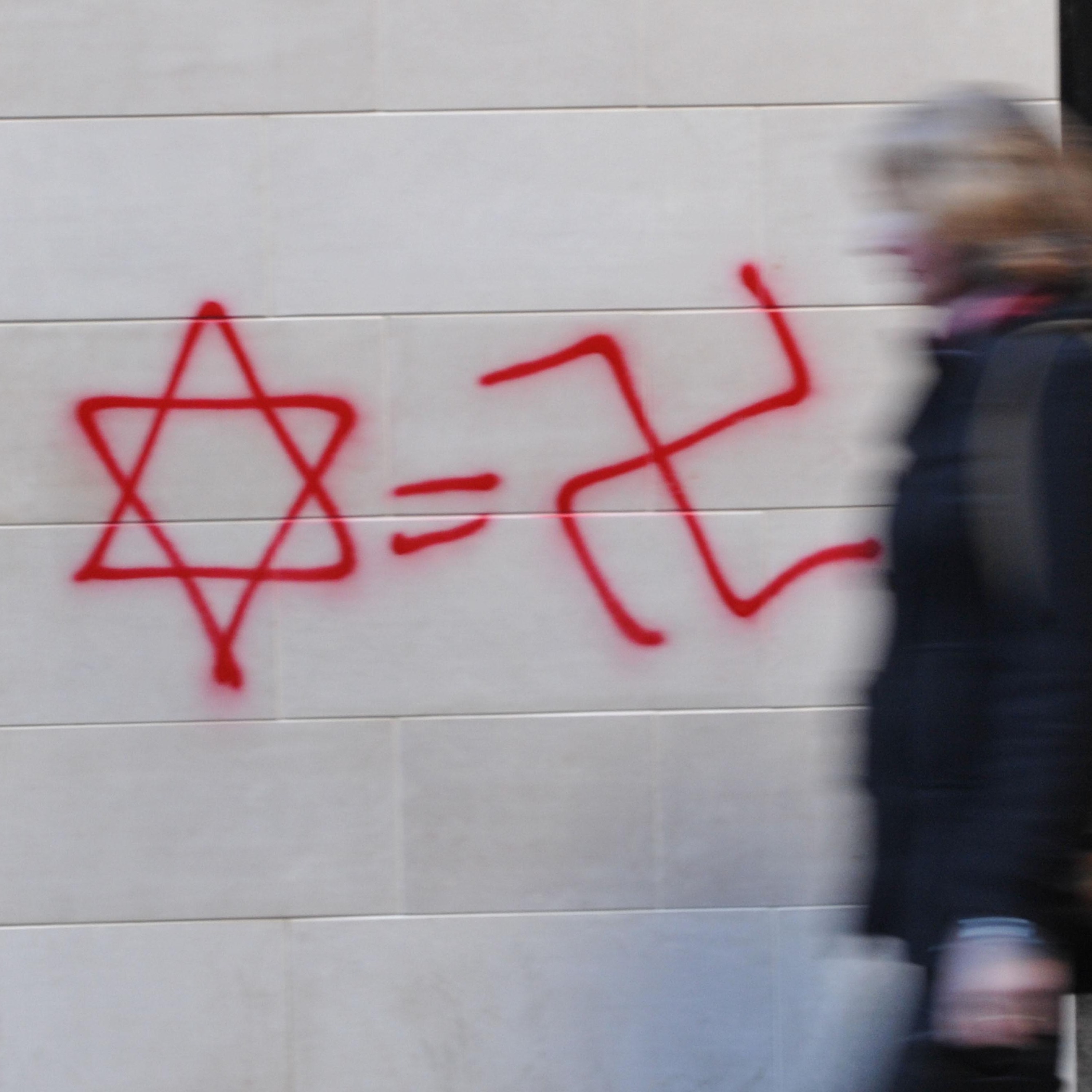4d ago
AJC's Asia Pacific Institute on How Australia's Government Ignored the Warning Signs Before Bondi
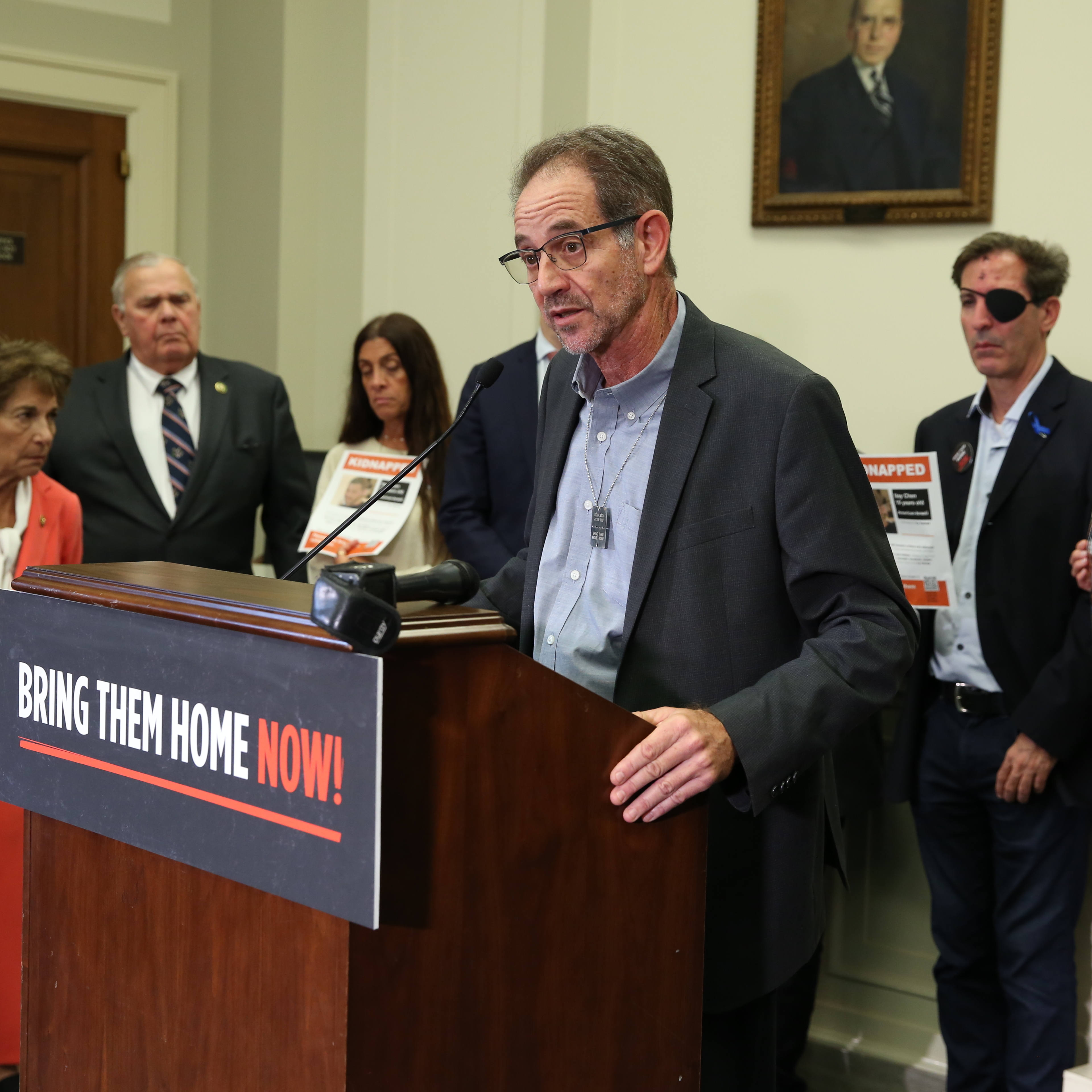
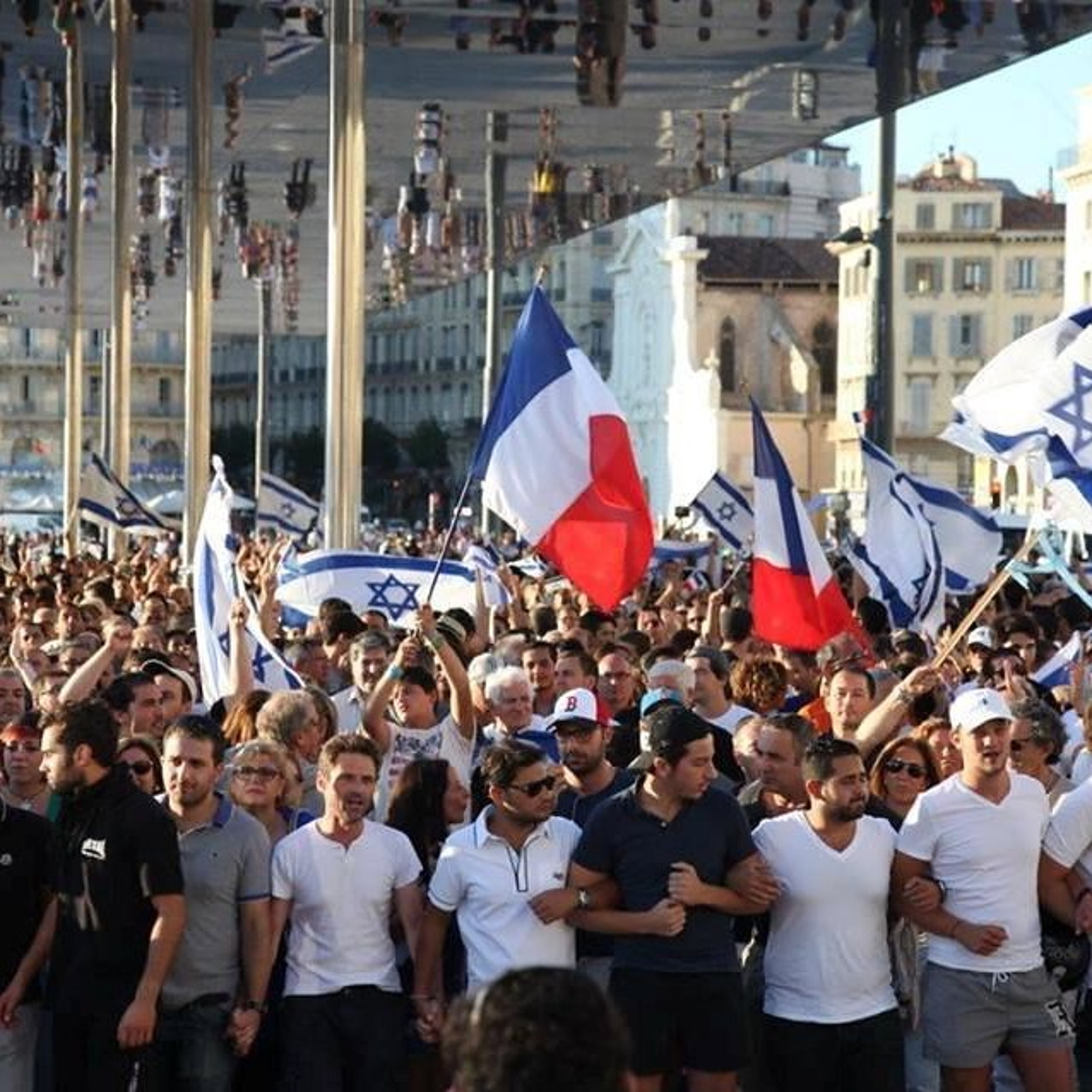
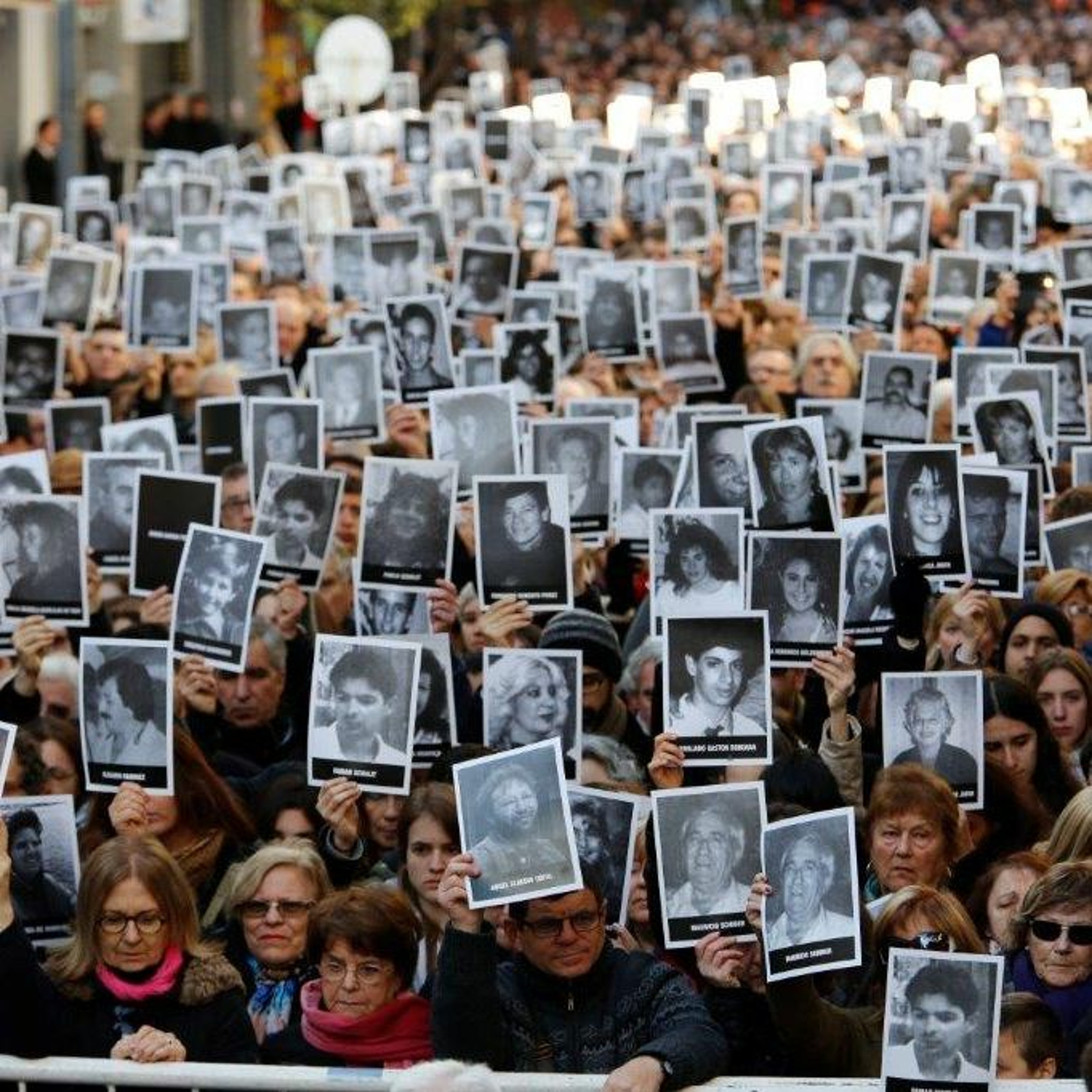
Once considered a haven for Jews, Australia is reeling after a deadly Hanukkah terror attack at Bondi Beach left 15 dead—the tragic outcome of skyrocketing hate. AJC Asia Pacific Institute Associate Director Hana Rudolph joins the podcast to unpack the crisis, revealing that despite over 2,000 antisemitic incidents in the year following October 7, the government dropped the ball. Hana details how political inaction and a fear that "supporting Jews is not politically popular" have allowed extremism to fester. She criticizes the delay in implementing the recommendations set forth by Australia's Special Envoy to Combat Antisemitism, noting the government's failure to move beyond basic security measures. Listen as she explains why global pressure is now urgent to ensure Australia takes this massive gap seriously before more lives are lost. Read the Full Transcript : https://www.ajc.org/news/podcast/ajcs-asia-pacific-institute-on-how-australias-government-ignored-the-warning-signs-before Resources: - What To Know About the Antisemitic Terror Attack in Sydney -Take action: Urgent: Confirm U.S. Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Antisemitism Listen – AJC Podcasts: - Architects of Peace - The Forgotten Exodus - People of the Pod Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: For more than 30 years, American Jewish Committee's Asia Pacific Institute has found Australia to be a nation that has stood shoulder to shoulder with the Jewish people and Israel. But that sense of steadfast support has started to fray as antisemitism has risen exponentially. The massacre at Bondi Beach on the first night of Hanukkah was only the latest and deadliest in a string of antisemitic incidents over the past two years. Here to discuss how we got here is Hana Rudolph, associate director of AJC's Asia Pacific Institute. Hana, welcome to People of the Pod. Hana Rudolph: Thank you so much for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, I want to ask you first, can you kind of introduce our listeners to the Australian Jewish community? How many people are we talking about? What is their history in Australia? Hana Rudolph: The Australian Jewish community is one of the most historic, long standing communities in the Asia Pacific. It dates back to 1788. So we're talking 18th century over 100,000 Jews. They're a diverse community. They reside primarily in the cities of Melbourne and Sydney, but they range in terms of practice, in terms of political views, similar to as we see in Europe or the US. There's some level of debate in terms of what, what percentage of the population it comprises, but somewhere between .5- 1% of the population. Manya Brachear Pashman: And has Australia been a friendly country for the Jewish community for all of that time, and at least until recently? Hana Rudolph: Yeah, absolutely. It has been a deep, close friend of Israel. Israeli diplomats have described Australia as an even closer partner to Israel at the UN and in other global forums than even the US. Jews have been living there for centuries, and have oftentimes described Australia as being like a haven. No matter the antisemitism that increases in Europe or in the US, Australia has been safe. It is the one place besides Israel, where they feel they can live in security. So the surge in antisemitism we've seen, especially since October 7, has just been so much more alarming and frightening and shocking for the community, because they just haven't seen incidents at this level anytime prior. Manya Brachear Pashman: What is it about Australia's community? I mean, I know that there's been a lot of emphasis on a kind of, give everyone a fair go, right? There's a lot of emphasis on equality. Is that what guides this kind of welcoming atmosphere? Or why are they such good friends with Israel? Is there something about the culture? Hana Rudolph: Yeah, Australia takes a lot of pride in its multiculturalism, the harmony and diversity, social cohesion, so they've placed a lot of emphasis on that in terms of, like, the national culture, and I think that's part of what's led to such a safe, thriving space for the Jewish community for so long until now. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what changed? Hana Rudolph: Million dollar question, right? October 7. It's really important to note that, you know, there have been threads of antisemitism from well before October 7, right? Things don't just happen overnight. And in the Hamas attack took place on October 7, before Israel had even begun its defensive war to recover the hostages and to complete its aims, on October 9, there was a massive protest in front of the Sydney Opera House, and people were yelling, were holding signs, yelling slogans of, where is the Jews, F the Jews. Some accounts of them saying, gas the Jews. I mean, we're talking about, there's no linkage here of like, Israel's counter defensive war. It's simply about terrorists attacked Israel. Now is a good time for us to talk about like, go find and hunt down the Jews. So October 7 was the trigger. But in the years since, there has been what the Australian Jewish community has really pointed to, a failure of the Australian Government to take the concerns of antiSemitism seriously. So in the year following October 7, there were over 2000 incidents of antiSemitism, which, if you if you break it down by day like it's horrific, especially when you think about the fact that the Jewish community primarily resides in two cities. So we're talking about 2000 incidents over two cities, primarily. And then in this last year, it was over 1600 incidents. And the Australian government has sought to be responsive. In many ways. They've done $30 million grants for security. They have committed to restoring synagogues that were fire bombed and all of that. But in a lot of ways that matter, kind of going beyond just simply police protection, but more about how do you fundamentally change the way that a society thinks about its Jewish community? They've really dropped the ball and we're seeing the impact of that now. Manya Brachear Pashman: What efforts have been made on the part of the Jewish community to change that? In other words, what advocacy have we seen from Australian Jews and their partners? Hana Rudolph: They've done everything we can, right, like in this they the Australian Jewish community is well established. They operate very similarly to European Jewish communities or American Jewish communities. So they have both umbrella organizations, and they also have advocacy organizations that run the gamut in terms of political viewpoints. AJC's partner organization, AJAC, the Australia Israel Jewish Affairs Council, has been very active in this space. And they have sought to work with leaders in both Maine political parties to call for various reforms. There has been a special envoy that was appointed by the government, which we laud in July 2024 in July 2025 she released a report containing about 50 recommendations for whole of society action, so some highest levels of government going all the way down to society, museums, media, schools, other institutes and just nothing has been done with the report. The government has not considered it. It has not acted on the recommendations, and we're talking about five months since that report was released. The Jewish community has really sought to emphasize that this is not simply a reaction to understandable public concerns about Israel's foreign policy, but rather, there is a deeper issue of antisemitism going on that the government needs to take seriously, and that's really where we're seeing just inaction. Manya Brachear Pashman: We talk a lot here at AJC about the sources of antiSemitism from the right, from the left, from Islamist sources. Where is it coming from? Primarily in Australia? Hana Rudolph: Yeah, it's a really interesting question, especially in Melbourne. My understanding is that the protests that were taking place weekly until the cease fire, and even now it's continued on, but it's morphed a little bit. But those weekly protests were drawing in, similar to what we see in the US, both the far left, people wearing keffiyehs, people calling for Palestinian rights. The same as we see in the US, and then also people on the far right. So it does draw an interesting mix of political views, united in their hatred of Jews and Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: And what about Islamist sources? Is that separate? Hana Rudolph: Yeah, so especially cities like Melbourne, that is part of the challenge. Melbourne has a high Muslim population. In all of Australia there, the Muslim population is something like 3% but it's one of the largest growing demographics. And in places like Melbourne, I don't know the number offhand, but it has a significantly larger impact on in terms of demographics, in terms of like, how politicians think about their voting, and so that's why you see Australian Jewish leaders pointing to like Alex rivchin from The Executive Council of Australian Jewry, has talked publicly about supporting Jews is not politically popular. Politicians aren't willing to risk that support because of the political costs they see, I think, primarily from Muslim voters. So Melbourne, especially where the protests have been particularly violent. Obviously, this took place in Sydney, so the violence is happening there too. But in Melbourne, where we've seen protests that turned violent previously, too, there's been real concern about the Muslim population. They're kind of feeding that. The Executive Council of Australian Jewry recently won a lawsuit. Within the last year, won the lawsuit against a Muslim clergy member who was in November 2023 so we're talking one month after the Hamas terrorist attacks. So one month later, he was doing a series of lectures describing Jews as pigs, as treacherous, like all these kinds of horrific caricatures. And so thankfully, this lawsuit, the Jewish community won. But this is the kind of situation, and that's one example, and maybe a more extreme example, but these are the kinds of situations that the community is running up against. Also in February 2024 there was a viral video of two Muslim nurses talking about how they would kill any Jews who were their patient, or Israeli or Israelis who were there. I'm sorry, I don't actually know what I just said. There was a video. There was a video that went viral of two Muslim nurses talking about how they would kill any Jewish or Israeli patients that they had and that they had already, was the insinuation as well. And so the lawsuit is ongoing for them, but they have faced criminal charges. They have had their licenses revoked, but there was also significant Muslim community pushback to the consequences that they face, which is also really alarming and disturbing. Manya Brachear Pashman: Of the 49 recommendations that were mentioned in the special envoy's report, Which ones do you think should be the priority going forward? You can't implement them all at once. Hana Rudolph: There's a lot of overlap between what the antisemitism envoy Jillian Siegel has recommended in her report, and what has been recommended through things like the Global Guidelines for Countering Antisemitism, which AJC supports. So I would say things like the enforcement of hate crime that's a huge priority. There are various ways in which the special envoys plan notes how Australia's law enforcement can deepen their efforts. And I think there is, there is some positive there is some positive movement to that end. Now, following this attack, there was an announcement following the recent cabinet meeting of the Australian Prime Minister and his cabinet talking about a hate crime database and so forth. So these are positive things we're also highlighting from the Special Envoys report, things like engaging social media, countering the disturbing narratives that we see there, and establishing better standards. And then also education, and I think that's a really core point. So how do you promote Holocaust education, antisemitism education and so forth and that we need the government's help, but also it can be done through other institutions as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you kind of share, kind of what AJC's advocacy, what you've learned, and what is AJC hearing and doing for Australia? Hana Rudolph: I mean, I think the number one takeaway that Ted [Deutch] and Shira [Lowenberg] had after visiting Australia, and they visited Melbourne, Canberra and Sydney. Canberra being the capital. Was just the the other shock at how much the community has been shaken by this massive spike in incidents. I think the last year's total of over 2000 incidents was something like three times higher than the previous year. So we're really talking about a spike. So just the shock that the Jewish community is facing and reeling from. And the sense from government and law enforcement that the only reaction needs to be about keeping them safe. So in terms of like, the protests that were happening weekly in Melbourne, the government's response was to encourage the Jewish community to stay at home, to not go into the city center where the protests were taking place for their own safety, as opposed to how, like, how do you protect free speech, of course, but also you don't allow it to reach A level where you're concerned about a Jewish person's safety if they come close to the protest. And similarly, just all of these measures that the Australian government has taken has really focused on security, you know, putting money towards law enforcement and and so forth, which is good, but nowhere near enough in terms of changing the slurs, the vandalism, the the arson attacks that has that have been on the rise over the past couple of years. So I think that was the first and primary takeaway that you know this, this massive gap between where the community is and how the government is responding. And in terms of AJC's advocacy, we're really trying to amplify the Australian Jewish community's message here, which is exactly that, that there is not enough being done. The problem is immense, and the government needs to take this seriously. This is not so easy as just putting some money towards security, but we need to go much further. And why is this report from the antiSemitism envoy appointed by the government sitting there for five months without any recommendations being considered or implemented. So things like this, we're we're amplifying that message, not just to Australian diplomats and leaders that we have connections with, but also in the US, because the US Australia relationship is so important, and we know that the US administration cares about antisemitism, and they care about antisemitism abroad, so we're working in close coordination with the White House, with state, to make sure that Canberra also hears this message from the US. Manya Brachear Pashman: Hana, thank you so much for joining us. Hana Rudolph: Thank you, Manya. It's a pleasure to join you.
4d ago
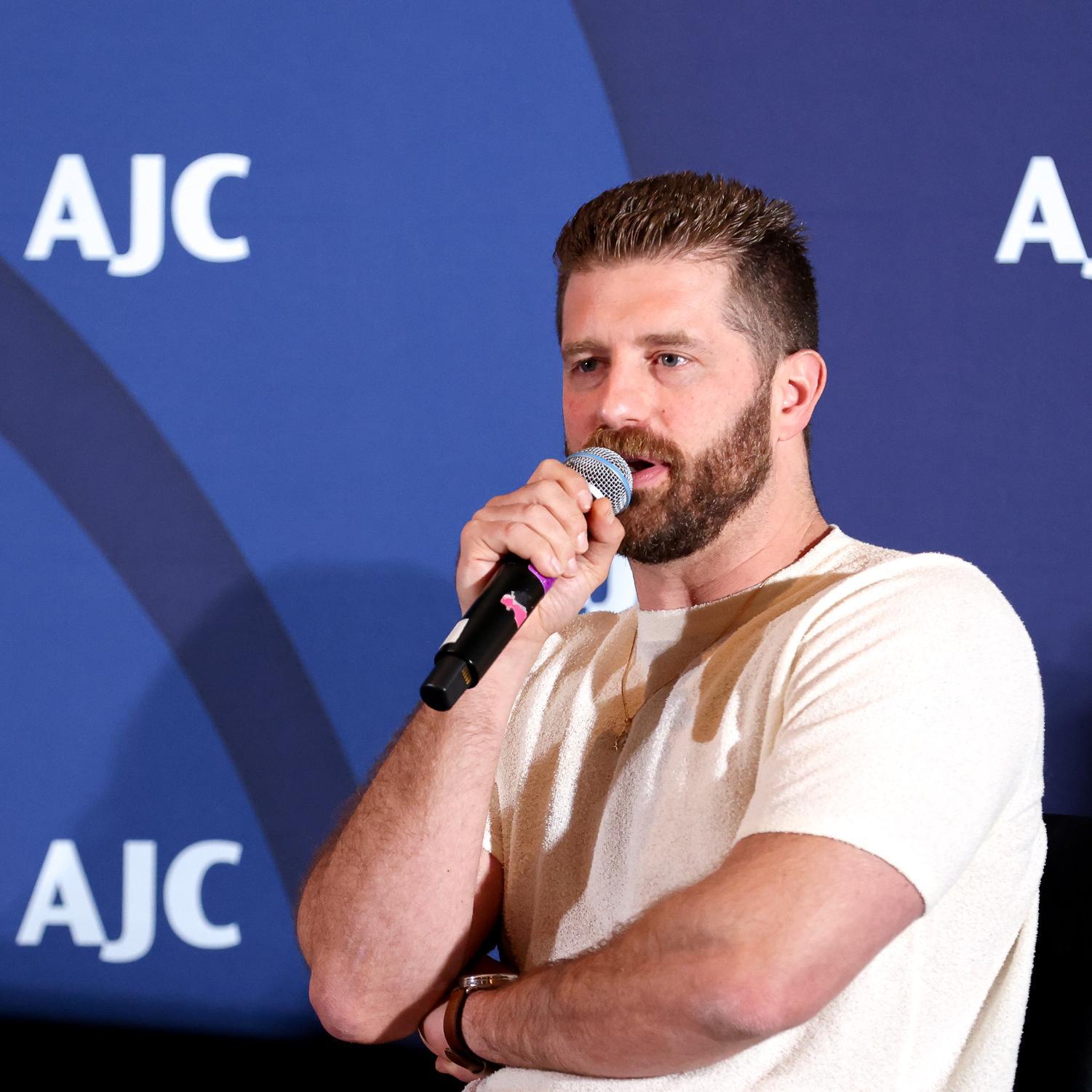
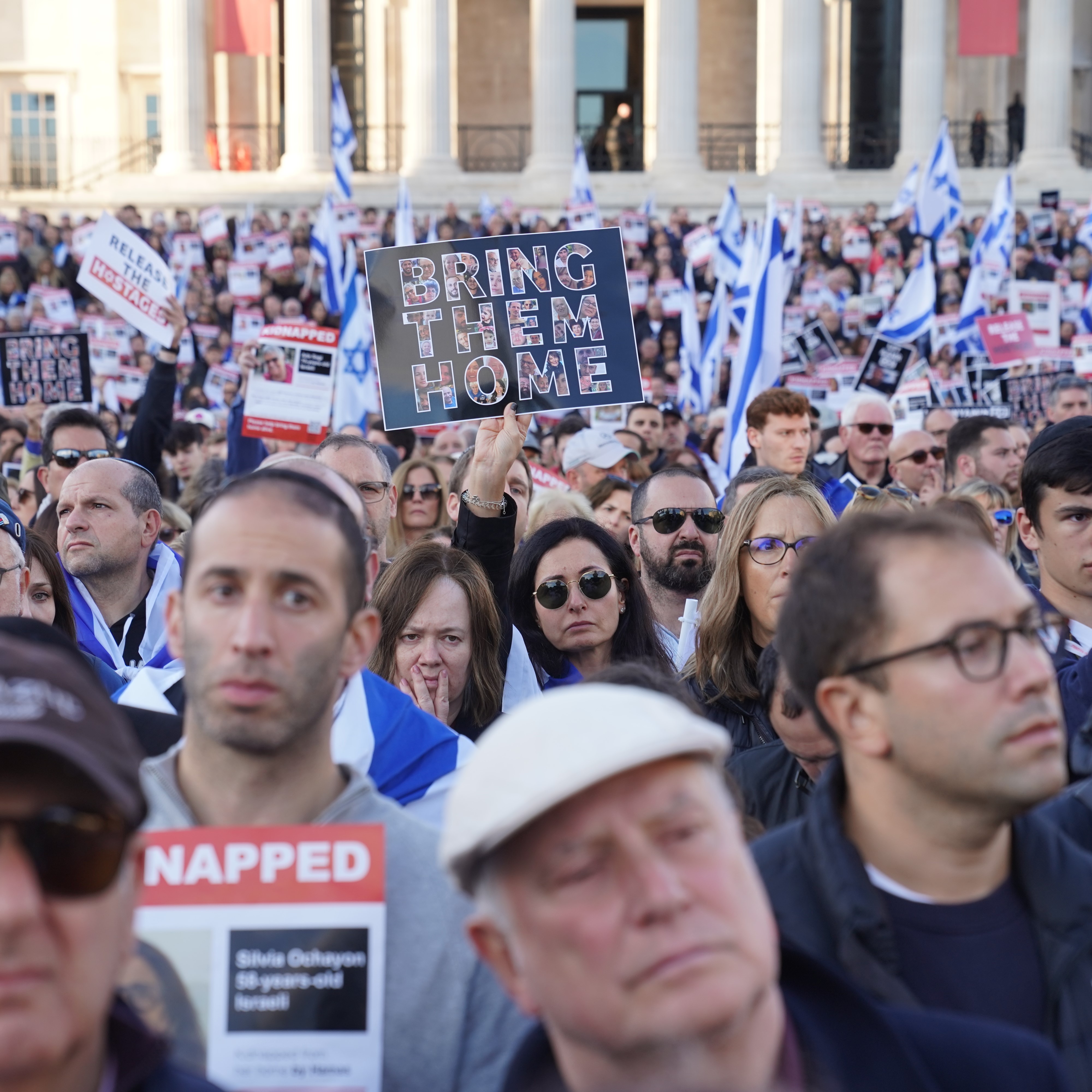
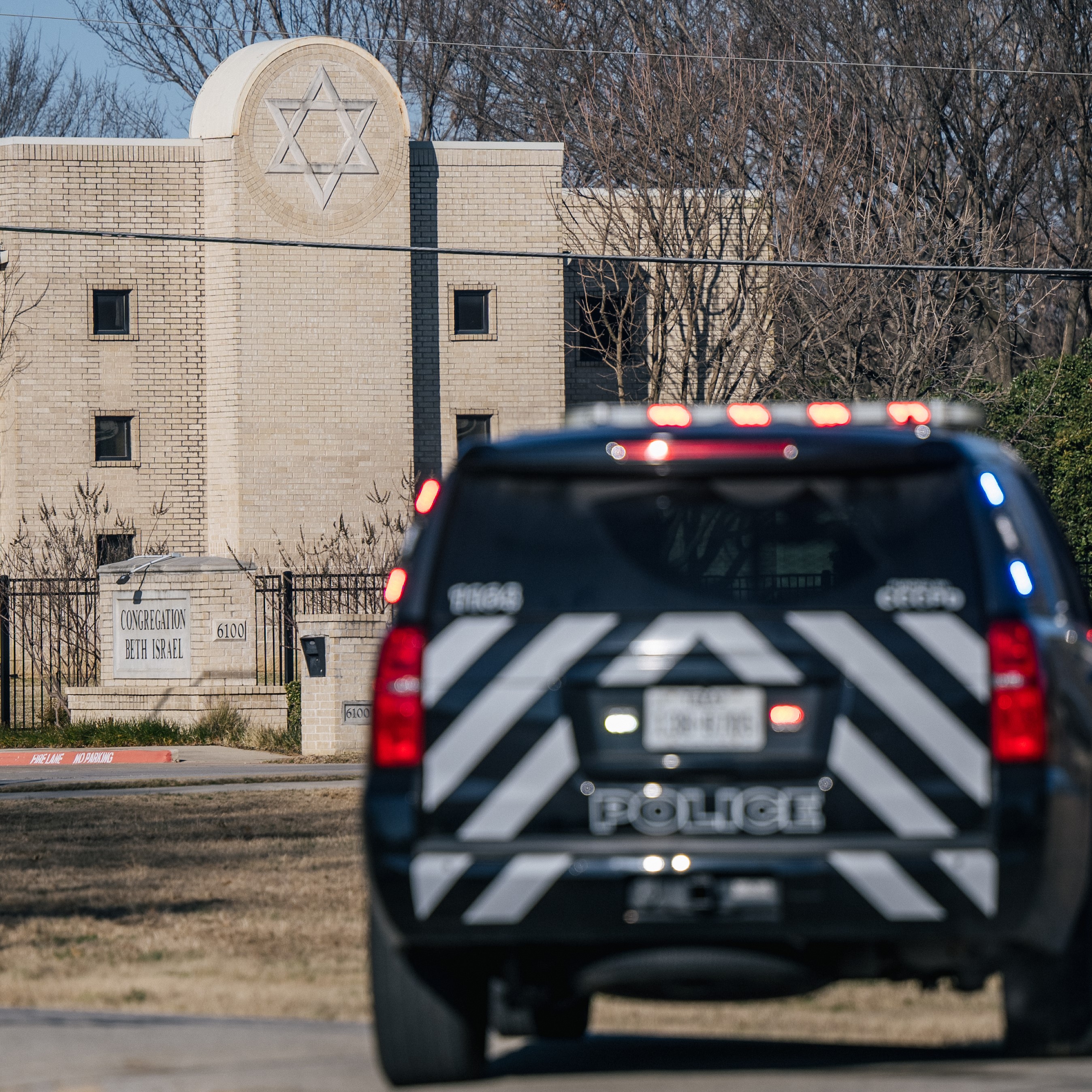
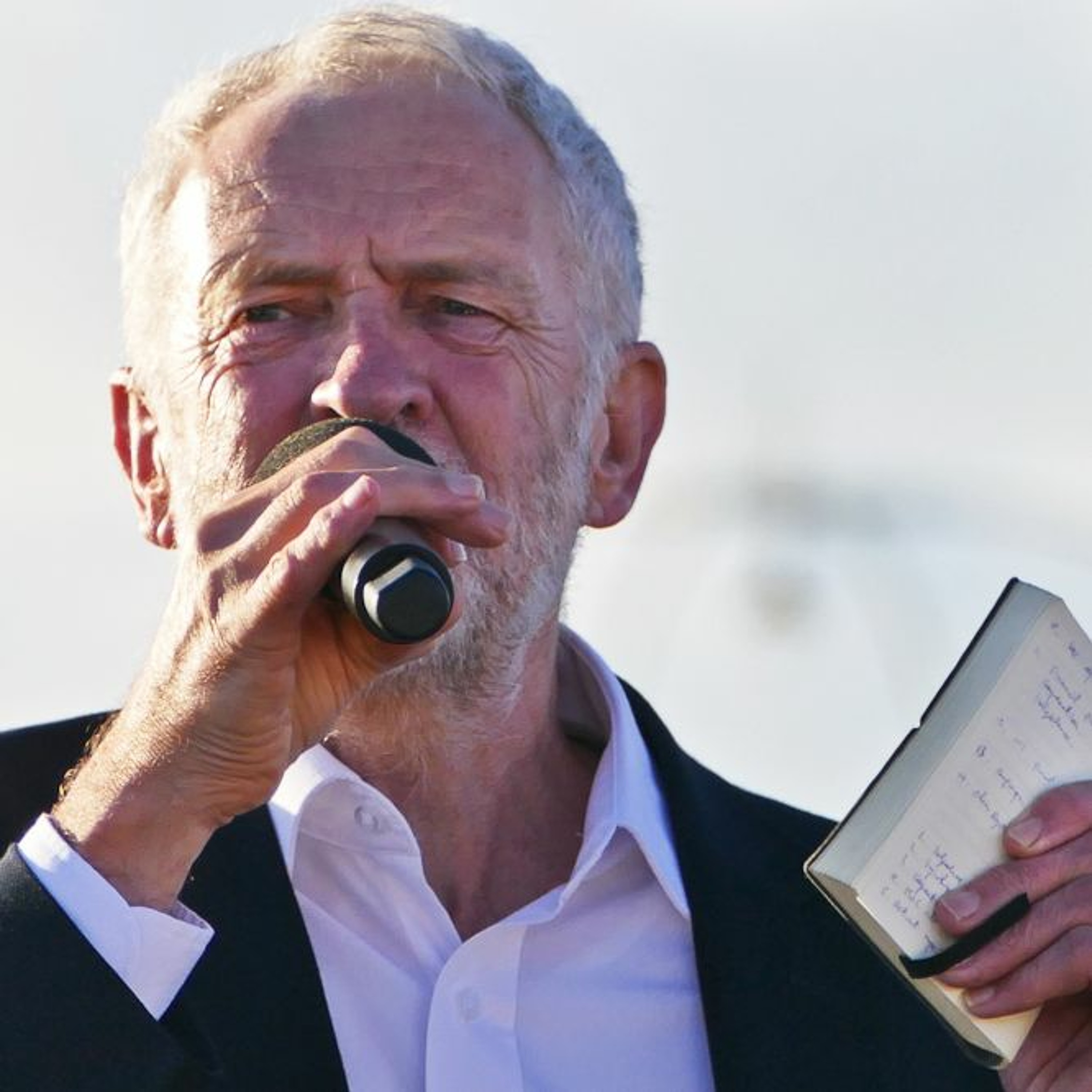
Sheltering in Place in Sydney: What AJC's Moshe Lencer Witnessed at Bondi Beach the Day After an Antisemitic Massacre
AJC Director of Campus Affairs Moshe Lencer was on his first visit to Australia when the unimaginable happened. Hours after he enjoyed the sun at Sydney's Bondi Beach, it became the site of an antisemitic terrorist attack, leaving 15 people, including a child and a Holocaust survivor, dead. Moshe recounts attending a student leadership shabbaton, in partnership with Australia's Union for Jewish Students (AUJS), and the immediate aftermath on the ground—a mix of helplessness and resolve—and the powerful scene at Bondi Beach the following day, as Jews and non-Jews gathered to mourn and show solidarity. Reflecting on the rise of antisemitism in Australia, Moshe—speaking as an outsider to the community—underscores the guiding principle of Australian Jews at this moment: "If we stop celebrating Jewish identity, it means they won." Read Full Transcript : https://www.ajc.org/news/podcast/ajcs-asia-pacific-institute-on-how-australias-government-ignored-the-warning-signs-before Resources: - What To Know About the Antisemitic Terror Attack in Sydney -Take action: Urgent: Confirm U.S. Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Antisemitism Listen – AJC Podcasts: - Architects of Peace - The Forgotten Exodus - People of the Pod Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: As the sun began to set in Australia on Sunday, more than 1000 gathered on Bondi Beach in Sydney to celebrate the first night of Hanukkah by the Sea, but at about 6p m, terrorists fired into the crowd, killing at least 15 and wounding dozens more. Students with the Australasian union of Jewish students had just wrapped up a Shaba tone before they headed to Bondi Beach and our own AJC, Director of Campus affairs, Moshe Lencer, whom we affectionately call Moosh, was there with him shortly before the attack, and he's with us now. Moosh, welcome to people of the pod. Moshe Lencer: Thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, I wish it were under very different circumstances. How are you doing and how are the students doing that you are spending time with there? Moshe Lencer: It's a wonderful question, and the more I think about it, the less I have a clear answer. It's a combination of helplessness, and in the same time, desire towards hope and trying to figure how to move through this very dark time. The last 24 hours, a little bit more than that have been very interesting is this has been my first time ever in Australia. I landed here Friday morning. Right now, for context, it's Monday night, and until about 6pm on Sunday, it was a very pleasant, positive experience, filled with moments of Jewish pride and joy. The reason I'm in Australia, even in this moment, is time, is AJC has a partnership with the Austra Asian union of Jewish students known as AJUS. Which is the student organization that focuses on Leadership for Jewish students in Australia and New Zealand. And I was invited to take part in a shabaton that was held just outside of Sydney with student leaders from both Australia and New Zealand. The weekend was filled with laughter and joy and happiness, and we were making edible chanukias before the holiday, we were talking about ways to advocate for what students needs and for what they need. We even finished the day with kayaking, and there was a lot of happiness and a lot of desire, because, as I learned recently, and I should have understood before by being in the southern hemisphere. This is the beginning of summer. This is the first few weeks when people finish the school year and they're enjoying it. They're celebrating. And that's why the dates were chosen. So it's like beautiful and it's sunny, and we were expelled and everything. And as we were about to start celebrating a holiday that's all about our community and resilience, our resilience was tested again, and now as just over a day into it, we're still trying to see what we can do and how to move forward and support the community right now as it's hurting. Manya Brachear Pashman: You were actually at Bondi Beach shortly before the attack. Can you kind of describe the environment and why you were there in the first place? Moshe Lencer: Yeah, of course, as mentioned, we were doing the shabbaton, and the programming ended around 3pm and it's summer. It's the first few days of summer. If you Google, what can you do, or what should you do and see in Sydney, the first few things people will see will be the Opera House, which is, I think, the most iconic place in the city. And then the second thing is go. It says, Go to Bondi Beach. It's such a big piece of the community here and where people go. It's also super close to where most of the Jewish community lives. So we were saying, okay, the shabbaton is done. A lot of the people are now local. What can we do in between? Before people hop on trains and flights and everything? Let's go to Bondi Beach. We all met up at the frozen yogurt location that's very iconic there very that chain itself was very connected to Sydney, and the participants just went there as an unofficial thing. I got there a little bit after just exploring. I said, my first time in Australia, like, Okay, what do I do? I go to Bondai beach. I walked around there. I was seeing this. It's the first week of summer school. Just ended. The beach was packed. It was sunny, beautiful, everything. I don't think there was a person in Sydney that wasn't at the beach yesterday, and I left the beach at around 510, ish, heading towards dinner with the student leaders at the Opera House. Because if I'm already there, I need, I should see everything else. Manya Brachear Pashman: And so why having, having walked that beach, why was there a Hanukkah celebration there? Can you tell our listeners who may not be familiar with who organized it, and why was the first night celebration? Operation scheduled for that, but that Hanukkah by the sea? Moshe Lencer: Yeah, of course, Hanukkah by the Sea was one of several events that were held yesterday by the Jewish community. Here. It had over 2000 people, but and it wasn't the only one. There were many events that were designed to celebrate, to have joy. Hanukkah is a holiday of lights, the community here, the geography here is that for a lot of us, Hanukkah, as a holiday, happens in the cold, in the winter, and this is the beginning of summer. You know, it's summer we go to the beach. I was joking with them that their Christian friends do Christmas in July, just so they can have snow or cold associated with the holiday. And just to think about it, right? So going to the beach, going to the where that's part of their culture, the culture here. So there were other events not even far from it. It was the best way to celebrate it. And Chabad of Bondi is a community that's growing, and it's community. It's beautiful, and it's using different aspects of of the tapestry that is the Jewish community of Sydney. So it's more of like, why not do it here? Why not have it there? It's, you know, it's the most connected to what's going on. It's, would have been surprising if they weren't doing something here. Manya Brachear Pashman: Was there in a giant menorah on the sands of the shore? Or how did they have it set up there? Moshe Lencer: I will be honest that I missed the preparation. But from what I've seen, though, you know, it's Chabad. They bring giant menorahs wherever they go. I even today they brought a giant menorah to light right there, because this is the core of what Chabad is, is to bring the light, to bring the essence of Judaism, where everyone might go. I walked also today by another location that wasn't far, which had another Hanukkah event yesterday with rides and everything. And they still had the hanukkiah there. That also was a huge Hanukkah. It was, there wasn't hiding of what is going on. You know, the people saw the flyer for what was going on. It was very public. There wasn't a feeling that this holiday should be celebrated in closed doors and hidden from the public. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you had mentioned earlier offline that you went back to Bondai Beach with the students that you were there to observe the Shabbaton with. Can you tell me what the scene is the day after? Moshe Lencer: I arrived there today with, with the senior leadership of AJAS who, for context, these are college age students that have tremendous amount of responsibility and leadership and ability. They oversee Jewish students across the whole continent and New Zealand, just to explain. And these are people there in their early 20s, and today, it was very important for them to make sure that we stop by and pay their respects. We have flowers and we want to go and stop at the site. And we weren't the only people with this idea. And what, from everything in my understanding, was a combination of very structured and a very spontaneous situation. People showed up with flowers and stones to mark they were there, and candles and stuffed animals and ways to make sure that the location is not going to be seen as something that isn't important and isn't marked what the horrible scenes was there. We got there, and I would say, there were, let's say about 100-120 sets of flowers. And then we stood there for another hour and a half, and I think it quadrupled, if not more, in that hour and a half. And it was just lines and lines of people. And what was very also noticeable, these were not just Jewish people, not Jewish and just Jewish individuals. I saw people of faith from different religions. I saw people walking with groceries and putting on flowers and heading back. I said, Children, I don't think there's someone in this whole area, and could have been even outside of Sydney that didn't want to stop and pay their respects because of how horrible that's the situation last night was, and how much it hurt the community, the Jewish community, of course, as being a part of the victims, not just the Jewish community that goes to Bondi, but also the community of Sydney. Many dignitaries have visited the sites in the last 24 hours, and. Um, there were several moments of spontaneous singing. There were, it was Hebrew singing, and it was started by different groups in different moments. It was just ways to those standing there to kind of find some silence in it. It was an attempt. And I'm saying an attempt, because I don't think anything can really help but an attempt to try to start processing, and I'm not going to be worried, and I cannot speak to the community itself as because I'm an outsider, I am fortunate enough to be connected to the members here and to those that are really trying to do what they can to continue and to move forward, but it is an outsider seeing something like this actually, there's some beauty and community and very, very dark times, and to know that it's not just the Jewish community helping each other, but It's the whole community here that they're showing up, just shows there might be some, some hope. Manya Brachear Pashman: Was this out of the blue? I mean, in your conversations with people there on the ground, was this shocking? Or have they sensed a slow motion journey to this point? Moshe Lencer: Antisemitism in Australia has been on the rise for a while now. Since October 7, a lot of events have happened, if it's been synagogues that were set on fire, and if it was individuals that would threaten children right outside of their kindergarten, if it was swastikas being spray painted, as I mentioned, the shabbaton started Friday. I landed at 9am on Friday, and I needed to be at our meeting place that was a main synagogue in Sydney at 11am meaning that my time I went through customs, got all my stuff, I just Uber directly there with my luggage. When I got to the synagogue, I was greeted by a security guard who looked at me and he was very confused of why a person he doesn't know stands outside of his synagogue with luggage. The first thing he told me is like, you're not allowed to walk in with luggage into a synagogue in Australia, and I understood exactly why he was saying this. They don't know me. They don't know what's in my luggage. Don't what can come out of my luggage. All of this story to say is that there, there is this tension. And I said it to him, and I said it when I walked in it I really was appreciative that would everything the security guard, no matter what, no matter what I was saying that was like, You're gonna open your luggage, I'm gonna go through everything you have to make sure that you're no matter we're gonna tell me, I'm making sure that there's nothing here that can harm this community. So the people are taking their job seriously with that being said, Australia as a whole has been lucky to never have events like this, not just on the antisemitism. They have never had this large of a terrorist attack and its soil. So it's one of those they're preparing to for what they know, not what they thought would ever be gun laws on like the US are a lot more stricter there. It's very uncommon to even have weapons so easily. I'm not going to say that people saw it specifically coming. They felt like there is a slow simmer of events. Something's going to happen. No one thought this scale of horrible event can happen, because there was never a scale of this horrible event to a point where it's not a culture like the Jewish community in the US that checks its media and the updates every five minutes that three four hours after event yesterday in downtown Sydney, people were not even aware what was going on in other places, because what they didn't have to check the news. The Jewish community, of course, did. We were told to shelter in places. Everything happened. But if you were someone that is not connected Jewish community in Sydney, and you were in downtown Sydney, and which is in a different part by the Opera House, there's a huge chance you had no it was going on because you didn't need to, because you didn't think that you didn't think that you need to think that something's going to happen. And then moving forward to today, the whole feeling shifted. I got into an Uber that took me to the area, and his first reaction was, I really hope nobody's going to try to shoot you without even knowing I'm Jewish or not, he just like all he knows it was that there was a horrible attack last night in that geographical area. Manya Brachear Pashman: So it's kind of shocking that you landed at 9am and by 11am you were already introduced to the precautions. That they took and the severity with which they with which they took them, and then not even 48 hours later, the worst. What can we do here in the United States or anywhere in the world where people might be listening to this podcast? What can we do to bring comfort, to bring solace, to show support that really will make a difference. Moshe Lencer: Everything I've noticed, I'll say that out of what I've been noticing. And then AJUS has actually just launched about 45 minutes ago, a new initiative that they're asking the community, and when I say in community, I mean the Jewish community at large around the world, to share how they're spreading light right now and this holiday, send videos and pictures of lighting the menorah. It's already the second night of Hanukkah. Here it's right now, 10:34pm on Monday, while the day is only starting in the US. So they're, you know, they're far ahead at 16 hour difference. They want to see, they want to feel that the community and the Jewish pride and joy is still going through this. They're the community as it's hurting and it's trying to recover from this, is also trying to show that there is still a vibrant Jewish community, because at the core of this event is to have us hide and is to have us stop being who we are, and to have an if we stop celebrating Jewish identity means they won. They mean that they got exactly what they wanted by actively attacking us and killing us. They're also stopping us from continuing to be the community that we want to be. So that's one thing. The other thing we're that I am seeing again, I don't want to speak for the community itself. I'm just saying from my experiences with it is to make sure that if you have any interaction with decision makers, if it's in Australia, or diplomats that represent Australia around the world, or even in your own country, that can make any type of public comments. As I said, it was simmering for a while, this didn't show up out of nothing. They didn't expect this horrible thing because, like I said, there was no precedent. But it didn't mean they weren't saying something's going to happen. Australia understood something's going on. But I think right now, what we need to do is putting some pressure to make sure that they're taking a lot more seriously here in Australia, they're taking it a lot more seriously around the world that after two years, when we were saying, this is not just about what they are using, the word of Israel is the fault. We're not against the Jews. It is. It is against the Jews. The lighting of a Hanukkah and Sydney, well, there's a cease fire. Has nothing to do with Israel has all to do with Jewish identity and community, and that's what we need right now to make sure that, you know, we're speaking out. We're making sure that elected officials, those that can make difference, are making a difference. Manya Brachear Pashman: You talked about the past two years that there has been a rise of antisemitism since October Seventh. And just a few days after October 7, you also mentioned the Opera House. The Sydney Opera House was illuminated in blue and white, the colors of the Israeli flag to show solidarity after the terror attack, and yet, there were protesters outside yelling and some yelling antisemitism, and I'm curious if there has been any indication or expression of similar sentiments in the days after this terror attack. Moshe Lencer: From my conversation so far with the community and from everything I saw, at least today at Bondi, it seems like the larger community is right now hurting for the Sydney, its own geographical syndicate community, for the Jewish community within its community, said I saw people Fate of different faiths there, very visibly from others right now, and I don't want to, want to knock on wood, I haven't heard or seen anything with that being said. Sorry, let me track this. I do know this morning, as people were putting down flowers, there were some videos of people wearing kefirs, they were actively trying to explain the connection between the shooting in their beliefs, and were trying to intimidate and interrupt as people were trying to mourn and the site. But it was very anecdotal. I believe was one or two people at most, and that does not represent a much larger thing. Just in comparison, as you mentioned that on October 9 that the bridge area in Sydney saw a protest that had hundreds of people. So it's a very different thing. With that being said, we're only 24 hours into this. Our community knows that sometimes we get a short grace period and then it flips. So I'm hoping that by the time this airs what I am saying won't change. Manya Brachear Pashman: You and me both. Well, you reminded me of the 16 hour time difference. It reminded me that on New Year's Eve, I always tune in to watch the fireworks in Australia, because they're always the first to ring in the new year. And it, to me, is kind of a early first sign of hope for great things to come in the new year, and then I don't want to wait. In other words, I always tune into Australia for that sign of hope and of newness. So I hope that this is I hope that a page turns in Australia for the better, not for the worst. So moosh, thank you very much for joining Moshe Lencer: Thank you for having me.
Dec 11
The Producer of Pulp Fiction on His New 10/7 Docu-series Red Alert on Paramount+
Join host Manya Brachear Pashman for a powerful conversation about Red Alert , the Critics Choice Award-nominated Paramount+ docu-series that confronts the October 7 Hamas massacre with unflinching honesty. Producer Lawrence Bender ( Pulp Fiction, Good Will Hunting ) shares why this project couldn't wait—launched in real time to push back against denial, disinformation, and a world struggling to absorb the scale of the tragedy. Bender reflects on the courage and trauma of the ordinary Israelis whose stories anchor the series, including survivors like Batsheva Olami, whose resilience changed the production team forever. Hear how filming during an active war shaped the storytelling, the emotional toll on everyone involved, and why capturing these true accounts is essential to ensuring October 7 is neither minimized nor forgotten. Key Resources: AJC.org/Donate : Please consider supporting AJC's work with a year-end gift today. Right now, your gift will be matched, dollar-for-dollar, making double the impact. Every gift matters. Every dollar makes a difference in the fight for a strong and secure Jewish future. Listen – AJC Podcasts: Architects of Peace The Forgotten Exodus People of the Pod Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: [Clip from Red Alert ] Manya Brachear Pashman: Academy Award nominated film producer Lawrence Bender has quite a repertoire for both feature films and documentaries: Pulp Fiction, Inglorious Bastards, Good Will Hunting and Inconvenient Truth. In fact, his works have earned 36 Academy Award nominations. His most recent TV miniseries is a more personal project on the second anniversary of the October 7 Hamas terror attacks on Israel, Paramount Plus began streaming a four episode series called red alert about the attack on festival goers, innocent passers by and families waking up to terrorists inside their Israeli homes that day, a tragedy that many of us, either on this podcast or listening have watched with overwhelming grief for the last two years. Lawrence is with us now to talk about how he grappled with this attack on Israel and the rise of antisemitism that followed. Lawrence, welcome to People of the Pod. Lawrence Bender: Thank you, Manya, it's good to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So that clip that we played at the top of this episode, it's one of the few clips in English. Most of the dialog in this show is in Hebrew with subtitles. But that scene is a woman, Bathsheba and her two daughters. They're walking across a field trying to return home, and her son has been taken. Her husband is gone. This series weaves together her story and three or four other ordinary civilians fighting for their lives on October 7, 2023. You know, as someone personally who's been immersed in this subject matter for two years, to be honest, I had to muster the energy to watch this, and I'm so glad that I did. But why are, I mean, as we're still waiting for the last hostage to be returned, why was it important for this show to air now? Lawrence Bender: Well, thank you so much for doing this with me, and thank you for playing that clip. I have to tell you first, I love that clip. I love that scene because one of the things about the show and the stories that we portrayed is that even with the horrific things that happened on that day, people still were able to fight back. People were still able to be strong. A mother with her daughter and her infant stood in the face of a terrorist and stood him down in real life, this happened. Now, not everybody was so fortunate, and her husband Ohad was not fortunate, and her son was taken hostage, as you mentioned, but it does show her personal power in this horrific situation. And I just thought, you know, this woman is a real hero. I've spent a lot of time with her, Batsheva Olami, she's really an extraordinary human in all ways. So thank you for playing that clip. So in terms of the show, I felt on October 8, it's just amazing how quickly, before Israel did anything, the entire world quickly turned against the very people who were the victims and having spent subsequently, a lot of time with people on the set, because, as you mentioned, this show was about real people, and those real people spent a lot of time on the set with us. And the very people that were traumatized, felt isolated, they felt alone, and they're the very ones that need to be loved, that need to be hugged, they need to be supported. Anyway, I just felt like I needed to do something fast to try to show the world what really happened. AndRed Alert is the result of that. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you fear that the world has already moved on? Lawrence Bender: Oh, that's a good question. It feels like we've passed a tipping point, actually, in terms of Jew hatred and anti-Israel and antisemitism. Even as we are now trying to have a peace process, right, that somehow we are stumbling forward, and if that's going to happen, people need to understand why we're here and why we're here happened on October 7. And if you watch the show, hopefully you're pulled into the show, and you have a, you know, you have an emotional journey, and then you understand, oh, this really happened. And you understand that's the truth. And only when you really understand the truth of October 7 do I really think that you can really get some sort of peace. Manya Brachear Pashman: So is this different from other historical events? You know, a lot of movies and television shows commemorate historical events, like the Holocaust, for example, but they happen years later. They're made years later. I kind of call it the never forget genre. But is October 7 unique in that it's not a question of whether people will forget or move on. It's a question of whether they believe that this present is actually true. Lawrence Bender: That's right, there's the deniers. There's people that just don't know. There's people that forgot, maybe you know, there are people who I know that I had to explain. Like, you know, it's interesting. As an example, when you see the show and you see all these Hamas terrorists invading the kibbutz, and Ohad says to her, his wife, Bathsheva, he whispers in her ear, I just saw about 20 terrorists, and someone said to me, who's not unintelligent, I didn't realize there are that many. I didn't realize that. And if you're not really paying attention, maybe you don't really know. And look, they're the haters, haters which are never going to change. But I think there's a large group of people that just don't really understand, and they're the ones that I feel we have a shot at showing this to and having a conversation with. Manya Brachear Pashman: In fact, are you actually introducing or experimenting with a new genre of truth or facts in the face of fiction. Lawrence Bender: I guess that's true. I mean, this just happened. And some people ask over this last, you know, when I released, and we were paramount, released the show. You know, I've been asked a question, is it too soon? And my answer is, I feel like it's not soon enough. And I felt like immediately I needed to work on something, and this is the result of that. For me, personally, there are many collaborators of people on this show that incredible Israeli partners, my American partners. I mean, there's a lot of amazing people that came together to work on this, to make this show, but we really felt like time was of the essence, because the world was shifting so quickly, we wanted this to get out there, to show the world what really happened. Manya Brachear Pashman: One of the reasons I'm pressing you on this, this was not a fiction film. This was based in reality. You said you met Bathsheba, the actors prepared for their roles by meeting with the very real people who they were portraying in this show whose stories they were recreating. I'm curious what some of the takeaways were for you, for your colleagues, from your encounters with these victims, with these survivors, and did anything about the production ever change after they got involved? Lawrence Bender: It was truly a life changing experience for myself, but really for everyone involved, of course, myself and my partner, Kevin Brown and Jordana Rubin, and we were basically the only non Israelis that were full time producing the show. And everyone else was a citizen of the country. Everyone else, you know, was affected dramatically, everything but from like our key grips brother ran the kibbutz Raim, where we filmed that area that was a kibbutz overrun by terrorists, right? His brother survived. So it was really like every single person at some point, you know, we call it triggered, but it really happened quite often where you have a scene and people just have to stop for a second and take a moment, whether it's an actor finishing a scene or a crew member, you know, partaking in the making of the scene. But lots of things happen. I'll tell you one story which was, you know, quite interesting. We're working at the Nova festival scene, and one of the actors, Moran, her niece, was on vacation in Greece, and her niece told her, if a red headed police woman shows up on the set, she's the one who saved my life. And indeed, her name was Bat, she showed up, and we said, we need you to meet somebody. And we FaceTimed Moran's niece with Bat, and the young lady she's like in her early 20s, said, You're the one who saved my life. You're the one I was hiding by your feet while you were firing. And we asked, Did you remember the people that you saved? And she said, I really only remember the people I didn't save. You really felt the pain that she is still at that point a year and a half later, this is. In April, May, suffering from what she went through. RPG hit nearby her. She went flying through the air. She had had half reconstructive surgery, on and on and on. It was obviously an extremely traumatic day for her to you know, a moment where there's a woman on the set whose daughter was murdered, and someone on my crew, actually, Mya Fisher, has said, you know, there's someone here I want to introduce you to. It's after lunch. And I spent some time with her, and I asked her, you know, like, how do you go? Fine, I can't, you know, I can't imagine losing my son in this way. It's just unimaginable. And I asked her, do you have a rabbi? What do you do to survive? And it was a very difficult emotional exchange. And sometime later, she had sort of retold that encounter to somebody else on the set who came to me and said, you know that woman you're talking to. She told me what happened, you know this conversation? And she said, You know this Hollywood producer came all the way from California, she doesn't know me, from Adam, and sat down with me for an hour to hear my story, and it clearly meant a lot to her. And again, you realize that the very people who are traumatized directly are not getting the love, are so isolated and people are against them, and it made me feel even more determined to tell these stories for the world to understand. Every day we had these type of difficult, emotional and to be honest, I was extremely honored every time I met someone. I spent every Saturday night at Hostage Square because we were making the show, I got to spend time backstage with all the families who had loved ones in the tunnels. There was a deep dive into this. Now, I have to tell you, on the other hand, the filming while a war is still going on is quite it's like things you don't have to think about normally, right? So, as an example, we were in a town and we're shooting a shootout. We're filming a shootout between the IDF actors and the Hamas actor. They're actors. I keep saying they're actors, right? Because they are actors. But the mayor and the chief of police in the town were extremely worried, because they look real, right? They look like real people. And unfortunately, the cemetery is littered with people who have been murdered and killed by the Hamas. And all the other men who are there, they have guns, they carry, and if something's happening, they're going to run towards the problem. So he's worried, what if someone walks by, or someone's up in a building. He looks down and they see an actor who looks like Hamas, they are going to shoot him. So we literally had speakers every 10 yards, like all up and down the street, and every like 15-20 minutes, saying, don't worry, in Hebrew, of course, this is a movie, everything's okay. We had a drone up in the air, never coming down, on a tether with a police officer. They're a full big screen watching case someone walks down the street. We dressed up the Hamas actors as they're walking from the holding area to the area where they're filming, we put them in these kind of white hazmat-like suits so that they couldn't confuse them, and when they got done filming, we put them right back in these hazmat white suits and brought them back to the holding area. We all had to dress up, and we had to wear these very, very light blue shirts the entire crew, so nobody looked like anything but a crew member. It was something, right? Manya Brachear Pashman: I did not even think about that. I mean, I knew that you had filmed on location in Israel, and I knew you had filmed during the war. In fact, I was going to explain to listeners who don't know Red Alert is what Israelis call the sirens and the phone alerts when there are rockets being fired upon Israel and they have time to seek shelter. I was going to ask you if you had been there during a red alert and had to seek shelter, but I didn't even think about the possibility of people confusing the filming with actual war activity. I imagine you were there during a red alert, and did have to seek shelter, yes? Lawrence Bender: so there's different types of alerts in the south. We did shoot in the guys called the Gaza envelope. We shot within less than a mile away from the Gaza border. So a scene that comes soon after the one that you showed. They're resting under a tree, and we are in the Gaza envelope. And this is a scene where they're running from the Hamas. They're running, they're bare feet, and they're out of breath, and they stop under this tree that's hot, and so forth. And you can hear, just a mile away, the war going on in Gaza. Hear the bombs and everything, and we weren't worried about we're going to be attacked, but it was eerie hearing a war go on, and we're filming a scene where they're running from that war, right? So it was dramatic every week or so still at that point, the Hamas would lob a missile bomb into southern Israel and an alert would go off. You have 15 seconds to. Get into. So we had to bring these portable concrete safe rooms with us so that crew, at any given moment can run quickly into one of these concrete things. We couldn't always do it. So there's always this conversation, and by the way, it costs a lot of money, so everything you're always carrying these things. There's a lot of planning that went on. But I have to tell you, as an American showing up in Israel for the first time after October 7, I wasn't used to these alarms going off, so we were fortunate that while we were filming in the south, no missiles were lobbed at us. However, my first day there, I'm in a meeting on the eighth floor. It was a Friday morning. I got in there on a Thursday evening, 10 o'clock in the morning, the alarm goes up. I mean, just like that, right? And it's loud. And you have these buzzers. Everyone's phone is buzzing, not like the Amber Alerts we have, like, really buzzing loud. And everyone stops and looks at me, and they apologize to me. They apologize and they go, Oh, we're really sorry, but it's an alert. We have to go into a safe room. Oh, don't worry, it's just from the Houthis. It takes eight minutes to get here. Now it's an intercontinental ballistic missile. These are real big missiles. They can really do bad damage. Don't worry, the Iron Dome usually gets them. It's really okay. So we go, you know, we go into and they pick up their danish and their coffee, and of course, I take out my cell phone and I'm videotaping. And then we go in there, and when it's off, we go back to the meeting. The meeting starts as if it never happened. And then they stop, and they go, Oh, how was that for you? And then I just didn't realize, what with the emotion that was going on because we're not used to having missiles shot at us. It's not normal. And I started to bubble up with emotion, and I had to, like, stop myself, I didn't want to cry in front of all these people that I barely knew. So I had to suppress my feelings. Like, don't worry, it's okay. You're having a normal reaction, right? And that happened quite often while I was there. Now, you do get used to it. And the last night I was there, I was having dinner outside, tables outside, you know, in restaurants everywhere. So we're having a typical outside dinner, and they're handing the fish, and the alarm goes off, and we go, let's eat. And we don't go into the restaurant where they're called maamads. You don't go into the safe room. So that's kind of the quote, unquote normal life. Now you imagine here in the United States we get a missile from Mexico or Canada or wherever. No one's going to put up with that. That's just insane. It's insane what people in Israel have to go through. Manya Brachear Pashman: it really is. But it's interesting that you've kind of adopted the nonchalance that your colleagues had at the very beginning of the trip, and wow, certainly no apologies. I want to know if there's a missile headed my way. Thank you. It does sound like October 7 changed you personally. And I'd like to know as a progressive Jew, on what level did it change you as a human being. I mean, how did it change you the most? Lawrence Bender: I've been an active Jewish person for maybe 20, somewhere, 2025, years. I went to Israel My first time. I was ready. As far as I'm concerned. I was too old already to go for the first time. It was like 2003 I went with the Israeli policy forum, and we met with a lot of people there, and we ended up going to Ramallah, met with Abu Mazen, we went to Cairo and met with the president there, Barak, and met with a lot of people in Israel and so forth. And I've been involved one way or another for quite a while. But of course, October 7 was dramatic. Of course, I was safe in my house in Los Angeles, but I still watched in horror. And of course, October 8, it's just hard to understand what happened. It was the latent antisemitism, Jew hatred, that sits there. I still don't quite understand that. It feels like antisemitism never went away, but it was underneath, and it just gave a good excuse to come out, and now the world is where it is. So yeah, for me, I became much more active than I was before. It became much more important to me, my Jewishness, my relationship to Israel. I want to protect Israel as much as I have that power to you know, whatever my ability is, like a lot of people, I know it's become a really important part of my existence, and it's like a new chapter in my life. I'm absolutely looking for more Jewish or Israeli projects. You know, I'm looking to do as much as possible in this area. Manya Brachear Pashman: A number of your colleagues in Hollywood have proposed boycotting Israeli film festivals, institutions, projects, they're going the opposite direction that you are. And I'm curious if you had difficulty finding an American network to air this series, and what do you say when you confront colleagues who do want to boycott and are hostile toward Israel? Lawrence Bender: You know, there's different groups of people. They're the true haters. I don't think that you can ever even have a conversation with them. There are people who just don't understand, and there's people you can and there are people who you know they're trying to be good people. They're trying to understand, like, What don't you understand about women being brutally raped and murdered? It's a little hard for me to understand that, actually. But there are a lot of good people who just are either confused or got too much of the wrong message. But the one thing I would say straight up is, let's take an analogy. You know, there's very few people that I know that you see on TV, on any news show, that is very empathetic with the regime in Iran as an example, right? That means a brutal regime. If you're a liberal or if you're a conservative, there's very few people who support that regime here in this country, right? But they don't boycott their filmmakers, right? They actually give their filmmakers Academy Awards. So why is that with Israel? I feel like there's something very misguided here in Hollywood. Now, we got really lucky when it came to distribution. I just have to say, because we were supposed to go out to sell the show like it was fully financed from equity and from Keshet, who's the local Israeli. This is the biggest network in Israel, by the way. It's the biggest drama in Israel in the last decade. It really performed well there. But now we're going to go sell it here in the United States and the rest of the world, and it's early September, which is our deadline to do that, and Israel bombs Qatar, and then this boycott letter is signed. And I have to tell the investors. You know, it's like, this is not a good time. We cannot go sell. We're just gonna fail, and there's no second chances. And you know, I was getting into dramatic arguments with my investors because they really felt strong. You got to be like that character in your show, the police officer is going to save his wife and you know, nothing's going to stop you. And I said, Yes, I'm with you. I developed that character I know in the Middle East arguments. I was at Skip Brittenham's memorial. Skip is like this beautiful man who was like the Mount Rushmore of lawyers here in LA. He's just a great human and one of those guys that wants to make deals, not just take everything and have the other guy get nothing. He was just like a he's just a real mensch, right? And well, loved anyway. Unfortunately, he passed, but I was at his memorial, and I ran into David Ellison. Now, I know David a little bit, not well, but I know him a little bit, and I also know that, you know, he loves Israel, from what I've read and so forth. And so I went up to him and said, Hey, man, we talked. I said, you got to know what I'm doing. And it probably got three words out of my mouth, and you can see him go, I'd love to see this. This sounds amazing, and sounds like it's exactly the timing we need. And we sent him the material, and he watched every episode himself, and then he gave it to Cindy Holland, who runs paramount, plus his main person. And you know, they said, we do this. We want this. It would be an honor to be your partner in this is actually quite humbling. And it was an incredible moment for us to have David Ellison, Cindy Holland, say, hey. You know, we want this now. Then they said, We need to drop it. We want to drop all the episodes on October 7? Well, by the time they got those episodes, it was like two weeks to go before October 7, or a couple days before, because we couldn't give it to them in the midnight before October 7, obviously. And they had pretty much final picture edit, but we had temporary sound, temporary music, temporary effects, and so we had to work double triple shifts to get it done. But of course, we did. Manya Brachear Pashman: This actually reminds me of a conversation I had with playwright, screenwriter, Oren softy for the Forgotten Exodus, which is a podcast series we did about Jews from the Middle East. He spoke about his father's side of the family, which hails from Aleppo, Syria, and he shared a lot of his frustrations with the modern anti Israel movement and sentiments in Hollywood, the protests which he's been trying to combat in theater and on the stage. And he actually said that investors had pulled out of a film project about Israel when tensions flared. So it's interesting to hear your investors took the opposite approach, but he told me in our conversations, he told me that being Jewish is about stepping up. That's how he sees it. It's about stepping up. And I'm curious if that rings true to you, and do you feel like this series and your plans to do more, is that your way of stepping up? Lawrence Bender: Hmm, that's beautiful, and I'm so glad to hear you recount that story with him. I'd love to talk to him about that I feel like, without really understanding that it's built into me genetically, right? My grandparents, far as you go back, my family is Jewish, right? From Romania, from Hungary, from Minsk Belarus. So it's the way that you're brought up as a Jew. It's just always been a part of our lives, and we're pretty much taught that that's part of being Jewish, right? So, you know, I've always felt like it's important for me. Now I tell you, you know, it's interesting, and I think about as we're talking so in the 90s, when I was getting started, and I was actually doing pretty well this one year, I had Good Will Hunting and Jackie Brown and a price above Rubens, those three movies, and things were going well, but I felt like something was missing in my life. And then we screened Good Will Hunting and Camp David in 1998 and it was an amazing moment. And that was like one of these light bulb moments for me. You know, I met the President and Mrs. Clinton and Madeleine Albright, Secretary of State, and Secretary of Defense, Sandy Berger and the Chief of Staff and Senate Majority Leader, and on and on, right? They're all there. And it was Matt Damon, Ban Affleck, Gus Van Zant, Robin Williams, et cetera, et cetera, right? And I felt like these guys are making a difference, and that's what was missing in my life. And so since 1998 I've been always looking for ways that I'm and that's that's that becomes like a more of a fulfilling way of living right for myself. So yes, I would answer that. That's a long way to get to yes. Manya Brachear Pashman: Wow, Camp David, that's awesome. Lawrence, thank you so much for joining us and for talking about the impetus behind this series. I encourage everyone to take some time, brace yourself emotionally, but do sit down and watch Red Alert. It is really quite worthwhile. Thank you so much. Lawrence Bender: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with AJC colleague, Dr Alexandra Herzog, the granddaughter of Chaim Herzog, Israel's Irish born sixth president. She shared how an attempt by Dublin officials to strip her grandfather's name from a community park illustrates how criticism of Israel can veer into an effort to erase Jewish memory. As I mentioned in my conversation with Lawrence, it took some degree of wherewithal to watch Red Alert, as we've spent the last two years on this podcast speaking with the families of hostages, former hostages themselves, and survivors of the October 7 massacre. I've wanted nothing more than to make sure their voices are heard. We end this week's episode with the voice of Orna Neutra, the mother of Omer Neutra. Orna recently spoke at the AJC Long Island meeting, shortly after the return of her son's remains more than two years after his death, followed by a word from AJC Long Island Director Eric Post. Orna Neutra: When Omer was taken, our world collapsed. But something else happened too. People stood up. People showed up. And many of you here showed up. This community, the broader Long Island Jewish community, AJC, our friends, colleagues, neighbors, complete strangers, carried us. You wrote, you marched, you advocated, you pressured you called you consoled and refused to let the world look away. To our personal friends and honorees here tonight, Veronica, Laurie, and Michael, your leadership has not been symbolic. It has been practical, steady and deeply felt by our family. Like you said, Veronica, on the first days when we were barely understanding what was going on, you connected us to Senator Schumer's office, and Michael, you helped us write a letter to the White House on October 8, and that was the first sign from hostage families that the White House received. We know that Secretary Blinken had the letter in his hands on October 8, indicating that Omer was probably a hostage. And AJC as an organization, beyond your many actions and advocacy, I want to specifically acknowledge your DC team. It was mentioned here tonight, throughout our many, many, many visits to Capitol Hill, AJC professionals were instrumental. They arranged meetings, they walked us through endless hallways, opened doors, prepared us and stood beside us, and they're still doing that for us, and we will see them this week. Always professional, with purpose and humanity, and we will never forget that. Over these two years, we learned something essential: that when Jewish families are in danger, the responsibility belongs to all of us, across movements, across generations, across continents. This work is the work that AJC does every day. This is the work that everyone here in this room understands. Eric Post: Since the horrors of October 7, AJC has been empowering leaders around the world to take action against antisemitism and stand with Israel. But we cannot succeed alone. Please consider supporting AJC's work with a year-end gift today. Right now, your gift will be matched, dollar-for-dollar, making double the impact. Every gift matters. Every dollar makes a difference in the fight for a strong and secure Jewish future. Donate at AJC.org/donate – that's www - dot - AJC - dot org slash donate.
Dec 4
Erasing Jewish History: Why What Happened in Ireland Should Alarm All Jews
When Dublin officials moved to strip the name of Chaim Herzog—Israel's Irish-born sixth president—from a community park, it wasn't just a local dispute. It was an act of erasure. In this emotional episode, Dr. Alexandra Herzog, AJC's Director of the William Petschek Global Jewish Communities Department, explains why this attempt to rewrite history should alarm not only Jews, but all citizens of goodwill. As anti-Zionist fervor increasingly targets Jewish identity across the West, the push to remove a Jewish name from a park beside Ireland's only Jewish school sends a chilling message: Jewish heritage has now become a political battleground. Alexandra shares personal memories of her grandfather and illustrates why this fight isn't about a plaque in Ireland—it's about halting the slide from criticism of Israel into the deletion of Jewish memory. Tune in to understand why defending this history is essential to protecting Jewish dignity everywhere. Key Resources: AJC Welcomes Dublin City Council's Decision to Shelve Renaming of Herzog Park Letter in the Irish Times: Renaming Herzog Park in Dublin Would Be An Act of Erasure Against Ireland's Jews Listen: Will Ireland Finally Stop Paying Lip Service When it Comes to Combating Antisemitism? AJC Directly Addresses Antisemitism and Vilification of Israel in Ireland with the Prime Minister Listen – AJC Podcasts: Architects of Peace The Forgotten Exodus People of the Pod Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Read the full transcript : https://www.ajc.org/news/podcast/erasing-jewish-history-why-what-happened-in-ireland-should-alarm-all-jews Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: Members of the City Council of Dublin, Ireland have withdrawn a proposal to rename a park that since 1995 has honored former Israeli President Chaim Herzog. The park, located near Dublin's only Jewish school, is named after Herzog, Israel's sixth president, who was born in Belfast. Here to talk about the now withdrawn proposal is Alexandra Herzog, AJC's Director of the William Petschek Global Jewish Communities Department, and Chaim Herzog's granddaughter. Alexandra, welcome to People of the Pod. Alexandra Herzog: Thank you so much for having me, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you have joined us before, but on a different podcast, The Forgotten Exodus , which is our narrative series about Jews from the Middle East and North Africa. You were joining us to talk about your maternal grandfather, Nessim Gaon , the longtime president of the World Sephardi Federation. He came to Israel from Sudan. But this time, we're talking about your paternal grandfather, Chaim Herzog. How did someone born in Ireland later become President of Israel? Alexandra Herzog: Yes, that's a great question. Manya, so my grandfather, Chaim Herzog, was, as you said, born in Belfast. He grew up in Dublin in a very proudly Jewish home. His father actually was a Rabbi Isaac Halevi Herzog, and he served as the Rabbi of Belfast before becoming the chief rabbi of Ireland. So he moved from Belfast to Dublin in 1919. He was affectionately known as the Sinn Féin rabbi, and he was highly respected and close to many of the leaders of the Irish independence movement. So my grandfather really grew up in a house that was deeply steeped in Jewish learning, in Irish patriotism, and he had a very strong sense of moral responsibility. And as a young man, he had to leave Ireland to study, and he later enlisted in the British Army during World War Two, he fought the Nazis as an intelligence officer. He was one of the first soldiers actually to enter the concentration camp of Bergen Belsen, and he interrogated senior Nazi officials. Now, after the war, he moved to what would become the State of Israel, and he helped build the very young country, almost from its founding, in different positions. And you know, then later, he became Israel's ambassador to the UN and a member of the Israeli parliament, the Knesset. And by the time he was elected as Israel's sixth president in 1983 he was widely seen really, as a statesman who combined Irish warmth and some storytelling with a very deep sense of Jewish history and Jewish responsibility. He never stopped describing himself, actually, as an Irish born man. and he often spoke about how Ireland really shaped his worldview, and his commitment to freedom and to democracy. Manya Brachear Pashman: And you mentioned that he was the ambassador to the United Nations. He was, in fact, Ambassador when the resolution Zionism is Racism was, was part of the conversation. Alexandra Herzog: That's right. Yes, one of the two UN resolutions ever to be withdrawn and canceled, very important one. That's right. Manya Brachear Pashman: In fact, if I'm not mistaken, he tore it in half. Alexandra Herzog: He did. He tore it in half saying that this was nothing but a piece of paper, and explained how, you know, we could not equate Zionism to racism in any sort of way. Manya Brachear Pashman: So were those the reasons why, in 1995, the Dublin City Council decided to name the park after your grandfather? Or were there other reasons? Yeah. Alexandra Herzog: I mean, I think that, you know, I think it was a gesture, really, of recognition, of pride. I mean, Dublin was basically honoring an Irish man, you know, one of its own, an Irish born Jew who had gone to become, it's true, a global statesman, the President of Israel, but who really never stopped speaking about his Irish roots. And I think that that was really a source of pride for him, but also for Ireland in general, for many, many years. And as you said, you know, Herzog Park really sits in a very historically Jewish neighborhood. It's near, actually, where my family lived, where my grandfather grew up, and it's right next to the country's only Jewish school. So naming a park for my grandfather was, I think, really a way of acknowledging this deep Irish Jewish history, and the fact that it is part of Irish history. So I think that my family story is very much woven into the country's broader story of independence, of democracy and of moral courage, really. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yet 30 years later, there has been an attempt to rename that park and strip that name from the park. Why? What happened in 30 years? Alexandra Herzog: It's a great question. I think that in the past three decades, you know, we've really seen the Israeli Palestinian conflict become a proxy battlefield for broader political debates in Europe, but also really everywhere around the world. In Ireland, the criticism of Israeli policies, of the Israeli government, has increasingly blurred into hostility towards Israel as a whole, and at times even towards Israelis and towards Jews. What is really striking about this proposal is that it doesn't target a policy or even a government decision within Ireland. It targets a piece of Jewish and Irish history. So instead of creating a new space or a memorial, the proposal really sought to erase an existing Jewish name. And I think that that shift from debate to erasure, because that's really what we're talking about, is what worries me the most. It reflects really a climate in which maybe some feel that expressing solidarity with Palestinians require overriding an important part of Jewish history and Jewish presence. Jewish memory, really. So one of their proposals is actually to rename it Free Palestine park, or to rename it after, you know, a Palestinian child. Obviously from a personal perspective, it's extremely problematic to remove a Jewish name to replace it by another group. We don't need to do that. We can recognize the realities and the lived experiences of both groups without having to erase one over another. Manya Brachear Pashman: I should note that last year, Israel recalled its ambassador, and in December, closed its embassy in Dublin, accusing the Irish government of extreme anti-Israel policies, antisemitic rhetoric and double standards. So really, taking the debate to extremes, and that the, in fact, the tiny Jewish community that is still there about–would you say about 3000 people in the Irish Jewish community? Alexandra Herzog: That's right. Manya Brachear Pashman: They're facing antisemitism as well. We actually interviewed our colleague, AJC's Director of International Jewish Affairs, Rabbi Andrew Baker, at the time, just about a year ago, because he also serves as the Personal Representative on Combating Antisemitism and the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe. So he had just met with the Irish Prime Minister whose administration had recently adopted the international Holocaust Remembrance Alliance's Working Definition of Antisemitism. So I'm curious now with this attempt to rename the park and do something so harsh to erase Jewish history, has that definition been implemented, or has it failed to be implemented? Alexandra Herzog: Yeah, I think that the adoption of the IHRA working definition of antisemitism by the Irish government was really an important and a very welcome step. On paper, you know, it gives officials and institutions, law enforcement, a shared framework, really, for recognizing antisemitism, including when it appears in the guise of anti-Israel rhetoric. I think that the challenge, really, as always, is implementation. So from what I hear in conversations with the Irish Jewish community, and you know, Jewish community leaders and colleagues who follow these issues very closely, there's still a significant gap between the formal adoption of the IHRA and the day to day practice. Whether it's in, you know, political discourse or in education, or even how incidents are simply discussed or understood. And I think that the current controversy here that we're talking about with Herzog Park is a perfect example of that. If you apply the IHRA seriously, then you see very quickly how targeting a specifically Jewish symbol in a Jewish neighborhood, in order to make a political point about Israel, actually crosses the line into antisemitism. So I think that if we could really work on the implementation much more, that would be extremely positive. Manya Brachear Pashman: And in fact, the prime minister himself actually condemned the attempt by the Dublin City Council to rename the park, correct, he encouraged the withdrawal of this proposal? Alexandra Herzog: That's correct. Both the Prime Minister and the Deputy Prime Minister actually issued statements saying that this proposal should not have come to even be considered, and that they should be withdrawn. And I'm very grateful for their leadership in that. And I think that it's important, though, to underline the fact that it is not, you know, just a global form of antisemitism, but that it is really an expressed form of antisemitism on the ground, really erasing Jewish history and blaming an entire Jewish population for what is happening miles and miles away is antisemitism. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what are you hearing from the tiny Jewish community there? Are you in touch with people there? Do you still have relatives who live in Ireland? Alexandra Herzog: I sadly don't have relatives there anymore, but I am in contact with the Jewish community. And I think that, you know, it's a community that really has a lot of pride in their Jewish history and their Irish history and in their Irish roots. I think there is a feeling, what I'm hearing from them, that there is a bit of a mix of fatigue also, and of anxiety. And you know this, we're talking, as we said before, about a very small community, about 3000 Jews. It's a close knit community that has contributed far beyond its size to Irish society. They love Ireland, and they feel deeply Irish, but in the past years, and especially since October 7, they have felt increasingly targeted, and they often have felt exposed, misunderstood. So I think that incidents like the proposed renaming of the park lands particularly hard because it's not abstract. It's a park that's in their neighborhood, that's next to their children's school, and bearing the name of someone who for them symbolizes their connection to Ireland. So to see this name singled out really sends a chilling message that, you know, Jewish presence, Jewish history are negotiable. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, we talked about similar issues when we talked about your maternal grandfather in Sudan and the erasure of Jewish history across the Middle East and North Africa in these countries where Jews fled. Would you say that there are parallels here? Or is that, is that an unfair statement? Is that taking it too far? Alexandra Herzog: I mean, I think that, in general, the notion of commemoration, the notion of really talking about one's history is, is a problematic one, when those commemorations, or those celebrations of memory, of Jewish memory and Jewish impact, are being erased because of the connection with Israel. And when people use the platform to accuse Israel of genocide, they distort history. They weaponize really Jewish suffering. I think that there is something to be said there. And, you know, it's the same idea as, you know, removing a Jewish name from a park in order to make that political point about Israel. I think that it is something that we're seeing way too much. It is a very slippery slope, and it's something that we should be 100% avoiding. Because Jewish memory, whether it be, you know, like a commemoration about like, what happened to Jews from our fleeing Arab lands, what happened during the Holocaust, anything that has to do with Jewish memory, it needs to be preserved. It needs to be honored on its own terms. It cannot be repurposed or overwritten to serve certain political narratives or even certain political accusations that like the ones that we're hearing right now, to me, that is very deeply troubling, and it's something that Jewish communities worldwide, I think, are experiencing more and more unfortunately. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I wanted to ask you, your grandfather passed away in 1997. This park was named two years earlier. Was he present for that dedication? Alexandra Herzog: Yeah, unfortunately, he wasn't able to attend the inauguration. He was still alive, that's true when the park was named, and he was deeply touched by the gesture. I think that for him, it really symbolized a bit of a full circle somehow. You know, the Irish boy who became President of Israel, who's being honored in the neighborhood where his story really began. I think that there was something very powerful and beautiful about it. For the 100th anniversary of my grandfather's birth in 2018 the family actually went to the park and got the dedication plaque up. And you know, that was a very meaningful event. Manya Brachear Pashman: It must be heartbreaking for you to know that they want to tear that plaque down now. Alexandra Herzog: I know how proud my grandfather was of his Irish roots. I know the work that my great-grandfather did in Ireland for Irish independence. And I think that it's completely uncalled for right now to rewrite history and to pretend that our family's story has no place in this country that meant so much for two generations of my family, and really even as a statement for Israel. My grandfather always, you know, talked about Ireland, and really always had this pride. So it touches very deeply. I think it really gives the very wrong message to young Jews and children who are growing up in a country where they are such a minority, I think that we have to put things in perspective a little bit. And, you know, I imagine being a kid and seeing like the name of somebody who maybe symbolizes something for you, their name being removed.It sends a message that really should not be out there in any kind of way and is not justified. Manya Brachear Pashman: You knew your grandfather. Did he share stories about his childhood, and was there anything as you were standing in that park that reflected those stories? Alexandra Herzog: Yeah, I had the very big privilege to know my grandfather very well, to spend a lot of time with him. I'm his first grandchild, so we spent a lot of time together. We shared a deep passion together for history, for literature, for politics, but also for nature. For me, before any before being a public figure, he really was my grandfather, my Saba. Someone who was warm, who was funny, who was very present as a grandfather, who would take me to the garden and show me all of his fruit trees that he was so very proud. And I had this feeling, I mean, the park, this park is very small. It's a tiny, you know, it's a tiny park, but somehow is so meaningful to him. And I know that he loved living in that neighborhood. It was very hard for him to leave Ireland and, you know, go to what was then Palestine. So it's something that I really felt very strongly when I was there, and that I think that our family thinks about often. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Alexandra, I am so glad that the Dublin City Council tabled this proposal for the time being. And I appreciate you sharing some memories about your grandfather and putting this in perspective for our listeners. Alexandra Herzog: Thank you very much. It was an honor. Manya Brachear Pashman: You can hear the story of Alexandra Herzog's maternal grandfather Nissim Gaon and the challenges he and his family faced in Sudan in the first season of our award-winning series The Forgotten Exodus. In 12 episodes, we also share the erased or often-forgotten stories of Jewish families who left or were driven from their homes in the Middle East and North Africa. And don't forget to listen to our most recent series about reconciliation in the region: Architects of Peace: The Abraham Accords Story.
Nov 26
Architects of Peace: Episode 6 - Building What's Next
Five years after the signing of the Abraham Accords, the Middle East looks very different—defined by both extraordinary cooperation and unprecedented challenges. In this episode, we unpack how Israel's defensive war on seven fronts affected regional partnerships, why Abraham Accords nations have stood by the Jewish state, and what expanded normalization could look like as countries like Saudi Arabia and others weigh making such monumental decisions. We also explore the growing importance of humanitarian coordination, people-to-people diplomacy, and the critical role AJC is playing in supporting deeper regional collaboration. From shifting narratives to new economic and security opportunities, we chart what the next five years could mean for peace, stability, and integration across the region. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. This episode is up-to-date as of November 25, 2025. Read the transcript : Building What's Next | Architects of Peace - Episode 6 | AJC Resources: AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace - Tune in weekly for new episodes. The Abraham Accords, Explained AJC.org/CNME - Find more from AJC's Center for a New Middle East Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus People of the Pod Follow Architects of Peace on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace You can reach us at: podcasts@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript: ANNE DREAZEN: One thing that I have learned from my many years at the Department of Defense is that military instruments of power are not sufficient to really build longlasting peace and stability. The importance of trade, of economic development, of people-to-people ties, is so essential to what we think of as an enduring or a lasting peace. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: In September 2020, the world saw what had been years–decades–in the making. Landmark peace agreements dubbed the Abraham Accords, normalizing relations between Israel and two Arabian Gulf States, the United Arab Emirates and the Kingdom of Bahrain. Later, in December, they were joined by the Kingdom of Morocco. Five years later, AJC is pulling back the curtain to meet key individuals who built the trust that led to these breakthroughs and build bonds that would last. Introducing: the Architects of Peace. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: It has been five years since Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and Bahrain signed the Abraham Accords on the South Lawn of the White House. In those five years, Russia invaded Ukraine, sparking a massive refugee crisis. The U.S. elected one president then re-elected his predecessor who had ushered in the Abraham Accords in the first place. And amid news that Saudi Arabia might be next to join the Accords, the Hamas terror group breached the border between Israel and Gaza, murdered more than 1,200 people and kidnapped 251 more. Israel suddenly found itself fighting an existential war against Iran and its terror proxies on multiple fronts – Gaza, Lebanon, the West Bank, Yemen, Syria, Iraq, and Iran itself. At the same time, Israel also fought a worldwide war of public opinion – as Hamas elevated the death toll in Gaza by using Palestinian civilians as human shields and activists waged a war of disinformation on social media that turned international public perception against the Jewish state. Through it all, the Abraham Accords held. ALI RASHID AL NUAIMI: There are those who work hard to undermine what we are doing. And this is where many question: 'How come the UAE is still part of the Abraham Accords?' MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: Dr. Ali Rashid Al Nuaimi is a leading parliamentarian and educator in the United Arab Emirates. He has served as the Chancellor of the United Arab Emirates University and the Chairman of the Abu Dhabi Department of Education and Knowledge. He currently serves as the Chairman of the International Steering Board of Hedayah, The International Center of Excellence for Countering Extremism and Violent Extremism. The center is based in Abu Dhabi. He was one of the first to go on Israeli and Arab media to talk to the general public about the Abraham Accords and was known for correcting news anchors and other interview subjects, that the UAE had not simply agreed to live in peace with the Jewish state. It had agreed to actively engage with the Israeli people. ALI RASHID AL NUAIMI: We saw the importance of engaging with both sides. We saw the importance of talking to the Israeli general public. We saw the importance of dialogue with the government in Israel, the Knesset, the NGO, the academician, businessman. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: That engagement started almost immediately with flights back and forth, musical collaborations, culinary exchanges, academic partnerships, business arrangements–much of which came to a halt on October 7, 2023. But that simply meant the nature of the engagement changed. Since the start of the Israel-Hamas War, the UAE has provided extensive humanitarian aid to Gaza, delivering more than 100,000 tons of food, medical supplies, tents, and clothing, by land, air and sea—about 46% of the total assistance that entered Gaza. It established six desalination plants with a combined capacity of two million gallons per day. And, in addition to operating field and floating hospitals that treated 73,000 patients, the UAE also provided five ambulances, facilitated a polio vaccination campaign, and evacuated 2,785 patients for treatment in the UAE. From Dr. Al-Nuami's point of view, the Abraham Accords made all of that humanitarian aid possible. ALI RASHID AL NUAIMI: This is why we were able to have these hospitals in Gaza, we were able to do these water solutions for the Palestinians, and we did so many things because there is a trust between us and the Israelis. That they allowed us to go and save the Palestinian people in Gaza. So there were so many challenges, but because we have the right leadership, who have the courage to make the right decision, who believe in the Abraham Accords principles, the vision, and who's working hard to transform the region. Where every everyone will enjoy security, stability, and prosperity without, you know, excluding anyone. Why the UAE didn't pull out of the Abraham Accords? My answer is this. It's not with the government, our engagement. The government will be there for two, three, four years, and they will change. Our Abraham Accords is with Israel as a nation, with the people, who will stay. Who are, we believe their root is here, and there is a history and there is a future that we have to share together. And this is where we have to work on what I call people to people diplomacy. This is sustainable peace. This is where you really build the bridges of trust, respect, partnership, and a shared responsibility about the whole region. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: On October 9, two years and two days after the start of the war between Israel and Hamas, the White House announced a ceasefire would take effect, the first step in a 20-point peace plan proposed for the region. Four days later, President Donald Trump joined the presidents of Egypt and Turkey, and the Emir of Qatar to announce a multilateral agreement to work toward a comprehensive and durable peace in Gaza. Since then, all but the remains of three hostages have been returned home, including Lt. Hadar Goldin, whose remains had been held since 2014, ending the longest hostage ordeal in Israel's history. Finally, the prospect of peace and progress seems to be re-emerging. But what is next for the Abraham Accords? Will they continue to hold and once again offer the possibilities that were promised on the White House Lawn in September 2020? Will they expand? And which countries will be next to sign on to the historic pact, setting aside decades of rejection to finally formalize full diplomatic relations with the Jewish state? The opportunities seem endless, just as they did in September 2020 when the Abraham Accords expanded the scope of what was suddenly possible in government, trade, and so much more. ANNE DREAZEN: The Abraham Accords really opened up lots of opportunities for us in the Department of Defense to really expand cooperation between Israel and its partners in the security sphere. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: Anne Dreazen spent the last 18 years as a civil servant in the U.S. Department of Defense. For most of that time, she worked on Middle East national security and defense policy, focusing on Iran, Iraq and Lebanon. And most recently serving as the principal director for Middle East policy, the senior civil service job overseeing the entire Middle East office. She was working at the Pentagon when the Abraham Accords were signed under the first Trump administration and immediately saw a shift in the region. ANNE DREAZEN: So, one thing that we saw at the very end of the first Trump administration, and it was made possible in part because of the success of the Abraham Accords, was the decision to move Israel from U.S. European Command into U.S. Central Command. And for many decades, it had been thought that that wouldn't be feasible because you wouldn't have any Middle East countries in CENTCOM that would really be willing to engage with Israel, even in very discreet minimal channels. But after the Abraham Accords, I think that led us policymakers and military leaders to sort of rethink that proposition, and it became very clear that, it would be better to increase cooperation between Israel and the other Gulf partners, because in many cases, they have similar security interests, specifically concerns about Iran and Iranian proxies and Iranian malign activity throughout the region. And so I think the Abraham Accords was one item that sort of laid the groundwork and really enabled and encouraged us to think creatively about ways through which we could, in the security and defense sphere, improve cooperation between Israel and other partners in the region. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: But sustaining peace in the region is more than a matter of maintaining security. Making sure young people can fulfill their dreams, make a contribution, build relationships and friendships across borders, and transcend religion and ideologies – even those in the security sphere know those are the necessary ingredients for peace and prosperity across the region. Despite the efforts of Hamas and other Iran-backed terror proxies to derail the Abraham Accords, the U.S., Arab, and Israeli leaders had continued to pursue plans for an Israeli-Saudi peace agreement and to explore a new security architecture to fight common threats. This spirit of optimism and determination led AJC to launch the Center for a New Middle East in June 2024. In October, Anne joined AJC to lead that initiative. ANNE DREAZEN: One thing that I have learned from my many years at the Department of Defense is that military instruments of power are not sufficient to really build long lasting peace and stability. The importance of trade, of economic development, of people-to-people ties is so essential to what we think of as an enduring or a lasting peace. And so at AJC, we're actually focused on those aspects of trying to advance normalization. Really trying to put more meat on the bones, in the case of where we already have agreements in place. So for example, with Jordan, Egypt, Bahrain, the UAE and Morocco, trying to really build out what more can be done in terms of building economic ties, building people-to-people ties, and advancing those agreements. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: Of course, that work had already begun prior to Anne's arrival. Just two years after the Abraham Accords, Retired Ambassador to Oman Marc Sievers became director of AJC Abu Dhabi: The Sidney Lerner Center for Arab-Jewish Understanding, the first and only Jewish agency office in an Arab and Islamic country. After more than 30 years as a U.S. diplomat serving across the Middle East and North Africa, Marc has witnessed a number of false starts between Arab nations and Israel. While the Abraham Accords introduced an unprecedented approach, they didn't suddenly stabilize the region. Marc's four years in Abu Dhabi have been fraught. In January 2022, Houthis in north Yemen launched a drone and missile attack on Abu Dhabi, killing three civilians and injuring six others. In 2023, the October 7 Hamas terror attack on Israel, Israel's retaliation, and Israel's war on seven fronts dimmed Emiratis' public perception of Jews. As recently as this past August, the U.S. Mission to the UAE issued a dire warning to Israeli diplomats and Jewish institutions in Abu Dhabi – a threat that was taken seriously given the kidnapping and murder of a Chabad rabbi in 2024. But just as the UAE stood by its commitment to Israel, Marc and AJC stood by their commitment to the UAE and Arab neighbors, working to advance Arab-Jewish and Muslim-Jewish dialogue; combat regional antisemitism and extremism; and invigorate Jewish life across the region. From Marc's vantage point, the Abraham Accords revolutionized the concept of normalization, inspiring a level of loyalty he's never before seen. It's worth noting the precursor to the Abraham Accords: the Peace to Prosperity Summit. For decades, diplomats had frowned on the idea of an economic peace preceding a two-state solution. MARC SIEVERS: That idea's been out there for a long time. …It was just never embraced by those who thought, you know, first you have a two-state solution. You have a Palestinian state, and then other things will follow. This approach is kind of the opposite. You create an environment in which people feel they have an incentive, they have something to gain from cooperation, and that then can lead to a different political environment. I happen to think that's quite an interesting approach, because the other approach was tried for years and years, and it didn't succeed. Rather than a confrontational approach, this is a constructive approach that everyone benefits from. The Prosperity to Peace Conference was a very important step in that direction. It was harshly criticized by a lot of people, but I think it actually was a very kind of visionary approach to changing how things are done. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: The conference Marc is referring to took place in June 2019 – a two-day workshop in Bahrain's capital city of Manama, where the Trump administration began rolling out the economic portion of its peace plan, titled "Peace to Prosperity." The workshop's host Bahrain, as well as Egypt, Jordan, Morocco, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the Emirates participated, to varying degrees. The plan called for large scale investment, mostly by other countries in the Gulf and Europe, to advance the Palestinian economy, to integrate the Palestinian and Israelis' economies and establish a small but functional Palestinian state. Angered by Trump's recognition of Jerusalem, Palestinian leadership rejected the plan before ever seeing its details. But as former U.S. Ambassador to Israel David Friedman pointed out in an earlier episode of this series, that was expected. The plan enabled Israel to demonstrate that it was open to cooperation. It enabled the Trump administration to illustrate the opportunities missed if countries in the region continued to let Palestinian leadership call the shots. It was economic diplomacy at its finest. And it worked. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: Benjamin Rogers, AJC's Director for Middle East and North Africa Initiatives, who also serves as Deputy Director of the Center for a New Middle East, said the Center has focused heavily on expanding private sector engagement. Israelis and Arab entrepreneurs have quietly traveled to the U.S. as part of the Center's budding business collectives. BENJAMIN ROGERS: So people who are focused on med tech, people who are focused on agri tech, people who are focused on tourism. And what we do is we say, 'Hey, we want to talk about the Middle East. No, we do not want to talk about violence. No, we don't want to talk about death and destruction. Not because these issues are not important, but because we're here today to talk about innovation, and we're here to talk about the next generation, and what can we do?' And when you say, like, food security for example, how can Israelis and Arabs work together in a way that helps provide more food for the entire world? That's powerful. How can the Israelis and Arabs working together with the United States help combat cancer, help find solutions to new diseases? If you really want to get at the essence of the Abraham Accords – the ability to do better and work together, to your average person on the street, that's meaningful. And so one of the initiatives is, hey, let's bring together these innovators, these business leaders, private sector, and let's showcase to Arabs, Israelis, non-Jewish community, what the Middle East can be about. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: People-to-people connections. That's what AJC has done for decades, traveling to the region since 1950 to build bridges and relationships. But providing a platform to help facilitate business ventures? That's a new strategy, which is why AJC partnered with Blue Laurel Advisors. The firm has offices in Tel Aviv, Dubai, and Washington, D.C.. It specializes in helping companies navigate the geopolitics of doing business in Saudi Arabia, UAE, Bahrain, and Israel. At AJC Global Forum in April, founder and Managing Director Tally Zingher told an audience that the Abraham Accords, which effectively lifted the UAE's ban on business with Israel, brought already existing deals above the radar. TALLY ZINGHER: We've been wowed by what the Center for a New Middle East has been able to do and put forth in the very short time that it's been incubated and Blue Laurel Advisors are really delighted to be part of this project and we're really aligned with its mission and its vision. It's quite simple in the region because the region is really driven by national agendas. I think it's no surprise that the appendix to the Abraham Accords was a direct parallel to the Abu Dhabi national vision. It's the key areas of growth in UAE and Saudi Arabia that are now really well aligned with Israeli strength. We're talking about the diversification efforts of the UAE and of Saudi Arabia. At Blue Laurel, we're quite focused on Saudi Arabia because of the real growth story underway there created by the diversification efforts. But they're focused on water, energy, renewable energy, healthy cyber security, tourism. Ten years ago when you were doing this work, 15 years ago there wasn't as much complementarity between Israel and the start-up innovation ecosystem and what was going on. The region is really ready and ripe to have Israeli innovation be a part of its growth trajectory. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: Benjy said there's another advantage to building bridges in the business world – continuity. BENJAMIN ROGERS:Out of the three sectors that we're focused on – diplomatic, business, and civil society – business relations are the most resistant to political conflict. There's this element of self interest in it, which I'm not saying is a bad thing, but when you tie the relationship to your own worth and your own value, you're much more likely to go through kind of the ebbs and flows of the political. Whereas, if you're a civil society, you're really at the mercy of populations. And if the timing is not right, it's not impossible to work together, but it's so much more difficult. Business is even more resistant than political engagement, because if political engagement is bad, the business relationship can still be good, because there's an element of self interest, and that element of we have to work together for the betterment of each other. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: The economic diplomacy complements AJC's partnership with civil society groups, other non-profits that work to bring people together to experience and embody each other's realities in the Middle East. The Center also has continued AJC's trademark traditional diplomacy to expand the circle of peace. Though Marc prefers to call it the circle of productivity. MARC SIEVERS: I think it achieved new relations for Israel that were perhaps different from what had happened with Egypt and Jordan, where we have long standing peace agreements, but very little contact between people, and very little engagement other than through very specific official channels. The Abraham Accords were different because there was a people-to-people element. The UAE in particular was flooded with Israeli tourists almost immediately after the Accords were signed, Bahrain less so, but there have been some. And not as many going the other way, but still, the human contacts were very much there. I think it was also building on this idea that economic engagement, joint partnerships, investment, build a kind of circle of productive relations that gradually hopefully expand and include broader parts of the region or the world that have been either in conflict with Israel or have refused to recognize Israel as a sovereign Jewish state. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: It being all of those things explains why the potential for expansion is all over the map. So where will the Abraham Accords likely go next? The Trump administration recently announced the addition of Kazakhstan. But as the Central Asian country already had diplomatic relations with Israel, the move was more of an endorsement of the Accords rather than an expansion. In November 2025, all eyes were on the White House when Saudi Arabia's Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman paid a visit. In addition to the customary Oval Office meeting, President Trump also hosted the Saudi royal at a black-tie dinner. ANNE DREAZEN: Right now, everyone is really talking about and thinking, of course, about Saudi Arabia, and certainly I think there's a lot of promise now with the ceasefire having been achieved. That sort of lays a better groundwork to be able to think about whether we can, whether the United States can play an important role in bringing Saudi Arabia and Israel to the table to move forward on normalization. Certainly from the Saudis have have made they've cautioned that one of their prerequisites is a viable path toward Palestinian statehood. And we've known that, that's in President Trump's 20-point plan. So I think it remains to be seen whether or not Israel and Saudi Arabia can come to a mutually agreed upon way of addressing that key concern for Saudi Arabia. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: But there are also countries who only a year ago never would have considered a relationship with Israel. With Hezbollah diminished and a moderate and forward-leaning Lebanese government in place, quiet conversations are taking place that could lead to a significant diplomatic achievement, even if not as ambitious as the Abraham Accords. The same in Syria, where Ahmed al-Sharaa is sending positive signals that he would at least be willing to consider security arrangements. ANNE DREAZEN: Even if you don't have a Syrian Embassy opening up in Jerusalem or Tel Aviv, even if you don't have an Israeli embassy opening up in Damascus, there could be other arrangements made, short of a full diplomatic peace accord that would lay the groundwork for some understandings on security, on borders. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: Marc said it remains to be seen whether Oman, his final diplomatic post, will join the Accords. Two years before the signing of the Accords, while serving as ambassador, there was a glimmer of hope. Well, more than a glimmer really. MARC SIEVERS: In Oman, the late Sultan Qaboos, a good, almost two years before the Abraham Accords, invited Prime Minister Netanyahu to visit him in his royal palace in Muscat. Netanyahu came with his wife, Sarah, but also with a lot of the top senior leadership. Certainly his military secretary, the head of the Mossad, a few other people. As soon as Netanyahu landed in Israel, the Omanis put it all over the media, and there were some wonderful videos of the Sultan giving Netanyahu a tour of the palace and a choir of children who came and sang, and some other things that the Sultan liked to do when he had important guests. And it was quite an interesting moment, and that was two years before. And that was not initiated by the United States. Unlike the Abraham Accords process, that was an Omani initiative, but again, other than the meeting itself, nothing really came of it. The Omanis took a lot of pride in what they had done, and then they backed away. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: Instead, Marc points to the country with the largest Muslim population in the world: Indonesia – especially following recent remarks to the United Nations General Assembly by Indonesia's President Prabowo Subianto. PRABOWO SUBIANTO: We must have an independent Palestine, but we must also recognize, we must also respect, and we must also guarantee the safety and security of Israel. Only then can we have real peace. Real peace and no longer hate and no longer suspicion. The only solution is the two-state solution. The descendants of Abraham must live in reconciliation, peace, and harmony. Arabs, Jews, Muslims, Christians, Hindus, Buddhists, all religions. We must live as one human family. Indonesia is committed to being part of making this vision a reality. MARC SIEVERS: We've heard that, you know, Indonesia needs some time to consider this, which makes a lot of sense. It's not something to be done lightly, and yet that would be a huge achievement. Obviously, Indonesia has never been a party to the conflict directly, but they also have never had relations with Israel, and they are the most populous Muslim country. Should that happen, it's a different kind of development than Saudi Arabia, but in some ways, it kind of internationalizes or broadens beyond the Middle East, the circle of peace. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: But in addition to adding signatories, Anne said AJC's Center for a New Middle East will work to strengthen the current relationships with countries that stayed committed during Israel's war against Hamas, despite public apprehensions. Anne recently traveled to Bahrain and the UAE with AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson, who has long led AJC's Middle East outreach. There, Anne discovered a significant slowdown in the momentum she witnessed when the Accords debuted. ANNE DREAZEN: I saw a real hesitancy during my travels in the region for politicians to publicly acknowledge and to publicly celebrate the Abraham Accords. They were much more likely to talk about peaceful coexistence and tolerance in what they characterize as a non-political way, meaning not tied to any sort of diplomatic agreements. So I saw that as a big impediment. I do think that among the leadership of a lot of these countries, though, there is a sense that they have to be more pragmatic than ever before in trying to establish, in time to sustain the ceasefire, and establish a more enduring stability in the region. So there's a bit of a disconnect, I think, between where a lot of the publics lie on this issue. But a lot of the political leaders recognize the importance of maintaining ties with Israel, and want to lay the groundwork for greater stability. We are very interested now in doing what we can as CNME, as the Center for New Middle East, to help rebuild those connections and help reinvigorate those relationships. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: This is especially the case in Bahrain, which has not seen the same economic dividends as the UAE. ANNE DREAZEN: Bahrain is a much smaller country than the UAE, and their key industries – they have less of a developed startup tech ecosystem than the UAE. And frankly, many of Bahrain's sectors don't overlap as neatly with some of Israel's emerging tech sectors, as is the case with the UAE. So, for example, Bahrain is very heavy on steel and aluminum manufacturing, on logistics. Manufacturing is a big part of the sector. Israeli tech doesn't really, in general, provide that many jobs in that type of sector. Tourism is another area where Bahrain is trying to develop as a top priority. This obviously was really challenged during the Abraham Accords, especially when direct flights stopped over Gulf air. So tourism was not a natural one, especially after October 7. Bahrain has really prioritized training their youth workforce to be able to take on jobs in IT and financial services, and this is one area we want to look into more and see what can be done. Bahrain is really prioritizing trying to build relationships in areas that can provide jobs to some of their youth. It is not as wealthy a country as the UAE, but it has a very educated young workforce. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: Again, fulfilling dreams, giving youth an opportunity to contribute. That's the necessary narrative to make the Abraham Accords a success. ALI RASHID AL NUAIMI: It's very important to focus on the youth, and how to create a narrative that will gain the heart and the mind of all youth in the region, the Israeli, the Palestinian, the Arabs, the Muslims. And this is where it is very important to counter hate that comes from both sides. Unfortunately, we still see some hate narratives that come from those far-right extremists who serve the extremists on the Arab side, taking advantage of what they are saying, what they are doing. From the beginning, I convey this message to many Israelis: please don't put the Palestinian people in one basket with Hamas, because if you do so, you will be saving Hamas. Hamas will take advantage of that. This is where it's very important to show the Palestinian people that we care about them. You know, we see them as human beings. We want a better future for them. We want to end their suffering. We want them to fulfill their dream within the region, that where everybody will feel safe, will feel respected, and that we all will live as neighbors, caring about each other's security and peace. We have to engage, have a dialogue, show others that we care about them, you see, and try to empower all those who believe in peace who believe that Israeli and Palestinian have to live together in peace and harmony. And it will take time, yes, but we don't have other options. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: But Dr. Al Nuaimi emphasizes that it can't be just a dialogue. It must be a conversation that includes the American voice. The UAE has been clear with the Israeli public on two occasions that attempts by Israel to unilaterally annex the West Bank would be a red line for the relationship between their two countries. But even as the five-year anniversary of the Abraham Accords approached, a milestone that should've been a reminder of the countries' mutual commitments, it took U.S. intervention for Israel to heed that warning. Anne Dreazen agrees that the U.S. plays an important role. She said Israel must continue to defend itself against threats. But in order to create a safe space for Israel in the long term, the U.S., the American Jewish community in particular, can help bridge connections and overcome cultural differences. That will keep the Accords moving in the right direction. ALI RASHID AL NUAIMI: I believe many Arab and Muslim leaders are eager to join it, but you know, they have to do their internal calculation within their people. We have to help them, not only us, but the Israelis. They are looking for a way, a path, to have them as neighbors, and to have a solution that the Palestinian will fulfill their dreams, but the Israeli also will be secure. I think having such a narrative that will take us to the next level by bringing other Arab countries and Muslim country to join the Abraham Accords. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: Thank you for listening. Atara Lakritz is our producer. T.K. Broderick is our sound engineer. Special thanks to Jason Isaacson, Sean Savage, and the entire AJC team for making this series possible. You can subscribe to Architects of Peace on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you listen to podcasts, and you can learn more at AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace. The views and opinions of our guests don't necessarily reflect the positions of AJC. You can reach us at podcasts@ajc.org. If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to spread the word, and hop onto Apple Podcasts or Spotify to rate us and write a review to help more listeners find us. Music Credits: Middle East : ID: 279780040; Composer: Eric Sutherland Inspired Middle East : ID: 241884108; Composer: iCENTURY Mystical Middle East : ID: 212471911; Composer: Vicher
Nov 6
Zohran Mamdani and the 2025 Elections: What It Means for Jewish Communities
From New York to California, the 2025 elections carry important implications for the Jewish community. AJC New York Director Josh Kramer addresses concerns over New York City mayor-elect Zohran Mamdani, who has questioned Israel's right to exist as a Jewish state and accused it of genocide. Kramer highlights fears over rising antisemitism in New York and outlines AJC's plan to engage the Mayor-elect on combating hate crimes while remaining vigilant against policies that could target Israel. Looking beyond New York, AJC's Director of National Political Outreach, Rebecca Klein, provides an overview of broader election results, including the victories of Democratic governors in New Jersey and Virginia, as well as the political impact of California's Proposition 50 on redistricting. She explains what these outcomes could mean for Jewish communities and national advocacy efforts. Key Resources: A Letter to Mayor-Elect Zohran Mamdani AJC's Efforts to Support the Hostages Listen – AJC Podcasts: Architects of Peace The Forgotten Exodus People of the Pod Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: The first election season since last year's presidential elections is behind us, giving New York City a new mayor, New Jersey and Virginia new governors and California a green light to redraw its map of congressional districts. We asked Rebecca Klein, AJC's Director of National Political Outreach, to explain what the 2025 election results mean for the American Jewish community. But first we wanted to hear from Josh Kramer, regional director of AJC New York, about the election of Zohran Mamdani as the 111th mayor of New York City, the largest Jewish community outside the state of Israel. Josh, if you could please tell us why that matters, why it matters that the largest Jewish community outside Israel is in New York City, and why the prospect of Mr. Mamdani at the helm of City Hall is a concern. Josh Kramer: So as you noted, New York has the largest Jewish population in the country and outside of Israel as well. Jews in New York City are scratching their heads today. They're asking themselves, how could it have come to be that a candidate has been elected to the highest office in the land who espouses views that are contrary to so much of the bulk of the mainstream Jewish population in New York City. Views that isolate and demonize and hold Israel to a double standard. This is a challenging day for many in the Jewish community. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you could rewind, for listeners who have not been following the mayoral election in New York City, because it's sometimes hard for us here in the New York metropolitan area to remember we are not the center of the world. People are more concerned with issues in their own backyard. But if you could please just kind of fill those listeners in on why Mr. Mamdani was a concern and how he expressed those views that you just spoke of being contradictory to the mainstream Jewish community. Josh Kramer: Absolutely, but I will take issue with New York not being the center of the Jewish world, of course, as the director for the AJC New York Regional Office. So I'll say that we know a lot about mayor-elect Mamdani's views on Israel from his long track record, from his statements that he's made along the campaign trail, from bills that he had proposed as a member of the state legislature. And mayor-elect Mamdani has espoused strong views in support of the BDS movement to isolate and dismantle Israel. He's called into question the Jewish nature of the world's only Jewish state, and he has had a very difficult time consistently calling out and labeling Hamas as a terrorist organization, condemning their actions of holding hostages and otherwise. So it has been a concern that these issues have been at issue during this election. But of course, we know that this election wasn't about the issues that AJC cares most about. Most people who went to the polls were voting about affordability issues or about bread and butter issues or filling potholes. Some were voting in alignment with their views on Israel. Many in the Jewish community, many who supported the mayor elect were misaligned with the candidates views on Israel. But I think most people were going to the polls based on those affordability issues. Manya Brachear Pashman: You answered my next question, which was, why did he win? And it sounds like you do not believe that it was necessarily a referendum on Israel. Josh Kramer: I think that there's been a lot of writing and a lot of discussion along the campaign trail about these issues. He has been, and other candidates have been asked about their support for the Jewish community and about what they would do to combat the rising tide of antisemitism, which has been a part of the campaign the entire time. But his non-support of the State of Israel has been a major issue in the campaign. It's just not the issue that I think that people were going to the polls and making their decisions based on. I think that there certainly were people who are motivated either by or repulsed by the now mayor-elect's views on Israel, but I don't think that it was their top issue. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you actually penned a letter to the mayor elect after his victory was announced. What did you say in that letter? What did you tell him? Josh Kramer: So AJC will work with this new mayor where we can, and that's one of the two core messages, I think, of the letter. We will work with this mayor on his pledge to quadruple, or octuple, the funding to combat hate crimes in New York City. We want to make sure that that funding is spent wisely and appropriately in the city government. We will work with him on a number of issues where we can align. Modeling, Muslim-Jewish dialog, if that is an area where we can work with the mayor elect. But the second message, and perhaps the more important message, is we will be there to speak out where we need to and understanding that this mayor elect has espoused BDS views for years now, since his days in college, and perhaps before. That we will speak out where we need to, should BDS principles be attempted by the city government as a result of those views. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned the funds that he has pledged for combating hate crimes, and I imagine that will require some input from community organizations, especially Jewish organizations, since the Jewish population is often targeted by hate crimes, do you worry that weighing in as much as you did during campaign season will harm your chances of being able to work with and and negotiate and yeah, work in harmony with this mayor. Josh Kramer: AJC did feel the need to be on record for this election. And in fact, even prior to the election, we felt we needed to be on record given some of the rhetoric we've seen from this candidate. At the same time, we have engaged with representatives of the mayor's team of the now mayor elects team, and we hope to continue that dialog, to hope to continue to work together where we can. I hope that we haven't harmed our chances to provide input to where hate crimes funding should be spent or could be spent. You're right. Hate Crimes against Jews in New York City, they differ from national statistics in that in New York City, we are the victims of the majority of hate crimes, not just the victims of the religiously motivated or just religious, religiously based hate crimes. And that means, on average, Jews in New York City are subject to hate crimes, on average, about once per day throughout the year, at least that was the case in 2024 and so we hope very much to be able to monitor and affect how this funding will be spent and make sure that it's spent appropriately in combating the majority of hate crimes, which comprise the Jewish hate crimes. In fact, there was a hate crime that took place earlier today, one of our on average, one hate crimes per day that we experience against the Jewish community in New York City, and it was a swastika spray painted on a yeshiva in Brooklyn. And just earlier today, mayor elect Mamdani tweeted out, this is a disgusting and heartbreaking act of antiSemitism. It has no place in our beautiful city, and as mayor, he will stand steadfast with our Jewish neighbors to root out the scourge of antiSemitism from our city. So it's an area of interest for us to continue to engage and to see that kind of rhetoric from our leaders is very helpful. So that's, that's what we will continue to look for and also be vigilant at the same time. Manya Brachear Pashman: In fact, do you see that as being an entree into conversations and dialog that perhaps just did not, did not happen during the campaign season, for whatever reason, sometimes campaigns can get a little heated and the rhetoric can get a little fiery to fire up the base. Do you have hope? Are you optimistic that perhaps a more rational dialog will emerge during his tenure, and that perhaps this hate crime conversation will be part of it? Josh Kramer: I do think that that can happen. It can be that strong relationships can be built out of open and very much public dialog, like the letter that was sent out, and it's happened before in New York, we've started very strong relationships with elected leaders in New York City by first starting with very public disagreements. Now that's not our typical way of advocating. Of course, our typical way is diplomatically and behind closed doors, holding very open and frank conversations, but in circumstances like these, perhaps this is the best way to start a conversation. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Josh, thank you so much for sharing your views on the mayoral election, and now we'll turn to Rebecca Klein to talk about some of the other election results from this week. Rebecca, welcome to People of the Pod. Rebecca Yoskowitz Klein: Thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So now that was one major municipal election this week. We also had smaller municipal elections across the country. There was an election in a suburb of Boston where voters voted to divest from Israel. In this Boston suburb, were there other examples of that in elections across the country, and why did this happen? Rebecca Yoskowitz Klein: So, you know, Boston has been sort of a challenge for us for some time now, and we as an organization have been addressing this. And I think this is a movement, the BDS movement, is one that we've been sort of countering for years now, and really had made a lot of progress, and it's coming back up again now you see sort of in the wake of 10/7 and in some of the concerns about the Israeli government. But I see this too as sort of these more symbolic gestures, right? And I think there is a movement out there. The Jewish community is paying attention. We are doing everything we can to counter these measures. I do think they are few and far between, and I think largely again, really, to get their messaging out there. These are sort of messaging points, but please know that we are doing everything we can to sort of quiet that noise, that these are not city issues, and we need to be sort of supportive of the Jewish community, especially now in the wake of rising antisemitism everywhere. Manya Brachear Pashman: So we'll go up from municipal elections and look at some statewide elections, some gubernatorial votes. We had Mikie Sherril win in the state of New Jersey against Republican candidate Jack Ciattarelli, and then we also had Abigail Spanberger in Virginia become governor. So two women as the head of states. What does this mean for the Jewish communities in those states and also across the country? Rebecca Yoskowitz Klein: So it's some good news, because I think both these candidates, these governors-elect have been really pro-Israel, pro-support of the Jewish community. Have loudly spoken out and shared their support. Have condemned antisemitism, and have really made it a part of their campaign, a part of their statements. I'll also just note that I think the truth is, is that whoever had won both of these elections, we were going to have a friend in the Jewish community. And this is a really important thing to note, because it sometimes can feel like there's a partisan divide between support for the Jewish community right now on Israel and antisemitism. And I'll say, when I see these races, where I look at it and I say, You know what, whoever wins, regardless of what else is going on in the background, I know that we can have lines in, we can have communication, and I feel we can have trusted partners. I'll also say that the interesting thing about, you know, we go right from the New York mayor's race to these two gubernatorial races, and you see a real shift from, you know, a very far side of the party to really moderate, centrist Democrats, both winning their primaries and now winning these elections, which I think says a lot. It's something I'm going to be looking for absolutely going into these midterms. But I do think it's very loud, and I think it's a counterbalance. For people who are concerned about the extremes of the parties, and I am too as well. Of course, I'm concerned, especially as AJC, as a nonpartisan organization that strives to be bipartisan and bring people together, that we have these now very moderate, reasonable voices leading these two very important states. Manya Brachear Pashman: And in fact, in New Jersey, AJC hosted a candidates forum, and all of the candidates had an opportunity to share their views about combating antisemitism. Correct? Rebecca Yoskowitz Klein: Absolutely, they did, and it really is a testament not to AJC and our influence, but also to the way that these candidates felt that they did need to address our issues, that they wanted to come to our forum in order to really go on the record. They felt that it was important to the population of the state of New Jersey that they had to be on the record for our issues. And absolutely, I think that's an important thing. And I'm glad to see that more and more candidates are taking these positions. They're not shying away from these positions, and they're creating important relationships within the Jewish community. Manya Brachear Pashman: And just speaking of these two candidates, Governor-elect Spanberger And Governor-elect Sherril, were they aware and alarmed by a rise of antisemitism in their states? Rebecca Yoskowitz Klein: Absolutely, and particularly some of the rhetoric so in the primary some of this antisemitism or anti-Israel rhetoric came up. And Abigail Spanberger really spoke to it. I think she spoke to it really nicely. She talked about, you know, it's okay to have differences of opinions, but ultimately, we can never cross the line into antisemitism. Mikie Sherril too really has been supportive of the IHRA working definition of antisemitism. Both really have addressed it. They understand that in a post 10/7 world, we really can't take these things for granted. And I know that both of these leaders, I think, will be good friends of the Jewish community and will absolutely be on the forefront of combating antisemitism in their states. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I'm going to move over to the west coast and talk about the election in California. I know we have some listeners in California who care about this, about Prop 50, but should people in other states across the nation be looking at California's Prop 50 and thinking about how it might affect them? Rebecca Yoskowitz Klein: Look, I think it's an important conversation. I think it's a difficult conversation, especially for us as we think about what democratic values really mean, when we talk about that as an ideal. Are these major redistricting efforts really the way we want to be thinking about our elections from now on? There are cases to be made on both sides. I think to some degree, if this is going to be the state of the future, you have to level the playing field. I think that's what California's voters said. They said, We need a level playing field. We need those extra five seats. You know, again, my concern is, where are we going to see the ripple effects of this? Now some states are absolutely backing off these redistricting efforts immediately after this election, which I probably think is maybe the better or the safer way to go. Because, again, one of the things to keep in mind is, when you create these new seats, you have to think about who are going to be the people running in these seats, whether we're talking about California or Texas. Are we now inviting people from the more extreme parts of the party to be running for these offices, and are we going to like what we get when those people win? Manya Brachear Pashman: Could you go back and explain to listeners what prop 50 is? Rebecca Yoskowitz Klein: Absolutely. So basically, prop 50 was on the ballot and California voters got to vote for it yesterday in the election. Basically it allows California to now create a new map, and it'll be with five seats that likely, I should say, will heavily favor Democrats. It will change the map of California pretty drastically in the upcoming midterm elections. Manya Brachear Pashman: And it's similar to the redistricting that happened in Texas, for example, although it wasn't as drastic a change, correct? I believe that's true, yes, but other states are redistricting as well, or at least discussing redrawing their maps. Rebecca Yoskowitz Klein: Yeah, other states are now talking about it. But like I said, I'm seeing some early sort of signs from some of these states that they may be backing off of that conversation. Again, you don't really know how it's going to play out when you do these efforts. I'll also say that it seems like the campaign to run this prop 50, it seemed a little disorganized all around and so again, if you're going to do this sort of thing, you really want to know that you're going to win it, because it can have really detrimental effects from cycle to cycle, election to election. So we'll sort of see, when we look at them, at these elections, these off-year elections, they're signals. They're signals to the major parties, they're signals to state parties, they're signals to voters. And so I think everyone's sort of now doing the analysis in just the hours after this election to see, okay, what does it mean? You know, should we be pivoting our messaging? Are we pivoting the way that we're doing things? And I think we're going to see some shuffling. And you can, again, you can already sort of see it. You'll hear it in some commentary. You'll see it on Twitter. People are a little bit, there are nerves out there. There's a lot of spin. Every party is going to sort of present their case here. But again, I think there's a lot to learn from what happened yesterday, and we're going to see these effects in the days ahead, in the weeks ahead, and absolutely in the months ahead. Manya Brachear Pashman: So where else should we be talking about? We mentioned Virginia, we mentioned New York and New Jersey and California. Were there any other elections of note? Rebecca Yoskowitz Klein: Yeah, there were some local Supreme Court races in Pennsylvania that went democratic, that could have gone either way. There was something in Maine, an absentee ballot measure that was a Republican-led measure that was voted down, and many viewed that as a way to sort of bring voter participation down. So that was considered, I'd say, a win from a democratic perspective. Manya Brachear Pashman: Wonderful, well Rebecca, thank you so much for joining us and putting this week's election in perspective. Rebecca Yoskowitz Klein: Absolutely. Thank you so much for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with former White House speechwriter Sarah Hurwitz about her new book As a Jew: Reclaiming Our Story from Those Who Blame, Shame, and Try to Erase Us.
Oct 30
Amid Blame and Shame, Reclaiming Jewish Identity with Sarah Hurwitz
"To me, that ark is: engaging deeply with our traditions. It's reclaiming some of what we lost when we were assimilating and trying to fit in. We have thousands of years of text that have such wisdom about the human condition, about how to be a good person, and lead a worthy life . . . What we can really do is, we can be Jews. And to be a Jew has always been to be different." Sarah Hurwitz—former White House speechwriter and New York Times bestselling author of Here All Along—returns to People of the Pod to discuss her new book, As a Jew: Reclaiming Our Story from Those Who Blame, Shame, and Try to Erase Us. Hurwitz reflects on why antisemitism remains, in her words, "the least mysterious phenomenon," and how Jews can reclaim pride, wisdom, and purpose through Jewish text, practice, and community. Drawing from her work as a hospital chaplain and her conversations with Jewish students on campus, she makes a powerful case for reconnecting with the depth and resilience of Jewish tradition. Key Resources: AJC's Translate Hate Glossary AJC's Efforts to Support the Hostages Listen – AJC Podcasts: Architects of Peace The Forgotten Exodus People of the Pod Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: During the Obama administration, Sarah Hurwitz served as senior speech writer for President Barack Obama and chief speech writer for First Lady Michelle Obama. But after she left the White House, she did a little bit of soul searching, and in her mid 30s, reconnected with her Judaism. She wrote about it in a book titled Here All Along, and joined us at the time to talk about it. Sarah has returned with us this week to talk about the book that followed, titled As a Jew: Reclaiming Our Story from Those Who Blame, Shame, and Try to Erase Us. Sarah, welcome back to People of the Pod. Sarah Hurwitz: Thank you so much. I'm thrilled to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So your title has a very powerful accusation. So tell us who is blaming, shaming and trying to erase us? Sarah Hurwitz: Yeah. So, you know, it's funny. My first book, as you know, was this love letter toJudaism. This, this journey of discovery of Jewish tradition, and I loved it so much, and I wanted to share it. You know, as I was writing it, I was thinking, Oh, where has this been all my life. Kind of a lovely, almost rhetorical question. But after it came out, a few things kind of happened that made me actually ask that question more seriously. Like, Wait, why did I not see any of the 4000 years of Jewish wisdom growing up? The first thing was, I trained to be a volunteer hospital chaplain, and you know, chaplaincy is multifaith, open to chaplains of all backgrounds. But you know, the training was kind of weirdly Christian. You know, we would talk about our ministry and our theology. And I was told that prayer is God, please heal so and so who's right here in front of me, and I'm just making this prayer up spontaneously, and they can hear me, and that's prayer. And everyone prays that way, I was told. I said, You know that that's not really a common form of Jewish prayer. But I was told, No, no, as long as you don't say Jesus, it is universal. That's interesting. And then something else that happened is I visited a college campus probably a year before October 7, and I was talking to students there at the Hillel, talking to a bunch of Jewish students. And one of them asked me, What did you do to respond to antisemitism when you were in college? And I was so stunned, I didn't even understand the question at first. And then I said, I didn't, not once, never. Not a single time did I deal with antisemitism. And the kids just looked kind of shocked, like they didn't believe me. And they started sharing stories of the antisemitism they were facing on campus. And I thought, uh oh, something's going on here. And then I really began kind of taking a deep dive into my identity. Of like, wait, so why did I spend my whole life being like, oh, I'm just a cultural Jew. I knew nothing about Jewish culture. Which is a beautiful way to be Jewish, being a cultural Jew, but I knew nothing about history, language, anything like that. When I said I'm an ethnic Jew, but Jews are of every ethnicity, so that's nonsense. Or I'd say social justice is my Judaism, but I didn't know anything about what Judaism said about social justice. Unlike these wonderful Jews who do know about social justice and spend their lives acting out Jewish social justice. And so I took a deep dive into history, and what I discovered was 2000 years of antisemitism and anti-Judaism and 200 years of Jews in Western Europe in a very understandable attempt to escape that persecution, kind of erasing many of our traditions. And I think that was kind of my answer to, where has this been all my life? And also my answer to, why did I have such an apologetic Jewish identity for so much of my life? Manya Brachear Pashman: In my introduction, I left off half the title of your first book because it was very long, but I am curious, kind of, when did you realize . . . well, let me give the full title of your book, it's Here All Along: Finding Meaning, Spirituality, and a Deeper Connection to Life--in Judaism (After Finally Choosing to Look There). So I guess, how was that delayed connection to Judaism, can you elaborate a little bit more about how it was tied to these forces that you just talked about? Sarah Hurwitz: Yeah, so, you know, something that I didn't really fully understand, I had intimations of this, but didn't really understand this, is that, you know, 2000 years ago, early Christianity very much defined itself against Judaism. There was actually a name for this, the Aversos Judeos tradition, which means against the Jews in Latin. And you know, early Church Fathers very much were defining Christianity against Judaism, because back then, both of these traditions had originated from Judaism. And you know they parted ways at some point, and the Church Fathers were really trying to distinguish Christianity from Judaism, and to get people to stop kind of practicing both traditions. This tradition really continues with Judaism defined as unspiritual, legalistic, depraved, dead, spiritually superseded. A lot of very, very ugly tropes that kind of have common themes that say that Jews are diabolically powerful, so supernaturally powerful, you can't even believe it. They are also profoundly depraved, evil, bloodthirsty, perverse, and they're in a conspiracy to hurt you. So there may be very few of them, but man, they are working together to really do harm. And you see these three themes kind of making their way through history, unfortunately, all the way basically, until the Holocaust. And I based a lot of my writing on the work of a number of really distinguished Christian scholars who make this argument. It's actually a pretty common argument among Christian scholars. And, you know, in recent decades, the church has very much disavowed its historic anti-Judaism and has worked very hard to, you know, fight antisemitism in the church. But, you know, these things really did kind of continue on through the 20th century. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you do describe in your book moments when you got oddly defensive about your Judaism, or perhaps a bit revisionist about Jewish history and the origin of Jewish traditions, or the reason why they exist now in modern day. Can you elaborate on some of those moments for our listeners and explain how you've self-corrected thatdefense? Sarah Hurwitz: You know, I think a lot of it took the form of, oh, I'm Jewish, but not that Jewish. It was just sort of this immediate, but I'm not one of those Jews. You know, those really Jewish Jews. Well, I'm sorry, would it be a problem if I were? What if social justice wasn't my Judaism, but Judaism was my Judaism? Would that be okay? You know, just beginning to notice, like, Why am I always kind of pushing it away, claiming that I'm not too Jewish? That's a very strange way to announce someone's identity. I think, you know, Dara Horn has actually a really, quite an amazing essay called The Cool Kids, and she talks about these two different types of antisemitism. And one is this kind of eliminationist antisemitism which says the Jews are bad, there's nothing they can do to be good. We must kill them. And you know, that is the Holocaust, pogroms. We learn about that kind of antisemitism in school. But there's another kind of antisemitism, which is conversionist, which says, yes, the Jews are bad, but there is something they can do to be okay and saved. And that is, they can disavow whatever we, the majority, find disgusting about Jewish civilization. So you know, back in the day, it was, reject Jewish religion and convert to Christianity, and you'll be saved, maybe. For some amount of time, possibly. In my parents and grandparents generation, it was, you know, reject your last name, get a nose job. Stop being so "Jewy", be a little bit more "waspy," and then maybe we'll let you into our club. Then maybe we'll accept you. And today, what you see is you have to reject your ancestral homeland, you know, reject Israel, and then you'll be okay. And, you know, I visited 27 college campuses, and I kind of saw how this sometimes takes on the format of almost like a Christian conversion narrative, where it goes something like, you know, growing up, my rabbi and my parents told me Israel was perfect and amazing and a utopia. And then I got to college, and I realized that actually it's a colonialist, Nazi, racist society, and I had an epiphany. I saw the light, and I took anti-Zionism and anti-colonialism into my heart, and now I'm saved. Now I'm a good Jew. And their classmates are like, now you're a good Jew. And as Dara Horn puts it, this kind of antisemitism involves the weaponization of shame. It involves really trying to convince Jews that there is something fundamentally shameful about some aspect of themselves, their identity, their tradition. And today, that thing is Israel. This idea that there's something fundamentally . . . it's like the original sin of the world. Manya Brachear Pashman: And you also talk about the tradition of circumcision, and how that came up, and you found yourself explaining this to someone. Can you elaborate on that for our listeners? Which I thought was really interesting. Sarah Hurwitz: This was during an encounter with a patient. I was doing a chaplaincy shift, and usually I don't tell my patients my religious background, I'm very neutral, unless they're Jewish, in which case, I do tell them I'm Jewish. But, you know, I was finishing up a conversation with this very lovely lady. And she was very curious about my background. And so I told her, you know, I'm Jewish. And her eyes kind of lit up, and she said, Oh, you know, many of my neighbors are Jewish. I've actually been to two brisses in the past month. And she just, you know, and she was so lovely, like, she actually seemed to be just really happy to be included in this tradition of her neighbors. And I got weirdly defensive, and was like, Oh, well, you know, just so, you know, medical professionals, they say whether you circumcise or don't circumcise, it's really, it's equally safe either way. And you know, we often, you know, when we do brisses, they're often done by a medical provider. And I'm going on and on and like, this woman did not say the slightest negative thing about this tradition, but suddenly I am defensive. Suddenly it's like, Huh, interesting. You know, I think that it was an illustration to me of the way that we can sometimes really imbibe all of the kind of negative views about Jews and Jewish traditions that are around us, and become defensive, and sometimes we don't even realize that they're there. It's almost like they're the air that we breathe. Manya Brachear Pashman: But let me challenge that and push back a little bit. I mean, is it okay to not agree with some of the traditions of the Jewish faith and be open about your disagreement with that? I certainly know a lot of Christians who don't like things that emerge from their tradition or from their community. Is that okay? Or is it not when Judaism is threatened? Sarah Hurwitz: So I actually do think that's okay. You know, I have no problem with that, but I think the problem in this situation was that I have no problem with circumcision, but I'm suddenly getting defensive and trying to convince this woman that it's not weird. And I'm thinking, why am I doing this? It was very interesting to me that I felt so suddenly defensive and anxious. You know, it was very surprising to me. Manya Brachear Pashman: And similarly, it's okay to criticize Israeli policy too, right? I mean, it's totally acceptable. Sarah Hurwitz: Absolutely. This is the thing that I'm so confused about. Where people are saying, well, you know, you're saying that it's not okay to criticize Israel. And I'm like, I'm sorry. Have you been to Israel? It's like the national pastime there to criticize the government. I criticize the Israeli government all the time, as do millions of American Jews. This idea that this is somehow… that we're somehow reacting to criticism of Israel, that's ridiculous. I think what we're reacting to is not criticism of Israel, but it's something else. You know, when you have students on a college campus saying from water to water, Palestine should be Arab, or Israelis are Nazis. I just, with all due respect, I don't see that as criticism. Nor would I see it as criticism if, God forbid, a Jewish student ever said from water to water, Israel should be Jewish, or, Palestinians are terrorists. That is hateful, disgusting, racist, eliminationist language. And if I ever heard a Jewish student say that, I mean, let me tell you, I would have quite a talking to with that kid. So that's not criticism. Criticism is, I am vehemently opposed and abhor, this policy, this ideology, this action, for these reasons. That's criticism. And I think you can use real strong language to do that kind of criticism. But there's a difference between a criticism and slurs and baseless accusations. And I think we need to be just clear about that. Manya Brachear Pashman: All right, so you just use the term from water to water instead of from river to sea. Was that on purpose? Sarah Hurwitz: Not necessarily. It's just a clearer illustration of what I think from the river to the sea really means, you know, I think that is the Arabic that is used. Infrom the river to the sea, Palestine shall be free. It's like, you can kind of make an argument that this is about Palestinian Liberation. And okay, fair enough. But I think when you get the from water to water, it shall be Arab, that's when I think there's less of an argument that it's about freedom, and it seems a little bit more eliminationist to me. Manya Brachear Pashman: Interesting. I've not heard that before. But I like that. So you call antisemitism the least mysterious phenomenon. Can you please explain what you mean by that? Sarah Hurwitz: Yeah, you know, I think, like a lot of young people, my antisemitism education was mainly just Holocaust education. And I kind of walked away thinking like, huh, how wild that the civilized world just lost its mind in the mid-20th century and started killing Jews. That's so shocking and disturbing, you know, why is that? And the answer was kind of like, well, you know, the Germans lost World War I. They blamed the Jews. There was a depression. They blamed the Jews. And when you ask why the Jews, it's like, well, because of prejudice and scapegoating. I'm like, Okay, right. But again, why the Jews? Prejudice and scapegoating, that's the answer. It's like, well, actually, the answer really is because of 2000 years of Christian anti-Judaism that preceded that. It wasn't mysterious why the Jews were targeted. This was a 2000-year neural groove that had been worn into the Western world psyche. And this is not my argument. This is the argument of countless Christian scholars whose brilliant work I cite. And so I think that the unfortunate thing about some forms of Holocaust education is that it leaves you with the impression that, oh, this is so mysterious, it's just kind of eternal and kind of comes out of nowhere. Or even worse, you might even think maybe we did something to deserve this. But it's not mysterious. I can show you its path through history. And I think it's very important that Jews understand this history. And look, I think this is very hard to teach in an average American public school. Because, you know, we live in a country where, you know, saying Happy Holidays instead of Merry Christmas is very upsetting for some people. They feel very threatened and triggered by that. So for a teacher to say, like, Okay, kids today we're going to learn about how 2000 years of Christian anti-Judaism paved the way for the Holocaust . . . I don't think that's going to go well. Even if many mainstream Christian scholars would agree that that's true, this is a challenge that we face. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you have continued, as you said, to visit college campuses where antisemitism has been an issue since October 7, more of an issue than it even was beforehand. And yet, when you were at Harvard and Harvard Law, you've said you could have walked through Harvard Yard wrapped in an Israeli flag and no one would have said a word or reacted negatively. So what has changed, and does it signal a more general shift on campuses of kind of uncensored, unbridled speech? In other words, if black students support black lives matter, or gay students are marching for pride, do you feel like there's a sense that students who disagree with that from either the right or the left, have kind of claimed a license to criticize that too? Sarah Hurwitz: No. I try to explain to college students when they say, Well, okay, my campus isn't that bad, you know, I can wear my Jewish star, and I won't get, you know, harassed or ostracized. And I say, like, okay, great, if it's not that bad, I'll just wear my Israel t-shirt and we'll see how it goes. They're like, No. And then I have to go through this long litany of like, okay, if your black classmate said to you, well, this campus isn't so bad for black students, but I can't wear my Black Lives Matter t-shirt or else I'll be harassed and ostracized. I hope you would say that's not okay, that's racism, pretty clear. Or if your queer classmate said, Well, this campus is pretty good for queer people, but I can't wear my pride t-shirt, I hope you would say, That's not pretty good. That's homophobia. You know, when the majority feels entitled to decide how the minority can embody and express their identity, I think we have a really serious problem. And sometimes the kids will push back on me. Well, no, no, but the problem isn't being Jewish. It's Israel. I'm like, okay, but if your Chinese American classmate wore a t-shirt that said China, even if all your classmates knew that the Chinese government had been interning a million Muslim Uighurs in camps and subjecting them to horrific human rights violations, would they harass and ostracize her? And they're like, Well, probably not. Right, because they would assume that she has a relationship to China that maybe involves having heritage there, or maybe she studied abroad there, or maybe she's studying Chinese, maybe she has family there. I think they would assume that she has some connection to the country that doesn't involve agreeing with the policies of the Chinese government, and Jewish students on campus really aren't afforded that courtesy. And I'll tell you, most of the Jewish students I spoke with on campus, they, like me, are extremely critical of this current Israeli government. Extremely, extremely critical. They have all sorts of criticisms about what's happening in Gaza, of the occupation. You know, their views are quite nuanced and complex, but there is no room given for that. You know, I think on some college campuses, Israel has been put into the same bucket as the KKK and the Nazi party. So I can't say to you, look, you know, I'm a Nazi, but I'm a liberal Nazi. Or, oh, you know, I'm in the KKK, but I'm not racist. It's like, come on, right? These are vile entities with which no connection is acceptable, period. And I think once Israel ceases to be a country and instead becomes the representation of all evil in the world, there's really no relationship that you can have with it that's acceptable. And I think that is a pretty devastating place for it to be today. And I'll tell you, I think it's a really challenging moment right now where I, like a lot of American Jews, I'm a Zionist. I believe that Jews have a right to a safe and secure home state in their ancestral homeland. I believe we have the right to national independence and self determination, like Japanese people have in Japan and Latvians have in Latvia, and on and on. And you know, we've run that experiment of Jewish powerlessness for 2000 years, and it didn't go well. Even as late as the 20th century. It wasn't just that two thirds of Jews in Europe got wiped out because of the Holocaust. It's that nearly a million Jews who lived in Arab lands had to flee persecution, most of them to Israel. It's that 2 million Russian Jews had to flee persecution, half of them to Israel. It's that 10s of 1000s of Ethiopian Jews, I can go on and on. So we know, we've run that experiment of Jewish statelessness, and it doesn't go well. And at the same time, we are looking at this current Israeli government, and we are appalled. We're appalled by the ideology, we're appalled by many of the policies. And you know, for me as an American, this feels very familiar, because I love this country. I'm a proud, patriotic American, and I happen to very much disagree with the current president. I happen to be very much appalled by the current president's policies and ideology. And so, I think many people are able to hold that, but somehow it's harder with Israel, because of what is in the air right now. Manya Brachear Pashman: So, really you're saying that antisemitism has distorted history. Distorted people's understanding of Israel's history, their understanding of modern Israel's rebirth and existence. It spawned anti-Zionism. Correct? Sarah Hurwitz: Yes. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did you encounter that during your time in the Obama administration? Do you see it now, in hindsight or or is it a more recent emergence? Sarah Hurwitz: I think this is more recent. I mean, you know, probably in some spaces it was, you know, I was in the administration from 2009 to 2017. I never once saw any kind of anti-Zionism or antisemitism. I mean, it was one of the best places to be a proud, passionate Jew. I knew my colleagues could not have been more supportive of my Jewish exploration. They were so proud when I wrote my first book. So I never saw any of this ever, once. And I think, you know, I think what is so confusing about this is that we often think about antisemitism as a kind of personal prejudice, like, oh, you know, Jews are fill in the blank, nasty thing. They are dirty, cheap, crass. I don't want my daughter to marry one. I don't want one in my country club. You don't really see that kind of antisemitism in the circles where I travel anymore. What you see instead is more of political antisemitism, which is antisemitism as a kind of conspiracy theory that says that we, the majority, are engaged in a grand moral project, and the only thing stopping us are these Jews. We the majority are Christianizing the Roman Empire. The only thing stopping us, these Jews who won't convert. We the majority are bringing about the brotherhood of man, the great communist revolution. The only thing stopping us, these capitalist Jews. We the Germans, are bringing about the great, racially pure Aryan fatherland. The only thing stopping us – these race-polluting Jews. And today in America, you see it on the right and the left. On the right, it's, you know, we white Christian Americans are bringing back white Christian civilization to America. And the only thing stopping us are these Jews who are importing black and brown immigrants to replace white people. That is the extremely racist and antisemitic theory known as the Great Replacement theory. It is an ugly, disgusting lie. On the left you have, you know, we this very moral group of people. we are bringing about the revolution of anti-colonialism, anti-Zionism. And the only thing stopping us are these colonialist Zionists, which is a polite way of saying Jews. And so, you know, I think it's very important to understand, as Yossi Klein Halevi, the journalist, puts it, you know, what you see again and again is whatever is the worst thing in a society, that is what the Jews are deemed to be. Whatever is the worst thing among a particular population, that is what the Jews are deemed to be. And I think we're kind of seeing that on both the right and the left today. Manya Brachear Pashman: If antisemitism defines so much, or has defined so much of Jewish identity, how do we reclaim that? How have you reclaimed that? And how have you found joy in your Jewish identity, especially after doing this book and immersing yourself and all of this extremely depressing perspective? Sarah Hurwitz: I hear this kind of line among many Jews that breaks my heart. It's this sort of self-flagellation, of like, if we just had the right PR campaign, if we just had the right tweet, then we would fight antisemitism. It's our fault, we're doing such a bad job fighting antisemitism. And, you know, I love the ambition there. I think that is so sweet. But there are 16 million of us in the whole world. That's with an M, million, like the size of like, the fifth largest city in China. We are a Chinese city. There are billions of people who don't really love us out there. And the idea that we, this tiny group of people, is going to somehow change the minds of billions of people. I really respect the ambition, but I think that's a tough one. I think it's sort of like trying to bail out a tsunami with buckets. You know, if enough of us do it, I'm sure we can make a difference. And I have such respect for the people who are doing that work. I think it's very important. But I also would just suggest that maybe we should put a little more of our energy into building an ark to weather the storm. And you know, to me, that ark is, engaging deeply with our traditions. It's reclaiming, I think, some of what we lost when we were assimilating and trying to fit in. You know, we have thousands of years of text that have such wisdom about the human condition, about how to be a good person and lead a worthy life and find profound spiritual connection. We have just so many beautiful traditions. And so I think that what we can really do is, we can be Jews. And to be a Jew has always been to be different. That was kind of our value proposition thousands of years ago when we came along and said, hey guys, monotheism. Totally different way of thinking. We said, hey, every human being is created in the image of God, which is an idea that every human being is infinitely worthy. Which, again, this is the idea that underlies things like liberalism, democracy, human rights. These are really Earth-shatteringly different counter cultural ideas, and we have so many more of those that I still think the world needs today. So I think that rather than just being anti-anti-semites, that we can be proud Jews instead, and we can really focus on becoming more learned, more vibrant members of our communities, you know, engaging in more of our traditions and our rituals. I also think, you know, Dara Horn has been doing a lot of great work about educating kids about Jewish civilization. Rather than having young people only know about the Jews via the Holocaust, she really wants to teach young people about Jewish civilization, ideas, and people. I think that is a very, very powerful and very helpful idea. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how are you doing this? How do you spend each week? How do you reclaim some of these traditions and joy? Sarah Hurwitz: For me, it's studying. That's really how I engage, you know, I have various chavrutas or I study Jewish texts. I love reading Jewish books, and I love participating in the Jewish community. You know, I love engaging with various Jewish organizations, you know, serving on various committees, and just trying to be part of this project of reclaiming Judaism, of making it more accessible to more Jews. This is what I love doing, and I'll be starting in January. I'm actually going to be starting a rabbinic program at the Hartman Institute. It's a part time program. And I'm not not planning to be a congregational rabbi, but I do want to keep writing books, and I am really grateful for this opportunity to get a much deeper, more thorough Jewish education than the one I've kind of given to myself, and, you know, kind of cobbled together. I think this is going to be a really extraordinary opportunity. So I'm very excited about that. Manya Brachear Pashman: Oh, wow. Well, congratulations. I look forward to welcoming you back to the podcast and calling you Rabbi. Sarah Hurwitz: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much for joining us, Sarah. Sarah Hurwitz: Such a pleasure. Thank you for having me.
Oct 23
How the War with Hamas Has Impacted the Israeli Economy
How did the Israeli economy react to the war against Hamas? Hear from a major player on the ground – Dr. Eugene Kandel, former economic adviser and Chairman of the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange, discusses Israel's financial resilience after the war against Hamas. Having made aliyah from the Soviet Union in 1977 with his family, Dr. Kandel covers the stock market rebound, missed economic opportunities with Jordan and Egypt, and the success of the Abraham Accords. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Take Action: Elected Leaders: Demand Hamas Release the Hostages Key Resources: AJC's Efforts to Support the Hostages Listen – AJC Podcasts: Architects of Peace The Forgotten Exodus People of the Pod Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: Professor Eugene Kandel served as economic adviser to the Prime Minister of Israel from 2009 to 2015, and with Ron Sor is a co-founder of Israel's Strategic Futures Institute. He is also chairman of the Tel Aviv stock exchange, the only public stock exchange in Israel, known locally as the Bursa. He is with us now to talk about the impact of Israel's war against Hamas in Gaza on Israel's economy, the potential and impact so far of the Abraham Accords, and how history could one day view October 7 as a turning point for Israel's democracy. Dr. Kandel, welcome to People of the Pod. Eugene Kandel: Thank you. Thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: Before we begin, your family came to Israel in 1977. Can you share your family's Aliyah story? Eugene Kandel: Yeah, when I was 14, my family was living very comfortably in the Soviet Union. My father was a quite known writer, playwright, a script writer. And around him was a group of Jewish people of culture that were quite known in their domains, mostly Jewish. And so at some point in 67 he sort of had this vision and started studying Hebrew. But 1970 and then by '73 when I was 14 years old, he came to me and said, Look, your mom and I decided to immigrate to Israel. What do you think about it, and I said, I don't know what I think about it. Okay, you know, if we want to immigrate, let's immigrate. I never felt too much belonging there. So unfortunately, Soviet authorities had other ideas about that. So we spent four years as refuseniks. My father, together with Benjamin Fine, were the editors of the underground publication called Tarbut. And for people who did not live there, they put their names on it. So this was, these were typewritten copies of Jewish culture monthly. And there were two names on it. You could go to jail for this. My father was always pretty brave man for his petite size, because during the Second World War, he was very, very hungry, to say the least. So he didn't really grow very much. But he's very big inside. And so the following four years were pretty tough on them, because he couldn't work anywhere. Just like in McCarty years in this country, people would give work to their friends and then publish it under their own name. That's what he did for his friends, and they would share the money with him, or give him most of the money. There were very, very brave people. And then, you know, there was an incident where they wanted to send a message to my father to be a little less publicly outspoken. And so two KGB agents beat me up. And that started a whole interesting set of events, because there was an organization in Chicago called Chicago Action for Soviet Jewry. Pamela Cohen. And I actually met Pamela when I was studying at the University of Chicago. And thanked her. So they took upon themselves to harass Soviet cinema and theater and culture officials. And so they were so successful that at some point, the writers league from Hollywood said that nobody will go to Moscow Film Festival unless they release us because they do not want to associate with people who beat up children. I wasn't a child, I was 17 years old, but still. And that sort of helped. At least, that's how we think about it. So it's worthwhile being beaten up once in a while, because if it lets you out, I would take it another time. And then we came to Israel in a very interesting time. We came to Israel four hours after Anwar Sadat left. So we came to a different Israel. On the brink of a peace agreement with Egypt. And so that was it. We came to Mevaseret Zion, which was an absorption center. A small absorption center. Today I actually live probably 500 yards from where we stayed. Sort of full circle. And today, it's a significant, it's about 25,000 people town. And that's the story, you know, in the middle, in between then and now, I served in the military, did two degrees at Hebrew University, did two degrees at the University of Chicago, served as professor at the University of Rochester, and then for 28 years, served as professor of economics and finance at the Hebrew University. So I keep doing these circles to places where I started. Manya Brachear Pashman: You say you arrived four hours after Sadat's visit to Israel on the brink of a peace agreement with Egypt. Did that peace agreement live up to expectations? Eugene Kandel: Well, it depends what are your expectations. If your expectation will continue in the war, it definitely did, because, you know, for the last, you know, whatever, 48 years, we didn't have any military activity between Israel and Egypt. And we even have security collaboration to some extent. But if you're thinking about real peace, that would translate into people to people peace, business to business peace, it did not generate that at all. Because there was a very, very strong opposition on the street level and on the intellectuals level. It actually started to break a little bit, because today you can find analysts on Egyptian television that are saying that we are, we are stupid because we don't collaborate with Israel. It is allowed today, It's allowed to be said in, you know, 20-30, years [ago], that person would have been ostracized and would never be allowed to speak. So there is some progress, but unfortunately, it's a huge loss for the Egyptian economy. For Israeli economy, it is probably also a loss, but Israeli economy has a lot of alternatives in other countries. But Egyptians don't seem to be able to implement all the things that Israelis implemented a long time ago. You know, whether it's water technologies, whether it's energy technologies. Lots of lots of stuff, and it's really, really unfortunate that we could have helped Egyptian people, the same people who rejected any relations with us. And that's a pity. Manya Brachear Pashman: The next peace agreement that came was with Jordan in 1994, quite some time later. Did that peace agreement live up to expectations, and where were you in 1994? Eugene Kandel: 1994, I was a professor at the University of Rochester, so I wasn't involved at all. But again, it was a very, very similar story. It was the peace that was sort of forced from above. It was clearly imposed on the people despite their objections, and you saw demonstrations, and you still see. But it was clear to the leadership of Jordan that Israel is, in their case, is absolutely essential for the survival of the Hashemite Dynasty. In the end the Israeli intelligence saved that dynasty, many, many times. But again, it wasn't translated into anything economic, almost anything economic, until in the early 2000s there were some plants in Jordan by Israeli businessmen that were providing jobs, etc. But I was privileged to be the first to go to Jordan together with American officials and negotiate the beginning of the gas agreement. We were selling gas to Jordan, because Jordan was basically going bankrupt because of the high energy costs. Jordan doesn't have its own energy, apart from oil shale. Sorry, shale oil. And for some reason they weren't able to develop that. But Israeli gas that we are selling to them as a result of what we started in 2012 I believe. Actually very important for the Jordanian economy. And if we can continue that, then maybe connect our electrical grid, which is now in the works, between the water-energy system. And now maybe there is a possibility to connect the Syrian grid. If we have an agreement with Syria, it will help tremendously these countries to get economic development much faster. And it will help Israel as well, to balance its energy needs and to maybe get energy, provide energy, you know, get electricity, provide gas. You know, there's all these things where we can do a lot of things together. If there is a will on the other side. There's definitely will on the Israeli side. Manya Brachear Pashman: In addition to gas, there's also water desalination agreements, as well, right? Eugene Kandel: Yeah, there was a Red to Dead project, which was to pump the water all the way from the Red Sea along the Arava Valley. And then there is a 400 meter, 500 meter drop. And so to generate electricity through that desalinate that water that you pump, and then send that water to Egypt, send the electricity that was generated and not needed to Israel and then dump this salt stuff into the Dead Sea. Frankly, I don't know where this project is. Nobody talks about it for the last seven, eight years. I haven't heard. Now there are different projects where you would get energy generated in Jordan and sold to Israel in Eilat, for example, because it's difficult for us to bring electricity all the way South. And so if the Jordanians have large fields of photovoltaic energy they can sell, they can satisfy the needs of a lot, and then in return, we can desalinate water and send it to them. So there's all kinds of projects that are being discussed. Manya Brachear Pashman: But Israel does provide water to Jordan, correct? Eugene Kandel: There are two agreements. One agreement, according to our peace agreement, we are supposed to provide them with a certain amount of water. I don't remember the exact amount. But that's not enough, and so we also sell them water. So think about it. There is a sweet water reservoir called Tiberius, Kinneret, in the north, and we sending water from there into two directions according to the agreement. We're sending it to Amman, pumping it up to the mountains, and then we're sending it throughout the Jordan Valley, all the way along the Jordan River, to the Jordanian side. So it's quite striking when I used to go between Jerusalem and Amman, it's actually an hour and a half drive. That's it. You go down, you go up, and you're there. And so when you're passing the Israeli side, you see the plantations of date palms that are irrigated with drip irrigation. So very, very economically, using the brackish salt water that is pumped out of the ground there. You cross two miles further, you see banana plantations that are flood irrigated at 50-centigrade weather, and the water that comes from them comes on an open canal. So basically, 50% of the water that we send this way evaporates. Growing bananas in that climate and using so much water, it's probably, if you take into account the true cost of water, it's probably money losing proposition, but they're getting the water. The people that are the settlements on that Bank of Jordan River, are getting it for free. They don't care. And if somebody would just internalize that, and instead of sending the water down in an open canal, would send the whole water up to Amman, where there is a shortage of water, enormous shortage of water. And then you would take the gravity and use that water to generate electricity, to clean that water, the sewage, clean it and drip irrigate plantations, everybody would make enormous amounts of money. Literally enormous amounts of money. And everybody's lives would be better, okay? And I'm not talking about Israelis. It's within Jordan. And you can't say that there's no technology for that, because the technology is two miles away. You can see it. And it just puzzles me. Why wouldn't that be done by some entrepreneurs, Jordanian entrepreneurs. We could really help with that. We could even help by buying the water from them back. The water that we give them, we can buy it back. Because in Israel, the water is very expensive. So we could finance that whole thing just by sending the water back, but that would be probably politically unacceptable, I don't know. But it's really, really . . . for an economist, it's just a sad story. Manya Brachear Pashman: Missed opportunities. Well, let's go back. I introduced you as the chair of the Tel Aviv stock exchange, the Bursa. And I am curious. Let's talk about the economy. Does Israel treat its stock market the same way we do? In other words, are there opening and closing bells at the beginning and end of every day? How does the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange work compared to the United States? Eugene Kandel: Well, we do have the opening bell, but it's usually reserved for some events. We don't have the events every day. Usually, if there's a new listing, or there's somebody celebrating, like, 20 years of listing, we have all kinds. Recently, we had Mr. Bill Ackman came and gave a speech and opened the trading together with us. There are events around Jeffries Conference. But it's much more, you know, ceremony, I mean, it's not really connected to anything. Trading starts whether you press the button or don't. But Israeli stock exchange is unique in the following sense: it is an open limit book. What means that there is, you know, buyers meet sellers directly, and it works like that, not only in stocks, which is similar to what it is everywhere, but it's also in bonds, government bonds, corporate bonds, and in derivatives. So in that sense, we do have our ceremonies, but the interesting thing is, what is happening with the exchange in the last two years. Accidentally, I joined two years ago as the chairman, and over the last two years, the stock exchange, the indices of Israeli Stock Exchange were the best performing out of all developed countries, by far. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did that have something to do with the war? Eugene Kandel: Well, it should have been, you know, in the opposite direction, but, the war is, not this length of war, not this intensity of war . . . but if you look back over at least 25 years, the Israeli economy responds very robustly to military conflict. Usually they're much shorter. If you look at even quarterly returns of the stock exchange, you would not know that there was a war in the middle, definitely not annual. If you look over the last 25 years, and you look at this stock, annual returns of the indices, you would not know that there was anything wrong, apart from our 2003 crisis, and Corona. Even the great financial crisis, you would not see it. I mean it was basically past us, because we didn't have a financial crisis in Israel. We had repercussions from, you know, the rest of the world's financial crisis, but we didn't get our own. And so we do have resilience built in, because we're just so used to it. However, having said that, it's the first time that we have such a long and intensive war on seven, whatever fronts. So it is quite surprising that just like any other time, it took about three months for the stock market to rebound after October 8. It was a big question whether to open the market on October 8. We struggled with it, and we decided that we do not want to give anybody the right to disrupt the Israeli economy. I mean, it was a really tough decision, because there was certain people were saying, Well, how can you do that? It's a national tragedy. And of course, it was a national tragedy. But closing the market would have meant two things. First of all, it would have shown the world that our economy can be interrupted. It would have given the benefit to those people that did these atrocities, that they managed to do more damage than they already did. And we didn't want to do that. And it didn't collapse. It went down, of course, but it rebounded within less than three months. By the end of that year, it was back on the same level. And then it did this comeback, which was quite phenomenal. And it's an interesting question, how come? Because during that time, we had some cases where Israel was boycotted by investors, very few, by the way, but we also saw many, many new investors coming in. You could look at the war from the negative side. Of course, huge costs. But with all that, it was about 10% of annual GDP, because we are, you know, we're a big economy, and we borrowed that very easily because we had a very strong macro position before that. So we now 76% debt to GDP ratio. It's much lower than majority of developed countries. But we still had to borrow that. It was a lot of money, and then the defense budget is going to go up. So there is this cost. But vis a vis that, A, Israeli technology has been proven to be unmatched, apart from maybe us technology in certain cases, but in some cases, even there, we have something to share. And so we have huge amounts of back orders for our defense industries. During the war, and they were going up when some of the countries that are making these purchases were criticizing us. They were learning from what we did, and buying, buying our equipment and software, etc. And the second thing, we removed the huge security threat. If you look before October 7, we were quite concerned about 150,000 missiles, some of them precise missiles in Hezbollah's hands, an uninterrupted path from Iran through Syria to Hezbollah, constantly replenishing. We would bomb them sometimes in Syria, but we didn't catch all of them. We had Hamas, we had Hezbollah, we had Syrians, we had Iranians. We had, you know, not, you know, Iraqi militia. So, Hezbollah doesn't exist. Well, it exists, but it's nowhere near where it where was at. And the Lebanese Government is seriously attempting to disarm it. Syria, we all know what happened in Syria. We didn't lift a finger to do that. But indirectly, from what happened in Hezbollah, the rebels in Syria became emboldened and did what they did. We know what happened with Hamas. We know what happened with Iran. Okay, Iran, even Europeans reimposed the sanctions. So that's the side effect. So if you look at the Israeli geopolitical and security situation, it's much, much better. And in that situation, once the war is over and the hostages are returned, and hopefully, we will not let this happen again, ever, to work hard so we remember that and not become complacent. It's an enormous, enormous boost to Israeli economy, because this security premium was quite big. So that is on the positive side, and if we play smart, and we play strategically, and we regain sort of good relations with some of the countries which are currently very critical of us, and somehow make them immune to this anti Israeli antisemitism propaganda, we can really get going. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned investors. There were more investors after the war. Where were those investors coming from, internally or from other countries? Eugene Kandel: It's interesting that you asked this question, because in 2020, early 2024 a lot of Israeli institutions and individuals moved to S&P 500, and they got really hammered. Twice. Because A, S&P 500 was lagging behind the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange. So there was some other players coming in, because otherwise, when you move money, usually, you should see a drop, but you saw an increase. That meant that there are others came in. But the more interesting thing is that shekel was very weak when they bought dollars, and now shekel is about 15% stronger, so they lost 15% just on the exchange rate. And so a lot of money that went to S&P came back in the last six, eight months. So the internal money came back. But on top of internal money, we looked at the behavior of foreign investors right after October 7. They didn't flee the country. Some of them sold stocks, bought bonds. And then so Israeli institutions made money on that, because Israeli institutions bought stocks from them at about 10%, 15% discount, and then when it rebounded, they made money. But that money didn't leave, it stayed in Israel, and it was very costly to repatriate it, because the shekel was very weak. And so buying dollars back was expensive. And the money slowly went into stocks. And then people made quite a lot of money on this. Manya Brachear Pashman: The last topic I want to cover with you is external relations. You mentioned Syria, the potential of collaborating with Syria for water, gas. Eugene Kandel: Electricity. Manya Brachear Pashman: Electricity. And I presume that you're referring to the possibility of Syria being one of the next members to join the Abraham Accords. That has been mentioned as a possibility. Eugene Kandel: Maybe. But we can, we can do something much less. Manya Brachear Pashman: Outside of the Accords. Eugene Kandel: Outside of the Accords, or pre-Accord, or we can, we can just create some kind of collaboration, just we had, like as we had with UAE for for 15 years before the Accord was signed. Was a clear understanding. Maybe. But we can, we can do something much less outside of the Accord, or pre-Accord, or we can, we can just create some kind of collaboration, just we had, like as we had with UAE for for 15 years before the Accord was signed. Was a clear understanding. You know, I was in UAE, in Dubai on the day of signing of the Accord. I landed in Dubai when they were signing on the on the green loan, on the White House lawn. And we landed. It was amazing. It was the degree of warmth that we received from everybody, from ministers in the economy to ministers that came to speak to us, by the dozen to people in the hotel that were just meeting us. They issued, for example, before signing the Accord, there was a regulation passed by by UAE that every hotel has to have kosher food. We don't have that in Israel. I mean, hotels mostly have kosher food, but not all of them, and, and it's not by law. This was, like, clear, we want these people to feel comfortable. It was truly amazing. I've never, I could never imagine that I would come to a country where we didn't have any relations until today, and suddenly feel very, very welcome. On every level, on the street, in restaurants. And that was quite amazing, and that was the result of us collaborating below the surface for many, many years. Manya Brachear Pashman: Parity of esteem, yes? Suddenly. Eugene Kandel: Yeah, they didn't feel they did exactly the important part when the UAE businessman or or Ambassador order you feel completely no chip on the shoulder whatsoever. They feel very proud of their heritage. They feel very proud of their achievements. They feel and you feel at the same level. They feel at the same level, just like you would with the Europeans. We always felt that there was something like when, when, Arab delegations, always tension. I don't know whether it was superiority or inferiority. I don't know. It doesn't matter, but it was always tension in here. I didn't feel any tension. Was like, want to do business, we want to learn from you, and you'll to learn from us. And it was just wow. Manya Brachear Pashman: Same in Bahrain and Morocco? Eugene Kandel: I haven't been to Bahrain and Morocco. I think Bahrain wants to do business. They were very even, sort of some of, we sent the delegation to Bahrain to talk about sort of Israeli technology and how to build an ecosystem in the same with Morocco. I think it's a bit different. I think it's a bit different because we didn't see much going on from from these two countries. Although Morocco is more advancing much faster than Bahrain. There are a lot of interesting proposals coming out of it. There's a genuine desire there. In the last two years, of course, it was difficult for for anybody to do anything in those but interestingly, when almost no European airlines or American airlines were flying to us, Etihad and Emirates were flying to Israel. They were flying. Manya Brachear Pashman: Past two years? Eugene Kandel: Yeah, they would not stop. And you're just like, wow. Manya Brachear Pashman: So would you say the Abraham Accords have had a significant impact on Israel's economy at all? Eugene Kandel: I do not know. I mean, I don't have data on that by the sheer number. I mean, the the number of Israeli tourists Sue UAE, it's probably 10 or 20 to one to the vice versa. So we've been Israelis flooding UAE. In terms of investments, there are some technology investments. There's some, some more infrastructural investors, like they bought 20% of our gas field. There are collaborations between universities and research centers. So it's hard to measure, but you have to remember that there was a huge amount of trade and collaboration under the surface. So it surfaced. But that doesn't mean that there was an effect on the economy, just people suddenly saw it. So you don't know what the Delta was. If the same amount of business was suddenly coming out of Jordan, we would have seen, you know, big surge. So I'm not sure how much . . . I don't mean to say that there was no impact. I'm just saying that the impact was much more gradual, because there was so much already, right? But I'm sure that it is continuing, and the fact that these airlines were continuing to fly, indicates that there is a demand, and there's a business. Initially a lot of Israelis thought that there was, this was a money bag, and they would go there and try to raise money and not understanding culture, not understanding. That period is over. I mean, the Emiratis conveyed pretty clearly that they not. They're very sophisticated investors. They know how to evaluate so they do when they make investments, these investments make sense, rather than just because you wanted to get some money from somebody. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, thank you so much. Eugene Kandel: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed our last episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with AJC's Director of Congressional Affairs Jessica Bernton. We spoke shortly after receiving the news that a deal had been reached and the hostages from the October 7 Hamas terror attack might finally come home after two years in captivity. That dream was partially realized last week when all the living hostages returned and the wait began for those who were murdered.
Oct 10
Inside the Advocacy Effort to Bring the Hostages Home
"Since before he was President, he [Trump] has made it clear that this is a priority, and he has instructed his team to work on this issue day in and day out . . . " More than two years after the October 7 massacre, Hamas has agreed to return the 48 hostages still in Gaza under the U.S.-brokered peace deal. Jessica Bernton, AJC's Director of Congressional Affairs, shares details of AJC's joint advocacy with the hostage families of returned hostages—how personal stories, bipartisan meetings with Congress and the White House, and coordinated delegations kept the issue at the forefront. She reflects on the emotional weight of this work, its impact on the U.S. administration, and the ongoing need to press policymakers to ensure that all hostages are safely returned. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Take Action: Elected Leaders: Demand Hamas Release the Hostages Key Resources: AJC's Efforts to Support the Hostages Listen – AJC Podcasts: Architects of Peace The Forgotten Exodus People of the Pod Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: More than two years after the October 7 massacre, the Hamas terror group has reportedly agreed at long last, to return the 48 hostages that remain in Gaza. With us now is Jessica Bernton, AJC's director of Congressional Affairs, who has been working with the families of hostages since day one to bring them all home. Jessica, welcome to People of the Pod. Jessica Bernton: Thanks so much, Manya, it's a pleasure to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you must be so relieved. I know you've been so immersed in all of this. When can we celebrate though? Is now too soon? Jessica Bernton: Oh, what a great question. I would say, I have this cautious optimism at the moment. There have been many ups and downs. There have been starts and stops throughout these long months and now two years, but this one does feel different. I would say, you know, this is the most progress we've seen since the spring, and we have to continue to have hope. We also cannot afford to let up the pressure until every single hostage is returned home. And so I would say we cannot exhale until everyone is returned. And once everybody is walking across the border, or the deceased are returned home for burial, that is when we can truly celebrate. Once every single person is returned. Manya Brachear Pashman: You said it feels different? How? How does it feel different? Jessica Bernton: You know, there's been a lot of pressure exerted in recent weeks. I'd say the US administration has stepped up their efforts as well, working with other countries, including partners across the world here. And a deal was signed. And so I think a lot can happen, though, between this announcement and actually, again, when hostages are returned, or when the first phase begins, and both sides need to continue to adhere to each side of the agreement. But this really is the most progress that there has been in some time. Manya Brachear Pashman: As I said in the introduction, you've been working since day one, bringing delegations to Washington to meet with members of Congress, meet with White House staff, including both President Biden and President Trump. What has happened most recently that might have made a difference here? Jessica Bernton: I think the most important thing here is that the families as well as the returned hostages, because we've been so far down in this process that we were advocating for the release of certain hostages, and now those individuals have come to DC and have been traveling across the world to make sure that their voice is heard. And they're speaking up for those that they were held in captivity with, who don't have a voice at the moment. And so it's been really incredible and emotional to have advocated, let's say, for somebody like the return of Keith Siegel or Doron Steinbrecher. And now we have joined them in going to the Hill, into these meetings, advocating for the return of every single hostage, and that's been really incredible. But I think the most important thing here is that these conversations have continued. And keeping this issue at the forefront of everybody's minds. The American public, government officials, foreign officials, community leaders, ensuring that the hostages have not been forgotten has been our top priority here, and ensuring that this remains a foreign policy priority for the US government in particular. And clearly it has paid off, because these hostages have been able to continue to tell their story, and we are where we are today, and hopefully this progress will continue. But it's been really incredible to see this, especially in the past couple months, as those who have been returned or released have now come to Washington, DC as well and are able to do this type of advocacy. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned Keith Siegel, one of the American-Israeli hostages, who was released earlier this year. They've been able to talk about their experiences, former hostages have been able to talk about their experiences in captivity and share that with President Trump in a way that their loved ones who were advocating for their release could not. What have they revealed about their experience that their loved ones could not possibly have known? Jessica Bernton: You know, I think it's one thing to read articles or, you know, hear about what happened to them, and then it's another thing to hear it firsthand. And I think hearing about the brutality and the heartbreak and everything that they suffered, as well as what they've shared publicly about who they were held with and the information that they've been able to also offer to families and hope that they've been able to give to the families who don't know the status of their loved one. Again, it's one thing to read an article and it's another to be sitting in a room listening to these incredibly powerful, emotional, and moving stories. And I think, you know, having them be able to share this has been incredibly important, and I think very impactful. Manya Brachear Pashman: Is there a particular story or experience that stands out in your mind, that perhaps someone shared with you first intimately, before they shared it publicly? One that really stands out. Jessica Bernton: I think I'll share a little bit about Ilana Gritzewsky, because we've hosted her for delegations, and our CEO, Ted Deutch joined with her at a press conference on Capitol Hill on Tuesday, on the second anniversary of the October 7 attacks. And she was also on Capitol Hill earlier this year, testifying at the House Foreign Affairs Committee at a bipartisan round table there. And she was brutally kidnapped alongside her partner, Matan Zangauker, who's still being held captive. And the words that have stuck with me about Ilana, and also sort of you know the story with her partner, Matan, is that she said she cannot heal until everyone has returned home, and the rest of the hostages who have come home also cannot heal until every single person has been returned. And I think that is something that we've heard time and time again, this process, you know, in order for them to grieve, to heal, to process. I don't think there will ever be getting back to a normal life, but as much as they can, it will begin once everybody is returned home. Manya Brachear Pashman: Former hostages, families of hostages have met with President Trump. He's welcomed them into the Oval Office. It seems like President Trump has made this a personal mission of his to get the hostages home. Perhaps that's why we've finally seen success and a deal made. Why do you think that might be the case? What moved the needle finally? Jessica Bernton: Yeah, I mean, I think since before he was President, he has made it clear that this is a priority, and he has instructed his team to work on this issue day in and day out, and to have this access to a president like this is very notable. And we've seen these incredibly powerful images of released hostages, returned hostages, and also family members of those who are still captive meeting in the Oval Office. And one can only assume that this has to be a priority for the President here, he's shown his seriousness. And again, we've now ended up with this current deal, which hopefully can be seen to fruition and can be implemented all the way. But it does seem like this has taken on greater importance as the months have gone on this past year, and it's truly incredible. Manya Brachear Pashman: Any final thoughts, Jessica, as we wait to see the hostages actually return and the various components of this deal come to fruition? Jessica Bernton: Yeah, I think you know, again, going back to this cautious optimism, I saw a video posted online where there's several returned hostages and released hostages, as well as family members who are in town this week, they've been in town for the second anniversary, and have been doing different meetings and events this week in Washington, DC. And they were on the phone with the President last night, you know, expressing their gratitude. And I think again, that's a powerful symbol here. But going back to your initial question, and, is it too early to celebrate? We need to be cautiously optimistic and keep the pressure on, and hopefully we really can be celebrating on Monday, if that's when everyone is returned. But AJC will not stop until everybody, every single hostage, has been returned, and that's when we will truly celebrate here. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much, Jessica. Really appreciate you joining us, and may we see all of this materialize in the days to come. Jessica Bernton: Absolutely thank you, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: Prior to the High Holidays, we brought you five episodes of our limited podcast series, architects of peace, the story of the Abraham accords. Our final episode deals with the challenges presented by the Israel-Hamas war. As we approach a potential end to that war, we are pressing pause on that episode to make sure we include any significant developments. Until then, People of the Pod will resume its regular weekly interviews. Stay tuned for the final episode of Architects of Peace.
Oct 1
Architects of Peace: Episode 5 - Accords of Tomorrow
On the sidelines of the UN General Assembly, AJC hosted a conversation with Jason Greenblatt, a key architect of the Abraham Accords, and former U.S. Ambassador to Israel Dan Shapiro. They discussed the challenges threatening regional stability, from unilateral moves on Palestinian statehood to political pressures within Israel, and underscored what's at stake—and what it will take—to expand the Abraham Accords and advance peace. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode lineup: Dan Shapiro (1:00) Jason Greenblatt (18:05) Full transcript : https://www.ajc.org/news/podcast/accords-of-tomorrow-architects-of-peace-episode-5 Resources: AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace - Tune in weekly for new episodes. AJC.org/AbrahamAccords - The Abraham Accords, Explained AJC.org/CNME - Find more on AJC's Center for a New Middle East Listen – AJC Podcasts: AJC.org/ForgottenExodus AJC.org/PeopleofthePod Follow Architects of Peace on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace You can reach us at: podcasts@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: In September 2020, the world saw what had been years – decades – in the making: landmark peace agreements dubbed the Abraham Accords – normalizing relations between Israel and two Arabian Gulf states, the United Arab Emirates and the Kingdom of Bahrain. Later, in December, they were joined by the Kingdom of Morocco. Five years later, AJC is pulling back the curtain to meet key individuals who built the trust that led to these breakthroughs and turning the spotlight on some of the results. Introducing the Architects of Peace. On the sidelines of the United Nations General Assembly in September, American Jewish Committee hosted conversations with former Middle East envoy Jason Greenblatt, a key architect of the Abraham Accords, and former U.S. Ambassador to Israel Dan Shapiro:. Both diplomats discussed the dangers threatening peace in the region, including some countries' unilateral calls for Palestinian statehood. They shared what's at stake and what it will take to expand the Abraham Accords and make progress toward peace in the region. We're including those conversations as part of our series. AJC's Chief Strategy and Communications Officer Belle Yoeli starts us off with Ambassador Shapiro. Belle Yoeli: Ambassador Shapiro, thank you so much for being with us. We're going to speak primarily about unilateral recognition of Palestinian statehood, but I, of course, want to ask you a couple of questions, because you have so much to share with us before we dive in. First and foremost, as we've said, It's been almost two years, and at AJC, we're all about optimism and playing the long game, as you know, but it does feel like the challenges for the Jewish community and the state of Israel continue to build. And of course, the war looms very large. What is your analysis of the geopolitical horizon for the war in Gaza. Dan Shapiro: First, thanks for having me. Thank you to American Jewish Committee and to Ted and everybody for all you do. Thank you, Ruby [Chen], and the families, for the fellowship that we can share with you in this goal. I'll just say it very simply, this war needs to end. The hostages need to come home. Hamas needs to be removed from power. And aid needs to surge into Gaza and move forward with a reconstruction of Gaza for Palestinians who prepare to live in peace with Israel. This is something that is overdue and needs to happen. I think there have been a number of missed opportunities along the way. I don't say this in a partisan way. I think President Trump has missed opportunities at the end of the first ceasefire, when the first ceasefire was allowed to expire after the Iran strike, something I strongly supported and felt was exactly the right thing to do. There was an opening to create a narrative to end the war. I think there have been other missed opportunities. And I don't say in a partisan way, because the administration I served in, the Biden administration, we made mistakes and we missed opportunities. So it can be shared. that responsibility. But what I do think is that there is a new opportunity right now, and we saw it in President Trump's meeting with Arab leaders. It's going to take very significant, deft, and sustained diplomatic effort. He's got a good team, and they need to do the follow through now to hold the Arabs to their commitments on ensuring Hamas is removed from power, on ensuring that there's a security arrangement in Gaza that does not leave Israel vulnerable to any possibility of a renewal of hostilities against it. And of course, to get the hostages released. That's pressure on the Arabs. And of course, he's got a meeting coming up with Prime Minister Netanyahu, and I do think he's going to need to lean on Prime Minister Netanyahu to overcome the resistance that he has to deal with in his cabinet, from those who want to continue the war or who those who rule out any role of any kind for the Palestinian Authority in something that will follow in the day after in Gaza. So there is a real opportunity here. Once the war is over, then we have an opportunity to get back on the road that we were on. Two years ago at this UN General Assembly, I was serving as the Biden administration's Senior Advisor on regional integration, the first State Department position to hold that, trying to follow through on the excellent work that Jason Greenblatt and Jared Kushner and, of course, President Trump did in the first term in achieving the Abraham Accords. And we were building out the Negev Forum. And in fact, at that UNGA meeting, we had planned the next ministerial meeting of the Negev Forum. It was to take place October 19 in Marrakesh. Obviously, no one ever heard about that summit. It didn't happen. But getting back on the road to strengthening and expanding the Abraham Accords, to getting Saudi Arabia to the table as a country that will normalize relations with Israel, to expanding regional forums like the Negev Forum. Those are all still within reach, but none of them are possible until the war ends, till the hostages are home, till Hamas is removed from power. Belle Yoeli: Absolutely. And we look forward to talking more about the day after, in our next segment, in a segment coming up. Ambassador, you just got back from Israel. Can you tell us about your experience, the mood, what's the climate like in Israel? And any insights from your meetings and time that you think should be top of mind for us? Dan Shapiro: I think what was top of mind for almost every Israeli I spoke to was the hostages. I spent time in the hostage square in Tel Aviv, spent time with Ruby, spent time with other hostage families, and everywhere you go as everybody who spin their nose, you see the signs, you hear the anxiety. And it's getting deeper because of the time that people are worried is slipping away for, especially for those who are still alive, but for all of those hostages to be returned to their families, so deep, deep anxiety about it, and candidly, some anger, I think we just heard a little bit of it toward a government that they're not sure shares that as the highest priority. There's a lot of exhaustion. People are tired of multiple rounds of reserve duty, hundreds of days. Families stressed by that as well the concern that this could drag on with the new operation well into next year. It's allowed to continue. It's a lot of worry about Israel's increased isolation, and of course, that's part of the subject. We'll discuss how countries who have been friends of Israel, whether in the region or in Europe or elsewhere, are responding in more and more negative ways, and Israel, and all Israelis, even in their personal lives, are feeling that pinch. But there's also some, I guess, expectant hope that President Trump, who is popular in Israel, of course, will use his influence and his regional standing, which is quite significant, to put these pieces together. Maybe we're seeing that happening this week. And of course, there's some expectant hope, or at least expectant mood, about an election next year, which will bring about some kind of political change in Israel. No one knows exactly what that will look like, but people are getting ready for that. So Israelis are relentlessly forward, looking even in the depths of some degree of anxiety and despair, and so I was able to feel those glimmers as well. Belle Yoeli: And relentlessly resilient, absolutely resilient. And we know that inspires us. Moving back to the piece on diplomatic isolation and the main piece of our conversation, obviously, at AJC, we've been intensely focused on many of the aspects that are concerning us, in terms of unfair treatment of countries towards Israel, but unilateral recognition of Palestinian state is probably the most concerning issue that we've been dealing with this week, and obviously has gotten a lot of attention in the media. So from your perspective, what is this really all about? Obviously, this, this has been on the table for a while. It's not the first time that countries have threatened to do this, but I think it is the first time we're time we're seeing France and other major countries now pushing this forward in this moment. Is this all about political pressure on Israel? Dan Shapiro: Well, first, I'll say that I think it's a mistake. I think it's an ill advised set of initiatives by France, by Canada, Australia, UK and others. It will change almost it will change nothing on the ground. And so to that sense, it's a purely rhetorical step that changes nothing, and probably does little, if anything, to advance toward the stated goal of some sort of resolution of the Israeli Palestinian conflict. And in many ways, it may actually set it back in part because of the way it appears to and certainly many Israelis understand it too. And I'm sorry to say, many Arabs understand it to reward Hamas. Hamas is celebrating it as an achievement of October 7, and that October 7 will find its place in the pantheon of the Palestinian Liberation story that should never be allowed to happen. So doing it this way, doing it without conditioning it on the release of hostages, on the disarming and removal of Hamas from Gaza, is a mistake. And of course, it tells Israelis that their very legitimate concerns about obviously the hostages, but also that some future Palestinian state, wherever and whatever form it might take, could become a threat to them from other parts, from parts of the West Bank, as it was from Gaza on October 7. And you cannot get to that goal unless you're willing to engage the Israeli public on those concerns, very legitimate concerns, and address them in a very forthright way. So I think it's a mistake. I'm sure, to some degree, others have made this observation. It is motivated by some of the domestic political pressures that these leaders feel from their different constituencies, maybe their left, left wing constituencies, some right wing constituencies, and some immigrant constituencies. And so maybe they're responding to that. And I think that's, you know, leaders deal with those types of things. I think sometimes they make bad decisions in dealing with those types of pressures. I think that's the case here, but I it's also the case. I think it's just fair to say that in the absence of any Israeli Government articulated viable day after, plan for Gaza, something we were urged Israel to work with us on all the time. I was serving in the Biden administration, and I think the Trump administration has as well, but it's remained blurry. What does what is that vision of the day after? Not only when does it start, but what does it look like afterwards? And is it something that Arab States and European states can buy into and get behind and and put their influence to work to get Hamas out and to do a rebuild that meets the needs of both Israelis and Palestinians. There hasn't been that. And so that could have been a way of satisfying some of those domestic pressures, but it wasn't really available. And so I think some of the leaders turn to this ill advised move instead. Belle Yoeli: So perhaps catering to domestic political concerns and wanting to take some sort of moral high ground on keeping peace alive, but beyond that, no real, practical or helpful outcomes, aside from setting back the cause of peace? Dan Shapiro: I think it has limited practical effects. Fact, I think it does tell Israelis that much of the world has not internalized their legitimate concerns, and that they will be, you know, cautious at best for this. Everybody knows that there are many Israelis who have been long standing supporters of some kind of two state resolution to the Israeli Palestinian conflict. And post October 7, they've, they don't still hold that position, or at least they say, if it can happen, it's going to take a long time, it's going to look very different. And I think that actually is some a real practical takeaway, that if we are going to talk about some future establishment of a Palestinian state and some two state arrangement, certainly separation between Israelis and Palestinians, so they don't try to live intermixed in a way that they govern each other. I think that is that is desirable, but it's not necessarily going to look like two state outcomes that were envisioned in the Oslo period, in the 90s and the 2000s it's going to look different. It's going to take longer. And so that is something that I think we have to make sure is understood as people raise this initiative, that their goal is not the goal of 1993 it's going to have to look different, and it's going to have to take longer. Belle Yoeli: So as more and more countries have sort of joined this, this move that we find to be unhelpful, obviously, a concern that we all have who are engaged in this work is that we've heard response, perhaps, from the Israelis, that there could be potential annexation of the West Bank, and that leads to this sort of very, very, even more concerning scenario that all of the work that you were discussing before, around the Abraham Accords, could freeze, or, perhaps even worse, collapse. What's your analysis on that scenario? How concerned should we be based on everything that you know now and if not that scenario? What else should we be thinking about? Dan Shapiro: We should be concerned. I was actually in Israel, when the UAE issued their announcement about four weeks ago that annexation in the West Wing could be a red line, and I talked to a very senior UAE official and tried to understand what that means, and they aren't, weren't prepared to or say precisely what it means. It doesn't necessarily mean they're going to break off relations or end the Abraham Accords, but that they would have to respond, and there's a limited range of options for how one could respond, with moving ambassadors or limiting flights or reducing certain kinds of trade or other visits. Nothing good, nothing that would help propel forward the Abraham accords and that particular critical bilateral relationship in a way that we wanted to so I think there's risk. I think if the UAE would take that step, others would probably take similar steps. Egypt and Jordan have suggested there would be steps. So I think there's real risk there, and I think it's something that we should be concerned about, and we should counsel our Israeli friends not to go that route. There are other ways that they may respond. In fact, I think we've already seen the Trump administration, maybe as a proxy, make some kind of moves that try to balance the scales of these unilateral recognitions. But that particular one, with all of the weight that it carries about what how it limits options for future endpoints, I think would be very, very damaging. And I don't think I'm the only one. Just in the last hour and a half or so, President Trump, sitting in the Oval Office, said very publicly that he, I think you said, would not allow Netanyahu to do the Analyze annexation of the West Bank. I think previously, it was said by various people in the administration that it's really an Israeli decision, and that the United States is not going to tell them what to do. And that's perfectly fine as a public position, and maybe privately, you can say very clearly what you think is the right course, he's now said it very publicly. We'll see if he holds to that position. But he said it, and I think given the conversations he was having with Arab leaders earlier this week, given the meeting, he will have his fourth meeting. So it's obviously a very rich relationship with Prime Minister Netanyahu on Monday, I think it's clear what he believes is necessary to get to the end of this war and not leave us in a worse position for trying to get back on the road to his goals. His goals of expanding the Abraham accords his great achievement from the first term, getting Saudi Arabia to normalize relations, of course, getting hostages released and getting Arabs involved in the reconstruction of Gaza in a way that Gaza can never become the threat it was again on October 7, those are his goals. They'll be well served by the end of the war that I described earlier, and by avoiding this cycle that you're referencing. Belle Yoeli: Putting aside the issue of unilateral recognition, I think we've seen in our work with our Israeli counterparts, sort of differences in the political establish. Around how important it is in thinking about the day after and seeing movement on the Palestinian issue. And we've seen from some that they perhaps make it out that it's not as important that the Palestinian having movement towards a political path. It's not necessarily a have to be front and center, while others seem to prioritize it. And I think in our work with Arab countries, it's very clear that there does have to be some tangible movement towards the political aspirations for the Palestinian for there to really be any future progress beyond the Abraham accords. What's your take? Dan Shapiro: My take is that the Arab states have often had a kind of schizophrenic view about the Palestinian issue. It's not always been, maybe rarely been their highest priority. They've certainly had a lot of disagreements with and maybe negative assessments of Palestinian leaders, of course, Hamas, but even Palestinian Authority leaders. And so, you know, it's possible to ask the question, or it has been over time, you know, how high do they prioritize? It? Certainly those countries that stepped forward to join the Abraham accords said they were not going to let that issue prevent them from advancing their own interests by establishing these productive bilateral relations with Israel, having said that there's no question that Arab publics have been deeply, deeply affected by the war in Gaza, by the coverage they see they unfortunately, know very little about what happened on October 7, and they know a lot about Israeli strikes in Gaza, civilian casualties, humanitarian aid challenges, and so that affects public moods. Even in non democratic countries, leaders are attentive to the views of their publics, and so I think this is important to them. And every conversation that I took part in, and I know my colleagues in the Biden administration with Arab states about those day after arrangements that we wanted them to participate in, Arab security forces, trainers of Palestinian civil servants, reconstruction funding and so forth. They made very clear there were two things they were looking for. They were looking for a role for the Palestinian Authority, certainly with room to negotiate exactly what that role would be, but some foothold for the Palestinian Authority and improving and reforming Palestinian Authority, but to have them be connected to that day after arrangement in Gaza and a declared goal of some kind of Palestinian state in the future. I think there was a lot of room in my experience, and I think it's probably still the case for flexibility on the timing, on the dimensions, on some of the characteristics of that outcome. And I think a lot of realism among some of these Arab leaders that we're not talking about tomorrow, and we're not talking about something that might have been imagined 20 or 30 years ago, but they still hold very clearly to those two positions as essentially conditions for their involvement in getting to getting this in. So I think we have to take it seriously. It sounds like President Trump heard that in his meeting with the Arab leaders on Tuesday. It sounds like he's taking it very seriously. Belle Yoeli: I could ask many more questions, but I would get in trouble, and you've given us a lot to think about in a very short amount of time. Ambassador Shapiro, thank you so much for being with us. Dan Shapiro: Thank you. Thank you everybody. Manya Brachear Pashman: As you heard, Ambassador Shapiro served under President Obama. Now AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson speaks with Jason Greenblatt, who served under President Trump. But don't expect a counterpoint. Despite their political differences, these two men see eye to eye on quite a bit. Jason Isaacson: Jason first, thank you for the Abraham Accords. The work that you did changed the history of the Middle East. We are so full of admiration for the work of you and your team. Jared Kushner. Of course, President Trump, in changing the realities for Israel's relationship across the region and opening the door to the full integration of Israel across the region. It's an unfinished work, but the work that you pioneered with the President, with Jared, with the whole team, has changed the perspective that Israel can now enjoy as it looks beyond the immediate borders, Jordan and Egypt, which has had relations with a quarter a century or more, to full integration in the region. And it's thanks to you that we actually are at this point today, even with all the challenges. So first, let me just begin this conversation by just thanking you for what you've done. Jason Greenblatt: Thank you. Thank you, and Shana Tova to everybody, thank you for all that you do. Jason Isaacson: Thank you. So you were intimately involved in negotiations to reach normalization agreements between Israel and the Kingdom of Morocco, the Kingdom of Bahrain, of course, the United Arab Emirates. Can you take us behind the scenes of these negotiations? At what point during the first term of President Trump did this become a priority for the administration, and when did it seem that it might actually be a real possibility? Jason Greenblatt: So I have the benefit, of course, of looking backward, right? We didn't start out to create the Abraham Accords. We started out to create peace between the Israelis and the Palestinians, which, as Dan knows, and so many people here know, including you Jason, seems to be an impossible task. But I would say that if I follow the breadcrumbs, my first meeting with Yousef Al Otaiba was a lunch, where it was the first time I actually ever met an Emirati, the first time I understood the psychology of the Emiratis. And others. I realized that the world had changed tremendously. Everything that you heard about anti-Israel wasn't part of the conversation. I'll go so far as to say, when I went to the Arab League Summit that took place in Jordan in March of 2017 where I met every foreign minister. And I'm not going to tell you that I loved many of those meetings, or 85% of the conversation, where it wasn't exactly excited about Israel and what Israel stood for. There were so many things in those conversations that were said that gave me hope. So it was multiple years of being in the White House and constantly trying to work toward that. But I want to go backwards for a second, and you touched on this in your speech, there are many parents and grandparents of the Abraham Accords, and AJC is one of those parents or grandparents. There are many people who work behind the scenes, Israeli diplomats and so many others. And I'm sure the Kingdom of Morocco, where the architecture was built for something like the Abraham Accords, everybody wanted regional peace and talked about Middle East peace. But we were fortunate, unfortunately for the Palestinians who left the table, which was a big mistake, I think, on their part, we're very fortunate to take all of that energy and all of that hard work and through a unique president, President Trump, actually create that architecture. On a sad note, I wouldn't say that when I left the White House, I thought I'd be sitting here thinking, you know, five years out, I thought there'd be lots of countries that would already have signed and all the trips that I take to the Middle East, I thought would be much. Now they're easy for me, but we're in a very, very different place right now. I don't think I ever would have envisioned that. Jason Isaacson: Thank you. The administration has talked a great deal about expanding the Abraham Accords, of course, and as have we. Indeed, at an AJC program that we had in Washington in February with Special Envoy Steven Witkoff, he talked publicly for the first time about Lebanon and Syria joining the Accords. Obviously, with both of those countries, their new political situation presents new possibilities. However, the ongoing war in Gaza, as we've been discussing with Ambassador Shapiro, and Israel's actions, including most recently striking Hamas in Doha, have further isolated Israel in the region and made an expansion of the accords harder to envision. At least, that's the way it seems. Given the current situation in the Middle East. Do you think the Trump administration can be successful in trying to broker new agreements, or do the current politics render that impossible in the short term? How hopeful are you? Jason Greenblatt: So I remain hopeful. First of all, I think that President Trump is a unique president because he's extremely close to the Israeli side, and he's very close to the Arab side. And he happens to have grandchildren who are both, right. I think, despite this terrible time that we're facing, despite hostage families, I mean, the terrible things that they have to live through and their loved ones are living it through right now, I still have hope. There's no conversation that I have in the Arab world that still doesn't want to see how those Abraham Accords can be expanded. Dan, you mentioned the Arab media. It's true, the Arab world has completely lost it when it comes to Israel, they don't see what I see, what I'm sure all of you see. I'm no fan of Al Jazeera, but I will say that there are newspapers that I write for, like Arab News. And when I leave the breakfast room in a hotel in Riyadh and I look at the headlines of, not Al Jazeera, but even Arab News, I would say, Wow, what these people are listening to and reading, what they must think of us. And we're seeing it now play out on the world stage. But despite all that, and I take my kids to the Middle East all the time, we have dear friends in all of those countries, including very high level people. I've gotten some great Shana Tovas from very high level people. They want the future that was created by the Abraham Accords. How we get there at this particular moment is a big question mark. Jason Isaacson: So we touched on this a little bit in the earlier conversation with Dan Shapiro:. Your team during the first Trump administration was able to defer an Israeli proposal to annex a portion of the West Bank, thanks to obviously, the oped written by Ambassador Al Otaiba, and the very clear position that that government took, that Israel basically had a choice, normalization with the UAE or annexation. Once again, there is discussion now in Israel about annexation. Now the President, as Ambassador Shapiro just said, made a very dramatic statement just a couple of hours ago. How do you see this playing out? Do you think that annexation is really off the table now? And if it were not off the table, would it prevent the continuation of the agreements that were reached in 2020 and the expansion of those agreements to a wider integration of Israel in the region? Jason Greenblatt: To answer that, I think for those of you who are in the room, who don't know me well, you should understand my answer is coming from somebody who is on the right of politics, both in Israel and here. In fact, some of my Palestinian friends would say that sometimes I was Bibi's mouthpiece. But I agree with President Trump and what he said earlier today that Dan had pointed out, I don't think this is the time. I don't think it's the place. And I was part of the team that wrote the paperwork that would have allowed Israel to . . . you use the word annexation. I'll say, apply Israeli sovereignty. You'll use the word West Bank, I'll use Judea, Samaria. Whatever the label is, it really doesn't matter. I don't think this is the time to do it. I think Israel has so many challenges right now, militarily, hostages, there's a million things going on, and the world has turned against Israel. I don't agree with those that are pushing Bibi. I don't know if it's Bibi himself, but I hope that Bibi could figure out a way to get out of that political space that he's in. And I think President Trump is making the right call. Jason Isaacson: So, I was speaking with Emirati diplomats a couple of days ago, who were giving me the sense that Israel hasn't gotten the message that the Palestinian issue is really important to Arab leaders. And we talked about this with Ambassador Shapiro earlier, that it's not just a rhetorical position adopted by Arab leaders. It actually is the genuine view of these Arab governments. Is that your sense as well that there needs to be something on the Palestinian front in order to advance the Abraham Accords, beyond the countries that we've established five years ago? Jason Greenblatt: You know, when I listened to Dan speak, and I told him this after his remarks, I'm always reminded that even though we disagree around the edges on certain things, if you did a Venn diagram, there would be a lot of overlap. I agree with how he sees the world. But I want to take it even back to when I was in the White House. There are many times people said, Oh, the Arabs don't care about the Palestinians. They don't care. We could just do whatever we want. It's not true. They may care more about their own countries, right? They all have their visions, and it's important to them to advance their own visions. The Palestinian cause may not have been as important, but there is no way that they were going to abandon the Palestinians back then, and I don't think the UAE or the Kingdom of Morocco or others having entered into the Abraham Accords, abandoned the Palestinians. I think that was the wrong way to look at it, but they are certainly not going to abandon the Palestinians now. And I think that how Dan described it, which is there has to be some sort of game plan going forward. Whether you want to call it a state, which, I don't like that word, but we can't continue to live like this. I'm a grandfather now of three. I don't want my grandchildren fighting this fight. I really don't. Is there a solution? Okay, there's a lot of space between what I said and reality, and I recognize that, but it's incumbent on all of us to keep trying to figure out, is there that solution? And it's going to include the Palestinians. I just want to close my answer with one thing that might seem odd to everybody. I'm not prone to quoting Saeb Erekat, who I disagreed with, the late Saeb Erekat, who I disagreed with just about on everything, but he used to tell me, Jason, the answer isn't in the Koran, it's not in the Torah, it's not in the Christian Bible, and the Israelis and the Palestinians are not leaving the space. So let's figure out a solution that we could all live with. So that's how I see it. Jason Isaacson: Thank you for that. One last question. I also heard in another conversation with other em righty diplomats the other day that the conflict isn't between Arabs and Israelis or Arabs and Jews, it's between moderates and extremists, and that the UAE is on the side of the moderates, and Morocco is on the side of the moderates, and the Kingdom of Bahrain is on the side of the moderates, and Israel is on the side of the moderates. And that's what we have to keep in our minds. But let me also ask you something that we've been saying for 30 years across the region, which is, if you believe in the Palestinian cause, believe in rights for the Palestinians, you will advance that cause by engaging Israel, not by isolating Israel. Is that also part of the argument that your administration used five years ago? Jason Greenblatt: 100%. I think, I mean, I kept pushing for it and eventually they did it, for the Israelis and the Arabs to engage directly. Yes, the US plays a role, and they could play a moderating role. They could play somewhat of a coercive role. Nobody's going to force the Israelis, or frankly, even the Palestinians, to do anything they don't want to do, but getting them in the room so there are no missed signals, no missed expectations, I think, is the key part of this solution. I'm still hopeful, just to go back to your prior question, that they could get the right people in the room and somebody like President Trump, together with Emirati diplomats, Moroccan diplomats and others. They could talk rationally, and sanely, and appropriately, and we'll get somewhere good. Jason Isaacson: Ok, look ahead. We just marked the fifth anniversary of the Abraham Accords. Will there be a 10th Anniversary of the Abraham Accords, and will it look the same that it is now? Jason Greenblatt: No, I think it's going to be better. Yes, I think there's going to be a 10th Anniversary. I think there will be challenges. But maybe the best way I could answer this is, when the, I'll call it, the beeper incident in Lebanon happened. Okay, quite, quite a feat. I was in a conference room at a client of mine in the Middle East. Most of the room was filled with Lebanese Arabs, Christians and Muslims and some Druze. And it was unusual for everybody's phone to buzz at once, because I'm usually following the Israeli and American news. They're following Arab news. All the phones buzz. So somebody stopped talking, and we all picked up our phone to look at it. And I'm looking at the headlines thinking, oh, boy, am I in the wrong room, right? And after a minute or so of people kind of catching their breath, understanding what happened, two or three of them said, wow, Jason. Like, that's incredible. Like, you know, I wasn't in the White House anymore, but they also want a different future, right? They are sick and tired of Lebanon being a failed state. Their kids are like my kids, and they're just . . . they're everything that they're building is for a different future, and I see that time and time again. So to go back to the UAE diplomats comment, which I hear all the time as well. It really is a fight of moderates against extremists. The extremists are loud and they're very bad. We know that, but we are so much better. So working together, I think we're going to get to somewhere great. Jason Isaacson: Very good. Okay. Final question. You can applaud, it's okay. Thank you for that. Out of the Abraham Accords have grown some regional cooperation agreements. I too, you too, IMEC, the India, Middle East, Europe, Economic corridor. Do you see that also, as part of the future, the creation of these other regional agreements, perhaps bringing in Japan and Korea and and other parts of the world into kind of expanding the Abraham Accords? In ways that are beneficial to many countries and also, at the same time, deepening the notion of Israelis, Israel's integration in the region. Jason Greenblatt: 100% and I know I think AJC has been very active on the IMEC front. People used to say, Oh, this is not an economic peace. It isn't an economic peace, but nor is economics not a very important part of peace. So all of these agreements, I encourage you to keep working toward them, because they will be needed. In fact, one of the fights that I used to have with Saeb Erekat and President Abbas all the time is, I know you're not an economic issue, but let's say we manage to make peace. What's going to happen the next day? You need an economic plan. Let's work on the economic plan. So whether it's IMEC or something else, just keep working at it. Go, you know, ignore the bad noise. The bad noise is here for a little while, unfortunately, but there will be a day after, and those economic agreements are what's going to be the glue that propels it forward. Jason Isaacson: Jason Greenblatt, really an honor to be with you again. Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: In our next episode of the series, we will explore more of the opportunities and challenges presented by the Abraham Accords and who might be the next country to sign the landmark peace agreement. Atara Lakritz is our producer. T.K. Broderick is our sound engineer. Special thanks to Jason Isaacson, Sean Savage, and the entire AJC team for making this series possible. You can subscribe to Architects of Peace on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you listen to podcasts, and you can learn more at AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace. The views and opinions of our guests don't necessarily reflect the positions of AJC. You can reach us at podcasts@ajc.org. If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to spread the word, and hop onto Apple Podcasts or Spotify to rate us and write a review to help more listeners find us. Music Credits: Middle East : ID: 279780040; Composer: Eric Sutherland Inspired Middle East : ID: 241884108; Composer: iCENTURY Mystical Middle East : ID: 212471911; Composer: Vicher
Sep 19
Architects of Peace: Episode 4 - Partners of Peace
Tune into the fourth installment of AJC's latest limited podcast series, Architects of Peace. Go behind the scenes of the decades-long diplomacy and quiet negotiations that made the Abraham Accords possible, bringing Israel, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, and later Morocco, together in historic peace agreements. From cockpits to kitchens to concert halls, the Abraham Accords are inspiring unexpected partnerships. In the fourth episode of AJC's limited series, four "partners of peace" share how these historic agreements are reshaping their lives and work. Hear from El Mehdi Boudra of the Mimouna Association on building people-to-people ties; producer Gili Masami on creating a groundbreaking Israeli–Emirati song; pilot Karim Taissir on flying between Casablanca and Tel Aviv while leading Symphionette, a Moroccan orchestra celebrating Andalusian music; and chef Gal Ben Moshe, the first Israeli chef to ever cook in Dubai on his dream of opening a restaurant in the UAE. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode lineup: El Mehdi Boudra (4:00) Gili Masami (11:10) Karim Taissir (16:14) Gal Ben Moshe (21:59) Read the transcript : https://www.ajc.org/news/podcast/partners-of-peace-architects-of-peace-episode-4 Resources: AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace - Tune in weekly for new episodes. The Abraham Accords, Explained AJC.org/CNME - Find more on AJC's Center for a New Middle East Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus People of the Pod Follow Architects of Peace on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace You can reach us at: podcasts@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript: El Mehdi Boudra: All the stereotypes started like getting out and people want to meet with the other. They wanted to discover the beauty of the diversity of Israel. And this is unique in the region, where you have Arabs Muslims, Arab Christians, Druze, Beta Yisrael, Ashkenazi, Sephardic Jews, Jews from India, from all over the world. This beauty of diversity in Israel is very unique for our region. Manya Brachear Pashman: In September 2020, the world saw what had been years – decades – in the making: landmark peace agreements dubbed the Abraham Accords – normalizing relations between Israel and two Arabian Gulf states, the United Arab Emirates and the Kingdom of Bahrain. Later, in December, they were joined by the Kingdom of Morocco. Five years later, AJC is pulling back the curtain to meet key individuals who built the trust that led to these breakthroughs and turning the spotlight on some of the results. Introducing: the Architects of Peace. ILTV correspondent: Well, hello, shalom, salaam. For the first time since the historic normalization deal between Israel and the UAE, an Israeli and an Emirati have teamed up to make music. [ Ahlan Bik plays] The signs have been everywhere. On stages in Jerusalem and in recording studios in Abu Dhabi. [Camera sounds]. On a catwalk in Tel Aviv during Fashion Week and on the covers of Israeli and Arab magazines. [Kitchen sounds]. In the kitchens of gourmet restaurants where Israeli and Emirati chefs exchanged recipes. Just days after the announcement of the Abraham Accords, Emirati ruler Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan formally ended the UAE's nearly 50-year boycott of Israel. Though commerce and cooperation had taken place between the countries under the radar for years, the boycott's official end transformed the fields of water, renewable energy, health, cybersecurity, and tourism. In 2023, Israel and the UAE signed a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) to advance economic cooperation, and by 2024, commerce between the UAE and Israel grew to $3.2 billion. Trade between Bahrain and Israel surged 740% in one year. As one of the world's most water-stressed countries, Bahrain's Electrical and Water Authority signed an agreement to acquire water desalination technology from Israel's national water company [Mekorot]. Signs of collaboration between Israeli and Arab artists also began to emerge. It was as if a creative energy had been unlocked and a longing to collaborate finally had the freedom to fly. [Airplane take off sounds]. And by the way, people had the freedom to fly too, as commercial airlines sent jets back and forth between Tel Aviv, Casablanca, Abu Dhabi, and Manama. A gigantic step forward for countries that once did not allow long distance calls to Israel, let alone vacations to the Jewish state. At long last, Israelis, Moroccans, Emiratis, and Bahrainis could finally satisfy their curiosity about one another. This episode features excerpts from four conversations. Not with diplomats or high-level senior officials, but ordinary citizens from the region who have seized opportunities made possible by the Abraham Accords to pursue unprecedented partnerships. For El Medhi Boudra, the Abraham Accords were a dream come true. As a Muslim college student in 2007 at Al Akhawayn University in Ifrane, Morocco, he founded a group dedicated to preserving and teaching the Jewish heritage of his North African home. El Mehdi knew fostering conversations and friendships would be the only way to counter stereotypes and foster a genuine appreciation for all of Morocco's history, including its once-thriving Jewish community of more than 100,000. Five years later, El Mehdi's efforts flourished into a nonprofit called Mimouna, the name of a Moroccan tradition that falls on the day after Passover, when Jewish and Muslim families gather at each other's homes to enjoy cakes and sweets and celebrate the end of the Passover prohibitions. Together. El Mehdi Boudra: Our work started in the campus to fill this gap between the old generation who talk with nostalgia about Moroccan Jews, and the young generation who don't know nothing about Moroccan Judaism. Then, in the beginning, we focused only on the preservation and educating and the promotion of Jewish heritage within campuses in Morocco. In 2011, we decided to organize the first conference on the Holocaust in the Arab world. Manya Brachear Pashman: So did the Abraham Accords make any difference in the work you were already doing? I mean, I know Mimouna was already a longtime partner with AJC. El Mehdi Boudra: With Abraham Accords, we thought bigger. We brought young professionals from Morocco and Israel to work together in certain sectors on challenges that our regions are overcoming. Like environment, climate change, water scarcity and innovation, and bring the best minds that we have in Morocco and in Israel to work together. But we included also other participants from Emirates and Bahrain. This was the first one that we started with. The second was with AJC. We invited also young professionals from United States and France, which was an opportunity to work globally. Because today, we cannot work alone. We need to borrow power from each other. If we have the same vision and the same values, we need to work together. In Morocco, we say: one hand don't clap. We need both hands. And this is the strategy that we have been doing with AJC, to bring all the partners to make sure that we can succeed in this mission. We had another people-to-people initiative. This one is with university students. It's called Youth for MENA. It's with an Israeli organization called Noar. And we try to take advantage of the Abraham Accords to make our work visible, impactful, to make the circle much bigger. Israel is a country that is part of this region. And we can have, Israel can offer good things to our region. It can fight against the challenges that we have in our region. And an Israeli is like an Iraqi. We can work all together and try to build a better future for our region at the end of the day. Manya Brachear Pashman: El Mehdi, when you started this initiative did you encounter pushback from other Moroccans? I mean, I understand the Accords lifted some of the restrictions and opened doors, but did it do anything to change attitudes? Or are there detractors still, to the same degree? El Mehdi Boudra: Before the Abraham Accords, it was more challenging to preserve Moroccan Jewish heritage in Morocco. It was easier. To educate about Holocaust. It was also OK. But to do activities with civil society in Israel, it was very challenging. Because, first of all, there is no embassies or offices between Morocco. Then to travel, there is no direct flights. There is the stereotypes that people have about you going to Israel. With Abraham Accords, we could do that very freely. Everyone was going to Israel, and more than that, there was becoming like a tendency to go to Israel. Moroccans, they started wanting to spend their vacation in Tel Aviv. They were asking us as an organization. We told them, we are not a tour guide, but we can help you. They wanted to travel to discover the country. All the stereotypes started like getting out and people want to meet with other. They wanted to discover the beauty of the diversity of Israel. And this is unique in the region where you have Arab Muslims, Arab Christians, Druze, Beta Israel, Ashkenazi, Sephardic Jews, Jews from India, from all over the world. This beauty of diversity in Israel is very unique for our region. And it's not granted in this modern time, as you can see in the region. You can see what happened in Iraq, what's happening in Syria, for minorities. Then you know, this gave us hope, and we need this hope in these dark times. Manya Brachear Pashman: Hm, what do you mean? How does Israel's diversity provide hope for the rest of the Middle East North Africa (MENA) region? El Mehdi Boudra: Since the MENA region lost its diversity, we lost a lot. It's not the Christians or the Yazidis or the Jews who left the MENA region who are in bad shape. It's the people of the MENA region who are in bad shape because those people, they immigrated to U.S., to Sweden, they have better lives. But who lost is those countries. Then us as the majority Muslims in the region, we should reach out to those minorities. We should work closely today with all countries, including Israel, to build a better future for our region. There is no choice. And we should do it very soon, because nothing is granted in life. And we should take this opportunity of the Abraham Accords as a real opportunity for everyone. It's not an opportunity for Israel or the people who want to have relation with Israel. It's an opportunity for everyone, from Yemen to Morocco. Manya Brachear Pashman: Morocco has had diplomatic relations with Israel in the past, right? Did you worry or do you still worry that the Abraham Accords will fall apart as a result of the Israel Hamas War? El Mehdi Boudra: Yes, yes, to tell you the truth, yes. After the 7th of October and things were going worse and worse. We said, the war will finish and it didn't finish. And I thought that probably with the tensions, the protest, will cut again the relations. But Morocco didn't cut those relations. Morocco strengthened those relations with Israel, and also spoke about the Palestinians' cause in the same time. Which I'm really proud of my government's decisions to not cut those relations, and we hope to strengthen those relations, because now they are not going in a fast dynamic. We want to go back to the first time when things were going very fastly. When United States signed with the Emirates and Bahrain in September 2020, I was hoping that Morocco will be the first, because Morocco had strong relations with Israel. We had direct relations in the 90s and we cut those relations after the Second Intifada in 2000. We lost those 21 years. But it's not [too] late now. We are working. The 7th of October happened. Morocco is still having relations with Israel. We are still having the Moroccan government and the Israeli government having strong relations together. Of course, initiatives to people-to-people are less active because of the war. But you know, the war will finish very soon, we hope, and the hostages will go back to their homes, Inshallah, and we will get back to our lives. And this is the time for us as civil society to do stronger work and to make sure that we didn't lose those two years. [ Ahlan Bik plays] Manya Brachear Pashman: Just weeks after the White House signing ceremony on September 15, 2020, Israeli music producer Gili Masami posted a music video on YouTube. The video featured a duet between a former winner of Israel's version of The Voice, Elkana Marziano, and Emirati singer Walid Aljasim. The song's title? Ahlan Bik, an Arabic greeting translated as "Hello, Friend." In under three weeks, the video had garnered more than 1.1 million views. Gili Masami: When I saw Bibi Netanyahu and Trump sign this contract, the Abraham Accords, I said, 'Wow!' Because always my dream was to fly to Dubai. And when I saw this, I said, 'Oh, this is the time to make some project that I already know how to do.' So I thought to make the first historic collaboration between an Israeli singer and an Emirati singer. We find this production company, and they say, OK. We did this historic collaboration. And the first thing it was that I invite the Emirati people to Israel. They came here. I take them to visit Jerusalem, Tel Aviv, and then I get a call to meet in Gitix Technology Week in the World Trade Center in Dubai. Manya Brachear Pashman: Gitix. That's the Gulf Information Technology Exhibition, one of the world's largest annual tech summits, which met in Dubai that year and invited an Israeli delegation for the first time. Gili Masami: They tell me. 'Listen, your song, it was big in 200 countries, cover worldwide. We want you to make this show.' I said, OK. We came to Dubai, and then we understand that the production company is the family of Mohammed bin Zayed al Nayhan, the president of UAE. And now we understand why they agree. The brother of Muhammad bin Zayed Al Nahyan, Sheik Issa Ben Zahid Al Nahyan, he had this production company. This singer, it's his singer. And we say, 'Wow, we get to this so high level, with the government of Dubai.' And then all the doors opened in Dubai. And then it was the Corona. 200 countries around the world cover this story but we can't do shows because this Corona issue, but we still did it first. Manya Brachear Pashman: The song Ahlan Bik translates to "Hello, Friend." It was written by Israeli songwriter Doron Medalie. Can you tell our listeners what it's about? Gili Masami: The song Ahlan Bik, it's this song speak about Ibrihim. Because if we go to the Bible, they are cousins. They are cousins. And you know, because of that, we call this Abraham Accords, because of Avraham. And they are sons of Ishmael. Yishmael. And we are sons of Jacob. So because of that, we are from back in the days. And this is the real cousins. Saudi Arabia, UAE, Morocco. They are the real ones. And this song speak about this connection. Manya Brachear Pashman: After Morocco joined the Abraham Accords, you also put together a collaboration between Elkana and Moroccan singer Sanaa Mohamed . But your connection to UAE continued. You actually moved to Dubai for a year and opened a production company there. I know you're back in Israel now, but have you kept in touch with people there? Gili Masami: I have a lot of friends in UAE. A lot of friends. I have a production company in UAE too. But every time we have these problems with this war, so we can do nothing. I was taking a lot of groups to Dubai, making tours, parties, shows, and all this stuff, because this war. So we're still friends. Manya Brachear Pashman: Given this war, do you ever go back and listen to the song Ahlan Bik for inspiration, for hope? Gili Masami: I don't look about the thinking that way. These things. I know what I did, and this is enough for me. I did history. This is enough for me. I did [a] good thing. This is enough for me. I did the first collaboration, and this is enough for me. Manya Brachear Pashman: Moroccan pilot and music aficionado Karim Taissir also knows the power of music. In 2016, he reached out to Tom Cohen, the founder and conductor of the Jerusalem Orchestra East & West and invited him to Morocco to conduct Symphonyat, an orchestra of 40 musicians from around the world playing Jewish and Arab music from Morocco's past that often has been neglected. Karim Taissir: In 2015 I contacted Tom via Facebook because of a story happening in Vietnam. I was in a bar. And this bar, the owner, tried to connect with people. And the concept was a YouTube session connected on the speaker of the bar, and they asked people to put some music on from their countries. So when he asked me, I put something played by Tom [Cohen], it was Moroccan music played by the orchestra of Tom. And people said, 'Wow.' And I felt the impact of the music, in terms of even, like the ambassador role. So that gave me the idea. Back in Morocco, I contacted him. I told him, 'Listen, you are doing great music, especially when it comes to Moroccan music, but I want to do it in Morocco. So are you ready to collaborate? And you should tell me, what do you need to create an orchestra that do this, this excellency of music?' And I don't know why he replied to my message, because, usually he got lots of message from people all over the world, but it was like that. So from that time, I start to look of musician, of all conditions, asked by Tom, and in 2016 in April, we did one week of rehearsals. This was a residence of musician in Casablanca by Royal Foundation Hiba. And this is how it starts. And from that time, we tried every year to organize concerts. Sometimes we succeed, and sometimes not. Manya Brachear Pashman: I asked this of El Mehdi too, since you were already doing this kind of bridge building Karim, did the Abraham Accords change anything for you? Karim Taissir: In '22 we did the great collaboration. It was a fusion between the two orchestras, under the conductor Tom Cohen in Timna desert [National Park], with the presence of many famous people, politician, and was around like more than 4,000 people, and the President Herzog himself was was there, and we had a little chat for that. And even the program, it was about peace, since there was Moroccan music, Israeli music, Egyptian music, Greek music, Turkish music. And this was very nice, 18 musicians on the stage. Manya Brachear Pashman: Oh, wow. 18 musicians. You know, the number 18, of course, is very significant, meaningful for the Jewish tradition. So, this was a combination of Israeli musicians, Moroccan musicians, playing music from across the region. Turkey, Greece, Egypt, Israel. What did that mean for you? In other words, what was the symbolism of that collaboration and of that choice of music? Karim Taissir: Listen, to be honest, it wasn't a surprise for me, the success of collaboration, since there was excellent artists from Israel and from Morocco. But more than that, the fact that Moroccan Muslims and other people with Israeli musicians, they work together every concert, rehearsals. They became friends, and maybe it was the first time for some musicians, especially in Morocco. I'm not talking only about peace, happiness, between people. It's very easy in our case, because it's people to people. Manya Brachear Pashman: How have those friendships held up under the strain of the Israel-Hamas War? Karim Taissir: Since 7th October, me, for example, I'm still in touch with all musicians from Israel, not only musicians, all my friends from Israel to support. To support them, to ask if they are OK. And they appreciate, I guess, because I guess some of them feel even before they have friends from all over the world. But suddenly it's not the case for us, it's more than friendships, and if I don't care about them, which means it's not true friendships. And especially Tom. Tom is more than more than a brother. And we are looking forward very soon to perform in Israel, in Morocco, very soon. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I should clarify for listeners that Symphonyat is not your full-time job. Professionally you are a pilot for Royal Air Maroc. And a week after that concert in Timna National Park in March 2022, Royal Air Maroc launched direct flights between Casablanca and Tel Aviv. Those flights have been suspended during the war, but did you get to fly that route? Karim Taissir: They call me the Israeli guy since I like very much to be there. Because I was kind of ambassador since I was there before, I'm trying always to explain people, when you will be there, you will discover other things. Before 7th of October, I did many, many, many flights as captain, and now we're waiting, not only me, all my colleagues. Because really, really–me, I've been in Israel since 2016–but all my colleagues, the first time, it was during those flights. And all of them had a really nice time. Not only by the beauty of the Tel Aviv city, but also they discover Israeli people. So we had really, really, very nice memories from that period, and hoping that very soon we will launch flight. Manya Brachear Pashman: Chef Gal Ben Moshe, the first Israeli chef to earn a Michelin Star for his restaurant in Berlin, remembers the day he got the call to speak at Gulfood 2021, a world food festival in Abu Dhabi. That call led to another call, then another, and then another. Before he knew it, Chef Gal's three-day trip to the United Arab Emirates had blossomed into a 10-day series: of master classes, panel discussions, catered dinners, and an opportunity to open a restaurant in Dubai. Gal Ben Moshe: Like I said, it wasn't just one dinner, it wasn't just a visit. It's basically from February '21 to October '23 I think I've been more than six, eight times, in the Emirates. Like almost regularly cooking dinners, doing events, doing conferences. And I cooked in the Dubai Expo when it was there. I did the opening event of the Dubai Expo. And a lot of the things that I did there, again, I love the place. I love the people. I got connected to a lot of people that I really, truly miss. Manya Brachear Pashman: When we first connected, you told me that the Abraham Accords was one of your favorite topics. Why? Gal Ben Moshe: I always felt kind of like, connected to it, because I was the first Israeli chef to ever cook in Dubai. And one of the most influential times of my life, basically going there and being there throughout basically everything from the Abraham Accords up to October 7. To a degree that I was supposed to open a restaurant there on the first of November 2023 which, as you probably know, did not happen in the end. And I love this place. And I love the idea of the Abraham Accords, and I've had a lot of beautiful moments there, and I've met a lot of amazing people there. And, in a way, talking about it is kind of me missing my friends less. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you were originally invited to speak at Gulfood. What topics did you cover and what was the reception like? Gal Ben Moshe: The journalist that interviewed me, he was a great guy, asked me, 'OK, so, like, where do you want to cook next?' And I said, 'If you would ask me six months ago, I would say that I would love to cook in Dubai, but it's not possible.' So having this happened, like, anything can happen, right? Like, if you would tell me in June 2020 that I would be cooking in Dubai in February 2021, I'm not sure I was going to believe you. It was very secretive, very fast, very surprising. And I said, 'Yeah, you know, I would love to cook in Damascus and Beirut, because it's two places that are basically very influential in the culture of what is the Pan-Arabic kitchen of the Levant. So a lot of the food influence, major culinary influence, comes from basically Aleppo, Damascus and Beirut. Basically, this area is the strongest influence on food. A lot of Jordanians are probably going to be insulted by me saying this, but this is very this is like culinary Mecca, in my opinion.' And I said it, and somebody from the audience shouted: 'I'm from Beirut! You can stay at my place!' And I was like, it's just amazing. And the funny thing is, and I always talk about it is, you know, I talk about my vegetable suppliers in Berlin and everything in the Syrian chefs and Palestinian chefs and Lebanese chefs that I met in the Emirates that became friends of mine. And I really have this thing as like, I'm gonna say it is that we have so much in common. It's crazy how much we have in common. You know, we have this war for the past two years with basically everyone around us. But I think that when we take this thing out of context, out of the politics, out of the region, out of this border dispute or religious dispute, or whatever it is, and we meet each other in different country. We have so much in common, and sometimes, I dare say, more than we have in common with ourselves as an Israeli society. And it's crazy how easy it is for me to strike a conversation and get friendly with the Lebanese or with a Palestinian or with the Syrian if I meet them in Berlin or in Dubai or in New York or in London. Manya Brachear Pashman: I should clarify, you run restaurants in Tel Aviv, but the restaurant that earned a Michelin star in 2020 and held on to it for four years, was Prism in Berlin. Tel Aviv was going to be added to the Michelin Guide in December 2023, but that was put on hold after the start of the Israel-Hamas War. Did your time in the Emirates inspire recipes that perhaps landed on your menu at Prism? Gal Ben Moshe: I was approached by a local journalist that wrote cookbooks and he did a special edition cookbook for 50 years for the Emirates. And he wanted me to contribute a recipe. And I did a dish that ended up being a Prism signature dish for a while, of Camel tartar with caviar, quail yolk, grilled onion, and it was served in this buckwheat tortelet. And at the time, it's a concept dish. So basically, the story is this whole story of Dubai. So you have the camel and the caviar, so between the desert and the sea. And then you have the camel, which basically is the nomadic background of Dubai, with the Bedouin culture and everything, and the caviar, which is this luxurious, futuristic–what Dubai is today. And it was really a dish about the Emirates. And I was invited to cook it afterwards in a state dinner, like with very high-end hotel with very high-end guests. And basically the chef of the hotel, who's a great guy, is like, sending, writing me an email, like, I'm not going to serve camel. I'm not going to serve camel in this meal. And I was like, but it's the whole story. It's the whole thing. He's like, but what's wrong with Wagyu beef? It's like, we're in Dubai. Wagyu beef is very Dubai. And I was like, not in the way that the camel is in that story. Listen, for a chef working there, it's a playground, it's heaven. People there are super curious about food. They're open-minded. And there's great food there. There's a great food scene there, great chefs working there. I think some of the best restaurants in the world are right now there, and it was amazing. Manya Brachear Pashman: There have been other Israeli chefs who opened their restaurants in Dubai before October 7. I know Chef Eyal Shani opened with North Miznon in a Hilton hotel in Dubai. You recently closed Prism, which really was a mom and pop place in Berlin, and you've now opened a hotel restaurant in Prague. Would you still consider opening a kitchen in Dubai? Gal Ben Moshe: I have not given up on the Emirates in any way. Like I've said, I love it there. I love the people there. I love the atmosphere there. I love the idea of being there. I would say that there is complexities, and I understand much better now, in hindsight of these two years. Of why, basically, October 7 meant that much. I live in Berlin for 13 years, and I work with my vegetable suppliers for the past, I would say nine or eight years. They're Palestinians and Syrians and Lebanese and everything. And even though October 7 happened and everything that's happened afterwards, we're still very close, and I would still define our relationship as very friendly and very positive. The one thing is that, I don't know, but I think it's because we know each other from before. And I don't know if they would have taken the business of an Israeli chef after October 7. So having known me and that I'm not a symbol for them, but I am an individual. For them it is easier because we're friends, like we worked together, let's say for five years before October 7. It's not going to change our relationship just because October 7 happened. But I think what I do understand is that sometimes our place in the world is different when it comes to becoming symbols. And there are people who don't know me and don't know who I am or what my opinions are, how I view the world, and then I become just a symbol of being an Israeli chef. And then it's you are this, and nothing you can say at that moment changes it. So I don't think that me opening a restaurant in Dubai before October 7 was a problem. I do understand that an Israeli chef opening a restaurant in Dubai after October 7 was not necessarily a good thing. I can understand how it's perceived as, in the symbolism kind of way, not a good thing. So I think basically, when this war is over, I think that the friendship is there. I think the connection is there. I think the mutual respect and admiration is there. And I think that there is no reason that it can't grow even further. Manya Brachear Pashman: In our next episode, expected to air after the High Holidays, we discuss how the Abraham Accords have held during one of Israel's most challenging times and posit which Arab countries might be next to join the historic pact. Atara Lakritz is our producer. T.K. Broderick is our sound engineer. Special thanks to Jason Isaacson, Sean Savage, and the entire AJC team for making this series possible. You can subscribe to Architects of Peace on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you listen to podcasts, and you can learn more at AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace. The views and opinions of our guests don't necessarily reflect the positions of AJC. You can reach us at podcasts@ajc.org. If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to spread the word, and hop onto Apple Podcasts or Spotify to rate us and write a review to help more listeners find us. Music Credits: Middle East : ID: 279780040; Composer: Eric Sutherland אלקנה מרציאנו & Waleed Aljasim - אהלן ביכ | Elkana Marziano AHALAN bik أهلاً بيك Moroccan Suite : Item ID: 125557642; Composer: umberto sangiovanni Medley Ana Glibi Biddi Kwitou / Ma Nebra - Symphonyat with Sanaa Marahati - Casablanca - 2022 Middle East : Item ID: 297982529; Composer: Aditya Mystical Middle East : ID: 212471911; Composer: Vicher
Sep 11
Architects of Peace: Episode 3 - From the White House Lawn
Dive into the third episode of AJC's latest limited podcast series, Architects of Peace. Go behind the scenes of the decades-long diplomacy and quiet negotiations that made the Abraham Accords possible, bringing Israel, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, and later Morocco, together in historic peace agreements. On September 15, 2020, the Abraham Accords were signed at the White House by President Trump, Prime Minister Netanyahu, and the foreign ministers of the UAE and Bahrain. In this third installment of AJC's limited series, AJC CEO Ted Deutch and Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson—who stood on the South Lawn that day—share their memories and insights five years later. Together, they reflect on how the Accords proved that peace is achievable when nations share strategic interests, build genuine relationships, and pursue the greater good. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Read the transcript : https://www.ajc.org/news/podcast/from-the-white-house-lawn-architects-of-peace-episode-3 Resources: AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace - Tune in weekly for new episodes. The Abraham Accords, Explained AJC.org/CNME - Find more on AJC's Center for a New Middle East Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus People of the Pod Follow Architects of Peace on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace You can reach us at: podcasts@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript: Ted Deutch: It was a beautiful day and there was this coming together, this recognition that this was such an historic moment. It's the kind of thing, frankly, that I remember having watched previously, when there were peace agreements signed and thinking that's something that I want to be a part of. And there I was looking around right in the middle of all of this, and so excited about where this could lead. Manya Brachear Pashman: In September 2020, the world saw what had been years, decades in the making, landmark peace agreements dubbed the Abraham Accords, normalizing relations between Israel and two Arabian Gulf States, the United Arab Emirates and the Kingdom of Bahrain. Later, in December, they were joined by the Kingdom of Morocco. Five years later, AJC is pulling back the curtain to meet key individuals who built the trust that led to these breakthroughs. Introducing: the Architects of Peace. Announcer : Ladies and gentlemen, the President of the United States. Accompanied by the Prime Minister of the State of Israel; His Highness the Minister of Foreign Affairs and International cooperation of the United Arab Emirates, and the Minister of the Foreign Affairs of the Kingdom of Bahrain. Manya Brachear Pashman: The guests of honor framed by the South Portico of the White House were an unlikely threesome. Two Arab foreign ministers and the Prime Minister of Israel, there to sign a pair of peace agreements that would transform the Middle East. Donald Trump : Thanks to the great courage of the leaders of these three countries, we take a major stride toward a future in which people of all faiths and backgrounds live together in peace and prosperity. There will be other countries very, very soon that will follow these great leaders. Manya Brachear Pashman: President Trump's team had achieved what was long thought impossible. After decades of pretending Israel did not exist until it solved its conflict with the Palestinians, Trump's team discovered that attitudes across the Arab region had shifted and after months of tense negotiations, an agreement had been brokered by a small circle of Washington insiders. On August 13, 2020, the United Arab Emirates agreed to become the first Arab state in a quarter century to normalize relations with Israel. Not since 1994 had Israel established diplomatic relations with an Arab country, when King Hussein of Jordan and Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin signed a treaty, ending the state of war that had existed between them since Israel's rebirth. A ceremony to celebrate and sign the historic deal was planned for the South Lawn of the White House on September 15, 2020. Before the signing ceremony took place, another nation agreed to sign as well: not too surprisingly the Kingdom of Bahrain. After all, in June 2019, Bahrain had hosted the Peace to Prosperity summit, a two-day workshop where the Trump administration unveiled the economic portion of its peace plan – a 38-page prospectus that proposed ways for Palestinians and Arab countries to expand economic opportunities in cooperation with Israel. In addition to Bahrain, Egypt, Jordan, Morocco, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE all participated in the summit. The Palestinians boycotted it, even as Trump's senior advisor Jared Kushner presented plans to help them. Jared Kushner : A lot of these investments people are unwilling to make because people don't want to put good money after bad money. They've seen in the past they've made these investments, they've tried to help out the Palestinian people, then all of a sudden there's some conflict that breaks out and a lot of this infrastructure gets destroyed. So what we have here is very detailed plans and these are things we can phase in over time assuming there's a real ceasefire, a real peace and there's an opportunity for people to start making these investments. Manya Brachear Pashman: Now Israel, the UAE, and Bahrain would open embassies, exchange ambassadors, and cooperate on tourism, trade, health care, and regional security. The Accords not only permitted Israelis to enter the two Arab nations using their Israeli passports, it opened the door for Muslims to visit historic sites in Israel, pray at Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem, the third holiest site in Islam, and finally satisfy their curiosity about the Jewish state. Before signing the accords, each leader delivered remarks. Here's Bahrain's Foreign Minister Abdullatif bin Rashid Al-Zayani. Abdullatif bin Rashid Al-Zayani : For too long, the Middle East has been set back by conflict and mistrust, causing untold destruction and thwarting the potential of generations of our best and brightest young people. Now, I'm convinced, we have the opportunity to change that. Manya Brachear Pashman: UAE's Minister of Foreign Affairs Sheikh Abdullah bin Zayed Al Nahyan echoed that sentiment and also addressed accusations by Palestinian leadership that the countries had abandoned them. He made it clear that the accords bolstered the Emirates' support for the Palestinian people and their pursuit of an independent state. Sheikh Abdullah bin Zayed Al Nahyan : [speaking in Arabic] Manya Brachear Pashman: [translating Sheikh Abdullah bin Zayed Al Nahyan] This new vision, he said, which is beginning to take shape as we meet today for the future of the region, full of youthful energy, is not a slogan that we raise for political gain as everyone looks forward to creating a more stable, prosperous, and secure future. This accord will enable us to continue to stand by the Palestinian people and realize their hopes for an independent state within a stable and prosperous region. Manya Brachear Pashman: The Truman Balcony, named for the first American president to recognize Israel's independence, served as the backdrop for a few iconic photographs. The officials then made their way down the stairs and took their seats at the table where they each signed three copies of the Abraham Accords in English, Hebrew, and Arabic. The brief ceremony combined formality and levity as the leaders helped translate for each other so someone didn't sign on the wrong dotted line. After that was settled, they turned the signed documents around to show the audience. When they all rose from their seats, Prime Minister Netanyahu paused. After the others put their portfolios down, he stood displaying his for a little while longer, taking a few more seconds to hold on to the magnitude of the moment. Benjamin Netanyahu : To all of Israel's friends in the Middle East, those who are with us today and those who will join us tomorrow, I say, 'As-salamu alaykum. Peace unto thee. Shalom.' And you have heard from the president that he is already lining up more and more countries. This is unimaginable a few years ago, but with resolve, determination, a fresh look at the way peace is done . . . The blessings of the peace we make today will be enormous, first, because this peace will eventually expand to include other Arab states, and ultimately, it can end the Arab Israeli conflict once and for all. [clapping] [Red alert sirens] Manya Brachear Pashman: But peace in Israel was and still is a distant reality as Palestinian leadership did not participate in the Accords, and, in fact, viewed it as a betrayal. As Netanyahu concluded his speech to the audience on the White House Lawn, thousands of miles away, Israel's Iron Dome missile defense system intercepted 15 rockets fired by terrorists in Gaza, at least one striking Israel's coastal city of Ashdod. Iran's regime condemned the agreement. But across most of the region and around the world, the revelation that decades of hostility could be set aside to try something new – a genuine pursuit of peace – inspired hope. Saudi journalists wrote op-eds in support of the UAE and Bahrain. Egypt and Oman praised the Abraham Accords for adding stability to the region. Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Spain commended the monumental step. United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres welcomed the deal for paving the way toward a two-state solution. AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson was one of more than 200 domestic and foreign officials on the White House Lawn that day taking it all in. The guest list included members of Congress, embassy staff, religious leaders, and people like himself who worked behind the scenes – a cross section of people who had been part of a long history of relationship building and peacemaking in the Middle East for many years. Jason Isaacson: To see what was happening then this meeting of neighbors who could be friends. To see the warmth evident on that stage at the South Lawn of the White House, and then the conversations that were taking place in this vast assembly on the South Lawn. Converging at that moment to mark the beginning of a development of a new Middle East. It was an exciting moment for me and for AJC and one that not only will I never forget but one that I am looking forward to reliving. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jason, of course, is talking about his confidence in the expansion of the Abraham Accords. Through his position at AJC he has attended several White House events marking milestones in the peace process. He had been seated on the South Lawn of the White House 27 years earlier to watch a similar scene unfold -- when Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and Palestinian Leader Yasser Arafat met to sign the Oslo Accords with President Bill Clinton. Yitzhak Rabin : What we are doing today is more than signing an agreement. It is a revolution. Yesterday, a dream. Today, a commitment. The Israeli and the Palestinian peoples who fought each other for almost a century have agreed to move decisively on the path of dialogue, understanding, and cooperation. Manya Brachear Pashman: Brokered secretly by Norway, the Oslo Accords established mutual recognition between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization, which claimed to represent the Palestinian people. It also led to the creation of a Palestinian Authority for interim self-government and a phased Israeli withdrawal from parts of the West Bank and Gaza. Jason Isaacson: I mean, 1993 was a tremendous breakthrough, and it was a breakthrough between the State of Israel and an organization that had been created to destroy Israel. And so it was a huge breakthrough to see the Israeli and Palestinian leaders agree to a process that would revolutionize that relationship, normalize that relationship, and set aside a very ugly history and chart a new path that was historic. Manya Brachear Pashman: While the Oslo Accords moved the Israelis and Palestinians toward a resolution, progress came to a halt two years later with the assassination of Prime Minister Rabin. In July 2000, President Clinton brought Arafat and then Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Barak to Camp David to continue discussions, but they could not agree. In his autobiography, "My Life," President Clinton wrote that Arafat walked away from a Palestinian state, a mistake that Clinton took personally. When Arafat called him a great man, Clinton responded "I am not a great man. I am a failure, and you made me one." Arafat's decision also would prove fatal for both Israelis and Palestinians. By September, the Second Intifada – five years of violence, terror attacks, and suicide bombings – derailed any efforts toward peace. Jason says the Abraham Accords have more staying power than the Oslo Accords. That's clear five years later, especially after the October 7 Hamas terror attacks sparked a prolonged war between Israel and Hamas in Gaza. Two years into the war, the Abraham Accords have held. But Jason recalls feeling optimistic, even as he sat there again on the South Lawn. Jason Isaacson: It's a different kind of historic moment, maybe a little less breathtaking in the idea of two fierce antagonists, sort of laying down their arms and shaking hands uneasily, but shaking hands. Uneasily, but shaking hands. All those years later, in 2020, you had a state of Israel that had no history of conflict with the UAE or Bahrain. Countries with, with real economies, with real investment potential, with wise and well-advised leaders who would be in a position to implement plans that were being put together in the summer and fall of 2020. The Oslo Accords, you know, didn't provide that kind of built in infrastructure to advance peace. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jason pointed out that the only source of conflict among the signatories on the Abraham Accords was actually a point of mutual agreement – a frustration and desire to resolve the conflict with the Palestinians. UAE and Bahrain were part of the League of Arab States that had sworn in 2002 not to advance relations with Israel in the absence of a two-state solution. But 18 years later, that had gone nowhere and leaders recognized that perhaps it would be more beneficial to the Palestinian cause if they at least engaged with Israel. Jason Isaacson: I had no fear, sitting in a folding chair on the White House Lawn on September 15, that this was going to evaporate. This seemed to be a natural progression. The region is increasingly sophisticated and increasingly plugged into the world, and recognizing that they have a lot of catching up to do to advance the welfare of their people. And that that catching up is going to require integrating with a very advanced country in their region that they have shunned for too long. This is a recognition that I am hearing across the region, not always spoken in those words, but it's clear that it will be of benefit to the region, to have Israel as a partner, rather than an isolated island that somehow is not a part of that region. Donald Trump : I want to thank all of the members of Congress for being here … Manya Brachear Pashman: AJC CEO Ted Deutch also was at the White House that day, not as AJC CEO but as a Congressman who served on the House Committee on Foreign Affairs and chaired its Subcommittee on the Middle East, North Africa and Global Counterterrorism. Ted Deutch: It was a beautiful day and there was this coming together, this recognition that this was such an historic moment and it's exactly the kind of thing, frankly, that I remember having watched previously, when there were peace agreements signed and thinking that's something that I want to be a part of. And there I was looking around right in the middle of all of this, and so excited about where this could lead. Manya Brachear Pashman: Despite his congressional role, Ted learned about the deal along with the rest of the world when it was initially announced a month before the ceremony, though he did get a tip that something was in the pipeline that would change the course of the committee's work. Ted Deutch: I found out when I got a phone call from the Trump administration, someone who was a senior official who told me that there is big news that's coming, that the Middle East is never going to look the same, and that he couldn't share any other information. And we, of course, went into wild speculation mode about what that could be. And the Abraham Accords was the announcement, and it was as dramatic as he suggested. Manya Brachear Pashman: It was a small glimmer of light during an otherwise dark time. Remember, this was the summer and early fall of 2020. The COVID pandemic, for the most part, had shut down the world. People were not attending meetings, conferences, or parties. Even members of Congress were avoiding Capitol Hill and casting their votes from home. Ted Deutch: It was hard to make great strides in anything in the diplomatic field, because there weren't the kind of personal interactions taking place on a regular basis. It didn't have the atmosphere that was conducive to meaningful, deep, ongoing conversations about the future of the world. And that's really what this was about, and that's what was missing. And so here was this huge news that for the rest of the world, felt like it was out of the blue, that set in motion a whole series of steps in Congress about the way that our committee, the way we approach the region. That we could finally start talking about regional cooperation in ways that we couldn't before. Manya Brachear Pashman: The timing was especially auspicious as it boosted interest in a particular piece of legislation that had been in the works for a decade: the bipartisan Nita M. Lowey Middle East Partnership for Peace Act. Approved by Congress in December 2020, around the same time Morocco joined the Abraham Accords, the law allocated up to $250 million over five years for programs advancing peaceful coexistence between Israelis and Palestinians and supporting a sustainable two-state solution. Passed as part of a larger appropriations bill, it was the largest investment of any single country in Israeli-Palestinian civil society initiatives. Ted Deutch: Here we were having this conversation about increasing trade and increasing tourism and the countries working more closely together and being able to freely fly back and forth on a regular basis – something that we've seen as the tourism numbers have taken off. The trade has taken off. So it really changed what we do. Manya Brachear Pashman: The other thing Ted recalls about that day on the White House lawn was the bipartisan spirit in the air. Although his own committee didn't tend to divide along party lines, Congress had become quite polarized and partisan on just about everything else. On that day, just as there was no animus between Israelis and Arabs, there was none between Republicans and Democrats either. And Ted believes that's the way it always should be. Ted Deutch: It was a bipartisan stellium of support, because this was a really important moment for the region and for the world, and it's exactly the kind of moment where we should look for ways to work together. This issue had to do with the Middle East, but it was driven out of Washington. There's no doubt about that. It was driven out of the out of the Trump administration and the White House and that was, I think, a reminder of the kind of things that can happen in Washington, and that we need to always look for those opportunities and when any administration does the right thing, then they need to be given credit for it, whether elected officials are on the same side of the aisle or not. We were there as people who were committed to building a more peaceful and prosperous region, with all of the countries in the region, recognizing the contributions that Israel makes and can make as the region has expanded, and then thinking about all of the chances that we would have in the years ahead to build upon this in really positive ways. Manya Brachear Pashman: On that warm September day, it felt as if the Abraham Accords not only had the potential to heal a rift in the Middle East but also teach us some lessons here at home. Even if it was impossible to resolve every disagreement, the Abraham Accords proved that progress and peace are possible when there are shared strategic interests, relationships, and a shared concern for the greater good. Ted Deutch: I hope that as we celebrate this 5th anniversary, that in this instance we allow ourselves to do just that. I mean, this is a celebratory moment, and I hope that we can leave politics out of this. And I hope that we're able to just spend a moment thinking about what's been achieved during these five years, and how much all of us, by working together, will be able to achieve, not just for Israel, but for the region, in the best interest of the United States and in so doing, ultimately, for the world. That's what this moment offers. Manya Brachear Pashman: In the next episode, we meet Israelis and Arabs who embraced the spirit of the Abraham Accords and seized unprecedented opportunities to collaborate. Atara Lakritz is our producer. T.K. Broderick is our sound engineer. Special thanks to Jason Isaacson, Sean Savage, and the entire AJC team for making this series possible. You can subscribe to Architects of Peace on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you listen to podcasts, and you can learn more at AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace. The views and opinions of our guests don't necessarily reflect the positions of AJC. You can reach us at podcasts@ajc.org. If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to spread the word, and hop onto Apple Podcasts or Spotify to rate us and write a review to help more listeners find us.
Sep 4
Architects of Peace: Episode 2 - Behind the Breakthrough
Tune into the second episode of AJC's newest limited podcast series, Architects of Peace. Go behind the scenes of the decades-long diplomacy and quiet negotiations that made the Abraham Accords possible, bringing Israel, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, and later Morocco, together in historic peace agreements. Former U.S. Ambassador to Israel David Friedman, U.S. Army General Miguel Correa, and AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson unpack the first Trump administration's Middle East strategy, share behind-the-scenes efforts to engage key regional players, and reveal what unfolded inside the White House in the crucial weeks before the Abraham Accords signing. Full transcript: https://www.ajc.org/news/podcast/behind-the-breakthrough-architects-of-peace-episode-2 Resources: AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace - Tune in weekly for new episodes. AJC.org/AbrahamAccords - The Abraham Accords, Explained AJC.org/CNME - Find more on AJC's Center for a New Middle East Listen – AJC Podcasts: AJC.org/ForgottenExodus AJC.org/PeopleofthePod Follow Architects of Peace on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace You can reach us at: podcasts@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript: Donald Trump : I think we're going to make a deal. It might be a bigger and better deal than people in this room even understand. Manya Brachear Pashman: In September 2020, the world saw what had been years – decades – in the making: landmark peace agreements dubbed the Abraham Accords -- normalizing relations between Israel and two Arabian Gulf states, the United Arab Emirates and the Kingdom of Bahrain. Later, in December, they were joined by the Kingdom of Morocco. Five years later, AJC is pulling back the curtain to meet key individuals who built the trust that led to these breakthroughs. Introducing: the Architects of Peace. Shortly after he was elected in 2016 and before he took office, President Donald Trump nominated his company's former bankruptcy attorney David Friedman to serve as U.S. Ambassador to Israel. He gave Friedman two simple tasks. Task No. 1? Build peace across the Middle East by normalizing relations between Israel and its Arab neighbors. Task No. 2? Solve the Israeli Palestinian conflict that a half dozen previous White House residents had failed to fix. After all, according to conventional wisdom, the first task could not happen before the second. The future of cooperation between Israel and 20-plus other Arab countries hinged on peace between the Israelis and Palestinians. Here's former Secretary of State John Kerry. John Kerry : There will be no advance and separate peace with the Arab world without the Palestinian process and Palestinian peace. Everybody needs to understand that. Manya Brachear Pashman: Ambassador Friedman disagreed with this conventional wisdom. David Friedman: We were told initially by most countries that the road to peace began with the Palestinians. This was a hypothesis that I rejected internally, but I thought: 'OK, well, let's just play this out and see where this can go. And so, we spent a couple of years really working on what could be a plan that would work for Israel and the Palestinians. The Palestinians, you know, rejected discussions early on, but we had a lot of discussions with the Israelis. Manya Brachear Pashman: The son of a rabbi who grew up in Long Island, Ambassador Friedman had been active in pro-Israel organizations for decades, He had advised Trump on the importance of the U.S.-Israel bond during the 2016 presidential election and recommended nothing less than a radical overhaul of White House policy in the region. Not long after his Senate confirmation as ambassador, that overhaul commenced. In February 2017, President Trump invited Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu to the White House – his first invitation to a foreign leader — and a symbolic one. After their meeting, they held a joint press conference. Donald Trump : With this visit, the United States again reaffirms our unbreakable bond with our cherished ally Israel. The partnership between our two countries, built on our shared values. I think we're going to make a deal. It might be a bigger and better deal than people in this room even understand. That's a possibility. So, let's see what we do. He doesn't sound too optimistic. But he's a good negotiator. Benjamin Netanyahu: That's the art of the deal. Manya Brachear Pashman: Nine months later, President Trump made another symbolic gesture -- recognizing Jerusalem as Israel's capital city and moving the American embassy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem. Though such a move had been approved by Congress in 1995, no president had ever acted upon it. When Trump's son-in-law, businessman, and senior White House advisor Jared Kushner opened conversations about that 'bigger and better deal,' Palestinians refused to participate, using the pretext of the Jerusalem decision to boycott the Trump administration. But that didn't stop Ambassador Friedman and others from engaging, not only with Israel, but with Arab countries about a new path forward. AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson, who has been building bridges in the region since the early '90s, recalls this strategy at the time. Jason Isaacson: It was very clear for many months, 2019 on into early 2020, that there was a team working under Jared Kushner in the White House that was going from country to country in the Gulf and North Africa, looking to make a deal, looking to make deals that would lead to normalization with Israel, would involve various benefits that the United States would be able to provide. But of course, the big benefit would be regional integration and a closer relationship with the United States. Manya Brachear Pashman: The pitch for a new path forward resonated in the United Arab Emirates, a Gulf country of 10 million residents, some 11% of whom are Emiratis — the rest expats and migrants from around the world. The UAE had designated 2019 the Year of Tolerance, an initiative aimed at promoting the country as a global capital for tolerance and respect between diverse cultures and nationalities. That year, the Emirates hosted a historic visit from Pope Francis, and 27 Israeli athletes competed in the 2019 Special Olympics World Games held in the capital city of Abu Dhabi. The pitch also resonated in Bahrain. In June of that year, during a two-day workshop in Bahrain's capital city of Manama, the Trump administration began rolling out the results of its Middle East tour – the economic portion of its peace plan, titled "Peace to Prosperity." Jason Isaacson: The White House plan for Peace to Prosperity was a kind of an early set of ideas for Israeli Palestinian resolution that would result in a small, but functional Palestinian state, created in a way that would not require the displacement of Israelis in the West Bank, and that would involve large scale investment, mostly provided by other countries, mostly in the Gulf, but not only, also Europe, to advance the Palestinian economy, to integrate the Palestinian and Israelis' economies in a way that had never happened. And there was discussion that was taking place that all led up to the idea of a very fresh approach, a very new approach to the regional conflict. Manya Brachear Pashman: The 38-page prospectus set ambitious goals — turning the West Bank and Gaza into tourism destinations, doubling the amount of drinkable water there, tripling exports, earmarking $900 million to build hospitals and clinics. The Palestinians, angered by Trump's recognition of Jerusalem and viewing the Manama workshop as an attempt to normalize Arab-Israel ties while sidelining their national rights, boycotted the meeting and rejected the plan before ever seeing its details. But the workshop's host Bahrain, as well as Egypt, Jordan, Morocco, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the Emirates participated, to varying degrees. Trump's team rolled out the rest of the plan in January 2020, including a map of land carved out for Palestinians and for Israel. The plan enabled Palestinians and Arab countries to expand economic opportunities. It enabled Israel to demonstrate that it was open to cooperation. It enabled the Trump administration to illustrate the opportunities missed if countries in the region continued to let Palestinian leadership call the shots. David Friedman: The expectation was not that the Palestinians would jump all over it. We were realistic about the possibility, but we did think it was important to show that Israel itself, under some circumstances, was willing to engage with the Palestinians with regard to a formula for peace that, you know, had an economic component, a geographic component, a governance component. Manya Brachear Pashman: The Palestine Liberation Organization accused the United States of trying to sell a "mirage of economic prosperity." Hamas leader Ismail Haniyeh criticized the Arab leaders attending the al-Manama conference, saying "The (Palestinian) people, who have been fighting for 100 years, did not commission anyone to concede or to bargain." But that's the thing. Arab leaders weren't there solely on behalf of the Palestinians. They wanted to learn how their own countries' citizens could enjoy peace and prosperity too. David Friedman: The real point of all this that got the Abraham Accords jump started was not the fact that the Palestinians embraced this, but more so that they rejected it in such a way that enabled these other countries to say: 'Look, guys, you know what? We can't be more pro-Palestinian than you.' Here you have, you know, the U.S. government putting on a table a proposal that gets you more than halfway there in terms of your stated goals and aspirations. Maybe you don't like all of it, that's fine, but you're never going to get everything you wanted anyway. And here's the first government in history that's willing to give you something tangible to talk about, and if you're not going to engage in something that they spent years working on, talking to everybody, trying to thread the needle as best they could. If you're not willing to talk to them about it, then don't ask us to fight your fight. There's only so far we can go. But we thought that putting this plan out on a table publicly would kind of smoke out a lot of positions that had historically been below the surface. And so, beginning right after the 28th of January of 2020 when we had that ceremony with the President's vision for peace, we began to really get serious engagement. Not from the Palestinians, who rejected it immediately, but from the countries in the region. And so that's how the Abraham Accords discussions really began in earnest. Manya Brachear Pashman: AJC had been saying for years that if Arab leaders truly wanted to foster stability in the region and help the Palestinians, engaging with Israel and opening channels of communication would give them the leverage to do so. Isolating Israel was not the answer. Nothing underscored that more than the COVID-19 pandemic, the worst global health crisis in a century. As everyone around the world donned N95 masks and went into self-imposed isolation, some governments in the Middle East concluded that isolating innovative countries like Israel was perhaps not the wisest or safest choice. In May 2020, UAE Ambassador to the United Nations Lana Nusseibeh said as much during a virtual webinar hosted by AJC. Lana Nusseibeh : Of course, we've had Israeli medics participate in previous events in the UAE, that wouldn't be unusual. And I'm sure there's a lot of scope for collaboration. I don't think we would be opposed to it. Because I really think this public health space should be an unpoliticized space where we all try and pool our collective knowledge of this virus. Manya Brachear Pashman: A month later, UAE Minister of State for Foreign Affairs Dr. Anwar Gargash echoed that sentiment, during AJC Global Forum. Anwar Gargash : I think we can come to a point where we come to a given Israeli government and we say we disagree with you on this, we don't think it's a good idea. But at the same time there are areas, such as COVID, technology, and other things that we can actually work on together. Manya Brachear Pashman: Not surprisingly, the UAE was the first Arab country to begin negotiating with the White House to normalize relations with Israel. However, talks that summer hit a stalemate. Israel was moving forward with a plan to annex a significant portion of the West Bank, including Israeli settlements and the Jordan Valley. Even though President Trump himself had cautioned Prime Minister Netanyahu to hold off, Ambassador Friedman was not about to stop them. David Friedman: I thought that the idea of Israel walking away from its biblical heartland. Anything that required Israel to make that commitment was something I couldn't support. I was so dead set against it. Israel cannot, as a price for normalization, as great as it is, as important as it is, Israel cannot agree to cede its biblical heartland. Manya Brachear Pashman: Not only was this personal for Ambassador Friedman, it was also a major incentive for Israel, included in the Peace to Prosperity plan. The ambassador didn't want to go back on his word and lose Israel's trust. But annexation was a dealbreaker for the Emirates. In June, UAE's Ambassador to the U.S. Yousef Al Otaiba wrote a column speaking directly to the Israeli public. He explained that the UAE wanted diplomatic relations with Israel – it really did – but unilateral annexation of land that it considered still in dispute would be viewed as a breach of trust and undermine any and all progress toward normalization. David Friedman: It was a kind of a tumultuous period, both internally within our own team and with others, about what exactly was going to happen as a result of that Peace to Prosperity Plan. And even if there was an agreement by the United States to support Israeli annexation, was this something that was better, at least in the short term? Manya Brachear Pashman: Otaiba's message got through, and the team ultimately agreed to suspend the annexation plan — not halt, but suspend — an intentionally temporary verb. In addition to writing the column, Otaiba also recommended that a friend join the negotiations to help repair the trust deficit: General Miguel Correa, a U.S. Army General who had spent part of his childhood in the Middle East, served in the Persian Gulf War and as a peacekeeper maintaining the treaty between Israel and Egypt. General Correa had joined the National Security Council in March 2020 after serving as a defense attaché in Abu Dhabi. He had earned the respect of Emiratis, not as a dealmaker so much as a lifesaver, once orchestrating a secret rescue mission of wounded Emirati troops from inside Yemen. Among those troops, the nephew and son-in-law of Crown Prince Mohamed bin Zayed, the then-de facto ruler and now the current president of the UAE. Kushner and Friedman had never met Correa. Miguel Correa: I didn't know them, and they didn't know me. No one else had any military experience on the team. I had a unique perspective of the Arab side of the equation. And had relationships. So, it was a match made in heaven. Jared, David Friedman, these guys obviously understood Israeli politics and understood the Israeli side, and somewhat Jewish American side. I could provide a different dynamic or a different view from the Arab side, as someone who's kind of grown up with this. It really got serious when the team came together and, and we could start working on real, concrete things. Manya Brachear Pashman: Months of negotiations had already unfolded. It was already late July, first of August, when General Correa became the last person to join the tiny circle of a half dozen negotiators – kept intentionally small to keep a lid on the conversations. It's hard to keep a secret in Washington. David Friedman: The secrecy here was very, very important, because to be honest with you, I think anything bigger than that group of six or seven, we would have put it in jeopardy. Manya Brachear Pashman: In this situation, leaks not only threatened the deal, they could threaten lives. Though word trickled out that a deal was in the works, no one guessed just how transformational the result might be. In General Correa's opinion, the UAE had the most to lose. Miguel Correa: That was the concern that, frankly, guys like me had, that, I hurt a nation of good people that is incredibly tolerant, that builds synagogues and churches and Sikh temples, or Hindu temples, and tolerance 101, that everybody can pray to who they would like to pray to. And I was worried that all these extremists were going to come out of the woodwork and hurt that trajectory in the UAE, that was going to be a great nation with or without the normalization. But this ruler said: 'No, no, it's the right thing to do. Peace is the right thing to do.' Manya Brachear Pashman: General Correa actually had quite a few concerns. He didn't want the negotiations to be hijacked for political gain. He wanted leaders to have a security and public relations response in place before anything was announced. And the agreement? It lacked a name. Miguel Correa: A lot of it has to do with my military side. We love to name cool task forces, and things like that. And then I felt like: 'Hey, it has to be something that rolls off the tongue, that makes sense and that will help it, you know, with staying power. Let's do something that ties the people together. There was going to be a shock, a tectonic shock that was going to occur. From 1948, we're going to do a complete 180, and wow. So what do we do to take the wind away from the extremists? As a guy who's fought extremism, militant extremism, for most of his military career, I figured, hey, we've got to do what we can to frame this in a super positive manner. Manya Brachear Pashman: To the general's dismay, no one else shared his concern about what to call their project. A lot was happening in those last few weeks. Landing on a name – not a priority. On the morning of August 13, once all the details were hammered out, the team sat in the Oval Office waiting to brief the President before it was announced to the world. David Friedman: It came about 10 minutes before the end, we were all sitting around the Oval Office, waiting for this announcement about the UAE. And somebody, not me, said: 'Well, we need a name for this,' and I said, why? And they said, 'Well, you know, you have the Oslo Accords, you have the Camp David Accords. You need a name.' And I said, you know, Who's got an idea? And General Miguel Correa, he said: 'How about the Abraham Accords?' And I said: 'That's a great name.' And then we had a rush to call the Israelis and the Emiratis to make sure they were OK with it. Five minutes later we're broadcasting to a few hundred million people this groundbreaking announcement. And the President looks at me and says, 'David, explain why you chose the Abraham Accords?' So that was when we explained what the name was, which I hadn't really thought of until that point. We just thought it was a good name. So at that point I said, 'Well, you know, Abraham was the father of three great religions. He's referred to as Abraham in English, and Ibrahim in Arabic, and Avraham in Hebrew. And no single individual better exemplifies the opportunity and the benefits of unity among all peoples than Abraham.' And that was sort of on the fly how we got to the Abraham Accords. Manya Brachear Pashman: General Correa said he chose a name that would remind people of all faiths that what they have in common far outweighs what separates them. It was also important that the name be plural. Not the Abraham Accord. The Abraham Accords. Even if only one country – the UAE – was signing on at that moment, there would be more to come. Indeed, Bahrain came on board within a month. Morocco joined in December. Miguel Correa: I felt in my heart that this has to be more than one. As a guy that's been affected by this extremism and it allowed this, this craziness and that people decide who can get to know who and and I felt like, No, we can't allow this to be a one-shot deal. We have to prove that this is an avalanche. This could be sustained, and this is the way it should be. Everyone has to come into this one way or another. And it's not, by the way, saying that, hey, we're all going to walk lockstep with Israel. That's not the point. The point is that you have a conversation, the leaders can pick up the phone and have that conversation. So it has to be, has to be plural. By the way, this is the way that it was. This isn't new. This isn't like a crazy new concept. This is the way it was. It's not an introduction of Jews in this region, in society. This is a reintroduction. This is the way it's supposed to be. This is what's happened for thousands of years. So why are we allowing people to take us back, you know, thousands of years? Let's go back to the way things should be, and develop these relationships. It makes us all better. Manya Brachear Pashman: Next episode, we step out from behind the scenes and on to the South Lawn of the White House where leaders from the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, Israel and the U.S. signed the Abraham Accords, while the world watched in awe. Atara Lakritz is our producer. T.K. Broderick is our sound engineer. Special thanks to Jason Isaacson, Sean Savage, and the entire AJC team for making this series possible. You can subscribe to Architects of Peace on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you listen to podcasts, and you can learn more at AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace. The views and opinions of our guests don't necessarily reflect the positions of AJC. You can reach us at podcasts@ajc.org. If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to spread the word, and hop onto Apple Podcasts or Spotify to rate us and write a review to help more listeners find us. Music Credits: Middle East : ID: 279780040; Composer: Eric Sutherland Frontiers : ID: 183925100; Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI); Composer: Pete Checkley (BMI) Meditative : ID: 115666358; Composer: DANIELYAN ASHOT MAKICHEVICH (IPI NAME #00855552512), UNITED STATES BMI Arabian : Item ID: 214336423; Composer: MusicForVideos Arabian Strings : ID: 72249988; Publisher: EITAN EPSTEIN; Composer: EITAN EPSTEIN Desert : Item ID: 220137401; Publisher: BFCMUSIC PROD.; Composer: Andrei Marchanka Middle East Violin : ID: 277189507; Composer: Andy Warner Arabic Ambient : ID: 186923328; Publisher: Victor Romanov; Composer: Victor Romanov Oriental : Item ID: 190860465; Publisher: Victor Romanov; Composer: Victor Romanov Mystical Middle East : ID: 212471911; Composer: Vicher
Aug 28
Architects of Peace: Episode 1 - The Road to the Deal
Listen to the first episode of AJC's new limited podcast series, Architects of Peace. Go behind the scenes of the decades-long diplomacy and quiet negotiations that made the Abraham Accords possible, bringing Israel, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, and later Morocco, together in historic peace agreements. Jason Isaacson, AJC Chief of Policy and Political Affairs, explains the complex Middle East landscape before the Accords and how behind-the-scenes efforts helped foster the dialogue that continues to shape the region today. Resources: Episode Transcript AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace - Tune in weekly for new episodes. The Abraham Accords, Explained AJC.org/CNME - Find more on AJC's Center for a New Middle East Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus People of the Pod Follow Architects of Peace on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace You can reach us at: podcasts@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript: Jason Isaacson: It has become clear to me in my travels in the region over the decades that more and more people across the Arab world understood the game, and they knew that this false narrative – that Jews are not legitimately there, and that somehow we have to focus all of our energy in the Arab world on combating this evil interloper – it's nonsense. And it's becoming increasingly clear that, in fact, Israel can be a partner. Manya Brachear Pashman: In September 2020, the world saw what had been years – decades – in the making: landmark peace agreements dubbed the Abraham Accords -- normalizing relations between Israel and two Arabian Gulf states, the United Arab Emirates and the Kingdom of Bahrain. Later in December, they were joined by the Kingdom of Morocco. Five years later, AJC is pulling back the curtain to meet key individuals who built the trust that led to these breakthroughs. Introducing: the Architects of Peace. Manya Brachear Pashman: On the eve of the signing of the Abraham Accords, AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson found himself traveling to the end of a tree filled winding road in McLean, Virginia, to sip tea on the back terrace with Bahraini Ambassador Shaikh Abdulla bin Rashid Al Khalifa and Bahrain's Minister of Foreign Affairs Dr. Abdullatif bin Rashid Al Zayani. Jason Isaacson: Sitting in the backyard of the Bahraini ambassador's house with Dr. Al Zayani, the Foreign Minister of Bahrain and with Shaikh Abdulla, the ambassador, and hearing what was about to happen the next day on the South Lawn of the White House was a thrilling moment. And really, in many ways, just a validation of the work that AJC has been doing for many years–before I came to the organization, and the time that I've spent with AJC since the early 90s. This possibility of Israel's true integration in the region, Israel's cooperation and peace with its neighbors, with all of its neighbors – this was clearly the threshold that we were standing on. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you're wondering how Jason ended up sipping tea in such esteemed company the night before his hosts made history, wonder no more. Here's the story. Yitzchak Shamir : The people of Israel look to this palace with great anticipation and expectation. We pray that this meeting will mark the beginning of a new chapter in the history of the Middle East; that it will signal the end of hostility, violence, terror, and war; that it will bring dialogue, accommodation, co-existence, and above all, peace. Manya Brachear Pashman: That was Israel's Prime Minister Yitzhak Shamir speaking in October 1991 at the historic Madrid Peace Conference -- the first time Israel and Arab delegations engaged in direct talks toward peace. It had taken 43 years to reach this point – 43 years since the historic United Nations Resolution that created separate Jewish and Arab states – a resolution Jewish leaders accepted, but Arab states scorned. Not even 24 hours after Israel declared its independence on May 14, 1948, the armies of Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, and Syria attacked the new Jewish state, which fought back mightily and expanded its territory. The result? A deep-seated distrust among Israel, its neighboring nations, and some of the Arab residents living within Israel's newly formed borders. Though many Palestinian Arabs stayed, comprising over 20 percent of Israel's population today, hundreds of thousands of others left or were displaced. Meanwhile, in reaction to the rebirth of the Jewish state, and over the following two decades, Jewish communities long established in Arab states faced hardship and attacks, forcing Jews by the hundreds of thousands to flee. Israel's War of Independence set off a series of wars with neighboring nations, terrorist attacks, and massacres. Peace in the region saw more than a few false starts, with one rare exception. In 1979, after the historic visit to Israel by Egyptian President Anwar Sadat, he and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin joined President Jimmy Carter for negotiations at Camp David and signed a peace treaty that for the next 15 years, remained the only formal agreement between Israel and an Arab state. In fact, it was denounced uniformly across the Arab world. But 1991 introduced dramatic geopolitical shifts. The collapse of the Soviet Union, which had severed relations with Israel during the Six-Day War of 1967, diminished its ability to back Syria, Iraq, and Libya. In the USSR's final months, it re-established diplomatic relations with Israel but left behind a regional power vacuum that extremists started to fill. Meanwhile, most Arab states, including Syria, joined the successful U.S.-led coalition against Saddam Hussein that liberated Kuwait, solidifying American supremacy in the region and around the world. The Palestine Liberation Organization, which claimed to represent the world's Palestinians, supported Iraq and Libya. Seizing an opportunity, the U.S. and the enfeebled but still relevant Soviet Union invited to Madrid a joint Jordanian-Palestinian delegation, along with delegations from Lebanon, Jordan, Syria, Egypt, and Israel. Just four months before that Madrid meeting, Jason Isaacson had left his job on Capitol Hill to work for the American Jewish Committee. At that time, AJC published a magazine titled Commentary, enabling Jason to travel to the historic summit with media credentials and hang out with the press pool. Jason Isaacson: It was very clear in just normal conversations with these young Arab journalists who I was spending some time with, that there was the possibility of an openness that I had not realized existed. There was a possibility of kind of a sense of common concerns about the region, that was kind of refreshing and was sort of running counter to the narratives that have dominated conversations in that part of the world for so long. And it gave me the sense that by expanding the circle of relationships that I was just starting with in Madrid, we might be able to make some progress. We might be able to find some partners with whom AJC could develop a real relationship. Manya Brachear Pashman: AJC had already begun to build ties in the region in the 1950s, visiting Arab countries like Morocco and Tunisia, which had sizable Jewish populations. The rise in Arab nationalism in Tunisia and rebirth of Israel eventually led to an exodus that depleted the Jewish community there. Emigration depleted Morocco's Jewish community as well. Jason Isaacson: To say that somehow this is not the native land of the Jewish people is just flying in the face of the reality. And yet, that was the propaganda line that was pushed out across the region. Of course, Madrid opened a lot of people's eyes. But that wasn't enough. More had to be done. There were very serious efforts made by the U.S. government, Israeli diplomats, Israeli businesspeople, and my organization, which played a very active role in trying to introduce people to the reality that they would benefit from this relationship with Israel. So it was pushing back against decades of propaganda and lies. And that was one of the roles that we assigned to ourselves and have continued to play. Manya Brachear Pashman: No real negotiations took place at the Madrid Conference, rather it opened conversations that unfolded in Moscow, in Washington, and behind closed doors in secret locations around the world. Progress quickened under Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin. In addition to a peace treaty between Israel and Jordan, reached in 1994, secret talks in Norway between Israel and PLO resulted in the Oslo Accords, a series of agreements signed in 1993 and 1995 that ended the First Intifada after six years of violence, and laid out a five-year timeline for achieving a two-state solution. Extremists tried to derail the process. A Jewish extremist assassinated Rabin in 1995. And a new terror group launched a series of suicide attacks against Israeli civilians. Formed during the First Intifada, these terrorists became stars of the Second. They called themselves Hamas. AP News Report: [sirens] [in Hebrew] Don't linger, don't linger. Manya Brachear Pashman: On March 27, 2002, Hamas sent a suicide bomber into an Israeli hotel where 250 guests had just been seated for a Passover Seder. He killed 30 people and injured 140 more. The day after the deadliest suicide attack in Israel's history, the Arab League, a coalition of 22 Arab nations in the Middle East and Africa, unveiled what it called the Arab Peace Initiative – a road map offering wide scale normalization of relations with Israel, but with an ultimatum: No expansion of Arab-Israeli relations until the establishment of a Palestinian state within the pre-1967 armistice lines and a so-called right of return for Palestinians who left and their descendants. As the Second Intifada continued to take civilian lives, the Israeli army soon launched Operation Defensive Shield to secure the West Bank and parts of Gaza. It was a period of high tension, conflict, and distrust. But behind the scenes, Jason and AJC were forging ahead, building bridges, and encountering an openness in Arab capitals that belied the ultimatum. Jason Isaacson: It has become clear to me in my travels in the region over the decades that more and more people across the Arab world understood the game, and they knew that that this false narrative that Jews are not legitimately there, and that somehow we have to focus all of our energy in the Arab world on combating this evil interloper – it's nonsense. And it's becoming increasingly clear that, in fact, Israel can be a partner of Arab countries. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jason led delegations of Jewish leaders to Arab capitals, oversaw visits by Arab leaders to Israel, and cultivated relationships of strategic and political consequence with governments and civil society leaders across North Africa, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. In 2009, King Mohammed VI of Morocco bestowed on him the honor of Chevalier of the Order of the Throne of the Kingdom of Morocco. Jason's priority was nurturing one key element missing from Arab-Israeli relations. An element that for decades had been absent in most Middle East peace negotiations: trust. Jason Isaacson: Nothing is more important than developing trust. Trust and goodwill are, if not synonymous, are so closely linked. Yes, a lot of these discussions that AJC's been engaged in over many years have been all about, not only developing a set of contacts we can turn to when there's a crisis or when we need answers to questions or when we need to pass a message along to a government. But also, develop a sense that we all want the same thing and we trust each other. That if someone is prepared to take certain risks to advance the prospect of peace, which will involve risk, which will involve vulnerability. That a neighbor who might have demonstrated in not-so-distant past animosity and hostility toward Israel can be trusted to take a different course. Manya Brachear Pashman: A number of Israeli diplomats and businesspeople also worked toward that goal. While certain diplomatic channels in the intelligence and security spheres stayed open out of necessity – other diplomats and businesspeople with dual citizenship traveled across the region, quietly breaking down barriers, starting conversations, and building trust. Jason Isaacson: I would run into people in Arab capitals from time to time, who were fulfilling that function, and traveling with different passports that they had legitimately, because they were from those countries. It was just a handful of people in governments that would necessarily know that they were there. So yes, if that sounds like cloak and dagger, it's kind of a cloak and dagger operation, a way for people to maintain a relationship and build a relationship until the society is ready to accept the reality that it will be in their country's best interest to have that relationship. Manya Brachear Pashman: Privately, behind the scenes, signs emerged that some Arab leaders understood the role that Jews have played in the region's history for millennia and the possibilities that would exist if Muslims and Jews could restore some of the faith and friendship of bygone years. Jason Isaacson: I remember sitting with King Mohammed the VI of Morocco just weeks after his ascension to the throne, so going back more than a quarter century, and hearing him talk with me and AJC colleagues about the 600,000 subjects that he had in Israel. Of course, these were Jews, Israelis of Moroccan descent, who are in the hundreds of thousands. But the sense that these countries really have a common history. Manya Brachear Pashman: Common history, yes. Common goals, too. And not for nothing, a common enemy. The same extremist forces that have been bent on Israel's destruction have not only disrupted Israeli-Arab peace, they've prevented the Palestinian people from thriving in a state of their own and now threaten the security and stability of the entire region. Jason Isaacson: We are hopeful that in partnership with those in the Arab world who feel the same way about the need to push back against extremism, including the extremism promoted, promulgated, funded, armed by the Islamic Republic of Iran, that we can have enough of a network of supportive players in the Arab world, in the West. Working with Israel and working with Palestinian partners who are interested in the same future. A real future, a politically free future, where we can actually make some progress. And that's an ongoing effort. This is a point that we made consistently over many years: if you want to help the Palestinian people–and we want to help the Palestinian people–but if you, fill in the blank Arab government official, your country wants to help the Palestinian people, you're not helping them by pretending that Israel doesn't exist. You're not helping them by isolating Israel, by making Israel a pariah in the minds of your people. You will actually have leverage with Israel, and you'll help the Palestinians when they're sitting at a negotiating table across from the Israelis. If you engage Israel, if you have access to the Israeli officials and they have a stake in your being on their side on certain things and working together on certain common issues. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jason says more and more Arab leaders are realizing, with some frustration, that isolating Israel is a losing proposition for all the parties involved. It has not helped the Palestinian people. It has not kept extremism at bay. And it has not helped their own countries and their own citizens prosper. In fact, the limitations that isolating Israel imposes have caused many countries to lag behind the tiny Jewish state. Jason Isaacson: I think there was just this sense of how far back we have fallen, how much ground we have to make up. We need to break out of the old mindset and try something different. But that before the Abraham Accords, they were saying it in the years leading up to the Abraham Accords, with increasing frustration for the failure of Palestinian leadership to seize opportunities that had been held out to them. But frankly, also contributing, I think, to this was this insistence on isolating themselves from a naturally synergistic relationship with a neighboring state right next door that could contribute to the welfare of their societies. It just didn't make a whole lot of sense, and it denied them the ability to move forward. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jason remembers the first time he heard an Arab official utter the words out loud – expressing a willingness, daresay desire, to partner with Israel. Jason Isaacson: It took a long time, but I could see in 2016, 17, 18, 19, this growing awareness, and finally hearing it actually spoken out loud in one particular conference that I remember going to in 2018 in Bahrain, by a senior official from an Arab country. It took a long time for that lesson to penetrate, but it's absolutely the case. Manya Brachear Pashman: In 2019, Bahrain hosted an economic summit where the Trump administration presented its "Peace to Prosperity" plan, a $50 billion investment proposal to create jobs and improve the lives of Palestinians while also promoting regional peace and security. Palestinians rejected the plan outright and refused to attend. Bahrain invited Israeli media to cover the summit. That September, on the sidelines of the UN General Assembly, AJC presented its inaugural Architect of Peace Award to the Kingdom of Bahrain's chief diplomat for nearly 20 years. Shaikh Khalid bin Ahmed Al Khalifa, Bahrain's Minister of Foreign Affairs at the time, told Jason that it was important to learn the lessons of the late Egyptian President Anwar Sadat and late Jordanian King Hussein, both of whom signed peace treaties with Israel. He also explained the reason why Bahrain invited Israeli media. Shaikh Khalid bin Ahmed Al Khalifa : President Anwar Sadat did it, he broke a huge barrier. He was a man of war, he was the leader of a country that went to war or two with Israel. But then he knew that at the right moment he would want to go straight to Israeli and talk to them. We fulfilled also something that we've always wanted to do, we've discussed it many times: talking to the Israeli public through the Israeli media. Why not talk to the people? They wake up every day, they have their breakfast watching their own TV channels, they read their own papers, they read their own media, they form their own opinion. Absolutely nobody should shy away from talking to the media. We are trying to get our point across. In order to convince. How will you do it? There is no language of silence. You'll have to talk and you'll have to remove all those barriers and with that, trust can be built. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jason had spent decades building that trust and the year to come yielded clear results. In May and June 2020, UAE Ambassador to the UN Lana Nusseibeh and UAE Minister of State Dr. Anwar Gargash both participated in AJC webinars to openly discuss cooperation with Israel – a topic once considered taboo. So when the Abraham Accords were signed a few months later, for Jason and AJC colleagues who had been on this long journey for peace, it was a natural progression. Though no less dramatic. Sitting with Minister Al Khalifa's successor, Dr. Al Zayani, and the Bahraini ambassador on the evening before the White House ceremony, it was time to drink a toast to a new chapter of history in the region. Jason Isaacson: I don't think that that would have been possible had there not been decades of contacts that had been made by many people. Roving Israeli diplomats and Israeli business people, usually operating, in fact, maybe always operating with passports from other countries, traveling across the region. And frankly, our work and the work of a limited number of other people who were in non-governmental positions. Some journalists, authors, scholars, business people, and we certainly did a great deal of this over decades, would speak with leaders in these countries and influential people who are not government officials. And opening up their minds to the possibility of the advantages that would accrue to their societies by engaging Israel and by better understanding the Jewish people and who we are, what we care about, who we are not. Because there was, of course, a great deal of decades, I should say, centuries and millennia, of misapprehensions and lies about the Jewish people. So clearing away that baggage was a very important part of the work that we did, and I believe that others did as well. We weren't surprised. We were pleased. We applauded the Trump administration, the President and his team, for making this enormous progress on advancing regional security and peace, prosperity. We are now hoping that we can build on those achievements of 2020 going forward and expanding fully the integration of Israel into its neighborhood. Manya Brachear Pashman: Next episode, we hear how the first Trump administration developed its Middle East policy and take listeners behind the scenes of the high stakes negotiations that yielded the Abraham Accords. Atara Lakritz is our producer. T.K. Broderick is our sound engineer. Special thanks to Jason Isaacson, Sean Savage, and the entire AJC team for making this series possible. You can subscribe to Architects of Peace on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you listen to podcasts, and you can learn more at AJC.org/ArchitectsofPeace . The views and opinions of our guests don't necessarily reflect the positions of AJC. You can reach us at podcasts@ajc.org. If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to spread the word, and hop onto Apple Podcasts or Spotify to rate us and write a review to help more listeners find us. ___ Music Credits: Middle East : ID: 279780040; Composer: Eric Sutherland Middle East Violin : ID: 277189507; Composer: Andy Warner Frontiers : ID: 183925100; Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI); Composer: Pete Checkley (BMI) Middle East Tension : ID: 45925627 Arabic Ambient : ID: 186923328; Publisher: Victor Romanov; Composer: Victor Romanov Arabian Strings : ID: 72249988; Publisher: EITAN EPSTEIN; Composer: EITAN EPSTEIN Inspired Middle East : ID: 241884108; Composer: iCENTURY Middle East Dramatic Intense : ID: 23619101; Publisher: GRS Records; Composer: Satria Petir Mystical Middle East : ID: 212471911; Composer: Vicher
Aug 15
3 Ways Jewish College Students are Building Strength Amid Hate
"Our duty as Jewish youth is paving the way for ourselves. Sometimes we may feel alone . . . But the most important thing is for us as youth to pave the way for ourselves, to take action, to speak out. Even if it's hard or difficult." As American Jewish college students head back to their campuses this fall, we talk to three leaders on AJC's Campus Global Board about how antisemitism before and after the October 7 Hamas terror attacks revealed their resilience and ignited the activist inside each of them. Jonathan Iadarola shares how a traumatic anti-Israel incident at University of Adelaide in Australia led him to secure a safe space on campus for Jewish students to convene. Ivan Stern recalls launching the Argentinian Union of Jewish Students after October 7, and Lauren Eckstein shares how instead of withdrawing from her California college and returning home to Arizona, she transferred to Washington University in St. Louis where she found opportunities she never dreamed existed and a supportive Jewish community miles from home. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Key Resources: AJC Campus Global Board Trusted Back to School Resources from AJC AJC's 10-Step Guide for Parents Supporting Jewish K-12 Students AJC's Center for Education Advocacy Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: War and Poetry: Owen Lewis on Being a Jewish Poet in a Time of Crisis An Orange Tie and A Grieving Crowd: Comedian Yohay Sponder on Jewish Resilience From Broadway to Jewish Advocacy: Jonah Platt on Identity, Antisemitism, and Israel Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: MANYA: As American Jewish college students head back to their campuses this fall, it's hard to know what to expect. Since the Hamas terror attacks of October 7, maintaining a GPA has been the least of their worries. For some who attend universities that allowed anti-Israel protesters to vandalize hostage signs or set up encampments, fears still linger. We wanted to hear from college students how they're feeling about this school year. But instead of limiting ourselves to American campuses, we asked three students from AJC's Campus Global Board – from America, Argentina, and Australia – that's right, we still aim for straight A's here. We asked them to share their experiences so far and what they anticipate this year. We'll start on the other side of the world in Australia. With us now is Jonathan Iadarola, a third-year student at the University of Adelaide in Adelaide, Australia, the land down under, where everything is flipped, and they are getting ready to wrap up their school year in November. Jonathan serves as president of the South Australia branch of the Australian Union of Jewish students and on AJC's Campus Global Board. Jonathan, welcome to People of the Pod. JONATHAN: Thank you for having me. MANYA: So tell us what your experience has been as a Jewish college student in Australia, both before October 7 and after. JONATHAN: So at my university, we have a student magazine, and there was a really awful article in the magazine that a student editor wrote, very critical of Israel, obviously not very nice words. And it sort of ended with like it ended with Death to Israel, glory to the Intifada. Inshallah, it will be merciless. So it was very, very traumatic, obviously, like, just the side note, my great aunt actually died in the Second Intifada in a bus bombing. So it was just like for me, a very personal like, whoa. This is like crazy that someone on my campus wrote this and genuinely believes what they wrote. So yeah, through that experience, I obviously, I obviously spoke up. That's kind of how my activism on campus started. I spoke up against this incident, and I brought it to the university. I brought it to the student editing team, and they stood their ground. They tried to say that this is free speech. This is totally okay. It's completely like normal, normal dialog, which I completely disagreed with. And yeah, they really pushed back on it for a really long time. And it just got more traumatic with myself and many other students having to go to meetings in person with this student editor at like a student representative council, which is like the students that are actually voted in. Like student government in the United States, like a student body that's voted in by the students to represent us to the university administration. And though that student government actually laughed in our faces in the meeting while we were telling them that this sort of incident makes us as Jewish students feel unsafe on campus. And we completely were traumatized. Completely, I would say, shattered, any illusion that Jewish students could feel safe on campus. And yeah, that was sort of the beginning of my university journey, which was not great. MANYA: Wow. And that was in 2022, before October 7. So after the terror attacks was when most college campuses here in America really erupted. Had the climate at the University of Adelaide improved by then, or did your experience continue to spiral downward until it was addressed? JONATHAN: It's kind of remained stagnant, I would say. The levels haven't really improved or gotten worse. I would say the only exception was maybe in May 2024, when the encampments started popping up across the world. Obviously it came, came to my city as well. And it wasn't very, it wasn't very great. There was definitely a large presence on my campus in the encampment. And they were, they were more peaceful than, I would say, other encampments across Australia and obviously in the United States as well. But it was definitely not pleasant for students to, you know, be on campus and constantly see that in their faces and protesting. They would often come into people's classrooms as well. Sharing everything that they would like to say. You couldn't really escape it when you were on campus. MANYA: So how did you find refuge? Was there a community center or safe space on campus? Were there people who took you in? JONATHAN: So I'm the president of the Jewish Student Society on my campus. One of the things that I really pushed for when the encampments came to my city was to have a Jewish space on campus. It was something that my university never had, and thankfully, we were able to push and they were like 'Yes, you know what? This is the right time. We definitely agree.' So we actually now have our own, like, big Jewish room on campus, and we still have it to this day, which is amazing. So it's great to go to when, whether we feel uncomfortable on campus, or whether we just want a place, you know, to feel proud in our Jewish identity. And there's often events in the room. There's like, a Beers and Bagels, or we can have beer here at 18, so it's OK for us. And there's also, yeah, there's bagels. Then we also do Shabbat dinners. Obviously, there's still other stuff happening on campus that's not as nice, but it's great that we now have a place to go when we feel like we need a place to be proud Jews. MANYA: You mentioned that this was the start of your Jewish activism. So, can you tell us a little bit about your Jewish upbringing and really how your college experience has shifted your Jewish involvement, just activity in general? JONATHAN: Yeah, that's a great question. So I actually grew up in Adelaide. This is my home. I was originally born in Israel to an Israeli mother, but we moved, I was two years old when we moved to Adelaide. There was a Jewish school when I grew up. So I did attend the Jewish school until grade five, and then, unfortunately, it did close due to low numbers. And so I had to move to the public school system. And from that point, I was very involved in the Jewish community through my youth. And then there was a point once the Jewish school closed down where I kind of maybe slightly fell out. I was obviously still involved, but not to the same extent as I was when I was younger. And then I would say the first place I got kind of reintroduced was once I went to college and obviously met other Jewish students, and then it made me want to get back in, back, involved in the community, to a higher level than I had been since primary school. And yeah, then obviously, these incidents happened on campus, and that kind of, I guess, it shoved me into the spotlight unintentionally, where I felt like no one else was saying anything. I started just speaking up against this. And then obviously, I think many other Jews on campus saw this, and were like: 'Hang on. We want to also support this and, like, speak out against it.' and we kind of formed a bit of a group on campus, and that's how the club actually was formed as well. So the club didn't exist prior to this incident. It kind of came out of it, which is, I guess, the beautiful thing, but also kind of a sad thing that we only seem to find each other in incidences of, you know, sadness and trauma. But the beautiful thing is that from that, we have been able to create a really nice, small community on campus for Jewish students. So yeah, that's sort of how my journey started. And then through that, I got involved with the Australsian Union of Jewish Students, which is the Jewish Student Union that represents Jewish students all across Australia and New Zealand. And I started the South Australian branch, which is the state that Adelaide is in. And I've been the president for the last three years. So that's sort of been my journey. And obviously through that, I've gotten involved with American Jewish Committee. MANYA: So you're not just fighting antisemitism, these communities and groups that you're forming are doing some really beautiful things. JONATHAN: Obviously, I really want to ensure that Jewish student life can continue to thrive in my city, but also across Australia. And one way that we've really wanted to do that is to help create essentially, a national Shabbaton. An event where Jewish students from all across the country, come to one place for a weekend, and we're all together having a Shabbat dinner together, learning different educational programs, hearing from different amazing speakers, and just being with each other in our Jewish identity, very proud and united. It's one of, I think, my most proud accomplishments so far, through my college journey, that I've been able to, you know, create this event and make it happen. MANYA: And is there anything that you would like to accomplish Jewishly before you finish your college career? JONATHAN: There's a couple things. The big thing for me is ensuring, I want there to continue to be a place on campus for people to go and feel proud in their Jewish identity. I think having a Jewish space is really important, and it's something that I didn't have when I started my college journey. So I'm very glad that that's in place for future generations. For most of my college journey so far, we didn't have even a definition at my university for antisemitism. So if you don't have a definition, how are you going to be able to define what is and what isn't antisemitic and actually combat it? So now, thankfully, they do have a definition. I don't know exactly if it's been fully implemented yet, but I know that they have agreed to a definition, and it's a mix of IHRA and the Jerusalem Declaration, I believe, so it's kind of a mix. But I think as a community, we're reasonably happy with it, because now they actually have something to use, rather than not having anything at all. And yeah, I think those are probably the two main things for me, obviously, ensuring that there's that processes at the university moving forward for Jewish students to feel safe to report when there are incidents on campus. And then ensuring that there's a place for Jewish students to continue to feel proud in their Jewish identity and continue to share that and live that while they are studying at the university. MANYA: Well, Jonathan, thank you so much for joining us, and enjoy your holiday. JONATHAN: Thank you very much. I really appreciate it. MANYA: Now we turn to Argentina, Buenos Aires to be exact, to talk to Ivan Stern, the first Argentine and first Latin American to serve on AJC's Campus Global Board. A student at La Universidad Nacional de San Martin, Ivan just returned to classes last week after a brief winter break down there in the Southern Hemisphere. What is Jewish life like there on that campus? Are there organizations for Jewish students? IVAN: So I like to compare Jewish life in Buenos Aires like Jewish life in New York or in Paris or in Madrid. We are a huge city with a huge Jewish community where you can feel the Jewish sense, the Jewish values, the synagogues everywhere in the street. When regarding to college campuses, we do not have Jewish institutions or Jewish clubs or Jewish anything in our campuses that advocate for Jewish life or for Jewish students. We don't actually need them, because the Jewish community is well established and respected in Argentina. Since our terrorist attacks of the 90s, we are more respected, and we have a strong weight in all the decisions. So there's no specific institution that works for Jewish life on campus until October 7 that we gathered a student, a student led organization, a student led group. We are now part of a system that it's created, and it exists in other parts of the world, but now we are start to strengthening their programming and activities in Argentina we are we now have the Argentinian union with Jewish students that was born in October 7, and now we represent over 150 Jewish students in more than 10 universities. We are growing, but we are doing Shabbat talks in different campuses for Jewish students. We are bringing Holocaust survivors to universities to speak with administrations and with student cabinets that are not Jewish, and to learn and to build bridges of cooperation, of course, after October 7, which is really important. So we are in the middle of this work. We don't have a strong Hillel in campuses or like in the US, but we have Jewish students everywhere. We are trying to make this grow, to try to connect every student with other students in other universities and within the same university. And we are, yeah, we are work in progress. MANYA: Listeners just heard from your Campus Global Board colleague Jonathan Iadarola from Adelaide, Australia, and he spoke about securing the first space for Jewish students on campus at the University of Adelaide. Does that exist at your university? Do you have a safe space? So Hillel exists in Buenos Aires and in Cordoba, which Cordova is another province of Argentina. It's a really old, nice house in the middle of a really nice neighborhood in Buenos Aires. So also in Argentina another thing that it's not like in the U.S., we don't live on campuses, so we come and go every day from our houses to the to the classes. So that's why sometimes it's possible for us to, after classes, go to Hillel or or go to elsewhere. And the Argentinian Union, it's our job to represent politically to the Jewish youth on campus. To make these bridges of cooperation with non-Jewish actors of different college campuses and institutions, as I mentioned before, we bring Holocaust survivors, we place banners, we organize rallies. We go to talk with administrators. We erase pro- Palestinian paints on the wall. We do that kind of stuff, building bridges, making programs for Jewish youth. We also do it, but it's not our main goal. MANYA: So really, it's an advocacy organization, much like AJC. IVAN: It's an advocacy organization, and we are really, really, really happy to work alongside with the AJC more than once to strengthen our goals. MANYA: October 7 was painful for all of us, what happened on university campuses there in Argentina that prompted the need for a union? So the impact of October 7 in Argentina wasn't nearly as strong as in other parts of the world, and definitely nothing like what's been happening on U.S. campuses. Maybe that's because October here is finals season, and our students were more focused on passing their classes than reacting to what was happening on the Middle East, but there were attempts of engagements, rallies, class disruptions and intimidations, just like in other places. That's why we focused on speaking up, taking action. So here it's not happening. What's happening in the U.S., which was really scary, and it's still really scary, but something was happening, and we needed to react. There wasn't a Jewish institution advocating for Jewish youth on campus, directly, getting to know what Jewish students were facing, directly, lively walking through the through the hallways, through the campus, through the campuses. So that's why we organize this student-led gathering, different students from different universities, universities. We need to do something. At the beginning, this institution was just on Instagram. It was named the institutions, and then for Israel, like my university acronym, it's unsam Universidad national, San Martin unsam. So it was unsam for Israel. So we, so we posted, like every campaign we were doing in our campuses, and then the same thing happened in other university and in other universities. So now we, we gathered everyone, and now we are the Argentinian Union of Jewish students. But on top of that, in November 2023 students went on summer break until March 2024 so while the topic was extremely heated elsewhere here, the focus had shifted on other things. The new national government was taking office, which had everyone talking more about their policies than about Israel. So now the issue is starting to resurface because of the latest news from Gaza, So we will go where it goes from here, but the weight of the community here, it's, as I said, really strong. So we have the ability to speak up. MANYA: What kinds of conversations have you had with university administrators directly after. October 7, and then now, I mean, are you, are you communicating with them? Do you have an open channel of communication? Or is are there challenges? IVAN: we do? That's an incredible question there. It's a tricky one, because it depends on the university. The answer we receive. Of course, in my university, as I said, we are, we are lots of Jews in our eyes, but we are a strong minority also, but we have some Jewish directors in the administration, so sometimes they are really focused on attending to our concerns, and they are really able to to pick a call, to answer back our messages, also, um, there's a there's a great work that Argentina has been, has been doing since 2020 to apply the IHRA definition in every institute, in every public institution. So for example, my university, it's part of the IHRA definition. So that's why it was easy for us to apply sanctions to student cabinets or student organizations that were repeating antisemitic rhetorics, distortioning the Holocaust messages and everything, because we could call to our administrators, regardless if they were Jewish or not, but saying like, 'Hey, this institution is part of the IHRA definition since February 2020, it's November 2023, and this will be saying this, this and that they are drawing on the walls of the of our classrooms. Rockets with Magen David, killing people. This is distortioning the Jewish values, the religion, they are distortioning everything. Please do something.' So they started doing something. Then with the private institutions, we really have a good relationship. They have partnerships with different institutions from Israel, so it's easy for us to stop political demonstrations against the Jewish people. We are not against political demonstrations supporting the Palestinian statehood or anything. But when it regards to the safety of Jewish life on campus or of Jewish students, we do make phone calls. We do call to other Jewish institutions to have our back. And yes, we it's we have difficult answers, but we but the important thing is that we have them. They do not ghost us, which is something we appreciate. But sometimes ghosting is worse. Sometimes it's better for us to know that the institution will not care about us, than not knowing what's their perspective towards the problem. So sometimes we receive like, 'Hey, this is not an antisemitism towards towards our eyes. If you want to answer back in any kind, you can do it. We will not do nothing. MANYA: Ivan, I'm wondering what you're thinking of as you're telling me this. Is there a specific incident that stands out in your mind as something the university administrators declined to address? IVAN: So in December 2023, when we were all in summer break, we went back to my college, to place the hostages signs on the walls of every classroom. Because at the same time, the student led organizations that were far left, student-led organizations were placing these kind of signs and drawings on the walls with rockets, with the Magen David and demonizing Jews. So we did the same thing. So we went to the school administrators, and we call them, like, hey, the rocket with the Magen David. It's not okay because the Magen David is a Jewish symbol. This is a thing happening in the Middle East between a state and another, you have to preserve the Jewish students, whatever. And they told us, like, this is not an antisemitic thing for us, regardless the IHRA definition. And then they did do something and paint them back to white, as the color of the wall. But they told us, like, if you want to place the hostages signs on top of them or elsewhere in the university, you can do it. So if they try to bring them down, yet, we will do something, because that this is like free speech, that they can do whatever they want, and you can do whatever that you want. So that's the answers we receive. So sometimes they are positive, sometimes they are negative, sometimes in between. But I think that the important thing is that the youth is united, and as students, we are trying to push forward and to advocate for ourselves and to organize by ourselves to do something. MANYA: Is there anything that you want to accomplish, either this year or before you leave campus? IVAN: To keep building on the work of the Argentinian Union of Jewish Students is doing bringing Jewish college students together, representing them, pushing our limits, expanding across the country. As I said, we have a strong operations in Buenos Aires as the majority of the community is here, but we also know that there's other Jewish students in other provinces of Argentina. We have 24 provinces, so we are just working in one. And it's also harder for Jewish students to live Jewishly on campus in other provinces when they are less students. Then the problems are bigger because you feel more alone, because you don't know other students, Jews or non-Jews. So that's one of my main goals, expanding across the country, and while teaming up with non-Jewish partners. MANYA: You had said earlier that the students in the union were all buzzing about AJC's recent ad in the The New York Times calling for a release of the hostages still in Gaza.Are you hoping your seat on AJC's Campus Global Board will help you expand that reach? Give you some initiatives to empower and encourage your peers. Not just your peers, Argentina's Jewish community at large. IVAN: My grandma is really happy about the AJC donation to the Gaza church. She sent me a message. If you have access to the AJC, please say thank you about the donation. And then lots of Jewish students in the in our union group chat, the 150 Jewish students freaking out about the AJC article or advice in The New York Times newspaper about the hostages. So they were really happy MANYA: In other words, they they like knowing that there's a global advocacy organization out there on their side? IVAN: Also advocating for youth directly. So sometimes it's hard for us to connect with other worldwide organizations. As I said, we are in Argentina, in the bottom of the world. AJC's worldwide. And as I said several times in this conversation, we are so well established that sometimes we lack of international representation here, because everything is solved internally. So if you have, if you have anything to say, you will go to the AMIA or to the Daya, which are the central organizations, and that's it. And you are good and there. And they may have connections or relationships with the AJC or with other organizations. But now students can have direct representations with organizations like AJC, which are advocating directly for us. So we appreciate it also. MANYA: You said things never got as heated and uncomfortable in Argentina as they did on American college campuses. What encouragement would you like to offer to your American peers? I was two weeks ago in New York in a seminar with other Jewish students from all over the world and I mentioned that our duty as Jewish youth is paving the way for ourselves. Sometimes we may feel alone. Sometimes we are, sometimes we are not. But the most important thing is for us as youth to pave the way for ourselves, to take action, to speak out. Even if it's hard or difficult. It doesn't matter how little it is, but to do something, to start reconnecting with other Jews, no matter their religious spectrum, to start building bridges with other youth. Our strongest aspect is that we are youth, Not only because we are Jewish, but we are youth. So it's easier for us to communicate with our with other peers. So sometimes when everything is, it looks like hate, or everything is shady and we cannot see the light at the end of the tunnel. We should remember that the other one shouting against us is also a peer. MANYA:. Thank you so much, Ivan. Really appreciate your time and good luck going back for your spring semester. IVAN: Thank you. Thank you so much for the time and the opportunity. MANYA: Now we return home. Campus Global Board Member Lauren Eckstein grew up outside Phoenix and initially pursued studies at Pomona College in Southern California. But during the spring semester after the October 7 Hamas terror attacks, she transferred to Washington University in St. Louis. She returned to California this summer as one of AJC's Goldman Fellows. So Lauren, you are headed back to Washington University in St Louis this fall. Tell us what your experience there has been so far as a college student. LAUREN: So I've been there since January of 2024. It has a thriving Jewish community of Hillel and Chabad that constantly is just like the center of Jewish life. And I have great Jewish friends, great supportive non-Jewish friends. Administration that is always talking with us, making sure that we feel safe and comfortable. I'm very much looking forward to being back on campus. MANYA: As I already shared with our audience, you transferred from Pomona College. Did that have anything to do with the response on campus after October 7? LAUREN: I was a bit alienated already for having spent a summer in Israel in between my freshman and sophomore year. So that would have been the summer of 2023 before October 7, like few months before, and I already lost some friends due to spending that summer in Israel before anything had happened and experienced some antisemitism before October 7, with a student calling a pro-Israel group that I was a part of 'bloodthirsty baby killers for having a barbecue in celebration of Israeli independence. But after October 7 is when it truly became unbearable. I lost hundreds of followers on Instagram. The majority of people I was friends with started giving me dirty looks on campus. I was a history and politics double major at the time, so the entire history department signed a letter in support of the war. I lost any sense of emotional safety on campus. And so 20 days after October 7, with constant protests happening outside of my dorm, I could hear it from my dorm students going into dining halls, getting them to sign petitions against Israel, even though Israel had not been in Gaza at all at this point. This was all before the invasion happened. I decided to go home for a week for my mental well being, and ended up deciding to spend the rest of that semester at home. MANYA: What did your other Jewish classmates do at Pomona? Did they stay? Did they transfer as well? LAUREN: I would say the majority of Jewish students in Claremont either aren't really–they don't really identify with their Jewish identity in other way, in any way, or most of them identify as anti-Zionist very proudly. And there were probably only a few dozen of us in total, from all five colleges that would identify as Zionists, or really say like, oh, I would love to go to Israel. One of my closest friends from Pomona transferred a semester after I did, to WashU. A few other people I know transferred to other colleges as well. I think the choice for a lot of people were either, I'm going to get through because I only have a year left, or, like, a couple years left, or I'm going to go abroad. Or I'm just going to face it, and I know that it's going to be really difficult, and I'm only going to have a few friends and only have a few professors I can even take classes with, but I'm going to get through it. MANYA: So have you kept in touch with the friends in Pomona or at Pomona that cut you off, shot you dirty looks, or did those friendships just come to an end? LAUREN: They all came to an end. I can count on one hand, under one hand, the number of people that I talked to from any of the Claremont Colleges. I'm lucky to have one like really, really close friend of mine, who is not Jewish, that stood by my side during all of this, when she easily did not need to and will definitely always be one of my closest friends, but I don't talk to the majority of people that I was friends with at Pomona. MANYA: Well, I'm very sorry to hear that, but it sounds like the experience helped you recognize your truest friend. With only one year left at WashU, I'm sure plenty of people are asking you what you plan to do after you graduate, but I want to know what you are hoping to do in the time you have left on campus. LAUREN: I really just want to take it all in. I feel like I haven't had a very normal college experience. I mean, most people don't transfer in general, but I think my two college experiences have been so different from each other, even not even just in terms of antisemitism or Jewish population, but even just in terms of like, the kind of school it is, like, the size of it and all of that, I have made such amazing friends at WashU – Jewish and not – that I just really want to spend as much time with them as I can, and definitely spend as much time with the Jewish community and staff at Hillel and Chabad that I can. I'm minoring in Jewish, Islamic, Middle Eastern Studies, and so I'm really looking forward to taking classes in that subject, just that opportunity that I didn't have at Pomona. I really just want to go into it with an open mind and really just enjoy it as much as I can, because I haven't been able to enjoy much of my college experience. So really appreciate the good that I have. MANYA: As I mentioned before, like Jonathan and Ivan, you are on AJC's Campus Global Board. But you also served as an AJC Goldman Fellow in the Los Angeles regional office this summer, which often involves working on a particular project. Did you indeed work on something specific? LAUREN: I mainly worked on a toolkit for parents of kids aged K-8, to address Jewish identity and antisemitism. And so really, what this is trying to do is both educate parents, but also provide activities and tools for their kids to be able to really foster that strong Jewish identity. Because sadly, antisemitism is happening to kids at much younger ages than what I dealt with, or what other people dealt with. And really, I think bringing in this positive aspect of Judaism, along with providing kids the tools to be able to say, 'What I'm seeing on this social media platform is antisemitic, and this is why,' is going to make the next generation of Jews even stronger. MANYA: Did you experience any antisemitism or any challenges growing up in Arizona? LAUREN: I went to a non-religious private high school, and there was a lot of antisemitism happening at that time, and so there was a trend to post a blue square on your Instagram. And so I did that. And one girl in my grade –it was a small school of around 70 kids per grade, she called me a Zionist bitch for posting the square. It had nothing to do with Israel or anything political. It was just a square in solidarity with Jews that were being killed in the United States for . . . being Jewish. And so I went to the school about it, and they basically just said, this is free speech. There's nothing we can do about it. And pretty much everyone in my grade at school sided with her over it. I didn't really start wearing a star until high school, but I never had a second thought about it. Like, I never thought, oh, I will be unsafe if I wear this here. MANYA: Jonathan and Ivan shared how they started Jewish organizations for college students that hadn't existed before. As someone who has benefited from Hillel and Chabad and other support networks, what advice would you offer your peers in Argentina and Australia? LAUREN: It's so hard for me to say what the experience is like as an Argentinian Jew or as an Australian Jew, but I think community is something that Jews everywhere need. I think it's through community that we keep succeeding, generation after generation, time after time, when people try to discriminate against us and kill us. I believe, it's when we come together as a people that we can truly thrive and feel safe. And I would say in different places, how Jewish you want to outwardly be is different. But I think on the inside, we all need to be proud to be Jewish, and I think we all need to connect with each other more, and that's why I'm really excited to be working with students from all over the world on the Campus Global Board, because I feel like us as Americans, we don't talk to Jews from other countries as much as we should be. I think that we are one people. We always have been and always will be, and we really need to fall back on that. MANYA: Well, that's a lovely note to end on. Thank you so much, Lauren. LAUREN: Thank you. MANYA: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Adam Louis-Klein, a PhD candidate at McGill University. Adam shared his unexpected journey from researching the Desano tribe in the Amazon to confronting rising antisemitism in academic circles after October 7. He also discussed his academic work, which explores the parallels between indigenous identity and Jewish peoplehood, and unpacks the politics of historical narrative. Next week, People of the Pod will be taking a short break while the AJC podcast team puts the finishing touches on a new series set to launch August 28: Architects of Peace: The Abraham Accords Story. Stay tuned.
Aug 7
From the Amazon to Academia: Antisemitism, Zionism, and Indigenous Identity
As the school year kicks off, Adam Louis-Klein shares his unexpected journey from researching the Desano tribe in the Amazon to confronting rising antisemitism in academic circles after October 7. He discusses his academic work, which explores the parallels between indigenous identity and Jewish peoplehood, and unpacks the politics of historical narrative. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: War and Poetry: Owen Lewis on Being a Jewish Poet in a Time of Crisis An Orange Tie and A Grieving Crowd: Comedian Yohay Sponder on Jewish Resilience From Broadway to Jewish Advocacy: Jonah Platt on Identity, Antisemitism, and Israel Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: Adam Louis-Klein is a PhD candidate in anthropology at McGill University, where he researches antisemitism, Zionism, Jewish peoplehood, and broader questions of indigeneity and historical narrative. His work bridges academic scholarship and public commentary, drawing on field work with indigenous communities in the Amazon and studies in philosophy at Yale, The New School and the University of Chicago. He writes on translation and the politics of peoplehood across traditions, and is committed to developing a Jewish intellectual voice grounded in historical depth and moral clarity. He blogs for The Times of Israel, and he's with us today to talk about his experience emerging from the Amazon, where he was doing research after October 7, 2023, and discovering what had happened in Israel. Adam, welcome to People of the Pod. Adam Louis-Klein: Thank you so much for having me. It's a real pleasure to be here on this podcast with the American Jewish community. Manya Brachear Pashman: So tell us about the research that you are doing that took you into the depths of the Amazon rainforest. Adam Louis-Klein: So I work with a group called the Desano people who live in the Vaupés region, which is a tributary of the upper Rio Negro. Part of it's in Brazil, part of it's in Colombia today. I went there because I was really interested in trying to understand how people were often seen at the margins of the world, the periphery of the global economy. See themselves and their own sort of role in the cosmos and in the world in general. And what I found actually is that these people see themselves at the center of it all, as a unique people, as a chosen people. And that was something that really inspired me, and later led me to rethink my own relationship to Jewish peoplehood and chosenness, and what it means to be a kind of indigenous people struggling for survival and recognition. Manya Brachear Pashman: So were you raised Jewish? Did you have a Jewish upbringing? Adam Louis-Klein: Yeah, I was raised as kind of a cultural and reform Jew. I wouldn't say that Israel was super present in our lives, but we did travel there for my younger brother's Bar Mitzvah at the Kotel, and that did have an impression on me. And then later on, I wear a wristband of Brothers for Life, which is a charity for injured Israeli soldiers. But as time went on, I got involved in these radical academic scenes. And you know, my own field, anthropology, has fundamentally turned against Jewish peoplehood and Israel, unfortunately. But it was really in the Amazon, actually, that my journey of Teshuvah and rediscovering my Jewishness and the importance of Jewish peoplehood was really re-awoken for me. Manya Brachear Pashman: You were involved in these radical circles. Did you ascribe to some of the beliefs that a lot of your academic colleagues were ascribing to? Did you start to question the legitimacy of Israel or the actions of the Israeli government? Adam Louis-Klein: I think I started to ascribe to them in a kind of background and passive way. In the way that I think that many people in these communities do. So I had actually learned about Israel. I did know something. But as I wanted to kind of ascribe to a broader social justice narrative, I sort of immediately assumed when people told me, that Israelis were the ones doing the oppression and the injustice, that that had to be true. And I didn't question it so much. So it's ironic that those spaces, I think, that are built around critical thought, have become spaces, in my opinion, that are not so critical today. And I think we really need a critical discourse around this kind of criticism, sort of to develop our own critical discourse of what anti-Zionism is today. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what inspired the research? In other words, so you're involved in these radical circles, and then you go and immerse yourself with these tribes to do the research. What inspired you to do it, and was it your Jewishness? Adam Louis-Klein: So I think what led me to anthropology was probably a kind of diasporic Jewish sensibility. So I'd studied philosophy before, and I was very entrenched in the Western tradition. But I was kind of seeking to think across worlds and think in translation. I've always kind of moved between countries and cities, and I think that's always been an intuitive part of who I am as a Jew. And anthropology was founded by Jews, by Franz Boas, Emile Durkheim, Claude Lévi-Strauss, so I think that's kind of part of what brought me there. But I ended up rediscovering also the meaning of, you know, homeland as well, and what it means to be part of a people with a unique destiny and relationship to territory and land. And that made me understand Zionism in a completely new light. Manya Brachear Pashman: And did you understand it when you were there? Did you come to these realizations when you were there, or did you start to piece all of that together and connect the dots after you emerged? Adam Louis-Klein: So part of my research looks at how indigenous people engage with Christian missionaries who try and translate the Bible into indigenous languages. So when that encounter happens, it's actually quite common throughout the world, that a lot of indigenous people identify with the Jewish people quite strongly. So this might sound a little counterintuitive, especially if someone's used to certain activist networks in which indigeneity is highly associated with Palestinians, Jews are treated now as settler colonists, which is basically the opposite of indigeneity. And that's become a kind of consensus in academia, even though it seems to fly in the face of both facts and our own self understanding as Jews. So I saw that in the Amazon, in the way people at the margins of the world who might not already be integrated in the academic, activist kind of scene, sort of organically identify with the Jewish people and Israel. And they admire the Jewish people and Israel, because they see in us, a people that's managed to maintain our cultural identity, our specific and distinct civilization, while also being able to use the tools of modernity and technology to benefit us and to benefit the world. So I think that also kind of disrupts some primitivist notions about indigenous people, that they should remain sort of technologically backwards, so to speak. I think that they have a more nuanced approach. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I guess, what did you discover when you did emerge from the Amazon? In other words, October 7 had happened. When did you emerge and how did you find out? Adam Louis-Klein: So I'd been living in a remote Desano village without internet or a phone or any connection to the outside world for months. And then I returned a couple days after October 7 to a local town, so still in the Amazon, but I was signing onto my computer for the first time in months, and I remember signing onto Facebook and I saw the images of people running from the Nova Festival. And that was the first thing that I saw in months from the world. So that was a very traumatic experience that sort of ruptured my sense of reality in many ways, but the most difficult thing was seeing my intellectual milieu immediately transform into a space of denial or justification or even just straightforward aggression and hate to anyone who showed any solidarity with Israelis in that moment, or who saw it as a moment to to say something positive and inspiring and helpful about the Jewish people. That was actually seen as an act of violence. So I went to Facebook, and I don't remember exactly what I said, I stand with the Jewish people, or with Israelis, or Am Yisrael Chai, or something like that. And many people in my circles, really interpreted that as an aggression. So at that point, it was really strange, because I'd been living in the Amazon, trying to help people with their own cultural survival, you know, their own struggle to reproduce their own civilization in the face of assimilation and surrounding society that refuses to validate their unique identity. And then I came back to the world, and I was seeing the exact same thing happening to my own people. And even stranger than that, it was happening to my own people, but in the language of critique and solidarity. So the very language I'd learned in anthropology, of how to support indigenous people and sort of to align myself with their struggles was now being weaponized against me in this kind of horrible inversion of reality. Manya Brachear Pashman: Had you sensed this aggressive tone prior to your time in the Amazon and when you were involved with these circles? Adam Louis-Klein: No, I'd never witnessed anything like this in my life, and so it took some real searching and going inward, and I was still in the jungle, but encountering all this anti-Zionist hate online from people I thought were my friends. And I had to really ask myself, you know, maybe I'm in the wrong, because I've never seen people act like . . . people who are scholars, intellectuals who should be thinking critically about antisemitism. Because antisemitism, you know, we talk a lot about in the academy, critical race theory. So we look at ideologies, tropes, and symbols that are used to dehumanize minority groups, and we learn to be skeptical. So we learn that there are discourses that speak at times, in languages of reason, of justice, even that are actually biased, structurally biased, against minorities. So then I was deeply confused. Why did these same people not know how to apply those same analytics to Jews? And not only did they not know how, they seemed to think it was offensive to even try. So that was really strange, and I had to kind of think, well, you know, maybe I'm wrong, you know, I think there's a process of they've attempted to sort of stabilize this consensus at such a degree. That Israel is committing genocide, that Israel is a settler colonial entity that is fundamentally evil, basically. And Israelis are fundamentally oppressors. They've created a space it's almost impossible to question them. And it took me a long time to emerge and to come to that realization that I think anti-Zionism is really a discourse of libel, fundamentally. And these accusations, I wouldn't say, are offered in good faith. And it's unfortunately, not much use to try and refute them. And so instead, I started writing, and I started trying to analyze anti-Zionism itself as an object of critique and as an ideology that we can deconstruct. Manya Brachear Pashman: So did this change the course of your academic research? In other words, you said you started writing, are you writing academic articles, or is it more The Times of Israel blog and your more public writings? Adam Louis-Klein: So I've been writing publicly. I started writing on Facebook, and then the readership on Facebook started to grow, and then I sent it to the Times of Israel. And I do have some plans lined up to try and get this material out in the academic context as well. Because I think that's really important, that we build parallel academic spaces and our own language of academic legitimacy. Because I think that academic language, and as well, that kind of activist language, critique of oppression is valuable, but it's also culturally hegemonic today. And so I think that as Jews, if we abandon that language, we will have trouble telling our story. So I think there are also projects like this. I'd like to mention the London Center for the Study of contemporary antisemitism. I think that's a great model. So they're doing serious academic work on contemporary antisemitism, not just classical antiSemitism, which we're all familiar with, Neo Nazis, etc. You know, what does it look like today? You know, red triangles, Hamas headbands. This is a new language of hate that I think we need to be on top of. Manya Brachear Pashman: In fact, you presented a paper recently, there, correct, at the London Center, or at a conference sponsored by the London Center? Adam Louis-Klein: Yeah, I did. I presented a paper. It was called the Dissolving the Denotational Account of Antisemitism. So denotational means, what words refer to. Because what I found very often is that it's a trope that's become really familiar now. Anti-Zionists, they say, we don't hate Jews, we only hate Zionists. We don't hate Judaism, we hate Zionism. We're not antisemitic, we're critical of Israel. So these distinctions that are made are all about saying, you can't point to us as attacking Jews, because our language is such that we are denoting we are referring to something else. So in my talk, I was trying to explain that I like look at anti-Zionism more like a symbolic anthropologist. So when an anthropologist goes and works with an indigenous culture, we look at the kinds of symbols that they use to articulate their vision of the world. The Jaguar, for example, becomes a symbol of certain kinds of potency or predation, for example. So I look at anti-Zionism in the same way. It's not important to me whether they think they're referring to Israel or Jews. What's important to me is the use of conspiratorial symbols, or a symbol of child killing, for example. So we see that classical antisemitism accused Jews of killing children. Anti-Zionism today constructs Israelis as bloodthirsty and desiring to kill children. So when we see that, we see that even if they say not Jews, Zionists, they're using similar symbols that have mutated. So I think that's what I'm trying to track, is both the mutation of classical antisemitism into anti-Zionism, and also the continuities between the two. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did you ever experience antisemitism from your academic circles or really anywhere in life through from childhood on? Adam Louis-Klein: Not particularly. So I went to a northeastern prep school, and we were, there were very few Jews, so I think we were sort of seen as another to the kind of traditional northeast New England aristocracy. But it wasn't something that overt, I would say. I think that antisemitism is something that occurs more so in cycles. So if you look at the 19th century, emancipation of Jews and integration of Jews into society, that was the up part of the cycle, and then the reaction to that came on the down part of the cycle. So unfortunately, I think we're in the same thing today. So Jews have very successfully assimilated into American society and became very successful and integrated into American society. But now we're seeing the backlash. And the backlash is taking a new form, which is anti-Zionism, which allows itself to evade what classical antisemitism looks like, and what we're used to identifying as classical antisemitism. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I do want to talk about the word indigenous or indigeneity. Jews celebrate the creation of Israel as a return to their indigenous homeland, and Palestinians also consider it their indigenous homeland. So how are their definitions of indigeneity, how are those definitions different or distinct? I mean, how are their experiences distinct from each other's and from the people and the tribes with whom you immersed yourself in the Amazon? Adam Louis-Klein: So I think indigeneity, in its fundamental meaning, captures something very real that's common to tons of different groups across the world. Which is a certain conception of the way that one's genealogical ancestry is connected to a specific territory where one emerged as a people, and through which one's own peoplehood is defined. So as Jews, our own peoplehood is connected to the land of Israel. It's the Promised Land, it's the place where our civilization first flourished, and it's the place we've always looked to return to. And so that is very similar to indigenous groups around the world. Now, at the same time, I think there's another concept of indigeneity that gets thrown in and sometimes confuses the issue a little bit, and that's that being indigenous relates to a specific history of dispossession, usually by European colonialism, starting in the 16th century. Now, in fact, there have been many colonialism throughout history. So there have been Islamic civilization practiced widespread colonialism. The Romans practiced colonialism. The Babylonians. But there is a tendency to only look at this form of colonialism. And now when we look at the Middle East, what we find then is these analytics are becoming confused and applied in strange ways. So we see that Palestinians, for example, their genealogical traditions, they understand themselves as tribally derived from tribes in Arabia that expanded with Muhammad's conquest, and that's very common. And Arabian culture and Arabic language is what they practice. And so at that level, from a factual perspective, Palestinians are not indigenous in the genealogical sense. However, there's a tendency to believe, since Jews have a state today, then since they appear not as dispossessed, because Jews have actually repossessed our ancestral land, that Jews can't be indigenous. But so I think that's a confusion. The basic understanding of what indigenous means, and largely what the UN definition is based on, is this notion of continuous identification with the territory. So I really think that this isn't so much a question of who can live where. I think Palestinians' right to live in the land has largely been recognized by the UN Partition Plan in 1947, or the Oslo Accords, and other peace deals, but it's a question of conceptual clarity and fact. And so at this level, I believe that the UN and other institutions should formally recognize Jews as indigenous to the land of Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: You have written, and I want to read this line, because it's so rich you have written that the recursive logic of an antiSemitic consensus builds upon itself, feeds on moral certainty, and shields its participants from having to ask whether what they are reproducing is not justice at all, but a new iteration of a very old lie. I. So are there other examples of that phenomenon in academia, either currently or in the past? Adam Louis-Klein: So what I was trying to grasp with that was my sense of despair in seeing that it was impossible to even point to people, point people to fact within academia, or debate these issues, or explain to non Jews who Jews even are. So I got the sense that people are talking quite a lot about Jews, but don't seem to really care about our voices. So some of that writing that you're quoting is an attempt to understand anti Zionism, not just not only as libel, but also as a kind of practice of exclusion, where Jews feel silenced in spaces. And where, where for all the talk of Academic Freedom versus antisemitism, which I think can sometimes be a tricky issue, I believe that Jews own academic freedom has fundamentally been violated by this discourse so that recursive logic is the way rumor and repeating slogans and repeating notions, regardless of their factual content, like the Jews or settler colonists, sort of builds on itself, as well as on social media, with this algorithmic escalation until it's almost impossible to talk back to it. So an example would be in 2024 the American Anthropological Association had its big conference, and the Gaza genocide was the main theme. But it wasn't a theme we were all going to go and debate. It was a theme that we assumed was true, and we were going to talk about it as a thing in the world, and then the Society for cultural anthropology released an issue with the exact same premise. It was glorifying Ismail Haniyeh of Hamas and Nasrallah of Hezbollah. And then, interestingly enough, just the other day, they released another edition, which was about settler colonialism, and saying, We want to come back to this issue and and reaffirm that settler colonialism applies to Israel and Palestine against people who are attacking the concept, and we're against the exceptionalization of Israel in their terms. And so I searched through the document, but I couldn't find anywhere where Jews were talked about as indigenous, not even as a fact, but even as a claim. I couldn't find anywhere in this journal where Jew it was even acknowledged that Jews might believe that we are indigenous. So it's almost as if the very notion is just completely erased by consciousness within academia. Which is quite frightening. Manya Brachear Pashman: And do you feel able to push back on that. In other words, as a fellow anthropologist, are you able to ask, why is this omitted from this paper, from this journal? Adam Louis-Klein: No, because they will simply ignore you. So that's why I believe these parallel spaces are so important and what I see my work trying to do is to help build a Jewish intellectual discourse. And unfortunately, I think we have to start a little bit internally. So we've been somewhat ghettoized. But if we build up that space, and construct these spaces where we have, where we can share the same premises and we don't have to argue from the bottom up every time. I think that will give us strength and also more clarity on our own understanding of what's happening. You know, both of the level of what is anti-Zionism, what is this new discourse? And at the level of, how can we speak from Jewish peoplehood as a legitimate place to even theorize from or build academic theories from. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned earlier that you held on to doubt. You kept open the possibility that Israel is in the wrong here, and you were watching for, looking for signs or evidence that your colleagues were correct. But as you've watched the horrors unfold, and wondered to yourself whether maybe Israel isn't really defending itself, why have you not concluded that that is indeed the case? Why have you reached the opposite conclusion? Adam Louis-Klein: Yeah, so I talked earlier about using, like a critical race theory analysis, so thinking about ideologies and the kind of tropes they're using and the way they're talking about Israelis, but I think that's only one part of the picture. So what I noticed is, one, they didn't want to do that kind of analysis, but two, they also weren't interested in empirical fact. So when I would sometimes try and do that analysis like this. This sounds like antisemitic, right? They would say, oh, but it's true. Israel is doing this stuff. Israel is intentionally killing Palestinian children. Israel is going completely beyond the laws of war. This is a genocide of unique proportions. Completely irrational and exaggerated statements. They also didn't want to engage with fact. I spent a lot of time digging up the sources of this material, given disinformation. For example, the Al-Ahli incident, where it was claimed by the Hamas health ministry that Israel had intentionally bombed the Al-Ahli hospital, killing 500 people. Al Jazeera promoted it. Western outlets also promoted it, and I had people all over my wall attacking me, saying that I'm justifying this by standing with Israel. And I saw what happened after, which was that they looked into it. The casualty count was tragic, but it was far lower than reported. It was about 50 people, and it was an Islamic Jihad rocket, so Israel was not even responsible. So I think that any rational person who sees what happened in that incident becomes skeptical of everything else they're being told and of the information circuits. And so when I also saw that the people who were talking about the Gaza genocide, weren't seemed completely unfazed by that. That made me have to rethink also what they were doing, because if they're unfazed by something like that, that suggests this isn't a truth that they're being forced to acknowledge, it sounds a bit more like a truth that has its own sort of incentive to believe in despite fact, rather than being pushed towards it because of fact. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I'm curious, if you went back to the people that you had been immersed with and had been studying for the matter of months before October 7, did you go back to them and tell them what had happened, or did they somehow know what had happened? And I'm just curious if there was any kind of response from them? Adam Louis-Klein: Interesting. Yeah, I speak with them regularly, on a regular basis. They don't know exactly what's happened. I think they see sometimes news, but it's largely their understanding, is that there's a lot of wars in the Western world. And they ask why? Why is there so much war? Why is there so much suffering? I mean, they were particularly interested in in the Ukraine war, because they couldn't wrap their head around why Putin was doing this, which I think is pretty similar to a lot of people, but they do see, some of them see Israel as kind of, you know, a figure of strength, and compare Israel almost to their own notions of ancestral, sort of potency or power. So they have a very different understanding of the relationship between, let's say, power and victimhood. They don't necessarily fetishize being powerless. Manya Brachear Pashman: Tell me a little bit about this tribe, these people that you spent time with. Adam Louis-Klein: So the Desano there, they're one of a number of many ethnicities who inhabit the Northwest Amazonian region in northwest Brazil and southeast Columbia. They live in an extremely complex world in which there are over 25 languages in the region. And they have a very unique form of marriage, where you have to marry someone who speaks a different language than you. And so any community has a kind of nucleus of people who speak the same language, and they're from the same tribe. But the women in the community all speak different languages and come from different tribes. So I think it's a kind of space where you have to think across difference. You're constantly confronted with people who are other than you, who are from different tribes and different communities, as well as the relationship between the Western world and the indigenous world itself. And I think that's really part of the promise of anthropology, like coming back to what I was saying earlier about a diasporic Jewish sensibility, I think it's also just a Jewish sensibility. Part of being a distinct people is that we need to think with other people, and I think that includes Muslims and Arabs and Christians as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: That is such an enlightened approach that they have taken to marriage. Isn't that what marriage is all about, crossing those differences and figuring out and they just do it from the very beginning. And I'm also curious, though, are they also mixing with Western cultures. In other words, have they broadened that, or do they keep it within those villages? Adam Louis-Klein: Yeah, so they've taken on a lot of features of the surrounding, Colombian Spanish language culture, and that is the struggle today. Because there's a lot of economic pressures to move to the towns and the cities in order to get work and employment. And that can pose problems to the reproduction of the traditional village community. And so that's part of what we've been struggling with and part of the project with them. So we're currently translating an old book about anthropology, about them into their language, so they have the Bible, which was translated into the language by missionaries. And now we also want to translate their own cultural material into their language so that can help them preserve the language and preserve their own cultural knowledge. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what's next for you, Adam? Adam Louis-Klein: So I'm hoping to continue writing and to continue getting out this work. I'm hoping to also work with grassroots organizers to try to put some activist meat onto this opposition to anti-Zionism. So I believe that, as I was talking about parallel academic spaces are really important, I also think it's important to be able to speak back to anti-Zionism with activist language. Not only the academic side, but the activist side. So I'm working with the group now, a decentralized group, developing infographics, memes, things that can circulate to educate people about anti-Zionism as the new form of antisemitism today. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you for taking on this work and for sharing your story. Adam Louis-Klein: Thank you so much. It was a pleasure.
Aug 1
War and Poetry: Owen Lewis on Being a Jewish Poet in a Time of Crisis
"The Jewish voice must be heard, not because it's more right or less right, but it's there. The suffering is there, the grief is there, and human grief is human grief." As Jews around the world mark Tisha B'Av, we're joined by Columbia University professor and award-winning poet Owen Lewis, whose new collection, "A Prayer of Six Wings," offers a powerful reflection on grief in the aftermath of October 7th. In this conversation, Lewis explores the healing power of poetry in the face of trauma, what it means to be a Jewish professor in today's campus climate, and how poetry can foster empathy, encourage dialogue, and resist the pull of division. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: An Orange Tie and A Grieving Crowd: Comedian Yohay Sponder on Jewish Resilience From Broadway to Jewish Advocacy: Jonah Platt on Identity, Antisemitism, and Israel Sexual Violence as a Weapon of War: The Dinah Project's Quest to Hold Hamas Accountable Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Owen Lewis: Overheard in a New York Restaurant. I can't talk about Israel tonight. I know. I can't not talk about Israel tonight. I know. Can we talk about . . . Here? Sure. Let's try to talk about here. Manya Brachear Pashman: On Saturday night, Jews around the world will commemorate Tisha B'av. Known as the saddest day on the Jewish calendar, the culmination of a three week period of mourning to commemorate several tragedies throughout early Jewish history. As a list of tragedies throughout modern Jewish history has continued to grow, many people spend this day fasting, listening to the book of Lamentations in synagogue, or visiting the graves of loved ones. Some might spend the day reading poetry. Owen Lewis is a Professor of Psychiatry in the Department of Medical Humanities and Ethics at Columbia University. But he's also the award-winning author of four poetry collections which have won accolades, including the EE Cummings Prize and the Rumi Prize for Poetry. His most recent collection, A Prayer of Six Wings documents in verse his grief since the October 7 terror attacks. Owen is with us now to talk about the role of poetry in times of violence and war, what it's been like to be a Jewish professor on the Columbia campus, and a Jewish father with children and grandchildren in Israel. And also, how to keep writing amid a climate of rising antisemitism. Owen, welcome to People of the Pod. Owen Lewis: Thank you so much, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you opened with that short poem titled overheard in a New York restaurant. I asked you to read that because I wanted to ask whether it reflected how you felt about poetry after October 7. Did you find yourself in a place where you couldn't write about Israel, but yet you couldn't not write about Israel? Owen Lewis: Among the many difficult things of that First Year, not only the war, not only the flagrant attacks on the posters of the hostages one block from where I live, 79th and Broadway, every day, taken down every day, put back up again, defaced. It was as if the war were being fought right here on 79th and Broadway. Another aspect that made this all so painful was watching the artistic and literary world turn against Israel. This past spring, 2000 writers and artists signed a petition, it was published, there was an oped about it in The Times, boycotting Israeli cultural institutions. And I thought: artists don't have a right to shut their ears. We all need to listen to each other's grief, and if we poets and artists can't listen to one another, what do we expect of statesmen? Statesmen, yeah, they can create a ceasefire. That's not the same as creating peace. And peace can only come when we really listen to each other. To feel ostracized by the poetry community and the intellectual community was very painful. Fortunately, last summer, as well as this past summer, I was a fellow at the Yetzirah conference. Yetzirah is an organization of Jewish American poets, although we're starting to branch out. And this kind of in-gathering of like-minded people gave me so much strength. So this dilemma, I can't talk about it, because we just can't take the trauma. We can't take hearing one more thing about it, but not talk about it…it's a compulsion to talk about it, and that's a way to process trauma. And that was the same with this poetry, this particular book. I feel in many ways, it just kind of blew through me, and it was at the same time it blew through me, created this container in which I could express myself, and it actually held me together for that year. I mean, still, in many ways, the writing does that, but not as immediately and acutely as I felt that year. Manya Brachear Pashman: This book has been praised as not being for the ideological but for the intellectually and emotionally engaged. So it's not it's not something that ideologically minded readers will necessarily be able to connect to, or is it actually quite the opposite? Owen Lewis: Well, it's very much written from the gut, from the experience, from in a sense, being on the ground, both in Israel and here in New York and on campus, and trying to keep a presence in the world of poetry and writers. So what comes from emotion should speak to emotion. There are a few wisps of political statements, but it's not essentially a politically motivated piece of writing. I feel that I have no problem keeping my sympathies with Israel and with Jews. I can still be critical of aspects of the government, and my sympathies can also be with the thousands of Palestinians, killed, hurt, displaced. I don't see a contradiction. I don't have to take sides. But the first poem is called My Partisan Grief, and it begins on October 7. I was originally going to call the bookMy Partisan Grief, because I felt that American, Jewish, and Israeli grief was being silenced, was being marginalized. And I wanted to say, this is our grief. Listen to it. You must listen to this. It doesn't privilege this grief over another grief. Grief is grief. But I wanted ultimately to move past that title into something broader, more encompassing, more humanitarian. Manya Brachear Pashman: And did that decision come as the death toll in Gaza rose and this war kept going and going and the hostages remained in captivity, did that kind of sway your thinking in terms of how to approach the book and frame it? Owen Lewis: Yes, but even more than those kind of headlines, which can be impersonal, the poetry of some remarkable Palestinian poets move me into a broader look. Abu Toha was first one who comes to mind Fady Joudah, who's also a physician, by the way. I mean his poetry, I mean many others, but it's gorgeous, moving poetry. Some of it is a diatribe, and you know, some of it is ideological, and people can do that with poetry, but when poetry really drills down into human experience, that's what I find so compelling and moving. And that's what I think can move the peace process. I know it sounds quite idealistic, but I really think poetry has a role in the peace process here. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to I want to unpack that a little bit later. But first, I want to go back to the protests that were roiling Columbia's campus over the past year and a half, two years. What was it like to be, one, writing this book, but also, teaching on campus as a Jewish professor? Owen Lewis: Most of my teaching takes place up at the Medical Center at 168th Street. And there I have to say, I didn't feel battered in any way by what was happening. I had a very shocking experience. I had a meeting that I needed to attend on, or that had been scheduled, I hadn't been quite paying attention. I mean, I knew about the encampments, but I hadn't seen them, and I come face to face with a blocked campus. I couldn't get on the campus. And what I'm staring at are signs to the effect, send the Jews back to Poland. I'm thinking, Where am I? What is this? I mean, protest, sure. I mean we expect undergraduates, we expect humans, to protest when things really aren't fair. But what did this have to do…why invoke the Holocaust and re-invoke it, as if to imply the Jews should be punished? All Jews. And what it fails to account for are the diversity of Jewish opinion. And you know, for some Jews, it's a black or white matter, but for most thinking Jews that I know, we all struggle very much with a loyalty to Israel, to the Jewish people, to the homeland and larger humanitarian values. So that was quite a shock. And I wrote a piece called "The Scars of Encampment," in which I say, I can't unsee that. " And I go to campus, and, okay, it's a little bit more security to get onto campus. It's a beautiful campus. It's like an oasis there, but at the same time, I'm seeing what was as if it still is. And in a way, that's the nature of trauma that things from the past just roil and are present with almost as much emotion as when first encountered. Manya Brachear Pashman: So did you need to tune out those voices, or did that fuel your work? Owen Lewis: No, that fueled my work. I mean, if anything, it made me feel much more, a sense of mission with this book. And a commitment, despite criticism that I may receive, and no position I take is that outlandish, except to sympathize with the murdered on October 7th, to sympathize with their families, to resonate with what it must be like to have family members as hostages in brutal, brutal conditions. Not knowing whether they're dead or alive. So I really felt that the Jewish voice must be heard, not because it's more right or less right, but it's there. The suffering is there, the grief is there, and human grief is human grief. Manya Brachear Pashman: Owen, if you wouldn't mind reading another poem from the collection. Of course, many of us remember the news out of Israel on Thanksgiving Day 2023, right after October 7th. And this poem is titled, "Waiting for the Next Release, Reported by the New York Times, November 23 2023". Owen Lewis: Waiting For the Next Release, Reported N.Y. Times, Nov. 23, 2023 Maybe tomorrow, if distrust doesn't flare like a missile, some families will be reunited. How awful this lottery of choice; Solomon would not deliberate. Poster faces always before my eyes, Among them, Emma & Yuli Cunio. Twins age 3, Raz Katz-Asher, age 4, Ariel Bibas, another four year old. What do their four year old minds make of captivity? What will they say? What would my Noa say? What will the other Noas say? Remembering Noa Argamani, age 26, thrown across the motorcycle to laughter and Hamas joy. I have almost forgotten this American day, Thanks- giving, With its cornucopian harvests, I am thinking of the cornucopian jails of human bounty. (What matter now who is to blame?) Manya Brachear Pashman: Really beautiful, and it really captures all of our emotions that day. You have children and grandchildren in Israel, as I mentioned and as you mentioned in that poem, your granddaughter, Noa. So your grief and your fear, it's not only a collective grief and fear that we all share, but also very personal, which you weave throughout the collection. In another poem, "In a Van to JFK", you talk about just wanting to spend one more hour with your family before they fly off to Israel. And it's very moving. But in addition to many of the poems, like the one you just read, they are based on and somewhat named for newspaper headlines, you said that kind of establishes a timeline. But are there other reasons why you transformed those headlines into verse? Owen Lewis: Yes, William Carlos Williams in his poem Asphodel, says, and I'm going to paraphrase it badly. You won't get news from poems yet, men die every day for wanting what is found there. And I think it's a very interesting juxtaposition of journalism and poetry. And I mean, I'm not writing news, I'm writing where my reflections, where my heart, goes in response to the news, and trying to bring another element to the news that, you know, we were confronted. I mean, in any time of high stress, you swear off – I'm not watching any more TV. I'm not even gonna look at the newspaper. And then, of course, you do. I can't talk about Israel today. I can't not talk about it. I can't read the paper. I can't not read the paper. It's kind of that back and forth. But what is driving that? And so I'm trying to get at that next dimension of what's resonating behind each one of these headlines, or resonating for me. I mean, I'm not claiming this is an interpretation of news. It's my reaction, but people do react, and there's that other dimension to headlines. Manya Brachear Pashman: That seems like it might be therapeutic, no? Owen Lewis: Oh, totally, totally. You know, I'm very fortunate that having started a career in medicine, in psychiatry, and particularly in child and adolescent psychiatry. I always had one foot in the door academically. I spent, you know, my life as, I still teach, but I'm very fortunate to have, maybe 10+ years ago, been introduced to a basically a woman who created the field of Narrative Medicine, Rita Sharon. And now at Columbia in the medical school, we have a free-standing Department of Medical Humanities and Ethics, of which she's chairman. So I've had the fortune of bringing psychiatry and medicine and writing together in a very integrated way. And yes, writing is therapeutic, especially, I could say in medicine, which has given itself over to electronic medical record keeping, but our whole society is moving towards the electronic. And what happens when you sit and write, and what happens when you then sit and read, you reflect. Your mind engages in a different way that is a bit slower than the fast pace of electronic communications and instant communications and instant thinking. And now with AI, instant analysis of any situation you want to feed data from. So that's sorely lacking in the human experience. And the act of writing, the act of reading has huge therapeutic values, huge salutary benefits for humans in general, but particularly in times of stress. In a lot of work on Post Traumatic Stress Disorder, finding an outlet, an artistic outlet, it doesn't have to be writing, but that's often a way of transcending the trauma. And medicine is filled with trauma. People trying to come to terms with acute illnesses, chronic illnesses. Doctors and caregivers trying to come to terms with what they can and can't do. And you know, we're coming up against limitations. But how do you make peace with those limitations? And it's not that it's a magical panacea, but it's a process of engagement, not only with the subject, but with yourself in relation to the subject. Manya Brachear Pashman: I mean, I imagine dialogue is really the healthiest way of conversation and speaking through and interacting with a topic. And so I would imagine poetry, or, as you said, any art form, responding to news reports, it makes that a two way conversation when you're able to process and it's not just the headlines shouting at you, you're actually interacting and processing it by writing and reaction, or painting and reaction, whatever you choose to do. Owen Lewis: Exactly. Manya Brachear Pashman: You have said that poetry can serve a purpose during times of war. Is this one of the purposes to to be therapeutic or are you talking more in terms of what statesmen could learn from it? Owen Lewis: Well, yes, of course, what statesmen could learn from it, but it's human nature to want to take sides. I mean, that's kind of just what we do. But I think we can always do better than that. So I'm really talking about the people. I mean, there are also many Jews who are so angry at Israel that they can't listen to the story of Jewish grief. They should be reading mine and others poetries from this era. I wish the Palestinian poets were. I wish the Palestinian people. I mean, of course, in their current situation, they don't have time when you're starving, when you're looking for your next glass of fresh water. You don't have time for anything beyond survival. But once we get beyond that, how long are these positions going to be hardened. I mean, I think when the people of all sides of the dilemma really listen to the others, I mean, they're, I mean, if, unless as Hamas has expressed, you know, wants to push Israel into the sea, if Israel is going to coexist with the Palestinian people, whether they're in a nation or not in a nation, each has to listen to the other. And it's, you know, it's not one side is right, one side is wrong. It's far too complex a history to reduce it to that kind of simplicity. And I think poetry, everyone's poetry, gets at the complexity of experience, which includes wanting to take sides and questioning your wanting to take sides and moving towards something more humanitarian. Manya Brachear Pashman: You said earlier, you recommend Abu Toha, Fady Joudah, two Palestinian poets who have written some beautiful verse about– tragically beautiful verse–about what's happening. But there have been some really deep rifts in the literary world over this war. I mean, as you mentioned before, there was a letter written by authors and entertainers who pledged to boycott Israeli cultural institutions. Some authors have refused to sell rights to their books to publishers in Israel. So why not reciprocate? And I know the answer. I think you've already addressed it pretty well. What's wrong with that approach? Owen Lewis: In any conflict, there are at least three sides to the conflict. I mean, claims to nationhood, claims to who shoved first, who. I mean, you don't entangle things by aggressively reacting. I mean, if we learned anything from Mahatma Gandhi, it's what happens when we don't retaliate, right? And what happens when we go the extra mile to create bridges and connections. There are a host of people in Israel who continue to help Palestinians get to medical facilities, driving them back and forth, working for peace. I mean, there's a Palestinian on the Supreme Court of Israel, and well, he should be there. You know, that's the part of Israel that I am deeply proud of. So why not retaliate? I think it entrenches positions and never moves anything forward. Manya Brachear Pashman: So have you gotten any negative feedback from your writing colleagues? Owen Lewis: Some cold shoulders, yes. I mean not nothing overtly. I haven't been slammed in a review yet. Maybe that's coming. But when I publish pieces, I tend not to look at them. I had an oped in the LA Times. I've had some other pieces, you know, that precipitates blogs, and I started to read them. And the first blog that came off of the the LA Times oped was, God, is he an opportunist, just taking advantage of having a daughter in Israel? And trying to make a name for himself or something. And I said, You know what, you can't put yourself out and take a position without getting some kind of flack. So occasionally, those things filter back, it's par for the course. Manya Brachear Pashman: Right, not really worth reading some of those. You included Midrash in this book. You also spelled God in the traditional sense in the poems. Why did you choose to do that? Owen Lewis: Well, I felt it honors a tradition of Jewish writing. It mean we have yud, hey, vav, hey, you know, which in English comes down as Yahweh, but it's unpronounceable. The name of God is unpronounceable. And, you know, yud, hey, vav, hey is just a representation. It isn't God's name. And there's a tradition that the name of God, when it's written down, can't be destroyed. And it's a way of honoring that tradition. Millennium of Jewish writers, you know, it's similar to say Elokim, instead of Elohim when the text is written. To sort of substitute. We know what we're talking about, but really to honor tradition, to pay respect and sort of to stay in the mind frame that, if there is a God, he, she, they, are unknowable. And somehow it creates, for me, a little bit of that mystery by leaving a letter out. It's like, G, O, D, seems more knowable than G-d. It's leaving that white space right for something bigger, grander, and mysterious, for the presence of that right in the word itself. Manya Brachear Pashman: And what about including Midrash? Owen Lewis: That's a very interesting question. You know Midrash for me, when you steep yourself in traditional Midrash, there's stories that exemplify principles and they fill in gaps. I mean, some of the most important. I mean, we have this notion of Abraham breaking the idols of his father before he left. No. That's Midrash, thats not in the Torah. And yet, nine out of ten Jews will say that's in the Torah, right? So, it kind of expands our understanding of the traditional text. But it also very much allows a writer to creatively engage with the text and expand it. It's like a commentary, but it's a commentary in story, and it's a commentary in terms that evoke human responses, not necessarily intellectual responses. So frankly, I think it's every Jews' responsibility to write Midrash. That reinvigorates the stories, the texts, and the meanings, and then we write midrashes upon midrashes. And you know, we get a whole community buzzing about a single story. Manya Brachear Pashman: Which is very much what you've done with this collection, you know, writing poetry in response to news stories and engaging it in that way. It's very Jewish response, I would argue. Do you observe Tisha B'av? Owen Lewis: You know what I do. You're gonna laugh. My grandmother always warned us, don't go in the water on Tisha B'av, the sea will swallow you up. So I'm a big swimmer. I love swimming. I don't swim on Tisha B'av, because I hear my grandmother's voice, I'm going to be swallowed up. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you could please wrap up this conversation by sharing a poem of your choice from your latest collection. Owen Lewis: A poem I love to read again starts with a headline. 2000 Pound Bombs Drop, Reported N.Y. Times, Dec,, 22 2023. In Khan Younis, the call to prayer is the call of a dazed Palestinian child crying baba, standing at the brim of a cavernous pit of rubble biting his knuckles–baba, baba . . . It's so close to the abba of the dazed Israeli children of Be'eri, Kfar Azza. There is no comfort. From his uncles he's heard the calls for revenge– for his home and school, for his bed of nighttime stories, for his nana's whisper-song of G-d's many names. His Allah, his neighbor's Adonai, cry the same tears for death and shun more blood. No miracle these waters turning red. Who called forth the fleets of avenging angels? By viral post: Jewish Plagues on Gaza! A firstborn lost, then a second, a third. What other plagues pass over? Hail from the tepid sky? From on high it falls and keeps falling. Though we've "seen terrible things," will you tell us, Adonai, Allah, tell us– do You remember the forgotten promise? From the pile once home of rubble stone, a father's hand reaching out, baba, abba crushed by the load. We know the silence of the lost child . . . G-d "has injured us but will bind up our wounds . . ." Mothers Look for us, called by the name yamma, calling the name imma. Our father of mercy, not the god of sacrifice. Our many crying heads explode. Manya Brachear Pashman: Owen Lewis, thank you so much for talking to us about how this book came about and for sharing some of these verses. Owen Lewis: Thank you so much. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to listen to my conversation with Israeli comedian Yohay Sponder on the sidelines of AJC Global Forum 2025. Hear how his Jewish identity shapes his work, how his comedy has evolved since the Hamas terror attacks, and what he says to those who try to silence him.
Jul 24
An Orange Tie and A Grieving Crowd: Comedian Yohay Sponder on Jewish Resilience
What do you do when you're an Israeli comedian set to perform in Paris on the very day the world learns the fate of the Bibas family? Yohay Sponder faced that moment in February 2025—and chose to take the stage. Wearing an orange tie in their honor, he brought laughter to a grieving crowd. Since October 7th, he has used comedy to carry pain, affirm his identity, and connect through resilience. Hear how his Jewish identity shapes his work, how his comedy has evolved since the Hamas attacks, and what he says to those who try to silence him. Recorded live at AJC Global Forum 2025. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: From Broadway to Jewish Advocacy: Jonah Platt on Identity, Antisemitism, and Israel Sexual Violence as a Weapon of War: The Dinah Project's Quest to Hold Hamas Accountable Journalist Matti Friedman Exposes Media Bias Against Israel Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: Israeli stand up comedian Yohay Sponder: first gained popularity for his funny Monday shows in Tel Aviv, which attracted a following on YouTube. A few years ago, Sponder made the decision to perform Israeli comedy in English to reach a wider audience and a wider audience it has reached. He has hundreds of thousands of followers on social media, and in May, launched the North American leg of his international tour in Baltimore. Sponder is with us now on the sidelines of AJC Global Forum 2025. Sponder, welcome to People of the Pod. Yohay Sponder: Thank you so much for this eulogy. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm curious how you found your way to stand up comedy and tell us a little bit about your upbringing in general. Yohay Sponder: Doing comedy, I always been fascinated about the laughing reaction of humans. You know, it's fascinating, if you think about it, if you have the ability to improve the frequency in the room. As a kid, I was really intrigued by that. So you saying few things, and people go, haha. It's like designing a vibe. So as a kid, I was attracted to that. So as a kid, you watch video cassettes, back in the day, I would watch all of the comedy stuff. I had all of them cassettes. I was very, very affected by it, impersonations, imitating them, doing jokes of my own, and always around that. And in my show, I'm talking about comedy. I have a bit about comedy in my show that I'm saying that I was, I wasn't just the class clown in my school. I was the jokes technician. If you had a broken joke or a joke that didn't work, you would come to me. I would fix it for you, bring it back. Not using it as my own resume. I would bring it back, when it's fixed. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's great. So you helped others clown around as well. Yohay Sponder: Yeah, I was a clown teacher. Manya Brachear Pashman: Were you raised in a secular home, a particularly Jewish home? Yohay Sponder: I was raised in a, let's say secular but Jewish, celebrated holidays, family Friday night family dinners. But we weren't like super Shabbat keepers. I think I became closer now, when, after my father passed away, I for the Kaddish and I put tefillin a little bit. And the war, you know, this war, activated a lot of Jews to the to this kind of level. Manya Brachear Pashman: Right. You're sitting across from me, and you're wearing a gigantic Star of David. On your chest. Yohay Sponder: Yeah, you see what she did, you see what she did? You're sitting across and you're wearing a gigantic Star of David. Manya Brachear Pashman: Have you always worn that or did you put it on after October 7? Yohay Sponder: No, it's after the war kicked in. I don't know. I had a vision that that's what we should do right now. We need to be out there and show other Jews that we're there. That's what I felt. And I imagine that, I need a big star of David. And the day I thought about it, I saw that. So there was a sign for me, like I had this vision, that I need a big star of David here. And less than 24 hours, that one find me. I didn't look for it. It came across my eyes. Manya Brachear Pashman: Which I imagine you'll be wearing your Magen David on tour. The tour itself is called Self Loving Jew. What is the meaning of that title? Yohay Sponder: So, basically, you know, this is so awesome, because before October 7, you could argue of other opinion. You could hear some people saying, Yeah, but maybe we should this. After October 7 that we know so all these monsters that came and attack us, the self hating Jews that they're doing now, super horrific, disgusting job of mocking us. And I find it really bad, and I think so I'm I'm bringing the other side. I'm just bringing the you know, it doesn't mean that I hate someone that is not Jewish. I'm just, I want to inspire other people to be to love themselves, even if they're not Jewish. But as Jews, we have to love us, because we're probably the last ones to love us, and if we won't love us, that's that's over for us. And people, people saying that it's very harsh to compare the self hating Jews of now to the Kapos and and I'm saying, yes, it's it's not fair for the Kapos, because they didn't have a choice. You guys have a choice, and you did it just for likes and for other people from other cultures to like you. I really, I really believe. I really deeply believe I'm coming from there. I'm coming from the war. I really believe that the people that don't, they don't give us the credit, people that not supporting Israel, they're uneducated. I really believe in that they don't know enough. They might be not bad people, but they might be stupid people. Self hating Jews, like whatever Dave Smith, all these guys that try to be liked by, you know, others, and they they just out of their own idiocy. Listen, you don't know anything about what's going on. As Douglas Murray told them, ou've been there. You saw those things that you're talking about when you're saying, Israel, starving the Gazans you're never seeing the the trucks that going every day. You're You're an idiot. You're just an idiot. You listen to other people, and you listen to other lies. And they will say, No, I just want peaceful. We all want peace. Just the fact that you're Jewish, it means that you want peace. We say Shalom when we see each other, when we say Shabbat Shalom. The holiest day of the week. We say telech bshalom, tachzor bshalom. Go in peace, come back in peace. You don't want peace more than I want. We all want peace, but we're willing to fight for peace because we have to make sure that no innocent people from both sides, by the way, will get hurt. So yeah, it's really bad and shitty situation, war, but you blame us without checking it. So anyway, I don't want it to make it too much political. It's not political, by the way, Self Loving Jew. It's about loving yourself and being, you know, being in touch with what's going on right now. Manya Brachear Pashman: So there is so much misinformation out there, you launched your you started doing English language comedy to reach a wider audience. Now you're doing an English language international tour. Do you have a message that you want to get out to the wider world to especially this region where there is so much misinformation and misunderstanding? Yohay Sponder: Yeah, the message is that, we're living in a time that it's very hard to agree on something, and I really miss the days that we all agree that the world is round. You know, a little long ago, a few years ago. But yeah, the message is that you do your research and come to laugh with us. Manya Brachear Pashman: It's an important message that gets forgotten. October 7, and its aftermath were so horrific. Did you press pause on your comedy career for a little while? At what point did you find it acceptable to make people laugh again in the aftermath? Yohay Sponder: No, it took time. It took time. It took a day. Manya Brachear Pashman: One day. Okay. Yohay Sponder: Because right after that, after the attack, they start to arrange people to go to volunteer in squads and families that got evacuated from their house and soldiers and hospitals, people got wounded. So I've been around. I did that. That was my duty service. And also I did regular reserves duty, stuff like that. Manya Brachear Pashman: And what did you do on reserve duty? Yohay Sponder: I was in Ramat Gan patrol. So not super serious, but I did what I did. Manya Brachear Pashman: And at what point did you go back to the stage and so more standup? Yohay Sponder: So I'm running the show Funny Monday, I think roughly a month after October 7, we get. Maybe two months, yeah, something like around that. January, maybe, I remember, like a little bit after that, the show went back and we did stand up in English. People really followed what's going on in Israel. No matter what you do from the country, they follow that. And we had strong they were saying, Wait, Shahar Hassan, my co-host, very good friend. Really funny man, serious comedian, like one of A-list, Top list. And people follow, people watching what we have to say. That was the main purpose of Funny Monday, when we launched it in 2016 nine years ago. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did it shift? When you restarted it after October 7, was it different? How so? Yohay Sponder: Yeah. We always talked about current events, what's going on in the world? It's the international perspective of not just news, but Israel perspective and stuff like that. So in that case, you're talking about Iran's attack. What the news with Biden, Benjamin Netanyahu? Whatever is happening politically, or current events and yeah, people were more attached to the screen those days. And also in comedy. It's a great form of art to deliver, you know, your point of view, or your, yeah, your what you want to say. So it's, it was great to do that, and till this very day, that's what we do. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you really though, have to read the room, right? I mean, different audiences, I imagine, receive your comedy in different ways, especially in different regions of the world. So I'm curious if there are differences in the kind of humor that resonates with an Israeli audience, and the kind of humor that resonates with an American audience or a European audience. Yohay Sponder: So that's the thing, why I love my country so much, because you can just stand up in any form you want. You can go as dark as you want in Israel or as political as you want. We have some issues right now with people having fight with each other, of political issues, and we have a lot of demonstrations and stuff. So there's that. But beside that, you can get away with a lot of what people say here in America, woke culture, politically correct. In Israel, we don't have it. You don't stand up like in the 80s. If someone looks gay in the audience, you say, Hey, you look gay man. That's very gay. You're fat. You these, you're old, you're very brown. We just say that, and that's fine. No one canceled. We don't even know what it means to cancel someone. No one get canceled in Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: Holocaust humor, is that acceptable in Israel? Yohay Sponder: Yeah, it's not just it's acceptable. For example, from my wife's point of view, she was shocked when people came back to say, wow, mitlachot poh shoah—the shower was like, it's the Holocaust. Holocaust shower. They sang that. There's something that you say in the army and it's kind of fine. No one like, hey, how can you compare this? Because the water was cold, so they were called. So they say, but in the Holocaust, no water at all, was gas. And also, when my wife told me, Don't honk like this, it's ghetto. You know, it's American thing to say, Don't honk. It's ghetto. It's like, I'm pretty sure that in Auschwitz, they didn't have cars. Manya Brachear Pashman: She's talking about a different kind of gheto. Yohay Sponder: And she said, like, you can't do these jokes. Yeah, you can't do this. She's like, she's from American perspective, you can't do these jokes. It's horrible. It's like, that's jokes we do here all the time. And in Israel, you use Nazi sometimes, like, as a, not only as a bad thing. It's like, accuracy. You say, like, Nazis coming on time. I need a Nazi plumber, not . . . someone that is a good commander. When I'm having the perspective of my wife and American people, I understand how horrible that is. However, some Holocaust survivors testify that they had humor in the camps. They used humor, even dark humor, in the camps, and it helped them raise their frequency and raise their morality and maybe survive, maybe humor saved them. So when you saying too soon, sometimes it's, yeah, it's too soon for someone but it's okay for someone else. I see black humor as spicy food. We all have our own scale for it. You can, you can eat spicy like a crazy mental person, and I can just taste it. And, you know, it's too harsh for me, and vice versa. So I did jokes about October 7, in November 7, and horrible ones, and it was also with the Holocaust. That's how horrible that was. So maybe it's too soon for the Holocaust. It's too soon for October 7. I said, the people that compare compared October 7 to the Holocaust. And I'm saying at least in the Holocaust, no one kidnapped Holocaust survivors. It's not even a funny, like, haha, funny. It's like, oh shit, yeah, yeah, that's the joke. It's not a joke of a punch line. It's a punch in your belly. Yeah. Manya Brachear Pashman: What have been some of the most memorable moments from your shows, from your live shows, and I'm talking good and bad, have there been really positive responses and have there been really ugly? Yohay Sponder: So let's just take this afternoon in Paris that I'm sitting in my hotel and Instagram and social media exploding from what's going on with the releasing of the Bibas babies. That we're getting back coffins, and I'm getting, I don't know, hundreds of messages from people that like we don't know if we're coming to the show. Two shows sold out in a huge theater in Paris. I'm not there every day. That's the show. That's it. One day since October 7, and no one knows when I'm going to come again. And my heart is broken, and people tell me we want to come but we can't. What do you think we should do? Now, I responded to all of them, my wife and I responded to all of them, you do what you feel. I totally support your feelings. And the show is going to happen, and we get together tonight, and it's going to be a group hug, but if you can't make it, that's fine. I went on stage with an orange tie that I bought, and we talked it through. Arthur is the comedian and producer of those shows. He opened the show, he talked about the situation, and we did the shows. Now, that's the beauty of it, that's, that's the genome of the Jewish people. That's so in us to . . . . what we talked earlier about the Holocaust survivors that testify that they want to laugh, they want to have a good time. They don't want to let these terrorists decide for us what we gonna feel. Yeah, we feel bad. Yes, you're the worst people on the planet. I wish God will wipe you out, or IDF as fast as possible. You're a disgusting dirt of…but for us, for what we can do right now, we're gonna, we're gonna do our best to raise our morality and frequency. And I did the shows. I'm not gonna lie to you, I was very sad. But you know, the people that, that's what Bob Marley said after, he got shot, you know, and he did the show anyway, and he said, the people that want us to feel bad, they don't take a day off. So how could I? That's a very nice thing to say. Manya Brachear Pashman: You had a show at City Winery where some people in the audience came with, maybe with intentions to protest, or at least they expected to disagree with you, and they met up with you after the show. And what happened? Yohay Sponder: After my show, one of the presidents of the BDS organizations. She approached me and she said, we came to hassle the show. We came to ruin your show. So like, why you didn't do it? And she said we were waiting for the right moment, but the more the show went on, the more we liked what you said. You talk a lot about peace, you talk a lot about mutual values and how to solve problems, and you talk about the nice things of the Jewish tradition and the Jewish religion. We couldn't ruin that. We have conscience and we also liked you. They liked the show. They wanted to ruin it, but they loved it, and they laughed. I told her, that's exactly what I do. In my stand up show, when you see that bit, it's with the whole structure of what happened there and how I almost made peace with these guys, but it didn't work out. Manya Brachear Pashman: Maybe you need to do your stand up routine in Gaza and that would solve everything. Yohay Sponder: I checked that. They don't have comedy clubs there. I said that when I hosted the show, we have an Arab comedian, a friend of ours. You know, people like they don't know that, but Arab-Israelis, are Palestinians. To their definition, to the Palestinians definition, it's the same thing, but they don't identify as Palestinians. It's like we're Muslims, we're Arabs. Anyway, they're with us. They're like siblings to us. So when I introduced him, I also made fun of the situation. I said, When is going to be in Palestine? When it's going to be the Jewish comedian goes on stage like you going here and stuff like that, and there is no comedy clubs in Ramallah or in Gaza, but Inshallah, when there will I go and I do a spot. Manya Brachear Pashman: How many of your shows, as you've been traveling around, have actually been canceled or moved or postponed. I read something about your Amsterdam show, for example, was moved to an undisclosed location because of security concerns. Has that happened elsewhere? Yohay Sponder: Australia. And they tried to cancel my show in Brussels, didn't make it. They tried to cancel my show in Paris. They couldn't make it, but demonstrated outside. And every time that thing happened, I got a lot of press covers and interviews, and people get insane. And like, oh, we have to support and come to see the show. So every time it happens, I doubling or sometimes tripling the amount of people. Which is so weird, you know, because they're always the people they hate us. Always go, oh, Jews, money and you guys this, and you made me make more money. I didn't want to make that much money. I want to make third of the amount of money. But because of your protesting. Your hate, that's how bad you are of what you do. And how amazing we are what we do. You know, I didn't want to make that much money, so now I hire them, the protesters. So they work for me. Manya Brachear Pashman: They do your marketing, generate publicity. So none of the shows have been successfully cancelled? Yohay Sponder: No, the Amsterdam show canceled. The Boom Chicago, which also surprising. Your name is Boom Chicago. What's your security concerns. That's gonna be a boom. Let it be. Manya Brachear Pashman: But I thought it was moved. Yohay Sponder: We moved that like because they a week before the show, they said we're not doing the show. And was like, guys, let me respond. Let me say something. No, no. Police said that. We called the police. We have their numbers, you know, we call them. They say, No, we didn't talk to them. And then they wrote, we can help you find a Jewish venue. So I told him, we can help you find a Jewish lawyer. Manya Brachear Pashman: So there was no show? Yohay Sponder: Not in the Boom Chicago. Manya Brachear Pashman: Got it. Yohay Sponder: And I'll never go there. Manya Brachear Pashman: And not in Amsterdam? Yohay Sponder: No, it was in Amsterville. Manya Brachear Pashman: Got it, okay. Amsterville, is that next to Amsterdam? Yohay Sponder: Turns out, yeah, they didn't know that too. Was was a very nice theater, I think, three times' size of the Boom Chicago, and we had a great time. And I'll go there again. And it's not just the Boom Chicago, when we try to rebook it, a lot of other venues, more than 30 venues, didn't want to have me there. Manya Brachear Pashman: So is there anything else that I haven't asked you that you really want to share with our audience? Yohay Sponder: Yeah. I mean, listen, I'm not sure that the audience is going to be 100% Jewish, right? So the message is going to be split for both. So I'll talk to them. So if you guys are Jews, I wanted to know that everything's going to be fine, and we got this, and raise your head, and we're good. We're going to be good. This is probably the last one. It's the last one. I think Messiah is coming, right? We're going to be fine, all right? And if you're a non Jewish person watching it, you're an ally. So I want to thank you. We don't take it for granted. It's very important that you're around. Manya Brachear Pashman: Sponder, thank you. Yohay Sponder: Thank you so much.
Jul 17
From Broadway to Jewish Advocacy: Jonah Platt on Identity, Antisemitism, and Israel
Being Jewish podcast host Jonah Platt—best known for playing Fiyero in Broadway's Wicked—joins People of the Pod to discuss his journey into Jewish advocacy after October 7. He reflects on his Jewish upbringing, challenges media misrepresentations of Israel, and shares how his podcast fosters inclusive and honest conversations about Jewish identity. Platt also previews The Mensch, an upcoming film he's producing to tell Jewish stories with heart and nuance. Recorded live at AJC Global Forum 2025. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: Sexual Violence as a Weapon of War: The Dinah Project's Quest to Hold Hamas Accountable Journalist Matti Friedman Exposes Media Bias Against Israel John Spencer's Key Takeaways After the 12-Day War: Air Supremacy, Intelligence, and Deterrence Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: Jonah Platt: is an award winning director of theater and improv comedy, an accomplished musician, singer and award winning vocal arranger. He has been on the Broadway stage, including one year as the heartthrob Fiyero in Wicked and he's producing his first feature film, a comedy called The Mensch. He also hosts his own podcast, Being Jewish with Jonah Platt:, a series of candid conversations and reflections that explore the many facets of Jewish identity. Jonah is with us now on the sidelines of AJC Global Forum 2025. Jonah, welcome to People of the Pod. Jonah Platt: Thank you so much for having me, happy to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So tell us about your podcast. How is being Jewish with Jonah Platt: different from Jewish with anyone else? Jonah Platt: That's a great question. I think it's different for a number of ways. I think one key difference is that I'm really trying to appeal to everybody, not just Jews and not just one type of Jews. I really wanted it to be a very inclusive show and, thank God, the feedback I've gotten, my audience is very diverse. It appeals to, you know, I hear from the ultra orthodox. I hear from people who found out they were Jewish a month ago. I hear from Republicans, I hear from Democrats. I hear from non Jews, Muslims, Christians, people all over the world. So I think that's special and different, especially in these echo-chambery, polarized times online, I'm trying to really reach out of that and create a space where the one thing we all have in common, everybody who listens, is that we're all well-meaning, good-hearted, curious people who want to understand more about our fellow man and each other. I also try to really call balls and strikes as I see them, regardless of where they're coming from. So if I see, let's call it bad behavior, on the left, I'll call it out. If I see bad behavior on the right, I'll call it out. If I see bad behavior from Israel, I'll call it out. In the same breath that I'll say, I love Israel, it's the greatest place. I think that's really unfortunately rare. I think people have a very hard time remembering that we are very capable of holding two truths at once, and it doesn't diminish your position by acknowledging fault where you see it. In fact, I feel it strengthens your position, because it makes you more trustworthy. And it's sort of like an iron sharpens iron thing, where, because I'm considering things from all angles, either I'm going to change my mind because I found something I didn't consider. That's going to be better for me and put me on firmer ground. Or it's going to reinforce what I thought, because now I have another thing I can even speak to about it and say, Well, I was right, because even this I checked out, and that was wrong. So either way, you're in a stronger position. And I feel that that level of sort of, you know, equanimity is sorely lacking online, for sure. Manya Brachear Pashman: Our podcasts have had some guests in common. We've had Dara Horn, Sarah Hurwitz, you said you're getting ready to have Bruce Pearl. We've had Coach Pearl on our show. You've also had conversations with Stuart Weitzman, a legendary shoe designer, in an episode titled Jews and Shoes. I love that. Can you share some other memorable nuggets from the conversations you've had over the last six months? Jonah Platt: I had my dad on the show, and I learned things about him that I had never heard about his childhood, growing up, the way his parents raised him. The way that social justice and understanding the conflict and sort of brokenness in the world was something that my grandparents really tried to teach them very actively, and some of it I had been aware of, but not every little specific story he told. And that was really special for me. And my siblings, after hearing it, were like, We're so glad you did this so that we could see Dad and learn about him in this way. So that was really special. There have been so many. Isaac Saul is a guy I had early on. He runs a newsletter, a news newsletter called Tangle Media that shows what the left is saying about an issue with the right is saying about an issue, and then his take. And a nugget that I took away from him is that on Shabbat, his way of keeping Shabbat is that he doesn't go on social media or read the news on Shabbat. And I took that from him, so now I do that too. I thought that was genius. It's hard for me. I'm trying to even start using my phone period less on Shabbat, but definitely I hold myself to it, except when I'm on the road, like I am right now. When I'm at home, no social media from Friday night to Saturday night, and it's fantastic. Manya Brachear Pashman: It sounds delightful. Jonah Platt: It is delightful. I highly recommend it to everybody. It's an easy one. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what about your upbringing? You said you learned a lot about your father's upbringing. What was your Jewish upbringing? Jonah Platt: Yeah, I have been very blessed to have a really strong, warm, lovely, Jewish upbringing. It's something that was always intrinsic to my family. It's not something that I sort of learned at Hebrew school. And no knock on people whose experience that is, but it's, you know, I never remember a time not feeling Jewish. Because it was so important to my parents and important to their families. And you know, part of the reason they're a good match for each other is because their values are the same. I went to Jewish Day School, the same one my kids now go to, which is pretty cool. Manya Brachear Pashman: Oh, that's lovely. Jonah Platt: Yeah. And I went to Jewish sleepaway camp at Camp Ramah in California. But for me, really, you know, when I get asked this question, like, my key Jewish word is family. And growing up, every holiday we spent with some part of my very large, amazing family. What's interesting is, in my city where I grew up, Los Angeles, I didn't have any grandparents, I didn't have any aunts or uncles or any first cousins. But I feel like I was with them all the time, because every holiday, someone was traveling to somebody, and we were being together. And all of my childhood memories of Jewish holidays are with my cousins and my aunts and my uncles and my grandparents. Because it was just so important to our family. And that's just an amazing foundation for being Jewish or anything else, if that's your foundation, that's really gonna stay with you. And my upbringing, like we kept kosher in my house, meat and milk plates. We would eat meat out but no pork, no shellfish, no milk and meat, any of that. And while I don't ascribe to all those things now, I'm grateful that I got sort of the literacy in that. In my Jewish Day School we had to wrap tefillin every morning. And while I don't do that now, I'm glad that I know how to do that, and I know what that looks like, and I know what that means, even if I resisted it very strongly at the time as a 13 year old, being like what I gotta wrap this up every day. But I'm grateful now to have that literacy. And I've always been very surprised to see in my life that often when I'm in a room with people, I'm the most observant in the room or the most Jewish literate in the room, which was never the case in my life. I have family members who are much more observant than me, orthodox. I know plenty of Orthodox people, whatever. But in today's world, I'm very grateful for the upbringing I had where, I'll be on an experience. I actually just got back from one in Poland. I went on a trip with all moderate Muslims from around the North Africa, Middle East, and Asia, with an organization called Sharaka. We had Shabbat dinner just this past Friday at the JCC in Krakow, and I did the Shabbat kiddush for everybody, which is so meaningful and, like, I'm so grateful that I know it, that I can play that role in that, in special situations like that. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you've been doing a lot of traveling. Jonah Platt: Yes. Manya Brachear Pashman: I saw your reflection on your visit to Baku, Azerbaijan. The largest Jewish community in the Muslim world. And you went with the Jewish Federation's National Young leadership cabinet. Jonah Platt: Shout out to my chevre. Manya Brachear Pashman: And you posted this reflection based on your experience there, asking the question, how much freedom is too much? So can you walk our listeners through that and how you answered that question? Jonah Platt: Yes. So to be fair, I make very clear I don't have the answer to that question definitively, I just wanted to give people food for thought, and what I hoped would happen has happened where I've been getting a lot of people who disagree with me and have other angles at which they want to look and answer this question, which I welcome and have given me a lot to think about. But basically, what I observed in Azerbaijan was a place that's a little bit authoritative. You know, they don't have full freedom of the press. Political opposition is, you know, quieted, but there's no crime anywhere. They have a strong police presence on the streets. There are security cameras everywhere, and people like their lives there and don't want to mess with it. And so it just got me thinking, you know, they're an extremely tolerant society. It's sort of something they pride themselves on, and always have. It's a Muslim majority country, but it is secular. They are not a Muslim official country. They're one of only really two countries in the world that are like that, the other being Albania. And they live together in beautiful peace and harmony with a sense of goodwill, with a sense of national pride, and it got me thinking, you know, look at any scenario in our lives. Look at the place you work, look at the preschool classroom that your kid is in. There are certain rules and restrictions that allow for more freedom, in a sense, because you feel safe and taken care of and our worst instincts are not given space to be expressed. So that is what brought the question of, how much freedom is too much. And really, the other way of putting that is, how much freedom would you be willing to give up if it meant you lived in a place with no crime, where people get along with their neighbors, where there's a sense of being a part of something bigger than yourself. I think all three of which are heavily lacking in America right now that is so polarized, where hateful rhetoric is not only, pervasive, but almost welcomed, and gets more clicks and more likes and more watches. It's an interesting thing to think about. And I heard from people being like, I haven't been able to stop thinking about this question. I don't know the answer, but it's really interesting. I have people say, you're out of your mind. It's a slippery slope. The second you give an inch, like it's all going downhill. And there are arguments to be made there. But I can't help but feel like, if we did the due diligence, I'm sure there is something, if we keep the focus really narrow, even if it's like, a specific sentence that can't be said, like, you can't say: the Holocaust was a great thing. Let's say we make that illegal to say, like, how does that hurt anybody? If that's you're not allowed to say those exact words in that exact sequence, you know. So I think if it's gonna be a slippery slope, to me, is not quite a good enough argument for Well, let's go down the road and see if we can come up with something. And then if we decide it's a slippery slope and we get there, maybe we don't do it, but maybe there is something we can come to that if we eliminate that one little thing you're not allowed to say, maybe that will benefit us. Maybe if we make certain things a little bit more restrictive, it'll benefit us. And I likened it to Shabbat saying, you know, on Shabbat, we have all these restrictions. If you're keeping Shabbat, that's what makes Shabbat special, is all the things you're not allowed to do, and because you're not given the quote, unquote, freedom to do those things, you actually give yourself more freedom to be as you are, and to enjoy what's really good about life, which is, you know, the people around you and and having gratitude. So it's just something interesting to think about. Manya Brachear Pashman: It's an interesting perspective. I am a big fan of free speech. Jonah Platt: As are most people. It's the hill many people will die on. Manya Brachear Pashman: Educated free speech, though, right? That's where the tension is, right? And in a democracy you have to push for education and try to make sure that, you know, people are well informed, so that they don't say stupid things, but they are going to say stupid things and I like that freedom. Did you ever foresee becoming a Jewish advocate? Jonah Platt: No. I . . . well, that's a little disingenuous. I would say, you know, in 2021 when there was violence between Israel and Gaza in the spring over this Sheik Jarrah neighborhood. That's when I first started using what little platform I had through my entertainment career to start speaking very, you know, small things, but about Israel and about Jewish life, just organically, because I am, at the time, certainly much more well educated, even now, than I was then. But I was more tuned in than the average person, let's say, and I felt like I could provide some value. I could help bring some clarity to what was a really confusing situation at that time, like, very hard to decipher. And I could just sense what people were thinking and feeling. I'm well, tapped into the Jewish world. I speak to Jews all over the place. My, as I said, my family's everywhere. So already I know Jews all over the country, and I felt like I could bring some value. And so it started very slowly. It was a trickle, and then it started to turn up a little bit, a little bit more, a little bit more. I went on a trip to Israel in April of 2023. It's actually the two year anniversary today of that trip, with the Tel Aviv Institute, run by a guy named Hen Mazzig, who I'm sure, you know, well, I'm sure he's been on the show, yeah. And that was, like, sort of the next step for me, where I was surrounded by other people speaking about things online, some about Jewish stuff, some not. Just seeing these young, diverse people using their platforms in whatever way, that was inspiring to me. I was like, I'm gonna go home, I'm gonna start using this more. And then October 7 happened, and I couldn't pull myself away from it. It's just where I wanted to be. It's what I wanted to be spending my time and energy doing. It felt way too important. The stakes felt way too high, to be doing anything else. It's crazy to me that anybody could do anything else but be focusing on that. And now here we are. So I mean, in a way, could I have seen it? No. But have I sort of, looking back on it, been leaning this way? Kinda. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you think it would've you would've turned toward advocacy if people hadn't been misinformed or confused about Israel? Or do you think that you would've really been more focused on entertainment. Jonah Platt: Yeah, I think probably. I mean, if we lived in some upside down, amazing world where everybody was getting everything right, and, you know, there'd be not so much for me to do. The only hesitation is, like, as I said, a lot of my content tries to be, you know, celebratory about Jewish identity. I think actually, I would still be talking because I've observed, you know, divisions and misunderstandings within the Jewish community that have bothered me, and so some of the things I've talked about have been about that, about like, hey, Jews, cut it out. Like, be nice to each other. You're getting this wrong. So I think that would still have been there, and something that I would have been passionate about speaking out on. Inclusivity is just so important to me, but definitely would be a lot lower stakes and a little more relaxed if everybody was on the same universe in regards to Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: You were relatively recently in Washington, DC. Jonah Platt: Yeah. Manya Brachear Pashman: For the White House Correspondents Dinner. I was confused, because he just said he was in Krakow, so maybe I was wrong. Jonah Platt: I flew direct from Krakow to DC, got off the plane, went to the hotel where the dinner was, changed it to my tux, and went downstairs for the dinner. Manya Brachear Pashman: Wow. Jonah Platt: Yeah. Manya Brachear Pashman: Are you tired? Jonah Platt: No, actually, it's amazing. I'll give a shout out. There's a Jewish businessman, a guy named Andrew Herr, who I was in a program with through Federation called CLI in LA, has started a company called Fly Kit. This is a major shout out to Fly Kit that you download the app, you plug in your trip, they send you supplements, and the app tells you when to take them, when to eat, when to nap, when to have coffee, in an attempt to help orient yourself towards the time zone you need to be on. And I have found it very useful on my international trips, and I'm not going to travel without it again. Yeah. Manya Brachear Pashman: Wow. White House Correspondents dinner. You posted some really thoughtful words about the work of journalists, which I truly appreciated. But what do American journalists get wrong about Israel and the Jewish connection to Israel? Jonah Platt: The same thing that everybody who gets things wrong are getting wrong. I mean, we're human beings, so we're fallible, and just because you're a journalist doesn't make you immune to propaganda, because propaganda is a powerful tool. If it didn't work, people wouldn't be using it. I mean, I was just looking at a post today from our friend Hen Mazzig about all the different ways the BBC is getting things horribly, horribly wrong. I think part of it is there's ill intent. I mean, there is malice. For certain people, where they have an agenda. And unfortunately, you know, however much integrity journalists have, there is a news media environment where we've made it okay to have agenda-driven news where it's just not objective. And somehow it's okay for these publications that we've long trusted to have a story they want to tell. I don't know why that's acceptable. It's a business, and I guess maybe if that, if the dollars are there, it's reinforcing itself. But reporters get wrong so much. I'd say the fundamental misunderstanding that journalists as human beings get wrong, that everybody gets wrong, is that Jews are not a group of rich, white Europeans with a common religion. That's like the number one misunderstanding about Jews. Because most people either don't know Jews at all on planet Earth. They've never met one. They know nothing about it except what they see on the news or in a film, or the Jews that they know happen to maybe be white, rich, European ancestry people, and so they assume that's everybody. When, of course, that's completely false, and erases the majority of Jews from planet Earth. So I think we're missing that, and then we're also missing what Israel means to the Jewish people is deeply misunderstood and very purposefully erased. Part of what's tricky about all of this is that the people way behind the curtain, the terrorists, the real I hate Israel people agenda. They're the ones who plant these seeds. But they're like 5% of the noise. They're secret. They're in the back. And then everybody else, without realizing it, is picking up these things. And so the vast majority of people are, let's say, erasing Jewish connection to Israel without almost even realizing they're doing it because they have been fed this, because propaganda is a powerful tool, and they believe it to be true what they've been told. And literally, don't realize what they're doing. And if they were in a calm environment and somebody was able to explain to them, Hey, here's what you're doing, here's what you're missing, I think, I don't know, 75% of people would be like, holy crap. I've been getting this wrong. I had no idea. Maybe even higher than 75% they really don't know. And that's super dangerous. And I think the media and journalism is playing a major role in that. Sometimes things get, you know, retracted and apologized for. But the damage is done, especially when it comes to social media. If you put out, Israel just bombed this hospital and killed a bunch of doctors, and then the next day you're like, Oops, sorry, that was wrong. Nobody cares. All they saw was Israel bombed a bunch of doctors and that seed's already been planted. So it's been a major issue the info war, while you know, obviously not the same stakes as a real life and death physical war has been as important a piece of this overall war as anything. And I wouldn't say it's going great. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did it come up at all at the Correspondent's Dinner, or more of a celebration? Jonah Platt: No, thank God. Yeah. It was more of a celebration. It was more of just sort of it was cool, because there was no host this year, there was no comedian, there was no president, he didn't come. So it was really like being in the clubhouse with the journalists, and you could sense they were sort of happy about it. Was like, just like a family reunion, kind of a vibe, like, it's just our people. We're all on the same page. We're the people who care about getting it right. We care about journalistic integrity. We're here to support each other. It was really nice. I mean, I liked being sort of a fly on the wall of this other group that I had not really been amongst before, and seeing them in their element in this like industry party, which was cool. Manya Brachear Pashman: Okay, so we talked about journalists. What about your colleagues in the entertainment industry? Are you facing backlash from them, either out of malice or ignorance? Jonah Platt: I'm not facing any backlash from anybody of importance if I'm not getting an opportunity, or someone's written me off or something. I don't know that, you know, I have no idea if I'm now on somebody's list of I'm never gonna work with that guy. I don't know. I don't imagine I am. If I am, it says way more about that person than it does about me, because my approach, as we've discussed, is to try to be really inclusive and honest and, like, objective. And if I get something wrong, I'll delete it, or I'll say I got it wrong. I try to be very transparent and really open that, like I'm trying my best to get things right and to be fair. And if you have a problem with that. You know, you've got a problem. I don't have a problem. So I wouldn't say any backlash. In fact, I mean, I get a lot of support, and a lot of, you know, appreciation from people in the industry who either are also speaking out or maybe too afraid to, and are glad that other people are doing it, which I have thoughts about too, but you know, when people are afraid to speak out about the stuff because of the things they're going to lose. Like, to a person, maybe you lose stuff, but like, you gain so many more other people and opportunities, people who were just sort of had no idea that you were on the same team and were waiting for you to say something, and they're like, Oh my God, you're in this with me too. Great, let's do something together, or whatever it is. So I've gotten, it's been much more positive than negative in terms of people I actually care about. I mean, I've gotten fans of entertainment who have nasty things to say about me, but not colleagues or industry peers. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you would declare yourself a proud Zionist. Jonah Platt: Yes. Manya Brachear Pashman: But you wrote a column in The Forward recently over Passover saying, let's retire the word Zionist. Why? Jonah Platt: Yes. I recently wrote an op-ed and actually talked about on my pod as well about why I feel we should retire the word Zionism. Not that I think we actually are. It's pretty well in use. But my main reasoning was, that the way we all understand Zionism, those of us who actually know what it is, unlike a lot of people –is the belief that Jews should have self determination, sovereignty in some piece of the land to which they are indigenous. We have that. We've had it for almost 80 years. I don't know why we need to keep using a word that frames it as aspirational, that like, I believe we should have this thing. We already have it. And I feel by sort of leaving that sentence without a period, we're sort of suggesting that non-existence is somehow on the table. Like, if I just protest enough, Israel's going to stop existing. I want to slam that door closed. I don't think we need to be the, I believe that Israel should exist people anymore. I think we should be the I love Israel people, or I support Israel people. I'm an Israel patriot. I'm a lover of Israel, whatever the phrase may be. To me, the idea that we should continue to sort of play by their framework of leaving that situation on the table, is it only hurts us, and I just don't think we need it. Manya Brachear Pashman: It lets others define it, in their own terms. Jonah Platt: Yeah, we're playing, sort of by the rules of the other people's game. And I know, you know, I heard when I put that out, especially from Israelis, who it to them, it sort of means patriot, and they feel a lot of great pride with it, which I totally understand. But the sort of more universal understanding of what that word is, and certainly of what the Movement was, was about that aspirational creation of a land, that a land's been created. Not only has it been created, it's, you know, survived through numerous wars, it's stronger than ever. You know, third-most NASDAQ companies in the world. We need to just start talking about it from like, yeah, we're here. We're not going anywhere, kind of a place. And not, a we should exist, kind of a place. Manya Brachear Pashman: So it's funny, you said, we all know what Zionism is. And I grinned a little bit, because there are so many different definitions of Zionism. I mean, also, Zionism was a very inclusive progressive ideology packaged in there, right, that nobody talks about because it's just kind of not, we just don't talk about it anymore. So what else about the conversation needs to change? How do we move forward in a productive, constructive way when it comes to teaching about Jewish identity and securing the existence of Israel? Jonah Platt: In a way, those two things are related, and in a way they're not. You can have a conversation about Jewish identity without necessarily going deep down the Israel hole. But it is critical that people understand how central a connection to Israel is, to Jewish identity. And people are allowed to believe whatever they want. And you can be someone who says, Well, you know, Israel is not important to me, and that's okay, that's you, but you have to at least be clear eyed that that is an extreme and fringe position. That is not a mainstream thing. And you're going to be met with mistrust and confusion and anger and a sense of betrayal, if that's your position. So I think we need to be clear eyed about that and be able to have that conversation. And I think if we can get to the place where we can acknowledge that in each other. Like, dude, have your belief. I don't agree with it. I think it's crazy. Like, you gotta at least know that we all think you're crazy having that idea. And if they can get to the base, we're like, yeah, I understand that, but I'm gonna believe what I'm gonna believe, then we can have conversations and, like, then we can talk. I think the, I need to change your mind conversation, it doesn't usually work. It has to be really gently done. And I'm speaking this as much from failure as I am from success. As much as we try, sometimes our emotions come to the fore of these conversations, and that's–it's not gonna happen. You know, on my pod, I've talked about something called, I call the four C's of difficult conversation. And I recently, like, tried to have a conversation. I did not adhere to my four C's, and it did not go well. And so I didn't take my own advice. You have to come, like, legitimately ready to be curious to the other person's point of view, wanting to hear what they have to say. You know, honoring their truth, even if it is something that hurts you deeply or that you abhor. You can say that, but you have to say it from a place of respect and honoring. If you want it to go somewhere. If you just want to like, let somebody have it, go ahead, let somebody have it, but you're definitely not going to be building towards anything that. Manya Brachear Pashman: So before I let you go, can you tell us a little bit about The Mensch? Jonah Platt: Yeah, sure. So the Mensch is one of a couple of Jewish entertainment projects I'm now involved with in the last year, which, you know, I went from sort of zero to now three. The Mensch is a really unique film that's in development now. We're gonna be shooting this summer that I'm a producer on. And it's the story of a 30 something female rabbi in New Mexico who, life just isn't where she thought it would be. She's not connecting with her congregation. She's not as far along as she thought things would be. Her synagogue is failing, and there's an antisemitic event at her synagogue, and the synagogue gets shut down. And she's at the center of it. Two weeks later, the synagogue's reopening. She's coming back to work, and as part of this reopening to try to bring some some life and some juzz to the proceedings, one of the congregants from the synagogue, the most eccentric one, who's sort of a pariah, who's being played by Jennifer Goodwin, who's a fantastic actress and Jewish advocate, donates her family's priceless Holocaust-era Torah to the synagogue, and the rabbi gets tasked with going to pick it up and bring it. As things often happen for this rabbi, like a bunch of stuff goes wrong. Long story short, she ends up on a bus with the Torah in a bag, like a sports duffel bag, and gets into an altercation with somebody who has the same tattoo as the perpetrator of the event at her synagogue, and unbeknownst to the two of them, they have the same sports duffel bag, and they accidentally swap them. So she shows up at the synagogue with Jennifer Goodwin, they're opening it up, expecting to see a Torah, and it's full of bricks of cocaine. And the ceremony is the next day, and they have less than 24 hours to track down this torah through the seedy, drug-dealing, white nationalist underbelly of the city. And, you know, drama and hilarity ensue. And there's lots of sort of fun, a magic realism to some of the proceedings that give it like a biblical tableau, kind of sense. There's wandering in the desert and a burning cactus and things of that nature. So it's just, it's really unique, and what drew me to it is what I'm looking for in any sort of Jewish project that I'm supporting, whether as a viewer or behind the scenes, is a contemporary story that's not about Jews dying in the Holocaust. That is a story of people just being people, and those people are Jewish. And so the things that they think about, the way they live, maybe their jobs, even in this case, are Jewish ones. But it's not like a story of the Jews in that sense. The only touch point the majority of the world has for Jews is the news and TV and film. And so if that's how people are gonna learn about us, we need to take that seriously and make sure they're learning who we really are, which is regular people, just like you, dealing with the same kind of problems, the same relationships, and just doing that through a little bit of a Jewish lens. So the movie is entertaining and unique and totally fun, but it also just happens to be about Jews and rabbis. Manya Brachear Pashman: And so possible, spoiler alert, does the White Nationalist end up being the Mensch in the end? Jonah Platt: No, no, the white nationalist is not the mensch. They're the villain. Manya Brachear Pashman: I thought maybe there was a conversion moment in this film. Jonah Platt: No conversion. But sort of, one of the themes you take away is, anybody can be a mensch. You don't necessarily need to be the best rabbi in the world to be a mensch. We're all fallible, flawed human beings. And what's important is that we try to do good and we try to do the right thing, and usually that's enough. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, I thought that kind of twist would be… Jonah Platt: I'll take it up with the writer. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Jonah, you are truly a mensch for joining us on the sidelines here today. Jonah Platt: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: Safe travels, wherever you're headed next. Jonah Platt: Thank you very much. Happy to be with you.
Jul 11
Sexual Violence as a Weapon of War: The Dinah Project's Quest to Hold Hamas Accountable
"In so many cases, as is the case of October 7, there are no direct victims who are able to speak – for the very grim reason that Hamas made sure to kill almost each and every one of them. The very few that did survive are too traumatized to speak . . . " Shortly after the October 7 Hamas terror attacks on Israel, witness accounts emerged of women brutally raped and mutilated before they were murdered and silenced forever. For Ruth Halperin-Kaddari, Professor of Law at Bar-Ilan University, that silence was deafening. And the silence of the international community unwilling to hold Hamas accountable, disturbing. "Does that mean that [Hamas] can walk away without being prosecuted, without being charged, and without being pointed to as those who perpetrate sexual violence and use it as a weapon of war?" she asks. In this episode, Halperin-Kaddari explains how she and her colleagues have erased any doubt to make sure Hamas is held accountable. Their initiative The Dinah Project, named for one of Jacob's daughters, a victim of rape, just published A Quest for Justice, the most comprehensive assessment to date of the widespread and systematic sexual violence that occurred during and after the October 7, 2023 attack on Israel by Hamas terrorists and their allies. The report demonstrates that sexual violence was widespread and systematic during the October 7 attack, that there are clear patterns in the methods of sexual violence across geographic locations, and that sexual violence continued against hostages in captivity. It concludes that Hamas used sexual violence as a tactical weapon of war during and after the October 7 attack. Resources: Read: The Dinah Project's groundbreaking new report, A Quest for Justice Read: Hamas' Most Horrific Weapon of War: 5 Takeaways from UN Report on Sexual Violence Against Israelis Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: Journalist Matti Friedman Exposes Media Bias Against Israel John Spencer's Key Takeaways After the 12-Day War: Air Supremacy, Intelligence, and Deterrence Iran's Secret Nuclear Program and What Comes Next in the Iranian Regime vs. Israel War Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: Shortly after the October 7 Hamas terror attacks on Israel, witness accounts emerged of women brutally raped and mutilated before they were murdered and silenced forever. For Ruth Halperin-Kaddari, Professor of Law at Bar Ilan University, that silence was deafening. And the silence of the international community unwilling to hold Hamas accountable, disturbing. In response, Ruth and colleagues, former military prosecutor Sharon Zagagi-Pinhas and retired judge Nava Ben-Or founded The Dinah Project, an effort to seek justice for the victims of sexual violence during conflicts, particularly in Israel, on October 7, 2023. This week, together with visual editor Nurit Jacobs-Yinon and linguistics editor Eetta Prince-Gibson, they released A Quest for Justice, the most comprehensive report yet on the sexual violence committed on October 7 and against hostages afterward. Ruth is with us now. Ruth, welcome to People of the Pod. Ruth Halperin-Kaddari: Thank you very much for having me on your podcast. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, it's really an honor to have you. I should note for our listeners that you are also the founding Academic Director of the Rackman Center for the Advancement of the Status of Women, and you've served on the UN Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination Against Women. So you're no newcomer to this subject matter. You know, we've talked a lot about how Hamas sexually assaulted women and men during the October 7 terror attacks on Israel. Without getting too graphic, or at least getting graphic enough to make your point clear and not sanitize these crimes, what new information and evidence does this report offer? Ruth Halperin-Kaddari: The specific new finding in the report is to actually take all the already published and existing information and put it together and come down with the numbers that prove that sexual violence on October 7 was not sporadic. Was not isolated. It was systematic. It happened in at least six different locations, at the same time, with the same manner, the same patterns. And the, I think, most significant finding is that there are at least 17 survivors who witnessed the sexual violence, and they reported on at least 15 different cases. So there were 17 people who either saw or heard, in real time, the rapes and the gang rapes, some of them involving mutilation, some ending, and the witnesses saw, the execution at the end of the assaults. And this is the first time that anybody came with the actual aggregation and the classification and the naming of all the various sexual assaults and all the various cases that occurred on October 7, and then also later on in captivity. What we did is to, as I said, take all the testimonies and the evidence and the reports that people had already given, and they published it, either on social media or regular media, in addition to some information that was available to us from from other sources, and grouped it into specific categories according to their evidentiary value. So the first group is, of course, those who were victims or survivors of sexual violence themselves, mostly returned hostages, but also one survivor of an attempted rape victim, attempted rape, on October 7, who had actually not spoken before. So that's the first time that her testimony is being recorded or reported. But then the returned hostages, who also report on repeated and similar patterns of sexual abuse and sexual assaults that they had been subjected to in captivity. Manya Brachear Pashman: So the United Nations has acknowledged that women were raped, mutilated, murdered, executed, as you said, but did it attribute responsibility to Hamas? Ruth Halperin-Kaddari: We have to differentiate between the first report of the Assistant Secretary General, Special Representative on sexual violence in conflict, Ms. Pramila Patten, who refrained from specifically attributing these atrocities to Hamas, saying that there needs to be more or follow up examination or investigation into the question of attribution. But then in June of 2024, the Commission of Inquiry on Palestinian Authority, Gaza, Israel, and East Jerusalem, did attribute in their report, they did attribute the sexual violence to Hamas in at least two different places in their report. So in our view, this is already a settled issue. And the information that we gathered comes on top of these two reports. We have to bear in mind the issue of time that passes, first of all, with respect to those survivors, mostly of the Nova music festival, who themselves were victims of the terror attack. And as can be expected, took time before they could recount and speak in public about what they had seen, what they had witnessed, suffering also from trauma, being exposed to such unbelievable acts of human cruelty. And then the other group of the returned hostages, who, some of them, were freed only after 400 or 500 days. So obviously we could not hear their reports before they were finally freed. So all these pieces of information could not have been available to these two investigative exercises by the United Nations. Manya Brachear Pashman: And when the UN Secretary General's annual report on the conflict related sexual violence, when it comes out in August, right, it's expected out next month, there is going to be more information. So do you have high hopes that they will hold Hamas accountable for using sexual violence as a tactical weapon of war, and that this will be included in that report? Ruth Halperin-Kaddari: So this is, in fact, our first recommendation request, ask, if you want to put it that way. We call upon the Secretary General to blacklist Hamas, to include Hamas in the list of those notorious organizations, entities, states that condone or that actually make use of sexual violence as a weapon of war, side by side with ISIS, with Boko Haram, with other terrorist organizations and terrorist groups around the world. And expose them, finally, for what they are, not freedom fighters and not resistance fighters, but rapists and terrorists that use the worst form of violence of human cruelty, of atrocities to inflict such terror and harm on the enemy. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, we talk about the dangers of nuclear warfare, especially lately, in the context of Iran, we talk about cyber attacks. What are the broader implications of sexual violence when it's used as a weapon of war? Ruth Halperin-Kaddari: Perhaps this is where we should clarify the sense in which sexual violence as a weapon of war is different from the regular term of sexual violence, and from the phenomena of, for lack of a better word, everyday sexual violence. It's really very important to bear this in mind when thinking about those broader implications and when seeking justice for victims of sexual violence when used as a weapon of war. It is directed not against the individual. It is directed against the community as a whole. Against the group of the enemy, the nation of the enemy. So the bodies of women, and sometimes also of men, are used as vessels, as symbols, symbolizing the body of the whole nation, and when the specific body is targeted and when the specific woman is invaded, conquered, violated, it is as if the whole body of the of the nation, of the enemy's nation, is being invaded and conquered. So the target is the total dehumanization and destroying of the whole community, of the whole group of the enemy. And these are the ramifications of using sexual violence as a weapon of war. It inflicts such a degree of terror, and then also of shame and of stigma, so as to paralyze the whole community. And it goes on and on. And we know from sadly, from other cases of the usage of sexual violence as a tool of war that it is transmitted to generation after generation, this collective trauma. And it's important, not just in understanding and perhaps being prepared for treatment, for healing, etc. But it is also important in the sense of seeking justice. Of attempting to prosecute for these crimes of sexual violence in conflict or in war. We know that it is always a very difficult challenge for the legal system, for institutions, legal institutions, institutions of justice, to prosecute perpetrators of CRSV, of conflict related sexual violence, because of the of the unique aspects and the unique nature of this kind of crime, which are different from everyday sexual violence. In so many cases, as is the case of October 7, there are no direct victims who are able to speak for the very grim reason that Hamas made sure to kill almost each and every one of them so as to leave no traces, to silence them forever. And the very few that did survive, are too traumatized to speak, are unable to come up and say what they had been through. But this is very often the case in CRSV. And then the next challenge is that it is almost always impossible to identify or to point to a specific perpetrator and it's almost impossible to know who did what, or to connect a specific perpetrator to a specific victim. In the case of October 7, the victims were buried with the evidence. The bodies were the evidence and they were buried immediately, or as soon as it was possible, according to Jewish tradition. So does that mean that they can walk away without being prosecuted, without being charged, and without being pointed to as those who perpetrate sexual violence and use it as a weapon of war? That is why we, in our work at The Dinah Project and in the book that we had just published this week, on top of the evidentiary platform that I already described before, we also develop a legal thesis calling for the prosecution of all those who participated in that horrific attack, all those who entered Israel with the genocidal intent of total dehumanization and total destruction. And we argue that they all share responsibility. This is a concept of joint responsibility, or joint criminal enterprise, that we must make use of, and it is a known concept in jurisprudence, in criminal law, and it has to be employed in these cases. In addition to understanding that some of the usual evidence that is sought for prosecution of sexual violence, namely the evidence, the testimony, of the victim herself or himself is not available. But then those eyewitnesses and ear witnesses in real time, 17 of them reporting 15 different cases, these are no less credible evidence and acceptable evidence in evidentiary, in evidence law. And these should be resorted to. So there has to be a paradigm shift in the understanding of the prosecutorial authorities and the law in general. Justice systems, judicial systems in general. Because otherwise, perpetrators of these crimes have full impunity and there will never be accountability for these crimes. And any terrorist organization gets this message that you can do this and get away with it, as long as you don't leave the victims behind. This is a terrible message. It's unacceptable, and we must fight against it. Manya Brachear Pashman: Ruth, can you explain to our audience the origins of The Dinah Project? How old is it? When did you found it, and why? Ruth Halperin-Kaddari: The Dinah Project is really a very interesting case. Can be seen as a case study of the operation of civil society in Israel, from the bottom up, forming organically, without any plan, at first, without any structure. Each of us found ourselves working in parallel channels immediately after October 7. I was very much involved and invested in the international human rights arena. My colleagues were more invested on the national front in seeking to, first of all, to raise awareness within the Israeli authorities themselves about what had took place, and then collecting the information and putting all the pieces of the puzzle together. And then we realized, as we realized that we are all working towards the same goal, we first of all formed a WhatsApp group. This is how things are being done in Israel, and we called it: Sexual Atrocities War Room. And then we understood that we have to have some kind of a structure. And it was only natural that the Rackman Center that I established, and I'm still heading more than 25 years ago, would be the natural organization to host The Dinah Project. As an organization that has always been leading justice for Israeli women, for women in Israel, gender justice, we realize that we are now facing a new front of where justice needs to be done for women in Israel. And we also can utilize the human power that we have in the academia, in the university, of course the organizational structure. So we expanded The Rackman Center, and for the past almost year and a half, The Dinah Project is part of the Rackman Center. And the book that we published now is really the culmination of a very, very careful and meticulous work, thousands of hours, as I said. I would like to add that we are, I'm trying to think of the proper words. It's actually a subject matter where you so often find yourself looking for the proper words. So I want to say we're pleased, but it's really not the right expression. But we see, we acknowledge that there is a huge amount of interest in our work since we launched the book this week and handed it over to the First Lady of Israel, Michal Herzog, at the presidential residence. And I hesitate to say that perhaps this demonstrates that maybe there is more willingness in the international media and in the world at large to hear, maybe to accept, that the situation is more nuanced than previously they prefer to believe. And maybe also because more time passed on. Of course, new information was gathered, but also when this is a work by an academic institution, coming from independent experts and a very solid piece of work, maybe this is also what was needed. I'm really, really hopeful that it will indeed generate the change that we're seeking. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, that denial that we encountered in the very beginning, where people were not believing the Israeli women who said that they were sexually assaulted, you find that that is shifting, that is changing. Ruth Halperin-Kaddari: I hope so. I hope that this media interest that we are experiencing now is a signal for some kind of change. It is our aim to refute the denialism. Manya Brachear Pashman: There are some that point to Israeli Forces as well and say that they are also using sexual violence as a weapon of war. Does The Dinah Project address that, has it worked with the IDF to try to figure out . . . in other words, is it a broad application, this report? Ruth Halperin-Kaddari: This is not our mission. Our mission is concerned with the victims of Hamas. We are aware of the allegations against Israeli soldiers, against IDF. We are aware, and we made some inquiries to know the facts that investigations are ongoing against those who are being accused of perpetrating sexual violence against Palestinian detainees. But we must point out a major difference, at least in our understanding. Hamas entered Israel on October 7 under a genocidal indoctrination. Just reading the Hamas charter, going through those writings that were found in the vessels of Hamas terrorists here in Israel, or later on in Gaza, the indoctrination there is clear. And they all entered civilian places. They attacked civilians purposefully, with the intent of total dehumanization and destruction. Whatever happened or not happened with respect to Palestinian detainees, and I do trust the Israeli authorities to conduct a thorough investigation and to hold those accountable, cannot be compared to a structured and planned and ordered attack against the civilian population. Manya Brachear Pashman: And total lack of accountability as well. Ruth Halperin-Kaddari: Obviously there is absolutely no accountability on the part of the Palestinian people, of Hamas leadership, or Palestinian Authority, if that's relevant. Obviously there are no investigations there and no accountability, no acceptance of responsibility on their part. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Ruth, thank you so much for producing this report, for continuing to investigate, and keeping the fire lit under the feet of the United Nations and authorities who can hold people accountable for the crimes that were committed. Thank you so much. Ruth Halperin-Kaddari: Thank you. Thank you very much. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for a replay of a conversation with award-winning journalist Matti Friedman at AJC Global Forum 2025. He breaks down the media bias, misinformation and double standards shaping global coverage of Israel.
Jul 3
Journalist Matti Friedman Exposes Media Bias Against Israel
How has the media distorted Israel's response to the October 7 Hamas attacks? In this powerful conversation from AJC Global Forum 2025, award-winning journalist and former AP correspondent Matti Friedman breaks down the media bias, misinformation, and double standards shaping global coverage of Israel. Moderated by AJC Chief Communications and Strategy Officer Belle Etra Yoeli, this episode explores how skewed narratives have taken hold in the media, in a climate of activist journalism. A must-listen for anyone concerned with truth in journalism, Israel advocacy, and combating disinformation in today's media landscape. Take Action: Take 15 seconds and urge your elected leaders to send a clear, united message: We stand with Israel. Take action now . Resources: Global Forum 2025 session with Matti Friedman: : Watch the full video. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: John Spencer's Key Takeaways After the 12-Day War: Air Supremacy, Intelligence, and Deterrence Iran's Secret Nuclear Program and What Comes Next in the Iranian Regime vs. Israel War Why Israel Had No Choice: Inside the Defensive Strike That Shook Iran's Nuclear Program Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: I've had the privilege of interviewing journalism colleague Matti Friedman: twice on this podcast. In 2022, Matti took listeners behind the scenes of Jerusalem's AP bureau where he had worked between 2006 and 2011 and shared some insight on what happens when news outlets try to oversimplify the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Then in 2023, I got to sit down with Matti in Jerusalem to talk about his latest book on Leonard Cohen and how the 1973 Yom Kippur War was a turning point both for the singer and for Israel. Earlier this year, Matti came to New York for AJC Global Forum 2025, and sat down with Belle Yoeli, AJC Chief Strategy and Communications Officer. They rehashed some of what we discussed before, but against an entirely different backdrop: post-October 7. For this week's episode, we bring you a portion of that conversation. Belle Yoeli: Hi, everyone. Great to see all of you. Thank you so much for being here. Matti, thank you for being here. Matti Friedman: Thanks for having me. Belle Yoeli: As you can tell by zero empty seats in this room, you have a lot of fans, and unless you want to open with anything, I'm going to jump right in. Okay, great. So for those of you who don't know, in September 2024 Matti wrote a piece in The Free Press that is a really great foundation for today's discussion. In When We Started to Lie, Matti, you reflect on two pieces that you had written in 2015 about issues of media coverage of Israel during Operation Protective Edge in 2014. And this piece basically talked about the conclusions you drew and how they've evolved since October 7. We're gonna get to those conclusions, but first, I'm hoping you can describe for everyone what were the issues of media coverage of Israel that you first identified based on the experience in 2014? Matti Friedman: First of all, thanks so much for having me here, and thanks for all of the amazing work that you guys are doing. So it's a real honor for me. I was a reporter for the AP, between 2006 and the very end of 2011, in Jerusalem. I was a reporter and editor. The AP, of course, as you know, is the American news agency. It's the world's largest news organization, according to the AP, according to Reuters, it's Reuters. One of them is probably right, but it's a big deal in the news world. And I had an inside view inside one of the biggest AP bureaus. In fact, the AP's biggest International Bureau, which was in Jerusalem. So I can try to sketch the problems that I saw as a reporter there. It would take me seven or eight hours, and apparently we only have four or five hours for this lunch, so I have to keep it short. But I would say there are two main problems. We often get very involved. When we talk about problems with coverage of Israel. We get involved with very micro issues like, you call it a settlement. I call it a neighborhood. Rockets, you know, the Nakba, issues of terminology. But in fact, there are two major problems that are much bigger, and because they're bigger, they're often harder to see. One of the things that I noticed at the Bureau was the scale of coverage of Israel. So at the time that I was at the AP, again, between 2006 and the very end of 2011 we had about 40 full time staffers covering Israel. That's print reporters like me, stills photographers, TV crews. Israel, as most of you probably know, is a very small country. As a percentage of the world's surface, Israel is 1/100 of 1% of the surface of the world, and as a percentage of the land mass of the Arab world, Israel is 1/5 of 1%. 0.2%. And we had 40 people covering it. And just as a point of comparison, that was dramatically more people than we had at the time covering China. There are about 10 million people today in Israel proper, in China, there are 1.3 billion. We had more people in Israel than we had in China. We had more people in Israel than we had in India, which is another country of about 1.3 billion people. We had more people in Israel than we had in all of the countries of Sub-Saharan Africa. That's 50 something countries. So we had more people in Israel than we had in all of those countries combined. And sometimes I say that to Jews, I say we covered Israel more than we covered China, and people just stare at me blankly, because it's Israel. So of course, that makes perfect sense. I happen to think Israel is the most important country in the world because I live there. But if the news is meant to be a rational analysis of events on planet Earth, you cannot cover Israel more than you cover the continent of Africa. It just doesn't make any sense. So one of the things that first jumped out at me– actually, that's making me sound smarter than I am. It didn't jump out at me at first. It took a couple of years. And I just started realizing that it was very strange that the world's largest organization had its largest international bureau in the State of Israel, which is a very small country, very small conflict in numeric terms. And yet there was this intense global focus on it that made people think that it was the most important story in the world. And it definitely occupies a place in the American political imagination that is not comparable to any other international conflict. So that's one part of the problem. That was the scope, the other part was the context. And it took me a while to figure this out, but the coverage of Israel is framed as an Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The conflict is defined in those terms, the Israeli Palestinian conflict, and everyone in this room has heard it discussed in those terms. Sometimes we discuss it in those terms, and that is because the news folks have framed the conflict in those terms. So at the AP bureau in Jerusalem, every single day, we had to write a story that was called, in the jargon of the Bureau, Is-Pals, Israelis, Palestinians. And it was the daily wrap of the Israeli Palestinian conflict. So what Netanyahu said, what Abbas said, rockets, settlers, Hamas, you know, whatever, the problem is that there isn't an Israeli=Palestinian conflict. And I know that sounds crazy, because everyone thinks there is. And of course, we're seeing conflicts play out in the most tragic way right now in Gaza. But most of Israel's wars have not been fought against Palestinians. Israel has unfortunately fought wars against Egyptians and Jordanians and Lebanese and Iraqis. And Israel's most important enemy at the moment, is Iran, right? The Iranians are not Palestinian. The Iranians are not Arab. They're Muslim, but they're not Arab. So clearly, there is a broader regional conflict that's going on that is not an Israeli Palestinian conflict, and we've seen it in the past year. If we had a satellite in space looking down and just following the paths of ballistic missiles and rockets fired at Israel. Like a photograph of these red trails of rockets fired at Israel. You'd see rockets being fired from Iraq and from Yemen and from Lebanon and from Gaza and from Iran. You'd see the contours of a regional conflict. And if you understand it's a regional conflict, then you understand the way Israelis see it. There are in the Arab world, 300 million people, almost all of them Muslim. And in one corner of that world, there are 7 million Jews, who are Israelis. And if we zoom out even farther to the level of the Islamic world, we'll see that there are 2 billion people in the Islamic world. There's some argument about the numbers, but it's roughly a quarter of the world's population. And in one corner of that world there, there are 7 million Israeli Jews. The entire Jewish population on planet Earth is a lot smaller than the population of Cairo. So the idea that this is an Israeli-Palestinian conflict, where Israelis are the stronger side, where Israelis are the dominant actor, and where Israelis are, let's face it, the bad guy in the story, that's a fictional presentation of a story that actually works in a completely different way. So if you take a small story and make it seem big. If you take a complicated regional story and you make it seem like a very small local story involving only Israelis and Palestinians, then you get the highly simplified but very emotive narrative that everyone is being subjected to now. And you get this portrayal of a villainous country called Israel that really looms in the liberal imagination of the West as an embodiment of the worst possible qualities of the age. Belle Yoeli: Wow. So already you were seeing these issues when you were reporter, earlier on. But like this, some of this was before and since, since productive edge. This is over 10 years ago, and here we are. So October 7 happens. You already know these issues exist. You've identified them. How would you describe because obviously we have a lot of feelings about this, but like, strictly as a journalist, how would you describe the coverage that you've seen since during October 7, in its aftermath? Is it just these issues? Have they? Have they expanded? Are there new issues in play? What's your analysis? Matti Friedman: The coverage has been great. I really have very I have no criticism of it. I think it's very accurate. I think that I, in a way, I was lucky to have been through what I went through 10 or 15 years ago, and I wasn't blindsided on October 7, as many people were, many people, quite naturally, don't pay close attention to this. And even people who are sympathetic to Israel, I think, were not necessarily convinced that my argument about the press was right. And I think many people thought it was overstated. And you can read those articles from 2014 one was in tablet and one was in the Atlantic, but it's basically the two chapters of the same argument. And unfortunately, I think that those the essays, they stand up. In fact, if you don't really look at the date of the essays, they kind of seem that they could have been written in the past year and a half. And I'm not happy about that. I think that's and I certainly wrote them in hopes that they would somehow make things better. But the issues that I saw in the press 15 years ago have only been exacerbated since then. And October seven didn't invent the wheel. The issues were pre existing, but it took everything that I saw and kind of supercharged it. So if I talked about ideological conformity in the bureaus that has been that has become much more extreme. A guy like me, I was hired in 2006 at the AP. I'm an Israeli of center left political leanings. Hiring me was not a problem in 22,006 by the time I left the AP, at the end of 2011 I'm pretty sure someone like me would not have been hired because my views, which are again, very centrist Israeli views, were really beyond the pale by the time that I left the AP, and certainly, and certainly today, the thing has really moved what I saw happening at the AP. And I hate picking on the AP because they were just unfortunate enough to hire me. That was their only error, but what I'm saying about them is true of a whole new. Was heard. It's true of the Times and CNN and the BBC, the news industry really works kind of as a it has a herd mentality. What happened was that news decisions were increasingly being made by people who are not interested in explanatory journalism. They were activists. Activists had moved into the key positions in the Bureau, and they had a very different idea of what press coverage was supposed to do. I would say, and I tried to explain it in that article for the free press, when I approach a news story, when I approach the profession of journalism, the question that I'm asking is, what's going on? That's the question I think you're supposed to ask, what's going on? How can I explain it in a way that's as accurate as as possible? The question that was increasingly being asked was not what's going on. The question was, who does this serve? That's an activist question. So when you look at a story, you don't ask, is it true, or is it not true? You ask, who's it going to help? Is it going to help the good guys, or is it going to help the bad guys? So if Israel in the story is the villain, then a story that makes Israel seem reasonable, reasonable or rational or sympathetic needs to be played down to the extent possible or made to disappear. And I can give you an example from my own experience. At the very end of 2008 two reporters in my bureau, people who I know, learned of a very dramatic peace offer that Prime Minister Ehud Olmert had made to the Palestinians. So Olmert, who was the prime minister at the time, had made a very far reaching offer that was supposed to see a Palestinian state in all of Gaza, most of the West Bank, with land swaps for territory that Israel was going to retain, and a very far reaching international consortium agreement to run the Old City of Jerusalem. Was a very dramatic. It was so far reaching, I think that Israelis probably wouldn't have supported it. But it was offered to the Palestinian side, and the Palestinians rejected it as insufficient. And two of our reporters knew about this, and they'd seen a map of the offer. And this was obviously a pretty big story for a bureau that had as the thrust of its coverage the peace process. The two reporters who had the story were ordered to drop it, they were not allowed to cover the story. And there were different explanations. And they didn't, by the way, AP did not publish the story at the time, even though we were the first to have it. Eventually, it kind of came out and in other ways, through other news organizations. But we knew at first. Why were we not allowed to cover it? Because it would have made the Israelis who we were trying to villainize and demonize, it would have made Israel seem like it was trying to solve the conflict on kind of reasonable lines, which, of course, was true at that time. So that story would have upended the thrust of our news coverage. So it had to be made to go away, even though it was true, it would have helped the wrong people. And that question of who does this serve has destroyed, I want to say all, but much, of what used to be mainstream news coverage, and it's not just where Israel is concerned. You can look at a story like the mental health of President Biden, right. Something's going on with Biden at the end of his term. It's a huge global news story, and the press, by and large, won't touch it, because why? I mean, it's true, right? We're all seeing that it's true, but why can't you touch it? Because it would help the wrong people. It would help the Republicans who in the press are the people who you are not supposed to help. The origins of COVID, right? We heard one story about that. The true story seems to be a different story. And there are many other examples of stories that are reported because they help the right people, or not reported because they would help the wrong people. And I saw this thinking really come into action in Israel 10 or 15 years ago, and unfortunately, it's really spread to include the whole mainstream press scene and really kill it. I mean, essentially, anyone interested in trying to get a solid sense of what's going on, we have very few options. There's not a lot, there's not a lot out there. So that's the broader conclusion that I drew from what I thought at the time was just a very small malfunction involving Israel coverage. But Israel coverage ends up being a symptom of something much bigger, as Jews often are the symptom of something much bigger that's going on. So my problems in the AP bureau 15 years ago were really a kind of maybe a canary in the coal mine, or a whiff of something much bigger that we were all going to see happen, which is the transformation of the important liberal institutions of the west into kind of activist arms of a very radical ideology that has as its goal the transformation of the west into something else. And that's true of the press, and it's true of NGO world, places like Human Rights Watch and Amnesty International, which were one thing 30 years ago and are something very different today. And it's also true of big parts of the academy. It's true of places like Columbia and places like Harvard, they still have the logo, they still have the name, but they serve a different purpose, and I just happen to be on the ground floor of it as a reporter. Belle Yoeli: So obviously, this concept of who does this serve, and this activist journalism is deeply concerning, and you actually mentioned a couple other areas, academia, obviously we're in that a lot right now in terms of what's going on campus. So I guess a couple of questions on that. First of all, think about this very practically, tachlis, in the day to day. I'm a journalist, and I go to write about what's happening in Gaza. What would you say is, if you had to throw out a percentage, are all of them aware of this activist journalist tendency? Or you think it's like, like intentional for many of them, or it's sort of they've been educated that way, and it's their worldview in such a way that they don't even know that they're not reporting the news in a very biased way. Does that make sense? Matti Friedman: Totally. I think that many people in the journalism world today view their job as not as explaining a complicated situation, but as swaying people toward the correct political conclusion. Journalism is power, and the power has to be wielded in support of justice. Now, justice is very slippery, and, you know, choosing who's in the right is very, very slippery, and that's how journalism gets into a lot of trouble. Instead of just trying to explain what's going on and then leave, you're supposed to leave the politics and the activism to other people. Politics and activism are very important. But unless everyone can agree on what is going on, it's impossible to choose the kind of act, the kind of activism that would be useful. So when the journalists become activists, then no one can understand what's what's going on, because the story itself is fake, and there are many, many examples of it. But you know, returning to what you asked about, about October 7, and reporting post October 7, you can really see it happen. The massacres of October 7 were very problematic for the ideological strain that now controls a lot of the press, because it's counterintuitive. You're not supposed to sympathize with Israelis. And yet, there were a few weeks after October 7 when they were forced to because the nature of the atrocities were so heinous that they could not be ignored. So you had the press covering what happened on October 7, but you could feel it. As someone who knows that scene, you could feel there was a lot of discomfort. There was a lot of discomfort. It wasn't their comfort zone, and you knew that within a few weeks, maybe a month, it was gonna snap back at the first opportunity. When did it snap back? In the story of the Al Ahli hospital strike. If you remember that a few weeks in, there's a massive global story that Israel has rocketed Hospital in Gaza and killed about 500 people and and then you can see the kind of the comfort the comfort zone return, because the story that the press is primed to cover is a story about villainous Israelis victimizing innocent Palestinians, and now, now we're back. Okay. Now Israel's rocketing hospital. The problem was that it hadn't happened, and it was that a lot of stories don't happen, and they're allowed to stand. But this story was so far from the truth that even the people involved couldn't make it work, and it had to be retracted, but it was basically too late. And then as soon as the Israeli ground offensive got into swing in Gaza, then the story really becomes the same old story, which is a story of Israel victimizing Palestinians for no reason. And you'll never see Hamas militants in uniform in Gaza. You just see dead civilians, and you'll see the aftermath of a rocket strike when the, you know, when an Israeli F16 takes out the launcher, but you will never see the strike. Which is the way it's worked in Gaza since the very end of 2008 which is when the first really bad round of violence in Gaza happens, which is when I'm at the AP. As far as I know, I was the first staffer to erase information from the story, because we were threatened by Hamas, which happened at the very end of 2008. We had a great reporter in Gaza, a Palestinian who had always been really an excellent reporter. We had a detail in a story. The detail was a crucial one. It was that Hamas fighters were dressed as civilians and were being counted as civilians in the death toll, an important thing to know, that went out in an AP story. The reporter called me a few hours later. It was clear that someone had spoken to him, and he told me, I was on the desk in Jerusalem, so I was kind of writing the story from the main bureau in Jerusalem. And he said, Matti, you have to take that detail out of the story. And it was clear that someone had threatened him. I took the detail out of the story. I suggested to our editors that we note in an Editor's Note that we were now complying with Hamas censorship. I was overruled, and from that point in time, the AP, like all of its sister organizations, collaborates with Hamas censorship in Gaza. What does that mean? You'll see a lot of dead civilians, and you won't see dead militants. You won't have a clear idea of what the Hamas military strategy is. And this is the kicker, the center of the coverage will be a number, a casualty number, that is provided to the press by something called the Gaza health ministry, which is Hamas. And we've been doing that since 2008, and it's a way of basically settling the story before you get into any other information. Because when you put, you know, when you say 50 Palestinians were killed, and one Israeli on a given day, it doesn't matter what else you say. The numbers kind of tell their own story, and it's a way of settling the story with something that sounds like a concrete statistic. And the statistic is being, you know, given to us by one of the combatant sides. But because the reporters sympathize with that side, they're happy to play along. So since 2008, certainly since 2014 when we had another serious war in Gaza, the press has not been covering Gaza, the press has been essentially an amplifier for one of the most poisonous ideologies on Earth. Hamas has figured out how to make the press amplify its messaging rather than covering Hamas. There are no Western reporters in Gaza. All of the reporters in Gaza are Palestinians, and those people fall into three categories. Some of them identify with Hamas. Some of them are intimidated by Hamas and won't cross Hamas, which makes a lot of sense. I wouldn't want to cross Hamas either. So either. And the third category is people who actually belong to Hamas. That's where the information from Gaza is coming from. And if you're credulous, then of course, you're going to get a story that makes Israel look pretty bad. Belle Yoeli: So this is very depressing. That's okay. It's very helpful, very depressing. But on that note, I would ask you so whether, because you spoke about this problem in terms, of, of course, the coverage of Israel, but that it's it's also more widespread you talk, you spoke about President Biden in your article, you name other examples of how this sort of activist journalism is affecting everything we read. So what should everyone in this room be reading, truly, from your opinion. This is Matti's opinion. But if you want to you want to get information from our news and not activist journalism, obviously The Free Press, perhaps. But are there other sites or outlets that you think are getting this more down the line, or at least better than some, some better than others? Matti Friedman: No, it's just The Free Press. No. I mean, it's a question that I also wrestle with. I haven't given up on everyone, and even in publications that have, I think, largely lost the plot, you'll still find good stuff on occasion. So I try to keep my eye on certain reporters whose name I know. I often ask not just on Israel, but on anything, does this reporter speak the language of the country that they're covering? You'd be shocked at how rare that is for Americans. A lot of the people covering Ukraine have no idea what language they speak in Ukraine, and just as someone who covers Israel, I'm aware of the low level of knowledge that many of the Western reporters have. You'll find really good stuff still in the Atlantic. The Atlantic has managed, against steep odds, to maintain its equilibrium amid all this. The New Yorker, unfortunately, less so, but you'll still see, on occasion, things that are good. And there are certain reporters who are, you know, you can trust. Isabel Kirchner, who writes for The New York Times, is an old colleague of mine from the Jerusalem report. She's excellent, and they're just people who are doing their job. But by and large, you have to be very, very suspicious of absolutely everything that you read and see. And I'm not saying that as someone who I'm not happy to say that, and I certainly don't identify with, you know, the term fake news, as it has been pushed by President Trump. I think that fake news is, you know, for those guys, is an attempt to avoid scrutiny. They're trying to, you know, neuter the watchdog so that they can get away with whatever they want. I don't think that crowd is interested in good press coverage. Unfortunately, the term fake news sticks because it's true. That's why it has worked. And the press, instead of helping people navigate the blizzard of disinformation that we're all in, they've joined it. People who are confused about what's going on, should be able to open up the New York Times or go to the AP and figure out what's going on, but because, and I saw it happen, instead of covering the circus, the reporters became dancing bears in the circus. So no one can make heads or tails of anything. So we need to be very careful. Most headlines that are out there are out there to generate outrage, because that's the most predictable generator of clicks, which is the, we're in a click economy. So I actually think that the less time you spend following headlines and daily news, the better off you'll be. Because you can follow the daily news for a year, and by the end of the year, you'll just be deranged. You'll just be crazy and very angry. If you take that time and use it to read books about, you know, bitten by people who are knowledgeable, or read longer form essays that are, you know, that are obviously less likely to be very simplistic, although not, you know, it's not completely impossible that they will be. I think that's time, that's time better spent. Unfortunately, much of the industry is kind of gone. And we're in an interesting kind of interim moment where it's clear that the old news industry is basically dead and that something new has to happen. And those new things are happening. I mean, The Free Press is part of a new thing that's happening. It's not big enough to really move the needle in a dramatic way yet, but it might be, and I think we all have to hope that new institutions emerge to fill the vacuum. The old institutions, and I say this with sorrow, and I think that this also might be true of a lot of the academic institutions. They can't be saved. They can't be saved. So if people think that writing an editor, a letter to the editor of the New York Times is going to help. It's not going to help. Sometimes people say, Why don't we just get the top people in the news industry and bring them to Israel and show them the truth? Doesn't help. It's not about knowing or not knowing. They define the profession differently. So it's not about a lack of information. The institutions have changed, and it's kind of irrevocable at this point, and we need new institutions, and one of them is The Free Press, and it's a great model of what to do when faced with fading institutions. By the way, the greatest model of all time in that regard is Zionism. That's what Zionism is. There's a guy in Vienna in 1890 something, and his moment is incredibly contemporary. There's an amazing biography of Herzl called Herzl by Amos Elon. It's an amazing book. If you haven't read it, you should read it, because his moment in cosmopolitan Vienna sounds exactly like now. It's shockingly current. He's in this friendly city. He's a reporter for the New York Times, basically of the Austro Hungarian empire, and he's assimilated, and he's got a Christmas tree in his house, and his son isn't circumcised, and he thinks everything is basically great. And then the light changes. He notices that something has changed in Vienna, and the discourse about Jews changes, and like in a Hollywood movie, the light changes. And he doesn't try to he doesn't start a campaign against antisemitism. He doesn't get on social media and kind of rail against unfair coverage. He sits down in a hotel room in Paris and he writes this pamphlet called the Jewish state, and I literally flew from that state yesterday. So there's a Zionist model where you look at a failing world and you think about radical solutions that involve creation. And I think we're there. And I think Herzl's model is a good one at a dark time you need real creativity. Belle Yoeli: Thank God you found the inspiration there, because I was really, I was really starting to worry. No, in all seriousness, Matti, the saying that these institutions can't be saved. I mean the consequences of this, not just for us as pro-Israel, pro-Jewish advocates, but for our country, for the world, the countries that we come from are tremendous. And the way we've been dealing with this issue and thinking about how, how can you change hearts and minds of individuals about Israel, about the Jewish people, if everything that they're reading is so damaging and most of what they're reading is so damaging and basically saying there's very little that we can do about that. So I am going to push you to dream big with us. We're an advocacy organization. AJC is an advocacy organization. So if you had unlimited resources, right, if you really wanted to make change in this area, to me, it sounds like you're saying we basically need 15 Free Presses or the new institutions to really take on this way. What would you do? What would you do to try to make it so that news media were more like the old days? Matti Friedman: Anyone who wants unlimited resources should not go into journalism. I have found that my resources remain limited. I'll give you an answer that is probably not what you're expecting or not what you want here. I think that the fight can't be won. I think that antisemitism can't be defeated. And I think that resources that are poured into it are resources wasted. And of course, I think that people need legal protection, and they need, you know, lawyers who can protect people from discrimination and from defamation. That's very important. But I know that when people are presented with a problem like antisemitism, which is so disturbing and it's really rocking the world of everyone in this room, and certainly, you know, children and grandchildren, you have a problem and you want to address it, right? You have a really bad rash on your arm. You want the rash to go away, and you're willing to do almost anything to make it go away. This has always been with us. It's always been with us. And you know, we recently celebrated the Seder, and we read in the Seder, in the Haggadah, l'chol dor vador, omdim aleinu l'chaloteinu. Which is, in every generation, they come at us to destroy us. And it's an incredibly depressing worldview. Okay, it's not the way I wanted to see the world when I grew up in Toronto in the 1990s. But in our tradition, we have this idea that this is always gonna be around. And the question is, what do you do? Do you let other people define you? Do you make your identity the fight against the people who hate you? And I think that's a dead end. This crisis is hitting the Jewish people at a moment when many of us don't know who we are, and I think that's why it's hitting so hard. For my grandfather, who was a standard New York Jew, garment industry, Lower East Side, poor union guy. This would not have shaken him, because he just assumed that this was the world like this. The term Jewish identity was not one he ever heard, because it wasn't an issue or something that had to be taught. So if I had unlimited resources, what I would do is I would make sure that young Jewish people have access to the riches of Jewish civilization, I would, you know, institute a program that would allow any young Jewish person to be fluent in Hebrew by the time they finish college. Why is that so important? Why is that such an amazing key? Because if you're fluent in Hebrew, you can open a Tanakh, or you can open a prayer book if you want. Or you can watch Fauda or you can get on a plane to Israel and hit on Israeli guys. Hebrew is the key to Jewish life, and if you have it, a whole world will open up. And it's not one that antisemites can interfere with. It does not depend on the goodwill of our neighbors. It's all about us and what we're doing with ourselves. And I think that if you're rooted in Jewish tradition, and I'm not saying becoming religious, I'm just saying, diving into the riches of Jewish tradition, whether it's history or gemara or Israel, or whatever, if you're if you're deep in there enough, then the other stuff doesn't go away, but it becomes less important. It won't be solved because it can't be solved, but it will fade into the background. And if we make the center of identity the fight against antisemitism, they've won. Why should they be the center of our identity? For a young person who's looking for some way of living or some deep kind of guide to life, the fight against antisemitism is not going to do it, and philanthropy is not going to do it. We come from the wisest and one of the oldest civilizations in the world, and many of us don't know how to open the door to that civilization, and that's in our hands. And if we're not doing it, it's not the fault of the antisemites. It's our own fault. So if I had unlimited resources, which, again, it's not, it's not going to happen unless I make a career change, that's where I would be putting my effort. Internally and not externally. Belle Yoeli: You did find the inspiration, though, again, by pushing Jewish identity, and we appreciate that. It's come up a lot in this conversation, this question about how we fight antisemitism, investing in Jewish identity and who we are, and at the same time, what do we do about it? And I think all of you heard Ted in a different context last night, say, we can hold two things, two thoughts at the same time, right? Two things can be true at the same time. And I think for me, what I took out of this, in addition to your excellent insights, is that that's exactly what we have to be doing. At AJC, we have to be engaging in this advocacy to stand up for the Jewish people and the State of Israel. But that's not the only piece of the puzzle. Of course, we have to be investing in Jewish identity. That's why we bring so many young people to this conference. Of course, we need to be investing in Jewish education. That's not necessarily what AJC is doing, the bulk of our work, but it's a lot of what the Jewish community is doing, and these pieces have to go together. And I want to thank you for raising that up for us, and again, for everything that you said. Thank you all so much for being here. Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in as John Spencer, Chair of Urban Warfare Studies at West Point, breaks down Israel's high-stakes strike on Iran's nuclear infrastructure and the U.S. decision to enter the fight.
Jun 26
John Spencer's Key Takeaways After the 12-Day War: Air Supremacy, Intelligence, and Deterrence
John Spencer, Chair of Urban Warfare Studies at West Point, joins guest host Casey Kustin, AJC's Chief Impact and Operations Officer, to break down Israel's high-stakes strike on Iran's nuclear infrastructure and the U.S. decision to enter the fight. With Iran's terror proxy network reportedly dismantled and its nuclear program set back by years, Spencer explains how Israel achieved total air superiority, why a wider regional war never materialized, and whether the fragile ceasefire will hold. He also critiques the international media's coverage and warns of the global consequences if Iran's ambitions are left unchecked. Take Action: Take 15 seconds and urge your elected leaders to send a clear, united message: We stand with Israel. Take action now . Resources and Analysis: Israel, Iran, and a Reshaped Middle East: AJC Global Experts on What Comes Next AJC Advocacy Anywhere - U.S. Strikes in Iran and What Comes Next Iranian Regime's War on America: Four Decades of Targeting U.S. Forces and Citizens AJC Global Forum 2025: John Spencer Breaks Down Israel's War and Media Misinformation Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: Iran's Secret Nuclear Program and What Comes Next in the Iranian Regime vs. Israel War Why Israel Had No Choice: Inside the Defensive Strike That Shook Iran's Nuclear Program Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Casey Kustin: Hi, I'm Casey Kustin, AJC's Chief Impact and Operations Officer, and I have the pleasure of guest hosting this week's episode. As of the start of this recording on Wednesday, June 25, it's been 13 days since Israel launched precision airstrikes aimed at dismantling the Iranian regime's nuclear infrastructure and degrading its ballistic missile capabilities to help us understand what transpired and where we are now, I'm here with John Spencer, Chair of Urban Warfare Studies at the Modern War Institute at West Point, co-director of the Urban Warfare Project and Executive Director of the Urban Warfare Institute. John, welcome to People of the Pod. John Spencer: Hey, Casey, it's good to see you again. Casey Kustin: Thanks so much for joining us. John, you described Israel's campaign as one of the most sophisticated preemptive strike campaigns in modern history, and certainly the scope and precision was impressive. What specific operational capabilities enabled Israel to dominate the Iranian airspace so completely? John Spencer: Yeah, that's a great question, and I do believe it basically rewrote the book, much like after the 1973 Yom Kippur War, where Israel did the unthinkable, the United States military conducted 27 different studies, and it fundamentally changed the way we fight warfare. It's called Air-Land Battle. I think similarly with Operation Rising Lion, just the opening campaign rewrote what we would call, you know, Shock and Awe, Joint Forcible Entry, things like that. And the capabilities that enabled it, of course, were years of planning and preparation. Just the deep intelligence infiltration that Israel did before the first round was dropped. The Mossad agents texting the high command of the IRGC to have a meeting, all of them believing the texts. And it was a meeting about Israel. They all coming together. And then Israel blew up that meeting and killed, you know, in the opening 72 hours, killed over 25 senior commanders, nine nuclear scientists, all of that before the first bomb was dropped. But even in the opening campaign, Israel put up over 200 aircrafts, almost the entire Israeli air force in the sky over Iran, dominating and immediately achieving what we call air supremacy. Again, through years of work, almost like a science fiction story, infiltrating drone parts and short range missiles into Iran, then having agents put those next to air defense radars and ballistic air defense missile systems. So that as soon as this was about to begin, those drones lost low cost drones and short range missiles attacked Iranian air defense capabilities to give the window for all of the Israeli F-35 Eyes that they've improved for the US military since October 7 and other aircraft. Doing one of the longest operations, seconded only to one other mission that Israel has done in their history, to do this just paralyzing operation in the opening moment, and then they didn't stop. So it was a combination of the infiltration intelligence, the low-tech, like the drones, high-tech, advanced radar, missiles, things like that. And it was all put together and synchronized, right? So this is the really important thing that people kind of miss in military operations, is how hard it is to synchronize every bit of that, right? So the attack on the generals, the attack on the air defenses, all of that synchronized. Hundreds of assets in a matter of minutes, all working together. There's so much chance for error, but this was perfection. Casey Kustin: So this wasn't just an operational success, it was really strategic dominance, and given that Iran failed to down a single Israeli Aircraft or cause any significant damage to any of Israel's assets. What does that tell us about the effectiveness of Iran's military capabilities, their Russian built air defenses that they have touted for so long? John Spencer: Absolutely. And some people say, I over emphasize tactics. But of course, there's some famous sayings about this. At the strategic level, Israel, one, demonstrated their military superiority. A small nation going against a Goliath, a David against a Goliath. It penetrated the Iranian myth of invincibility. And I also failed to mention about how Israel, during this opening of the campaign, weakened Iran's ability to respond. So they targeted ballistic missile launchers and ballistic missile storages, so Iran was really weakened Iran's ability to respond. But you're right, this sent a signal around the Middle East that this paper tiger could be, not just hit, it could be dominated. And from the opening moments of the operation until the ceasefire was agreed to, Israel eventually achieved air supremacy and could dominate the skies, like you said, without losing a single aircraft, with his really historic as well. And hit what they wanted with what they wanted, all the military infrastructure, all the senior leaders. I mean, eventually they assigned a new commander of the IRGC, and Israel found that guy, despite him running around in caves and things. It definitely had a strategic impact on the signal to the world on Israel's capabilities. And this isn't just about aircraft and airstrikes. Israel's complete dominance of Iran and the weakness, like you said. Although Israel also taught the world back when they responded to Iran's attack in April of last year, and in October of last year, is that you probably shouldn't be buying Russian air defense systems like S-300s. But Iran still, that was the backbone of their air defense capabilities, and Israel showed that that's a really bad idea. Casey Kustin: You mentioned the component of this that was not just about going after infrastructure sites, but targeting Iranian military leadership and over 20 senior military and nuclear figures, according to public reporting. This was really a central part of this campaign as well. How does this kind of decapitation strategy alter the regime's military capability now, both in this immediate short term, but also in the long term, when you take out that kind of leadership? John Spencer: Yeah, absolutely. I mean, much like when the United States took out Qasem Soleimani, the head of the Quds Force, who had been decades of leadership of the Quds Force, the terror proxies, which I'm sure we'll talk about, overseeing those to include the ones in Iraq, killing my soldiers. It had a ripple effect that was, it's hard to measure, but that's decades of relationships and leadership, and people following them. So there is that aspect of all of these. Now we know over 25 senior IRGC and Iranian basically leadership, because they killed a police chief in Tehran and others. Yet that, of course, will ripple across. It paralyzed the leadership in many ways during the operation, which is the psychological element of this, right? The psychological warfare, to do that on the opening day and then keep it up. That no general could trust, much like Hezbollah, like nobody's volunteering to be the next guy, because Israel finds him and kills him. On the nuclear though, right, which all wars the pursuit of political goals. We can never forget what Israel said the political goals were – to roll back Iran's imminent breakout of a nuclear weapon, which would not only serve to destroy Israel, because that's what they said they wanted to do with it, but it also gives a nuclear umbrella, which is what they want, to their exporting of terrorism, and the Ring of Fire, the proxy networks that have all been defanged thanks to Israel. That's the reason they wanted. So in taking out these scientists.So now it's up to 15 named nuclear scientists. On top of the nuclear infrastructure and all the weaponization components. So it's not just about the three nuclear enrichment sites that we all talked about in the news, you know, Fordow, Natanz, and Esfahan. It's about that complete, decades-long architecture of the scientists, the senior scientists at each of the factories and things like that, that does send about, and I know we're in right now, as we're talking, they're debating about how far the program was set back. It holistically sets back that definitely the timeline. Just like they destroyed the Tehran clock. I'm sure you've heard this, which was the doomsday clock that Iran had in Tehran, which is the countdown to the destruction of Israel. Israel stopped that clock, both literally and figuratively. Could they find another clock and restart it? Absolutely. But for now, that damage to all those personnel sets everything back. Of course, they'll find new commanders. I argue that you can't find those same level of you know, an Oppenheimer or the Kahn guy in Pakistan. Like some of those guys are irreplaceable. Casey Kustin: So a hallmark of Israeli defense policy has always been that Israel will take care of itself by itself. It never asks the United States to get involved on its behalf. And before President Trump decided to undertake US strikes, there was considerable public discussion, debate as to whether the US should transfer B2s or 30,000 pound bunker busters to Israel. From purely a military perspective, can you help us understand the calculus that would go into why the US would decide to take the action itself, rather than, say, transfer these assets to Israel to take the action? John Spencer: Sure. It's a complex political question, but actually, from the military perspective, it's very straightforward. The B2 stealth fire fighter, one of our most advanced, only long range bomber that can do this mission right, safely under radar, all this stuff. Nobody else has it. Nobody else has a pilot that could do it. So you couldn't just loan this to Israel, our strongest ally in the Middle East, and let them do the operation. As well as the bomb. This is the only aircraft with the fuselage capable of carrying this side. Even the B-52 stratomaster doesn't have the ability to carry this one, although it can push big things out the back of it. So just from a logistics perspective, it wouldn't work. And then there's the classification. And there's many issues with, like, the somebody thinking that would have been the easiest, and even if it was possible, there's no way to train an Israeli pilot, all the logistics to it, to do it. The Israel Begin Doctrine about, you know, taking into their own hands like they did in Iraq in 1981 and Syria in 2007, is still in full effect, and was shown to be literally, a part of Israel's survival is this ability to, look, I understand that allies are important. And I argue strongly that Israel can never go at it alone, and we should never want it to. The strength of any nation is its allies. And the fact that even during this operation, you saw immense amounts of American military resources pushed into the Middle East to help defend Israel and US bases but Patriot systems on the ground before this operation, THAAD systems on the ground before the system. These are the advanced US army air defense systems that can take down ballistic missiles. You had Jordan knocking down drones. You had the new Assad replacement guy, it's complex, agreeing to shoot things down over their airspace. That is part of Israel's strength, is its allies. I mean, the fact that you have, you know, all the Arab nations that have been helping and defending Israel is, I think, can't be underscored under Israel doesn't, shouldn't need to go it alone, and it will act. And that's the Begin Doctrine like this case. And I do believe that the United States had the only weapon, the only capability to deliver something that the entire world can get behind, which is nuclear proliferation, not, you know, stopping it. So we don't want a terror regime like the Islamic regime, for so many different reasons, to have a nuclear weapon close to breakout. So United States, even the G7, the United Nations, all agree, like, you can't have a nuclear weapon. So the United States doing that limited strike and midnight hammer, I think, was more than just about capabilities. It was about leadership in saying, look, Iran's double play that the economic sanctions, or whatever, the JCPOA agreement, like all these things, have failed. Conclusively, not just the IAEA statement that they're 20 years that now they're in violation of enrichment to all the different intelligence sources. It was not working. So this operation was vital to Israel's survival, but also vital for the world and that too, really won in this operation. Casey Kustin: Vital both in this operation, in the defense of Israel, back in April 2024 when Iran was firing missiles and we saw other countries in the region assist in shooting them down. How vital is Israel's integration into CENTCOM to making that all work? John Spencer: Oh, I mean, it's life saving. And General Carrillo, the CENTCOM Commander, has visited Israel so much in. The last 20 months, you might as well have an apartment in Tel Aviv. It's vital, because, again, Israel is a small nation that does spend exponential amounts of its GDP in its defense. But Iran, you know this, 90 million much greater resources, just with the ballistic missile program. Why that, and why that was so critical to set that back, could overwhelm Israel's air defense systems. Could. There's so much to this, but that coordination. And from a military to military perspective, and this is where I come and get involved, like I know, it's decades long, it's very strong. It's apolitical on purpose. It's hidden. Most people don't know it, but it's vital to the survival of our greatest ally in the Middle East. So it meets American interest, and, of course, meets Israel's interest. Casey Kustin: Can you help us understand the Iranian response targeting Al Udeid Air Base in Qatar, because this seemed like a very deliberate way for the regime to save face and then de-escalate. But if the ceasefire falls apart, what are the vulnerabilities for us, troops and assets in the region. How well positioned are our bases in Qatar, Al Dhafra in the UAE, our naval assets in Bahrain, our bases in Iraq? How well positioned are we to absorb and deter a real retaliatory response? John Spencer: Yeah, it's a great question. I mean, first and foremost, you know, there is a bit of active defense. So, of course, all of our US bases are heavily defended. A lot of times, you can see things are about to happen, and you can, just like they did, they moved to naval aircraft that would have been even vulnerable in some of these locations, out to sea, so they can't be touched. Heavily defended. But really, active defense is absolutely important, but really deterrence is the greatest protection. So that has to be demonstrated by the capability, right? So the capability to defend, but also the capability to attack and the willingness to use it. This is why I think that supposedly symbolic to the 14 bunker busters that the United States dropped during Operation Midnight Hammer. Iran sent 14 missiles. President Trump says, thanks for the heads up. You know, all of it was evacuated, very symbolic, clearly, to save face and they had a parade, I guess, to say they won something. It's ludicrous, but sometimes you can't get inside the heads of irrational actors who are just doing things for their own population. Our bases, the force protection is heavy. I mean, there's never 100% just like we saw with all the air defenses of Israel, still about 5% or if not less, of the ballistic missiles got through one one drone out of 1000 got through. You can never be 100% but it is the deterrence, and I think that's what people miss in this operation. It set a new doctrine for everyone, for the United States, that we will use force with limited objectives, to send an immense amount of strength. And when somebody says there's a red line now that you should believe that, like if you would have injured a single American in the Middle East, Iran would have felt immense amount of American power against that, and they were very careful not to so clearly, they're deterred. This also sent a new red line for Israel, like Israel will act just like it did in other cases against even Iran, if they start to rebuild the program. War is the pursuit of political objectives, but you always have to look at the strategic on down. Casey Kustin: On that last point, do you think we have entered a new phase in Israeli military doctrine, where, instead of sort of a more covert shadow war with Iran, we will now see open confrontation going forward, if necessary? John Spencer: Well, you always hope that it will not be necessary, but absolutely this event will create, creates a new doctrine. You can see, see almost everything since October 7, and really there were just things that were unconceivable. Having studied and talked to Israeil senior leaders from the beginning of this. Everybody thought, if you attacked Hezbollah, Iran, was going to attack and cause immense amounts of destruction in Israel. Even when Israel started this operation, their estimates of what the damage they would incur was immense. And that it didn't is a miracle, but it's a miracle built in alliances and friendships with the United States and capabilities built in Israel. Of course, Israel has learned a lot since October 7 that will fundamentally change everything about not just the military doctrine, but also intelligence services and many aspects that are still happening as they're fighting, still to this day in Gaza to achieve the realistic, measurable goal there. Yes, it absolutely has set forth that the old ways of doing things are gone, the you know, having these terror armies, the ring of fire that Israel has defanged, if not for Hamas dismantled and destroyed. It sets a new complete peace in the Middle East. But also a doctrine of, Israel is adapting. I mean, there's still some elements about the reserve forces, the reigning doctrine, that are evolving based on the magnitude of the war since October 7. But absolutely you're right about they will, which has been the doctrine, but now they've demonstrated the capability to do it to any threat, to include the great, you know, myth of Iran. Casey Kustin: So when you talk about this defanging of the Iranian proxy network obviously, Israel undertook significant operations against Hezbollah. Over the last year, they've been in active conflict with the Houthis. How does this operation now alter the way that Iran interacts with those proxies and its capacity to wage war against Israel through these proxies? John Spencer: Yeah, cripples it, right? So Iran's nuclear ambition and its terror campaign are literally in ruins right now, both literally and figuratively. Hezbollah was defanged, the leadership, even taking out Nasrallah was believed to have caused catastrophic consequences, and it didn't. So, absolutely for Iran, also during this operation, is sniffing because all of his proxies were silent. I think the Houthis launched two missiles because thanks to Israel and the United States, the Houthi capabilities that should never have been allowed to amass, you know, this pirate terror empire. They didn't make those greatest shore to sea arsenal out of falafels. It got it straight from Iran, and that pipeline has already been cut off, let alone the capabilities. Same thing with Hezbollah, which relied heavily on pipelines and infrastructure of missiles and everything being fed to it by Iran. That's been cut. The Assad regime being the drug empire, support of Hezbollah to rule basically, in Lebanon, has been cut. Hezbollah couldn't come to the aid of Assad. All of these variables. And of course, Hamas will never be able to do anything again, period. It all causes Iran to have to rethink everything. From, you know, not only their own national defense, right air defense capabilities and all this, but their terror campaign, it isn't just in ruins. There's a new doctrine, like it's not acceptable. Now, of course, that's going to be hard to fully reign in. You have Shia backed groups in Iraq, you have a lot of bad things going on, but the Quds Force, which is its job, it's all shattered. Of course, they'll try to rebuild it. But the fact that these terror proxies were already so weakened by Israel that they couldn't do anything and remain silent. Hezbollah just was silent basically during this, is very significant to the peace going forward. I mean, there, there's still a lot of war here, but Israel and the United States have rewritten the map of the Middle East. Casey Kustin: in the hours days that followed the US deciding to engage here. A lot of the conversation focused on the possibility of triggering now broader regional escalation, but we didn't see that, and it sort of shattered that myth that if Israel or the US were to go after Iran, that it would spiral into a broader Middle East conflict. Why did we not see that happen? Why did this remain so controlled? John Spencer: So many reasons that really go back a few months, if not years? Mean going back to the first the Abraham Accords, President Trump's recent tour of the Gulf states and his story. Turic financial deals Israel's like we talked about with the Arab nations that were part of protecting it, the fact that the so on, that very geopolitical aspect. And we saw Iran turn to Russia, because there's always geopolitical considerations. Iran turned to Russia. Said, you're going to help us out. We signed this security agreement last year. We've been helping you in Ukraine do the awful things you're doing there. And Russia said, No, that's not what we said. And it called called President Trump. President Trump says, how about you worry about mediating a ceasefire in Ukraine? And well, so they turned to China and the fact that there was nobody again, and that all the work that had been done with all the people that also disagree, nation states like Saudi Arabia, Qatar, all those others. Those are many of the contributing factors. But war also, I wrote this piece about, this isn't Iraq, this isn't Afghanistan, this isn't Libya. I really hate the lazy comparisons. This was contained and not able to spill out by constant communication from day one of what the goals were. Limited objective to roll back a threat to the world nuclear program and the ballistic program as well. That prevents the ability for even the Islamic regime to say, you know, my survival is at risk, I need to escalate this, right? So, being clear, having strategic clarity from Israel, and when the United States assisted, from the United States. You know, war is a contest of wills, not just between the military is fighting it, but the political element and the population element. So, you know, being able to communicate to the population in Israel and like, what's the goal here? Like, how long are we gonna have to do this? And to the United States. Like, what are our interests? Keeping it the goal limited, which all parties did. And even, in fact, you had the G7 meeting during this and they signed an agreement, we agree Iran cannot have a nuclear weapon. That is a big part of how you permit the spill out. But it does have many contextual elements of the broader, this isn't black and white between Israel and Iran. It's much bigger than that. And that, and we saw all that work that has been done to show strength through peace, or peace through strength, in all the forms of national power that have been rallied against what is chaos that the Islamic regime wants in the Middle East. Casey Kustin: So now that we've had a few days to begin to assess the impact of both the US and the Israeli strikes based on what's publicly available. I think you wrote that the nuclear timeline has been pushed back years. We saw some reporting in the New York Times yesterday saying it's only set back months. It seems this morning, the US is concurring with the Israeli assessment that it's been set back years. A lot of talk about where certain Where did certain stockpiles of enriched uranium, and how confident can we be at this point in any of these assessments? John Spencer: So yes, as we're talking, people are trying to make it political. This should be a non partisan, non political issue. I'm an objective analyst of war. If you just write down all the things that Israel destroyed, validated by satellite imagery. then the fact that somebody And even the spinning of words where like we saw with that leaked report, which was the preliminary thoughts about something, it isn't comprehensive, right? So one, BDA has never come that fast. Two, we do know, and Iran has validated, like all these scientists dead, all these generals dead, all these components of the nuclear program, damaged or destroyed. The idea that somebody would say, well, you only set it back a couple months to me, it's just anti-intellectual. Look, Natanz, Esfahan, Fordo, we can debate about how much stuff is inside of that mountain that was destroyed, although 14 of the world's best bunker buster munitions, 30,000 pounds punching through. I just think, it's not a silly argument, because this is very serious. And yes, there could be, you know, hundreds of pounds of enriched uranium up there, a certain percentage that got floated around. That's not the, the things that set the timeline of breakout. Breakout included all the components of the knowledge and capability to reach breakout and then weaponization of a nuclear bomb. There's nobody, I think, who can comprehensively, without nuancing the words say that Israel wasn't very effective, and the United States assistance in only what the United States could do, at setting this program back and actually stopping the immediate danger. Of course, Iran is still a danger. The program is still a danger, but I just think it's so political that they're trying to say that, well, you only said it back a couple months. That's like, that's ridiculous. Casey Kustin: So as an objective analyst of war, but also as someone who's really been a voice of moral clarity and has called out the international media over the last 18 months for a lot of this disinformation, misinformation, bias reporting. Before we go, John, what is one consequence of this operation that the international media is just missing? John Spencer: One is that, I think the international media who are debating whether Iran was literally using an opposing opinion against global thought that Iran was close to a nuclear bomb, they missed that completely and tried to politicize it to where, just giving disinformation agents that tidbit of a headline that they need. I do believe in journalistic standards, fact checking, those elements and holding those people accountable. I live in the world of experts. People on the platform X who think they're experts. But when you have national media running headlines for sensationalism, for clicks, for you know, struggling for opposition to just political administration, we should learn to really question a single report as valid when there's overwhelming opposition. I don't know how to put that succinctly, but you think we would learn over the last, you know, 20 months of this lies, disinformation, statistical warfare, the things like that that, yeah, it's just crazy that that somebody would think in any way this wasn't an overwhelming success for the world, that this program was set back and a new doctrine for treating the program was established. Casey Kustin: Finally, John, before we wrap up here, the question on everyone's mind: can the ceasefire really hold? John Spencer: So, you know, I don't do predictions, because I understand wars uncertainty. It's human. It's political. It looks by all signs, because of how Iran was dominated, and how the United States showed that if it isn't contained, then immense amounts of force and of course, Israel's superiority, I believe that the ceasefire will hold. It was normal. And I made some some posts about the historical examples of wars coming to an end, from the Korean War, to the Yom Kippur war, Bosnia War, where you had this transition period where you're rolling back forces and everything. But the by the fact that Iran has said, Yeah, we agreed. We have stopped our operation. All signs for me are saying that this ceasefire will hold, and now the world's in a better place. Casey Kustin: John, thank you so much for the insight, for, as I said, your moral clarity that you bring to this conversation. We appreciate you joining us today on People of the Pod. John Spencer: Thank you so much.
Jun 18
Iran's Secret Nuclear Program and What Comes Next in the Iranian Regime vs. Israel War
Since Israel launched Operation Rising Lion—a precise and defensive military campaign aimed at preventing the Iranian regime from acquiring nuclear weapons—Iran has responded with a barrage of ballistic missiles and drones, indiscriminately targeting Israeli civilians. Dr. Matthew Levitt, director of the Reinhard Program on Counterterrorism and Intelligence at the Washington Institute for Near East Policy, and a leading expert on Iran's global terror network, explains what's at stake—and what could come next. Take Action: We must stop a regime that vows to murder millions of Israelis from gaining the weapons to do it. Urge your elected leaders to assure that Israel has all the necessary support to end Iran's nuclear threat . Resources and Analysis: Iranian Regime vs. Israel War Explained: What You Should Know AJC Advocacy Anywhere: Israel and Iran: Latest Updates, Global Responses, and the Path Ahead 5 Key Reasons Behind Israel's Defensive Strike on Iran's Imminent Nuclear Threat Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: Why Israel Had No Choice: Inside the Defensive Strike That Shook Iran's Nuclear Program What Rabbi Lord Jonathan Sacks' State of the Jewish World Teaches Us Today Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Israel's shadow war with the Iranian regime, the world's leading state sponsor of terrorism, erupted into open conflict last week following a stunning report from the International Atomic Energy Agency that confirmed Iran was much closer to obtaining nuclear weapons than previously known. Since Israel launched a wave of attacks on nuclear sites and facilities, Iran has fired missiles toward Israel's most populated cities. Joining us to discuss what this all means is one of the foremost experts on Iran and its global threats, and a regular guest when trouble arises with Iran. Dr. Matthew Levitt, director of the Reinhard Counterterrorism Program at the Washington Institute for Near East Policy. Matt, welcome back to People of the Pod. Matthew Levitt: It's a pleasure to be back, but I need to come sometime when the world's okay. Manya Brachear Pashman: That would be nice. That'd be nice. But what will we talk about? Matthew Levitt: Yeah, just call me one of the Horsemen of the Apocalypse. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, you are one of the foremost experts on the dangers posed by Iran, especially its terror proxies. And you've written the definitive book on Hezbollah, titled Hezbollah: the Global Footprint of Lebanon's Party of God. And I say that whole title, I want to get in there, because we are talking about global threats here. Can you explain the scale of Iran's global threat and the critical role that its terror proxies, like Hezbollah, Hamas, the Houthis, play in advancing that strategy? Matthew Levitt: So I really appreciate the question, because it's really important to remind listeners that the Israel Iran war did not start Thursday night US time, Friday morning, Israel time. In fact, it's just the latest salvo where the Israelis, after years and years and years of Iranian we call it malign activity, but that's too soft a term. We're talking about Iran sending weapons and funds to proxies like Hamas to carry out October 7, like Hezbollah to fire rockets at Israel almost daily for almost a year. Like the Houthis, who were much more than a thorn in the Saudi backside until the Iranians came and gave them more sophisticated capabilities. We're talking about an Iran that a few years ago decided that instead of making sure that every gun that it sent to the West Bank had to go to Hamas or Islamic Jihad. They decided to just flood the West Bank with guns. Who cares who's shooting at the Israelis so long as somebody is. And an Iran that not only carries out human rights abuses of all kinds at home, but that threatens Israel and its neighbors with drones, low altitude cruise missiles, short range ballistic missiles, and medium and long range ballistic missiles. And so the totality of this, much like the totality of Hezbollah's striking Israel for almost a year, ultimately led Israel to do what most people thought couldn't be done, and just tear Hezbollah apart, that the Israel war on Hezbollah is the prequel to what we've been seeing over the past few days in Iran. Similarly, for the Israelis, it got to be too much. It wasn't even really that President Trump's 60 days expired and Israel attacked on day 61. It wasn't only that the IAEA came out with a report saying that the Iranians have refused to explain certain activities that can only be explained as nuclear weaponization activities. It was that the Israelis had information that two things were happening. One, that Iran was working very, very hard to rebuild its capability to manufacture medium, long range ballistic missiles that can hit Israel. After the Israeli reprisal attack last October took out a key component of that program, the mixers that are important for the solid propellant, without which you can't make ballistic missiles. And Iran is believed to have, at least the beginning of this recent round of the conflict –Thursday, Friday–about 2000 such missiles. Far fewer now, the Israelis say they've taken out about a third of them, plus launchers, plus radars, et cetera. But that Iran had a plan within just a few years to develop as many as 8000 of these. And that simply was not tolerable for the Israelis. And the second is that the Israelis say that they compiled evidence that Iran had a secret, secret nuclear weapons program that had been going on predating October 7, but was fast tracked after October 7, that they were planning to maintain this program, even as they were negotiating over the more overt program with the Trump administration. President Trump has even taken issue with his own Director of National Intelligence Tulsi Gabbard, who testified in March that the US intelligence committee does not assess that Iran is weaponizing. And President says, I don't care what she says, I think they were very close to weaponizing. The Israelis say they have shared this information at least recently with their US counterparts and that was not tolerable. So the primary goals that Israel has set out for itself with this campaign is beyond the critically important shattering the glass ceiling. Think where people in particular, in Iran thought this would never happen, was two things, one, addressing and significantly degrading and setting back the Iranian ballistic missile production program, and second, doing the same to the nuclear program. They've already carried out strikes at Isfahan, Natanz, even at the upper parts of Fordow. And there is an expectation that the Israelis are going to do something more. The Israeli national security advisor said on Israeli television today, We are not going to stop without addressing the nuclear activities at Fordow. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, you called it a prequel, Israel's operations against Hezbollah last year. Did you know that it was a prequel at the time and to what extent did it weaken Iran and leave it more vulnerable in this particular war? Matthew Levitt: I'm going to be the last person in Washington, D.C. who tells you when he doesn't know. And anybody who tells you they did know is lying to you. None of us saw what Israel did to Hezbollah coming. None of us saw that and said, Oh, they did it to a non-state actor right across their border. So they'll definitely be able to do it to Iran, 1000+ kilometers away, big nation state with massive arsenals and a nuclear program and lots of proxies. One plus one does not equal three in this. In other words, the fact that Israel developed mind boggling capabilities and incredible intelligence, dominance and then special tools, pagers and walkie talkies, in the case of Hezbollah, did not mean that they were going to be able to do the same vis a vis Iran. And they did. The same type of intelligence dominance, the same type of intelligence, knowing where somebody was at a certain time, that the protocols would be that certain leaders would get in a certain secret bunker once hostilities started, and they'd be able to take them out in that bunker. As they did to a bunch of senior Hezbollah commanders just months ago. Drone operations from within Iran, Iran being hit with missiles that were fired at Iran from within Iran, all of it. One case did not necessarily translate into the other. It is exponentially impressive. And Israel's enemies have to be saying, you know, that the Israelis are just all capable. Now you're absolutely right. You hit the nail on the head on one critical issue. For a very long time, Israel was at least somewhat deterred, I would say very deterred, from targeting Iran. Because Iran had made very, very clear if Israel or the United States or anybody else targeted Iran or its nuclear program, one of the first things that would happen would be that Hezbollah in Lebanon, Israel, Iran's first, most important proxy would rain hellfire in Israel in the form of 1000s upon 1000s of rockets. Until Israel addressed the problem, Hezbollah is believed to have had 150 to 200,000 different types of projectiles, up to and including precision guided munitions. Not only have the overwhelming majority of those been destroyed, Hezbollah still has 1000s of rockets, but Hezbollah leadership has been decimated. There's a new sheriff in town in Lebanon. There's a new government that immediately, when hostility started with Iran's, went to Hezbollah and said, You're not doing this, not dragging Lebanon back into a war that nobody wanted again. We are finally coming out of this economic crisis. And so Iran was faced with a situation where it didn't have Hezbollah to deter Israel. Israel, you know, paved the way for a highway in the air to Iran, taking out air defense systems. It was able to fly over and through Syria. The Syrians are not shedding any tears as they see the Quds Force and the IRGC getting beaten down after what Iran did in Syria. And the Israelis have air dominance now. President Trump said, We, using the we term, air dominance now, earlier today. And they're able to slowly and methodically continue to target the ballistic missile program. Primarily, the medium and long range missiles that target Israel, but sometimes it's the same production lines that produce the short range missiles that Iran uses to target U.S. Forces in the region, and our allies in the Gulf. So Israel is not just protecting itself, it's protecting the region. And then also taking out key military security intelligence personnel, sometimes taking out one person, then a couple days later, taking out the person who succeeded that person, and then also taking out key scientists who had the know-how to potentially rebuild all the things that Israel is now destroying. Manya Brachear Pashman: But Israel is also not hearing from the Houthis, is not hearing from Hamas. It's not hearing from other terror proxies either. Very few attacks from Iran's terror proxies in the aftermath of this wave. Why? Why do you think that is? Matthew Levitt: The crickets are loud. The crickets are loud. Look, we've discussed Hezbollah. Hezbollah understands that if it were to do something, the Israelis will come in even harder and destroy what's left. Hamas is still holding hostages. This is still an open wound, but it doesn't have the capabilities that it once had, and so there have been a couple of short range things that they tried to shoot, but it's not anything that's going to do huge damage, and the Israeli systems can deal with those. The Houthis did fire something, and it hurt some Palestinians near Hebron. You know, the Houthis and the Iranians in particular, in this conflict have killed Palestinians, and in one case, Syrians. They're continuing to hurt people that are not Israelis. One of the things that I think people are hopeful for is that as Iran tries to sue for peace, and it already is, it's been reaching out to Cyprus to pass messages, etcetera. The hope is that Iran will recognize that it's in a position whereby A) there has to be zero enrichment and the facilities have to be destroyed, whatever's left of them. And B) there's a hope that Israel and the United States together will be able to use this diplomatic moment to truly end the conflict in Gaza and get the hostages home. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, that was what I was going to ask. I mean, if Israel achieves its objectives in this war, primarily eliminating Iran's nuclear threat, how significant a setback would that be for Hamas and Iran's other terror proxies, and could it indeed pave the way for an end of the war in Gaza and the return of the hostages? Matthew Levitt: Like everybody else, I'm so scarred, I don't want to get my hopes up, but I do see this as a distinct possibility, and here's why. Not Hezbollah, not the Houthis, not Hamas, none of them, and plenty of other proxies that don't start in the letter H, none of them could have been anywhere as capable as they've proven to be, were it not for Iranian money and weapons. Also some training, some intelligence, but primarily money and weapons. And so Hamas is already on its back foot in this regard. It can still get some money in. It's still being able to make money off of humanitarian aid. Iran is still sending money in through money exchange houses and hawaladars, but not weapons. Their ability to manufacture weapons, their military industrial complex within Gaza, this is destroyed. Hezbollah, we've discussed, discussed, and a lot of their capabilities have been destroyed. And those that remain are largely deterred. The Houthis did shoot up some rockets, and the Israelis did carry out one significant retaliatory attack. But I think people are beginning to see the writing on the wall. The Israelis are kicking the stuffing out of Iran with pinprick attacks that are targeting the worst of the bad guys, including people who have carried out some of the worst human rights transgressions against Iranians. Let's not pretend that this is not affecting the average Iranian. It is. The president says, Everybody get out of Tehran. That's just not possible. People, average Iranians, good people. It must be just an absolute terror. But Israel's not bombing, you know, apartment buildings, as Iran is doing in Israel, or as Russia is doing in Ukraine. And so it really is a different type of thing. And when the Houthis, when Hamas, when Hezbollah, look at this, you don't you don't poke the tiger when it's angry. I think they also understand now's the time to get into survival mode. What you want is for the regime in Iran not to be destroyed. This is no longer a moment, as it's been since long before October 7, but certainly since then, of how Iran as proxies, export Iran's revolution. This is now a question of how they maintain and preserve the revolution at home. And it's extremely important to the proxies that Iran remain, so that even if it's knocked down over time, hopefully, theoretically, from their perspective, it can regain its footing. It will still have, they hope, its oil and gas, etcetera, and they will get back to a point where they can continue to fund and arm the proxies in. Maybe even prioritize them as it takes them longer to rebuild their ballistic missile, drone, and nuclear programs. Manya Brachear Pashman: Which is a scary prospect as well to know that terror proxies could be spread throughout the world and empowered even a little bit more. President Trump left the G7 summit a day early to meet with security advisors, and just a few hours ago, prior to this interview, President Trump called for Iran's, quote, unconditional surrender, saying that the US knows where the Supreme Leader is, and some other threatening language. But I mean, this appears to be a kind of a clear commitment to Israel. So I'm curious how you assess his administration's actions before and during the war thus far, and do you see the United States edging toward direct involvement? Matthew Levitt: All politics is local, and there is a tug of war within the MAGA movement over whether or not the US should be getting involved. Not only in supporting an important ally, but in removing a critical threat. The President is clearly frustrated that Iran was not being more forthcoming in the negotiations. He said many times, we'd offered you a great deal, you should have taken the deal. He's very aware that his deadline ended, and they didn't particularly seem to care. There's also the background that once upon a time, they tried to assassinate him, I think, after the Israelis did what they did, the President appreciates capabilities. He appreciates success. He likes backing the winning horse. And so the New York Times is reporting that after getting off the phone with Prime Minister Netanyahu, President Trump reportedly turned to some aides and said, maybe we need to help him. Now it's not clear that's what's going to happen, and my understanding is that the Israelis have plans of their own for things like the heavily fortified facility at Fordow, which is the most important and highly fortified, protected of the nuclear installations. The Israeli National Security Advisor spoke today and said, you know, we're not going to be done until we do something with Fordow. The United States can do multiple things only the United States has the MOP: the Massive Ordinance Penetrator, and the airplanes to deliver it, and they could end Fordow if they wanted. Short of that, they could do other things to support Israel. There's been defensive support for the State of Israel already, but there's other things they could do, refueling and other things if they wanted to. And at a minimum, I don't see the president restraining Israel at all. Now, I've heard some people say that so far, the President has fired nothing more than some social media postings, some of them even in all caps. But the truth is, those do have an effect, and so long as Israel is not restrained. I think the Israelis went into this with a plan. That plan is not necessarily to entirely destroy the entire nuclear program, but if the ballistic missile program and the nuclear program are sufficiently degraded so that it will take them years and a tremendous amount of time and money to rebuild, knowing that Israel has broken the glass ceiling on this idea of targeting Iran, that if the Israelis feel they need to, they will come back. If the Iranians rebuild their air defense systems, the Israelis will address them and create a new highway going if they need to. I think the Israelis are making that clear. Knowing that it's going to be a little bit of a road for Iran, especially when it will have to deal with some domestic issues coming out of this. Finally, the Israelis have started signaling there's other things they could do. The Israelis have not yet fully targeted oil and gas fields and facilities. For example, they had one set of attacks where they basically knocked at the front door of some of these facilities without walking in the house. That's signaling, and I think it's one of the reasons you're seeing Iran quietly trying to reach out for some type of a ceasefire. Other signaling, for example, is the Israelis deciding to fly all the way to Mashhad, which is in far eastern Iran, to take out an airplane. That airplane was not particularly important. It was the message. There is nowhere in Iran we can't go. It's not a question of distance, it's not a question of refueling, it's not a question of air defense systems. We can do what we need to do. And I think the Iranians understand that now. Manya Brachear Pashman: So we talked about the commitment to Israel, and how clear, how important it is to clarify that commitment to Israel. How important is it to clarify the United States commitment to Arab partners in the Middle East to help defend them in other words, if this conflict escalates? Matthew Levitt: This is critically important. You know, one of the individuals who was taken out, for example, was the person who was in charge of the drone attack on the Abqaiq oil facility in Saudi Arabia. If you look, for example, at the Saudi statement condemning the Israeli actions, it was issued by the Foreign Ministry without a single name attached to it. Wasn't issued by the Crown Prince, wasn't issued by the foreign minister. So I think you should expect a whole lot of public criticism. I imagine there's a different conversation going on behind closed doors. It's not necessarily, you know, pom-poming. This makes the Gulf states very, very nervous, in part because they understand that one way Iran could try and get out of this is to expand the conflict. And that the reason they haven't is because, short of trying to prevent Iranians from taking to the streets and potentially doing something to maybe overthrow the regime, short of that, the number one thing that the Iranian regime is most desperate to avoid is getting the United States involved militarily. And I think the Iranians really understand and the messaging's been clear. If you target US Forces in the region, if you target our allies in the region, we'll get involved. If you don't, then we might not. Now the President now is talking about potentially doing that, and as a lot of maybe this, maybe that, nothing very clear. I think what is clear is that the Israelis are going to continue doing what they need to do for another one to two weeks. Even going so far as doing something, though they haven't made clear what to address the really complicated problem of the fortified facility at Fordow. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how important is it for global security if Israel is successful in eliminating the nuclear threat in Iran? Matthew Levitt: Look, Iran has been the single most destabilizing factor in the region for a long time now. Imagine a region without a destabilizing revolutionary regime in Iran without a regime that is supporting Shia militants in Saudi Arabia and other Gulf countries. Imagine the Shia militias in Iraq suddenly without a funder and a patron, enabling the Shia government in Iraq to actually be able to take control of the country and establish a monopoly over the use of force. At a time when the Shia militias, because of Iran's backing, are becoming more dangerous and more powerful in Iraq. Imagine the Lebanese government being able to be more forward leaning in their effort to establish a monopoly over the use of force in that country, reclaim bases that Hezbollah has used for all this time, and establish a new Lebanon that is not beholden to Iran and Hezbollah. And imagine an Israeli-Palestinian situation where you didn't have Hamas and Palestinian Islamic Jihad as spoilers. Recall that October 7 happened in large part because Hamas and Hezbollah and Iran could not tolerate the prospect of Israeli-Saudi normalization. For most Palestinians, this was great news. The Saudis were demanding real dividends for the Palestinians from the Netanyahu government, which was likely going to do them. This was great for Palestinians, bad for Hamas. Imagine Hamas no longer getting that support from Iran. Imagine Iran no longer able to send or being interested in sending millions upon millions of dollars to its proxies, and instead spending what money it has on helping its population, instead of cracking down on it with human rights violations. You could have a very, very different region, let alone imagine Iran no longer carrying out acts of terrorism, kidnapping plots, abduction plots of dissidents and Jews and Israelis and others around the world of the type that we've seen throughout Europe and throughout the Middle East and even in the United States over the past few years. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's quite an imagination you have. But I take your point. Let me ask you this then. Did you ever imagine that Israel would take this dramatic step? Matthew Levitt: What the Israelis have achieved, when you are so against the wall and you're forced to come up with solutions, because it's a matter of life or death – you make the impossible possible. And I think that perhaps the Iranians assumed that the Israeli post-October 7 doctrine applied to non-state actors only. And that doctrine is very simple. Israel will no longer allow adversaries who are openly committed to its destruction to build up weapons, arsenals that they can then use at some point to actually try and destroy Israel. They will not allow that to happen. They allowed it to happen with Hamas. It was a mistake. They allowed it to happen with Hezbollah. It was a mistake that they corrected. And Iran is the biggest, arguably, really, the only existential threat as huge, as a tasking as that was, clearly they invested in doing it. And the question became, not, why can't it be done? What is it that has to be overcome? And I don't think sitting here with you right now, you know, what is it, 3:30 on Tuesday, the 17th, that we've seen the last of the tricks up Israel's sleeve. Manya Brachear Pashman: I only have one last question for you, and that is about the United States. The importance of the United States getting directly involved. I mean, we've talked about previously undisclosed nuclear sites, and who knows how many there could be. We're talking about more than what, 600,000 square miles of Iran. If the goal is a non nuclear Iran, can Israel finish this war without the United States, or does it even matter? I mean, is this just a step to force Iran back to the negotiating table with virtually zero leverage? Matthew Levitt: So look, I don't think the goal here is completely destroying the Iranian nuclear program, or even completely destroying the Iranian ballistic missile program. The goal is to so degrade it that it is set back many, many years, and break that ceiling. People now understand if Israelis need to come back, they're coming back. I think they would like to do as much damage to these destructive programs as possible, of course, and I don't think we've seen the end of it. I think there are more tricks up Israel's sleeve when it comes to some of these complicated problems. Judged by this yardstick, by the way, the Israeli operation is a tremendous success, tremendous success, even though there have been some significant casualties back in Israel, and even though this has caused tremendous trauma for innocent Iranians who have no love for the regime. This is a situation that the Iranian regime has brought down on all of us. I do think that the Israelis have made very, very clear that this doesn't end until something is done to further disrupt and dismantle Fordow, which is the most important and the most heavily fortified, underground, under a mountain facility. It's not clear what the Israelis have in mind. It seems they have something in mind of their own. It's clear they would love for the United States to get involved, because the United States could do real damage to that facility and potentially end the Iranian nuclear program. But at the end of the day, if it can't be completely destroyed, I anticipate it's going to be damaged enough to significantly set it back. This phase of the Israel-Iran war, which didn't start last week, is not about pushing them back a week or a month or two months. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Matt, thank you so much for your wise counsel and perspective on this matter, and yes, hopefully we can have you back another time to talk about peace and love and things that have nothing to do with war and conflict with Iran or its terror proxies. Matthew Levitt: I would really look forward to prepping for that interview. In the meantime, I want to thank AJC for all the important work it does, and thank you guys for having me on the podcast. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episodes, be sure to tune in for our crossover episode with Books and Beyond: The Rabbi Sacks Podcast, a podcast of the Rabbi Sacks Legacy, and my conversation with AJC's Jerusalem Director Avital Liebovich. During a special breaking news episode the day after Israel launched Operation Rising Lion, the latest in Israel's ongoing war of self-defense against the Iranian regime.
Jun 13
Why Israel Had No Choice: Inside the Defensive Strike That Shook Iran's Nuclear Program
Why did Israel launch defensive strikes against Iran's nuclear sites — and what does this mean for regional security? AJC Jerusalem Director Lt. Col. (res.) Avital Leibovich joins from IDF reserve duty to explain Operation Rising Lion — Israel's precision military strikes aimed at dismantling Iran's nuclear and missile capabilities. Find out why Israel saw this defensive action as vital to protect millions of lives and prevent Iran's nuclear breakout. Resources: 5 Key Reasons Behind Israel's Defensive Strike on Iran's Imminent Nuclear Threat Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: What Rabbi Lord Jonathan Sacks' State of the Jewish World Teaches Us Today AJC's CEO Ted Deutch: Messages That Moved Me After the D.C. Tragedy Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman Late Thursday night, Israel launched a series of preemptive strikes against Iran in a military offensive dubbed Operation Rising Lion. The wave of strikes comes after the International Atomic Energy Agency censured Iran for obstructing its inspections after the revelation of a secretive nuclear site. What is happening on the ground, what's next, and what are the implications for Israel, Iran, and the broader Middle East? AJC Jerusalem director, Avital Leibovich, who also serves as Lieutenant Colonel in the IDF reserves, joins us now from reserve duty as counterattacks from Iran have begun. Avital, thank you for joining us with pleasure. Avital, negotiations for a new nuclear deal with Iran have been underway since April. There have been five rounds, maybe six, and another was going to begin on Sunday. President Trump also asked Israel to hold off on this preemptive operation. So why did Israel choose to launch these strikes? At this particular time, Avital Leibovich Israel took a decision already to prepare for a preemptive attack on Iran. Since November, what happened in November? In November, Hezbollah lost the majority of its capabilities, of its military capabilities, and also of its leadership. Actually, a lot of his leaders, military leaders, have been eliminated, starting with Nasrallah, Hassan, Nasrallah, and going on to all the major generals of the organization. And basically the Shiite axis, as we call it here in Israel, was broken. Add to this, what happened a month later in December, when Assad's regime crashed, collapsed and was replaced by an anti Iranian man, jihadist, which jihadist background, by the name of Ahmed al Shara. So Iran was actually by on its own, really, because instead of circling Israel from the north, both from Syria and from Lebanon. Now it was circling in a very one dimension way, only from the east. So in order to do that, Iran figured out it needed to really upscale its nuclear capabilities, and for that, they sped up a few processes, for example, uranium enrichment, but not only that, also the weaponization of a potential nuclear bomb. And all of these steps actually brought us to a point that we are today, the point of no return. Iran will not be able to return to 20 years ago, 30 years ago, when it did not have those capabilities as it has today. For us in Israel, this is an issue of existence, either we exist or we don't, and that is the sole reason why the preemptive strike actually began today. This is according to Israeli intelligence, we have all the indications and data showing us this really major leap. And look the IAEA, you know, they issue reports every couple of months. It's their kind of responsibility for us. It's a matter of life and death. We cannot, you know, comply only with reports. And the reports sit on some shelf somewhere and and there's a lot of dust which is piling up on these reports for us, we needed action. So based on this very accurate intelligence, and some of this intelligence that has been accumulated for many, many years, you can see in the attack in Iran, you can see the very accurate attacks, the pinpointed strikes, which actually are directed at specific terrorists and not causing damage to uninvolved civilians, just To the locals. Yeah, Manya Brachear Pashman And how do you evaluate the Trump administration's response so far, given the diplomatic efforts underway? Well, Avital Leibovich I think that he is using the attacks to leverage and put pressure on Iran to resume the negotiation table in a few days. And as you know, there were six rounds of talks, and the best of my knowledge, there were huge gaps between the two sides, the American side and the Iranian side. I'm not sure these gaps can be bridged. We heard over and over again, President Trump say that Iran will never be able to enrich uranium. And then we heard Iranian leaders like Hamina say, this is the basic right of the Iranian people to enrich uranium. So I'm not sure how you can get you can bridge such a deep gap overall, I think that the President. Uh, has been congratulating Israel on its excellent attacks until now. But again, we are in the beginning. We're in the beginning phase of the attacks, although they're spread all over Iran. This is still the first day. We need to keep this in mind. Manya Brachear Pashman The targets included more than nuclear sites. It included ballistic missile sites as well, and we're receiving word that Iran has fired ballistic missiles toward Israel as we speak, they fired ballistic missiles on Israel in April. If this counterattack continues, do you expect the United States to step in to defend Israel, and do you expect some of your neighbors to step in and help as well as they did in April the United Arab Emirates or Bahrain Avital Leibovich So as for the neighbors, I think that if their aerial space will be violated and breached by Iran, then of course, they have the right, like any other country, they're sovereign, to protect their own airspace. First of all, they will be protecting themselves and their people, not Israel, as for the US. This really depends on what Iran chooses to do next. The retaliation that Iran had practiced until now was launching 100 plus drones, explosive drones, to Israel. Almost all of these drones have been intercepted. This happened in the morning today. Now if Iran will decide that the ballistic missiles or the cruise missiles that it will launch here, will attack not only Israel, but also US bases across the region. Then here, there's a question, how will the US respond? Will the US retaliate as well? If that would happen, we could have even a more significant strike together the US and Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman These attacks killed two lead scientists, IRGC commanders, Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps leaders. Is there a long-term goal of prompting a regime change? Avital Leibovich So first of all, there are few types of targets in Iran, and you mentioned some of them. Physics and nuclear scientists are, of course, a critical human resource to the Iranian regime, as they rely on their long term knowledge and expertise on producing the bomb as soon as possible, as quick as possible, and by eliminating them in a way, you are removing the immediate threat. Other options are economic options. For example, really Iran relies on oil and buys it from China and maybe other countries as well. So obviously, Israel could decide to target its oil reserves, and this will be, of course, a significant economic blow. The third option is to target the government, leadership, politicians. Now, Israel, up to this moment, did not choose an economic target or a political target, but this may change in the future. The military targets, of course, are the most immediate targets that Israel is attacking, and the idea is to eliminate the immediate threat on Israel for the long range? Well, in the Middle East, in this part of the world, unfortunately, long range is something we can only put as a vision which is not bad. I'm happy to dream. I'm dreaming often Iran, which is similar to the Iran we knew before 1979 before the revolution, a moderate country, a human, loving country with values that I can share and adopt just the same. I'm looking at a different Middle East, maybe in a few years, with an expansion of the Abraham Accords, and creating an axis of moderate countries and other Shiite countries. So all of these changes that we're witnessing right now in the region and may still witness in the future, may all have an impact also on the long range outcome of the current war, which is unprecedented. Manya Brachear Pashman I know Israel calls this a preemptive attack, but what do you say to countries who have already expressed concern about what they call an unprovoked attack? Avital Leibovich Well, I think it's enough for them just to look at the many kind of materials, which Israel and the Israeli. Army released today, showing what they have done, what Iran has done on its own soil. Now, when you follow the targets we just spoke about, you can see that these are not civilian targets. In other words, Israel is not attacking a school or a building just in the middle of Tehran for nothing. It's attacking deliberate military related sites. Actually, I think that, if I'm daring to dream again, I think that the people of Israel and the people of Iran have a lot in common. They're both people with deep heritage, with beautiful cultures. So I do envision one day a different regime in Iran, such a regime that could really bring the two countries together, opening a new page. And I think it will do a better Middle East here for all of us. Manya Brachear Pashman We have talked about how Hamas embeds itself among the Palestinian civilians in Gaza. So no matter how precise Israel's attacks are, civilians are killed. Does Iran do the same thing? Or, I should say, does the Iranian regime do the same thing in Iran? Avital Leibovich Obviously, Iran is not a democracy, and there is a similarity here with Hamas. We are talking about almost a fanaticist religious kind of aspect, which is also very similar to Hamas. Actually, Hamas and Iran have been connected for decades, for many, many decades, so they do share a lot of similarities. But unfortunately, the freedom of movement, freedom of speech, freedom of of culture, is not something which is of an ordinary situation in Iran. It's very unfortunate. You know, I'm sometimes following the social media in Iran, and I see how people speak about the regime. I see how they curse the regime. I see how they aspire for better lives. I see them organize parties in basements and so so the regime will not find out. I see them the women wearing jeans underneath hijabs long dresses, trying to conceal them for God forbid, so they would not be considered as not modest. So it's very unfortunate that the public is suffering in Iran, and we see that, not only in the general atmosphere, but also we see it with the standards of life, they have only electricity a couple of days of couple of hours a day. Water is scarce. The the prices of food, they are huge. Take, for example, today, one American dollar, it equals almost 1 million rials. For comparison, $1 equals three point 60 Israeli shekels. So yeah, they're suffering from many, many perspectives. Manya Brachear Pashman Thank you so much for joining us stay safe. Avital Leibovich Thank you, Manya, and I'll just thank everybody for their support. I'm Israel. If Manya Brachear Pashman you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for a special crossover episode between people of the pod and Books and Beyond, the podcast of the Rabbi Sacks legacy, Dr Tanya white, host of Books and Beyond, and Joanna benaroche, global, Chief Executive of the legacy, sit down with my colleague, Maggie wishegrad Fredman to discuss how the wisdom and perspective of the late Rabbi Lord Jonathan Sacks still endures today.
Jun 12
What Rabbi Lord Jonathan Sacks' State of the Jewish World Teaches Us Today
In 2014, the late Rabbi Lord Jonathan Sacks stood on the AJC Global Forum stage and delivered a powerful call to action: "We have to celebrate our Judaism. We have to have less oy and more joy… We never defined ourselves as victims. We never lost our sense of humor. Our ancestors were sometimes hated by gentiles, but they defined themselves as the people loved by God." Over a decade later, at AJC Global Forum 2025, AJC's Director of Jewish Communal Partnerships, Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman, revisits that message in a special crossover episode between People of the Pod and Books and Beyond, the podcast of the Rabbi Sacks Legacy. She speaks with Dr. Tanya White, one of the inaugural Sacks Scholars and host of Books and Beyond, and Joanna Benarroch, Global Chief Executive of the Legacy, about Rabbi Sacks's enduring wisdom and what it means for the Jewish future. Resources: The State of the Jewish World Address: Rabbi Lord Jonathan Sacks The Inaugural Sacks Conversation with Tony Blair Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: "They Were Bridge Builders": Remembering Sarah Milgrim and Yaron Lischinsky AJC's CEO Ted Deutch: Messages That Moved Me After the D.C. Tragedy Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: On this week 16 years ago, the late Rabbi Lord Jonathan Sacks published Future Tense, a powerful vision of the future of Judaism, Jewish life, and the state of Israel in the 21st Century. Five years later, he delivered a progress report on that future to AJC Global Forum. On the sidelines of this year's Global Forum, my colleague Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman spoke with two guests from the Rabbi Sacks Legacy, which was established after his death in 2020 to preserve and teach his timeless and universal wisdom. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: In 2014, Rabbi Lord Jonathan Sacks addressed our Global Forum stage to offer the state of the Jewish world. Modeled after the US President's State of the Union speech given every year before Congress and the American people, this address was intended to offer an overview of what the Jewish people were experiencing, and to look towards our future. The full video is available on AJC's website as well as the Sacks Legacy website. For today's episode, we are holding a crossover between AJC's People of the Pod podcast and Books and Beyond, the Rabbi Sacks podcast. On Books and Beyond, each episode features experts reflecting on particular works from Rabbi Sacks. Channeling that model, we'll be reflecting on Rabbi Sacks' State of the Jewish World here at AJC's 2025 Global Forum in New York. AJC has long taken inspiration from Rabbi Lord Jonathan Sacks and today, AJC and the Rabbi Sacks legacy have developed a close partnership. To help us understand his insights, I am joined by two esteemed guests. Dr. Tanya White is one of the inaugural Sacks Scholars and the founder and host of the podcast Books and Beyond, the Rabbi Sacks podcast. Joanna Benarroch is the Global Chief Executive of the Rabbi Sacks legacy. And prior to that, worked closely with Rabbi Sacks for over two decades in the Office of the Chief Rabbi. Joanna, Tanya, thank you for being with us here at AJC's Global Forum. Tanya White: It's wonderful to be with you, Meggie. Joanna Benarroch: Thank you so much, Meggie. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: I want to get to the State of the Jewish World. I vividly remember that address. I was with thousands of people in the room, Jews from different walks of life, Jews from around the globe, as well as a number of non-Jewish leaders and dignitaries. And what was so special is that each of them held onto every single word. He identifies these three areas of concern: a resurgence of antisemitism in Europe, delegitimization of Israel on the global stage, and the Iranian regime's use of terror and terror proxies towards Israel. This was 2014, so with exception of, I would say today, needing to broaden, unfortunately, antisemitism far beyond Europe, to the skyrocketing rates we're living through today, it's really remarkable the foresight and the relevance that these areas he identified hold. What do you think allowed Rabbi Sacks to see and understand these challenges so early, before many in the mainstream did? And how is his framing of antisemitism and its associated threats different from others? And I'll let Tanya jump in and start. Tanya White: So firstly, I think there was something very unique about Rabbi Sacks. You know, very often, since he passed, we keep asking the question, how was it that he managed to reach such a broad and diverse audience, from non Jews and even in the Jewish world, you will find Rabbi Sacks his books in a Chabad yeshiva, even a Haredi yeshiva, perhaps, and you will find them in a very left, liberal Jewish institution. There's something about his works, his writing, that somehow fills a space that many Jews of many denominations and many people, not just Jews, are searching for. And I think this unique synthesis of his knowledge, he was clearly a religious leader, but he wasn't just uniquely a religious leader. He was a scholar of history, of philosophy, of political thought, and the ability to, I think, be able to not just read and have the knowledge, but to integrate the knowledge with what's going on at this moment is something that takes extreme prowess and a very deep sense of moral clarity that Rabbi Sacks had. And I would say more than moral clarity, is a moral imagination. I think it was actually Tony Blair. He spoke about the fact that Rabbi Sacks had this ability, this kind of, I think he even used the term moral imagination, that he was able to see something that other people just couldn't see. Professor Berman from University of Bar Ilan, Joshua Berman, a brilliant Bible scholar. So he was very close to Rabbi Sacks, and he wrote an article in Israeli, actually, an Israeli newspaper, and he was very bold in calling Rabbi Sacks a modern day prophet. What is a prophet? A prophet is someone who is able to see a big picture and is able to warn us when we're veering in the wrong direction. And that's what you see in the AJC address, and it's quite incredible, because it was 11 years ago, 2014. And he could have stood up today and said exactly the same thing. Rabbi Jonathan Sacks: But there is nonetheless a new antisemitism. Unlike the old it isn't hatred of Jews for being a religion. It isn't hatred of Jews as a race. It is hatred of Jews as a sovereign nation in their own land, but it has taken and recycled all the old myths. From the blood libel to the Protocols of the Elders of Zion. Though I have to confess, as I said to the young leaders this morning, I have a very soft spot for antisemites, because they say the nicest things about Jews. I just love the Protocols of the Elders of Zion. Because, according to this, Jews control the banks, Jews control the media, Jews control the world. Little though they know, we can't even control a shul board meeting. Tanya White: So what's fascinating is, if you look at his book Future Tense, which was penned in 2009.The book itself is actually a book about antisemitism, and you'll note its title is very optimistic, Future Tense, because Rabbi Sacks truly, deeply believed, even though he understood exactly what antisemitism was, he believed that antisemitism shouldn't define us. Because if antisemitism defines who we are, we'll become the victims of external circumstances, rather than the agents of change in the future. But he was very precise in his description of antisemitism, and the way in which he describes it has actually become a prism through which many people use today. Some people don't even quote him. We were discussing it yesterday, Joanna, he called it a mutating virus, and he speaks about the idea that antisemitism is not new, and in every generation, it comes in different forms. But what it does is like a virus. It attacks the immune system by mutating according to how the system is at the time. So for example, today, people say, I'm not antisemitic, I'm just anti-Zionist. But what Rabbi Sacks said is that throughout history, when people sought to justify their antisemitism, they did it by recourse to the highest source of authority within that culture. So for example, in the Middle Ages, the highest recourse of authority was religion. So obviously we know the Christian pogroms and things that happen were this recourse the fact, well, the Jews are not Christians, and therefore we're justified in killing them. In the Enlightenment period, it was science. So we have the and the Scientific Study of Race, right and Social Darwinism, which was used to predicate the Nazi ideology. Today, the highest value is, as we all know, human rights. And so the virus of antisemitism has mutated itself in order to look like a justification of human rights. If we don't challenge that, we are going to end up on the wrong side of history. And unfortunately, his prediction we are seeing come very much to light today. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: I want to turn to a different topic, and this actually transitioned well, because Tanya, you raised Prime Minister Tony Blair. Joanna, for our listeners who may have less familiarity with Rabbi Sacks, I would love for you to fill in a larger picture of Rabbi Sacks as one of the strongest global Jewish advocates of our time. He was a chief rabbi, his torah knowledge, his philosophical works make him truly a religious and intellectual leader of our generation. At the same time, he was also counsel to the royal family, to secular thought leaders, world leaders, and in his remarks here at Global Forum, he actually raised addressing leading governing bodies at the European Union at that time, including Chancellor Merkel. These are not the halls that rabbis usually find themselves in. So I would love for you to explain to our audience, help us understand this part of Rabbi Sacks' life and what made him so effective in it. Joanna Benarroch: Thanks, Meggie. Over the last couple of weeks, I spent quite a bit of time with people who have been interested in learning more about Rabbi Sacks and looking at his archive, which we've just housed at the National Library in Israel. Then I spent quite a significant amount of time with one of our Sacks Scholars who's doing a project on exactly this. How did he live that Judaism, engaged with the world that he wrote so eloquently about when he stepped down as chief rabbi. And a couple of days ago, I got an email, actually sent to the Sacks Scholar that I spent time with, from the gifted archivist who's working on cataloging Rabbi Sacks' archive. She brought our attention to a video that's on our website. Rabbi Sacks was asked by a young woman who was a student at Harvard doing a business leadership course, and she asked Rabbi Sacks for his help with her assignment. So he answered several questions, but the question that I wanted to bring to your attention was: what difference have you sought to make in the world? The difference that he sought to make in the world, and this is what he said, "is to make Judaism speak to people who are in the world, because it's quite easy being religious in a house of worship, in a synagogue or church, or even actually at home or in the school. But when you're out there in the marketplace, how do you retain those strong values? And secondly, the challenge came from University. I was studying philosophy at a time when there were virtually no philosophers who were religious believers, or at least, none who were prepared to publicly confess to that. So the intellectual challenges were real. So how do you make Judaism speak to people in those worlds, the world of academic life, the world of economy? And in the end, I realized that to do that credibly, I actually had to go into the world myself, whether it was broadcasting for the BBC or writing for The Times, and getting a little street cred in the world itself, which actually then broadened the mission. And I found myself being asked by politicians and people like that to advise them on their issues, which forced me to widen my boundaries." So from the very beginning, I was reminded that John–he wrote a piece. I don't know if you recall, but I think it was in 2005, maybe a little bit earlier. He wrote a piece for The Times about the two teenagers killed a young boy, Jamie Bulger, and he wrote a piece in The Times. And on the back of that, John Major, the prime minister at the time, called him in and asked him for his advice. Following that, he realized that he had something to offer, and what he would do is he would host dinners at home where he would bring key members of either the parliament or others in high positions to meet with members of the Jewish community. He would have one on one meetings with the Prime Minister of the time and others who would actually come and seek his advice and guidance. As Tanya reflected, he was extremely well read, but these were books that he read to help him gain a better understanding into the world that we're living in. He took his time around general elections to ring and make contact with those members of parliament that had got in to office, from across the spectrum. So he wasn't party political. He spoke to everybody, and he built up. He worked really hard on those relationships. People would call him and say so and so had a baby or a life cycle event, and he would make a point of calling and making contact with them. And you and I have discussed the personal effect that he has on people, making those building those relationships. So he didn't just do that within the Jewish community, but he really built up those relationships and broaden the horizons, making him a sought after advisor to many. And we came across letters from the current king, from Prince Charles at the time, asking his guidance on a speech, or asking Gordon Brown, inviting him to give him serious advice on how to craft a good speech, how long he should speak for? And Gordon Brown actually gave the inaugural annual lecture, Memorial Lecture for Rabbi Sacks last in 2023 and he said, I hope my mentor will be proud of me. And that gave us, I mean, it's emotional talking about it, but he really, really worked on himself. He realized he had something to offer, but also worked on himself in making his ideas accessible to a broad audience. So many people could write and can speak. He had the ability to do both, but he worked on himself from quite a young age on making his speeches accessible. In the early days, they were academic and not accessible. Why have a good message if you can't share it with a broad audience? Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: What I also am thinking about, we're speaking, of course, here at an advocacy conference. And on the one hand, part of what you're describing are the foundations of being an excellent Jewish educator, having things be deeply accessible. But the other part that feels very relevant is being an excellent global Jewish advocate is engaging with people on all sides and understanding that we need to engage with whomever is currently in power or may who may be in power in four years. And it again, speaks to his foresight. Joanna Benarroch: You know, to your point about being prophetic, he was always looking 10, 15, 20 years ahead. He was never looking at tomorrow or next week. He was always, what are we doing now that can affect our future? How do I need to work to protect our Jewish community? He was focused whilst he was chief rabbi, obviously on the UK, but he was thinking about the global issues that were going to impact the Jewish community worldwide. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Yes. I want to turn to the antidote that Rabbi Sacks proposed when he spoke here at Global Forum. Rabbi Jonathan Sacks: I will tell you the single most important thing we have to do, more important than all the others. We have to celebrate our Judaism. We have to have less oy and more joy. Do you know why Judaism survived? I'll tell you. Because we never defined ourselves as victims. Because we never lost our sense of humor. Because never in all the centuries did we internalize the disdain of the world. Yes, our ancestors were sometimes hated by gentiles, but they defined themselves as the people loved by God. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: So he highlights the need to proudly embrace the particularism of Judaism, which really in today's world, feels somewhat at odds with the very heavy reliance we have on universalism in Western society. And underpinning this, Rabbi Sacks calls on us to embrace the joy of Judaism, simchatah, Chaim, or, as he so fittingly puts it, less oy and more joy. How did both of these shape Rabbi Sacks's wider philosophy and advocacy, and what do they mean for us today? Tanya White: Rabbi Sacks speaks about the idea of human beings having a first and second language. On a metaphorical level, a second language is our particularities. It's the people, it's the family we're born. We're born into. It's where we learn who we are. It's what we would call today in sociology, our thick identity. Okay, it's who, who I am, what I believe in, where I'm going to what my story is. But all of us as human beings also have a first language. And that first language can be, it can manifest itself in many different ways. First language can be a specific society, a specific nation, and it can also be a global my global humanity, my first language, though, has to, I have to be able to speak my first language, but to speak my first language, meaning my universal identity, what we will call today, thin identity. It won't work if I don't have a solid foundation in my thick identity, in my second language. I have nothing to offer my first language if I don't have a thick, particular identity. And Rabbi Sacks says even more than that. As Jews, we are here to teach the world the dignity of difference. And this was one of Rabbi Sacks' greatest messages. He has a book called The Dignity of Difference, which he wrote on the heels of 9/11. And he said that Judaism comes and you have the whole story of Babel in the Bible, where the people try to create a society that is homogenous, right? The narrative begins, they were of one people and one language, you know, and what, and a oneness of things. Everyone was the same. And Rabbi Sacks says that God imposes diversity on them. And then sees, can they still be unified, even in their diversity? And they can't. So Rabbi Sacks answers that the kind of antidote to that is Abraham. Who is Abraham? Abraham the Ivri. Ivri is m'ever, the other. Abraham cut this legacy. The story of Abraham is to teach the world the dignity of difference. And one of the reasons we see antisemitism when it rears its head is when there is no tolerance for the other in society. There is no tolerance for the particular story. For my second language. For the way in which I am different to other people. There's no real space for diversity, even when we may use hashtags, okay, or even when we may, you know, proclaim that we are a very diverse society. When there is no space for the Jew, that's not true dignifying of difference. And so I think for Rabbi Sacks, he told someone once that one of his greatest, he believed, that one of his greatest novelties he brought into the world was the idea of Torah and chochma, which is torah and wisdom, universal wisdom. And Rabbi Sacks says that we need both. We need to have the particularity of our identity, of our language, of our literacy, of where we came from, of our belief system. But at the same time, we also need to have universal wisdom, and we have to constantly be oscillating and be kind of trying to navigate the space between these two things. And that's exactly what Rabbi Sacks did. And so I would say, I'll actually just finish with a beautiful story that he used to always tell. He would tell the story, and he heard this story from the late Lubavitcher, Menachem Schneerson, Rabbi Menachem Schneerson, who was a very big influence on Rabbi Sacks and the leader of the Chabad movement. So in the story, there's two people that are schlepping rocks up a mountain, two workers, and one of them just sees his bags that are full of rocks and just sees no meaning or purpose in his work. The other understands that he's carrying diamonds in his bag. And one day they get a different bag, and in that bag there's rubies, and the person who carries the rocks sees the rubies as rocks, again, sees that as a burden. But the person who's carrying the rubies and understands their value, even though they may not be diamonds, understands the values of the stones, will see them in a different way. The Lubavitcher Rebbe said, if we see our identity, our Judaism, as stones to carry as a burden that we have to just schlep up a mountain, then we won't see anyone else's particular religion or particular belief system or particularity as anything to be dignified or to be valued. But if we see our religion as diamonds, we'll understand that other people's religions, though for me, they may be rubies, they're still of value. You have to understand that your religion is diamonds, and you have to know what your religion is, understand what it is. You have to embrace your particularity. You have to engage with it, value it, and then go out into the world and advocate for it. And that, to me, was exactly what Rabbi Sacks did. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: So much of what you're outlining is the underpinning of being a successful engager in interfaith and inter religious work. And Rabbi Sacks, of course, was such a leader there. At AJC, we have taken inspiration from Rabbi Sacks and have long engaged in interfaith and inter-religious work, that's exactly a linchpin of it, of preaching one's own faith in order to engage with others. Tanya White: That's the oy and the joy. For Rabbi Sacks, it's exactly that, if I see it as the oy, which is schlepping it up the mountain, well, I'm not going to be a very good advocate, but if I see it as the joy, then my advocacy, it's like it shines through. Joanna Benarroch: It's very interesting, because he was interviewed by Christian Amanpour on CNN in 2014 just after he stepped down, as she she quoted the phrase "less oy and more joy" back to him, referring to his description of the Jewish community. When he came into office in 1991 he was worried about rising assimilation and out-marriage. And she said: How did you turn it around? He said, "We've done the book of Lamentations for many centuries. There's been a lot of antisemitism and a lot of negativity to Jewish identity. And if you think of yourself, exactly as you're describing, as the people who get hated by others, or you've got something too heavy to carry, you're not going to want to hand that on to your children. If you've got a very open society, the question is, why should I be anything in particular? Being Jewish is a very particular kind of Jewish identity, but I do feel that our great religious traditions in Judaism is the classic instance of this. We have enormous gifts to offer in the 21st century, a very strong sense of community, very supportive families, a dedicated approach to education. And we do well with our children. We're a community that believes in giving. We are great givers, charitably and in other ways. So I think when you stay firm in an identity, it helps you locate yourself in a world that sometimes otherwise can be seen to be changing very fast and make people very anxious. I think when you're rooted in a people that comes through everything that fate and history can throw at it, and has kept surviving and kept being strong and kept going, there's a huge thing for young people to carry with them." And then he adds, to finish this interview, he said, "I think that by being what we uniquely are, we contribute to humanity what only we can give." What Rabbi Sacks had was a deep sense of hope. He wore a yellow tie to give people hope and to make them smile. That's why he wore a yellow tie on major occasions. You know, sunshine, bringing hope and a smile to people's faces. And he had hope in humanity and in the Jewish people. And he was always looking to find good in people and things. And when we talk about less oy and more joy. He took pleasure in the simple things in life. Bringing music into the community as a way to uplift and bring the community together. We just spent a lovely Shabbat together with AJC, at the AJC Shabbaton with the students. And he would have loved nothing more than being in shul, in synagogue with the community and joining in. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Thank you Joanna, and that's beautiful. I want to end our conversation by channeling how Rabbi Sacks concluded his 2014 address. He speaks about the need for Jewish unity at that time. Let's take a listen. Rabbi Jonathan Sacks: We must learn to overcome our differences and our divisions as Jews and work together as a global people. Friends, consider this extraordinary historical fact: Jews in history have been attacked by some of the greatest empires the world has ever known, empires that bestrode the narrow world like a colossus. That seemed invulnerable in their time. Egypt of the pharaohs, Assyria, Babylonia, the Alexandrian Empire, the Roman Empire, the medieval empires of Christianity and Islam, all the way up to the Third Reich and the Soviet Union. Each one of those, seemingly invulnerable, has been consigned to history, while our tiny people can still stand and sing Am Yisrael Chai. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: In Rabbi Sacks' A Letter in the Scroll, he talks about the seminal moment in his life when he most deeply understood Jewish peoplehood and unity. And that was 1967, the Six Day War, when the Jewish people, of course, witnessed the State of Israel on the brink of existential threat. To our AJC audience, this may ring particularly familiar because it was evoked in a piece by Mijal Bitton, herself a Sacks Scholar, a guest on our podcast, a guest Tanya on your podcast, who wrote a piece about a month after 10/7 titled "That Pain You're Feeling is Peoplehood'. And that piece went viral in the Jewish world. And she draws this parallel between the moment that Rabbi Sacks highlights in 1967 and 10, seven, I should note, Tanya, of course, is referenced in that article that Mijal wrote. For our audiences, help us understand the centrality of peoplehood and unity to Rabbi Sacks' vision of Judaism. And as we now approach a year and a half past 10/7 and have seen the resurgence of certain communal fractures, what moral clarity can we take from Rabbi Sacks in this moment? Tanya White: Okay, so it's interesting you talked about Mijal, because I remember straight after 7/10 we were in constant conversation–how it was impacting us, each of us in our own arenas, in different ways. And one of the things I said to her, which I found really comforting, was her constant ability to be in touch. And I think like this, you know, I like to call it after the name of a book that I read to my kid, The Invisible String. This idea that there are these invisible strings. In the book, the mother tells the child that all the people we love have invisible strings that connect us. And when we pull on the string, they feel it the other side. 1967 was the moment Rabbi Sacks felt that invisible pull on the string. They have a very similar trajectory. The seventh of October was the moment in which many, many Jews, who were perhaps disengaged, maybe a little bit ambivalent about their Jewish identity, they felt the tug of that invisible string. And then the question is, what do we do in order to maintain that connection? And I think for Rabbi Sacks, that was really the question. He speaks about 1967 being the moment in which he says, I realized at that moment every, you know, in Cambridge, and everything was about choice. And, you know, 1960s philosophy and enlightenment philosophy says, at that moment, I realized I hadn't chosen Judaism. Judaism had chosen me. And from that moment forth, Rabbi Sacks feels as if he had been chosen. Judaism had chosen him for a reason. He was a Jew for a reason. And I think today, many, many Jews are coming back to that question. What does it mean that I felt that pull of the string on the seventh of October? Rabbi Sacks' answer to that question of, where do we go from here? I think very simply, would be to go back to the analogy. You need to work out why Judaism is a diamond. And once you understand why Judaism is a diamond and isn't a burden to carry on my back, everything else will fall into place. Because you will want to advocate for that particularity and what that particularity brings to the world. In his book, Future Tense, which, again, was a book about antisemitism, there was a picture of a lighthouse at the front of the book. That's how Rabbi Sacks saw the antidote for antisemitism, right? Is that we need to be the lighthouse. Because that's our role, globally, to be able to be the light that directs the rest of the world when they don't know where they're going. And we are living in a time of dizziness at the moment, on every level, morally, sociologically, psychologically, people are dizzy. And Judaism has, and I believe this is exactly what Rabbi Sacks advocated for, Judaism has a way to take us out of that maze that we found ourselves in. And so I think today, more than ever, in response to you, yes, it is peoplehood that we feel. And then the question is, how do we take that feeling of peoplehood and use it towards really building what we need to do in this world. The advocacy that Judaism needs to bring into the world. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: We all have a role, a reason, a purpose. When Rabbi Sacks spoke to us a decade ago, more than a decade ago, at this point, those who were in the room felt the moral imperative to stand up to advocate and why, as Jews, we had that unique role. I am so honored that today, now with Rabbi Sacks not here, you continue to give us that inspiration of why we are a letter in the scroll, why we must stand up and advocate. So thank you, Tanya and Joanna, for joining us at Global Forum and for this enlightening conversation. Tanya White: Thank you so much for having us. Thank you. Joanna Benarroch: Thank you so much. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, please be sure to listen as two AJC colleagues pay tribute to their friends Sarah Milgrim and Yaron Lischinsky who were brutally murdered outside the Capital Jewish Museum in May.
Jun 6
"They Were Bridge Builders": Remembering Sarah Milgrim and Yaron Lischinsky
We remember Sarah Milgrim and Yaron Lischinsky through the voices of those who knew them. Hear about Sarah's peacebuilding in Morocco and Yaron's diplomatic efforts to forge stronger ties between Israel and its neighbors. Both were members of the Israeli diplomatic corps and AJC's extended family. They were tragically murdered after leaving an AJC event in Washington, D.C. Dr. Dana Walker, the director of AJC ACCESS, the young professional program that hosted the reception, shares memories of traveling with Sarah to Morocco last fall as part of the Michael Sachs Fellowship for Emerging Leaders, organized by AJC and the Mimouna Association. Then, Benjamin Rogers, AJC's Director for Middle East and North Africa Initiatives, reflects on his conversations with Yaron, who held a parallel diplomatic portfolio at the Israeli Embassy. Benjy and Yaron spoke quite often about their diplomatic work and the importance of Israel's relationship with its neighbors. Benjy recalls their last exchange, just moments before Yaron was gunned down. Resources: What To Know About The Murder of Sarah Milgrim z"l and Yaron Lischinsky z"l in Washington, D.C. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episode: AJC's CEO Ted Deutch: Messages That Moved Me After the D.C. Tragedy Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: American Jewish Committee and Jews around the world have been left completely shaken by the devastating events in Washington, D.C., where two members of the Israeli diplomatic community and AJC's community—Sarah Milgrim and Yaron Lishinsky were brutally murdered after leaving an AJC reception. Last week, AJC CEO Ted Deutch returned from Sarah's funeral in Kansas City to share what he's learned about Sarah and Yaron. He also shared how graciously people have reached out to express their support, including families of Israeli hostages. This week, to remember Sarah and Yaron, we invited two AJC colleagues who knew them personally to help us remember. Dana Levinson Walker is the director of AJC ACCESS, the program for young Jewish professionals. In that role, she traveled to Morocco with Sarah and two dozen other young bridge builders as part of the Michael Sachs Fellowship for Emerging Leaders organized by AJC and the Mimouna Association. Dana is with us now to share her memories. Dana, thank you for being here. Can you please tell us about that trip last fall? Dana Walker: I had the privilege of traveling with Sarah and 25 other young professionals and staff from the US, Israel, Morocco and France. And it was an extraordinary seven days. We traveled to six different cities in seven days. Normally, we backend an Israel trip as a part of this delegation. But due to some geopolitical issues happening in the region, we made a decision to just go to Morocco at that time, and then we were going to go to Israel later. And we are indeed scheduled to go to Israel in September of 2025. It was an extraordinary experience for all different kinds of reasons. I think that the environment that we were walking into in Morocco was not only an embracing one, but it was also a challenging one. The day that we arrived in Morocco was the day we found out that the six hostages had been murdered in Gaza, and it was an incredibly painful moment for the Jewish participants, many of whom had a connection to the hostages or their families. And especially for someone like Sarah, who worked at the embassy, it felt really personal, because she had been advocating, of course, for their release, but also had just been a voice for many of them. And it was deeply devastating. But the trip could have taken a really depressing and sad turn, and in reality, it actually took an incredible turn where I've often told people that it wasn't necessarily the trip we planned for, but it was the trip we needed. In that it really fostered and created a family that is bound together now for life. They wept together, they laughed together. And I think what was so powerful is that it was Sarah's first time in Morocco, and she really just had this look of awe most of the time we were there. It was a look of deep reflection, a look of kind of taking it all in. We have really amazing photos of her, where she's just kind of looking very ethereal and like looking up in awe walking around the kind of old city of Marrakesh and things like that. And she was an incredible addition to our trip. She was a calming figure, a grounding figure. She spent a lot of late nights with the folks, just talking on the bus, talking by the pool. I know that on the last night of our trip in Marrakech, she and a couple of other participants, Israelis and Moroccans and Americans, were up until 5:30 in the morning just talking about life and their ambitions and their goals and just understanding one another by the pool for hours and hours and hours. And Sarah was one of the people in that conversation. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you share what perspectives she added to the conversations? What did she contribute? And also, if you know anything about those ambitions and life goals that she shared with others. Dana Walker: Sarah was really passionate about the environment. She was really passionate about sustainability. She loved her dog. She was really passionate about animals, and specifically dogs. I remember one of the things that we were talking about when she was preparing to go on the trip, and we had to kind of navigate when we were going and if we were still going, because of the geopolitics of the region, and she was really concerned about boarding her dog. It's just so clear that she cares so much about everyone in her life, and especially in this case, her dog, who was a really focal part of her heart. You know, she studied agriculture and sustainability, primarily sustainability. She was really interested in leaving the world a better place than she found it. And when we were going through the acceptance process for the Sachs Fellowship, we had a ton of applicants. And I think really what drew us to Sarah's application was that she was someone who was literally about to start her job at the embassy. We decided to put her in the agriculture and sustainability track because that's what she cared about. She was really passionate about finding sustainable solutions, especially in the region, because the region is growing hotter with each kind of succeeding year. Food and water security is becoming a challenge. Although, you know, after she started her role at the embassy, she really was doing a little bit of everything, but one of the key features that she worked on was working with survivors who had experienced gender and sexual based violence after October 7, and we couldn't really fathom anyone being more suited to do that work because of her gentle and calm and compassionate, assuring disposition. So she was ambitious in that she had a lot of big dreams for the future, about what she wanted to do, and she was really figuring out what was going to come next for her. The diplomat's life is never easy, especially in these incredibly uncertain and overwhelming times after October 7, and she and Yaron were planning a future, and they were really figuring out what was coming next for them. Manya Brachear Pashman: Was that trip to Morocco the only time you spent with Sarah? Dana Walker: I met her in person for the first time at last year's AJC Young Diplomats reception, where we focused on talking about regional integration, which was something she was really passionate about. She was with her other embassy friends and colleagues, and it was great to meet her, because I knew I was going to be traveling with her in the fall. So it was great to meet her in person. And then I saw her a few more times in DC over the course of our year, getting to know her. And then the last time I saw her was at the AJC Global Forum in April of just this year. Manya Brachear Pashman: The Sachs Fellowship is named in memory of Michael Sachs. He was someone who dedicated his life to promoting Arab-Israeli engagement. We've heard a lot of people talk about Sarah's commitment to that as well. How could you tell? Is there a moment in your mind that stands out? Illustrates her belief that interfaith, intercultural engagement could and should happen? Dana Walker: I believe in Essaouira–I believe that's where we were–and they had given us the option that we could either go around the souq and do a little bit of shopping, or we could go to a mosque and participate in an opportunity with this incredible singer and spiritual leader. And there were a few of us who said, Okay, we're gonna go. And Sarah was one of them, and she came with me and with the others. And it was so extraordinary, not only the experience of being in the mosque and hearing this unbelievable. Whole singing and just being kind of enveloped in this like spiritual warmth, which was just so wonderful. But she could have gone shopping, and she chose to go to the mosque, and she chose to put herself out there and experience something that she would likely not get to experience again, in this kind of environment. She really took advantage of it. She was really eager to learn. In order to be a peace builder, in order to be someone who can really transform hearts and minds, you have to understand the people that you're working with, and she really took advantage of that in the best way possible. I have some really great photos and videos of us in the mosque. And of course, they have this amazing tea ceremony. So the spiritual leader of the mosque had this really, really, really cute child who must have been maybe four or something. And, you know, hospitality is one of the pillars of Moroccan society, and everybody always does kind of the double cheek kiss. And the spiritual leader wanted to make sure that his child went around and gave everybody these little kisses. And I remember Sarah, and I were like, Oh my God, this kid is so cute and so well behaved. Like, I can't believe it. So he came over and gave us these little you know, these little bissou or, you know, whatever, the cheek kisses. And we were just melting. He was so adorable. Manya Brachear Pashman: It sounds like you were met with so much warmth and kindness in Morocco. As you said, it was what it was the trip you needed. And it sounds like she didn't hesitate to immerse herself, to really engage with that, that kind of cross-cultural experience. Do you know of any examples of when she engaged with a not-so friendly crowd? Dana Walker: One of the things that Sarah talked a lot about on the trip, and I know that my ACCESS leader and friend Laura mentioned this at the vigil yesterday is that, after Sarah started working for the embassy, a lot of her friends from graduate school and other places were really unkind to her and were really, really awful to her about her decision to work for the Israeli embassy. And in many cases, they stopped talking to her, they blocked her, they cropped her out of photos, they excluded her, and that was the kind of hostility she was facing. So I think what's really telling is that the people who love her and embrace her so much include Moroccan Muslims who saw her for the kind of person that she was. Which was this extraordinarily warm and caring and kind and compassionate person, but also someone who had a vision for securing a better future for everyone in the region, regardless of whether they were Jewish or Muslim, regardless of whether they were Israeli or Palestinian or Moroccan. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did she ever talk about how she handled those broken friendships? Dana Walker: I think they were just really painful for her. I think they were really hard. I think she found a lot of comfort in hearing from the other Americans on the trip who had also lost friendships and relationships and relationships after October 7. It was a very common refrain from a lot of the participants that some of their coworkers or long friendships, relationships, even with family, had been fractured or damaged or kind of beyond a place of repair. And I think in many ways, not misery loves company, but you know, she was surrounded by others who understood her experience and vice versa. That they all could appreciate, because they had all been through it in some way or another. So her experience was a familiar one, unfortunately, and a familiar one for many American Jews. So I think she took comfort in knowing that other people on the trip were experiencing similar things. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Dana, how are you finding any glimmers of hope going forward, after that evening? Dana Walker: You know, I . . . in my almost seven years of working at AJC, which is a long time, I think at this point, have discovered that the key to keep doing what we do is looking at our work through a glass, half full lens, because If we don't, it's just exhausting and debilitating. And I what gives me hope is knowing that even in her last sort of moments, that she was fulfilling her desire to be a glass half full person. She had vision for how to support a sustainable region, how to deeply invest in her relationships with her colleagues and friends across many nations and many backgrounds. And I urge others to try and embody that sense of optimism and glass half full approach, because the person who perpetrated this brutal act sought to destroy the work, and the only way forward is to amplify it and double down on it. So that's the hope that I get out of this experience. Is just knowing that we owe it to Sarah and to Yaron to keep amplifying their vision for what was possible. Manya Brachear Pashman: Sadly, Sarah is not the first Sachs Fellow that the current cohort lost this past year. At AJC Global Forum in New York in April, AJC honored Laziza Dalil, a co-founder of Mimouna Association. She was a Moroccan Muslim who dedicated her life to repairing Arab Israeli relations. She posthumously received the Ofir Libshtein Bridge Builder Award at Global Forum. Dana, how are you and the Sachs Fellows doing through what I can only imagine has been a difficult time? Dana Walker: It just all seems so unfair. Deeply unfair and deeply painful. That two of the best and brightest were taken from us. Were stolen from us, really. And it's something that we are grappling with. We're still processing. We're still dealing with it. I think what has been tremendously helpful is that we are grieving as a family. We are grieving as a group of not Moroccans or Israelis or Americans or French people, but as a collection of people who by fate and circumstance, are now bound to each other forever by both the trauma and the joys of what we've experienced as a community in service of trying to make the world a better place. And it's hard. But we are going to keep going because of it. Manya Brachear Pashman: If only that shared sense of grief was as powerful in the region. Dana, thank you so much. Dana Walker: Thank you, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: As AJC's Director for Middle East and North Africa Initiatives, Benjamin Rogers handles the Middle East portfolio for American Jewish Committee. The same portfolio that Yaron Lischinsky handled for the Israeli Embassy. Benjy and Yaron spoke quite often about the importance of Israel's relationship with its neighbors. Benjy is with us now to recall his last conversation with Yaron, moments before his death. Thank you for joining us, Benjy. You were at the event in Washington that night. Where were you when the shots were fired just after 9 p.m.? Benjamin Rogers: I left the museum around 8:55pm and I was in a taxi heading home, when I got a text message letting me know that there's been shots fired. Talked to a lot of people from the Israeli embassy, from AJC, trying to get a sense of what was happening. I remember calling Yaron, asking if he was okay, texting him if he was okay. And then everything kind of unfolded once I got home. A lot of confusion initially, and then kind of everyone's worst fears were soon realized. Manya Brachear Pashman: You knew Yaron through the particular work that you both did, correct? Benjamin Rogers: I have the privilege of working on the Middle East file for AJC and Yaron also had the privilege of working on the Middle East file for the Embassy of Israel. And the Embassy of Israel is quite large, but believe it or not, there's only two people that really focus on the Middle East–Yaron and then his supervisor, Noa Ginosar. So Yaron was someone who I used to see frequently in Washington. He would always be at various events. It was always fun to have Yaron, an Israeli representative at different programming with Arab diplomats, Arab representatives. Something that was clearly important to us at AJC, but also deeply personal to Yaron. Israel at the time of the Abraham Accords, Israel post October 7, Israel at a time of difficulty, how could we work together on a shared mission of advancing regional integration. And this was something that – you know, Yaron was not the loudest person in the room ever. He, in that sense, was not your typical Washingtonian. But he always had this presence. He always had this smile on his face. So whenever he was there, you knew you felt this comfort. People have been saying a lot, who have been meeting his family, that he comes from a very noble family, and I think that perfectly describes Yaron. He was a noble guy. He was always somebody who was happy to be where he was. You could tell the work meant a lot to him, and someone who I always enjoyed being able to see. That night, I got to spend a good amount of time with him. I had seen him a few weeks prior, but we didn't really have the time to catch up, and it was just a great opportunity to be able to talk with him. He shared, he was very excited to go home. He hadn't been home in close to a year. Was going to see his family. He was going to go over Shavuot. Again, with that typical Yaron smile, calm energy, noble engagement. He was really happy that night, and that's something, the more I talk about this, the more that's important for me to share. Just because I am a new father, I can only imagine what his parents are going through. But he was happy that night. He was at a really good place. And I think that that, I hope, that brings some solace and meaning to all who knew and loved him. Manya Brachear Pashman: I know people did more than mingle at this reception. Much has been said about the cruel irony that this was a program about humanitarian aid to Gaza. Could you speak a little more about that? Benjamin Rogers: The event on Wednesday night was one that I moderated, and one that I was actually quite nervous to moderate. It was on humanitarian diplomacy. This is not an easy topic to discuss right now. There's a lot of complexity, a lot of hardship, a lot of heartbreak, but the fact that he was there for this conversation showed his willingness to engage, his willingness to hear a conversation. It was not a political discussion. It was a discussion with representatives from IsraAID and representatives from Multifaith Network–that was really working on showcasing how interfaith engagement, how IsraAID came together to say, how do we do something good? How do we do something good at a time when there's not so much humanity right now. And it was about trust. It was about doing better. It was about looking forward. And that I think encapsulates not only Yaron's spirit, but very much Sarah's as well, who I knew less well, but was very much part of the AJC family. Very much also deeply believed in being a bridge, bringing people together. Manya Brachear Pashman: Is there a conversation or a moment, an encounter that really stands out for you as your key memory, core memory, if you will, of Yaron? Benjamin Rogers: We always used to joke about diplomats that we had engaged together. There's a lot of sensitivities in this, but we would always seem to be at events where it was a great networking opportunities and great opportunities to expand understanding throughout the Middle East. And we would always kind of laugh and talk about how happy we were to be able to do some of those small engagement, small steps together. That and his smile. This was always somebody who walked into a room and again, not the loudest person, but someone who you could just tell was good natured, had a good heart, and that's essential in this work. There are a lot of good people in this field. Not everybody, though, is to the level of Yaron and to the level of Sarah, and I think…I've been going through many different emotions. Most of it is just this feeling of surrealness. This is somebody who I just saw and is now gone. I still haven't fully processed that. But what I'm coming to more and more is that we've got to do better. We're better than this. We're all better than this. Yaron and Sarah were better. We need to find a way to live up to their ideals. Professing kind of what he stood for. How do we get out of this period? How do we find a more understanding, a more hopeful, more empathetic world where we pull away from this black and white, good and bad, explain this to me in a tweet or a five second clip. This is complex. We've seen just how tragic this environment can be, how tragic and costly words can be, and I hope that for everyone, it is a rallying call to be better. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much, Benjy. Benjamin Rogers: Thanks Manya.
May 29
AJC's CEO Ted Deutch: Messages That Moved Me After the D.C. Tragedy
In this episode about the week following the antisemitic murders of Israeli embassy employees Yaron Lischinsky and Sarah Milgrim, AJC CEO Ted Deutch shares how leaders and allies around the globe, as well as hostage families, despite their own state of grief, have reached out to offer comfort and condolences, and what we all must do to shape a new future for the Jewish people. Resources: What To Know About The Murder of Sarah Milgrim z"l and Yaron Lischinsky z"l in Washington, D.C. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: Why TikTok is the Place to Talk about Antisemitism: With Holocaust Survivor Tova Friedman Related Episodes: Higher Education in Turmoil: Balancing Academic Freedom and the Fight Against Antisemitism Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of the Interview: Manya Brachear Pashman: On May 21, Sarah Milgrim and Yaron Lischinsky were murdered outside the Capital Jewish Museum in Washington, D.C., following the Young Diplomats Reception hosted annually by American Jewish Committee. Yaron returned to his home in Israel to be buried on Sunday. Sarah's funeral in Kansas City took place on Tuesday. AJC CEO Ted Deutch was there and is with us now to talk about this incredibly sad and significant loss for the Jewish community – really for the world. Ted, thank you so much for joining us. Ted Deutch: Thanks, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Ted, I have to ask, Where were you when you heard the news of what happened? Ted Deutch: Well, I had been in Washington with the team there. I had done meetings in the capital. I've had some meetings in Atlanta. I flew to Atlanta, and there were some questions as I was flying. But it wasn't until I landed that it was clear what had happened. And the rest of the night on into the morning, obviously, we're all completely tied up trying to address the crisis and make sure that everything was being addressed for our people. For those who were there with law enforcement, with the administration, was a really, really horrible, horrible night. Manya Brachear Pashman: This was an annual reception for Young Diplomats. What was the theme of the event this year, though, was it different from years past? Ted Deutch: The theme was humanitarian diplomacy, which is the cruel irony here. This brutal, violent terror attack came immediately after a big group of young leaders from across Washington came together. AJC leaders, Jewish leaders, young diplomats, literally Young Diplomats from across the diplomatic corps all came together to focus on how to bring people together to provide humanitarian assistance, ultimately, to make life better for everyone. For Jews and Muslims and Christians, for Israelis and Arabs, Palestinians. Everyone coming together with this sense of hope, and then that was, of course, followed with the despair that we felt immediately after, as a result of this tragedy. Manya Brachear Pashman: Given the climate since October 7, given the rise in antiSemitism and the virulence of a lot of the protests, was this predictable, sadly, or was it really unimaginable? Ted Deutch: Strangely, I think both of those things can be true. It was, on the one hand, absolutely predictable. We've been saying since before October 7, but certainly since we've seen these horrific protests and people chanting to globalize the Intifada and Palestine from the river to the sea and calling for the destruction of Israel, and the attacks against Jews on the streets. We've been saying that words can lead to violence. We've seen this happen. We've seen it happen throughout our history. We've seen it happen across Europe, and we've seen the kind of deadly violence here in the United States. At Tree of Life and Poway and elsewhere. And so, on the one hand, completely predictable, at the same time, unimaginable. How is it that a group of dedicated young Jewish leaders and their allies from around the world could come together in a Jewish museum, to focus on the hope for a better future for everyone and be a target for a brutal, vicious antisemitic killer? And that's the point we've been trying to make since. Is that sure, that incitement, that words aren't just words because they can lead to violence, but also that we shouldn't live in a place where we just expect that the Jewish community is always going to be under threat. That's not normal. It's not normal in the United States. It shouldn't be normal anywhere. Manya Brachear Pashman: What have you learned about Yaron and Sarah, since last Wednesday? Ted Deutch I have…Yaron was a partner of AJC on a lot of work, but among the many messages that I received since last Wednesday, there was a really touching message from a diplomat, from an ambassador in Washington, who had just recently met with a group of hostages, hostage families, I should say, that Yaron brought to them, and he wanted to share how meaningful was, and in particular, the care that Yaron showed for these families who have been struggling now as we're recording this, 600 days. I thought that was really meaningful to hear from someone who had only recently spent considerable time with him. In Sarah's case, I just got back from her funeral and Shiva in Kansas City, and I learned a lot. And I had met her before, but I didn't know a fraction of the ways that she's made so many meaningful contributions to her community in Kansas City, to the work that she's done in all of the jobs that she's had, to the incredible work that she's done at the Embassy in Washington, working to go out into the community, to groups. In particular groups that included people who had ostracized her because of her strong positions, and when she took this job at the Israeli embassy and worked to bring people together and to build bridges in all of these different communities across Washington and around the country, really, really meaningful. We knew that both of them, I've said this a lot, and you can tell, even just from the photo, they're a beautiful couple, and they really represented the best of us. But when you hear her rabbis, her friends, her family talk about all that Sarah really was. It's a really, really tremendous loss. And there's this feeling in Kansas City. There was this feeling in the synagogue yesterday, which was, of course, filled to overflowing, that–everyone there felt invested in Sarah's life, her development, her success, the impact that she's had on the Jewish community and the world. And everyone felt the loss personally, and it really speaks to the way that we've all reacted to this. The more that we get to know about Sarah and Yaron the more we understand just how dramatic a tragedy this really was. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, your story about Yaron, bringing the hostage families together just is heartbreaking, because I just can't imagine the pain that's amplified now for those families having met and worked with Yaron, and now this. Ted Deutch: Manya, among the most powerful messages that we've received since last week were the many messages from the hostage families that we at AJC have gotten to know so well now for 600 days, because of all of the times that we've spent with them and getting to know them and trying to lift up their voices with leaders in Washington around the world, to think about what they have experienced, the loss that some of them have felt, the tragedy of knowing that their loved ones are gone, but being unable to bury them and have closure, and yet the decency and the humanity to reach out to express their sadness over these losses, it's just really, really powerful. Also, not in the Jewish community, but along these same lines. I mean, as you know, when I was in Congress, I got to know many of the families who lost loved ones in the school shooting in Parkland, and after spending a lot of time with them and trying to be there for them, it's just unbelievable to me, the number of those families who almost immediately reached out to see if there's anything they could do. Manya Brachear Pashman: Oh, wow, wow. That's amazing. That encounter you had with gun violence that took other young lives–how was that experience similar to this one, and how is it very different? Ted Deutch: Well, I've actually been thinking about this a lot. And the greatest similarity, is really beyond the sadness, obviously, which is profound. It's the outrage in in the case of Parkland, it's the fact that students went to school that day to a place that should be safe and never returned to their families, that their school became the most dangerous place they could have been. And last Wednesday, for Sarah and Yaron, they were with peers, friends, leaders in the Jewish community and beyond in a hopeful setting, talking about the way to address suffering, really the best of what we would want anyone, anyone, especially our young people, to be spending their time on. And this was the most dangerous place for them. And ultimately, when, when the event ended and they walked outside, they lost their lives as well. And the world that we live in, in which both of those things happen, that's what I've really struggled with. Manya Brachear Pashman: We're all struggling with this. What is the takeaway? How do we find any glimmer of hope in any of this? Ted Deutch: Well, Rachel Goldberg-Polon has, we've all heard her say over and over that hope is mandatory. And for the hostages and look, I think, for where we go as a Jewish people, hope is also mandatory. But hope alone isn't enough. We have work to do. We if, if we're going to if, if we're going to come through this as a community that is, that is different and, and, frankly, safer and living in a world which is different than the one that we live in now, then, then we have to, we have to honor Sarah and Yaron's lives by making this conversation different than it normally is. Yes, we have to focus on increasing security and making sure that the community is safe and but if all we're doing is, if the only thing that we're doing is talking about how to get more money for security and and police officers with bigger guns and metal detectors and and and creating turning our synagogues and day schools and JCC's into fortresses. Some of that is necessary at this moment, but we have to change the conversation so that no one thinks that it's normal in America for Jews to be the only group that has to think about how they represent a target, just by being together, that that has to change It's not just about making people care about antisemitism and fighting antisemitism and acknowledging this, the loss of the tragic loss of life that has happened. I mean, there the messages from around for the highest levels of government, from around the United States, from around the world, so much sympathy and and it's important. But as I told one governor yesterday, I am grateful for the additional security that you'll be providing. But there is so much more than that in terms of changing this conversation, the conversation about why it's not normal for Jews to be afraid, why we have to recognize once and for all, that calls for globalizing the Intifada are not the calls of a social justice movement. They're the cause of a terrorist movement. We have to understand that when people that when people decide that because of something that's happening in Gaza, that they're going to they're going to protest outside of synagogues and and they're going to vandalize Jewish owned restaurants, and they're going to get on the subway in New York, and they're going to march in other places, and they're going to accost Jews, that can't be tolerated, and that's a different conversation than we then we've been willing to have, and we need to force that conversation and force it upon our leaders. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, I do hope that this is a turning point in that direction so Ted, thank you so much for joining us. Ted Deutch: Manya, I appreciate it. Since you had asked about hope, I want to make sure that we try to end on a hopeful note, which is, what's been especially striking for me is not the responses from all of the leaders for which we are really grateful. It's the responses from people, especially young people, especially like the ones that I saw yesterday at Sarah's funeral, who understand that the world has to change, and that they have to play a role, helping to change it and to really honor Sarah and Yaron's memory, providing more and more opportunities for young people to play exactly the roles that the two of them were playing on the night that they were killed, where they were trying to change the conversation, to build bridges, to bring people together. That's what has to happen. Those are the opportunities that we have to provide going forward. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much, Ted. Ted Deutch: Thanks, Manya. I appreciate it.
May 15
Modern-Day Miriams: Jewish Women Shaping Global Diplomacy
"This has been my favorite session of the three days. Thank you," said one attendee following a powerful live conversation at AJC Global Forum 2025. This exclusive episode of AJC's People of the Pod, presented by AJC's Women's Global Leadership Network, features a candid discussion on the critical impact of Jewish women leaders in global diplomacy and conflict resolution. Casey Kustin, AJC's Chief Impact and Operations Officer, joins former U.S. Deputy Assistant Secretary of State Mira Resnick and Dana Stroul, Research Director and Kassen Family Senior Fellow at The Washington Institute for Near East Policy, to share how they've navigated the corridors of power, shaped international policy from the Middle East to Europe and beyond, and opened doors for the next generation of women in foreign affairs. ___ Resources– AJC Global Forum 2025 News and Video AJC Global Forum 2026 returns to Washington, D.C. Will you be in the room? Listen – AJC Podcasts: Most Recent Episodes: A United Front: U.S. Colleges and AJC Commit to Fighting Campus Antisemitism What is Pope Francis' Legacy with the Jewish People? Why TikTok is the Place to Talk about Antisemitism: With Holocaust Survivor Tova Friedman The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Interview Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: Live from AJC Global Forum 2025, welcome to People of the Pod. For audience members who are not in this room, you are listening to a show that was recorded in front of a live studio audience on April 29 at AJC Global Forum 2025 in New York. I'm your host, Manya Brachear Pashman. Thank you all for being here. In countries around the world, women are working more than ever before. But compared to men, they are not earning as much or being afforded an equal voice – at work, at home, or in the community. In no country in the world do women have an equal role. Let me repeat that. In no country in the world, do women have an equal role–when it comes to setting policy agendas, allocating resources, or leading companies. With us today are three modern-day Miriams who have raised their voices and earned unprecedented roles that recognize the intellect and compassion they bring to international diplomacy. To my left is AJC Chief Impact and Operations Officer, Casey Kustin. Casey served as the staff director of the Middle East, North Africa, and Global Counterterrorism Subcommittee on the House Foreign Affairs Committee for 10 years. She has worked on political campaigns at the state and national level, including on Jewish outreach for Barack Obama's presidential campaign. Welcome, Casey. To Casey's left is Dana Strohl. She is the Director of Research for the Washington Institute for Near East Policy. She was the Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense for the Middle East. In this role, she led the development of U.S. Department of Defense policy and strategy for Bahrain, Egypt, Israel, Iran, Iraq–I'm not done–Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestinian Authority, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Prior to that, she also served on Capitol Hill as the senior professional staff member for the Middle East on the Senate Foreign Relations Committee. Welcome, Dana. And last but not least, Mira Resnick. Mira was the former Deputy Assistant Secretary of State for Israeli and Palestinian Affairs and Arabian Peninsula Affairs, in which she handled two crucial Middle East portfolios, usually helmed by two separate people. Previously, she oversaw the Department's Office of regional security and arms transfers, where she managed foreign arms sales and shepherded the Biden administration's military assistance to Ukraine and Israel after Russia's invasion and after the October 7 Hamas attacks. Like Casey, Mira has also served as a senior professional staff member with the House Committee on Foreign Affairs, focusing on the Middle East and North Africa. Thank you for being here, Mira. Welcome to all of you, to People of the Pod. I think it's safe to say, this panel right here, and all the knowledge and experience it represents could solve the Middle East conflict in one day, if given the chance. Casey, you served for a decade as staff director for the Middle East, North Africa and Global Counterterrorism Subcommittee. A decade, wow. You witnessed a lot of transition, but what were the constants when it came to regional cooperation and security needs? Casey Kustin: What's the saying? The enemy of my enemy is my friend. And that's the world that we're all trying to build. So, you know, from an American perspective, which we all came from in our government work, it was trying to find those shared interests, and trying to cultivate, where we could, points of common interest. And even with the challenges of October 7 now, perhaps stalling some of those areas of progress, you still see that the Abraham Accords haven't fallen apart. You saw when Iran launched missiles at Israel. You saw other countries in the region come to, maybe they wouldn't say Israel's defense. It was their airspace defense. But you saw that still working. You see that still working now. And it's every day when we come to work at AJC, we're thinking about how to increase and strengthen Israel's place in the world. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Mira, your role encompassed both Israel and the Gulf for the first time, right? Mira Resnick: That was the first time at my level. Yes. Manya Brachear Pashman: Okay, so whose idea was that, and did that put you or the US in a position to work for the good of the neighborhood, rather than just Israel, or just the Gulf States? Mira Resnick: Yeah, this was an opportunity for the State Department to be able to see all of the different threads that were coming throughout the region. This is something that Dana did on a daily basis. This is something that our colleagues at the NSC did on a daily basis. The Secretary, of course, needs to be able to manage multiple threads at the same time. When I was overseeing arms sales, of course, I would have to consider Israel and the Gulf at the same time. So this wasn't a new idea, that our interests can be aligned within one portfolio, but it was particularly important timing for the United States to be able to see and to talk to and to hear our Gulf partners and our Israeli partners at the same time within the same prism, to be able to truly understand what the trends were in the region at that particularly critical moment, post-October 7. Manya Brachear Pashman: Dana, in your role as Assistant Deputy Secretary of Defense, you met with military leaders in the Middle East, around the world, and you were often the only woman at the table. What do women contribute to international conflict resolution that's missing when they're not given a seat at the table? Dana Strohl: Well, let me start out by stating the obvious, which is that women make up 50% of the global population of the world. So if 50% of the world is missing from the negotiating table, from the peacemaking table, from conflict prevention mechanisms, then you're missing 50% of the critical voices. There's evidence, clear evidence, that when women are part of peace processes, when they are part of negotiations, the outcomes on the other side are 35% more sustainable. So we have evidence and data to back up the contention that women must be at the table if we are going to have sustainable outcomes. When I think about the necessity, the imperative, of women being included, I think about the full range of conflict. So there's preventing it, managing it, and then transitioning to peace and political processes in a post-war or post-conflict situation. In every part of that, there's a critical role for women. As examples, I always think about, when you make policy, when you have a memo, when there's a statement that's really nice, in the big capital of some country, or in a fancy, beautiful palace somewhere in the Middle East or in Europe. But peace only happens if it's implemented at a local level. Everyone in the world wants the same things. They want a better life for their kids. They want safety. They want access to basic services, school, health, clean water and some sort of future which requires jobs. Confidence you can turn the light on. You can drive your car on a road without potholes. Those are details that often are not included in the big sweeping statements of peace, usually between men, that require really significant compromises. But peace gets implemented at a very local level. And at the local level, at the family level, at the community level, at the school level, it's women. So how those big things get implemented requires women to champion them, to advance them. And I will also just say, you know, generally we should aspire to prevent conflict from happening. There's data to suggest that in countries with higher levels of gender equality, they are less likely to descend into conflict in the first place. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you recall a particularly consequential moment during your tenure, when you were at the table and it mattered? Dana Strohl: So my view on this is that it was important for me to be at the table as a woman, just to make the point. That women can serve, just like men. Do the same job. And frankly, a lot of the times I felt like I was doing a better job. So what was really important to me, and I can also just say sitting up here with Mira and Casey, is that all of us have worked together now for more than a decade, at different stages of, getting married, thinking through having kids, getting pregnant, taking parental leave, and then transitioning back to work. And all of us have been able to manage our careers at the same time. That only happens in supportive communities, in ecosystems, and I don't just mean having a really supportive partner. My friends up here know, I ask my mom for a lot of help. I do have a partner who really supported me, but it also means normalizing parenthood and being a woman, and having other obligations in the office space. I would make a point of talking about being a parent or talking about being a woman. To normalize that women can be there. And often there were women, really across the whole Middle East, there were always women in the room. They were just on the back wall, not at the table. And I could see them looking at me. And so I thought it was really important to make the point that, one, a woman can be up here, but I don't have to be like the men at the table. I can actually talk about, well, I can't stay for an extra day because I have a kindergarten, you know, theater thing, and I have to run back and do that. Or there were many times actually, I think Mira was Zooming for parent teacher conferences after we were having the official meeting. But I think it's important to actually say that, at the table, I'm going to leave now and go back to my hotel room because I'm making a parent teacher conference. Or, I have to be back by Friday because I'm taking a kid to a doctor's appointment. So all the women that come after us can see that you can do both, and the men at the table can understand that women have a right to be here. Can do the jobs just as effectively and professionally as the men, and do this other absolutely critical thing. Manya Brachear Pashman: But your point about, it requires a supportive network, a supportive work community. You told me a story before we got up here about just how supportive your colleagues were in the Department of Defense. Dana Strohl: I will give a shout out to Lloyd Austin, the Secretary of Defense. So one of the things you do in our positions is travel with the Secretary of State or the Secretary of Defense. And these are not the kind of things where they get on a plane and you land in whatever country. There's a tremendous amount of planning that goes into these. So on a particular trip, it was a four country trip, early in 2023. Secretary Austin was going to multiple countries. He had switched the day, not he, but his travel team, of his departure, which then caused us to switch the day of my son's birthday party. And then they switched the time of his departure from Andrews Air Force Base, and we could not change the birthday party. So I called Secretary Austin's office and said, Listen, I want to be at my son's birthday party. So I've looked and it looks like I can take this commercial flight. So I won't be on the Secretary of Defense's plane, but I can largely land around the same time as you all and still do my job in the region. And to their credit, they said, okay, and then one of the things that you do in my position is you get on the airplane and you talk to the Secretary of Defense about the objectives and the goals and the meetings. So they said, Okay, we'll just change that to earlier. You can do it the day before we depart, so that he can hear from you. You're on the same page. You can make the birthday party. He can do the thing. So we were actually going to Jordan for the first stop. And it turns out, in his itinerary, the first thing we were doing when we landed in Jordan, was going to dinner with the King. And it was very unclear whether I was going to make it or not. And quite a high stakes negotiation. But the bottom line is this, I finished the birthday party, had my mother come to the birthday party to help me clean up from the birthday party, changed my clothes, went to Dulles, got on the airplane, sort of took a nap, get off the airplane. And there is an entire delegation of people waiting for me as you exit the runway of the airplane, and they said, Well, you need to go to this bathroom right here and change your clothes. I changed my clothes, put on my suit, ran a brush through my hair, get in a car, and they drove me to the King's palace, and I made the dinner with the king. It's an example of a team, and in particular Secretary Austin, who understood that for women to have the opportunities but also have other obligations, that there has to be an understanding and some flexibility, but we can do both, and it took understanding and accommodation from his team, but also a lot of people who are willing to work with me, to get me to the dinner. And I sat next to him, and it was a very, very good meal. Manya Brachear Pashman: I find that so encouraging and empowering. Thank you so much. Casey, I want to turn to you. Mira and Dana worked under particular administrations. You worked with members of Congress from different parties. So how did the increasing polarization in politics affect your work, or did it? Casey Kustin: It's funny, I was traveling last week for an AJC event, and I ended up at the same place with a member of Congress who was on my subcommittee, and I knew pretty well. And he looked at me and he said, the foreign affairs committee, as you know it, is no longer. And that was a really sad moment for me, because people always described our committee as the last bastion of bipartisanship. And the polarization that is seeping through every part of society is really impacting even the foreign policy space now. As you see our colleague, our Managing Director of [AJC] Europe, Simone Rodan[-Benzaquen], who many of you know, just wrote a piece this week talking about how, as Israel has become to the progressive, when Ukraine has become to the far right. And I think about all the years I spent when Ted Deutch, our CEO, was the top Democrat on the Middle East subcommittee, and Ileana Ros-Lehtinen (R-FL), a great friend of AJC, was the chair of the subcommittee. And Ted and Ileana would travel around together. And when she was the chair, she always made a point of kind of joking like Ted's, my co chair, and we did so many pieces–with Mira's great support of legislation for the US, Israel relationship, for Syria, for Iran, that we worked on together, really together. Like at the table with my staff counterparts, trying to figure out, you know, what can your side swallow? What can your side swallow? And I hear from so many of our former colleagues that those conversations aren't really taking place anymore. And you know, the great thing about AJC is we are nonpartisan, and we try so hard to have both viewpoints at the table. But even that gets harder and harder. And Dana's story about the King of Jordan made me laugh, because I remember a very similar experience where I was on a congressional delegation and Chairwoman Ros-Lehtinen, and I was six months pregnant at the time, and I wanted to go on the trip, and the doctor said I could go on the trip. And we were seated around the table having the meeting. And I, as you won't be able to hear on the podcast, but you in this room know, look very young, despite my age. And you're self conscious about that. And I remember Ileana just being so caring and supportive of me the entire trip. And I wasn't even her staffer, and I remember she announced to the King of Jordan that I was six months pregnant, and you could kind of see him go, okay. That's very like, thank you. That's very nice. But even just having that moment of having the chairwoman on the other side of the aisle. That whole trip. I think I've told some AJC people another funny story of on that same trip, we met with the Greek Orthodox Patriarch in Jerusalem, and she pulled me up to him, and she said to the patriarch, will you bless her unborn child? Knowing I'm Jewish, she leaned over and said to me: Can't hurt. So I hope that we return to a place like that on Capitol Hill. I think there are really good staffers like us who want that to happen, but it is just as hard a space now in foreign policy as you see in other parts of politics. Manya Brachear Pashman: Mira, I want to ask you another policy related question. How did the Abraham Accords change the dynamics of your combined portfolio, and how could it shape the future? Mira Resnik: My first, one of my first trips, certainly my first trip to the Middle East, when I was the Deputy Assistant Secretary for Regional Security, overseeing security assistance and security cooperation, was to Dubai, as the State Department representative for the Dubai Airshow. And it is a huge event that showcases the world's technology. And I remember walking into the huge hangar, that every country that has a defense industry was showcasing their most important, their most important munitions, their most important aircraft. And I remember seeing the enormous Israeli pavilion when I was there. And I was staying at a hotel, and I get to the breakfast and they said, Would you like the kosher breakfast or the non-kosher breakfast. And I'm like, Am I in Israel? And I was blown away by the very warm relationship–in the security space, in the humanitarian space. I agree with Casey that things have gotten a little tougher since October 7, and since the aftermath in Gaza. But what I would also point out is that April and October, during the time when when we witnessed Israel under cover, when we witnessed Iran's missiles and projectiles going toward Israel and going toward other regional airspace, our diplomats, our militaries, our intelligence officials, all had earlier warning because of the work of other Gulf governments, even those who have not joined the Abraham Accords. And that is a prime example of where this security cooperation really matters. It saves lives. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Casey, so much of what AJC does has to do with international diplomacy and maintaining that regional cooperation and security, and that sounds a lot like your previous role. So I'm really curious how much your job truly has changed since you came to AJC? Casey Kustin: You're absolutely right. There are so many similarities in what we do at AJC and what we did in the government. And the core of that is really those relationships that you build with partners and interlocutors in other countries and other governments, and the foundation, over decades that AJC has laid. Particularly in the Middle East, thanks to 30 years of quiet travel to the region. It struck me when I first came here, the access that AJC has is nearly the same that we had traveling as members of Congress. And the meetings and the quality and the level of meetings that AJC is afforded in these other countries. Our missions, which many of you have been on, often feel like congressional delegation trips to me, and the conversations and the candor with which partners speak to AJC is almost the same that was afforded to members of Congress. And that has been comforting, in a way, as you said Manya, Because there feels like there's continuity in the work that we're doing, and it has made me realize that organizations, non-governmental organizations, advocacy organizations, play such a crucial role in supporting the work of a government, of your country's government. And in reinforcing the values and the interests that we as AJC want to communicate that very much dovetail, with hopefully any US administration. I think that the role that an organization like ours, like AJC, can play in a particular moment, like we're in, where, as we've discussed, there's hyperpartisanship, and we hear a lot, Dana mentioned this. We hear a lot from foreign partners that the way our democracy works with a change in administration every four years is unsettling to some of them, because they don't know if a particular policy or agreement is going to continue the role that we can play, providing some of that continuity and providing a nonpartisan and thoughtful place to have conversations. Because they know that we have that kind of nuanced and thoughtful and nonpartisan insight. Manya Brachear Pashman: I really appreciate your insights on the roles that you've played, and I think the audience has as well. But I want to pivot back to your role as women. Dana, I mentioned that you were often the only woman at the table. Would you discover that when you arrived at meetings and events? Dana Strohl: In Washington, DC, and in particular, I'm very proud to have served in the Biden administration, where there were always women at the table. And I will also say that there was a network of women, and it was the same on the Hill. On the hill, there was actually a box of maternity clothes that was kept in then-Senate Leader Harry Reid's office. And his National Security Advisor called me when she heard I was pregnant the first time, which was during the 2015 JCPOA negotiations on the Hill, which meant that I was super tired and doing all of those congressional hearings and briefings, but there was a network of women who were supporting each other and giving me clothes as I got bigger and bigger. And it continued into the Pentagon and the State Department, where there were always women and when we saw each other at the White House Situation Room or in the different meetings, there was always the quiet pull aside. How are you doing? How are your kids? Are you managing? What's the trade off on your day to day basis? Can I do anything to help you? And in particular, after October 7, that network of people really kicked into high gear, and we were all checking in with each other. Because it was the most intense, most devastating time to work in the government and try to both support Israel and prevent World War III from breaking out across the Middle East. So that was DC. In the Middle East, I largely assumed that I was going to be the only woman at the table, and so I decided to just own it. There are some great pictures of me always in a pink jacket, but the point you know, was that I expected it, and there were always women, again, against the back walls. I made an effort whenever possible to make sure everyone at the table, regardless of your gender, had an opportunity to speak and participate, but I was also not just the only woman. A lot of times, I was the co-chair with whatever partner it was in the Middle East, so I had a speaking role, and I felt was incumbent upon me to present a model of leadership and inclusivity in how we engage with our partners, spoke to our partners, listened to our partners concerns, and that that was part of the job. And only once, I remember it very clearly. We were at a dinner after a big meeting, and somebody looks at me, it's a meeting with all, y7all men, all men for a dinner. And they said, Is this what it's like for you all the time? And I said, Yes, it is. And you know, it took two and a half years for somebody to notice, so. Manya Brachear Pashman: Mira, what have you experienced? And have you ever worried as a woman that you weren't being taken seriously? Mira Resnick: I think that every woman in one of these jobs has imposter syndrome every so often, and walking into the room and owning it, fake it till you make it right. That's the solution. I will. I agree with Dana wholeheartedly that in Washington, I was really proud to walk into the room and never fear that I was the only woman. And I even remember traveling where another delegation was all women, and our delegation was all women, and how surprising that was, and then how disappointing, how surprising that was, but to take notice of the moment, because they don't happen very often. I think that in Washington and throughout diplomacy, the goal is to pay it forward to other women. And I wasn't the last person to pump in the Ramallah Coca Cola factory, and I wasn't the first person to pump in the Ramallah Coca Cola factory. But that is, that was, like, my moment where I was like, Oh, this is a strange place to be a woman, right? But I do find that women really bring holistic views into our policy making, and whether it's meeting with civil society, even if your job is strictly security cooperation to understand the human impacts of your security decisions, or making sure that you are nurturing your people, that you are a good leader of people. I remember post-October 7, I was looking for some way that I could nurture in the personal life. And I see Nadine Binstock here, who goes to my shul, and Stephanie also. Stephanie Guiloff is also in the audience. She's my neighbor, and also goes to my shul. And after October 7, I took on the Kiddush Committee Coordinator at my shul. So that every week, no matter what I was experiencing at the office and no matter where I was in the world, our community would be a little bit more nurtured. And it was a way for me to like to give back to the community, and at the same time be able to continue to do the hard power work of security cooperation. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Mira, Casey, Dana, thank you so much for joining us, sharing your modern-day Miriam experiences. I want to open it up for questions from the audience. Just raise your hand and someone will bring you a microphone. Audience Member: Hi, I'm Maddie Ingle. I'm a Leaders for Tomorrow alum. What is some advice that any of you have for young women like me in the advocacy space and in general. Casey Kustin: First of all, thank you for taking the time to come to Global Forum and for joining LFT. You've already taken the first step to better arming yourself as an advocate. I think there is, I wish someone had said to me, probably before I met the two of them who did say it to me, that it was okay to take up space around the table. I remember sitting in secure facilities, getting classified briefings from ambassadors, male ambassadors who were 30 years my senior, and watching the two of you in particular i. Not be scared to challenge the back and forth when I as a probably still, you know, mid 20s, early 30s, did have fear of speaking up. And I wish someone, when I was your age as a teenager, had, and obviously, I had supportive parents who told me I could do anything, but it's different. It's different than seeing it modeled by people who are in the same space as you, and who are maybe even just a couple years older than you. So I would just say to you not to ever be afraid to use your voice. This is a memory that has stuck with me for 15 years. I was in a meeting, sitting next to my congressman boss, with two men who were probably in their 60s, and a vote was called. And you never know on the Hill when a vote is going to be called. So it interrupts a meeting. And he had to go vote, and he said, Casey will finish the meeting with you. And they looked at him and said, Does she know what we're talking about? Dana Strohl: We have all been there, Casey. Casey Kustin: We have all been there. So even if you're met with a response like that when you try to use your voice, don't let it deter you. Audience Member: Hi, guys. I'm Jenny. This has been my favorite session of the three days. Thank you guys. My mom is the first female, woman brakeman conductor on Amtrak. So you guys are just so empowering. As a long time Democrat, you guys talked about bipartisan issues. With how the Democratic Party is. I know you guys probably can't go fully into this. Do you have any inspiring words to give us hope when it feels very scary right now, as a Democrat, how divided our party is. Casey Kustin: I work for a nonpartisan organization now, so I'll let them handle that one. Dana Strohl: I, so were we all on the Hill during the first Trump administration? And there was still bipartisanship. And what I'm looking for right now is the green shoots of our democracy. And I see them. There is thinking through what does it mean to be in this country, to be an American, to live in a democracy? What does democracy do? I think, first of all, it is healthy and okay for Americans to go through times of challenge and questioning. Is this working for us? And you know, the relationship between the government, whether it's legislative, judicial, executive and the people, and it's okay to challenge and question, and I think it's okay for there to be healthy debates inside both the Republican and the Democratic Party about what what this stands for, and what is in the best interest of our country. And you can see both in polling data and in certain areas where there actually are members of Congress coming together on certain issues, like economic policy, what's in the best interest of our constituents and voters. That there is thinking through what is the right balance between the different branches of our government. I was talking to somebody the other day who was reminding me this actual, you know, we are, we are in a time of significant transition and debate in our society about the future of our country and the future role of the government and the relationship. But it's not the first time, and it won't be the last. And I found to be that part of my job was to make sure I understood the diversity of voices and views about what the role of the government should be, general views about American foreign policy, which was our job, was just such a humble reminder of democracy and the importance of this back and forth. Audience Member: [My name is Allie.] My question for you is, what are your hopes and dreams for generation alpha, who will be able to vote in the next election? Casey Kustin: I think we all have, all our kids are still in elementary, or Mira, your one is going into middle school now– Mira Resnik: To middle school. Casey Kustin: So the vast majority of our children are still elementary school age. And for me, I have a very interesting experience of moving my family out of a very diverse community in Washington, DC to Jacksonville, Florida. And it's a very different environment than I thought that my children were going to grow up in, because at the time, we didn't anticipate leaving DC anytime soon, and it's made me realize that I want them to live in a world where no matter what community They are growing up in, they are experiencing a world that gives them different perspectives on life, and I think it's very easy now that I have gone from a city environment to suburbia to live in a bubble, and I just, I hope that every child in this next generation doesn't have to wait until they're adults to learn these kinds of really important lessons. Dana Strohl: I have two additional things to add. I'm very concerned at what the polling suggests, the apathy of young people toward voting, the power of voting, why it matters. And participation, that you need to be an active citizen in your governments. And you can't just vote every four years in the presidential election, there's actually a ton of voting, including, like the county boards of education, you got to vote all the way up and down you continuously. And that it's okay to have respectful debate, discourse, disagreements in a democracy. So I would like this generation to learn how to have respectful discourse and debate, to believe that their votes matter and just vote. And three, on the YouTube thing, which is terrifying to me, so I'm hoping the educators help me with this is, how to teach our kids to separate the disinformation, the misinformation, and the fiction that they are getting because of YouTube and online. So mine are all elementary schoolers, and I have lost positive control of the information they absorb. And now I'm trying to teach them well, you know, that's not real. And do I cut off certain things? How do I engage them? How do I use books and when? So they need to not just be active participants in their society, all up and down the ballot, multiple times every year, but they need to know how to inform themselves. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Mira? Mira Resnick: I do hope that our children, as they approach voting age, that they see the value in cooperation with each other, that they see the value of face to face conversation. I think that honestly, this is the value of Shabbat in my household. That you take a break from the screens and you have a face to face conversation. My children understand how to have conversations with adults now. Which is, I think, a critical life skill, and that they will use those life skills toward the betterment of their communities, and more broadly, our Jewish community, and more broadly than that, our global community. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much. Thank you to everyone.
May 9
A United Front: U.S. Colleges and AJC Commit to Fighting Campus Antisemitism
This week, groups representing more than 1,600 colleges and universities pledged reforms to fight campus antisemitism —a major breakthrough in the effort to end anti-Jewish hatred and create campuses where Jewish students feel safe. In collaboration with American Jewish Committee (AJC), the groups urged the Trump administration to continue making the eradication of antisemitism a priority, but without endangering the research grants, academic freedom and institutional autonomy of America's colleges and universities. Here to discuss this collaboration are Sara Coodin, Director of Academic Affairs for AJC, and Ted Mitchell, president of the American Council on Education. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Resources: Watch – Creating Safe Spaces for Jewish Students: Education Leaders Speak at AJC Global Forum 2025 Listen – AJC Podcasts: Most Recent Episodes: What is Pope Francis' Legacy with the Jewish People? Why TikTok is the Place to Talk about Antisemitism: With Holocaust Survivor Tova Friedman Related Episodes: Higher Education in Turmoil: Balancing Academic Freedom and the Fight Against Antisemitism Meet the MIT Scientists Fighting Academic Boycotts of Israel Spat On and Silenced: 2 Jewish Students on Fighting Campus Hate University of Michigan Regent Jordan Acker: When Antisemitism Hits Home The Forgotten Exodus : Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of Conversation with Ted Mitchell and Sara Coodin: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week, groups representing more than 1,600 colleges and universities pledged reforms to fight campus antisemitism -- a major breakthrough in the effort to end anti-Jewish hatred and create campuses where Jewish students feel safe. In collaboration with American Jewish Committee, the groups urged the Trump administration to continue making the eradication of antisemitism a priority, but without endangering the research grants, academic freedom and institutional autonomy of America's colleges and universities. Here to discuss this collaboration is Sara Coodin, Director of Academic Affairs for AJC and Ted Mitchell, president of the American Council on Education. Ted, Sara, welcome to People of the Pod. Ted Mitchell: Thanks, Manya, good to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Ted, if you could please give our listeners an overview of who signed on to this. Who are the six organizations, and do they encompass all of the higher ed institutions in the country? Ted Mitchell: We represent everybody. And so it's everybody, from the Community College Association to the land grant universities, to AAU, the big research universities, the state colleges and universities, and then ACE is an umbrella organization for everybody. So we've got built in suspenders, and we've got every institution in America on the side of eliminating antisemitism. Manya Brachear Pashman: And then, I guess, the next question is, why? I mean, why was it necessary for American Council on Education and these other associations to join this effort? Ted Mitchell: Well, a couple, a couple of things. I mean, first of all, we have partnered. AJC and Ace have partnered for a number of years to identify and try to address issues of antisemitism. So feel like we've been in partnership for some time on these issues. And unfortunately, the need has continued to grow. I think that last spring was a real wake up call to a lot of our institutions, that they might have been comfortable believing that there was no antisemitism on their campus, but boy, they got up. They got a notice in the mail. So I think that we have, as a group, all six of us, we have worked with our institutions since last spring to create opportunities for institutions to do better. And so we had long conversations over the spring and summer about changes in disciplinary policy, everything from masks to how to make sure that every group that was seeking to have a voice make a protest was operating under the same rules, make sure that everybody understood those rules. And frankly, I think we've made great progress over the course of the summer. There are still things that we can do better. There are always things we can do better. But I think the call for this letter was the conflation by the Trump administration of antisemitism and efforts to eradicate antisemitism with all of the other activities that go on on a university campus that are not really related to antisemitism. And case in point is the administration's willingness to hold research funds hostage to institutional changes and behaviors that have never been stipulated. So we're in this interesting spot where we want to do better. We're working on doing better, and the administration is saying, well, just do more. We can't tell you when you'll get there. Not only is that sort of fruitless, we also think it's illegal. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Sara, I know AJC published an action plan for university administrators last year, and that not only includes concrete steps to address antisemitic incidents when they happen immediately, but also ways to cultivate a healthier culture. Does AJC expect the member schools of these six associations to draw from that action plan? Sara Coodin: So, we hope so. You know, we don't have the power to mandate that any university in particular, much less a range of universities representing all of higher ed the entire spectrum adopt our specific action plan, but our action plan is really, I think, quite thoughtful, and covers a lot of territory. So we're thinking about all of the citizens of campus. We're thinking about administrators. We're thinking too about how administrators can create frameworks so that students can get the education that they're meant to receive on site, and for which they, you know, attend university in the first place, we're thinking too about the role of faculty, and specifically at this crucial moment, because so much attention has been paid to the experience of students and to what happens when you create clear expectations and convey them to students through codes of conduct and other kinds of regulatory initiatives. We're thinking very seriously about what it would mean for administrators to convey those expectations to their faculty as well, and we think that there are lanes through which they can do this that have been under scrutinized and underutilized, and usually that falls into the bucket of professionalization. What do you do with faculty who are showing up fresh out of grad school on your campus? How do you as an institutional leader or a provost, convey the expectations that you have about the rights and responsibilities of being a teacher, a research supervisor, someone who might be supervising student activities and clubs like the student newspaper. How do you convey your institutional expectations and your expectations of these folks who are in positions of leadership for a generation or more? So it's it's an area that we think is really ripe for conversation and for folks to be convening in meaningful discussions about what the next steps consist of. Ted Mitchell: Manya, if I can, if I can interject, I really applaud the framework. I think is a great place for us to start. And I know that one of the things that was important and beginning to get support from my members and other people's members was the convening that we that we held a while ago in Washington that drew 85 college presidents together, and that was a solutions focused meeting. And I think it really suggests to me that there is quite an opening for us to work together on creating a framework that could be adopted either formally or informally by many institutions. As you say, none of us can mandate what's going to happen. That's also true for the government, frankly. But I think the more and the sooner we can build a common common consensus around this, the better. And to your point about faculty responsibilities. We hear a lot about academic freedom. We hear a lot about faculty rights. We often forget that there is a responsibility for faculty to be the adults in the room and to expand the dialog and raise the level of discussion, and we need, we need to promote that. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, I'm curious, are there any examples of institutions that have made a change have drawn from that action plan, and it created positive results. Sara? Sara Coodin: So I think we're seeing the effects of time, place and manner restrictions, and we first saw those being articulated through the task force at Columbia. And we know Columbia is not, not exactly an ideal institution right now for for a lot of different reasons, but that's not to disparage the efforts of the folks who sat on that antisemitism Task Force who came up with very specific and extremely thoughtful recommendations for their school. And I pride myself on having worked with a team that took those ideas and made sure that other schools were aware of them, so that they weren't trying to reinvent the wheel. And I think that's often the function that we've served, and particularly in the last year, because schools can and do operate in silos, whether they're geographical silos or silos within their own particular brand of school, big research institutions, Ivy League institutions, sometimes they're in conversation, but it can be very useful to serve, for us to serve as a convening function. We're not also not reinventing the wheel necessarily, but we're working in partnership to try to bring a solutions focused kind of perspective to this, because we think there are solutions in view? Obviously, leadership plays a key role in any institutional context. Are people emboldened enough to actually feel like they can convey those solutions to their communities and stand by them? And that's something that we have seen happen. I wish it were pervasive. I wish it were happening in every case. It's not, but there are certainly institutions that have taken the lead on this, whether quietly or very loudly, and I think it's important to bring our solutions to the attention of other institutions as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: Ted, I'm curious, can you shed light on the conversations that have unfolded since October 7, 2023 I mean, as students were setting up encampments and staging sit ins. Was there hand wringing, or was it considered, well, at least at first, typical college activism part of university life, Ted Mitchell: I think it started off as I certainly would never say ho hum. It started off with a sense that there has been a horrific event in the world. And of course, our campuses are going to be places where students need to respond to that and reflect on it. So I think in the early days, there was a sense that this was a right thing for campuses to be engaged in. I think the surprise came in the following weeks. 90s when the pro Palestinian, anti Israel and antisemitic counter protests began to happen and and that was something that we really didn't expect, certainly not in the volume and intensity that took place. And I think I've said this from from the beginning, I think that we were taken by surprise and on our back foot, and so I can't, I don't know a college president who would say, stand up and say we did everything right after October 7. And you could see this in, you know, presidents making a statement on a Tuesday that they had to either retract or revise on a Thursday, and then by Monday, everything was up in the air. Again, I think that there was a lack of a sense of what the framework is looking for. There's a there was a lack of a sense of, here's where we stand as an institution. Here's what's permissible, here's what's not permissible, and we're going to be even handed in the way we deal with students who are protesting and expressing expressing their beliefs. We need them to be able to express their beliefs, but under no circumstances can those expressions be violent. Under no circumstances can they discriminate against other groups or prevent other groups from access to the education that they came for. Manya Brachear Pashman: Is some of what you're saying informed by 2020, hindsight, or is it informed by education? In other words, have you? Have you yourself and have have college presidents learned as as this year has progressed, Ted Mitchell: Well, this goes to Sara's really good point. I think that there have been two kinds of learning that have taken place. One is sort of informal communication back and forth between Presidents who sort of recognize themselves in other circumstances. And I think that that's been very powerful. We for a while, in the spring, had informal Friday discussion discussions where any president who wanted to come and talk would come and talk, and they were avidly taking notes and trying to learn from each other in real time. I think the second kind of learning was after students went home, and there really was a broad agreement that institutions needed to tackle their policies. We ran into presidents in the spring who had not read their student conduct policies, and from from there to people who had very elaborate Student Conduct policies but weren't actually following them very well, or had a lot of exceptions, or, you know, just crazy stuff. So summer was an incredible time of calculated learning, where people were sharing drafts of things. Sara was deeply involved in, in making sure that institutions were learning from each other, and that Sara and her colleagues were pulling these together in the framework, in the framework that we have, you know it's still happening. I talk often with with presidents, and they're still exchanging notes and tactics about things that are going on, going on this fall, but they're doing so from a position of much more stability, Manya Brachear Pashman: Having taken that breath over the summer and prepared. Ted Mitchell: Having taken that breath, having sort of been through the fire, having taken that breath and having really regrouped. And one of the things that has been most essential in that regrouping is to make sure that all parties on campus understand what the rules and regulations are. From faculty to staff to Student Affairs personnel, to make sure that when a campus takes an action that it's understood to be the appropriate response to whatever the event might have been. Sara Coodin: And just to add to that point, about how, many institutions were caught flat footed. And I won't attest to whether I experienced this first personally, but thinking back to the history, the days of, you know when, when protests were either about apartheid in South Africa or it, it seemed like there was a very clear position and a clear kind of moral line there when it came to protests. So that's one example where it seems like there was a right side to be on. And I think that that is much, obviously we look at the protests from last year as being far more out of line with any sense of a moral right, they were in some cases host to horrific antisemitism and directly responsible for making Jewish students feel unsafe on campus. So the other example of protest, which is before my time, were the Vietnam protests on college campuses. Were really directed against the government. And last year and two years ago, we saw protests where one group of students was effectively protesting against another student group, another student population. And that is something that university administrators haven't seen before. If they were caught flat footed, it's because this was a novel set of circumstances and a really challenging one, because if you have students being activists about a geopolitical event, the focus is somewhere out there, not a population that has to live and learn on your campus. And so we're seeing the kind of directed impact of those protests on a particular group of students that feel like they no longer have a home on campus or on particular campuses, and that is a uniquely challenging set of circumstances. Of course, we would have loved it if everyone had a playbook that worked, that could have really caught this stuff from the get go and had a very clear plan for how to deal with it, but that simply wasn't the case. And I think there are good reasons to understand why that was the case. Those codes of conduct hadn't been updated, in some cases, in 70 years. Ted Mitchell: Your insight is really powerful, that this was one group of students against another group of students, and that's very different. But taking it back, not historically, but just sociologically, one of the things that we also learned is that this generation of students comes to our campuses with almost zero muscle and no muscle memory of how to deal with difference. And so this generation of students is growing up in the most segregated neighborhoods since the Civil Rights Act. They're growing up in the most segregated schools since Brown. And they are parts of these social media ecosystems that are self consciously siloing. And so they come to our campuses and they confront an issue that is as divisive as this one was last spring, and they really don't know how to deal with it. So that's the other learning that we've taken. Is that we need to get very serious about civic education, about how to have conversations between left and right, Jewish students and non-Jewish students, Muslim students and others, and white and black. And we need to get better at that, which, again, comes into the where's the faculty in this? And if they're not a part of that kind of engagement, especially if they take sides, then we've really lost a lot of our power to create a kind of contentious but productive democratic citizenship. Sara Coodin: What we have been privy to, and in the conversations that we've had with, I think leading university presidents and chancellors who really have have done the right thing, I think in the last year, they're, they're affirming a lot of what you're saying, Ted, about this inability to engage in in civil discourse. And in some ways, it's an admissions problem. It's admitting students who are, you know, they're writing to an audience that is looking for world-changing activism. And when you do that, you're going to get a lot of really inflamed activists on your campus. I think the faculty piece is more complicated. I think that speaks to a couple of generations' worth of lack of framing, of what academic freedom even is, and a kind of entry into the conversation through all kinds of back channels, that the most powerful thing you can be as a teacher is a world changer. And that means gravitating towards the extremes. It doesn't mean cultivating civil discourse, because that's boring. Why would you want to do that? That's, that's not the way to make a splash. It's disappointing to see that kind of ethos take hold. But I think there are ways in which it can be more actively discouraged. Whether it's through admissions, through looking to hire on the basis of different criteria when you're looking for faculty. And it's also a K-12 problem, and we affirm that, and that's something our Center for Educational Advocacy looks at very seriously in the work that we do in the K-12 space. How do we work with instructors and heads of school in that space to better prepare students who arrive on a college campus, knowing how to engage in civil discourse, knowing how to disagree in a way that doesn't have to result in everyone holding hands at the end and singing Kumbaya. But it shouldn't produce the culture that we saw last year. It shouldn't. It's incredibly damaging. And I think we've seen how ineffective that model is and how turbulent it is. Ted Mitchell: It's interesting that you raise the admissions question, because I think that, Manya, to your question about what have people done? A lot of this gets really granular, like, what essay questions do you ask? And a lot of them are, what have you done to advance something you believe in? And I was talking with a president who came in right before the springtime, who changed the essay question to be a question about bridging. Tell the committee of a time when you helped, you know, bridge an issue, a group, whatever. And I think that the attention on antisemitism in particular is really that is driving us to think about those micro-elements of our processes that actually foster, in some ways, this kind of segregation and combat that we saw in such grotesque detail last spring. Sara Coodin: Yeah, it's interesting. I know you work with faith-based colleges as well, and that notion of service, which is not part of the infrastructure for most schools, seems like a productive part of, maybe, a future conversation about a different model for being in the world. Ted Mitchell: I think that that's right, and I love all of our members, but the faith based institution, because this has always been front and center for so many of them, who will you be in the world as a question to ask every single student, who are you in the world, to ask every faculty member that those are natural questions in many of our many of our faith based institutions. And I really admire them. Admire them for it. Manya Brachear Pashman: And of course, that's the purpose of going to a college or university, is to figure that out, right? Who you are going to be in this world. I want to ask both of you, what is the next step? Will there be an effort to reverse some of the measures that have been taken by the federal government to get universities to comply, or is this more about proactive measures? Sara Coodin: I mean, I can say, for our part, we have no leverage over the federal government. We're not in a position to tell them to do anything. We can appeal to them to be more measured, as we have, and we've appealed to them to be part of a larger conversation about what's going on right now and we make those efforts routinely. I think the path forward is for universities to really think carefully about who their partners are in this work. And that's, I think part of the effect of this statement is that we are, we, AJC, are there to work towards constructive solutions, and that has always been our basic mission in terms of our advocacy, but we now have it in a very public form. And we're not there to simply hold accountable. I mean, we all hold one another accountable perpetually. We are actually there to do the work and to engage in constructive solution seeking. And I think we're at a moment now where we've seen enough, we've kind of seen enough of this film, that we can come up with some better solutions going forward. It's not catching us kind of flat footed in the same way, because we've had some time to reflect. And I think that's where the future of this leads to. It leads to constructive solutions. It leads to coming up with really effective strategies to migrate knowledge and approaches, and tailor them to the specifics of campuses that you know are very unique, are very distinctive, and are broad in this country. As you know, Ted, this is a country with so many types of educational institutions, so many. Ted Mitchell: So the statement is important from a number of different perspectives. One is that it's great that we have come together to ask the federal government to separate the important issue of antisemitism from the other interventions that the federal government is attempting. But the other really important thing that we want the letter to signal is our helping institutions develop the right way to combat antisemitism and, more importantly, prevent it, and through its work on antisemitism, really develop this kind of more inclusive civic culture on our campuses. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, AJC does a state of antisemitism in America report every year, and the most recent report found that roughly a third of current American Jewish college students or graduates had experienced antisemitism personally at least once in the past year, and about little over 20% reported being excluded from a group because they were Jewish. And I'm curious if university administrators pay attention to these kinds of statistics, or maybe, did they pay attention before October 7, and are they paying attention? Ted Mitchell: Now, I think, with some embarrassment, I'll say that before October 7, antisemitism was a back burner issue, and in many cases, was seen as yesterday's problem or even a historical problem. History has that nasty way of never quite going away. And you know, we see it again here. You know I remember. Was it three years ago that we co hosted a symposium in New York on antisemitism on campus, and it was it was striking. It was well attended, and people really heard a lot. But the the most striking thing that we all heard was testimony from Jewish students, not only about the frequency of antisemitic activity, but their exclusion from what we used to be able to call DEI initiatives, and that somehow whatever was happening to Jewish students wasn't the same thing. And I went away heart's sake about that. And I think that we, you know, we let two years pass without doing much about it. And we were called, we were called to account for that. So I think that, now that antisemitism has the attention of colleges and universities, we can't squander it. But instead, we really need to move forward and say, what is it that institutions need? Can I take one more second about data and statistics? When I read that report the first thing that I noted was that those numbers are almost precisely the same numbers that women on American colleges have experienced assault, sexual assault, 30% of women on college campuses have felt that they were assaulted in one way or another verbal and 20% feel like they were physically endangered. And so it's not a good thing, but it speaks to the scope of the problem. And in our little world, there really was a lot of attention placed on safety and security for female students, prevention sexual assault prevention, identification of the places where sexual assault was more prevalent, fraternities, alcohol as a as a fixture of that and I hope that we're going to have the same data driven conversations about antisemitism that we did about women's women's safety issues on our on our campuses. Manya Brachear Pashman: That is such an interesting observation. Sara Coodin: Just to latch on to that point, about data and about how, how. I mean, we too, were surprised by some of the returns this year. We knew it had been a tough year, but we didn't exactly know what students were going to report. We asked specific questions about specific aspects of their experience. But I think you know, one of the things that stands out about the data, for me is, is the framing that we had for students when we asked about their experiences, we asked about their subjective experience, something that's occasionally used to discount our data. Hey, you're asking about people's feelings, but actually, we want to know about the experience, the subjective experience. This is a key component of what the college experience actually amounts to for students going through it. And of course, we want a solid record of the number of incidents that students are exposed to, whether it's violence or, you know, whether it's coming through the form of words. There's a range of different options, but I think when you look at things like numbers of Jews on college campuses, you get a particular story about the presence of a fractionally tiny minority at elite institutions. Particularly, the numbers are fairly good, although they've dropped in the last number of years. But I think that that doesn't tell the full story. And I think you need that subjective aspect to find out how Jewish students are feeling in those roles in those institutions. And I kind of want to use this just as an opportunity to double down on the importance of that, the feeling that student have about their experience in college, which is an experience they've worked terribly hard to arrive at, and that they tend to take extraordinarily seriously once they've arrived it is It is unthinkable to allow that experience to continue to be shaped by antisemitism. It's flatly unacceptable. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Sara, Ted, thank you so much to you both for elaborating and explaining what this means, and I wish you both luck in carrying out the mission. Ted Mitchell: Thank you so much. Sara Coodin: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's special episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Holocaust Survivor Tova Friedman and Lisa Marlowe, director of the Holocaust Awareness Museum and Education Center outside Philadelphia – a conversation that was recorded live at the Weizmann National Museum of American Jewish History in Philadelphia. Be sure to listen.
Apr 23
Why TikTok is the Place to Talk about Antisemitism: With Holocaust Survivor Tova Friedman
Tova Friedman was just six years old when she walked out of Auschwitz. Now, 80 years later, Tova is devoted to speaking about her experiences as a child survivor of the Holocaust and being vocal about the threat of antisemitism. She knows how easily a society can transition from burning books to burning people, and she is determined to ensure that never happens again. Tova speaks to audiences worldwide–in person and on the social media platform TikTok, where she has amassed over half a million followers. Listen to Tova's harrowing, miraculous testimony of survival, as part of a live recording at the Weizmann National Museum of American Jewish History in Philadelphia, in partnership with AJC Philadelphia/Southern New Jersey. Lisa Marlowe, director of the Holocaust Awareness Museum and Education Center (HAMEC), joined us to discuss the museum's mission to bring Holocaust survivors to schools, the importance of teaching history through eyewitness accounts, and the significance of preserving stories of righteous individuals like her Danish great-grandmother, who saved thousands of Jews during WWII. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Photo credit: Christopher Brown Resources: - About Tova Friedman and TovaTok - Holocaust Awareness Museum and Education Center (HAMEC) - AJC Philadelphia/Southern New Jersey Listen – AJC Podcasts: - The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran - People of the Pod Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of Interview with Tova Friedman and Lise Marlowe: Manya Brachear Pashman: Yom HaShoah, Israel's Holocaust Remembrance Day, begins on the evening of April 23. To mark this remembrance, our broadcast this week features our recent live event at the Weitzman National Museum of American Jewish History in Philadelphia. There I had a conversation with Lise Marlowe, of the Holocaust Awareness Museum and Education Center in suburban Philadelphia and author and Holocaust survivor Tova Friedman. __ Thank you to all of you for being here today to participate in a live recording of People of the Pod, American Jewish Committee's weekly podcast about global affairs through a Jewish lens. I'm your host, Manya Brachear Pashman. Down here on this end is Lise Marlowe, our partner and organizer of this wonderful event. She is the program and Outreach Director of the Holocaust awareness Museum and Education Center, otherwise known as HAMC in Elkins Park, Pennsylvania, which is just outside here in Philadelphia. She is also a long time teacher who has come up with some quite innovative ways to teach Holocaust history to middle school students. But before we begin and get to all of that, I do want to turn to Lisa for a few minutes. If you could just tell us a little bit about HAMC. What is it? Because we are in a different museum venue now. Lise Marlowe: Thank you Manya, and thank you everyone for being here today. So HAMC is America's first Holocaust Museum, which started in 1961 by Holocaust survivor named Jacob Riz, who lost 83 family members to the Nazis. Our Museum's mission is to bring Holocaust survivors to schools and organizations. We believe it's important to give students the opportunity to learn history through an eyewitness. When we host a school program, we tell students that they are the last generation to meet a survivor, and once they hear a survivor's story, it becomes their story to tell. It also becomes their responsibility to speak up and stand up to the Holocaust deniers of the world and to say, I know you're lying because I met a survivor. It's not easy for our survivors to tell their story, but they want to honor the family they lost. And to make sure students know what happened so history hopefully doesn't repeat itself. Hearing about the rise of antisemitism, seeing hate towards other groups, can bring trauma to our survivors, but our survivors teach students that there are things we can do to stand up to hate. We can remember that words matter, kindness matters, that we can support and help each other when bad things happen. The Holocaust did not begin with concentration camps. It began with words. Our museum brings hundreds of programs all over the world, so please reach out to us at HAMC.org. Because we believe education is stronger than hate. We find that students are inspired by the messages our survivors tell them, which is to not hate others. Even though they lost everything. Their families, their property, their identity, their childhood, they teach students that hate can only destroy yourself. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much, Lise. I met some of Lise's former students who are here in the audience today. You have some really remarkable ways of teaching Holocaust history so that it sticks. I would like to get into that a little bit later. And you also have your own family story to share, and we'll learn more about that later, as she is one of our two guests on today's podcast. You see, there are three pieces to our podcast today, including the traditional format of a conversation with our guests, which will come later, and then your opportunity to ask questions. But to really comprehend what we discuss, you must first hear the powerful story that our guest of honor, the woman next to me, Tova Friedman, one of the youngest people to emerge from Auschwitz, the Nazi's concentration camp and extermination camp in occupied Poland. You must hear her story first. Tova has worked tirelessly to share her story in every format possible, to reach the widest audience. In addition to telling her story in person, at venues such as this, she worked with a journalist to produce an accurate and comprehensive memoir, and next month, a young adult version of that memoir will be released. She's worked with her grandson, Aaron, a student at Washington University, to share portions of her story on Tiktok on a channel called TovaTok , that has about 522,000 followers, and she is here today to reach our podcast listeners. And you. After her presentation, Tova will have a seat once again, and we'll continue the conversation. But right now, it is my honor to turn the mic over to Tova Friedman:. Tova Friedman: Thank you. I have no notes and I can't sit because I'm a walker. You know, I think better when I walk. I think better on my feet. Let me tell you, a few months ago, I was in Poland. I was invited as a speaker to the 80th commemoration of Auschwitz liberation. Five years ago, I was there also–75th. And there were 120 Holocaust survivors there with their families and their friends from Auschwitz. This time there were 17 [survivors], and we'll have no more commemoration. We're done. People, the lucky people, are dying from old age. You know, they're, or they're Florida, or they're gone, okay, they're not available. So what's scary is that many young people will not meet a survivor, and they will be told in colleges and high schools, probably it never happened. It's an exaggeration. You know, the Jews. They want everybody to be sorry for them. That will happen. And that's been happening here and there to my grandchildren. Right now, I've got eight grandchildren, but two are in colleges, and one is in Cornell. And I got the saddest phone call on Earth. To me it's sad. He got a beautiful Jewish star when we went to Israel. He called me to ask me if he should wear it inside, hidden, or if he should wear it outside. That's so symbolic. And I said to him, do you want to be a visible Jew, or do you want to be a hidden Jew? Do what you want. I will not criticize you. I know that life is changed from when I went to college. America is different, and I'm just so upset and unhappy that you, at age 18-19, have to go through that. One of my grandkids had to leave the dormitory because of the absolute terrible antisemitism. She is in McGill in Canada, and she has to live by herself in an apartment because even her Jewish friends stopped talking to her. So what kind of a world are we living in? Extraordinarily scary, as far as I'm concerned. That's why I talk. You can hear my voice. I talk as much as I can for a number of reasons. First, I talk in order for those people who were murdered, million and a half children, some of the faces I still remember, and a total 6 million Jews, they cannot be forgotten. They cannot be forgotten. This is such a wonderful place here that I hear you have classes and you have survivors talking to kids. You take them to schools. I think it's fabulous, but you got to do it fast, because there's just not many of us going to be here for a long time. So one thing is memory. The other reason I speak is a warning. I really feel that this world is again turning against us. We have been scapegoats all through history. Books have been written. Why? Why this? Why that? Why this? Why that? I can't figure out why. They're jealous, we feel with the chosen people. Oh, my God, it goes on and on. But why us? It started 2000 years ago. So I'm here to remember, so that all those people didn't just die and became ashes. But we're living in a world where we have to be aware. We have to be aware. You heard statistics that were scary. You know, I didn't even know some of the statistics. That Jews are stopping to use their Jewish last name when they make reservations somewhere? In America.? You know, I remember when I walked out from Auschwitz with my mother. My mother survived, and I'll take you back and just give me a certain amount of time. What happened? She said to me, remember I was exactly six and a half years old. And I do, I remember. And one of the reasons I remember is because my mother was a big talker. Talker just like I am. I inherited it from her. She would tell me everything. We were in all kinds of conditions. And I'd say, Mom, what is that? She says, Yeah, that's the smoke, people are being burned. She didn't say, you know, Oh, it's nothing. Don't worry about it. No, no, no, no. She talked and she talked as long as I was with her, until we were separated. That's why my memory is so sharp, and I always tell the younger generation: stop texting and start talking. Texting, you won't remember anything. It doesn't go into your brain. When somebody talks to you, you will never forget. When your mom or dad says things to you, you will remember them. If they text it to you, it lasts a few minutes and it's gone. So that's why I remember so much. My mother lost 150 people. She was the only survivor of Auschwitz. The only survivor, brothers, sisters, nieces, nephews, all gone, and she died very young. She died at 45. Her war never ended. Her Auschwitz, she brought with her to America because she just couldn't get over it. My father lost about all his brothers and sisters except two, and he was able to handle life a little bit better, but she wasn't. In my town, there were hundreds of Jewish children at the end of the war. There were five left. Five. I'm the youngest. That's why I'm still here talking. Two have died, and one is in her 90s, and she doesn't talk much anymore. So I feel like I'm representing an entire town that's gone, just gone. A town that had synagogues and they had football and they had a very vibrant town. Where my mother was a young woman. She was studying. My father was an actor, a singer, and a tailor, so he should have some money, but they were all functioning. It's all gone. When I went to visit, because I took my grandchildren so they can see, there was no sign the Jews even were there. It's like we disappeared. My memory of the war starts when I was four, not so much before. My parents lived in a very modern town. And because they left the shtetl, my mother wasn't interested in all the religious and the sheitles, and you know, the wigs people used to wear, which, by the way, my daughter now is wearing a wig, which is sort of strange, right? And they went to live a modern life. As soon as Kristallnacht came, he knew right away that this is not a place for him. And what do you do when you're scared? You go home, you go to your parents. So my mother and father, I was one year old, went back to their parents' home. What did they find there? That they were already in a ghetto. Now, I remember the ghetto at the age of four, there were lots and lots of people in a tiny apartment, no running water, no bathrooms, no food, no room. So I was under the table. All my memories were under the table. And I knew things that were going on. How did I know? Because I heard it. You know, a kid at four, four and a half, people make mistakes. The children don't know. Children know everything. They may not be able to verbalize it, but they know. And I knew what was the issue. I knew that they killed children and that I have to be under the table. I knew that. I knew that my grandparents are going to die soon. I heard it. I heard my father talking. I heard my mother talking. I heard the other people talking in the apartment in Yiddish. I still remember the words, oh, they name it. They're taking the elderly. They're taking this. Well, one day they came in, they took my grandmother, and they shot her, right outside our window, you know, took her outside. You know what's amazing when I think about this? Because I've tried to get some perspective. I've always tried to figure out, how did that happen? Why? How is it possible? Hitler was brilliant, and if he wasn't brilliant, he had brilliant people helping him. Idiots could not have done what he did. They were educated people. He had therapists. He had a nutritionist. And you know what they said, break up the family, and you will break up people. People die when their family is killed, they die sometimes physically, sometimes emotionally. Listen, I'm a grandmother. I have eight grandchildren. I know what it means to be a grandmother in my role, and I'm sure many of you feel the same way. So they took away the elderly. One day, my father comes in, and he says to my mother, I just put them on the truck. I know what he meant. I was exactly four and a half because I was standing by a table. I could tell my size. The table went up to my chin, and I knew that there were because the day before these people in their 20s and 30s, they were the strong guys. They dug graves for their own parents. We, the Jews, dug graves for our children and our parents. You know when the Nuremberg Trials came, some of the guys said, we didn't do anything. We never killed any…you know why? Because they used us to kill our own people. So that time, my father told my mother what was going on. He was sitting, his tears were coming down. And I could picture it, because, by the way, whatever I tell you, multiply by hundreds. This was a template, you know, like you have a template on a computer, you just fill in the name and everything is the same. You can fill in all kinds. You apply for a job. There is a special way. That's what happened. The Germans when they came to a town, they didn't have to think what happened. They had the piece of paper, kill the elderly, kill the children, as soon as possible. So I knew. I knew exactly what was going on. I knew that my grandparents were gone, my father's parents, my mother's mother was killed. Her my grandpa died before the war from some disease. He was very lucky. So here we are. One day. I had this uncle, James. He was a German Jew. He spoke a perfect German. So he thought, look at our minds. He thought, he speaks German. He's going to volunteer. He didn't have working papers, and he was scared to die. His wife, my aunt, she had working papers. So he went to the Gestapo, and he said, I'll be your translator. I speak a perfect German. I was born in German. And they shot him on the spot. So I remember he used to come and visit us. I sat on his lap one day. My father said, you won't go to see Uncle James anymore. He's not coming back. I didn't say anything. I know he was dead. I didn't know how he was dead. So the reason I'm telling you all the different things is because this happened in every other ghetto. We were living 16,000 Jews in 250 apartments, and we couldn't go in, and we couldn't get out, except certain people who had privileges. They had working papers, they had special papers. They could go out. That's how the smuggling started. Also, certain people could go out, bring some food, because we were starving. We were starving to such a point. You know why? Because the nutritionist, the PhD, the best nutritionist in Germany, told Hitler how much to feed us in order to die. You want them to die in two months? Give them that much bread. You want them to die in two weeks? Give them that. My town, which was called Tomaszow Mazowiecki, has no Jews anymore. I just wanted to mention the name because my family was there for 200 years, because the Poles in the beginning were very good to the Jews. They wanted the Jews because we were good business people. Every time the Jews were there, the place thrived. There were close to 100 tailor shops in town, all Jewish. So how could you go wrong? They brought business from everywhere. But now, of course, there isn't anybody. And slowly, all those people were sent to Treblinka. There were left about 50-60, people, my parents, I among them. There were very few kids left. And we were the cleanup squad. Not only did my father had to dig the graves, I don't think my mother did. My father, dig the graves, but afterwards you have to clean up. You can't leave a town so dirty because they wanted to leave no witnesses. Hitler had an order all the way from Berlin, no witnesses. That's another reason he killed the children. Kids can grow up and be a witness like me, and that was very dangerous for him. Because, you know, it's interesting from the psychological point of view, no matter what atrocities he and his people did, in the back of their mind, they were afraid of the consequences. They were afraid of consequences. That's why you leave no witnesses. But at that time, my father buried people and he said Kaddish. I didn't know what Kaddish was. I didn't know what being Jewish was. I don't remember any Jewish holidays. I knew that being Jewish means death, but I wasn't sure what that meant, Juden. What is this Juden business? But look at four and a half. I wasn't going to think about it. Anyhow, they moved the camp. We cleaned it up. We came to the next camp, and the next camp was the labor camp. Only work. We worked for more, not me, my parents did, and I want to tell you something about that. Slowly they did the same exact thing they did in every other camp. People were taken away. The moment you were sick, the moment you were tired, straight into some camp. One day, I heard, I heard– my mother told me, I didn't hear anything. She said they're taking the children, whoever, whatever, there were very few children left, maybe 20-30–we've got to hide you. And she hid me in like a crawl space, like they had these tiles or something. I don't know it was tile, something. And she put me in there, and she followed me, just the two of us, my father didn't get in there. And she put me on her lap, I remember. And she put her hands on my mouth. I shouldn't scream. I remember it was so tight that for weeks I had blue marks right here. And from the little window, I see where all my friends that I was playing with outside, because my parents were gone a whole day, I was outside with the other kids, put on trucks, but I knew where they were going. They were going to the place where the big graves were dug for them. So anyhow, when my mother said, we have to hide, we were there for maybe an hour or two. After it was all done, the kids were gone. We went up downstairs in a little room. She said, from now on, you can no longer be on the street. Okay, so I couldn't go out. I stayed in the dark room for a few weeks. It's another story, but one day I remember, and she came every day from work, she gave me food, and I slept with my parents. Because they were in the room with me. One day, she said, Oh, you don't have to go to the room anymore. I was delighted. I said, I don't have to? No, you can go outside. I haven't been outside for weeks, and I saw she was sort of packing, moving things. We had so few things. I said, What are you doing? She says, We're packing. We're going to Auschwitz. Again, they had, you know, cleaned up the ghetto. The place was called Starachowice. It was a Polish place. Had a town next to it even, and people who lived around, the non Jews, knew what was going on. They all knew, because there was always a town nearby. There was also a town near Auschwitz. Auschwitz, people lived a normal life there. So anyhow, I knew. I said, Auschwitz. We're going to Auschwitz, okay? I didn't care. I was so happy that I was outside. Within a very short time, we started walking. The train was waiting. My parents were separated. That's the first time. We were always together. My father was crying, and I remember I was little, so my mother picked me up, because I don't know if anybody of you either have been either to Auschwitz or to New York City. They have the cattle car by the museum, right outside, right. You saw the cattle car and it's that high, very hard to get on it. So she had to pick me up. She put me in and my father said, Be a good girl. I said, Yeah, I'll be a good girl. And he went to another cattle car. I was with my mother, and then a 36 hour drive began, no food, no no food and no drink, very hot, because they were all women. 150 women, and no bathrooms. And I remember, I said, Mom, I have to go. I have to go. She didn't answer me. And then I said to myself, Oh, I know everybody's going where they're standing. I think that that was a dividing line between being human and being inhuman. We're all dressed like normal kids. I had braids, you know, when we walked out, we were all covered with feces, because everybody was going everywhere. And many people had died, and I am outside standing watching all this going on, and my mother says to me, Get undressed. And I said, why? It was about July, August. It was summertime. Why? She said to me, they want to check if we're healthy. So I, very obedient, by the way, very, very. My mother taught me rules, and I'll tell you about the rules. So I took off my clothes, and she said, don't look at the eyes of the dogs. Don't look at anybody's eyes, because these the Germans came with their dogs. And When I was by myself, in the in the labor camp, she also taught me, because I was alone, never have eye contact. She said, eye contact will make you recognize and when you see a dog stand still, which is counterintuitive. I was frightened, terrified of the dogs more than of the Germans, but she said, the dogs will think that you're running away, and they are trained to kill when somebody's trying to run away. So in other words, she always trained me how to be self sufficient, how to recognize danger and what to do with it. So eye contact is pure danger, and running is pure danger. So I learned very, very easily how to do that. So when I'm there, I'm standing very still, the dogs are passing by. And then I say, what's the smell, it stinks here. I said, it stinks. She pointed to the crematorium. They were taking the burning bodies from the gas chamber, and it was all black, and you could smell it. And you know what? She didn't have to say anymore. I knew it. So I remember saying, Mom, how do I look? How do I look? And she said, Oh, you look good. I said, Am I healthy? She said, Yeah, you're very healthy. I said, what about you? Oh, I'm healthy too. She said. And somehow we made it. I tried to find out. I wrote a book together with a researcher. He tried to research. He lives in England. What happened that day? Every child under the age of 12 or 13 was taken straight to the crematorium. We're useless. Old people, pregnant people, sick people. What is old, 50 and over, because you can't work. Even in Auschwitz, you had to work. Even when you waited for your death, there was some job they gave you. So that you had to be healthy, at least. Anyhow, I don't really know. I was told that we arrived on a Sunday, and Sunday they were the Germans were Christians, so they didn't want to open another crematorium. They had four going. They didn't want the fifth. That's somehow how I and my mother survived. My whole transport, not just me. We were all, you know, a bunch of people. We went to another room. They shaved my head. I remember that very well, because they picked me up and I was, I was quite small, so they picked me up, put me on a bench, and the woman did my hair. And she herself, and I couldn't find my mother, and they gave me some clothes, because they've taken my clothes by the train. And then she found me, and then she took my hand, and we followed a whole bunch of people into Auschwitz proper. This was outside of Auschwitz before you were like, ready, and so you went inside. We got a middle bed, and then she started teaching me again. She said, you know, there'll be a lot of people here sleeping. More women, so when you're asleep, you can't move around so much, because then everybody else has to move. Okay. And I said, What about if I have to go to the bathroom? She says, No, you can't. That was a terrible thing for me as a child. I had to hold it, because they had it twice a day to the bathroom. And then she said, Look, you're going to get a cup. I didn't get it yet. We were going to be getting a cup, a tin cup, a spoon and a bowl. If tyou lose it, and if somebody steals it, you'll go hungry and you'll die. She said, they don't look at you. You take out the bowl. Somebody gives you something to eat. Nobody touched it, by the way. I was so aware of it. I just want to go a little fast forward, because I need your questions. I need to know what you want to know. And then one of the things I told you is bathroom for kids. It was hard for me to hold it. Well one day, we were all on line, and I really had to go. So I went in front of the line, and I was in such a hurry that I fell. The way the bathrooms were, I don't know if anybody's been to Auschwitz. The slabs of the boards. It was big, gigantic holes. The holes were like, maybe this size. My grandkids, who are, one of them is 6"2, got the privilege, because of me, to try out those bathrooms. He sat on it and he said, Grandma, I don't know how you didn't of course, you fell in. He said, It's too big for me. I fell inside. And of course, they got me out and they hosed me down, but I must have picked up some kind of a bug. There were rats there, there were feces up to here. And I got very sick, but I knew that sickness meant death, so I was very careful not to tell anybody, but that somebody saw me, and they said, this child, this child is ill. And they were so scared of illness, because illness meant death immediately. Because every morning they came, they picked up the dead, the sick, on one of those three wheel things. Wheelbarrow, wheelbarrow, to the crematorium. So I was afraid to be one of them. And then somebody said she's sick. She's going to infect all of us. They picked me up. I don't remember much about that, because I was really ill, and they took me to one of those places, a hospital, without doctors. When I woke up, I must have had fever, they told me no more. You can't go back to your mother. And that's when they took me to the children's place. For the first time, I saw so many children, I never knew they even existed, and they tattooed me. I remember. They said, Oh, your name is such and such. No, it's 27,633. And the woman said, Say it. Say it. I couldn't say it. I don't know what numbers were. Never went to school, but she was so kind. She taught me. She said it again. She said, just say the words, say the words. And I did it, and I learned. And she gave me a rag with cold water. She said, press it hard. Don't rub. It'll swell. I was there just about towards the end of the war. But one day, I got a package and it said, Happy sixth birthday. I'm six. I didn't know it. I said, Oh, my mother must be somewhere, and she's alive, because she gave me a package. It was a piece of bread, but I was going to save it until I'm dead. I imagine there's a little girl I'm going to be dying, dying, dying, like everybody is dying, but I won't, because I'll take that piece of bread and I'll eat it. I didn't know anything about bread getting stale. I know nothing about bread, so I remember keeping it here, just like that, because it was on a piece of string. In the middle of the night, rats came, ate up everything, tore my clothing, but they didn't touch me. Miracle. There were a number of miracles that, I should have been dead. All I can tell you is, within a few weeks, something weird was going on at Auschwitz. I did not know. Terrible noise, terrible shooting. Dogs were barking, and the person who was in charge of us, it was always a kapo, an adult woman, was gone. The door was open, but we didn't dare open the door. We heard the dogs outside, and shooting. We were frightened and we were hungry. There wasn't even the little bit that we got every day, even that wasn't there. And all of a sudden, the door opens, and my mother–I didn't know it was my mother–a woman comes in full of rags. She looks terrible. She looks around. Nobody's saying a word. She looks around, she looks around, she comes over to me, and she looks at me, and she bends down like on her knees a little bit. She says my name, and she says, You don't know me. I'm your mother. I thought to myself, my mother, she doesn't look like my mother. I only saw my mother six, seven months earlier, but she didn't look anything like it. She just looked just, I can't even describe it. But she convinced me and listen to what she said. She looked at me. She said, You look like you can survive. Look at me. Her feet were swollen, and she said, listen, we're going to try to hide. We will either survive together or die together. What do you think? I said, I want to be with you. I don't care what. She takes my hand and we snuck, we didn't even have to sneak out because the door was open, but the other kids refused to leave. We were all so frightened, but somehow we got out. She's walking. She's walking. Outside the dogs are barking. It's terrible. We're walking very close to the barracks, and she comes to a house, door. She walks. She must have had a plan. I didn't know that. And it's a hospital without doctors. All these people are screaming and crying and she goes from bed to bed. She touches everybody. I don't ask a question. And I'm wondering, why is she doing that? She found a corpse that she liked. It was a corpse of a young woman, maybe twenty, now I look back at it to me, she was an adult, in the 20s, nice, nice looking woman who must have just died because she was warm. So she could manipulate her body. I remember my mother took off my shoes, picked me up, and she said, Listen, don't breathe. I'm going to cover you up. No matter what you hear–because she knew I couldn't see anything–what you hear don't get uncovered. Try to breathe into the ground. She takes my face, she puts it towards the floor, and she manipulates my body, and she puts me very close to the corpse, and then she covers it up, and outside, you only see the head of the woman who died, and her hands, and her hands are holding like the blanket, so you can't see. All of a sudden, I can hear screaming and yelling. I don't move. I obey orders. And I can hear steps. I remember the steps, and somebody stopped, and I say to myself, Oh, I'm going to stop breathing. I stopped breathing. I was afraid that the blanket would move. Well, I just couldn't anymore. The person walked away, and then screaming and yelling went on, I didn't move. And all of a sudden I smelled smoke, and I said, How can I not get uncovered? In the beginning, I still breathed very shallow, but I couldn't. And I said, I'll have to get uncovered to get air. And then all of a sudden, my mother pulls the blanket off me and says in Yiddish, they're gone. The Germans are gone. And she must have hidden with another corpse. And when I sit up in the bed, all these people have been hiding with other corpses. And in order to get out, they were pushing the corpses off the beds, so the corpses were flying everywhere, you know, while the people who were hidden under the corpses. So she says to me, come. I couldn't find my shoes, so I walked without and she takes my hand, and we were all walking. It was January 25, 1945. Germans have all gone. Taken with them, 50,000 people. Other people were just dying everywhere, and the Russians had not come yet. The Russians came two days later. So we had two days inside the camp, without anybody, without the Germans. And we waited until they came, but there was electrified still. We couldn't get out. There was electricity everywhere. So we waited till the Russians came. And while we were standing by the barbed wires, I saw all these soldiers jump off trucks, and they were doing something with electricity. Then they could open the doors. And it was January 27 the liberation of Auschwitz, where children, whoever was left, was left. But many were in the process of dying, and you couldn't stop it. Hundreds and hundreds of people died while the Russians were there, because you couldn't stop whatever they had, you know. And I remember, the Russians said, show us your number. Some kids were standing there. There's a picture of it, and I'm standing in front showing my number. And I'm talking for all the kids who didn't make it to that day. So thank you for listening. Did I take too much time? I'm sorry. Manya Brachear Pashman: I don't think you can take too much time sharing that story. I know that there's so much more to share. So many miracles, Tova. Tova Friedman: Yes. Manya Brachear Pashman: You have spent most of your adult life sharing your story to advance Holocaust education, and I'm curious what was the catalyst for that? Did someone ask you to share your story? Tova Friedman: I tried to talk to people when I came to America. Because my teachers, I could read. I didn't go to school till I was 12. So I wanted to tell them why, but nobody heard me. Nobody cared. Nobody wanted to talk about it. But one day, when my oldest daughter was 15, she said to me, they're looking for a Holocaust survivor in school. Can you come to my class? That's how I started. Manya Brachear Pashman: And then your grandson, many years later, introduced you to this thing called Tiktok, right? Tova Friedman: I didn't know what Tiktok was because my daughter worked for a candy company called Tic Tac. You know the Tic Tac that you eat, the little white things that you have, like they make noise and stuff. So that's her company. Well, it's not her. She works for them. So I said to my son, what would a candy company be interested in the Holocaust? It's the same word. In fact, I still don't know the difference. Tik tok? Tic Tac? Manya Brachear Pashman: Tic Tacs. Tova Friedman: Tic Tac and TikTok? Manya Brachear Pashman: Yes. Right, that's what you're on, TikTok. Tova Friedman: A refugee is always a refugee. So he said to me, we had Shabbos dinner in his house, and he said, Can you give me two minutes? I said, Of course. He said, Just tell me something about yourself. Two minutes, because the people who are going to hear it have a two minute span. They can't listen to more than two minutes. I said, What should I say? Anything? Okay, my name and two minutes. Goes very quickly. And then all of a sudden, a half hour later, he said, people are interested. I said, what people? He said, on this. I said, on what? You have a phone in your hand. What are they, who? And that's how it started. He first explained to me the system, what it means, and he got questions. He said, Would you like to answer the questions? I said, Who's asking? You know, I mean, I'm not in the generation of social media. I don't even have Facebook. I don't know any of that stuff. So he explained to me, he taught me, and he's very good at it. He's a wonderful guy. He's now 20. He's at WashU. And he became the person who's going to try to keep it going. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, your presence on Tiktok is really this wonderful, really, very innovative way of reaching people, of reaching young people, Jewish and non-Jewish. Tova Friedman: Right. Manya Brachear Pashman: Lisa, you've come up with some unusual ways to reach young people. You were a middle school teacher until two years ago. Is that right? But you had this project where you had your students draw stick figures, and this was more than two decades ago when you started this. Can you tell us a little bit about the stick figures, which is like the polar opposite of Tiktok, but just as innovative? Lise Marlowe: So when I started teaching the Holocaust, and the first thing you say is 6 million Jews were murdered just for being Jewish, I realized the number did not shock students. I mean, it was sad, and they were empathetic, but the number 6 million…when we think about this generation and our sports heroes and our celebrities making millions of dollars, 6 million didn't sound like a big number. So at the time, I just had students take out a piece of paper and draw 20 stick figures across the paper. And to keep doing that for five minutes to see how many we could draw in five minutes. And my class, on the average, could draw, almost all of our elementary schools and middle schools in five minutes time, thousands of stick figures in five minutes time. And then the next day, when I went to my lesson, I'm teaching the Hitler's rise to power, one of my students stopped me and said, Wait, Mrs. Marlowe, aren't we going to draw stick figures? And I said, What do you mean? And she said, Well, I went home and I talked to my grandmother, and the other students were jealous that we're drawing stick figures. And I think if we get together, my church and all of our friends, we pull together, I think we can draw 6 million. Tova Friedman: Wow. Lise Marlowe: And I said, you want to do this? And she said, Yes, I want to do that. So it warms my heart that every year I had hundreds and hundreds of students drawing stick figures, mostly not Jewish students. We are in a very diverse community in Shawnee school district, one of the most diverse in the state, mostly students of color, and I had them handing me in 1000s of stick figures every week, it covered our whole entire gym floor. And when I retired, sadly, we did not get to all the children, because we know 1.5 million children were murdered. There was 1.6 million children to start with, and that means 94% of all the Jewish children were murdered in Europe, and we did not reach that milestone. And that shows that 6 million is a big number. And I have students like, you know, they're in their 30s and 40s now, who will always stop me on the street and say, did you get to 6 million. They always remember that's that project, and I have to, sadly tell them, we didn't even finish the children. Manya Brachear Pashman: Tova, I would say that teaching is your side gig, right? You certainly have done so much to advance education, but professionally, you're a therapist, and I'm curious if your experience, your lived experience, has informed how you communicate with your patients? Tova Friedman: I think it does. You know, to me, time has been always of essence. Time is the only thing we have. Money comes and goes. You look at the stock market. Tight now, it goes. Sometimes it goes up, sometimes it goes down. Time is the only thing. Once you lose it, it's done. So when I get a therapist, that's how I always thought, because timing to me, like, how many people just died that didn't have the time, like those 6 million people that you drew. And the children, how much they could have accomplished, had they had time, right? Time was taken from them. So when I get a client, the first thing I say, listen, we're not going to be here forever. We're not going to sit and talk about your parents and your grandparents. Five years from now, you'll be able to maybe. No, it's going to be time-limited, and it's going to be quick. And you have to accept my style, or there's so many people who love having you for 10 years. I need 10 weeks or less. That means that their goals, you accomplish them. I'm a little tough, and I say I'm not going to hold your hand, even if I could. I can't anymore because of COVID and because a lot of it is on Zoom. But even when I had them in my office, I said, I will not be a therapist who's going to sympathize, sympathize, sympathize. I'll sympathize for five minutes, then we're going to work. And a lot of people will say to me, Oh, that's exactly what I needed, somebody to really push me a little bit. I said, Yeah, but that's the way it's going to be. And others say, Wow, you're a mean person. I don't want to want to be here. I said, there are hundreds of other therapists. So yes, Holocaust has taught me, eat it fast, or somebody else will take it. I'm sorry, but also that's one thing. But let's talk about the good things. This is good too, but. My degree was in gerontology, because Hitler was, that's the most vulnerable in our society. You know, the elderly become alcoholics. Loneliness is among the elderly, financial issues. You know, loneliness is a killer. And I worked with the elderly to help them. I felt that's, that's the people that are sort of redundant. So that's where I worked with. I did it for years. And then I went to other age groups. I feel that my experience gives them courage. You know, come on, come on. Let's do it. Try it. Don't worry. What can happen? What can happen if you speak to your to your father or to your mother and you say this and this, what can happen? In my mind, I said–I don't tell them that, and don't say I said that–I said there are no gas chambers here. So just you know, in my mind, I said, the consequences are minor, so let's do it. And it works. Manya Brachear Pashman: And I wondered if it was the level, the level of trauma, pales in comparison to what you went through? Tova Friedman: No, no. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's what I was wondering. Tova Friedman: I feel that every trauma is different than, you know. You can't say, Well, my foot hurts, and it's so, big deal. So your foot hurts, my two feet hurt. No. Every pain deserves a healing, even if it's a little toe, it deserves it. And I take it very seriously. Most clients don't know about me, hopefully. I don't talk about anything personal. But I'm a little bit, you know, we don't have time on this earth. Let's make it as good as possible. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you, thank you for sharing that. Lisa, I want to ask about your family, about your great grandmother's efforts. She was not Jewish, but she saved thousands of Jews in Denmark, and I'm curious how that story was passed down in your family. Lise Marlowe: So I started learning the Holocaust at a very young age, because my grandfather was from Denmark, and he actually fought against the Nazis for the Danish Navy, and he would share with me how his mother rescued Jews in boats, in fishing boats, and take them to Sweden. And I never really heard that story before. And I was able to go to Denmark and go to Sweden and do more research. And I learned that she was actually the editor of Land of Folk newspaper, which was a major resistance newspaper. 23 million copies were given out secretly to make sure that people knew what was happening. But I was so proud, you know, being Jewish that my non-Jewish side of my family helped to rescue people, and I think it really helped me with the work that I do now, and standing up, and social justice, that's always been a passion of mine, and I think just her story inspired me to stand up for others. And they literally saved 99% of the population by getting them to Sweden. And it's really a truly heroic story that's not told that much. But the Danish people, if you ask them, they're very humble, and their attitude is, it's what people are supposed to do. So I'm just very proud of that Danish heritage. Tova Friedman: Do you think that their king or something has something to do with it? Leaders? Tell me about that? Lise Marlowe: It's a myth, right, that King Christian wore a Jewish star. He did say, if the Nazis require our Danish Jewish people to wear the star, I will wear it with the highest dignity. Along with my family. And Danish people didn't treat the Jews as the other. They considered them their friends and their neighbors, and that's why they did what they did. Tova Friedman: Wonderful. Lise Marlowe: They didn't see them as the other, which is such an incredible lesson to teach students. Tova Friedman: Yes, yeah. Manya Brachear Pashman: Preserving these stories is so important, your experiences. Have you witnessed as lasting an effort to preserve the stories and pass down the stories of the righteous among us, like your great grandmother. And I ask you both this question, is it as important? Tova Friedman: I think it's, you know, Israel, there is this wonderful, in Yad Vashem, the big museum, there's a whole avenue of the righteous. You know, I ask myself, what would I do if my family would be in danger in order to save somebody else, and the answer is, I don't know. But I am so utterly amazed that people do that. And there are many–well, not enough–but this is very impressive, your story, and I would love to learn. I don't know the answer, what separates one person from the other, that one is selfless and looks at humanity and one only at their own families? I wish some studies would be done and so forth. Because we have to do something right now. We are now considered the others. You know, we are, in this world, all over Europe, except, ironically, not in Germany. I was in Germany, and I spoke to German kids, high school kids in German. I didn't know I knew German. I just got up and I saw they were trying so hard to understand. I had an interpreter, and I didn't understand the interpreter. And I said, Let me try. Let me try. I speak Yiddish fluently and German a little bit like that. Also, I lived three years in Germany, so I didn't speak it, but it must have come into my head. And do you know what they did after my speech? 250 kids? They came over. They apologized. I mean, they're a generation separated. I went to Dachau, where my father was, and there were two women whose parents or grandparents were Nazis, and they said to me, we're dedicating our entire life to preserve this Dachau andcamp and and they they have, they give talks and Everything, because my family killed your family, but they admit it. So right now, Germany has laws against it. But what about the rest of the world? What's happening in America? So I would love to know how the Danish did that. It's a wonderful story. It makes your heart feel good, you know. Thank you for the story. Lise Marlowe: I would just add, the survivors we have today were the children who survived, right? Most of the adults are gone. And they were the hidden children. And most of them were hidden by non-Jewish people. Actually, all of them were. The Catholic Church, a farm lady, you know, who said, she took kindness on them. So you know, the hidden children were mostly hidden by non-Jewish people in terms of the righteous of the nations. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you both so much for your insights. This has been a really illuminating conversation. If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Advisor Jason Isaacson, about legacy of the 2015 Iran Nuclear Deal, the U.S. withdrawal from that deal in 2018, and Iran's dangerous stockpiling of uranium that's getting them closer to nuclear weapons capabilities. You can also listen to our latest episode about the impact of Pope Francis on Jewish-Catholic relations. From April 27-29, 2025, we will be at AJC Global Forum in New York City. Join American Jewish Committee (AJC) and over 2,000 committed activists at the premier global Jewish advocacy conference of the year. After the horrific attack on October 7, 2023, and in this fraught moment for the global Jewish community, escalating threats worldwide underscore the importance of our mission. All who care about the fate of the Jewish people, Israel, and the values of the civilized world must respond now with action, urgency, and resolve. If ever there was a time to stand up and be counted, that time is now. Your voice is needed now more than ever. If you won't be with us in person, you can tune into the webcast at AJC.org/GlobalForum2025 .
Apr 22
What Is Pope Francis' Legacy With the Jewish Community?
Rabbi Noam Marans, AJC's Director of Interreligious Affairs, reflects on Pope Francis' legacy—from his deep ties with Argentina's Jewish community to his historic visit to Israel and strong stance against antisemitism. He also addresses recent tensions over the Pope's comments on the Israel-Hamas War and highlights the ongoing collaboration between AJC and the U.S. Conference of Catholic Bishops in combating hate and building interfaith understanding. ___ Resources: The Francis I Knew: A Warrior Against Antisemitism, a Sometimes Impolitic Critic of Israel Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran People of the Pod : Latest Episodes: Inside the New U.S.-Iran Nuclear Talks: What's at Stake? This Often Forgotten 1929 Massacre is Key to Understanding the Current Israel-Palestinian Conflict Related Episodes: The Next Chapter in Catholic-Jewish Relations What We Can All Learn from Rabbi Heschel on Confronting Injustice Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify.
Apr 11
Inside the New U.S.-Iran Nuclear Talks: What's at Stake?
As new negotiations begin to tackle Iran's nuclear program, missile development, and support for terror proxies, tensions are escalating. Jason Isaacson, AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer, joins us to unpack the legacy of the 2015 Iran nuclear deal (JCPOA) and withdrawal in 2018, and Iran's dangerous stockpiling of uranium, getting them closer to nuclear weapons capabilities. With U.S. Special Envoy Steve Witkoff leading talks and key UN sanctions expiring soon, the stakes are higher than ever. Don't miss Jason's insights on what the U.S. is demanding, the potential for successful diplomacy, and the global risks posed by Iran. ___ Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran Social media influencer Hen Mazzig on leaving Tunisia Chef Einat Admony on leaving Iran Playwright Oren Safdie on leaving Syria Cartoonist Carol Isaacs on leaving Iraq Novelist Andre Aciman on leaving Egypt People of the Pod : Latest Episode: This Often Forgotten 1929 Massacre is Key to Understanding the Current Israel-Palestinian Conflict Higher Education in Turmoil: Balancing Academic Freedom and the Fight Against Antisemitism Held Hostage in Gaza: A Mother's Fight for Freedom and Justice Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of Interview with Jason Isaacson: Manya Brachear Pashman: Negotiations begin on Saturday to curtail Iran's nuclear fuel enrichment, infrastructure, missile program and support of Hezbollah Hamas and other terror proxies around the world. US Special envoy to the Middle East, Steve Witkoff, will shepherd the talks. At the same time he's handling discussions around Gaza and Ukraine with us to discuss the potential of these negotiations and their impact is AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer, Jason Isaacson. Jason, welcome back to People of the Pod. Jason Isaacson: Thanks, Manya. It's good to be back. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Jason, the Obama administration sealed the deal in 2015 to curtail Iran's nuclear program, which President Trump then withdrew from in 2018. What did that original deal look like? Jason Isaacson: Of course, the United States pulled out of the deal in 2018 as you said, whereupon, after a period of reflection and some uncertainty, the Iranians started violating the agreement. The original agreement that was called the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action allowed the Iranians to enrich their uranium up to 3.67% purity of uranium. You need something like 90% in order to make a bomb. They were allowed to keep just 300 kilograms of that enriched uranium. The rest of their stockpile of uranium had to be shipped out of the country, which it was. There were other restrictions that were imposed on Iran. They had to disable a plutonium facility that also was a possible avenue toward a nuclear device. They had to allow intrusive inspections, not as intrusive as some had hoped, and they had to limit the degree of sophistication of their centrifuges. They had a very robust centrifuge production capacity, which had to be limited. They had to disable certain centrifuges that they already had, and they couldn't advance them further. There were a number of these other restrictions that were imposed in the return for which the Iranians were going to have sanctions removed, sanctions that had held back their economic growth, limited the degree to which they could ship their oil and gas to vendors, to customers around the world. It was a good trade for the Iranians, but from our perspective, it lacked certain things. It certainly lacked objectives that the administration, at that time, the Obama administration, we thought, had been pursuing, which was not only to limit the ability of the Iranians to produce a nuclear weapon, but to affect other aspects of Iranian behavior, their missile program, their advanced ballistic missile program, their support for proxies that endangered stability and security across the region and beyond. Those issues ended up getting dropped in the nuclear negotiations. They were just focused on nuclear program, which was a reason why AJC opposed the deal when it was announced in 2015 and why Donald Trump campaigning for president and then after he became president, after giving it a run to try to find a way to perhaps induce European partners to go back to the negotiating table and impose additional restrictions on the Iranians, including covering the missile program, lengthening the amount of time that would be held in check the nuclear program of Iran for maybe not just 15 years, but 20 or 30 or 40 or 50 years. Those efforts were ultimately abandoned. Was impossible to reach an agreement between the United States and the European allies, and so in 2018 the president pulled out. Manya Brachear Pashman: So besides the man in charge, what has changed in the last decade since that time? Jason Isaacson: Iran has serially and outrageously violated the terms that were agreed to 2015 they were initially allowed, as I said, to have 300 kilograms of low enriched uranium. They now have 8200 kilograms plus, according to the IAEA, the International Atomic Energy Agency, and some of that is enriched up to a level of 60% which is really, frankly, just below the level needed for a nuclear device. So they're way out of alignment, way out of the agreement that they had reached in 2015 now, of course, in addition to that, the Iranian economy has suffered a decade of sanctions, high inflation, high unemployment, rolling. Blackouts in major cities, the brain drain. Smart Iranians realizing there's no economic future in their country and have left and of course, over the last year and a half, after the Hamas attacked on Israel of October 7, 2023 Iran, a supporter of Hamas, a funder and supplier of Hamas, after a few months, it posed its own attacks, fired missiles and drones at Israel in support of Hamas' activities and also in support of Hezbollah, the other Iranian proxy on Israel's northern border. So twice in the last year and a half, we've had attacks by Iran against Israel, which Israel responded to, and significantly weakened terrorists in Lebanon, Hezbollah. And of course, the Hamas, they decapitated Hezbollah, and they also struck back at Iran, after Iran fired missiles and drones that had mostly been intercepted by Israel's air defenses in cooperation with the United States, and frankly, some Arab partners and also France and the UK. Manya Brachear Pashman: So does Iran have as much leverage as it had in 2015? Jason Isaacson: It must be said that Iran is weakened. It's weakened economically, it's weakened militarily, its air defenses have been exposed and significantly damaged, and it has seen that its attempts to strike at Israel are deflected. By a combination of us and and especially Israeli forces, and also with the support of some regional allies and European allies as well. So Iran goes into this negotiation with the Trump administration in a poorer position to make its demands heard and enforced, except for the fact that Iran is proud and it has shown under enormous economic duress, they have continued to advance their nuclear program. They clearly believe that this is part of their right and necessity if they are going to provide some kind of a defense for themselves against what they see as a US led us in cooperation, in partnership with Israel, led effort to weaken them and drive them away from their power in the Gulf, to limit their ability to exert influence across the region. So they may be in a poorer position. Whether that will be evident in the negotiating table is another question. Manya Brachear Pashman: President Trump criticized the Obama administration for not walking away when Iran didn't meet America's demands. Do you see this negotiation unfolding quite differently than that one did? Jason Isaacson: Well, there are a couple of factors here. One the Iranians are famous negotiators, famous for being exacting and excruciating and insistent on certain points in the texts that they discuss. They have their own interpretations for texts. This was an issue in the past. And the pain that is exerted on their counterparts in negotiations, I have heard people talk about, both from the Gulf and from US officials, how difficult it is to actually have the negotiation with the Iranians. They will insist on going again and again and again through every codicil, every agreement, every annex, to a point that will sort of drive people up a wall until they, according to, I think the Iranians calculation, give up and say, Okay, fine, we'll concede you on that point. I'm concerned that they are so practiced at this negotiating style, which I suppose you have to say they've been practicing for thousands of years. I am not sure that in this kind of rushed effort to move into negotiations with, frankly, a very capable negotiator in Steve Witkoff, who certainly has the trust of the President. And he was successful in helping move forward hostage negotiations very early on. In fact, frankly, the day before the inauguration of President Trump, Steve Witkoff was instrumental in advancing that cease fire and hostage release deal. But there's a lot on Steve Witkoff's shoulders. He's also involved in the Ukraine, Russia negotiations. He is not and I'm sure he would say this himself, an expert on the Iranian nuclear file and all the details of the nuclear enrichment and the capabilities of the Iranians to deceive their negotiators. So I am hopeful that we will have something to celebrate after these negotiations get off the ground. But I think it's also fair to say that it's with some trepidation that we look ahead to the possibility of sitting down with practiced negotiators who have been doing this for decades. Manya Brachear Pashman: Is there a sense of urgency here? How long do you anticipate these negotiations taking? Jason Isaacson: Frankly, the negotiation over the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action took something like two years. We had a preliminary agreement in 2014 the final agreement in 2015 then the Biden administration, after the Trump administration, pulled out of the deal. When the Biden administration came in, in 2021 there was an effort for about two years to go back to the negotiating table with the Iranians. Very complicated, very difficult. Ultimately unsuccessful. It is not easy to negotiate with these guys. I'm hopeful that this administration have taken lessons from the experience of the past. Have experts around them who know the Iranian file, who have actually sat across the table from Iranians and can work with them to a successful conclusion. The other issue that must be put on the table here is that come October, one key point of leverage in this entire process, the ability to snap back the United Nations sanctions that were put in place years ago and that were then suspended when the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action took effect, with the support of the United Nations. The ability to snap back those very heavy UN sanctions, which don't only apply to oil, energy sector applies to transportation and banking and other aspects of Iranian behavior, would really be crippling sanctions. The ability to snap those back, put those back in place, will expire on October 18 of this year, which means that we have just a few months to come up with some kind of agreement with Iran that is better than what we had in 2015. If we don't, all bets off. Then we're back to a place where we have lost the ability to have the entire international community, all UN member states, comply with a renewed set of sanctions. And then it'll be a whole process of trying to get other countries on board. If we're going to try to exert maximum pressure, really maximum pressure. That means not just us pressure, but maximum pressure applied by the international community at large. We're going to lose that if we don't reach some kind of an agreement or snap back before October 18. So the clock is ticking. The pressure is on. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, certainly the scope of what the Trump administration is pursuing with Iran is much broader. The Obama era agreement, for example, limited Iran's stockpiles of nuclear material. The Trump administration wants to take it all apart, completely dismantle the country's nuclear infrastructure, dismantle its missile program, its longtime support for Hamas and Hezbollah. Certainly, that's what everyone wants. But is it realistic? Jason Isaacson: What we've heard from President Trump and from Mike Waltz, the national security adviser and Secretary Rubio others who have commented on this in recent days, they are insisting that the Iranians dismantle, fully dismantle, in the words of the National Security Advisor, their ability to enrich uranium to have the stockpile necessary for an eventual nuclear bomb. You know, countries can have a nuclear program, but they don't have to enrich their own uranium. They can buy uranium for their nuclear reactors, for energy purposes and research and medical purposes. The Iranians want the full nuclear cycle. They basically got that in the negotiations a decade ago. This administration clearly wants to remove that ability for the Iranians. That's going to be a very hard thing to sell to the Iranians. And in addition to that, the administration has made it clear that preventing the Iranians from advancing a military nuclear program is just one of their objectives. It's a main objective, but the other objectives are eliminating their ability to advance their ballistic missile program, which was really designed for the sole purpose of being able to carry a nuclear warhead to Europe, to the United States, to Israel, other neighbors, other enemies of the Iranians. And then also, very clearly that this administration wants to negotiate an end to Iranian support for its proxy network, for the militias in Iraq and Syria. Used to be in Syria for Hezbollah, for Hamas, for other terrorist groups. That's a very tall order. You're basically saying, Iran, get down on your knees and give up all of the weapons that you have assiduously assembled over the last decades to protect yourself against the depredations of the horrible West and of your longtime neighbors who have maybe some designs on your territory, you might think. And they're not going to do that. So it's going to be very difficult. We have sanctions, we have influence, we have pressure that we can put on the Iranians, and there are two aircraft carrier battle groups that are stationed not very far away that will exert military pressure on the Iranians. So very complicated negotiations, a lot of assets, a lot of equities at play here, I wish the administration well. It will be a very difficult road to get the Iranians to see ground on all of these points. Manya Brachear Pashman: It is hard to believe that a hostile country, especially, that supports terrorism around the world, would agree to become essentially defenseless. But there is a history of it, right? I mean, in the early aughts, Libya, they agreed to dismantle their nuclear program under the Bush administration in 2003. Could something similar happen here? Or does the United States just not have that same leverage? Jason Isaacson: Look, we've heard the reference to Libya. In fact, it was made by the administration just in recent days as well. And yes, it's true that in 2003 the Libyans did relinquish their nuclear weapons program. There were, I think, 10 sites across Libya that international inspectors were allowed to visit. And dismantle the program that had been going on for a number of years. But then, of course, we all know, eight years later, Muammar Gaddafi was toppled, was overthrown and hunted down and later killed. Another example in 1994 is the Budapest Memorandum in which Ukraine and Belarus and Kazakhstan gave up their nuclear weapons that were part of the arsenals that have been kept there by the former Soviet Union. Relinquished those weapons, those warheads were sent back to Russia. It was a very complicated negotiation. The United States and the United Kingdom and Russia all agreed at that time, 1994, that they would never attack Ukraine and Belarus and Kazakhstan. They would not use military force, they would not use economic coercion unless an act of self defense. But the agreement very controversial in Ukraine at the time, to give up what had been the world's third largest nuclear stockpile was relying on these assurances from the West that they would not be attacked if they gave up their nuclear deterrent and turned it back to now, what was Russia, which is the seat of power of the Soviet Union. Two decades later, Russia comes along and annexes Crimea and attacks in the Donbas region of eastern Ukraine. And now, of course, you know, here we are a decade after that, where Russia is seizing a significant portion of Ukrainian territory and killing 1000s of Ukrainians. So the lesson, yes, is that you can negotiate away a nuclear program. But the other lesson that follows from that is, yes, you can negotiate it away, and you can find yourself facing terrible dangers, having lost that deterrent capacity. Manya Brachear Pashman: Okay, so the US did previously hammer out a deal in 2015. Are there any details of that deal that are worth bringing back to the table, or is the Trump administration starting from scratch? Jason Isaacson: Well, look, if they're able to, in these negotiations, come to an agreement on the dismantling, really the destruction, of the capacity of the Iranians to with any centrifuges advanced or otherwise, to enrich uranium, to create a stockpile from which they could later secretly advance a military nuclear program. If that's what we agree to, there have to be very comprehensive and intrusive and unannounced inspections by the IAEA, perhaps by other national agencies as well. If the Iranians could agree to that the United States overseeing the destruction of these facilities, that would pick up on sort of the inspection aspect of the 2015 agreement. And go, of course, significantly farther. If they're able to provide other assurances on other research facilities that the Iranians have, making sure that any research is unearthed, is exposed, is destroyed, ceases to present the possibility that the Iranians could actually advance the military nuclear program if all those steps could be put in place, which again, would be taking what happened in 2015 and JCPOA, and just magnifying it, intensifying it way beyond what was possible to negotiate at that time, according to those who tried very hard to negotiate a stronger agreement, but we're left with what they actually were able to accomplish in 2015. Let's hope that's possible. I don't know if it will be possible. But there would be, of course, in any agreement going forward, there would be certain elements that are related to and are outgrowths of and are really expansions on what happened in the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, except that this administration has set a very high bar, and there will be many critics in the United States and Congress, around the world, in Israel but elsewhere in the region, if the administration rushes to a deal that falls short of its very ambitious expectations. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned Israel, if President Trump follows through on his threats of military strikes on Iran, if negotiations don't go as he has planned, could that put Israel at more risk than it already is. Jason Isaacson: It could. I think there is really no one in the region who wants a war, as everyone knows, as everyone has seen in successive military conflicts, the outcome of war is unpredictable, usually worse than what is expected. I think Israel does not want a war, but Israel cannot live with an Iranian nuclear threat, and if there is not the possibility of negotiating away this nuclear threat, I think that everyone would understand that a small country that has already been attacked twice in the last year by Iran, which had demonstrated its intention to strangle and destroy Israel again and again, and says it at every opportunity that it gets, everyone would understand if Israel had to take certain action, and if Israel and the United States were to act together. Are providing a greater chance of success, I think that would be understandable and, frankly, laudable. The best possible option is a negotiation in which the Iranian nuclear program is forever put out of business. Let's hope we can get to that. Let's hope that the Trump administration is successful in these efforts. Manya Brachear Pashman: And also, speaking of Israel, how much did or should Israel be contributing to these negotiations? Jason Isaacson: Well, let's hope that, unlike in 2014 2015 when the United States negotiated with Iran, alongwith France and Germany and Great Britain and the European Union and Russia and China. Let's hope that the neighbors of Iran, those who were most affected by Iranian threats, are involved in this process in a much more serious way. There was a great deal of complaining in the Gulf, in Israel, justifiably, in 2015 that the JCPOA, which really was designed to make the region safer. And of course, American security interests of being advanced took place in the absence of real input on the part of those who would be most affected. And let's hope that this goes in a very different direction. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, not just Israel, but all of their neighbors in the Gulf. Jason Isaacson: Not just Israel, but the neighbors in the GCC who themselves have been attacked from time to time by Iran and by Iran's proxies, the Houthis, which I did not mention before, of course, in Yemen, have attacked their neighbors on the Arabian Peninsula. Saudi Aramco was attacked by Iranian missiles a number of years ago. Ships on their way to and from the UAE have been attacked. So they all have an interest in limiting the ability of Iran to project force and to threaten the region, particularly with the nuclear capability. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jason, thank you so much for your time and expertise on this matter. I suspect we will be talking again soon as this develops. Jason Isaacson: I look forward to it, Manya, thank you very much. Manya Brachear Pashman: Be sure to tune in for my conversation with journalist Yardena Schwartz about her first book, Ghosts of a Holy War , the 1929 Massacre in Palestine that ignited the Arab Israeli conflict. Yardena shared how history repeated itself on October 7, 2023 and why understanding the past is essential to making sense of the present. From April 27 to 29th we will be at AJC Global Forum in New York City, join American Jewish Committee and over 2000 committed activists at the premier global Jewish advocacy conference of the year after the horrific attack on October 7, 2023 and in this fraught moment for the global Jewish community, escalating threats worldwide underscore the importance of our mission. All who care about the fate of the Jewish people Israel and the values of the civilized world must respond now with action, urgency and resolve. If ever there was a time to stand up and be counted, that time is now. Your voice is needed now more than ever. If you won't be with us in person, you can tune in to the webcast at AJC.org/GlobalForum2025.
Apr 3
This Often Forgotten 1929 Massacre is Key to Understanding the Current Israel-Palestinian Conflict
On October 7, 2023, Hamas launched the deadliest attack on Jews since the Holocaust, calling it Operation Al Aqsa. For journalist Yardena Schwartz, the massacre was a chilling echo of the 1929 Hebron Massacre—the brutal slaughter of nearly 70 Jews, incited by propaganda that Jews sought to seize the Al Aqsa Mosque. At the time, she was deep into writing her first book, Ghosts of a Holy War: The 1929 Massacre in Palestine That Ignited the Arab-Israeli Conflict. In this episode, Yardena shares how history repeated itself, how the October 7 attack reshaped her book, and why understanding the past is essential to making sense of the present. ___ Read: Ghosts of a Holy War: The 1929 Massacre in Palestine That Ignited the Arab Israeli Conflict Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus: Untold stories of Jews who left or were driven from Arab nations and Iran Social media influencer Hen Mazzig on leaving Tunisia Chef Einat Admony on leaving Iran Playwright Oren Safdie on leaving Syria Cartoonist Carol Isaacs on leaving Iraq Novelist Andre Aciman on leaving Egypt People of the Pod : Latest Episode: Higher Education in Turmoil: Balancing Academic Freedom and the Fight Against Antisemitism Held Hostage in Gaza: A Mother's Fight for Freedom and Justice Yossi Klein Halevi on the Convergence of Politics and Religion at Jerusalem's Temple Mount Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Interview with Yardena Schwartz: Manya Brachear Pashman: Hello, and welcome to People of the Pod, brought to you by American Jewish Committee. Each week, we take you beyond the headlines to help you understand what they all mean for America, Israel and the Jewish people. I'm your host Manya Brachear Pashman:. In October 2023 journalist Yardena Schwartz was in the middle of writing her first book exploring the rarely talked about 1929 Hebron massacre, in which nearly 70 Jews were murdered, dozens more injured by their Muslim neighbors during riots incited by the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem, who spread lies that Jews wanted to take over the Al Aqsa Mosque. When she heard reports of the October 7 terror attacks by Hamas dubbed Operation Al Aqsa, she realized just how relevant and prescient her book would be, and began drafting some new chapters. Yardena is with us now to discuss that book titled Ghosts of a Holy War: The 1929 Massacre in Palestine that ignited the Arab Israeli conflict. Yardena, welcome to People of the Pod. Yardena Schwartz: Great to be here, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: So full disclosure to you and our audience. You attended Columbia Journalism School 10 years after I did, and you took Professor Ari Goldman's class on covering religions 10 years after I did that, class had always traveled to Israel, and I had hoped it would be my ticket to go to Israel for the first time, but the Second Intifada prevented that, and we went to Russia and Ukraine. Instead, your class did go to Israel, and that was your first visit to Hebron, correct? Yardena Schwartz: So it was in 2011 and we went to Hebron for one day out of our 10 day trip to Israel, and it was my first time there. I was the only Jewish student in our class. It was about 15 of us, and I was the only one who had been to Israel. I had been all over Israel, but I had never been to Chevron. And our tour was with Breaking the Silence, an organization of former Israeli soldiers who had served in Hebron or in other parts of the West Bank and wanted Israelis to know what was happening in Hebron and how Palestinians were living there, and the various restrictions that were put in place as a result of terrorist attacks. But nevertheless, you know, those restrictions were extremely disturbing, and that brief visit in 2011 made me really never want to go back to Hebron. And when I moved to Israel two years later to become a freelance journalist there, and, you know, to move to Israel because I loved Israel, and still obviously love Israel, I didn't really go back to Chevron because I, you know, was really troubled by what I saw there. But this book took me, of course, back to Chevron hundreds of times, spending hundreds of hours there. And it came to be, you know, my expertise in this conflict, in my reporting. And you know, of course, Heron is kind of the main character in this book, Manya Brachear Pashman: Tell us how you came to find out about this massacre. Was it mentioned during that class visit in 2011 or was it later that you learned about it? Yardena Schwartz: So that was one of the most interesting things about my early adventure into writing this book, was that I had of course been to have Ron, and yet, during that day that we spent there learning so much about the history of this place, this deeply holy place to so many people, there was no mention of the massacre of 1929, so, you know, I knew that Chevron is, you know, the second holiest city in Judaism, the burial place of Abraham And the matrix and patriarchs of the Jewish people. And you know the first place where King David established his kingdom before Jerusalem. So it was holy before Jerusalem. And yet I had no idea that this ancient Jewish community in Hebron had been decimated in 1929 in one of the worst pogroms ever perpetrated. We all know about the kishineff pogrom of 1904 and yet the pogrom in 1929 in Hebron, perpetrated by the Muslim residents of Hebron, against their Jewish neighbors, was more deadly and more gruesome than the kishineff pogrom, and it effectively ended 1000s of years of Jewish presence in this holy city. And so when I was told by my mentor, Yossi Klein Halevi, the amazing writer, that there was a family in Memphis, Tennessee that had discovered a box of letters in their attic written by a young American man from. Memphis, who had traveled to Chevron in 1928 to study at the Hebron yeshiva, which was at the time, the most prestigious yeshiva in the land of Israel in what was then, of course, British Mandate Palestine. And that this young man had been killed in that massacre. Yet his letters, you know, painted this vivid portrait of what Chevron was before the massacre that took his life. I was immediately fascinated. And I, you know, wanted to meet this family, read these letters and see how I could bring the story to life. And I was introduced to them by, yes, in 2019 so that's when I began working on my book. And you know, as you mentioned, I was still writing the book in 2023 on October 7, and this book I had been writing about this massacre nearly a century ago immediately became more relevant than I ever hoped it would be. Manya Brachear Pashman: The young American man from Memphis. His name was David Schoenberg. Give our listeners a history lesson. Tell us about this 1929 massacre. So Yardena Schwartz: On August 24 1929 also a Shabbat morning in crevorone, every Jewish family had locked their doors and windows. They were cowering in fear as 1000s of Muslim men rioted outside their homes, throwing rocks at their windows, breaking down their doors and essentially hunting down Jews, much like they did on October 7, families were slaughtered. Women and teenage girls were raped by their neighbors in front of their family members. Infants were murdered in their mother's arms. Children watched as their parents were butchered by their neighbors, rabbis, yeshiva students were castrated and Arabic speaking Jews, you know, Sephardi, Mizrahi, Jews, who composed about half of the Jewish population in Hebron at the time, and were very friendly with their Arab neighbors. You know, they went to each other's weddings and holidays, went to each other's shops, and these people were also slaughtered. It wasn't just the yeshiva students who had come from Europe or from America to study there, or, you know, the Ashkenazi Jewish families. It was, you know, Arabic speaking Jews whose families had been there for generations and had lived side by side in peace with their Muslim neighbors for centuries. They too were slaughtered. Manya Brachear Pashman: Why did their Muslim neighbors turn on them so suddenly and violently? The Yardena Schwartz: rioters that day were shouting Allahu Akbar. They claimed to be defending Islam and Al Aqsa from this supposed Jewish plot to destroy Al Aqsa in order to rebuild the Third Temple. This is what they had been told by their leaders and by Imams and their mosques and in Hebron, that Lai had also extended to the tomb of the patriarchs and matriarchs, which is known in Arabic as the Ibrahimi mosque. Imams there had told Muslims in Hebron that the Jews of Hebron were planning to conquer Ibrahimi mosque in order to turn it into a synagogue. So this incitement and this disinformation that continues to drive the conflict today. Really began in 1929 the rumors about this supposed Jewish plot to destroy Al Aqsa that began in 1928 around the same time that David Schoenberg arrived in Palestine to study at the yeshiva. Manya Brachear Pashman: So in addition to the letters that David Schoenberg wrote to his family back in Tennessee. How else did you piece together this history? How did you go about reporting and researching it? Who kept records? Yardena Schwartz: So it's really interesting, because I was so surprised by the lack of literature on this really dramatic moment in history, in the history of Israel, the history of this conflict. And yet, despite the fact there are really no books in English, at least, about the massacre and about these riots and what led to them, there were mountains of, you know, testimony from victims and survivors. The British carried out this commission after the riots that produced this 400 page report filled with testimony of British officials, Arab officials, Jewish officials, survivors. So there was just so much material to work with. Also, survivors ended up writing books about their experiences in Hebron, very similar to David's letters, in a way, because they wrote not only about the riots and the massacre itself, but also what they experienced in Hebron before they too, wrote about, you know, the relatively peaceful relations between the city's Jewish minority and the Arab majority. And I also relied on archival newspaper reports so the. Riots really occupied the front pages of American newspapers for about a week, because it took about a week for the British to quell the riots, and they did so with an air, land and sea campaign. They sent warships and war planes from across the British Empire and sent troops from other parts of the British Empire. Because one of the reasons the riots were so effective, in a way, you know, were so deadly, especially in kharag, was because there was just no military force in Palestine. At the time, the British did not have a Palestine military force, and it was only after the 1929 riots that they did have troops in Palestine. Until then, they had the Palestine police force, and that police force was mostly Arabs. In Hebron, for example, there were about 40 policemen under the stewardship of one British police chief, and all but one of those policemen were Arabs, and many of them participated in the massacre or stood by outside of Jewish homes and allowed the mobs to enter the homes and carry out their slaughter. And Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm curious. There was a lot of newspaper coverage, but what about the international community's response beyond the British Empire? Yardena Schwartz: So there were actually protests around the world against the massacre in New York. 35,000 people marched through the streets of Manhattan to protest the British failure to protect their Jewish subjects from these riots. Most of the marchers were Jewish, but nevertheless, I mean 35,000 people. We didn't see anything like that after October 7. Of course, we saw the opposite people marching through the streets of New York and cities around the world supporting the mass of October 7. You know, I mentioned this March in New York, but similar protests were held around the world, mostly in Jewish communities. So in Poland, Warsaw and in England, there were protests against the British failure to protect Jews in Palestine from these riots. And the American government was livid with the British and they sent statements put out, statements to the press, criticizing the British inaction, the British failure to protect the Jewish subjects and the American citizens who were in Palestine at the time, there were eight Americans killed in Hebron on August 24 1929. Out of the 67 Jewish men, women and children who were killed, and all of them were unarmed. The Haganah at the time, you know, the underground Jewish Defense Force that would later become the nucleus of the IDF, the Haganah was active then, mostly in Jerusalem and Tel Aviv, there were no Haganah members in Hebron. The Hebron Jewish community was very traditional, very religious, and when Haganah came to Hebron two days before the riots erupted, they because they knew that these riots were going to happen. There had been calls from Arab officials to riot, to attack Jewish communities across Palestine. And so the Haganah came to Hebron to warn Jewish leaders of Hebron that they could either come there to protect them or evacuate them to Jerusalem to safety until the riots subsided and the Jewish leaders of Hebron were unanimous in their opposition. They said, No, you know, we're friends with our Arab neighbors. They'll never hurt us. We trust them. If anything happens elsewhere, it won't happen here. And they believed that because, not only because they had such a good relationship with their Arab neighbors and friends, but also because in previous outbursts of violence in other years, like in 1920 1921 when they were much smaller riots and much less deadly riots. When those riots reached other parts of Palestine, they didn't reach Hebron because of those relations and because they weren't fueled by incitement and disinformation, which was what led the riots of 1929 to be so massive and so deadly, and what led them to be embraced by previously peaceful neighbors. Manya Brachear Pashman: How did that disinformation travel in 1929 How did it reach those neighbors in Hebron? Yardena Schwartz: When we talk about disinformation and misinformation today, we think of it as this, you know, modern plague of, you know, the social media era, or, you know our fractured media landscape. But back in 1929 disinformation was rampant, and it also traveled through Arabic newspapers. They were publishing these statements by Arab officials, mostly the Grand Mufti Hajime Husseini, who was the leader of Palestinian Muslims under British rule, he began this rumor that the Jews of Palestine were plotting to conquer Al Aqsa mosque to rebuild their ancient temple. Of course, Al Aqsa is built upon the ruins of the ancient temples. Temple Mount is the holiest place for Jews in the world. And in 1929, Jews were forbidden from accessing the Temple Mount because it was considered, you know, a solely holy Muslim site. But the closest place they could pray was the Western Wall, the Kotel. And Jews who were demanding British protection to pray in peace at the Western Wall without being attacked by Muslims as a result of this disinformation campaign were then painted by the Arabic press as working to conquer the Western Wall, turn it into a synagogue, and then from there, take Al Aqsa Mosque. So this disinformation traveled from the very highest of Muslim officials. So the imams in mosques across Palestine, specifically in Al Aqsa and in Hebron, were repeating these rumors, these lies about this supposed Jewish plot. Those lies were then being published in flyers that were put in city squares. Jewish officials were warning the British and telling, you know, they should have known and they should have done more to end this campaign of disinformation, not only to achieve peace in this land that they were ruling over, but also because they were responsible for installing hajamina Husseini, the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem, into his position they had chosen him for that position, that all powerful position. And so they were responsible, in a way, for all of these lies that he was spreading. And yet they took no responsibility. And even in the commission that they sent to Palestine from London to investigate the causes of the riots, despite the fact that, you know, if you read these, you know, 400 pages, I don't recommend it. It's a tough reading. But, you know, I did that for this book. And it's so clear from all of these hearings that this disinformation campaign was very obvious, very clear and very clearly to blame for the riots. And yet, because saying so would have made the British responsible for so much death, their conclusions in this commission was that it was Jewish immigration to Palestine and Jewish land purchases at the time that had sparked the riots, and that it was this Jewish demonstration, peaceful demonstration at the Western Wall on to Shabaab in August of 1929 that had sparked these riots. So there's just, you know, this absolute lack of accountability, not only for the Mufti, who retained his position and became even more powerful and more popular as a leader after these riots, but also for the British and instead, you know, the Jewish victims were blamed for their suffering. At the time, Jews were just 20% of the Palestinian population, which was just 1 million people. Of course, today, Israel is home to more than 10 million people. So you know, clearly there was room for everyone. And the Jews at the time were very peaceful. The Haganah was a very, you know, weak, decentralized force, and after these riots, it became much stronger, and Sephardi Jews and Mizrahi Jews, more traditional Jews who had not joined the Haganah before 1929 had not really embraced Zionism before 1929 now agreed that if Jews were going to be safe in our homeland, then we would need our own army. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can we talk a little bit about the turn toward radicalization and extremism during this time, and what role that has played in the years since? Yardena Schwartz: you know, the Zionist leadership was very adamant that Jews in Palestine should not be carrying out attacks against Arabs in Palestine. You know, it should be really about defending Jews, preventing attacks, but not carrying out retaliatory attacks. But as we've seen throughout the century, of this conflict. You know, extremism begets extremism. And you know, when violence is being used by one side, it is going to be used by the other side as well. And so the rise of a more militant form of Zionism was a direct result of 1929 and this feeling of just helplessness and this feeling of relying on this foreign power, the British, to protect them, and realizing that no foreign power was going to protect the Jews of Palestine and that Jews would have to protect themselves, and the radicalism and the extremism within the Muslim population, particularly the Muslim leadership of Palestine, really just accelerated after the massacre, because they saw that it succeeded. I mean, the British punished the Jewish population of Palestine for the riots by vastly limiting Jewish immigration, vastly limiting Jewish land purchases. Notice, I use the word land purchases because, contrary to a lot of the disinformation we hear. Much today, none of this land was being stolen. It was being purchased by Jews from Muslim land owners. Many of them were absentee landowners. Many of them were from the wealthiest families in Palestine. And many of them were members of, you know, this anti Zionist, pro Mufti circle, who were then telling their own people that Jews are stealing your land and evicting you from your land, when, in fact, it was these wealthy Arab landowners who were selling their land to Jews at exorbitant prices. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did you establish a motive for the Mufti and what were his intentions spreading this disinformation? Yardena Schwartz: Great question. So it was very clear. I mean, he never admitted this, but it was very clear what his motives were, and that was to counter the criticism and accusations of corruption that had dogged him for years, until he began this campaign of propaganda which led much of that criticism and much of those stories of his corruption within the Arabic press and among his Arab rivals to essentially disappear, because now they had a much more threatening enemy, and that enemy was the Jewish community of Palestine, who was plotting to destroy Al Aqsa, conquer Al Aqsa, rebuild their temple, take over Palestine and his campaign worked. You know, after that propaganda campaign became so successful, there were very few people willing to stand up to him and to criticize him, because after 1929 when he became so much more powerful, he began a campaign of assassinations and intimidation and violence used against not only his political rivals and dissidents, but also just Anyone who favored cooperation between Arabs and Jews in Palestine. So there were various mayors of Arab cities who wanted to work together with the Jewish community of those cities or with other Jewish leaders to bring about various economic initiatives, for instance. And some of those mayors were assassinated by the muftis henchmen, or they were just intimidated into silence and into kind of embracing his platform, which was that Palestine is and has always been and should always be, a purely Muslim land, and that there is no place for any kind of Jewish sovereignty or Jewish power in that land. So, you know, the Mufti, in 1936 he ended up leading a violent rebellion against the British. And the British at that point, had gotten tired of ruling Palestine. They realized it was much more work than they were interested in doing, and they were interested in leaving Palestine, handing over governance to the local population to the Jews and Arabs of Palestine, and they had been interested in figuring out what could be done. Could there be a binational state with equal representation, or representative governance? If Jews are 40% of the population and Arabs are 60% then there could be some kind of governance on those ratios, all of those solutions, including a two state solution, which was presented in 1937 all of those solutions were rejected by the grand mufti, and his platform was embraced by the other Arab officials within Palestine, because if it wasn't, they could face death or violence. And he even rejected the idea of Jews remaining in Palestine under Arab rule. You know when the British said to him, okay, so what will be done with the 400,000 Jews who are in Palestine right now? He said they can't stay. So he didn't only reject the two state solution. He rejected, you know, this bi national, equal utopian society that we hear proposed by so many in pro Palestine movement today. You know, all of these solutions have been on the table for a century and always. They have been rejected by Palestinian leaders, whether it was the Grand Mufti or his apprentice, his young cousin, yas Arafat. Manya Brachear Pashman: Ah, okay, so what happened to Grand Mufti Husseini? Did he stick around? So The Mufti was eventually, finally wanted for arrest by the British after his rebellion claimed the life of a British official. Until then, it had only claimed the lives of Jews and Arabs, but once a British official was killed, then the British had decided that they'd had enough of the Mufti, and they ordered his arrest. He fled Palestine. He ended up in Iraq, where he was involved in riots there the far hood in which many Jews were massacred, perhaps hundreds, if not over 1000 Jews were slaughtered in Baghdad, which was at the time home to about. 100,000 Jews. He then fled Iraq and ended up in Berlin, where he lived from 1941 to 1945 in a Nazi financed mansion, and he led the Arab branch of Joseph Goebbels Ministry of Propaganda. He was the Nazi's leading voice in the Arab world, he spread Nazi propaganda throughout the Muslim world and recruited 10s of 1000s of Muslims to fight for the Nazis, including in the Waffen SS and when the war ended, when world war two ended, and the UN wanted him for Nazi war crimes, he was wanted for Nazi war crimes, placed on the UN's list of Nazi war criminals. Once again, he fled, first to France, then to Cairo, eventually settling in Beirut, where he continued to lead his people's jihad against the Jews of Palestine. So when, in 1947, when the UN voted to partition British Mandate Palestine into an Arab state and a Jewish state so that the British could finally leave Palestine. He declared jihad, and he rejected the Partition Plan, along with every other Arab state which also rejected it. Of course, the Jews of Palestine embraced it, celebrated it, and the very next day after the UN vote, riots erupted throughout Palestine, and he helped. He was kind of pulling the strings of that Jihad taking place in Palestine. And in fact, 1000 Muslim men who he had recruited for the Waffen. SS joined that holy war in Palestine. The Mufti helped create the army of the holy war. Yasser Arafat, who was also in Beirut at the time, also assisted the army of the holy war. He actually fought in the war that began in 1947 alongside the Muslim Brotherhood. So, you know the legacy that the Mufti had? You know, it doesn't end there. It continued to his dying day in 1974 and Arafat took over his mantle as the leader of the Palestinian people. And you know, we see how the disinformation and incitement and rejection of Jewish sovereignty in any part of the ancient land of Israel has continued to be a prominent force in Palestinian politics no matter who was in charge. You know, the Fatah, Mahmoud, Abbas and Hamas, of course, perpetuate the same lies about Al Aqsa. They perpetuate the same denial of a Jewish right to live in peace in our homeland, deny the history of Jewish presence in Israel. So, you know, it's really astounding to me how little is known about the Grand Mufti and how little is known about his impact on this conflict, and particularly in the very beginnings, the ground zero of this conflict in 1929 Manya Brachear Pashman: It's so interesting. We talk so much about Hitler, right? And his antisemitism, but we don't talk about Husseini. Yardena Schwartz: Yeah, and they were good friends. I mean, they met in 1941 shortly after the Mufti arrived, he had a private chauffeur. He was lavishly paid by the Nazis, and he was good friends with Himmler. He toured concentration camps. He knew very well about the final solution. Hitler himself considered the Mufti an honorary Aryan. I mean, the Mufti had blue eyes, fair skin, light hair. Hitler believed that Husseini had Roman blood, and he saw him as someone who could lead the Nazi forces once they arrived in the Middle East. He saw him as, you know, a great ally of the Nazis. He didn't just participate in the Nazis quest to eradicate the Jewish population of Europe and eventually arrive in Palestine, but he also the Mufti worked to convince various European leaders not to allow Jewish refugees from fleeing Europe and not allowing them to come to Palestine. He told them, send them to Poland, and he knew very well what was happening in Poland. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I want to go back to this family in Tennessee, the genesis of this story, and I'm curious. David Schoenberg's niece said that at one point in the book, she said they're Southern, so they sweep ugly under the rug in the south. And so they just didn't talk about that. And when I read that, I thought, actually, that's kind of a Jewish approach, not a southern approach, except we wouldn't say we sweep things under the rug. We move on, right? We treasure our resilience, and we move on from that pain and we build anew. But is moving on really in the Jewish community's best interest? Is that how we end up forgetting and letting this history and this very important history fade?. Yardena Schwartz: Yeah, absolutely. You know, I think it is possible to do both. It is possible to take great pride in our resilience and in our strength and our ability to experience so much devastation and suffering, and yet every time emerge stronger. I mean, think about the Holocaust. First of all, for many years, we did sweep that under the rug. Survivors were discouraged from speaking about what they went through. They were seen as, you know, especially in Israel, they were seen as, you know, people who went like sheep to the slaughter. It wasn't something to talk about. It was something to move on from. And yet now we are able to hold both in both hands. You know. We're able to honor and commemorate the memory and speak about the atrocities that millions of Jews suffered during the Holocaust, while also celebrating where we went after the Holocaust. I mean, three years after the Holocaust, Israel was born. You know, that's just, on its own, you know, a remarkable symbol of our resilience and our strength as a people. But I think the way we commemorate the Holocaust is a really great example of how we do both how we honor the memory and use that as a lesson so that it never happens again. And yet, I think that when it comes to the conflict and the various forces that have led us to where we are today, there is this tendency to kind of try to move on and not really speak about how we got here. And it's really a shame, because I think that this is the only way we'll ever find a way out of this tragic cycle of violence, is if we learn how we got here, the forces that continue to drive this conflict after a century, and you know, the people who brought us here. Not only the Grand Mufti, but also, you know, the leaders today who are very much capitalizing on fear and religion, exploiting religion for their own, their own interests, and utilizing disinformation to remain in power. And I think that, you know, we can't afford not to speak about these things and not to know about our own history. It's really telling that, you know, even in Jewish communities, where people know so much about Israel and about this conflict, there is just a complete lack of knowledge of, you know, the very bedrock of this conflict. And I think without that knowledge, we'll never get out of this mess. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yardena, thank you so much. This is such a wonderful book, and congratulations on writing it. Yardena Schwartz: Thank you so much. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Dr Laura Shaw Frank, Director of AJC Center for Education Advocacy. We discussed the delicate balance between combating antisemitism, safeguarding free speech, and ensuring campuses remain safe for all students. Thank you for listening. This episode is brought to you by AJC. Our producer is Atara Lakritz. Our sound engineer is TK Broderick. You can subscribe to People of the Pod on Apple podcasts, Spotify or Google podcasts, or learn more at ajc.org/PeopleofthePod . The views and opinions of our guests don't necessarily reflect the positions of AJC. We'd love to hear your views and opinions or your questions. You can reach us at PeopleofthePod@ajc.org. If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends. Tag us on social media with hashtag People of the Pod and hop on to Apple podcasts to rate us and write a review to help more listeners find us. Tune in next week for another episode of People of the Pod.
Mar 27
Higher Education in Turmoil: Balancing Academic Freedom and the Fight Against Antisemitism
Following the Trump administration's decision to revoke $400 million in federal funding over Columbia University's failure to protect Jewish students, the university announced sweeping policy changes. Meanwhile, the U.S. moved to deport former Columbia student and pro-Palestinian activist Mahmoud Khalil, accusing him of concealing his ties to UNRWA and participating in antisemitic campus protests. Dr. Laura Shaw Frank, Director of AJC's Center for Education Advocacy, joins People of the Pod to discuss the delicate balance between combating antisemitism, safeguarding free speech, and ensuring campuses remain safe for all students. ___ Resources: Leaders for Tomorrow : AJC's Flagship Leadership Development Initiative for High School Students AJC Supports Action on Antisemitism, Warns Against Overly Broad Funding Cuts Guidance and Programs for Higher Education Spaces The State of Antisemitism in America 2024 Report AJC Statement on ICE Proceeding Against Mahmoud Khalil Listen – AJC Podcasts: - The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . - People of the Pod : Spat On and Silenced: 2 Jewish Students on Fighting Campus Hate Meet the MIT Scientists Fighting Academic Boycotts of Israel Will Ireland Finally Stop Paying Lip Service When it Comes to Combating Antisemitism? Held Hostage in Gaza: A Mother's Fight for Freedom and Justice Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Laura Shaw Frank: Aaron Bregman: Hi, this is Aaron Bregman, AJC's Director of High School Affairs. If you're the parent of a Jewish high school student, you've probably asked yourself, "How can I help my teen feel proud and prepared to lead in today's world?" Well, that's exactly what AJC's Leaders for Tomorrow program, or LFT, is all about. LFT gives Jewish teens the tools to navigate challenging conversations and advocAte about antisemitism and Israel—whether in the classroom, online, or in their community spaces. Our monthly deep-dive sessions into the issues faced by Jews - both historically and today - become the place where LFT students find community, build confidence, and strengthen their Jewish identity. If your teen is ready to expand their understanding of what it means to be a Jewish leader — have them visit AJC.org/LFT to learn more. Let's give them the tools they need to step up, speak out, and lead with pride. Again, that's AJC.org/LFT . Manya Brachear Pashman: Three federal agencies said this week that they welcomed the policy changes that Columbia University announced Friday, following the Trump administration's revocation of $400 million in federal funding. The government recalled the funding in response to the university's failure to enforce its own rules to protect Jewish students after the terror attacks of October 7, 2023. Masked protesters of the Israel Hamas War spewed antisemitic rhetoric, built encampments that blocked students from attending classes and, in some cases, took over classes. Also this week, the government announced new charges against Mahmoud Khalil, an Algerian citizen and green card holder here in the United States, and a former Columbia University graduate student who was detained due to his activism on campus. International students on other campuses also have been detained in the weeks since. As a community that values academic freedom, as well as freedom of expression, and democracy, how do we balance those values with the importance of fighting antisemitism and making sure our campuses are safe for Jewish students? With me to discuss this balancing act is Laura Shaw Frank, director of the AJC Center for Education Advocacy and director of AJC's Department of Contemporary Jewish Life. Laura, welcome to People of the Pod. Laura Shaw Frank: Thanks, Manya. Good to be with you. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's start with the issue of Mahmoud Khalil, a former Columbia University graduate student. He was detained due to his activism on campus. And we're learning from government this week that he reportedly did not disclose that he was a member of the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestinian Refugees (UNWRA) as a political officer. And he was also part of Colombia's Apartheid Divest movement when he applied to become a permanent resident in 2024. He was taken into custody, though, in a very troubling way. And frankly, he was one of the few who didn't conceal his identity during the protests and encampments. He negotiated with the University. What is AJC's stance on this? Laura Shaw Frank: Great question Manya, and it deserves a very, very careful and nuanced answer. So I want to start by saying that AJC, as it has always done, is striving enormously to remain the very nuanced and careful voice that we always have about every issue, and particularly about the issues that we're talking about here, which are so so fraught in a moment that is so so fraught. AJC issued a statement that we published on X and on our website that talked about the fact that we deplore so many of Mahmoud Khalil's views and actions. And at the same time, it is critically important that the government follow all rules of due process and protections of free expression that we have in our country. And I wanted to emphasize, while I am an attorney, my law degree is incredibly rusty, and I'm not going to pretend to know all the legal ins and outs here, but I do know this, that free speech does attach, even for non-citizens in this country. So we're trying to express a very careful position here. It is possible that Khalil needs to be deported. It is very possible. What has to happen, though, is a trial with due process that is open, transparent and legal. And once those factual findings are determined, if it is the case that Khalil has violated United States law, and has provided material support for terror, and I know the government is actually no longer relying on that particular statute, or has endangered US interests, I don't remember exactly the language that the statute has, but endangered US interests, then he can be deported. But we want to make sure that even as we deplore so much of what he has stood for--he's been the spokesperson for Columbia University Apartheid Divest, which is sort of an umbrella organization for many, many other student organizations at Columbia, including Students for Justice in Palestine, which was banned from campus, and some other groups which have espoused terribly antisemitic and anti-Israel views and actions on campus. They have engaged in protest activity that has been at times violent and exclusionary of Jewish students. There's a lot to be horrified by there. And even as we abhor all of that, we love America, we love due process, we love democracy, and we feel very fiercely that those norms have to be upheld, and we hope that the government will uphold them. We expressed that concern because of the circumstances of his detention, and we're watching the case closely. Manya Brachear Pashman: We also have the government threatening to cancel about $400 million in federal grants and contracts to Columbia. This is a separate matter, but those cuts could include funding for scholarship and research and law. Education and health care. You know, a number of students and scholars alike are very afraid that this could backfire, if indeed, this is done at other universities across the country, in the name of protecting Jewish students. That the backlash could actually hurt the Jewish community. Do you think that there is some credence to that? And if so, how do we prevent that? Laura Shaw Frank: It's a great question, so I want to stop for a second before I answer the question, and talk a little bit about the position AJC has taken with respect to the $400 million. We issued a statement, a letter to the government, to the task force, about the $400 million. Where we, again, expressed our enormous gratitude to the administration for shining a light on antisemitism and for taking it seriously. Which it needs to be taken incredibly seriously in this moment. And we fear that it has not been taken seriously enough until this moment, so we're very grateful that the administration is taking it seriously. And at the same time, we expressed our concern about the $400 million dollars being withheld because of what that $400 million will fund. That $400 million is largely funding for research, scientific and medical research, and we know that in this moment, there is a great deal of research money that is being withheld in various places in this country from universities that is funding really critical research. Pediatric brain cancer, Parkinson's disease, COVID. Whatever it is, that research is incredibly important. So we want to make sure that even as the government is doing the good work of shining a light on antisemitism and ensuring that our higher education institutions are not harboring and fostering atmospheres of antisemitism. We want to make sure that they are simultaneously not using a hatchet rather than a scalpel in order to attack the problem. We are keenly aware that much of the most antisemitic discourse that occurs on campus among faculty is discourse that comes out of humanities departments and not generally out of science, research, medicine departments. And it feels wrong to perhaps be withholding the funds from those who are not the problem. Generally, humanities departments don't get hundreds of millions of dollars in funding from the federal government. The research that they do is of a different scale. It's less expensive. Frankly, they don't have to run labs, so the funding is really mostly in that medical and science realm. So I wanted to just start by saying that, and would definitely encourage folks to take a look at the letter that AJC sent to the task force. With respect to your question about whether this is going to backfire against the Jewish community. It is definitely a concern that we've thought about at AJC. There have been many moments in Jewish history where Jews have become scapegoats for policies of governments, or policies in a society, or failures of a society. I'm thinking of two in this particular moment that are just popping into my head. One of them was the Khmelnytsky massacres in 1648 and 49. I know that sounds like a long time ago, but feels kind of relevant. When Jews, who were representing the nobles in exchanges with peasants, collecting taxes, things of that nature, were attacked and murdered in tens of thousands. And Jews were really, you know, was there antisemitism involved? Absolutely. Were Jews being scapegoated for rage against nobles? Also, absolutely. So I'm thinking about that. I'm also thinking about the rise of the Nazi Party in Germany in the 1920s and 30s, where this myth of the German population being stabbed in the back by the Jews who quote, unquote, made them lose World War I–which is, of course, obscene and ridiculous–led the way for Nazi ideology finding a foothold in German society. So I'm thinking of those moments when Jews became a scapegoat. And I'm keenly aware of how much our universities rely on research dollars to do their work, and also the anger that so many who are working in that space must be feeling in this moment. It does make me fearful to think that those who are working in the research and those who need the research, you know, people who are struggling with health issues, people who are relying on cutting edge research to help them, could say, No, this is all the Jews' fault. It's all because of them. They're causing the government to do this and that. You know, it feeds into that antisemitism trope of control. I do worry about the Jews becoming the target. What should we do about that? I think it's very important for us to have the open lines of communication that we're grateful to have with government officials, with elected officials and appointed officials in the Administration and across the aisle in Congress, with Democratic and Republican elected officials. I think it's important for them to understand, at least, you know, from AJC's perspective, that we hope that as they continue to shine that very important spotlight on antisemitism, and continue to ensure that we hold our institutions of higher education to the standard which they must be held to, taking antisemitism very seriously and combating it with all of their power and strength. That at the same time, we want to make sure that the strategies that the government is using to address this issue are strategies that will truly address the problem. And we hope that our statements, our transparency about our stance, will help this country see the views of the Jewish community in this moment. That there are diverse views in the Jewish community, that we do care deeply about the success of higher education, about the success and the importance of research dollars, and that we also care deeply that the administration is taking antisemitism seriously. So really trying to hold that very special AJC nuance. Manya Brachear Pashman: I know AJC offers an entire package of strategies to combat antisemitism in many different arenas, including university campuses. And I want to take a look at some of the changes that Columbia announced in response to the government's threats to cut funds, to restore those funds. They said that they would make it easier to report harassment and enable the provost to deal with disciplinary action against students who are involved in protests. These seem to reflect some of the strategies that AJC has shared, Yes? Laura Shaw Frank: Yes, for sure. I want to say, before I respond, that there seems to be a bit of murkiness right now, as we are recording, regarding sort of where some of the some of the agreement stands. So I'm just going to just note that, that it could be that by the time we air this episode, things will be different. But AJC's strategy for higher education administrators, which could be found on our website, and you can probably link to that in the show notes too, calls for very clear codes of conduct. Calls for enforcement, clear enforcement of those codes of conduct. We don't specifically say where discipline should be situated, because every university has a different kind of plan for how, how that should be situated. And I know that's an issue that appears to be ongoingly unclear between the government and Columbia right now, so I'm not going to say where that's landing. It's not clear to me where it's landing, yet. But there's no question that the kinds of asks that the federal government or demands, really that the federal government has made of Columbia, are demands that are rooted in the same issues that we have highlighted on campus. So there's this issue of discipline. Not just codes of conduct, but also the enforcement of codes of conduct. We've seen very often, including at Columbia, that there are rules that are on the books, but they're not actually enforced in reality. And they're useless if they're not enforced in reality. So that's one thing that we have been very clear about in our plan. We also have encouraged universities to think about faculty, to think about the role that faculty plays on a campus, and that's also been a part of the Columbia agreement with the federal government. Again, this is a little bit murky, still, but the federal government had asked for the Middle East and African Studies Department, maybe Asian Studies. I'm not sure exactly what the title of the department is to be put in receivership. That is a very extreme thing that can be done. Universities do it if a department is completely failing in whatever way. They could put it in receivership, give it over to somebody else to head. And it seems, at least as of this moment, that what Columbia has done is appoint a new Vice President who is going to oversee studies in the Middle East and Jewish studies, but it's not really exactly receivership. So I'm not going to opine on what they've done, but what I will opine on is what AJC is asking campuses to do in this moment. We've alluded to it in our campus plan that we have up on the website, but we are going to shortly be issuing updated guidance specifically about how we think universities should be addressing the issue of faculty members who are creating an atmosphere that's making Jews feel harassed, or that they're advancing antisemitism. Our State of Antisemitism Report that was released about a month and a half ago showed that, I think it's 32% of students felt that their faculty members were advancing an antisemitic atmosphere or an atmosphere that was harassing of them. And I want to be clear that obviously this is a question of feel, right? We ask the students, do you feel that way? And we know that feelings are not empirical data. Every person has their own set of feelings. And what some students might feel is antisemitic. Other students might say, no, no, that's not antisemitic. That's simply a different viewpoint. That's a perfectly legitimate viewpoint. So with that caveat, I want to say that we're very concerned about that statistic, and we do think that it reflects a reality on campus, specifically on campuses like Columbia. And what we are asking universities to do at this moment is to think really carefully about how they're talking to faculty. How are they professionalizing their faculty? Our Director of Academic Affairs, Dr. Sara Coodin, has been working a great deal on coming up with a plan of what we would like to ask universities to work on in this moment, to work on the summer when they have some downtime. How are they going to talk to their faculty, especially emerging faculty, TA's,graduate students and young, untenured faculty about what their responsibilities are. What are their responsibilities to have classrooms with multiple viewpoints? What are their responsibilities to not treat their classrooms as activist spaces for their own political ideologies? What are their responsibilities to not require students to take actions that are political in nature. Such as, we're going to hold class in the encampment today, or I'm canceling class in order for students to go to protest. Those are not appropriate. They are not responsible actions on the part of faculty. They do not fall under the category of academic freedom, they're not responsible. So academic freedom is a very wide ranging notion, and it's really important. I do want to emphasize very important. We do want faculty members to have academic freedom. They have to be able to pursue the research, the thinking that they do pursue without being curtailed, without being censored. And at the same time, faculty has that privilege, and they also do have responsibilities. And by the way, we're not the only ones who think that. There are national organizations, academic organizations, that have outlined the responsibilities of faculty. So as we kind of look at this issue with Columbia, the issue of those departments that are the government has asked for receivership, and Columbia has appointed this vice president, the issue that we would like to sort of home in on is this issue of: what are we doing to ensure that we are creating campuses where faculty understand their role in pedagogy, their role in teaching, their role in upholding University spaces that are places of vibrant dialog and discourse–and not activism for the professor's particular viewpoints. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm curious, there's been a lot of talk about Columbia failing its Jewish students, and these measures, these threats from the government are really the government's way of trying to repair that. Trying to motivate Columbia to to fix that and serve its Jewish students. But I'm curious if it's not just the Jewish students that Columbia is failing by not protecting Jewish students. In what ways are–and not just Columbia, but–universities in general failing students in this moment, maybe even students including Mahmoud Khalil? Laura Shaw Frank: I'm so glad you asked that question. I think it's such an important question. We look at universities, at the Center for Education Advocacy, and I think that so many Americans look at universities this way, as places where we are growing the next generation of citizens. Not even the next, they are citizens, many of them, some of them are foreign students and green card holders, et cetera. But we're raising the next generation of Americans, American leadership in our university and college spaces. And we believe so firmly and so strongly that the ways that antisemitism plays out on campus are so intertwined with general notions of anti-democracy and anti-civics. And that solving antisemitism actually involves solving for these anti-democratic tendencies on certain campuses. And so we do firmly believe that the universities are failing all students in this moment. What we need as a society, as we become more and more polarized and more and more siloed, what we need universities to do is help us come together, is: help us think about, what are the facts that we can discuss together, debate together, even as we have different interpretations of those facts. Even if we have different opinions about where those facts should lead us. How do we discuss the issues that are so problematic in our society? How will we be able to solve them? And that, for antisemitism, plays out in a way about, you know, Jewish students are a tiny minority, right, even on campuses where there's a large Jewish population. What does large look like? 10, 15%? On some campuses it's more than that, but it's still quite small. And Jews are two and a half percent of American society. So Jews are a minority. It's very important for us to be in spaces where different views will be included, where different opinions are on the table. Additionally, of course, discourse about Israel is so important to Jews, and we know from the Pew study and from our AJC studies that four in five Jews, over 80% of Jews, see Israel as important to their Jewish identity. So discourse on campus about Israel that ends up being so one-sided, so ignoring of facts and realities, and so demonizing of Israel and of Zionists and of the Jewish people, that's not healthy for Jews and fosters enormous antisemitism, and it simultaneously is so detrimental, and dangerous for all of us. It's not solely discourse about Israel that is at issue. It is any time that a university is sending faculty members into the classroom who are all of the same mindset, who all have the same attitude, who are all teaching the same views and not preparing young people with the ability to debate and come up with their own views. Fact-based views, not imaginary views, fact-based views. That's incredibly, incredibly important. One other piece that I want to mention, that I think when campuses fail to enforce their rules, why they're damaging not just Jewish students, but all students. When you think about a campus that has their library taken over by protesters, or their classrooms taken over by protesters, or the dining hall being blocked by protesters. That's not just preventing Jewish students from accessing those university facilities. It's preventing all students. Students are on campus to learn, whether they're in a community college, a state university, a small liberal arts college, a private university, whatever it is, they are there to learn. They are paying tuition, in many cases, tens of thousands of dollars, close to $100,000 in tuition in some places, to learn and for these students to have the ability to take away other students' ability to learn is a way that the university is failing all of its students. That has to be stopped. Manya Brachear Pashman: You talked about using classroom space, using library space, as you know, co-opting it for protest purposes or to express particular points of view. But what about the quad? What about the open space on campus? You know, there appears to be, again, it's still murky, but there appears to be an outright ban now on protests on Columbia's campus. Is that a reasonable approach or should campuses have some sort of vehicle for demonstration and expression, somewhere on its property? Laura Shaw Frank: Absolutely, campuses should allow for protest. Protest is a right in America. Now, private campuses do not have to give students the right to protest, because that's private space. The government isn't allowed to infringe on protests, so public universities would not be able to do that. But most private campuses have adopted the First Amendment and hold by it on their campuses, including Columbia. It is critically important that students, faculty members, anyone in American society, be permitted to peacefully protest. What can be done in order to keep campuses functional, and what many campuses have done, is employ time, place, and manner restrictions. That's a phrase that probably a lot of our listeners have heard before. You're not allowed to curtail speech–which, protest is, of course, a form of speech–you're not allowed to curtail speech based on a particular viewpoint. You can't say, these people are allowed to talk, but those people, because we don't like their opinion, they're not allowed to talk. But what you can do is have something that is viewpoint-neutral. So time, place and manner restrictions are viewpoint neutral. What does that mean? It means that you can say, on a campus, you're allowed to protest, but it's only between 12 and 1pm on the south quad with no megaphones, right? That's time, place, manner. I believe, and I think we all at AJC believe, that protests should be allowed to happen, and that good, solid time, place, and manner restrictions should be put into place to ensure that those protests are not going to prevent, as we just talked about, students from accessing the resources on campus they need to access, from learning in classrooms. There was a protest at Columbia that took place in a classroom, which was horrifying. I have to tell you that even the most left wing anti-Israel professors tweeted, posted on X against what those students did. So campuses can create those time, place and manner restrictions and enforce them. And that way, they're permitting free speech. And this is what the Supreme Court has held again and again. And at the same time, prevented protesters from kind of destroying campus, from tearing it all down. And I think that that's really the way to go. Some campuses, by the way, have created spaces, special spaces for protest, like, if you're going to protest, you have to do it in the protest quarter, whatever it is, and I think that's a really good idea. I'm an alum of Columbia, so I know how small Columbia's campus is. That might not work on Columbia's campus, but certainly time, place, and manner restrictions are critical, critical to campus safety and peace in this moment, and critical to protect the rights of all students, including Jewish students. Manya Brachear Pashman: And on the topic of protests, as I was reading up on the latest developments, I saw a student quoted, she was quoted saying, 'It's essentially going to ban any protest that it thinks is antisemitic slash pro-Palestine. I guess we're mixing up those words now.' And I cringed, and I thought, No, we're not. And what are universities doing to educate their students on that difference? Or is that still missing from the equation? Laura Shaw Frank: So I actually want to start, if I may, not in universities, but in K-12 schools. The Center for Education Advocacy works with people across the education spectrum, starting in kindergarten and going all the way through graduate school. And I think that's so important, because one of the things we hear from the many university presidents that we are working with in this moment is: we can't fix it. We are asking our K-12 schools to engage in responsible education about the Israel-Palestinian conflict, and we have particular curricular providers that we recommend for them to use in this moment, I want to say that they are terrified to do that, and I understand why they're terrified to do that. Everyone is worried that the minute they open their mouth, they're going to be attacked by some person or another, some group or another. And I get that. And I also believe, as do the presidents of these universities believe, that we cannot send students to campus when this issue is such a front burner issue. We cannot send students to campus with no ability to deal with it, with no framework of understanding, with no understanding of the way social media is playing with all of us. That education has to take place in K-12 spaces. So I wanted to say that first. And now I'll talk about campus. Universities are not yet there at all, at all, at all, with talking about these issues in a nuanced and careful and intelligent way. We can never be in a position where we are conflating antisemitism and pro-Palestinian. That is simply ridiculous. One can be a very proud Zionist and be pro-Palestinian, in the sense of wanting Palestinians to have self determination, wanting them to be free, to have life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. AJC has long, long been on the books supporting a two-state solution, which I believe is pro-Palestinian in nature. Even as we have very few people who are also in the Middle East who are pro two-state solution in this moment. And I understand that. Education of students to be able to think and act and speak responsibly in this moment means helping students understand what the differences are between being pro-Palestinian and being antisemitic. I'm thinking about phrases like 'from the river to the sea, Palestine will be free,' which lands on Jewish ears, as we know from research that's been done at the University of Chicago, lands on the majority of Jewish ears as genocidal in nature. I'm thinking about phrases like 'globalize the Intifada,' which also lands on Jewish ears in a very particular way is targeting them, us, and education needs to take place to help students understand the way certain phrases the way certain language lands with Jews and why it lands that way, and how antisemitism plays out in society, and at the same time, education has to take place so students understand the conflict that's going on in the Middle East. They might think about having debates between different professors, faculty members, students, that are open to the public, open to all, students that present this nuanced and careful view, that help people think through this issue in a careful and educated way. I also think that universities should probably engage in perhaps requiring a class. And I know some universities have started to do this. Stanford University has started to do this, and others as well, requiring a class about responsible speech. And what I mean by that is: free speech is a right. You don't have to be responsible about it. You can be irresponsible. It's a right. What does it mean to understand the impact of your words? How do we use speech to bring people together? How do we use speech to build bridges instead of tear people apart? So I think those are two ways that universities could look at this moment in terms of education. Manya Brachear Pashman: Anything I haven't asked you, Laura, that you think needs to be addressed in this murky moment? Laura Shaw Frank: I hope that our listeners and everyone who's following the stories on campus right now can take a breath and think carefully and in a nuanced way about what's going on and how they're going to speak about what's going on. I hope that people can see that we can hold two truths, that the government is shining a necessary light on antisemitism, at the same time as universities are very concerned, as are we about some of the ways that light is being shined, or some of the particular strategies the government is using. It is so important in this moment where polarization is the root of so many of our problems, for us not to further polarize the conversation, but instead to think about the ways to speak productively, to speak in a forward thinking way, to speak in a way that's going to bring people together toward the solution for our universities and not further tear us all apart. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much for this conversation, Laura, it is one that I have been wanting to have for a while, and I think that you are exactly the right person to have it with. So thank you for just really breaking it down for us. Laura Shaw Frank: Thank you so much, Manya.
Mar 20
Will Ireland Finally Stop Paying Lip Service When it Comes to Combating Antisemitism?
In late 2024, Israel closed its embassy in Dublin, accusing the Irish government of extreme anti-Israel policies, antisemitic rhetoric, and double standards. Meanwhile, the small Jewish community in Ireland, numbering nearly 3,000, has faced antisemitism in the streets. AJC's Director of International Jewish Affairs, Rabbi Andrew Baker, joins us to discuss his recent meeting with Irish Prime Minister Micheál Martin, examples of antisemitic activity in Ireland, including Holocaust inversion and the chilling impact of widespread anti-Israel sentiment on Irish Jews. He also shares insights on Ireland's adoption of the IHRA working definition of antisemitism and the future of Holocaust remembrance in the country. ___ Resources: AJC Directly Addresses Antisemitism and Vilification of Israel in Ireland with the Prime Minister Listen – AJC Podcasts: - The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . - People of the Pod : U.S. Special Envoy Steve Witkoff on Gaza Reconstruction, Israeli Security, and the Future of Middle East Diplomacy Why Germany's Antisemitic Far-Right Party is Thriving Instead of Disappearing Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Andrew Baker: Manya Brachear Pashman: In December, Israel closed its embassy in Dublin, accusing the Irish government of extreme anti-Israel policies, antisemitic rhetoric, and double standards. Meanwhile, the small Jewish community in Ireland, numbering nearly 3000 has faced antisemitism in the streets. With us now to discuss the situation in Ireland, and his meeting with the Irish Prime Minister last week, is AJC's Director of International Jewish Affairs, Rabbi Andrew Baker, who also serves as the personal representative on combating antisemitism in the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe. Andy, welcome to People of the Pod. Andrew Baker: Great to be here, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: This situation did not develop overnight. Can you take our listeners back to the first clues that the relationship between Israel and Ireland was deteriorating? Andrew Baker: Ireland has a small Jewish community, perhaps about 3000 people. And a significant number of them, maybe upwards toward 1000, also people with Israeli citizenship who moved to Ireland to work there with a number of the social media tech companies based in Ireland. Over the years, and certainly even predating October 7, in Ireland there's been a fairly high degree of anti-Israel animus. It's not dissimilar to what we may find in a number of other northern European countries. They view the political scene in the Middle East through a certain prism that creates and maybe amplifies this form of animus. But that said, there have also been, I think, issues between this community and government policy, even as it's reflected in ceremonies marking Holocaust remembrance in Ireland. In many cases, the particular focus in that history of what happened to the Jewish people in Europe during World War II, the genocide of the Holocaust. While there may be commemoration events, in principle to market, they've really, in many ways, washed out the Jewish nature of that. In 2016 I was an invited speaker to the official Holocaust Commemoration Day in Ireland. Almost the entire focus was on the refugees, at the time coming in from North Africa and the Middle East. I was actually the only person who spoke the word antisemitism at that event. You also had an effort through legislation to really separate out Israel, the occupied territories, as they understood it, and the name of this bill that was passed by the legislature was called the Occupied Territories Bill. Which sought to separate Israel, at least the territories commercially from Ireland, but it would have a very onerous impact, frankly, on any anyone, certainly members of the Jewish community, who would choose to visit Israel. If they purchased a kippa in The Old City of Jerusalem, brought it back with them to Ireland, under this law, if it were enacted, they could literally be arrested for that action. So I think also at the time I made a visit there in 2019 in my OSC role, Israel was preparing to host the Eurovision Song Contest in Tel Aviv, and there was a very public campaign in Ireland to boycott the Eurovision contest. Advertisements calling for this on the side of buses, people in the state media already indicating that they were going to refuse to attend. So you had this sort of environment in Ireland, again, a good number of years before what happened on October 7, which really changed everything throughout Europe. Manya Brachear Pashman: And now there has been a more moderate government recently elected in Ireland. Prime Minister Micheál Martin was in the United States last week in Washington, DC, and you actually met with him when he was here, correct? Andrew Baker: That's correct. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did you share some of these concerns? Did you address, for example, the Occupied Territories Bill with him? Andrew Baker: Yes, we spent a bit over an hour together. I was joined also by Marina Rosenberg from the ADL. Our two organizations met. There were some initial plans that other organizations would also participate, but in the end, it was the two of us. One of the most significant issues that has arisen, it's partly why Israel closed its embassy, was the fact that Ireland has joined with South Africa in the charges brought before the ICJ, the International Court of Justice, accusing Israel of genocide. So our goal at this meeting was to raise a number of these issues, including that, including the status of the Occupied Territories bill. But also, really to impress on him that the community itself was feeling, sieged, if you will, by these developments. And so we wanted him to understand that the anti-Israel animus, which at times, crosses over to a form of antisemitism, has had a direct impact on the Jews in Ireland. It also was brought to the fore only this past January at this year's International Holocaust Remembrance event, Michael Higgins, the Irish president, spoke, even though the Jewish community had actually urged that he not be given a platform. He used the opportunity to focus on the suffering of Palestinians in Gaza. And again, by that, drawing an analogy between Israel, between the Jewish experience during the Holocaust and somehow Israel's treatment of Palestinians today. So this, too, was an issue we brought up with the Prime Minister. Manya Brachear Pashman: But this prime minister has made some overtures to address antisemitism, right? I mean, his administration, for example, just announced it was adopting the working definition. Andrew Baker: Yes, in fact, several weeks before coming to Washington, the prime minister did announce that Ireland would accept the international Holocaust Remembrance Alliance, the IHRA working definition of antisemitism. And we also have a set of global guidelines that some, I think, over over 30 countries now have adopted, that lay out measures that government should take. So we did, of course, discuss this with the prime minister. He indicated to us that he was in the process of appointing a national coordinator, someone who could sort of oversee the development of national strategy to combat anti semitism. This is a very important step, by the way, it's one that almost all, with only a couple of exceptions, EU Member States, have already done. So. It is good that Ireland is doing this. Of course, it comes quite late to the game in this the IHRA definition is very important, because it offers old and new examples of antisemitism, and to digress only for a moment, this IHRA definition began as the definition endorsed presented by the European monitoring center on racism and xenophobia, already 20 years ago. And in my AJC role at that time, I worked closely with the EUMC in the drafting and the adoption of that definition. And notably, it speaks about antisemitism related to Israel. Frankly, if one had that definition in front of him or her, you would be able to look at some of the actions, even by members of government, and certainly the President's own remarks in January, and say, well, this could constitute a form of antisemitism itself. Manya Brachear Pashman: And did he address the bill legislation that is so troublesome? Andrew Baker: Yes, he did. He indicated to us that the Occupied Territories Bill as drafted is probably unconstitutional, since it really concerns international trade and economics. This is the purview of Brussels for all EU member states. So in that regard, they're really not expected or permitted to have their own economic international policy. He also said it was probably unenforceable. Now I asked him to simply dispel with this bill altogether. That was not something that he could agree to, but he did inform me that it would be, at least for now, off the legislative calendar. So we know there are others in Ireland who are pushing for that law to be redrafted and enacted. So this was somewhat reassuring to be told that no, at least this will not happen this year. Manya Brachear Pashman: Though he adopted the IRA working definition, I know that he also received some pressure from activists to dispense of that, to not adopt it and to reject it. And he assured them that it was not legally binding. Was that discouraging to hear? Or did he seem to be willing to implement it in training of law enforcement and education of students? Andrew Baker: Look, these are the very elements that we speak of when we speak about employing the IHRA definition. And as you said, it's identified as a non legally binding definition, but it ought to be used to advise, to inform law enforcement, the judiciary, if and when they address incidents of antisemitism. Again, he made the decision to adopt the definition, to accept the global guidelines only, only a few weeks ago, really. So how it will be used to what extent remains to be seen. I have to say we, and my ADL colleague indicated we're certainly prepared to work with the government to offer advice on how these things can be employed. We hope that they'll consider and take up our offer, but at this point, we have to see what happens. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned that the small Jewish community there is largely Israeli expats doing business. And they were certainly uncomfortable at Holocaust Remembrance event. Are there other examples of harassment or antisemitic behavior, assaults, protests. What are they seeing on a day to day basis? Andrew Baker: Yes, first, I mean, the majority of the community are not Israelis, but there's a significant number who are. And I think what they're finding is, it's not unique, but it's intensive for them, that in schools, in the workplace, there's a high level of discomfort. And a result of this, where people may have the choice they will try not to identify publicly in some way that would signal to others that they're Jewish. There are incidents. There haven't really been violent attacks but clearly kids in school have been harassed and made to feel uncomfortable. Because they're Jewish because of this sort of strong anti-Israel animus. There was, only shortly after we had our meeting, an incident in one of the resort towns in Ireland where Israeli tourists in a restaurant were harassed by other patrons. They were cursed. They were spit at. It was the sort of thing, and the local council did issue a kind of apology. But I think it illustrates that when you have such a high level of anti-Israel animus, which at times can be just a harshly critical view of Israel or Israel's government, but it can spill over and create a sense that there is, as we've termed it, a kind of ambient antisemitism. It is sort of in the atmosphere, and so it does have an impact on this small Jewish community. Manya Brachear Pashman: Last year, Israel recalled its ambassador to Dublin. It closed its embassy in December, but in May, it actually recalled its ambassador, after Ireland announced, along with other countries, Norway, Spain, Slovenia, that it would recognize a Palestinian state. And I'm curious if there's something about Ireland's history that informs this approach? Andrew Baker: I think that's partly true. Look, first of all, Ireland had a somewhat checkered role, even during the Holocaust. You know, the Irish Ambassador government signed a condolence book when Adolf Hitler died. And it accepted German refugees after the war, but it was really quite reluctant to accept even some small number of Jewish refugees. And I think over time, Ireland in its own fight for independence with Great Britain, maybe drew the same analogy to Palestinians. This notion of being a colonialist subject. Perhaps there are those connections that people make as well. But in the case with the Israeli ambassador first being withdrawn, and then the embassy closed, unfortunately, much of the normal diplomatic relations that an ambassador wants to do, is expected to do, were really precluded from Israeli Ambassador Erlich. Gatherings of political parties where diplomats as a kind of standard rule, invited to attend, she was not invited. Other events the same was true. So there was also a frustration to be ambassador in what ought to be a friendly country, a fellow democracy, a member of the European Union, and yet to be made a kind of de facto persona non grata was a quite troubling experience. Manya Brachear Pashman: So whether there was an ambassador or an embassy there didn't seem to matter. They were still being excluded from diplomatic events already. Andrew Baker: The Israeli government made the decision that they needed to do something dramatic to express the state of affairs and this discomfort, and that was first through recalling the ambassador, but ultimately, As you pointed out, essentially closing the embassy, that's a dramatic step, and some might disagree, particularly if you have Israeli citizens that would otherwise want the services of an embassy in that country, but they believe this was one way of sending a message, and I think it was a message that was received. I would point out that following our meeting with the Prime Minister, it drew significant attention in the Irish press. Perhaps one of the most prominent read newspapers in Ireland, The Independent, this past Sunday, had an editorial that spoke about our meeting with the Prime Minister and really called on the government to reassess its relationship with Israel. In other words, to try and repair that relationship. So if it leads to that, then I think we will feel it was well worth it. Manya Brachear Pashman: Going back to the Holocaust Remembrance events that seem to be a continuing issue. Did you speak with the Prime Minister about the Jewish community perhaps having a role in organizing those commemorations from now on? Andrew Baker: We did. The fact is, there has been a Holocaust Educational Trust [Ireland] organization that had some government support, but it's separate from the Jewish community that has been responsible for organizing these events. As I noted when I was invited in 2016, this was the organization that organized it, but it has sort of fallen out of favor with the Jewish community. There have been internal tensions, and again, as a result of this last event in January, the Jewish community has asked the government to really be given the authority to to organize these events. I have to point out that it does have, typically, the participation of senior figures in the government. When I was there, the prime minister at the time spoke, and members of the High Court participated, the Mayor of Dublin. So I think that level of participation is important and should continue. But I think the problem we're seeing is that even that history is being instrumentalized, so we need to be certain that doesn't continue. Manya Brachear Pashman: Andy, a number of Jewish leaders declined to meet with Prime Minister Martin, given the tension and animosity Jews in Ireland have been facing. Why did you meet with him? Andrew Baker: AJC values, sees itself as playing an important diplomatic role, not simply with Ireland, but with various countries. And while some other organizations felt in the end, they should not participate, because by not talking to the Irish Prime Minister that was sending a message, our approach is rather quite the opposite. It's important to talk. I'm not sure that it's always the easiest conversations, and the results may not always be all that we would hope them to be, but I want to say we're in this for the long haul. We've been back and forth to Ireland, with other countries, of course, as well over the years. We hope that those visits and these meetings will continue. Frankly, it's only by this kind of ongoing engagement, I believe that we can really make a difference, and that's what we're all about. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well Andy, thank you so much for joining us. Andrew Baker: You're welcome, Manya.
Mar 13
Held Hostage in Gaza: A Mother's Fight for Freedom and Justice
"He told me: 'We are the same. We are the same.' Meaning, me and the terrorists who penetrated the kibbutz are the same. They received the mission to murder and to burn, and I received the mission to hold you as bargaining chips for the release of the Palestinian prisoners. And this was a very cruel sentence, because while we were in captivity . . . they could do anything to us." Former Israeli hostage Shoshan Haran, abducted during the Hamas terror attack on October 7, 2023, shares her harrowing story of survival and resilience. Shoshan was abducted from her home in Kibbutz Be'eri alongside her family, including her son-in-law Tal Shoham, her daughter, and her young grandchildren. While she and the other women and children were released after 50 days in November 2023, Tal remained in Gaza for 505 days and was released in February 2025. Now, as she welcomes Tal home, Shoshan opens up about the unbearable anguish of captivity, the emotional toll of waiting, and the devastating losses her family has endured. She sheds light on the humanity that persisted even in the darkest moments and issues a powerful call for continued global action to free the 59 hostages who are still being held. Resources: Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : U.S. Special Envoy Steve Witkoff on Gaza Reconstruction, Israeli Security, and the Future of Middle East Diplomacy Why Germany's Antisemitic Far-Right Party is Thriving Instead of Disappearing Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Shoshan Haran: Manya Brachear Pashman: After 505 days as a hostage in Gaza, Tal Shoham returned to Israel to his wife and two young children and to an extended family whose lives have been on hold since the Hamas terror attacks on October 7, 2023. Tal had been taken hostage from his home in Kibbutz Be'eri with his wife, his children, his wife's aunt, his 12-year-old niece, and his mother in law, Shoshan Haran. Shoshan returned home with the other women and children on November 26, 2023. She is with us now to talk about welcoming Tal home, the tremendous loss she and her family have suffered, and the endless fight to get the rest of the hostages home. Shoshan, welcome to People of the Pod. Shoshan Haran: Thank you. Nice being here. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, I'm glad that you are here to at least partially celebrate the return of your loved ones. It has been more than 500 days since that awful day in October. Can you take our listeners back a few days before the 7th, to October 4th: what were you doing that day? Shoshan Haran: On October 4, we had a very big event of Women Making Peace in the Dead Sea, together with a sister movement, Women of the Sun. It's a Palestinian movement. Both women-led movements working for peace on both sides. And I went there with my sister Lilach and with the founder of this movement, Vivian Silver , who was my neighbor in Kibbutz Be'eri. And it was such an optimistic event, and heartwarming, we were there with thousands of women, some men also, and we were talking about the power of women to bring peace and how we should stop the bloodshed and how we should find a new way to live together in peace. That was on October 4. Two days later, on October 6, we are getting ready for Simchat Torah, to celebrate with our family. We had the sukkah already since a week ago, and we invited my daughter, Adi, and her husband Tal and the little kids, Naveh, who was then eight years old, and Yahel (Yula), three years old, to join us for Simchat Torah. So we were cooking, getting ready for the holidays. It was a shabbat dinner, so cooking. And then we got a call from Avshal, Avshalom, he's my husband, his nickname is Avshal, and we got a call from his sister, Sharon, that wanted to join us for that evening with her daughter, Noam who was then 12 years old. And we celebrated together in the sukkah, having fun. The kids were playing all over. And then we went to sleep. We had kind of a loft above our house for hosting our guests, and that's where Tal and Adi and the kids stayed overnight. Sharon and her daughter stayed with us on the ground level, and we went to sleep. And then at 6:29am, we heard the red . . . color red is the code for attack. And we thought it is, I shouldn't say it, but the usual missile attack on us. So we went to the safe room. And then after a few minutes, we went out. My husband went up to the second floor to get Adi, Tal, and the kids down to be with us, and I started making hot chocolate for the grandkids. And then we got the warning on our–we have a community WhatsApp for alarms. And they told us that they suspect that some terrorists penetrated the kibbutz, and then we should go into the safe room. And a few minutes later, they confirmed that a terrorist attack was launched on the kibbutz. Manya Brachear Pashman: Who was in that safe room with you? Shoshan Haran: We were in the safe room, seven people. Tal, Adi, my daughter, the kids–my [2] grandkids, Sharon and Noam. Avshal stayed outside with a knife ready to protect his family, and also looking through the windows to understand what was going on. And then we started hearing shooting and grenades, and they got closer and closer to us. My cell phone was the only one that had reception inside the safe room. And after one hour and a half of terror, Tal texted my husband to join us in the safe room, because he understood that a knife is not gonna protect us, so there was no way. And so Avshal joined us, and Tal and him–we had a very large dinner table when we have guests, and the extensions were in the safe room, so very heavy pieces of wood. And they used it to protect the handle of the safe room door because there was no lock, but they were just pushing it against the safe room door. I heard them breaking into my neighbor's home. I heard a lot of glass and a lot of shooting and grenades. I didn't know what was happening there. And then they left. And then they penetrated our house. They just broke into it. It's easy. It was full of windows that you could easily break into. And they started shouting at us: open the door, open the door. We did not. And then they had steel penetrating bullets that went through the safe room's iron door. And I even saw one bullet passing very close to my head. The movement of the bullet was a little bit slowed, so I could see it. And my husband shouted at me, just lie down, you know, because my head was a little bit upwards, looking at the cell phone and trying to call for help. They couldn't break in the safe room door, and then they left, and we thought that maybe we were saved. But then after a few minutes, they brought a bulldozer, and they just cracked the safe room window. And the safe room window is composed of two steel parts that should be connected. But with the bulldozer, they were able to dismantle the window and create a crack. And then we had a few seconds to decide to surrender or not. And then my husband and Tal decided to surrender. We were under the bed, so we didn't see much, but they understood that the crack will allow the terrorists to throw grenades into the room. So they decided to surrender. And then the terrorist opened the window so we stopped resisting. They opened the window, and then my husband and Tal went out first, and that was the last glance that I had of my husband. And it took us a while, because we were under the bed, and we were three women and three little kids. So we went out of the room. They grabbed us through the window. And when my daughter was out, she saw her kids. They took her kids separately. And she just shouted at them, mother, kid, mother, kids. And she, she just kidnapped. She grabbed them from the terrorist. She's a real hero, my daughter. And then they pushed us with a gun pointed at us. And when we were out of the safe room, which I saw already, six or seven members of the kibbutz were already murdered and were lying near our home, and they were pushing us towards the fence around the kibbutz, which they already destroyed. And one of them that looks really lunatic, he handcuffed me with my hands behind my back, and they just pushed us into the car that they brought from Gaza and drove towards the Gaza Strip. We didn't see any IDF soldiers. The border was completely abolished. There was no border. We didn't see any Air Force. We saw nothing. It was just driving through the open fields into the Gaza Strip. We were sitting in the back seat of the car. I had Naveh, my grandson, on my lap. Adi was holding Yula, and Sharon was holding her daughter, Noam. And the two terrorists were sitting in front. And when we crossed the border into Gaza–the theoretical border, there was nothing there–one of the terrorists told us, welcome to Gaza. And I said, thank you. And then we just entered into Gaza. Manya Brachear Pashman: You said that was your last glance of Avshal when he climbed out the window. Shoshan Haran: So we were in captivity for 50 days, and during these horrible days, I was almost sure that both Tal and Avshal were hostages in Gaza, because they were kidnapped a few minutes before us, and I understood that the goal of the terrorists was to have hostages. And so I was very confident, I should say, that both of them are hostages in Gaza. And I knew, I knew by intuition, that Israel will demand to release women and children first. I just knew it. And I told Adi and Sharon all the time. I said, we need to survive. Every day that we survive will get us closer to our release, because I knew that the terrorists see us as bargain chips to get their prisoners released. So I said our mission is just to survive. I need to keep my family. I need to survive. And I thought that Tal and Avshal are also hostages, and I learned about the fact that they murdered my husband on October 7, only after I was released and I met my daughter and my son, and they had to tell me the horrible truth that he was murdered, but not only him. My sister was murdered, my little sister, my younger sister. Her husband, his caregiver. 102 people from my kibbutz, from the little community that we know, every one were murdered on October 7. Manya Brachear Pashman: This was your sister, Lilach, who had been at the event on October 4 with you. Yes? Shoshan Haran: Yes, yes. Manya Brachear Pashman: I am so sorry. May all of those memories be a blessing, every one of them in the kibbutz. Did you stay with your daughter and grandchildren in Gaza the entire time? Or were you separated? Shoshan Haran: No, we were together, luckily. We were handed over by the kidnappers to what I used to term as guards in Gaza. And I use the term guards because we wanted the children to live in the belief that these people are guarding us, so we didn't call them terrorists, not even between ourselves. We call them guards. We were moved from one house to another. So we were not in the tunnels. We were in top Hamas leaders' houses. What they did in all of these houses, they created a separate room for us, where we did not see the family of the Hamas leader, but we heard the voices. We heard the voices of the commander. We heard the voices of his wife and the children. So it was like a provisoric arrangement. And the guards were always in between us and the family. I mean, we didn't see the family, but we heard them. And the guards were the ones who brought us food and they were kind of in between. We had an event in the second house that we stayed. We had an event of knock on the roof. Knock on the roof is a term that the IDF is using when the Air Force is aiming to hit a specific house without harming the people who live inside the house. One time it was supposed to be two blocks away from us, so the terrorists, they know exactly the address, and they told us to get away, just to stay away from the window. So if the window is, if the glass is breaking, we will not be wounded. The second time, it was very close to where we stayed, maybe even the place we stayed, specifically so they evacuated us and the family of the Hamas terrorist who was holding us. We were evacuated to the street, and then we were taken to another house. And eventually we were taken to a fourth house, where we stayed 43 days. And in that house, the Hamas person who joined us knew English. So I started to talk. Before that the guards or the captors, didn't speak any English. They knew some very basic words, like bomb, far, go, come. You know, simple words. But in the fourth house that we stayed 43 days, the Hamas terrorist knew quite good English. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did you seize on that and try to have conversations with your captors? We had lots of conversations and talks. I'm a very passionate reader, so I read a lot of books, including Holocaust survivors' books. I used a lot of the wisdom on how to survive when I was in Gaza. So the first thing I knew: that I should not show any weakness. I looked in their eyes, I talked straight forward, I didn't show any panic or hysterical or crying or stuff like that. The other thing is, I knew I had to keep hope and be determined that we will be released. So that was very important, and that gave us strength. And also I counted the days. I knew the day of the week. And I knew the date. And to eat when you can. To sleep when you can. So to be very determined and very focused on the present. You don't have the capacity to think about the past or the future, you just focus on survival every second, every minute, every hour, how to protect your family and how to create some kind of a relationship with your captors. So they will get to know us, and this will give some some layer of protection. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did you feel like you successfully fostered a relationship? Shoshan Haran: Yeah, it's a very tricky situation. So on one hand, I used to thank–his mother was cooking, was providing the food. We never saw her, but we heard her voice. We heard the babies on the other side of the apartment, but there was no eye contact. But when I knew that she was the one who is preparing food for us and for the captors and for her family. So every time that this guy, her son, brought us the food, I said, I want you to thank your mother. And I mentioned a few times that I appreciate the fact that they are guarding us and they are providing us the food, although it was very minimal, but still. And after a few days, we started to talk about life. I know about their salaries. I know their problems. I know how they get married or why they're not married yet. I know about their mission. Their mission is very clear. They want to destroy Israel. It's a jihadistic mission. It's very clear. They talk about it very openly. And actually, they tried to convince us to leave Israel. He was saying, why don't you go back to Europe or go to Florida. I don't know for some reason, Florida is like, simple for them, for the Jewish community in the US. And he said, next time we're going to come harder on Israel, and I'm not sure that you'll have such a nice team to take care of you, so I advise you go, leave Israel. And at a certain point he said, he asked me, if you go back to Israel, will you go back to the kibbutz? So said to him, I don't want to hear the word if. When we go back to Israel. And regarding the kibbutz, I said, it's a very good question, but I never gave him an answer. I knew what he wanted to hear. They were in a state of mind that, on one hand, you do create human interactions. And they played with the children. The children were so sweet, and they started to play. His family had the same age kids at the other side of the house, so there were human interactions, but it was very clear that their mission is to keep us as bargaining chips. And at one point after I felt more, I don't know, relaxed with the interaction with him, because all my talks were with this specific guy, because he was the only one who talked English. I said, you know, I am very, I don't know which expression I said, but I'm very angry about the people I saw who penetrated the kibbutz and murdered my my friends. And I saw the house of my sister was on fire. It was already bombed. You know, with, I don't know what, with whatever. Actually, I gave her and her husband like, 1% chances to be alive. What I saw in the house was, it would require a miracle for them to survive. So I told him that I'm angry at the people who penetrated the kibbutz and did these horrible things, but I do thank him and the guards and his family, to protect us and to feed us. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did you get any glimmer of remorse or compassion or empathy from them at that point? Shoshan Haran: He told me: We are the same. We are the same, meaning me and the terrorists who penetrated the kibbutz are the same. They received the mission to murder and to burn, and I received the mission to hold you as bargaining chips for the release of the Palestinian prisoners. And this was a very cruel sentence, because while we were in captivity, we were fully dependent on every expression of their faces, they could do anything to us. So my mind couldn't handle this sentence, and I kind of buried it, I just put it aside. I didn't want to think about it, because it was so cruel. But I was sure that if anybody tried to rescue us, they will murder us. I was sure, I was not confused in that sense. I knew that they use us as assets. They see us as assets. And if they will feel that somebody is trying to rescue us by force, then they will kill us. And going to the situation now, you know that Tal, my son in law, Tal Shoham, was released two weeks ago. And actually it's the first time I started to breathe after a year and some months of fighting for his life, and, you know, taking care of helping my daughter and the grandkids and everybody, but we need To remember there are 59 more hostages in Gaza. And when we must keep on the fight. We must not give up. Manya Brachear Pashman: A religion reporting colleague of mine, Dave Schechter in Atlanta, is a cousin of yours. When Tal was released, he wrote about how the extended family all around the world fought for and celebrated his release . Were you able to feel that love or sense that family energy? Shoshan Haran: When I was a hostage in Gaza, I knew that my family and friends in Israel will not stay quiet, just because I know them. But as I said before, most of the time you don't think of anything else besides what's going on in your cell. Actually, I I looked at our situation as if we are astronauts in a hostile world, but unfortunately with terrorists pointing guns at our heads inside the satellite. So when I was in Gaza, I thought about the fact that my family and friends will not stay quiet and will fight, but only on the way to Gaza. Once I was there, the focus is survival, focus. You just don't have any capacity to think of the past or the future or on anything that is beyond here and now. After I returned, first of all, Yuval, my son, told me that he organized a march from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem with 50,000 people when we were in captivity. And Shaked, my daughter, she was then nine months pregnant, and she flew to the US with AJC, by the way. Without insurance. She was nine months pregnant, no insurance company would cover her flight, but she still went, and she was all over. And when they told me, I suddenly felt the connection. And of course, I mean, I got, while I was there, I got millions of emails and, well, WhatsApp I didn't have, because my phone was stolen, but emails from all over the world, including from Africa, the places that my my NGO is working with smaller farmers, Fair Planet, we call it. Now I think it's a bit naive name, but still. Manya Brachear Pashman: And really the Jewish people as a collective have come together at this moment in history. Were you able to feel that sense of community in your circumstance? Or if not, can you feel it now that Tal is home and you can, as you just said, breathe? Shoshan Haran: 10 days after I was released on 26 of November, 50 days after we were taken, I came to the US and AJC people helped us get meetings with congressmen and Senate members. They took us all over. I was just in the meetings. But, you know, in the corridors of the Senate, at the corridors of the Congress and in and out with meetings. And I really, really, really appreciate not only this help, but this was my personal feeling. I mean, we just landed. I was still half in Gaza and half in my freedom. And here I am in the US, talking to decision makers and influencers, and this was done with the help of you guys, so I think it's a nice opportunity to thank you. Thank you for all the help that you are doing since then. I know it started very early on. Actually, my daughter, my younger daughter, Shaked, came to the US to meet you guys and to meet Congressmen a few days after I was kidnapped. So, when I was in Gaza, actually. So I think, the way I see it, I always knew the importance of the Jewish people all over the world, and of course, the importance of Israel being an independent Jewish democratic country, the importance of Israel to the Jews in the world, and the importance of the Jews in the world for Israel. I knew it, but the strength of these connections was much more evident after this horrific October 7 attack. So I felt that the Jewish world is is not only with us, but on a very practical level with us, and using all the network and all the professionals in Washington, in New York, I was invited to synagogues a few times, to big synagogues in Manhattan, what I felt is that a lot of Jewish people abroad that were not so much active in their connection to Israel understood the importance of Israel to them. And the urgency to work together on this crisis. And I think this will not go away. That's my feeling. But now we need to focus on the 59 hostages. I know the feeling I had until two weeks ago. I couldn't breathe. I couldn't smile. I mean, it's your you look at the news and you get heart attacks every single news piece, and you just cannot breathe, and the families of these 59 hostages are still in this situation, we are not allowed to forget and let go. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you for expressing your gratitude. And I must echo that gratitude to you for sharing that story and reliving all of that trauma. I'm sorry that you had to remember some of those horrible moments, though I do think that they are illuminating for those who just simply can't grasp what your family went through. You did not see Tal again until he returned to Israel. Is that correct? Shoshan Haran: Yes. Well, about my husband, I heard only when I returned. But there were evidence from October 7 that Tal was taken alive. People saw him in Gaza. So we knew that he was taken. We were just hoping and praying that none of the horrible things that could happen while you are in captivity will not happen to him. He had a horrible time, but it was released, and my daughter, Adi, his wife, told me it's either zero or one. Either you get your husband, your loved ones back alive, and you can rebuild your future and unite your family, or it's a zero. And for the 59 hostages who are still in Gaza, we need to do anything that we can keep keep the pressure, keep the energy, keep the fight. If you care about the civilian Palestinians in Gaza, like I do–that all my life, I was working for peace–the only thing you need to focus on is releasing the hostages. Because the hostages, the fact that the Hamas terrorists are still keeping them there, is a devastating fact for the Palestinians, because the Hamas, they don't care about their own people. Manya Brachear Pashman: Is it too soon to ask, once all the hostages return and they will, what comes next? Is there a movement already afoot to make sure Israel and others never forget what happened on October 7? Or is it too soon to ask that question? Shoshan Haran: I think once all the hostages are back, there will be as we will need, and also the Jewish people in the world will need to cheshbon nefesh (accounting of the soul). I don't know how to say it in English. To rethink and reconsider our views and our actions looking forward. I think we cannot be naive anymore and say to ourselves, you know that just saying that they want to kill us all, but they don't really mean it, and they will not be, they will not dare to do it and so and so forth. I think now we need to look at the facts as they are and recalculate our stance, our thoughts. I think, first of all, we need to follow the money. Because one thing I can tell you, without funding, Hamas would never get to this stage, and neither Iran or the Houthis or Hezbollah, there are forces in the world who are supporting financially, the organizations or the countries who declare that they want to destroy and abolish Israel. We need to follow the money. We need to be smart. That's one. The other, and that's a big question. I'm just putting it on the table, but it's a big question how to do it, but this, we must do it. And the other thing is, the key for mutual existence is education. And what I learned recently, for example, is that the Palestinian Authority, or the people in Gaza, they do not teach about the Holocaust. They do not know about the Holocaust. The people that my captors, they were 24, 25, and 31 and then the commander was 40. Looking at the dates of the decision not to teach about the Holocaust, I'm sure they had no understanding why we are here. They think that we just came here like a colonialist or, you know, and then, if they will give us enough trouble, we will go away. But we're not going to go away. We are staying, and until they change their mission to destroy us. We need to be stronger and smarter than them. Manya Brachear Pashman: Shoshan, thank you so much for being with us, for sharing your story, and for giving us hope, sharing your hope, and then giving us hope that the hostages are all coming home, and that there is a future for Israel. Shoshan Haran: There is a future for Israel. This, I'm sure, yes, but we need the Jewish people with us, and we need to work together. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much. Shoshan Haran: Thank you. Thank you. And regards to my friends at AJC. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with two scientists at MIT who have created a foundation to ensure Israeli scholars and their American colleagues can collaborate freely, and foster research and innovation that benefits all of humanity.
Mar 7
Meet the MIT Scientists Fighting Academic Boycotts of Israel
The American Studies Association has boycotted Israeli academic institutions since 2013. The Association for the Advancement of Anthropology has refrained from formal collaborations with Israeli academic institutions. And just this past summer, the American Association of University Professors opened the door to academic boycotts against Israel. Enter: two scientists at MIT who see firsthand the consequences of academic boycotts and the damage it can cause to scholarship and scientific progress. To ensure Israeli scholars and their American colleagues can collaborate freely, and foster research and innovation that benefits all of humanity, they formed The Kalaniyot Foundation (pronounced Ka-la-nee-yought), named after Israel's national flower. Hear from Drs. Or Hen and Ernest Fraenkel, co-founders of this initiative, on the impact of anti-Israel boycotts on academic collaboration with Israeli scholars, and what they're doing to rehabilitate the reputation of Israeli researchers in the eyes of the world. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : U.S. Special Envoy Steve Witkoff on Gaza Reconstruction, Israeli Security, and the Future of Middle East Diplomacy Why Germany's Antisemitic Far-Right Party is Thriving Instead of Disappearing Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Drs. Or Hen and Ernest Fraenkel: Manya Brachear Pashman: Since the Hamas terror attacks of October 7, 2023 many university campuses have been riven by anti-Israel protests, demonstrations, often unfortunately fueled by disinformation and rife with rhetoric that too often crosses the line into antisemitism. But even before October 7, Israeli scholarship had become a target of the boycott divestment sanctions movement. The American Studies Association has boycotted Israeli academic institutions since 2013. The Association for the Advancement of Anthropology has refrained from formal collaborations with Israeli academic institutions. Even study abroad programs that give students an opportunity to live and study in Israel have come under scrutiny. Enter: two scientists at MIT who see firsthand the consequences of academic boycotts and the damage it can cause to scholarship and scientific progress. To ensure Israeli scholars and their American colleagues can collaborate freely, foster research and innovation that benefits all of humanity, they formed The Kalaniyot Foundation, named after Israel's national flower. Dr. Or Hen and Ernest Fraenkel are with us now to discuss this initiative. Dr. Hen, Dr. Fraenkel, welcome to People of the Pod. Ernest Fraenkel: Thank you very much. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I want to work backward here a bit with a purpose. I want to start by sharing with our audience a little about your research. Dr Fraenkel, you work in health science, technology. What is the goal of your research and scholarship? Are there particular diseases you're trying to cure or treat? Ernest Fraenkel: We are interested in the diseases that are the hardest to treat, ones like Alzheimer's, ALS, Parkinson's, where we don't really know the root cause, and we believe that by gathering many different kinds of data about genes and molecules, about RNA and also about people's lived experience of these diseases, and using computational models, we can identify new targets for drugs and hopefully better therapies. Manya Brachear Pashman: Have you collaborated with Israeli scientists on this? Ernest Fraenkel: Yes, we collaborate with quite a few scientists all over the world, including top researchers in Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Dr. Hen, you are a nuclear physicist, and you study the strongest force in nature, right? What is the goal of your research? Or Hen: So my research is very much on the fundamental curiosity driven science side of things, I am trying to understand how the fundamental building blocks of matter come about. We're building a new particle collider in the US called the electron hand collider. It's a $3 billion project funded by the Department of Energy, where we will try to understand why the proton and from that nucleus and all of us have mass. Trying to understand how we get the proton to a specific spin, which is the reason that we can go into an MRI machine and image ourselves. And I also try to understand things like, how do protons and neutrons interact with each other at extremely short distances, which tell us about exotic phenomena in the universe, like neutron stars. So trying to understand, really, the fundamental building blocks of matter and how they come about. Manya Brachear Pashman: Wow. And is there promising scholarship in this realm in Israel? Or Hen: Yes, there's quite a few groups working in this area. I did my own training in Israel. I am a graduate of the Hebrew University for undergrad and Tel Aviv University for grad school. And actually, ever since I came to MIT, I've still been collaborating with colleagues from Technion, Tel Aviv, Hebrew University, Weizmann, Ben Gurion. I've always had a strong collaboration with Israel, actually. Manya Brachear Pashman: So after October 7, or maybe even leading up to it, what were you seeing when it came to support of Israeli scholarship and collaboration in your institutions, in your fields, in academia in general? Ernest Fraenkel: I think before October 7, we were living in a bit of a bubble, because MIT is a special place which is very deeply immersed in science and technology. Where really, quite honestly, before October 7, I had no hint that there were biases against Israel, Israelis or Jews. I know that was not the experience in many other areas, especially in other fields. But things really turned 180 degrees on October 7, and what we've seen since then has been deeply disturbing. That some of the boycotts that have been bubbling for years in the humanities suddenly burst forth into the sciences and the engineering fields in ways that are both global and also very local. Seeing bias against individual researchers inside laboratories, as well as these kind of blanket attempts to boycott Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Dr Hen, did you see the same? Or Hen: Yes, definitely. I work with a lot of international collaborations, actually, within collaborations, because there's structured bodies with bylaws and rules, It was very hard for anyone to object the presence of Israeli researchers. But what we have observed in many places is peer to peer collaborations dying down. We've seen a very significant social tax being applied to people who continue to collaborate with Israelis, and honestly, maybe in contrast a bit to what we know from academic boycotts in other areas, but are very much politically driven, within the STEM, within exact sciences, biosciences, etc, the social taxing is actually much stronger because we are people who usually instead, people keep a very clear separation between the politics and then, you know what they view from the work in the lab, which is very clear and data driven, and not a lot of room for opinions. It's very much exact. But on the other hand, the second that walking within Israel, and you know collaborating with Israel, is start costing other corporations, other people will now not work, then you get a problem. And that's what people really avoid and that's how an academic boycott within the STEM areas is progressing. It's a very deeply bound social tax that is just running in the air of the institutions. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what is the Kalaniyot Foundation doing to promote these collaborations? Can you give us some specific examples, or projects or partnerships? Or Hen: Yeah, so one of the things that we really believe in is that, at the end of the day, actually, what we see, also data shows, is, well, there is existing strong collaboration, that peer to peer, that person to person connection, is so strong that it's very hard to break that. You can go into my department and you can talk to people about Israel. And they know Or, and they know the person, right? And they might have a positive opinion about, you know, negative opinion about me. But whatever that opinion is, right, it's stronger than anything. They will try to protest and say, Okay, maybe there's a political issue. But you know, we know the researcher. We know the scientists. We know our colleagues. So the approach of Kalaniyot is to actually bring in more Israelis to campus, to bring in brilliant people who are excellent researchers that will come and enrich the academic environment, first and foremost, through this quality, and second, by the people that they are. Maybe Ernest, you want to continue with this? Ernest Fraenkel: So it's really this dual mission. We think that if we bring more top notch Israeli scholars to us campuses, it will normalize interaction with Israelis, humanize the Israeli, but there's a problem, right? Because if you just bring Israelis into campus environments that are hostile, they won't thrive. Many of them won't want to come, right? And so the other piece of it that's necessary is to build community, and that's something that we've been doing since October 7 of last year, trying to figure out how to do that, and what we found is face to face interaction is really critical. And so at MIT, we've been having weekly lunches of the Israelis, Jews, allies, everybody who felt isolated and left out of society by all the protests that were taking place. And the beautiful thing is that that started as a reaction, right, a sort of a safe place to retreat to, and it's actually become a wonderful, positive place. And still, now, you know, so far into this crisis, people are coming, and actually the numbers are even growing. And so on a typical week, we get more than 100 people in person. We, of course, feed them lunch, and it's just a wonderful place where you can make friendships, develop academic collaborations, and Israelis realize that there is a community here that appreciates them and welcomes them and it helps them thrive. Manya Brachear Pashman: Because, of course, food is a vital currency, both on college campuses as well in Jewish as in Jewish life. Food heals all. But I am curious, do you? In addition to building these thriving communities, are you also so that people are surrounded and comfortable but are you also trying to build bridges with people who perhaps do tend to throw the word Israeli around in a negative capacity, but you need to actually have some face to face contact. Or is that really not the purpose of Kalaniyot. Or Hen: I mean, it's a yes and a no. We certainly have done that, right. So if you think about how it all started very soon after October 7, basically after the first protest on campus at MIT. We went to talk to our president, three Jewish Israeli faculty, and we asked her. We said, Look, we hear from the students about what's happening in the dorms, what they're experiencing. It's really bad, and it's very hard to handle through the existing mechanisms. Please actually give us the budget. We'll get kosher food. I'm a Mizrahi, that's what I know how to do, feed people. Let's put everybody together, and let's make sure everybody feel welcome. And we also said, you know, we'll be your bridge. We'll help the students communicate with administration through our guidance, right? We'll be able to filter, to guide them, but also to pick up on the important things that you need to know. But then we said something else. We said, Look, this is going to become very tough, also for the students who are protesting out there right now. It was before Israel responded, but we knew exactly what happened in the kibbutzim, and we knew this is not going to be just another round with Gaza. This is going to be something different. So we actually suggested to the President that alongside starting our group, we will start a parallel group of peers who we might disagree with politically and have different perspectives on the Middle East, but we know that they are reasonable people that we can talk to, that we can collaborate with, that we can work with, despite or alongside disagreements. And so the idea was to start our lunch, to start a second lunch, and slowly, through the faculty leadership, bring the groups together. Some of it has worked. Some of it didn't work. We used to meet once a week as the faculty and say, students tell us that this and this is happening. Can you maybe walk with your students to tone that down, and they would tell us what's bothering them, etc. Getting the students to come together, that was a bigger lift, a challenging one. And there was another initiative that came about called the Third Space Lunch, that maybe Ernest can elaborate more on. Ernest Fraenkel: So just to add a little bit to that. So the faculty leads from the other group came to speak to our students. Were very respectful to them. The faculty listened quietly to the concerns of the Jewish students. And I think we did see an attempt by many of the faculty to bridge the gaps. Obviously, faculty are an extremely, you know, diverse group. We have extremists, we've got centrists, we've got moderates. And not everybody was trying to help, but many, many were, and I think that was very encouraging, and I've seen that continue throughout this. There are hidden allies. Probaby the average faculty member probably doesn't really want to know too much about Israel or Palestine. Doesn't want to have to understand the conflicts. They just want to go about their daily lives, teach what they love to teach, do the research they love to do, and they are natural allies in trying to bring order back to campus. And the more that we can engage them, the better off it is. Or Hen: But I think in terms of the formal program for Kalaniyot - Kalaniyot is really meant to bring in researchers and make sure that they have a supporting environment. And if people want to take that extra step of building bridges and building, that's all great, but it's not kind of a mandatory part of the program. Manya Brachear Pashman: I get it. You really just want to foster academic research and progress and innovation, right? Put political strife aside. You've named this foundation Kalaniyot after Israel's national flower. Can you describe for our listeners that flower and why you chose that name for this initiative? Ernest Fraenkel: The Kalaniyah looks a lot like a poppy. It's a red poppy, and during good times, there actually was an annual festival where Israelis would flock to the south in the area right around Gaza to see the bloom of this flower that would cover the otherwise fairly barren, quite honestly, countryside. And it was called the South Red, Darom Adom, and people would rush there to see it. And it was a symbol, which actually takes place right around the time we're recording. People have been sending us photos from from Israel the last few weeks of these flowers, the more they hear about the program. And it's a sign that the winter is going to end and spring is going to come, and everything will be renewed. And so it was the South in red, in a sense, that was all positive. And we think the same sort of thing is possible here, that while Israel is right now a touch point for conflict on campus, we want to see a time when Israel, this is something like, Oh, of course. You know, everybody wants to have some connection to Israel. That's where the best researchers are in every field. I often tell the story, when I was first on the faculty here, one of my first assignees as an undergraduate advisee was somebody from Hawaii, and he told me, asked him what he was going to do this summer, and he said he's going to Israel. So no, really, what's, what's your connection to Israel? He said, Oh, I don't have any I thought, maybe he's a strong Christian. I asked him about that. Said, no, no, I don't have any particular faith. I just heard it's startup nation, and I want to go and experience it. And I just think, how many students today is their first association with Israel, startup nation? Probably not that many anymore, but we can get back to that and realize that it's more than startups, right? It's basic science, it's the arts, it's culture. And so there's much that Israel has to offer the world, and we want to get back to the point where that's the first thing people think about Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: So this initiative did start at MIT, but it appears to be sprouting, to use a pun, it appears to be sprouting on other campuses. Dartmouth is developing a chapter and Penn, right, the University of Pennsylvania. Are they being led by fellow scientists who have seen the consequence of this scholastic snub, for lack of a better word? Ernest Fraenkel: So at each university, and there are several others in the works that are still working their way through the administration at each university, and by the way, this is not a renegade effort. At each university, the faculty form a faculty board, we encourage them to find a diverse group. So it's not all the sciences on our board. And on those boards, there seem to be many members of humanities departments. Not all Jews, not all Israelis. And these diverse faculty boards are people who are allied with the goals, and we have bylaws. This is a program entirely about positivity. It's not attempting to suppress anybody else's speech. It's not attempting to make any political points. It's a purely academic program that will help restore the image of Israel as a place of academic excellence and help the United States maintain its academic edge through those collaborations. Or Hen: And I think you're hitting on a very unique point, right? And that is that this is entirely faculty led program. When you think about the role of faculty in universities, especially faculty from STEM fields, right, we don't lead a lot of things in the academic world that are not our research, right? Honestly, that's kind of, why am I here and not in Google, right? I would probably make a much bigger salary for Google these days. I'm here because I really care about my research, those open questions I really want to explore, and that's what I'm doing. So I'm teaching my class, and I'm focusing on my research. And me is everybody else around me, that's what we do. So there is a very high activation energy to get the faculty to do something that is not their research, their own research, but once you do that, faculty is a force of nature at the university. That's kind of what we're here to stay, right? We'll tenure, we're going to be at the retirement. We run the place eventually. So it's both to activate the people who can really make an impact from within in a very strong way. That's number one, who have these decades of connections, right? Well before the challenge, you know, I've had my 10 years of collaborations here at MIT, and this has a lifetime of more than 10 years of collaborations here, right? And many of us and people remember those connections, right? Remember how we teach together, how I lent them something from my lab, and stuff like that, right? We have these personal connections. So it is really the first and uniquely faculty led program that is very helping to come back, see faculty do that. There's a lot of power, and that's also why it's such an academically focused program, because that's what we know how to do. There's many other who can combat antisemitism and can give antisemitism training and title six and all that. And we don't do it, not because it's not important, just because we are not the people who bring in unique expertise in those areas, but when it comes to research collaboration, connections with Israel around those things, we are the ones who can really promote it from within in a way that's unpowered and parallel to anyone else. And that's the, I think the strongest point of Kalaniyot, the faculty leadership. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, you're not activists, you're not advocates. That's not what you set out to do. You are researchers, scientists who just want to do research in science. Or Hen: And when I see everybody around us do the best research and science possible, which means engaging with the brightest minds anywhere in the world, and that includes Israel. And we don't want to see that door shut down. There's no hiding it – Ernest and I are Zionists, we're not going to shy away from that. And we think that an academic boycott in the STEM is a risk to Israel. Israel doesn't have oil, right? What Israel has is the Jewish mind, and that mind is the thing that helps Israel, and that mind is the thing that helps the world. And we can go on and on about inventions and discoveries that came out of Israel and Israelis and Jews for the benefit of mankind. So both for the benefit of Israel and all of humanity, we don't want to see the Israeli Academy get isolated. It's going to be bad for all of us. Manya Brachear Pashman: Now I know that there is a program at Indiana University called Olamot, focusing on the humanities. Does this only apply to STEM fields, or do you also have partnerships and collaborations developing across multiple disciplines? Ernest Fraenkel: Yes, absolutely, this is a program that's open to all academic fields, and each university will craft a slightly different program, we're sure. At MIT, because we're STEM dominated, our Kalaniyot program is dominated by STEM, but it's not exclusively STEM here, either. We do have deep involvement with several of our board members in the humanities. Many of the people who come to our programming are in humanities. We're hoping that some of the scholars whom we will select in our first cohort of post doctoral and sabbatical visitors will be in the humanities, but that's going to be much a bigger component of it at other universities such as Dartmouth and Penn, where they have huge humanities programs. Manya Brachear Pashman: And are you getting mostly support, or are you getting any pushback from faculty members? Ernest Fraenkel: So this is really fascinating. Early on, when we first started formulating this program, we wrote a memo explaining, a letter, explaining why we were doing this for something called the faculty newsletter, which is usually a place where people write fairly anti-Israel things, and we kind of braced ourselves for the pushback. And nothing came back. There was no pushback. Because if you believe in academic values in the United States, unless you're a hardcore BDS person, there's really nothing objectionable here. Our goal is to bring brilliant scholars to campus and encourage them to be able to work broadly, without regard to nationality, religion, anything else, any other protective category. And so we were very pleased. And initially, you know, the administration was curious. They were interested. They wanted to review exactly what we're doing. The MIT administration went through everything we're doing, and they gave us the thumbs up, and they've now been helping us make connections and behind the scenes, I believe, I understand that, you know, some provosts and presidents occasionally talk about this when they meet and they, you know, tell each other it's not a bad thing to have at your University. Or Hen: I remember when we kind of got people to know the program, we met with a very high ranking individual at MIT. And that person said, Look, MIT stands on three legs: research, education, and entrepreneurship. Israel excels in all three. Of course, we want those connections. Of course we want those collaborations. And who in the right mind can say that this is anything political, right? Now I'm sure that some people will try at some point. But like Ernest said, we've worked very hard on the language and the messaging to make sure that the language and messaging reflects the way we really see it, as a very strong academic program. Manya Brachear Pashman: So, Dr. Hen, I do want to ask you a personal question. I have read that as a child, you navigated some pretty significant learning disabilities stemming from dysgraphia. You have difficulty translating your thoughts into written form, but the assessment to determine those disabilities also determined that you had a unique gift for abstract comprehension, the ability to conceptually pare down complex ideas to their fundamental core. So I wanted to ask you, in your opinion, what is at the fundamental core of these academic boycotts? Or Hen: Honestly, I do believe that the academic boycotts come from antisemitism. That's the core. I do believe that there are a lot of people who engage in that, not understanding that is what they're doing. I'd like to give people the benefit of the doubt. I think that a lot of people do see a difference between anti-Zionism, anti-Israel, antisemitism, right, which I personally do not share. And that's a different point of view, which is allowed. But I think at the end of the day, trying to isolate Israel, eventually is from a top level, and attempt to bring down the country, because that's the core. Core of Israel is its academics. That's really where it all starts. And if we don't have academia, if we're attacking the Israeli Academy, you're attacking Israel. And any person who takes the time to learn about the Israeli Academy, who listens to speeches by the head of Tel Aviv University about the judicial reform in Israel. Who listens to the head of the Israeli National Academy about how he sees democracy and what he sees about the war, situation, you would learn that the Israeli Academy is really the hallmark of independent academia that stands by itself, as an independent body that really promotes research and good for the world. And anyone who attacks that either doesn't know or doesn't care to know, and I'd like to hope that most people don't know, and once they'll know and appreciate the people, they will see different people. There is a core that doesn't want to know, and okay, we need to make sure that that call remains as small as possible. Manya Brachear Pashman: Dr. Fraenkel, do you agree? Ernest Fraenkel: I'm by nature, a centrist and not a political person, and I also have learned over time that it's very hard to understand other people's motivations. But I do think that one of the paths to it, to solving the problem, is to re-humanize Israel and Israelis in the minds of the people who are currently protesting. And I think we'll have good results if we do that. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm curious, we've been talking a lot about Israeli research and innovation. Can you kind of share a piece of Israeli innovation that you've heard about recently, that maybe our audience has not and should know about? Ernest Fraenkel: I was just at a conference yesterday, and one of the best talks yesterday, this was at a conference on ALS, was given by a researcher from the Weitzman Institute, Eran Hornstein. And he spoke about an entirely new way to analyze what goes on inside cells in the course of disease. He calls it organellealomics, I think. It's kind of a mouthful, but it was completely innovative. No one has anything similar. It allows you to get a wonderful view of all the different processes that are going on in the cell at a very high level, in a way that is experimentally very accessible. And I think it's really going to transform a lot of how we research diseases, and may lead to some rapid advances in some of these tough cases. Or Hen: Yeah, I can add to that, you know, from the more industry side of things, right? We all have technology in our pockets, in our homes, in our offices, developed in Israel. The most advanced processors by Intel are built on architecture that was developed in Haifa. Apple has engineering centers in Israel. Facebook has engineering centers in Israel, Nvidia. All of us use Israeli technology day in and day out. We either know it or we don't. But there's not a single person in the western world that does not rely on Israeli technology sometime, someplace, some point in his day. Manya Brachear Pashman: And when you were at that conference, Dr. Fraenkel, or Dr. Hen, consider that, when you pull out your phone and consider the many ways in which we use Israeli technology, does that further validate, does it affirm that what you are doing is the right thing to do, and that this will only benefit humanity at large? Ernest Fraenkel: In biology, we often do these experiments where we delete a gene, we make it stop working, and we see what happens to the cell or to the animal that we're studying, right? And just do the thought experiment. What would happen to American science if it didn't have these strong collaborations with Israel? And be weaker in consumer electronics, and be weaker in AI, we would be weaker in all the underpinnings of all the technology that we're all walking around with every day. We'd be weaker in healthcare. Think about the contribution that Israel made to understanding what was going on during the COVID pandemic, right? It's just shocking how much we would lose from this small country not being there. And absolutely, when we think about that, it just drives us even more to try to get this program to spread across all the best universities in the United States, and hopefully we'll make inroads in Europe as well and really bring Israel back to the forefront in everybody's mind as a place where positive things are happening. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, thank you both for joining us so much and for sharing about this program. Really do appreciate it. It's fascinating and refreshing to learn that academics are supporting academics. Ernest Fraenkel: Thank you very much. Real pleasure to speak with you.
Feb 27
U.S. Special Envoy Steve Witkoff on Gaza Reconstruction, Israeli Security, and the Future of Middle East Diplomacy
AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson sits down with U.S. Special Envoy to the Middle East, Steve Witkoff, for a live discussion in Washington, D.C., to introduce AJC's Center for a New Middle East. They cover plans for rebuilding Gaza, the future of Israeli-Arab relations, and the evolving geopolitical landscape, including the impact of the Abraham Accords and shifting regional alliances. Tune in for insights on diplomacy, security, and what's next for the Middle East. The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Resources: AJC Center for a New Middle East Initiatives and Policy Recommendations Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : Why Germany's Antisemitic Far-Right Party is Thriving Instead of Disappearing Spat On and Silenced: 2 Jewish Students on Fighting Campus Hate University of Michigan Regent Jordan Acker: When Antisemitism Hits Home Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Jason Isaacson and Steve Witkoff: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week, AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer, Jason Isaacson, sat down for a live conversation with Steve Witkoff, the US Special Envoy to the Middle East. They discussed plans to rebuild Gaza, political upheaval in Syria and Lebanon and expansion of the Abraham Accords. For this week's episode, we bring you that live conversation to you. Jason Isaacson: Good evening, everyone. Thank you for being here, and thank you Special Envoy Witkoff for participating in this evening's program, introducing AJC Center for New Middle East, and extension and refocusing of the work that we've been doing for decades to advance Arab Israeli understanding, cooperation and peace. Your presence here means a great deal to us. As you've heard from my colleagues, AJC looks forward to working with you and your team in any way that we can to help ensure the success of a secure Israel, fully integrated in the Middle East. Now let me begin by thanking you again, renewing our thanks and thanking President Trump for your relentless efforts, which began even before the President took office, to assure the liberation of the hostages still held by Hamas and Gaza now for 508 days, we know how dedicated you are and the President is, to gaining the release of Edan Alexander, the last living American hostage, and the remains of the four other Americans, Itai Chen, Gadi and Judy Weinstein-Haggai, and Omer Neutra, and all of the hostages living and dead, still held captive by the terrorists. So I want to point out that leaders of the Hostage Families Forum are with us here this evening. As is Emmet Tsurkov, whose sister Elizabeth Tsurkov was kidnapped by terrorists in Iraq two years ago. We are all counting on your and your colleagues' continued efforts to free them all. Thank you again, Steve. Now my first question to you, how does a successful real estate developer make the transition to Middle East diplomacy, as you certainly have. Clearly, there are profound territorial issues at play here, but there are also powerful and tangible factors, perhaps less easily negotiated, factors of historical narrative, of religion, of nationalism. How do you cut through all that? How do you achieve success given the very different career that you've pursued up to this point? Steve Witkoff: Well, first of all, Jason, thank you for having me, and welcome everybody and to the hostage families, I just want to welcome you here. Some of the people I probably have talked to already, and just know that my heart is always with you. You know, President, I'm a very close friend of President Trump's, and I think he felt that, hopefully, that I could do a good job here. And so I think the job had a lot to do with miscommunication and correcting that. It had a lot to do with getting over to the region and understand what was happening, and maybe most importantly, it had a lot to do with his election and peace through strength and the perception that he was not he was going to take a different path, that the old policy prescriptions that that had not worked in the Middle East were not going to be tolerated by him anymore. And I think that's in large part what allowed us to get a positive result. Adding to that, of course, was all of the good work that Prime Minister Netanyahu in his administration had achieved with Nasrallah Hezbollah in Lebanon, he had basically gutted Hamas. So many good things that happened. And you know, on top of that, the raids in Iran, and it created this perception that a lot of the a lot of what emanated out of October 7 was never going to be tolerated again. And that began the, you know, that began the pathway to achieving the result we achieved in the first phase. But that's just half of the problem. So we've got a lot more to go. Jason Isaacson: I've got some questions about that, as well as you can imagine. Help us understand the President's priorities and therefore your focus in this very complicated region. There's the continued trauma of October 7, 2023 dozens of Israeli and other hostages still held by Hamas terrorists in Gaza, and the deep wounds inflicted on Israeli society in that attack. There's the need to rebuild Gaza and to assure it is no longer governed by Hamas. There's the prospect of advancing normalization between Israel and Arab states building on the Abraham Accords of the first Trump administration. There are also political upheavals and some hopeful signs, although the jury is still out in Lebanon and in Syria, and there's the ongoing threat to peace and stability posed by the Iranian regime. How do you prioritize? What are your expectations for success on these many tracks. It's an awful lot to deal with. Steve Witkoff: That was, I think I counted like 14 questions. Jason Isaacson: This is my specialty, by the way. Steve Witkoff: I can see. I have to, now you're testing my memory on all of this. Jason Isaacson: Priorities. Steve Witkoff: Yeah, I would say, How does the President think about it? Well, first and foremost, he wants something different for the region, yeah, and different in the sense that the old way of thinking we've they've rebuilt Gaza three or four times already. Like that's just an unacceptable use of resources. We need to do it in a much more in a much better way, a. B, we need to get rid of this crazy, ideological, psychopathic way of thinking that Hamas thinks. What they did, it can never be tolerated. I saw a film that many in this in this room did not see, made by Southern Command when I was in Gaza, and it's horrific. I mean, it is a horrific film. What happened in this film and what they did to people. So this is not, this is not the act of people who are going to war. This is the act of barbarians, and it can never be tolerated. Normalization is critical for the region. Saudi Arabia embraces it because they can't finance in their own markets today. And why? Because there's so much war risk. I actually saw Jamie Diamond today, and I discussed it with him, and I said to him, you know, think about an area like Saudi Arabia. They have tons of money, but they can't leverage their money. And they can't because the underwriting risk on war, it can't be underwritten. So you're not going to see typical senior financing. Go into those marketplaces they can finance if they do a deal in New York and they can't finance in their own country. Makes no sense. And that's going to lead to a lot of stability. In terms of the Iranian crescent, it's basically been decimated. Look at what's happened with Syria. No one ever thought that that was going to happen. We've got an epic election in Lebanon. And so tons of things happening. Lebanon, by the way, could actually normalize and come into the Abraham Peace Accords, as could even potentially Syria. So so many profound changes are happening there, and yet it's been a flash point of conflict, and I think that there's a possibility that we end it. Now, do we have to make sure that Egypt is stabilized? Yes, they've got some issues, economic and financial issues, and also on their streets. Same thing with Saudi Arabia, and we have to be cognizant about that. But all in all, I think there are some really good, good things that are happening. Jason Isaacson: Yeah, and I hope with your intervention and the president's power, more good things will happen in the coming months. Steve Witkoff: We're hopeful. Jason Isaacson: So you've recently returned from your latest trip to the region with meetings at the highest levels in Israel, in Saudi Arabia, in the United Arab Emirates, next Tuesday in Cairo, will be a meeting of the Arab League to discuss the future of Gaza. What is your sense of, drills down on your last answer, what is your sense of the region's readiness to advance to the next phase of negotiations, to free the Israeli hostages, to shift to a new Israeli force posture in and around Gaza, and put a governing structure in place that excludes terrorists. Can we assure that Hamas no longer rules, no longer poses a threat, that its missiles, tunnels and other infrastructure in Gaza are destroyed? Steve Witkoff: Well, you know, central to the May 27 protocol that was signed with the Biden administration and the Israelis. Central to that is that Hamas cannot have any part of a governor governing structure in Gaza. And that's from that's a red line for the Israelis, but it's a red line for us, too. You see the film. And we have to thread that needle in phase two of the negotiations. Jason Isaacson: How do we get there? Steve Witkoff: We're not entirely sure yet, but we are working. You know, we're making a lot of progress. There is, Israel is sending a team right now as we speak, it's either going to be to Doha or to Cairo, where negotiations will begin again with the Egyptians and with the Qataris, and I may if that negotiation goes positively enough. This is the initial phase of the negotiation where we've set, we've set some boundaries, some contours about what we want to talk about and what the outcomes we expect to happen. This is from the United States at the direction of President Trump. If it goes well, maybe I would be able to go on Sunday to execute and finish an arrangement. That's what we're hoping for. Jason Isaacson: Put phase two on track. Steve Witkoff: Put phase two on track and have some additional hostage release, and we think that that's a real possibility. We had a lot of conversation this morning about that, and with all of the parties I'm talking about, and people are responsive. Doesn't mean it's going to happen. That's a very chaotic place the Middle East. Jason Isaacson: But you've got cooperation from the Quint, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Jordan, Egypt, Qatar. Steve Witkoff: Yes. All of those countries in that region, they want to see, they want to see stability. There's new young leadership there. Everybody understands that it's untenable to be at war all the time. It just doesn't work, and it's setting everybody back. Look at Israel, by the way, they're drafting, they're conscripting people at 50 years old to go to go to the fight. That's, uh… Jason Isaacson: And reservists are being called back to duty again and again. Steve Witkoff: Correct. People can't work, by the way, economies are suffering throughout there. But on the other hand, Hamas can't be tolerated either, and yet, we need to get the hostages back to their families. Pardon me? Jason Isaacson: Israel is still resilient. Steve Witkoff: Of course it is. Of course it is. But we, you know, look, I don't want to talk about all these things and not acknowledge that the most that the primary objective has got to be to bring those hostages home. It has to be. Jason Isaacson: I mentioned the Quint before: Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Jordan, Egypt, Qatar. Egypt and Jordan, longtime peace partners with Israel, were proposed by the president as the possible place in which Palestinians evacuated from Gaza could be housed temporarily, or perhaps more than temporarily. What is your sense of the possibility of the dislocation of Palestinians from Gaza? Is that essential to the idea of rebuilding Gaza, or not essential? Steve Witkoff: Well, first of all, let me acknowledge King Abdullah, and also the Egyptians, General Hassan, who runs their intelligence unit. President Sisi, their ambassador. They're dug in. They're focused on solutions. It's a complicated situation right now, but they've done a great job, and they've been available, and whenever I call them, they're responsive. The Jordanians have had a tough trip here, but, you know, they've managed through it. But let's just talk sort of about what the President talks about. Why is he talking about Gaza in the way he's talking about it? Because all the for the last four decades, the other ways of thinking have not worked. We sort of always get back to this place. First of all, it's a giant slum. It really is, by the way, and it's a slum that's been decimated. On top of that, I was the first American official to go there in 22 years. I was literally there in the tunnels, on the battlefield. It is completely destroyed. There's 30,000 shells that are laying all over that battlefield, in large part because the Biden administration held up munitions shipments to the Israelis, and they were firing 1973 vintage ammunition that didn't explode. Who would let their children wander around these places? In New York, there would be yellow tape around it. Nobody would be allowed to come in the they were digging tunnels. So everything underneath subterranean is swiss cheese, and then it got hit by 2000 pound bunker bombs. So you could have dust down there. It's so devastated. I just think that President Trump, is much more focused on, how do we make a better life for people? How do we change the educational frameworks? Right now, people are growing up there, in textbooks, in the first grade, they're seeing AK47's, and how you fire them. That's, that's, this is just insanity. What's going on out there. So we have to directionally change how people are thinking there, how they're going to live together. People talk about two state we at the Trump administration, talk about, how do you get to a better life if you have a home in Gaza in the middle of a slum that hasn't been fixed up correctly, is that as good as aspirationally having a great job and being able to know that you can send your kids to college and they can become lawyers and doctors and so forth? That to me, is what we want to achieve. And when, when we began talking about Gaza, we were not talking about a giant eviction plan. What we were talking about was the fact, unlike the Biden administration, and this is not a knock on them, it's that they didn't do their work correctly, the Biden administration, that May 27 protocol is based on a five year redevelopment plan. You can't demolish everything there and clean it up in five years, let alone x-ray it on a subterranean level and figure out what foundations exist, or what, what conditions exist to hold foundations, and then what we should build. It's easily a 15 year plan, and it might be 20 or 25 years. And the Wall Street Journal, one of the most mainstream publications, two days ago, finally came out with a major article talking about that and basically validating what we've been talking about. Once you understand it from that perspective, you understand it's not about an eviction plan. It's about creating an environment there for whoever's going to live there that's better than it's ever been in the last 40 years. Jason Isaacson: Steve, thank you. Before October 7, 2023 the betting in many foreign policy circles, as you know, was that the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and Israel were closing in on a deal to normalize relations, coupled with an enhanced security agreement between the US and Saudi governments and Saudi access to the full nuclear fuel cycle under US safeguards. Where would you say that formula stands today? Is that still the framework that you're expecting will describe the relationship between the United States and Saudi Arabia and between Saudi Arabia and Israel? Steve Witkoff: Well, that's why I keep on going back to the May 27 protocol, because it's chock full of misinformation. And so the Saudis were operating, as were the Israelis, as if you could redevelop and reconstruct Gaza in five years. You can't. You can finish demolition, you can finish refuse removal, you can do all of that in five years. But for that, there's nothing else is going to get accomplished. So when the Saudis talked normalization with the Israelis and defense treaty, they were thinking about it on a five year time frame. Once you begin to think about it as a 15 or a 20 year deal, it almost begs the question, are Gazans going to wait? Do they even want to wait? I mean, if you're a mother and a father and you've got three kids, do you want to wait 20 years to maybe have a nice, safe home there? And this has nothing to do with relocation. Maybe we should be talking about relocation, or, excuse me, the ability to come back and, you know, later on. But right now, right here, right now, Gaza is a long term redevelopment plan, and I think once the Saudis begin to incorporate that into their thinking, and the Egyptians and UAE and everybody who has a vested interest in Gaza, I think you're going to see development plans that more mirror the way the President is thinking than what the May 27 protocol contemplated. Jason Isaacson: Are you suggesting that the possibility of normalization between Israel and Saudi Arabia will come after there is a fully formed Gaza redevelopment plan? Steve Witkoff: I think so. Because I believe that. I believe it's just sequentially logical, because that's when you begin to think about how Gazans are going to think about it. Right now, we're talking about it in the abstract. And there are many countries, by the way, out there, that from a humanitarian standpoint, we've talked to many of them, are actually extending themselves and saying, Hey, look, we'd, we'd love to be a part of some sort of permanent solution for the Gazan people. No one wants to see the Gazan people in some sort of diaspora, they're sort of disengaged, and that doesn't work. That only is going to fester and lead to more radicalism in the region. So we've got to get a solution for it, but we need to levelset the facts first. And the facts have not been levelset. They've been thinking about this from a perspective of facts that are inaccurate. Now we've level set those facts. We're going to conduct a summit pretty soon with probably the biggest developers in the Mideast region, many of the Arab developers, lots of master planners. I think when people see some of the ideas that come from this, they're going to be amazed. Jason Isaacson: Steve, thank you. Final question, from AJC's many contacts and visits over many years across the Arab world, including regular exchanges over three decades in Gulf Cooperation Council countries, we've come to believe in the inevitability of Israel's full integration in the region, that the more the region's leaders and elites focus on the potential advantages to their societies, including their security of normal relations with Israel, the more likely it is that we'll achieve that goal. Is that the sense that you have as well, from where you sit? Steve Witkoff: I do. I think, look, I think that the people of Israel want to live in peace with with the people of the Middle East. And it could be incredible. Jason Isaacson: And vice versa. Steve Witkoff: And vice versa. I had a discussion with His Royal Highness, His MBs, his brother yesterday, the defense minister, an exceptional man, by the way, and we talked about how Saudi could become one of the best investable markets out there, when it can be financed. Think about this. The United States today has the greatest capital market system that the world knows. And when you have a great capital market system, when. You can borrow, when you can lease a car, when you can buy a home and mortgage it all those different things. It drives an economy. It propels it. Right now in the Middle East, it's very difficult to finance. The banks don't want to operate it. Why? Because tomorrow a Hootie missile could come in if you're building a data center, and puff it's gone. We don't have to. Banks don't have to underwrite that risk in New York City or Washington, DC or American cities. So I think as you get more stabilization there, I think the real estate values are going to go through the moon. And we talk about this, Israel is a bedrock of great technological innovation. I think you know, all of the Arab countries, UAE, Saudi, Qatar, they're into blockchain robotics. They're into hyperscale data centers. These are the things that interest Israel, and yet they're driving so much of the tech surge out there. Imagine all of them working together. It could be an incredible region, so we're hopeful for that prospect. That's that's the way the President thinks about it. We've we talk at length about this, and he gives us the direction, and we follow it, and that's his direction. Jason Isaacson: I thought I heard applause about to begin, but I will, I will ask you to hold for a second, because I just want to thank you, Steve whitco, for sharing your vision and the President's vision for how to move forward to build a more stable and prosperous and peaceful Middle East and and you've laid it out for us, and we very much appreciate your Thank you. Steve Witkoff: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with AJC Berlin director Remko Leemhuis about the victory of a centrist right government in Germany's recent election and its plans to build a coalition excluding the far-right, antisemitic political party, Alternative for Germany. Remko and I discussed why that party's unprecedented post war election returns are a cause for concern.
Feb 25
Why Germany's Antisemitic Far-Right Party is Thriving Instead of Disappearing
"In Germany after 1945 . . . it was always sort of an unwritten rule or law that the more radical these [right wing populist] parties become, the less votes they get, and at some point they just disappear. And what is troubling with the AfD is that the more radical they become, the more votes they get." Following Germany's recent election results, the far-right party AfD, or Alternative for Germany, is now a more prominent force than ever, doubling its support. Director of AJC Berlin Lawrence and Lee Ramer Institute for German-Jewish Relations Remko Leemhuis breaks down the rise of AfD, the role of Christian Democrat's Friedrich Merz—widely expected to be Germany's next chancellor—and the challenges ahead for Germany's relationship with Israel and the United States. Leemhuis also discusses the dangers of political polarization and its consequences for the Jewish community in Germany. As the Christian Democrats form a coalition and Merz takes the lead, how will Germany navigate the rise of populism while strengthening its alliances on the global stage? Resources: -What is the Alternative for Germany or AfD Party? Listen – AJC Podcasts: -The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . -People of the Pod : Unpacking Trump's Gaza Plan The Oldest Holocaust Survivor Siblings: A Tale of Family, Survival, and Hope Israeli Hostages Freed: Inside the Emotional Reunions, High-Stakes Negotiations, and What's Next Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Remko Leemhuis: Manya Brachear Pashman: German citizens went to the polls on Sunday for the fourth snap election in that nation's postwar history. Public opinion surveys indicated that the far right party, AFD Alternative for Germany, was poised to play a larger political role than ever before. The party also has attracted significant attention from US political leaders of late, including US Vice President JD Vance, who, in addition to visiting a Holocaust concentration camp during a recent trip to Europe, also met with Alice Weidel, the head of Germany's AFD party. Here to discuss the outcome of the election, its impact on Germany's relationship with Israel, and the German Jewish community is AJC Berlin director Remko Leemhuis. Remko, welcome to People of the Pod. Remko Leemhuis: Hello, and thanks for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So if you could just brief our audience on who exactly AfD is- what their history is and their ideology? Remko Leemhuis: So the party started out in 2013 and started out as a – I don't want to make it a joke, but they started out as a sort of party of professors who were in opposition to the European austerity policy during the financial crisis. Meaning, especially keeping Greece, who was in a deep financial crisis, and they advocated for expelling Greece, for example, from the European Union, because they were afraid that their debt will be then sort of distributed among all member states of the Europeans. So that was their starting point. But that was also their only issue. And I remember that in 2015 they were around 3-4%. But then the party changed. We had, as many of your listeners know, the influx of over a million refugees from mostly Syria, and the party sort of reinvented itself. And from then on, migration policy, illegal migration, all of the issues connected to these issues were at the center. And from there, they rose, and again, radicalized ever since. And right now, the migration issue is their central issue on which they are campaigning. And it doesn't matter what you ask. I've seen a lot of these debates that we have before elections with all the heads of the parties, and it is really astonishing how the party is always able to tie every single issue to migration, be it taxes, be it–you can come up with every issue. At the end, it's always about migration, illegal migration, and migrants. And that is something that is their central platform. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well the Trump administration also made illegal immigration central to its platform, but I think what AJC here in America found so alarming about Vance's meeting with Weidel, perhaps there was alarm there in Germany too, was the party's clear record of antisemitism and hostility to America. Weidel herself has called Germany a "slave state" to America and Germany's Holocaust remembrance culture a "guilt cult". AJC pointed these things out after the vice president's meeting. So did AfD do as well as expected, Remko? What are the election results so far? Remko Leemhuis: So we had the highest voter turnout since 1990. We were above 80%. 83-84% which is the highest turnout since 1990, so the elections after reunification. The AfD was able to double their result. In the last general election that around 10%, now they came in with 20%. And just for comparison, the Social Democrats came in with 15, close to 16%. So this is something that should concern us very much. The Christian Democratic Union, so the German conservative center right party won the election. Although not with that many votes as expected. So their aim was 30% plus X. They now have 28-29% but still they are the strongest party. And given German election tradition, the party with the most votes then forms the government and invites other parties to form a government. Manya Brachear Pashman: And that means that Friedrich Merz is poised to be the next chancellor. Is that correct? Remko Leemhuis: Yes, if he's able to form a government, yes. I mean, at this point, he still has to talk to one party, and this will be the Social Democrats, even though they lost almost 10% compared to previous elections. Together, they have a majority, and everything indicates that they will form the next government. Manya Brachear Pashman: Is there a possibility that Alternative for Germany or AfD could be part of the coalition as well? Remko Leemhuis: No, that has been ruled out by Friedrich Merz, given that he was ahead on the polls for at least over a year, he has ruled this out on numerous occasions. He has ruled it out yesterday in interviews, so there's no chance that the AfD will be part of a federal government. Manya Brachear Pashman: So is there any reason for concern, given the trajectory of this election, and given AfD's results in this election? They came in second, correct? Remko Leemhuis: There's a lot of reason for concern, because we can say, of course, this is a broader trend in Europe and in the Western world, that you have the rise of these right wing populist parties. But in Germany, after 1945, it's not the first time that we have right wing extremist parties in Parliament, state or federal, but it was always sort of an unwritten rule or law that the more radical these parties become, the less votes they get, and at some point they just disappear. And what is troubling with the AfD is that the more radical they become, the more votes they get. And this is something that is pretty hard to grapple with, and where I very honestly, also don't have an answer why they are able to sort of break with this rule. But this is very, very troubling, especially in light of the fact, and that is something that is well known to the German public, that the German domestic security services are surveilling the AfD and classifying them as a case of suspected right wing extremism. So the whole party and three regional branches of this party are officially confirmed by German domestic security as far right. So which means that they are in opposition to liberal democracy. And this is something that, again, is very, very concerning. Manya Brachear Pashman: Of course, AfD did not win. The Christian Democratic Union won. Could that victory have any impact on the special relationship between Germany and Israel? This is, of course, the return of the party of Angela Merkel, correct? Remko Leemhuis: First of all, we have to get credit for the outgoing government coalition, because since October 7, this coalition has been a reliable ally of Israel. Of course, there were issues where there were differences, but in general, the outgoing coalition has stood by Israel's side, which was also recognized by Israel. And it is not just a talking point for Israel diplomats when they say that Germany is Israel's second most important ally. And they have done it despite the fact that they had a lot of pressure from their respective voter bases, especially the Greens and the Social Democrats. So this is something where we really have to credit these parties. Now, the Christian Democratic Union, as you have mentioned, is the party of Angela Merkel, and it's the party that and she came up with the term of the staatsräson (reason of state), and that Israel's security is essential to Germany's policy. I think there are areas where the relationship will even improve. And just to give you one example, we are talking, today on Monday, the day after the election. And it's really astonishing. Freidrich Merz gave a press conference today, the first after the election yesterday. And really the first question was about his call that he had with the Israeli Prime Minister yesterday. And he stated very clearly that he has invited the Israeli prime minister to Germany, and that he will find a way to make sure that the Israeli prime minister will be able to visit Germany without being arrested, given the ICC warrant, something that the outgoing coalition didn't say this clearly or said they will adhere to the ICC arrest warrant. So this is something that, from our perspective, is very positive. And also, I think that the military cooperation and the defense cooperation between Israel and Germany will again, first of all, all of that will not be, again openly debated, but again in the formats where they belong. And so in general, I would say the relations will improve. But this will not mean that also this government or the next government will only say, and do what Israel wants. But I think in general, the trend and the relationship will be more positive and even improve. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what about relations with the United States? As I mentioned before, Vice President Vance met with one of the AfD leaders. Do you foresee that relationship changing significantly? Remko Leemhuis: Well, first of all, I have to say Freidrich Merz is very committed to the transatlantic relationship. But yesterday, again, in a post-election interview, he said something that I thought I would have never hear from him. But he said that, We in Europe maybe have to grapple with the fact that the US will not be the sort of ally that it was before, and that we in Europe have to think about a situation where the US will only be very little or not present at all in Europe. Especially when it comes to war in Ukraine and the support for Ukraine. So even though he is very committed to the transatlantic relationship, given the recent developments he looks much more concerned to Washington and what is happening and what is coming out of Washington. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, he sees a bit of a destabilizing effect when it comes to transatlantic relations and security from the direction of the United States, not within Europe itself. Remko Leemhuis: Yes, destabilizing is the right word. And that doesn't mean that he doesn't see the failures that Europe and Germany has made over the past years. And I think that's something we also, as AJC, try to highlight every time. That the Europeans, especially the Germans, for decades, haven't lived up to their commitments when it comes to defense spending. And 11 years ago now, after Russia annexed Ukraine and the NATO states agreed on the 2% goal, Germany hasn't met this. And a lot of other European countries that are member of NATO haven't met that 2% goal. And the discussion about this goes even, you know, way back longer. I think it was even started with President George W. Bush, who always highlighted this issue and that the Germans, the Europeans, have to do more. And especially the Germans as the third-largest economy in the world and the biggest economy in Europe, has to shoulder more responsibility, which means they have to spend more. So he's very aware of the fact of all these shortcomings, and he's very willing to fix that and to spend more money on defense if the US cuts its spending here, if the US withdraws troops from the European continent. And still being aware that even if you know, Europe does its best, we will not be able to fill these gaps, because we just don't have the resources or the infrastructure to do that. So we still need the US, no matter what. So he will need to find a line, sort of working with the US, and then looking at what can Europe do to become a bit more independent from the US in all of these questions. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's zoom in and talk about the impact of the rise of AFD on the German Jewish community. Has it given license to those who might otherwise keep antisemitic attitudes to themselves? Remko Leemhuis: So in general, as I said at the beginning, nothing of this is a big surprise. The AfD in the polls over the past year or so, I would say, you know, fared around 20%. So the result yesterday wasn't a surprise, and it was also not a surprise because we have seen the AfD having even bigger successes in state elections. But of course, this is concerning. This is concerning because the AfD is also a symbol of polarization, and polarization that we see across the western world, in all democracies at this point, I think, and historically speaking, times of polarization have never been good times for the Jewish community. But I also have to say that the German Jewish community is also very aligned in how to deal with the AfD, and that means no Jewish organization speaks to the AfD. Every Jewish organization at some point in time has come out against the AfD. We as AJC have had numerous publication on highlighting the threat to democracy, and by that also to the Jewish community, by the AfD. And the AfD so far, hasn't been successful in using Jews, or, you know, Israel, or pretending to be Israel's biggest friend and the Jewish community's biggest friends. No one, no one buys into that, and everyone can see through that, and everyone understands that this is performative at best. Manya Brachear Pashman: Here in the United States, people of opposite political persuasions are honestly having a hard time facing each other. Those who voted for Kamala Harris, they see the speed with which Trump is enacting his campaign promises. They're having a hard time facing their neighbors who voted for him, or who had yard signs up for him. People are organizing boycotts of businesses and CEOs who are aligning themselves with Trump. Is the same dynamic playing out on the ground in Berlin or Munich, for example. Do you see that kind of, as you said, the polarization. Does it play out on the very personal level? Can neighbors face each other? Remko Leemhuis: Yes. I'm not sure if we see it to the extent that we see it in the US. But of course, we see that and that political questions, political issues, have become a dividing line among friends, among families, and that people stop talking to each other. And that is a very worrying trend, that this happens. I mean, of course, there is a line, where I would say it is legitimate to say, I'm not going to discuss these issues. And I personally, and we as AJC, don't talk to AFD. For the reasons we have talked about there's nothing for us to discuss with them. But yes, I have to say that, especially over the past weeks, we have seen even an increase in this polarization and in this lack of unity, at least in terms of, everyone agrees that it is okay to fight and to fight about the issues and to have even hard debates on issues. And this is part of democracy. And I guess we Germans also have to learn that, more that democracy means debating things and having hard debates about issues. But the last weeks have seen that it then ventures into contempt and denigration, and if you are not having this position, then you're automatically on the other side, not even to be talked to. And that you don't often run into people that have an opposing view, because we all live in a bubble, and that, I guess, the only place where you encounter people with different opinions is social media. And I guess we can all agree that social media is, for sure, not the best place to debate controversial issues. We all have to come out of our bubbles, that we all have to you know, even if we have political differences with other people, still see that there's much more that aligns us with most of these people, and that if one person doesn't exactly hold the same view as you on any given policy, doesn't mean that it is an inherently bad person. But still, someone that isn't just inherently bad, but your neighbor, your co-worker. And I think that is the biggest challenge for all democratic societies in the West at this point. Manya Brachear Pashman: Remko, thank you so very much for joining us and for explaining the outcome of this election and what it narrowly avoided. Remko Leemhuis: Not narrowly but, one thing is clear, and I think that is that is much more what I'm thinking about is that certain issues aren't addressed in a way that people feel, you know, they are addressed and they are taken serious. I mean, we just have to look to our neighbor, Austria, where an openly right wing extremist party is now the strongest party. And we should do everything we can to avoid that scenario. But that means then even having difficult debates and making also difficult decisions. But, if we want the center to hold, there is no alternative. And that's why our appeal as AJC is. And a lot of people find this lame or undecided, that we have appealed on numerous occasions, also in this campaign cycle, on all democratic parties to find solutions for the pressing issues and to find a middle ground. And this is what we will continue to do. And also we'll try to continue to then bring together people from different parties to debate these issues and give, you know, these conversations a platform, and do what we can do in order to facilitate such discussions, and hopefully by that, have a healthier culture of debate and a healthier political culture. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much, Remko. Remko Leemhuis: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for the second installment of our two-part series on the faces behind antisemitism as part of AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2024 Report . I ask two Jewish college students about the report's findings that nearly a third of Jewish students in the U.S. reported feeling uncomfortable or unsafe at a campus event because of their Jewish identity. Our guests shared their own experience.
Feb 21
Spat On and Silenced: 2 Jewish Students on Fighting Campus Hate
Imagine being spat on as you walk across your college campus simply because you're Jewish or being asked whether you're a "good Jew" or a "bad Jew." As part of AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2024 Report , AJC and Hillel International partnered to document the experiences of Jewish students on campus over the past year. The findings are deeply troubling: nearly a third of Jewish students in the U.S. reported feeling uncomfortable or unsafe at a campus event because of their Jewish identity, and 43% avoided expressing their views on Israel due to fears of antisemitism. In the second installment of this two-part series, meet two students whose experiences reflect these alarming statistics: Evan Cohen, a senior computer science major at the University of Michigan and Vice Chair of Hillel International's Israel Leadership Network, and Daniel Solomon, a junior studying political science and urban studies at Brown University who serves on AJC's Campus Global Board. Resources: - AJC's Center for Education Advocacy - 5 Takeaways from AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2024 Report - Go Behind the Numbers: Hear directly from American Jews about what it's like to be Jewish in America Test Your Knowledge: -How much do you really know about how antisemitism affects Americans? Take this one-minute quiz and put your knowledge to the test. Start now . Listen – AJC Podcasts: - The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . - People of the Pod : Unpacking Trump's Gaza Plan The Oldest Holocaust Survivor Siblings: A Tale of Family, Survival, and Hope Israeli Hostages Freed: Inside the Emotional Reunions, High-Stakes Negotiations, and What's Next Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Evan Cohen and Daniel Solomon: Manya Brachear Pashman: As part of AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2024 report, AJC and Hillel International partnered to document Jewish students' experiences during their time on campus. Last year, the report found that 43% of Jewish college students avoided expressing their views about Israel on campus or to classmates because of fears of antisemitism. 22% of Jewish students report feeling or being excluded from a group or an event on campus because they're Jewish, and 32% of American Jewish students said they have felt uncomfortable or unsafe at a campus event because of their Jewish identity. Here to share their perspective on the ground are two students who have become advocates for their Jewish peers. Evan Cohen, a senior computer science major at the University of Michigan, is the vice chair of Hillel International's Israel Leadership Network. And Daniel Solomon, a junior political science and urban studies major at Brown University who serves on AJC's Campus Global Board. Evan, Daniel, welcome to People of the Pod. Evan Cohen: I wish it was under better circumstances, but, you know, it's a pleasure to be here. Daniel Solomon: Thank you so much for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So gentlemen, I just read a bunch of findings from the most recent report. Do they seem too high or too low based on your national vantage points? Evan? Evan Cohen: So I think these findings are, sadly, not that surprising. We've seen and experienced an unprecedented amount of antisemitism over the past year and a half, give or take. Clearly, it's rising. Clearly students are experiencing this on their campuses, myself included. I definitely think that, you know, there's probably some cases where students are experiencing it more. In some cases it's less, but I think, you know, in general, it's way too high, like we should not be seeing as much antisemism on campuses. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Daniel, what do you think? Daniel Solomon: You know, the numbers seem about right. I have the opportunity of helping lead AJC's Campus Global Board, which really has a very wide perspective across the world and also across the United State. And we recently just met as a board in Lisbon where we discussed at length new trends over the past year in college antisemitism and around the world. And this really holds. We really found that this data is reflective of what we find in our qualitative experiences. Manya Brachear Pashman: One finding I did not just share at the beginning is that roughly 35% of American Jewish college students or recent graduates report having personally experienced antisemitism at least once during their time on campus. Did either of you have a personal encounter of your own over the past year? Evan Cohen: So a number of months ago, I was walking through the center of campus with a rabbi and a friend of mine, and we were spat at. And the unfortunate reality is, not only were we spat at, but when I tried to report this, I was basically told that, without identifying the individual by name, there was nothing that the university could do. And this was extremely frustrating, because we were spat at. That was a deeply upsetting experience. It's something that no one should have to go through just for being Jewish, but the fact that there was almost nothing that could be done about it. Besides, you know, maybe you know, here's how we can support you, which was not something that I was particularly in need of. It was disappointing to see that there was no strong response to that. Daniel Solomon: So shortly after October 7, my friends and I in our apartment, we held a small gathering, and you know, some friends brought mutual friends, and their friends brought mutual friends, which is totally fine. And so someone who I didn't know came up to me and looked at my door frame, and I have a mezuzah on my door frame. And she said, is that your Jew thing? Which, yes, it is, but it's called a mezuzah. And she said, Well, are you a good Jew or a bad Jew? And I said, What do you mean by that? And I knew exactly what she meant by that. She meant, are you a Zionist? Or are you an anti-Zionist Jew? And the conversation ended shortly thereafter, and we asked her if she would leave. Manya Brachear Pashman: This report came after the protests and the encampments that roiled college campuses, mostly in the spring of 2024 of the Jewish students who witnessed anti-Israel demonstrations after the October 7 terrorist attacks, 51% said that these protests or encampments made them feel unsafe on campus. How did your universities handle the encampments that popped up on your campuses? Evan Cohen: There was an encampment on our campus, it sprung up the morning of the first Passover Seder of last year. And I remember receiving a text at six in the morning or something. I woke up, the first message I saw was, Evan, Do you know what's going on? And I said, Oh my god, another thing to deal with. You know, it's about to be Passover like we're supposed to be preparing for the Seder. And, you know, I think that at our university was handled extremely poorly, you know? We were told the encampment is contained, yet it grew in size, you know. So at first it took over the main part of the center of the Diag, which is the main center of campus area at the University of Michigan, and slowly crept out into farther and farther areas of that center of campus Diag. And it was really disappointing, because at the end of the year, when it's finally warm, students are out there, they're hammocking, they're playing sports, even just reading and studying. And at that point, there was nobody besides those in the encampment. And so it really destroyed the end of year atmosphere that everyone always looks forward to. And again, like I said, I think it was handled very poorly. The university did not contain it. The university waited until after graduation. They were hoping, I believe they were hoping, that if they waited until after graduation, there wouldn't be disruptions at the graduation. While I personally did not graduate last spring, I had friends who did, and there were disruptions at that graduation. So clearly, that strategy did not work, did not pay off. Sometime after graduation, they announced that the encampment was being removed because of fire hazards. Now these fire hazards were hazards the entire time the encampment was there, I saw students plugging in various electronic devices, keeping themselves warm with space heaters. That's not something that you're supposed to be able to do there, and I do have experience, because I've had to reserve that space for, you know, pro-Israel activities in the past, and so I very much understand, first, what the rules and regulations are and how that process works. Very clearly, these rules were violated. And not only that, there was clear antisemitic imaging and speech that was spewing out of this encampment. Daniel Solomon: So, you know, first and foremost, our campus is a very big advocate of free speech, just collectively. So, you know, when the encampment originally went up, you know, the university made sure to emphasize the fact that, you know, it is free speech. But free speech, you know, has, you know, consequences, in the sense that setting up an encampment is against the university policy. So, within those guidelines, you know, the encampment was up for probably a day or two, and then I remember one evening, the members of the encampment started yelling to globalize the Intifada. And this was sort of the call on the university's end to say this is actually not okay. This is when it teeters on free speech and free expression. And, you know, voicing your opinions, however different they might be than most, this is actually when it gets into hate speech. And so that's sort of the moment that our university leadership really, really took, took control of the encampment, and it ended shortly thereafter. Manya Brachear Pashman: Of course, most antisemitic content and the anti-Israel vitriol is primarily spread online and on social media, and the data back that up, almost seven in 10 American Jews, 67% reported seeing or hearing anti semitism online or on social media in the past 12 months. The number jumps to 83% for young American Jews between the ages of 18 and 29 so your peers, how has social media, the digital landscape, shaped your encounters with antisemitism? Daniel Solomon: Social media is a big part of of our generation, and a part of how we how we bond together. Similar to other universities, Brown has a platform called side chat. Other universities, they might be called Yik Yak or something else. But the only way to access this app, which is a private a private company, not, you know, affiliated with brown, but the only way to actually access the brown only channel in Sidechat is to use your Brown email. So it's sort of an anonymous message board where anyone can post whatever they feel, whatever they think. Sometimes it's funny memes. Sometimes it's satire. In the context of the post October 7 world on Brown's campus, it was nothing, but, you know, atrocious really. It was really just a cesspool and a hotbed of antisemitism. And anti-Israel rhetoric that absolutely veered into antisemitism, but also really just classic, flat out antisemitism, you know, pointing out Jews in in, in great positions of authority in the country, and on college campuses specifically, and sort of trying to connect dots that really aren't connectable. And so Side chat was really just a really terrible hotbed of antisemitism. And then also, you know, those who were more bold antiSemites would really just blatantly, you know, leave comments in Instagram posts, you know, with their profile name visible, so you knew exactly who they are. And so, you know, the digital, the digital landscape, was absolutely a pretty crucial part of what comprised, you know, the anti semitism happening. You know, as I mentioned before, the campus, the campus that we see now is really the one, is really the one that I that I remember, you know, in my freshman year, the one that I made some of my closest friends, on the one where I developed some of my, you know, some of my academic ambitions. The campus that I really fell in love with is the one that I'm seeing now, and much different than the situation that we were in last year. Evan Cohen: I could talk about, you know, two specific examples. One example was the president of our SJP chapter. Sometime, I want to say, around last March, posted something to her personal public account that said something along the lines of death to everyone who supports the Zionist state, death and more, death and worse. And I believe that Regent Acker, who was on the podcast relatively recently, actually spoke about this, I think. And that was deeply disappointing to see, because, you know, studies have shown. I even read a study recently, I think it said that about 80% of American Jews support Israel, meaning they believe in Zionism, the right for Israel to exist safely and securely, for Jews to live there in our ancestral homeland. And so to say that, you know, that's basically calling for the death of Jews, the death of fellow classmates, fellow students. So that was, you know, extremely challenging to see and to deal with. And ultimately, there were effectively no consequences. The student graduated last, last spring. And you know, we saw, we saw nothing, no repercussions from this, this activity. Another example of online anti semitism. What I experienced was during a trip to Israel last May. As part of this trip, I was going to be bearing witness to the atrocities of October 7, and so we were sharing, me and another student from the University were sharing some of our experiences, and a screenshot was taken of us, and then over, over, on top of it were overlaid messages like settlers scum, and these students were celebrating genocide. Manya Brachear Pashman: Evan, how have these encounters, both on campus with the encampments and on social media? How have they informed your time working with Hillel on an international level? Evan Cohen: You know, it's very clear that antisemitism is extremely prevalent. It's clear that anti-Zionism, anti-Israel sentiment, is very prevalent, and that we need to be constantly working toward combating it and supporting students on different campuses, this manifests in different ways. So it requires different tactics, different strategies, depending on what school you're at, depending on what your individual needs are. But now being in this leadership position, it's amazing to be able to try to offer that support and use my experiences to then help other students on their campuses deal with the troubles that they are going through and what they are experiencing. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to point out that a lot of this happened after the October 7 terrorist attack. A lot of what you're talking about, of course, the survey itself. But antisemitism doesn't just come from anti-Israel corners and Evan I know there were instances of demonstrators waving Nazi flags in Howell and Fowlerville outside a production of The Diary of Anne Frank. Those are small towns about 30 or 40 miles away from Ann Arbor. Have there been expressions of antisemitism from the far right on Michigan's campus? I think Evan Cohen: I think it was like the 2022-2023, academic year, the students received hate mail specifically targeting Jews, saying that Jews run the media, that they're responsible for COVID messages similar to that. I want to say that was even around the High Holidays timeframe. And so this was found like, you know, passed out around off campus, student housing. And so a number of students received messages like that. You know, we also saw post October 7 swastikas on or near Jewish buildings, for example, at Hillel one time. And so, you know, we're definitely seeing anti semitism from both sides. Manya Brachear Pashman: Daniel, your campus Antisemitism Task Force, for lack of a better term, it initially formed in response to hatred from the far right. Is that right or is that correct? Daniel Solomon: Yeah. So when I was a when I was a freshman, in my freshman fall, a terrible anti semitic threat was sent to the campus rabbi and executive director of the Brown-RISD Hillel that serves both Brown University and the Rhode Island School of Design, and that's sort of where we sort of came together and started really having very proactive and very productive meetings with with Brown's administration. Partially, I, you know, I will plug just a little bit that. I think that part, you know, the reason why I was so zealous to get involved was the training I received with American Jewish Committee, with the LFT program, the Leaders for Tomorrow High School Program. So we really came together. Started having these conversations with Brown's administration, and created this really, really positive relationship, which I think is a pretty Hallmark component of being a Brown student, is this really, is this really great relationship that we formed? And I think that, you know, leading into October, 7, part of what made Brown's response so effective was that we had this really dynamic relationship with administrators already, and that, you know, there's really no gap in between Brown's institutional Jewish leaders and Brown's administration. We have, you know, an incredibly supportive administration. And I think that was something that we saw following the incident and fall of 2022, and something that we continue to see all throughout you know, the post October 7 world. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Daniel, I'll ask you the same question I just asked Evan, how has that experience, that experience on Brown's campus, informed your time on AJC's Campus Global Board? Daniel Solomon: To be honest, it's actually a little bit of the opposite. I feel as though my time on AJC's campus global board has really provided such an incredible opportunity to understand the global landscape of campus antisemitism. And also, of course, you know, we want to emphasize the global landscape of Jewish joy that's happening on college campuses, because that is definitely not in short supply. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, I'm curious, do you get questions from your peers back home, your younger peers, questions about whether or not your campuses are the right choice, the right fit for them? Evan Cohen: I think it's really important to mention that the Jewish students on campus do absolutely have a home here. We're working extremely hard to ensure that there is Jewish joy on campus, and there are organizations here to support Jewish students. It's imperative that Jews come to campus, that we continue to build a supportive community and that, you know, we're not just hiding, we're not just shying away from this. We're actively working towards improving campus and campuses drastically improved in the 2024-2025 school year compared to the 23-24 school year. So, you know, we're standing strong. We're standing proud, and we're not going to back down. There is a thriving Jewish community, and we're here to support you. We want you to come here. The University of Michigan has such a large Jewish population in part because a long time ago, the Ivy League schools had quotas on the number of Jews who could attend, and so the University of Michigan did not as such. We have a very strong Jewish community here, and I highly recommend coming here as long as you can bear, as long as you can bear and withstand the cold. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you both for joining us, and reflecting on the difficulties of 2024. May 2025 be more peaceful on your campuses. Evan Cohen: Thank you very much for having me. Daniel Solomon: Thank you for having me.
Feb 13
University of Michigan Regent Jordan Acker: When Antisemitism Hits Home
What would you do if jars of urine were thrown through the windows of your house in the middle of the night? How would you feel if antisemitic messages were spray painted on your cars? How would you respond if you were targeted simply because you're Jewish? In the first installment of a 2-part series, meet a face behind the alarming findings of AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2024 Report , the first analysis of the impact of antisemitism on American Jews and the U.S. general public for the full-year following Hamas' October 7, 2023 massacre of Israelis. In this week's episode, Jordan Acker, a lawyer and member of the University of Michigan's Board of Regents, shares what happened to him and his family in late 2024 when they were personally targeted by anti-Israel and antisemitic protesters. He criticizes the broader campus climate and faculty's response, while emphasizing the need for productive dialogue and understanding as a way forward, all the while stressing the importance of standing up to antisemitism. Resources: - AJC's Center for Education Advocacy -5 Takeaways from AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2024 Report -Go Behind the Numbers: Hear directly from American Jews about what it's like to be Jewish in America Test Your Knowledge: -How much do you really know about how antisemitism affects Americans? Take this one-minute quiz and put your knowledge to the test. Start now . Listen – AJC Podcasts: - The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . - People of the Pod : Unpacking Trump's Gaza Plan The Oldest Holocaust Survivor Siblings: A Tale of Family, Survival, and Hope Israeli Hostages Freed: Inside the Emotional Reunions, High-Stakes Negotiations, and What's Next Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Jordan Acker: Manya Brachear Pashman: For six years now, AJC has published the State of Antisemitism in America Report , and each year the findings become more alarming and sad. This year's report found that 77% of American Jews say they feel less safe as a Jewish person in the United States because of the Hamas terrorist attacks on October 7, 2023. A majority of American Jews, 56%, said they changed their behavior out of fear of antisemitism, opting not to wear a Star of David, or put up a mezuzah. And a third of American Jews say they have been the personal target of antisemitism, in person or virtually, at least once over the last year. While the numbers alone are telling, the encounters with antisemitism behind those numbers are even more powerful. Here to discuss these findings, and sadly, his own family's experience with antisemitism in 2024 is Jordan Acker, a member of the University of Michigan's Board of Regents. Mr. Acker, welcome to People of the Pod. Jordan Acker: Thank you so much for having me. On such an unpleasant topic, but . . . Manya Brachear Pashman: Despite the circumstances, it's a pleasure to speak with you as well. So I want to tell our audience a little bit about what you experienced in the last year. Last May, the doorbell camera at your home showed a stranger, with their face covered, walking up to the front door, laying a list of demands, signed by the University of Michigan Gaza Solidarity Encampment. Laid those demands on your front porch. And then a month later, your law office in suburban Detroit was vandalized with anti-Israel phrases, profanity, directed at you personally. And then in December, you and your family awoke one morning to a pretty horrifying sight. So could you kind of walk through what you encountered last year? Jordan Acker: Yeah, absolutely. So you know, what's interesting about this is that as much as I oppose BDS, I was not the person on the board who was speaking about it, the people that were speaking about it were actually my non-Jewish colleagues. We're an elected body, six Democrats, two Republicans, and universally, we oppose the idea of boycotts, divestment and sanctions, and we said so. We've affirmed this in 2018, we affirmed this in 2023. And at some point, while we had an encampment on our campus, it remained relatively peaceful to what other campuses have dealt with, until they started showing up at our homes. We had this happen, a list of demands. Ironically, including, defunding the police was one of the demands. And then, you know, it went to a different level, when it went from all of my colleagues to just me getting the treatment. My office is an Orthodox Jewish neighborhood. They went to my office in the middle of the night and spray painted messages all over it, including profanities. But they caused over $100,000 worth of damage. And I don't think that location was unintentional. I think that as people were waking up in the neighborhood, going to synagogue the next day, they wanted to make sure that people in that neighborhood saw what had been done. It was certainly on purpose. And what was so disturbing about it was that three student groups actually posted photos of it in the middle of the night on Instagram, before the police knew about it, before we knew about it, and then quickly took them down, obviously, because, you know, they realize this is a crime. And then things had remained relatively quiet through the fall. Experiences had been much different than prior semesters, until I was awoken about two in the morning to jars of urine being thrown through my window. And this had followed up several instances of similar incidents. On October 7, the president of our university, who's not Jewish, his personal home was vandalized. The Jewish Federation in Metro Detroit was also vandalized. The head of our endowment, a member of law enforcement, all of their homes were vandalized with pretty much the same messages. Ethnic related, calling them cowards, demanding divestment. Of course, the worst part for me was obviously the jars flying through my home. I have three small children, and having my oldest woken up to that was terrible. But they spray painted my wife's car with messages to divest, but also upside down triangles, which I think most Jews now take to see as a direct threat. That is a Hamas symbol for a target. And as I've said before, I'm not in the Israeli military. I'm not a military target. I'm not a target at all. I'm a trustee of a public university in the Midwest. And this kind of behavior, frankly, is unacceptable. It's unacceptable from any members of our community, regardless of where you stand on the political spectrum. And frankly, it's deeply antisemitic. And the fact that there's some people that are questioning that, or wonder why, is part of the problem, part of why we've gotten here. It's a deeply troubling time, I think, for American Jews, for a lot of these reasons. Manya Brachear Pashman: You said that you are the only Regent who has been targeted in this way any any sense of why. Jordan Acker: It's a good question. You know, I think there's a few different layers to this. I think being Jewish is a big part of the layer, obviously. But also a part of it is that I have a public social media presence. It's something I've maintained since, frankly, when I was running for this office. This is an elected office, obviously, in Michigan. And I think that has something to do with it, for sure. But the degree in the manner is very, very different. And it's really hard to understand why it would happen in this particular way. Again, except for, you know, an excuse to engage in violent behavior. You know what's so disturbing about this, and what is so heartbreaking to me is that, I understand, you know, for those who are on the other side of this issue, who care deeply about Palestinian rights and Palestinians having their own state? I care about that. I'm the only regent that actually met with SJP prior to October 7. Not because we agree on everything. We do not. But because there's some things that we do agree on. And by the way, the vast majority of American Jews agree on. I think that's what's been so disturbing about everything that's happened since October the 7th in America, is that you probably have no group of Americans that's more empathetic or sympathetic to Palestinians than American Jews. And yet, there's obviously a large group of this protest movement, or the remains of it at this point, that are deeply antisemitic and are using Palestinians essentially as a weapon to go after and to isolate American Jews. Manya Brachear Pashman: Are you the only Jewish regent? Jordan Acker: I'm not. At the time, we had three actually, of our eight-member board, were Jewish. But our board is almost universally pro-Israel and almost universally opposed to BDS, and has been for a very long time. And there are lots of reasons for that, but this is, you know, perhaps the person who's been most outspoken about this, interestingly enough, is Denise Ilitch, who, you know, if they were looking to attack a pro Israel business. Well, there are two Little Caesars locations on campus. Right, again, this has nothing to do with being pro-Israel. Coming to my office has a very distinct, very specific message that they're trying to send. Manya Brachear Pashman: You said there are a number of reasons why the Board of Regents is universally opposed to BDS. Can you explain those reasons? Jordan Acker: I think the first one, and I can only obviously speak for myself on this. The board speaks through its pronouncements and its decisions, but the biggest one actually is that, generally speaking, academic boycotts do not add anything to the conversation. They don't get people closer to resolving conflict. They don't even get people talking about conflict. And to me, that's antithetical to the purpose of the American University. One of the incidents that has most disturbed me over the last few months, other than obviously, the physical violence, but what's disturbed me is a group of mass protesters went to a lecture by a professor named Marc Dollinger, a guest professor on campus, and Marc Dollinger was teaching, as he does, about the relationship between the black community and the Jewish community during the Civil Rights Movement. And a group of mass protesters came in and said, We don't engage with Zionists here. And what I've told people is actually the second part of that phrase is deeply offensive, but the first part of that phrase, "we don't engage with" is actually antithetical to the existence of the University of Michigan, and should be tossed aside. We do engage. We engage with everyone, and we especially engage with the people that we disagree with. And so, that kind of speech and behavior is, to me, the most problematic. Because, again, American universities are places where deeply unpopular ideas should be thrown around. That doesn't give it as an excuse for violence, but it certainly is a place for deeply unpopular ideas, or for popular ideas, or for anyone who's different than you. That's the purpose of this. And yet, this movement has again decided that Jews, or people who are affiliated with Israel are uniquely deserving of being tossed out. And it's unacceptable and it's un-American. Manya Brachear Pashman: Is it just this movement, or has the campus climate been changing more and more in recent years, when it comes to a refusal to engage or the treatment of Jews on campus? Jordan Acker: I think that. It's a great question. So what I think is that what has changed actually is not the values of the students. Because, look, college students protest lots of things. When I was a student, BDS was an issue 20 years ago. What's actually changed is the faculty. And that's actually what's most concerning to me, is the way that our faculty has behaved, not all of them, and certainly not even a majority or a minority, but a small group, has behaved since this happened. Throughout this process, throughout these protests, any criticism of the methods has been responded to by the faculty as criticizing everything about the movement. And so I think the faculty has actually, frankly, made the situation a lot worse. You know, one of the things that I that I learn in conversations with other regents and other trustees across the country, and I'll never forget the story, because it's so telling about where we are here, a person was who's a professor at Columbia now, was telling a story about how he protested the Vietnam War. His mentor at Columbia, who was also opposed to the war, after they invaded Hamilton Hall, came up to him and said, I agree with you on what you're thinking. I don't agree with what you're doing. And we've gotten to this place now for some reason that we can't do that anymore, that our faculty can't say this is bad behavior, period and deserves punishment, while we also may agree with the underlying politics. What has been most disturbing is, is that, for example, our faculty senate still hasn't condemned the attack on the academic freedom of Professor Dollinger, and only condemned the attack on what happened to my family after I called out the Faculty Senate Chair publicly because she feels the need to publicly defend open antisemitism. And yet, when it comes to the safety of Jews, she's too busy. And it's really disturbing, quite frankly, and it's a disturbing reflection on our faculty. But I will say that since I pointed this out, I've had dozens of faculty members reach out to me and say, Thank you, thank you for speaking out about this. I don't feel comfortable either, but I can be fired. You know, these promotion decisions come from this group of faculty. So what I would say is, that there's real problems with the way faculty have been responding, and unlike students, they're grown ups, they're adults. And certainly, I don't want to infringe on academic freedom, but academic freedom does not include the freedom from criticism, and they deserve a lot of how we've gotten here. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's interesting that you heard from faculty who were grateful that you spoke up. And I'm curious, you said in an interview last year that since the October 7 attacks in 2023 many of us have been asked to distance ourselves from our Jewish identity. And I'm curious if you are hearing that from some faculty, if you're hearing that from students, can you explain what you meant by that? Jordan Acker: I will admit that I stole this phrase from Josh Marshall from Talking Points Memo, is 'protest koshering,' right? And that's a really interesting way, I think, of what has been asked of a lot of Jews, that Jews have to apologize for their heritage or for their love of the people of Israel, even if, like me, they don't like the government of the people of Israel, right? And that's, I think, been a big challenge. But what I've seen mostly is, on our campuses, it's not so overt. It shows up in students avoiding certain classes, students avoiding certain professors, or students simply not speaking up at all. And again, those are really disturbing breaches of student academic freedom to have to choose. Oh, well, I can't take this class or that professor, even if that professor might be good, because I might be judged differently, or I might have to listen to a completely unrelated lecture about the Middle East. Or even worse, we've had professors, and frankly, they're mostly graduate student instructors, canceling class and encouraging people to go to protests. It's an unacceptable place to be. And again, part of the issue here with the faculty is, knowing where the border of your own political activism is and your taxpayer funded job is, right? They're different, and we have to get back to a place where we respect both of those. We can't stop someone from going out, engaging politically, nor should we. But the person also has a responsibility to not bring that into the classroom, especially when it's not directly related to their class. Manya Brachear Pashman: And so, what specific examples have you heard from students and faculty in terms of wanting to hide their Jewish identity? Are you hearing any examples of people who perhaps aren't wearing a Star of David necklace or aren't participating in Jewish events because they don't want to be identified as such? Jordan Acker: I'm not seeing much of that, to be honest with you, and I think that's a great thing. You know, I was really worried about this myself. I attended the last Shabbat dinner at Hillel prior to the end of the previous school year, and there were hundreds of students there, and it felt like any other Friday night. What I've gotten most from students is that they've been annoyed by it, but they haven't necessarily been, they haven't been overwhelmed. It hasn't been like UCLA or Columbia. It's like I said, it's been less overt. But I do think that there's been some level of, people keep their heads down right. And that's, I think, a big challenge and a big problem here. But I think, again, I think it's worse among the faculty, far worse among the faculty than it is among our students. I mean, imagine being a Jewish or Israeli professor on campus right now and thinking that someone like this is going to be responsible for your promotion, for your tenure decisions. Those things are highly disturbing, and we see this all the time. Just last night, you know, we see an epidemiologist who people want to protest because he's Israeli. Well, at some point it says, Well, how is this person able to get a fair shake on their own academic research at our university, if this is what happens every time you know, they're singled out in a way that, frankly, no Chinese student, or Chinese professor would ever be singled out. Because you would know that that would be clearly anti-Chinese racism. Somehow, this seems to be acceptable when it comes to Israelis and to Jews generally. And it's not. And you know, it's a big problem in the academy, quite frankly. Manya Brachear Pashman: You had also said in a previous interview that there has been an intense policing of Jews' ability to determine for themselves what is antisemitic and what is not. Is that one example, are people actually willing to say, Oh, that's not antisemitic, that just because we protest him, because he's Israeli or Jewish, I would do people, is that what people argue or are there other examples that you can share? Jordan Acker: Well, you know, I had professors come to me and say, How could you say what happened to your office is antisemitic? How could you say what happened to your house is antisemitic? And I think that, honestly, in a lot of places, it doesn't come from a bad place. I think it comes from a place of not knowing, right? And I think it comes from a blind spot. And I think that's really the big issue here, is that there's a real lack of education and interest on the far left with, engaging with us. And I think it's frankly, you know, to say, Oh, it's a failure, the far left is not actually doing the Jewish community generally, a service. I think the Jewish community has also, quite frankly, failed when it comes to helping people on the left who are not antisemitic, but have very real, legitimate criticisms of Israel, helping them do so and engage in a way so the conversations are productive, while pushing out actual antisemitism. And that's, I think, a big difference. I think that we know, and we're very clear, and I know this, having just come back from from Israel about a month ago, that the criticisms of the Israeli government are quite harsh among other Israelis. And I don't think that stopping the Israeli government from being criticized in America is helpful at all either. I think it, frankly, deserves a lot of criticism, just like any other democratically elected government does. But it's the how, it's the what, who's the messenger? How does the message come across, that I think things are really lacking, and people are are really not understanding why it veers so frequently into antisemitism and how to tell people, you know, that language is not acceptable. The person who was the head of the coalition that did our encampment put out a bunch of posts on Instagram saying that anyone who believes in the Zionist entity should die and worse. The problem, obviously, is her own personal antisemitism, which is obvious. But more importantly, the problem here is that nobody says: that's not acceptable, you're gone. That, to me, is the biggest failure. Because it says we are not policing ourselves in our own behavior, and it discredits movements. But more importantly, it shows what a utter failure this movement has been in order to get anything for Palestinians without hurting American Jews, which has ultimately been the target of so much of this. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to share more findings from the antisemitism report. The survey found that 81% of American Jews are able to divorce their displeasure with the government from their spiritual connection to Israel. In other words, they say caring about Israel is important to what being Jewish means to them. I think this is perhaps, is what you mean, or maybe it isn't, by a blind spot. I mean, is part of the problem on college campuses, that lack of understanding about the American Jewish spiritual connection to Israel? Jordan Acker: I think that's a big part of it. And I think that's I think that's a big thing that we're lacking when it comes to understanding the story of the Jewish people, but frankly, it's a story that could be told on the other side as well, about Palestinian connection to the land and to the region as well. You know when we talk about where Jews pray, what direction we pray, the importance of Jerusalem, the importance of so many places in Israel, and of that spiritual connection. I think that there is a lack of understanding of that. You know, one of the things that I got out of my own trip to Israel and meeting with Jewish and Palestinian students, was, they understand, and they believe, correctly, in my view, that the protest movement America has simply Americanized a non-American conflict. This is not settler colonialism or, or some, you know, academic theory. These are two peoples with very deep connections to this land who have a very, very difficult challenge in front of them, and it's different. And I think that, yeah, I think we have failed at that. I think the whole concept, you know, and I've had this conversation with my friends in the Arab American community, the whole concept of not knowing that, you know, they talk about the Nakba and this, you know, ejection of Palestinians in 1948 and, there is some truth to it, but what they don't know or speak about at all is the ejection of the Jewish communities that were also thousands of years old from the Arab world – at that exact same time. And so I bring this up not to say that one group has more of a claim than the other, or one group has more of a claim for having suffered than the other, but to say that we need to talk about both sides of this narrative, and we're not. And you know, too much of this movement has brought forward Jews who say things like, you know, as a Jew, I blah, blah, blah, and I have no connection to the Jewish community, or in Israel. But it misses out what the vast majority of American Jews say, and the vast majority of world Jewry says, which is, they do have a spiritual connection to Israel. And it's fine not to, by the way, that's your personal belief, but there's been this mistaken belief that that viewpoint is representative of all of the Jewish community, and while it's a small group certainly, it is not the majority at all. Most American Jews do have an understandable connection to the land of Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: Has the conversation on campus been a debate or discussion about the two people who have a connection to the land, or has it focused more on whether Jews have a right to self determination? Jordan Acker: So I met with students at Tel Aviv University, Ben Gurion University, and Hebrew University, all three of which have very large Palestinian and Arab and Muslim populations. And they recognize the complexity of the conflict. And when I left there, my first, my big feeling about this was deep embarrassment for the way that our students had or so it's not all of our students, but a group of students had acted, you know, this whole concept of genocide and settler colonialism and and it is completely removed from the everyday experiences and understandings of both peoples. I think the conversation on campus has been wildly counterproductive. I think it has done no good for anyone over there and has only served to hurt people here. You know, I think there's a lot of folks on the other side who genuinely believe that protesting is helpful for the Palestinian people, and do not understand why these specific attacks are so harmful to American Jews. And I don't think, you know, again, I don't think the American Jewish community has done a great job in helping to educate and to push people into places that are not anti semitic, but I think generally, the conversations have been particularly unproductive that they just put people into camps, and people are not able to listen and talk to each other because they use extremely loaded language, and have are looking for social media points. They're not looking for discussions and understanding. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, I will say that the State of Antisemitism in America report found that a majority of Americans, 85% the same number of American Jews, agree that the statement Israel has no right to exist, that foundational core of anti Zionism, that that statement is antisemitic. So I'm curious, does that give you hope that meaningful dialog is still possible? It still could be on the horizon, or has that ship sailed? Jordan Acker: No. I think that. I think no ship has ever sailed permanently. I think we're in a far worse place off than we were before October 7. I think everyone is actually in a far worse place off. It gives me hope and understanding that Jews are an accepted mainstream part of American life, and I think that's for a lot of Jews myself included. There was a feeling that we were being intentionally isolated, that our allies weren't standing up and talking for us at the times when we needed them the most. But I think that it's pretty clear at this point that positions like that are a minority that harassing my family. And engaging in violent behavior. Those are a minority. You know, the group that has been most that called me first, the leadership of the community called me first when this happened to me, was the Arab American community in Metro Detroit, community that I have long relationships with, good relationships with. You know, I've had the mayor of Dearborn over for Shabbat dinner, and I appreciate and love those and cherish those relationships, but I think that it is totally separate from the question of Israel in whether Jews have a right to exist in America as full citizens, right that we don't have to take we're only citizens if we take certain positions, right? I think that's what, to me, that is most hopeful about, is it shows that that particular position is rejected by the vast majority of Americans. And I think that's a really good thing for American Jews at a time when world Jewry is in a pretty precarious state. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned that you have three young daughters who awoke to that vandalism in your home that morning. How are they processing all of this? Jordan Acker: It's been really hard. You know, I think trying to explain to a nine and a seven year old why someone would do this to your family is really difficult. My seven year old said to one of her friends that there are people who are trying to bully daddy. And I guess that's true, and in the technical sense of the word, I think that that's right, but I think that it's really a challenging thing. You know, my girls are fortunate to go to great public schools with Jews and non-Jews. They're fortunate they do gymnastics in a very diverse community on the east side, which we love. So they get to see and know people of all races, colors, religions, you name it. I mean, Detroit is a remarkable and diverse place, and to think that they were being singled out, I think, is something that they can't quite put their heads around, because it doesn't exist to them. You know, for them, you know, the black girls that they do gymnastics with are the same as the Lebanese girls who they do gymnastics with, same as the Jewish girls they do gymnastics with. It's just, can you complete your round off, right? And that's where I'd like them back to being again. But it's really, really challenging when you've had something like this happen to you. So because the sound is so visceral and it's just so violative of your family, and frankly, of the way America should work, it's, it's, that's why I said at the beginning of this pod, it's un-American to engage in this kind of violence. It's the kind of violence that the Klan would engage in. And you know, that's why we have laws like here we do in Michigan to prevent people from masking in public like this. It's for this exact reason, because that's what the Klan did. And we have to toss it out because it has no place in our society, period. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jordan, thank you so much for joining us and for kind of explaining the situation on University of Michigan's campus, but also your own family's encounter. Jordan Acker: Thank you so much for having me, and for your wonderful CEO, I have to end this with a Go Blue, and thanks again.
Feb 7
Unpacking Trump's Gaza Plan
During a White House press conference with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, U.S. President Donald Trump made a stunning proposal: that the United States take control of Gaza. His remark sparked intense global debate. This week, we break down the implications with Jason Isaacson, AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer. Jason examines the proposal and shares AJC's perspective on what it means for the future of the region. Resources: AJC Welcomes Trump Affirmation of U.S.-Israel Alliance; Expresses Concern over Proposal for Gaza Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : The Oldest Holocaust Survivor Siblings: A Tale of Family, Survival, and Hope Israeli Hostages Freed: Inside the Emotional Reunions, High-Stakes Negotiations, and What's Next Bring Them Home: Understanding the Israel-Hamas Hostage Deal and Its Impact Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Jason Isaacson: Manya Brachear Pashman: During a press conference with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu at the White House this week, US President Donald Trump proposed that the United States "take over and own the Gaza Strip", suggesting long term control and suggesting the Israel Hamas war would soon come to an end. Whether one considers the proposal innovative or absurd, the surprising declaration underscored the need for a new approach to Gaza's future. With us now to discuss the impact of the President's words is Jason Isaacson, AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer. Jason, thank you for joining us. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Manya. It's good to be back. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Jason, I'll just ask you straight up, is this proposal innovative or absurd? Jason Isaacson: Well, of course, there are people who will say it's both. From my sense of the conversations I've been having in the Middle East over the last several days, last couple of days. First of all, it caught everybody by surprise. It does seem to be a little bit half baked, because there are many questions that arise when one starts digging into some of the details, which have been lacking. And it's also very important to point out that the day after the President presented this very surprising, innovative, out of the box proposal, there were comments from various White House officials that suggested, you know, don't take it quite so literally as the way it was laid out by the President. Even Mike Waltz, the National Security Advisor, suggested that it really, in many ways, is an attempt to kind of change everyone's thinking in the region, and force, urge, somehow move the Arab states to put forward their own innovative proposals. Because clearly, we're stuck, and we've been in a rut for decades, certainly since the Hamas takeover of the Gaza Strip almost two decades ago. And over the last year and a half of terrible conflict, the last 16 months of war, it's clear that no reasonable plan has been put forward that will really nail down not only the release of the hostages right away–which is insane that you've had hostages held for 16 months–but not even achieving the objectives that had been laid out at the very beginning of this conflict by the Israeli government, which was the necessity of Hamas no longer ruling Gaza. Because with Hamas ruling Gaza, you will never have a two state solution. You'll never have Palestinian rights. You'll never have peace in that region. You won't have 10s of 1000s of Israelis moving back to their homes in southern Israel, you will not be able to make the kind of progress toward regional peace that is necessary. Hamas is an extremist terrorist organization that wants to kill Jews. Wants to destroy the State of Israel. They don't want a 2-state solution. They want the end of Israel. So they can no longer be in charge. They can no longer threaten the Palestinian people with their aspirations for political change, and they can no longer threaten the people of Israel. They can no longer govern Gaza. And no one has come up yet with the definitive path forward to eliminate that continued Hamas threat. So there is a ceasefire agreement, ceasefire hostage release deal, that is in progress right now. Ultimately, the third stage of all of that, after we get through the second stage, which is yet to dawn, would be a new governing structure, but that is still in the future, and it's still not clear that we're going to get there anytime soon. So the idea of putting forward something bold and new and totally different has a certain logic to it, even if elements of what the President was saying the other night seem to be wanting certain degrees of logic. But we're still trying to figure out whether it was a genuine proposal, or just a slap in the face of the region saying, Okay, let's do something different and bold. Let's move forward. Manya Brachear Pashman: Even if we aren't supposed to take this proposal quite that literally, can you explain the proposal and what led to it? Jason Isaacson: Well, the proposal, basically says, if I understand it correctly, that the United States would kind of take charge and would conduct demining and clearing of the rubble and coordinating the reconstruction of Gaza. Which would require, according to the President's formulation, the removal of the Palestinian population. Some 1.7, 1.8 billion Palestinians who live there and are living in terrible conditions right now because so much of the infrastructure and the homes have been either badly damaged or destroyed. And so there's a certain logic, certainly, if you're a real estate man and you know how to redevelop property, if you're knocking down lots of buildings and you're trying to put up something new, you've got to get the people out of the way. So I can understand that reason, that reasoning. But this is a population that doesn't necessarily want to leave. Obviously, maybe some do, but it's very clear that there is a long embedded national movement among the Palestinians, which clings to that land, as miserable as the conditions may be there. And so therefore, if you are going to follow the President's plan, which would require the removal of people, they will be removed against their will, many of them, at least, and where would they be moved to? Unclear. The President originally said several days ago that he thought that they should go to Egypt and Jordan. Both countries have said clearly, as clear as day, no thank you, we do not want them. Palestinians belong in Palestine, which doesn't yet exist. They don't belong in our countries. This was a long standing position of both the Kingdom of Jordan and Egypt. And then where else would they go? There is no market internationally for accepting hundreds of thousands, let alone more than a million Palestinian temporary dislocated persons. Not clear that they would be away for very long, although I think the way the President was describing this project, we could be talking about a 10 or 15-year redevelopment plan in which he envisions a Riviera on the Mediterranean, another Riviera on the eastern Mediterranean, which is, you know, a wonderful vision, but how we actually get from here to there with so many complications in the way is totally unclear. There will be so much resistance. There already is. Within hours, there were immediate statements of pushback from the region. So what I hope this will mean is people across the region, and AJC is staying in the region. We've been in Israel for the last several days, we had an AJC Board of Governors solidarity mission to Israel earlier this week, and then a number of us are staying on and talking to people across the region. We'll get a sense for how the region is responding and whether this plan to prod the region to come up with something decisive that will actually help resolve this problem in Gaza, end the terrorist scourge that makes it impossible to move forward on peace, makes it impossible for Israelis to live in peace alongside their Palestinian neighbors. We'll get a sense of that. Right at this point, really, the ball is in both courts. The American court, because clearly the president wants ownership of some kind of a solution to this problem. Israel obviously has a huge stake in this, a security stake, especially. And the region also wants to move forward, and wants to see a resolution of the Palestinian-Israeli conflict, and frankly, relief for the Palestinians who have suffered through this terrible war over the last 16 months, brought about by Hamas' attacks on Israel of October 7, 2023. So it's a period in which the people in the region cannot tolerate the continued misery in Gaza, the continued threat that Hamas poses to Israel, the continued holding of hostages, dozens of hostages who have not yet been released. We need to see an end to all of this. The President has put forward a dramatic proposal. It may or may not make sense. It's up for the region to actually step forward and see what else, what else could be put down that will allow us to move forward. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you are on the ground there. What has been the reaction to it so far on the ground? Jason Isaacson: Well, I mean, so far, there have been statements issued by regional governments. Some quite detailed. Others, just commentary. Making it very clear that they have no interest in the dislocation of the Palestinian population. And some have really been quite harsh in how they have phrased that. But I think there is also a realization, and I expect to dig into this further in the coming days, that something bold, something that we haven't tried before, is necessary. Because what we have tried before simply hasn't worked. And you even have, 16 months into this terrible war Hamas, still, as the basically the governing authority in Gaza. Even with the Palestinian population there, I think clearly understanding that this misery that they have faced for the last 16 months has been brought about by Hamas, by their cynical policy of placing their entire military infrastructure embedded in a civilian population, so that when they made this brutal series of attacks on October 7 and killed 1,200 people and captured 251 and kidnapped them and been holding them for months, knowing that there would be a massive Israeli retaliation, a massive Israeli effort to bring back these hostages and to punish those who came across the border and killed and raped and pillaged southern Israel. They knew that that was going to bring about enormous destruction. Palestinians in Gaza recognize that it was Hamas that did this. But still, they're stuck in this terrible cycle of being governed by the very people who have brought about this terrible misery to the people of the Gaza Strip. So we all know that we have to move forward into something different. The ceasefire and hostage release deal allows us in stages, to get to a better place to release all of the hostages. Some 18 were released as of yesterday. I think we're on track to release several more in the coming days and we hope all of them and the conclusion of the second phase. But we have to get through the second phase, and then we have to get to someplace else. So Hamas can no longer govern. We have to see a way forward to a resolution that allows us to envision peace between Israelis and Palestinians, the well being of the Palestinian population, the return of Israelis to the southern cities and towns and clearly, the release immediately, as quickly as possible, of the hostages who have been suffering for 16 months. Manya Brachear Pashman: Why do you think the White House has tried to walk back his comments? Jason Isaacson: Well, President Trump is famous for big ideas and bold statements and also sometimes saying things that kind of upset the norms of discourse. He's known for doing this in lots of different contexts, domestic policy, foreign policy. And it was very clear, the reaction from the region was so sharp, so immediate, that they had to find some way of explaining what the President intended. And the way they have framed it is that basically, this wasn't about the United States owning Gaza. It wasn't necessarily about the United States building luxury resorts and condominiums on the shores of the Mediterranean and Gaza, because there was also a statement that made it clear that there weren't going to be US troops involved, and maybe not even US investment involved. So it was just clear that there were holes in this plan. It was a kind of a big, dreamy vision, intended as we are hearing from the White House in the days after the President spoke to kind of shake up the establishment, the establishment in the region, the establishment in the sort of the foreign policy community and and force people to come up with a better idea, a clear path forward that would rebuild Gaza without Hamas, and allow the Palestinian people some relief from all of this, and obviously assuring the security, the release of the hostages, and the security of the people of Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: You've mentioned the hostages coming home in the days to come. But do you think this declaration could derail the hostage agreement the first stage of it, especially given second stage negotiations have not even begun yet? Jason Isaacson: Well, there is that danger, and that is one of the points that that AJC made in the statement that we issued immediately after, the day after the President spoke. While also recognizing that what he did say about the alliance between the United States and Israel was hugely important. The fact that he received Prime Minister Netanyahu as the first foreign visitor to the White House in this second Trump administration sends a powerful signal to the region. Certainly to our community, but to the region, that Israel's security is vital to the United States' national interest. He was very clear about that, and also very clear about the threat posed by Iran and the necessity of pushing back against the Iranian nuclear threat, but also its support for proxies like Hamas and Hezbollah, of course, in Lebanon and others in Yemen and Iraq. And other changes that will have to be made to this ring of resistance, of fire that the Iranians tried to strangle Israel with. The President's been very clear about all of that, and it's really welcome, and we welcome that. But we had to express concerns about the policy, the proposal that was put forward on Gaza, because it clearly rattled the region, and it could–if the signal to Hamas which is in negotiations with Israel through Qatar and Egypt and the United States, if Hamas, which continues to hold hostages, sees that there is some alternate universe that the administration is proposing in which they would just clear out the whole area–how does that affect their thinking about their hopes that they can still have some kind of a presence in Gaza, which we don't want. Israel can't stand. Frankly, the region doesn't want either. But it could be that if Hamas is negotiating with a sense that they have some future in which they will still have some role to play in the conduct of affairs in Gaza. This remaking of the entire map could force them to retreat and to say, You know what? Maybe we're not going to go ahead with these negotiations right now. We're going to rethink our position, and that would be terrible. It is imperative that the process that was set in place on January 19, the last full day of the Biden administration, with very strong support from the incoming Trump administration, move forward. It is essential that we move forward on the hostage release deal. And Israel will continue to protect itself, will continue to have a security presence in the region. But will end the war at least while this is going forward, assuming that Hamas abides by the agreement, and Hamas, then, in the next stage, no longer governs Gaza. Manya Brachear Pashman: We've talked about the impact of this proposal on the hostage negotiations. What about expansion of the Abraham Accords, which was certainly one of the major milestone achievements of the first Trump administration. You are in the region now, that is something that you have worked very hard for for decades. How could this derail the expansion of the Abraham Accords? Jason Isaacson: Well, the Abraham Accords, the whole idea of expanding Arab-Israeli peace, of Israel's integration into the region, is so abundantly clearly in the interest of the region. We have seen again and again instances in which it's been proven, demonstrated of the advantage that accrues to the region by having Israel as part of the region, instead of pretending that it's somehow separate from the region. What happened last April, what happened last October, when Iran fired missiles and drones to Israel and the region joined Israel a couple of countries, not the entire region, couple of countries in the Arabian Gulf, joined with Israel and with Israel, but also with the United States and with the UK and other navies and air forces to combat this incursion. You have the creation, the emergence, of a regional security architecture in which Israel plays a significant role. The benefit of that is so clear to wise leaders across the region that I am completely confident that that progress will continue. Even if this weird statement was made by the White House the other day. I want to read that, and I'm hoping that I will hear from contacts across the region that they want to hear that as just simply a clarion call for something new and bold and different that can break us out of the. Paralysis that we are suffering in Gaza without having any effect on the natural course of progress in Arab Israeli peace and cooperation, security infrastructure, exchange programs of various kinds, medical technology, the public health, education, water resources, environmental issues. There are so many things that are happening at a lower level right now that when the cover is removed and it's allowed to kind of move forward, is extremely exciting to people across the region. Which is why, by the way, last June, at the AJC Global Forum in Washington, AJC CEO Ted Deutsch announced the creation, launch of the AJC Center for a New Middle East, which builds on the work that we've been doing for decades to introduce people to each other across the Arab world, with Israel, with our community to talk about the benefits that will accrue to the people of the region from Israel's integration in the region, the contributions that Israel continues to make and will make in a much amplified way if it is accepted and normally interacting with its neighbors, as It does with now, in the last four years, with the UAE and Bahrain and Morocco. And of course, has had long standing peace agreements with Egypt and Jordan, with which, even though there are many disagreements and dissatisfaction with these agreements, they have been enormous contributors to regional peace and stability, and frankly, the welfare of both of those countries as well. So the advantages are clear. We've been part of this process for a long time. We will continue to be part of this process. Whatever is said in the way of unusual statements from the White House about new ways forward that don't fit into the normal pattern of diplomacy. The leaders of the region understand that this is the direction that they should be pursuing, and we will continue to encourage that process. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jason, thank you so much for joining us. Jason Isaacson: Happy to be here, Manya.
Jan 30
Empathy Is Who We Are: Rabbi Elliot Cosgrove on Being Jewish Today
"To be a Jew is to know that because of who we are, because of our historical experience, we care for the other. This is really one of the great tensions of our moment. Of how to be eyes wide open to Israel's need for self-defense, and at the same time recognize the real suffering that's going on in Gaza and to know that we need to find a way to hold both of those together." Rabbi Elliot Cosgrove, spiritual leader of Park Avenue Synagogue in New York, explores the complexities of Jewish identity in a post-October 7th world in his new book, For Such a Time As This: On Being Jewish Today. In this conversation, he unpacks the tension between Israel's need for self-defense and the suffering experienced by Gazans and Israelis and the challenge of balancing empathy with vigilance. He also shares his personal journey to the rabbinate and what it means to live as a Jew in this pivotal moment. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Sign up for AJC Global Forum: Register at AJC.org/GlobalForum2025 for the premier global Jewish advocacy conference of the year, in New York City, April 27-29 2025 Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : The Oldest Holocaust Survivor Siblings: A Tale of Family, Survival, and Hope Israeli Hostages Freed: Inside the Emotional Reunions, High-Stakes Negotiations, and What's Next Bring Them Home: Understanding the Israel-Hamas Hostage Deal and Its Impact Pack One Bag: Stanley Tucci and David Modigliani Uncover His Jewish Family's Escape from Fascism and Antisemitism in 1930s Italy Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Rabbi Elliot Cosgrove: Josh Kramer: AJC Global Forum is returning to New York City, April 27 to 29th 2025. I'm Josh Kramer. AJC New York Regional Director, and I hope to see you there. You won't want to miss this opportunity to join with more than 2000 other activists and engage in thought provoking discussions on the future of the Jewish people, Israel, America, and the world. Our program will feature large plenary sessions with headline speakers, smaller breakout sessions designed to explore the key political, strategic and social concerns affecting the global Jewish community, and exclusive opportunities to engage with diplomats, decision makers, interfaith partners, community leaders and more. Will you be in the room? Register today at AJC.org/GlobalForum2025 to take part in the premier global Jewish advocacy conference of the year. Now is the time to join AJC in shaping a new future. Head to AJC.org/GlobalForum2025 . Manya Brachear Pashman: I've done quite a bit of soul searching in the 15 months since October 7. How do I grapple with the tragedy in Israel and Gaza and the hatred Jews face on American soil without scaring my children away from Judaism? Then came our Temple's Purim spiel last spring. That story of Queen Esther's bravery, in some ways, helped. It was about that same time that Rabbi Elliot Cosgrove, the spiritual leader at Park Avenue Synagogue in New York, picked up his pen and began to write his latest book, named for a line in Queen Esther's tale – For Such a Time As This: On Being Jewish Today. Rabbi Cosgrove is with us now. Rabbi, welcome to People of the Pod. Elliot Cosgrove: Thank you. It's great to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I have to tell you, rehearsals began for this year's Purim spiel as I was reading this book, which made it all the more powerful. What inspired you to write this? Elliot Cosgrove: Well, for me, I draw wisdom from text, and I was trying to think of what would be an analogous moment for what we were going through as American Jews from the ancient text. And for me, as you say, this is now on the cusp of Purim 2025, it was the story of Esther that we read. And in many of our synagogues, we have Purim spiels, where we act out the story, which is basically the story of a Jewish community of ancient Shushan who believed themselves to have it good, that they were comfortable in the diaspora. And the wicked decree of Haman came down and Esther, whose name actually means to hide, she hid herself, her Jewish identity in the king's palace, and believed that she was comfortable there. When the decree came down, Mordechai, her uncle, by way of an emissary, sent a message to her. "Don't think yourself to be safe from Haman's decree. Who knows, if it was not for such a time as this that you've arrived at your station." And I saw this as really the calling card of our moment that we all felt ourselves in the wake of October 7, Esther-like called to action. The trauma of October 7, but also the call to action, to step up to the moment, the needs of our people. Manya Brachear Pashman: Tell us about your writing process. Elliot Cosgrove: I buried myself in my writing from before dawn until mid-morning, and then I would hit a wall. And I didn't take a sabbatical. I actually went into my day job as a congregational rabbi. It was a very intense writing process and then in the course of about three to four months sent the manuscript off to the publisher. Manya, the thing about the book is it was very disorienting to write as the events were playing out, both in Israel and in the States. And one of the worries that I had that I spoke to the publisher about was, well, what if this becomes dated? You know, it was not journalism, but I was writing as the news was happening, and the good news and the bad news is that the themes that I pick up on: the trauma of Israel, the blurred line between anti-Zionism and antisemitism, how we balance empathy and vigilance, the question of the hostages, of thinking about a day after for Israel and the Palestinians, these questions are not only still relevant, but they're actually more pressing than ever. So unfortunately, the themes that I hit on in the book, very much present right now. Manya Brachear Pashman: How did that writing process help you personally process what you were witnessing and experiencing as a Jew in America? Elliot Cosgrove: I'll say this, that as a rabbi, I often see my job–someone calls, they've just gotten bad news in the hospital, a loved one has passed away. Or a happy thing, that their child has just gotten engaged, or they themselves have just become new parents. And people turn to clergy to get the first line of constructing the narrative of what it is they are experiencing. And for me, there is something deeply personal and deeply pastoral about this book, because I feel like it's seeking, hopefully, to give the language to American Jews as to how to construct this new reality of a post October 7 existence, the jumble of emotions, of trauma, but also the emergence of Jewish identity, the likes of which we've never seen before, the argument for continued defense of Israel's right to self determination, as well as an assurance that the traumas of October 7 never happen again. And in the same breath to think actively about what does the day after look like. I think we're all searching for language for these and other tensions of our moment, and I'm hoping that the book is sort of a vocabulary builder for our time. Manya Brachear Pashman: One word that you used many times in the book, and it stuck with me, just because maybe it's one of my favorite words, and that is empathy. And you used it in different chapters, different contexts. And I'm curious if you could share with the audience the role of empathy and how it is a guiding force, how it has been a guiding force since October 7. Elliot Cosgrove: Empathy, both its presence and its absence, has been a subplot of this moment, because I think empathy is ingrained into the Jewish DNA. You open up the Passover Haggadah, and on the one hand, we know that we are vigilant against every generation a pharaoh arises to destroy us. We are guards up. We are a people who knows the importance of ancient hatreds, of being vigilant against them, and also the ring of fire that Israel sits in by way of Iran and its proxies. I mean, Israel's in a very tight spot, and American Jewry is in a very tight spot. And at the same time, empathy is who we are. You were once a stranger in a strange land. Therefore you should know the heart of a stranger. To be a Jew is to know that because of who we are, because of our historical experience, we care for the other. And I think that this is really one of the great tensions of our moment of how to, you know, be eyes wide open to Israel's need to self defense, and at the same time recognize the real suffering that's going on in Gaza and and to know that we need to find a way to hold both of those together. That Israel needs to fight this war as if there's no tomorrow, and Israel has to fight this war with an eye to tomorrow, with the same ferocity that it prosecutes this war, it has to pursue a day after plan. And I think that somewhere along the way, it's the voices on the extremes who are speaking with the loudest megaphones. And the goal of this moment is to realize that we need to find a way to embrace both. I think it was Fitzgerald who said the test of a great mind is the ability to hold two opposing ideas and retain the ability to function. I think the test of the Jewish community right now is the ability to hold both vigilance and empathy at the same time and retain the ability to move forward with hope. Manya Brachear Pashman: And how can empathy help here on American soil, where we're facing protesters, we're facing all kinds of opposition and questions and hatred because of what's happening overseas. How do we use empathy here on American soil? Elliot Cosgrove: First of all, it's hard. It's hard. When you are under attack, the last thing anyone wants to do is feel someone else's pain. When someone is calling me a colonialist oppressor, when someone is calling for the destruction of the Jewish state, something which is part and parcel to my identity, core to my very being – my initial instinct is not to inquire into how they feel and have empathy. My initial instinct is to have shields of self-defense, prioritize the needs of my people over anyone else's. I think that's a human thing to do. And as long as the hostages are hostages, as long as Israel stands in a vulnerable position, I think we need to be eyes wide open to that, and then we need to breathe, and we need to remember what it means to be a Jew. And we need to remember that it takes two to tango, and that if we are going to create a future whereby Jews and Palestinians can live side by side in safety and self determination, then we need to realize that there are two peoples worthy of realizing that dream, and that requires empathy, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: You were not always that religious or observant of your religious tradition. Can you tell our audience how you became a rabbi? Elliot Cosgrove: How long do we have? This is a big question, but, look as with any way we construct our realities and tell our origin stories, there are a million ways to tell it. The truth of the matter is, I am the grandson of a congregational rabbi, an orthodox rabbi. So to say that I had somehow strayed from the path is a little bit of an overstatement. But I will say that I grew up in a traditional Jewish background. I'm very proud of the home I grew up in, but when I went off to college, it was very much something I did, Judaism was something I did at home. And I can't say that my first few years at my alma mater at University of Michigan were known by way of my religious affiliations and commitments. And then I got a phone call my junior year of college, that a figure from my youth, a grandfather figure I never really knew. My grandparents had passed away, and he was a guy who used to sit next to us in synagogue and slip me up peppermint candy as the rabbi was about to start the sermon or come over for Passover Seders or Shabbat dinner, Mr. Gendun, and he had passed away. And I got the phone call. I said, What would Mr. Gendun want me to do? And I thought, maybe I'll say Kaddish. So I called one of my Jewishy friends. I had never been inside the Hillel building up until that moment. And I called up one of my Jewishy friends and I said, What's, where's the Hillel? And they said, you're an idiot, Elliot. It's this huge building right on campus at Michigan. And I went in and I said my Kaddish, and I was getting up like it was the end of an airplane ride just to run back out to whatever my evening plans were. And a man stood between me and the door, boxing me out, and I was trying to shimmy one way and the other. And he said, I notice you've never been here before. And he said, Well, I'm wondering if you'd like to come to Shabbat dinner. And I lied, truth be told, because I figure he didn't want to know about dollar pitcher night. And I said, I already have Shabbat plans. And he said, Well, do you have Shabbat plans next week? And I was caught in my tracks, and I said, No, and before I could say another word, he said, Good, then you'll come over for Shabbat dinner. And that man was Michael Brooks, who was the Hillel Director of the Michigan Hillel. I went over to Shabbat dinner. I got involved in the Israel group. I was an editor of the student journal. I sat on the Hillel governing board. One thing led to the other, and I became a rabbi. But important [as] that story is obviously in my own religious formation and choice of vocation, is how it informs my own life and my own rabbinate. It's that ability to look around the room when you're in a class, a Jewish event, a service, and who's the person who looks a little out of place like they might have been there for the very first time, and just do that small human act of reaching out to them, and whether you're going to invite them to Shabbat dinner or not, but just to acknowledge their humanity, that has been the north star of my rabbinate ever since. We're all just human beings looking for a place to hang our hats. Manya Brachear Pashman: You talk about empathy. I think empathy caught my attention every time you mentioned it in the book, because I think it's so key to journalism. It's such an important component of it. And then I think hospitality is such an important component to Judaism and to congregational life, Elliot Cosgrove: Absolutely. Hospitality is something that is key to our text at the beginning of the Passover Seder. But hospitality is also a spiritual demeanor that we welcome people into our souls, into our presence, into our life. Hachnasat Orchim in Hebrew, this idea that there's always space within our souls, within our hearts. Manya Brachear Pashman: Having had such an important turning point on a university campus, how did you interact with, council, university students during this time, as they were facing such pressures and such opposition, crushing opposition during this past year and a half? Elliot Cosgrove: So there's a chapter about that in the book. It's really the part of the book that I think has struck a nerve, and appropriately so, because I'm the father of four college age or thereabouts children. And that story I tell about Maya, and Maya is a young woman who, I joke, shares half a brain with my own college age daughter. She's grown up in my household, and she is what you or I might identify as a non Zionist Gen zer, and she approached me and perhaps reproached me for having a Israeli flag on the pulpit, for doing the prayer for the State of Israel in the midst of the service, and said, you know, and she grew up in the Jewish Day School. She grew up going to Jewish summer camp. She did gap year programs in Israel. Not a small amount of money has been invested in the Mayas of the world, and she herself is asking whether or not her liberal, American Jewish self can be simpatico with the policies of this or that Israeli government, because they don't speak for her sensibility. And to this question of empathy, I think the first move one makes in any such situation is to try to understand where the other person is coming from. And I think a 21, 22, 23 year old is coming of age in a moment of time where the only Prime Minister they know of is Bibi Netanyahu, who either is or is beholden to the most right-wing elements of Israeli society. The only policies they know of the Israeli government are an expansionist policy in the West Bank, which has precluded the possibility of a two state solution. The only paradigm they have is an Israel which is a Goliath to the Palestinian David, this is their reality. You can't blame someone for the time into which they are born. I can pick apart and engage in a dialog on what's true and what's not true. But to tell someone that their reality is not, their reality is is not, you know, a move that one can make. And by the way, if they're during the time of the judicial reform, and to this day, there are 1000s of Israelis marching on the streets on a Saturday night protesting the Israeli government as an expression of their love of country. To tell the Mayas of the world, a college age student today, that they are treif, they are beyond the bounds of Jewish discourse, for doing the exact same thing is just an argument that doesn't hold water anymore. And so the the the goal here, Manya, is to engage with their questions, to listen intently, to prompt that young mind to come up with their own answers for the defense and the well being of the Jewish people, given the harsh realities that Israel faces, and also to make room for their very real question. So I look long on the Maya generation. It's actually a controversial moment within the organized Jewish community –do we write them off, do we not write them off? I think they're our future, and I think we do terrible damage to ourselves if we write them off. Manya Brachear Pashman: Because it is such a time as this. We have to pay attention to the context, right, and to where we are in history, without losing sight of history. Elliot Cosgrove: Look, it's very easy to take pot shots from the left and from the right. You know where this brave space is. The brave space is standing in the middle and dignifying the claims and counterclaims of both sides, and knowing that real leadership is trying to keep our people together. Manya Brachear Pashman: Your book does such a beautiful job of inspiring that sense, sparking those, those right emotions in my head. So thank you so much for writing it. And I encourage all of our listeners to pick up a copy of Rabbi Cosgrove's book–For Such a Time as This: On Being Jewish Today. It is full of challenges, and I think that the challenge is worth facing and taking on. Thank you. Elliot Cosgrove: Thank you so much, Manya.
Jan 23
The Oldest Holocaust Survivor Siblings: A Tale of Family, Survival, and Hope
When the USC Shoah Foundation named three sisters and their brother from Sanok, Poland the oldest surviving siblings of the Holocaust, Canadian Jewish filmmaker Allan Novak, the son of one of those shvesters (sisters in Yiddish), realized it was time to use the footage he'd been collecting for years to tell their story. The result? Crossing the River: From Poland to Paradise – a heartwarming short documentary about how members of one family miraculously survived the Holocaust by staying together with each other and their parents. Listen to this conversation with Novak on his family's dream of moving to Israel, unwavering resilience, and positive outlook, despite losing 80 family members to the horrors of Nazism. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Resources: Watch the film: Crossing the River Artist Zoya Cherkassky print created in the spirit of the film: 250 signed and numbered prints will be sold with 100% of proceeds going towards Holocaust education through a series of initiatives developed and implemented in collaboration with AJC. The cost of the prints is $250. They can be purchased by credit card by calling 212-891-1454 or by emailing contribute@ajc.org. Or, you can send a check made out to AJC to the address below. In all instances, please be sure to mention that this is for a Zoya print. American Jewish Committee - 165 E. 56th St., New York, NY 10022 Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : Israeli Hostages Freed: Inside the Emotional Reunions, High-Stakes Negotiations, and What's Next Bring Them Home: Understanding the Israel-Hamas Hostage Deal and Its Impact Pack One Bag: Stanley Tucci and David Modigliani Uncover His Jewish Family's Escape from Fascism and Antisemitism in 1930s Italy Gov. Josh Shapiro and AJC CEO Ted Deutch on Combating Antisemitism Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Allan Novak: Trailer: Ruth Zimmer: That's a camera. Allan Novak: No, this records sound. Sally Singer: [in Yiddish: It's so small.] Ruth Zimmer: Ok, Sally. Allan Novak: Meet the shvesters: Auntie Ruthie, Auntie Sally, and my mum, Anne. Anne Novak: I'm the quiet one. Ruth Zimmer: And I'm the pisk (loudmouth). Allan Novak: Along with my uncle Saul, they've been together since the 1920s. As they began to hit 100 the media started to take notice, and when the USC Shoah Foundation named them the oldest Holocaust survivor siblings in the world, I knew I needed to tell their story now. Ruth Zimmer: What do you want us to . . you want to ask questions? Okay, that's easier. Allan Novak: I want to talk about the war. ____ Manya Brachear Pashman: When the Shoah Foundation named three sisters and their brother from Sanok, Poland the oldest surviving siblings of the Holocaust, filmmaker Allan Novak, the son of one of those sisters, realized it was time to use the footage he'd been collecting for years to tell their story. The result? Crossing the River: From Poland to Paradise – a heartwarming short documentary about how members of one family miraculously survived the Holocaust by staying together with each other and their parents. Allan is with us now to talk about his extraordinary aunts, uncle and mom and this equally extraordinary Holocaust story. Allan, welcome to People of the Pod. Allan Novak: Thank you, Manya, great to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you had been recording interviews and kind of a life with your family for decades, right, while kind of working on various other projects. But what finally moved you to make this a project? Allan Novak: Sure, well, I've been filming them since I got my Bar Mitzvah Super Eight camera a while ago, in the 70s, actually. And, yeah, I've been collecting footage, you know, at different times. Was inspired to interview, to capture their story, but really, more is just kind of a personal archivist kind of project. But then when the Shoah Foundation identified them as the oldest Holocaust survivor siblings in the world, as you mentioned, I kind of posted that in my social media. And then there was a huge reaction. People just loved this idea that these people survived all this, and we're still together and survived, and we're thriving, in fact. And actually had a producer friend of mine inquire about where the rights available to their story. So I had to laugh, because, you know, I'm a filmmaker, so I immediately realized that somehow, you know, my little family story had kind of broken in a way, and it didn't deserve to be told and shared with the world. Manya Brachear Pashman: So without giving too much away, can you tell our listeners a little bit about these extraordinary family members and what your relationship with them was like growing up? When did you realize they had such an extraordinary backstory? Allan Novak: Well, you know, they often talked about, you know, Siberia, which is where they survived the war. And they were, they were kind of small little stories. And I understood they were hungry and it was cold and that kind of a thing, but it was always kind of light hearted, and there was laughter. You know, my auntie Ruthie, who is prominent in the film, she was an actress in the Yiddish theater, and she's really a natural comedian, and so she would always, they would make it funny. And my uncle, Saul, I call him the most positive person in the world. He actually also would look on the bright side of things. So although they went through, you know, really tremendous trauma, somehow the way they processed it was with a positive outlook. And that kind of rubbed off on me. So I never felt, you know, unlike the people whose parents were unfortunate enough to have been in places like Auschwitz and under the Germans, I didn't have that sort of really, really dark sense of a traumatic story, but rather kind of this sort of triumphant survivalist story. So survival is kind of the key word and positivity together. So that's how I saw them growing up, as sort of somewhat fun old country of uncles and aunts. Manya Brachear Pashman: Now one of the reasons your mother and most of her siblings survived is because the river that ran through Sanok also divided it into German and Russian territory, and your family fled to your great grandparents home on the Russian side, but about 80 of your family members stayed on the Nazi occupied side of Sanok and were murdered. One of them was your uncle Eli? Allan Novak: Yeah, yeah. Eli. Manya Brachear Pashman: Eli, yeah. Who did not stay with the siblings and parents. He had a bad feeling about where the Russians might take them. Did you ever get a sense of why the rest of the family stayed on the west side of the river in Nazi occupied Sanok? Allan Novak: You know, it's a sad thing, but part of it was economic. You know, my grandfather had a relatively prosperous butcher shop. It was unusual because he supplied meats to the Polish military regiment there, but also to Jews. So he sort of had a half kosher, half not kosher shop, which was, I didn't even realize that could exist, but it did. He was quite Orthodox, and so they were sort of comfortable, but they shared a house, for instance, with my grandfather's brother, and he had like nine kids, and he wasn't so successful. And so when I asked them, like, Why didn't everybody go over to the other side? It's like they didn't have the money to hire a driver, horseman, get across the river. And so it was just unfortunate. And as well, it was my mother's grandmother that had the property, so on the father's side, they didn't really have that option to sort of show up on the other side of the family. So it was kind of cruel twists of family and economics and also nobody knew, like they didn't know that that would be the right side. Nobody knew what would happen. You know, the week the Germans marched into Poland in September. So, you know, they went with their instinct, stay with the grandmother. But nobody knew what would happen. And of course, Eli, the brother, thought he was making the clever choice. He thought he was going to survive because he didn't want to get on the train. Manya Brachear Pashman: How old were these people when they made these decisions to stay together or stay in Sanok? Allan Novak: So there were five siblings. Sally, the oldest, would have been 19. So they were like 1917--15, 13, and 11. So Eli was 11, so they stuck together. They were young, you know, it probably seemed like a bit of an adventure, you know, to a 13 year old Auntie Ruthie, they didn't know, nobody knew what was to come. But Eli was 11, and he was, by all accounts, a stubborn child and a willful kid. A tough cookie, as my uncle Saul says. And so there's a point in the story where everybody was told you have to get on this train by the Russians, and the family huddled together. And this 11 year old boy who thought he was smarter than everyone and was more willful, said, I'm not getting on that train. I'm going to stay with my grandparents, who were not being sent out. The others were deported because they were Polish citizens, and on the other side, they weren't. So that's what happened. So he was 11, strong willed, and he made a choice. And then in the end, obviously, like one of those sort of lessons of the story is families that stay together do better than not. Manya Brachear Pashman: As you mentioned, your family ends up in Siberia. That's where this Russian train takes them. I'll let listeners kind of watch the film to find out exactly how that unfolds. There is a story that did not make it into the film, but I read about the spilled milk, and I'm hoping that you can share that story as I think it's so sweet, but it also just gives listeners an idea of the conditions that your aunts, uncle and mom survived. Allan Novak: I mean, they were living essentially in a small wooden room inside of a long wooden barrack, and every family didn't matter how many people you got this, this wooden room. There were no beds. There were just sort of boards that came down from the wall. And there was like a bucket where they would put wood in and that sort of all they had to kind of keep them warm. But sometimes they could do things like they could trade. There were Siberian peasants around. And if you had an earring or something, you could get some milk, right, from a farmer nearby. And so, yeah, I think my Aunt Sally, she was able to kind of get this milk for the family. And it was this huge, huge treasure to have this small little pail of milk. And she put it under the bed for safekeeping until she could share it the next morning, and then she knocked it over in the night, and this precious, precious milk spilled on the floor, and she really like, for her whole life, she just had this deep sense of regret and shame for spilling this milk, because it was just so precious to have anything to eat other than the few grams of bread they were given. Manya Brachear Pashman: She literally cried over spilled milk for decades. Allan Novak: Yes. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did her siblings know about this? And I'm just curious, what was the dynamic? You actually asked this very question in the film. You asked them, what is the dynamic between all of you? And they interpreted that as the difference. But I'm curious, just from your perspective, what was the dynamic of these siblings through the years? Allan Novak: Well, you know, they came from a traditional family. The father was Orthodox, you know, Shomer Shabbos, kosher, as probably were most of the Jews in Poland at that time, in the 20s and 30s. So they had a great deal of respect for the mother and father, would be nothing like today. It was just pure respect and love. And so between them, Sally, who's in the film, they called her the smart one. She was the most educated one. So she kind of ruled the roost, in a way. But Ruth, the youngest, she was a troublemaker. She's my auntie Ruthie, the comedian. And so she would make trouble. She would follow them. If somebody had a date, like if Sally had a date with a boy, you know, Ruthie would be sneaking up behind and, like, harassing them and not going home, or chasing after them. She was kind of wild and incorrigible. My mother was always the middle child, so she was the peacemaker, which you see in the film, always trying to bridge between Sally and the younger Ruth. And Saul was kind of, he was the boy, the only boy, and they really just cherished him. He was good with his hands. He could fix anything. There's a story in the film of how he had to kind of steal little parts, pieces of wood and things to end up building a cart that he could sell to get milk, that kind of thing. So they really appreciated each other, and they each had their positions, you know, judging by birth order, in a way. Manya Brachear Pashman: You also talk in the film about how Saul and your aunt Ruthie, they were determined to fulfill their dream of going to Israel and going to a kibbutz in Israel. Spoiler alert, they did not make it, because, again, they put family first. Was this family first theme, a through line of your upbringing? And also, did they ever make it to Israel as just tourists? Allan Novak: Yeah, family first, certainly. Yeah. I grew up with a lot of cousins, the uncles and aunts, and they all lived very close to each other for their entire adult lives. You know, every night, one of the uncles and aunts would be walking over down the street and sitting there, so yeah, and we would hang with my cousins during the summer. So yeah, family first, definitely. We were all very close with our cousins, and we still continue to be. With respect to Israel, I mean, it was really something. They really wanted to be in Israel. You know, they were part of Zionist groups called Akiba growing up. My father, this story isn't in the film, was actually the head of, like, a whole group of Kibbutzim in Poland, and he ran the organization getting people over to Israel, you know, in 1947-48 and it was actually a great embarrassment to him that he ended up going with his new wife to Canada versus Israel. And he was very embarrassed because, you know, Oscar, you know, she and Novak, the organizer, ended up going to Canada. So it was a bit awkward. But, you know, they went where they got their immigration, and there was already family there. And just a very quick sidebar, so my father had one sister. My father lost like nine siblings, but he had one sister who emigrated to Palestine at the time in the 20s, and she had one son. And so my only living relative in Israel was the greatest living soccer star of his era. It's the equivalent of like having Pele as your cousin. His name is Nahum Stelmach. They called him Rosh Zahav, the golden head, because he won a famous match against Russia in the 60s. And this small country beat Russia, and he won. Sidebar. So they did get to Israel. It took until the mid 60s to get there to visit his, you know, Nahum, and then they went subsequently a few more times, but, you know, it was expensive, particularly, you know, in the 50s, and you know, until the 60s. So it took until the 60s, till they got there. But, yeah, it was a lifelong regret, but it was just kind of the twists of fate. Well, it's in the film. They might have ended up in Israel. They were on the Exodus. They were booked on the boat the Exodus, and then my grandfather had a stroke just before. So part of the themes of the film is kind of the random twists of fate and the choices that we make, and what happens is unknowable. Manya Brachear Pashman: The film includes footage of your mother turning 100, the birthday party, and she would always say that the best revenge against Hitler was to live long lives. What do you think has kept your family members alive for so long, what has kept them alive? Allan Novak: Coincidentally, Uncle Saul just had his 100th birthday party three days ago. Now, three of them hit 100 and over, and Ruthie just is gonna have her 90th birthday next week. One of the things I say is they live with intense moderation. Everything they did was moderate. They didn't eat too much, they didn't tan too much, they didn't smoke, they didn't travel, just everything was just kind of this moderate lifestyle and exercise, right? So I believe that's part of it. They really were well preserved, physically and mentally like, right to the end. And then, of course, you know the closeness, I think, the social cohesion that the fact that they, three of them, moved in together to assisted living facilities, you know, in their late 90s together. You know, as they lived in a condo. They all had three apartments next to each other for 20 years as well, with Saul close by. So I think that family cohesion and closeness and they didn't fight. They never fought, never saw a feuding moment. So, you know, we know things like stress and all of that contribute to long lives. So I think they sort of had this mild and loving long life. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm sure their experience gave them some perspective. There's nothing really worth fighting about when you've survived what you did together. Allan Novak: Yes, absolutely right. Manya Brachear Pashman: What has kept them so young, not so old? What lessons can we take away from the shvesters story today? Allan Novak: Certainly take care of your siblings. Stay close. Keep them close, keep relations good. Choose togetherness over isolation when the chips are down. Positive spirit, Uncle Saul's positive spirit and their positive outlook. Again, never wallowing in what had happened to them and the things that were lost, even the family members that were lost, moving forward and cherishing what they have. And you know, loving your children, if you have them, and their caring family gave them a lot of meaning. They did everything for us, everything for the kinder, even to the point of when the film initially premiered, actually at Lincoln Center last January, and my mother was in the hospital at 100 and a half, and she stayed alive and alert until we had this premiere. We flew back, and then it was kind of like three days later, she let herself go with us there and said proper goodbyes. And I firmly believe that she just held on for the kinder, as they would say, for the children. So I think that's part of what kept them vital and youthful and alive. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much. Allan, thank you for making this documentary and sharing it with the world. Allan Novak: My complete and utter pleasure, and I hope people take as much joy and uplifting positive and laughter, which is ironic for a film dealing with that time period, but they won. Hitler lost, and they won. And so it's kind of a triumphant story. And there's a final image which people would see of them on their balcony, you know, all around 100. In the snow in Winnipeg, holding hands, just persistent and alive. And they're together, immortalized now in the film. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much, Allan. Allan Novak: My pleasure. Manya Brachear Pashman: To watch the short film, head to the link in our show notes . And a special thank you to Debi Wisch, AJC Board of Governors member and the producer of Crossing the River, for her work to further Holocaust education through the arts. If you missed our last two episodes, be sure to tune in for my conversations with AJC Jerusalem Director Avital Leibovich and AJC Managing Director of Policy and Political Affairs Julie Fishman Rayman about the high stakes negotiations to bring the October 7 hostages home.
Jan 21
Israeli Hostages Freed: Inside the Emotional Reunions, High-Stakes Negotiations, and What's Next
After 471 harrowing days in Gaza, Israeli hostages Emily Damari, Romi Gonen, and Doron Steinbrecher are finally reunited with their families. Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC's Managing Director of Policy and Political Affairs, discusses the emotional impact of these reunions, the high-stakes prisoner exchange deal, and the collaboration between the outgoing Biden administration and newly inaugurated President Donald Trump. This breakthrough highlights the broader societal trauma in Israel, the complexities of negotiating with Hamas, and the ongoing efforts to bring all hostages home. Learn how this pivotal moment could reshape U.S.-Israel relations and Middle East policy moving forward. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : Bring Them Home: Understanding the Israel-Hamas Hostage Deal and Its Impact Pack One Bag: Stanley Tucci and David Modigliani Uncover His Jewish Family's Escape from Fascism and Antisemitism in 1930s Italy Gov. Josh Shapiro and AJC CEO Ted Deutch on Combating Antisemitism Mijal Bitton on What It Means to Be a Jew Today The Next Chapter in Catholic-Jewish Relations Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Julie Fishman Rayman: Manya Brachear Pashman: The world watched Sunday as three women held hostage in Gaza for 471 days reunited with their families. The moving footage was juxtaposed against the frightening prospect of more than 1000 Palestinian prisoners, many of them convicted murderers and terrorists, would eventually return to freedom as well in exchange for the hostages. There was also the strange irony of a hostage crisis nearing an end amid a transition in the White House, just a week after President Carter, who departed the White House as the Iran hostage crisis neared the end, was laid to rest. Here to discuss the painful and painstaking process of bringing the hostages home is Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC's Managing Director of Policy and Political Affairs. Julie, welcome. Julie Fishman Rayman: Thank you so much, Manya, for having me. I appreciate the opportunity to tell this amazing story. Manya Brachear Pashman: It has been a long 470 days now for you and your team as you have worked so closely with hostages' families. What was it like for you to watch those reunion videos? Julie Fishman Rayman: Pure, pure joy. One of the things that I talk about with my team a lot is that we missed an opportunity during the last agreement, during the last releases, to really celebrate. You know, we sort of thought, oh, okay, this, this is it. Now we're going to soon be able to celebrate everyone coming home. But what we missed in that moment was that that was just the end of the sprint and the start of the marathon that we've been in now for so long. So being able to see these three released, all I could think was dayenu, this would be enough. You know, after all of this, after all the work, after all the agony, and certainly, you know, the families don't feel that way, and our work must continue. There's no question, we have to keep going until they're all home. But even, even if it were just Emily, just Romi, just Doron, this, to me, personally, feels enough. Manya Brachear Pashman: There was also talk of the very high price that was paid for these, for these hostages to return. It was so wonderful to see Gilad Shalit return home, but at the cost of more than 1000 prisoners, including Yawah Sinwar, who was the architect of the October 7 attack. And so I know there is this huge fear among Israelis now and that there are efforts underway to prevent this kind of deal, specifically, this kind of deal, from happening again. But where do you stand on this? Where does AJC stand on this? And where do the families stand on this? Julie Fishman Rayman: Well, I'll start by answering your question with regards to the families, because they are not a monolith. They're not unanimous in their opinions on this, and a lot of them, you know, even within families, feel very ambivalent, and don't even necessarily feel the same way in the morning that they do in the evening, because there's just so so so much emotion around this. Any deal to get hostages, to get political prisoners, to get anyone unjustly held, released, is ugly. If you peel back the onion layers or or look behind the curtain, you see all of the really yucky things that we don't want to acknowledge about, you know, negotiating with terrorists, about allowing people who have committed the most heinous crimes to be free. But that's the only way it works, right? That's the only way you get to an agreement. So unless you are fully confident, as you know, a government or a power that has citizens held unjustly, that you are going to be able to complete many heroic rescues, as the Israeli Defense Forces has done, the only viable solution is to get to a deal. And I think that there is, there's a recognition in the United States, in Israel that a deal was the only way to get these folks released, finally. But there are really heavy costs to be paid, and I do feel as though there is, there's a nervousness, you know, what comes? What happens next? Manya Brachear Pashman: And then, of course, there's also the trauma that a number of survivors are feeling out there, whose family members were murdered by these prisoners who are going free. Has AJC worked with them in any way and connected with them in any way? Julie Fishman Rayman: I believe our Jerusalem office knows a number of those families. It has some of those connections on the ground. We have not engaged with them in Washington or in our work, sort of throughout the United States, in the same way that we have with hostage families. But one of the things that I think is incumbent, not just on AJC, but really on the Jewish community and all who care about Israel, is to lift up those stories and to sort of collectively hold the pain of those families who felt when the murderers of their family members, when they were imprisoned, they felt okay, we have justice, you know, like we have a sense of closure, and that this pain that we've endured has has not, has not been for, for no reason. And now they have to go back into that trauma and go back into that pain and without that sort of sense of closure. So there's a lot of trauma that those families are going to be going through. And if we've learned one major lesson from this big hostage ordeal that we're going through now, is that the pain of one family in Israel is not exclusive to that family, that it reverberates throughout society, that it ripples throughout the entire population. And so as one family is grieving or suffering, all of the families are. That's one thing that we've seen throughout the course of the last you know, 478 days in Israel. That the families are not alone, that the tragedy and the horror that they have experienced has created this terrific rift in a lot of ways, in Israeli society, this feeling of a lack of trust that the that the government, that the Israeli Defense Forces, that the population as a whole, could protect them to this point. And we can only hope that this deal will be concluded, that as we're in phase one, that phase two will continue to be negotiated. That we will get to the end, so that the families can all be reunited, and this feeling of cohesion in Israeli society and throughout the diaspora can continue. Manya Brachear Pashman: Julie, can you share with our audience--I said you worked closely, you and your team worked closely with the hostages' families, and have been ever since this ordeal on October 7. Can you explain to our audience what that means? What have you been doing? What have you been working toward, and how have you been working toward it? Julie Fishman Rayman: Absolutely. So since the very early days after October 7, we've been deeply engaged with families, and it started just, I think five or six days after the seventh, my phone rang, and it was a number from Israel. I didn't know the number, but of course, you know, it's a number from Israel. I'm going to answer, so my answer and the caller explained that he was Jon Polin, the father of Hersh Goldberg-Polin. That his son had part of his arm blown off by a grenade. They knew that, and that he was being held hostage, and that he was one of many, many parents who are going through this experience, and he didn't really know what to do, and could we help? And choking back tears right, choking them back, I said, Yes, of course, we can help, like, what's Let's talk this out. Let's make you know, let's make a plan. But AJC is here. We're here for your family. We can be here for the families . And it started what I think none of us could have imagined, in terms of this ongoing, continuous support, not just for Jon and Rachel, although we continue to stay very closely engaged with them, but for more than 50 families who started seeing elected officials when they traveled to Israel, who started to come to Washington, DC. Because they felt like in Washington, the elected officials that they could meet wit had power, had influence, would hear their stories and try to move heaven and earth for their children. So virtually, you know, every month, at least sometimes every week, every other week, we opened our doors in Washington, DC, we opened our rolodexes and said, we'll help you with meetings. Whether that was with members of Congress, with the administration, with members of the media, with the diplomatic corps, with other partners. Sometimes the delegations were random. It was whoever, whichever family members wanted to come. Sometimes they were specific, right? Sometimes we would bring family members of female hostages to talk specifically about their concerns related to gender based violence, and just simply try to give them the biggest and broadest platform that we could to tell their stories. And that's what they've been doing for 470 days, and that's what needs to continue, really and truly, until every single hostage comes home. Manya Brachear Pashman: Clearly, Monday was also a big day here in the United States, President Joe Biden left the White House, handed the keys back to Donald Trump, who was inaugurated as the 47th president. And really, I could not help but think about the Carter-Reagan transition and the Iran hostage crisis that came to an end soon after. Clearly, Trump has made the issue of releasing the hostage as a core foreign policy priority for his administration. What is the reaction you're hearing from the families about the Trump administration's efforts and as well as the efforts by the former Biden administration? Julie Fishman Rayman: The families had really great access within the Biden administration, really at the very top. Know, a lot of the families, especially the families of the American hostages, met with some frequency with the President himself, with Jake Sullivan, with Roger Carstens, the special envoy for hostages, and really felt as though this administration was was with them on this horrific journey, and they always spoke with and continue to speak with a lot of gratitude towards the Biden administration. But it also became very clear that when Trump was elected, that they were eager to seize on any opportunity. And so you talk about this, this Carter-Reagan sort of moment. The families, for some time, had been talking to the president elect, now President, and his team, and saying, we need a Reagan moment. This can be President Trump's Reagan moment. They've been planting that seed and really playing to the hope that this would be something that would be meaningful as well for him. And I think we're deeply successful in doing this. We would not be where we are today without this amazing display of collaboration between the Biden administration and the incoming Trump administration. The ability for the two of them to work together, build on what the Biden administration had been doing for so long, and then also come in with the sort of bravado of President Trump, and a commitment, really, he said he's going to rain hell down if the hostages aren't released. So sort of the combination of these efforts, I think, was so remarkable and really got us to where we are today, but we're not, we're not there yet. And so, as we celebrate Emily and Doron and Romi's return, their triumphant return. We also know that there's a lot that could continue to go wrong at any stage of this, of this agreement, and even President Trump himself said, I'm not confident. And this is from a man who is sort of eternally confident. So the fact that he's expressing that caution, that nervousness about the ability to get to the finish line, means that we still, and the families still have a lot of work to do. Manya Brachear Pashman: I find it interesting that you are referring to it as a collaboration, because, because my next question was going to be, I mean, how much credit does the incoming administration deserve for the hostage deal versus the outgoing administration? Would you say it really was a genuine collaboration? Julie Fishman Rayman: All signs point to a genuine collaboration. I think there's a lot that we don't know, and we will know for some time, just as when we look at, you know, the last 470 days, there's so much of this amazing story that needs to be told. I feel very proud about the role that AJC played. But success has many people to credit, always. And there were tons of players, not just in Washington, DC, across the country, across the globe, who made it possible to get to where we are today. So it will be very interesting at this point, we sort of see a jockeying for credit amongst the Biden administration and the incoming Trump administration. I am willing to give that credit out like candy on Halloween. Everyone who had the smallest part should be taking that victory lap, patting themselves on the back and then preparing themselves for the next round of advocacy and pressure. Manya Brachear Pashman: President Trump did have former hostages at his rally at the arena on Monday night. What message do you think he was trying to send, and I'll follow that with, what message do you think they are taking back home to Israel? Julie Fishman Rayman: I am ecstatic that he brought the families up on stage with him. I think that was such a meaningful moment, and certainly deeply meaningful to them. Because amidst all of this, there must be some there must be some fear that, okay, we've started to bring people home. What if we don't get across the finish line, right? So the commitment, even after Emily, Doron, and Romi were returned, to bring them up and to show the importance of their families and their cause, I think, was deeply, deeply important. Cynically, I think part of that was to show, look, I've just come into office and look at the win that I've already had. But if it takes that sort of seizing of credit to keep the push going, I welcome that 100%, without question. The families will no doubt take tremendous comfort in the fact that they were called up to stage. That representatives of this really large and robust community, sad community, of the hostage families that they had representatives called up on that stage. I think they'll see that as a really important signal that their cause is not forgotten, that even as there are celebrations welcoming Romi and Emily and Doron back, that this is not a box that has been checked, but rather a recognition that this is a job not yet finished. Manya Brachear Pashman: So with that in mind, Julie, what are your priorities? What are AJC's priorities with this new administration? Julie Fishman Rayman: We are looking for every opportunity to engage with this administration, as closely as we did with the last around the issues that are really important to AJC. First and foremost, of course, that is support for Israel, that is making sure that the US-Israel relationship remains strong, that the United States is continuing to play a vital role in supporting Israel on the world stage, whether that's at the UN, with European partners and so on. And lifting up our vital ally in this moment. And not secondarily, just secondarily in terms of how I'm talking about it, but of equal importance is working with this administration to counter antisemitism. In all its forms, from all its sources. We worked really hand in glove with the Biden administration on not just creating but implementing the first ever US National Strategy to Counter Antisemitism. And I think it's, it's fair to say that there were a lot of phenomenal successes that came out of that strategy. And now it's a matter of working with the incoming administration officials, and the President himself, to make sure that we are moving forward. That this idea that it requires the whole of government and all of society to be working together, to be working in tandem and coordination, in lock step to counter antisemitism. That strategy in and of itself, is critical. So whether it's something written on paper or implemented in that way, or whether it's, you know, appointing a coordinator, or what have you, we are here, and we're ready to be a part of that process. Manya Brachear Pashman: Julie, thank you so much for joining us the day after the inauguration and all of the many changes that began to unfold. Thank you. Julie Fishman Rayman: Thanks for having me, Manya.
Jan 16
Bring Them Home: Understanding the Israel-Hamas Hostage Deal and Its Impact
After 467 days of anguish, Israel and Hamas have reached a pivotal agreement to begin releasing hostages. AJC Jerusalem Director Lt. Col. (res.) Avital Leibovich breaks down the deal's details, the phased approach to releases, and the emotional toll on families and the nation. Hear about the complexities of the negotiations, the potential political fallout, and the profound resilience of those waiting for their loved ones to come home. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : Pack One Bag: Stanley Tucci and David Modigliani Uncover His Jewish Family's Escape from Fascism and Antisemitism in 1930s Italy Gov. Josh Shapiro and AJC CEO Ted Deutch on Combating Antisemitism Mijal Bitton on What It Means to Be a Jew Today The Next Chapter in Catholic-Jewish Relations Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Avital Leibovich: Manya Brachear Pashman: On Wednesday, the Israeli government and Hamas terror group, at long last, 467 days, to be exact, announced a deal to bring the hostages home. The deal, which will unfold in phases, calls for Hamas to ultimately release the 98 remaining hostages in exchange for Palestinian prisoners convicted of terrorism and serving life sentences. The first exchange could happen as early as Sunday. Here, on day 468, to explain the deal and the mood on the ground in Israel, where families wait to see whether the Israeli cabinet will sign the agreement, is AJC Jerusalem director Avital Leibovich. Avital, thank you so much for joining us. Wow. 468 days, and this seems like such a breakthrough, at least on this end. Can you walk us through the details of what has been agreed upon? Avital Leibovich: So currently, the Israeli delegation is still in Doha in Qatar, and have not returned to Israel. When they will turn to Israel, after the agreement will be finalized, then the Cabinet will meet, the government will gather, and they will approve the agreement. So according to the draft that has been leaked to the Palestinian media, the agreement has a few stages. The first one has to do with releasing 33 hostages. That's the first stage. The 33 hostages, as we know, most of them, are alive, but unfortunately, there will be around 10 hostages that either have been murdered on October 7 by Hamas, and their bodies hijacked to Gaza, or those that have been murdered in captivity by Hamas. Now we know that the first ones to be released, hopefully on Sunday, we are praying for that, are women, children, female soldiers, and also men over the age of 50 with some illnesses or some health issues or humanitarian condition. Which, I think everybody is in a humanitarian condition after such a long time. So that is the first stage. The first stage will last 42 days. 42 days is a long time, and as we've seen and based on our past experience, Hamas can actually turn away, decide to change things last minute, halt the agreement and so on. In the course of those 42 days, Israel will release Palestinian prisoners. I have to say that the price is extremely high, because I'm talking about around 1000 Palestinian prisoners. When I look at the scale of how many prisoners will be released, versus a hostage, it's unbelievable. The price, quote, unquote, of an Israeli soldier, a female soldier, is very high compared to just an ordinary civilian. So around 1000 prisoners will be released in this duration. In addition to this, the IDF will gradually leave some areas, and then on day 16, there will be discussions regarding the second phase. Israel would like to see, on the second phase, the remaining hostages released. That's 65 additional hostages. And then we're talking about the third phase, which will be the reconstructing of Gaza. So these are the three phases. This is what we know for now. There are other components, like humanitarian aid, increasing significantly the number of trucks filled with aid going into Gaza, and we can talk about the implications of these prices, which Israel will be paying. Manya Brachear Pashman: Now a lot of American media are reporting this as a cease fire. Is that accurate? Avital Leibovich: No, the Israeli policy is very clear. Only after the last hostage we leave Gaza, this means 98 hostages will be out of Gaza. Only then Israel will be willing to cease fire. That's the reason why it's called a hostage agreement, and not a ceasefire agreement. Now we know Hamas. Hamas is a vicious enemy. It's a cruel enemy. You know, I just watched Palestinian media, and you'll be amazed to see how many civilians in Gaza, not Hamas related or Hamas oriented Palestinians, are saying that they wish that October 7 will return every year. They're supporting the repetition of October 7 year after year. And so, you know, this is the atmosphere that we are seeing. And Hamas can be affected by this atmosphere, and this would maybe lead even to the possibility that there will never be a second phase to this agreement. So this is definitely something that Israel wants to be very, very cautious, and this is the reason why it's not called a ceasefire deal at this point of time. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you said 33 hostages, but 10, possibly who have died either in captivity or on October 7, those are the hostages that will be released in the first phase. Do we know who those hostages might be? Avital Leibovich: We don't know who. I mean, there are some kind of lists, so there are some indications, but it's based on rumors, and until the agreement is signed, the families themselves do not know. So you can imagine what's going on in the homes of 98 families of hostages, and of course, the second circles of these families, not sleeping, not eating, not breathing, just waiting for any kind of an announcement, the potential light in their lives. The tension is really unbearable. Manya Brachear Pashman: I cannot imagine. Can you also speak to the tension in the nation? What about those who don't have relatives in a hostage situation, but who are still part of this nation? Can you kind of talk about the emotion there. Avital Leibovich: Yeah, it's a great question. We know the hostages by name. We know what music they like. We know who the parents are. We know what their hobbies are. At this point of time, we all know the hostages, almost like it's another child of ours, or another aunt or another uncle or a grandfather or a son in law. This is how we feel. And if you were to visit now Israel, and you would take any road, you will most likely see yellow flags symbolizing the hostages alongside the road. And if you'll enter a school, you'll probably hear in the yard the songs which the hostages love to play. And if you go to a supermarket and check yourself out at the self checkout counter, you want to swipe your credit card, you'll see a picture of a hostage. So the issue is surrounding us, 24/7. Manya Brachear Pashman: Does the prospect of an agreement that would finally bring them home – has that generated a unified sense of hope or optimism there on the ground? Avital Leibovich: Even among the families, there are different opinions. So today, for example, families of hostages blocked the main road to Jerusalem and protested later near the prime minister's office because they think that the agreement is a bad one. And they have kids held in Gaza. They think it's a bad one because they think that we may never reach the second phase, and their loved ones will stay forever in Gaza. And then there are other parts of the families who protest in Tel Aviv to make sure that the government signs this agreement. And there is no right and wrong answer here. Families are torn. The country is torn. In order to patch the situation, we need the hostages back. There is no question about it. Manya Brachear Pashman: You raise a very good point. There is a divide, and it is a political divide, and so I am curious what your thoughts are on the prospect of the cabinet actually signing this agreement and going forward with this–and then also what the political implications are if the cabinet does or does not sign the agreement? Avital Leibovich: It is a political divide, but both sides are blaming the same person, the Prime Minister, doesn't matter from which side of the political map they are, they still see one person responsible to get them out of the situation. Look, I do think that there will be a majority in the government. I do think that the Cabinet will vote for the agreement. I think that most of the ministers understand there is really no chance. And this is the turning point. This should be a turning point. I can say that one of the ministers in the cabinet, Minister Zohar, which is the Minister of Culture, actually wrote a letter to all the other cabinet members and ask them to vote to support the agreement and release the hostages. So I do have reason to believe that it will be approved, by the way, according to the law in Israel, after it will be approved, both in the cabinet and in the government. Then the very long list of Palestinian terror prisoners will be published publicly. Because, according to the law in Israel, anybody who wants to object –t can be my next door neighbor, it could be a family of a hostage. It could be an NGO. They could go and sue. They have 48 hours to go and file a lawsuit against the release of a specific or a few people on the prisoners list. So the High Court of Justice will discuss these appeals, and it will take 48 hours maximum. This brings us to Sunday as the closest possible point of the return of the hostages. Manya Brachear Pashman: Could those names change on that list, and would that void the agreement? Avital Leibovich: So one of the arguments I understood that rose today in Doha in Qatar is exactly on that point Israel wants to veto the list, although it has agreed to release prisoners which are sentenced not to one life sentence, but even to two and three life sentences, so it is willing to pay the price, but it is not willing, for instance, to release those symbols of leadership of Palestinian prisoners, because there will be implications for that. And by the way, even to those who are only one sentence for only one life sentence, there's also implications. Because Hamas, from a military perspective, is in a very dire situation, and they need all the professional manpower they could get. So this is a situation that we may see these prisoners return to the lines of Hamas tomorrow morning, right after they're being released. So it is, it is a heavy price. So I think that if this will come through, and I think it will come through, Israel will need to set up a whole list, a new kind of security measure, list that will be compatible with the new situation, the new challenge in Gaza, and take it from there. And of course, this cannot go back to what, where we were on October 6. Manya Brachear Pashman: And just going back to the political implications, you said, everyone, no matter what side they're on, they all point to Prime Minister Netanyahu as being responsible, good or bad. So what are the implications for him, for his future as the leader? Avital Leibovich: So you're basically asking me about the chance of survival for the Netanyahu government. Currently, they have 68 seats, because, as you remember, Gideon Saar, who was in the opposition, alongside three other politicians, members of Knesset joined Netanyahu's coalition, and now it's more stable. The coalition needs 361 seats to survive, and the planned elections will be in 2026, so the question is, what will happen with Ben Gvir and Smotrich? One is holding six seats. The other one is holding seven seats. What I'm hearing now about Smotrich, that he will agree to the first phase of the agreement, the hostage agreement, and then he wants some guarantees regarding the second stage, mainly with security issues, which is kind of ridiculous, because this person who does not have any background in military or security or things like that. And then Ben Gvir is a bit more on the radical side, and he is actually in a political landslide with Netanyahu for the past couple of weeks. So the situation with him is just deteriorating. Having said all of that, you know, he fulfilled his dream to be a minister, and he would never have dreamt of it a few years ago. And now that he's there, and now that we have President Trump going in in a few days, he may understand that the potential here for him is a lot bigger, and then he should take advantage of it, rather than just walk away. So I think that, if I would have to bet, I would say that this government will stay until 2026. Manya Brachear Pashman: I don't want to end with politics, so I want to go back to the personal side of this. You are there on the ground, as you said, you see the faces of the hostages when you check out at the supermarket. You see these families pleading. You also are in a very key advocacy position there. Have you met with families recently? Have you spoken with anyone recently? And can you share that conversation? Avital Leibovich: Yeah, I've been in touch with a few of the huh, maybe 20 of the hostages families. And I'll share one story, which, of course, a lot of the stories are very emotional, and you get attached to them. But once in particular is a young mother. Her partner is in hostage in Gaza, and she gave birth to a beautiful girl when he's in Gaza. And she was here, as a matter of fact, on October 7, 2023 when she was sitting hiding in the shelter with her two other kids, she was eight months pregnant, and for her, it's about an everyday kind of survival, because on the one hand, she needs to be strong mother for three toddlers, but on the other hand, she's fighting constantly to bring her husband home, and so there's a conflict there, and I keep on asking her, how does she not break down? And she is surrounded by families and so on, but at the end of the day, when she goes to sleep, she's alone, and if the baby cries in the middle of the night, then it's only her. And of course, there is work to be done and the kids to be taken and picked up and going to the doctors and, you know, whatever kids need. And three small kids, I mean, one is in first grade. And again, the first grade, for example, she started school, and she was only escorted by her mother and and also, the kids are asking these naive questions, but they understand they know because they've seen many times their parents being kidnapped. So this is something they will carry on for the rest of their lives, and the fact that a baby has never met her father, that's really heartbreaking. But I do want to say that I think they're finding inner strength, inner sources of strength for themselves, which is maybe a symbol of resilience of the Israeli people. This resilience, I think, is something very common in Israeli society. So this is a little bit of positivity in all the darkness. Manya Brachear Pashman: Absolutely well, I really do hope that her prayers are answered, that her partner returns home safely, as well as the other 97 hostages who are still in captivity. And those who do not return alive, may their memories be for a blessing. Avital, thank you so much. Avital Leibovich: Thank you.
Jan 9
Pack One Bag: Stanley Tucci and David Modigliani Uncover His Jewish Family's Escape from Fascism and Antisemitism in 1930s Italy
As Stanley Tucci reflects, "Given the circumstances in today's world, the parallels between then and now are impossible to ignore. It's an incredible story, but it's also happening today, to millions of people . . . It's a story about people in a certain place and time, and what happened to them, and what happened to them has happened before, and has happened since, and will continue to happen. Unless we as the human race begin to understand that we are all the same." What would you do if fascism and antisemitism seized your homeland? In his award-winning podcast, Pack One Bag, documentarian David Modigliani takes listeners on a gripping journey through his family's escape from Italy in 1938. The podcast series features actor Stanley Tucci as Modigliani's great-grandfather, who was known as Italy's "King of the Books," and once advised Mussolini but later turned against him. As Modigliani retraces his family's steps across Italy, he uncovers hidden Fascist spy documents, personal family diaries, and the poignant Jewish love story of his grandparents that echoes through time. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : Gov. Josh Shapiro and AJC CEO Ted Deutch on Combating Antisemitism Mijal Bitton on What It Means to Be a Jew Today The Next Chapter in Catholic-Jewish Relations What's Next for the Abraham Accords Under President Trump? You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with David Mogdiliani and Stanley Tucci: Manya Brachear Pashman: As a documentary filmmaker, David Modigliani has created a variety of works on politics in America, improv comedy, and the improv comedy of politics in America. But during the pandemic, he discovered the love letters of his grandparents, written moments before they fled fascist Italy. Those letters led him to produce a more personal project – an award-winning podcast series starring Stanley Tucci, titled Pack One Bag. David is with us now to talk about that journey. David, welcome to People of the Pod. David Mogdiliani: Thank you so much for having me. I'm so glad to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So, at the core of your podcast, Pack One Bag, is the story of your grandfather, a Nobel Prize winner who fled Italy in 1938 and this was a story that you heard as a young man, as a teenager, right? But if you could share with our listeners what that story was, when you originally heard it. David Mogdiliani: Yeah, so my grandfather, I was just a five year old kid when he won the Nobel Prize for Economics in 1985. But as I became a teenager and started to grow up, I became sort of fascinated by their love story, the story of escape. Which was basically that my grandfather, Franco Modigliani, had been a 19 year old kid in Rome when Mussolini passed the racial laws against Jews like him, and he didn't know quite what to do, and he was so fortunate that he had fallen in love with this girl from Bologna named Serena Calabi, whose family had really been planning for this moment for many years, had had the foresight and the privilege to move resources outside of the country, put together an exit strategy, and when they fled Italy for Paris in the fall of 1938 they invited him to join them. They invited their daughter's boyfriend to join them. And the family was in Paris for about nine months and then made it onto the Normandie, a French ocean liner that left the coast of France in August of 1939 and turned out to be the last boat out of mainland Europe before Hitler invaded Poland and World War II began. So that kind of fairy tale escape, a whirlwind romance, that getting married, you know, in Paris on the run, and arriving in the US, kind of just in the nick of time, was the kind of origin story that I grew up with as a kid. Manya Brachear Pashman: And how did your grandmother's family know how to read those tea leaves? David Mogdiliani: My grandmother's father had been known as ile de libri, the king of the books in Italian because he had founded and run along with his wife, something called La messaggerie italiane, which was the biggest book distribution business in all of Italy. It gave him resources and an understanding of where things might be going in Europe in the 1930s so I had known all of that. But when I sort of became more interested in this project and wanted to learn more, and dug into some boxes that my dad had, 19 boxes of my family's documents, we found inside them, a couple of letters from Benito Mussolini to my great grandfather, the king of the books, and that kind of was a staggering moment to see the signature of the future dictator of Italy there at the bottom of the page. Mussolini had been a lefty socialist newspaper editor in 1914, 1915, and when he had been kicked out of the Socialist Party for supporting Italy's intervention and involvement in World War I, the Socialist Party had kicked him out, and he had decided to start his own newspaper. He needed help doing that, and it turns out that my great grandfather had not only advised him on sort of launching his startup newspaper, but had also funneled a secret subsidy from the French government to Mussolini to fund this paper. So I was relieved to learn that he later had broken with Mussolini, you know, didn't follow sort of the whole fascist experiment, but that he had a sense of Mussolini's temperament, his character. And really, after Mussolini killed a political opponent of his in 1924, a couple of years after coming into power, that is when my great grandfather said, if things continue this way, there's no future for us in this country. Manya Brachear Pashman: And when you say your great grandfather, the king of the books, concluded that there was no future for us, did he mean your family, or did he mean the Jewish community? David Mogdiliani: I think at that time, in 1924, he meant our family, and I suppose also those who were not interested in kind of following a blindly fascist authoritarian dictator to the extent that he might transform the country. One of the things that I was sort of fascinated to learn in this project was that Italy was, in fact, a very inclusive place for Jews. In 1870, the country was sort of unified, and the Jews who had been in ghettos across Italy for hundreds of years, were released, became really central part of Italian society, which was a very tolerant society. Mussolini, in fact, had a couple of Jews in his cabinet. As late as 1935 had a Jewish lover. And it was not really until a later stage of Mussolini's fascism that he very swiftly turned against the Jews, eventually passing the Leggi Razziali, the racial laws, which really instituted a whole set of restrictions that only got worse. Manya Brachear Pashman: So talk a little bit about your process. I mean, how did you piece together this saga and all of the many pieces of this story that you had not known before, this saga that eventually became 10 episodes of your podcast. David Mogdiliani: Yeah, you know, during COVID, a lot of people baked banana bread. I pulled out my grandparents' love letters. I had always wanted to interview them to document– I had been a documentary filmmaker for many years and to capture their story–and I kind of just never got around to it. Before I did it, they died. They passed away. And so I had kind of been living with a sense of guilt about that. But I was in a new romance with a woman named Willa. We had become quarantine mates during the pandemic, she was really curious about the seeds of this family story that I'd shared with her. And we pulled out these love letters, which, in fact, my grandmother had translated into English for her grandchildren, because she really wanted them to know how you know, love had gotten them through the horror of that period. And pulling out those love letters, I was sort of stunned by how fresh and relevant they seemed. Not these kind of black and white mementos from a time gone by, but in a world where there was increasing authoritarian leadership around the world where antisemitism was on the rise, again, their letters to one another, which were going back and forth between Rome and Bologna. They were dealing with these questions, how do we deal with rising fascism? How bad is the antisemitism getting, and what do we do about it? And inside of those boxes, we found not only letters from Mussolini, but kind of the other part of the story. You asked me about the story I grew up with the fairy tale escape that was kind of the baseline that I was operating from. What I had not fully understood was that when my grandfather fled Italy with his girlfriend, and the king of the books, and was so fortunate to escape with them, he left behind his whole family, including his mother and his older brother, Giorgio. And eventually, as World War II kicked off, as they got into the Nazi occupation of Rome, all he could do was read about, you know, the Nazis invading his hometown, what was going on abroad, and he had lost touch entirely with his brother, and yet, what We found inside of these 19 boxes was a 25 page letter from my grandfather's brother, Giorgio, from the older brother that he'd left behind. And that 25 page letter, it had come just after the war ended. And it said, essentially, you know, we survived. And there's so much to tell you, you know, here's how. And it was just this page turning epic of how my grandfather's brother had shepherded his young family through the war, how they had hid in a small hill town outside of Rome, how he had taken on fake identity, and his little children had learned their fake names and identities and how to cross themselves and go to church and pose as though they were Catholic, and ultimately, how they had made it all the way through to the liberation of Rome. And that, to me, felt like this whole other world, the kind of parallel universe that my grandparents had escaped, the experiences that they might have had if they'd not been so fortunate to be among. Those who were able to flee, and that, along with the question of, why do we have these letters from Mussolini, you know, in the basement, and what's going on with the king of the books, all of that made me want to go back to Italy to dig into my family's past, to better understand this story, to find, you know, answers that could inform my present moment. At the time, you know, I thought, well, I'll need someone to help me, an audio engineer, at least if we're going to do a podcast. And Willa said, Well, you know, or I could do it. She had learned some audio skills in film school, and I had this question of, like, is this a good idea? Like mixing my budding romance with, you know, digging into my family's, you know, unknown history, but her curiosity had kind of inspired me to dig into this story in the first place, and so we set off together back to Italy with kind of no idea of just how far that adventure would take us. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I should explain that that saga, you tell that saga in the 10 episodes of the podcast, and the voice of your grandfather is actually that of actor Stanley Tucci. How did you connect with Stanley about this project, and what was it about the project that appealed to him? David Mogdiliani: I knew that we wanted to bring not only the personal investigative nature of kind of solving some of these mysteries, putting together the pieces, but also to bring to life the experiences and the stories of the characters in this podcast. And so I knew that I could bring to life the voices of my grandparents, which I remembered so well, but I really wanted to bring to life as well the king of the books, my great grandfather, and whenever I thought about him as this kind of debonair Italian, you know, media magnate who got his family out of dodge just in time, he seemed like this kind of cultured, congenial hero that someone like Stanley Tucci might play. And I'd been in touch with Stanley Tucci a few years prior in regards to his searching for Italy series, we almost worked together on that the scheduling didn't work out, but we'd formed a relationship, and so I shared with him, Hey, I'm digging into the story. I'm finding all this incredible stuff. I want to tell it in audio. And he said, I'd love to help. How can I be part of this? In addition to those more standard documentary techniques. We also do a little bit of kind of creative storytelling, and it's wonderful to have Stanley Tucci do that. We travel to London, where he lives, and did two long recording sessions with him, and he, having Italian parents and grandparents of his own, speaking Italian well, was able to snap right into that character. He needed very little direction, and it was a great joy to hear him kind of bring that character to life. Manya Brachear Pashman: And in fact, you had a conversation with him about his own family history and the importance of connecting to that. And I want our listeners to hear a clip of that conversation. __ David Mogdiliani: Okay, so tell me, I guess what drew you to the story. Why spend some time doing this? Stanley Tucci: Well, a number of things. I'm interested in Italian history, Italian stories, Italian people. I'm interested in World War II, and given the circumstances in today's world, you can't help but be interested in the parallels of that time and our time. It's your family story. It's an incredible story, but it's something that's happening today. It's happening as we speak. It's happening all over the world to literally millions of people. David Mogdiliani: I know you get asked this a lot, but what was your first connection to learning about Italy and its history and what happened to there? Stanley Tucci: My mother's father fought in World War I. He was a corpsman, and he was up in the Alps, and I mean, like the worst fighting, but he never spoke of that. But we were always told about our family history. We were able to live in Italy when I was a kid, and we were able to go visit my family. This is in the early 1970s down in Colombia, and that was fascinating, because it wasn't even 30 years after the war. But that history was really important to us, and the way that those stories were really funny that they would tell, or really frightening that they would tell. And like basically every Italian family, those stories were always told at, you know, dinner parties, at gatherings, at holidays, and you always had a connection with your family. You were always doing things with your family. Sometimes you were like, Why are we here? No one seems to be getting along, you know. But that said, it's invaluable. Understanding that history, knowing those people. And I really love this story because it's a universal story. It is an Italian story, but it's not an Italian story. It's a Jewish story, but it's not a Jewish story. It's a story about people in a certain place and time, and what happened to them. And what happened to them has happened before and has happened since and will continue to happen. Unless we as the human race begins to understand that we are all the same. That's why I like this story. It's about hope for equality. ___ Manya Brachear Pashman: David, you use the word refugee. I'm just curious if your grandparents considered themselves refugees, given the timing of their departure and then the timing of what their relatives that they left behind experienced. David Mogdiliani: Yeah, and I know actually they specifically did. There's a letter, when my grandmother fled with her parents in early September of 1938. Her father had told her, we're going to leave in the morning. We're going to make this look just like we're going on vacation so we don't draw any undue attention. And I want you to pack one bag and we'll take off in the morning. And they went ahead to Paris, and they were joined there a few weeks later by my grandfather, who had to settle some of his affairs in Rome and get his act together. And so there are letters from my grandmother, having just arrived in Paris, writing to her boyfriend back in Rome and hoping that he's going to come soon. And she says, quite specifically, we're in this tiny hotel room, and we're really refugees now, everything feels quite different. She, of course, had come from this privileged background. She grew up in this beautiful villa on the hill above Bologna that her father had built, a villa that they had to abandon very quickly. And so she was sort of encountering the reality of being outside of her comfort zone, of not having sort of the comforts that she had grown up with and wishing and hoping that her beloved would join her soon, which would kind of allay some of her anxiety as a refugee. I think they also felt that sense of being unsettled through their nine months in Paris, from the fall of 1938 until the summer of 1939 being unsure of whether war might break out during that period, my great grandfather, my grandmother's father, the king of the books, he found that his bank accounts inside of Italy had been blocked by the fascist regime, something that we uncovered in more detail in the archives in Rome as we dug into these fascist documents that were kept about all of this persecution, and they had this sense of being unsure of quite when they would leave and how far kind of the tentacles of the fascist regime might extend. And so I do think that they felt like refugees, even if they themselves did not encounter one tenth of the horrors that the family members who remained behind did. Manya Brachear Pashman: We have a narrative podcast series called The Forgotten Exodus that really speaks to that. It's about Jews fleeing the Middle East and leaving their homes behind. I mean, that's what you're doing, is you're leaving your home behind, even if you were hated in your home, even if you faced violent antisemitism, it was still home. I'm curious how much your family was fleeing fascism, or were they fleeing antisemitism? Were they fleeing more of one than the other, or did they go hand in hand? David Mogdiliani: Yeah, well, I think that their initial plans that my great grandfather, the king of the books, was making, were related more to fascism, to his understanding of Mussolini and to political violence and how far things might go. But in the summer of 1938 as he began to get information about the coming racial laws against Jews, and in early September of 1938 when the racial laws were passed such that Jewish children could no longer go to public schools. Teachers couldn't teach at public schools or universities if they were Jewish. Jews could not own a business with more than 99 employees. They couldn't have domestic help of non Jews. And that initial, you know, set of restrictions against them only increased that fall in the following months, you know, obviously getting to the point eventually that Jews could own nothing, that even the debts that they owed to other people should be diverted to the state. But the beginning of those racial laws is quite literally what they were fleeing when they then decided to execute their exit strategy. It was the promulgation of the racial laws that caused them to leave. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, they began to develop that exit strategy because of fascism. It was initially kind of envisioned as a flight from fascism, but when the culture became antisemitic. That was the trigger. David Mogdiliani: Exactly. Manya Brachear Pashman: What have I not asked you, David, that you think is a really important point to mention. David Mogdiliani: I would say, just about the love and humor that's such a big part of this story. My grandparents were, you know, constantly bickering at one another in this very loving way that we capture in the podcast, just the jump start of their romance was amazing to me. I mean, my grandmother came into Rome with her father, the businessman. She encountered this young kid who she later called il tipo ridiculo, meaning the ridiculous character, because he was just sort of a pesky all over the place, you know guy. And when she came back a second time, he had this plan to take her out, and he had concocted this outing up the Via Appia Antica, which is the ancient road outside of Rome. They got to know each other a little better, and she let him just steal a little kiss at the end of that little date. And the next morning, when she was going back to Bologna, he showed up at the train station in this suit, you know, two sizes too big for him. He's pacing the platform, and he had come to declare his undying love for her. He was so worried that she was going to get a marriage proposal from a fancy guy in Bologna, and he felt like he had to state his case. And she was like, you know, you got to calm down. You know, it was just a kiss. You know, this is really over the top. And she told him, I want you to not write to me for three months. She really wanted this kind of cooling off period. She said, then write to me if you want. And let's see, you know, if we really have a connection. And so three months later, she's in Bologna, and she gets this package from Rome, and on the top it says: Oh aspettato tre meze, signora di tatoreza. (I waited three months, Madam Dictator.) Ma ogna notte teo scritto. (But every night I wrote to you.) And she opens it up, and there's 91 little letters inside. So every night he had written to her, and then he had saved them and sent them all at the end. So these kind of dramatic, you know, acts of romance and love, the way that they got married inside of the fascist Italian consulate in Paris, that was a huge part of their story, and I think a huge part of what got them through that very anxious, you know, experience. Manya Brachear Pashman: You talk about how this moment in history jumpstarted your grandparents' romance. Do you mind sharing with listeners what happened to that girlfriend who tagged along and helped you with this project? David Mogdiliani: It's probably about 3% you know, of the overall story. We're really focused on the story of my grandparents, my great grandparents. But yes, this girlfriend Willa that I had, that had sparked curiosity about my grandparents story when we pulled out the love letters four years ago, as she then came with me as we went back to Italy, digging into the archives, interviewing our cousins, bringing this story to life, and of course, brought us a lot closer together. Our own relationship continued on, and we were married last year. And just about three and a half months ago, we welcomed our first child, Marcello Vita Modigliani, Vita meaning life in Italian which was a family name. So yes, my own romance has been part of this story as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: David, thank you so much. I really appreciate you doing this project and then coming and speaking with us about that. It really is quite relevant and quite instructive. And so thank you so much. David Mogdiliani: Thank you. It's been a pleasure to be here, and folks can find pack one bag anywhere they listen to podcasts, Apple, Spotify, but really anywhere, including at packonebagshow.com. You can stream it straight from the website there at packonebagshow.com and thanks so much for this wonderful conversation. I really enjoyed it. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed the last episode, be sure to tune in for the conversation between AJC CEO Ted Deutch and Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro. In that conversation on the ground in Philadelphia, Governor Shapiro and Ted talked about the antisemitism the governor has faced, the importance of nuance and how simply there is none when it comes to expressions of anti-Jewish hatred.
Dec 23, 2024
Gov. Josh Shapiro and AJC CEO Ted Deutch on Combating Antisemitism
Last week, AJC CEO Ted Deutch traveled to Philadelphia to meet with Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro for an in-depth discussion on combating antisemitism, ensuring the future vitality of Jewish communities in Pennsylvania and beyond, and addressing the challenges posed by rising political polarization both locally and nationally. "When it comes to antisemitism . . . there is no nuance. Antisemitism, bigotry, and hatred in all forms is not okay. Everyone in a position of public trust . . . has a responsibility to speak and act with moral clarity and speak out against it," said Governor Shapiro. AJC is a 501(c)3 not-for-profit organization. AJC neither supports nor opposes candidates for elective office. Watch: AJC CEO Ted Deutch, Gov. Josh Shapiro Say Fight Against Antisemitism Must Be Bipartisan Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : Mijal Bitton on What It Means to Be a Jew Today The Next Chapter in Catholic-Jewish Relations What's Next for the Abraham Accords Under President Trump? Honoring Israel's Lone Soldiers This Thanksgiving: Celebrating Service and Sacrifice Away from Home The ICC Issues Arrest Warrants: What You Need to Know Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Ted Detuch and Josh Shapiro: Manya Brachear Pashman: Last week, AJC CEO Ted Deutch traveled to Philadelphia and sat down with Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro for a conversation about antisemitism, the future of Jewish communities in Pennsylvania and across the nation, and growing political polarization not only in Philadelphia but throughout the country. The conversation was so powerful, we wanted to share it with a wider audience. So, I turn it over to Ted and Governor Shapiro. Ted Deutch: I'm going to start just by fessing up to something that I tried to do, that I fortunately failed at. I don't often tout my failure, but there was a time some number of years ago, Governor, where I thought that your future should take you to the United States House of Representatives. I tried to convince you to run for Congress, and you had other plans. Fast forward many years, thank God I was wrong, and thank you for the remarkable job you've done as governor of Pennsylvania. Josh Shapiro: Thank you. It's so good to be with you. Ted Deutch: Obviously, it's a really great to be with you. But I had, I wanted to break the ice just a little bit, if I may, with just some quick questions, just to lose, just to loosen you up a little, if that's alright. Josh Shapiro: Do I not seem loose? I feel pretty loose. Ted Deutch: Alright, very quickly. Favorite eagle of all time? Josh Shapiro: You know what I was on Eagles pregame live just yesterday, before the Birds played the Steelers. Birds beat the Steelers, by the way. And I got to sit next to Jaws. Ron Jaworski, and like, it was just a normal day. I was a little bit starstruck. So I guess I'd go with Jaws. Yeah. Ted Deutch: Alright. Better play-by-play announcer– Merrill Reese, Gene Hart? Josh Shapiro: Oh my God, come on. All right. That's like asking me to pick between my kids. Ted Deutch: Alright, I'll move on. Moving on, moving on, moving on. Some people here who don't, the handful who don't really get this at all, and my staff, who's saying, why are you doing this. Josh Shapiro: Merrill Reese by the way is about to get inducted into the Hall of Fame for, they do once a year, they do an announcer, and Merrill just won that award this year. Pretty amazing. Ted Deutch: He is amazing. Best Philly movie ever made? Josh Shapiro: Rocky. Ted Deutch: Easy. Thank you. Inappropriate question, perhaps at an AJC dinner, provolone or swiss? Josh Shapiro: I do enjoy provolone, but I'm not a cheesesteak guy, so. We have a kosher governor's residence. I can't be out eating cheesesteaks. Ted Deutch: It was a bit of a trick question, I'll admit. And then we'll just finish this off. Favorite Israeli food? Josh Shapiro: Falafel, but not from some fancy restaurant, though I do love Goldies and I love Michael, but on some like stand in the middle of nowhere in Israel, it's always delicious. Ted Deutch: This also gives me an opportunity to acknowledge Tsach Saar, who is the Consul General of Israel. Thank you very much for being here. All right, I tried. Thanks for playing along. Josh Shapiro: Did I not do well? You did try. Ted Deutch: You did great. You did great. Thank you. Josh Shapiro: No more lightning round? Ted Deutch: I have more. Josh Shapiro: Now we got to do this serious stuff? Ted Deutch: We do. And frankly, look, your answer to the silly question about cheesesteaks is the perfect lead in to my first question for you. The first governor, I grew up in Bethlehem, the first governor I remember was governor Milton Shapp, who was born Milton Shapiro. So in that respect, you're actually the second Governor Shapiro in Pennsylvania's history. He was governor from 1971 to 79. But you are Governor Shapiro. You're a proud Jew who dismisses a question about cheesesteaks because you have a kosher home. You quote Pirkei Avot in your life as governor and the speeches that you give. It's so clear, and we and everyone has come to know how important Shabbat dinner is for you, with your family. Your Judaism matters to you a lot, and for those of us who are so involved in the community, it's something that obviously we admire. But I would love to hear a little bit more about how it informs what you do and why it's so important. Josh Shapiro: I want to just say on a serious note, how grateful I am to AJC for the important work that you do every day, how grateful I am to Ted, who's been a friend for more than a decade. How thankful I am to the leaders here who raise money and do this important work. For Mark, who I think asked me to do this like a year ago, and has checked in with me each month to make sure he's going to do it. I'm proud to do it, and to the Liebmans, and everyone, I appreciate what you all do. I just celebrated, Lori noted the other night that I've been in public office for 20 years, and I'm a proud public servant. I think public service is a noble profession, and the reason I am in public service, it's fitting that my dad is here tonight, is because of my family and because of my faith. Both draw me to service. Our faith teaches us that, as you mentioned, I quote Pirkei Avot. I quote it in a synagogue. I'll quote it at a Kiwanis Club. I was proud to quote it from the pulpit at Ebenezer Baptist Church in Atlanta, Georgia, just a couple months ago, that no one is required to complete the task, but neither are we free to refrain from it. Meaning each of us has a responsibility to get off the sidelines, get in the game and do our part. Now, doing our part can come in a lot of different ways. Some people do their part in a courtroom. Some people do their part in a business. Some people do their part through charitable work, like here at AJC. For me, my part is through public service. My part is through serving my community, and I'm honored to do it. I share that with you because as I was getting ready to launch my campaign for governor, you may recall I was attorney general at the time, a group of us came together and said, Well, how do we want to kind of reintroduce you to the good people of Pennsylvania as you launch your campaign? You could start by talking about a policy or for some initiative you want to get past, but actually what I wanted to do was talk about the issue I just mentioned to you, what drew me to want to serve in the first place. Why I was even contemplating running to be your governor. And so we had a long conversation about what motivates me, Ted, and why I do this. To me, being able to bring together family and faith was really important, and the best way to show that is by doing what I do every single Friday night since I was a kid, and what we continue to do, and that is having Shabbat dinner with my family. And so the first ad in my campaign was all of us sitting around the Shabbat dinner table. Now, fun fact for all of you, I think we filmed it like on a Tuesday, so it really wasn't Shabbat. My kids remind me of that, but we did have everything on the table. And what was so interesting about it was, after the ad started running, and I would show up in communities where there aren't a lot of Jews, if any Jews, in Pennsylvania. Folks would grab me and say, Hey, I saw your ad. That was great. I want to tell you what Sunday lunch is like after I get home from church. I want to tell you what Christmas dinner is like in our family. I want you to know what we experience when we leave our place of worship. And in a lot of ways, it actually brought me closer together with the community. We were able to see one another in a deeper way. I think faith has allowed me to get into living rooms and conversations and communities in a much deeper way than perhaps I ever could before, as I think it is critically important if you want to be a public servant, to be true to who you are and express that to folks. So I'm proud of who I am. I'm proud of the way I've lived my life. I'm proud of the way Lori and I are raising our four children, and I appreciate the fact that the good people of Pennsylvania acknowledge that and open themselves up and share that back with me as I go out serving them as their governor. Ted Deutch: The importance of Shabbat dinner, part of it, obviously is your Judaism, but it also anchoring for your family. And for everyone that you interact with to know that on Friday nights, that's the time for your family. There's something there in a time of really polarizing politics and fragmentation of society, there's something there that we should learn from, right? Josh Shapiro: I just think making sure you're committed to family, you're committed to yourself at some key moments, each day, each week, is really important. Lori and I live crazy lives right now, running all over the place. I'm not complaining. I asked for this, and I love what I do. I hope you can tell the joy that I have every day in serving you as your governor. And no matter where we are during the week, we always know, Friday night we're going to be together. We always know that it's going to be a moment where we can be with the kids and have conversations with them. And I'll be honest with you, Ted. I mean, some of it, of course, is the prayers and the rituals and the religious aspect of it, but so much of it is just the family part of it, and being grounded in that, and knowing that that will be our moment during the week, whether we're at the governor's residence or our home in Montgomery County, we are always together Friday night, and it's something we don't compromise on. I think it's important that you've got to set those boundaries. You got to say what's important. And that's exactly what we do. Ted Deutch: It's especially important to have time to be together in this period where, for almost 15 months, the community has really, in so many ways, struggled. We had the deadliest attack on the Jewish community since the Holocaust, the equivalent, just in terms that people in America can try to understand. The 1200 people, the equivalent of 45,000 Americans, God forbid, if you use the same ratios, the equivalent of 7000 people being taken hostage. Now still, 100 hostages still being held beneath Gaza. It's been really hard for the community. And yes, Israel has fortunately made advances, and from a geostrategic standpoint, is doing better. But this has still been really difficult for the community, for those of us who care about Israel, and then layer on top of that, the antisemitism that we've seen, that you've been so outspoken about in the work that you do. How, again, given what's at your core, is it hard sometimes with the way that we're feeling, the way that you feel as a committed Jew, in the face of all this, to speak about it? Do you ever feel that you need to hold back because this is all so personal to you? Josh Shapiro: I never feel like I need to hold back. I think it is always important to speak out. But I also think it is important that we have two separate conversations, one about antisemitism and the other about Israel. When it comes to antisemitism, I think it is critically important that folks understand: there is no nuance in that conversation. Antisemitism, hatred, bigotry in all forms. It is not okay. And everyone, everyone in a position of public trust, everyone has a responsibility to speak and act with moral clarity, to speak out against it, and it doesn't matter who is sharing those sentiments. If they're members of your own party, if they're people who you otherwise might agree with on some other issue, we have a responsibility to speak out against it, and we have a responsibility as a community to be unified against antisemitism, hatred, bigotry, in all forms. There is no nuance on that. When it comes to the issue of Israel and foreign policy and Middle East policy, that's a far more gray area. And I think it is important to continue to speak out in support of Israel, and I think it is also acceptable, if one wants to respectfully criticize a policy coming from the Israeli government, there is a difference there. And so what I try and do is not hold back in any way, but to make sure folks understand we are having two different conversations. We got to speak out and stop antisemitism in our communities, and yes, we can express an opinion as it relates to the policies in Israel or by the Israeli government. And I think it is also critically important to acknowledge the very real fact that there is antisemitism in this country. There is antisemitism in this Commonwealth, and it is on the left and it is on the right, and there is no one party that has a clean record on it, and we've got to make sure that no matter who is putting forth those words of hate, they are condemned. Ted Deutch: AJC is fiercely non-partisan in the way that we do our work and recognize and talk constantly, try to make the point exactly the way you have. That there's antisemitism, wherever it is, we have to call it out. But that it's harder for some to see it or to call it out when it's among their friends, in their own party, than if it's in the other party. This was something that I dealt with as a member of Congress. But when it when conversations turn to you during the election and people refer to you as Genocide Josh. Josh Shapiro: Yeah, I saw that. Ted Deutch: Yeah. There are those, I think we have to acknowledge it's on both sides. And clearly there are those on the far left who don't want to criticize Israel, but have now taken the position that Israel essentially has no right to exist. That then bring that into that kind of language, which is clearly antisemitic in the way it's applied. How do you deal with that? Josh Shapiro: I must tell you, it did not upset me and it didn't affect me. What did upset me was the way those attacks against me made other people feel. As I was traveling across this commonwealth, across the country, folks would come over to me and tell me, you know, I saw what they said about you, and it was making them feel less safe in their communities. It was making them feel less safe in their schools or on their college campuses. That upset me. And on that I felt a responsibility to try and lift them up and strengthen them, and let them know that they should be proud of who they are. I'm proud of who I am, and sort of help them brush off the noise and recognizing and I think this is an important point, that while a lot of that noise did exist, and it is empirically true that antisemitism is on the rise, and thank God for groups like AJC doing this work. The vast, vast, vast majority of people that I come across every day, they're good people. They're not bigots, they're not spewing hate, they're actually looking to try and figure out ways in which we can bring people together. That is what I see. And so I'm comforted by that every day. I'm not offended or upset by the attacks that people make against me, even the antisemitic attacks against me. What I get upset about, what I worry about, is how it makes other people feel, and whether that causes them to retreat or causes them to maybe not do something they were going to do or not, go somewhere where they were going to go. That is upsetting to me, and I try and spend as much time as I can with the people who are affected by that, to try and make sure they have the strength to continue to go forward and lead by example in a way that gives them the strength that they need to move forward. Ted Deutch: And sometimes, while the overwhelming majority of people are good, I agree with you, and I think it's important for us to realize that the data tells us that the vast majority of Americans are supportive of Israel as well, and are overwhelmingly opposed to antisemitism. Small numbers can do real damage. And that's what we saw on a number of college campuses, where the the protests, some of them going back to October 8, which were not protests about, obviously, about the Israeli government, but just protests in support of Hamas, some of these protests in support of a terror group, really put people at risk. And you were very clear in the way that you approach that, right here in Philadelphia and around the state. How should, now that we're 15 months in, AJC has worked with universities around the country to try to ensure that they're doing what they need to to fight antisemitism. From your perspective, how are they doing, how are we doing, 15 months later? Josh Shapiro: I commend AJC for the important work they've done on college campuses. And I don't know if John Fry is still here, the president of Temple University, and an outstanding leader who was at Drexel University for some time and now is at Temple. He's an example of a strong leader dealing with these challenges on campus. And there are others to be sure. Look, I think it is critically important that we protect people's first amendment rights to be able to protest on campus, protest on our streets, they of course, have to follow the rules of the road, whether on campus or in a city, Commonwealth, you name it, but they should be able to express themselves. But that expression is not okay if you're violating the rules of the campus, the rules of the city or the community. It's also not okay if it puts other people at risk. Universities have a moral and a legal responsibility to the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and to this country to keep all students safe on campus. And for some universities, I think they were willing to forgo that responsibility, or it got a little bit out of balance. Some universities were willing to accept a little bit of hate over here, but no hate over here, and that's not okay. Hate and bigotry in all forms, needs to be condemned. All students need to be safe on campus, and yes, there should be places where students can express themselves and have their views heard. So while I realize there's a lot of gray area when it comes to figuring out exactly where that line is, I do think it's important everybody adhere to those basic principles. And there are many colleges and universities here in Pennsylvania that are. I think, candidly, Penn lost its way. They are working to get back. I think Susanna Lachs-Adler and others. Susanna has done really wonderful work, and there's some important work there happening under their interim president. I think they are moving in the right direction there, and many other universities are as well. And so I hope, to get to the heart of your question, 15 months later, we're in a position where students feel safe, to be able to both go to class and to be able to protest within the bounds of the rules on campus, and that we continue to be balanced in our approach there. Ted Deutch: When there is messaging sent, whether from faculty or from student groups or from other places on campus that say you are not welcome in this group, or, frankly, in this classroom, simply because you are a Zionist, simply because you believe in the modern state of Israel, that that also can't be acceptable because of what it says, the message that it sends to students, and how it puts people at risk. Josh Shapiro: Without question. I mean, if you're a student on one of these campuses, you literally have a legal right to be safe in these communities and on these campuses. And university leaders have to remember that. I gotta tell you, these students, they're scared. You know, Hanukkah last year was sort of right around the time that these protests were really kicking up and students were incredibly scared. I heard from a number of students at Penn who reached out to me, reached out to my wife, and we decided to forgo lighting our hanukkiah for the first night at the governor's residence. Got in the trucks, drove to Penn, and we lit the hanukkiot at Penn's Hillel with those students. We wanted to make sure that they knew their governor, their first lady, had their backs, and that they were going to be safe on campus. And that we were going to make sure that university leaders ensured their safety and their well being on campus. Again, I want to be really clear. Students have a right to protest. Their voices should be heard. I think students have helped usher in change in this country for generations. We want to hear their voices, but not at the expense of the safety and well being of any other student. That's where you got to draw a line. Ted Deutch: You have, you've talked a lot about building a coalition to combat hatred, and you've invoked Rabbi Heschel, and you've invoked his work with Dr. King during the Civil Rights era. And it's, I think it's true for so many of us, that having invested so much time in those really important relationships, there was some disappointment with response after October 7, and yet, the only option, from our perspective, is to double down. One, because it's the right thing to do, and two, because the Jewish community represents .02% of the population in the world. We need allies. And this has been really central to AJC. And I know Stephanie Sun is here, co-chair of Papaja, and I think Anthony Rosado, co-chair of the Latino Jewish Coalition is here. And I appreciate their being here and their leadership. This is a really important way to continue to combat antisemitism and simultaneously to make sure that Zionists, the people who believe in Israel, aren't excluded. Can you just talk about, I know this is important to you. Can you talk about how to build those kinds of coalitions that will help our community and and beyond? Josh Shapiro: You have to build coalitions if you want to make any progress here in this Commonwealth and in the country. I'm actually the only governor in the entire country with a divided legislature, right? So I've got a State Senate led by Republicans, State House led by Democrats. I literally can't get a bill to my desk unless some number of Democrats and some number of Republicans support it. And so you're forced to have dialogue. You're forced to come together. That's naturally who I am, trying to bring people together. But I want you to know it is. It is required here in Pennsylvania if we want to make progress. We made a hell of a lot of progress, fixing an unconstitutional education system, cutting taxes six times, hiring over 1000 new state troopers and police officers in Pennsylvania, and passing some of the most sweeping criminal justice reforms ever in the history of Pennsylvania. At the same time, we've been able to invest $3 billion in private capital investment to create over 130,000 new jobs. I've only been governor two years. We're getting a lot of stuff done. I share this with you because we understand the critical importance of building coalitions. Now I'll tell you who else understood that, the person whose portrait hangs in my office right above my desk, William Penn. I share that with you because when William Penn helped build what is now the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, he built this as a place that would be warm and welcoming for all, where people of all different faiths would be forced together to actually work together to make progress in this commonwealth. That was his vision, and I view it as my responsibility, as someone who's been handed the baton from William Penn, and actually a whole lot of people in between, of course, to pick up on the work that was done before I got here and to continue it, in the spirit that that Penn started. A spirit where we want to make sure we respect people, no matter what they look like, where they come from, who they love, who they pray to, and that those folks are represented around the table. And when they're around the table, and they feel like they have the freedom and the safety to be able to talk and to share their ideas and their views and their policies, that's what's going to allow us to build a coalition, to be able to get meaningful things done, to be able to make progress. You mentioned Heschel and King. I've had a lot of conversations about Heschel and King with Reverend Warnock, who I think is one of the great leaders in our country. He gave me the privilege of being able to speak at the pulpit at Ebenezer Baptist Church where Dr. King was, of course, the prayer leader there. We spoke about Heschel and King from Ebenezer, the need to be able to bring the black community and the Jewish community closer together, to be able to do this important work. My friend David's here. He's done work with Operation Understanding and other organizations like that, that bring people from different walks of life together. And if we can do that more, we can understand one another, we can reduce the amount of hate and bigotry in our community, and we can make progress in the spirit of William Penn, to fill in the work that Heschel and King started, and to be able to create a safer community for all of us. Ted Deutch: I want to follow up on this note of bipartisanship. You talked about the division and the legislature in Harrisburg, and I want to just focus on Israel for a moment. We have, you have, sorry, it's been a long time since I lived in Pennsylvania. Josh Shapiro: You're still one of us. You're a Birds fan. Ted Deutch: Thank you. Thank you very much. Josh Shapiro: And he went to Camp Ramah. This guy's got a whole pedigree. Ted Deutch: Lehigh Valley, in my blood. Look, if you think about support for Israel in Pennsylvania, there were two pro Israel Democratic senators. There will now be a pro Israel Democratic senator in Senator Fetterman, whose support has been nothing short of spectacular. You have strong Republican support, including from my good friend, Congressman Fitzpatrick from the area as well. And in many ways, it's a good reminder of the importance of bipartisan support for Israel. As we look into the future, given the challenges that Israel faces, is that Pennsylvania model of bipartisan support from both senators and bipartisan support from House members and a Democratic governor, is that the model that we should continue to expect to see around the country and will both parties continue to be as strongly pro Israel as they could be? Josh Shapiro: Look, I'm a proud Democrat, and I want to make sure that the Democratic Party continues to stand with Israel, and I'm going to continue to do my part to raise my voice, to ensure that it does. I lament the fact that in recent years, the issue of Israel, so to speak, has become weaponized in our political system. I think Israel is far safer and far stronger when the relationship that elected officials in America have is on a really bipartisan or nonpartisan basis. And I think there have been some organizations, quite candidly, that have tried to throw a monkey wrench in that idea, and instead have injected too much partisanship into that relationship. In the long run that makes Israel less safe. Maybe in the short run, given the way the political dynamics are in the country today, it could work to Israel's advantage. But mark my words, in the long run, politicizing America's relationship with Israel is not in the best interest of Israel long term, from a safety and a security standpoint. And so I believe the Pennsylvania model is the right way, where we've got Republicans and Democrats alike standing up and speaking out in support of Israel, and by the way, challenging Israel, where Israel needs to be challenged, and also making sure that we are speaking with a unified bipartisan voice against antisemitism, and where antisemitism rears its ugly head, no matter what political party or affiliation or left leaning or right leaning person said it, or group said it, that we join together in standing up and speaking out against it. I think there's something to our Pennsylvania model, and I'd like to see it more across the country. Ted Deutch: I want to thank you really so much for this conversation, and I want to give you a chance to end with this, for all of the challenges that we're facing, it's kind of a heavy conversation. What is it that you're most hopeful about at this moment, thinking about our community and the future and your life and your world? Josh Shapiro: You know, I get asked a lot like, how do you stay so optimistic and so upbeat, given all the challenges there are out in the world, and there are so many challenges, there's challenges like what we're talking about here tonight with antisemitism. There's other challenges that the world is confronting, and probably in another 40 days or so, we're going to confront even more challenges in this country. But what, what I think keeps me so up and so hopeful every day is the privilege I have to serve as your governor and travel around to different communities and different neighborhoods and just meet people who are doing remarkable things every day. It is a privilege I wish every Pennsylvanian had. To go and to see these nonprofits who are doing life saving and life changing work. To see the incredible work that's happening in some of our skyscrapers here in Philly and our farmlands out in rural communities across Pennsylvania. There are so many people who are literally changing the world, doing tikkun olam in their neighborhoods. And you know what? They're not down by the news cycle that I know really can bum a lot of people out. These people give me hope, and these people fuel my energy every day to go out and do this work as governor, and they make me optimistic and hopeful. And so while I leave you with this, while I understand the critically important role AJC plays to continue to combat hatred and bigotry and antisemitism, and you do a great job doing that work, while we're focused on those negative things that we've got to combat, I hope you'll also take a moment to appreciate the positive in our communities and understand that there is so much good out there and so many people doing so much good. And that is what fuels me. That's what keeps me up and excited. And that is what I think you know, really, in many ways, in the spirit of Penn, we get to see every day in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. So we need to continue to do this hard work that AJC calls us to do. But let's never lose sight of the positivity that's out there that fuels my optimism every day. Ted Deutch: We're so grateful. Governor Shapiro, thank you very, very much. Josh Shapiro: Thank you. Thank you, Ted.
Dec 19, 2024
Mijal Bitton on What It Means to Be a Jew Today
As many Jews deepen their sense of Jewish identity, Dr. Mijal Bitton joins the podcast to explore the significance of our Jewish heritage, texts, and peoplehood and what it means as we enter the Hanukkah season. Bitton is a sociologist, storyteller, podcast host, and Jewish advocate who also serves as the spiritual leader of the Downtown Minyan in Manhattan. As one of the first Sacks Scholars, she helps young people reclaim and reimagine Jewish traditions. In this week's episode, Dr. Bitton discusses Sephardic Jewry, Jewish peoplehood, academia, the needs of young Jews, and the realities of intergroup and interfaith after October 7. Resources: The Morality and Ethics of Global Jewish Advocacy: Lessons from Rabbi Lord Jonathan Sacks - AJC Advocacy Anywhere Jewish Unpacked - Wondering Jews podcast, with guest AJC CEO Ted Deutch Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : The Next Chapter in Catholic-Jewish Relations What's Next for the Abraham Accords Under President Trump? Honoring Israel's Lone Soldiers This Thanksgiving: Celebrating Service and Sacrifice Away from Home The ICC Issues Arrest Warrants: What You Need to Know Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Mijal Bitton: Manya Brachear Pashman: Dr. Mijal Bitton is a sociologist, storyteller and Jewish advocate. As the spiritual leader of the Downtown Minyan in Manhattan and one of the first Sacks Scholars, she helps young people reclaim and reimagine Jewish traditions. Michal is no stranger to our AJC audiences. Earlier this month, she delivered a powerful Advocacy Anywhere to commemorate Rabbi Lord Jonathan Sacks, for which the Sacks Scholars are, of course named. And as co-host of Jewish Unpacked's podcast Wondering Jews , she and Jewish educator Noah Weisman explore questions we all ask about the Jewish experience, from the mundane to the miraculous. In fact, just recently, they interviewed AJC CEO Ted Deutch . The podcast has covered topics spanning from how summer camp shapes Jewish lives, how to constantly juggle joy and pain, the impact of the Jewish vote in the most recent election, and in turn, the impact of Trump's resulting victory on Jewish America. Mijal is with us now in our Midtown Manhattan studio to rehash a little of that, but also to discuss what led her to take on her many roles, including her newest project. Mijal, welcome to People of the Pod. Mijal Bitton: Thank you, thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you could please share with our listeners about your heritage, about your upbringing. You were born in Argentina, correct? Mijal Bitton: I was born in Argentina. My father's family moved to Argentina from Morocco and Syria. My mother is from Spain. And part of what shaped my interest in Jews from the Middle East and North Africa, is that when we moved to America, we moved to a Persian Jewish community. So that was like my introduction to American Jews, this very tight knit Persian community in Long Island. Eventually, I met my husband, who is a Syrian Jew, with Egyptian and Iraqi background, and I wrote my PhD on the Syrian Jewish community in Brooklyn, which all just shows you a little bit my fascination. It's not just an identity, it's a tradition that I draw from and that I believe can actually give us very powerful tools right now. Manya Brachear Pashman: Now, is this a Syrian Jewish community from Aleppo or Damascus? Mijal Bitton: Historically, there is a big difference. I would say that a lot of these communities, you can think of them as pre-immigration and then new settlement in America. Right now in America, it's one community. The differences between Aleppo and Damascus are not that pronounced, maybe like when you cook a little bit the recipe that you use, or slightly different songs that you might have, depending where your family is from. Manya Brachear Pashman: You are, in fact, a visiting researcher at NYU, and you are the director of the National Study of the Sephardic and Mizrahi in the United States. What is that study all about? Mijal Bitton: Yeah. So when I wanted to do a PhD at NYU, which I did, on Syrian Jews, and I wanted to study Sephardic Jews, what I realized very quickly, and you might have seen this from your other podcast, is that there is very little good scholarship, good literature to explain to us who these Jews are. This is a problem, both in terms of historical research, and for me, I'm really interested in contemporary Jewish life. There was a huge gap of not having resources to understand Sephardic Jews in the United States. So I had to do my PhD, kind of trying to reconstruct, you know, even, like the categories of study, how do we think about Jewish observance and really religiosity with Jews from the Middle East. So this study is an early attempt by early I mean, we hope it's the first of many studies to begin to tease out the main pillars of what we need to know to understand Sephardic and Mizrahi Jews roughly. And again, we'll go into this more in the actual report, which will come out in a couple of months, roughly 10% of American Jews are Sephardic or Mizrahi, very similar to, let's say, the Orthodox Jewish population, the Russian-speaking Jewish population, but much less understood, much less studied. So it's an important first attempt to begin to lay out the foundations of knowledge. Manya Brachear Pashman: So would you say that study is overdue? Mijal Bitton: Yes, very much overdue. I think it's overdue for many reasons. One of them is that in the American Jewish community we've had for many years now, conversations around diversity, around inclusion and the like. And Sephardic Jews have not really been part of this conversation. Or let me say this with more precision, they have not been part of this conversation in terms that they would want to be part of this conversation. Maybe I'll be a little bit more explicit as to what I mean. Many of the Jews that we've cited that I know tend to reflect more socially conservative, Middle Eastern forms of Jewish life, and these communities don't fit in very neatly in diversity efforts that tend to align with progressive understandings of diversity. So that means that there's been a real gap in how Sephardic Jews are included or not included in many spaces that are trying to be more inclusive. So we really believe that diversity is not easy, and that it begins with listening and understanding, who are the individuals and communities that we want to include. Manya Brachear Pashman: I mean, how does kind of a deeper and broader knowledge of one's Jewish identity, one's Jewish history, how does your deeper and broader knowledge of your identity and history help you be a better advocate? And how can it help others be better Jewish advocates? Mijal Bitton: That's a great question. So you know, you mentioned before that I started a weekly Jewish wisdom Substack. It's called Committed and I'll be grateful to share the link with everyone. The first piece that I wrote there on Genesis was actually about Jewish pride, and it was an idea that I had been thinking for a long time about, and it was that, especially since October 7, I have been in all of these spaces with people who are newly reawakened, energized, outraged about what's been happening. And they speak constantly about the need for Jewish pride, Jewish pride. We need more Jewish pride, more Jewish pride, more Jewish pride. And on the one hand, I love that. I love that awakening. It resonates with me strongly. On the other hand, I had like this little voice whispering to me, because, as a sociologist, I've actually done research that talks about pride as something, I want to try to say this carefully, as something that is sometimes the last thing a group holds on to before assimilating fully. So in very simplistic terms, if you think about Italian Americans or Irish Americans right over three or four generations in this country, they will slowly lose a lot of their communal elements. They will move away from their neighborhoods. They will stop only cooking Italian food. They will stop working in certain professions. But they will still have a little bit of that Irish pride in St Patrick's Day. So I have been concerned when we speak about Jewish pride, that Jewish pride can be seen as unsustainable if we don't know what we are proud of. There is a world of a difference between someone who says there's something here, that seems really good, and I think I'm proud. I'm proud. And it's different that if you're standing there and you say, I am proud of a heritage spanning 1000s of years, I stand on the shoulders of giants. I am continuing a legacy of Jews who have survived persecutions, who've survived assimilation, who've survived living in different countries and in different times, and I am holding all of this when I stand up as a Jew. That, to me, is the kind of confident pride that can help us as advocates when we are facing challenges, because we are facing challenges and we're going to continue to face challenges. So we desperately need that sense of Jewish history, that sense of spiritual sustenance. We have to know what we are proud of, what we are fighting for. Manya Brachear Pashman: You wrote a piece shortly after October 7, and it was titled, The Pain You're Feeling is Peoplehood . And it was incredibly powerful. It went viral. Because it so perfectly captured what so many Jews were feeling at that moment. And for those who haven't read it, can you share what led you to write it and kind of summarize it for our listeners. Mijal Bitton: I lead a community, I'm the spiritual leader of a community called the Downtown Minyan. And like many spiritual leaders and clergy on that Simchat Torah. I had to, you know, I'm not saying anything new. Here I was, I was heartbroken, reeling. I don't use a phone on Shabbat didn't always happening. My family in Israel, the reports that were coming in, I felt like my soul, my heart was being ripped. I think many of us felt this. And I had a Shul to run, and I had to figure out, like, what Jewish wisdom can I use right now? And it was very primal and instinctive. There was a teaching that I had taught before because I thought it was important, but at that moment, it felt essential, and it just like, came out. I stood in front of my community who were in pain, and I wanted to give them names to explain what was happening. And I described, I use a very famous teaching by Rav Soloveichik, who speaks about who asked the question, can we still speak of ourselves as Jewish people, even with all of our diversity and differences and disagreements? And it brings up a Talmudic question about, if you have a man of two heads, is this considered one person or two? And it's a complicated question, if you take it seriously, and he offers a gruesome test to figure this out. You pour boiling water on one head, and then you look at the other, and if it cries out in pain, it is one people. If it doesn't, it is two. The reason that this teaching was important for me to say, and I think the reason you said it went viral is because, you know. I haven't said this like this before, so I am expressing this now, thinking with you. I think for very long, for us Jews in America, we have been pushed and compelled to think of Judaism along Protestant religious terms. What I mean by this, it's a faith, it's a set of beliefs, it's a value system. It has to fit in like some universalistic framework, and that pain that we felt on October 7 was different. It was a reminder that to be a Jew is to be part of a family. That it doesn't matter how different we are from each other, how much we disagree. When your relative is in pain, you cry with them. And it's almost like that pain, to me was like a way of saying we are reminded that we're part of a family. And there's something. I don't have the right words here. There's something almost to treasure about the pain, because it reminds us that we are connected to each other, committed to each other, responsible for each other. And I think we all felt it, and it took away some of the layers of conditioning that many of us have had, to pretend like we aren't a family. That's what I think was one of the things that were so powerful about the tragedy that we all experienced. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yeah, because we're so trained to be individuals, right, especially here in America, right, that individual spirit, and that's, that's not part of peoplehood. Or is it? I don't know. Maybe that's not the point. Mijal Bitton: Yeah, listen, I think our tradition is amazing and complex, and there's strands of faith that brings up individualism and agency, but there's powerful strengths that talk about us as a family, as a collective, as a tribe, and there's powerful elements in our culture that have been pushing against that. And in many parts of our community, I think we drank the Kool Aid and we said we are not like, you know, that's backwards. That's not who we are anymore. And then we were reminded that there's something there that we all felt was true. It existed before October 7, but I think October 7 kind of like woke it up. When I've shared this metaphor of the two headed men with people, many of them have offered an objection, and they've said, how awful is it for us to speak about who we are based on antisemitism? It shouldn't have to be like that. But, I mean, I would agree with that critique on theoretical terms. On sociological human terms, there is nothing that is more potent than having a shared enemy, a shared tragedy. Think about a family again, how tragedy brings us together. So I think that unfortunately, the fact that there is still antisemitism vibrant in our societies and our streets has served to continue to reinforce that initial sense that we had after October 7. Of course, there are rifts. We can talk about debates that are happening. We are not as united as right after the tragedy. But, you know, I wrote a piece for CNN basically saying that the virulent anti semitism in the anti-Zionist movement is creating more Zionists. It's creating more Jewish solidarity. And it hasn't gone away. I am a religious woman. When I pray to God, I ask God that God should give us the challenge of having to remain connected in good times. I prefer that, but being that we don't have that right now, I do think that we have to double down on what our response is. Manya Brachear Pashman: You wrote another piece for CNN that had to do with the anti-Israel protests on university campuses and the fear that it was inducing in so many Jewish young people, and the solidarity that was coming out of that. So with that in mind, one thing that the Jewish communal world is experiencing, we're certainly seeing it here at AJC, is an influx in involvement. Not just solidarity, but activism and advocacy, people who want to be more involved. Have you given any thought to this influx, and whether or not the infrastructure is in place here in America especially, to kind of sustain that, that level of involvement and activism. Mijal Bitton: So one of the things that I've seen, and I'll be honest, that I'm still trying to understand it, but one of the things that I'm seeing is, there's, there's the thing called the organized Jewish community, okay? And it's a powerful ecosystem, you know, with lovers of power and influence. And I'm also privy, partially because of my work with young Jews, to a whole world of people who are wanting to be active, but who either don't have the access or the orientation to do so, you know, within the organized Jewish community And for me, part of what's still missing are the bridges between these different ecosystems. There's all of these people who are active on social media, right? The world of influencers, there's these groups of young Jews who are creating pop up Shabbat dinners, like all over the place, and like creating new clubs to celebrate Shabbat with each other and Jewish identity. And there is a lot of energy there. And what I'm trying to figure out is, I'm thinking of this as almost two powerful ecosystems, and I think that they would both be more powerful if they're in better conversation with each other. So that, to me, again, it's a little bit abstract. I'm still thinking it through. I am a scholar in residence at the Maimonides Fund, and this is one of the questions that I have right now in this post-October 7 world: what would it mean to better bridge between these different ecosystems? Manya Brachear Pashman: We just talked about the campus protests and the solidarity that they fuel, and we've also talked about the lack of research and scholarship out there about Jews in the Middle East and and North Africa and the diversity of the Jewish community. Do you think if young people had a better grasp of the thousands of years of history, of Jewish history in the Middle East, do you think that would shift the conversation at all, that education? And I don't mean obviously just within the Jewish community, I mean more broadly. Mijal Bitton: I mean, broadly speaking, yeah. So I would say two things I take to heart with my friend Haviv Retig Gur, who's a brilliant analyst. He speaks a lot about the fact that Jews, we don't know our own story. And I do think there is, like, huge lack of literacy in understanding that there were nearly 1 million Jews all across the Middle East and North Africa, and they left, fled, or were expelled in like massive Arab nationalist, anti-Zionist regimes that were propped up across the region. So I do think that for people to know these stories would be incredibly powerful. I do want to note something, though, as someone who has been active in academia, I still have one foot there. I think that in many places, and we need to not be naive. In many places, people have vested interest in certain narratives, and they are emotionally attached to this narrative, and they have no incentive to change them, no matter how many counterfactuals you provide to them. So there are definitely many parts in academia that want to think of the world as divided between the oppressors and the oppressed, and who want to think of Jews and Israel and Zionists as aligned with the oppressors, who they equate to Europeans and white and Westerners. And no matter how many counterfactuals you will give to them, they will find a way again, and I'm happy to explain this. They will find ways to make it fit into their narrative. So we need a multi-pronged approach. One approach is to give the literacy to those who are seeking it as a way to have greater strength and intellectual tools at their disposal. Also, there's like a huge middle to convince, you know that can be moved. And when it comes to those ideologues, we have to battle their narratives. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, offering that literacy to the Jewish community first, to those who actually want it, who are curious enough to want it, that's step one. Mijal Bitton: Yeah, Jewish community, friends of the Jewish community, people who are intellectually honest and want to have a better discourse around Israel, the Middle East and current reality. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Mijal, I am curious how your conversations have changed and evolved since October 7. Initially I wanted to ask you about interfaith dialog, but maybe intercultural dialog is a better way to put it. But did you have more intercultural dialog before October 7 or after October 7, or is your work really immersed in the Jewish community and Jewish dialog? Mijal Bitton: Yeah, so I would say like this: I think before October 7, I had spent many years focused on interfaith work. I think that the interfaith work was often anchored in more liberal and progressive spaces, and many of those efforts really imploded. And I think that I represent, because I've heard this from so many people who basically said, we've invested years into showing up for others and into relationships. And then if I can't get someone to say that–you don't need to like Israel, you don't need to like Netanyahu, but just that Hamas raping and murdering is wrong and evil–then what am I doing here? So I think that definitely, I have been affected by that, by seeing that. And right now, I think we're in a place a year out when there is new energy in trying to figure out, okay, like, who are those people that we can still talk to, and they exist. And also I think that, and this is like work that is ongoing, there is a real sense that we need to re-examine the work that we were doing. Perhaps we were investing in the wrong interfaith relationships and spaces. Which doesn't mean interfaith work is bad, but maybe we need to invest in other parts of interfaith work. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you expand on that a little bit? Mijal Bitton: I mean, yeah, this is like, personal. I am not going to be spending time in interfaith work with people who give Hamas a pass. I'll just say this, you know, like that. And I think there's a lot for me. I am much more interested right now in pursuing relationships with socially conservative leaders of other faiths, that perhaps in the past, we wouldn't have been in the same tables around interfaith work and who have spoken up with clarity when it comes to defending Jews and speaking up against antisemitism. This doesn't mean, again, I don't want to imply that we should walk away from spaces you said before, it's important to have people fighting in many different areas. I think the real question we have to ask ourselves is, what are the lines, that if they are crossed, we walk away? Because I think too many Jews, for too long, have stayed in spaces where our basic story, dignity and humanity, was trampled, and we accepted that price. And that is not something we can do anymore. So we have to figure out, how do we reconfigure relationships? How do we stand up for ourselves in different ways? How do we, and I'll say this: in many places Jews showed up and agreed to, you know, like, pound their chest about, like, their white Jewish privilege as a price of entry into coalitions and relationships in ways that just were not honest. We need to fight all of this. Manya Brachear Pashman: You recently hosted AJC CEO Ted Deutch on your podcast Wondering Jews, and I'm curious what you learned from that exchange with him, both on and off the air. Mijal Bitton: Yeah, it was wonderful. I co-host the podcast Wondering Jews with Noam Weissman, and it was really nice. I mentioned this on that episode, but I have a very fond personal memory of my first encounter with Ted. It was the March in Washington. I was one of their earliest featured speakers at the March. You know, 300,000 people in person, many watching live. And I was very nervous. And I was like, pacing behind backstage. And I see Ted. I've never met him before, but I had read about him. And when I read about him, I was very curious. I'm like, who leaves sitting Congress to go and work for the Jews? So I was already, fascinated by like, who would make this career switch? And then I saw him, and I don't know why, I turned to him, and I asked him if I could practice with him. And he literally had me practice my speech. I memorized it, and I practiced, and he gave me some feedback, and I changed some of the words, and his wife lent me a hostage tag necklace because I wanted to have one on stage. And it was early days, I didn't have one. So my first encounter with him was that it felt like a very personal one, and that's what came across, I think, in the in the podcast, that Ted is this, you know, was a member of Congress, like runs AJC, but he just, he's so warm, and it is so obvious in everything that he says, that this is not like a job for him, but it is a passion and a life's mission. And the way that he spoke about just his love for the Jewish people, for spirituality, for what it means to stand up in the world, his hope and optimism. He speaks about relationships that you can insist on and make sure that you can have right now. It's very moving to find leaders who are running institutions and who themselves are able to embody a very powerful sense of conviction. We need more leaders like that. Manya Brachear Pashman: So tell us about your newest project. Mijal Bitton: Yeah, it's called Committed. That's the name of the Substack. I started it on Simchat Torah. I'm still tinkering with it. Like you know, how long it should be, the tone, this, that. I'm very lucky to have a lot of readers and students who eagerly give me feedback as to what works and what doesn't, which is lovely, because I love learning Torah with them. But really, as many conversations that I've had with people about anti semitism and advocacy and Zionism on campus, as many conversations that I've been having around like antisemitism and Israel and politics, I have been having the same number of conversations about Judaism and spirituality and the soul and what it means to be part of this magnificent tradition. I have been taken aback that often in my my classes and lectures, it will end with people coming to me afterwards and wanting to speak about their Jewish journeys, what it means to raise Jewish children, what it means to learn Torah, if you didn't grow up learning Torah, and now you want to what it means to to know that we are souls with bodies, as opposed to bodies with souls, all of these things. I have felt that it's really important to try to to have weekly touch points that we can have to ask big questions and to be able to address them using Jewish tradition. So I've in my Substack so far, I've explored, like I mentioned before, Jewish pride, what it means to have Jewish pride. I've explored what it means to have, using the stories of Abraham and Rebecca, what it means to, when the world is burning, to know that we have multiple modes of responses. One of them is to provide justice, put out the flame. Another mode is to help those who have burn marks and to just show care to them and be with them in times of need. The one that I wrote that I think went the farthest. One was around sacrifice, the binding of Isaac, which I wrote about what it means to from America. Look at Israeli parents and know that they are raising children who are willing to sacrifice in a way that American children are just not being taught. I use the story of Jacob and Esau, and I did a beautiful thought experiment. What would have happened if a Chabad emissary would have met the bad twin of Jacob? And there's all of this text that actually allow us to imagine that Esau could have become a leader of the Jewish people if he would have been shown the kind of love that Chabad emissaries give. So I think there's amazing ways to approach Jewish tradition and to use those as and use Jewish tradition as a way to ask the most critical questions about what it means to live as a Jew today. Manya Brachear Pashman: I imagine you'll be lighting candles soon for Hanukkah. Any other special traditions? Mijal Bitton The one thing I would say that I love that we do in our Sephardic communities, we light a little bit differently. And this is a traditional way. There's some Sephardic Jews that have changed this a little bit, but traditionally we light one Hanukkiah (menorah) as a family. So in many Ashkenazic communities, each individual lights their own. Classically, in the Sephardic tradition, a family has one Hanukkiah, and we try to light it either by a window or, even better, outside. So my family, my parents, my siblings, they have a special Hanukkiah with glass panels, and we always light it outside the house, facing the streets in a very real way. And I think that's an important symbol for us, what it means to insist on our lights in public spaces, what it means to fight for public spaces, and what it means, I would say . . . you know, Hanukkah has become such a commercialized holiday in America that, like lives alongside Christmas, and that feels good. And it's become not just a watered down version of its original premise, but in many ways the opposite, because what the Maccabees did is they took on not just the Greek Empire in military terms. They took on the Greek Empire in cultural and spiritual terms, and they resisted assimilation with everything they had. So in a funny way, in America, to fit in, we've remade Hanukkah in terms that have been opposite in its original meaning. And I think this last year asked us to reconsider what Hanukkah should look like, and what would it mean, you know, we shouldn't, I'm not saying we should be like the Maccabees exactly. You know, they're a complicated story as well. But what would it mean to make sure that we're not only lighting a light outside, but that we are expressing our Judaism in Jewish terms, even when it's a little bit uncomfortable for others. Manya Brachear Pashman: Mijal, thank you so much for joining us. Mijal Bitton: Thank you for having me. Really great to be here.
Dec 17, 2024
The Next Chapter in Catholic-Jewish Relations
Bishop Joseph Bambera marks the launch of a groundbreaking Catholic-Jewish initiative - Translate Hate: The Catholic Edition - with a wide-ranging interview with AJC's People of the Pod. At a time when recent events have challenged Catholic-Jewish relations, Bambera, the Chairman of the U.S. Conference of Catholic Bishops Committee (USCCB) on Ecumenical and Interreligious Affairs, details why the church has made combating antisemitism a priority. Translate Hate: The Catholic Edition, a joint project of AJC and the USCCB, features Catholic commentary on various entries of AJC's renowned Translate Hate glossary of antisemitic terms, themes, and memes. It comes as Catholic and Jewish communities prepare to mark six decades of trust-building and mutual learning beginning when the Catholic Church reached out to the Jewish people and the world with Nostra Aetate , the historic Second Vatican Council document disseminated on October 28, 1965, which dramatically and publicly decried antisemitism and transformed the Church's approach to the Jewish people for the better.Resources: New Glossary Breaks Ground in Tackling Antisemitism Through a Catholic Lens Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : Bernard-Henri Lévy and AJC CEO Ted Deutch on How to Build a Resilient Jewish Future Post-October 7 What's Next for the Abraham Accords Under President Trump? The ICC Issues Arrest Warrants: What You Need to Know Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Bishop Bambera: Manya Brachear Pashman: Nearly 60 years ago, the Roman Catholic Church issued a declaration called Nostra Aetate, a groundbreaking document that, among other things, aimed to heal the Church's strained relationship with the Jewish community at large. But over the past year, since the start of the Israel-Hamas war, there have been some tense moments: a call from Pope Francis to investigate whether Israel is committing genocide, a photograph of the Pope before a Nativity scene–featuring a keffiyeh. Now AJC and the US Conference of Catholic Bishops have unveiled Translate Hate: the Catholic edition, the glossary of antisemitic terms, tropes and memes, originally published in 2019, also features Catholic commentaries to explain why the church has made combating antisemitism a priority. Here to talk about this partnership is Bishop Joseph Bambera, Chairman of the US Conference of Catholic Bishops Committee on Ecumenical and interreligious affairs. Bishop, welcome. Most Reverend Joseph C. Bambera: Thank you for the honor of being with you today. Manya Brachear Pashman: Bishop Bambera, please walk us through the Catholic edition of Translate Hate and how the Catholic Church became involved in this initiative together with the Jewish community. Most Reverend Joseph C. Bambera: I think the best way to walk us through the Translate Hate Catholic edition is to first take us back to 1965 and the Second Vatican Council and the declaration on the church's relationship with non-Christian religions, and particularly with the Jewish community. There was this really milestone declaration Nostra Aetate that I think many of us would be familiar with, and that really speaks about our relationship as it stands today. A relationship that I would say. tragically prior to the Second Vatican Council was not what it should have been. And on the heels of the Council, for almost 60 years, an anniversary that we'll celebrate next year, we have grown together in mutual respect and understanding. That particular declaration Nostra aetate speaks very, very clearly about the fact that Catholics and Jews really share a common patrimony. We Catholics, our roots are in Judaism. Jesus was Jewish. His family was. And so many members of the early church were as well. And we recognize and affirm in that document the fact that the Jewish people were the first to hear the Word of God and are a part of a covenant relationship that certainly has not been in any way broken, but has been maintained. And something that we affirm and that we teach in that document. A very important thing, from my perspective. And as well, the document reminds all those who would be familiar with it, and certainly who should be, if they are not, of the importance of us coming to a deeper sense of mutual respect and understanding. Of decrying any sense of hatred, persecution, or antisemitic efforts on the part of individuals that really have been such a burden to the Jewish people. So that particular document really laid the groundwork, for the very simple fact that I am here today and a part of this initiative. But to fast forward a bit, the reality of antisemitism, as you know better than I, it has hardly diminished, and sadly, has intensified in recent years. And well before October 7 of 2023. So much so that the bishops of the United States, many of them, brought to the attention of the committee that I chair, the Bishops Committee for Humanism and Interreligious Affairs, have brought to our attention the fact that we need to begin to do something in a more concrete way. To walk more intimately and closely and lovingly with our Jewish brothers and sisters and to address the reality of antisemitism in a very real and concrete manner. And so in 2022 this committee that I just referenced, they issued a document that they shared with all of the bishops. It's called the Fruits of Dialogues: Catholics Confronting Antisemitism. And in many respects, I would say that that particular document was the impetus for this initiative that we are a part of today, the Translate Hate Catholic Edition, hopefully it's been the impetus for other efforts on the part of many bishops in their own particular dioceses and archdiocese to work with their Jewish partners, to help to eradicate this, or certainly to address it in a way that is hope filled. So this document has been in the works now for quite a while particularly with the leadership of the Bishop's Committee and the American Jewish Committee as well. What you will find is building upon the antisemitic themes and tropes that were placed in the document when the American Jewish Committee put it together; we have provided commentary on a number of them from a Catholic perspective. So you know, if you look at the notion of deicide, the commentary that we provide there offers very clear Catholic theological teaching on the fact that that whole reality is certainly not something that we would ever intend to insinuate today is the responsibility of all of the Jewish people. In the midst of these commentaries, we offer current theological teaching. We offer teaching on human dignity, which is so much a part of our tradition and our hope and prayer for humankind, and we acknowledge, as well, in some of those commentaries, the fact that, you know, some members of the Church throughout history have been insensitive and inappropriately offered, and perhaps even negligently offered, words and actions that led to antisemitic efforts, sadly on the part of so many. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what is the expectation? This document is going out. How are you expecting or wanting parishes and pastors to implement it? Most Reverend Joseph C. Bambera: Given the fact that it the document that the Bishops Committee came out with in 2022 was really at the initiative of many bishops in the United States, I would like to believe and think that the vast majority of our bishops will embrace this and use it in whatever way speaks to the situation within their own territory, their own region, relative to the Jewish community there. So for example, once this is officially promulgated today, later on in the day, we will be releasing from the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops on our bishops-only website. We will be releasing a letter from me as the chair of this committee, and the document, and that will be followed up with a hard copy that will be sent to every bishop in the near future, following the online version that they'll receive today. We anticipate that this will be used by other committees that might have some relationship to the work that our committee does, and the hope that they would use them. We will be disseminating it to ecumenical officers who are appointed in every one of our dioceses to do the work of ecumenism and interreligious affairs folks. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned Nostra Atate. In 1965 you were just a child then. And I should also mention AJC played a leading role in those conversations, as well with Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel. You were ordained 20 years later. And I'm just curious if this major turning point in Catholic Jewish relations, did it come up in your theology training, or 20 years later, was it just accepted as the norm? Most Reverend Joseph C. Bambera: You know, I will be frank with you, the term that you used in asking the question was, did it come up? Yes, it did. It did. But given the scope of issues that would be necessary to prepare a man for ministry in the church as a priest in the seminary, it was one of many things that everything rose to the level of being absolutely vital, all right, to our preparation. So this was but it took its place in a whole line of other things that were just as vital. So maybe the best way to answer your question was, you know, a great deal of the teaching of the Second Vatican Council was integrated into many of the theology courses that I would have taken, all right, and the same would go for something like Nostra Atate. All right. We were, I was certainly familiar with it. All right. It was certainly something that was communicated as a very significant teaching, a milestone moment in our church, a clear refocusing of our relationship with the Jewish community. Prior to that, there were no relationships officially. So it was put before us as something that was vital to consider. But I would not be honest in wanting to suggest that in some way it was a major focus. It was one of many. Manya Brachear Pashman: I do want to fast forward and talk about today. Of course, Catholic Jewish relations are quite complicated now, especially given the Israel Hamas war, I imagine educating inspiring your flock on the moral complexities of that war, while also rallying the faithful to combat the rise of antisemitism against Israel and the Jewish Diaspora at large is very complicated, and there have been some tense moments. Recently, a letter from Pope Francis, one year after the October 7 terror attacks, included a couple kind of eerily iconic phrases from John 8:44, a verse that's long been understood as a fundamental, eternal indictment of the entire Jewish people. He was even cited by the Pittsburgh synagogue shooter. A lot of Jews are irate that the Pope has called for an investigation into whether Israel is committing genocide in Gaza. And most recently, some people were upset that the nativity scene at the Vatican featured a baby Jesus resting in a manger draped with a keffiyeh, Palestinian national symbol, and I know that has since been removed from that scene. But how do you talk about all of these moments with your Jewish friends, friends like the Hollanders, when they arise? Most Reverend Joseph C. Bambera: First of all, the concern that you share in that question, maybe the hurt or the confusion that some of these things have caused. It's rather palpable. I spoke about it just coming into the studio today with Rabbi Marans. I would first say that the very fact that in this exchange that we are having here today, on a day that is a real positive step. I believe in Catholic Jewish relations with the promulgation of the Translate Hate Catholic Edition, I would say it's a testimony to the relationship that we have developed. And I want to thank you for that. I want to thank you for the question, you know, they're, not easy questions to address, but they are of great concern to you and so many others. And you, on behalf of your people, have a responsibility to ask me that question, and I need to say to you that my presence here today is meant to speak a word of encouragement regarding our relationship. It is one that is deeply valued. I treasure it. I'm grateful for it. I am honored to be here today. Now with that, let me, let me speak a little bit more directly to the question and how these types of things are addressed. I look at the work that I have done in ecumenism and interreligious affairs, and I've been privileged to be chairman of this committee for a term now, for three years. I was previously back in 2017 elected chairman of this very same committee. So I've been at the helm of it twice now, and I've learned so much, so much from Christian partners, so much from our Jewish partners. One of the things that I have learned in the midst of the work that I have done with ecumenism is that I can't create a false sense of unity and harmony. For us to journey together in a positive way, I need to hear what you have to say, and I need to receive it, and I can't say something that is contrary to where my church is. Now, another dimension of the dialogue work that I have learned relates to listening. How do we listen to what we hear about this relationship? What are we hearing when we read something about Pope Francis? How is that speaking to our hearts? What is it saying to this relationship? I hear from you hurt. I hear from you confusion. I said that a moment ago. For me, and perhaps this is the best thing that I can say, and I would say it across all three areas or topics that you raised in your question, I would say this much. I can't speak for Pope Francis. But what I can do is reflect to you what I hear from him and what I have heard from him throughout his 11 years as Pope. I have heard from him very, very early on, and you're all familiar with this quote that he offered to a Jewish interreligious organization way back, I think, in 2013 or 14, shortly after he was elected Pope, that a true Christian cannot be an antisemite. That's something that I would affirm, and that's something that I have never heard him go back on. I have heard him embrace better than probably I have heard prior to his election, a deep commitment to the documents of Vatican Council, Vatican Two, and particularly, a deep commitment to the tenets of Nostra Aetate. The other thing that I've heard from Pope Francis, and perhaps this speaks to some of the struggle that you raise that in the face of terrorism and war and the loss of innocent lives, of Jewish lives that were lost in 2023 and of countless other lives that are lost throughout our world in the midst of war. I hear him speak over and over again about human dignity, the value of life and the reason for why we treasure life, and that's rooted in a common scripture that we both cherish, in the first book of the Torah, Genesis, the first chapter. In the image of God man was created, in the image and likeness of God. I think that that speaks for me to this moment. It does not take away, and I would not imagine that for a moment some of the struggle that you experience, but that's what I hear when I look at his papacy. I also look at some more personal dimensions of it. And I know that his experience as the archbishop of Buenos Aires was an experience that found him deeply connected to the Jewish community, particularly to a close friend of his, whom I've been privileged to meet, Rabbi Abraham Skorka. So I share these things with you in response to your observation. And by the same token, I would say to you that we have miles to go before we achieve the end for which we are about here today. Manya Brachear Pashman: In this moment, Bishop, do you believe that Translate Hate, specifically this new Catholic edition has particular value in this, in this moment that we talked about, where the relationship can get complicated? Most Reverend Joseph C. Bambera: I think, in any moment in time when there is suffering because of hatred, because of an antisemitic perspective that so many people so horrifically bring to life, I think this particular initiative is vital, and I think today more than ever, we have recognized it in our church, the sufferings of our Jewish brothers and sisters. We have recognized it globally. We have recognized it in our country, and we experience it in in my community, Scranton, relatively, you know, small city of about 100,000 people, you know, we it's sadly, it's sadly everywhere. I believe this moment is a bit of a clarion call for all of us to walk a little bit more authentically and closely with our Jewish brothers and sisters. It's one thing to have issued a document 60 years ago. You can forget the intensity and the significance that document was and meant 60 years ago, 50 years ago, maybe even 40 years ago. But as time goes on and generations pass, we sometimes need to refocus our attention, don't we? And we need to recognize the fact that as our society, becomes more secularized, we can't possibly circle the wagons to just preserve what we have. Every one of our congregations, many of yours and many of mine, are diminishing in terms of numbers since the pandemic, but also before that as well. And I think sadly, what you see in many congregations is this sense of trying to preserve what one has and therefore excluding others. Not just, I certainly don't necessarily mean from being in a church or a synagogue or temple, but I mean excluding from life by one's attitudes and one's actions and one's words. And I think we are, at this moment, really at risk of losing a sense of what we learn and how we grow from dialogue. I'm here to tell you today that I am so much richer personally because of this opportunity that I have been given to be a part of this initiative, frankly, to even prepare for today. It's just been a wonderful experience for me that has really re-energized me. This wonderful mission. But it's also reminded me of how much people who are involved in in faith traditions, in a leadership position, can be somewhat academically connected to something. It's it's got to be translated to the heart, and I hope that that's what happens here. Manya Brachear Pashman: I mentioned that you were just a child when Nostra Aetate came about. Can you tell us a little bit about your upbringing and when you heard the calling to seek ordination and become a priest? Most Reverend Joseph C. Bambera: I grew up in a Catholic family. I didn't have a lot of Jewish friends. There weren't a lot of Jewish people living in our community, although I did develop friends as as I went off to college. Okay, when I when I got the call to be a become a priest. I was actually at the University of Pittsburgh with every intention of becoming a dentist. It was kind of the family business, okay? And and I got involved in an ecumenical Christian campus ministry program. But, you know, it was just an experience that really called me to develop a deeper sense of authenticity, I think, in my faith journey, and, and, and so that's what ultimately prompted me to go into the seminary and become a priest. Did you grow up in Pittsburgh? I grew up in Scranton, where I serve as bishop, which is very unusual. So I my mom, who, at 97 still lives nearby. We I've spent my entire ministry in the Diocese of Scranton, and 15 years ago was appointed Bishop. Manya Brachear Pashman: Wow, wow. That that is indeed rare, and that is indeed rare. So you get to see the parish in which you you grew up. Most Reverend Joseph C. Bambera: I do. I do, yeah. And I've journeyed with this community, there's, there's pluses and minuses to something like that. You know, sometimes people say, What's the best thing about being bishop in your home diocese? I say, you know people, and they know you and and what's the most challenging thing? You know people and they know you. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Bishop, thank you so much for sharing what the church's teaching now and how it's collaborating with AJC to build bridges and educate your flock. Thank you so much, and thank you for joining us. Most Reverend Joseph C. Bambera: It's been a real pleasure.
Dec 12, 2024
Bernard-Henri Lévy and AJC CEO Ted Deutch on How to Build a Resilient Jewish Future Post-October 7
What lessons can be drawn from the post-October 7 era? Amid growing isolation and antisemitism, where do opportunities for hope and resilience lie for the Jewish people? In a compelling discussion, AJC CEO Ted Deutch and Bernard-Henri Lévy—renowned French philosopher, public intellectual, and author of Israel Alone—explore these critical questions. Guest-hosted by AJC Paris Director Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache, this conversation offers insight into the challenges Jewish communities face and the possibilities for a brighter future. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : What's Next for the Abraham Accords Under President Trump? Honoring Israel's Lone Soldiers This Thanksgiving: Celebrating Service and Sacrifice Away from Home The ICC Issues Arrest Warrants: What You Need to Know Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Bernard-Henri Lévy and Ted Deutch: Manya Brachear Pashman: What lessons can be drawn from the post-October 7 era? Amid growing isolation and antisemitism, where do opportunities for hope and resilience lie for the Jewish people? I'm throwing it off to AJC Paris Director Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache to explore these critical questions. Anne-Sophie? Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: Thank you, Manya. Welcome everyone to today's special episode of People of the Pod. I'm sitting here in our office near the Eiffel Tower for a special and unique conversation between Ted Deutch AJC CEO and Bernard-Henri Lévy, one of the most, if not the most prominent French philosopher and public intellectuals. Bonjour. Bernard-Henri Lévy: Bonjour. Hello. Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: Today, we will speak about loneliness, the loneliness of the Jewish people in Israel, the explosion of antisemitism in Europe and the United States, the attacks on Israel from multiple fronts since October 7. We will also speak about the loneliness of Western democracies, more broadly, the consequences of the US elections and the future for Ukraine and the European continent. Bernard-Henri Lévy:, you've recently come back from a tour in the United States where you presented your latest book titled Israel Alone. Ted, you've just arrived in Europe to sound again the alarm on the situation of Jewish communities on this continent after the shocking assault on Israeli soccer fans in Amsterdam. Israel alone, the diaspora alone, actually the Jewish people, or Am Yisrael alone. As if Israel and Jews all over the world have merged this year over a common sense of loneliness. So I ask the question to both of you, are we alone? Bernard, let's start with you. Bernard-Henri Lévy: I am back from a campus tour in the United States of America. I went in USC, in UCLA, in Columbia, in Ohio, University in Michigan. I was in many places, and in these places, in the campuses, it's not even a question. The loneliness is terrible. You have Jewish students, brave, resilient, who have to face every day humiliation, provocations, attacks, sometimes physical attacks. And who feel that, for the first time, the country in the world, America, which was supposed to be immune to antisemitism. You know, we knew about antisemitism in Europe. We knew about antisemitism in the rest of the world. But in America, they discovered that when they are attacked, of course there is support. But not always from their teachers, not always from the boards of the universities, and not always from the public opinion. And what they are discovering today in America is that, they are protected, of course, but not as it was before unconditionally. Jews in America and in Europe are supposed to be protected unconditionally. This is minimum. Minimum in France, since French Revolution, in America, since the Mayflower. For the first time, there are conditions. If you are a right wing guy, you say, I protect you if you vote for me. If you don't vote, you will be guilty of my loss, and you will be, and the state will disappear in a few years. So you will be no longer protected. You are protected under the condition that you endorse me. On the left. You have people on the left wing side, people who say you are protected under condition that you don't support Israel, under condition that you take your distance with Zionism, under condition that you pay tribute to the new dark side who say that Netanyahu is a genocide criminal and so on. So what I feel, and not only my feeling, is the feeling of most of the students and sometimes teachers whom I met in this new situation of conditional security and support, and this is what loneliness means in America. Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: Thank you, Bernard. How about you, Ted? Ted Deutch: Well, it's interesting. First of all, thank you Anne-Sophie, and Bernard, it's an honor to be in conversation with you. It's interesting to hear you talk about America. Your observations track very closely. The comments that I've heard since being in Europe from students in the UK, and from students here who, speaking about America, tell me that their conclusion is that whatever the challenges they face here and the challenges are real, that they feel fortunate to be in university in Europe rather than in the United States. But the point that you make that's so important everywhere, is this sense that it's not only the Jewish community that expects to have unconditional security. For the Jewish community now, it feels as if expecting that security, the freedom to be able on college campuses, the freedom to be able to pursue their studies and grow intellectually and have different experiences. That when that security is compromised, by those who wish to exclude Jews because they support Israel, for those who wish to tag every Jewish student as a genocidal baby killer, that when those positions are taken, it's the loneliness stems from the fact that they're not hearing from the broader community, how unacceptable that behavior is. That it's become too easy for others to, even if they're not joining in, to simply shrug their shoulders and look the other way, when what's happening to Jewish students is not just about Jewish students, but is fundamentally about democracy and values and the way of life in the U.S. and in Europe. Bernard-Henri Lévy: Of course, except that the new thing in America, which is not bad, is that every minority has the right to be protected. Every community, every minority has the right to have a safe space and so on. There is one minority who does not have the same rights. The only minority who is not safe in America, whose safety is not granted, is the Jewish one. And this is a scandal. You know, we could live in a sort of general jungle. Okay, Jews would be like the others, but it is not the case. Since the political correctness and so on, every minority is safe except the Jewish one. Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: So if we are alone, if American Jewish students feel alone, as European Jewish students, we are probably not the only one to feel that way, right? I turn over to you, Mr. Levy, and go to another subject. Since day one of the Russian invasion, and even before that, you have been a forceful advocate for a steadfast European and American support for Ukraine. Is Ukraine alone today? And will it be even more during America's second Trump administration? Bernard-Henri Lévy: I've been an advocate of Ukraine, absolutely and I really believe that the freedom for liberty, the battle for liberty, the battle for freedom today, is waged on two front lines. For the moment, it might be more, but Israel and Ukraine. I wish to make that very clear, it is the same battle. They are the same stakes, the same values, and the same enemy. I'm not sure that every Ukrainian, every Jew, knows that they have the same enemy. The axis between Iran, Putin, China, more and more, Turkey, and the same axis of authorisation countries. So it is the same battle. The Ukrainians have not been exactly alone. They have been supported in the last two years and half, but in a strange way, not enough. The chancellery, the West, spoke about an incremental support. Incremental support meant exactly what is not enough, what is necessary for them not to lose, but not to win. This is what I saw on the ground. I made three documentaries in Ukraine on the field, and I could elaborate on that a lot, precisely, concretely in every spot, every trench they have exactly what is needed for the line not to be broken, but not to win. Now we enter in a new in a new moment, a new moment of uncertainty in America and in Europe, with the rise of populism. Which means the rise of parties who say: Who cares about Ukraine, who don't understand that the support of Ukraine, as the support of Israel, is a question of national interest, a question of national security for us, too. The Ukrainian ladies and gentlemen, who fight in Ukraine, they fight for the liberty. They fight for ours, French, yours, American. And we might enter in a new moment. It's not sure, because history has more imagination than the man, than mankind. So we can have surprises. But for the moment, I am really anxious on this front line too, yes. Ted Deutch: There are additional connections too, between what's happening in Ukraine and what's happening in Israel, and clearly the fact that Iranian killer drones are being used by Russia to kill Europeans should be an alarming enough fact that jars all of us into action. But the point that you make, that I think is so important Bernard, is that Israel has in many ways, faced the same response, except with a much tighter window than Ukraine did. Israel was allowed to respond to the attacks of October 7, that for those few days after the World understood the horrific nature of the slaughter, the rape, and the babies burning, the terrible, terrible mayhem, and recognize that Israel had a right to respond, but as with Ukraine, only to a point Bernard-Henri Lévy: Even to a point, I'm not sure. Ted Deutch: But then that point ended. It was limited. They could take that response. But now we've moved to the point where, just like those students on campus and in so many places around the world, where only the Jews are excluded, that's a natural line from the geopolitical issues, where only Israel is the country that can't respond in self defense. Only Israel is the country that doesn't have the right to exist. Only a Jewish state is the one state that should be dismantled. That's another reason, how these are, another way they are all tied together. Bernard-Henri Lévy: Don't forget that just a few days after Israel started to retaliate. We heard from everywhere in the West, and United Nations, calls for cease fire, call for negotiation, call for de-escalation. Hezbollah shell Israel for one year. We never heard one responsible of the UN called Hezbollah for not escalating. The day Israel started to reply and retaliate after one year of being bombed, immediately take care to escalation. Please keep down. Please keep cool, etc, etc. So situation of Israel is a unique case, and again, if you have a little memory, I remember the battle for Mosul. I made a film about that. I remember the battle against the Taliban in 2001 nobody asked the West to make compromise with ISIS and with al-Qaeda, which are the cousins of Hamas. Nobody asked the West not to enter here or there. No one outside the ground said, Okay, you can enter in Mazar-I-Sharif in Afghanistan, but you cannot enter in Kandahar. Or you can enter in the western part of Mosul. But be careful. Nobody had even this idea this happened only for Israel. And remember Joe by then asking the Prime Minister of Israel about Rafa? Don't, don't, don't. At the end of the day, he's not always right and he's often wrong, but the Prime Minister was right to enter into Rafa for obvious reasons, which we all know now. Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: Ted, let me come back to you more specifically on the US. At AJC, we support democracy. This is in our DNA. Since the organization was founded 1906 we've been strong supporters of the Transatlantic Partnership since day one. We believe in the alliance of democracies in the defense of our common values. And you know here, there's a lot of anxiety about Donald Trump's re-election. So what is your take on the U.S. elections' consequences for Europe, for transatlantic relations? Ted Deutch: I've been coming to Europe for years, as I did as an elected official. Now in this capacity there is that our friends in Europe are always rightly focused on US policy and engaging the level of commitment the US makes to Europe. The election of Donald Trump, this isn't a new moment. There is history. And for four years in the last administration, the focus that the President had on questioning the ties to Europe and questioning NATO and questioning the commitment that has been so central to the transatlantic relationship rightfully put much of Europe on edge. Now, as the President will come back into power, there is this question of Ukraine and the different opinions that the President is hearing. In one side, in one ear, he's hearing from traditional conservative voices in the United States who are telling him that the US has a crucial role to play, that support for Ukraine is not just as we've been discussing, not just in the best interest of Ukraine, but that it relates directly back to the United States, to Europe. It actually will, they tell him, rightly so, I submit, that US involvement and continued support for Ukraine will help to prevent further war across the continent. In the other ear, however, he's hearing from the America first crowd that thinks that America should recognize that the ocean protects us, and we should withdraw from the world. And the best place to start is Ukraine, and that means turning our back on the brave Ukrainians who have fought so nobly against Russia. That's what he's hearing. It's imperative that, starting this weekend, when he is here at Notre Dame, that he hears and sees and is reminded of not just the importance of the transatlantic relationship, but why it's important, and why that relationship is impacted so directly by what's happening in Ukraine, and the need to continue to focus on Ukraine and to support NATO. And to recognize that with all of the challenges, when there is an opportunity for American leadership to bring together traditional allies, that should be the easiest form of leadership for the President to take. It's still an open question, however, as to whether that's the approach that you will take. Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: Thank you, Ted. Let me sum it up, our conversation for a minute. We said that the Jewish people feels alone, but we said that we are not the only ones. Didn't you feel that on that lonely road of this year, we've also never felt as strong as who we are, both our Jewishness. A French intellectual I know, Bernard Levy would say our Jewish being, être juif, and Jewish unity. Are they the best answers to overcome our loneliness? Let's start with our philosopher. Bernard-Henri Lévy: I don't believe only in Jewish unity. I believe in Jewish strength. And in one of my previous books, the genius of religion, I spoke about about that Jewish strength, not military strength in Israel, but spiritual strength, and I think that this strength is not behaving so bad. I told you about the campuses. I told you the dark side. But there is also the bright side, the fact that the students stand firm. They stand by themselves, by their position. They are proud Jews in the campuses. In Israel, come on. Israel is facing the most difficult war and the most terrible war of its history. We know all the previous wars, and alas, I have the age to have known personally and directly, a lot of them since 1960s about this war with terrorists embedded in the civilians, with the most powerful terrorist army in the world on the north, with seven fronts open with Houthis sending missiles and so on. Israel never saw that. So the people of Israel, the young girls and young boys, the fathers, even the old men of Israel, who enlist, who are on the front, who fight bravely. They do a job that their grandfathers never had to do. So, resilience. Also in Israel. The most sophisticated, the most difficult, the most difficult to win war, they are winning it. And in Europe, I see, as I never saw, a movement of resistance and refusal to bow in front of the antisemite, which I never saw to this extent in my long life. You have groups today in France, for example, who really react every day, who post videos every day. Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: Some are in this room. Bernard-Henri Lévy: Some are in this room. Pirrout is in this room, for example, every day about the so called unbound France. Mélenchon, who is a real antisemite as you know, they publish the truth. They don't let any infamy pass without reacting, and this again, is new, not completely new, but I never saw that to this extent. Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: Thank you, Rene. How about you Ted, what do you think? Ted Deutch: more important than ever that as Jews, as Jewish community, As Zionists, that we don't allow our opponents to define what's happening, that the response is never to to feel defensive, that the response. Is to be bold, boldly Jewish, boldly Zionist, unapologetically Zionist. To to do exactly what those students are doing across the United States, that I've seen, the students here who have that I that I've met with that in Europe, a student in in London a few days ago, said to me, she said, when someone yells at me, when they when they scream at me and accuse me of genocide, she said it only makes me want to get a bigger Magen David. The person that that stood up at a meeting in New York a few months ago who told me that, before announced in front of a big crowd that that for years, she's been involved in all of these different organizations in her community to to help feed the hungry and to help kids to read, and all these worthy causes. She said, since October 7, she said, I am all Jewish all the time, and I want everyone to know it the and Israel is perhaps the best example of this. It's impossible to imagine the kind of resilience that we see from Israelis. The taxi driver that I had in Israel. He said, This is so difficult for all of us. We've all known people. We've lost people. It's affected all of us, but we're just never going to give up, because our history doesn't allow it. We have prevailed as a people for 1000s of years and have gotten stronger every single time. Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: Thank you, Ted. I can keep thinking about this overwhelming challenge that we face as the Jewish people today, which seems to confine us to solitude. Anyway, Jews and Israel are attacked with alternative truths, false narratives. We've witnessed how international justice, our common, universal values, have been turned upside down in the Jewish tradition, we say that we have a mission to repair the world, Tikkun Olam. But how can we make sure to recreate the common world in the first place? Bernard-Henri Lévy: It's on process number one, continue to try to repair the world, I remind you, and you know that, and Simone Rodan knows it also, in many occurrences, in many situations of the last 30 years when real genocides happened. Real genocide, not imaginary. Real one. In Rwanda, in Srebrenica, in Darfur, when I met with in Chad, with Simone, and so on. The first whistleblowers, the first to tell the world that something terrible was happening, were not exactly Jews, but were ladies and men who had in their hearts the memory of the Shoah. And the flame of Yad Vashem. That's a fact, and therefore they reacted and what could be repaired. They contributed to repair it. Number one. Second observation, about what Ted said, there is in Europe now, since many years, a tendency to step out, to give up to and to go to Israel. Not only by love of Zionism, but thinking that this is not a safe place any longer for them. I tell you, this tendency starts to be reversed now you have more and more Jews in Europe who say, no, no, no, no. We built this country. We are among the authors of the French social contract. For example, we will not leave it to those illiterate morons who try to push us away. And this is a new thing. This reaction, this no of the Jews in Europe is something relatively new. And third little remark. 10 years ago in the States, I met a lot of young people who were embarrassed with Israel, who said we are liberal and there is Israel, and the two don't match really well. 10-15, years ago, I met a lot. Less and less today. You have more and more students in America who understand that Israel should be supported, not in spite of their liberal values. But because of their liberal values. And come on, this for a liberal, is a treasure, and it is unprecedented, and there is no example. Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: How about you, Ted? How do you think we can overcome the challenge of those parallel realities we feel we live in? Ted Deutch: Those students, and I think broadly the Jewish community, after October 7, came to realize that as Hamas terrorists rolled into southern Israel, they made no distinctions about the politics of the Israelis. That great irony, of course, is that the peaceniks, or the brunt of these attacks, living along the southern edge of Israel by Gaza, they didn't make determinations on who to kill based on how they practiced, what their politics were, how they felt about Bibi. And I think what the Jewish world, certainly it's true for young people that I talk to, came to realize is that connection between Israel and the Jewish people is not theoretical, that that ultimately, what's gone on for the past year is is an attack against Israel, Israel as the stand in for the Jewish people, and that defending Israel is really defending all of us. And I think they've come to understand that. But going forward, I think what you described, Bernard, is new, this is what it means now to be an Or Lagoyim. This is what it means to be a light unto the nations. That in the face of all of these attacks, that Israeli democracy continues to thrive. That the conversation by those, ironically, the conversation that has attempted to demonize Israel by demonizing Bibi, has highlighted the fact that these protests have continued during the time of war. As you point out that this is this is unlike anything you would see, that what's permitted, the way democracy is thrives and is and is vibrant in Israel, is different than every place else, that this is a message that the world will see, that that the that in the face of these ongoing challenges, that the Jewish community stands not just against against these attacks against the Jews, but stands against what's happening In the streets of so many places in America. Where people march with Hezbollah flags, where they're openly supporting Hamas. It's going to take some time, but ultimately, because of the strong, because of the resilience, because of the strong, proud way that Jews are responding to this moment and to those protests, eventually, the world will realize that standing in support of Hamas terrorism is not just something that is dangerous to the Jews, but puts at risk the entire world. Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: Thank you. I'm a Sephardic Jew, so I cannot just end this conversation speaking about loneliness. How about hope? Can we find some? Bernard-Henri Lévy: I compare the situation of the Jews today to the situation in the time of my dad, for example, there are some change, for example, the Christians and the Catholic Church. 50 years ago, a huge cultural revolution in the world. It is the change of position of the Catholic Church on anti semitism. It was the Vatican Two Council and the Nostra aetate. It seems tiny, but it is huge revolution, and it consisted in a single word, one word, the Catholic Council of Vatican Two said Jews are no longer the fathers of the Christians, as it was said before, in the best of the case, they are the brothers of the Christians. This is a huge revelation. Of course, Catholics are not always faithful to this commitment. And popes, and especially the pope of today do not remember well the message of his ancestor, but on the whole, we have among the Christians, among the Catholics in Europe and in. Real friends in America among the new evangelical I don't know if they are friends, but they are strong allies. Abraham agreements was again another big revolution which has been underestimated, and the fact that the Abraham agreements, alliance with Morocco, Emirates, Bahrain stands, in spite of the war on seven fronts. Is a proof. It is solid. It is an ironclad alliance, and it holds. And this is a new event, and we have in the not only in the top of the state, but in the public opinions of the Muslim world. We have a lot of people who who start to be who are more and more numerous, to believe that enough is enough. Too much war, too much misunderstandings, too much hatred, and who are really eager to make the real peace, which is the peace of hearts and the peace of souls with their other brothers, who are the Jews. So yes, there are some reasons to be optimistic. Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: Thank you very much, Bernard. Ted? Ted Deutch: I don't think that we can ever give up hope. And optimism is necessary, and I think justified. The things Bernard talks about, I mean, at AJC, our focus on on building democracy, our focus on interreligious work, the work we've done with the Catholic Church around Nostra aetate, now 60 years old and and continuing to build the relationship our Muslim Jewish Advisory Council always looking for opportunities to to find those voices that are tired of all of the war. And in our office, in Abu Dhabi, we've, we've continued to go to the Gulf, to the Abraham Accord states, and beyond, even through this entire war, because there is the hope of of getting to a place where, where Israel is in a more normalized position in the region, which will then change the perception and push back against the lies that those who wish to to see a world without Israel continue to espouse. All of that is hopeful, and we work toward it. But for me, the most hopeful thing to come from this moment is, AJC works around the world and because the Jewish community now understands how connected we all are as a result of the threats that we face, the opportunity to strengthen diaspora Jewry, to help people realize that the connections between the Jewish community in Paris and the Jewish community in Mexico City and the Jewish community in Buenos Aires in Chicago, in Miami and New York, that they're interrelated and that we don't have the luxury of viewing our challenges as unique in our countries. By standing together, we're in a much, much stronger position, and we have to continue to build that. That's why AJC's Global Forum is always the most important part of the year for us, bringing together the Jewish community from around the world. That's why the antisemitism summit that we'll be doing here with the CRIF is going to be so critical to building those relationships. We have an opportunity coming out of this incredibly dark time to take the strength and the resolve that we feel and to and to channel it in ways that that will lead the Jewish community to places that a year ago seemed absolutely impossible to imagine. Those 101 hostages need to return home. We stand together calling for them to return home. We stand together in our support of Israel as it wages the seven-front war, and ultimately, we stand together as Jewish people. That's what gives me hope every day. Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache: Thank you so much. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for the conversation between my colleague Benji Rogers, AJC's director for Middle East and North Africa initiatives, and Rob Greenway, director of the Allison center for national security at the Heritage Foundation, and former senior director for Middle Eastern and North African Affairs on the National Security Council, they discuss the opportunities and challenges President-elect Trump will face in the Middle East.
Dec 5, 2024
What's Next for the Abraham Accords Under President Trump?
The Abraham Accords marked a significant foreign policy achievement for President Donald Trump at the end of his first term in 2020. What's next for the Abraham Accords under a new Trump administration? Joining us is Rob Greenway, Director of the Allison Center for National Security at the Heritage Foundation and former senior director for Middle Eastern and North African Affairs on the National Security Council, to discuss the opportunities and challenges President Trump will face in the Middle East. Guest hosted by Benjy Rogers, AJC's Director for Middle East and North Africa Initiatives, Greenway draws on his firsthand experience with the Abraham Accords to explore how these agreements can be expanded and how security and economic cooperation between Israel and its neighbors can be strengthened. Resources: AJC Experts Assess the Global Impact of Trump's Election What President-Elect Trump's Nominees Mean for Israel, Antisemitism, and More The Abraham Accords, Explained Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : Honoring Israel's Lone Soldiers This Thanksgiving: Celebrating Service and Sacrifice Away from Home The ICC Issues Arrest Warrants: What You Need to Know What President-Elect Trump's Nominees Mean for Israel, Antisemitism, and More Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Rob Greenway: Manya Brachear Pashman: The landmark achievement of the first Trump Administration was President Trump's ability to successfully broker peace treaties between Israel and the Arab countries of the UAE, Bahrain, and Morocco. While much has changed since the September 2020 signing of the Abraham Accords, there are high hopes that a second Trump Administration will once again focus on brokering Arab-Israeli peace. This week, my colleague Benjy Rogers, AJC's Director for Middle East and North Africa Initiatives, invited an expert from the first Trump administration to share his insights on what to expect. Benjy, the mic is yours. Benjamin Rogers: What can we expect from the incoming Trump administration, particularly when it comes to the committee's policy and the future of the Abraham Accords and regional integration? To help us break it all down, we're joined by someone who's been at the center of these historic developments, Rob Greenway. Rob is the director of the Allison Center for National Security at the Heritage Foundation, where he formulates policy to defend American freedom and prosperity. Rob has first hand experience with the Abraham Accords, having served as Deputy Assistant to the President and senior director of the National Security Council's Middle Eastern and North African Affairs Directorate during the first Trump administration. Rob has more than 30 years in public service, including as President and Executive Director of the Abraham Accords Peace Institute, advocating for the expansion of the agreements he helped craft. Rob has also served as Senior Intelligence Officer at the Defense Intelligence Agency, and is a decorated combat veteran within the US Army Special Forces. Rob, welcome to People of the Pod. We are honored to have you here. Rob Greenway: It's my great pleasure. Thanks for having me. Benjamin Rogers: Let's jump right into it. Much has changed in the Middle East since the last Trump administration, while the hope of the Abraham Accords continued into the Biden administration, the horrors of October 7 in its aftermath have transformed the region. How do you think the next Trump administration will address the ongoing conflicts in the Middle East, and do you see renewed hope for continuing to deepen and expand the Abraham Accords? Rob Greenway: It's a great question. I'll start in reverse order, because that's the optimistic part, right? The hope in all of the relatively dark circumstances and the escalation of the conflict that's really accelerated, but didn't begin in October the seventh, but it certainly accelerated dramatically. I certainly judge that there is hope. And there's hope because the shared interest between Israel and its neighboring countries is, in fact, very strong. And that the US fundamentally, and certainly under a Trump administration, I think, will reprioritize efforts to normalize Israel's relations with its neighbors, to confront shared adversaries, which obviously is Iran, its surrogates and proxies, including Hamas and Hezbollah. But also because the economic potential has to be unlocked through integration of Israel and its neighbors and the countries within the region. They all know this, and they all recognize the intrinsic importance of it, so both for security purposes and for economic reasons, the normalization process will be resumed, certainly under a Trump administration as a matter of policy. It is, in many ways, the solution to the problems we're seeing in the region right now. Benjamin Rogers: Say a little bit more about that, Rob, if you would, what particular solutions do you think can come as a result of expansion of Abraham Accords, regional integration? Rob Greenway: Sure. On the one hand, the practical side of it is Israel's defense is better done working with and through with other partners, not just the United States, but its neighbors, so the extent to which cooperation could be expanded, they can jointly meet the threat from Iran, and will, in fact, have to do so. Iran, unfortunately, has been fed too long by appeasement the last four years. It's flush with cash. It's at nuclear threshold. The only way for Israel to effectively defend itself is more often than not, working with like-minded partners, and certainly the United States. Together, I think it's easier to provide a defense. Remember the ballistic missile attacks against Israel, which now unfortunately, have happened twice. It took a regional neighborhood response to that in order to effectively detect and intercept the range of missiles and drones and cruise missiles coming from Iran. That's a picture of what the potential is and should be. It's also a strong deterrent. When Israel's standing with its partners and allies in the region, it discourages the escalation that Iran is responsible for. And again, the economic potential is also critical, and it's so important that they would protect and defend the relationship, because it's so vital to all of their future potential. Benjamin Rogers: I appreciate what you said on defense, and I think that makes a lot of sense, but I want to drill into a little bit more on the economic side of things, because it's easiest to say, hey, look, there's greater ties, there's greater business. This is a region that, little over 10 years ago, went through the Arab Spring. This is a region that is not all the Gulf. This is a region where there's lots of poverty and there's lots of struggles. A region that is impacted by the daily changes throughout the globe. How does economic cooperation address some of those concerns? Address some of those issues? How does a more integrated Middle East, will it actually make your average person on the streets, life better? How do you get there? Rob Greenway: So first, a couple of points. If you talk to countries in the region. They all share similar concerns. They look a little different, but they have similar concerns. One is the security environment. Again, each of them have a different focus, but they're all concerned about the security environment, largely again, the threat from Iran. Second is that they've got a domestic population that, in all too many cases, ultimately will have difficulty finding employment for its large youth population, growing population below the age of 25. They're all very cognizant of this, and they know that the solution is economic integration, regionally and perhaps globally. And so they know that they have a problem. They know that the solution is better integration. It's historically not been the case. Intra-GCC trade has always been less than 15% historically, Europe and Russia are probably still trading more than that now, even though they're at war essentially in Europe, but the GCC has not done so, but they know that they can't sustain it. Second, how it helps average individuals. The employment opportunities. And look, it's not just integrating the country's economies. The reality is, the strongest economic potential is allowing market markets to be connected between Europe and Asia, through the Middle East. So to move goods and services between Asian and European markets, the Middle East has to be transited. If you integrate the countries from a transportation standpoint and from an economic standpoint, the potential becomes vast. That's the real economic promise. Integrating a company's bilateral trade with UAE, with Israel, is absolutely spectacular to watch, but that's the beginning. The end is to better integrate economies and markets globally through which the region is a critical transport link. It can happen. They want it to happen, and I think we can make it happen, and I hope we do. Benjamin Rogers: That's fascinating. I think it's just such a stark difference in the way we've been approaching the region recently, which is doom and gloom. This is cause for hope. This is a cause for a way forward. But October 7, we saw, and you've mentioned this country repeatedly, we saw how spoilers can completely upend this hope. You mentioned a little bit, but can you say a little bit more about how the Trump administration is thinking about countries like the Iranian regime, how the Trump administration will ensure that terror organizations like Hezbollah, like Hamas, will not ever be able to threaten this, this pretty remarkable vision that you're sharing today. Rob Greenway: It's a great question. Maybe the central question. First, we didn't see this threat manifest itself, even though it was there, latent. It didn't just come into creation on October the seventh. Obviously, it existed during the first Trump term, but it never manifested itself this way because it had boundaries. The boundaries come in two ways. First is an absolute, demonstrable commitment to Israel's security, not question, not speculative, not changing or dynamic as it is now and unfortunately, wanting in too many cases, it was ironclad. Everyone in the region knew it, and everyone saw it, and that's an incredibly important part of deterrence. The second and perhaps even more important is denying resources to your adversaries. It sounds fundamental. You shouldn't pay your enemies to attack you, but that's what appeasement is, and that's what's happened in the last four years of the Biden administration. You can't give the world's largest state sponsor of terrorism $120 billion of excess revenue and not expect them to engage in terrorism. And so they did. The principal applied the first Trump term will absolutely come back in the second and that's denying them the resources. And so for us, you know, I watched Hezbollah for decades, and to see them ask for members to donate their organs to raise funds at the end of the maximum economic pressure campaign, by the end of 2020, as a sign of success, in a sense that they were they were deprived and unable to conduct attacks and enter into that risk. I know that that will have a similar result. It's going to take a while to get back to it, but I strongly believe it has to happen, and I believe that it will happen. Benjamin Rogers: Thanks Rob. I want to also dive into what's been front and center on a lot of people's rights now, which is Israeli-Palestinian relations. What do you think the Trump approach will be? And this, to me, is particularly interesting, because, you know, we saw early in the Trump administration, the focus on the deal of the century, focus on peace and prosperity. We saw an initial rejection by the Palestinian Authority, by the PLO to any sort of agreement. We know that many in the Israeli government have a range of views, quite strong views. And I would say the population as a whole, any mechanisms of peace while an ongoing war is happening, particularly in the aftermath of October 7 and something that is more challenging than ever to talk about. How do you see the Israeli Palestinian conflict, and how do you see a Trump administration approaching it? Rob Greenway: I believe I've read somewhere. I'm sure you did too. There's nothing new under the sun. And in most cases, there are precedents and examples. Look, for over four decades, people pursued the Israel-Palestine conflict as the central issue in the region, and they made no progress on either front. The region didn't get better, and Israel's relationship with the Palestinians didn't improve, empirically and objectively. The approach in the Trump administration was, what are the most pressing threats to our interest in the region's interest, including Israel? The answer is Iran, its surrogates and proxies. And ISIS in 2017 as you recall. And so the premise is, start with the highest order of threat. If you get the sequence wrong, you know you're going to inevitably have adverse consequences. You can't paint the kitchen when your house is on fire. It's not a perfect analogy, but the idea is, we have to deal with the most primary threats first, and if you don't deal with Iran as the principal source of instability in the region, you can't make progress on anything else, including this issue. Second, as we heard from, John Kerry's famous remarks in 2016, deeply held belief then, and I fear still now, you cannot make progress on Israel-Arab relations without making progress on the Palestinian file. And he emphasized, you can't. And obviously you can. We proved it in the form of the Abraham Accords, and President Trump led the way. And I think that will come back again. And that, I think, is the key to success. But everyone I talked to in Israel tells me the same thing, the two state solution is dead after October the seventh. At some point it may resurrect itself. I think at the end of the day, we focus on the primary threat, build a stronger relationship between Israel and its neighbors, and then we can also improve the lives of the Palestinian people in a variety of ways, which the Abraham Accords were designed to do and its members insisted on. And second, as you mentioned, the peace to prosperity plan, I think we'll end up leveraging the work done there, the fantastic work that Jared did, just he did with the Abraham Accords, and resurrect that for what needs to happen next in places like Gaza and South Lebanon. And I think that will improve the lives of the Palestinian people. So it's a reverse sequencing, essentially. I think that gets to a different outcome. But if you start with an impossible, intractable problem, everything else becomes difficult. Benjamin Rogers: Fascinating. Saudi Arabia. What do you think can be done? What do you think relations are between the US and Saudi Arabia, between Israel and Saudi Arabia. I know there's been strong comments that have got a lot of attention as of late, but where do you see that relationship going? Rob Greenway: I think the good news is that President Trump's relationship with the kingdom and with Saudi leadership like the region, was exceptional. His first visit as President of the United States on May 17, was to Riyadh and then to Jerusalem, and then to Rome, very deliberately and very intentionally. And the policies he set forth were what we carried as guidance for the four years that followed. And I think it bore fruit. That relationship is key, and I think it's going to be restored. It was deeply damaged on a number of fronts under the Biden-Harris administration, I think that damage is going to be undone by a different relationship and approach. And second, look, we've had decades, generations of cooperation with Saudi Arabia, as we have with Israel, and that puts President Trump in a unique position to be able to broker the inevitable peace between the two. But I think it's something that, like most negotiations, and certainly in the Middle East, we should give space for the new administration to do this privately and not have a public negotiation, because all that's going to do is complicated for all parties, and it'll make the end objective more difficult. I think it'll happen. I think it needs to happen. Last thing I'll say is, it isn't as much about security, although that's certainly a critical part of it. It's also, again, about managing global markets between the United States and Saudi Arabia, because this is what, obviously, for our purposes and for the region's purposes, we've got to be able to do. As long as China is dependent upon Middle Eastern oil and gas, we've got to be able to exercise some control over it. And we can't let Russia, as an exporter and our partners and allies in the region, manage global exports to China. So this isn't limited to the region itself. Our relationship with Riyadh is vital. It is strategic. It is necessary. It helped us prevail in the Cold War against the Soviet Union. It'll be absolutely vital in competition with China and with Russia. So it's critical on a number of fronts. President Trump instinctively understands this better than I think anyone, and I think he's in a unique position to close the real deal of the century. Benjamin Rogers: Staying on this topic, for a little bit, where else, what other countries in the Middle East do you think are going to be of a particular focus to the incoming Trump administration? Rob Greenway: So not surprisingly, Riyadh would unlikely be the only country to join the Accords, not followed by others. So I could think of most other countries in the Gulf would be good candidates. But I also think it's not limited to the region, right? There are a number of other Muslim majority countries that are not necessarily Arab, that reside outside the region that would be enormously beneficial from an economic standpoint and from a diplomatic standpoint. And we had a number of conversations with many countries that fall into this category. So there's, I think, a new vista that opens with the successful conclusion of getting the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia to establish normalized diplomatic relations. And again, I think if you confront Iran, this becomes possible. If you don't confront Iran, it's virtually impossible. Benjamin Rogers: I want to zoom out, but before I do, you have, you have explained how you've explained in detail, where the Trump administration may go. You've expressed some criticism of the Biden administration. Is there anything related to Middle East policy that the Biden administration pursued? Things like the Negev Forum, things like the concept of I2U2, of IMEC, things where do you think those are actually helpful mechanisms that may continue into a Trump administration? Or do you think this is essentially going to be a return to priorities that were started in the first Trump administration? Rob Greenway: I think it's going to be more of the latter than the former. Negev ultimately was taking the Abraham Accords and introducing it into a multilateral fora. But the attempt, I think, was ultimately not successful, not because of October the seventh, but because one they made it a diplomatic conference, which we deliberately didn't do with the Abraham Accords. We were more focused on getting the businessmen together and the parts of the government that dealt with trade and concrete relationships, because that's what they wanted. So we didn't try and impose a forum on them. We tried to allow it to grow organically in the areas where they were interested, and, frankly, where you could measure the progress. I mean, as you know, having a diplomatic conference is not a difficult thing to do. Having one with an outcome might be a bit of a challenge. So we were inclined to approach it from an economic perspective. Ultimately, we'd like to see it get to the security domain. I think there is a difference. But again, it's an extension of the Accords that were built during the Trump administration. They also intended to insert the Palestinian issue into the equation, and they worked to get it introduced into the forum. I don't know the wisdom behind it, and ultimately, I think it became an impediment, but I will say that ultimately, they did come to the conclusion the Abraham Accords was a good thing. The Abraham Accords was beneficial to the region, and the region wanted to see the US invested in it. Unfortunately, I think it came too late, and it was overshadowed by the intrinsic policy contradiction of feeding Iran and attempting to deal with the consequences of it. So you can't feed the greatest threat to instability in the region and attempt to work together towards normalization at the same time, the two objectives are in complete opposition to one another. And so they were working across purposes, and the region saw it, and I think they were unable to get progress because of it. Sudan is probably the only accord member country that unfortunately has collapsed into virtual civil war, which was again a very tragic and unnecessary result of bad policy choice. And it can and it must be reversed. And I trust the Trump second Trump administration would make that a priority as well. Benjamin Rogers: I'm happy to hear that, because that's an area that we have focused on, and I think absolutely heartbreaking to see what's unfolding in Sudan right now. I'd be remiss if I didn't make a plug for AJC Center for a New Middle East, which is something our CEO Ted Deutch announced in June, and essentially our concept is, let's take the decades of trust that AJC has cultivated over the last 70+ years. Let's take the network that we have in places like Europe, in the Middle East, with our office in Abu Dhabi and in Jerusalem. We have offices across Asia. We've got offices in Africa. How can we use that architecture to be a helpful model in bringing people together? So I wanted to ask you, as someone with so much experience on this, what role do you see for civil society organizations in being able to help cultivate, reinvigorate, bring together more hope to a region that is really reeling? Rob Greenway: Having come from the Abraham Accords Peace Institute, where this was our purpose, and having worked with your offices and your organization and many others, I'm convinced that there is an absolute necessity for private organizations to help contribute to and to ensure that there's continuity and successes are sustained. Especially in the people to people contact, but areas like education, in sports and athletics, enormous potential. And it will require private organizations. This is one of many areas where government doesn't do it well. So I think government has opened a door. It can open others. Private organizations ultimately are going to determine success and failure, and that includes, of course, businesses. So I think it's absolutely essential, and I think that organizations like AJC and others are uniquely positioned to be able to translate the potential into concrete success in a number of different fronts that either government can't do or it's just not well equipped to do. So 100% agree, and in fact, again, this is too, where more people external to the region can really make a contribution, and small ways can have a massive impact. And we had the luxury of being able to work on a number. And we saw the fruits of that, and I think we'll continue to see. Some of them take decades to materialize, but it's worth it. Benjamin Rogers: Amazing. Thanks, Rob. So I promised I would zoom out a little bit, because I know you're not only an expert in the Middle East, but look at the whole globe. Outside of the Middle East, where do you think when it comes to foreign affairs, the Trump administration will be focused? How will it address issues like Russia, Ukraine? How will it address issues like China? Rob Greenway: So if you just consider the staggering array of security challenges that the new Trump administration is going to inherit and confront, it can be overwhelming. For two reasons. First, because it's happening on virtually every continent, right, in every cardinal direction you look, there's not just a crisis, but in many cases, a conflict that is unprecedented or hasn't been seen at this level in a generation. First land war in Europe since the Second World War, a Middle East that hasn't been this unstable since, I think at least 1979, perhaps earlier. These are generational challenges. And I could add to that, of course, China in both the first second island chains and the potential threat against Taiwan. Massive challenges to the international order and the US vital national security interests. Number two, they're not just connected in a temporal space. Yes, unfortunately, Russia, China, Iran, North Korea, are working together in unprecedented ways. The provision of ballistic missiles and drones from Iran, nuclear technology going in the other direction. All horrible. But the fact that they are connected in ways that are impossible to segregate, so you can't solve one problem while you're waiting to solve the other two. Because the solution to each is integrated to the problem in the other. And energy, as I mentioned already, is just one of those ways, and perhaps one of the most important. So if you want to restore maximum economic pressure against Iran–and we have to–you're going to be taking them gradually off the international market. Without disrupting prices in everyone's economies, including ours, you've got to compensate for it. There are ways to do it, but Russia is an exporter too, and China is a consumer. So you think about the sequencing behind how to confront these challenges, it is going to be absolutely one of the most complex I think any presidential administration has faced. And again, economic insecurity is integral. And I say that too, because the Trump administration thankfully at the top, with the President himself and many of his trusted advisors and cabinet officials come from a business background, and they understand the economics, because that's the world in which they grew up in. As well as the security domain. And I think they're uniquely configured to be able to solve this. And they have the experience of working in these regions. A daunting series of challenges. And I think all of us watching this progress need to give them time and patience, because the scope of these challenges are massive. And I didn't mention, you know, the interior crisis at the border and the millions of illegal immigrants, tens of thousands of which are terrorists or known criminals. And that just adds to the complexity, and also can't be addressed in isolation. So massive challenges, all of them connected, security and economic standpoint, and it's going to take time, but this team and the president, I think, are uniquely postured to be able to do it. Benjamin Rogers: Rob, I really want to thank you for everything today. Before we conclude, any final thoughts? Rob Greenway: So I'd like to end again on a positive note, because it's easy to get distracted with the crises. The solution to these problems are what make them possible. Seeing the potential is what gives you the drive, the resolve, to fix it, and it also makes it possible. So if there wasn't a good solution to these problems, they would persist. The reality is that integrating the Middle East and Israel and its neighbors and connecting global markets is key to solving these problems. It's also what's going to prevent it from happening again. If we can lean into it and do it successfully and follow through on what was started, we'll be able to see not only a cessation of these problems, we'll be able to see a real improvement in regional quality of life, and hopefully peace and prosperity will again dominate, rather than conflict and chaos. Benjamin Rogers: Alright Rob, thank you so much for your time. We really appreciate it. Rob Greenway: My great pleasure. Thanks for having me.
Nov 26, 2024
Honoring Israel's Lone Soldiers This Thanksgiving: Celebrating Service and Sacrifice Away from Home
Supporting lone soldiers in the Israel Defense Forces (IDF)—those serving without immediate family in Israel—has never been more crucial. These soldiers face challenges such as language barriers, adjusting to a new culture, and coping with the emotional and physical demands of service, all while navigating feelings of loneliness, especially during holidays. This Thanksgiving, hear from lone soldiers Kerren Seidner and Nate LeRoy about their experiences and how they support fellow soldiers through Ach Gadol (Big Brother), an organization dedicated to helping those serving without family support. Resources: Ach Gadol: Big Brother Organization for Lone Soldiers Be Kind As Omer Balva Instagram page Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : The ICC Issues Arrest Warrants: What You Need to Know What President-Elect Trump's Nominees Mean for Israel, Antisemitism, and More What the Election Results Mean for Israel and the Jewish People The Jewish Vote in Pennsylvania: What You Need to Know Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Nate LeRoy and Kerren Seidner: Manya Brachear Pashman: Lone soldiers are members of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) who don't have immediate family to support them while they're serving. They face many challenges, including learning Hebrew, adapting to a new culture, and the physical and emotional demands of IDF service. And it may come as no surprise that lone soldiers also experience loneliness, especially on holidays celebrated back home. For two decades, AJC Jerusalem has held a special Thanksgiving dinner for lone soldiers. But after the Hamas terror attacks on October 7, 2023 as many lone soldiers were dispatched across the country, AJC sent boxes of sweets and other Thanksgiving delicacies to 48 lone soldiers deployed at different bases. Here to talk about why they served as lone soldiers, and the unique way they have volunteered their services since October 7, are two former lone soldiers, Kerren Seidner and Nate LeRoy. Kerren, Nate, welcome to People of the Pod. Nate LeRoy: Hi, thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: Kerren, I'll start with you, if you wouldn't mind sharing with listeners your back story. You were born in China, and then an Israeli couple living in the United States adopted you. Kerren Seidner: Correct. So I was adopted around 11 months old, both my parents, my Israeli Jewish family, my parents, they were living in Los Angeles, California at the time. They adopted me. They went to China to come adopt me, and I have an older brother who is biological to my parents. And then I grew up, my entire family, in a Jewish Israeli home. Manya Brachear Pashman: And so had you ever been to Israel? What inspired you to go to Israel for the first time and then later to serve? Kerren Seidner: For me, I always grew up in Israeli household. Growing up with the Israeli culture. I heard Hebrew every single day in my life. Although I did not learn Hebrew, my parents did not teach me. I think the first time I went to Israel was for my brother's Bar Mitzvah when I was six years old, and so ever since then, we would always go to Israel for the summer vacation. So I always grew up going to Israel. I've always been in touch with all my family and cousins, aunts and uncles that I have here in Israel. But I never thought I would ever come to Israel to serve until the age 18, where you grew up in American house, like in the American lifestyle, where at age 18, you need to decide if you want to go to college or university, or figure out what you want to do in life. So then I started thinking, You know what, maybe studying in Israel might be an option. But then my older brother, decided that he had just decided to draft to the army. So I thought maybe that might be a possibility for myself. And then overnight, it just kind of happened that I wanted to make Aliyah and draft to the army. My mom said, you know, you should be a combat soldier. It was very new at that time for girls to be in combat. Manya Brachear Pashman: So why did she encourage you to do combat? Kerren Seidner: Growing up, I've always done sports. I played soccer for 11 years. So I was always active. And I think my mom knew, coming from my dad, because most of the time I would spend with my dad, my mom in our household was different, where my mom was out working and my dad was a stay at home dad mostly. So I was always with him, and I always heard the stories of him being an officer in combat, and then right at age 16, my brother had just drafted to Said Golani. So hearing all these stories, my mom just knew it was very fitting for me to go to combat as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: Nate, you grew up in Charleston, South Carolina, and did you first come to Israel on a gap year, or had you been before? Nate LeRoy: So my first trip to Israel was actually with my Jewish day school. We have a small, strong Jewish day school in Charleston called Addelstone Hebrew Academy. Every eighth grade there does each year, does a trip. So that was my first experience in Israel. I came back with Young Judea on a summer program before senior year of high school, and then lived here on my gap year, Young Judea Year Course immediately after high school as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: And then what drew you to serve as a lone soldier? Nate LeRoy: I think a huge part of it, like Kerren was talking about, was growing up with, for me, it wasn't an Israeli family, but a really strong, close, tight knit community in Charleston. And I have to give a lot of credit to Young Judea as well, especially to Camp Judea, where I grew up in just an extremely Zionist, welcoming, loving environment. And we had dozens of Israelis working on our staff every summer. So having that kind of constant flood growing up of Israelis each summer, even if it wasn't in the house. Camp is really that home for a month each year, especially later on in high school, working there, and ultimately the gap year as well. Being here, living here for a year, being able to experience Israel, really feeling like you get kind of absorbed into society, was a huge part of it. And I kind of looked around at the time, at Israelis my age, and felt okay, I'm 18 years old. They're 18 years old. We hear all the time that Israel is the Jewish nation, the Jewish state. We never hear that it's the Israeli nation, the Israeli state. So why do only the people who are born here have to serve? And I kind of felt like, for me, the best way to do something and to serve the Jewish people and the Jewish state in Israel was through the army. And kind of like, my service for myself was also mandatory, and that was the path I chose, was to serve through that way. Manya Brachear Pashman: And what year did you serve Nate? Nate LeRoy: I drafted in 2020. Manya Brachear Pashman: In 2020, and then served until when? Nate LeRoy: I served until the end of 2021, through the Machal program. Which allows you to draft before you make Aliyah, so you do a shortened service of 18 months. Manya Brachear Pashman: And then, Kerren, when did you serve? Kerren Seidner: I drafted December 2019. Manya Brachear Pashman: And served for how long? Kerren Seidner: Until August 2022. Manya Brachear Pashman And so you said, Kerren, that you wanted to be, you sought to be in combat. Did you see combat as an IDF soldier? Kerren Seidner: Yes, I was in Ariot Ha'edan. It's a coed unit in Israel. It's a regular reconnaissance unit, like Golani, Tzanchanim, but coed, and we're just mostly on the border, so the main underneath the unit Kchi Gvulot, so that translates to Border Patrol. So there's other units like Caracal, which was very much known in the recent war, and Bardelas, they're on the borders, mostly with Egypt. I was on the Jordanian border within the West Bank. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Nate, how did you serve? Or where did you serve? Nate LeRoy: I served in Golani, in dud chamishim v'achat. So the 51st brigade. And we serve kind of all around. We did our training in the Merkaz Israel, the middle of Israel, in the north, and then served on various borders, on Gaza and up north and throughout the West Bank as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: Now, are you both in reserves now? Nate LeRoy: I currently serve in reserves. I'm not at this moment, I finished reserves in the summer. We were in Gaza for two months with my unit most recently. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Kerren, how about you? Are you still a reservist? Kerren Seidner: Yes, from October 7. I served about two months, and then I got released for about half a year, and then I just did about two months in the summer as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: All right. And can you say where? Kerren Seidner: They put me wherever they need. In the first part, I moved eight times in the span of two months. So wherever they put me. Manya Brachear Pashman: When you're not serving, when you're not fighting or seeing combat, you volunteer in a very unique way. Can you tell our listeners how you have continued to serve those who are in the IDF? Kerren Seidner: For me, for us, we volunteer with Ach Gadol. It's a special program where people like us, who are post lone soldiers who, we have lone soldiers who are currently serving, and we mentor them throughout their entire service. I currently have three soldiers, and two of them are actually combat soldiers. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Nate? Nate LeRoy: Yeah. So like Kerren said, it's a great summary. Ach Gadol, which means big brother, can translate it to big sister as well. We both volunteer with the organization. I have the privilege of being volunteering in a lone soldier house in Tel Aviv as well. So it's just a place where lone soldiers can stay on the weekends when they're off base, if they don't have a place to go, or some of them who might do kind of daily jobs where they go to and from their army service each day. If they're in intelligence, they can stay there as well if it's closer to base. So I volunteered there a little bit, and have a little brother. It's funny to say, because he's my age. We actually both overlapped at Tulane University in the States for a year, but didn't meet each other, and so we got here and got matched through the organization, so he's my one little brother right now, and it's been great. It's a great way to have a connection with someone. I personally received a lot of help from the generations before me. And I think most lone soldiers did because you really can't do this by yourself. As funny as that is being called a lone soldier, you really can't do it alone. And it's just great. It felt definitely like the right thing to do, to turn around and give it to the current generation and future generations. Manya Brachear Pashman: What do lone soldiers need now, that's different from when you served? Nate LeRoy: I think a lot of the challenges stay the same. In terms of, you encounter adulthood all of a sudden, when you get here, in terms of finding an apartment, figuring out how to live your life by yourself, figuring out all that sort of adulthood stuff. And on top of it, you have the army, which is a massive thing to navigate, a massive language issue. And I think right now I'll speak personally with my own relationship with the person I volunteer with, with Josh, when you throw war on top of that, which by itself, is more than enough to deal with, you know, how can you figure out your apartment in your contract when you've been in Gaza for the last two months? How can you figure out, you know, you have to leave combat in a war zone and go back and do your own laundry? And it's those little things that really make a difference. Where someone who is Israeli and has a family here and has the support they need, you know, they go back and they're in that support circle. And no matter what you come back from, even if you come back from, you know, when I was serving just the most regular week in the army, when you come back and you just want to check out for the weekend and be with your friends, and you have this kind of list of errands piling up, it's difficult. And coming back from combat, from war, from fighting, from losing friends, you know, it just 100 times more difficult. I think it's super important to make sure people have the support they need in all of those things, and also know that they have the space to talk about stuff and to share things that are difficult for them, and to reach out to someone who's going through similar things. Kerren Seidner: For me, it's a very deep question, but I think that, like how Nate said the whole thing about being a lone soldier, no matter times of war or normal times. We like to say normal times, but it's still hard. You need the support no matter what I think, especially just during the times of this war, and in any war, just the mental because I feel like, having to have been in miluim, I also struggled with it as well, going to miluim, being in the duty of being in the Army and that mindset as a soldier, and then coming home to civilian life, it's very different. Especially then you come to civilian life, and I'm here, like in Herzliya, and you also don't feel necessarily safe, because you have also rockets all the time, like I had one this morning as well. So it's really can be scary at times, but I think what's so special about Israel, we have the support from one another, not just from people like me, who was a lone soldier trying to help out with other lone soldiers, but just random civilians on the street, really just uplifting. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you kind of describe what you're talking about? What do you mean by that? Kerren Seidner: I think for me, ever since I moved to Israel, I say, Israel is definitely home, the people here are very different. I grew up in the Los Angeles area, so I really feel like there was very materialistic. But I think there's so many people that just want to help one another. And I really seen that a lot throughout the war, even through my service, being a lone soldier, people would just hand me money left and right. People constantly are asking, Do you have a place for Shabbat to not feel alone on Shabbat, which means a lot. Manya Brachear Pashman: And what about Thanksgiving and other holidays that you traditionally celebrated in Los Angeles or in Charleston. How have you been able to mark those occasions in Israel? Nate LeRoy: I think for me, in going off of a big thing, Kerren spoke about. I also lived in Herzliya during my service, and there's a fantastic self made group of just moms and dads and everyday people from the community there of Israelis who, whenever we'd go home, especially on holidays, Rosh Hashanah and stuff, people would either volunteer to host us, or a lot of times we just receive Friday afternoon, someone would come by. They have a list of all of our addresses, if we're in this group chat, and they just drop off home cooked meals and say, you know, this Friday night, you and your roommates, have this Shabbat dinner. Enjoy. Don't worry about cooking. And having that home cooked meal, even if it's not my mom, you know, mom's cooking. It's a great feeling and a great experience. And another thing that I've had, and I've been super fortunate to and I know a lot of us do as well. A lot of lone soldiers. Is in the absence of your immediate family, your friends really become your family. And I'm still lucky to this day to have people who I met during my time in the army and I served with who, we're still in touch. We still hang out together, and some of us, Thanksgiving specifically, you know people who can get home, and it works out with work, they go, and I'm jealous of them. I wish I could as well, but we do our best to cook a great Thanksgiving dinner. And turkeys are a little hard to come by here, but we get a couple of rotisserie chickens, and a bird's a bird, and we try to do the best we can to have this sort of family experiences and family holidays. Manya Brachear Pashman: Kerren, how about you? Do you mark Thanksgiving in any particular way or other holidays? Kerren Seidner: For me, Thanksgiving, honestly, I don't think I do, only because for me, every Friday night is like Thanksgiving to me. For me, yom shishi, the arcuchat shihi is super important for me. I because we are lone soldiers. I always try to make sure I spend it with friends who how, like Nate said, it's become like family. So living here in Herzliya, there is a big community of people, olim like myself. So we became like a little family of our own. So I would always do Shabbat together, or I am in touch with, when I moved here and did the army, I had a host family. So I am still in touch with my host family from the army. And I see them. They just live in the north in a moshav. So it's kind of hard for me to get there all the time, but I try to celebrate the Hebrew holidays, the Jewish holidays, mostly. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do your families get to Israel throughout the year? Have they traveled there to see you, even if you aren't able to get to, back to Los Angeles or Charleston to see them? Kerren Seidner: For me, my dad was really nervous when the war first broke out and Nefesh b'Nefesh opened up flights for one parent to come to Israel for lone soldiers. So he was able to get one of those flights and was able to see me during the war. And then my mom came not too long after that for a wedding, our cousin's wedding was canceled throughout the war, so it was postponed, and so she came for our cousin's wedding. But I haven't gone home in a year and a half, so I'm luckily going back in February to visit. Nate LeRoy: My family was able to come to visit at the end of my service, which was really important for me, for them to be able to see me. I guess we both, you drafted just a few months before me, but we both served during COVID. Kerren Seidner: Yeah. Nate LeRoy: Which is just also just, I mean, now, nothing compares to serving now, but it was a super weird, wild time of all sorts of closures and rules and different things. So for my family to be able to come after the kind of general lockdown and everything of COVID was really great for them, to be able to be here while I was in the army, and they haven't been able to come visit since then, but they still want to, and still will. I think sometime in this coming year, my parents may be able to come out to visit. Manya Brachear Pashman: And when was the last time you went to Charleston? Nate LeRoy: I was lucky enough. I was able to go back a few months ago, when I finished my reserve service, over the summer, I went back for a little bit to see my family and see some friends. Manya Brachear Pashman: What did you gain from serving in the IDF? Nate LeRoy: I think it's kind of immeasurable to an extent. I think that the person I was when I went in, it's still very much the person I am now. But you experienced so much, and you changed so much. And I drafted at 21 years of age, but growing so much over those kind of really formative years, but I think that I learned more about myself than I ever expected to. I learned about the importance of commitment to other people and the reaffirmment of committing to the greater good. And I think something I learned about people is just always, always to give people the benefit of the doubt and to know that people usually do try their best and they have their best intentions in mind, and to give them the space to be able to show that, improve that, you're in a lot of really just within your team and people you're shoulder to shoulder. You know, you never get a minute by yourself, and it gets very intense. A lot of situations with you or the people you serve with. But just learning to kind of give them that space and trust people and know that they want what's best for you and you want what's best for them, no matter how much each moment might get kind of chippy at certain points. It's something that you can only really experience through those tougher, tougher ordeals. Manya Brachear Pashman: Kerren, what did you take away from your service in the IDF? Kerren Seidner: I think for me, it was really hard. I was going through a lot. I also, when I first moved to Israel, I was 18, and I didn't necessarily want to leave LA at that moment, I was finally in a friend group where I felt like I belonged. So it was really hard for me to have just decided to move across the country or the world, not the country, and I didn't really know the language. So it was still hard, which is always going to be a little hard, but then getting put somewhere in the middle of nowhere, not knowing anything. I think I definitely change in a way that I've opened up a lot more. I was very closed off. And I tell people all the time, like my friends today, they didn't know me when I was 18, and I was very closed off. I don't even think I would be doing something like this even today. And in the army, you're just put with a bunch of girls, and you don't know the full language, but you just got to get to know them. And I even tell my friends today that the girls who are with me in the army, who are my best friends today, hang out with them all the time. And they will even say that the first year, I did not talk to them, and I think because we were stuck in quarantine for two weeks, we were forced to spend time. I had to just open up and actually get to know them. And I regretted not getting to know them earlier, and I'm so much happier that I open up and reach out. And that's something with Ach Gadol, where you just kind of maybe need to make that extra step, the first step, because there's new lone soldiers today who are just maybe scared to do that first step because they're in a new country, and we've been there before. Manya Brachear Pashman: I asked you both what you gained from your time in the IDF, but it is a sacrifice. For which we are very grateful that you made. What did you lose by serving in the IDF? What did you sacrifice? Nate LeRoy: I think, without the risk of being overly cheesy, I feel very lucky to have had a great service and to have experienced the army in a I got lucky, and I had a great service. And there are a lot of people around me who weren't so lucky, and kind of you know, things didn't fall their way, and they had a less good service or a bad service to a certain extent. So I'm very fortunate. That I can say I didn't lose anything that I wasn't willing to and I didn't know I was going to sacrifice beforehand. I did a year at Tulane before, and chose to leave that behind and come and do the army, and knew I had finished my studies at some point, which I'm doing now. And I guess I lost, you know, two or three more years of partying in college in the States and a lot of experiences with close friends, who I'm fortunate to still be close with. But that's a decision and choice that I made, and knew I was making when I came over here. And, you know, a couple of Mardi Gras would have been great. COVID softened the blow a little that it, you know, they were canceled or didn't happen to the full extent. But again, I'm just fortunate to have. You know, only missed the experiences that I thought I would be able to miss. Kerren Seidner: Yeah, I honestly, I think I lucked out, that I really enjoyed my service, and I don't regret anything about it. And I always say that I'm, I'm going to stay here in Israel forever. This is home. I always say, like to my friends who are drafting now and to my soldiers now that: I'll support them no matter what. If they have any regrets, or if they went to combat and they regretted that decision, or any other decision. I really do believe God has a path for every single person, and I think that we make mistakes, we have to learn, and we may regret some things, but I think that doing the army was the path that I was meant to do, and I don't regret any of it. Manya Brachear Pashman: One more question for you both, and that is, I asked you, what you lost from serving in the IDF, but so many people lost loved ones and friends on October 7. Did you lose anyone, or know anyone who was killed or kidnapped on October 7? Kerren Seidner: For me, not on October 7. I have a friend of mine. His name is Omer Balva. They actually have an Instagram page called Be Kind as Omer . And we did Garin Tzabar together. He was in the Moshav next to me. And he actually started university with me at the same time, so that was really hard for me. And I was able to go to his funeral. That was the first time I was out of miluim. And then throughout, after I got released in July, my mifached, unfortunately, was killed in a motorcycle accident, and he did miluim and everything. It was just very unfortunate to have lost him in such an unfortunate way. And then a far relative cousin on my dad's side is actually kidnapped still to this day. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to let listeners know you are referring to your cousin Tzachi Idan. Kerren, I hope you don't mind me sharing that his 18-year-old daughter Ma'ayan was murdered in their home on October 7 before her father was taken into Gaza. In fact, she was helping her father hold the door to the safe room closed and she was shot through the door. It is a horrific story. Thank you, Kerren, for sharing that about your friend and your cousin. Nate? Nate LeRoy: So I was fortunate to not have anyone that I was close with who passed away on the seventh. There were several people I served with kind of an extended, extended relationship with, or distant relationship with, who passed away fighting in the Kibbutzim in the south and about a month after the seventh, someone in my extended family, one of my cousins, a lone soldier from Atlanta, Rose Lubin, was killed in a terrorist attack in Jerusalem, and actually, this coming week is her the yard site for the first time. So a lot of the family, a lot of family on her side, live here in Israel. So everyone's kind of has a fantastic week of really meaningful, important events taking place. Everyone's coming over for it from the States as well, so it'll be a really meaningful, moving week to remember her. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you both so very much for your service, for all you've done to and you're doing to support the soldiers, especially at this time. Thank you both for joining us. Nate LeRoy: Thank you. And just one last thing, anyone who's interested in Ach Gadol wants to find us online. I'm sure there'll be a link somewhere with this podcast, but feel free to search us on Google or wherever Ach Gadol or in Hebrew, Ach Gadol L'Ma'an Chayalim Bodedim, and thank you so much for having me on the show. Kerren Seidner: What he said. Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, tune in for my conversation with Belle Yoeli, AJC's Chief Advocacy Officer, about the International Criminal Court's charges against Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and former Defense Minister Yoav Gallant. She explains why regardless of political views about this Israeli administration, the charges tied to Israel's defense operations in Gaza are unjust.
Nov 22, 2024
The ICC Issues Arrest Warrants: What You Need to Know
The International Criminal Court (ICC) announced arrest warrants for Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and former Defense Minister Yoav Gallant, accusing them of crimes tied to Israel's defense operations in Gaza. Why should supporters of Israel—regardless of political views—reject these accusations? Belle Yoeli, AJC's Chief Advocacy Officer, explains why the ICC's charges are not only baseless but also undermine justice, distort international law, and fuel harmful narratives following the deadliest antisemitic attack since the Holocaust. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : What President-Elect Trump's Nominees Mean for Israel, Antisemitism, and More What the Election Results Mean for Israel and the Jewish People The Jewish Vote in Pennsylvania: What You Need to Know Go Deeper – AJC Analysis: Statement: American Jewish Committee Appalled by ICC's Issuance of Arrest Warrants Against Israelis Explainer: What You Need to Know About the ICC and the Israel-Hamas War Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Belle Yoeli: Manya Brachear Pashman: The International Criminal Court announced on Thursday that it issued arrest warrants for Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and former defense minister. You have Galant as well as Hamas terrorist Mohammed, if the Court said it had found reasonable grounds to believe that Netanyahu and Galant quote, each bear criminal responsibility for starvation as a method of warfare and crimes against humanity, end quote. All tied to Israel's military operations in Gaza focused on defeating Hamas terrorists, securing the return of the 101 remaining hostages and preventing more attacks. Here to talk about why the court is prosecuting Israel's leaders for its defense operation after the country suffered the deadliest antisemitic attack since the Holocaust, and why that's dangerous, is Belle Yoeli, AJC's Chief advocacy officer. Belle, welcome to People of the Pod. Belle Yoeli: Thanks so much, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do Belle, why have warrants been issued for Netanyahu and Gallant. Belle Yoeli: Right. So first and foremost, I just want to make it abundantly clear, and it really needs to be said, that this decision is absolutely outrageous. It's a gross distortion of international law and so many other things. It undermines the credibility of the court, and it fuels a lot of malicious lies about the state of Israel and its self defensive activities in Gaza since October 7. I will share the Court's reasoning for the warrants, and you alluded to it, quote, crimes against humanity and war crimes committed from at least the eighth of October, until at least the 20th of May 2024. The court claims they found reasonable grounds that Netanyahu and Gallant, again, quote, bear criminal responsibility for the following crimes as co-perpetrators for committing the acts jointly with others. The war crime of starvation as a method of warfare, and the crimes against humanity of murder, persecution and other inhumane acts. That's the direct quote, obviously very hard to read. And of course, AJC fundamentally rejects these claims, as do the United States and many, many leading international law and warfare experts. This is just a total and complete failure of justice. Manya Brachear Pashman: So why should supporters of Israel stand firmly against this accusation, no matter what their political views are? In other words, if they're not fans of Netanyahu, but they are ardent supporters of Israel, why should they stand firm against this? Belle Yoeli: Yeah, it's an important question, and we have to be clear. I mean, the court has politicized this by sort of taking this unprecedented action. But this is not about political issues, it's not about Netanyahu or Gallant. This is about the truth. This is about right and wrong, and the claims that are being made here are so outrageous and malicious. I mean, Israel is not intentionally starving Palestinian civilians or committing crimes. It just doesn't make sense. If it were, it would not be facilitating tons and tons of aid into the Gaza Strip every day, not to mention polio vaccines. I mean, the list goes on and on. Israel, like any other country, is defending itself, and not just in Gaza against Hamas, but on seven fronts, including Hezbollah and Lebanon, against Iranian proxies. And look, we've said it from the beginning, since Israel responded in this self defensive way, and we'll say it again: civilians die in war, and that is a terrible, horrible thing. But Israel is fighting its war in Gaza in response to Hamas' actions on October 7. It's about bringing the hostages home and preventing the ability of Hamas to attack Israeli civilians. And it's been said by many experts that Israel is conducting itself in this war in an unprecedented manner, in a positive way. And I know that's hard for people to grasp, because, again, people have died, Palestinians have died, and, yes, civilians have died, and that's terrible. But that doesn't take away from the fact that Israel is trying to prevent civilian death and why it's fighting this war, and none of that has to do with intentionally harming civilians. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I want to back up here and talk about who is actually pressing these charges, who is actually issuing these warrants and making these accusations in this case. For people who may not be familiar or they may be confused between the International Criminal Court and another international court, the International Court of Justice, which has a separate case against Israel and is connected to the United Nations. So what is the International Criminal Court? How is it different than the ICJ? Belle Yoeli: So you mean, not everybody is a legal scholar? It's quite confusing, and I'm grateful for my colleagues who have really helped us try to explain this to everyone, and I'll try to break it down for you as simply as I can. So the ICC is an independent, international judicial tribunal. It's based in the Hague, and it was created in 2002 by the Rome Statute. And that's a treaty that essentially spells out what crimes this specific body, the ICC, should investigate and adjudicate when it can. And the ICC's jurisdiction is essentially that it can prosecute individuals for war crimes, crimes against humanity, genocide and aggression. That's four categories. And it's allowed to prosecute not just state actors, but also non-state actors. And when you think about the ICC, as colleagues have explained to me, you really are supposed to think about it as a court of last resort. So when you think about national legal systems, and respecting the right that sovereign states have their own courts and that should be respected, the ICC would step in when an important crime or a crime did not get prosecuted. That's what this body is meant for, and again, trying to respect sovereign states. Now, by contrast, the ICJ is the judicial arm of the UN, the United Nations, and the ICJ is supposed to settle legal disputes between states, and it also can issue opinions upon requests by UN entities. So there are two different bodies, two very different purposes. Manya Brachear Pashman: So is Israel a member of the ICC? Belle Yoeli: So Israel is not a member of the ICC. And this is actually sort of interesting. Israel was involved in drafting the Rome Statute that I mentioned, that created the ICC, that treaty. But things got a little complicated, which is not so surprising when you hear why. Essentially, the ICC, as we discussed, was intended to focus on these most heinous crimes, right? But eventually the entity was urged by several Arab countries, and the majority of the countries that are party to the ICC agreed, to add as one of the categories of things that can be investigated and prosecuted, the transfer of civilians into occupied territory. And so if you hear that, I'm sure a ping goes off, obviously based on Israel and its situation and dynamics in the region. Israel took this as a sign that countries were aiming to distort the purpose of the body and really to try to just prosecute Israelis for actions in the West Bank, for example. So it ended up refraining from joining. Manya Brachear Pashman: So now, countries cannot be prosecuted by the ICC, right? I mean, I understand that Israel as a country can't be prosecuted, but Israelis can be, and that's why the warrants issued named Netanyahu and Gallant. Belle Yoeli: So technically, the body is supposed to go after individuals. But the question here, of the warrants is about jurisdiction, right? And clearly there's a disagreement. The Israelis, the United States and others have said that the ICC has no jurisdiction over, you know, for the warrants they've issued. And AJC agrees. The Palestinians and actually, the court itself have said that it's based on certain technicalities which are actually quite complicated, and you can read about in our explainer on our website about this subject, that there is jurisdiction. But for me, the thing that is most clear here is that as we reference, Israel has a strong, independent judiciary, and even when it comes to the conflict. Most recent conflicts is October 7, Israel's own military Advocate General has in fact, opened dozens of investigations into incidents. So when you consider the fact that Israel has a mechanism for investigating things that are happening in Gaza, that in itself, should tell everyone that the ICC has no jurisdiction here based on its own treaty. So yes, these warrants were issued, but from our perspective, there's really no jurisdiction. Manya Brachear Pashman: Okay, so would you say the fog of war makes this almost impossible to adjudicate, or is this, in your eyes, an open and shut case? Is it abundantly clear that Israeli leaders have avoided committing these crimes they're accused of? Belle Yoeli: So, I mean, to me, it's open and shut for a few reasons, right? We've mentioned them. One, the ICC has no jurisdiction. Two, the claims are, of the crimes are, are false and really offensive. And, you know, there is, of course, this phrase, the fog of war, and there's always fog in war. But this is really not what it's about. The travesty in all of this is that Israel does so much in an unprecedented environment that shows that the claims that are being made are untrue. So, yes, the technicalities, yes, there's no jurisdiction. The claims are offensive. But it's more than that. This is so clearly being politicized, because, yes, people are upset about what's happening and the conflict, and we understand that the entire world is reacting, but it's just not true. It's just about truth here, and what the court is suggesting is simply not true, and really targeting Israel in a way that is against justice and is really unheard of. Manya Brachear Pashman: So here in America, we are amid a leadership transition. Has the response differed between the Biden administration and the incoming Trump administration? Belle Yoeli: So from what we've seen so far, I mean, the Biden administration and incoming administration officials from the Trump administration have both spoken out and both rejected the decision outright. You'll see, and I think we'll see in the coming days, there are differences of opinion also in Congress about how to deal with this action. And this been, this has been in conversation, you know, discussion for months when this was first raised, that this could possibly happen, questions around sanctions and different actions that can be taken. But I think we'll know a lot more about concrete potential proposals and next steps in the coming days. Manya Brachear Pashman: And what about the international community? Belle Yoeli: You know, it's interesting, at this point, when we're as of this recording, the international response has actually been quite muted, and I think that's because countries are trying to balance upholding the respect for the court and the idea of the court and its jurisdiction with this really outrageous decision that I think many of them know is is false and wrong and has really bad implications for what the court is meant to do. You know, some have been quite clear. Just to name a few, Argentina and Paraguay spoke out forcefully. Some responses have been a bit more murky. I think, trying to thread that needle that I mentioned, like the United Kingdom had a pretty murky response. And actually, the EU high representative who's thankfully on his way out, Joseph Burrell, really fully embraced the decision in a sort of grotesque way. But this isn't new for him. He's fairly problematic on these types of issues. So we'll see how other countries react. You know, more things are in play, and I'm sure Israel and the United States are having close conversations with allies. I think the US even alluded to that, and we'll have a better sense of what's to come soon. Manya Brachear Pashman: And so what does this mean for Israel and for the ongoing Israel-Hamas war? Belle Yoeli: I mean, I don't have a crystal ball. I can say, look, it remains to be seen what will happen next. I think countries who are party to the ICC need to do the right thing. They need to reject the jurisdiction and really refuse to enforce the warrants. That's the most important piece here. That's what we're hoping to see. I think we'll see that international pressure likely be applied by the United States and others. But the bigger picture here, I mean, again, it speaks to the travesty that I spoke about before. It's this larger attempt to delegitimize Israel and really discredit and slander Israel, I would even go so far to say, is just unjust, and it fuels all of the disinformation that we're seeing. And what does that lead to? It leads to hate. It leads to hate against Israelis, and let's be honest, it puts Jews around the world at risk at a time when there's already surging antisemitism. This isn't new. Look at what happened in Amsterdam. So more broadly, this just, this hits. This is an issue and so problematic in so many ways, and it just, it does so much harm and the ideals of democracy and the ideas of justice, it's really unprecedented and unforgivable. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you think it gets in the way of bringing the hostages home? Belle Yoeli: Unfortunately, the reality is that it's been difficult enough as it is to bring the hostages home, and we just haven't seen movement in negotiations. And obviously we're praying for that every day. I couldn't tell you how this will impact that. I don't, I don't see an immediate connection. I think, look, we need to be clear that every action like this contributes to a feeling in Israel of already, sort of, as they say in conflict negotiation or resolution speak. like a siege mentality, right? Israelis feel under attack. The government likely feels under attack, and so it certainly doesn't help when Israel is trying to defend itself, to carry out war and to bring the hostages home, it certainly doesn't help, but how it will affect actual negotiations, I couldn't say. Manya Brachear Pashman: Belle, thank you so much for sharing your insights and trying to explain this to our listeners. Belle Yoeli: Thank you so much for having me.
Nov 18, 2024
What President-Elect Trump's Nominees Mean for Israel, Antisemitism, and More
From Marco Rubio to Elise Stefanik: who are the nominations that President-elect Trump has announced, and what does their selection say about how the administration may take shape? Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC Managing Director of Policy and Political Affairs reviews the names announced thus far, how, if confirmed, they could impact efforts to counter antisemitism, support Israel, and uphold democratic values, and how AJC is advocating to advance these critical issues. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : What the Election Results Mean for Israel and the Jewish People The Jewish Vote in Pennsylvania: What You Need to Know Sinwar Eliminated: What Does This Mean for the 101 Hostages Still Held by Hamas? Go Deeper – AJC Analysis: Explainer: What to Know About President-elect Trump on Antisemitism, Israel, and Iran Policy AJC Briefing — Post-Election Analysis: What to Expect Under the New U.S. Administration | Tuesday, November 19 | 1:30 p.m. Eastern | Register Here Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript of Conversation with Julie Fishman Rayman: Manya Brachear Pashman: President Elect Donald Trump has named and nominated eight of the 24 officials, including his chief of staff, most of whom would make up his cabinet. Returning to discuss the nominees so far and where they stand on AJC missions of fighting antisemitism, defending Israel and safeguarding democracy, is AJC Managing Director of Policy and Political Affairs, Julie Fishman Rayman. Julie, welcome back to People of the Pod. Julie Fishman Rayman: Thanks for having me, Manya, glad to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you have worked with some of these nominees, and you know their track record on these issues. First of all, from a 30,000-40,000 foot view, what is your overall take on the slate so far? Julie Fishman Rayman: I feel like if you had asked me that yesterday, I would have had a totally different answer. And so I imagine even by the time People of the {od airs, my answer maybe would have even changed, so I will answer, but I want everyone, including our listeners, to take it with a grain of salt that I am speaking from a very specific moment in tim while the clock is rapidly changing and the situation is rapidly changing. So I think the initial slate of potential nominees that were announced gave a lot of folks, especially in sort of the foreign policy world, a good deal of comfort, right? So people like Representative Mike Waltz, people like Senator Marco Rubio, those types of folks. Even Governor Huckabee, are sort of these, these names of traditional conservatives who we say, Oh, they have a record. They have governed. They have a voting record. We know exactly where they stand and what they believe, and that it's not vastly dissimilar from any other previous Republican administration. Then, of course, there was the news about the potential coming in of Matt Gaetz, representative, Matt Gaetz, a Republican from Florida and Tulsi Gabbard. And I think those names and what they represent put everyone in a bit of a tailspin. Not simply because of who they are, although they come with a lot of really interesting backstory that we can unpack, if you want to, but not just because of who they are, but because they represent a really different part of the Republican Party. A really different part of the right wing world view that had not theretofore been represented in Trump's cabinet picks, definitely less of the traditional conservative mindset and much more in line with a, dare I say, like populist kind of perspective. And so there's tension now that people are trying to sort of understand and unravel. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's talk about each individual. And you mentioned Marco Rubio, who is Trump's nominee for Secretary of State, the Florida Senator. He currently serves on the Foreign Relations Committee. He's the top Republican on the Intelligence Committee. And I mean, he and the President Elect seem to agree on America's approach to Iran and Ukraine, but not NATO, right? I mean, where do he and Mr. Trump agree and disagree? Julie Fishman Rayman: You're asking a question as though we have a full sense of what incoming president, former President Trump believes, which I think is a bit of an assumption. They're certainly deeply aligned on sort of big picture principles as they relate to support for Israel, no question. A tough, tough approach to whether it's an actor like Iran or China, you know, sort of these nefarious global players that seek to disrupt our world order, they're aligned there. There is a potential disconnect on Ukraine. Right? We've heard statements from Senator Rubio recently where you almost see him trying to channel the former president, the president-elect, and say, like, what would Trump say? What would Trump do? You can like, see the wheels spinning in his mind as he talks about how we have been funding a stalemate and how something needs to change. But I'm not sure that if you put them both in a room and ask them blindfolded, apart from each other, what to do about Ukraine, if you would get the same answer, I think there would probably be a good deal of daylight. And I think the same could be said about the future of NATO and others. But it all remains to be seen. And then, of course, also will have to be balanced with other forces that are coming into the administration, not least of which Senator JD Vance, colleague of Marco Rubio, who definitely comes with a different sort of world view. Manya Brachear Pashman: And next on the list, Congresswoman Elise Stefanik of New York, she has been nominated for the role of UN ambassador. We kind of know her as an outspoken supporter of Israel, given her high profile role in the congressional hearings about anti-Israel protests on college campuses after the Hamas terror attacks on October 7. Those hearings actually led to the resignation of a couple of university presidents. How do you foresee that outspoken support playing out in the UN arena, or maybe even in the Trump administration's approach to higher education? Julie Fishman Rayman: In terms of the UN and antisemitism, there will be a lot of very vocal, very strident affirmations that antisemitism is not something that the US will abide. That same sort of force that Congresswoman Stefanik brought to the Education Committee, she will bring to the UN and she won't take any bones about it, and she's not going to sit down to anybody. Of that we can be sure what that looks like, though, beyond pontification, beyond promulgations of support for the Jewish community across the globe, remains to be seen. Right? How will she engage in a UN that she certainly will perceive to be at least biased towards Israel and possibly antisemitic at its core. Right? We can make that assumption on her world view. How will she seek to engage with a system that she presumably views as fundamentally flawed? We know that a Republican House and Senate are already sort of gearing up towards cutting funding of major UN institutions, if not the UN across the board. So what does that mean for her role? What does that mean for the voice that the United States will have and the ability for her very strong voice, to even be at the table, and that's sort of where some of that tension arrives is also, do you get in the room? Do you get the seat at the table? Or are you on the menu? Right? The United States is never going to be on the menu, but are we going to, by virtue of our own sort of principles, going to push our seat back in and stand in the hallway. There's a lot of calculi that she's going to have to make there. In terms of the Department of Education and Congress and how they're dealing with these really important issues that that Congresswoman Stefanik has put at the fore for so long, there's no question that the threat of pulling federal funding that we've heard from the Biden administration repeatedly will be more believed under a future Trump administration. I think there are universities all over the country that already are saying, oh, like, what do we have to do? We don't want to get caught in these crosshairs. What do we need to do to make sure that we are not either under fire with the light shining on us or on the chopping block for federal funding? So if you're an educational institution that really believes that there is a true threat that you're to your federal funding, you're reconsidering a lot of steps. And if in fact, federal funding is leveraged or cut, I think we have to be really mindful of three things. One, we have to make sure that it doesn't look as though the Jews are behind this crushing blow, because that's scapegoating. And we have to make sure that shuttering these major academic institutions doesn't foreclose the creation, the necessary creation, of future American doctors and engineers and others. And finally, we have to make sure that we're not creating a void in funding that could really easily be filled by foreign actors that are already known to use university funding to advance a particular ideology, to advance their own interests. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to go back to another name you mentioned at the top, and that is the Florida congressman, Michael Waltz. He has been named as National Security Advisor to head up the National Security Council, and he has been a huge champion of the Abraham accords. So what can we expect to see from him if he indeed does take this post. Julie Fishman Rayman: So one of the things that I think is really interesting about, you know, looking back on the last trump administration, while we sort of forecast for the next, is that the National Security Council, this body that Mike Waltz will lead, was always the brain trust for him in the previous administration. Of course, there was the State Department. It was filled, it was supported. But generally, I think he thought of the State Department as a place of a foreign policy bureaucracy, where passports got stamped, that kind of, step by step, day by day, keeping the wheels turning, but not where real change happened. So if we're, you know, we're talking about Marco Rubio at State, we're talking about Mike Waltz as National Security Advisor, I think we really need to sort of dig into what's Waltz gonna bring. And of course, like, as you said, Manya deeply supportive of Abraham Accords, very hawkish when it comes to China, and very, very embedded in the military establishment himself, right? He's not the DoD pick, but he's a Green Beret vet. He served in Afghanistan, he served in the Middle East. He served in Africa. In addition to being on the foreign affairs committee and Congress, he was on the Armed Services Committee and the Intelligence Committee, if there are, if there's a trifecta of committees that someone could serve on to be as informed and at sort of the pinnacle of information about what's going on in this world, it's those three committees. Ukraine is the big question mark here. He's criticized aid to Ukraine, and has talked about getting Putin to the negotiating table, getting a diplomatic solution, or some sort of settlement to this war. And that I think remains this major looming question for a lot of folks about, as we're looking at these various picks whose voice is going to win here. Or, you know, if we're channeling the last Trump administration again, who's going to be the last person in his ear before he goes and makes a major announcement. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned DoD. Let's talk about President Elect Trump's DoD pick. Fox News anchor Pete hegseth, he is a retired US Army Major. He served in Iraq and Afghanistan, but a surprising pick to head the Department of Defense. Julie Fishman Rayman: It's interesting that you asked that question, because I think for folks who just think of him as a, you know, the guy on the Fox News couch, everyone who I've talked to who really knows Pete Hegseth and really is engaged with him for a long time, they they're not surprised, and they say, Oh, that does make sense. I don't know how much we can anticipate his fox views translating into a DoD cabinet pick. I don't really know how to manage that, right? He's talked about, like the Joint Chiefs, for example, in sort of a disparaging way. So, he's definitely one of these picks that you know shows the future President's desire to be at the vanguard, right? He wants to shake things up. He wants to keep people on their toes. Manya Brachear Pashman: Okay, so now let's move on to some of the names you mentioned that are curious, curious choice. Other curious choices. Former Hawaiian Congresswoman Tulsi Gabbard, she has been nominated to serve as Trump's chief intelligence advisor, the Director of National Intelligence. That would mean she would be responsible for overseeing 18 spy agencies and keeping the President informed of the nation's international intelligence as anti semitism rises around the world, incidents like what we saw in Amsterdam this past weekend continue to flare up. Do you foresee her prioritizing that kind of news for the president elect? Julie Fishman Rayman: This is a position that has to be confirmed by the Senate, and it's not, I think, a slam dunk in a lot of ways. She's not always been a Republican. She certainly hasn't always been a Trumpist Republican. She had a major leadership role in the Democratic Party for quite some time. She was the vice chair of the Democratic National Committee, and not rank and file, she resigned from that position to endorse Bernie Sanders in 2016 she supported the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, the Iran deal that many Democrats broke with the administration to oppose that. AJC opposed, I think that there's a lot of baggage that she brings, and not personal baggage, but policy baggage that might make it very, very difficult for her to make the step through that confirmation process, and someone very smart said that'll be the test. Maybe I'll give him credit. Josh Kraushauer, the editor of Jewish insider, said this will be the test for how Senate leadership is going to respond to the calls from President Trump. You know, if they're able to just sort of if Senator Thune, in this new role that he has just received is able to push through the nomination of Tulsi Gabbard, then we can expect a lot of confirmations legislation Trump desires to move through the Senate. If she gets a little bit held up. If it's not as easy, then we can anticipate just a little bit more gridlock, as much gridlock as one could expect from one party control of the House, Senate and the White House. But a little bit more of a pushback. It'll be a real test. Manya Brachear Pashman: She is nominated to be his chief intelligence advisor, and yet she has posted blatantly false propaganda on her social media channels. And people know that, people have called her out for that. Is that concerning? Julie Fishman Rayman: I think it's deeply concerning whenever anyone puts out blatantly false propaganda, particularly that which emanates from Russia, that is problematic at any level of elected official, appointed official, period. We need to constantly, as a society and as a nation, be on fierce guard against that, because it is real and it is pervasive. I anticipate that, you know, when the confirmation hearings are up, there's going to be a lot of questions about, you know, what has she posted, where is she getting her information, and from whom does she rely on for real, authoritative information that is truthful? Manya Brachear Pashman: So another name that you mentioned at the top of the conversation, and that is Congressman, well now former Congressman Matt Gaetz from Florida, since he resigned immediately after his nomination for attorney general. He was one of, I think, 21 republicans who voted against the Antisemitism Awareness Act in May, saying he couldn't support a definition of antisemitism that labeled claims of Jews killing Jesus as antisemitic. I think Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel might have had some choice words for him, if he is indeed, if he indeed progresses through this process toward Attorney General, what could we see from him? What can we see, period, of this whole process? Julie Fishman Rayman: So first off, I just, I want to speak a little bit about it was sort of him in his record, because I think that it's important for our community to to be refreshed about exactly who Matt Gaetz is it there were a number of Republicans who voted against the Antisemitism Awareness Act because they did not think that it was appropriate for there to be a law that says the Jews didn't kill Jesus. This is, of course, like a sort of gross mischaracterization of what the international Holocaust Remembrance Alliance working definition of anti semitism says and purports to do. But he wasn't alone. And it was, it was very interesting to see how this, this sort of trope that I think a lot of us thought was over about the Jews killing Jesus. You know, Nostra Aetate was in the 70s, right? So we thought that this was done and behind us. But to hear, particularly from the evangelical set, that, okay, like, maybe the Jews didn't kill Jesus, or maybe they did. He also invited a Holocaust denier and a white supremacist to be his guest at the State of the Union later, he said, like, Oh, I didn't really know. But either he got terrible staffing or he knew, and he just didn't want to get caught. He's deeply, deeply scandal ridden, without question. And he, you know, is constantly defending Marjorie Taylor Green, who, you know, compared the COVID mask laws to, you know, the Holocaust and things like that. He called the ADL racist. He is not representative of any stream, really, within the Republican Party. He is emblematic of the most populist of the populace, the most MAGA of the MAGA. So we should remember who he is, first and foremost. Beyond that, I cannot imagine an America that would confirm him as Attorney General. I'm a congressist by heart. I believe that Congress does the right things, if given enough time to do so, and I cannot believe that they'll let this one go through. So forgive my rant. I think it needs to be said about him. But in terms of, you know, who are we watching, and what do we think is going to happen in the long term? I don't think there's a long term there. Manya Brachear Pashman: Let's talk about another pick, and that is his pick for Homeland Security, who I don't think is so outlandish, and that is South Dakota Governor Christie gnomes. She could play a really vital role in his immigration the proposal that he's made for the immigration system. She has been a strong ally of AJC in the past. Julie Fishman Rayman: Yes, she has. When she signed North South Dakota's bill, um on the international Holocaust Remembrance Alliance, working definition of antisemitism, when she signed into law, AJC was there. She's been outspoken about anti semitism, and has consistently, sort of done, she's done the right things there. That being said, South Dakota has a very small Jewish population. So it's not, the same as if she were the governor of New York or Florida or even California that has major Jewish populations that are constantly calling with various, you know, security needs or something like that. So she's been there when she's needed to be there. Manya Brachear Pashman: And I know South Dakota is not a border state, but didn't she send army reserves to the border to help Texas Governor Greg Abbott, at one point? Julie Fishman Rayman: She has. A lot of Republican governors sort of backed Abbott in that way. I think that her crew in the governors, in the Republican Governors Association, etc, will be much aligned with the incoming administration. And of course, you know, that's why she's picked. Manya Brachear Pashman: We also have the choice of John Ratliff, who Trump has named as a potential CIA director. And you know, technically, CIA director is the person who's nominated as head of intelligence is the CIA director's boss, and so he was the former director or chief intelligence advisor. So in a way, it's kind of a demotion. However, what I've read is President elect Trump believes that the CIA director is actually more important. So what are we looking at here? Are we looking at a smoother confirmation process for the CIA director, perhaps, and are we looking at kind of an elevation of that job? Julie Fishman Rayman: I think we can probably assume it's an elevation, and in the same way that we talked about the previous Trump administration prioritizing the National Security Council almost above the State Department, I think we'll see that sort of shift in alignment, the CIA being sort of the new center of gravity, if it wasn't already within the the intelligence community. So I think that we probably will see him playing a much more dominant role. That being said, I think America has always held this deep fascination with CIA directors, FBI directors. They always, because of the really interesting and critical roles they play, they always sort of punch above their weight in terms of, you know, how much are they on TV? How much are people watching what they're saying and what they're doing? So I think that we can absolutely anticipate that. And you know, he has some skeletons in his closet, but I don't think that there's anything that will prohibit or impede his nomination for that role. Manya Brachear Pashman: And as a religion reporter, I found the naming of former Governor Mike Huckabee as the ambassador, a potential ambassador to Israel, to be very interesting, given that he is an evangelical Christian, a Baptist pastor. Aren't too many non-Jewish ambassadors to Israel. There have been some, but not too many. And I thought that this was a really interesting selection. What can we see or expect to see from that choice? Julie Fishman Rayman: You know, part of me kind of loves this for America. I think there's, Governor Huckabee has always been a stalwart supporter of Israel, without question, deeply, deeply supportive. There are questions about, what is he going to do with regard to like, the question of settlements or annexation and things like that. And and I think we're going to have to be watching that very, very closely. But if we're looking sort of at the macro level, the issue of Israel and America has become so polarized and in some ways so toxic, that this reminder that it's not just the Jews that care about Israel, I think, couldn't come at a better time. I do think that it's really interesting to now have someone going to sit at the embassy that President Trump moved to Jerusalem, who is not representing the Jewish community there, but representing the massive Evangelical community in the United States and even frankly, around the world. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Julie, thank you so much for sharing your perspectives. As these names keep trickling out each day, many things are said, some important, some not so important. So I'm glad I appreciate you kind of focusing our audience on what matters to AJC, what matters to the Jewish community and for those who support Israel. So thank you so much. Julie Fishman Rayman: It's been my pleasure and many and if I can just say, as we conclude that the personalities take up a lot of space, they take up a lot of oxygen. But for AJC, we're always singularly focused on the policies, and we'll continue doing what we've been doing already for months, and that's reaching everyone who will have influence in this next administration, to advance our policy perspective, to share our agenda and to talk about what we think needs to form the policy priorities of the next administration. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much, Julie. Julie Fishman Rayman: Thank you.
Nov 13, 2024
Honoring Felice Gaer: A Lifelong Champion for Human Rights
Felice Gaer, esteemed Director of AJC's Jacob Blaustein Institute for the Advancement of Human Rights, was an internationally respected human rights advocate who dedicated more than four decades to championing the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and enforcing international commitments to prevent severe human rights violations globally. On November 9, Felice passed away after a prolonged battle with metastatic breast cancer. In honor of her legacy, we revisit her insightful conversation on People of the Pod, recorded last year during Women's History Month and on International Women's Day. As we remember and celebrate Felice's profound contributions, we share this interview once more. May her memory continue to be a blessing. __ Music credits: Drops of Melting Snow (after Holst, Abroad as I was walking) by Axletree is licensed under a Attribution 4.0 International License. Learn more about Felice Gaer: Felice Gaer, Legendary Human Rights Champion Who Inspired Generations of Global Advocates, Dies at 78 Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : What the Election Results Mean for Israel and the Jewish People The Jewish Vote in Pennsylvania: What You Need to Know Sinwar Eliminated: What Does This Mean for the 101 Hostages Still Held by Hamas? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Felice Gaer: Manya Brachear Pashman: This past weekend, AJC lost a phenomenal colleague. Felice Gaer, the director of American Jewish Committee's Jacob Blaustein Institute for the Advancement of Human Rights, was an internationally renowned human rights expert who, for more than four decades, brought life and practical significance to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and international commitments, to prevent grave human rights abuses around the world. She died on November 9, following a lengthy battle with metastatic breast cancer. I had the honor of interviewing Felice last year during Women's History Month and on International Women's Day. We bring you that interview now, as we remember Felice. May her memory be for a blessing. _ Felice is with us now to discuss today's human rights challenges and the challenges she has faced as a woman in the Human Rights world. Felice, welcome to People of the Pod. Felice Gaer: Thank you, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's start with the beginning. Can you share with our listeners a little about your upbringing, and how Jewish values shaped what you do today? Felice Gaer: Well, I had a fairly ordinary upbringing in a suburb of New York City that had a fairly high percentage of Jews living in it–Teaneck, New Jersey. I was shaped by all the usual things in a Jewish home. First of all, the holidays. Secondly, the values, Jewish values, and awareness, a profound awareness of Jewish history, the history of annihilation, expulsion, discrimination, violence. But also the Jewish values of universality, respect for all human life, equality before the law, sense of realism, sense that you can change your life by what you do, and the choices that you make. These are all core Jewish values. And I guess I always have found the three part expression by Rabbi Hillel to sum up the approach I've always taken to human rights and most other things in life. He said, If I'm not for myself, who will be, and if I'm only for myself, what am I? And if not now, when? So that's a sense of Jewish particularism, Jewish universalism, and realism, as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: You went to Wellesley, class of 1968, it's an all-women's college. Was there a strong Jewish presence on campus there at a time? And did that part of your identity even play a role in your college experience? Felice Gaer : Well, I left, as I said, a town that had a fairly sizable Jewish population. And I went to Wellesley and I felt like I was in another world. And so even as long ago as 1964-65, that era, I actually reached out to Hillel and participated in very minor activities that took place, usually a Friday night dinner, or something like that. But it really didn't play a role except by making me recognize that I was a member of a very small minority. Manya Brachear Pashman: Here on this podcast, we've talked a lot about the movement to free Soviet Jewry. As you pursued graduate work at Columbia, and also during your undergrad days at Wellesley, were you involved in that movement at all? Felice Gaer: Well, I had great interest in Russian studies, and in my years at Wellesley, the Soviet Union movement was at a very nascent stage. And I remember arguments with the Soviet Ambassador coming to the campus and our specialist on Russian history, arguing about whether this concern about the treatment of Soviet Jews was a valid concern. The professor, who happened to have been Jewish, by the way, argued that Jews in the Soviet Union were treated badly, but so was everybody else in the Soviet Union. And it really wasn't something that one needed to focus on especially. As I left Wellesley and went to Columbia, where I studied political science and was at the Russian Institute, now the Harriman Institute, I found that the treatment of Soviet Jews was different in many ways, and the capacity to do something about it was serious. We knew people who had relatives, we knew people who wanted to leave. The whole Soviet Union movement was focused around the desire to leave the country–not to change it–that was an explicit decision of Jewish leaders around the world, and in the Soviet Union itself. And so the desire to leave was something you could realize, document the cases, bring the names forward, and engage American officials in a way that the Jewish community had never done before with cases and examples demanding that every place you went, every negotiation that took place, was accompanied by lists of names and cases, whose plight will be brought to the attention of the authorities. And that really mobilized people, including people like me. I also worked to focus on the agenda of internal change in the Soviet Union. And that meant also looking at other human rights issues. Why and how freedom of religion or belief was suppressed in this militantly atheist state, why and how freedom of expression, freedom of association, and just about every other right, was really severely limited. And what the international standards were at that time. After I left Columbia, that was around the time that the famous manifesto from Andrei Sakharov, the world famous physicist, Nobel Prize winner, was made public. It was around the time that other kinds of dissident materials were becoming better known about life inside the Soviet Union post-Khrushchev. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you left Colombia with a master's degree, the Cold War ends, and you take a job at the Ford Foundation that has you traveling all around Eastern Europe, looking to end human rights abuses, assessing the challenges that face that region. I want to ask you about the treatment of women, and what you witnessed about the mistreatment of women in these regions. And does that tend to be a common denominator around the world when you assess human rights abuses? Felice Gaer: Well, there's no question that the treatment of women is different than the treatment of men. And it's true all over the world. But when I traveled in Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union in the height of those years, height of the Cold War, and so forth, the issues of women's rights actually weren't one of the top issues on the agenda because the Soviet Union and East European countries appeared to be doing more for women than the Western countries. They had them in governance. They had them in the parliament. They purported to support equality for women. It took some years for Soviet feminists, dissidents, to find a voice and to begin to point out all the ways in which they were treated in the same condescending, patriarchal style as elsewhere. But in those years, that was not a big issue in the air. It was unusual for me, a 20-something year old woman from the United States to be traveling around Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union, meeting with high officials and others, and on behalf of the Ford Foundation, trying to develop programming that would involve people to people contacts, that would involve developing programs where there was common expertise, like management training, and things of that sort. And I was really an odd, odd duck in that situation, and I felt it. Manya Brachear Pashman: I mentioned in my introduction, the Beijing World Conference on Women, can you reflect a little on what had a lasting impact there? Felice Gaer: Well, the Beijing World Conference on Women was the largest, and remains the largest conference that the United Nations has ever organized. There were over 35,000 women there, about 17,000 at the intergovernmental conference. I was on the US delegation there. The simple statement that women's rights are human rights may seem hackneyed today. But when that was affirmed in the 1995 Beijing Outcome Document, it was a major political and conceptual breakthrough. It was largely focused on getting the UN to accept that the rights of women were actually international human rights and that they weren't something different. They weren't private, or outside the reach of investigators and human rights bodies. It was an inclusive statement, and it was a mind altering statement in the women's rights movement. It not only reaffirmed that women's rights are human rights, but it went further in addressing the problems facing women in the language of human rights. The earlier world conferences on women talked about equality, but they didn't identify violations of those rights. They didn't demand accountability of those rights. And they said absolutely nothing about creating mechanisms by which you could monitor, review, and hold people accountable, which is the rights paradigm. Beijing changed all that. It was a violations approach that was quite different from anything that existed before that. Manya Brachear Pashman : Did anything get forgotten? We talked about what had a lasting impact, but what seems to have been forgotten or have fallen to the wayside? Felice Gaer: Oh, I think it's just the opposite. I think the things that were in the Beijing conference have become Fuller and addressed in greater detail and are more commonly part of what goes on in the international discourse on women's rights and the status of women in public life. And certainly at the international level that's the case. I'll give you just one example, the Convention Against Torture. I mean, when I became a member of the committee, the 10 person committee, I was the only woman. The committee really had, in 11 years, it had maybe said, four or five things about the treatment of women. And the way that torture, ill treatment, inhuman, degrading treatment may affect women. It looked at the world through the eyes of male prisoners in detention. And it didn't look at the world through the eyes of women who suffer private violence, gender based violence, that is that the state looks away from and ignores and therefore sanctions, and to a certain extent endorses. And it didn't identify the kinds of things that affect women, including women who are imprisoned, and why and where in many parts of the world. What one does in terms of education or dress or behavior may lead you into a situation where you're being abused, either in a prison or outside of prison. These are issues that are now part of the regular review, for example, at the Committee Against Torture, issues of of trafficking, issues of gender based violence, the Sharia law, the hudud punishments of whipping and stoning, are part of the concern of the committee, which they weren't before. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, having that woman's perspective, having your perspective on that committee was really important and really changed and broadened the discussion. Felice Gaer: Absolutely. When I first joined the committee, the first session I was at, we had a review of China. And so I very politely asked a question about the violence and coercion associated with the population policy in China, as you know, forced abortions and things of that sort. This was a question that had come up before the women's convention, the CEDAW, and I thought it was only appropriate that it also come up in the Committee Against Torture. In our discussion afterwards, the very stern chairman of the committee, a former constable, said to me, 'You know, this might be of interest to you, Ms. Gaer, but this has nothing to do with the mandate of this committee.' I explained to him why it did, in some detail. And when I finished pointing out all of those elements–including the fact that the people carried out these practices on the basis of state policy–when I finished, there was a silence. And the most senior person in the room, who had been involved in these issues for decades, said, 'I'm quite certain we can accommodate Ms. Gaer's concerns in the conclusions,' and they did. That's the kind of thing that happens when you look at issues from a different perspective and raise them. Manya Brachear Pashman: You talked about being an odd duck in your 20s, as a woman traveling around Eastern Europe, trying to address these challenges. I'm curious if that woman in her 20s would have been able to stand up to this committee like that, and give that thorough an explanation? Or did it take some years of experience, of witnessing these issues, perhaps being ignored? Felice Gaer: Well, I think as we go through life, you learn new things. And I learned new things along the way. I learned about the universal norms, I learned about how to apply them, how they had been applied, and how they hadn't been applied. And in that process, developed what I would say is a sharper way of looking at these issues. But the Bosnian conflict in particular, made the issue of gender based violence against women, especially in war, but not only in war, into a mainstream issue, and helped propel these issues, both inside the United Nations and outside, the awareness changed. I remember asking the International Red Cross representatives in Croatia, just across the border from Bosnia, if they had encountered any victims of gender based violence or rape, and they said, 'No.' And I said, 'Did you ask them about these concerns?' And they sort of looked down and looked embarrassed, looked at each other and looked back at me and said, 'Oh.' There were no words. There were no understandings of looking at the world this way. And that has changed. That has changed dramatically today. I mean, if you look at the situation in Ukraine, the amount of gender based violence that has been documented is horrifying, just horrifying, but it's been documented. Manya Brachear Pashman So is the world of human rights advocacy male-dominated, female-dominated, is it fairly balanced these days? And has that balance made the difference in what you're talking about? Felice Gaer: You know, I wrote an article in 1988, the 40th anniversary of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, about why women's rights weren't being addressed. And one of the points I drew attention to was the fact that the heads of almost all the major organizations at the time were all male. And that it wasn't seen as a concern. A lot of that has changed. There's really a real variety of perspectives now that are brought to bear. Manya Brachear Pashman: So we've talked a lot about the importance of [a] woman's perspective. Does a Jewish perspective matter as well? Felice Gaer: Oh, on every issue on every issue and, you know, I worked a great deal on freedom of religion and belief, as an issue. That's a core issue of AJC, and it's a fundamental rights issue. And it struck me as surprising that with all the attention to freedom of religion, the concern about antisemitic acts was not being documented by mainstream human rights organizations. And it wasn't being documented by the UN experts on freedom of religion or belief either. I drew this to the attention of Dr. Ahmed Shaheed, who was recently ending his term as Special Rapporteur on Freedom of religion or belief. And he was really very struck by this. And he went, and he did a little bit of research. And he found out that since computerized records had been prepared at the United Nations, that there had been no attention, no attention at all, to cases of alleged antisemitic incidents. And he began a project to record the kinds of problems that existed and to identify what could be done about it. We helped him in the sense that we organized a couple of colloquia, we brought people from all over the world together to talk about the dimensions of the problem and the documentation that they did, and the proposals that they had for addressing it. And he, as you may recall, wrote a brilliant report in 2019, setting out the problems of global antisemitism. And he followed that up in 2022, before leaving his position with what he called an action plan for combating anti semitism, which has concrete specific suggestions for all countries around the world as to what they can do to help combat antisemitism and antisemitic acts, including and to some extent, starting with adopting the working definition on antisemitism of the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance, but also activities in in the area of education, training, training of law enforcement officials, documentation and public action. It's a real contribution to the international discourse and to understanding that freedom of religion or belief belongs to everyone. Manya Brachear Pashman: And do you believe that Dr. Shaheed's report is being absorbed, comprehended by those that need to hear it that need to understand it? Felice Gaer I've been delighted to see the way that the European Union has engaged with Dr. Shaheed and his report has developed standards and expectations for all 27 member states, and that other countries and other parts of the world have done the same. So yeah, I do think they're engaging with it. I hope there'll be a lot more because the problem has only grown. Manya Brachear Pashman: On the one year anniversary of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, JBI issued a report that sounded the alarm on the widespread violations committed against Ukrainians, you mentioned the amount of gender based violence Since that has taken place, and the other just catastrophic consequences of this war. Felice, you've been on the front row of Eastern European affairs and human rights advocacy in that region. From your perspective, and I know this is a big question: How did this war happen? Felice Gaer: I'll just start by saying: it didn't start in 2022. And if you have to look at what happened, the events of 2014, to understand the events of 2022. Following the breakup of the Soviet Union, or even during the breakup, there was a period where the 15th constituent Union republics of the Soviet Union developed a greater national awareness, really, and some of them had been independent as some of them hadn't been, but they developed a much greater awareness. When the Soviet Union collapsed, the 15 countries, including Russia, as one of the 15, became independent entities. And aside from having more members in the United Nations and the Council of Europe and places like that, it led to much more robust activity, in terms of respecting human rights and other areas of endeavor in each of those countries. The situation in Russia, with a head of state who has been there, with one exception, a couple of years, for 20 years, has seen an angry desire to reestablish an empire. That's the only thing you can say really about it. If they can't dominate by having a pro-Russian group in charge in the country, then there have been invasions, there have been Russian forces, Russia-aligned forces sent to the different countries. So whether it's Georgia, or Moldova, or Ukraine, we've seen this pattern. And unfortunately, what happened in 2022, is the most egregious and I would say, blatant such example. In 2014, the Russians argued that it was local Russian speaking, little green men who were conducting hostilities in these places, or it was local people who wanted to realign with Russia, who were demanding changes, and so forth. But in the 2022 events, Russia's forces invaded, wearing Russian insignia and making it quite clear that this was a matter of state policy that they were pursuing, and that they weren't going to give up. And it's led to the tragic developments that we've all seen inside the country, and the horrific violence, the terrible, widespread human rights violations. And in war, we know that human rights violations are usually the worst. And so the one good spot on the horizon: the degree to which these abuses have been documented, it's unprecedented to have so much documentation so early in a conflict like this, which someday may lead to redress and accountability for those who perpetrated it. But right now, in the middle of these events, it's just a horror. Manya Brachear Pashman: What other human rights situations do we need to be taking more seriously now? And where has there been significant progress? Felice Gaer: Well, I'll talk about the problem spots if I may for a minute. Everyone points to North Korea as the situation without parallel, that's what a UN Commission of Inquiry said, without parallel in the world. The situation in Iran? Well, you just need to watch what's happened to the protesters, the women and others who have protested over 500 people in the streets have died because of this. 15,000 people imprisoned, and Iran's prisons are known for ill treatment and torture. The situation in Afghanistan is atrocious. The activities of the Taliban, which they were known for in the 1990s are being brought back. They are normalizing discrimination, they are engaged in probably the most hardline gender discrimination we've seen anywhere where women can't work outside the home, girls can't be educated, political participation is denied. The constitution has been thrown out. All kinds of things. The latest is women can't go to parks, they can't go to university, and they can't work for NGOs. This continues. It's a major crisis. Well, there are other countries, from Belarus, to Sudan to Uzbekistan, and China, that we could also talk about at great length, lots of problems in the world, and not enough effort to expose them, address them and try to ameliorate them. Manya Brachear Pashman So what do we do about that? What can our listeners do about that, when we hear this kind of grim report? Felice Gaer: Work harder. Pay attention when you hear about rights issues. Support rights organizations. Take up cases. Seek redress. Be concerned about the victims. All these things need to be done. Manya Brachear Pashman: I don't know how you maintain your composure and your cool, Felice, because you have faced so much in terms of challenges and push back. So thank you so much for all you have done for women, for the Jewish people, and for the world at large. Thank you, thank you, thank you. Felice Gaer: Thank you, Manya.
Nov 13, 2024
What the Election Results Mean for Israel and the Jewish People
What do the results of the 2024 U.S. presidential election, a sweeping victory for President-elect Donald Trump and Vice President-elect J.D. Vance, mean for the U.S. Jewish community and Israel? How did the Jewish community vote? What are the top takeaways from the Senate and the House elections? Get caught up on all the latest election data points and analysis in this week's episode, featuring Ron Kampeas, JTA's Washington Bureau Chief and guest hosted by Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC's Managing Director of Policy and Political Affairs. AJC is a 501(c)3 not-for-profit organization. AJC neither supports nor opposes candidates for elective office. The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. AJC's Policy Priorities: AJC Congratulates President-Elect Donald J. Trump Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : The Jewish Vote in Pennsylvania: What You Need to Know Sinwar Eliminated: What Does This Mean for the 101 Hostages Still Held by Hamas? From Doña Gracia to Deborah Lipstadt: What Iconic Jewish Women Can Teach Us Today Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. Transcript: Julie Fishman Rayman: Hello, I'm Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC's Managing Director of Policy and Political Affairs. Today, I have the pleasure of guest hosting People of the Pod and speaking with Ron Kampeas, JTA's Washington Bureau Chief, to discuss the results and the implications of the 2024 U.S. presidential election. As the nonpartisan global advocacy organization for the Jewish people, AJC congratulates Donald J. Trump on his election as the 47th President of the United States, and Senator JD Vance as Vice President. AJC looks forward to working with the President-elect and his administration on the domestic and foreign policy concerns that are AJC advocacy priorities to learn more about our policy priorities for the incoming administration. Head to the link in our show notes. As a reminder, AJC is a 501(c)3 non-partisan, not for profit organization. AJC neither supports nor opposes candidates for elected office. Ron, welcome to People of the Pod. Thank you for being here. Ron Kampeas: Of course. Julie Fishman Rayman: Well, I'd like to start asking you if you have a sense about the Jewish vote, because there have been a number of different exit polls, which, I guess, not surprisingly, because exit polls are what they are, say vastly different things. There are some that say it's the biggest Jewish vote in support for a Democratic candidate ever, and then also the highest percentage ever for a Republican candidate. What do we know to be true? And what would you sort of be looking at in terms of, you know, as we're examining this moving forward, what are we looking for? Ron Kampeas: So first of all, I know I've seen those very extreme assessments as well, and I know what they're based on, and even based on what they're based on, and we, I'll talk about that too, that's just not correct. So they're talking about a 79% turnout, according to a poll, the consortium of a number of organizations like CNN and the New York Times. And that poll is not reliable yet. It does show 79% and think 21%, in other words, an even split. Nobody seemed to have voted for, at least among the Jews, for third party candidates. And I'm not sure what number of Jews who were included in that poll were. I mean, it's a vast, vast poll. They do talk to a lot of people, but even they will say, and I think they put it on their things, that it's just preliminary. The more reliable analysis is considered to be the one that came out of the Fox-AP analysis that showed 66%-67% for Harris, 32%-31% for Trump. And I think that's what the Trump people are talking about in terms of the highest for Republicans. It's just not the highest for a Republican. I think if you count in the margin of error, that's not even like recently the highest for a Republican. Nothing's changed in the last four years. I think what it is showing is that whereas Republicans, when I started at JTA in 2004 they were happy to get 25%. They've gone up from 19% with George W. Bush in 2020 to 25% with John Kerry a few years later. Now they can comfortably say they're getting about 30% of the Jewish community. People love to attach everything that happens to the very current politics of the day. So however you count it, nothing seems to have changed. Julie Fishman Rayman: So interesting, because for I think a lot of Jews around America, we feel as though so much has changed. But when you go to the voting booth, Jews consistently aren't necessarily thinking just about either Israel or antisemitism. AJC does a survey looking at American Jewish opinion, not every year, but almost every year. And we did it in June, and asked questions about political affiliation. Who are you going to vote for? And one of the things that we asked was, what drives your vote? And foreign policy is always low down on the list. On election night, CNN asked that same question, of course, to all Americans, and I think 4% said that their vote was driven by foreign policy. Has there been a moment where the American Jewish vote is more focused on issues that feel perhaps a bit more parochial? Ron Kampeas: No. Certainly within the Orthodox subset, and it's always difficult to tell, because the smaller the subset, the bigger the margin of error. But when there's consistency over time and survey after survey after survey, I think you can conclude that, yes, Orthodox Jews do attach more importance to the U.S.-Israel relationship and how it's manifesting, how they're perceiving it. The only time that a Democrat, at least since FDR, I think, a Democrat, didn't receive a majority of the Jewish vote was Jimmy Carter, who, in 1980 got a plurality of the Jewish vote, I think, about 45%. People sort of conflate things in their head. In his post-presidency, Carter became very identified with being very critical of Israel. And it's true, in 1980 he'd had difficult relationships with Menachem Begin, but he brokered the most important peace treaty in Israeli history. He saved a lot of lives. So I don't think people were feeling bad about Carter in 1980 because of Israel. I like to tell people, Jews are like everybody else. You know it's true that a majority of us vote for Democrats, and there are other subsets where, a majority vote for Republican more majority for Democrats. But we vote for the same reasons as everybody else. Our votes will get more enthusiastic for a Democrat on one circumstance, just like everybody else's will, or might get less enthusiastic just like everybody else's will. We're susceptible to the same things. Julie Fishman Rayman: It's really interesting. So at this moment, there's so much Monday morning quarterbacking happening, and I don't want to look too far in the rear view, but I do want to ask you for your take on this question of, would the result have been different had the Vice President selected Shapiro, Governor Shapiro from Pennsylvania, as her running mate? Ron Kampeas: Maybe, it's hard to say. Vice presidents have had such a little impact on nominations. But on the other hand, Pennsylvania was close enough, and Shapiro is popular enough there that perhaps it might have made the difference. She might have had Pennsylvania, and then if she had Pennsylvania, I don't know, she would have gotten to 270. But you know, Nevada and Arizona are still being counted. They might still go in her column. If they do go in her column, although I don't think they will, I think it looks like they're going to go into Trump's column. If Nevada and Arizona go into her column and she missed out on Pennsylvania, you could say that her decision to go with Tim Walz instead of Josh Shapiro was fateful. On the other hand, everybody's a cynic. Nobody actually believes anything anybody says. But I try to get away from that. I try not to be too much of a cynic. And when Josh Shapiro said afterwards that he had second thoughts about taking on VP, because he's like a hugely successful governor so far in Pennsylvania is this is two years into his first term. You know, if I'm Josh Shapiro, I'm thinking about my legacy, and I'm thinking about running for president in the future and two years, just, yeah, I'm not going to make an impact in Pennsylvania in just two years. If I'm the 60% governor who can get Republicans to vote for me in the middle of the state, I'm thinking two terms will make me like, well, you know, get me a statue in some building at one point. There's this whole narrative that there was an antisemitic pushback. It was an antisemitic pushback against Shapiro. It was anti-Israel at times. I really believe it did cross over antisemitism. I'm not sure that that had the effect on the Harris campaign in terms of its decision making. She clicked with Tim Walz. Shapiro wasn't so eager. Shapiro was going to be a co-president. Walz wanted to be a vice president. He made that very clear. He had no intentions of ever running for the presidency. So if you're a Harris, do you want to have a Dan Quayle, or do you want to have a Dick Cheney kind of thing? You know as somebody who's prone to take over, or somebody who's prone to do what needs to be done to be vice president. And obviously she preferred the latter. Julie Fishman Rayman: It's a great analogy. Can we talk for a minute about sort of Jewish representation in Congress where Israel was on the ballot? What are your perceptions there? Ron Kampeas: I think that it might have made a difference in NY-17th, where Mike Lawler defeated Mondair Jones. Mondair Jones was perceived when he first ran into 2020, and he was elected. He was perceived initially as somebody who would be very different from Nita Lowey, who he was replacing because she's a very solid, long time pro-Israel. Julie Fishman Rayman: And an AJC board member. Ron Kampeas: And an AJC board member. He actually declared before she retired, so he was a little bit confrontational with her, which happens, obviously. I don't know if Israel came up in that equation, though. Young progressive people thought he'd be a squadder, but he wasn't. In his two years in Congress, he wasn't a member of the squad, and he went out of his way to align with the pro-Israel community, and this because it was so important in his district. But Lawler, he's been, he's a freshman, but he's been out front. He's been very good at cultivating the Jewish people in his district. And he's not just led on a number of Israel issues, but he's always made sure to do it in a bipartisan way, partnering with Jared Moskowitz in Florida, or Josh got him or in New Jersey, and you know, that might have helped him in the district. It was a close race. He won by a close margin. So I think maybe that was definitely a factor there. I think that one of the group's decision desk that declares winners just declared for Jackie Rosen in Nevada. She's been reelected, according to them, but we'll wait. We'll see if and when AP calls it. But again, a state with a substantial Jewish population, she is, like, one of the premier Democrats. She's Jewish, but she also is very, very upfront about Israel. She co-chairs an Antisemitism Task Force. She has a bill that would designate a domestic antisemitism coordinator. So in such a close race or such close margins with the Jewish community, that's actually much larger than the margin that might have helped put her over the top. On the other side, you know, you have Michigan, which might have also, like we looked at Pennsylvania and Josh Shapiro. Michigan also might have cost Kamala Harris the presidency because of her support for Israel, because, you know, President Trump managed to peel away Muslim American and Arab American voters in in Michigan, in a kind of a weird slight of hand, because he said that he would be more pro their issue than Kamala Harris was, even though he's more pro-Netanyahu, definitely than Kamala Harris is. But also, there were third party voters, people who voted for Jill Stein. Julie Fishman Rayman: Pretty significant numbers for Jill Stein, from Michigan. Ron Kampeas: Pretty significant numbers for Jill Stein. But Elissa Slotkin got over the top. Very pro-Israel, centrist Democrat, Jewish. Very much a foreign policy, you know, specialist. She came out of the CIA and the Defense Department. Also very partisan. She was meeting with red constituents, like veterans, and she was doing a good job of it. She had that appeal. And I think that's why she ran for Senate. I think that's where Democrats are excited to have her run for Senate. And then October 7 happened, and she had to navigate a very difficult situation in her state, which has a substantial Jewish community, has an even bigger Muslim American and Arab American community. She had meetings with both leaders. She put out sensitive statements after the meetings. I think one of the most interesting sort of developments with her is that Rashida Tlaib, the Palestinian American Congresswoman attacked Dana Nessel for prosecuting people who were violent, were allegedly violent at protests. She put out a statement that, without saying it was because Dana Nessel was Jewish, she was said that Dana Nessel had other sort of considerations when she brought these prosecutions. Dana Nessel outright accused her of antisemitism, and then Rashida Tlaib was the subject of a lot of Islamophobic, anti-Palestinian vitriol. And it was interesting because there were two letters that went out at the time from Congress members. One condemning anything that insinuated that Dana Nessel had dual loyalties, or anything like that, and one condemning the anti-Islamic rhetoric that Rashida Tlaib faced, and the only person who signed both letters was Alyssa Slotkin. I thought that was interesting. Julie Fishman Rayman: I want to turn a little bit if we can, to the expectations for the next administration, even for the next Congress. When we last spoke, right after the Republican National Convention, JD Vance had been selected as the running mate, and you and I, we talked about what that means for a Trump foreign policy in the next administration. Will it go in a more isolationist direction, more aligning with JD Vance's worldview? What do you think now and what might we expect? Ron Kampeas: That's still a potential for sure, there are names being rooted about for Secretary of State. One of them is Rick Grinnell, who's completely a Trumpist, who will do what he wants, his former Acting CIA director. And the other is Marco Rubio, gave one of the best speeches at the convention, I thought, and who is very close to the pro-Israel community, who's an internationalist, but who has tailored his rhetoric to be more, to make sure he doesn't antagonize Donald Trump. He was, you know, he came close to being the vice presidential pick himself. I mean, if Marco Rubio becomes Secretary of State, I think that's a good sign for internationalists. I mean, you know, Israel has kind of a buffer, because the Republican Party is very pro-Israel. And there are people like JD Vance who say, you know, Israel is the exception when it comes to what I think about pulling the United States back from the world, even though he says it's not so much the exception. And then there are people like Marco Rubio who are internationalists. Does Marco Rubio get to run an independent foreign policy? That would be very good news, I think, for internationalists, if Donald Trump doesn't get in his way. But I don't know if that that happens. There's a view of pro-Israelism that says internationalism is necessary. I always like to say when a AIPAC used to have its policy conferences, and it's a shame it doesn't any more, they would have a little brief talk before on Tuesday morning, before going up to the Hill, they would have, like, some prominent Senator come out and give a rah rah speech. And then like, three officials would come out on the stage, Howard Core, the late Richard Fishman, and Esther Kurz. And Esther Kurz had handled congressional relations, and they would talk about the three items they were bringing up the Hill, usually two laws in a letter or a resolution or something like that. And she would always say, and this was like the one moment like they would sort of reveal this. They'd be very candid about this. You have to push not for assistance for Israel, but foreign assistance generally, because there is no such thing as sort of singling out Israel and saying, Okay, we're going to take care of Israel, but nobody else in the world. That it's all interconnected. And it's such a true thing now, because you can say, you know, let's just cut off Ukraine. But if you're cut off Ukraine, you're bolstering Putin. If you're bolstering Putin, you're bolstering somebody who has a substantial and military alliance with Iran. If you're bolstering Iran, that is not good for Israel. And it's kind of circuitous to get there, but it's also a very substantive point. I think those are the things the pro-Israel community is going to be looking at with genuine concern. Julie Fishman Rayman: Indeed, it's all about sort of the strength of the American global leadership regime. And when you start to whittle away at one, the overall package ends up being weaker. Speaking of Israel, I can't speak to you this week and not ask you about the news out of Israel, about Netanyahu firing the Defense Secretary Gallant and what that means. And also, if we can extrapolate, if we can prognosticate what might happen vis a vis Israel in this lame duck session, while we still have Biden as president, but moving through the transition towards a future Trump administration. Ron Kampeas: Yeah, you know, there a lot of Israelis are actually worried about that. Like, Oh, Biden's gonna take his frustrations out on Bibi in the lame duck. Doesn't have anything stopping him. I don't think that's going to happen. I think what's interesting is, like, you had a couple of instances in American history where a lame duck president used the fact that he didn't care, you know, what anybody thought of him, to push something through. In 1988 Ronald Reagan recognized the PLO because it's something George H. W. Bush wanted him to do. George H. W. Bush wanted to push like more Israel Palestinian peace. He did with the Madrid Conference, but he didn't want to be the one to invite the PLO into the room, so he got Ronald Reagan to do it in his last two months in office. In 2016 Barack Obama allowed through a Security Council resolution that condemned the settlements. The United States didn't vote for it, but it also didn't veto it. That really kind of shook Israel up. But what was interesting. I've done the reporting on this. When he was taking advice, Should I, should we vote for the resolution? Should we veto it, or should we just allow it through? There were people voicing opinions on all sides. Joe Biden and Jack Lew, who was then the Treasury Secretary, is now the ambassador to Israel, both said, veto it. Don't let it through. Don't let it through because, partly because it's going to really upset our Jewish supporters, if you let it through. You're not going to be president anymore, but somebody in the room is going to probably try and be president. I think that Joe Biden still has that sense of responsibility. I could be wrong. You know, four years or a year of like, from his perspective, being very strongly supportive of Israel and not getting anything back from Bibi, from his perspective, might have changed his mind. Something might occur now. But the question is, like, you can tell Israel if they hit anything, but if they hit anything, if they elevate it at all, they're going to need US assistance. And Trump hasn't said he's going to give that. Biden has. Biden's proven he's going to give it. So you've got two months of a president who will, who will back up Israel with American might, and then you have a president who has isolationist tendencies and who doesn't want to get involved with wars for another four years. Julie Fishman Rayman: Is there anything else that you're hearing, perhaps, from the Israeli perspective, about Gallant's departure, and what that signals? Ron Kampeas: I think that Netanyahu, you know, he's just trying to keep his government intact. Gallant is very vocal in opposing or in supporting drafting the ultra orthodox, the Haredi orthodox. Netanyahu's government relies on Haredi orthodox parties. So there's that. He's also facing a kind of spy scandal from his own circle. Just a weird, weird story. Somebody who's in his circle is alleged to have tried to help Netanyahu politically by leaking highly classified documents and altering them as well to foreign news outlets. The allegation is that whatever the guy's motivation was, he's actually put Israel at risk. So Netanyahu is suddenly in a position of facing allegations that he put Israel at risk. Now, he's faced a lot of scandals in his time. Israelis have a high level of tolerance for people who are alleged to have skimmed off the top, alleged to have helped themselves, and that's what the scandals are about. They have no tolerance for anybody who puts Israel's security at risk. So if this comes back to Netanyahu, that could be more damage than than any other scandal that he's endured so far. And so notably, I think, you know, when he was firing Gallant, he said he accused Gallant of leaking information. Although, I mean, what he seemed to be referring to was Gallant didn't leak anything. Gallant openly said that he disagreed with Netanyahu on certain tactics, and that, you know Netanyahu is casting is putting Israel at risk. Which is not to say that Netanyahu is necessarily going to be implicated by the scandal, but it's certainly not of a piece with leaking, actually classified documents that reveal methods and sources that can put Israel's intelligence gathering methods at risk. Julie Fishman Rayman: As always, there's so much more to the story, right? Ron Kampeas: Yeah, yeah. There always is. Julie Fishman Rayman: Ron, we could probably talk for a very long time about the American elections and what's going on in Israel and the degrees of various scandals and how populations will take them, and what the future of our country in the region looks like. But I know that you're very busy, especially this week, and I just want to say how grateful we are that you always make time for AJC and for People of the Pod. Ron Kampeas: Of course.
Oct 31, 2024
The Jewish Vote in Pennsylvania: What You Need to Know
As election day nears, Republican nominee and former President Donald Trump and Democratic nominee, Vice President Kamala Harris, are zeroing in on Pennsylvania, which has the largest Jewish community among the battleground states. Aaron Troodler, editor of the Philadelphia Jewish Exponent, breaks down what's influencing Jewish voter sentiment in Pennsylvania, from economic and social issues to the U.S.-Israel relationship amid rising antisemitism and Israel's defensive war against Iran-backed Hamas and Hezbollah. AJC is a 501(c)3 not-for-profit organization. AJC neither supports nor opposes candidates for elective office. The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : Sinwar Eliminated: What Does This Mean for the 101 Hostages Still Held by Hamas? From Doña Gracia to Deborah Lipstadt: What Iconic Jewish Women Can Teach Us Today The Nova Music Festival Survivor Saved by an 88-Year-Old Holocaust Survivor Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Aaron Troodler: Manya Brachear Pashman: It's the home stretch leading up to election day for the presidential campaigns of Republican nominee and former President Donald Trump and Democratic nominee, Vice President Kamala Harris. And both campaigns see Jewish voters in seven swing states as key to a potential victory. These seven swing states are swarming with canvassers, knocking on doors, handing out literature and engaging undecided voters in critical conversations. Joining us for a critical conversation about the Jewish vote in one of those swing states is Aaron Troodler, editor of The Philadelphia Exponent and The Washington Jewish Week. Aaron, welcome to People of the Pod. Aaron Troodler: Thank you, Manya, it's a pleasure to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: Aaron, you live in the Philadelphia area and have your finger on the political pulse there. Everyone's talking about the impact of Pennsylvania's voters. What makes Pennsylvania so key? Aaron Troodler: So I think they're going to have a very significant influence. There are a lot of people saying these days that the path to the presidency runs through Pennsylvania, and I do think that there's a degree of truth to that. But in fact, I believe that the path to the presidency may very well run through the Jewish community, not just in Pennsylvania, but more specifically, in the greater Philadelphia area. Manya Brachear Pashman: How much of an influence are they going to have in this election? Aaron Troodler: Ballpark, the Jewish population in Pennsylvania is estimated somewhere between 400,000, a little bit north of that figure. Of that 400,000 and change, it's estimated that approximately 300,000 or so are of voting age. And when you take into account that in 2020, Joe Biden beat then-President Donald Trump only by about 80,000 votes cast in Pennsylvania. And then, if you look back to 2016, Donald Trump won by only about 44,000 votes. We're talking about very slim margins here, and the outsized influence of the greater Jewish community is really going to shine through in this election. Manya Brachear Pashman: Now, are you talking about Philadelphia city proper, or suburban Philadelphia? Is there a difference in how the two vote? Aaron Troodler: Great question, Manya, focusing primarily on suburban Pennsylvania. You have, for example, in 2019, the Jewish Federation of Greater Philadelphia–and I know this goes back five years, but it's the most recent data we have–did a population study, a community profile. And they looked at basically five counties, give or take, including Philadelphia County, which includes the city, but also 4 suburban counties: Bucks, Chester, Delaware, and Montgomery. And approximately at that point– again, dating back five years–but there are approximately 195,000 Jewish households at the time. And that number has grown over the past several years. I won't be able to really quantify it, because we don't have the actual data, but it's a significant number. And you know, when you take into account that Pennsylvania's Fourth Congressional District, which is represented by Madeleine Dean, it's mostly Montgomery County, which is suburban Philadelphia County. It's got the largest Jewish population in the state, in terms of congressional districts. It's very significant. And then the second largest is Pennsylvania's first congressional district, which is represented by Brian Fitzpatrick. And again, there are about 40,000 Jewish adults in that district. 54,000 or so, give or take, in the Montgomery County area. We're talking about big numbers. And I think what's happening now is just by virtue of where we are as a Jewish community, whether it be antisemitism, and being very cognizant of the frightening rise of antisemitism, whether it be on college campuses, city streets, social media platforms. People are very mindful of that, and rightfully so. And then when you throw into the equation the current situation involving Israel and the reverberations felt around the world just resulting from the Israel-Hamas war post-October 7, the Jewish community, I think, is mobilized now, perhaps even more than ever, to make their voices heard. And to do that, they would be going and voting and making their voices heard through their choices in the election. Manya Brachear Pashman: You just mentioned the rise of antisemitism. What issues are guiding the Jewish vote? Because I know in years past, concerns about the economy have really steered the Jewish vote. Is that still true in the 2024 election? Aaron Troodler: It's an interesting point you raise Manya, because I think historically, the Jewish community, and I'm over-generalizing by saying the Jewish community. Obviously, it's comprised of several denominations who historically have had potentially different political leanings. But I think a lot of the domestic issues, whether it be the economy, reproductive rights, taxes, immigration, I mean, I think all these things are on people's radar screens. However, I think there is a particular emphasis now on Israel. I think that is front and center. I know historically in the Orthodox community, that has been the case. I think that has carried over to the conservative community, the reform community, other communities. And I think the survival of the Jewish state and the health and strength of the US-Israel relationship is paramount to Jewish voters. Not to the exclusion of the other issues that we're talking about on the domestic front. But I think people are viewing this election through a different lens, just by virtue of the circumstances that we're discussing, that our brethren in Israel are facing. And I think that is really informing people's votes, whether it be for Kamala Harris or Donald Trump. And that's a whole other conversation we could have, but I think that that really is front and center, maybe not the sole factor, but most certainly a primary factor. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how does that translate? I mean, many believe that the Biden administration has been quite supportive of Israel. Others believe it has not been supportive enough. Aaron Troodler: Right. Well, I think the answer depends on who you ask. I think there is a very strong case to be made that the Biden administration and Kamala Harris was obviously a pivotal part of that administration, has been supportive of Israel, and I think there's a lot of conversation that centers around President Biden's response and reaction to October 7, particularly in the immediate aftermath of the Hamas attacks, and how he handled it at that time. I think on the other side of the equation you have people pointing to Donald Trump's presidency and saying, Hey, he perhaps might be the best president that the Jewish community, slash Israel, has ever had, just by virtue of some of the things he did while he was in office. I think this is all leading to a very spirited debate, a very robust conversation about people who feel very passionate, you know, A or B. And I don't know that there's all that much consensus. I think people that are supportive of Kamala Harris are adamant and positive that she will be best for Israel. And conversely, people who are on the other side of the coin and feel that Donald Trump is their chosen candidate are making the same choice for Donald Trump. So I don't know that there's a particular answer to that question, but I do firmly believe that that has become a defining issue for the Jewish community. And it's just remarkable to me that people, perhaps I'm over generalizing, you know, 50% of the population is saying, you know, she is absolutely, unquestionably, the best friend that we've had and will have, and then you have the same people saying similar things about Donald Trump. So it's hard to quantify, but I do think that it has really, really become pervasive, meaning the notion of Israel and the central role that is playing this election, it's absolutely pivotal. And people are, I think, are really making their choices on who to support based on their assessment of those issues. Manya Brachear Pashman: Just to clarify, you said the same people are saying that about Trump. You meant the same percentage of people, right? Aaron Troddler: Correct, give or take. The Jewish Democratic Council of America (JDCA) has done a poll, and they found, you know, over 70% of the Jewish community is supporting Kamala Harris, as opposed to 20-25% for Donald Trump. You have polls, you have data from the Republican Jewish Coalition that shows that half the voters are supporting Donald Trump. These figures are bouncing around. I mean, obviously we've seen in the past polls definitely have value to them, but I think the real test, the real result, won't be really known until election day. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned denominational differences, but what about generational differences? Are younger Jewish voters leaning toward a particular candidate, or toward particular issues that are different than the ones that concern older voters? Aaron Troodler: Great question. I'm personally not seeing it. I have young adult children, let's call them, who are invested in terms of who they're voting for. You have people that I encounter that are on the opposite end of the spectrum, perhaps in their golden years, who are very opinionated in terms of who they want to vote for. I think what's, you know, an interesting thing here, and again, it's not really, I don't know if it's quantifiable by denomination. But I think another thing that is important to mention, Manya, is, you still have, I know we're only several days prior to election day. There's still a healthy amount of people that are, I think, truly undecided. I think a lot of people, particularly in the Jewish community, that I've spoken with and encountered, are really torn. In Pennsylvania we are getting an absolute barrage of campaign mail, TV ads, canvassers knocking on doors. There's a lot of that, particularly in the Philadelphia suburbs, and a good amount of those, again, I know they're targeting the Jewish community, focus on Israel and antisemitism. And you look at a piece of mail for one particular candidate, and it makes it sound like the other one is the devil. And then flip the coin and it's the opposite for the other candidate. I think people are really trying to cut through the noise and get to the heart of the matter and make their own assessment. You can't really focus on the demographics in terms of age and whatnot. I think it's an across the board issue that people are focusing on. The people who are pro-Trump are pro-Trump, the people who are pro-Harris are pro-Harris, and then you have this whole sliver in the middle that I think are truly undecided. Even with the election looming large. Manya Brachear Pashman: Is that just because they're getting conflicting messages, and they're just easily swayed one way or the other, and therefore they're torn, or are they waiting for something? Are they waiting for some deciding factor to reveal itself? Aaron Troodler: I'm actually not sure if it's either. I don't know that they're waiting for something per se, because if they are, that quote, unquote thing may never come and they have to make a determination. I do feel that there are some in the Jewish community, and I think the Harris campaign has acknowledged this in events that they've had featuring the Second Gentleman Doug Emhoff, who obviously is Jewish, who would become the first Jewish first spouse. But there's been an acknowledgement by renowned and well known surrogates of the Harris campaign that there are some reservations in the Jewish community. They're not giving credence to those hesitations that people might have, in terms of Kamala Harris and her position on Israel, or what that might look like. They're just acknowledging that it's there, and they recognize that they have to speak to that issue. I think on the flip side of the coin, you have people who are looking at Donald Trump, and say, oh he moved the embassy to Jerusalem, and he recognized Israel's sovereignty over the Golan Heights, and he said that the settlements in the West Bank are not illegal, you know, per se under international law. And people are looking at those and they say, Wow, he did some great stuff. And then those same people may look at Donald Trump as a candidate and say, Is he the best person for our country? And that's a determination that they're trying to make, and I think are having a lot of trouble doing so just because of the different packed factors that are kind of pulling and tugging at them in different directions. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to go back to the Israel-Hamas war. What about that war are people thinking about when it comes to supporting a candidate? In other words, are they looking at the 101 hostages that are still in captivity, and what the candidates are saying, or how they're treating that situation? Or are they looking at humanitarian aid issues when it comes to Gaza? What are they looking at? Aaron Troodler: Manya, I think they're looking at all of that, and I think that's all factoring into the equation and the decision making process. And this is where I believe the vice president might be at a little bit of a disadvantage, because she's a prominent member of the current administration, whereas Donald Trump is no longer the president at the moment. And so they're looking at actions of the administration and parsing each move and each statement. And whether or not that moves the needle, I don't know. But I do think that she has a harder hurdle to overcome vis a vis those issues, because people are really looking at statements that she's made, whether it be about the humanitarian aid that you referred to reaching Gaza and the need for that to happen. People are looking to statements that the President, perhaps, has made relative to Israel and their response. And on and off over the past year, there have been a number of times when, reportedly, the US has cautioned Israel or advised Israel not to proceed down a certain path. There's been talk about weapon shipments and delays and stuff of that nature. And I think all of those are issues that Kamala Harris has to contend with, just by virtue of association. And I think there's a lot of folks in the community saying, you know, what would a Harris presidency look like? You know, we know what a Trump presidency looks like vis a vis Israel. What would the Harris presidency look like? I will say, you know, the President, the Vice President, has seemingly been very supportive of Israel on the issue of antisemitism. Obviously, the National Strategy to Counter Antisemitism that was unveiled by this current administration was heralded by people as a very necessary move. And I know, obviously the Second Gentleman Doug Emhoff, was intimately involved in that as well. All those things, I think, are factoring into people's decision making process. It's a very complicated decision for many people. And I think that's really something that the Vice President is, I think trying to work through. How does she carve out her own path, and what does that path look like? Manya Brachear Pashman: How influential is Pennsylvania's Jewish Governor Josh Shapiro in this race? Aaron Troodler: So the saga of Josh Shapiro is obviously well known at this point. He's a governor who wears his Judaism on his sleeve, very proud of it. Will often quote passages relating to Jewish thought. He talks openly about his Shabbat observances and celebrations with his family. And obviously he was seemingly, reportedly, on the cusp of the vice presidency. I think what's interesting about Josh Shapiro, aside from his religion, is that he's universally well liked, let's call it. I think his appeal throughout Pennsylvania, it does transcend party lines in many places, just by virtue of his approach to government, his commitment to bipartisanship, and how he's been as a governor. I think there's a lot of appeal. I think the fact that he's become a primary surrogate for the Harris campaign across the country, quite frankly, but more particularly in Pennsylvania. I think people look at that, I think there's certainly a segment of the population that was definitely holding out hope that he might end up as the Vice President of the United States. But I think that you know his willingness to go out on the trail and to and to stump for Kamala Harris and to try and speak about her bona fides as a candidate, and her strengths and what she could do for the country and her vision. I think people are taking note of that, particularly the Jewish community. Whether that will sway everybody to a particular candidate, I don't know. But I definitely do know that people are taking notice of it because people are speaking about it in a favorable way. Manya Brachear Pashman: What is he saying when he stumps for her? What is he saying to get out all those voters? Aaron Troodler: Well, he's trying to paint her as basically, not just the best choice, but the only choice. Obviously, he, I guess it's no secret. I don't think he's really a fan of Donald Trump, and I don't think he pulls any punches when it comes to that regard. But I think in Josh Shapiro's mind, the governor really firmly believes that the Vice President is the best person to lead this country forward. And I think when you when you factor in all the issues, for example, we talked about domestic issues at the outset of the conversation, when you look at all those issues, and you don't only make it about Israel, there's a thought that perhaps Kamala Harris is that person, and that's the message that Josh Shapiro's trying to convey. You know, obviously Trump supporters look at that and shake their heads, because they don't buy into that. But I think in terms of the case that he's trying to make to the voters, particularly to Jewish voters, it is a compelling case, because he's a compelling messenger. Manya Brachear Pashman: You talked about canvassers being all over Pennsylvania, especially the greater Philadelphia area. Can you paint a scene for our listeners? I mean, do you see teams of people walking the streets? Have people knocked on your doors, rung your doorbell? Tell me what kind of things you're seeing. What you see day to day in Greater Philadelphia. Aaron Troodler: I think I can probably measure the amount of canvassers by the number of door hangers that have been left on my front door over the past several months. There's a huge effort. You have people coming from different states. All descending on Pennsylvania. And there is a particular emphasis on the Jewish community, particularly in suburban Philadelphia. I was covering an event for the Philadelphia Jewish Exponent a number of weeks ago, where Doug Emhoff came and was the featured speaker at a Get Out The Jewish [Vote] event in a Philadelphia suburb. Ben Stiller was there, the well known actor. Senator Ben Cardin, who is the chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, came up from Maryland. Debbie Wasserman Schultz, the congresswoman from Florida, was there. It's a full blown effort on the part of both campaigns to try and cultivate the Jewish vote, try to generate more Jewish support. Both sides of the coin. I think you know, the Republican Jewish Coalition has put a very significant emphasis on this election, whether it be through ads, whether it be through surrogates, whether it be through the canvassers, they're everywhere. And I think I think it's good. I think it's not only does it underscore the importance of Philadelphia's Jewish community in in an election that literally has national implications, but it enables people. When somebody knocks on your door, if you answer the door, you can engage in a dialogue. Obviously they are slanted to a particular candidate, whether it be Kamala Harris or Donald Trump, and that's fine, but it gives voters who perhaps are still undecided at this point the opportunity to have a conversation with the folks who are knocking on their doors about the issues that are important to them. But I think just by virtue of the sheer number of canvassers who have been kind of traversing our neighborhoods over the past several weeks, I think it's indicative of the outsized role that Philadelphia's Jewish community's playing in the presidential election. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned Governor Shapiro is kind of a surrogate for the Harris-Walz campaign. Does the Trump campaign have a surrogate in Pennsylvania or in the Philadelphia area? Aaron Troodler: So they have people who are coming around. There's Peter Deutsch, who's a former congressman from Florida, who's a democratic congressman from Florida, came up to not just Pennsylvania, but the greater Philadelphia area, in particular, to spend several weeks. I know he was here over the Sukkot holiday. You know, they are bringing folks in because they're trying to make the case to people that look, you know, when it comes to the issues that you, the Jewish community, cares about, Donald Trump's your man. And they are doing that, and they're trying to do it in a way that will resonate with people. And we mentioned some high profile people on the Democratic side. You know there are people on the Republican side, whether it's Congressman Deutsch, other people are coming in. The RJC has been very active in the community recently. And in addition to official campaign surrogates, you know you have conversations happening in synagogues, you know, community institutions, where regular folks are conversing with one another. So each campaign, in addition to the, let's call them the official surrogates, you have these armies of unofficial surrogates who are talking with one another and trying to convince their peers to vote for a particular candidate. And with all the holidays that we just had on the Jewish calendar, spent a lot of time in shul, in the synagogue, and there's a lot of folks talking about the presidential election. And I'll tell you, quite frankly, there's no consensus. There are people that are absolutely pro-Trump, and they're people that are absolutely pro-Harris. And I think those folks are trying to impart to what's called the undecided people, their feelings about the campaign and their particular candidates. Manya Brachear Pashman: I do want to clarify for listeners, Peter Deutsch should not be confused with Ted Deutch, AJC CEO, who has not been in Pennsylvania canvassing as a surrogate for either candidate. It's a different Deutsch. But what about rabbis? How involved are rabbis getting into this campaign? How involved have they been in these conversations? Aaron Troodler: So it's interesting. Whenever you broach the topic of politics from the pulpit, it becomes very tricky. Obviously, there's 501(c)(3) status considerations and stuff of that nature that I think rabbis are always mindful of. So what they talk about from the pulpit and how they talk about it is usually done very carefully and deliberately. That all being said, there's no question that maybe, behind the scenes, let's call it, rabbis, have very distinct opinions about this. How that will sway congregants in their respective congregations, it's hard to know. But I do think, I think because rabbis have spent so much time over the past year, post-October 7, talking about these issues of Israel's security and survival and the things that we need to do to help Israel, this is just another step in that process. Obviously, the next President of the United States is going to play a pivotal role in Israel's future and Israel's security. The relationship between the US and Israel is paramount, and Israel depends heavily on the United States, whether it be for the military aid, strategic aid and cooperation. And on the other side of the coin, the United States relies on Israel for many national and security considerations. But I think because rabbis have spent so much time talking about that stuff, it's top of mind for everybody. It's at the forefront of all of our minds. And whether or not they get up from the pulpit and endorse a particular candidate, I'm not sure that's going to happen in most situations, but there's no question that rabbis are trying to convey to their congregants the importance of ensuring that Israel has a strong friend and ally in the White House. Manya Brachear Pashman: Aaron, thank you so much for joining us and shedding a little light on what's going on in your neck of the woods. Aaron Troodler: Of course Manya, thank you so much for having me. It was a pleasure chatting with you. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for a conversation with AJC Jerusalem Director Lt. Col. Avital Leibovich, and AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer, Jason Isaacson, about the Israeli Defense Force's elimination of Yahya Sinwar, the architect of the October 7 terror attacks.
Oct 23, 2024
Sinwar Eliminated: What Does This Mean for the 101 Hostages Still Held by Hamas?
How will the killing of Hamas leader Yahya Sinwar affect Israel's security and regional stability? What are the implications for the 101 hostages still held by Hamas? Join us as AJC Jerusalem Director Lt. Col. (res.) Avital Leibovich and AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson discuss the Israeli Defense Forces' recent elimination of the terror leader responsible for orchestrating the October 7 attacks and thousands of deaths. They'll break down the impact of the unfolding situation and what comes next. Watch – Israel Update: Analyzing the Impact of Yahya Sinwar's Death - AJC Advocacy Anywhere Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : From Doña Gracia to Deborah Lipstadt: What Iconic Jewish Women Can Teach Us Today The Nova Music Festival Survivor Saved by an 88-Year-Old Holocaust Survivor Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Conversation with Jason Isaacson and Avital Leibovich: Manya Brachear Pashman: Last week, Israeli Defense Forces killed Hamas leader Yahya Sinwar, the architect of the October 7 terror attacks. His death comes two months after the murder of six hostages who he had been using as his human shields. What comes next? How will Sinwar's death impact the dynamics within Hamas and the broader conflict between Israel and other Iran-backed proxies? What are the potential implications for Israel's security and regional stability? And what does this mean for the 101 hostages still being held by Hamas? For answers to those pressing questions, AJC welcomed its Jerusalem director, Lt. Colonel Avital Leibovich and Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson, for an in-depth analysis of the unfolding situation. Here's a portion of that conversation. Jason Isaacson: Thanks very much. Before we begin our discussion, Avital, please allow me to again express to you, my and all our AJC colleagues and supporters' gratitude for your consistent availability throughout this difficult, dangerous period, to brief the AJC family on the challenges that Israel faces, the trauma that Israel suffered on October 7, on and onward, and the remarkable resilience of the people of Israel in the face of terrorism. Allow me also to wish you and your family and our AJC colleagues in Jerusalem a healthy and, let's hope, a more peaceful New Year. We are meeting now one week after a major development, perhaps even a turning point in Israel's necessary war against Hamas, the killing of the terrorist organization's leader, the murderous mastermind of October 7, Yahya Sinwar by the IDF in Rafah in southern Gaza. I want to hear your thoughts on the ramifications of that successful operation, which has been praised by the US and other world leaders. But first, let me ask you two questions. First, how was the IDF able to finally track down this most-wanted war criminal. And second, how did Sinwar's elimination figure in Israel's set of priority objectives for the self defensive campaign that it has been conducting in Gaza? Avital Leibovich: Thank you, Jason, for your kind opening words, and it's always good to be with you here on another what I think will be an interesting session for our listeners. So it was the day of October 16, few days ago, IDF troops, actually reserve units, were working in a neighborhood in Rafah called El Sultan neighborhood. This is approximately one kilometer from Israel, so it's a relatively short distance, they have identified. These soldiers have identified three suspicious figures, between moving from one area to another, between buildings. And they fired towards the suspects, and then the group split into two. Two of them stayed in one area and another one stayed in another building. And in order to make sure that buildings are not booby trapped, so the forces are not endangered, what the IDF often does, it sends a drone with a camera inside the building, searching and checking out to see who is exactly there, and then they saw on a couch in the corner of a living room. This was, by the way, a very fancy villa in this neighborhood. They saw a figure sitting there, with his head covered, with his face covered, and armed with a weapon, with grenades, and they fired. They understood that this is a terrorist, and they fired towards that person. Because, again, there was danger of the amount of explosives that were placed in this specific house, it took only 24 hours until the forces return and then search the house. When they got to this terrorist sitting on the arm chair, they suddenly realized that it looked very similar to Sinwar. But in order to check, you know whether it was Sinwar or not, they had to take a DNA sample from one of his fingers. And Sinwar has been in Israeli prisons for many years, and therefore his DNA samples is already there. So it took a few more hours, and then it was identified, finally, as Yahya Sinwar. And of course, it was a big press briefing announcement by the Prime Minister, by the army and so on. What else was found on his body was the following: a small gun, a big rifle, flak jacket filled with different kinds of grenades, 40,000 shekels, which is equivalent of something like $12,000 in cash, a passport--of someone else--an UNWRA certificate of another person. Another identity. And that's more or less what was found. The two others that split from him and went to another house were actually his bodyguards. Later on, when the army searched deeper, it reached a conclusion that the tunnel that six hostages were held in and were murdered viciously by Hamas just six weeks before, were just a few 100 meters from where Sinwar was, and they also found out that actually they served as human shields for Sinwar until he escaped. So basically he was running from one place to another until he was found that day, 16 of October in that building. Jason Isaacson: How high on the list of Israel's military objectives in Gaza was the elimination of Sinwar? Avital Leibovich: So, yeah, you can imagine that, since he's the number one terrorist of Hamas, and he is the mind behind October 7, obviously he was ranked very high on the list of Most Wanted. I can say that his brother, Muhammad, is still on that list. And Israel has announced already that it will hunt Muhammad as well. And I think that there was a ray of light on October 17. It was exactly when it was announced officially that Sinwar was eliminated. I think every Israeli home was as much as we could under the circumstances express joy that Sinwarwas gone. Jason Isaacson: You could imagine supporters of Israel around the world and our country, but all over, I think, shared that sentiment as well. But let's talk about the ramifications now of Sinwar's death for Hamas and also for the Islamic Republic of Iran, which has provided money, weapons training guidance to Hamas. I have a few related questions. First, Hamas has already put forward the claim that its fight continues, that it isn't relinquishing its hold on Gaza. Can Hamas still legitimately make that claim, that it is in control in Gaza? Avital Leibovich: So I think that if we're looking at, you know, the comments from all over the world regarding primarily the terror groups in Iran, we see a lot of support for the way of Hamas.. Sinwar was actually painted as a shahid, a martyr, as someone who fought until the very last minute, who act in a very brave way. In other words, it's some kind of glorification for Sinwar, but also for Hamas, in another way. I have to say that even the PLO, the Executive Committee of the PLO actually offered condolences for the death of Sinwar, which was also quite disturbing, I have to say. And Abu Mazen's party Fatah, one of the members of the Fatah, the guy by the name of Abbas Zaki, said that Sinwar has chosen, and I'm quoting, "An exit worthy of his heroism and the heroism of his people." So that's the mood in the Palestinian Street, and that's the mood among the other Arab terror groups, Muslim terror groups, extremists in Iran, in Hezbollah and other places. So the question is, what are now Israel's immediate goals in Gaza following Sinwar's death. So Israel has been concentrating in one main area, and this is an area very close to the envelope of Gaza. It's what we call northern part of Gaza, primarily an area called Jabalia. Jabalia is a place that, according to the Israeli intelligence, unfortunately, there has been a big crowding of Hamas terrorists who are taking shelters in schools or in local civilian facilities where civilians are. So Israel has been trying to encourage the population to go out of this part of Gaza, northern Gaza. It has been doing so by leaflets, by phone calls, by messages on their phones and so on. The problem was, the challenge was with this situation, that Hamas prohibited the population of leaving. But when Sinwar died, this has changed, and we saw two interesting things in the Palestinian Street in Gaza. Number one, people have started to move from the northern part of Gaza. Actually, 20,000 people already relocated from that area. We saw 150 Hamas terrorists turn themselves in. But we also saw, Jason, another thing which we have not seen in a long time. And these are multitudes of Gazans which are not being afraid to speak to the camera with their faces totally uncovered, exposed and cursing Hamas and cursing Sinwar and wanting a better future for themselves. So this is actually, this phenomenon is actually growing more and more. So while Israel is working in Jabalia, there's a still part of the army which is working in Rafah, in the Rafah area, Tel Sultan is one of the neighborhoods, as we mentioned before. So it's still very tactical. There are still a lot of rockets that are flowing in from from Gaza. We're not at the end, at this point of time. And if you'd like, we can dig into the numbers of you know, the achievements that Israel has in Gaza. Jason Isaacson: Yeah, stay on this for a second. This is fascinating. I mean, it sounds like what you're sayingis that the kind of the culture of fear that Hamas has used to basically make it impossible for Palestinians to think of an alternative form of governance or an alternative relationship with Israel, that culture is at least been been damaged by the death of Sinwar, not eliminated, probably, but certainly weakened, which does give you some hope that there can be a day after in which there's a very different governing structure, a very different mentality in that exists in Gaza. Avital Leibovich: About the whole part, I'm not so sure. I have to say I want to be very hopeful, but we're not there yet. And I'll tell you why. Jason Isaacson: Long term, long term. Avital Leibovich: Long term, for sure, I'll tell you, but I want to be more concise in my answer, because you know, one of the things I'm sure people are asking themselves, is: is Sinwar replaceable? So I want to share with you six figures that are the potential list for replacing Sinwar. Number one is Khaled Mashal, is a well known personality. He's currently the head of what we call the external Hamas leadership. As you know, Hamas has two other countries, which they are based in. Qatar in Turkey. He served also as the predecessor of Sinwar, and he lives in Qatar. That's number one. Number two, Musa Abu Mazug. It's another known figure. He was in Sinwar's position a long time ago. He lives in Qatar as well. Then we have Muhammad Al-wish. He is the head of the Hamas Shura Council. He's considered, actually a shadow figure, and does not appear in public too much, but he deals with Hamas policy, and he lives in Qatar. He's known for his connections with the Iranians. The next person is Khalil al Haya. He is the deputy head of the political bureau of Hamas. Actually, he is the deputy of Sinwar. I would say he's more kind of a gray kind of figure. He lives in Qatar. He also has some involvement on ceasefire and negotiation talks, release of the hostages. And then we have Muhammad Nazal, another member of the Hamas political bureau, one of the most prominent spokespeople for the Hamas terror group. And the last one is Zaher Jabarin, member of the Hamas political bureau since 2021 and he's also in charge of the Judea Samaria area, or the West Bank, and he lives in Turkey. So these are the potential replacements for Sinwar. And the question here really remains, who will take the lead, whether it will be another figure from Gaza, or will it be an external figure? And of course, each of the options has its own consequences. So if we're looking at Qatari based Hamas leaders, which have which are more prone to pressure from the US or from other countries. That's one reason to be optimistic vis a vis maybe a future deal with the hostages. But if we're looking at someone from Gaza, or someone from the West Bank will come to Gaza, then I think we're looking at more of the same kind of scenario. So this is where we are in terms of the current situation in Hamas and Hamas leadership. Let's see what conclusion they will reach. Jason Isaacson: Sinwar's brother is not considered in line for promotion? Avital Leibovich: So you know, the opinions here vary. There are those who say that since he's hunted by Israel, then he will not have the capability to deal with it. There are others that say that he is a natural replacement. But I gave you the list on purpose so you can understand that the options are not just one or two people, but more than that. Jason Isaacson: So let's talk about what the implications of Sinwar's death are for the fate of the hostages. It's been over a year. There are 101 still held, many of them no longer alive. We understand a desperate situation in brutal captivity held by Hamas. What AJC was hearing before the death of Sinwar, when we were having meetings on the sidelines of the UN General Assembly with people who had intimate knowledge of the negotiating process with Hamas,was that there had been no response for a month from Sinwar on the possibility of a hostage release-ceasefire deal. Does the death of Sinwar make it harder, make it easier to be able to resume negotiations? What is your sense? Avital Leibovich: So yeah, that's the big question. The big question is, now, who is in control? Because with Sinwar gone, obviously Hamas in Qatar will have the capability to influence more. He was the main barrier to any deal that was proposed. That's the reason that a few days ago, earlier this week, the head of Shabaq Secret Services was rushed to Egypt with some kind of an offer. And actually, when Secretary Blinken just ended his visit a few hours ago in Israel, what he said next to his plane before he left was about his, I would say, strategy for the potential hostage deal. And the strategy says that, instead of going for the big deal of 101 hostages with stages, you know, being released in different stages, let's try to feel the water. And let's say we are talking about a smaller deal with a minimal amount of time for ceasefire, with just a few hostages that will be released. So in other words, not a very threatening deal, but something to work with. And here again, the question is, if the Hama leadership in Qatar will be able to go along with this kind of deal, I think we're in a very, very narrow window of opportunities. And I think this is the reason why Secretary Blinken isnot leaving the area yet, and he's continuing from one Arab capital to another. I know that he is in Riyadh now, and he's still continuing to other areas tomorrow as well. So that really remains the question. Whether the leadership of Hamas in Qatar will have the capability to lead a deal, even a smaller deal. If that will come across, then we can open the window wider and we can shoot for a bigger deal. You're right. There are 101 hostages held in horrible conditions, terrible conditions. Some of the bodies, you know, Jason, that were retrieved to Israel, were weighed. And a girl who is 24 years old, was weighing 36 kilograms.That equals to a weight of a third grader, something like that. So we do understand that it'severy day that passes is critical. The estimation is that there are 44 hostages which are no longer living. But the number may be higher because the intelligence information isas you know, not 100%. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Avital. Manya Brachear Pashman: To listen to the rest of their conversation, head to the link in our show notes, and if you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in to the conversation between my colleague Alexandra Herzog and author Aliza Lavie about her latest book, "Iconic Jewish Women."
Oct 16, 2024
From Doña Gracia to Deborah Lipstadt: What Iconic Jewish Women Can Teach Us Today
What do Doña Gracia, Glückel of Hameln, and Deborah Lipstadt have in common? They are all celebrated as iconic Jewish women in Dr. Aliza Lavie's incisive book, "Iconic Jewish Women". Dr. Lavie's book features 59 remarkable role models, highlighting the significance of women's voices and leadership in the Jewish community. In a compelling conversation guest-hosted by Dr. Alexandra Herzog, the national deputy director of AJC's Contemporary Jewish Life department, Lavie reflects on her grandmother's strength and her own experiences serving in the Israeli army and parliament. By showcasing the resilience and leadership of Jewish women throughout history—some stories well-known, others less recognized—Dr. Lavie emphasizes the need to confront the pervasive silence surrounding antisemitism. She urges us to learn from those who have paved the way, advocating for greater awareness and action against this global issue. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : The Nova Music Festival Survivor Saved by an 88-Year-Old Holocaust Survivor Is Nasrallah's Death a Game-Changer? Matthew Levitt Breaks What's at Stake for Israel, Iran, and Hezbollah At the UN General Assembly: Jason Isaacson Highlights Israel's Challenges and the Fight Against Antisemitism Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Interview with Aliza Lavie: Manya Brachear Pashman: Former Israeli Knesset member, Aliza Lavie is the author of six books, including the award winning "A Jewish Women's Prayer Book". Her latest, "Iconic Jewish Women"–59 inspiring, courageous, revolutionary role models for young girls, introduces readers to amazing women from Queen Esther to Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg and others in between, many of whom have been overlooked, but offer inspiring tales. My colleague, Alexandra Herzog, is the national deputy director of AJC's Contemporary Jewish life department, and another amazing woman. She is our guest host this week, and she had the honor of speaking with Dr. Lavie. Alexandra, the mic is yours. Alexandra Herzog: It's an honor and great pleasure to welcome Dr. Aliza Lavie to People of the Pod today. She's the author of six books. I want to especially highlight the two latest ones, "A Jewish Women's Prayer Book," which won a National Jewish Book Award in 2008. And the latest one that we will be talking about today, "Iconic Jewish Women". In many ways, Aliza gives voice to women who have been forgotten from Jewish history, and for that, I and so many women are so very grateful. Since this book is about women, I want to make sure we don't forget all the women who are still held hostage by Hamas in Gaza. Not just our women, but also the children and the men. May we bring them all back. Okay, let's dive into the conversation. Aliza, welcome to People of the Pod. Aliza Lavie: Thank you so much, Alexandra. Alexandra Herzog: It's very interesting that you have focused much of your writing about and for women. Let's also remind our listeners that your academic and professional background show your very long standing interest in women's issues. During your time in the Knesset, you served as the chair of the Committee on the Status of Women and Gender Equality, and the chair of the Committee to Combat Women Trafficking and Prostitution. So let me ask you this. Why this interest? Where does it stem from? Aliza Lavie: I believe in equality, and we need to work for it. We need men and women together to build a society. My grandmother came from Afghanistan, together with her husband. It was 1920, many, many years ago. They came to Jerusalem as a Zionist before Israel was established and became part of Jerusalem. They built and established a Bukharian neighborhood in Jerusalem, very, very old neighborhood. But my granny, she lost her husband years after, two, three years after. Suddenly, she found herself without a voice, without a language, and she raised nine children. At that time, it was the big war just before Israel was established. And my granny, my granny, knew all the halachic code and all the Torah by heart. And always I asked myself, who told her? Who gave her the information? And more, I became, you know, part of the Israeli society, as an officer in the army, in the Israeli army, and later as a lecturer at the University, and later became a parliament member and activist in Israel. So I found myself asking questions without finding answers. And I say to myself, come on, be part of the tikkun, be part of changing the mood. Not because it's women's issue or problems, it's because the society needs men and women together, otherwise the society will lose. And more we have our part and position in Israeli society, in the Jewish world, in all of the world, we will build a better world for all of us. I can declare and give lectures about it, but the question is, what are you doing? How have you become a part of this? So I find myself starting as a social activist and at that time, I had a 20 years TV show in the Israeli broadcasting. And I find myself asking questions, bringing more women to the TV show, and you have to see role models around you. And I found that we have a lot of answers, but we need to continue working. Alexandra Herzog: Iconic Jewish Women offers readers 59 role models. And you were just now talking about role models, the book was designed as a bat mitzvah gift for girls celebrating their Jewish coming of age. But it's really about discovering one's Jewish identity and Jewish heritage. What is particularly compelling to you about that, about also the Bat Mitzvah practice in general? Aliza Lavie: I asked myself, what is going on? You know, the big roads in the streets, most of them named after men. How come there is not even one public place in Israel named after Golda Meir? How come? Why is that? And it's not only questions of awareness. It's a question of knowledge and position and role models. And the more I become familiar with the fact that I'm not that familiar with my heritage, with my history as a Jewish woman, as an Israeli woman. And even though women from the Bible, what really we know about Deborah the Prophet, or Miriam, the prophet or Esther the queen. Okay, so all of us, and the girls especially wants to be Esther the queen with a nice dress. But Esther the queen, she became from beauty queen to a leader. She was the one that told Mordechai, okay, you want me to go to the king without permission, so do something fast three days. And then it was a huge fight between still and old high. And what Mordechai told her, No, no, no, we can't fast three days. But she gave him the order, and she was the one that told him that we should do it, to have future. So suddenly, from a woman in the megila, she became the leader, and more than that, in the end, she wrote, remember me for the next generation. She knew that women in the future will need her knowledge, her help, her position, her role modeling. So more of you became familiar with the presence that our mothers, the women that were here before us, gave to us, so you will become much stronger. And more than that, Alexandra, you can find your only voice in a world that we are living in a very, very challenging time, increasing antisemitism and political instability, a lack of leadership and growing disconnected from a tradition, and we in Israel, in the middle of a war, where a brave soul who took responsibility. Alexandra Herzog: And I think that that's really a project that you did also in your previous book, Tefillat Nashim, A Jewish Women's Prayer Book, you explore Jewish identities through the rich tradition of women's prayers that is often absent from traditional historical or religious consciousness. Is Iconic Jewish Women, in some ways, also a project about restoring, reclaiming and recovering? Aliza Lavie: You are so right. And thanks for this question. My previous book, when I first spoke, Tefillat Nashim, A Jewish Women's Prayer Book. Actually, it's a collection of prayers that were written by women. When I start my journey, my research, nobody believed and felt that Jewish women wrote prayers. More than that, some professors wrote, Jewish women? They didn't know how to write, or they didn't allow the, you know, by the spiritual leaders to write, and they didn't know Hebrew or other languages. And always, when I find myself as a politician or social activist, in a position that I didn't know what to do, I thought: what other women did when you can't find answer yourself? You have to go and make your own research. And believe it or not, I found ancient prayers. Actually the most ancient one is from the 13th century written by Paula [dei Mansi], the daughter of Rabbi Abraham [Anau] in Milan, north of Italy. And actually, Paula, she copied the book we are talking about before the printing press time, and only men were allowed to copy books, because you need knowledge. So when I found this prayer in the end of the book named Yehudah de Trani, and she copied it. In the end, she wrote a prayer in Hebrew. Who was Paula, who taught her Hebrew, who gave her the thinking that you can add prayer for good days, for redemption, for coming back to Israel. 13th century. And what about us? What about our knowledge and level of Hebrew and the permission to write your own personal prayer. And we are talking 13th century, not our days. So a lot of understanding about our position. Sometimes we think that, you know, in our generation, everything is open, and we are brave people and I suggest that we need to be a little bit modest and bring back knowledge from the past with the tools of our days and continue to tell the story. Alexandra Herzog: I was particularly intrigued, really, by the choice of women that you picked, as well, actually, as the organizing format of the book. The women are not in chronological order, but rather in alphabetical order. So one of the things that I particularly love about the book is the fact that the reader is asked to actively engage with the content and to add their own stories to a vast historical network of political, scientific, activist, literary, and religious figures. What advice would you give to young women aspiring to make a difference in the world? Aliza Lavie: First of all, think about your dream. About your dream, and don't hesitate. You can make it. You can make it. And find role models for your lives. You know, you ask, Why I put alphabetic? By the way, in Hebrew, it's 71 women, and I hope in the next book to add much more women or in the technological project that I'm working on, and I invite girls, women men, to add their voice and to use the tools that they are professional with. Remind yourself that one of us can make a story in the TikTok, video about Doña Gracia. The richest Jewish woman in the 16th century. She was the one that took control during the Inquisition about her brothers and sister in Spain and Portugal. Who was she? And how come that, you know, she became back to her Hebrew name Chana, and what is all about her and why we are not that familiar with her? Take the opportunity during your Bat Mitzvah or family dinner to share a little bit or to ask people and to open a discussion and bringback, see something again new. Go out of your comfortable area and find and bring back and tell your friends and be ambassadors. Because it's not a history book. It's not a history book. And another thing I want to mention why I chose these amazing women, they didn't plan to be famous. They were in the right time for and chose to be helpful for the Jewish people and the Israeli society. When they found, like Henrietta, Golda, other names in this book, that the people of Israel need them. Need their help, or no one did something to stop the issue or to be there. They were there. Alexandra Herzog: And so you're basically inviting young women to really, by engaging also with all of those amazing role models. And by the way, I do think that the you know, the chronological–using an alphabetical order rather than a chronological order, actually adds a lot of dynamism, because it really creates a conversation across time periods between Queen Esther, Glückel of Hameln, Golda Meir, and Deborah Lipstadt. And so, you know, the person, the reader is really asked to add their voice to this amazing group of women that they can be a part of. And I think that that acts, that really adds a content and a component of leadership that they can take on into their own life. Aliza Lavie: In the end, you can also find timeline of iconic Jewish women, because we not always remember and now which year and Hebrew years and the area, etc, etc. Alexandra Herzog: And I love that. And so I was wondering, because the book really delves into Jewish identity across continents, across time periods, sewing together different pieces of our history as a people. And I would be remiss if I didn't connect the difficult time that we are in as a people since October 7 with the powerful examples of leadership we find in the book. And we are asked to look for, around us in our daily lives. What do you think makes the book even more important, at this particular time? Aliza Lavie: We're very upset to find a lot of our colleagues in all over the world, in United Nation and in universities, colleagues. I represent the Israeli parliament in the European Council, and I worked very hard together with other colleagues in the committee of status of women in the European Committee. And suddenly, when you saw all this blaming, and the way that nobody believe in what's happening October the seventh, and what Hamas did to our brothers and sisters and the situation, and the way the world treats us. First of all, you feel that you become betrayed. What is, what is going on? Why is that? First of all, the aims are laid out in the document of Hamas. But what about the democratic world? Why is that? And when you saw all of this, I think that first we have to put it in a frame that it's not the first time in our history. It's not the first time. So when you see the story of the Jewish people, and it's maybe a sign for us to understand who are we, where are we coming from, and to remember all the difficult time in Egypt. When Pharoh say to the people of Israel that you know should not have boys, the baby boys, and to kill them. And the fact that brave women, Miriam and her mother, Yocheved, they gave birth to the children, and they didn't pay attention to Pharaoh, and they took control about the future of the people of Israel the men didn't want. And by the way, thanks to them, to these women, the promise of redemption, got from God. And later in the Inquisition, more women took responsibility, and we know it from all the testimonies and all the understanding, and women that didn't, didn't lost Judaism, didn't lost and and become Christian. And when you see the numbers, you see that more men became Christian, or left the women together with the children. And later in the Holocaust, we see, and now we are in our days, we see that women, men, of course, brave people around us, men and women, but I see what women did. Women that didn't have a choice. They took control. They protect the people. They protect the children. And when Noa Argamani came back from Gaza, thanks to our soldiers. But Noa Argamani, she was the leader of the soldiers that kidnapped from their basic and Noa, without any help, she was the one that support. And I can share with you a lot of examples of women that lost their children and are going every day to other families and widows to support, to hug, to give help. Alexandra Herzog: The book was published, as you said, before, in both English and Hebrew. Of course, Hebrew and English are the languages spoken by the two largest Jewish communities in the world, Israel and the United States. So how do you think that a book like this can contribute to strengthening Jewish peoplehood and conversations in the Jewish world? Aliza Lavie: So knowledge is a power, and let's start with our common history. Let's start with our common heritage. So this book invites you to start, to begin, to continue the conversation between yourself, between you and your spouse, or your family. Of course, your children. That you know what, to bring back the responsibility, parents to the family. What's happened actually, that in ancient world, the family took responsibility to the Jewish education or belonging, and then later the communities, because when they saw what's happening in the families and later organizations, we can start, you know, discussion about your amazing organization that's taking the responsibility and think about new directions or legacy or tools to continue. This book is an invitation to, you know, maybe to grandmothers, to aunts, to teachers, to educators, to organizations, to take knowledge and inspiration from a book like this. Alexandra Herzog: Thank you, Aliza. So in a post October 7 world where Jewish women worldwide have had to make their voices heard even more than usual, to denounce the sexual violence that occurred on October 7, the deafening silence of many women's organizations, how has that impacted the conversations you're having? Could you tell us a little bit about how women have been engaging with you about the book? Aliza Lavie: When this book was established in Israel, it was before the war, but in Israel that time, it was not an easy time in between the people of Israel that start, you know, many, many voices, again, the government and again, the parliament and etc, etc. And we need to bring, you know, the peaceful and to understand that the enemy is out of us, and for the enemy, all the Jewish are the same. It doesn't matter if you are secular, religious, Orthodox, reconstruction, reform. For them, we had this experience. Remember? Yeah, we had it in the Holocaust. They count seven generations ahead. Your question is a wake up call, the answer is a wake up call for all of us, for all of us, the citizens, the governments, the Jewish people all over the world. And to start getting serious thinking about the day after. And even now, even now, when you ask yourself, how come that our brothers and sisters are still in Gaza, where is the Red Cross? So you can blame Israel all the time about that we are not, you know, delivering food to Gaza. But you know what is going on in Gaza. And you know who took all the food, etc. The Hamas. And it's not going to women and children. And what about our people? Where are they? So hypocrisy, yes, tikkun olam, of course. But in between, in between, we need to understand that we Jewish people have to work together and to bring back knowledge from the past. It's not a history lesson. Alexandra Herzog: Thank you so much. I love that we end on hope and a better future. So I'm going to keep these words as the last ones, and with the notion I'm going to add of: Bring Them Home. Thank you so much for joining us, Aliza, to People of the Pod. Aliza Lavie: Thank you so much, Alexandra, for having me, and we'll pray for good days. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Nova music festival survivor Daniel Vaknin about the horrific events that unfolded on October 7, 2023 and the brave Holocaust survivor who kept him and a handful of others safe and alive that day.
Oct 10, 2024
The Nova Music Festival Survivor Saved by an 88-Year-Old Holocaust Survivor
"I want to show the word that you can choose light . . . no matter how much dark you saw, or what's going on in Israel now, or what's going on in the world, there's still a choice." As we mark one year since Hamas' massacre of Israelis, Israeli DJ Daniel Vaknin, 30, shares his harrowing experience from the Nova Music Festival, where 340 attendees were brutally murdered in the deadliest event in music history. Vaknin recounts the chaos as rockets from Gaza struck, triggering a desperate evacuation and his narrow escape while being shot at, taking refuge in nearby Kibbutz Sa'ad at the home of an 88-year-old Holocaust survivor. Vaknin highlights the incredible resilience of the Israeli people and the pressing need for global support to bring the hostages home. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : with Hen Mazzig , Einat Admony , and more . People of the Pod : Is Nasrallah's Death a Game-Changer? Matthew Levitt Breaks What's at Stake for Israel, Iran, and Hezbollah At the UN General Assembly: Jason Isaacson Highlights Israel's Challenges and the Fight Against Antisemitism From Rocket Attacks to Exploding Pagers: Michael Oren on Escalating Tensions Between Israel and Hezbollah Paris 2024: 2 Proud Jewish Paralympians on How Sports Unites Athletes Amid Antisemitism Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Interview with Daniel Vaknin: Manya Brachear Pashman Daniel Vaknin is a 30-year old Israeli DJ and music event producer. He was not one of the DJs responsible for the soundtrack of the Nova Festival on October 7. He was there as a fan seeking a fun weekend. He arrived less than half an hour before Hamas terrorists stormed the border between Israel and Gaza, killing more than 1,200 people, including more than 300 at the music festival. Vaknin managed to survive, but since that day, he has dedicated his time to advocating for the hostages still in captivity. As we marked one year this week since the Hamas terror attacks, Daniel is with us now to share the story of his harrowing escape. Daniel, welcome to People of the Pod. Daniel Vaknin: Thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman I can't imagine, I don't want to imagine being at a music festival like Lollapalooza for example and it all coming to a sudden and terrifying end. But I think it's important for us to put ourselves in your shoes. Can you take us back to the Nova Festival that morning? Daniel Vaknin: So for me, the Nova festival, it's not only the Nova. It's the festival of the trance (with a c) music festivals. It symbolizes and it represents love. It's supposed to represent the connection to the nature it's supposed to represent our connection, no judgment, happiness, joyful, of course, at the end of the day, it's an amazing community of fans of specific genre of music that looking for more and more festivals and more and more events to enjoy, to celebrate, to dance, to express yourself in so many ways. So people think that the festivals or the trance (with a c) music, supposed to be about music, but it's not. When you go to this kind of festival, to this kind of event, you can walk around and people open up their tents and camps, and they're like way before they plan everything, and they bring their most colorful clothes, and they bring so much food and drinks. And you can really go through the sta;ls and see art and paints and clothes that you can buy and bags that people sell or made by themselves and want to express themselves. People are dancing, it's a festival. I think that's exactly the description that you're supposed to have when you ask Google, what is a festival? So it's not only about music. There's so many things in it, and that's what it represents for us, and that's what it represents for me, because not all the time I'm going only to dance. Sometimes I just want to hang out. Sometimes I just want to see new stuff, buy some stuff, and express myself with different people, to meet new people. Manya Brachear Pashman: Why did it take place on the Gaza envelope? Was it always in that field? Daniel Vaknin: So for the people that don't live in Israel, and I'm not saying it in a bad way. I'm just saying in general. I want you to know. I want you to understand. I work in the music industry, in the music production for almost 12 years. To make an event in Israel, unfortunately, Israel is a small country. Where it's a blessing and a curse, because it's a small country and everyone is together, but unfortunately, we don't have a lot of space. And we have a lot of borders, and that's okay. So 70% of Israel's open space, open fields, are military training. You cannot enter or make any kind of events in almost 70% of the country of the open fields, because the military is training there. And it's like you cannot. It's like high called area 51 that you got here, United States, nobody can enter, right? So that's why we got there. And let's say, and again, what I'm saying right now, it can be a percentage here, a percentage there, but let's say 30% that we got left it's or near borders, Lebanon, up north. We got Syria, we got Jordan, we got Egypt, and now we got Gaza. And not only that, it means that we got people that owns the lands and maybe doesn't want festivals around their houses, their farms. They don't want you to interrupt the quiet that they have next to their kibbutzim, or, you know, their families, and let's say, even more than that, some of the areas are not proper to have festivals. Like maybe it's too muddy, maybe it's too grassy, maybe it's forest. Maybe the country, the government there's like, I don't know you call it here, but we have this company. Or maybe it's not the right word, that take care of all the trees and all the forests in Israel, like the government official. And they don't want you to make festivals, because they want to take care of the lands, or they're taking care of the lands right now, or the farms. So it happened near Gaza only because of one reason. It's Israel. As long as it's Israel, as long as it's a place that's called Israel, that's a land of our country, I can make parties wherever I want, as long as it's called Israel. It was near Gaza, because the kibbutzim is near Gaza. It's like to ask Sarah Jackson, the Holocaust survivor that host me while I was escaping, why she is living in Kibbutz Sa'ad next to the border, 2.5 miles. If you ask her, that's her house, that's her home for 50 years, even before Gaza. So I think to explain the best way is that I cannot ask you why you're doing in your balcony a party, because that's yours. Once you're out of your balcony, and that's not your property, I can ask you why you decide, or why you chose to do this. But I think as long as my property, it's Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: There was also a ceasefire in place, and therefore a reasonable sense of confidence that it would remain peaceful and safe. Daniel Vaknin: Yes,right. So all this time we have a ceasefire. Everybody knows about it, and I won't tell you that once every three months, every five months, we're going to have a one missile launch from Gaza, and that's okay, you know, in the circumstances, because we have the Iron Dome, and we understand that sometimes it cannot be so peaceful, because things happen. But we have our military, we have our fences, we have our Iron Dome that costs Israel so much money. Every missile, every this kind of huge operation, costs a fortune, and we do the best we can to defend the country without interrupting the peace. So yeah, it was quiet and peaceful. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's talk about that day and when that piece was broken for you, where were you? And you mentioned the person who gave you shelter when you escaped. Can you kind of walk us through the events of October 7 for you? Daniel Vaknin: October 7 for me, started again a little bit before, because this festival was supposed to start on October 6, 10pm. And was supposed to be one of the biggest festivals that happened, and a good friend of mine was supposed to go. I didn't mean to go because I was supposed to work, and my girlfriend was working there as a bartender, and she arrived with my roommate (back then) around 2am. And both of them called me, and before they left the house, they told me, like, you have to come, if you're not working, I want you to come. And you know, when your girlfriend, your amazing friend and roommate, ask you to come, you do the best you can to make it happen. And I had a ticket from a good friend of mine, and then we plan to go around 5am to head to the party, and I pick up my friend Ilya, and we headed to the party, and we arrived to the parking lot at around six in the morning. So I know that everybody knows the details right now. So everybody knows that 29 minutes from now, my life's going to be changed forever. But the most important thing is that when people when I'm talking about it, I think what's important for me is that people need to understand that now you know the details, but we didn't know. We always have this amazing feeling above our heads. We always had this blessing that we're coming for the best festival ever, and everything gonna be amazing. I want people to understand it, to realize that we didn't had any attention or thinking about something else besides having the best time. So we arrived at the parking lot, we parked a car, and we had it towards the festival, and good friends of ours was coming outside of the party to go to the car, to bring some stuff, and we're so happy. And we hugged, and we had a great time talking, like, really, what's going on in the festival? We're so excited to go inside and see. And then it was the first second that we heard a whistle, and this whistle was a missile launches from Gaza to Israel, and there's no red alert. So we freaked out, of course, but I like to say that it's not a routine in Israel. I don't want to say it's a routine, but it's not something that didn't happen, missile launches from Gaza, or missile launches from somewhere, and the party is still on, because we got the Iron Dome. You stop the music for a second, you take over, it's done, and you go back to party. And it's not the first time, but this time wasn't the same. This time was a barrage of missiles launches from Gaza every second, hundreds of missiles just launches. So the party was over, and someone announced that we need to evacuate. And the party is not coming back. Because people were waiting. And he said, like guys, you have to evacuate. The party's not going on. Leave the perimeter, evacuate, go home. And I saw the opportunity of going back home, fast as I can, not because we want to run from the missiles, only because we realize it's going to be a traffic jam, right? So we saw, like, so many cars, and we're like, next to our car. And we said, Okay, let's go home like the car is right here. Let's go. And I called my girlfriend and she said, like, Daniel, don't come. The party is done. I was like, That's too late. I'm right here. And I told like, Babe, I'm going to pick you up. So go out. So I jumped back to the car, and we pick up my girlfriend, and we headed home. And at the same time, we're having a FaceTime with a good friend of mine from Israel. He was still in Tel Aviv. Was supposed to come to the party, but he woke up really late, so. We had a FaceTime, and we talked about what's going on, and we laughed about it, right? Like it was breaking news, a missile start and Nova festival is done. Are you coming back home? We're like, Yeah, we're coming to Tel Aviv. What a bummer. We want to have a great party. So we started head back home, and that was the moment that we on this route 232, making our way back home, and a police officer stopped us and signaled us to U turn, like we cannot go that way. And he asked us to U turn. And I want you to understand it that all this time, you have unstoppable missiles. The Red Alert is above your head all the time. The missiles is just hitting the ground. You can see so many cars stopping, people running, people sitting next to their car, smoking a cigarette, drinking something. And that's another thing that people need to know. People just finished an amazing festival in a second, they were drunk, they were high, and scared. We cannot forget it, that not anyone can handle this kind of situation smoothly, and you don't know where to go, right? Because the police officers, and it's really important for me, I'm not blaming them, I'm just saying they didn't know as well. So they stopped us no matter where we go. They asked us to stop here, to stop there, and we cannot go towards this way or that way. So my oldest brother called me and he asked me, What's going on. He knew that I will be in this kind of festival, and I told her, we gotta stop next to one of the kibbutzim to find a bomb shelter, because we have to hide. You cannot stay in the car once you have red alerts, and we're gonna take over, and I'm calling back when it's become a little bit more quiet, and we'll head back home. And I didn't have the chance even to hang up, because when I stopped the car and opened the door, that was the moment we were getting shot at with automatic rifles. I want to say that not everyone will recognize it, but the military, the IDF, are not supposed to shoot on automatic. We're not supposed to shoot automatically, only single bullets every time. That's like the rule. That's the law that we got in Israel. And when you're getting shot at by automatic rifles, it feels different, it sounds different, and you can hear the gunshots just above your head, just whistling next to you everywhere. And I told my brother, I'm getting shot and I will call him back. And I hung up, and I fell to the ground, and I took cover, and I crawled next to the side of the court, and I yelled to the car that we're getting shot at, so they have to go out. So Ilya was laying next to me, and I remember that we saw so many people stopping their car next to us and screaming and running and praying because nobody, no one understood what's going on. Nobody realized that we're in a war again. Now everybody knows it. Now we can picture that, but at the same moment you don't know. Nothing. You don't have a clue of what's coming up. So it's all blurry, right? You don't really understand what's going on. And you try to realize where, where you at, or why you're why you're getting shot at. And we took cover, and when I left my head, I didn't see Lala, I didn't see my girlfriend. So I asked Ilya, where, where Lala at and he's and he said that maybe she's in the car. Now, an important, an important thing that I took my mom's car and she got a child lock, so if someone's inside, you cannot open the door. So I crawl above Ilya, and I open up the door. And Lala was looking at me with his frightened look, and she was like, I can't, I can't open the door. I can't open it. I was like, I'm sorry, baby, I'm sorry. Just come next to us. So she crawled next to us, and we later cover hats for a few minutes, for a while. And all this time we have the missiles. All this time we're getting shot at all this time you can hear the bullets hitting the trees next to you. Can hear the bullets hitting the rocks, and people are running, people are screaming, and you don't know what to do. And we've been there for a while, and after a while, I felt like I don't want to stay here, like I don't know where I'm going or where I'm supposed to do but I don't want to stay here. So what we did is we said that we gonna crawl next back to the car. We're going to take our seats back so we won't be like in the horizon of the windows that people cannot see or do, or the gunshots won't hit us through the window, and we're going to drive somewhere. I'm going to press gas and run, I don't know where, so that's exactly what we did. And Lala was just laying like we're not in the seat, like where you put your dogs at, like, underneath the seat, and Ilya and I were taking the seats all the way back, and I crawled to the seat, to the driver's seat, and just press gas. And in the second I pressed gas, we felt all the car was shaken. And I remember that we really felt the the car moving once I press gas, and Ilya and I looked at his at each other, was like, there was a grenade. We felt it wasn't a missile. And I remember we were like, shocked looking at each other. So we drove, like, real fast. And again, imagine that all this time I'm lifting my head, I'm picking every time just to see where I'm heading. So we drove like this for, I don't know, a while, and then after, I don't know, 15 minutes of driving we we found ourselves getting stopped by two bicycle couple. So they went for Shabbat just to have a nice ride, and they stopped us, and they lift their hands, like, you have to stop, you have to stop. And she said, like, you cannot go forward. There's a terror attack ahead, and they're shooting it, anyone that comes, and that's the moment you start to realize that, okay, maybe I start to understand what's what I came from. So we're talking about it like, I think that's what happened there, and they tell us what happened there, and we we try to understand the bigger picture. And I remember that we didn't know where we're supposed to go. But I like to call it: the first angel came, and there was a car that is heading towards us, and a beautiful guy jumped from the car, and he looked at all the cars that stopped, and we're like, 20 or 30 cars. And it was like, Guys, Kibbutz Sa'ad is just ahead, and I want you all to follow me. They'll open up the gates and they will and they will let you in. So please follow my lead, park the car outside the gate, and just go inside the gate. And we follow his lead. It's a beautiful kibbutz. It's a religious kibbutz, so it was Shabbat for them, so the gate was supposed to be closed all the time, and everybody was praying in the synagogue, because it was Simchat Torah. And it was around eight in the morning, more or less. And I want to say between 50 to 60 people from the Nova, kids from the Nova, are running into the kibbutz. And we don't know what to do. We're just staying at the kibbutz, and there was a soldier that getting treatment next to the gate of the kibbutz because he had a gunshot wound in his stomach. And we see that he's getting a treatment from the city patrol. And even the city patrol that took us in, they didn't know what to do with us. They looked at us with the same look that we're looking at them like we don't know what's going on. Go inside and let's see. Let's figure it out. And I remember that we just scattered the kibbutz like we just walked and so many kids, so many girls, so many guys around my age are just crying, asking themselves, what's going on. And you start to hear this like people are looking for their friends, like, Hey, where's Rachel? She with you? Where is Avi? Did you see him? So it was a horrific moment at the same time, and you're so useless, and you don't even understand what's going on. And we made a lot of noise in this kibbutz. And this kibbutz is like a really quiet. I want you to imagine that when you entered the most quietest place in the world, it's like Yom Kippur. It's so beautiful, so nice. It's Shabbat Simchat Torah. All the porches are have decorations for the Sukkot. It's beautiful. It's quiet, but 60 people right now, with a lot of mud and dust from the party, from the festival, and running into your kibbutz. And the second angel appeared, and her name was Sarah Jackson. She's 88 years old. She's a Holocaust survivor, and she's an amazing, beautiful person, and she came outside of her house because of the noise we made, and she was standing at her porch. She looked at us with this beautiful look, and she's like, Who are you guys? And we said, it doesn't matter. Can we come to your house? Can we stay in your house? Can we can we hide for a second just to drink something? She was like, of course, come in, and when we came in, she offered us, of course, she gave us water and drinks, and she asked if we want coffee, and she asked us if we're hungry. And she always have this chill feeling. Always chill vibe, no nervousness. The Shabbat, it's Shabbat, it's quiet, the Shabbat will keep us safe, guys leave the phones. And we started talking with her, of course, and she told us a little bit about herself, and we told her a little about ourselves. And this time, the information start to come right? We're we're calling our friends that we don't know where they at, or that we lost at the same time, and and we start to gather the information. And I remember I called my my roommate at the same time, like, where, where you at? She was like, two of my friends got shot. Were taking them to the hospital. I was like, What do you mean? What do you mean? Got shot by who she was like, I don't know. They were getting shot at. And I got shot in the car, and two of my friend got shot, one in the knee, one at his shoulder, and I will talk to you later. I was like, okay, just be safe. And again, this talks that you have at the same time, it's not reasonable. It doesn't make any sense. You don't know that 3000 terrorists just enter your country. You don't know that right now, people are getting slaughtered in their houses, murdered. You don't know it. And you start to get this piece of information from the news, right? You open up the news, and we call our friends, and this friend is hiding in the bushes, and this friend, he's is running for his life, and this friend is hiding in another kibbutz, and some people managed to escape to Tel Aviv, and like they are heading home, they don't know what we're talking about. And so many, so many like different stories right at the same time. And all this time, we get all this piece of information that berries got invaded and and you can hear the people calling the news like the anchor, the anchorman, and like, gasping for help and whispering at the same time. And it's Be'eri, it's Kfar Aza and all this time, we ask, Sarah, and she was like, yeah, it's right here, why? Like, okay, never mind. Because we felt like, Sarah, I don't know if she didn't want to know. So she wasn't into all the details, but she was chilled. She didn't really realize what's going on. And we thought that maybe it's good for her not to know what's going on outside. And I remember that I was going out all the time, was running, and I have some videos that I was running outside to the gate to see if I can help, to see what's going on, to to ask maybe to patrol, maybe they know what's going on. And every time you're running outside, you're getting red alert. So you have to go back and you do this. And I did it like 5, 4, 6, times, and you can hear the gunshots from Kfar Aza. And now you know that they are inside Kfar Aza slaughtering people. And there was a rumor started, I don't know how, and that's how rumors start, that people saw terrorists in Kibbutz Sa'ad, so in the Kibbutz that I was hiding, and I remember that we thought that, Okay, that's it. They're inside. What are we gonna do? We don't have a lot of choice. And what we did is that I told Ilya. I was like, Okay, I'm gonna bring some knives to the bomb shelter, because if they're going to open up the door, at least we can fight, at least we're going to take one of them with us. I don't know, something that we can try to do. And I ran to the kitchen. And again, like I told you, Sarah was a chill, quiet person, so the only knife that she had was a butter knife. So Ilya and I was standing with butter knives for a few hours, holding the door. And it was you know, a funny moment, because I have to tell you, I think when I think when, when you filled and you don't have a lot to do, humor kicks in. So we were standing with this butter knives like this, holding the door with a knife that cannot do anything to anyone. And I remember that after a while, Sarah looked at us. She was like, What are you doing with my knives? I was like, oh, not a lot, so I don't know. Like, no, take it back. I was like, Okay. And every time she took, we took it back. We brought two others. It was a game like, you know, Cartoon Network we're running, taking it back. She's taking it back. And after 10 hours that we've been there, something happened. We had the opportunity to go back home, to drive back home, and I took my mom's car back to the kibbutz, and we jumped to the car, and we went to the other side of the gate, and we asked the commander the military that arrived already if we can go back home, because they told us that if you're going to stay here after six o'clock, you will stay all night because they're going to close the perimeter. No, nobody gets in or out. I don't want to stay in the war zone, so we asked the commander, and he asked us peacefully, like, Okay, if you're going home and I will let you go out, please. Are you going only to Tel Aviv? You don't you're not stopping anywhere. I was like, No, we're not going to stop anywhere, promise. Okay, don't look to the side. Just go straight. Just go home. Now, that's a weird, that's a weird thing to ask from you. But we're like, yeah, okay, we understand. But unfortunately, first of all, you cannot, when someone asks you not to do this, that's exactly what you're going to do, let's be honest. And second of all, we couldn't even if we wanted because once while I was driving, we saw we had to maneuver in the road that we're going home, between cars that was shattered to pieces. And inside these cars, and outside these cars, there was so many dead bodies of people from the festival. And from our left side, you can always see this black smoke coming up from all the kibbutzim and Gaza. Because now Gaza is getting hit really hard and really strong from the military and from the Air Force, and it was apocalypse. It was moments of apocalypse. It's one of the most beautiful places in the world, so quiet, so peaceful. And I know it sounds ironic, but it's the truth. Like, it's such a beautiful place, and to see it now a war zone, to see the smoke, to see these dead bodies all over and cars shattered. It's a polar [opposite]. It's 180 degrees from what you knew or saw. Manya Brachear Pashman: Have you shared what you just shared? Have you shared this story with college students in America, or do you rarely retell this story? Daniel Vaknin: I came to United States for the first time in May. I had an amazing opportunity to play as a DJ in a joyful Jewish event that happened in MIT, but it was for 1500 people, Jewish people, just to celebrate, just to be happy, not to talk. And I was supposed to come to this event to play as a DJ, to perform as a DJ, in front of these people, and headed back home after a while, like after eight days. But when I went down the stage, when I got off the stage, so many people ran towards me and asked me if I want to come and speak and to share my story in communities, in schools and in synagogue, in temples. I didn't know that at the same time, that's what's going to be, it's going to be something I'm going to do every day now. But I had almost 12 events, 12 speaking engagements in two weeks here in Boston, in Miami as well. And I had this amazing opportunity to share my story, to talk, to spread awareness. So I came here only for this purpose. I'm going to be here almost two months, speaking, talking to colleges, talking to communities, anyone and any place that will give me the opportunity and want to hear a Nova survivor experience, like a first hand experience. And to ask the questions and have this amazing dialog, to hear the truth again. I don't like to speak about politics. I like to speak about what I've been through. I like to speak about my beliefs. I want to speak about my community. I want to speak about my friends. I want to speak about the friends that I lost. I want to memorize them. I want to show the word that you can choose light, no matter how much dark you have, and no matter how much dark you saw, or what's going on in Israel now, or what's going on in the world, there's still a choice. Manya Brachear Pashman: And you have a yellow ribbon dangling from your left ear. Do you know people who are being held hostage? Daniel Vaknin: So a month and a half ago, our missing puzzle, our amazing friend Eden Yerushalmi was murdered in captivity after 11 months that she survived. And she was the last person that I knew personally, and we spent some time together, and she's a good friend. Yes, Eden was more closer to my heart and other friends that murdered the same day. But I can tell you that Eliya Cohen, that everybody's waiting for him to come back. He's a good friend of a lot of my friends, like I know so many people that he's a friend of them. So I cannot say that I'm his friend, but he's one of the family. And each person there, the Bibas, the babies that no one's talk about them anymore, the parents of the kids, nobody talk about them anymore. I want all of them to come back home, because again, guys, it's not about right or wrong. It's beyond insane. It's beyond insane that we got a kid that almost a year more than his life is in captivity, and nobody's talking about it. It's, it's not insane. I don't, I don't think there's a word for, for expressing it. So this ribbon, I know it represents hostages, and it's nice to put in my ear, but God, that's not enough. That's not enough, and we need to do more than that, to bring them back home and to bring them safe. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to note for our listeners. That you are in Boston for some speaking engagements, and we're actually speaking on October 2, a day after all of Israel went into bomb shelters following a barrage of missiles from Iran and a terror attack on a train in Tel Aviv. What have you heard from your family and friends back in Israel? Daniel Vaknin: My parents and my brothers are in Israel, and I got younger–my youngest brother is in the army right now. He's 19. He's a combat fighter. He's a commander. And my mom, she got four boys, so she is a lioness. All of us were fighters. All of us been through war. And now the youngest one, and that's the last one. Like she said, no more, no more boys, no more fighters. She wanted peace. And that's the reality right now. Imagine that yesterday I was waking up to the news that I know that Jaffa, I lived in Tel Aviv for nine years. So Jaffa, Tel Aviv was like so close, and I got a lot of friends that lives in Jaffa, and I'm waking up to this news that terror attacks start and they're killing people, they're murdering, they're slaughtering people in a train station. And I recognize the place immediately, because I've been there a lot, and there's so many heroes. You know what? I won't give the stage to this. I want to change it. There's so many heroes in Israel. My parents are sitting in a bomb shelter and smiling and doing the best they can to keep the morale high. And someone that I know well, and he's a good friend, he was the guy that yesterday went to buy groceries because he did had food with his flip flops and his pistol, because from the moment the war started, he had a license for a gun, and he only went down to buy some food, and he was the one that injured and killed one of the terrorists with flip flops yesterday. So that's the reality, but that's our heroes. They don't wear capes, they wear flip flops, and they're going to buy food. Manya Brachear Pashman: Daniel, this state of war seems to have no end, no boundaries. Attacks are coming from all directions. As you travel around the States and the world, speaking and listening, what do you find to be the biggest misconception? What do people outside of Israel seem to not understand? Daniel Vaknin: I think if we try to see and we try to fight every single day about religious and who is right and who is wrong, and all this excuses, why we're not supposed to be here. I don't know. Guys, if you don't, if you don't know what you're talking about, don't take a stand. Come to Israel. Talk to the Nova survivors. Talk to the kibbutzim. Talk to them, there are human beings that will tell you exactly what they saw, what happened, what they lost, what they're losing. You will see an amazing people and strong people that will tell you the truth. That they don't want it [war], not the kibbutzim, not the Nova survivors. No one wants it. But as long as it takes, we will do it. We'll defend ourselves, and we'll be the strongest people that we can. Because we have the right to live. Manya Brachear Pashman: Daniel, thank you so much for helping us remember what happened a year ago on October 7. Thank you for sharing what I know was a very painful story and journey, but I think it really will impact our listeners and remind them about the horrors we witnessed a year ago. Thank you. Daniel Vaknin: Thank you very much. Manya, it was a pleasure, and thank you for having me.
Sep 30, 2024
Is Nasrallah's Death a Game-Changer? Matthew Levitt Breaks Down What's at Stake for Israel, Iran, and Hezbollah
Could Israel's elimination of Hezbollah's leaders reshape the landscape of power in the Middle East? Matthew Levitt, Director of the Washington Institute's Program on Counterterrorism and Intelligence, answers that pressing question, discusses the impact of Israel's recent offensive against Hezbollah, following the death of its leader, Hassan Nasrallah, and analyzes the ongoing military operations on the Israel-Lebanon border. The conversation also delves into Iran's strategic calculations, the potential consequences for Lebanon's sovereignty, and the broader regional stability in light of Hezbollah's diminished military capabilities. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus , Season 2 – out now: Explore the untold stories of Jews from Tunisia , Syria , Yemen , Morocco , and more . People of the Pod : At the UN General Assembly: Jason Isaacson Highlights Israel's Challenges and the Fight Against Antisemitism From Rocket Attacks to Exploding Pagers: Michael Oren on Escalating Tensions Between Israel and Hezbollah Paris 2024: 2 Proud Jewish Paralympians on How Sports Unites Athletes Amid Antisemitism Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Interview with Matthew Levitt: Manya Brachear Pashman: Since October 8, Iran's terror proxy Hezbollah has escalated its attacks on Israel, launching rockets, drones, mortar shells toward Israeli civilians on a near daily basis, more than 10,000 to date, pushing 1000s of residents from their homes in Israel's North more than 11 months later, on September 27 Israel Defense Forces launched a massive retaliatory airstrike targeting Hezbollah's headquarters in Lebanon, killing the group's founder and leader, Hassan Nasrallah and other senior officials. Here to talk about how significant this development might be for Israel and its neighbors, is Dr. Matthew Levitt, director of the Reinhard Program on Counterterrorism and Intelligence at the Washington Institute. Matt, welcome to People of the Pod. I'm going to launch right into questions. Has Hezbollah been significantly disabled by Israel's attack, or is Nasrallah's death just a setback for the terrorist group? Matthew Levitt: This is extremely consequential, and it's not just this one attack. So we're talking about two weeks of activities that come straight out of Hollywood. Hollywood would have rejected the script for being too fanciful. First the pagers exploding 24 hours, then walkie talkies exploding. This, already coming on the heels of almost 500 Hezbollah operatives, some of them quite senior, being eliminated. So you already had the beginning of the kind of hierarchy of Hezbollah leadership being taken out, and now what you have is Fuad Shukr. Ibrahim Akil, members of the jihad Council, the Ohio Military Council for Hezbollah, being taken and then, of course, on Friday, taking out the Hezbollah Operational Command Center, which itself is extremely important. And in that operation, killing both Hassan Nasrallah and another member of the jihad council, Ali Karaki and a senior Quds Force General. It's so it's not one thing, it's the totality of all these things. And they haven't stopped. Seen over the weekend into Monday, more Israeli air strikes, where they are clearly taking out as much of the Hezbollah medium and long range rocket systems as possible, those are the systems that present the greatest threat to Israel. And there are even reports coming out today that Israeli special forces units have been sneaking across the border to take out tunnels and other things, all of which is to say, the Hezbollah that existed just a few days ago no longer exists. Hezbollah is there, but it will take a very long time and a whole lot of support for it to reconstitute itself. And when this part of the war is done and it's not done yet, clearly the next phase is going to be preventing Iran from resupplying them. So already, an Iranian plane tried to land in Beirut. The Israelis told the Lebanese Government, it lands. We shoot it. It didn't land. The Israelis targeted some type of smuggling operation all the way out on this Syrian Iraqi border over the weekend. Clearly the Hezbollah that exists today is nowhere near as capable of fighting a prolonged, full scale war as Hezbollah was, say, 10 days ago. Manya Brachear Pashman: And what does that mean for Iran in the region? Matthew Levitt: Look, Hezbollah was first among equals within Iran's proxy network, what it likes to call its access of resistance. And so it's not just effectively having lost Hamas as a fighting force in Gaza, and it's not even just losing another proxy. It's the pearl in Iran's proxy network. You know, we just published a new version of my book on Hezbollah with a new chapter that focuses on Hezbollah's role helping other Shia militant groups in the region make themselves more capable. On behalf of this Iranian proxy network, Hezbollah is no longer available to do that, and it really picked up the pace of that activity on behalf of other Shia militia groups in the region after the death of Qasem Soleimani. So this is something more than just another militant group, and Iran for itself, you might think, because Hezbollah is so important, then the Iranians would attack Israel. The Iranians are being very, very careful. They kind of got the message, right. If you attack Israel, Israel's going to hit back really, really hard. They understand that, unlike in April, where they shot some 300 projectiles at Israel, basically all of which missed, and then Israel had this very, very specific, limited attack back, shooting a small number of projectiles, all of which hit and took out air defense systems near Natanz, the one of the key nuclear facilities. The Iranians understand that this time around, the Israeli response to be very, very different. And no one can say after the April response, well, maybe they can't go the distance. Maybe they can't get past the air defense systems. And if anybody had any questions, even just over this weekend, the Israelis responded to Houthi attacks from Yemen with a very, very long range attack just about the same distance, or near the same distance they'd have to go to hit some things in eastern Iraq and in Iran. Manya Brachear Pashman: And speaking of Iran nuclear negotiations, where do those stand now, if there are any still underway, and how does, how does this affect that? Matthew Levitt: It's very connected, even though the nuclear negotiations are effectively nowhere. Now there's a new Iranian president who is very focused on trying to roll back. Sanctions. He is, in fact, a moderate when it comes to some domestic policy. He is not a moderate when it comes to, does he support Hezbollah, etc. He's part of the system, and the system is very much one of what they would call resistance. And so while he came to the UN General Assembly last week, and had a much more kind of calm, moderate, sort of pragmatic message about diplomacy as he was saying those words, Iran was doing all kinds of other things in the region to support Hezbollah. And more significantly for this issue, the nuclear issue, Iran has significantly ratcheted up its nuclear program activity over the past 11 months, authorities are concerned that we're maybe potentially weeks away from breakouts, should Iran make that decision, which it has not yet done, but that's a right on the cusp. And so this really does affect the calculations with Hezbollah, even before the Israeli actions to degrade Hezbollah's military capabilities, but certainly now, as Iran is trying to decide if it should conduct a retaliation of its own, because for Iran there's really only one red line. It doesn't want whatever regional war it kicks off to cross into Iran, and it wants the powder dry on most of Hezbollah's rockets, because it sees those rockets as the best deterrent against an Israeli or anyone else's attack on Iran's nuclear program, or if someone should attack the nuclear program, the best second strike capability. So it's not that the Iranians have become Zionists, nor have they backed off of their really serious desire to have Hezbollah take the fight to Israel just right now, there's a competing interest in their nuclear program, which is a much bigger strategic consideration, and so they actually want most of the power to drive as much of that powder is left after the Israeli airstrikes to defend against, to deter, against an attack on their nuclear program. Manya Brachear Pashman: So can I want to widen the lens of regional stability, not just Iran or Lebanon or Israel. I mean, some people have actually said September 27 was just as monumental for the Middle East as the Abraham accords. Is that a bit of a stretch? Or do you agree? Matthew Levitt: Look, it's premature to say exactly what September 27 will be, but it's something big, right? It's too early to tell the specific trajectory, but this is a watershed moment without question. I see the potential for very good things to come out of this. I see the potential for Lebanon to finally be able to declare sovereignty over its own country, Hezbollah, which is an unelected entity, the only sectarian militia to hold on to its weapons after the tight accords that ended the Civil War, has effectively been making decisions of life and death, war and peace for all Lebanese, without their say. So many, many Lebanese, the overwhelming majority of Lebanese, don't want a war, and are going to be angry to Hezbollah for a war of choice that they jumped into on October 8, that may have dragged Lebanon into this war. I see an opportunity for a significant setback, if not broader, dismantling of Iran's proxy network. Hamas in Gaza is not what it once was, period. It still exists. It can still do things in Gaza and the West Bank. It has leadership in Lebanon and Turkey and Qatar, but it is not what it once was, and the Israelis have demonstrated by killing Ismael Hania in Iran when he was there for the President's inauguration, in an IRGC safe house that they will take the fight where they need to to eliminate arch terrorists behind things like October 7 you saw over the weekend Hezbollah getting hit really, really hard again and again and again. This is not a one off like the assassination of Abbas Moussaoui, the original secretary general of Hezbollah in 1992. You saw this weekend after the Houthis attacked Israel again and the Israelis went in hard and hit Houthi infrastructure in Yemen, and so the next stage of this has to be doing much more to disrupt Iran's ability to send weapons and to send money to its proxies without those weapons, without that money, the Houthis, frankly, are an annoying prick in the Saudi backside. Without that funding, Hezbollah is nowhere near what it became over the past few decades, and the same goes for the rest of the Iranian proxies. Manya Brachear Pashman: How does this affect the conflict in Gaza with Hamas? Matthew Levitt: Look, Nasrallah hitched his wagon to Hamas by announcing that he would continue targeting Israel with near daily rocket attacks so long as there was not a ceasefire. That gave Hamas leader yikes in war and Gaza even more leverage. And while it's true that Prime Minister Netanyahu was sometimes playing hardball over control of the Philadelphi corridor, etc. US officials that I've spoken to have been involved in this process say that the reason there hasn't been a ceasefire deal of the past few weeks is entirely Hamas fault, because Hamas moved the goalposts on which specific Hamas leaders were to be in prison were to be released in the first round, wanting the worst of the worst now, probably thinking there wouldn't be a second round, and there's no way the Israelis were going to be able to do that. One thing that this does is it demonstrates to Hamas just how serious Israel is. I mean, Hamas is far less dangerous than Hezbollah, and if Israel's willing to do all of this against Hezbollah, Hamas has to understand like this is not ending anytime soon. There's also talk about whether or not the Iranians turn to Hamas at some point and try and find a face saving way for Hamas to say, Okay, well, we'll take a ceasefire, because that would provide Hezbollah face saving way to say, Okay, now we're going to stop the rockets, which maybe would end the Israeli onslaught targeting Hezbollah. I think that that is not a likely scenario, but it is a real scenario. Iran is not going to sacrifice Hezbollah its crown jewel in its proxy network for Hamas, and so there's lots of ways this goes, but it ultimately doesn't change the fact that Hamas is still holding hostages, that the time is running out for these hostages, as painful as it is to to articulate that And that Israel is still fighting on multiple fronts, Manya Brachear Pashman: How should the US respond? Or should the US even participate in this? Matthew Levitt: The US should not participate in this, and the Israelis will not ask Israel to the United States to participate in this. They never have. The United States, the administration has come out with very clear messages saying that Israel has a right to defend itself, and understanding that this is in response to 11 and a half months of your daily shelling. This is not an Israeli escalation. It is a long, long delayed Israeli response. They understand that the Israeli war cabinet, before this all started, before the pages went off, they expanded the war goals not to include the destruction of Hezbollah, not even to include a goal of destroying as many of Hezbollah's missiles as possible. The war goal is very clear, to enable the 60,000 plus Israelis displaced from their homes to be able to go home after 11 and a half months. And to do that, they have to deal with the rocket threat, and they have to deal with the threat of a cross border, October 7-style invasion by Hezbollah, of the type by the way, that Hezbollah is apparently plotting when Israel took out Ibrahim Akhil and a bunch of other Radwan special forces commanders last week. And so I think the administration understands that. The administration also just concluded a very significant arms deal with Israel that will provide Israel the weaponry it needs to defend itself. And the United States has also sent naval assets in particular to the region as a signal to Iran in particular, don't get involved. And I think that has been a message that the Iranians have also heard. Manya Brachear Pashman: Just as in the Gaza conflict, there have been calls for an immediate ceasefire in Lebanon because of the level of civilian casualties and the possibility of escalating violence. Matt, what's your take? Matthew Levitt: Two things can be true. There is more work to be done, and this is having devastating consequences. As we saw in Gaza we are seeing in Lebanon. The consequence of a militant terrorist group establishing military infrastructure behind and under civilian infrastructure, and hiding behind human shields. And there's only so much warning you can do, and the Israelis have sent warnings–get out of Dakia, they sent warnings on cell phones in Lebanon, you know, if there are rockets near your house, get out. There's only so much you can do. The Israelis are now, in a matter of days, dismantling more of the Hezbollah military infrastructure and firepower that has been built. Over decades now than they have over many, many, many, many years. And so there'll be calls in Israel to continue to push to not mitigate or even degrade, but to destroy as much of the military threat that Hezbollah has been posing as possible. There will also be calls for taking the win and not going in on the ground, because a ground war could be dangerous for Israeli soldiers. It could get Israelis bogged down, and there'll be a political debate there. But whether Israel really needs some type of new security zone in the south, plenty of people are kind of saying, we saw that movie. It didn't go so well. Don't go there again. But there is a real feeling in Israel that that they have to do whatever it is they have to do to not reassert deterrence, but to actually degrade the threat and enable people to go back to their lives after you know, it's, it's almost a year from the south and the north. These are not, these are not easy decisions, and we should not take lightly at all, the consequence for civilians in Gaza, the consequence for civilians in Lebanon, and, of course, consequence for civilians in Israel too. War is horrible, and I blame Hamas and Hezbollah for starting one on October 7th and 8th. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, it sounds like you need to write a new chapter for your book. Matthew Levitt: Wow. A week after the last new chapter came out, but you're not wrong. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much, Matt. Really appreciate you joining us. Matthew Levitt: It's really such a pleasure to be here. I really look forward to doing another AJC podcast on a much more uplifting topic sometime in the near future. But until then, let's hope that the region becomes more secure and that the ground is laid for us to have that kind of calmer conversation in the near future.
Sep 26, 2024
At the UN General Assembly: Jason Isaacson Highlights Israel's Challenges and the Fight Against Antisemitism
Jason Isaacson, AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer, joins us to share insights on the key priorities from the sidelines of this year's UN General Assembly. Each year, AJC experts spearhead diplomatic outreach to world leaders on crucial issues, from addressing anti-Israel bias and combating antisemitism to rallying global efforts against the Iranian threat. This year's discussions unfold against the backdrop of Israel's multi-front defensive war against Iran and its terror proxies, as well as a significant rise in antisemitism following Hamas' attacks on October 7. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus , Season 2 – out now: Explore the untold stories of Jews from Tunisia , Syria , Yemen , Morocco , and more . People of the Pod : From Rocket Attacks to Exploding Pagers: Michael Oren on Escalating Tensions Between Israel and Hezbollah Paris 2024: 2 Proud Jewish Paralympians on How Sports Unites Athletes Amid Antisemitism Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Interview with Jason Isaacson: Manya Brachear Pashman: World Leaders convened at the United Nations this week to open the 79th session of the General Assembly every year, AJC experts lead the Jewish community's diplomatic outreach on issues ranging from confronting anti Israel bias and anti semitism to uniting the world against the Iranian threat. This year's meetings come amid a backdrop of Israel's seven-front defensive war against Iran and its terror proxies and the surge of antisemitism since Hamas' October 7 attacks on Israel. Here to discuss the priorities on the sidelines of this year's UN General Assembly is Jason Isaacson, AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs officer. Jason, welcome to People of the Pod. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Manya. It's good to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I want to turn first to Israel's defense of military operations in Lebanon targeting Hezbollah. For years, AJC has been pushing the UN to designate all of Hezbollah a terrorist organization. How does Hezbollah's near daily attacks on Israel and this military operation change that plea. Jason Isaacson: I mean, it changes it only in that it emphasizes, once again, its demonstration of the danger posed by Hezbollah, which, of course, is a threat to the security, the safety of the people of Israel, to peace across the region. But also Hezbollah has arms tentacles that reach elsewhere, reach into Europe for fundraising purposes, for narcotics trafficking, for money laundering posing a real threat to security, not just for the people of Israel, but for people elsewhere in the world. But what's been happening since October 8, when Hezbollah started firing rockets, missiles, anti tank weapons into northern Israel, killing Israelis, civilians and soldiers, destroying property, inflaming the region, unprovoked, but they did it in response to or as an ally of Hamas, another Iranian backed terror organization has just destabilized the region, made it impossible for 10s of 1000s of Israelis to live in their homes. They've had to evacuate the north, disrupting the personal lives of so many And now, of course, over the last week or two weeks, we've seen repeated huge barrages of rockets, missiles that have been fired into Israel, killing and destroying property. And it's intolerable. Israel cannot live with that kind of a threat on its border, and no country would tolerate this. Israel will not tolerate it. And so we're seeing decisive action in various ways that Israel has responded to these multiple threats. In the case of Lebanon, we've seen missile attacks on rocket launchers and command centers and commanders, very precise, targeted. Of course, it is war, and there has been collateral damage, and that is terrible, but Israel has been attacked relentlessly, ruthlessly by Hezbollah. It must respond. We've also seen very interesting, really quite clever, use of technologies that Israel has mastered in other ways to attack Hezbollah commanders and fighters. We are hopeful that this will send a very clear message to Hezbollah leadership and to their backers in Tehran that they really have to pull this back. There does not have to be a wider war in the region. It is really Hezbollah's decision, Iran's decision, whether to return to some state of calm where we can have the people of Israel return to their homes, the people of Southern Lebanon return to their homes and get back to, kind of normal life. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do the diplomats you are encountering on the sidelines of the UN understand that? Do they acknowledge what you just said? Jason Isaacson: The word on the lips of most diplomats is deescalate, avoid a wider war. And of course, we can all appreciate that no one wants a wider war. But what is a country to do that is being attacked daily by hundreds of rockets and missiles fired into cities and towns? It cannot just simply say, Oh, well, we're just going to restrain ourselves because, we're more moral than our terrorist neighbors. No country would do that. No country could make that decision. So yes, there is understanding of the situation that Israel is in. There is an appeal for lessening the tensions, for de-escalating. But I think that privately, it is widely understood that Israel has no choice but to defeat the terrorist enemies that are at its throat. Manya Brachear Pashman: I spoke of the call to designate Hezbollah a terror organization in its entirety. Does Hamas need to be added to that plea for designation? Or do most diplomats already? Or I should say, do most countries already recognize Hamas as a terror organization? Jason Isaacson: Unfortunately, most countries do not already recognize Hezbollah as a terrorist organization, at least not formally. I mean, they may do it sort of rhetorically, and in a meeting with us, they may say that they of course recognize that. But for reasons that they will cite having to do with their need to continue to interact with the government of Lebanon, which of course has a very strong Hezbollah component in that government, they don't want to box themselves out as some kind of interaction with Beirut. We could point out, as we do repeatedly, that it's not necessary to exclude contact with Lebanese authorities by designating Hezbollah as a terrorist organization. Other countries find ways around that problem. France and others that have cited this argument to us repeatedly could do so as well. But it's important that Hezbollah be designated as a terrorist organization. It's also important that the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps of Iran also be designated fully as a terrorist organization. Of course, the United States has done that. A number of other countries have as well, but that must be universal. It is so clear who is lighting the fires across the region, who is threatening the sovereignty, the security of a neighboring state. And for countries to not take those simple steps to try to clamp down on funding, on money transfers, on freedom of movement internationally, for leaders of the IRGC, for leaders of Hezbollah, is just turning a blind eye to terrorism. That's not tolerable. Manya Brachear Pashman: What about Hamas? Has that been designated by more countries as a terror organization than Hezbollah or the IRGC? Jason Isaacson: Hamas is widely recognized as a terrorist organization, and I think that we need to press the countries that have not yet done so to add Hamas to the terrorist but we also have to not neglect the most important part of this equation, which is, of course, the support that Hamas and that Hezbollah get from Iran. And the fact that the sanctions that have been imposed on Iran are not always widely and carefully and universally enforced. The fact that Iran has been freed from certain restrictions that the UN imposed after the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action in 2015 in terms of its missile development, a lot of sanctions have to be restored, and the sanctions, particularly on the missile program of Iran, should be restored. And the United States in the next administration, whether it is a Harris administration or a Trump administration, I'm expecting a whole new playbook regarding the approach to Iran. Manya Brachear Pashman: So the October 7 attacks, which happened shortly after last year's General Assembly, killed more than 1200 people. 101 hostages still remain in captivity. Has the UN adequately condemned Hamas for the October 7 atrocities, the recent murder of six hostages, and has it called for the unconditional release of the remaining hostages? Jason Isaacson: No. Frankly, the UN response has been disappointing to say the least. It has failed repeatedly when efforts have been made to condemn Hamas specifically, even though we know that it is understood across the board around the world, the terrorist nature of the threat that Israel faces, no one doubts, if you have a conversation with a diplomat, that Hamas was responsible for the most horrific atrocities on October 7 and since. And of course, is holding 101 hostages, some of whom are not alive, but those who are in the most brutal conditions. We saw what happened just a few weeks ago, when Israel was preparing to actually liberate six hostages, including one American, American, Israeli, and they were executed before the Israeli soldiers could get to them by Hamas. Everyone knows the culpability of Hamas, and yet there has been a moral failure on the part of the United Nations to condemn Hamas. There have been a number of General Assembly and Security Council efforts to raise the issue of the hostages, to raise the issue of Hamas, and they've been deflected. They have not been allowed to move forward. There have been, of course, continual condemnations, as the United Nations has a long history of condemning Israel for its occupation of Palestinian territory, for its treatment of Palestinian civilians. That happens, you know, ritually in the United Nations. And, of course, every year in the General Assembly, there are, you know, a dozen or 20 or so resolutions against Israel, but to call out the terrorist organization that tells 1200 people and captured 251 others, men, women, children, grandparents, and has been holding 100+ still in captivity in Gaza. That just isn't quite on the UN's agenda. It's very disappointing. That's more than disappointing. It's outrageous. Manya Brachear Pashman: You did mention that targeting Iran, or just recognizing that Iran is pulling the strings on all of this with its nuclear ambitions, its advanced missile program, these proxy armies and terror organizations the regime does seem to pose a profound danger to Israel as well as the broader world. But do members of the UN seem to recognize this? And what is AJC pushing them to do about it? Jason Isaacson: There is wide recognition, certainly in the Gulf, but also increasingly in Europe, of the danger. Posed by Iran, not only on the nuclear file, where Iran is inching closer and closer to being a nuclear threshold state, if not an actual nuclear weapon state, but also the Iranian support for Subversion, for terrorism in countries across the region, Iranian support, Iranian regime support for assassination attempts and kidnapping attempts across Europe. In the United States as well, former Secretary of State of the United States, a former National Security Advisor of the United States, under protection by the US government because of those Iranian threats, and in Europe as well, this is recognized whether countries are prepared to impose Some economic hardship on their own countries because of imposing sanctions on trade with Iran is another question. It's sometimes been difficult for countries to make that decision. We have been pushing countries to impose further sanctions on trade with Iran, on the missile program that Iran has been pursuing, on Iran's cooperation, collaboration with Russia in Russia's brutal war of aggression in Ukraine, which is really getting the attention, especially of European leaders. So we have a lot of arguments that we've been deploying in our meetings over the last week and beyond the last week with the leaders around the world, but especially with European leaders to get much tougher in their dealings with Iran, to stop Iran Air from flying into Europe, which is now an action that is moving forward, but other forms of interaction just to make it impossible for the Iranian regime to continue to carry out its aggression in the region, threatening the security of countries in the Gulf. But of course, threatening Israel in multiple ways, by supporting terrorists who are acting against the Israeli people on seven fronts, we are hoping, and we are working hard through our advocacy in the United States, at the United Nations around the world, with our 15 offices across the globe, to make that case to foreign governments that it is time to call out and to act firmly against Iranian aggression. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm so glad you mentioned Russia, because I did want to ask you whether Ukraine is still a priority, whether it's still a priority for AJC, but also whether it's still a priority for the UN it's been more than two years Jason Isaacson: in AJC s meetings on the sidelines of the UN General Assembly. This week, we have repeatedly made the case that the territorial integrity of Ukraine, democracy in Ukraine, and frankly, the territorial integrity and democracy and security of Europe as a whole is at stake in the war that Russia is pursuing, that Vladimir Putin has launched against Ukraine, its neighbor. The importance of the United States and our allies continuing to supply Ukraine with the means to defend itself. We're not talking about American boots on the ground in Ukraine. We're talking about America doing whatever it can, and it has done a lot to help the people of Ukraine defend themselves against Russian aggression, not only for the good of Ukraine, but frankly, for the security, the safety of Europe, and frankly, of global security. If Russia is allowed to continue gobbling up pieces of Ukrainian territory unimpeded, unchallenged by the West, it will continue its rapacious ways, and that is just not acceptable in Europe. It's not acceptable for the security of the United States, for our interests across the world. So it is important that Russia be pushed back. It is important that we stand by Ukraine as they try to liberate themselves from Russian aggression. And frankly, it's a signal to other countries that may have territorial ambitions, designs on neighboring states, small, weaker states. You know what we're talking about here. So it's important that the line be drawn, and we stand by that line and continue to supply Ukraine with what it needs to defend itself, and it has actually made some impressive gains. It has still a challenge ahead. Russia is much larger and has many more missiles in its stockpile than Ukraine does, but Ukraine is fighting back, and is actually taking the fight to Russia, which is so important we need to stand by our friends in Ukraine as they beat back Putin's aggression. Manya Brachear Pashman: So that seems to be a popular sentiment, that it's okay for Ukraine to fight back, and we support that effort. So why do they not support the efforts of Israel to fight back? Is it just geography? Jason Isaacson: Well, Israel has always had a difficult challenge in the United Nations. Of course, the situation with the Palestinians has been a popular cause across the globe, and it's been very difficult for Israel to make the case that it does not want to rule over the Palestinian people. It was put in that position as a result of a war in which it defended itself against aggression in 67 and 73 and ended up occupying land or administering land that had been launching pads for strikes against the people of Israel themselves. It is hoping for, searching for, it has signed on to a process that would allow for a political resolution of the status of the Palestinians. Palestinian leadership has been such that it hasn't been able to move forward on any kind of a further settlement of that dispute with Israel. And in the meantime, the public around the world has grown frustrated and of course, has a continuing support for the underdog, less appreciation for the situation that Israel finds itself in. And that's just a fact of life that we've been we've been wrestling with for too long. At the same time, there is an appreciation of the contributions that Israel has made and continues to make to technological advancement, public health, a variety of fields in which, certainly the countries in the region, but countries beyond the region, can benefit from further interaction with Israel. We've seen the growth of the relationship between Israel and India, the growth of relationship between India and other states in the developing world, and we're hoping that at a certain point, public opinion will follow the trend that is so evident in our contacts with governments around the world. In many ways, what we've seen is an action in which Israel is the target, but the real target is the West. The real target is the United States, and Israel is an ally of the United States as the one democracy in the Middle East, closely connected to the United States, has been in many ways, the focal point for antagonism toward the west, and it puts Israel in a unique position. Sort of a positive position, in some ways, in that there's an affiliation and association of Israel with the United States, which is of benefit to countries in the region that want their own strategic partnership with the United States, that want to benefit from Israel's access to the west, technologically, in education, in public health, and a whole range of sectors. But for other parts of the world, where it's easy to blame the West for their own economic situation or political situation, it's very easy to link the United States with Israel, and therefore to hold Israel somewhat to a different, harsher standard. That's part of what's going on. Part of it is identification with the Palestinian cause, which has been very popular on the street, fueled in the Arab world by Al Jazeera and other media, but also very conveniently used over the generations by Arab governments to deflect from their own issues of governance in their own countries and elsewhere in the world, it's been a rallying cry for a range of despots and dictators and monarchs who have wanted to again, distract their countries from the real issues that they face, and target this western outpost in the eastern Mediterranean. Manya Brachear Pashman: Speaking of strategic partnerships, is the UN General Assembly the right forum to pursue discussions of expanding the Abraham Accords, and is this the right time, even if it is the right forum? Jason Isaacson: Well, in the General Assembly of the United Nations, no, because there is an automatic majority. And we just saw this on display just a week or so ago when the UN General Assembly adopted a one sided anti Israel resolution overwhelmingly by something like 50% more votes against Israel than occurred the last time a couple of years ago that there was a resolution regarding Israel the General Assembly a similar resolution. So no, not in the General Assembly itself, not in the UN system itself, but among individual countries, Israel is still quite popular at elite levels of many countries, and AJC has worked, I should say, tirelessly for decades, to open doors for Israel. Countries around the world, not just in the Arab world, but in the developing world and elsewhere. We continue to do so, and we continue to find great receptivity to the argument that there is much to be gained by a relationship with Israel. Maybe starting out quietly, but benefiting the people of your country. Prime minister, Foreign Minister, Mr. President, Madam President, these are arguments that we are making constantly, and we're seeing the openings of trade relations, of new business opportunities, investments, exchanges, people coming to Israel to learn about how they can benefit their own societies by a different kind of a partnership with counterparts in Israel. AJC has been part of that action for a long time. We continue to do so through our Center for a New Middle East, which was announced by AJC CEO Ted Deutch in June. We are expanding our efforts, especially across the Gulf and North Africa, to introduce societies, civil sector leaders, business people and governments, to the benefits that would accrue to them, to their societies through the embrace of this new Middle East, which has begun frankly with the Abraham Accords in 2020 and we are hopeful that the coming years will bring us greater success as well, but not just in that part of the world. Other countries, as we have seen through the advent of I2U2 and IMEC, which were efforts to bring India into more interaction with Israel and with Europe, this corridor from India to the. Middle East to Europe and Israel in cooperation with India and the United States and the United Arab Emirates. I2U2, all of these efforts are efforts to expand the circle of Arab Israeli peace, to expand the circle of Israel's interaction with for the benefit of those countries, countries around the world. And we're seeing great success there. We continue to work hard to broaden that success. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jason, thank you so much for shedding light on what you've been up to this week on the sidelines. Jason Isaacson: Always a pleasure, Manya, thank you.
Sep 20, 2024
From Rocket Attacks to Exploding Pagers: Michael Oren on Escalating Tensions Between Israel and Hezbollah
In this episode of People of the Pod , Ambassador Michael Oren dives into Israel's escalating conflict with Hezbollah, which has turned Israel's northern border into a war zone and caused 60,000 to remain displaced from their homes. Oren emphasizes Israel's need to defend itself on multiple fronts, including threats from Hamas, the Houthis, and Iran, warning of the risk of all-out war. He also discusses the formation of the Israel Advocacy Group (IAG) to bolster Israel's media and diplomatic efforts and shares how his vision for Israel's future, as outlined in 2048: The Rejuvenated State, remains critical post-conflict. Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : Explore the untold stories of Jews from Tunisia , Syria , Yemen , and more . People of the Pod : Paris 2024: 2 Proud Jewish Paralympians on How Sports Unites Athletes Amid Antisemitism The DNC with AJC: What You Need to Know about the Democratic Party's Israel Platform Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Interview with Michael Oren: Manya Brachear Pashman: Michael Oren served as Israel's ambassador to the United States between 2009 and 2013. As ambassador, he was instrumental in securing US support for Israel's defense and upholding Israel's right to security. His current role isn't all that much different. After October 7, he launched the Israel Advocacy Group (IAG), which has worked to strengthen diplomatic relations for the Jewish state and support Israelis during wartime. Ambassador Oren is with us now to explain the challenge Israelis are now facing. Ambassador Oren, welcome to People of the Pod. Michael Oren: Good to be with you, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: Ambassador, you are touring the US with residents of Northern Israel who've been displaced by near daily attacks from Hezbollah terrorists across the border with Lebanon. As we speak, Israel is conducting a military operation in Beirut. Can you tell us what is happening and why? Michael Oren: Okay, let me begin by saying that Israel has not taken credit from the pager and walkie talkie attacks Has not. And so we want to avoid that type of symmetry, because on one hand, Hezbollah is very proud of the fact that they're firing hundreds of rockets and hundreds of explosive drones at civilians in Israel. Literally. Israel's not taking that credit. Okay. So let's begin with this. October 8, a day after the horrendous Hamas assault on southern Israel. Hezbollah, out of a vowed desire to show solidarity with Hamas, opened fire on Northern Israel. To date, about 10,000 rockets, explosive domes, have been fired at Galilee. It began along the immediate border, some 18 communities along the immediate border, but it creeped downward. Creeped downward now where rockets are falling along the Sea of Galilee, which is in southern Galilee, and moving its way toward Haifa, nd the suburbs of Haifa, moving westward. 100,000 Israelis have been rendered homeless. 10s of 1000s of acres of farmland, forest land have been incinerated. 1000s of houses have been destroyed, and dozens of people have been wounded and killed, as well. Civilians, as well as military. The entire North has been transformed into a war zone. Cities that you know, like Kiryat Shmona, Metula, are ghost towns today. One of the members of our delegation, Her home was rocketed in Metula yesterday. Is the 215th home destroyed by Hezbollah in that once beautiful, beautiful town of Metula. So that's the objective situation. Is it an utterly, utterly unprovoked attack on the land and the people of Israel. And Israel, of course, has to defend itself. The great complaint among the people of the north, it is that the state has not done enough to defend the people of the north. And so any actions now taken, including last night, where Israeli warplanes were attacking Hezbollah emplacements and targets, not just in southern Lebanon, but throughout Lebanon, is very much welcomed by the people of the north. So they have yet to see how the state intends to return them and store them to their homes. I'll just add one more point that is widely misunderstood in this country. There's a notion that somehow, if a ceasefire is attained with Hamas in Gaza, which is highly, highly unlikely, but if it is attained, then Hassan Nasrallah, the head of Hezbollah, said, he too will accept a ceasefire, but a ceasefire will restore the status quo of October 6. And Israelis simply won't go back to their homes if the situation that obtained on October 6 where Hezbollah was exactly on the opposite side of the fence, no one's going back to communities that are opposite side of the fence, because now we know what terrorists can do to Israelis on the other side of that fence, our side of the fence. So there is really no alternative but to drive Hezbollah back. It's to drive them back beyond the Litani River, which meanders opposite our northern border, between 13 and 20 kilometers. There's a diplomatic initiative by American Special Envoy Amos Hochstein to try to convince Hezbollah to retroactively implement Resolution 1701, of the Security Council. It's from 200. They called on his Hezbollah to withdraw north of the Litani River. Hezbollah never accepted it. Hezbollah violates it daily, flagrantly. I wish Mr. Hochstein all the best of luck. I don't know what leverage he can bring to bear to convince Hezbollah to implement 1701 but barring that, Israel will have absolutely no choice to push Hezbollah back physically from that fence. Manya Brachear Pashman: In fact, returning residents home, to their homes in northern Israel has become a war goal. The cabinet has just announced this week, right? Michael Oren: Well, it's about time. It's about 11 months too late. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I guess, what does that mean? Does that mean that this conflict with Hezbollah or Lebanon could escalate? Michael Oren: Oh, I would expect it would escalate. Yes, and that we have to prepare it for any scenario, including an all out war. Now, an all out war is no small thing. It's a war that's many times more severe than that, with Hamas in the South. First of all, Hezbollah is one of the largest military forces anywhere, not just in the Middle East. It's got upwards of 170,000 rockets hidden under villages, under hundreds of villages. It has a fighting force of terrorists that's three, four times that of Hamas. It has cyber capabilities. And it's not just Hezbollah. It's the Shiite militias that are backed by Iran and in Iraq and Syria, the Huthi rebels in Yemen. We know that they can fire Israel well. And there's Iran itself. Iran, which, on April 14, launched 315 rockets at Israel. So the IDF estimate for rocket fire per day in any war with Hezbollah could reach as much as 10,000 rockets a day. And that will overwhelm our multi-tiered anti-missile system. We will require assistance from the United States, and even then, it will be quite a challenge. Manya Brachear Pashman: As you mentioned, this is all happening simultaneously with the war against Hamas in Gaza. Yes, Houthis also are firing rockets, one of which, I think at least one reached, or almost reached, central Israel just this past week. And I mean, how many fronts is Israel fighting on right now? And could this escalate? Could, though, that number of fronts grow even more? Michael Oren: Well, right now we're at about seven fronts, according to the defense Minister's calculation. So what is it? It the North. It is the south. It is the Huthis, very much to the south, but are capable of firing into Tel Aviv. It is the Judean Samaria, the West Bank front, which is very severe indeed. So that's just sort of the bottom line of the fronts we're firing. We're also fighting a front against Iran, more distantly, against the Shiite and militias in Iraq and Syria. So a multi, multiple front war. And make no mistake about it, this is an existential struggle for the State of Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: And you said that returning to October 6 or what the status was on October 6 is now not acceptable. I mean, was there a short window of time where that was, what the wish and the hope was? And that has shifted.? Michael Oren: I think it was lost on October 7. So if you were to go to Metula on October 6, you could stick your hand through the fence, and I wouldn't recommend you do this. You could stick your hand through the fence, and you would touch Hezbollah. They're right there. And the people of Matula and other communities along that border simply won't go back under those circumstances. And you can understand why. I don't know if you have young children, I don't think you put your children in a house that's looking at Hezbollah across from a fence. Now we know what terrorists can do to Israeli families, civilians, women, babies, who are on the other side of the fence. And a fence is no guarantee against any assault. The people from the north also believe that there are still tunnels under that fence that we haven't discovered all of the Hezbollah tunnels. There are people in our delegation from the north who believe that Hezbollah still has tunnels that have not been detected under that fence, because Hamas digs tunnels in sand, Hezbollah digs tunnels in rock, and they're deeper and harder to detect. Manya Brachear Pashman: You said that you wondered, if I have small children, I do. I have two small children. We go to well, they're not. They're getting less small by the day. But it made me think of a column that you wrote back in March for The Forward about how Jews are cursed to be a lonely people. And I actually gave a speech to our synagogue congregation just last week, talking about how I was so grateful to be part of a congregation on October 6, celebrating Simchat Torah when I woke up on October 7, because otherwise I would have felt and my children would have felt so alone. And I am curious where you were on October 7, and how you have combated that loneliness, that lonely feeling. Michael Oren: Hm. Well, I had an unusual experience. On October 5, I was giving a speech in Dallas, Texas, and the speech was interesting, because at the end of my remarks, I told the audience that I believe that Israel would soon be going to war. And everyone gasped, and I'd actually been briefing foreign diplomatic personnel about this for about two weeks. And the reason I thought Israel was going to war was because of the divisions within Israeli society, the divisions within American societies, that Iranians were following very, very closely. But the most important point was that the United States was trying to broker a peace agreement between Israel and Saudi Arabia, and as part of that deal, Saudi Arabia was going to get nuclear power. And my line was that if anybody thought that the Iranians would sit quietly while the Saudis got nuclear power, they were kidding themselves, and the Iranians would start a war. All right, I had other information, but that was the major thrust. So two days later, I was coming back to Israel. I was stopping off at my mother's house in New Jersey, woke up to the messages you never want to receive on your cell phone, which is, are you okay? Are you okay? Are you okay? And learned about this. Now for many years through the generosity of the Singer Foundation. Whenever there's a national emergency, I'm immediately put on television. So starting on the morning of October 7, I was on CNN, MSNBC throughout the day, called some friends in ElAl and got myself on the first flight out of Newark that night, and landed in a war zone the next morning and went immediately to work. So around a small kitchen table in my house, a group of volunteers together formed an emergency NGO called the Israel Advocacy Group, because what can I say, the state wasn't doing a particularly excellent job in defending itself in the media and other forums. And what began as a small sort of a ma and pa operation around the kitchen table has now become the Israel advocacy group, IAG, dealing with international media, mainstream, non mainstream, and with track two diplomacy. So track two diplomacy is what we're doing in Washington now by bringing the delegations to the hill. We've had meetings on the hill with both parties, both houses, and today we're in the White House. So we've gone to the White House twice with these delegations. That's tracked two diplomacy and so it's a big undertaking. So my way of dealing with the loneliness is certainly joining with other people, especially young people, who are committed to defending Israel in every possible form. I'm very blessed because I'm a member of a community in Jaffa, a kehilla, which is just wonderful and, of course, the family, the family, the family. Tammy, my, my beloved and children and grandchildren, 6.5 and counting. Manya Brachear Pashman: You are heading up this Israel advocacy group that's post October 7. But before October 7, you had started a think tank. I don't know if you would call it an advocacy group. I've been calling it a think tank. Called Israel 2048. You also wrote a book titled 2048: The Rejuvenated State. It was published in one single volume in English, Hebrew and Arabic, very, very symbolically. And I'm curious if this vision that you laid out for the next century of the Jewish state, is it stalled by all of this? Michael Oren: So first of all, 2048 it was a project that grew out of my time in Knesset, and I was the deputy in the prime minister's office, and sort of realizing that Israel is so bogged down in its daily crises, little do we know what a daily crisis was, that we never really think about our future. And the goal was to envision the Jewish state on its 100th birthday. Our 100th birthday would be 2048, and how can we assure a second successful century? What changes had to be made in the State of Israel? And they're pretty big, far reaching changes. And it began as a discussion group online. We had a 2048 seminar at the Hartman Institute with Natan Sharansky for about a year, then covid hit and retreated to the room and wrote this book. It's an 80 page manifesto that covers 22 aspects of Israeli society. Its educational policy, social policy, health policy, foreign policy, America-Israel diaspora relations, of course, the US relations and the peace process. Certainly the largest section on the peace process and our relationship with Israeli Arabs, the Haredi issue, the ultra orthodox issue, the Bedouin issue. It's all in 80 quick pages. And the idea of the book was to sort of to spur conversation, especially among young people within Israel and in the United States elsewhere in the diaspora. In the way Zionist thinkers used to think about the future Jewish state, starting in the 1880s up to the 1940s. Huge literature on what this Jewish state was going to look like. And we seem to have lost the ability to have that sort of broad discussion about our future. And it was going very, very well, the discussion. It was not a think tank. It was actually an anti think tank. I didn't want to produce any papers. I just wanted to have discussions. When the war broke out. Looking back at this book now, it is actually a better seller now than it was before the war, because many of the problems that were revealed by the war were anticipated by the book. And it's actually more crucial now than ever before. You know, Manya, I'm often asked, What wars does this war most resemble? Is it the 67 war where we were surrounded by enemies, the 73 war, when we were surprised by our enemies? But truly, the war that most resembles this one is the War of Independence, where we are fighting on multiple fronts, in our neighborhoods, in our communities, and everybody's in the army. And the tremendous, tremendous cost. So really, we're in a second Israel war of independence. And that's the bad news. The good news is we get to rebuild afterward the way we rebuilt post 1948. I don't know any other manifesto that sets out the goals that we have to strive if we're going to have a successful Second War of Independence. Certainly, we have to address the Haredi issue. That's not sustainable. We have to address the Bedouin issue, you know, the IDF secured the release of one of the hostages several weeks ago, a Bedouin gentleman. It was an extraordinary event, definitely praiseworthy, but that Bedouin had two wives, and had settled illegally on state land, and that sort of it was indicative of the type of problems we face with a Bedouin that no one's addressing. But it's also our education system. How can we proceed and a road to some type of better relationship with the Palestinians? How can we maintain unity within Israel, within the Jewish world? Everything from the Kotel to teaching math on a high school level in a Haredi school. Manya Brachear Pashman: How dismaying that there are so many wars to choose from for comparison. But I, but I appreciate the one that you the analogy that you've made and the hope that that carries with it. So, Ambassador Oren, thank you so much for joining us. Thank you. Michael Oren: Thank you. Let me say Shana Tova. Manya Brachear Pashman: Shana Tova. Michael Oren: I also want to give a special thank you to the American Jewish Committee. Yesterday morning, we through the office under the aegis of the the AJC, our delegation of displaced northerners met with about 20 representatives of the diplomatic community here in Washington, including the German ambassador, the Czech ambassador, the Slovakian ambassador, diplomats from Spain, Italy, and for the first time, this diplomatic community was able to hear firsthand what it is to live under daily Hezbollah rocket and drone fire, to be displaced from their homes, and it was extremely important. We're very, very grateful to AJC. Manya Brachear Pashman: Ambassador Oren, thank you so much for joining us. Michael Oren: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with two proud Jewish Paralympians on how sports can unite athletes amid antisemitism, which surfaced during the Paris 2024 Olympic Games.
Sep 9, 2024
Paris 2024: 2 Proud Jewish Paralympians on How Sports Unites Athletes Amid Antisemitism
Following Hamas' October 7 massacre of Israelis, antisemitism has infiltrated nearly every part of society – including the world of sports. At the 2024 Paris Olympic Games, Israeli athletes faced death threats and "Heil Hitler" salutes. U.S. Paralympian Tahl Leibovitz, an Israeli-American, knows this hatred firsthand, having been targeted both on and off the court simply for being Jewish. Together with fellow Paralympian Ian Seidenfeld, the Para Table Tennis champions reflect on how they've seen sports serve as a powerful unifying force, despite the challenges. ___ Listen – AJC Podcasts: The Forgotten Exodus : Season 2 out now exploring the untold stories of Jews from Tunisia , Syria , Yemen , and more. People of the Pod : The DNC with AJC: What You Need to Know about the Democratic Party's Israel Platform Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts or Spotify. __ Transcript of Interview with Ian Seidenfeld and Tahl Leibovitz: Manya Brachear Pashman: It is always a joy to watch the Olympic Games with my children. I must confess, not until I had children, did I watch the Paralympics. If you want to see strength, grit, and resilience on a heroic level, behold British cyclist Sarah Story claim her 18th gold. My son's favorite sports are wheelchair tennis and table tennis. So he was particularly excited when I told him that I had the opportunity to sit down with two proud Jewish athletes who competed in this year's Paralympic games in Paris. Twenty-three year old Ian Seidenfeld and 49-year-old Tahl Leibovitz are members of the USA 2024 Para Table Tennis team. They are here to talk about their approach to the sport and what it means to be a Jewish athlete. Ian, Tahl: welcome to People of the Pod. Ian Seidenfeld: Thank you. I'm happy to be here. Tahl Leibovitz: It is really good to be here. I'm very excited about this. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what drew you to this sport, to table tennis? Ian, how about you start us off? Ian Seidenfeld: Yeah, I don't know if I was ever interested in table tennis, but my dad was the table tennis coach, runs the table tennis in Minnesota with the Minnesota Table Tennis Federation, so it was always kind of just a part of life in that when I was four or five years old I'd want to go with my dad to work and kind of be around him and play. And it just happened to be table tennis that he was coaching. So I didn't even know what was going on, but it was something that I enjoyed to do to kind of hang out with my dad a little bit. Tahl Leibovitz: I was in the South Beach Boys and Girls Club that was kind of in Queens, South Richmond Hill. And I had a lot of different things. I was doing martial arts there, which I really liked a lot. And my trainer was saying, if you do table tennis it can help you with your reflexes. You're gonna be faster. And I started doing table tennis, and I kind of got drawn into it, and I really like the challenge of it. It's very similar to chess – it's like chess and running at the same time. I do a lot of jiu-jitsu now, it's similar to that. You're trying to solve things. So it's very interesting. Manya Brachear Pashman: Tahl, you were born with a physical disability that makes it difficult to kind of move on your feet and to straighten your arms or flex your wrists. So I'm curious how you've balanced that. How have you overcome that? Tahl Leibovitz: Another good question, and most people don't even ask that, and that's probably somebody that had been playing table tennis probably for like, 10 or 20 years would kind of notice I have osteochondromas, so I have limited supination and pronation. You can't really see if I'm walking, can't see any disability, but I have bone tumors all over my body. They're benign, so it restricts movement. So to answer that, I had to find a way to adapt. So when I hold the racket, I change the grip a lot. And I would say the two things that I never thought I would become this great player. You know, you never really know. But when I was watching the best athletes in the country in the world, I started competing against them eventually. And I started trying to think, 'Okay, what, you know, what would be difficult? How could I make their match difficult?' Not trying to beat them, but how can I make these matches very difficult for them? I started doing that a lot, and then I built the style. And then, of course, you know, really believing that you can compete against anyone. I say those two things, and then I don't know, I started, I don't know what happened after. It took about eight years, and I just started doing really well, both in the able-bodied and the para competition. Manya Brachear Pashman: Ian, can you talk a little bit about the preparation and training process for the Paralympics and other competitions as well? Ian Seidenfeld: Table tennis training, a lot of it happens on the table, as you might imagine. So we're on the table for two to three hour practice sessions. And then what I try and do outside of table tennis is, for me, cardio on the bike. I live near a lake, Lake Bde Maka Ska in Minnesota, and so it's a very beautiful lake to ride around and get that kind of cardio in, two to three days a week, and then playing on the table three to four days a week for myself. A lot of it is that hand-eye coordination is the biggest part, being able to react to the ball movement much quicker than others, I think is a defining factor, along with being able to understand spin. That's maybe the biggest difference in table tennis compared to other racquet sports, is the amount of spin we can get on the ball. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you have a signature move or kind of signature maneuver that you use to best your opponents? Ian Seidenfeld: I think my best thing is variation. Because of my disability of dwarfism, I have shorter limbs, so I can't reach or move as far as others. So I try and control the table with angle of play as well as spin and speed variation. So it's a very, we'll call it a thinker's game, trying to outsmart the opponent some ways and keep things very uncomfortable for them. That's kind of what I try and do to my opponents. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's great, keep them guessing as to what's coming their way. I love that. Well what have been some of your challenges? In other words, are there particular strategies or moves that other players use that you have really tried to get better at confronting? Ian Seidenfeld: Yeah, there's a lot of different things. As I said, with my disability, with dwarfism, a short stature and shorter limbs, I have had people use a short serve against me, so that I can't reach the serve to start off the point. And we've kind of fought over the last five or six years for me to be able to use a paddle extension, which will basically allow me to reach the first serve and then take the extension off and play like a normal point afterwards. So that's, for me, kind of a big difference. The other big difference for my disability would be I can't play as long because my joints are very malformed, so I have higher levels of inflammation sooner. So I kind of practice less than most people. Manya Brachear Pashman: So it seems like that would be something that they would regulate or accommodate. I'm kind of surprised that they would even allow a short serve in that kind of circumstance. Ian Seidenfeld: From how my dad described the Paralympics to me when he was playing in 1988 in Barcelona, he had won a gold medal there. At the time, it was probably more about building community and acceptance among disabilities. Just because we have a disability, we're not necessarily accepting of other disabilities. And so in those instances, you can see, back then it was, you were kind of learning to be around other people and accept their differences. I think now we've gotten to the point where a lot of it is about this higher level of competition, and so that competitive aspect has changed things a lot more. So maybe the short serves and things, tactics that might be considered underhanded are a little bit more accepted than I'd like it to be. But who am I to argue? I'm happy to just to be able to play. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned your father, Ian. He was a champion in the 1980s. He is now the coach of the U.S.A. Paralympic team. What other mentors or support systems have both of you had along the way? Ian Seidenfeld: Yeah, I think family is the biggest crutch for all of us. I know for my teammate, Jensen, he's the same age as me, and so he has a very good support system with his parents and his brother. And myself, with my parents and my sister, I think we were able to confide in them very honestly and speak candidly about everything that we're feeling. I recently had been talking to an energy coach as well, someone to kind of give better levels of positive energy, being able to stay more present in the moment and not get ahead of myself, and I tend to guide towards the negative aspects of things, getting upset or getting annoyed or frustrated. And so I'm trying my best to get out of that. And so I have been talking to someone to kind of help with staying positive in tougher times. So it's really about being able to be honest with yourself and with other people, and not afraid to reach out. Because, as an athlete that's competing in Paris, a lot of people want to help and do their best for you, and so you just have to be able to communicate in a mature way. Manya Brachear Pashman: And what about you Tahl – what does your support system look like? Tahl Leibovitz: Yeah, you know, that's probably one of the most important things, is when you connect to people that are, you know, trying to help you along the way. Of course, my coach Sean O'Neill has been a very good mentor. He's a two-time Olympian, five-time national champion. He's helped me greatly, helped me study for, you know, when I was doing my social work exams. We also have a lot of great coaches. Mitch Seidenfeld is our head coach. We have Vlad Farcas. He's amazing. He's, you know, a really good friend and somebody that runs the program as well. But I would say, yeah, those three individuals, and there's another person, Dr. Dov Copler, who's practicing medicine. He's helped me a lot as well. Of course, my wife, I've been married for more than 20 years, she's unbelievable, and we're, you know, best friends, and she's helped me, you know, without her, I probably couldn't make these achievements not be possible. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm curious, has your Jewish identity played a role in your athletic success, your academics or your professional careers? Ian Seidenfeld: Yeah, my Jewish identity. So I'm a reform Jew, but I think it's a lot about the community and family that I have that's really important to me, and I've been able to look up to them and what they've done in their careers and their lives, and how they kind of view life in a lot of ways, to just enjoy it, enjoy family. And so I think I've taken a lot of that as being very important to me, being able to try and pursue both career and being consistent with my family. Tahl Leibovitz: I was born in Israel. You know, I was born in Haifa. Obviously, I'm very connected to Israel. And I went to a thing called the Maccabi Games that was in 1997, that was my first games. And the people, the experience, it was just so amazing. And that's the first time I had been back to Israel. I'm trying to think, I was 22 years old, I think at that time. So I would say, yeah, Israel, I feel so good there. There's a very good connection to being there. So that's the positive note and, you know, and also coming up, you know, on a negative thing. You know, being Jewish, of course, it's not easy in some ways, you know, I went through, in a lot of obstacles and different things because of that. Manya Brachear Pashman: So can you talk a little bit about some of the obstacles that you have encountered along that being Jewish have presented? Tahl Leibovitz: When I grew up – well, I lived in the street when I was a boy, you know, for maybe 13 to about 21 but it's interesting before that, even when I was, I grew up in Howard Beach, and then eventually I was living in kind of, like, by Cypress Hills in New York City. And there's, like, a shame that being Jewish, like I was, you know, is like, in some way, from my peers, like I wasn't around a lot of Jewish people, and they were, you know, they make fun of you. They like, you feel this, and I didn't know anything really. I was only a kid, but I think having my grandfather was, like, a really good, I mean, he made a, you know, spending time with him was a big difference. He was a Holocaust survivor. One thing I learned from him, which I think is so important, I think more people should do. When you look at the Jewish community, it's like the family. There's a very strong sense of family. And I feel, even when I'm in Israel, because I'm very good friends with a lot of people on the table tennis team, the Israeli Center, I feel such a good connection, like I feel really a part of something, and that is really important. Manya Brachear Pashman: So in other words, being part of that sports community and a team, there's something kind of Jewish about that and that family feel. You spoke about the negative. Of course, Israeli athletes competing in Paris, some have received death threats and hate messages online, and then at the soccer match between Israel and Paraguay, spectators were yelling Heil Hitler during the Israeli national anthem. As a Jewish athlete, as an Israeli-born Jewish athlete, is this hate something that you have encountered along the way, or is this hate just reserved for the athletes representing Israel? Tahl Leibovitz: You know, I'll say two things to that. The first being that, you know, obviously, what happened, you know, in October of last year. You feel something. You could say whatever you want. There's no words. I feel like I've overcome a lot of adversity, but to feel that, like, that you can't do anything. You feel so badly, you know. So there's a connection, I think, you know from all of us that is the first thing. So, and you look at what's happening in the schools, Columbia University, and a lot of these things, so there is a heightened sense of antisemitism, for sure. And I would say that does happen. I'll give you one quick example, which is very, very interesting. I had to play a league match. This wasn't even too long ago, just two months ago, so to play a league match. And there were, you know, I'm not saying these people are bad or good, but they were from Egypt. There were two players, and then they, they came in and they said, 'Do you know where we were?' And I was like, 'Okay, where were you guys at?' And they said, 'Well, we're in the mosque, and we were praying for the destruction of Israel. We were praying that Israel would be destroyed.' I'm about to start a match with these guys, and, you know, obviously I'm a therapist, so, you know, I have a lot, you know, patients, and I ended up winning against them. So they were not too happy. But the point is that I tend to think about, like when people bring that, they have great difficulties within themselves. And of course, you can match that, you know, with it, with anything you know. You can be aggressive with them. But I find if people sit long enough in some of these, I don't know if you want to call it delusions that they have, because a lot of people, we're just human beings. People hate Jewish people for no reason, like, it's like, they don't even know me. It's like, you're hating somebody for something, you don't even know them. So I think when people sit with that, they tend to, you know, they spend a little more time with you. Sports can do that too. It kind of humanized people together. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's interesting. You have actually called your birthplace your favorite place on earth. And I'm curious, how do you honor both your American and Israeli identities while representing the United States in competition? Tahl Leibovitz: Yeah, that's a very good question. And I would say for me, the thing, because I've been to a lot of different tournaments, the Paralympics, a lot of different things, the most incredible experience for me has been like I mentioned the Maccabi Games. So that's one thing, and I stay connected, you know, and it's also not just what I'm doing. Look, I'm a table tennis player, I do the best I can. But, you know, there's some people that I've, you know, there's a student I work with. Her name is Estee Ackerman. She does a lot of public speaking. She was a great player. We, you know, I trained her for many years. So you, kind of, I would say the answer is this sort of community, you know, and to and to be connected to yourself, and also to be even in therapy, you know, actually, I'll say one other thing. I could say a lot. I work for a few, I have contracted a few different places. And I said to one place, you know, after this thing happened in Israel, I said, and again, I have no special ability. I just said, look, send me the people that were affected by Israel. I said, those are the people I want to work with now. I said, send me as many as you can, as much as you can. And then I started working with them. And it is, the truth is, it's profoundly effective. Like there were, you know, these people that can't function at work. You know, it's something, some of them were very connected, they're affected in some way, obviously. So I just give what I can. I can't change the world, but I know, like, I can give the best I can to people, and even if I do my small part, it's okay. Manya Brachear Pashman: So after this year's Paralympics, what's next? Ian Seidenfeld: I think the goal is really to just try and feel comfortable and try and have fun out there, and the results will come. But after the Paralympics, I work for a company called Allianz, a global insurance company, and so I plan to continue working for them afterwards, and they've been, they're a sponsor of the Olympics and Paralympics, so they've been very supportive of my training, and so I plan to continue working for them and continue training for the next World Championships and Maccabi Games, and we actually have our own Allianz Olympics coming up in 2026, so there's a lot more table tennis to be played, and ultimately I hope to compete in LA 2028 so I might take a month or two off, but other than that, it'll be back to training as usual. Tahl Leibovitz: Well I set a goal that I wanted to try to continue to 2028 since I won my first gold medal in 1996. That was my biggest achievement. And so now I'm saying, all right, we have 2028 in LA, so I will continue to 2028. I'm in pretty good, playing pretty well, doing a lot of fitness. So I feel okay. And yeah, probably do that, and then I will see. Most likely I will retire, I think, although people keep pushing me to do another two, but that would be 2036 would be my last one. So it's a little, I'm 50 years old, almost, so, but we'll see. I think 2028, then I'll reevaluate. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well thank you both so much for joining us. Is there anything I have not asked you that you definitely want to share with our audience before we go? Ian Seidenfeld: I think when we're talking about acceptance and love and trying to overcome our differences and challenges, I think the Paralympics can be a very good representation of what we can all do together, as the Olympics was founded as well to find common ground among nations, and I think there is a lot of hate and rhetoric that's spoken throughout the US and throughout the world, that hopefully people will be able to watch the Olympics and Paralympics and feel a more, a greater sense of unity among people. And hopefully we won't have death threats and that kind of hate, that's really unnecessary. I hope. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well said. Thank you so much. Ian, Tahl, Mazal Tov! Ian Seidenfeld: Thank you very much. I appreciate it. Tahl Leibovitz: Thank you. Thank you so much.
Aug 30, 2024
The Forgotten Exodus: Tunisia – Listen to the Season 2 Premiere
Listen to the premiere episode of the second season of The Forgotten Exodus, the multi-award-winning, chart-topping, and first-ever narrative podcast series to focus exclusively on Mizrahi and Sephardic Jews. This week's episode focuses on Jews from Tunisia. If you like what you hear, subscribe before the next episode drops on September 3. "In the Israeli DNA and the Jewish DNA, we have to fight to be who we are. In every generation, empires and big forces tried to erase us . . . I know what it is to be rejected for several parts of my identity... I'm fighting for my ancestors, but I'm also fighting for our future generation." Hen Mazzig, a writer, digital creator, and founder of the Tel Aviv Institute, shares his powerful journey as a proud Israeli, LGBTQ+, and Mizrahi Jew, in the premiere episode of the second season of the award-winning podcast, The Forgotten Exodus. Hen delves into his family's deep roots in Tunisia, their harrowing experiences during the Nazi occupation, and their eventual escape to Israel. Discover the rich history of Tunisia's ancient Amazigh Jewish community, the impact of French colonial and Arab nationalist movements on Jews in North Africa, and the cultural identity that Hen passionately preserves today. Joining the conversation is historian Lucette Valensi, an expert on Tunisian Jewish culture, who provides scholarly insights into the longstanding presence of Jews in Tunisia, from antiquity to their exodus in the mid-20th century. ___ Show notes: Sign up to receive podcast updates here . Learn more about the series here . Song credits: "Penceresi Yola Karsi" -- by Turku, Nomads of the Silk Road Pond5 : "Desert Caravans": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI), Composer: Tiemur Zarobov (BMI), IPI#1098108837 "Sentimental Oud Middle Eastern": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI), Composer: Sotirios Bakas (BMI), IPI#797324989. "Meditative Middle Eastern Flute": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI), Composer: Danielyan Ashot Makichevich (BMI), IPI Name #00855552512, United States BMI "Tunisia Eastern": Publisher: Edi Surya Nurrohim, Composer: Edi Surya Nurrohim, Item ID#155836469. "At The Rabbi's Table": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI), Composer: Fazio Giulio (IPI/CAE# 00198377019). "Fields Of Elysium"; Publisher: Mysterylab Music; Composer: Mott Jordan; ID#79549862 "Frontiers": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI); Composer: Pete Checkley (BMI), IPI#380407375 "Hatikvah (National Anthem Of Israel)"; Composer: Eli Sibony; ID#122561081 "Tunisian Pot Dance (Short)": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI); Composer: kesokid, ID #97451515 "Middle East Ident"; Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Alpha (ASCAP); Composer: Alon Marcus (ACUM), IPI#776550702 "Adventures in the East": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI) Composer: Petar Milinkovic (BMI), IPI#00738313833. ___ Episode Transcript: HEN MAZZIG: They took whatever they had left and they got on a boat. And my grandmother told me this story before she passed away on how they were on this boat coming to Israel. And they were so happy, and they were crying because they felt that finally after generations upon generations of oppression they are going to come to a place where they are going to be protected, and that she was coming home. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: The world has overlooked an important episode in modern history: the 800,000 Jews who left or were driven from their homes in the Middle East and North Africa in the mid-20th century. Welcome to the second season of The Forgotten Exodus, brought to you by American Jewish Committee. This series explores that pivotal moment in history and the little-known Jewish heritage of Iran and Arab nations. As Jews around the world confront violent antisemitism and Israelis face daily attacks by terrorists on multiple fronts, our second season explores how Jews have lived throughout the region for generations–despite hardship, hostility, and hatred–then sought safety and new possibilities in their ancestral homeland. I'm your host, Manya Brachear Pashman. Join us as we explore untold family histories and personal stories of courage, perseverance, and resilience from this transformative and tumultuous period of history for the Jewish people and the Middle East. The world has ignored these voices. We will not. This is The Forgotten Exodus. Today's episode: leaving Tunisia. __ [ Tel Aviv Pride video ] MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: Every June, Hen Mazzig, who splits his time between London and Tel Aviv, heads to Israel to show his Pride. His Israeli pride. His LGBTQ+ pride. And his Mizrahi Jewish pride. For that one week, all of those identities coalesce. And while other cities around the world have transformed Pride into a June version of the Macy's Thanksgiving Day Parade, Israel is home to one of the few vibrant LGBTQ communities in the Middle East. Tel Aviv keeps it real. HEN: For me, Pride in Israel, in Tel Aviv, it still has this element of fighting for something. And that it's important for all of us to show up and to come out to the Pride Parade because if we're not going to be there, there's some people with agendas to erase us and we can't let them do it. MANYA: This year, the Tel Aviv Pride rally was a more somber affair as participants demanded freedom for the more than 100 hostages still held in Gaza since October 7th. On that day, Hamas terrorists bent on erasing Jews from the Middle East went on a murderous rampage, killing more than 1,200, kidnapping 250 others, and unleashing what has become a 7-front war on Israel. HEN: In the Israeli DNA and the Jewish DNA we have to fight to be who we are. In every generation, empires and big forces tried to erase us, and we had to fight. And the LGBTQ+ community also knows very well how hard it is. I know what it is to be rejected for several parts of my identity. And I don't want anyone to go through that. I don't want my children to go through that. I'm fighting for my ancestors, but I'm also fighting for our future generation. MANYA: Hen Mazzig is an international speaker, writer, and digital influencer. In 2022, he founded the Tel Aviv Institute, a social media laboratory that tackles antisemitism online. He's also a second-generation Israeli, whose maternal grandparents fled Iraq, while his father's parents fled Tunisia – roots that echo in the family name: Mazzig. HEN: The last name Mazzig never made sense, because in Israel a lot of the last names have meaning in Hebrew. So I remember one of my teachers in school was saying that Mazzig sounds like mozeg, which means pouring in Hebrew. Maybe your ancestors were running a bar or something? Clearly, this teacher did not have knowledge of the Amazigh people. Which, later on I learned, several of those tribes, those Amazigh tribes, were Jewish or practiced Judaism, and that there was 5,000 Jews that came from Tunisia that were holding both identities of being Jewish and Amazigh. And today, they have last names like Mazzig, and Amzaleg, Mizzoug. There's several of those last names in Israel today. And they are the descendants of those Jewish communities that have lived in the Atlas Mountains. MANYA: The Atlas Mountains. A 1,500-mile chain of magnificent peaks and treacherous terrain that stretch across Algeria, Morocco, and Tunisia, separating the Sahara from the Mediterranean and Atlantic coastline. It's where the nomadic Amazigh have called home for thousands of years. The Amazigh trace their origins to at least 2,000 BCE in western North Africa. They speak the language of Tamazight and rely on cattle and agriculture as their main sources of income. But textiles too. In fact, you've probably heard of the Amazigh or own a rug woven by them. A Berber rug. HEN: Amazigh, which are also called Berbers. But they're rejecting this term because of the association with barbarians, which was the title that European colonialists when they came to North Africa gave them. There's beautiful folklore about Jewish leaders within the Amazigh people. One story that I really connected to was the story of Queen Dihya that was also known as El-Kahina, which in Arabic means the Kohen, the priest, and she was known as this leader of the Amazigh tribes, and she was Jewish. Her derrogaters were calling her a Jewish witch, because they said that she had the power to foresee the future. And her roots were apparently connected to Queen Sheba and her arrival from Israel back to Africa. And she was the descendant of Queen Sheba. And that's how she led the Amazigh people. And the stories that I read about her, I just felt so connected. How she had this long, black, curly hair that went all the way down to her knees, and she was fierce, and she was very committed to her identity, and she was fighting against the Islamic expansion to North Africa. And when she failed, after years of holding them off, she realized that she can't do it anymore and she's going to lose. And she was not willing to give up her Jewish identity and convert to Islam and instead she jumped into a well and died. This well is known today in Tunisia. It's the [Bir] Al-Kahina or Dihya's Well that is still in existence. Her descendants, her kids, were Jewish members of the Amazigh people. Of course, I would like to believe that I am the descendant of royalty. MANYA: Scholars debate whether the Amazigh converted to Judaism or descended from Queen Dihya and stayed. Lucette Valensi is a French scholar of Tunisian history who served as a director of studies at the School for Advanced Studies in the Social Sciences in Paris, one of the most prestigious institutions of graduate education in France. She has written extensively about Tunisian Jewish culture. Generations of her family lived in Tunisia. She says archaeological evidence proves Jews were living in that land since Antiquity. LUCETTE VALENSI: I myself am a Chemla, born Chemla. And this is an Arabic name, which means a kind of belt. And my mother's name was Tartour, which is a turban [laugh]. So the names were Arabic. So my ancestors spoke Arabic. I don't know if any of them spoke Berber before, or Latin. I have no idea. But there were Jews in antiquity and of course, through Saint Augustin. MANYA: So when did Jews arrive in Tunisia? LUCETTE: [laugh] That's a strange question because they were there since Antiquity. We have evidence of their presence in mosaics of synagogues, from the times of Byzantium. I think we think in terms of a short chronology, and they would tend to associate the Jews to colonization, which does not make sense, they were there much before French colonization. They were there for millennia. MANYA: Valensi says Jews lived in Tunisia dating to the time of Carthage, an ancient city-state in what is now Tunisia, that reached its peak in the fourth century BCE. Later, under Roman and then Byzantine rule, Carthage continued to play a vital role as a center of commerce and trade during antiquity. Besides the role of tax collectors, Jews were forbidden to serve in almost all public offices. Between the 5th and 8th centuries CE, conditions fluctuated between relief and forced conversions while under Christian rule. After the Islamic conquest of Tunisia in the seventh and early eighth centuries CE, the treatment of Jews largely depended on which Muslim ruler was in charge at the time. Some Jews converted to Islam while others lived as dhimmis, or second-class citizens, protected by the state in exchange for a special tax known as the jizya. In 1146, the first caliph of the Almohad dynasty, declared that the Prophet Muhammad had granted Jews religious freedom for only 500 years, by which time if the messiah had not come, they had to convert. Those who did not convert and even those who did were forced to wear yellow turbans or other special garb called shikra, to distinguish them from Muslims. An influx of Jews expelled from Spain and Portugal arrived in the 14th Century. In the 16th Century, Tunisia became part of the Ottoman Empire, and the situation of Jews improved significantly. Another group who had settled in the coastal Tuscan city of Livorno crossed the Mediterranean in the 17th and 18th centuries to make Tunisia their home. LUCETTE: There were other groups that came, Jews from Italy, Jews from Spain, of course, Spain and Portugal, different periods. 14th century already from Spain and then from Spain and Portugal. From Italy, from Livorno, that's later, but the Jews from Livorno themselves came from Spain. So I myself am named Valensi. From Valencia. It was the family name of my first husband. So from Valencia in Spain they went to Livorno, and from Livorno–Leghorn in English–to Tunisia. MANYA: At its peak, Tunisia's Jewish population exceeded 100,000 – a combination of Sephardi and Mizrahi. HEN: When we speak about Jews from the Middle East and North Africa, specifically in the West, or mainly in the West, we're referring to them as Sephardi. But in Tunisia, it's very interesting to see that there was the Grana community which are Livorno Jews that moved to Tunisia in the 1800s, and they brought the Sephardi way of praying. And that's why I always use the term Mizrahi to describe myself, because I feel like it encapsulates more of my identity. And for me, the Sephardi title that we often use on those communities doesn't feel accurate to me, and it also has the connection to Ladino, which my grandparents never spoke. They spoke Tamazight, Judeo-Tamazight, which was the language of those tribes in North Africa. And my family from my mother's side, from Iraq, they were speaking Judeo-Iraqi-Arabic. So for me, the term Sephardi just doesn't cut it. I go with Mizrahi to describe myself. MANYA: The terms Ashkenazi, Sephardi, and Mizrahi all refer to the places Jews once called home. Ashkenazi Jews hail from Central and Eastern Europe, particularly Germany, Poland, and Russia. They traditionally speak Yiddish, and their customs and practices reflect the influences of Central and Eastern European cultures. Pogroms in Eastern Europe and the Holocaust led many Ashkenazi Jews to flee their longtime homes to countries like the United States and their ancestral homeland, Israel. Mizrahi, which means "Eastern" in Hebrew, refers to the diaspora of descendants of Jewish communities from Middle Eastern countries such as: Iraq, Iran, and Yemen, and North African countries such as: Tunisia, Libya, and Morocco. Ancient Jewish communities that have lived in the region for millennia long before the advent of Islam and Christianity. They often speak dialects of Arabic. Sephardi Jews originate from Spain and Portugal, speaking Ladino and incorporating Spanish and Portuguese cultural influences. Following their expulsion from the Iberian Peninsula in 1492, they settled in regions like North Africa and the Balkans. In Tunisia, the Mizrahi and Sephardi communities lived side by side, but separately. HEN: As time passed, those communities became closer together, still quite separated, but they became closer and closer. And perhaps the reason they were becoming closer was because of the hardship that they faced as Jews. For the leaders of Muslim armies that came to Tunisia, it didn't matter if you were a Sephardi Jew, or if you were an Amazigh Jew. You were a Jew for them. MANYA: Algeria's invasion of Tunisia in the 18th century had a disproportionate effect on Tunisia's Jewish community. The Algerian army killed thousands of the citizens of Tunis, many of whom were Jewish. Algerians raped Jewish women, looted Jewish homes. LUCETTE: There were moments of trouble when you had an invasion of the Algerian army to impose a prince. The Jews were molested in Tunis. MANYA: After a military invasion, a French protectorate was established in 1881 and lasted until Tunisia gained independence in 1956. The Jews of Tunisia felt much safer under the French protectorate. They put a lot of stock in the French revolutionary promise of Liberté, égalité, fraternité. Soon, the French language replaced Judeo-Arabic. LUCETTE: Well, under colonization, the Jews were in a better position. First, the school system. They went to modern schools, especially the Alliance [Israélite Universelle] schools, and with that started a form of Westernization. You had also schools in Italian, created by Italian Jews, and some Tunisian Jews went to these schools and already in the 19th century, there was a form of acculturation and Westernization. Access to newspapers, creation of newspapers. In the 1880s Jews had already their own newspapers in Hebrew characters, but Arabic language. And my grandfather was one of the early journalists and they started having their own press and published books, folklore, sort of short stories. MANYA: In May 1940, Nazi Germany invaded France and quickly overran the French Third Republic, forcing the French to sign an armistice agreement in June. The armistice significantly reduced the territory governed by France and created a new government known as the Vichy regime, after the central French city where it was based. The Vichy regime collaborated with the Nazis, establishing a special administration to introduce anti-Jewish legislation and enforce a compulsory Jewish census in all of its territories including Tunisia. Hen grew up learning about the Holocaust, the Nazis' attempt to erase the Jewish people. As part of his schooling, he learned the names of concentration and death camps and he heard the stories from his friends' grandparents. But because he was not Ashkenazi, because his grandparents didn't suffer through the same catastrophe that befell Europe, Hen never felt fully accepted. It was a trauma that belonged to his Ashkenazi friends of German and Polish descent, not to him. Or so they thought and so he thought, until he was a teenager and asked his grandmother Kamisa to finally share their family's journey from Tunisia. That's when he learned that the Mazzig family had not been exempt from Hitler's hatred. In November 1942, Tunisia became the only North African country to come under Nazi Germany's occupation and the Nazis wasted no time. Jewish property was confiscated, and heavy fines were levied on large Jewish communities. With the presence of the Einsatzkommando, a subgroup of the Einsatzgruppen, or mobile killing units, the Nazis were prepared to implement the systematic murder of the Jews of Tunisia. The tide of the war turned just in time to prevent that. LUCETTE: At the time the Germans came, they did not control the Mediterranean, and so they could not export us to the camps. We were saved by that. Lanor camps for men in dangerous places where there were bombs by the Allies. But not for us, it was, I mean, they took our radios. They took the silverware or they took money, this kind of oppression, but they did not murder us. They took the men away, a few families were directly impacted and died in the camps. A few men. So we were afraid. We were occupied. But compared to what Jews in Europe were subjected to, we didn't suffer. MANYA: Almost 5,000 Jews, most of them from Tunis and from certain northern communities, were taken captive and incarcerated in 32 labor camps scattered throughout Tunisia. Jews were not only required to wear yellow stars, but those in the camps were also required to wear them on their backs so they could be identified from a distance and shot in the event they tried to escape. HEN: My grandmother never told me until before she died, when she was more open about the stories of oppression, on how she was serving food for the French Nazi officers that were occupying Tunisia, or how my grandfather was in a labor camp, and he was supposed to be sent to a death camp in Europe as well. They never felt like they should share these stories. MANYA: The capture of Tunisia by the Allied forces in May 1943 led the Axis forces in North Africa to surrender. But the country remained under French colonial rule and the antisemitic legislation of the Vichy regime continued until 1944. Many of the Vichy camps, including forced labor camps in the Sahara, continued to operate. Even after the decline and fall of the Vichy regime and the pursuit of independence from French rule began, conditions for the Mazzig family and many others in the Tunisian Jewish community did not improve. But the source of much of the hostility and strife was actually a beacon of hope for Tunisia's Jews. On May 14, 1948, the world had witnessed the creation of the state of Israel, sparking outrage throughout the Arab world. Seven Arab nations declared war on Israel the day after it declared independence. Amid the rise of Tunisian nationalism and its push for independence from France, Jewish communities who had lived in Tunisia for centuries became targets. Guilty by association. No longer welcome. Rabbinical councils were dismantled. Jewish sports associations banned. Jews practiced their religion in hiding. Hen's grandfather recounted violence in the Jewish quarter of Tunis. HEN: When World War Two was over, the Jewish community in Tunisia was hoping that now that Tunisia would have emancipation, and it would become a country, that their neighbors and the country itself would protect them. Because when it was Nazis, they knew that it was a foreign power that came from France and oppressed them. They knew that there was some hatred in the past, from their Muslim neighbors towards them. But they also were hoping that, if anything, they would go back to the same status of a dhimmi, of being a protected minority. Even if they were not going to be fully accepted and celebrated in this society, at least they would be protected, for paying tax. And this really did not happen. MANYA: By the early 1950s, life for the Mazzig family became untenable. By then, American Jewish organizations based in Tunis started working to take Jews to Israel right away. HEN: [My family decided to leave.] They took whatever they had left. And they got on a boat. And my grandmother told me this story before she passed away on how they were on this boat coming to Israel. And they were so happy, and they were crying because they felt that finally after generations upon generations of oppression of living as a minority that knows that anytime the ruler might turn on them and take everything they have and pull the ground underneath their feet, they are going to come to a place where they are going to be protected. And maybe they will face hate, but no one will hate them because they're Jewish. And I often dream about my grandmother being a young girl on this boat and how she must have felt to know that the nightmare and the hell that she went through is behind her and that she was coming home. MANYA: The boat they sailed to Israel took days. When Hen's uncle, just a young child at the time, got sick, the captain threatened to throw him overboard. Hen's grandmother hid the child inside her clothes until they docked in Israel. When they arrived, they were sprayed with DDT to kill any lice or disease, then placed in ma'abarot, which in Hebrew means transit camps. In this case, it was a tent with one bed. HEN: They were really mistreated back then. And it's not criticism. I mean, yes, it is also criticism, but it's not without understanding the context. That it was a young country that just started, and those Jewish communities, Jewish refugees came from Tunisia, they didn't speak Hebrew. They didn't look like the other Jewish communities there. And while they all had this in common, that they were all Jews, they had a very different experience. MANYA: No, the family's arrival in the Holy Land was nothing like what they had imagined. But even still, it was a dream fulfilled and there was hope, which they had lost in Tunisia. HEN: I think that it was somewhere in between having both this deep connection to Israel and going there because they wanted to, and also knowing that there's no future in Tunisia. And the truth is that even–and I'm sure people that are listening to us, that are strong Zionists and love Israel, if you tell them 'OK, so move tomorrow,' no matter how much you love Israel, it's a very difficult decision to make. Unless it's not really a decision. And I think for them, it wasn't really a decision. And they went through so much, they knew, OK, we have to leave and I think for the first time having a country, having Israel was the hope that they had for centuries to go back home, finally realized. MANYA: Valensi's family did stay a while longer. When Tunisia declared independence in 1956, her father, a ceramicist, designed tiles for the residence of President Habib Bourguiba. Those good relations did not last. Valensi studied history in France, married an engineer, and returned to Tunisia. But after being there for five years, it became clear that Jews were not treated equally and they returned to France in 1965. LUCETTE: I did not plan to emigrate. And then it became more and more obvious that some people were more equal than others [laugh]. And so there was this nationalist mood where responsibilities were given to Muslims rather than Jews and I felt more and more segregated. And so, my husband was an engineer from a good engineering school. Again, I mean, he worked for another engineer, who was a Muslim. We knew he would never reach the same position. His father was a lawyer. And in the tribunal, he had to use Arabic. And so all these things accumulated, and we were displaced. MANYA: Valensi said Jewish emigration from Tunisia accelerated at two more mileposts. Even after Tunisia declared independence, France maintained a presence and a naval base in the port city of Bizerte, a strategic port on the Mediterranean for the French who were fighting with Algeria. In 1961, Tunisian forces blockaded the naval base and warned France to stay out of its airspace. What became known as the Bizerte Crisis lasted for three days. LUCETTE: There were critical times, like what we call "La Crise de Bizerte." Bizerte is a port to the west of Tunis that used to be a military port and when independence was negotiated with France, the French kept this port, where they could keep an army, and Bourguiba decided that he wanted this port back. And there was a war, a conflict, between Tunisia and France in '61. And that crisis was one moment when Jews thought: if there is no French presence to protect us, then anything could happen. You had the movement of emigration. Of course, much later, '67, the unrest in the Middle East, and what happened there provoked a kind of panic, and there were movements against the Jews in Tunis – violence and destruction of shops, etc. So they emigrated again. Now you have only a few hundred Jews left. MANYA: Valensi's first husband died at an early age. Her second husband, Abraham Udovitch, is the former chair of Near Eastern Studies at Princeton University. Together, they researched and published a book about the Jewish communities in the Tunisian island of Djerba. The couple now splits their time between Paris and Princeton. But Valensi returns to Tunisia every year. It's still home. LUCETTE: When I go, strange thing, I feel at home. I mean, I feel I belong. My Arabic comes back. The words that I thought I had forgotten come back. They welcome you. I mean, if you go, you say you come from America, they're going to ask you questions. Are you Jewish? Did you go to Israel? I mean, these kind of very brutal questions, right away. They're going there. The taxi driver won't hesitate to ask you: Are you Jewish? But at the same time, they're very welcoming. So, I have no trouble. MANYA: Hen, on the other hand, has never been to the land of his ancestors. He holds on to his grandparents' trauma. And fear. HEN: Tunisia just still feels a bit unsafe to me. Just as recent as a couple of months ago, there was a terror attack. So it's something that's still occurring. MANYA: Just last year, a member of the Tunisian National Guard opened fire on worshippers outside El Ghriba Synagogue where a large gathering of Jewish pilgrims were celebrating the festival of Lag BaOmer. The synagogue is located on the Tunisian island of Djerba where Valensi and her husband did research for their book. Earlier this year, a mob attacked an abandoned synagogue in the southern city of Sfax, setting fire to the building's courtyard. Numbering over 100,000 Jews on the eve of Israel's Independence in 1948, the Tunisian Jewish community is now estimated to be less than 1,000. There has been limited contact over the years between Tunisia and Israel. Some Israeli tourists, mostly of Tunisian origin, annually visit the El Ghriba synagogue in Djerba. But the government has largely been hostile to the Jewish state. In the wake of the October 7 attack, the Tunisian parliament began debate on a law that would criminalize any normalization of ties with Israel. Still, Hen would like to go just once to see where his grandparents lived. Walked. Cooked. Prayed. But to him it's just geography, an arbitrary place on a map. The memories, the music, the recipes, the traditions. It's no longer in Tunisia. It's elsewhere now – in the only country that preserved it. HEN: The Jewish Tunisian culture, the only place that it's been maintained is in Israel. That's why it's still alive. Like in Tunisia, it's not really celebrated. It's not something that they keep as much as they keep here. Like if you want to go to a proper Mimouna, you would probably need to go to Israel, not to North Africa, although that's where it started. And the same with the Middle Eastern Jewish cuisine. The only place in the world, where be it Tunisian Jews and Iraqi Jews, or Yemenite Jews, still develop their recipes, is in Israel. Israel is home, and this is where we still celebrate our culture and our cuisine and our identity is still something that I can engage with here. I always feel like I am living the dreams of my grandparents, and I know that my grandmother is looking from above and I know how proud she is that we have a country, that we have a place to be safe at. And that everything I do today is to protect my people, to protect the Jewish people, and making sure that next time when a country, when an empire, when a power would turn on Jews we'll have a place to go to and be safe. MANYA: Tunisian Jews are just one of the many Jewish communities who, in the last century, left Arab countries to forge new lives for themselves and future generations. Join us next week as we share another untold story of The Forgotten Exodus. Many thanks to Hen for sharing his story. You can read more in his memoir The Wrong Kind of Jew: A Mizrahi Manifesto. Too many times during my reporting, I encountered children and grandchildren who didn't have the answers to my questions because they'd never asked. That's why one of the goals of this project is to encourage you to ask those questions. Find your stories. Atara Lakritz is our producer. T.K. Broderick is our sound engineer. Special thanks to Jon Schweitzer, Nicole Mazur, Sean Savage, and Madeleine Stern, and so many of our colleagues, too many to name really, for making this series possible. You can subscribe to The Forgotten Exodus on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you listen to podcasts, and you can learn more at AJC.org/theforgottenexodus. The views and opinions of our guests don't necessarily reflect the positions of AJC. You can reach us at theforgottenexodus@ajc.org. If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to spread the word, and hop onto Apple Podcasts or Spotify to rate us and write a review to help more listeners find us.
Aug 22, 2024
The DNC with AJC: What You Need to Know about the Democratic Party's Israel Platform
This week, on the sidelines of the Democratic National Convention, AJC hosted a program on Israel and the path to peace. Ambassador Thomas R. Nides, former U.S. Ambassador to Israel, Halie Soifer, CEO of the Jewish Democratic Council of America, and Illinois Congressman Brad Schneider (D-IL) joined us for the conversation. AJC's chief policy officer, Jason Isaacson, who is also the head of AJC's recently launched Center for a New Middle East, was moderating the program. AJC hosted a similar program on the sidelines of the Republican National Convention last month in Milwaukee. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. AJC is a nonpartisan, 501(c)3 nonprofit organization. AJC does not endorse or oppose political parties or candidates. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jason Isaacson, Halie Soifer, Brad Schneider, Tom Nides Show Notes: Watch: Israel and the Path to Peace - AJC at the Democratic National Convention Listen – People of the Pod: Is Centrism the Antidote to Political Polarization and Extremism? A Conversation with Yair Zivan Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Panel with Jason Isaacson, Halie Soifer, Brad Schneider, Tom Nides: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week, on the sidelines of the Democratic National Convention, AJC hosted a program on Israel and the path to peace. Joining us for the conversation was Ambassador Tom Nides, former US ambassador to Israel, Halie Soifer, CEO of the Jewish Democratic Council of America, and Illinois Congressman Brad Schneider. Moderating the program was AJC's chief policy officer Jason Isaacson, who is also the head of AJC's recently launched Center for a New Middle East. Just a reminder, AJC is a 501(c)3 nonpartisan organization, and AJC neither supports nor opposes candidates for elective office. Jason Isaacson: I really wanted to begin by citing some passages from the Democratic platform and some passages from the Republican platform relating to the Middle East. I'll just mention very briefly that the Republican platform's Middle East language is short and to the point. It says, We will stand with Israel and seek peace in the Middle East. We will rebuild our alliance network in the region to ensure a future of stability, peace, stability and prosperity. And it also promises, very quickly, to restore peace in Europe and the Middle East. The Democratic platform is much more extensive. It's an 80 page document, a long section on the Middle East. But it says that the administration opposes settlement expansion and West Bank West Bank annexation. Also opposes the Boycott Divestment and Sanctions Movement against Israel. But it's very clear that the administration believes a strong, secure and democratic Israel is vital to the interests of the United States. It's also quite specific about the necessity of defeating Hamas. I want to start my questioning with Halie Soifer. The question that's been on the minds of political reporters and many of us in the community, Haley, as you very well know, over the last 10 months of the war in Gaza, and has taken on new meaning in light of the change at the top of the Democratic ticket. How can a Democratic candidate for president in the current highly charged environment maintain the support of the party's pro Israel mainstream while also keeping or winning back the loyalty of the increasingly active pro Palestinian segment of its constituency. What have we heard from Vice President Harris, for whom you worked in the Senate, that suggests that she can balance these competing policy claims? Halie Soifer: Well, thank you, Jason, thanks to everyone. I was told to project. And for those of you who are at the Global Forum, you know I know how to project, so I will try my best. But thanks for having me. I did have the honor of working for then-Senator Harris, starting her first month in the Senate for two years as her national security advisor. And what I can tell you is, not only does she share the views of President Biden, we know that based on the past three and a half years, and their records standing with Israel in the lead up to and of course, in the aftermath of the horrific attacks of October 7. Giving an unprecedented amount of military assistance to Israel, standing with Israel, not only in the aftermath of these attacks, but demanding the release of all of the hostages, and continuing to stand with Israel as it faces this threat from Iran, pre positioning military assets in the region, not once, but twice in the lead up to The attacks of April 13. But also, I can tell you from personal experience, her views on Israel didn't start from day one in the White House. I saw it from day one when she was in the Senate. She came to this role with over a decade of experience working on these issues. I traveled to Israel with her in November of 2017. This is an issue that she feels deeply in terms of the importance of the US Israel relationship, Israel security, its right to self defense, and she is a staunch supporter of Israel. Have no doubt. I'm glad you started with the Democratic platform as well, because this also elaborates on what is the strongly pro Israel views of our party. And make no mistake, it's not a coincidence that we have three pages detailing our support of Israel in our platform. It's pages 82-85 for those who would like to look it up. And it is no mistake that the Republican platform is empty platitudes. Two, two bullet points that barely say anything. Because this is an issue of which our party is deeply committed. And it extends beyond Israel. It includes Israel's security in the Middle East and our platform, which has never been stronger. I testified before the platform committee. I was very happy to say this very strong pro Israel platform of 2020 not only should it not be diluted, it should be strengthened. Because, of course, we have seen the horror of October 7, we should reflect the fact that we stand with Israel in this moment. We call for the release of the hostages, and of course, we unequivocally condemn Hamas. All of that is reflected in this platform and more, including recognition of the horrific sexual violence that was perpetrated on that day, which the vice president herself has given voice to. So in terms of questioning how she can navigate this issue, she already has and she continues to stand with Israel. I have no doubt that when she's elected in 78 days, with the strong support of the Jewish community, that she will continue to do so as President. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Haile. Brad, I'm going to turn to you. The Republican Party platform had no specific references to Iran, but the Democratic platform went on at length about the need both to halt the regime's progress toward nuclear weapons capability and to confront Iran's and its proxies, destabilizing activities across the region. The Democrats document also pointed to instances of the Trump administration's failure to respond to certain Iranian provocations. Unfortunately, the Democratic platform didn't mention the fact that Trump administration was responsible for taking out IRGC Quds Force Chief, General Soleimani. Now talk about how you imagine a Harris administration confronting the Iranian threats differently from the Biden administration. We have seen over the last three years, Iran has continued to develop its nuclear weapons capability, although it's not yet passed that threshold apparently. Its proxies are on the march across the region. We haven't really been successful in confronting Iran. Do you see a Harris administration taking a different approach? Brad Schneider Great question. And before I start, let me just welcome everybody to Chicago, to our great city, and those from Chicago, can you raise your hand? And I'm also going to take the personal indulgence to say it's good to be home with Chicago AJC. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Brad. I should have said that. Brad Schneider Look, Iran is the greatest threat to Israel, to the region, but also to the United States. Our interests here in the region, but also here at home, and so we need to stand up to Iran and understand Iran is a threat on many different aspects. It's not just their nuclear program. It is their support of the proxies, Hamas, Hezbollah, the Houthis, and more. It is their efforts to expand their reach, their influence across the region, and they do so not by building up states, but by tearing them down, creating instability across the region. Their chant is not just Death to Israel, but Death to America. I have no doubt that the Harris-Walz administration will stay focused and understands the importance of first, ensuring that Iran never, ever gets a nuclear weapon. That has to be our number one priority. Because imagine where we would have been on April 13 if Iran had a nuclear weapon. Or this past couple of weeks, if Iran had a nuclear weapon. The second thing I think you will see is the continuation of the policy. Reflecting on April 13, Iran launched 350 drones, rockets and missiles at Israel. It was Israel, the United States, and a arrangement or alliance of other nations that defeated that attack. That sent a very clear message that we will stand up to Iran, not leaving Israel to stand alone, or the United States and Israel standing without the support of allies, but allies throughout the region. And just as important, if you look at who those allies are and what they believe in, they are countries, Arab countries, that are looking to the future. They're looking for a different dynamic in the Middle East. You mentioned that the Trump administration took out Soleimani. The Trump administration also laid the groundwork and helped establish the Abraham Accords. That is, I believe, the framework for the future that provides security and peace, not just to Israel, but to the other nations in the region. And so what I believe the administration, that the Harris-Walz administration will focus on is isolating Iran, ensuring Iran can never have a nuclear weapon. Thwarting Iran's effort to expand its reach through proxies and failed states, but at the same time building up and working towards a path towards peace, security and prosperity for Israel and the region. I think that reflection of forward thinking, it's not just about Israel. It's about everything. If you were watching last night, if you were there last night [Monday night], if you've been watching this campaign as it's unfolded. Now it'll be one month tomorrow. As it unfolds, what you're seeing is a view towards a different path that gives promise and hope to a better future that is absolutely dependent on the United States. United States leadership and US leadership on a global stage will empower and help us to ensure that Iran doesn't get that foothold on the global stage and doesn't have the ability to continue with threats to Israel in the region. Jason Isaacson: Well, let me stay on Iran for a second with you. Do you see a Harris administration try to return to the JCPOA? Brad Schneider No. Jason Isaacson: Or has that been totally discredited? Brad Schneider One thing you'll see is the Harris administration. I had a long conversation with Ilan Goldberg yesterday, the recognition that we are where we are now, we all would wish we were in a different place. 10 years ago, we were focused on getting to a place to move Iran back from the threshold of a nuclear weapon, and without relitigating the JCPOA, we moved Iran further away, a year away. Now a year away is not eliminating Iran's capacity or capability to develop a nuclear weapon, but it is buying time. And what we should have done, I will relitigate this. We should have used that time to strengthen our position, our allies' position to improve our prospects of moving Iran further back. Instead, what happened was the Trump administration pulled out of the JCPOA and Iran marched forward, and where they are today is far closer to a nuclear weapon than they were 10 years ago. Where they are today are talking about days away from having enough nuclear enriched uranium, highly enriched uranium, to build not one, but multiple nuclear weapons. And they just announced that they're working on developing the triggering mechanism, the ability to convert that enriched uranium into a nuclear weapon. So the stakes are higher. The risks are higher. Iran is closer. We've got to start where we are today, and I think the new administration coming in will start at that point and look for ways to push back, to create space, and to use that space to buy time, to use that time to get us to a place where we have more security. But we can only go there if the administration is clear. Congress is clear. It's not a partisan issue. This has to be Democrats and Republicans saying we will never allow Iran to have a nuclear weapon, and all options are available to us to ensure that Iran does not achieve their goal. Jason Isaacson: Brad, thank you. Ambassador Nides. We were talking earlier this morning about the Abraham Accords, and of course, Congressman Schneider just talked about that as well. How do you see a Harris administration, building on the Abraham Accords, success, building on what the Biden administration has tried to do in normalizing relations between Saudi Arabia and Israel. Will that be a priority for the Harris administration? What would be the obstacles that it will face as it tries to move forward in that direction. Thomas Nides: Well, first of all, thank you for having me. And let me give a little bit of shout out to Ted Deutch. Who is– Ted, you can't leave. I see you walking back there. Because when they decided to recruit Ted Deutsch to leave the Congress to come do this, that was your biggest, happiest day. So thank you very much for your leadership. Let me just say there were not many things I agreed about with the Trump administration, to be clear. And when my when I was being confirmed as ambassador, one of the very nice members on the Republican side asked me, Sir, it seems to be that the Biden administration won't even talk about the Abraham Accords, and they don't even call them the Abraham Accords, I remember seeing the Senate because I'm a bit of a smart aleck, and I said, Can I explain to you something? I love the Abraham Accords, okay? I love the Abraham Accords. The Abraham Accords was, in my view, then and is today, a foundational event. And as much as I believe that the Trump administration has done all sorts of other things, the Abraham Accords, in my view, has strengthened the State of Israel. So I congratulate them for doing it and supporting it as we have. So we should all applaud that. And as we think about the future. Because listen, what has happened here. Even after October 7, the Bahrainians, the Moroccans and the Emiratis, they didn't abandon Israel. Quite the opposite. They've stuck with, most all of them kept their ambassadors in Israel. Most of them continue to have long involved conversations with the Prime Minister about the strength of Israel. And in fact, several months ago, when the Iranians were attacking Israel, those same countries were indirectly helping with the United States and with Israel to protect the State of Israel, not directly, but indirectly. A lot of information sharing. So the foundation for the Abraham Accords should be the foundation for what comes next. And what comes next. Number one, we got to get a hostage deal. For any of you – I'm leaving here to go with the hostage families. I was in Israel a couple weeks and spoke at hostage square. For all of us, for any of us, we should sit and pray to get these hostages out. And for those of you who know some of the families, it breaks my heart. We've got to get a hostage deal. The time is now, okay? And this President and this Vice President are committed to get these hostages free, so once we can get that deal done, and that means putting pressure on Netanyahu and putting pressure on Hamas. Make no mistake, this idea that this is all about Bibi. Listen, I've got my issues with Bibi on occasions, but it's not only convincing Bibi to do what needs to be done, it also is pressuring Hamas, through the proxies, to get them to do a deal. Once there is a hostage deal, everything starts coming into place. And what does that mean? Ultimately, would have to have a plan to rebuild Gaza. Because this fight wasn't with the Palestinian people. This fight was with Hamas, and we've got to help rebuild Gaza with a new PA, with a new group of international parties, including the Saudis and Emiratis. That's a $15 or $20 billion operation to build, rebuild Gaza. Yes, we need a new PA leadership, a new what PA leadership looks like in the future. Needs to be talked about and then, and then we need to have a conversation about normalization with Saudi Arabia. Make no mistake, it is the single most important thing that we can do, including keeping in control of Iran, is getting a normalization with Saudi Arabia. Because it's not just Saudi Arabia, it's the rest of the Muslim world, and it's in our grasp. We can get this done. Now obviously it's a little dreamy. And how do you get the 67 votes? We'll let the geniuses on the Hill, including the congressman, figure that out. But I do believe there is an opportunity, because Joe Biden and Kamala Harris are completely committed to this. I will say one little note. Two years ago, when Joe Biden came for his 10th visit to Israel, I remember meeting him at the airport, and if you recall, it was the same it was middle of covid. It was the same time and where he decided to go to Saudi Arabia. And you remember Joe Biden during the campaign, said some fairly aggressive things about the Saudis during the Khashoggi thing and MBS. But he was convinced by a lot of people, mostly his national security adviser and his vice president to go to Saudi Arabia. Why? Because it was good for the security of the State of Israel. He fundamentally believed that the Saudi normalization could be and should be the keys for the security of the State of Israel. So we've got to get these hostages out. We get a plan, and we need moving on a side, normalization as quickly as humanly possible. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Yair Zivan, foreign policy advisor to Israel's opposition leader, Yair Lapid, about his new book of essays "The Center Must Hold." In that book, authors argue for a return to centrist politics as an antidote to the extremism around the globe today.
Aug 15, 2024
Is Centrism the Antidote to Political Polarization and Extremism? A Conversation with Yair Zivan
"We live in a complicated world . . . We have to balance those tensions, and the way that we do that is not by running away from them and looking for simplistic answers, but actually by embracing that complexity." In his new book of essays, "The Center Must Hold," Yair Zivan, Foreign Policy Advisor to Israel's Opposition Leader Yair Lapid, who heads Israel's largest centrist political party, argues for a return to centrist politics as an antidote to the extremism and polarized politics proliferating around the globe today. The essays, by authors including Israel's former Prime Minister Yair Lapid, American political commentator Jennifer Rubin, former New York Mayor Michael Bloomberg, and philanthropist Catherine Murdoch, call populism fatally flawed and prescribe centrism as the solution to political ire around the globe. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Yair Zivan Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod: What the Unprecedented Assassinations of Terror Leaders Means for Israel and the Middle East Aviva Klompas is Fighting the Normalization of Antisemitism on Social Media On the Ground at the Republican National Convention: What's at Stake for Israel and the Middle East? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Yair Zivan: Manya Brachear Pashman: Yair Zivan has served as an advisor to Israel's Foreign Minister, Prime Minister and President. Most recently, he has edited a series of essays that argue for a return to centrist politics as an antidote to the extremism and polarized politics we see proliferating around the globe today. The title of that book: "The Center Must Hold". The essays by authors including Israel's former Prime Minister Yair Lapid, American political commentator Jennifer Rubin, former New York Mayor Michael Bloomberg and philanthropist Catherine Murdoch, call out populism as fatally flawed and prescribe centrism as the solution to political ire around the globe. Yair, welcome to People of the Pod. Yair Zivan: Thank you very much. Thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's start with the title of this essay collection, which is a spin, your spin on the line from the Yates poem The Second Coming. And that poem was written more than a century ago, also during a time of worldwide angst after World War One and the flu pandemic and the poem's opening line is, things fall apart, the center cannot hold. Why do you argue the center must hold? Yair Zivan: So I think that the play on words there is about a kind of a fatalism that says it can't and saying, Well, we don't really have that luxury if we believe, as I do, that the center is the answer to the polarization and the populism and the extremism that's tearing us apart, then it simply has to hold. Now that's not to say that it will automatically or by default. It means we have to go out and fight for it, and that's what I've been trying to do with the book and with the events around it, is to make the case that the center can hold if we go out and make that happen. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what is centrism anyway? Yair Zivan: It's a good place to start. I'll start with what centrism isn't. Centrism is not the middle. It's not a search for some point on a map between where the left and the right happen to be at any given time. That just leaves you getting dragged around from place to place by whatever the political winds are. It's not useful as a political idea. It's also not successful as a political idea. Centrism says, here are a set of core values that we believe should be at the center of politics. They should be the things that are at the heart of our democratic political tradition, our political instinct. And you can trace it back to the early '90s, to Clinton and to Blair and the third way movement. You can trace it back much further, Oliver Wendell Holmes is often cited as a good example of a centrist political philosophy. But at its core, what centrism says is we live in a complicated world, and we have to manage that complexity. We have to balance those tensions, and the way that we do that is not by running away from them and looking for simplistic answers, but actually by embracing that complexity. And by saying when we find the best balance between these competing tensions, and that's not to say split the difference and find the middle. There are times when we go more one way and more another, it's to say that is the way that we can best hold within us the complexities of running a country today. And there are some very core values at the heart of that liberal patriotism, this idea that it's good to love your country. It's good to be a patriot without being a nationalist, without hating others, without having to degrade other people in order to affirm your sense of love for your own country. We talk about equality of opportunity, the idea that the role of government is to give everybody the best possible chance to succeed. It's not to guarantee an equality of outcome at the end, but it's to say we're going to make sure that children have a good education system and that their health care system gives them a chance to succeed, and they have a hot meal every day, and then people that want to work hard and take those opportunities and be innovative will be able to succeed in society. It talks about the politics of hope, as opposed to the politics of fear and division, so creating a national story that people can rally around, rather than one that divides us inevitably into camps and separates us, which is what I think populists and extremists try to do. So there's a whole host of them, and I would say one of the core ones, and maybe why it's so important and so relevant now, is that centrism is the place where you defend liberal democracy. It's fashionable today to talk about the death of liberalism and why liberalism can't possibly survive, and liberal democracy is an aberration in human history, and really we're meant to be ruled by kings and autocrats. And I say no, liberal democracy is good. It's actually the best system of government we've ever had, and we should work really hard to defend it and to protect it. And the only place you can do that is in the political center. You can't trust the political right and the political left to defend the institutions of liberal democracy, because they only do it up until the point when it's uncomfortable for them. The right has taken on itself the mantle of free speech, and the right is really great at protecting free speech right up until the point that it's speech they don't like and then they're banning books in libraries. And the left loves talking about protecting the institutions of liberal democracy until it disagrees with them, and then it's happy to start bending around the edges. The Center is the place where we say the institutions, the ideas, the culture of liberal democracy, is something that's worth defending and worth defending passionately and strongly. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I'm curious, are these core values universal to centrism, or are they really up to individual communities? Is it, in other words, is it up to communities, nations to decide what centrism is in their region, in their neck of the woods, if you will? Yair Zivan: So there is always variety in any political idea, in any political approach, where people adapt it to their own systems, but the core principles have to be the same core principles. And one of the things I set out to do in this book is to say, actually, centrism is something that works across the globe. So Malcolm Turnbull, the former Australian Prime Minister, and Andreas Velasco, a former presidential candidate in Latin America, and we have Argentinians, and we have a Japanese contributor, and the idea is to say centrism as the principles that I laid out as the core idea is the antidote to the extremism and polarization that we're seeing works everywhere, and that's actually a really important part. Now, sure, there are different issues that you deal with in different countries. Also say the threat is different in different countries, if part of what we're doing is an alternative to extremism and polarization. Then in Latin America, people are more worried today about the rise of a populist far left, whereas in Europe, they might be more worried about the rise of a populist far right. And so the challenge is different and the response is different, but the core principles, I think, are the same and they are consistent. Manya Brachear Pashman: So do you believe that this philosophy is eroding? I mean, it seems to be happening at the same time around the world, in various democracies, Europe, United States, Israel. But do you agree? I mean, is this eroding, or is that too strong a word? Yair Zivan: Look, I think one of the problems with centrist is we're often not very good at talking about our successes and pretty down on ourselves, rather than actually taking pride in really good things that we've done and in places where we win and places where we do well, the test of a political idea is not if it wins every election. No one wins every election, right? That's part of politics as a pendulum. Sometimes you win, sometimes you lose, but the more important thing is not whether you win every election. And don't get me wrong, I work in politics. I like to win. I like to get votes. I like to be in government so that we can do the things that we care about, right? That's why we're in politics. But the test of the idea is whether it can also survive, defeat, an opposition and a time when you're not in power and come back from that stronger. And I think centrism has done that, and can continue to do that. But part of the reason for the book is we haven't always been articulate enough, confident enough and coherent enough in the way that we present our case, and that's something that I hope this book will have some kind of role in changing. That is to say we need to be proud of our successes and our achievements. What happens when you have a successful centrist government, the next people in the political party that come along disavow it and move away from it. You saw it in Tony Blair's Labor Party. I would argue that new labor was an incredibly successful political project, and the thing that came next was a labor party that did everything it could to run away from that rather than embrace that legacy. And as the Labor Party reembrace that legacy, not coincidentally, it also came to power again in the UK, and you see that across the world. I think there are places clearly where we're struggling and places where we need to do a better job, but I also think there are enough examples to show that centrism can work, and the kind of politics that we're pushing for can work and can be successful. Manya Brachear Pashman: So where is it struggling and where is it succeeding the most? Yair Zivan: So look, I'll talk about something that is maybe close to our heart on this podcast, and that's the situation in Israel today, Israel is going through the most difficult time, I think, as a country that certainly in our lifetimes, if not since 1948 we October 7 was was the darkest day that any of us lived through. I'm a little reticent to talk about the political response to that, but one of the things that's interesting from a centrist perspective, is the response of the Israeli public has not been to move to the right. It's been to move to the political center. And if you look at opinion polls in Israel today, the next government, if elections were held today, would be a center center right government. And I'm confident that that will hold all the way through to whenever we have the next election. And I think that's because there is a sense in Israel that actually people want that type of governance. They want people who understand that you need to embrace compromise and moderation and pragmatism as values, rather than looking at them as kind of a political slur, as a vice, as something that we need to talk down about. And so I look at Israel as a place where, actually we lost the election. In November '22 we elected a government that was, to my mind, very right wing. And populist and incredibly problematic. I think we've paid a very high price for that in the last 18 months or so, and now there is a move back towards the political center. Look, I think Emmanuel Macron has been an example of the success of political centrism. The fact that he struggled in the parliament in the most recent parliamentary elections is not an indictment of the fact that he managed to build a political center in France that wasn't really there before. And the test, I guess, will be whether in two years, there is a successor from his party or not. So there are plenty of places I think that I can look out for being successful and where centrism does well. I think there's been some really good examples of political centrism in the US as well, despite the popular media narrative that everything is polarized. You look at groups like the problem solvers caucus in Congress, and you say, here is a group of members of Congress who are determined to work together, who are determined to cooperate and to find solutions to complicated problems and approach it in a really centrist way. Would I like to see centrists winning more in bigger majorities everywhere? Absolutely. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you give an example of an issue, pick a country, any country, but an issue that would really benefit from that pragmatic approach, that pragmatic centrist approach, sir Yair Zivan: Arne Duncan, who was President Obama's Secretary of Education, who writes about a willingness to take on teachers unions and a willingness to demand standards and a sense of what is the focus of education, right? Where the focus of education should be providing the best possible education to children, something we should all be able to rally around, and yet, something that we seem to have lost along the way. And I think education comes back again and again as a core centrist focus. That's one. The other one that I think is really interesting is the essay by Rachel Pritzker. Rachel writes about climate change and about environment, and in it, she makes what I think is a really compelling case that says we can't fight back against the need for energy abundance, because, particularly in the developing world, people need energy in order to improve their quality of life, and they need a lot more energy than they have now. And the idea that the solution to climate change is turning off the lights every so often for a bit longer, is just not practical. Now it comes from a perspective that says climate change is real and is a problem and it's something we need to address, but it kind of pushes away from, I think, most of the orthodoxies of much of the kind of climate change movement and the environmental protection movement, and says we need something different. And that thing is a focus on technology and on innovation that will allow people to create the energy that they need in order to raise their quality of life, rather than demanding that they use less. That is, I think, a really great centrist approach. It's not a splitting of the difference. It's clearly coming down on the side that says climate change is real and it's a problem and it's something we have to address. But it's rejecting orthodoxies and offering something I think that's different. Manya Brachear Pashman: And this seems like such a no brainer, right? I mean, it seems like these are our values, our principles that everyone should be able to agree upon, maybe not the methodology, right? Maybe that's what's up for debate. But it seems like these are just not points of contention. Yair Zivan: I think we're going against the grain of politics. I think today, people don't subscribe to a real full throated defense of liberal democracy, and people aren't really willing to defend free speech, including speech that they don't like. And people are taking advantage of feelings of patriotism and dragging them to a pretty ugly nationalism or rejecting patriotism altogether. And so I think a lot of the ideas are not the most natural grain of where politics is. I was on a panel a few days ago, and one of the panelists turned to me, looked at me deeply, and said, I don't think I've ever met a centrist before. And I thought, I think you probably have, right? And if not, then, nice to meet you, hi, I'm a centrist. But the idea that actually it's going against the trend in politics is one that troubles me. Part of what I'm trying to do is to say to people, if you are a centrist, then speak up. And it's difficult when you're a centrist, you are the biggest threat today. The fight in politics today is not between left and right, it's between the center and the extremes. And so what happens when you come out and say, I'm a centrist? This is what I believe, is you find yourself attacked by the extremes, and that's sometimes a difficult place to be. When I put the first tweet out about my book within half an hour, I was called every name under the sun. I was a communist and a Nazi all at once, depending on who was attacking me, right? You have to be able to withstand that too often. Centrists have been shy and have kind of hidden back and said, I don't really mean it, and actually, I don't want to have this fight. Or actually, let's not talk about politics now, rather than saying, here's a set of values I believe in, and I'm passionate about and I'm willing to fight for them, and you know what, I am as committed to them, I am as passionate about them, and I'm as willing to fight for them as the extremes are about theirs. And because I think the majority of people are centrist and are looking for that motivation, I think that allows us to win the political argument, because if we're proud enough, then people will line up behind us who already do agree with the principles, but maybe feel like they're alone or there aren't enough people that share their views. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, they're kind of anti confrontational. They avoid confrontation, or perhaps too many centrists don't want to sound too passionate about their values, because. As perhaps passion equates to extreme. Yair Zivan: You should be able to be a passionate centrist. You should be passionate about defending liberal democracy. You should be passionate about being a liberal patriot. You should be passionate about trying to give children equality of opportunity, right? Those things are things that it's good to be passionate about, and you should care about them. I just don't recognize in the centrism that I see being successful, this perception of timidity, or this perception of being scared, but what you have, I think, is too many centrists who have taken that path, and you have kind of backed off and backed away from being passionate about those arguments, and that's where we lose. So my call to centrists is to be loud and to be proud and to be passionate about the things that we really care about and where there are places where people might feel a little bit uncomfortable with it and not want to be confrontational, because maybe it goes with the more moderate and pragmatic mindset. Is to say we have to overcome it because the issues are too important for us not to. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do I also want to clarify, being a centrist is not at the exclusion of the right or the left, right? It's more a conversation between both, or a consensus or a compromise of both, whatever works right, whatever works best for the greater good? Yair Zivan: There is an element of a rejection of the left and the right, to some extent, right, particularly of the fringes, and I'm incredibly critical of even some of the more moderate left and moderate right, because they're too willing to appease the extremes on their side. They're very good at calling out extremism and populism from the other camp, but not always good enough for calling out on their own side, which I think is where the challenge really lies. The idea is not to find a compromise. The idea is not to split the difference between old ideas. It is about saying we should be focusing on what works. And I write a line in the book, slightly glibly, that, if it works, and if it makes people's lives better, does it really matter if it comes from Marx or from Hayek, right? The political philosophy behind it certainly matters less than if it works the way that compromise can be a successful political tool. And I think we all compromise in our lives all the time, and suddenly when we get to politics, we see it as a sign of weakness or non-committal-ness or something like that, whereas in our everyday lives, we see it as a part of being able to function as an adult in society. I think the goal of that, the way that you do that successfully, the way you compromise successfully, is by being really clear about what your values are and what your ideals are and what you believe. And only then can you go to a compromise. If I try to compromise with people without being very firm about what I believe and what's important to me, I'll just get dragged to wherever they are because they're passionate and I'm not. They're committed and I'm not. So you have to be really clear about what your values are. And I actually think the real test about compromise is whether you do it when you're in a position of power, not in a position of weakness. In politics, people compromise because they have to. I say you should compromise because you want to. And I'll give a kind of an example, I guess. If I had 51% of the votes in Parliament, and I could pass anything I wanted, and I had a belief, a reform that I passionately believed and wanted to get through, and I could pass it 100% the way that I wanted, or I could take it down to 80% of what I want, and take 20% from other people and increase my majority from 51% to 75% I would do that because I think it's right, because I think building consensus builds more sustainable policy, because I think it creates a healthier democracy and a healthier political culture. Because I have enough humility to say that maybe I don't know everything, and I'm not right about everything, and the other side has something useful to contribute, even to something that I'm really passionate about. That's the test of compromise. Do you do it when you don't have to, but because you think it's the right thing to do? And again, it's dependent on knowing what your values are and dependent on knowing what you're not willing to compromise on, because if you don't have that, then you don't have the anchor from which you take your political beliefs. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, kind of seeding a little bit to the other side, not because you have to, but because you need that little percentage bump to pass your legislation, but because you'll just build more of a consensus and more support on both sides of the aisle, or both sides of eight aisles, whatever, however it works. But yeah, I mean, it's really about building a consensus among lawmakers for the greater good, rather than just claiming that slim victory. Yair Zivan: Yeah, it creates better policy and more sustainable policy. But there's also limits to it. You very rarely in politics get 100% support for anything. And often, if you've got to the place where everyone supports it, then you've probably gone too far with the compromise, right, and you've probably watered it down too much. There are very rare moments in politics when everybody agrees about something, and there are cases, and there are cases when we can do that, but on the really big issues, it's rare for us to get to that level of consensus, and I don't think that's necessarily desirable either. But being able to build a little bit beyond your political comfort zone, a little bit beyond your camp, I think, is a really useful thing in politics, and there are models where it works really well. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let me ask you more specifically. Okay, what is eroding centrism? What forces really are working against it and in the places where the center is maintaining its hold, are those forces in reverse? In other words, have they found a way to conquer those particular forces, or have they found a way to conquer what works against centrism, or has it just not reached them yet? Yair Zivan: So I'll start by flipping the question, I don't think it's about, does centrism work when other people aren't strong enough to attack it and to take it apart? Centrism works when it's strong enough, in and of itself, and it's defining the political agenda. The goal of what I'm trying to do with the book and with the arguments that I'm making is to say, we define what is at the core of democratic politics. Now everybody else is going to have to respond to us. So that's the first thing. Is that switch in mindset away from Are we able to withstand, where the extremes are, to a place where we say, actually, we're the solid anchor, and now we are the ones that are defining the political moment and the political issues. Where is it that we do well? Is where we're confident, right? When we're able to stand up and be proud of ourselves, and then you're more easily able to rebuff some of those forces. Where do I think centrism struggles? One of the places where it struggles, and this is my criticism of my own camp, which I think is always important to have that kind of, I think, a little bit of self awareness. We're often not good enough at really connecting with people's fears and grievances and concerns that are genuine, right? People really are worried about technological innovation and the pace of automation, and people are worried about immigration. And you can be worried about immigration without being a racist and without being a person that should be shunned or that we should criticize. There is a genuine reason why people are worried about these things, and we have to be better at really connecting to those grievances and fears that people have to really understand them, to really empathize with them. That is the cost of entry, to be able to suggest different policies to them. If I want to convince someone that populist politics aren't going to work, I have to show that I care about them as much as the Populists do, and not seed that ground. And I don't think we're always really good enough at doing that. Where we are good at doing that, there's a huge reward. And ultimately, I believe that on every issue, the solutions that we offer from the political center are more successful than the solutions that are offered by the populists and by the extremists, but we have to be able to convince the public of that you can't disregard people who vote for somebody you find distasteful, even if you think that the candidate they're voting for is somebody that you have real problems with, and even if the candidate they're voting for is actually a racist or is actually illiberal and undemocratic. That doesn't mean all the people voting for them are and it doesn't mean you can afford to dismiss those people. It means you need to do a better job of listening to them and connecting with them and bringing them back to our political camp. When politicians fail to get their message across because they're not doing a good enough job, it's not because of the public. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yair, thank you so much for joining us and for giving us a little bit of a pathway to expressing these kinds of views that aren't heard of a whole lot. Yair Zivan: Thank you very much. I really appreciate it. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for a conversation between my colleague Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC's Managing Director of Policy and Political Affairs, and Ron Kampeas, the Washington, D.C. Bureau Chief at the Jewish Telegraphic Agency.
Aug 8, 2024
VP Picks, Media Bias, and Antisemitism: The 2024 U.S. Election and Its Impact on Israel and the Jewish People
Listen to an in-depth conversation on all the latest in the 2024 U.S. presidential election, from the vice presidential picks –Tim Walz and JD Vance – to Israel and antisemitism. Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC's Managing Director of Policy and Political Affairs, speaks with Ron Kampeas, the Washington, D.C. Bureau Chief at the Jewish Telegraphic Agency. Kampeas also discussed the importance of accuracy and empathy in reporting on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, highlighting the need for journalists to avoid biases and misrepresentations. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Ron Kampeas Learn: AJC's Call to Action Against Antisemitism U.S. Party Platforms Must Take a Stand Against Antisemitism Here are 5 Jewish Issues Republicans and Democrats Must Address at their Conventions Listen: What the Unprecedented Assassinations of Terror Leaders Means for Israel and the Middle East Aviva Klompas is Fighting the Normalization of Antisemitism on Social Media On the Ground at the Republican National Convention: What's at Stake for Israel and the Middle East? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Ron Kampeas: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week, my colleague Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC Managing Director of Policy and Political Affairs, spoke to Ron Kampeas, the Washington DC Bureau Chief of JTA, the Jewish Telegraphic Agency. They broke down the latest in the 2024 US presidential election. Julie, the mic is yours. Julie Fishman Rayman: Ron, thank you so much for joining us. I'm so pleased to have this conversation with you, because we get to flip the tables and someone who's really a beloved and renowned journalist in the Jewish space, and finally, I get to ask you questions. So thank you for making this opportunity available to us. Ron Kampeas: Thank you. Julie Fishman Rayman: I want to start by talking a little bit about the conventions. You were in Milwaukee covering AJC's event , alongside a number of other things. Thank you for being there with us. What were your biggest takeaways from the Republican Convention, particularly as they related to the issues of Israel and antisemitism? Ron Kampeas: I think Israel was front and center, and they made it front and center because it's an obvious advantage that they have over the Democrats right now. So, you know, I think the representative moment was, in a way, when Matt Brooks, the CEO of the Republican Jewish Coalition, he was invited for the first time to address the Republican Convention, and the first thing he said was, let's hear it for Israel, or something like that, or let's hear it for the hostages. And there were cheers, and then he says that couldn't happen in a month at the Democratic Convention. He might be right. And so that was a big plus for them. On antisemitism it's a little more opaque, but it's problematic, I think, because after Matt spoke, he called us Jewish media reporters together for a little gaggle, and we asked him, naturally, about the isolationism that the vice presidential or the running mate pick JD Vance represents. And it's interesting, the way that Matt put it. He said, yeah, it is a problem. He was candid. He said, it's a problem in the party, and we plan to fight it. And, you know, nobody prompted him, but he said, we plan to take on the Tucker Carlson wing of the party. The interesting thing about that is that he said, prevent Tucker Carlson wing from getting a foothold. And Tucker Carlson had very much a foothold at the convention. He spoke on the last night, setting up Donald Trump's speech. He was up in the balcony with Donald Trump. And of course, you know, Matt's point is that Tucker Carlson is very much an isolationist, particularly as far as Ukraine goes, but he's given hints as far as Israel goes. But it's more than that. He's platformed antisemites, and he's kind of ventured into that territory himself – antisemites like Candace Owens, Kanye West – and I think that that is something that Jewish Republicans are going to have to grapple with. Julie Fishman Rayman: One of the things that was discussed at AJC's event alongside the Republican National Convention was the policy positions of not just JD Vance, but others who sort of align with that faction of the Republican Party – I guess, the Tucker Carlson faction – and sort of reading the tea leaves on Ukraine and saying, you know, at what point does the hesitancy around support for Ukraine translate into hesitancy for support for Israel? And does it? What would you say to that question? Ron Kampeas: You know, it's interesting that at least as far as I could track, that played out an explicit sense only at your event, at the AJC event. There were people who were asking hard questions of the panelists, and two of the panelists were very much not stumping for Trump, they were defending Trump and the Trump policies. Kirsten Fontenrose, not so much. She was more critical, and even though she was part of the Trump NSC. And so the defense that they were saying is that simply, you know, whatever you may think of Trump's position, this is Rich Goldberg has particularly said this, but I think Ken Weinstein also said it, whatever you may think of Trump's positions on Ukraine, the strength he will project in the world. And this was right after the assassination, and Rich Goldberg kept on bringing up that Associated Press photo of Trump looking very defiant after being shot, that strength is going to deter the kind of actions that Putin has taken in Ukraine. But the flip side of that actually came up a couple of weeks later at a Christians United for Israel conference here in DC, where isolationism was very much on the mind, and what they were articulating and what might have been articulated in an AIPAC conference, if AIPAC still had conferences – it doesn't – but what they were articulating is that it's holistic, that you can't just say, like, JD Vance says, 'Oh, I'm all for assisting Israel, but we don't need to assist Ukraine, because Russia's bad actions in Ukraine are being supported by Iran. Iran is supplying arms to Russia in Ukraine that it then can, you know, see how those arms work in Ukraine, and they can use them theoretically against Israel.' We're seeing now, as tensions build up in the Middle East, that Russia has Iran's back. And then, you know, there's also China, which is also problematic and is buying Iranian oil and helping to prop up the Iranian economy that way. So it's not simply a matter of whether one side projects strength better than the other side, and this is the argument coming out of the Christians United for Israel thing. It's a matter of constant engagement and awareness of how all these things can interlock. Julie Fishman Rayman: I think that's a really great point, and I'm glad you made that connection. I know one of the other issues that was present or discussed at the Christians United for Israel conference was the issue of the hostages, and what you said before about the sort of rallying result of Matt Brooks' comments about, you know, let's hear it for Israel, let's hear it for the hostage families. And a similar cry might solicit or elicit at the DNC. What do you think we could expect? You know, would you expect that a hostage family will take to the stage as Orna and Ronen Neutra did at the DNC, and if so, what might the result be? Ron Kampeas: So that's a good question. I know that they've asked. I know that the hostage families have asked to appear at the DNC. I know that there are people who have told me that the DNC, especially like with Kamala Harris, who has spoken out for the hostages. I don't see how Kamala Harris could not have the hostages or some sort of representation of the hostages at the conference. On the other hand, the Democrats are going to have to worry about, I don't think they're going to be booed, but I think that they're not going to get the same sort of enthusiastic reception that maybe that they got at the Republican conference, and simultaneously the uncommitted movement. The movement was founded in Michigan and spread to some other states that when Biden was the nominee, particularly, they were upset that Biden wasn't doing enough to stop the war in Gaza, wasn't doing enough to force Israel into a ceasefire, and they wanted to show that they didn't necessarily have to vote for him in November, so they didn't vote for him in the primaries. And they had different effects in different states, but certainly in states like Michigan and Minnesota, I think that they had a pretty good turnout as far as that goes. And they want a doctor from Gaza to speak at the DNC. So you know which might be fine. It might be a legitimate enterprise in their part, but you know that the Democrats are going to be accused of "both sides-ing" it, that the Republicans wouldn't have somebody like that. So because of the Democrats of different constituencies, as much as the Republicans are now, at least the Trump campaign is now trying to reach out to Arab Americans. It's much more a constituency for the Democrats, as are the Jews. It's going to be like a tightrope for them to walk. And so I don't know how that's going to be a play out, but it's certainly something we're going to be tracking. Julie Fishman Rayman: Talking about that, that tightrope, and also, because you mentioned Michigan and Minnesota, let's talk for a moment about the selection of Minnesota Governor Tim Walz for the vice presidential nominee. He has both spoken at AIPAC's conferences, stood by Israel after the October 7 attacks, talked about Jewish students on campus dealing with encampments and anti-Israel protests and has really been outspoken about rising antisemitism in this country. On the flip side, he also speaks to the more progressive flank of the Democratic Party, and has urged the party to do more intentional kind of outreach to anti-Israel voters who aren't committed to voting the Harris-Walz ticket. What do you make of him in this moment, as both a campaigner and then presumably, if elected, what would you make of him as a vice president? Ron Kampeas: It's hard to say right now. Nobody was really aware of Tim Walz a lot outside of Minnesota until last week, but it's so funny because, you know, there was this whole push back against Shapiro from the far left because he was perceived as being – I'm talking about Josh Shapiro, the Pennsylvania Governor who was a front runner – because he was perceived as being too pro-Israel. But Yair Rosenberg did a really good job. I also did a little bit of reporting into this about how the other candidates, who other likelies that Kamala Harris were considering, are also pro-Israel, and Tim Walz has a long list of accomplishments, but you know, a measure of how fast this summer has gone, how crazy this political season has been, is this a week and a half ago, when Yair put up his story, he didn't even have Tim Walz in it. He was looking at Roy Cooper, he was looking at Mark Kelly from Arizona, and then, because nobody was even thinking about Tim Walz then, and now, he's the running mate. But from what you can see about him, and like, we just, JTA just did a big story about his master's thesis on Holocaust education, he's somebody who really wants to listen. His recommendation to the Republican Party, you know, he's coined this whole weird thing. That's actually why the Harris campaign noticed him, because he was the first to call the Republicans weird. I mean, the Republican candidates, but he said don't direct that at the voters, direct that only at the nominees, because we have to listen to the voters. And so I think that you can look at what he says about listening to the protesters on campuses in that context. For somebody who was born in Nebraska and lived most of his life in a town of 400 people in Minnesota, he shows, like, remarkably nuanced understanding of things that are of Jewish concern regarding the Holocaust. He's talked about how, you know, one can look at the Holocaust legitimately as an anomaly in history, but also understand it as something that could be repeated, which is actually Yehuda Bauer, the famous Holocaust historian's point. The way he boiled it down was that the Holocaust happened only to the Jews, but it can happen to anybody. And so that's Waltz's outlook, and it shows somebody who's really sort of read up on this and considered it in depth. Julie Fishman Rayman: Because you mentioned that Josh Shapiro had been very much in the running there, I want to get your take on the sort of social media trends of calling him "Genocide Josh" because of his pro-Israel statements and record. Is that just blatant antisemitism that we need to be mindful of, was it specific? Do you think it's just, you know, savvy opposition researchers? What do you make of that? Ron Kampeas: You know, we often think of antisemitism as, you know, planning to be antisemitic and putting out a statement. There are people who are consciously antisemitic, but the much greater, the much more vexing problem is that, how, it just seeps into the discourse. We have a polarized society, and it's just very easy when you're opposing somebody to grab whatever is in the toolbox to harm them. And for anybody who's Jewish, I mean, you see this and we talk about it openly, you see it when we talk about women in politics, about how attacks on them can be gendered. And nobody, at least nobody on the left, complains about that. Actually, maybe they did a little bit. You know, the Bernie Bros made gendered attacks on Hillary Clinton, and they didn't denied it. But anyways, so you can say that attacks can be gendered, but it's hard to explain how attacks can also be antisemitic, because that's a tool in the box. And then a lot of people on the left don't want to acknowledge that. They slip into that. And I think that's what happened with Josh Shapiro. I think that there is for some reason, I mean, I can speculate as to, not even speculate – people have said why, even though he was just as pro-Israel as Tim Walz. He's like he's not less pro-Israel. But Mark Kelly did things that I'm sure Josh Shapiro wouldn't have done. Josh Shapiro doesn't like Benjamin Netanyahu. Mark Kelly, the senator from Arizona, went to the Netanyahu speech, shook his hand afterwards and applauded, and they didn't get attacked in the same way. And if you look at some of the reasons that Shapiro was attacked, they talked about his upbringing, his going to a Jewish Day School in the Philly area, and the things that he was exposed to, they talked about his going to Israel when he was a teenager. And those are things that are part and parcel of a lot of American Jewish upbringings. And so you can say those things are indicting, but there's a point, because you're an American Jew coming up in American Jewish communities, going to be exposed to a lot of pro-Israel. But at what point does that become antisemitic? Because that's just the natural part of Jewish life. Julie Fishman Rayman: I want to ask you another question related to the media. I want to sort of get your take. Last week, AJC and the Jewish Federations of North America published an open letter to media outlets generally, really identifying how so many of them got the Hezbollah attack on the soccer field in the Golan so, so, so wrong that, after a dozen Druze kids playing soccer were murdered in the middle of the afternoon, Washington Post, Houston Chronicle, others, just totally misrepresented the facts. The Washington Post headlined a story "Hezbollah denies responsibility for the fatal rocket strike." It wasn't true. Hezbollah celebrated the attack until they learned that children were killed and then walked it back. And then doubling down, a later Washington Post story showed an image of the funeral of one of the children who was killed, but the headline read, "Israel hits target in Lebanon." So if you only look at the picture and you only read the headline, you think it's a Lebanese kid that has been killed by a strike in Israel, not that an Israeli Druze kid was killed by a Hezbollah attack. CNN, AP, they all sort of downplayed Hezbollah's role in these really horrific murders. Is this ignorance? Is it bias? Is it both? And regardless, if we're sort of operating under this principle of journalist integrity, is this OK? Ron Kampeas: No, it's not OK. I don't know what went on at the Washington Post. I was witness, kind of, to one of the most foundational episodes in bad media takes, which happened right after the Second Intifada began, and the AP put out a photo of a policeman helping up a Haredi Jewish kid who had just been knocked down or even beaten by Palestinian writers in Jerusalem. And the AP captioned the photo saying that the policeman was attacking a Palestinian on the Temple Mount, which is so funny because there's a gas station in the back of the picture and there's no gas stations on the Temple Mount. I mean, if you know Jerusalem, you know the Temple Mount, you know how crazy that is. And so, like, what had happened was that I knew the guy who was handling photo editing at the AP that night when he got this picture. And at the time – this is in the early days of the Internet and computers – the picture came across at the AP's, Israeli photo agency affiliate, and Hebrew couldn't work on that machine, so, like, the Hebrew was scrambled. They captioned it in Hebrew. It was scrambled. So the guy calls up the other guy who's also tired, and he said, was this like some cop beating up a Palestinian on the Temple Mount? He said, yeah, sure, and that's how the thing goes out. So it's just, like, journalists can screw up in ways that speak to a certain underlying bias about the conflict. They expect to see certain things, but it's also can be stupidity and laziness and just screw ups at the last minute. I mean, I imagine that's what happened with the Washington Post front page, but it's awful, and it needs to be remedied, and people need to be more educated, and they need to pay more attention. I think you're right. I think the way that the media has been treating the Hezbollah-Israel conflict in the north, in a way, differently than it treated, at least at the beginning, it treated Israel-Hamas. Hamas is clearly defined as a terrorist organization. Hezbollah is a terrorist organization. Hezbollah is an organization that's holding Lebanon hostage. Historically, people now think it was a big mistake to invade Lebanon in 1982. Hezbollah was partly an outgrowth of resentment of the Israeli occupation in southern Lebanon. But Israel withdrew to UN. They went to the UN and they said, you decide where the lines are. We're not going to decide where the lines are. You decide where the lines are, and we will withdraw that to that point. In 2000 Israel did that. Hezbollah continued to attack. Hezbollah launched a war in 2006 that Israel did not want, and conflict with Israel helps uphold Hezbollah within Lebanon. And so I think that because Hezbollah is a very proficient and weathered militia, they fought a war in Syria. They fought a terrible, genocidal war in Syria. They were on the wrong side of that, but they fought a war in Syria. They're good at what they're doing. So maybe there's a reflex to see this as a conflict between two militaries, but it's not. It's a conflict between Israel and a terrorist organization that unprovoked launched missiles inside Israel on October the eighth, even before Israel was striking back in Gaza as a means of solidarity with Hamas. And so I think that needs to be front, just as I think a lot of media, obviously JTA, but even a lot of like, you know, non-Jewish media always put out there that Hamas started this war. It needs to be reminded that Hezbollah also started its version of the war, and that Hezbollah, it's not an army that's accountable to any kind of civilian infrastructure, never mind a democratic one, like the Israeli army is accountable to elected officials. It's its own militia with a stranglehold on Lebanon. So yeah, I think that should be evident in everything that's written about that conflict, and maybe that's what helped distort at least the initial reporting from what happened in Majdal Shams, which is just horrible. Julie Fishman Rayman: One of the things that AJC is always trying to call on media outlets to do is to know who to call. Right, if there is an incident related to Israel that they don't fully understand, if there's an antisemitic attack and they need more context, to understand that there are Jewish individuals and organizations who can help to provide insight and texture and understanding so that their reporting can be more accurate. That's one of the recommendations in our Call to Action Against Antisemitism in America , recommendations for media. I wonder if, you know, journalist to journalist, if folks call you and say, "Ron, this is what we're writing, is this right?" Knowing that you are just such a font of knowledge, they should, this is what I'm saying. They should call you. Ron Kampeas: My son asks me, I mean, very occasionally, I do get calls more having to do with my alleged knowledge of the American Jewish community and how it works and how it functions. I get calls about that. I think on Israel, less so because everybody's an expert. Everybody considers themselves an expert. Everybody flies in. I think what was an unfortunate standard. 20 years ago, it wasn't just the AP, it was all mainstream media, that you get your best takes from a foreign correspondent between three and six months into the assignment, because it takes them three months to learn it, but it takes them six months to go native, which is to sort of really understand the nuances. I think that's unfortunate, because I think going native, really understanding the nuances, sort of delving into a story, becoming familiar with it, becoming sympathetic in ways, with all sides to the story, actually enriches a story. And I think that that's something that maybe you know, I've been doing JTA for 21 years. I've been in journalism for 35 years. I think it's great to have fresh outlooks. It's good. I think it's also good to sometimes rely on institutional knowledge and to listen to people who have been here before. It was weird at AP. I was in a position at AP when I wasn't allowed to use my institute for bizarre reasons. Institutional knowledge, you know. But it was funny, because at the outset of the Iraq War, the first day, the major Iraq war in 2002, 2003, I knew things that signal that it was going to go wrong, because I'd lived in the Middle East, and I wasn't the only one. By far, by far, there were a lot of people who knew those things institutionally. It means literally saying, like what the Israelis said in 1982, the Shiites are throwing rice and you had actual examples in 1982 of Shiites throwing rice at Israelis, and in 2003 of Shiites throwing rice at Americans. They want this. And it never works out that way. It goes awry. But nobody was listening, because people were too invested in a particular outcome to listen to the institutionalists. And I think that that's a problem. There's a reflex sometimes to say, oh, the institutionalists got it wrong in the past, because the world is still a mess, but that's not their value. The value of the institutionalists, and a great institutionalist just passed away, Martin Indyk, the value of the institutionalists is that sometimes they can actually say, this is where I went wrong, and this is what we misunderstood, and this is how we misunderstood it, and this is how we were deep in the weeds and we misunderstood it. And that's the kind of knowledge that I think shouldn't go wasted. Julie Fishman Rayman: Thanks so much for that perspective. I was going to ask you as a final question, if there was anything that you wanted to raise that we haven't discussed yet. But I would also add to that question, feel free to answer that question. Or is there something that we're getting wrong now institutionally? Ron Kampeas: Yeah, I think that, you know, there's a lot that we're getting wrong now institutionally. I think that people are, and every side of the Israel-Hamas conflict are they retreating into sort of easy, reflexive understandings of what could go right and what could go wrong. I think that there is a value in understanding how toxic Hamas ideology is, that was, I think, grasped at the beginning after October the seventh, but has slipped away as this seems to be just a conflict, and people are retreating into Israel's bashing Gaza. We have to get it to stop bashing Gaza, which is fine, it's an outlook. It's a legitimate outlook, but it's one that's not going to register at all with any Israeli, unless you take into account how Hamas is perceived among Israelis as a genocidal organization. If it wasn't before October 7, it is now. On the other hand, I think that sort of reflexive, we can never have a two state solution. I'm not saying, advocating, for two state solution. We never have a two state solution. We're just going to go on as we've gone with the Palestinians. I think that also reflects this kind of like a reflexive blindness that you have to account for the Palestinians, somehow. Nothing is going to be imposed on them. They have to be agents and actors and whatever happens, and it might not happen in my generation, it might not happen in my lifetime, but that has to be back of mind. And I think for a lot of people, particularly in parts of the Israeli establishment, it is not back of mind. So those are things that I think that people can maybe, you know, if, if these competing, they're not actually enemies, I'm talking about people who are on the same side. They can be on the same side in Israel, they can be on the same side in America, but they're rivals, and they don't like to listen to each other. But if they did talk to each other and listen to each other, maybe they would find nuances that could get everybody to a better place. Julie Fishman Rayman: If we could do a word cloud of some of the themes that have come out of this conversation, listening is definitely one of the words that would be prominent. And I think it's not only a good aspiration, but I also want to highlight that our listening to you on these really important issues is revelatory, truthfully, and we're grateful for all the work that you're doing with JTA every day, but also for being here on People of the Pod with us and for all the wisdom that you've shared. Thank you. Ron Kampeas: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, tune in for my conversation with AJC Jerusalem Director Avital Leibovich on what the widely reported deaths of two terror leaders last week could mean for Israel and the wider region.
Aug 1, 2024
What the Unprecedented Assassinations of Terror Leaders Means for Israel and the Middle East
This week, two major terrorist leaders were assassinated in the Middle East. Hamas' Ismail Haniyeh was killed in an explosion in Tehran, just a day after top Hezbollah leader Fuad Shukr was killed in an Israeli airstrike on Beirut in retaliation for the horrific rocket attack that killed 12 children on a soccer field in northern Israel. What does this mean for Israel and the wider region? Is this a major setback for Iran and its terror proxies? Tune in to hear what AJC Jerusalem Director Lt. Col. (res.) Avital Leibovich, who visited the site of the terror attack in Majdal Shams, has to say. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Avital Leibovich Learn: What to Know About Hamas Terror Leader Ismail Haniyeh What to Know About Hezbollah's Escalation Against Israel Listen: Aviva Klompas is Fighting the Normalization of Antisemitism on Social Media On the Ground at the Republican National Convention: What's at Stake for Israel and the Middle East? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Avital Leibovich: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week marked 300 days of captivity for the 115 remaining hostages kidnapped by Hamas terrorists on October 7. There was also a major development: confirmation that an operation in July led to the death of Hamas' military leader Muhammad Deif. But there were two more assassinations this week, the leaders of two terror groups targeting Israel. On Wednesday, we learned that Hamas terror leader Ismail Haniyeh was killed in an explosion in Tehran shortly after meeting with Iran Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. Haniyeh had been in Tehran for the inauguration of its new president. This just a day after top Hezbollah leader Fuad Shukr was killed in an Israeli airstrike on Beirut in retaliation for the horrific rocket attack that killed 12 children on a soccer field in Golan Heights. AJC Jerusalem director Avital Leibovich is with us now to discuss these developments. Avital, welcome back to People of the Pod. Avital Leibovich: Thank you. Manya. Good to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So, Avital, my first question is, are we safer now than we were at the start of the week? Do two fewer terror leaders lead to less terror? Avital Leibovich: Well, I would say the world in general is a safer place with the absence of Shukr and Haniyeh. However, the neighborhood here is not changing. And unfortunately, we are still surrounded by vicious enemies, who still are seeking to see our erosion and eradication. So while I'm very happy with your outcome in the last 24 hours, I also know there's still a lot of reason for concern. Manya Brachear Pashman: So tell us about these terror leaders. Who was Ismail Haniyeh? And what was his role with Hamas? Avital Leibovich: Sure. So Ismail Haniyeh, who's also, by the way, has another name, which is Abu al-Abed, he actually served as the number one political leader of Hamas since May 2017. He actually substituted in this role, Khaled Mashal and other terrorists, and before that, he actually served as the prime minister of the Palestinian Authority just for a very brief, short time between 2006 and 2007. And he actually became very close to a Hamas leader called Ahmed Yassin. And basically, he really grew into the very radical agenda of Hamas. Interesting enough, his background was totally different. I mean, even worked in Israel in the city closest to Gaza called Ashkelon. So he knows the country. He knows the mentality. So in addition to this, he also began to do some terror activity after the three years of working in Ashkelon in Israel. And then he initiated different kinds of activities. Among them was the kidnapping of Gilad Shalit, a soldier who we'll remember. And after being involved in the terror realm and the political realm, he decided to focus more on Hamas' agenda, on Hamas' charter. And basically, what we have seen in the last couple of years are a few things. Number one, Hania got very rich, because he received millions and millions of dollars from the Qataris. Number two, he left Gaza and he spent the last years of his life in Qatar, in lavish hotels and apartments, enjoying great life. And this is also an indication of how much does he care about the people of Gaza. And I want to connect to the current war and give you a quote of who Haniyeh was because I see that some of the media outlets have the nerve to call him a moderate negotiator. Therefore, I'd like to help them and share with you the following quote, which was said on October 27 — that was the first day where the IDF entered Gaza following the October 7 massacre. So he said, "We need the blood of women, children, and the elderly of Gaza, so it awakens our revolutionary spirit." This is the moderate guy that international media is referring to in their reports. He was a radical, he was a terrorist, and we had a very good opening of our day this morning when we heard the news. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Fuad Shukr, what was his role with Hezbollah? Avital Leibovich: He also, you know, this is a name which is not known, I think, to many people, but he does have a French connection and an American connection — of course, an Israeli connection. The guy was number two in the level of seniority in Hezbollah. He was actually the manager of the army in a way of the Hezbollah military apparatus. But more than that, he was a strategist, and he knew what direction should Hezbollah take in the next years. He was in charge of developing the entire missile industry that Hezbollah had, including the accurate missiles. In other words, he was a strategist but also was a practical man. Now, here's the connection that he had to the US and to France. In 1983, he was one of the orchestrators of the attack in the marine base in Beirut. On that terrible day, 241 American marines lost their lives, but 70 French soldiers were killed as well. So as you can imagine, this terrorist Fuad Shukr has 40 years of terror activities, primarily against Israel, but also against Israeli allies. So again, I think it was a very courageous and accurate Israeli operation. And more than anything, Manya, it shows the amazing level of intelligence, where that person was exactly in which room, in which building, in which floor, and to be able to very surgically act in the right time, at the right moment and target him, I think that shows a lot for the Israeli intelligence capabilities. Manya Brachear Pashman: Was Haniyeh part of the ceasefire and hostage release negotiations? Avital Leibovich: So if you look at the title that Hanieyeh had, which is the head of the political branch of Hamas, you could think that he had some impact on the decision making process with the hostage deals. But I can tell you that he had really no impact, very little impact. Because from the analysis that we have here in Israel, the main decision maker is Sinwar. Now the question is, will the death of Haniyeh have an impact, number one on Sinwar? And therefore, number two on the hostage deal? Now, I'm not sure it will have an effect. I have to say. Sinwar is known as the longtime rival of Haniyeh. So in other words, he will not be mourning his death. But he had the last word with regard to any of the discussions on the hostages. And at the end of the day, Sinwar said numerous times, that he's willing to die. And his ultimate goal is to make sure that Hamas has some sort of a controlling Gaza. He understands today Sinwar, that Hamas will no longer control the government, therefore, he's willing to compromise. For example, let's say Hamas will be giving the role of being in charge of the renovations in Gaza. Or perhaps they will be in charge of the education system and so on, in other words, just to have some sort of a stronghold inside Gaza in terms of governance of some sort. Now, if that will not be a part of any possible deal, then Sinwar has no interest to give a positive answer to a deal. Manya Brachear Pashman: I am curious why Haniyeh would have met with Ayatollah Ali Khamenei before his death? Avital Leibovich: Hamas and Iran have different kinds of cooperation. We have seen that across the region. In other words, we have seen Hamas representatives in Lebanon, working alongside Nasrallah, the health Hezbollah, but also meeting the Iranian foreign minister, when he came to Lebanon for visits. We understand that this time around there is a clear interest which Iran supports, is to target Israel as much as possible. And obviously Iran prefers a proxy like Hamas to be representative of its own goals and intentions. And therefore you saw Haniyeh last time, was last night paying respects for the inauguration ceremony in Iran. And according to what I'm hearing, he was also hosted in a Revolutionary Guards facility. In other words, whoever targeted Haniyeh had a great level of intelligence by knowing how to get to that specific building. But moreover, this is a very secure area, because the Revolutionary Guards are considered the body which is the most guarded of all bodies in Iran. They're the ones controlling the budget of the Iranian government. They're the ones operating Hezbollah and other militias and proxies. So in other words, the fact that it was a Revolutionary Guards headquarters, Antonia was there and despite of all this information, the security system around him cracked. I think that sends a very loud and clear message to the Iranians. Manya Brachear Pashman: How is the relationship between Iran and Hamas and the relationship between Iran and Hezbollah different? Can you explain that to our audience? Avital Leibovich: First of all, I mean, you know, Iran is the chief orchestrator of everything that we have been seeing here since October 7, but actually before that as well. Now, I would say that with Hezbollah, it's a long love story between the two. Actually, Hezbollah was founded by Iran, quite shortly after the revolution in '79. When the country became a fundamentalist Islamist and obviously, took the wrong path, distancing itself from the Western world. Iran actually built Hezbollah, founded Hezbollah, first the military wing, and then adding three years later the political wing. And the idea was to use them in order to attack Israel. And this is very convenient. Think about it, Iran is 1300 kilometers away from Israel. It's not convenient to fire a rocket all the way from that country to Israel. But let's say you want to use simpler means and within half an hour to take an operation out, it's easier to use someone who's bordering with Israel. So gradually, we saw Hezbollah taking over almost the entire country. And everything had to do with Iranian funding. Now, in order to have Iranian funding in terms of sanctions, Iran and Hezbollah, found alternative options like laundering money, like a whole chain of drug trafficking in Syria and other countries. So they found solutions to do that. By the way, Iran is doing the same thing with the Houthis in Yemen, also using them as a proxy. Because you know, this is the most poor country in the region, huge unemployment rates, you can recruit 10s of 1000s and hundreds of 1000s of people, as long as you pay them a very minimal salary. Now, as for Hamas, Hamas was built a little bit later. It's actually an offshoot of the Muslim Brotherhood, so not directly of Iran. However, sometimes there are joint interests between different terror groups. Actually, Iran founded the Islamic Jihad in Gaza, in 79, right after the revolution, because he thought this would be the main actor controlling Gaza with the best assets and so on. But with the course of the years, when Hamas controlled Gaza, and was able to develop its terror means rockets, drones, etc, then, of course, Iran moved to cooperate with Hamas, according to its needs for Iran, it's, of course, more worthwhile to use the blood of Palestinians than the blood of Iranians to sacrifice Palestinians and not the Iranians. This is how they see it. At the end of the day, Iran now wishes to resume to the situation of being a major empire as it used to be, a Persian empire decades and decades ago. So this is the longtime dream, I would say. And the proxies are just another, I would say detail in the path to reach that dream. Manya Brachear Pashman: Now, Hezbollah did not claim responsibility for the attack that killed a dozen children on a soccer field. Why not? They're usually proud of the death and destruction that they wreak. Why did Israel target the terror group anyway? Avital Leibovich: Look, say a few words about this tragic event that took place just a few days ago in a very small, beautiful, pastoral village called Majdal Shams, which, by the way, means the tower of sun. It's on the Syrian border, and the other side is on the Lebanese border. And, you know, people asked me if this is the first time that Hizballah ever targeted Druze or targeted Muslims. Now this specific village was targeted five times already by Hezbollah. Saturday, obviously, was the deadliest of all the five. It was 6:18 in the afternoon, beautiful summer day, lots of kids outside. I visited the soccer field where it happens. And the rockets left, really not a chance for those kids who were playing there. Although there was actually a shelter right there, maybe two feet from where the rocket hit the ground. They really didn't have a chance to make it and go into the shelter. And unfortunately, those poor 12 year old kids, ages 10-16, died in place. We still have over 30 people hospitalized, many of them are kids as well. And I have to say, Manya, that I saw a village who has been traumatized. People are still wearing black clothes. There are black flags hanging everywhere inside the village. The pictures of the kids are, you know, pasted everywhere, on the squares just on random villages and walls of buildings. I also went to one of the bereaved families. And you know, you sit there with a parent who lost his 12 year old boy named Johnny [Wadeea Ibrahim]. And he tells you about his dreams. And he says to me, you know, these dreams will never be fulfilled. And he says to me, we don't even know how to digest what happened to us. So, for Hezbollah, they don't really care who they're firing at, whether it's Jews or Arabs, or Muslims or Christians, whoever, they don't care if it's in the eastern Galilee, or the Western Galilee, or the Golan. All these areas are relevant for the Hezbollah fire since October 8. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Hezbollah did not take responsibility. Why not? Avital Leibovich: So here is the mistake. Hezbollah actually made the mistake. Hezbollah has a TV station, which is its mouthpiece, just like Hamas's TV station mouthpiece is Al Jazeera. Hezbollah's is Al Mayadeen. Now, immediately after an attack, a Hezbollah attack, Al Mayadeen immediately publishes responsibility taking by Hezbollah always every time. And by the way, we're talking about an average of eight attacks a day, every day. And that's what they did here too. On Saturday, they immediately took responsibility in the name of Hezbollah. Unfortunately, for them, after 20 minutes, they understood the extent of the mistake they did, and deleted, of course, this responsibility, and then they made up their own narrative. The narrative was that a misfiring of an Iron Dome interceptor, mistakenly killed the kids, like Israel's fault is that the kids died. Now, this narrative, if you think it was only the social media, then think again, they sent the foreign minister of Lebanon to the media to repeat it. But they also did something more. They sent the head of the Druze community. It's the same blood and flesh of the Druze in the Golan. They sent him to the press to declare that it was not a Hezbollah rocket. So they understood that they will pay a price of some sort. I'm sure they understood that I'm not sure they understood the extent of the intelligence Israel had. And now of course, they're threatening to target Israel. I think the next 48 hours will reveal where we're heading. Manya Brachear Pashman: And you talk about the incredible intelligence that led to the precise explosion in Beirut as well as the death of Haniyeh. Has Israel taken responsibility for his death and what it claimed credit if it was responsible, Avital Leibovich: Up to this minute, Israel did not take any responsibility for Haniyeh's death. Of course, yes, for the Hizballah number two guy Fuad Shukr, but not for Haniyeh. As a matter of fact, the Prime Minister ordered the Cabinet members and the ministers not to speak publicly on the issue. And basically, there's been a lot of quiet from the political echelon here since the morning. Manya Brachear Pashman: And you touched on what my last question is, and that is, how will this elevate the tensions? Does this raise the chance of a war between Israel and Lebanon, Israel, and Iran, these assassinations? Avital Leibovich: So I would say we are already in a war to some extent with Hezbollah, because Hezbollah has fired more than 6000 rockets since October 8. And I've counted 43 Israeli casualties since October 8. So we are talking about an active war in a sense, I think that there is a good reason to believe that both Hezbollah and Iran will react to these two targets. I'm not sure in which way. I do think that Hezbollah still has the notion and the strategy of not completely escalating the situation to a full scale war. I'm sure that Nasrallah is sitting in his bunker in the darkened neighborhood, seeing the footage from Gaza and understanding Israel's capability and does not want to turn Beirut into a similar kind of situation. And he also saw the building last night and he also understood the extent of the intelligence capability. So I think he will have to react in such a way that on the one hand, he could be proud that he did something but on the other hand, would not engage in a full scale war. Iran, on the other hand, is a different story. Because three months have passed since April 14 in which Iran decided to gift us with hundreds of drones and different kinds of ballistic missiles. And from their perspective, it failed. It failed because Israel has a great defense system. It also failed because the US led the great coalition of countries who supported the interception attempts in April 14. However, and this is a big however, Iran learned its lessons. Iran learned why it failed in April. And therefore, my concern is that they will take these lessons and implement them in whichever reaction they will have. I'm not sure it will be tomorrow morning. Tomorrow, they will celebrate Haniyeh in the big funeral in Iran, and then there will be additional mourning days in Qatar. So it may take a few days, but I have no doubt that they will both, Hezbollah and Iran react. Manya Brachear Pashman: Avital, thank you so much for just explaining all of these developments and what they mean. Avital Leibovich: Of course, I just hope that for once they will be able to talk about positive things and not only terror and wars. Manya Brachear Pashman: We hope so too. We hope so too. Thank you so much. Avital Leibovich: Thank you and Am Yisrael Chai.
Jul 26, 2024
Aviva Klompas is Fighting the Normalization of Antisemitism on Social Media
Aviva Klompas has long been a fierce advocate for Israel and is no stranger to the forces that try to delegitimize the Jewish state. Klompas, cofounder of Boundless Israel, a think tank dedicated to strengthening education about Israel while also keeping an eye on the surge of antisemitism in the U.S., joins us to discuss how she's working to combat antisemitism and shape the conversation, both online and off. Listen to this candid conversation, recorded on the sidelines of AJC Global Forum 2024 in Washington, D.C. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jason Isaacson, Ken Weinstein, Kirsten Fontenrose, Rich Goldberg Show Notes: Watch: Voices of Truth: Advocating for Israel on Social Media with Aviva Klompas and Michael Rapaport Listen – People of the Pod: On the Ground at the Republican National Convention: What's at Stake for Israel and the Middle East? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Aviva Klompas: Manya Brachear Pashman: Aviva Klompas has long been a fierce advocate for Israel and is no stranger to the forces that try to delegitimize the Jewish state. After leading Birthright trips, she became the speechwriter for Israel's Mission at the United Nations where she was always looking for ways to give voice to Israel's side of the story, amid a cacophony of anti-Israel sentiments. After working for Combined Jewish Philanthropies, she co-founded Boundless Israel, a think tank dedicated to strengthening education about Israel while also keeping an eye on the surge of antisemitism in the U.S. Aviva might still write the occasional speech, but on Instagram and X, that's where she's really shaping the conversation and confronting haters. We sat down with Aviva on the sidelines of AJC Global Forum 2024 in Washington D.C in early June. Aviva, welcome to People of the Pod's pop-up studio here in Washington. Aviva Klompas: Absolutely. Manya Brachear Pashman: Together with Rachel Fish, you co-founded a nonprofit called Boundless. can you tell us the purpose of boundless and the origins of its name? Aviva Klompas: The idea is to look at the larger issues that are plaguing the ecosystem in Israel in North America and to function both both as a think tank that does research to understand what's happening under the surface, but then to not just investigate and study for curiosity sake, but then to turn to action, and really to extract recommendations, and to pull together partners in order to take meaningful action in order to address some of the larger challenges. So the two areas in which we primarily focus are one, education. How do we reimagine Israel education in North America, for both Jews and for non-Jews? And the area where I spend most of my time has to do with the narrative war? Understanding how did we get here? What's happening below the surface, both in traditional and on social media? Manya Brachear Pashman: You previously served as the director of speech reading at the Israeli Mission to the United Nations. And at that time, did you find yourself not just talking to a traditional institution but actually trying to persuade or convince, maybe even combat the sentiments of that audience? Aviva Klompas: Working as a speechwriter for Israel at the United Nations is certainly an experience and an education unto itself. And my former boss, Ambassador Ron Prosor always used to say to us, it's not so much politics and diplomacy as it is theater and a game of chess. And so to some extent, it's about who you can convince in these speeches and in these conversations in the halls, in the corridors of the United Nations, but the meaningful action, the real relationship building, tends to happen behind the scenes where there's no camera, and when there's no public audience. What people tend to see, the speeches that are broadcast, statements that make headlines around the world, that's really theater. Manya Brachear Pashman: And you mentioned, when you were onstage with Michael Rapaport, at Global Forum yesterday , you mentioned how that job is very limiting compared to your job now and your representation on social media. Can you talk a little bit about why it's important to be on social media to use that as a platform. Aviva Klompas: Yeah, so I worked both for the Israeli delegation. So that was working for the Israeli government. I also worked as a policy advisor for the Canadian government. And certainly when you're working for a government, there are limitations on what you can say, and what you can do. And one of the great blessings of having co-founded Boundless and working in this nonprofit is that at this moment in time, there's a lot of flexibility and latitude for Rachel and I to really hone in on what we think needs to be done and spend our time and our energy there. The great education that I got when I was working at the United Nations, was the fact that people would always ask me, Well, why is it that Israel participates in the United Nations? This is an institution that is notorious for its bias against Israel. So why does Israel participate? Why would it be a member of an institution that notoriously demonizes, delegitimize, vilifies, ostracizes it. No country has to be a member of the United Nations. And more than that, in order to be a member in good standing, you have to pay dues. So Israel pays its membership dues to endure the sort of abuse that we see day in and day out at the United Nations. That's the number one question that I get asked, but it was never once a conversation that we had inside of the United Nations, because we never for a moment doubted that Israel has every right to participate in and contribute to global affairs. And that mentality is what I've taken with me throughout my career that Israel has, and the Jewish people have every right to participate in and contribute to our communities, our societies, our countries and bettering this planet. Manya Brachear Pashman: You also, since October 7, you have emphasized that it's very important to tell Israel's story, tell the story of October 7, day to day, hour to hour, which is how I viewed the news cycle of social media. Why? Why is it that it's so important? Aviva Klompas: It's a part of that mentality that I was describing, which says, I won't for a moment accept that any of this is either normal or acceptable. I'm not going to tolerate a world that speaks to us and treats us as if we had this coming. As if what happened on October 7 was due to us. As if it is normal to be holding over 100 people hostage. As if it is acceptable that Jewish people have to hide their Jewish identity. And I'm not interested in people that will speak with great sympathy about dead Jews, but not take any meaningful or consequential action to safeguard living Jews, which is ultimately what's most important. And at the end of the day, the reason that I'm spending so much time and energy on social media is because I refuse to allow the normalization of what we're seeing day in and day out. And the only way you stop that normalization is two things is one, you have to use your voice, you have to stand up. And we also have to use our Yiddishe kops a bit and try to think about what's happening under the surface. What are the root causes? What are the points of origin for what's taking place? And how can we outthink them? And that's the work we're doing at Boundless. Manya Brachear Pashman: You have primarily focused your messaging on X, or Twitter. You recently though moved your posts to Instagram as well. Aviva Klompas: After a lot of people told me that I had to, yeah, a lot. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, can you talk a little bit about your social media choices? In other words, is there a particular audience on X that you were trying to reach? Aviva Klompas: I joined X when I was actually speechwriter for Israel at the UN. And I was very at the time we're talking, I don't know, 10 or 11 years ago, I was opposed to the notion of joining social media, I thought, I don't think everybody needs to know my thoughts. That's ridiculous. And then one of my colleagues Israel Nitzan, a good friend, and a diplomat of Israel, he was the one that convinced me said, this is very much in line with Elon Musk, I would say is, it's the town square, this is where conversations are happening. This is where politicians and diplomats and reporters are having conversation. And it's important that you participate. And that is an idea that resonates with me very deeply, is that we need to have a voice in the public square. So that's how I got started on X. And I left my Facebook, and I did have Instagram, but I really left it for that personal private space. And then early on in the war, had to change the privacy settings because all of a sudden, it was being flooded with with requests, my Instagram, my personal Instagram, when you open it up, it's 1000s and 1000s of people that want to follow me and I'm like, It's my vacation photos and it's family. No. So that's not going to happen. So instead, after a lot of people said to me, there's obviously a whole other audience of much younger people and different people that are on Instagram, can you just pull your posts over? So I started a second Instagram account, which is just replicating the tweets and it's @AvivaKlompas. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm curious if you have developed relationships, either real or virtual with other social media influencers. In other words, did you know Michael Rapaport before October 7, before he became so vocal on social media and is that in particular and are others new and surprising friendships and partnerships? Aviva Klompas: So I met Michael Rapaport because I got a DM on X from him. That was three words. And they were: who are you? And I wrote back: who are you? And that's where we started chatting. And then we had the opportunity to meet in Israel and he's become a very good friend and a person that I admire enormously. And that's happened in other instances as well that there's been other influencers that I've met as a result of this that started his online conversation. chanson turned into real world relationships. And ultimately, all of us need to have a community social media is a very lonely place and it's a dystopia. When you pull people in the real world, which is what we do at Boundless, it asked her attitudes and opinions about Israel and anti semitism, you get one set of answers. When you look on social media you get a different set of answers. The world is much bleaker and darker. And that's because the rule on social media is if it enrages, it engages. So the most vitriolic, hateful, disgusting, vile content is the content that will trend that's most likely to appear in your feed. I always likened social media to the Coliseum in ancient Rome, where you have people battling it out in the center of the arena. And then you have the throngs of crowds surely, lustily screaming for them for someone's demise. It is not a venue that is conducive to relationships are conversations are chasing or changing minds, if you can sort of visualize that Coliseum analogy. And at the same time, because social media is this kind of dystopia, bleak place, you need to have a community. And that's what I have found with other pro-Israel pro-Jewish voices is that it makes you feel like you're not alone in this that you're not this like single voice that standing against an enormous tide. So I'm very grateful to the other people that have lent their friendship in this moment. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I want to pivot a little bit to what you put on social media, mostly the Israel-Hamas war. Why do you think Hamas terrorists are being treated as heroes in so many outlets and venues? Aviva Klompas: Yeah, what we're really seeing is new tactics and an old strategy. This strategy of how Israel and the Jewish people is being demonized. It's not new, the only new part of it is is the advent of social media as a way to more quickly and more spread the these lies and disinformation much further, but it really goes back to a Soviet strategy you had after World War Two, you had the Cold War, and you had the United States pitted against the Soviet Union. And you never want to fight a war on your own territory. So to the extent that you can you want to fight it on a different front, and that's really what the Middle East became. Israel as it moved away from its socialist roots and towards a capitalist roots, begins to align itself more with the United States. That poses a threat, the Soviet Union sees Israel in the Middle East as a forward operating base for the United States. And so it begins to align itself more closely with the Arab nations. And in order to fight this battle, it begins a disinformation campaign that has a number of strategies to it that I think will sound very familiar. The first is to claim that there's no connection between the Jewish people and land of Israel to paint us as colonizers. The second is to paint us as aggressors. And just to frame it in such a way as it is, isn't the Nakba, not the story of how a number of surrounding Arab armies attacked Israel, not the story of how Israel accepted a two state Partition Plan from the United Nations, but rather the story of the Nakba, and the demise. And the third is to paint the Palestinians as a people that have no agency, and that all of this is happening to them and that they are victims in this colonialist, racist world. And then what the Soviets did is they begin to use that type of language that says Zionists are Nazis, and Nazis are the epitome of evil. And so all of the worst racist colonialist, etc. Accusations that's not new, we saw that from the infamous Zionism is racism resolution at the United Nations in the 1970s. So this is a continuation of a very, very old strategy. And as we always see, it starts with the Jews, but it never ends with the Jews. Manya Brachear Pashman: On the morning that many of us traveled here to Washington for AJC's Global Forum, we woke up to the news of the IDS rescue for hostages. Headlines talked about the four hostages being freed, not rescued. And sadly, many more headlines focused on the hundreds of Palestinians who were killed in that rescue effort. I asked why Hamas terrorists are being treated as heroes and I ask this knowing the IDF has certainly made some tragic errors in this war. But do you get a sense that there is a concerted effort not to treat IDF as heroes? Aviva Klompas: So first off, I mean, I saw them being the hostages being spoken about as having been released, as if, as if commerce just opened the doors and let them go. And the level of condemnation about us going into rescue or hostages? What did they want us to do? Ask nicely. It's been eight months, we've tried a series of hostage deals in negotiations, and it's gone nowhere. I don't measure the standard of the IDF behavior by what the world says. That's going to be a failing strategy for us. I think it's measured by the values of the State of Israel and the Jewish people. And that's why the army has a code of conduct. The people that are more outraged that Israel went to get its people back than the fact that terrorists took them and held them for eight months. Those people need to check their thinking and their values. And that's one of the things that we need to call out all the time. And I think that's a question the mainstream media that's been reporting on it, it's been embarrassing to watch people just essentially regurgitate Hamas press releases. How about a little bit of journalistic integrity? How about asking some hard questions like, Do we even know the casualty figure? I saw it grow by 100, since yesterday. I don't think anybody actually knows the number of casualties. And then, if you had the number, how would you assess how many were actually combatants? If you're counting journalists and doctors that hold hostages in their home as civilians…I don't understand how mainstream media have sort of suspended rational analysis in this war. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you also get the impression that the hostages' stories have been downplayed by mainstream media? I mean these are truly ordinary people, ordinary families who now suffer extraordinary uncertainty, which, you know, I would argue, is worse than loss, this uncertainty. Do you feel like that has been lost in mainstream media coverage? Aviva Klompas: I think that for a while, we saw that the hostage family stories were prominent, and they were certainly getting a lot of attention. And now it's a lot harder. Now it's been eight months, and it's a very visual war. No war in the history of the world has had this level of scrutiny, and certainly not this level of playing out real or disinformation on social media. And people are being bombarded with very difficult and very honestly very, very tragic scenes from Gaza. And we haven't really seen that many new images emerging about the hostages, because there's so much silence. So in that sense, I can understand why there is a level to which humans can stay interested in a topic without new information. I think that's part of what we're struggling with. And at the same time, we have seen journalists be shockingly callous to the hostage families, and that's absolutely unacceptable. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you give an example of what you mean? Aviva Klompas: Well, we just saw a very prominent reporter from the hill roll her eyes while speaking to the sister of a hostage when she asked her to believe women. Manya Brachear Pashman: The New York Times broke a big story–I'm putting big and finger quotes–earlier this week that Israel's Ministry of diaspora affairs organized and paid for an influence campaign last year that targeted US lawmakers, American public with pro Israel messaging, but the story never mentioned the barrage of propaganda that pro Palestinian organizations have put out quite effectively. How do you guard against spreading disinformation as a social media influencer? Aviva Klompas: So I don't agree With what the Israeli government did, I think it was pretty inevitable that that was going to become public. And so I think we could have all seen that this was coming in, and it was not a wise decision to target American lawmakers. I'm not sure that I would call that a disinformation campaign. Disinformation is a deliberate attempt to spread fake information. And I don't think that was the case, but nonetheless, not wise. The difference is, is that my beloved Jewish people believe in truth and integrity. And we believe that if we just tell the same story one more time and maybe tell it a little bit differently, people will finally listen to us. And I think after trying that for a couple 1000 years, maybe we should adopt a different approach. And we again, have to look at what's happening under the surface. If we want to do better at social media. You're right, the other side will say anything, do anything and show whatever image, true or not. People say it immediately 6000 people were killed in the bombing, an intentional IDF bombing of a hospital, okay, based on what? It's been 15 minutes, nobody actually knows what happened. Same thing with the rescue mission. Day by day, the count of quote unquote, civilian casualty grows by 100. We don't know the facts on the ground, we're not relying on third party verification in the way that we should, and people are just soaking this up. And the other side has realized as much, and they understand that they have the freedom and latitude to say everything. Understanding that we have to rethink what this picture looks like. In understanding social media, we have to be thinking smarter about the type of information we're putting out and what some of the challenges are. You have algorithmic manipulation, you have bots and inauthentic activity, you have foreign intervention campaigns, you have the echo chambers that exist, we have the algorithms that even when they're not manipulated, as I said, what engages and engages. We know all of these things. But I don't think we're working hard enough and smart enough to design our campaigns and our messaging, in order to address some of them. One of the things that we're doing at Boundless is we started with the very simple question that says, Who do we need to be talking to? Any messaging, any communications, begins with understanding who's your audience because you need to tailor your message appropriately. And I'm not sure that we're doing that as much as we should. So at Boundless, we started with that question, we did a major study with a national research firm, and we identified six priority audiences. And we ask them their opinion, we want to learn from them, we want to understand why do you think what you think? Why do you believe what you believe? Where are you getting your news and information, we're very open about going to them and saying, We want to learn with you, we want to understand what your challenges are. One of the things that we learned is that every minority population in this country believes that they are the victim, they believe that they are one of the most highly targeted people for hate crimes. And the challenge that we have is that when we come we present them and say no, we're the most hated group, what we're doing is we're minimizing their experience. And we're catalyzing a sort of victim Olympics, it makes them feel defensive, it makes them feel like they're not being seen and heard. And we're not tailoring our messaging with that understanding. So we need to do a little more, a lot more, front work in order to understand who do we want to speak to? What are their values, what are their positions, what's informing how they feel, and think about different issues, before we start to construct messages. And then we really have to think about the distribution and dissemination techniques that we have. Which are right now, they're too uniform, we need to be doing a lot more and a lot differently. And we're hyper reliant on social media. And social media has a very important role to play. But we all know that if we see social media as sort of this coliseum, this arena in which people are thrashing it out, you're never going to really have a conversation. Manya Brachear Pashman: Shortly after October 7, you wrote, quote, The State of Israel was supposed to be a living promise that there would always be a place for Jews to be saved for the pogroms in the Holocaust that plague Jewish history. After the October 7, mass terror attacks, that promise is broken. Do you still feel that way? Aviva Klompas: I've been to Israel seven times in seven months. And I think a lot about when I first went the first time I went was two weeks after October 7 And I was in Jerusalem. And that was deserted. And I wanted to go walk to the Western Wall to the Kotel and I walked through the Old City and it was unbelievable. It was the middle of the week in the middle of the day and everything there was not a person in sight. Everybody was so scared. And I recall friends saying to me, we're having conversations as if it's the 1940s we're talking, we're whispering husbands to wives about where we would hide our children. Because exactly that sense of security, that sense of comfort had been shattered. The idea was that anybody could jump out and didn't matter where you were in Israel, the sense of safety had dissipated. And it wasn't that different here in the United States. And I think to some extent, people probably still feel it. Whereas in Israel, it's been more alleviated with the notion that antisemitism, that you're not safe in your places of worship in Jewish day schools and community centers that you have to think twice before you go to a walk for Israel, you have to think twice, about whether you're going to wear a kippa or a magen david. I think really, our sense of security has been shattered. And that's one of the great tragedies, beyond the enormous tragedy that is October 7, than the living tragedy of the hostages, is the fact that we are all shaken by this. And that it feels scary for a lot of people to be a Jew in the world right now. There's a lot to say about what social media does wrong and how harmful it is and how difficult it is. But also, the one thing that means the most to me, about being active on social media in the last eight months, is the number of messages I get, and people that come up to me in the real world and say to me, I'm scared. And I feel a little bit less scared because you have a voice in the world, you and other people, that people are feeling very alone, that people are saying I'm in workplaces where I'm the only Jew or I'm in schools where I'm being targeted where I feel like I can't speak up in class where I have to hide my head when I am choosing to stay in my room rather than go out. And it's a lonely, lonely feeling right now. And if the only thing that my social media is doing is helping people have a voice and to know that there's others who think this is not normal, this is not acceptable. And we're going to spend every single day raging against it. That will have been worth it. Manya Brachear Pashman: Aviva, thank you so much for joining us on the sidelines of Global Forum. Aviva Klompas: Thank you for having me.
Jul 18, 2024
On the Ground at the Republican National Convention: What's at Stake for Israel and the Middle East?
Israel's right to self-defense and security, governance in Gaza, the Iranian regime and its network of terror, the Jewish state's relationship with Arab countries in the Gulf, and much more were among the topics of discussion at an AJC-convened panel discussion at the 2024 Republican National Convention in Milwaukee. Listen to an excerpt of the panel, moderated by AJC's Chief Policy Officer and the head of AJC's Center for a New Middle East, Jason Isaacson, along with policy experts Dr. Ken Weinstein, Kirsten Fontenrose, and Rich Goldberg. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. AJC is a nonpartisan, 501(c)3 nonprofit organization. AJC does not endorse or oppose political parties or candidates. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jason Isaacson, Ken Weinstein, Kirsten Fontenrose, Rich Goldberg Show Notes: Watch: Israel and the Path to Peace - AJC at the Republican National Convention Listen – People of the Pod: Europe at the Ballot Box: Insights and Impact on Jewish Communities and Beyond Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Panel with Jason Isaacson, Ken Weinstein, Kirsten Fontenrose, and Rich Goldberg: Manya Brachear Pashman: America's political parties are kicking off the 2024 convention season, starting this week with the Republican National Convention in Milwaukee. AJC was on the sidelines of the RNC, with a live program titled Israel and the Path to Peace, moderated by AJC's chief policy officer, Jason Isaacson. Jason is also the head of AJC's recently launched Center for A New Middle East. Joining Jason was Dr. Ken Weinstein, former longtime CEO of the Hudson Institute and the Walter P. Stern Distinguished Fellow at Hudson; Kirsten Fontenrose, the President of Red Six Solutions and Senior Director of Gulf Affairs in the National Security Council under President Trump; and Rich Goldberg, Senior Adviser at the Foundation for Defense of Democracies and Director of Countering Iranian Weapons of Mass Destruction for the National Security Council, under President Trump. Just a reminder: AJC is a 501(c)3 nonpartisan organization and neither supports nor opposes candidates for elective office. A similar program will be offered at the Democratic National Convention in Chicago later this summer. Now onto today's episode: an excerpt from AJC's convention program. Jason Isaacson: Let me begin by reading to you a couple of passages from the Republican platform, which was adopted yesterday at the Republican National Convention. This is what it said about Israel. Quote, We will stand with Israel and seek peace in the Middle East, we will rebuild our alliance network in the region to ensure a future of peace, stability and prosperity. And then there was, as you may recall, for the Republican platform, his list of 20 promises. And it's described as 20 promises that we will accomplish very quickly when we win the White House and Republican majorities in the House and Senate. And number eight, on that list of 20 promises is the following, quote: restore peace in Europe and in the Middle East. So let's drill down with our panelists on those two statements in January 2025. That's more than six months away. It may be that the Israel Hamas war will be won over by them, and perhaps whatever conflict is so close to boiling over between Israel and Hezbollah, that that might not any longer be the case, might have boiled over, might be a thing of the past. But let's say for the sake of argument, that hostilities are in fact, continuing, and let's assume that the Republican Party is victorious this fall. What are you expecting the Trump administration to do to, quote restore peace in the Middle East and to accomplish that, quote, very quickly. And let me begin Kirsten, with you. Kirsten Fontenrose: Great, thanks so much for having us. All of us like to nerd out about these kinds of topics all the time when we're just grateful that there are other people who are as interested. What I expect to see in America is a revived peace plan. So you all remember the deal of the century, the vision for peace, we will see that come back. If there's a second Trump administration. Not in isolation, it will be part of a larger context. That will also include assurances about Israel security and governance for Gaza and the like. Why have we not seen this yet? Because no one's asked the Trump team. But that will come back and you will see that. There's an expectation, whether it's naive or not, which we'll see, that there will be a greater receptiveness among the Palestinian population for an economic plan that offers improvements in livelihood after this conflict. If there is a marginalized Hamas, there'll be more movement in this space for reviving these kinds of ideas. So we will definitely see a revived peace plan, you won't see less attention on this issue, you'll see very top level attention on the issue. You're also going to see, I think gloves off with the Houthis in the Red Sea. The US military has been very careful to make sure that all of our strikes so far had been from a defensive perspective. But you will see, I believe, because the world has not criticized any of these strikes, I think you're gonna see more latitude there. More room for movement for preemptive striking, for instance, because the perception is that for the whole world, this shipping interception problem is just out of hand. So I think we'll see more latitude there. And we'll see gloves come off a bit there. And then I think you're gonna see some tough talk, frankly, with Prime Minister Netanyahu. President Trump has watched the US be yanked around a bit by the current Israeli government. And I think you're going to see less tolerance for that recognition that Israel is a sovereign country, but more of an attempt to say the US is the superpower here, and we will be leading the ideas from hence. If we're expected to play a role, we will be leading in that role. What you will see, however, will be interesting to watch as there is division among Trump advisors about a two state solution. So you'll see that be debated out. Jason Isaacson: Thank you for that. Ken, let me ask you, restoring peace in the Middle East and Europe and doing it very quickly, you've had a very broad focus on a whole range of foreign policy issues at the Hudson Institute and before and since. Tell me how you see that playing out under a second Trump administration? Ken Weinstein: I'd say first of all, I think President Trump came to the conclusion early on, in his first term, he came in remember, talking about the deal of the century with you know, this peace agreement, he was booed at the Republican Jewish Committees event when he was a candidate. And he quickly came into office and understood he could not trust Mahmoud Abbas, because of the incitement to terror by the Palestinian Authority and the tensions that were given out, and the pay for slay efforts that the Palestinian Authority has. Whereby people who kill Jews, kill Americans, were getting Palestinian Authority pensions in prisons, for their families and the like. And so, Trump quickly came to understand that the challenge in the peace process wasn't bringing Israel and the Palestinians together, it was that the peace process itself was misconstrued. The peace process was being used by Middle Eastern governments, in particular, the Iranians, but also the Palestinians as a means to put leverage on Israel, exercise leverage on Israel, by a bunch of people who wanted to see the end of Israel's existence. And Trump quickly reversed that equation. He understood that the best way to move forward was to remove items from the table such as moving the embassy to Jerusalem, which didn't have any of the backlash that John Kerry and others predicted would happen. And he quickly understood the best way to move things forward was to put pressure on the Palestinians. Trump's a real estate guy. And so he understands leverage, he understands how to put pressure forth, and how to deter. I think we're going to see much more of that moving forward. We're not going to have a vice president of the United States who's going to get up and say, the Israelis can't evacuate Rafah, it's going to lead to 10s of 1000s of deaths. And here I actually disagree slightly, I think Trump will actually give the Israelis the latitude they need to finish the mission, which is to destroy Hamas, and eventually bring about a transformation in Gaza, with the assistance of the Saudis. Who were absolutely critical in de-radicalizing Gaza, they have done it successfully themselves, as has the UAE. And so I think we're going to look much more at a regional approach on these issues. Obviously, Iran is going to be, to borrow a term from Joe Biden, President Biden, in the crosshairs of the Trump administration, as they were before. You're gonna see massive sanctions again, we're gonna get them, we're gonna enforce those sanctions. And Rich can talk to this stuff far more deeply than I ever could. And you're gonna have the Iranians on the run so that they don't feel that they can work with Hamas or work with Hezbollah, to do more damage to Israel. And already we're seeing a deterrent effect on the Northern Front. And also with regard to Hamas. Because with regard to Hamas, we see that the fear of a Trump administration is leading to a greater willingness to negotiate with Israel. And on the northern front, I think it's less likely that the Israelis will take dramatic action before the US election, knowing that they will not be reined in by an administration that is somehow searching for a delusion of peace with Hezbollah and with Lebanon. Jason Isaacson: What about peace in Europe? Is is that something that you see, that you can envision under a Trump administration? Ken Weinstein: First, let me say something with regard to Europe and the Middle East. I think that the Trump administration, the Trump team has been infuriated by this notion of enforcing this ridiculous ICC policy with regard to Israel and those who threatened to arrest Netanyahu. I think you're going to see in places particularly, I can just think of the kinds of actions they'll take in Germany. I think you can expect individual sanctions on the people who were behind Nord Stream as a sign to not dare mess with Netanyahu, period. And you'll see other actions like that. I know the Spanish ambassadors here with regard to Spain with that we will be taking numbers, as Nikki Haley did so effectively at the UN, and as the Biden team does not. So with regard to Europe. Look, I think the situation with regard to Ukraine, as President Trump understands it, I think, Trump, you have to understand he comes to this. He's not a policy person. He thinks that policy people like the three of us, four us up here, we lack creativity, we have a sense the policy options run from the letter L or P to the letter Q or R. And in fact, for Trump, they run from A to Z. And so that meant fire and fury in Pyongyang, but it meant eventually potentially beachfront condominiums in North Korea and an economic vitality to North Korea, if it gave up its nuclear program. With regard to Iran, it was maximum pressure, but it was the new Iran deal that got rid of the nuclear program that got rid of the missile program that got rid of regional activities, and that internally reshaped Iran, and led to a new relationship with Iran, with not only the region but the rest of the world. And with China, it was massive tariffs on China, but a new trade deal in the phase one that was gonna get rid of intellectual property stuff, which was at the core of what President Trump saw correctly as the engine of the Chinese economy, and the engine of the China 2025 program. So I'd say with regard to Ukraine, the President is looking at options that will, as he himself has said, he would tell the, you know, the Ukrainians on day one, you've got to, you know, we've got to end the fighting, you would tell Putin, if you don't end the fighting, we're gonna arm the shit out of Ukraine, pardon my French, as he said something along those lines. And I think what we'll see at the end of the day, is a massive program to guarantee Ukrainian security, that is going to take massive security guarantees. But the Europeans are going to have to step up and step up in a very serious way. And we've seen since the announcement of the JD Vance nomination are ready to reaction in Europe, the Europeans, you know, have to understand they're not gonna be able to backchannel they're not going to be able to figure out some way out of this. They're gonna have to be big providers of security guarantees, we will do the same for the Ukrainians as well, but Europe has to take up a big portion of it. And Trump does not, he is not Joe Biden, he's not going to cut and run, as in Afghanistan, he doesn't want to be humiliated on the stage, he understands deterrence, he's going to send a very clear signal to the Russians, as he did to the Taliban. When they were talking about when they were negotiating with the Taliban, Trump was on a video call once with the Taliban leader, and said, I want to make this very clear, you're not to strike at any of our people. And if you do, and hit the button on Play, and he showed a video of I think, the Taliban leader's kid leaving their house to say we're watching you every moment, and we will take care of you. And there'll be some kind of a version of that with regard to Putin, that's going to be very clear. He was very blunt with Putin behind closed doors, from the White House in particular. And I think there was a good reason why Putin didn't go into Ukraine during Trump's term. And so I think that there's going to be some kind of a square in the circle solution that's going to have to come together. And I've been telling European foreign and defense ministers for the last few months, think about this now, how to do it, how to implement it. Jason Isaacson: Ken, thank you so much. Rich, let me turn to you. We've been talking about Iran, and you are an expert on Iran. It happened for years. I didn't see a reference to Iran and the Republican platform. But of course, we know, former President Trump's record on Iran. And Ken has been talking about that. Should he return to the White House next January, what do you foresee on this front to return to maximum pressure, or something more kinetic? And what is your sense of our regional strategic partners priorities? Are our friends in the Gulf hoping for a decisive showdown with Iran? Or are they sufficiently risk averse that they prefer a less confrontational approach? What do you think? Rich Goldberg: I think if you look at the top lines, right, and you compare the policy, the recipe, if you will, under the Trump administration: maximum pressure on Iran, maximum support for Israel gets you peace, gets you deterrence. And when you flip the narrative and you go to maximum deference to Iran and pressure on Israel, you get conflict in the Middle East. It's not disconnected from what Ken's just talking about in other regions of the world as well, whether in Europe, whether you're in the Indo-Pacific. This comes down to the ability to restore American deterrence. And then you have options. There are a lot of genies that are out of the bottle due to the last three and a half years. Iran today and its nuclear program is at the one yard line of nuclear weapons thresholds. They were not there four years ago. In fact, after the killing of Soleimani, in early 2020, the rest of the year the Iranians never escalated the nuclear program again. They waited until January of 2021. And that's when they started jumping to 20% high enriched uranium. And then they saw nothing's happening to us. So they went to 60% high enriched uranium. They started installing all the advanced centrifuges, they've advanced, so far accelerated to this incredible capacity to produce a dozen nuclear weapons in just a couple of months if they so chose. Plus Intel now coming in that the administration is trying to downplay work on weaponization. There's a lot of genies out of the bottle here that Donald Trump's going to have to try to put back into the bottle. And that will not be easy. But the formula remains correct. Restore deterrence, have maximum pressure and isolation on the Iranian regime and provide support to your allies. Now, the Gulf Arabs, by the way, the Saudis, the Emiratis, they've made some strategic decisions due to the policies that they saw, sustained by Joe Biden. They've cut deals with the Iranians and sort of cut their own JCPOA. with Iran with the Houthis. I'm not sure they're going to be on board for what's coming next. And they need to make some preparations for the return of a Trump administration and hawkishness towards Tehran and understand that we also won't tolerate them hedging with the Chinese. Now, that comes from the fact that America is hedging on them. And so there's going to be a lot of parts that have to come together like a puzzle, to try to put Humpty Dumpty back together again, actual restored turns and regain that peace through strength in the region. This is true in the Middle East. It's true in Europe, and it's true in the Indo Pacific. So what is deterrence? I think that's a major question. What is deterrence? Made up of two big things, capacity and will. Joe Biden and Donald Trump both have capacity. They were the commander in chief at some point of the most powerful military on Earth. Nobody doubts that you have capacity when you are the president of the United States. But our enemies do doubt the will. And they test the will early on. Every single administration gets tested, whether it's China, whether it's Putin, whether it's Iran, they get tested. At some point, Donald Trump got tested by the Iranians and Soleimani is dead. And that changed a lot of things in the world. And over the course of time, the unpredictability, the some of the craziness of the media went hysterical over the red button with Kim Jong Un did get the attention of people like Vladimir Putin. The Taliban tested Joe Biden, and he failed the test. And Kabul fell. And then Ukraine was invaded. And then now in China, they're expanding and starting to harass and actually attack in some ways, the Philippines and Taiwan. And what are we seeing? Nothing. So, the minute Donald Trump becomes president, when I hear Trump say, just my election is going to start bringing about a change on the Ukraine front, a change in the world. You might have laughed at that. I think after Saturday, you're not laughing anymore. A picture that if you're Xi Jinping, the Ayatollah, Putin, Kim Jong Un, looking at that on your desk every day of Donald Trump with his fist in the air blood dripping, right after being shot, saying fight. You're not questioning will. And that will be, I think, the big game changer. Now, they might still test it. And there's a Chinese proverb, which is, you have to kill the chicken to scare the monkey. And I think President Trump might have to kill a chicken. He'd have to pick the chicken wisely. I think it might be the Houthis. That makes no sense to me. There is a national interest, there's a strategic importance to it. And it will game change how you're trying to get the Gulf Arabs back on side, see that we are committed to the security in the Gulf in the broader Middle East, it will send a major signal to Tehran, and it'll be part of that pivot back to maximum pressure on Iran and maximum support for Israel. Jason Isaacson: Rich, thank you. But before I turn back to the Abraham Accords, let me ask you, what's your sense of the Saudi and UAE and Bahraini overtures to Iran? Are they just seeking some kind of stability, some kind of channel, but it doesn't have a whole lot of meaning, or what's your sense and how should the US respond? Rich? Rich Goldberg: I think there is meaning to it. I think that Mohammed bin Salman, the Crown Prince in Saudi Arabia has changed his strategic calculus over the last three years. I think that there was a game changing moment for him when the Houthis were raining down missiles, next to a Formula One race he was hosting out in Jeddah. And you're talking about major investors, world leaders, important people all driving into a race course already there. And you're seeing a ballistic missile explode within your line of sight. And the United States does nothing. And then Abu Dhabi comes under attack by the Houthis, and the United States does nothing. And they're saying, Wow, they're just at the table trying to give the Iranians whatever they can, they've taken the Houthis off the terror list. They're not defending us anymore. They've pulled the missile defense augmentation that Trump put in, in 2019-2020. And they're still trying to get this nuclear deal done. What are we doing here? Why are we just waiting around for Godot? Why are we exposed? We should cut a deal here. And why if the United States can hedge on us, can't we hedge on them, and they start cozying up to the Chinese and doing things that we probably don't like very much I need to put an end to. So I think it's very real. These channels are real. They're in a hedge. I think it's taken a while for others that are far more suspicious of Iran, like Bahrain to get on board this strategy. But everybody sort of signed up to this. There's a normalization process with Assad that I think is partially connected to it as well. All of that's going to have to change. You have Donald Trump is back in office. And I don't know that they appreciate that very much. Jason Isaacson: There's also a recollection of the Trump administration in this reaction or non reaction to this Iranian attack on Saudi Aramco facilities. So it's been a mixed bag. But But first, let me let me let me turn back to you. And we were talking about the Abraham accords before. That was a great foreign policy access success of the last months of the Trump administration, first of the UAE, then Bahrain and then with different terminology, but Morocco and Sudan. As you know, the Biden administration has been vigorously pursuing an effort to normalize Saudi relations with Israel, and objective that was also very much a part of the Trump administration's vision. What are your perspectives on the likelihood of that kind of a deal being closed in the last months of the current Biden administration, if they do move forward on such a deal with the Republicans getting the Senate joined with Democrats in the Senate to support such a deal before the election? Or perhaps in a lame duck session after the election? Kirsten Fontenrose: Well that's the big question. So I think if you have a deal that includes normalization with Israel, Saudi us still includes normalization with Israel, it has a shot of getting through, but the closer we get to the election, the smaller that shot gets, because the more Republicans Congress will want to hold out to grant that foreign policy when to potential Republican administration. But if you have a deal that is being discussed now, as a Plan B, that is just a US-Saudi deal, without normalization. And this is because of the Israeli government's decision, perhaps not to grant that the Saudis are fully on board, you won't get it through, there's just not enough in it. For the US. There are lots of questions about why we'd be granting Saudi assistance with civilian nuclear technology. And a security guarantee, when we're not really getting much out of it. There's nothing in this deal in terms of concrete asks on the relationship with China. And we can really go quite far in blocking Chinese influence in the Gulf by just improving our own foreign military sales process. We don't need to grant security guarantees, the Israeli Saudi relationship is so close right now. It's normalization and everything but public statement and name and that public statement name is important for the follow on effects you have around the world globally and with other Muslim populations. But in terms of their coordination, they're in a pretty good place. So we're not in some sort of crisis rush to make sure this happens in the next few months, unless you're the Biden team. And you're desperate for a foreign policy win, because your promises on other foreign policy fronts have not borne out. So I think you will still see this continue, though we have doubled down on the Saudi discussion, if there is a second Trump administration. But you will not see this granting of a deal to Saudi Arabia, even though they are a phenomenal partner. And we are quite close, without more concrete asks that benefit U.S. goals as well. It's not the opinion that just having Saudi on side with nothing we've actually signed them up to, would they grant overflight rights, if things came down with Iran. We need to make those more specific before we would do something that would require commitment of troops, large resources, equipment, perhaps to the detriment of other partners, we would be able to send those same troops and equipment. So I don't think we're going to see it in the last months of this administration. Manya Brachear Pashman: To hear the rest of the panel, head to the link in our show notes. Another reminder that AJC is a nonpartisan organization and will be at the DNC next month in Chicago. We hope to see some of you there. Next week on People of the Pod, tune in for our sit down with two Jewish Olympians before they head to Paris for the Summer Olympic Games.
Jul 12, 2024
Europe at the Ballot Box: Insights and Impact on Jewish Communities and Beyond
Election season in Europe is in full force, including recent elections in France, the United Kingdom, and the European Parliament. American Jewish Committee's offices across Europe have closely followed the results, which have had dramatic outcomes across the continent. Listen to an excerpt of this live podcast recording with AJC Europe Managing Director Simone Rodan-Benzaquen for expert analysis on what these developments mean for the future of Europe, European Jewry, Israel and the region, and more. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Simone Rodan Benzaquen Show Notes: Resources: European Elections: June-July 2024; Results and AJC Expert Analysis Listen – People of the Pod: Rebuilding Israel's Devastated Negev Region Post 10/7 The 2024 U.S. Presidential Election: What Does it Mean For Israel? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Simone Rodan-Benzaquen: Manya Brachear Pashman: Welcome to this live recording. Election season in Europe is in full force, including recent elections in France, the United Kingdom and the European Parliament. American Jewish Committee's offices across Europe have closely followed the dramatic results across the continent. Joining us to share what these developments mean for Israel and the Jewish people is someone who has become a fairly regular guest, thanks to her expertise, AJC Europe Managing Director Simone Rodan-Benzaquen. Simone, welcome back to People of the Pod. Simone Rodan Benzaquen: Thank you very much Manya. It's very good to be with you. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's start with the most recent election in France, which is home to the second largest diaspora Jewish community behind the United States. So President Emmanuel Macron surprised a lot of people by calling for a snap election after his party was pummeled by the far right in European Parliament elections. Why was a snap election his solution? And what was the outcome? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: So the President has said that after the European Parliamentary elections, which indeed have been a huge failure for his party, he only gained 17% of the French vote while the far right gained 33% – that he wanted to use this occasion to give back the voice to the people and use it basically as a means to clarify the situation. Now, there has been a little bit of clarification. The one clarification, I'd say, is the fact that after the first round, where it became very clear that the far right is gaining more and more weight within the French public opinion and therefore, possibly also in Parliament, where it was expected that the far right would become the first party and possibly be able to have a government–the clarification was nevertheless that the majority of the country doesn't want the National Rally, meaning the far right to rule the country. It has also been a clarification because it has also showed that to some extent, the National Front is probably not yet ready to rule apart from the fact that majority of the people don't believe it should be, because nearly 100 candidates were as, one could say, problematic. Some of them had a criminal past. Some of them had made antisemitic, racist statements in the past. Some of them were truly not very competent, broke down in all of the interviews or the confrontations, not being able to respond to any of the questions. So that was, I'd say, one part of the clarification. The other part of the clarification, which is to some extent, problematic, and brings us to the situation we're in today is the fact that France is now clearly split into I'd say, three blocks: the far right, which is strong, the center and the left. And so just to give you a little bit of an understanding of what the results look like after the second round of the of the elections, so it gave what we call the NFP basically an alliance of all of the left parties – the far left, the Socialist Party, the Greens and the Communists – 182 seats in the 577-seat National Assembly. A majority is needed of 289 seats, so they only have, as the largest bloc, 182 seats. Marine Le Pen's national rally party has, again, despite the fact that they were expecting to win only 143 seats, nevertheless gaining 50 seats compared to the previous election. And for President Macron's party, the results come as something probably of a relief, because they have 168 seats, down from the 250 seats it held in the outgoing parliament, but still far more than what people were expecting. So we now have basically three scenarios. We have, in theory, a left bloc that doesn't have an absolute majority, that could be the ones, nevertheless, to try and find a coalition to rule the country. You could have something of a sort of a grand coalition which would include the moderate left, the center, and the moderate right. But France is not really used to making coalitions. It's not how we work. It's not like in Israel, it's not like in Germany, or other European countries. Or, we could have a third option, again, one that we've not had previously, in the Fifth Republic. It's called something like a technical government as it was the case for example, in Italy, under the Draghi government. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what do these results mean for the French Jewish community? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: Now, first of all, I'd say that many Jews after the second round of the elections, probably felt, just as much of the country, a sigh of relief. In between the two rounds, everybody was talking about the fact that whether the National Rally would have an absolute majority, we would have Prime Minister Bardella from the far right ruling the country, what it would mean. And that's not happening. So I think a majority of French Jews, again, just as the majority of French people probably seem somewhat relieved. But I think it was very quickly gained by a sense of worry, because of the presence of the far left Unbowed party in the left coalition that is now the largest part. And so many, many questions arise, because we know that in that part of the coalition, there are very, very, very problematic elements, particularly with relation to Jews and antisemitism. And they have really made sort of, you know, "anti-Israelism," or even antisemitism a core part of the ideology. And I think more largely, I'd say, Jews, I think are very, very uncomfortable. We were really the Jewish question, if I may put it that way, was really at the center of this election. It was all day long about which party is antisemitic, which party isn't, who's trying to get the attention of the Jews. And so many people around us, around me, really had the impression that they were being instrumentalized in a very, very horrible manner. And I think that the large feeling within the Jewish community is uncomfortable. They are afraid. And all of this also particularly in a context where we have an explosion of antisemitism. Manya Brachear Pashman: So are you saying that that question of who is more antisemitic – the right, the left – was not actually, that question was not coming from the Jewish community? It was coming from another source. What were the origins of that question? And why is antisemitism the sin that has been instrumentalized? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: So first of all, you have to understand that the far left party from Jean-Luc Mélenchon has really used the issue of Gaza and of the Palestinians as a weapon. It's not about the Palestinians. It's about – how can I call it – "Palestinianism" – it's really become sort of a cultural marker for that party, constantly being at the border of antisemitism. So you have, for example, people within his party who considered that the October 7 terrorist attacks were not terrorist; you have those who say that it was actually resistance; you have those who deny that babies were killed. And the other side of the political spectrum, Marine Le Pen and Jordan Bardella, really made the issue of antisemitism, position themselves as basically, the defenders, the protectors of the Jews, all while at the same time, still having elements within their own party that were clearly problematic. The National Front also knows that this is the best way for them to become normalized to become a regular party that can actually be taken seriously by large parts of the French society. So basically, everybody was pulling at the Jews on all sides. And we all know that whenever you make the issue of antisemitism a political issue, or basically a political football game, or baseball game in the American context, it means that you're actually not serious about antisemitism. And the same can be said on the left, in particular, the far left always pretends not to be antisemitic, says how is it even possible that anyone could believe they would be antisemitic while they only believe that antisemitism only exists on the on the right and on the far right? So it's very problematic, because again, in the middle, are there actually Jewish citizens who the only thing they want is for everybody within the French society to take antisemitism seriously, and to fight it, collectively, knowing in particular that antisemitism is always the problem of society at large and should therefore be taken seriously by everybody. Manya Brachear Pashman: I mean, it is well known the history of antisemitism within France's far right party. Jean-Marie Le Pen, Marine Le Pen's father, was repeatedly convicted for hate speech, Holocaust denial, and it does appear that his daughter Marine Le Pen has taken steps to distance her party from that history. She has expressed support for Israel. She has expressed support for France's Jewish community, as you said. Are you saying that it's really nothing more than a political strategy, a facade? Or do you think there is an authentic evolution of principles in her party, that has, a party that has some residual antisemitism from this long history? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: First of all, it's better to have a party to say what they say than the opposite. Let's be very clear about that. It's better to have Marine Le Pen and Bardella say the same things that they say, meaning, expressing support for the Jewish community, expressing support for Israel, than the opposite, as her father used to say, who used to consider that the gas chambers were just the detail in history. But nevertheless, I spoke about the fact that Emmanuel Macron, in his decision to call for snap elections, has wanted to clarify things. And once the focus came back to actually looking at the party and looking at the candidates of those that were actually presented by the national rally as being candidates for the parliamentary elections, you could see that the problems were still there. So it's one thing to talk the talk, which is good, but at the same time, when you give nearly 100 seats to elements within your own party who are clearly problematic, I mean, we had a woman who wore a Nazi cap, like actually a cap from from from the Nazi era and took a picture of herself and posted it on social media. You have Holocaust deniers. You have people who actually had a library with where they sell Holocaust denying books, and the list goes on. You can't just consider that this is just residual, that this is just a small problem. And again, I think for the party to really be taken seriously and really make sure that to know that what they're doing is genuine, they will have to have a very serious inward-looking approach. Meaning, not using the issue of antisemitism and considering that it only exists ever on the far left, or that it only exists only within Islamist elements within the society, but actually agree and actually understand that it exists within their own ranks. Once that happens, we can take them a little bit more seriously. And we know that this will not only be part of a political strategy. In the meantime, I think we need to stay vigilant and call them out whenever that's necessary. Manya Brachear Pashman: So now let's turn to the left. I have to say I used the word "residual" in my previous question on purpose because that was a word that Jean-Luc Mélenchon, the far left leader, used to describe antisemitism in France. It's not rising, it's just residual. He's also called Israel's operation in Gaza genocide. I'm curious, should we be concerned about the far left's first place result? And what could be the ramifications of a far left victory in 2027 in the presidential election? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: So we did a survey, our biannual survey that we do together with IFOP, one of the largest polling institutes in France. And we found that 92% of French Jews consider Jean-Luc Mélenchon's unbound party to be the main reason why antisemitism is growing in the political sphere. So 92% of French Jews consider it to be antisemitic. A large majority or 54% of French Jews when they're being asked if Jean-Luc Mélenchon was to be president of France, would they leave the country or not, 55% say they would. So this is very, very clear. French Jews are very concerned about the far left. The different comments by himself, whether it's because he called, for example, when Jeremy Corbyn lost the election in the United Kingdom at the time, he said that the reason why he lost the elections was because of the Chief Rabbi of the United Kingdom, or because of the networks of the Likud. He, as you said, he's spoken about a Gaza genocide, but that's happening basically every single day. He considers antisemitism to be residual, all while knowing that 1,000% increase in antisemitism has happened since October 7. He has used the issue of Gaza, of the Palestinians really as a political game to create chaos within its parliament. He has had, they have had Palestinian flags. They have called Israel an apartheid state. I mean, this is basically happening every single day. So this is why Jews in France are extremely concerned and consider the far left to be the main cause of antisemitism today in the French political sphere. Now, what is very, very concerning, and this is we're paying the consequences today, is that when after the first round of the parliamentary elections, the traditional left wing parties, meaning the Socialists, the Green, the small Communist Party, decided to make an alliance with Jean-Luc Mélenchon's party, this was another not only a feeling of concern for French Jews, but probably a feeling of betrayal. Because it means that the moderate left does not consider antisemitism to be a red line. It doesn't consider antisemitism to be so important. For it not to create an alliance with a party that has very clearly made antisemitism one of its major causes. And let's be clear, in the Socialist Party, you have, for example, Francois Hollande, the former President of France, who was just elected in Parliament again, and who has, you know, indirectly considered that antisemitism is not a red line for him, and therefore, has decided to create an alliance with the far left. So for French Jews, it's both a sense of fear, but also clearly a sense of betrayal. Because how, what is the message not only to the French left, but what is the message to the rest of society? If you consider antisemitism not to be a red line? How do you want to continue to explain to the rest of society, to French children that antisemitism needs to be fought, that this is a priority for the country as such, if you don't consider it to be a red line? So we are now living with these consequences and therefore, the question arises, who will be in the government? Will it be, you know, will it be the far left, Jean-Luc Mélenchon, or will after the second round of the elections, the traditional moderate left decide to split off and, you know, take its distance with third party or again, continue in the same way, as they have until today, but it's a major issue, and one that we will possibly pay the price for in the future, again, beyond the very political issue, but in the country as such. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what role did the Israel-Hamas war play in this election and its outcome? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: The far left had a candidate, Palestinian woman by the name of Rima Hassan, who has a very, very radical approach to the Palestinian issue, considers that there needs to be a Palestinian state from the river to the sea. And this was really sort of the poster child of the unbowed party from Jean-Luc Mélenchon. And more largely, the issue of antisemitism played a role on the other side by all the other parties. We know, for example, of this horrible case of a 12-year-old Jewish girl who was raped by three boys of 12 and 13 years old, who hurled antisemitic insults and raped her. So all of this has really taken a center stage in the election, which makes many French people uneasy. I mean, so many friends of mine who said, you know, I wish we would be talking about something else. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to also look at the United Kingdom, another major country that also had elections last week, the UK Labour Party had a major victory ending 14 years of conservative rule. What can you tell us about that election and its results? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: This is major. The Labour Party led by Sir Keir Starmer really scored resounding victory in the general elections. Its majority is the largest one by any government since 1997. The party flipped seats in all corners, really, of the United Kingdom, defeating conservative candidates in constituencies that had been conservative since, really, the 19th century. The conservative vote collapsed by nearly 20 percentage points. It's the largest decline by any governing party in British political history. And voters abandoned the party not only in favor of the Labour Party, but also for other parties – for the Liberal Democrats, for reform UK, and also for the Green Party. And also plenty stayed at home. Fewer than three-fifths of the voters turned out to vote, and it's the second lowest turnout in the past century. Now, the Liberal Democrats took 60 seats held by the conservatives. The party increased its representation in the House of Commons from 11 seats in 2019 to 72, and seats in which the Liberal Democrats were competing against the conservative really saw substantial tactical voting to ask the governing party in the seats. The Tories vote share fell by an average of 24 percentage points, while that of the Liberal Democrats increased by 12. Also the Reform Party, Euro-skeptic, rather pro Russian anti-immigration party that was led by Nigel Farage was the biggest beneficiary of the conservative collapse in terms of vote share. Reform achieved 14% of the vote nationwide, which is basically 12 points compared with the Brexit party that Nigel Farage used in 2019. Nevertheless, the interesting thing, though, I think, for the Labour Party in particular, is that we see to some extent that when Labour becomes a normal social democratic center left party, it can win elections, which wasn't the case under the leadership of Jeremy Corbyn where the Labour Party very, very clearly lost the elections. Manya Brachear Pashman: But now, Jeremy Corbyn, as you mentioned earlier, very troubling history of antisemitism that spread throughout that party. So what should we know about the new prime minister Keir Starmer? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: Keir Starmer has made the issue of antisemitism a top priority. The party under Jeremy Corbyn had really become one could say institutionally antisemitic. And one of the first actions as Keir Starmer took over the party was the public apology to the Jewish community calling antisemitism a stain on the party that needed to be eradicated. And so I think as such, that needs to be clearly noted. Before Starmer also took over, before he now became Prime Minister, it's also important to note that the Jewish Labour MPs, like Luciana Berger, like Louise Ellman, who had left the party under Jeremy Corbyn, because basically they were being harassed, have decided to come back. So I think it's really sort of an endorsement of Labour as sort of a renewed confidence in the party's election. So, I think overall, the Jewish community is in the United Kingdom somewhat reassured by the stance that Keir Starmer has taken, since he has taken over the party, and there is no reason to believe that he will take a different stance. One should also probably note, even though this is, of course, his personal life, that Sir Keir Starmer knows the Jewish community very well. His wife is Jewish. She is the daughter of a Polish-British Jew, a Polish Jew who had emigrated to the United Kingdom in the 20s. Then was married to a non-Jewish woman who then converted to Judaism. So she was brought up Jewish. She is involved in Jewish community affairs. Keir Starmer has had in the past said that he would stop working at 6 pm on Friday night in order to be able to be with his family for Shabbat dinner. And so this is, of course, an important sign. That being said, there will also be pressure without a doubt from other elements within the political spectrum. There are other parties who did particularly well – the Green Party, the Reform Party, the Liberal Democrats, and there will be pressure, nevertheless, on many of the issues that in particular on foreign policy with relations to Israel and Gaza, that will be made. But overall, I think many in the Jewish community are reassured about the fact that the Labour Party was somehow cleansed of the most problematic antisemitic elements within the party. Manya Brachear Pashman: So put this all in context for us now. And how do these elections fit in with what we're seeing across the continent, from the recent EU Parliament elections to the Dutch elections? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: There is clearly, across the continent, a huge polarization. We see radicalization of the political spectrum. We see a certain inability of people to even talk with each other, to even share a common sense of reality, a common sense of shared values. And I think this is really what we're seeing across the European continent, and probably more widely across Western democracies. And this I think, needs to be seen, particularly also in a wider geopolitical point of view. We are clearly witnessing these days, an assault by autocratic nations or groups across the world, who have decided to team up despite their differences and to have to attack the Western worlds for their hegemony, to attack the Western world because they want to change the world order. So of course, militarily, by the war that is being waged by Russia against Ukraine, the war that is also being waged by Iranian proxies against Israel – Hamas, of course, since October 7, but also Hezbollah, the Houthis, etc, etc. And they're really, I think, trying to test the grounds. We see those autocrats teaming up – Russia, Iran, North Korea, China, to some extent – waging this war against the West, and we in the West, really falling apart to some extent from within both because there is a hybrid war that is being waged by those autocratic elements and countries from the outside, but also because we ourselves have our own huge problems, of course, as we know, and there I think, this is what we're seeing. This is the polarization of the political spectrum. And the fact that the far right is gaining more and more ground is part of that. It's part of the fact that many, many European citizens feel that what they used to believe Europe was about is falling apart. There is a lot of cultural insecurity. There's a lot of fear, and to some extent, the job that by the sort of traditional conservative and liberal parties on the left and right, that should have been there to address the concerns of European citizens, whether it's on immigration, whether it's on globalization, whether it's about the middle class have not been addressed by those parties. And so in this vacuum, and in this wider geopolitical context, the populist parties are exploiting that part. So my appeal to European and Western democracies and Western parties who care about Western values and European values is to start addressing the issues from within, stand up for themselves stand up for the minorities and in particular Jews. Knowing that antisemitism is always the first sign of societies falling apart, and deal with the very serious threats that are coming from the outside, and stand firm. Because we are at a crossroads of the world as we know it. Manya Brachear Pashman: Once again, thank you, Simone for joining us and informing all of our conversations on these matters.
Jun 28, 2024
Rebuilding Israel's Devastated Negev Region Post 10/7
The October 7 Hamas attack severely affected Israel's Ben-Gurion University (BGU) and its surrounding community. The university lost over 110 people, several students were taken hostage, including Noa Argamani, and thousands of students were called up for reserve duty. Doug Seserman, CEO of Americans for Ben-Gurion University, joins us to discuss the impact of the October 7 Hamas massacre on BGU and Israel's Negev region. Hear about the university's emergency response and volunteer efforts, highlighting the region's resilience and the university's innovation in sustainability, water conservation, and energy solutions. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Doug Seserman Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod: The 2024 U.S. Presidential Election: What Does it Mean For Israel? Seven Months In: What Israelis Think About the War Against Hamas, Campus Antisemitism in America, and More What Does it Mean to be a Jewish American Hero? A Jewish American Heritage Month Conversation with AJC CEO Ted Deutch Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Doug Seserman: Manya Brachear Pashman: The Negev, the vast desert region that covers 60% of Israel's territory is home to only 10% of its population. It's also home to Ben-Gurion University and many of the communities attacked by Hamas terrorists on October 7. Doug Seserman is the CEO of Americans for Ben-Gurion University. In that role, he has worked to highlight the innovations and technology know-how that Israel can offer America and the world when it comes to sustainability, water conservation, energy solutions and ecology. But since October 7 BGU's efforts have shifted from sustaining lives across Israel's south to rebuilding them. Doug Seserman is with us now to discuss those efforts. Doug, welcome to People of the Pod. Doug Seserman: Thank you so much for inviting me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So compared to other Israeli universities, the BGU community was disproportionately impacted by the October 7 massacre, correct? Can you give our listeners some perspective on the scope of loss? Doug Seserman: Sure. So as the crow flies our main campus in Beer-Sheva is only about 22 miles from Gaza. We had a number of students at the Nova music festival site, and a number of our employees and their families live in the western Negev or Gaza Envelope area. So as a university today, we have 111 dead. That includes those murdered on October 7, as well as fallen soldiers. We've had close to 6,600 of our students, faculty, employees, administration, called up to milu'im, reserve duty, and not all of them have come back. Some 2000 are still fighting. So that was a direct and disproportional impact. Now everybody in Israel has experienced this war. Every family knows somebody, but for us, it's definitely disproportional. Literally every colleague's kids are fighting. Every younger woman who's a colleague in her 30s, their husbands are fighting. People are on their WhatsApp just trying to hear what's going to happen next. It's a very surreal situation. Manya Brachear Pashman: Four hostages were rescued by the IDF earlier this month. Were there any faculty, staff, or students from Ben-Gurion taken hostage? Doug Seserman: Noa Argamani, you may recall her name. She was at the music festival and forcibly separated from her boyfriend Avinatan Or, who's a BGU alum. But Noa is a 26-year-old information systems student of ours. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yes, thank you. Of course, Noa was one of those hostages recently rescued. We are so thankful that Noa is now home. 124 hostages are still being held in Gaza. We are praying and advocating for the safe return home of all hostages, and will highlight those that are part of the BGU family : Sasha (Alexander) Trufanov, Avinatan Or, Alex Dancyg, and Segev Kalfon And Doug, how many at BGU were called up for reserve duty? Doug Seserman: That's about a third of the student body. Classes, obviously, they were supposed to start on October 15, and they didn't resume until December 31. The president of the University, Professor Daniel Chamovitz, did his best to have no student be left behind. But at some point, we had to resume classes. And so today, when you go to the campus, it's, I don't want to say it's thriving, but it's functioning. There's a normalcy about life in Israel and also on campus. But there's nothing normal about this new normal. Many of our reservists are back and they're in the classroom, but even going from being in Gaza, in conflict, to then studying for a test, you know, writing papers and things. People are traumatized, and the university has done an amazing job providing psychological support and counseling for the students and the faculty and the families who've been directly impacted. But still, it's a very difficult situation. Manya Brachear Pashman: In addition to those called up for reserve duty immediately after October 7, was there a sizable volunteer effort? Or was the community just too shell-shocked? Doug Seserman: Thank you for asking. Today when you go to campus, it's happening and it's alive and doing as well as it can. On October 7, that immediately pivoted from a university that was closing – had to close because of the war – to almost a hub for activity to support not only the faculty and students, but also the community – a logistics center, if you will. We were housing, in our dorms, evacuated families and also medical professionals from the center of the country that needed help. Soroka, which is the main hospital of the Negev and also the teaching hospital for our two medical schools. Very close relationship with Soroka Medical Center. Our medical students immediately became ER triage doctors. They learn by doing. If you talk with some of them today, they'll tell you in this strange way that October 7 may have really accelerated their knowledge in terms of their career, etc. And then we just started doing what we could. Students mobilized, as Israelis do, to create care packages and provide clothing and anything that was necessary for these evacuated families. We had, I want to say close to 1500 members of our community that were evacuated. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, I imagine it's even more than medical students getting this, you know, on the ground experience. I happened to be in journalism school in New York when 9/11 happened. I remember places in New York City all of a sudden transforming into emergency centers, like what you're describing, and I think a lot of my classmates got a crash course, right, in journalism from covering that. Doug Seserman: Absolutely. Even our social work and psychology students became kind of caseworkers. I mean, everybody was doing what they could and, in a way, we should feel really good about it. It's hard to say there are silver linings from October 7. But the resilience that the country has demonstrated in the university, in particular, is incredible and quite inspiring. One thing about Ben-Gurion University that's unique is, yes, we are an educational and research institution and one of the leading universities in Israel, and we're quite proud of those accomplishments. But we have a particular and very unique mandate to develop the Negev region. And it's almost in what we call the Ben Gurion DNA, to activate the social justice aspect of being a Jew, honestly. But it's particularly manifest at the University and we're proud of it. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, you know, let's talk a little bit more about that innovative spirit that I hear a lot about, that characterizes Israel and, obviously, BGU. And I mentioned earlier how BGU has introduced, you know, all of these technologies, innovative solutions for environmental concerns. I think David Ben Gurion said "making the desert bloom" – that was his goal and what the university aims for – but has the aftermath of October 7 highlighted other faculty, other fields? You talked about psychology and social work. Can you talk a little bit about how this kind of innovative spirit has been applied and has really shown itself since October 7? Doug Seserman: Yeah, absolutely. I'm happy to do that. And it's important to note also that Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, it was important on October 6. When you visit the Beer-Sheva campus, it's, in a way, it's startup nation on steroids. You have Ben-Gurion University and Soroka hospital, the advanced technology park that has 3000 employees and 70 multinational companies, right across the high speed train station to get you to Tel Aviv in just over an hour. And you have the IDF moving south and their IT and computing base literally adjacent to the university. It's an amazing place. I actually feel like a lot of people visit Israel, and they don't really go south. And the truth is, you haven't seen the future of Israel until you spend time in the Negev. And you don't really understand the Negev until you've spent time at the University. But in terms of areas that the University excels at, that are important in the aftermath. I mean, it's everything. But some of the things I would highlight is our strength in engineering, computer sciences, IT, cybersecurity. The cyber capital of Israel is actually Beer-Sheva. This IDF base that's adjacent to us, I call them 22nd century defense systems, remote sensing satellite defense technology. Hatzerim Air Force base is in the Negev, that's where all members of the Israeli Air Force get their wings, but they actually get their degree, their educational degree, from Ben-Gurion University. So when we think about the future, listen, it takes a village. And you can never do wrong by doing right. So I'd encourage your listeners to just get involved in something in Israel that's consistent with their values. Manya Brachear Pashman: I know the South has supplied much of Israel's kind of homegrown food, vegetable crops, barley, wheat, dairy, but obviously, I mean, many of the Palestinian and Thai workers who tended those fields, they're not returning anytime soon, neither are the residents of those kibbutzim. Has BGU played a role in filling that gap? Doug Seserman: The answer is yes, and doing our best and not enough. And very proud of all the volunteers and that you're seeing, especially also from the diaspora coming to Israel to help pick fruit and etc. We had faculty that basically stop because they weren't teaching and they had time, they just started going into the fields and helping the farmers, both with their hands and their heart. At the end of the day, there's a very close relationship and literally hundreds of our students and faculty and administration has been involved in volunteer efforts. At the end of our board of governors meeting last week, we had a whole afternoon dedicated for volunteers who came from around the world to volunteer as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to go back to campus real quick and talk a little bit more about the students. I know that BGSU has a really robust diversity and inclusion effort that covers Druze, other Arabs, women, disabilities, Ethiopian immigrants, ultra-Orthodox Jews – it's a very diverse campus. And I'm curious how this diverse student population views the scenes from some American university campuses. I mean, has there been vigorous debate on BGU's campus about how Israel is fighting this war? And does it look any different? Doug Seserman: Now that's a big question. I can say this: we're extremely proud of the diversity on campus and sometimes what we call a shared society. We have Sarab Abu-Rabia-Queder, who's the Vice President of Diversity and Equity and Inclusion in Israel. That DEI term has become controversial, in the United States, but in Israel, you know, in our campus, it's a thriving concept. We have approximately 20,000 students. Most of them are Israeli. We have about 1000 international students that study in English, mostly from China and India, but also from North America. And then we have about 2000 Arab-Israelis. So of the Arab-Israeli, a number of them are Bedouin. We're by far the largest university for Bedouin students in Israel. So we have robust discussions underneath that framework of the diversity, VP of diversity, to try to bring students together. Sometimes there have been, before October 7, protests, peaceful protests, with Arab students protesting and Jewish students also there. And we've never had issues. You know, there's a way to have civil discourse, and free speech and academic freedom is critical. I mean, it's a hallmark to a just society. So you know, you have to be able to have peaceful protests. Now going back to what's happening on American campuses. You know, I'm personally embarrassed. I wrote an op-ed recently in The Times of Israel about what do you do when your alma mater no longer reflects your values? I'm a proud Wildcat from Northwestern University. And we had a terrible situation on campus. And then our president Michael Schill, who's a smart guy, and also a Jew, negotiated with the encampment leaders and created a precedent almost like, it's not negotiating with terrorists, but it's compromising and rewarding, enabling bad behavior and creating a precedent that the way to make change is to be lawless and create hate speech. So something's happened in the US that on college campuses, that's absolutely out of control. But at the same time, freedom of speech, and especially in academic institutions, must be protected, but it has to be safe. We teach chemistry on university campuses all across the country, perhaps we should be teaching morality. And maybe that should be a required course. Now, I don't even know what that looks like. But I think people have lost a sense for the difference between proper behavior and improper behavior. And they sometimes use free speech to do hateful and wrongful things. And that's, that's not appropriate. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, you're suggesting social chemistry lessons? How do we get along? How do relationships work? Doug Seserman: I love that. I think what's happened is we all are talking in echo chambers. We've no longer figured out how to understand the narrative of the other, and how to find some sort of central place to move forward where people can agree to disagree, but you can move forward in some kind of democratic and civil way. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I don't want to lose sight of the fact that you head Americans for BGU, right, the arm of the university that works to garner American support? Has October 7 presented some unexpected challenges in that realm? Doug Seserman: You know the answer, to that is yes. And also, unfortunately, opportunities at the same time. There's been an October, I call it October 8 awakening, some people are calling it October 8 Jews – people in this country and in the diaspora are waking up, that something is happening out there with antisemitism, and the relationship between anti-Zionism and antisemitism. And as an American diaspora Jew, you have sort of like three options. You can do nothing, and no miracles are going to come from that. Or you can kind of wait and see and no miracles are gonna come from that. Or you can kind of double down your efforts and get involved with institutions that matter, can make a difference. And that's what we're encouraging. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Doug, thank you so much for joining us and for giving us a snapshot of what people are trying to do to rebuild Israel's south and help it recover after October 7. Thank you so much. Doug Seserman: Thank you so much for having me.
Jun 21, 2024
The 2024 U.S. Presidential Election: What Does it Mean For Israel?
In AJC's signature AJC Global Forum session, the Great Debate, Halie Soifer, CEO of the Jewish Democratic Council of America, and Morgan Ortagus, former Spokeswoman for the Department of State under the Trump administration, engaged in a debate on the 2024 presidential election and its impact on the global Jewish community, Israel, and the future of democracy. Listen to this session, moderated by AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson, recorded live on the AJC Global Forum 2024 stage in Washington, D.C. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. AJC is a 501(c)3 not for profit organization and does not endorse political candidates for elective office. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jason Isaacson, Morgan Ortagus, Halie Soifer Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod: Seven Months In: What Israelis Think About the War Against Hamas, Campus Antisemitism in America, and More What Does it Mean to be a Jewish American Hero? A Jewish American Heritage Month Conversation with AJC CEO Ted Deutch Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Debate with Morgan Ortagus and Halie Soifer: Manya Brachear Pashman: In AJC's signature AJC Global Forum session, the Great Debate, Halie Soifer, CEO of the Jewish Democratic Council of America, and Morgan Ortagus, former Spokeswoman for the Department of State under the Trump administration, engaged in a debate on the 2024 presidential election and its impact on the global Jewish community, Israel, and the future of democracy. Moderating the debate was AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson. Here's Jason now to explain the format. Jason Isaacson: We had a coin toss, and Morgan won the coin toss, and will go first. Each of them will have two minutes to provide opening statements. There will be the opportunity for a minute of rebuttal afterwards, then we'll plunge into a series of questions that I'll be posing to each of them. Morgan, you're up. Morgan Ortagus: Thank you so much for having me. I want to start this discussion today really telling a few stories from my time in the Trump administration, but also talking about this from a policy perspective. For those of you who don't know me, I've actually served in multiple administrations, including in the Obama administration, as well. And I say that to provide the context that I think the State of Israel cannot have a relationship with just one political party in the United States, just as we pray for the success of Israel. I pray for the success of our leaders, whomever wins in November. And I think no matter what happens today, in this debate in November, we must stand with our ally, we must stand with the State of Israel. You know, what's amazing is, I think about four years ago, I was standing in the Oval Office after many, many months of having worked with Secretary Pompeo, Jared Kushner, and the entire team on something that you all came to learn about called the Abraham Accords. And in that moment, I was pregnant with my daughter Adina Ann, this beautiful Jewish baby. And I thought to myself, the Middle East has entirely changed for her. This is going to be so radically different. Fast forward three and a half years later, to see October 7th and what happened that day, the worst killing of the Jewish people in any single day since the Holocaust. It felt like everything I had worked on in Abraham Accords had been shattered. But I am here to say that there is hope, with the right president, with the right policies. And that's what I really want to talk about today. With the right policies, we can get back to an era, not only have a strong America, a strong Israel, and a much stronger Middle East, happy to debate the policies. I'm not a campaign person. But I do believe that under the Trump administration, under Mike Pompeo, we had the right policies that were best for Israel, and best for the Middle East. So I guess as the famous song goes, all I'm here to say is give Trump a chance. Jason Isaacson: Morgan, thank you. Halie Soifer. Halie Soifer: Jason, Morgan, AJC, thank you for having me. And thank you for your efforts advocating for the Jewish people for Israel and defending democratic values. I'm grateful for your work, which has made a difference, and particularly grateful for the leadership of your CEO, my friend, Ted Deutch. This is the third time I've joined AJC's Great Debate in advance of an election with Joe Biden and Donald Trump on the ballot. The first was in 2019. The second was 2020. But 2024 is different for three reasons. First, the stakes of this election are higher. Second, the positions of the two candidates have never been more clear or divergent. And third, both candidates have been president before and can and should be judged on their records. Unlike the last debate, this is no longer a hypothetical in terms of what kind of President Joe Biden or Donald Trump would be. We know the answer. Joe Biden has sought to restore the soul of America by taking unprecedented steps to combat antisemitism and bigotry, while Donald Trump has emboldened, echoed and aligned with dangerous extremists and antisemites. Joe Biden is a self declared Zionist who has stood with Israel for more than five decades, including after October 7, when he pledged his staunch support of Israel and the Jewish people. While Donald Trump is a self declared dictator on day one, who marched Israel's leaders and praised Hezbollah after October 7. Best summarized by his former national security adviser John Bolton, who told the New York Times, Trump's support of Israel is not guaranteed in a second term. Joe Biden is an ardent defender of democracy, while Donald Trump incited a deadly insurrection in order to stop the peaceful transfer of power in the last election, and is preparing to weaponize the US government as an act of political retribution. If he wins the next one. And let's not forget, he's also a twice impeached 34 Time convicted felon. So three times is clearly a charm. There's plenty to debate and I'm happy to be here. Thanks. Jason Isaacson: Very good. Thank you, Halie. You can each rebut the others statements. Morgan, would you like to say a word? Morgan Ortagus: I think the only response I would have to that is do you feel safer as a Jew in America today than you did four years ago? That's it. Jason Isaacson: Halie, would you like to say anything in response? Halie Soifer: Sure. Four years ago, I mentioned I joined this debate. We did so via zoom, where we were in our home stuck for more than a year. It was an unprecedented pandemic that really epitomized Donald Trump's leadership. He was ignorant, chaotic or erratic, and demonstrated a reckless disregard for a fundamental Jewish value pickoff nephesh. The sanctity of life. Since Joe Biden has become president, we emerged from this dark period, the economy has grown. Unemployment is at a 50 year low. And yes, anti semitism has risen, including after the horrific attacks perpetrated by Hamas on October 7, and our unequivocal condemnation of this violence and of rising anti semitism is something on which I'm sure we agree, Morgan, and you know, who else agrees with us, Joe Biden. On May 2, he said in response to the campus protests, there should be no place on any campus or any place in America for antisemitism. It's simply wrong. Jason Isaacson: Thank you. Okay. Let's get into the questions if I could begin with you, Morgan. As you know, in election after election over the last century, a substantial majority of Jews have voted for Democratic presidential candidates over Republican candidates, the sharpest differences were under FDR in the 1940s and the Johnson Goldwater election of 1964, when Democrats were reported to have scored 90% of the Jewish vote, but Harry Truman, Bill Clinton, Al Gore and Barack Obama weren't far behind, and Joe Biden was reported to have led Donald Trump four years ago, according to Pew by 70%, to 27%. AJC's latest polling shows a somewhat narrower gap, but still has President Biden beating former President Trump by more than two to one among American Jews. If these numbers are predictive and accurate, how does the Republican Party break through that traditional Democratic predisposition among Jewish voters and why does it matter? Morgan Ortagus: I think there's a couple ways to unpack that first, I think there's a big difference between saying the right thing and doing the right thing. There's no doubt that the Biden administration, the Biden-Harris administration is great on the rhetoric. But I would say that the policy is lacking. First of all, I think most Jewish voters care about Israel care about antisemitism in this country. But let me just also say that I think Jewish voters, Jewish moms and grandmas in this audience, Jewish parents, you care about things that I care about in Nashville, Tennessee, which is the price of groceries, which is filling up your car with gasoline, which is all of the things that matter to all of us as consumers. And it is not a good time in America for the American family. People are making real decisions, whether to fill up their gas tank or whether to fill up their cart full of groceries. That happens in real America in Nashville, Tennessee, where I live. I would also say that, you know, Lindsey Graham said this to me once and it really made me laugh. He said about Trump, I've never seen somebody so willing to cut off their own arm just to spite him. And he certainly incites a lot of heated emotion and passion. But again, I would get back to the question that I asked you, do you feel more safe as a Jew in America today than you did four years ago? Do you think our policies are stronger at protecting Israel, with standing with our ally than they were four years ago, I would argue that we have turned the Middle East on its head in the past four years by beginning at the beginning of this administration to spend the past three and a half years, chasing the Islamic Republic around the world, begging and cajoling and pleading with them to get back into a nuclear deal, giving them billions of dollars in sanctions relief by not enforcing those sanctions. That was three and a half years of policies that led to events like October 7. We also saw multiple times at the UN, including yesterday, ways in which that I think the Biden administration has sold Israel down the river. has not stood up for them at the United Nations or on the world stage. And so I'm quite simply argue that the Middle East is chaotic today, specifically from the policies of the past three years that were put in place by the Biden Administration. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Morgan. Halie, you can respond if you wish. You have a minute. Halie Soifer: Well, as a Jewish mom, I can say I absolutely feel safer knowing that Joe Biden is in the White House because he shares our values, our fundamental values, our Jewish values, defending democracy, and of course, support of Israel. A lot of Republicans mentioned Donald Trump's move of the US embassy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem in 2017. Something we agree with–Jerusalem is the capital of Israel. What we don't mention enough is that in August of 2020, Donald Trump said he did that for the evangelicals, which demonstrates two things. One, Donald Trump's Israel policy has always been based on his self interests. His own former national security adviser has revealed that in an article in The New York Times in early April, and also it's clear that Donald Trump has great animus toward the vast majority of Jewish Americans, those who vote for Democrats because of it.. He has called us disloyal. He has called us uninformed. He has said we hate Israel, we hate our religion, we should be ashamed of ourselves. We're loyal to our values, which is why the overwhelming majority of us support Democrats. Jason Isaacson: Halie, I want to ask you a different version, or the pretty much the same version of the question that I asked Morgan at the beginning, why it matters where the Jewish vote is. Remembering that the Israeli newspaper Haaretz had a piece after the 2020 election, that maintained it was Jewish voters in Pennsylvania, Georgia and Arizona who actually made the crucial difference in that tight race moving those swing states and their deciding Electoral College votes into the Biden column. Although polling and voting history is obviously on your side, there are signs of slippage for President Biden in our own polling and in other samples. Some of that may have to do with the President's being seen as inappropriately pushing the Israeli government in ways that didn't want to go in the conduct of the war against Hamas. And in a post conflict path to Palestinian statehood. Some of it may be factors that have nothing to do with Israel or with the Jewish community, but reflect attitudes in the general population. Why the slippage and how are you addressing it? Halie Soifer: Well, Jason, you're right. The Jewish vote absolutely matters. The states you mentioned, Pennsylvania, Georgia, and Arizona determined the outcome of the 2020 election and may do so again in 2024. Joe Biden won those three states in total by just over 100,000 voters. And in those states the Jewish vote, and even more said the Jewish vote that supported Joe Biden was exponentially higher than the margin by which he won. So where are Jewish voters in 2024? Well, 74% of Jewish voters supported Democrats in our last election in the 2022 midterms. It's the same amount approximately three quarters who have supported Democrats historically, and it's the amount I predict will support Joe Biden in this election for two reasons. One, Joe Biden represents the vast majority of Jewish voters on every key issue, domestic policy, democracy, abortion, access, guns, climate change the economy, antisemitism, and foreign policy, Israel, Ukraine and defending democracy abroad. And too, Jewish voters overwhelmingly disapprove of and oppose Donald Trump in 2016, in 2020, and they're going to do it again in 2024. Because there's even more reasons to oppose him now, going into a potential second term. AJC's new poll only confirms this. The poll indicates that both Joe Biden and Donald Trump have essentially the same amount of support–61%/23%--among Jewish voters as they did among that same group of voters in 2020, when it was 64%/21%. Donald Trump has not broken 25%. It also shows that Jewish voters trust Biden more than Trump on Israel by a two to one margin and on antisemitism by three to one margin. So AJC is consistent in its polling, and it's consistent with what we've seen in other polling as well that Jewish voters will continue to overwhelmingly support Democrats and Joe Biden, especially with Donald Trump on the ballot. Jason Isaacson: Morgan, you may respond. Morgan Ortagus: Again, you know, I'd say there's a big difference between rhetoric and policy action. The truth is, the reality is, there has never been a more unsafe time in America, for Jews, especially young Jews on college campuses. Today, the antisemitism unveiled and unchecked during the Biden administration should scare all of us. The fact that Jewish students have to make decisions if they want to wear a yarmulke, if they want to wear a Star of David, if they want to openly embrace Judaism in the United States of America is a stain on the Biden administration. And something that I think that there has been no real action. In 2019, again, I'm going to keep going back to policy because when you have bad policy, you have to run on rhetoric. When you have good policy, you can talk about things that we did like the executive order to combat antisemitism in 2019. That executive order focused on criminalizing antisemitism, basically bringing it up to the level of any other persecution against, you know, sex, gender. We could go through everything in Title Six. That's incredibly important because we have real world ramifications for antisemitism that this administration has ignored. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Morgan. Let me ask you another question. And I'm going to turn to a foreign policy issue again. Since President Trump in May 2018 pulled the United States out of the 2015 Iran nuclear deal, the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, calling it a horrible one-sided deal that should never ever have been made. Iran has marched closer and closer to becoming a nuclear threshold state with a stockpile of enriched uranium calculated to be more than 6000 kilograms as of last month, more than 20 times the limit that was set in the nuclear deal. But enough of that uranium enriched to a near weapons grade level to fuel at least three atomic weapons. It's been said that the maximum pressure campaign waged in the last year and a half of the Trump administration had little effect on Iran's pursuit of nuclear weapons capability. How would you answer the charge that pulling the US out of an unsatisfactory nuclear deal actually made the problem worse? How would a second Trump administration approach this threat from Iran? Morgan Ortagus: Thanks, now we're getting to my favorite subject. So you don't even have to listen to President Trump on this. You can look at Senator Schumer, Majority Leader at the time in his speech and his debate why he did not support the JCPOA. We know of course, that the JCPOA was never brought before the Senate because it was a bad deal that would never get passed, including by Democrats. Let's also remember that under the JCPOA, we left the deal in 2018 in the Trump administration, at the time and during the entire Trump administration. Iran never exceeded the 5% enrichment. In fact, it didn't happen until the Biden administration and under Biden, they've gone up to an 84% enrichment strategy with zero ramifications. That's enough material to get a bomb within eight months if we wanted to. More importantly, Americans and Israelis are dying at the hands of Iran. And why is that? Because once again, you have a Democratic administration who have not enforced sanctions, they got billions of dollars in sanctions relief. About three weeks before October 7, this administration negotiated a deal that I didn't think that could be worse than the JCPOA. But they actually managed to top themselves by promising to give Iran $6 billion for returning five American hostages home. Now, I love getting American hostages home. In fact, in the Trump administration, we got two American hostages home from Iran, guess how much we paid for those hostages, zero. And so there is a way to negotiate to be tough with Iran and to protect Americans. But Americans are dying in places like Jordan, from Iranian made drones. We know that American ships are being taxed on a daily basis, again, from material that is supplied to the Hussein's by Iran. And so whenever you reward enemies, like the Islamic Republic of Iran and punish friends like Israel, the Arab states, then you end up with a chaotic Middle East. So the Middle East is on fire today principally because of the appeasement of the Islamic Republic of Iran. Iran will likely get a nuclear weapon in the next administration, if it isn't stopped. President Trump will stop it. President Biden will just beg and plead them to stop. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Morgan. Halie, you may respond. Halie Soifer: We talked a lot about, of course, the horrific acts of what happened on October 7. What I don't think we talked enough about is what happened on April 13, when Iran launched over 300 projectiles at Israel and an unprecedented direct attack. In the end, Israel survived that attack relatively unscathed. Miraculously, because Joe Biden had deployed two aircraft carriers to the eastern Mediterranean preparing for such attacks, and had encouraged a coalition, Arab partners, to stand with Israel and directly intercepted over 100 ballistic missiles. It was the first time the US military had been deployed to prevent a direct attack on Israel. Following the attack, Biden took steps to hold Iran accountable, including imposing new sanctions and exports control on Iran. The sanctions targeted leaders and entities connected to the IRGC, the Iran Revolutionary Guard Corps. During the Biden administration, the US has sanctioned over 600 individuals and entities including Iran and its proxies. And the President has directed the administration to continue to impose sanctions that further degrade Iran's military. This is on top of the Trump era sanctions against Iran that Biden kept in place. So Joe Biden has demonstrated great strength in defending against the threat of Iran, especially as it relates to the threat posed by Israel. Jason Isaacson: There are increasingly loud and influential voices in the Democratic Party, expressing harsh criticism of Israel's conduct of the war against Hamas in Gaza and among constituencies on which democratic election victories have often depended. There's opposition to Israel more generally, not just to the current war, but to the legitimacy of the Jewish state. Over the last two years, according to Gallup sympathy for Israelis over Palestinians has slipped among Democrats from a majority to a minority position, although there is still a plurality with more favorable views of Israel versus Palestinian Authority. For comparison among Republicans sympathy for Israelis earlier this year was recorded by Gallup is more than 10 times that for Palestinians. How can President Biden and the party counter the critics and assure that US support for the Middle East's sole democracy remains bipartisan. And how do you respond to the charge that Trump criticism of Israel in progressive circles contributes to attacks on supporters of Israel and incidents of antisemitism? Halie Soifer: Antisemitic and anti-Israel views have been expressed by elected officials on both sides of the aisle. Neither party is homogenous in their view on either issue. When antisemitism and or anti-Israel views have emerged among Democrats in Congress, JDCA, our organization has condemned it, and in some cases endorsed a primary opponent to anti Israel, Democratic incumbents. There are two such primaries that we're engaged in right now as we speak in New York and in Missouri, to elect Democrats who share our values. There are some Democrats who have opposed or proposed conditioning aid to Israel, something which JDCA opposes. But House Republicans, including their entire leadership, recklessly delayed essential military aid for Israel that Joe Biden pledged in October for six months, at a time when it could not have been needed more. When it comes to antisemitism, there is a sharp difference between how it is handled by the two parties. The Democratic Party marginalizes those who have used antisemitic rhetoric, while the Republican Party has elevated extremists and antisemites, one of whom is at the top of the ticket in the past three election cycles, including this one. Leadership matters, and the words and actions of our leaders matter. When the American people were faced with the same choice for president in 2020, on the debate stage, President Biden implored Donald Trump to condemn white supremacy, we all remember it. Trump blatantly refused, he could not, would not condemn this insidious ideology that motivated the perpetrator of the worst massacre of Jewish Americans in our history two years earlier at the Tree of Life synagogue in Pittsburgh. What did he do instead, he incited dangerous right wing extremists, the Proud Boys to stand back and stand by from the debate stage. And less than four months later, they heated his call on January 6. This election is a binary choice. There are two names on this ballot, two men vying to be leader of the free world. One has been a staunch friend and ally of the Jewish people in Israel, since he was first elected to the Senate in 1972. And the other who has always done and will continue to only do what is good for himself. Jason Isaacson: Morgan, I think you may want to respond. Morgan Ortagus: You know, I will concede, I don't watch MSNBC. And maybe they're just not covering what I see going on in America on a daily basis, which is a Charlottesville every single day in this country, which is the calling for not only supporting Hamas and other terrorist organizations, but calling for the genocide and the extermination of the Jewish people blatantly and openly every single day in this country. You also see yesterday in New York City, while there was a memorial to what happened on October 7, people there openly demonstrating support for more October 7, support for more terrorism. And while that was happening, the United States was shamefully at the United Nations calling for a ceasefire resolution that made us look like we were Hamas' personal lawyer. If you're a party that doesn't have the moral clarity, to stand by the Jewish faith to just stay defending itself against terrorism, how can you claim to have the moral clarity on anything. I was in Israel three weeks ago Prime Minister Bibi Netanyahu told me that in fact, the Biden administration is slow walking military aid that he needs. Just last week in the Congress, the Biden administration was whipping votes against bipartisan ICC sanctions, which are undermining again the leadership of a democratic elected Jewish state. We'll remember famously that after the attack that he talked about a few minutes ago from Iran, Biden famously told Prime Minister Bibi Netanyahu for Israel just to take the win essentially. At every turn, then not only tie one hand behind Israel's back, they tie both hands behind the back as they tried to defeat the terrorists that invaded them and by the way, killed Americans on October 7, and the last time I checked, we still have five Americans that are held captive eight months later by a terrorist organization behind enemy lines. Bring them home. Jason Isaacson: Morgan, you're up. Your last question and President Trump and other leaders of your party had been harshly critical of a range of diversity and equity programs, affirmative action and college admissions and educational curricula that cast a negative light on aspects of American history. And these stances have earned the support and loyalty of among others, individuals and groups with extremist views on race and ethnicity. How do you answer critics, including President Biden, who charge that this so-called anti-woke agenda lends legitimacy and support to forces of intolerance? As you know, there are also accusations that divisive rhetoric can fuel antisemitism. And the example of Charlottesville, which we've been talking about is often cited. How do you counter that, in a minute, if you may. Morgan Ortagus: I'll be very quick and say that I agree with Halie that there is antisemitic problems that happen on both the left and the right, and we must be countering them. And every time it happens, again, I'm a foreign policy professional. I look at the policies. I don't necessarily get involved in domestic politics. But I will say that what we have seen, especially on college campuses, is that DEI and intersectionality are the parents of antisemitism and fostering intolerance. Can anybody look at our college campuses and say this isn't true. I don't think President Biden and vice president Harris are doing enough to rein in anti-Jewish Jewish violence in this country. Let's look at Biden's so-called efforts, is there more or less antisemitism in our universities? Are there fewer encampments? How about what's happening to the American flag? The last I've seen, the Iranian people have more respect for the American flag and the Israeli flag than liberals on university campuses today. Many students who had to start college online and COVID have gone back to going online because it's unsafe to be Jewish in America in an American university today. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Morgan. And Halie, we're not going to have rebuttals to these questions. Halie, your last question: the Iranian threats, foreign policy question. The Iranian threat isn't confined to its accelerated nuclear program. Iranian proxies in Lebanon, Syria and Iraq firing missiles and drones at Israel sometimes with deadly effect. The Iranian supported Hutus in Yemen regularly attack ships in the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean. In recent years, Saudi Arabia and the UAE have come under attack from Iran or its proxies and vessels of many nations, including the US Navy, have been targeted or damaged or seized. Iranian agents abroad from the IRGC, Hezbollah, Hamas and other groups have been implicated in assassination plots, including in our own country. Critics charge the Biden administration, which yearned from day one to return to the 2015 nuclear deal has failed to confront Iran forcefully over these multiple threats. What's your response? In a minute, if you could? Halie Soifer: Ok, in order to answer this, you have to go back to May of 2018 when President Trump against the advice of many in the US intelligence community and Israeli security establishment, withdrew from the Iran nuclear agreement. While the JCPOA was not a perfect agreement, Iran was in compliance with it. According to international observers and American intelligence officials. It was effectively verifying restrictions on Iran's nuclear development, as AJC itself said at the time in its own press release, despite our many reservations, we had hoped to see the deal fixed, not next. It was with the same objective. And given the fact that Iran was at that time weeks away from acquiring a nuclear weapons capability. The Biden administration explored whether it was possible to reenter the JCPOA and reach a better deal if Iran came back into compliance. In the end, it wasn't possible because Joe Biden refuse to capitulate to Iranian demands, including lifting the terrorists designation on the IRGC, Joe Biden should be praised, not criticized, for working with our allies to explore whether the resumption of a multilateral deal that would contain Israel's nuclear aspirations was possible, and for standing up to Iran, not just by refusing to give in to their demands, but by continuing to implement sanctions against Iran. And as I mentioned, in an unprecedented act, defending Israel against an unprecedented direct attack by the Iranians on April 13. Jason Isaacson: Halie, thank you. We're gonna go directly to closing statements and Morgan, having won the coin toss, you go first. Morgan Ortagus: Okay. You know, Halie just talked about working with allies. How about last week at the IAEA, whenever the E three, the UK, France, Germany, had to actually go and beg and plead us to stand up against Iran at the IAEA which we didn't do. We just talked about the ICC in which bipartisan sanctions are before the Congress that the Biden administration is not only not supporting, they're whipping against and the multiple votes at the UN either abstaining or actually working on ceasefire, right. solutions that undermine the State of Israel. Listen, I would say there's a far big difference between bad rhetoric and bad policy. If you want pretty tweets, vote for Biden, if you don't want dead Israelis and dead Americans vote for Trump. When you look at the people that Biden has empowered in his administration look no further than his Iran envoy, Rob Malley, who was fired, who was under FBI investigation, and also the State Department inspector general investigation because of his leaking of classified information and potential ties to Hamas. These are not the people that we will promote and support in the Trump administration. President Trump will defend Israel, he will stand by Israel and things like October 7 won't happen under President Trump. You will have peace like under the Abraham Accords and you will have an Iran that is curtailed because we will actually stand up to them and we will stop them from getting a nuclear weapon. Jason Isaacson: Morgan, thank you. Halie Soifer, your closing comment? Halie Soifer: Well, you will soon hear from Joe Biden's National Security Adviser Jake Sullivan, there is no stronger champion of the US Israel relationship. You will see that Maya Angelou famously said when someone shows you who they are, believe them the first time. Whether it's acquainting Neo Nazis with peaceful protesters declaring very fine people on both sides as Donald Trump did after Charlottesville, dining with white supremacists, Nick Fuentes and Kanye West in Mar-a-Lago, quoting Hitler, and reportedly saying he did some good things. Donald Trump has shown us exactly who he is, time and time again. Don't believe me listen to his own words. As has President Biden. And the contrast could not be more stark. This past weekend, President Biden welcomed the heroic rescue of four Israeli hostages and pledged to not stop working until all the hostages are home. Donald Trump also mentioned those who he refers to as hostages. Are they the more than 100 Israelis and Americans and others being held by Hamas? No. He's referring to incarcerated January 6 insurrectionists. That's who he is. And the American people, the Jewish people, and Israel, deserve far better from a US president and we have far better. He's currently in the White House. President Biden recently said that democracy begins with each of us. He's right. It could also end with each of us. And we each have a responsibility to defend it at the ballot box in November. Jason Isaacson: Halie, Morgan, thank you. That closes our great debate. Our community, our country have a big decision to make this November. AJC will continue to provide information on the issues that are at stake. And we thank you guys very much and we thank all of you for your attention to this important debate.
May 24, 2024
Jews in the U.S. Military: Veterans' Stories in Honor of Jewish American Heritage Month
Explore the unique experiences of Jewish U.S. military veterans with Dave Warnock, U.S. Army Veteran, and Andrea Goldstein, U.S. Navy Veteran and Reservist. If you missed this conversation when it first aired for Veterans Day, here's your chance to honor Jewish American Heritage Month and pay tribute to those who serve our country. Our guests share what inspired them to join the military, how their Jewish heritage played a significant role in shaping their service, and what advice they have for IDF soldiers fighting now against Hamas in the Gaza Strip. Warnock and Goldstein are members of AJC's ACCESS Jewish Military Veterans Affinity Group, a space to convene young Jewish professionals who have served in the American military. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Dave Warnock, Andrea Goldstein Show Notes: Learn more: What You Need to Know About the ICC and the Israel-Hamas War Listen to AJC's People of the Pod: Seven Months In: What Israelis Think About the War Against Hamas, Campus Antisemitism in America, and More What Does it Mean to be a Jewish American Hero? A Jewish American Heritage Month Conversation with AJC CEO Ted Deutch Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Episode Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: Earlier this month, during my conversation with AJC CEO Ted Deutch about Jewish American heroes and Jewish American Heritage Month, we paid tribute to those who serve our country in a multitude of ways – teachers, doctors, nurses. As we approach Memorial Day and the end of Jewish American Heritage Month, we thought it would be appropriate to re-broadcast an episode that aired last fall. Guest hosting is my colleague Dr. Dana Levinson Steiner, Director of ACCESS Global at AJC, where she oversees an international program to engage young professionals, including a number of Jewish military veterans. Dana, the mic is yours. Dana Levinson Steiner: Thanks, Manya. I'm so happy that we're here today. It was just over two years ago that we formed the ACCESS Jewish Military Veterans Affinity Group, which is a space for us to convene young Jewish professionals who had served in the American military. And here we are now recording our first People of the Pod podcast episode in honor of and commemorating Veterans Day. With us today are: Dave Warnock, U.S. Army Veteran, joining us from his home in Seattle, Washington, and Andrea Goldstein, U.S. Navy Veteran and Reservist, who is based in Washington, D.C. Dave, Andrea, thanks for joining us today. Dave Warnock: Happy to be here, Dana. Andrea Goldstein: Yeah, I'm glad to be here. Dana Levinson Steiner: To kick off the conversation, please tell us a little bit about your journey as an American Jewish military veteran. What inspired you to join the United States Armed Forces? Dave, let's start with you. Dave Warnock: For me, there are two kind of main things when I look back on what propelled me to join the US Army. The first one was my great grandfather, Saul Fink. The family legend is like he emigrated over from the shtetl. His family settled in Harlem. And when he heard about what was going on in Texas at the time, and 1916 and 1914 with the Pancho Villa incursions, he felt so propelled by patriotism and love of America that he had to run away from home and enlist at 16 years old. Which he did. Joined the Horse Calvary, a proper Jewish cowboy chasing after Pancho Villa in New Mexico, in a forgotten war. And he made sort of a career out of the army. So that's the legend that he was propelled by patriotism, maybe hated the tenement, maybe just wanted to get out of Harlem, get some fresh air, see the American West, I don't know. But his service propelled him forward in American society, through the US Army in a way that I think would have been unavailable to a lot of Jews at the time. It's not to say that it was an easy journey. He was certainly discriminated against; he shortened his name from Finkelstein to Fink for reasons that are not kind of lost to history. One joke is that it couldn't fit on the nametag. But through this service, he was elevated in society, he became an officer in World War I. He served through World War II and in the army of occupation in Germany. And his stature, sort of the patriarch of my family, loomed large. My middle name is Solomon, I'm named after him. So that kind of tradition was part of it. Another part was, I enlisted in 2004. So three years after 91/1 when I was a freshman in high school, and that terrorist attack really did propelled, cemented my decision to serve you know, if that didn't happen, I don't know what I would have done differently. But those are the two main reasons that propelled me to join. And I joined the Army and I volunteered for the infantry because I wanted to be a soldier. Dana Levinson Steiner: In a lot of ways, it is our family that inspires us to make these kinds of decisions and we learn so much from our family history and our family lineage. Andrea, I'd love to hear a little bit more about your journey too and I'm curious if family played a role in your decision to join the Navy. Andrea Goldstein: My family decision to do the military was much more related to growing up in the United States, growing up in New York at a time actually, probably when we didn't have the NYPD outside of synagogues. I didn't really think about being Jewish, at least in New York in the 90s. But my family came here in mostly two waves, most in the early 20th century, and then another wave right before the Holocaust, and found everything they were looking for. And depending on which wave, either second generation or third generation where a sense of precarity and being American was gone. We just were American Jews. And I am currently sitting in a home that has embroidery on the wall that was sent to my great-grandmother, by family members who ended up–who perished in the shoah. This country really gave us everything and I wanted to give back to that. The value of tikkun olam is very central to everything that I do. And so serving my country and wearing the cloth of the nation to me felt like really the only way to do that. 9/11 was not a motivating factor for me, despite growing up in New York City and being in New York City on 9/11. My desire to serve in uniform predated that, in fact, 9/11 led me to really not so much reconsider, but really give even more thought to my military service, because I knew I would be serving in conflict zones, which, with the peacetime military of the 90s, that wasn't clear. But I ended up joining through an officer program. I didn't initially have any family support, because it was such a shocking choice. I had great-grandparents who'd served during World War Two great-uncles, but not from a military family at all. And what became very understood by my family, because it was, what was motivating me was, this desire to serve my country and wear the cloth of the nation, no matter what. Dana Levinson Steiner: I want to pivot a little bit, I want to get back to questions of Jewish identity in a moment. But when we're thinking about American Jews serving in the US armed forces, while there isn't a ton of data, the most recent-ish data suggests that just about 1% of the US armed forces, or the US military, is made up of American Jews. It's tiny, only 1%. And that 1% is of an already really small number of American Jews who already live in this country. So, you know, thinking about this statistic and also acknowledging American history in serving in the military. What do we make of this small number? And what would you like to tell young American Jews who may be considering joining the military but may have doubts or concerns? Andrea Goldstein: So there are a couple of things I would say to that. I would comment on that data–first of all, that's only commenting that that only includes self reported numbers because we don't collect demographic data on, it's seen as completely religious affiliation. The military does not collect demographics on Jews as being an ethnic group. So it's actually quite difficult to self-report your religion. So there's going to be an undercount, there are people who are Jewish, who may even practice privately, who are not reporting. And it also doesn't capture Jewish families. So it doesn't capture the number of people who may be not Jewish themselves, but their partner and spouse is Jewish, and they're raising Jewish children, and they're observing Jewish holidays with their families. So there's a lot that we really don't know. What I would also say is, if you were to overlay where the military struggles to recruit from, with the parts of the country where most Jews live in the United States, you would see probably some very interesting geographic trends. The military has become a family business. There has also been, there have been some comforts that the military has had in where they recruit from. And that typically is not New York, Los Angeles, Miami, Chicago, Washington, DC. So in addition to being one of the very few Jews that I know, in the military, I think I know probably even fewer people from New York City, especially officers. Dana Levinson Steiner: Dave, I'm curious, your thoughts on some of these numbers? And also maybe what you would tell–you and I have talked about this before about wanting to really engage in conversation with young American Jews about this experience and what it can mean for them, you know, acknowledging this number a while not perfect, I would imagine it's not so massive. So tell us a little bit about what you think and also maybe what you would tell a young American Jew who might be considering enlisting. Dave Warnock: Sure. First off, my mom was also very surprised when I joined, perplexed, flummoxed, aggrieved, perhaps she would have much rather me not join the army. But I just have to get that out there because she's certainly going to listen to this. Yeah, so, you know, I don't know where that number comes from, you know, the infantry's a different representation, I would say Jews were less than 1% of the infantry. But when I was at basic training, like for one station unit training, as they called it back then, after your red phase, like your hell phase, or whatever you want to call it, you are allowed to go to religious services on Sunday. So I went to Jewish services on Sunday, because, you know, it is the army. And I want to do it, like in my basic training company, there were no other Jews. So the company's like 200 guys, and then when you go to religious services, they're all of a sudden, like, 200 guys, they're like, Oh, my God, why so many Jews all of a sudden in every company in Fort Benning, except for mine? And then I realized is because they serve Kiddush lunch and you could get snacky cakes after services. And it turns out there were like three actual Jews at the services. Andrea Goldstein: I had a completely different experience in officer candidate school where we were allowed to leave on Friday nights. Dana Levinson Steiner: Oh, interesting. Dave, what was your experience? Dave Warnock: So again,, this is like 2005, things might have changed. But when you joined a Combat Arms significant you just went to one station unit training and it was a fairly intense experience. Think about Full Metal Jacket, whatever, people screaming at you, doing lots of push ups. And all your time is blocked out and accounted for. So you've trained on Saturdays and religious service time was Sunday morning. That's the time you got, so if you want to go to services, you had to do that. Something to consider if you join certain aspects of the military is, religious accommodations will be difficult. You know, I served with guys who were vegetarian. And there's one vegetarian MRE. You ate that a lot, like our rations for the field. So you eat that vegetarian ration a lot. Get real used to it. Certainly that is a consideration and it would be difficult to be religiously observant. In the infantry. I actually there was one guy in my company on the latter half of my service who was a religious Jew. And he basically got a lot of exceptions by his rabbi to serve. Because it was hard. The army would accommodate him to an extent, like, for example, we had to shave every day. And so he was allowed to use an electric razor. But it's something to consider if you are religious, that serving in the US military will be challenging. But you know, I encourage people to consider it. I don't regret my service, it's difficult to imagine my adult life without it. I'd say, I'm proud of it, too. But it carries costs. You know, when I was 19, on my first tour in Iraq, I was wounded, it took me six months to recover and get back to the line. The, almost five years I was in, I rarely saw my family because I was stationed in Germany and deployed to Iraq twice. So I was overseas, essentially, for the entire time of my service. And that's something to consider, but this is all my perspective. But the experiences you get, that will propel you forward in life in a way that I don't think you get through other things, certainly, when you're 18, or when I was. That being said, you know, a lot of soldiers in my unit did die in combat. A lot of guys, when they got out, they did struggle with PTSD and suicide. So it's not all sunshine and roses. But for me, it was the right decision. Andrea Goldstein: Military service is really incredible. My field does have more Jewish folks, especially in the reserves where I'm still serving. What's been very interesting is as an intelligence officer, the active duty component doesn't have a lot of Jewish people, but the reserve component, my last unit, we had enough people to have a minyan in a unit of 50 people. And I have found, similarly to just living in society. I mean, your exercises are not–you're going to have exercises that take place during Rosh Hashanah, you're going to be deployed around Christian holidays so that people can be home for Christmas. Maybe you'll be lucky if that's around Hanukkah. But I've also found people to who I've worked with to be incredibly accommodating up until, up to the extent that they can. So maybe I was going to be away for Rosh Hashanah or Yom Kippur. But people would change their shifts with me on watch so that I could run the service because I was the lay leader, or so that I could break my fast at the end of Yom Kippur war. And I experienced people being really curious and asking a lot of really good, in good faith questions. And I've had incredible experiences that range from serving with a lot of incredible, not just our military, but partner militaries. The most rewarding was my time with NATO where I got to teach in Norway and Greece and in Sweden and get to have these incredible experiences with people as the people who– actually the Germans all notice my last name, which was really interesting. And that's a whole other story. But you also see things you can't experience anywhere else. And it's not just the–I saw a meteor shower in the middle of the ocean, on my 26th birthday from the middle of a ship. Like there are certain experiences that you don't think about when you're going into the profession of arms. But you will get to experience these incredibly vibrant experiences just because you've, you've made this choice to go where no one else does. And so it's incredibly rewarding. I've also found that as a millennial, I mean, there are some very realistic things about the economic environment that we graduated into. And because of my military service, I have no debt, and I own a home. I have a master's degree that the GI bill paid for. So there's some other things. Dana Levinson Steiner: You talked about sort of the things that you learned and the experience that you got as a young person. Dave tell us maybe a little about some of the more rewarding experiences or things were really profoundly important to you in your service. Dave Warnock: I got out when I was 23. So 13 years ago now and memories once so vivid that I thought I would never forget him kind of faded away a little bit. One thing that I'll never forget, that was quite challenging, because after I was wounded, I was kind of serving in the rear just like in a limited duty capacity, like back in my garrison. And it was a tough tour, you know, lots of us got wounded, we had lots of members of our battalion killed. And I was asked by chain of command, as much as one can be asked in the military to escort a soldier's body back to his parents and to his burial in Arlington Cemetery. And I did that, and that was, I can't even describe just what that moment felt like to do that to be present there. It's kind of like a unit liaison. I didn't know the soldier, we were in different companies. But that was something I'll never forget. Actually escorting a soldier back to his parents. Another memory I'll never forget is like, because I have a photo of it. And it's on the wall in our living room is, the photo of me and my fire team. I was a sergeant on my second tour. And so I led like a small unit of four guys. And I have a picture when we were leaving Iraq for the last time. And just that sense of accomplishment of, everyone came home safe from my team on that tour. And that's why it's hung up on my wall. It's you know, we're smiling. We're happy. We're leaving. Yeah, so those are two things that tend to stand out in my service. Dana Levinson Steiner: So Andrea, you started off by saying that the value of tikkun olam, repairing the world is one of the things that really guides you. And what I want to ask both you and Dave is how has your identity as a Jew, also shaped your experience as a veteran, we talked a little bit about, you know, in the beginning about your experiences as Jews or maybe your family, being involved in the military not being involved, being surprised. But tell us a little bit about how your identity as a Jew has shaped your experience as a military veteran and as someone who served in our armed forces. Andrea Goldstein: So I left active duty in 2016 and stayed in the reserves but left full time service because I felt like I had reached a ceiling on what I could really do for others and that be my full time job. I wanted to keep serving, I wanted to keep serving my country. But a lot of that actually had to do with the way that I saw a lot of my teammates being mistreated by systemic issues, whether they be cultural or policy. And I wanted to spend a lot more of my time actively putting putting more good into the world versus preventing bad things from happening. Because that's what you do in the military, especially if you're in intel, you try to stop the bad you don't do anything that actively promotes the good. And so I've spent the last seven years in my civilian career, either in nonprofit or public service, doing just that. And about half of that time has been active either actively helping veterans, particularly women veterans, and people who have experienced sexual violence or other kinds of institutionalized harm, and currently serving members of the military. And I also firmly believe that our institutions need to live up to the ideals that we profess. And I want our nation to represent the ideals that my family came here believing it had. And so that's what I've been doing with my time. I spent two and a half years on the House Veterans Affairs Committee and helped write over 100 laws that particularly supported women veterans, members of the LGBTQ community, sexual trauma survivors, people living with PTSD, to help them get improved access to healthcare and benefits. And I'm also very proud that I've also had the opportunity to work with the IDF and provided some insight into the way that we've made some policy changes here in the US. Dana Levinson Steiner: Dave, tell us a little bit about your Jewish identity and how it plays into this experience. Dave Warnock: Well, my unit was very diverse in many ways, not gender, because the unit was closed to, or at the time that the MLS was close to females, so the unit was, the job was all male. And, you know, part of the pipeline and being new and being a private is your identity is kind of like stripped away and melted down, you're built up as part of this team, your individualism is kind of knocked away. So when that process happens, you know, whatever is the more like forefront of your identity kind of consumes it. In a sense that, like, if you have a very pronounced southern accent, everyone's going to call you a country guy, or whatever. And if you're from New York, there's a guy from Queens, so like, everything about him became like, you're the New York guy. And for me, it was like I was the Jew. Because that was the most forefront and center thing of my identity. Also, when you shave my head, I have a really big head. So it was all like, all my nicknames were either about having a big head or being a Jew. And then eventually, when I started to grow my hair back and settled more on the latter. So it was always very central to my service, because that was me, I was like the company's guy who was Jewish. And that was not meant in a derogatory term was more of like a statement of fact. And I think the only thing I really had to overcome was like, in 2005, when you're serving with people, like when I said it was diverse, you could be serving with people from all over the country, the US territories and guys from parts of the South I've never heard of, guys from the center of the country place have never been soldiers from Puerto Rico and Guam, like all over the world are serving in the US Army and then we have immigrant soldiers from, you know, Colombia, Nicaragua, Vietnam, like it was a very wide swath of representation and not very many of them had even met a Jew before. So in a way I was like the first Jew a lot of them had ever met. And I think, you know, rewind back 2005. If you know anything about Jews you probably know like Woody Allen and Jerry Seinfeld, which are exactly like pictures of guys you want in a foxhole with you. So I had to sort of maybe work a little harder to prove myself in the basic soldiering tasks, but like that didn't take very long. A lot of guys asked me questions about Judaism, because they genuinely didn't know. And I think one of the benefits of my service is, these guys take back their experiences with me, which I hope are positive, and then like, go back to wherever they're from. And they're like, if Judaism or Jews comes up, they're like, Hey, I served with a Jewish guy, he was pretty cool. But I think that was very important to me, and why it's so important for Jews to continue military service, because you just meet people from all over the country that you never would have met before. And it broadened my experiences too, serving with those guys. Dana Levinson Steiner: I think, hearing the story about how in many cases you might have been the first few that these folks have met is really important. I think in a lot of ways it helps to demystify, or in most important cases, maybe even act against antisemitic ideas or stereotypes. So I think that that's really important. And Dave, you and I have talked over the years, about how sort of the term of calling you a Jew was like a term of endearment. It wasn't in terms of a term of antisemitism. And in spending a lot of my time with this ACCESS Military Veterans Group, I've gotten to learn some of the interesting elements of how you communicate and what that can look like. So I have just one more question for us. And I think it's really important to acknowledge this moment that we're in. On October 7, Israel experienced one of the most horrific tragedies in its 75 year history. It was and continues to be a horrific day for Israelis and the Jewish community around the world. As of today's recording, over 300 soldiers have been killed and tens of thousands have been called up for active and reserve duty. So a question I have for both of you is, what is a message that you have, or that you can share, Jewish veteran to Jewish veteran. And I should even say just veteran to veteran because one of the amazing things about Israel is that there are many who serve in the IDF and who've been called up for reserve duty or who are in active duty who are not Jewish. They're a part of the Druze community. They're Arab Israelis. I think that's really what makes Israel such a remarkable country. So tell us a little bit about perhaps your reactions to that day. And also a message that you have for your fellow soldiers in Israel. Andrea Goldstein: I'm struggling to react because – the horror, rage, I'm just going to start crying on this podcast and not be able to actually give words. I was actually in touch on WhatsApp with several women who I've had the opportunity to work with who are veterans and reservists in the IDF. And there's definitely this kind of secret community of women around the world who have served in combat roles. Even if they weren't in combat, occupational specialties in their countries, where we know what we did, and our service has often gone unacknowledged and erased. And that service is also particularly called upon during the most desperate times, which we are in now. And the message that I have is we see you, we're with you and we want to run towards chaos with you. Dana Levinson Steiner: Thank you so much, Andrea. Dave? Dave Warnock: I mean, I can't say anything that hasn't already been said. You know, shock, anger. My wife and I are expecting our first child soon. And I didn't think we'd be having a daughter, be worried about like, I just thought, ignorantly, that these sorts of things were perhaps in the past. All I can say to those who are going to go serve is, keep your head on a swivel. Watch out for your battle buddy. All the things we used to say to each other then are still true now. Dana Levinson Steiner: Thank you. I think just knowing that you are in community with them, and that they have love and support is so powerful. And as I think both of you know, our ACCESS chapters are all over the world, including in Israel, where a huge number of our ACCESS leaders have been called up for active and reserve duty. So we're thinking of them in this moment. And we're thinking of all soldiers as we approach Veterans Day, and we're so grateful for the two of you sharing your story with us and sharing your time with us and giving a voice to the more than 1%, we will hope, of American Jewish veterans and perhaps even encourage some folks who may have been thinking that this is something that's been on their mind. Maybe perhaps it might be the moment for them to lean into that into that journey as a Jewish member of our armed forces. So thank you both for joining us. Wishing you a restful and restorative weekend. And Shabbat Shalom. Dave Warnock: Shabbat shalom, thank you. Andrea Goldstein: Thank you so much, shabbat shalom.
May 16, 2024
Seven Months In: What Israelis Think About the War Against Hamas, Campus Antisemitism in America, and More
Jacob Magid, U.S. Bureau Chief for the Times of Israel, provides his take on Israel's efforts to destroy Hamas in Gaza, the U.S-Israel relations, the anti-Israel campus protests, the Israeli public's reaction to rising antisemitism abroad, and the challenges he has faced as a journalist since October 7. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jacob Magid Show Notes: Learn more: Everything You Need to Know About Rafah, Its Importance to Hamas, and Protecting Its Civilian Population Listen to AJC's People of the Pod: What Does it Mean to be a Jewish American Hero? A Jewish American Heritage Month Conversation with AJC CEO Ted Deutch The Chaos at Columbia: What It's Like to be Jewish on Campus Right Now Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Episode Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: How important is American support for Israel? What message is the protest movement on American college campuses sending to Israel? Jacob Magid: is the U.S. Bureau Chief for The Times of Israel. Our colleagues in Washington D.C. hosted him this week in front of a live audience of about 200 guests. But we had some questions of our own and he joins us now. Jacob, welcome to People of the Pod. Jacob Magid: Hey there, thanks for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So there have been a lot of reports in the media lately about a strain in US-Israel relations, especially after Biden's announcement of a delay in the transfer of heavy munitions and concerns over Israel's plans in Rafah. Yet this week, Biden announced that it green-lit the transfer of over $1 billion in new arms for Israel, seemingly quelling any concerns about this rift. But what is your take on the situation? Is there a rift between President Biden and Prime Minister Netanyahu? Jacob Magid: It's interesting, because I think in the weeks and months immediately after October 7, support for President Joe Biden was at record highs. As at the same time, support for Donald Trump was plummeting, given the comments that he was making, shortly after October 7, kind of mocking Israel for not being able to foresee what what occurred on the seventh, as opposed to Biden who made this trip right after October 7, sent those aircrafts to the eastern Mediterranean, and warned Israel's adversaries not to get involved in the attack. I think there was real appreciation for what Joe Biden was doing. And I think it's amazing how much seven months can do because we've seen that support for President Biden completely, I'd say, plummet. There was a recent poll taken before this threat. But you can only imagine that it's only going to go down further, showing that now. Whereas earlier in the war, a plurality of Israelis supported President Biden over Trump in another election. Now those numbers have switched back, I think Israelis still do remember the steps Donald Trump took to re-open the Embassy in Jerusalem, to the Abraham Accords, the Golan Heights, all these different steps that he took when he was president. And I think that's more on their minds. And then they compare it to President Biden, they couldn't imagine President Trump taking those kinds of steps that he has taken, a public threat to withhold weapons that's a little bit harder for them to picture. And it's just more fresh on the minds of many Israelis when they're thinking about this current president. But I would note that it's not really clear what President Trump would do in this kind of scenario. I think there are a lot of US officials and Israeli officials I've spoken with who say that at least Prime Minister Netanyahu might prefer President Biden to President Trump because he's seen as someone who's more predictable, in regards with his ties with Israel, that while things have gotten bad, Netanyahu can also always frame himself as trying to stand up to the Americans. Whereas you'd have a much harder time doing that to Trump because I think he's a lot more beholden to him, will have a lot harder time saying no to Trump, I think Donald Trump, imagining a presidency where he's returning to the White House, I can't imagine he would be prepared to allow a war to continue for seven months, given his specific foreign policy agenda items, be it with Saudi Arabia or other places. But right now Israelis, for right or wrong, I think are very much shocked by the step that the President took. I don't think they saw a lot of the lead up that maybe the Biden administration was feeling, that there was a lot of warning given. And I think there's a degree of betrayal that I think a lot of Israelis feel right now. But again, things change so rapidly in this war. So that could switch again. And the Biden administration lately has been making a point to say this is just one shipment that we're holding. The vast majority of aid is still going to Israel, and we still have Israel's back. We're still determined to help them get rid of the threat of Hamas. But right now, Israelis, I think, are looking at it a little bit differently. Manya Brachear Pashman: How are Israelis viewing the possibility or the prospect of a more major Rafah operation and is there actually a difference of opinion among the Israeli population about how long this war should continue? Jacob Magid: Given the fact that over the past few weeks, we've seen, Israeli troops returned to areas that they were already fighting in several times, like in the Gaza City neighborhood of Zaytoun. IDF troops returned to again last week. This is the third time they were there and soldiers have been killed each time. And Hamas has managed to regroup and return to these areas the IDF previously cleared. But we haven't seen beyond leaks from the military establishment that has been frustrated with the Israeli government, with Prime Minister Netanyahu for not really forging some sort of plan for the day after in Gaza, some sort of body to replace Hamas be it the PA or anyone. Just something is what they're looking to be able to advance in order to complement the military achievements on the battlefield, you need some sort of diplomatic alternative as wel, diplomatic achievements. So I think we're getting to a point I would imagine where Israelis are going to start voicing some more frustration with the way the war is being handled. But I think it's going to start with a decision by Benny Gantz, the National Unity Party and also his deputy Gadi Eisenkot, two former IDF chiefs of staff who are highly respected among Israelis. A poll show that they're the strongest, most popular party right now in the Knesset. If elections were held today. That if they take that step to leave the government and demonstrate that they no longer have trust in the government's ability to get a hostage tool to wage the war, I think then you'll see a bit more frustration amongst Israelis and with the path that Netanyahu has taken, be it in Rafah or other places where they just don't trust that the war is being managed well. But until that happens, and I think Benny Gantz is very hesitant to take that step, because he knows that there are people he's able to straddle being at playing at both kind of dancing at both weddings right now, where he is very appreciated by both the more left wing people that might appreciate him being in the government to prevent the more far-right flank from taking steps that they don't agree with. And then on the right also for being a team player. And as Israelis like to say in Hebrew, to go under the stretcher and take part in the military offensive, I think he's able to beget appreciation from both. But once you take that step of crossing the Rubicon and leaving the government, and I think you'll lose some of those people that appreciate you. So I'm not sure when Gantz is going to take that step. But I don't think this war will be able to go on for months more without him leaving the government. I think that if we're two months on and there's no hostage deal, I would expect, I think, that step to be taken. Manya Brachear Pashman: Are Israelis growing more and more impatient, as the hostages remain in Gaza? Jacob Magid: Yeah, I think they are. I think we're seeing an escalation of these protests that are led by the hostages' families. And they're increasingly willing to be aligned with separate protests that were much more definitive at one point about just toppling the government and demanding new elections. I think that a lot of these families of the hostages are starting to believe that the only way to get their loved ones back is to have a new government in place. Now, that's still not the feeling amongst all families of hostages. Obviously, there's 132 families that come from different backgrounds and feel different things about this government. But I think there's definitely a feeling of desperation amongst them. And I think there's a lot of sympathy amongst the broader public with how they feel about this government. And I think at some point that that will dictate the direction that things take. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jacob, you mentioned earlier that the Biden administration's comments or threats, you refer to them as there's a sense of betrayal. Is there also a sense of despair? In other words, how critical is America's support in this war? Jacob Magid: I think, Israel, at least official Israel since Biden's comments, has insisted that Israel can continue fighting the war on its own, that it doesn't need, obviously would love the US support them, it's very important, but that it has no qualms with going into Rafah or just in general fighting this war on its own. It believes it's an existential war, and that it has the means to continue fighting without necessarily US support. That's been the implication of these comments that Prime Minister Netanyahu and Yoav Gallant have been making different framing of how they've responded to it. I think Gallant is a bit more sensitive to the US concerns than Netanyahu might appear to be. But that's basically the implication. However, if you look just I mean, even Ron Dermer, a few days, I believe it was yesterday, he issued a speech basically saying that we have proven that we can fight on our own when we need to. But I think he neglected the point that I think it was April 14, when Iran fired 200 missiles and drones at Israel at the same time. It wasn't Israel intercepting all these drones on its own. It required support from the US, from its European allies, from even Jordan and Saudi Arabia, which is less known, but that these countries were needed to come to Israel's aid in order to to really intercept all those rockets, all those missiles and drones. And then I don't think it's totally accurate to say that we can do this on our own, we would have had a very different picture. I think on April 14, that night, had those rockets been able to penetrate Israeli airspace and harm civilians. So I think, yes, Israel does have the means to continue fighting in Rafah on its own, and then Gaza on its own, but the question of Lebanon is a lot trickier, given how difficult it has been to fight against Hamas. And we've seen as I mentioned, that the Hamas fighters have been able to return to areas that were previously cleared by the IDF that this has taken seven months, and we're not on the edge of victory, as Netanyahu claims that we are. Just imagine how difficult it's going to be against Hezbollah. Which is even according to Israeli estimates, is far far far stronger than the kind of–it's a full fledged army in a way that Hamas might not necessarily be, as much as we underestimated Hamas. But I think nobody's under estimating Hezbollah and the firepower that it has, and the Iran backing that it has. And I think that Israel will need the US support in order to fight that kind of war. I think there was this feeling of betrayal. The Biden administration just sees it differently, that they feel that this war has been going on for seven months, and there's really no end in sight. And they are concerned about the civilian casualties. That of course, I think Hamas inflates the numbers. And we can talk about that shortly. But it's undeniable that the level of destruction that's been caused to Gaza. And there's just this feeling that without a strategy without a diplomatic path that Israel doesn't seem willing to approach, maybe it's starting to slowly talk a little bit privately about some sort of Palestinian Authority involvement in Gaza. But this feeling that we can't just kind of continue throwing our head into the wall without any real broader plan beyond this military approach, and that there is an understanding or a hope in the Biden administration that Israel will some at some point, at least, I think the military establishment is starting to get there, that it'll extend to the political establishment as well, except that we're not trying to do this out of spite. I think there's a real belief that this is not the best way to go about it going into Rafah the way that Israel wants to go to it. That's how the US sees it. And that we do need to look at other approaches in order to maintain the US support that we the US says that we want to continue giving that we do believe in this eliminating the threat of Hamas. That's different than eliminating Hamas entirely, which is how I think Israel framed it at the beginning of the war. So we're talking we're with you on eliminating the threat of Hamas. But let's take different steps to go about it. And we're still willing to continue providing our support in the meantime, not just for Hamas, but also the broader threats you face. The US have been very clear that they're not going to walk away from Israel on those. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you talked about protests by Israelis and hostage families in particular. Of course, we've had our own protest movement here in America, predominantly on America's college campuses. But they're very different. Most of the American protests are calling for a flat out ceasefire and criticizing Israel's response to the massacre on October 7. Very few if any call for a return of the hostages and many have been dominated by loud pro-Hamas and antisemitic elements. I'm curious how the Israelis have viewed those protests and what message they are sending? Jacob Magid: I think that Israelis are similarly disturbed, if not more disturbed by what they're seeing on these campuses. And I think it reinforces a lot of what they feel like the necessity of the evil that they're up against and Hamas is kind of similar to the evil that is being framed on college campuses. And the need to frame it as an existential war to some degree, whether or not that is accurate. I think it's debatable. But there is a growing sentiment of solidarity, I think with Jewish students in the US that of what they're feeling is comparable, maybe not into military scale by any means, but definitely into the ideological scale of what Israelis are facing in Gaza. Manya Brachear Pashman: Are they surprised by the growing sense of antisemitism abroad? Jacob Magid: I don't think entirely surprised. I think the fact that they live in Israel is testament to the belief that this is where they believe that Jews should be. I think there's less of an understanding I think amongst mainstream Israelis have the value and the necessity and even the it's totally okay for Jewish lives to take place abroad. I think there's a lot less of an understanding of the the Jewish experience abroad. I think there might be a little bit more understanding amongst diaspora Jews of the experience in Israel as much as possible, I think are two very unique experiences. There's not a Birthright for Israelis to come to America to really understand. I mean, a lot of them do after the army. But there isn't that same experience that I think that American Jews and many others are given privy to this real access and, and window into Israeli society. So I think given that I think I think there's just oftentimes when I've spoken to Israelis about this is there's just this assumption that, yeah, of course, there's a lot of antisemitism out there. And that's why you're supposed to be in Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: You work here in the United States, but what are some of the challenges you've faced as a journalist for an Israeli outlet, since 10/7? Jacob Magid: I have found myself frustrated trying to cover these campus protests where students aren't willing to speak to me because I work for an Israeli outlet. That was something I'm used to dealing with when I was over in the West Bank and covering Palestinian issues. And there were certain Palestinian officials who were willing to speak with me on background, as in not in name when it's published. That's something I'm used to, but now it's having to deal with that with American college students who aren't even, like there's no reason to be going to want to be anonymous, unless you don't like recognize the legitimacy of my newspaper, which I guess is fine, but even though I don't necessarily agree with them, I want to be able to tell their story and I'm unable to fully do so because I'm not getting full cooperation. So yeah, it would be definitely easier to work for in that regard a different news outlet where I wouldn't have to identify myself but it's just kind of I think shows the absurdity of the times of it. Manya Brachear Pashman: So we're speaking to you on Israel's Memorial Day, before the transition into Independence Day. Are Israelis observing these days differently after October 7? Jacob Magid: Oh absolutely. I spoke with a few family members and friends about the experience right now in Israel, they're just starting to transition to Yom Ha'atzmaut. There are some who are adamant about the need to celebrate this day, that the deaths aren't going to be in vain, that's our purpose. If we felt that it was always the case that we are supposed to celebrate Yom Ha'atzmaut right after Yom Hazikaron, the silver platter to make those soldiers and those who have fallen, their lives, give them meaning. And a reason to celebrate. That technically should stand true this year as well, even though the loss on October 7 was of a magnitude that Israel hadn't seen before. But of course, I think given the fact that we have hostages, who are still being held in Gaza, given the fact that the war is still going on, I think a plurality of Israelis, I'm sure are not going to be celebrating this year, the way they had. I think there are still interestingly parties happening; scheduled in Tel Aviv. I'm sure the clubs will be filled in a lot of these cities. I think that's still a sentiment that resonates. But I think Yom Ha'atzmaut is not going to be the same as it was in previous years. And Yom Hazikaron I think we saw what was happening in a lot of these ceremonies on military cemeteries across the country where government members were speaking. It's happened in the past where they've been heckled, but not to the degree that I think that we saw this year. From the Prime Minister down, a real feeling of anger, because this isn't just the average Israeli who might support the war, might support Netanyahu. These are people who lost the those closest to them, fighting a war that hasn't gotten to the total victory that Prime Minister Netanyahu has promised, or just a feeling of resentment. There's a pretty good example, a couple of weeks ago, where two names of casualties were determined dead by the IDF. One was Elyakim Liebman, from the settlement of Hebron, and one was [Dror Or] I believe from the Gaza periphery. And we saw over a dozen Knesset members, coalition members and ministers head to the funeral of Liebman, who was a real hero, who fought off terrorists during the Nova music festival as a security guard. Whereas this other person from the Gaza periphery, [Dror], who came from a community not necessarily aligned ideologically with the government. Nobody made any calls to them. Nobody visited, reached out to the family. And I feel like there's a real feeling of resentment and just dissonance between a government that a lot of Israelis feel like just doesn't represent them in increasing number. I think, even if they agree maybe with the broader goals of the war, that they don't feel like Netanyahu and the broader government is handling it in the way that they appreciate. Even earlier President Biden was seen as someone who was more in touch with the hostages and than Prime Minister Netanyahu was. He reached out to them before Netanyahu did. So there's that real dissonance there. And I think that that anger came out during Yom Hazikaron. And I think is, is going to probably carry over, beyond into Yom Ha'atzmaut, and until there's some sort of breakthrough, either a hostage deal, or some sort of end to the war that Israelis would like to see. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well may that war end very, very soon and may the hostages come home. Jacob, thank you so much for your work here, and for joining us. Jacob Magid: Thank you Manya. Thank you very much for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with AJC CEO Ted Deutch about Jewish American Heritage Month and what it means to be a Jewish American hero today.
May 10, 2024
What Does it Mean to be a Jewish American Hero? A Jewish American Heritage Month Conversation with AJC CEO Ted Deutch
AJC CEO Ted Deutch reflects on Jewish American Heritage Month, highlighting the historical contributions of Jewish Americans and discussing the concept of heroism in the face of rising antisemitism. Ted also shares what it means to be a hero today, especially in the wake of 10/7, and who he considers to be among his own heroes. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Ted Deutch Show Notes: Learn more: Join AJC in Celebrating Jewish American Heritage Month Quiz: Test your knowledge of the rich culture and heritage of the Jewish people and their many contributions to our nation Listen to AJC's People of the Pod: The Chaos at Columbia: What It's Like to be Jewish on Campus Right Now Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Episode Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: Amid the recent rise of antisemitism and the unease that brings, we are marking the month of May as Jewish American Heritage Month. This is a time when so many of us in the Jewish community are feeling misunderstood, unwelcome, and confronting hatred. But the American Jewish experience is so much more than standing up to hatred and bigotry. Over the past 370 years, Jewish Americans have served in government, the military, they've won Nobel Prizes, headed universities and corporations, advanced medicine, the arts and justice. Here to celebrate Jewish American Heritage is AJC's CEO Ted Deutch. Ted, welcome back to People of the Pod. Ted Deutch: Thank you very much. Manya Brachear Pashman: Ted, you began serving in Congress in 2010 A few years after a Jewish American Heritage Month was first proclaimed in 2006 Can you tell us a little bit of the history behind Jewish American Heritage or what we like to call JAHM. Ted Deutch: Well, Jewish American Heritage Month has been around for almost 20 years. Congress passed a resolution that was led by my former colleague Debbie Wasserman Schultz to acknowledge the important contributions that Jewish Americans have made throughout our history. And in 2006, President George W. Bush designated the month of May to be Jewish American Heritage Month, and there have been presidential proclamations every year since. This year, President Biden proclaimed May to be Jewish American Heritage Month and outlined the history of the American Jewish community and the fact that Jewish American culture is so inextricably woven into the fabric of our country. He talked about the importance of Jewish American suffragettes and activists and leaders marching for civil rights and women's rights and voting rights. He talked about the contributions of, of Jewish men and women in uniform and on the Supreme Court. And throughout multiple administrations. It's an acknowledgement that we are really forming an important part of the fabric of this country. And we have to spend time thinking about that, particularly in a moment when so many are really taking positions and saying things that challenge our contributions that are made, and that really put so many of us in the Jewish community on edge, make us feel at risk. This is an important opportunity to really stand proudly as Jewish Americans. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, during the month of March, Women's History Month, I always discover a new role model, a particularly amazing woman that I never knew existed. And the same is often true during Jewish American Heritage Month. But in reverse, I discovered that people whom I always thought to be amazing, and heroes in my book are Jewish. Do you have heroes growing up who you discovered were, or maybe you already knew, were Jewish? Ted Deutch: It's interesting. Our community is, I think, always looking to elevate those from our community who make a meaningful impact in society. I remember when I learned about Eddie Jacobson, that was one of those moments for me. Eddie Jacobson was a friend, business partner of Harry Truman. And, he played such a really interesting role during the war when, when he was focused on the plight of the Jews in Europe. His friendship led him to go advocate with then-Senator Truman to urge the us to do more for the Jews who are being discriminated against, harassed. Ultimately those who were being sent to concentration camps. That was a relationship that he had, and was able to use to help strengthen his own community. And what he did that I think was even more important than that, was following the war when he understood that there was this opportunity for the rebirth of the modern state of Israel. He went to urge his, again, his friend, then-President Truman, to to meet with Haim Weitzman, the leader of the Zionist movement, and President Truman was reluctant, but because of that relationship, that that personal relationship, Eddie Jacobson was able to convince the President to take that meeting, which then ultimately led to the recognition of the State of Israel by the United States just minutes after it declared, Israel declared its independence, being the first country to to recognize Israel. He's a hero in the history of the Jewish people. He played a really important role, I think, in the history of the country. And I think most people had no idea or may never have heard of him. There are also the heroes within the Jewish community that in Jewish American Heritage Month we have the chance to think about people who impacted us, impacted the way we work to strengthen the Jewish community who maybe aren't famous at all. When I think about the people, the Jewish leaders that I was privileged to know when I was a college student. Our [University of Michigan] Hillel director, Michael Brooks, and the professors who helped guide us where, at a moment years ago when we were facing antisemitism. When the student newspaper ran this series of outrageously anti-Zionist, antisemitic editorials, unfortunately, sounding familiar, the support from these heroic adults, for those of us who were students, to go out and to hold rallies and to protest outside of the student newspaper, to make sure that people understood what the facts were–that kind of heroism really resonates because it's a reminder of what we can do for young people now at a moment when they're looking to others in the community to help support them. It really carries right through to, to the work that I get to do every day, that I'm so privileged to do and, and really the ways that all of us can work behind the scenes to help lift up the voices of Jewish young people today. Manya Brachear Pashman: It's interesting that you kind of bring up who the heroes were for yourself when you were younger. I mean, I'm sure I'm sure you've been to baseball games, Yankees, Cubs, Mighty Mussels, whoever your team might be. Ted Deutch: The Mighty what? Manya Brachear Pashman: The Mighty Mussels, they're in Fort Myers, Florida. It's also the name of my son's baseball team. They're named after minor league teams. But I'm sure you've been to these games where the announcer calls the heroes to stand, be recognized by the crowd. And everyone knows that the announcer is calling on veterans, right members of the military, first responders, and they are undoubtedly heroes. But in those moments, I often wish they would list all the many types of heroes when they do that. The doctors, the nurses, the teachers, God bless them. How do you define hero? Ted Deutch: Well, you're exactly right, and what those moments feel like. And first of all, I think it's important that we acknowledge injury, Jewish American Heritage Month, the contributions of Jewish Americans throughout our nation's history, in defending our country, we've talked before, I mean, I talk a lot about my father, who graduated from high school and enlisted in the Army to go fight the Nazis, and earned a Purple Heart in the Battle of the Bulge. And all of the people like him who, whether it was in World War Two, or Korea or Vietnam, right on through the wars, in the Middle East wars in Afghanistan and, and in Iraq, the contributions from Jewish Americans who were proudly Jewish, as they served our country, those are really important to remember and every time at a sporting event where they ask the heroes to rise, I think it's important to think about that, you know, down here in South Florida, when they do that, at sporting events, it's not unusual, especially if they're recognizing someone from World War Two or the conflict in Korea in particular, it's just not that unusual for the veterans to be Jewish Americans. And there's always an extra amount of pride that you feel when they make those announcements. I do think it's important to think about all that we've contributed in defense of the country. But you're right. There are so many people who are heroes, who serve our country in other ways. We had a moment during COVID, where I think everybody recognized the heroism of our first responders, our doctors and nurses and people went in when COVID was raging, and people knew so very little about it. And every day, they went to work to take care of people and help save lives. And there was that moment. And I think it's important that we have more moments like that. It's true for police officers and firefighters and first responders. Again, too often, I think we sort of take for granted the work that so many people do, putting themselves out in service of others. And you mentioned teachers, there's just no question that the contributions of teachers and so many Jewish teachers among them, who have committed their lives to helping prepare the next generation, to help them become citizens in our country and understand our history and learn what they need to be able to thrive in our society and in their lives. They're doing an incredible service, and should be recognized as well. And so when we think about Jewish American Heritage Month, look, I'm all for thinking about, getting back to athletes. I'm all for thinking about Alex Bregman from the Astros. And for those of us who are hockey fans, it's the glory days for Jews in hockey, and Zach Hyman and the Hughs and others, but it's the people that we've not heard of whose names we don't know, who come from our own families that we need to hold up and think about as the real heroes for the work they do every day in their lives. Manya Brachear Pashman: It has been seven months now, since terrorists attacked Israel on October 7. And I'm curious if in your opinion, the last seven months have changed what it means to be a hero, especially in the Jewish world. Ted Deutch: Well, there are all kinds of people in the Jewish world right now who are doing heroic work since 10/7 in ways that either weren't necessary, or were unappreciated before 10/7. Because the challenge There's so much greater. We were just talking about people who served the country. IDF soldiers are heroes and what the IDF has done since 10/7 to defend Israel in the face of the horrific attacks by Hamas is heroic, and the loss of life is painful. And so even as we mourn those soldiers who have been killed, we have to take a moment to appreciate the heroism. But there are others, the hostage families who traveled to New York and Washington and around the world and we at AJC are so privileged to work with so many of them to help give them voice and make sure that they're heard. But as they struggle now, for more than 200 days that their loved ones have been held captive deep below Gaza, they continue to go out and advocate for the release of their loved ones. And to help people understand that these are real people, and we feel like we've gotten to know them. And that's because of the heroic actions that their loved ones have taken. There are people in social media who have become heroes for every day just going to battle against the lies and misinformation on so many of the social media outlets. In the United States, on college campuses right now, what we've seen from so many students, whether they're on our Campus Global Board, high school students from our LFT program, but wherever they are, the ability for students to stand up and to say, in the face of these protests that are often directed at the Jewish community, the language is horrific, and it is dangerous and unacceptable. And in the face of all of that. the number of students and young people who are standing up saying, I am a proud Jew who loves Israel. And I'm going to fight back in all of the ways I can to make sure that people know who we are, to make sure that they understand the truth of what's happening now. There are so many young people now who are doing heroic things, and will continue to do heroic things, I have no doubt, for the rest of their lives. And I think it's important to stop to acknowledge that. I know these days, it's not popular to talk about heroes in politics. But if you pause for a moment and think about what Richie Torres has done, as a member of Congress, a progressive member of Congress, standing firmly in support of Israel and Israel's right to defend itself and speaking with a moral clarity that we wish others could follow. Ritchie's a hero. John Fetterman, staring down the protesters day after day, the way that he does, is a hero. At a time when there is so little bipartisanship, the fact that Speaker Johnson decided to move forward with the aid package for Israel and Ukraine and Taiwan with humanitarian aid and got that done, we should be celebrating his contributions. There are a lot of people that we really need to stop and be grateful for. And obviously, they're not all Jews. But it's a moment when the Jewish community, as we're thinking about our own heroes, should pause to be grateful for those who have really been helpful to the community. Manya Brachear Pashman: Now you've just mentioned a lot of the people who've had a high profile since October 7. Any ordinary or overlooked heroes that we might not think to recognize? Ted Deutch: Being a parent of a Jewish child shouldn't be heroic. And yet, seeing parents find more ways for their kids to really understand who we are, as a community find more ways for them to be involved, by more ways for them to learn, especially after 10/7, really teaching more and more about who we are as Jews, to our kids, that's heroic. I don't think it should be heroic to be a rabbi, or a Hebrew school teacher, or someone who works at a day school or in the Jewish community. But in this post 10/7 world, that work in so many instances is heroic, because of all of the baggage that comes with, with the protesters, with the challenges to the community, with the things that we see on social media, to get up every single day, and to be there as leaders in the Jewish community in synagogues, in schools, in the organizational world. As we prepare to get ready for camp season. All of these Jewish professionals are doing heroic work, and the community is so much better and stronger for it and for them. Manya Brachear Pashman: How did October 7th change you and your approach to either public service or service to the Jewish people? Ted Deutch: First, there's an urgency with which I try to meet every single day, since 10/7, I think it's something that we all feel. I think a lot about the way that we felt on 10/7, that morning when we were learning about what happened and the fragility of Israel. And the notion that the Jewish community and Israel are so inextricably linked became more powerful than ever, and that both felt at risk that day and the days after. It's just required a constant and urgent focus on trying to make sure that people understand what's actually happening, putting out meaningful and factual information and pushing back against false narratives, something that we've tried so hard to do, literally since 10/7. Hlping people understand that the protests didn't start when IDF soldiers marched into Gaza to defend Israel and Jewish people. They started after Hamas slaughtered 1,200 people on October 7. These were protests in support of this vile terrorism. And helping people understand that when Iran launched close to 350 missiles and drones, it was part of an ongoing effort through Iran, with Iran to the head, but that includes Hamas and Hezbollah, and the militia in Iraq and the militia in Syria, and the Houthis, and others throughout the region, all to target Israel, again, urgently making that clear every single day. So there's an urgency, there is a passion to make sure that the commitment in the community, the way that people have stood up and said, You know what, there are a lot of things that are important, but man our community needs, it needs us to focus on ourselves. That ultimately, the only people that we know that we can count on are the Jewish people. And yes, we're going to continue to work with our friends and allies and partners. That's important. But working hard to retain the sense of unity within the Jewish community is also something that was never really a priority. But now that we've seen what that unity looks like, and what it means when we all stand together, in the face of this Hamas evil in the face of these protesters celebrating terrorism, and calling for the destruction of Israel, that's a unity that we have to desperately try to hold on to, and to bring people together around, not just while this war is going on, but on into the future. Manya Brachear Pashman: Ted, thank you so much for joining us. Ted Deutch: I hope people will use this as an opportunity to share their own stories, their family stories, the stories of the people that they know deserve some attention for what they've done to strengthen America. And I hope that they'll go out and they'll tell the story and they'll get others to listen. Our contributions to America have been so rich and varied and instrumental to the kind of country that we have and the kind of country that we know we need to continue to be. These are stories that everyone needs to hear. So I very much appreciate the opportunity.
May 3, 2024
The Chaos at Columbia: What It's Like to be Jewish on Campus Right Now
Noa Fay is a Jewish student leader at Columbia University, the epicenter of the anti-Israel protest movement that has unfolded on American college campuses in recent weeks. Pro-Hamas, antisemitic, and anti-Israel demonstrators have occupied academic buildings, set up overnight tent encampments, and staged demonstrations, while Jewish students have faced increasing threats, antisemitism, and violence. Noa shares her first-hand perspective on what it's like to be Jewish on campus right now. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Noa Fay Show Notes: Learn more: WATCH: Press Conference at Columbia/Barnard to Urge Action from University Leadership AJC – along with our partners at Hillel International, Columbia/Barnard Hillel, UJA-Federation of New York, and Jewish students – called on universities and their leaders to keep Jewish students safe on their campuses during a press conference last week. Watch the press conference. AJC Campus Library Resources to help Jewish students feel safe on campus and become well-informed and effective advocates for Israel and the Jewish people Listen to AJC's People of the Pod: What It's Like to Be Jewish at Harvard Among Antisemites and Hamas Supporters The Good, the Bad, and the Death Threats: What It's Like to Be a Jewish College Student Right Now Jewish College Student Leaders Share Their Blueprint for Combating Antisemitism Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Episode Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: Nearly seven months since the Hamas-led massacre on Israel that ignited Israel's current war with Hamas, chaos has unfolded on the campuses of Columbia University, Barnard College and other universities across the nation. Most recently, student demonstrators have built tent encampments on university quads and occupied academic buildings. They also have targeted Jewish students with antisemitic signs, slogans and in some cases, physical assaults to protest the war. But that's not all they're protesting. With us to discuss her perspective as a Jewish student leader on campus is Barnard College senior Noa Fay. Noa, welcome to People of the Pod. Noa Fay: Hi, thanks so much for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, thank you for joining us. And I'm sorry that you have been experiencing this on campus in recent weeks. We've seen plenty of images from the chaos there. But can you describe it from your vantage point, kind of walking through the crowds and seeing it up close? What do you see? What do you hear? Noa Fay: It's important to understand not only the amount of antisemitism, and that sort of violence that we're seeing–which has been incredibly painful, really, for every Jewish student at this point, I really believe I mean, it's just been absolutely horrifying. You know, I mean, it's pogrom style stuff that we're seeing. It has felt like now that everybody is affected, people are taking this seriously. But in reality, the Jewish students, we've been dealing with this literally since October 7, and it's taken up until now to even seem to get somebody's attention. So I think it's important to understand that, when I talk about this chaos, what I'm really thinking of is– there is, first of all, just so much press everywhere, which is just a bunch of people that are really swarming everyone and, you know, up and down Broadway, it's very disorienting. But more importantly, on top of that, we have a very significant police presence. I mean, it really is a police state. I can't even get to certain dining halls. I can't study in certain libraries. I can't get to my own gym. I mean, it's a really, really chaotic situation. Manya Brachear Pashman: Are they protesting the war? Is that the message that you're that you're hearing? Or are they protesting something else? Noa Fay: No. No, no, no. They sprinkle in a few things, I think, dedicated to the war. But by and large, these are anti-Israel demonstrations. And at this point, anti-Jewish demonstrations. So they are using the war to, I think, gain credibility. And the war is definitely fueling their ire, I guess you could say, but this is not about the war. And it's never been about the war. There was a very strong anti-Israel community on campus. And that was way before October 7, this was during ceasefires that were already taking place between Hamas and Israel. And still, we had this exact same rhetoric. The only difference now is that it's gained a lot of traction. So, no, it's not about the war at all. Manya Brachear Pashman: I was going to ask you, you headed to Barnard three years ago, you're a senior now. Did you get warnings? Did people prepare you for Jewish life on campus? And was it helpful advice? Noa Fay: Yeah, so people did advise me. I did have people tell me not to go anywhere near there. But I just didn't think that it was that serious. And honestly, I did take this anti-Israel movement seriously, obviously, I had dealt with it in high school, and I had come to learn that this was somewhat of a popular ideology within my generation. And so I was aware of this. But I basically wasn't daunted, I was honestly happy to debate these students, to basically point out why they're wrong. So I wasn't nervous about it at all. Of course, we could never have predicted that this would be the situation. But that's just to say, I did have somewhat of an idea, but I didn't take it seriously. And I'm clearly, I'm not the only one, none of us took it seriously, and here we are. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned before we started recording that before you started at Barnard, your parents similarly did not think that antisemitism was going to be an issue for you on campus. What are you hearing from your family now? How has this environment affected you personally? Noa Fay: My family, they've been very concerned. They've been talking to me about transferring, because I'm in a plus one program with our School of International and Public Affairs. So I'll be here for one more year finishing up my master's degree. And my parents have a few times now really asked me about transferring and stuff. Which I will say, I don't really have an urge to do that at all. But they are very concerned. But more than that, I have family in Israel and my family in Israel–they are the ones who are asking me if I'm physically ok. Which is just…again, not the only one who's been having that very bizarre, sad experience. My friends have the same issues. They're their family and Israel, their family is calling them to say, Are you as a Jewish student doing okay, at Columbia University in the city of New York? So it's just, everybody's very concerned. And rightfully so. It is just, honestly, the more we all talk about it, the fewer words I have to really describe because it is just such an experience that it leaves you speechless. It really does because it is that disturbing. Manya Brachear Pashman: You are black, Native American, Jewish. How does that inform your perspective on the messages that you hear such as you Jews are not indigenous to the land of Israel? Noa Fay: Right. Oh, my gosh, please. That's one of the worst ones. I'm just absolutely mind boggled by that. I will say that. I think that combination of identities for me, it gives me a bunch of different perspectives with which to use to understand a lot of political issues and social political issues. But I think for me, the number one I guess, benefit that all of these identities gives me in terms of analyzing antisemitism and just taking in everything that's going on right now, is that, and I've been trying to stress this to people but I think definitely the students who are demonstrating against Israel, they either ignore me or they don't take me seriously or whatever, but I am trying to stress that if only they would take me seriously because I am a person of color, from a few groups, which means: I know what it is like to be discriminated against. So please, because of that, if you can't hear me when I say I'm Jewish, so I know what it's like to be discriminated against, please hear me when I say I am black, and I am Native American, and I am a woman. Of course, I know what it feels like to be discriminated against. So please trust me when I say, I am Jewish, and I am now facing discrimination because I'm Jewish. Manya Brachear Pashman: I mean, are there people in these crowds, perhaps including your friends, that are holding multiple perspectives? In other words, they want the hostages released. They're sad about the devastation in Gaza, and what's happening to the civilians there. In other words, they're not calling for a ceasefire or calling for death to the Jews. They're just holding all of this and spending the night in tents with their friends. Does that exist? Noa Fay: So I have been told that it does. And in fact, a friend of mine, who has also been struggling with the same issue where her very close friends are participating in this and she's trying to understand it. She has told me, and so have other people, that the issue is that different people identify different parts of this movement to be significant to them, which is to say–apparently, this is the argument that's going around–is that everybody believes the movement means something different to everybody. That's what I'm being told. And I can understand that. My response, though, is that, I don't know that I need to know what it means to you. Because no matter what it means to you, you are putting aside the fact that this is a violently antisemitic movement, simply because I don't know, you want to protest police presence, which is necessary to begin with. So it's kind of a difficult argument for me to follow. You have forsaken all of these basic human rights issues, for something else that you have identified is more important. So that's why even if these students do have different explanations, which I know they do, it's ultimately, you can't get around the problem. That is, they're saying they don't care that it's antisemetic. That's what the message is. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'd like to take this back to the classroom, which is why you're getting at Barnard to begin with, I mean, have you gotten support from the faculty, from the staff, from the administration? Or have faculty members accused you of exaggerating the antisemitism you're experiencing? Noa Fay: So I have mostly not really opted to rely on faculty because I know that it's a bit of a gamble, shall we say? I've had one unfortunate experience with a professor. This is a course about slavery, American slavery. It was an amazing course up until this anti-Israel rhetoric made its way in here. But in this class, this professor has consistently communicated his anti-Israel sentiments and he's also done so by bringing in guest lecturers who have very outwardly demonstrated their anti-Israel nature. One guest lecturer came in and denied the rape of Israeli women on October 7. I was shaking. I was shaking in my seat. Just because like, what do you say to something like that? I mean, it was just horrific. And then another example is that another guest lecturer who came in celebrated Aaron Bushnell, the man who set himself on fire over all of this in front of the embassy, I believe it was, and she said he was a true patriot. That's a direct quote. And then obviously throughout all of this, everything that sprinkled in is, you know, Israel's, a genocidal state, it's colonialist, settler, imperialist, oppressive, all of these things, these are all the exact words that were used. And this is being told to a group of, as we know, very impressionable students. And I mean, obviously, all of that is just problematic in itself. But we can also identify it being problematic because at the very least, we don't have an Israeli coming in saying the, the Jewish side of the story and the Israeli side of the story. So it's just a baseline, poorly done, in terms of in terms of attempting to, quote, educate students about this issue. And because we have that lack of representation of perspectives. We know, it's indoctrination. It's indoctrination. And I and this is to say, I mean, this is I've had, honestly, my whole experience with all of this antisemitism stuff, including what I just described with this professor, that my experience has been mild compared to people who I mean, I've heard about really, really horrific things. Manya Brachear Pashman: Where are these protesters going awry? What's the solution here that would allow them to have adequate free speech, but not cross the line into harassment? Noa Fay: Yeah, I'm so glad you asked about this, because I am done with this freedom of speech debate. We know this is not an issue of freedom of speech. And we know that because we have students here who would be expelled in a second, if they're not black and say the N word, or if they celebrate the KKK, or anything like that. In fact, pulling from my high school experience, which was a private institution, just like Columbia. And because of that, they were able to rightfully dismiss a student who called his black peer the N word, and told him to go back to the cotton fields. For some reason, we've forgotten about this, that no one is entitled to an Ivy League degree. In fact, that's the entire point. Is that it's the most exclusive, elitist selective thing ever. So if the Ivy League had previously selected you, out of literally thousands of applicants, and you come here, and then you show that you are not worthy of that selection, in whatever way, the University reserves the right to say, Oh, you are not one of us, and you don't abide by our rules. These are our rules. This is our society that we get to dictate. And if you're not fitting into it in the way that you said you would implicitly or explicitly via your application, then the university absolutely has the right to tell them you're not allowed here and actually we're going to select from the thousands of applicants who would give anything to be in your position. That is the ultimate element of remember to check your privilege. Manya Brachear Pashman: I will say an Ivy League education is very expensive. I'm still paying for my graduate education at Columbia. And that brings me to this question. Are you learning anything? Are you getting anything for your tuition this year? Or is this experience infringing on that? Noa Fay: That's a great question. My friends and I literally just asked ourselves that the other day, and I responded by saying, Well, I've definitely learned that I'm surrounded by antisemites. So that's number one, which is, you know, for better or for worse, it's definitely good to know. But I mean, really, my answer is that I personally have learned so much at this institution. This, first of all, helps me realize why I feel so strongly about everything that I feel strongly about, which means that it is forcing me to think more deeply about my own values and why I have these values. And number two, is that it definitely has strengthened my debate skills, and just my ability to engage with people who are not only sitting across the table from me, in terms of, you know, arguments and ideology and stuff, but with people who are quite literally against my very existence. So I think that's a good way to look at it. But I think that as of right now, most of us, us being the Jewish community at Columbia, most of us are not at that point yet, because this is all happening right now. This is a very, very raw thing. And so I think it will be quite a while until we can all identify the potential positives from all of this. And I don't think we should have to identify the positives. This is a very negative and upsetting situation. But I think that it can be helpful to acknowledge at least the different ways in which this makes us stronger. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Noa, thank you. Thank you so much for joining us and sharing your experience. I hope things calm down for you there, and that you're able to walk across campus at ease again soon. Noa Fay: Thank you. Thank you so much for having me. I appreciate it.
Apr 19, 2024
Her Mother-In-Law Was Murdered at Tree of Life: Now Marnie Fienberg is Countering Antisemitism One Seder at a Time
Ancient texts, traditional foods, and friends and family: the markers of many Passover tables across America. But what if you added something new–or rather, someone new? Marnie Fienberg founded 2ForSeder, a program to combat antisemitism and honor her mother-in-law, Joyce Feinberg, who was one of the 11 victims murdered inside Tree of Life. The initiative is simple: extend a Seder invite to two people of another faith, who have never been to a Seder before, to build bridges and spread Jewish joy. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Marnie Fienberg Show Notes: Learn more: 2ForSeder.org Listen to AJC's People of the Pod: What the Iranian Regime's Massive Attack Means for Israel and the Region Meet Modi Rosenfeld – the Comedian Helping the Jewish Community Laugh Again A Look Back: AJC's Award-Winning "Remembering Pittsburgh" Series Jewish College Student Leaders Share Their Blueprint for Combating Antisemitism Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Episode Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: A few weeks ago, we re-aired excerpts from our award winning series Remembering Pittsburgh, which marked five years since the 2018 shooting at the Tree of Life synagogue. One of our guests in that series has returned today. Marnie Feinberg founded 2ForSeder, an initiative to honor her mother in law, Joyce Feinberg, who was one of the 11 victims murdered inside Tree of Life. As we approach Passover, Marnie is with us now to share why there's no time like the present to invite first timers to the Seder table, a superb way to introduce people to the beauty of Judaism, like Joyce often did. Marnie, thank you for joining us again. Marnie Fienberg: Thank you so much for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So we spoke a little about this project, when you joined us last fall. We have a little more time now to unpack why this initiative is such a meaningful way to preserve Joyce's legacy. Can you tell us about her Seders? Marnie Fienberg: My mother in law as most mothers and mother in laws, she trained me on how to actually hold the Seder. So as you know, holding the Seder is almost like your second bat mitzvah, it's a rite of passage. And it's also a very important thing that, you know, not only are you trained to do it, but you have to incorporate things from, if you have a partner or from their family, you incorporate things from your own life to your family traditions. And all that kind of comes together in this wonderful magical night that is really grounded in the Haggadah. But Joyce was of course instrumental and teaching me my mother lives kind of far away. And Joyce and I actually did Seders together for more than a decade. And they started at her house and gradually kind of came over to my house. But she really she helped me every single step of the way, to the point where when she wasn't there anymore, I almost didn't know how to do it. And I'm every time I'm thinking about the Seder and making a Seder. It's it's with her in my head as it has to be. But I still, you know, all of the traditions that she taught me we still utilize those once again, combined with the ones that I learned from my own family and she is a vise still a vibrant part of our personal Seder. Manya Brachear Pashman: So was Joyce in your head still when you found 2ForSeder? Marnie Fienberg: Oh, absolutely. Well, I am a Jewish woman. And I can't sit still. I need to do something. We have tikkun olam kind of almost in our DNA. Yes. So I really wanted to not only bring her back, which I think is a natural sort of a feeling. But I also wanted to push back on all of the antisemitism that had removed her from my life. And people were constantly coming up to me, I mean, the community in Pittsburgh and the community where I live in Northern Virginia, everybody was very supportive. But they were constantly asking me, What can we do? And it took me a little while to realize they didn't, they did mean, what can I do to help you? Of course, they did mean that. But what they really meant was, what can we do to stop this from ever happening again? I don't have the answer for that. But I thought that the seder kind of came into my mind because I was really inspired by what Joyce always did that she brought students or faculty, you know, because she was a campus researcher, and my father in law was actually at Carnegie Mellon. He was a professor there. And they always had people who weren't Jewish at our at the table. And the discussions were always not only very interesting, but you always saw a very different perspective, when they participated in something in a ritual that you knew so well. And it really created bonds of friendship, even with people who I didn't know. Which was wonderful. So that's what I really wanted to encourage, you know, this was 2018 when she was murdered. So 2019 was the Seder and I just wanted to encourage every Jew in America and in Canada, because Joyce was Canadian, that they, if they if they were holding the Seder, invite to people who had never been to a Seder before, start that dialogue, invite them to the intimacy of your home, and make them part of your family for that one night. And that will really help them understand the joy of Judaism, the happiness and the reason that we are Jewish is, it's right there in the Seder. In every Seder I've ever been to, it's always there, and to share that with someone who is not Jewish, starts the dialogue to understanding about the differences between us, the similarities, all these great things, that this is a thing that combats the hate that took my mother in law. Manya Brachear Pashman: These are uncomfortable times, they were certainly uncomfortable back in 2018, when the Tree of Life happened, but they're uncomfortable times again for the Jewish community. For everyone really? Who's watching what's been going on in Israel since October seventh. What does the Seder offer? And how do you avoid some of the pitfalls that can arise? When you do bring people perhaps have different perspectives around a dinner table? Marnie Fienberg: I'm glad you asked that question. Because my family and Joyce, you know, we feel very strongly about what's happening in Israel, we have a lot of family over there. A lot of friends, like everyone else, we all know someone in Israel. And it's a part of what's going to happen in your Seder this year, I assume almost everybody's going to do something to remind them about, you know, that the hostages are still not freed, that there are people that are starving, but are being helped. This is a difficult situation, it's not a simple, straightforward thing. And the Seder Absolutely, is a reprieve from that for a moment. I think the idea of the Seder is about reaffirming your Judaism, because it takes you on that journey from when we were a tribe, to a nation. It's that little piece in the middle. But it's when you reaffirm your Judaism every year. So it's still important to do it. It's so important to do it your way. And if you want to have a reminder of the hostages, an empty seat at the table, something on the Seder plate, there's so many different ways that you could do something. I think that all of those things would be absolutely important right now, something that reminds you that we're doing this, not just for our family, but we're going to be doing this for those families that are missing those members right now. So I think that the the Seder in general will be healing to some extent for everybody who participates. So inviting someone who's never been to a Seder before. I think it's important, not only do you explain the Seder, which you really do need to do, you have to explain it before you start. And then they can participate and feel comfortable. But also explain to them that if you are going to be doing something to remember the hostages and all the people that were lost, let them know ahead of time that that's what you're going to be doing. You don't want to surprise your guests, your other guests will know exactly what you're doing by the guests who are not Jewish. Don't assume that they know, make sure there's great communication, and everything should go very smoothly. Manya Brachear Pashman So I appreciate you kind of mentioning some of the rituals that we can do to honor the hostages and to remind the guests that the hostages are not free. But what about guests who come to the table who have been watching what's going on and disagree. They have really strong emotions and opinions about what's going on there between Israel and Hamas. And I asked this because I know Joyce worked at the University of Pittsburgh, as you said her husband Steven was a professor at Carnegie Mellon. And they often invited students to dinners and Seders. You might have seen the dean of Berkeley Law School has an annual custom of inviting students to his home for a dinner with students. And recently a group accepted that invitation showed up, but then got up from the table and pulled out their megaphones right there in his backyard. So it's hard to believe that that level of rudeness is possible. But it does appear to be a real risk. So can you offer some tools or tips on how to avoid that kind of a response? Or how to respond if you get that kind of behavior? Marnie Fienberg: Absolutely. And, you know, it's interesting, I think that we feel a heightened sense of that this year. But it's interesting, that is one of the most asked questions that I always get: How do I ensure that my guests don't veer into politics or if they have disagreements or things along those lines? Probably not the first year so much. But the other years, we've always had questions along those lines. So my recommendation is that you lay some ground rules ahead of time. So as the leader of the Seder, you're not just the head mom or the head Dad, you are the facilitator of what's going on around your table. And while some of us will have five people around the table, some of us will have 30 people around the table, and some of us will be in the backyard with I don't know how many people that the Dean had. But regardless of any people you have, you still have to manage their expectations. It's very important. So when you lay ground rules, it's your choice. You may want to actually have a lively debate. Many Seders are a lot of fun when there's a lot of debate. And if you know the guest, and you know that that's what they're interested in talking about. And the rest of your guests would be okay with it. That is your choice and you should manage that but even with that You might want to say, look, we're going to venture into politics, we can't talk about X, Y, and Z. Or I'll let you know when we've gone too far. Or, hey, this now it's time to bring out the dessert, because that'll stop everybody from talking. I don't know, that's going to be your choice. There is the other side of the coin. And this is actually I live in Washington, DC, where politics is always quite a big deal. But other politics, right, all sorts of politics. So one of the ground rules we always have at our Passover Seder is to have no politics at all, this is a little island, we're not going to talk about the fact that you might be one party, I might be another party, he is going to be another party and y'all work for those parties. I mean, it's not like these are just opinions. So one of our ground rules is always this is a time to focus on once again, the joy of Judaism, the joy of reaffirming my beliefs, and being with my family. And really kind of feeling like this is a very, very special time. And I personally have never wanted politics at my table, because I want that joy to fall through. But when I've been to other tables, it's been very different. So my ground rules are always this is a politics free space. If you'd like to talk about politics, let's go out for drinks after Passover. Manya Brachear Pashman: So it's a great point about being in Washington. But again, there's a chance that politics will be brought up at every table, whether it's California or Nebraska, or Texas or Maine. So if it does get tense if people ignore the ground rules, for example. Any suggestions on what to do? Marnie Fienberg: Yes, actually, we do have a couple of tools in our toolkit. So two first Seder, if you go to our website to crusader.org, we actually have two kits, when you hit the signup button, it's two free kits for you. One is for your guests to kind of set expectations about the Seder, not about politics, it doesn't touch about that. But it's still important. But the host kit actually has 20 discussion cards in it. And I would actually recommend it if you've started out with a little bit of excitement with politics, and you don't like the way it's going, or if you want to say, look, I really want to avoid it. But I know, this is a lively crew, which I mean, you know your people, right? So I would actually print them out, put the discussion cards out on the table, and actually start picking up some of them and you know, send them around the table and start having discussions about them. So they are more about the Seder. And some of them are pretty surface level, like, what do you think about the taste of matzah, and you're having a discussion about how all these things are cooked with matzah and how crazy that is and how difficult it is and what a genius your chef must be, you know, so you get to compliment the host or hostess. But on the other side of it, there's some deep waters that it goes into, to really talk about the philosophy behind the Seder in some deeper things. So you can really choose what you want. There's 20 different discussion cards. And I think when people are having a very tense discussion, if you say, look, I like where this is going. But it's just not appropriate for today. We've got an alternative here. Let's keep talking. But let's talk about these topics. It won't always work. But it tends to work me most people really, you know, they have strong opinions about many things. And that is what the Seder is for, right? We're supposed to be learning, we're supposed to be growing from each other. So if you can change the topic, if you're uncomfortable with it, the discussion cards are a wonderful tool to help kind of guide that. Manya Brachear Pashman: And those can be downloaded at the 2ForSeder.org site. Marnie Fienberg: Yes, yes, exactly. There's a host toolkit. And it's the last 20 pages of the host toolkit. You Manya Brachear Pashman: know, I'm so glad Ramadan has passed so that in a Muslim guests are able to come and enjoy these saders Without the concern of breaking their fast. But I know that a little has been written about how Jewish Muslim relations have been on edge. And honestly, I have a few Jewish acquaintances who were nervous about attending if tars during Ramadan or weren't invited to as many if tars during Ramadan this year, just because of the potential for tension. Are you hearing any concerns about or from the Muslim community? Or are you hearing that people are sadly turning down invitations for similar reasons? Marnie Fienberg: Yeah, I think that as you said, this is a very challenging year. And if you don't feel comfortable, you're not going to a particular place. And I have Muslim friends and normally I am invited to if tours across the month, and I received very few invitations this year, which was interesting. We're still friends. The friendships haven't ceased or anything like that, but the invitations were not their part. To the reason what I did ask part of the reason they felt that they shouldn't be celebrating when people are starving and Palestine so they actually toned down their celebrations out of respect which that's a longer conversation, but I respect that and I appreciate that. Would they be coming to my table? I don't know. We have a community Seder a community to for Seder that we hold every year. So most of to First Aiders about home Seders, you know, so the idea of doing it in your home that is the primary core of twofer Seder. But we've started a nice little thing on the side, where we do a community to for Seder, where everybody we actually invite interfaith groups. The spirit of twofer Seder is about building a bridge. And I hope actually in the past, if you've done too, for Seder before, thank you, but be I hope that those bridges are holding during these troubled times. And if you can't build them during a difficult time like this, you know, I'm hoping I'm praying that next year, there won't be no war, and we'll be able to mend some of these fences and you will be able to invite and accept invitations to Iftar invitations to your Seder for your Muslim friends, I think it's important to keep trying. That's one thing that we are obligated to do as Jews, that may not work, but you'd have to keep trying. Manya Brachear Pashman: One thing I've noticed over the years, and the many Seders I've attended is the diversity of traditions and the customs some families put an orange on the table and have a glass for Miriam, other stick to Elijah. So make sure the Afikoman is chocolate, others play it straight. Some change the lyrics of the songs to fit Beyonce tunes, I won't lie I've done that. But does that present a challenge to the purpose or the goal of two for Seder? You know, the goal being to teach a newcomer about Passover? How do you do that? When it's you know, the traditions can be so different. Marnie Fienberg: This is also very–well not the Beyonce piece. But that's a very common question. First of all, I want to say I would really like a copy of that, please. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'll dig it up for you. Marnie Fienberg: Thank you. But that's the whole point that the Seder is blue door for door right we are Lincoln a chain from generation to generation and the core of the Seder the Haggadah, regardless of if you do a traditional haggadah that is, you know, four hours long starts after sunset, maybe you eat by midnight, you know, if you're doing a modern Orthodox or an orthodox Seder, or if you're doing a very, very modern said Seder, which just has the basic four pieces in it. And Tiktok you're done. I'm starving. It's been 10 minutes. Welcome to my my dad. Actually, that's the way he does his. But I've been to all different types, because you know, almost all of our Jewish families, we have a variety in our family, we have Orthodox, we have reform, we have everything in between, right? That's what it's about. It's about the magic of what you bring to your Seder. The haggadah is going to ground you, you've got the grounding story about our journey to becoming a people. That's the core, but what you do a round it, that's you, you are bringing you and your family and all the things that bring you joy, into your Judaism, into your Seder. And these things are critical. If you just read the Haggadah, and then you walked away, it wouldn't be joyous it would be yes, I was here. But the joy behind it is removed. So the idea that you know, you almost always have children at your Seder, and there's a rule for the children. Why is that? There's a role for the adults to teach the children. There's the food, there's thinking about the future when you sing Eliyahu with the door open so that your neighbors can hear you and wonder what is going on. I mean, all of these things. There's personal ways to put a stamp on those. But we're going to do those. And even if you do it to Beyonce, once again, very excited to hear that. It's really bringing that modern tinge to it. When we're going to hand the hat over to our children. When they do it. They're going to do something different and there'll be wondering who's Beyonce? That's okay, that's okay. But they're still going to do the for questions. They're still going to do the monkey, they're still going to do the Eliyahu all these pieces will still flow. I have proof of this. When I was working to create the community to for Seder. I wanted to create our own Haggadah, and I use of course haggadot.com To start off with, but I really wanted certain things that weren't in there and and I got stuck and I'm sitting here staring at the screen and my teenage daughter walks in and And she actually wanted to help me right there. I know you don't believe me, but she sat down. She said, How can I help? And I was walking through some of the more traditional lines. I don't know why they always took my heart, you know, where they say, you know, in God with an outstretched arm and outstretched hand and the old language, right? Should I keep it in the Haggadah, or should I not? And she looked at me like I was nuts. And she said, of course, you have to, you must, it won't be the Haggadah without it. And that really made me feel like this is going to pass down, at least in my family. These words are so intrinsic to who we are, somehow it gets passed down. It's amazing. Manya Brachear Pashman My last question is, who will be coming to your site or table this year? Marnie Fienberg: So I'm holding two Seders, although I'm going to three. The first one is the community Seder that is being held in Temple Emanu-El in South Hills right outside of Pittsburgh. And I'm gonna be sort of emceeing it. And we're going to be using the Haggadah that we talked about. And that will be I think there are three different churches that are joining and all sorts of different folks. And one of the tables is actually just teenagers. So I'm really excited because, you know, sometimes to first seders is of interest to adults, and not so much the younger set. Although at our last community Seder, we had a lot of college kids, we had a huge table of college kids, which was great. So I think that that's gonna be a wonderful Seder. The next Seder is going to be the second night we'll be at my house, my friend is holding it the first night at her house. Second night will be in my house, we're having 25 people's the current count, although, you know, it's Wednesday, so somebody's gonna have too late of a night or whatever, so they won't be able to come. But we're really excited because this is more even though there will be some family coming in. This is more of like, a friend Seders the second night for us. So it's going to be a wonderful night. Who's gonna be my two for Seder. This is once again through my daughter. She has a friend who is actually Korean, and her family is going to be joining us. I'm so excited her families, they're wonderful folks. And the one thing I'm nervous about is that they are amazing cooks, and I'm not sure if my cooking is going to stand up to their skills. So hopefully it'll all work out. But it's gonna be a lovely night as it always is. Manya Brachear Pashman: That sounds truly lovely. 25 people, Marnie, you are a brave woman, a brave hostess. Marnie Fienberg: I wish there was one more that was coming, but she will be there in spirit. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yes, absolutely. And thank you because I know it's a lot of hard work to put together a Seder. But again, so important it is such an anchor, I think for families and preserving our traditions. So thank you for all that hard work that's going into that Seder. Marnie Fienberg: It is my pleasure and I think every single person who's putting together a Seder and participating in to for Seder, if you've done it before, thank you, if you're interested in doing it again, we've got little kids to help you but just be you and it's about inviting new people every year. And that's how we're going to help really make an awareness about what it really is to be Jewish, not what you hear, you know, the negative rumors, replace those with positive Jewish joy. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, thank you so much, Marnie. The website to download discussion cards and toolkits, all the instructions that you need to host a Seder with a guest is at two, the number two for seder.org Marnie, thanks again for joining us. Marnie Fienberg: Thank you so much for having me. This was a great discussion.
Apr 17, 2024
What the Iranian Regime's Massive Attack Means for Israel and the Region
AJC Jerusalem director Lt. Col. (res.) Avital Leibovich shares how the IDF — and its neighbors and allies — defended Israel with remarkable success. In the early hours of April 14, sirens and explosions were heard across the Jewish state. In an unprecedented, first-ever direct attack on the Israeli people, the Iranian regime launched a wave of more than 300 drones and missiles. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Avital Leibovich Show Notes: Take Action: Join AJC in urging Congress to call on the EU to designate all of Hezbollah and the IRGC as terror organizations. Read AJC's Explainers on Iran: Get the Facts About Iran's Unprecedented Attack on Israel 'Crimes Against Humanity:' Another UN Report Finds Sexual Violence by IRGC and Other Authorities in Iran; Similar to Crimes by Hamas What is Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps and Why is it Designated a Terror Group by the United States? Listen to AJC's People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: Meet Modi Rosenfeld – the Comedian Helping the Jewish Community Laugh Again A Look Back: AJC's Award-Winning "Remembering Pittsburgh" Series Jewish College Student Leaders Share Their Blueprint for Combating Antisemitism Matisyahu's Message to His Fellow Jews and to the Israel Haters Trying to Cancel Him Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Episode Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: Few of us slept well on Saturday night into Sunday knowing that Iran had launched a wave of more than 300 drones and missiles in its first ever direct attack on Israel. In the early hours of Sunday, sirens and explosions were heard across the Jewish state. Here to talk about how Israel definit itself from what many feared was inevitable, Director of AJC Jerusalem Avital Leibovich, who also serves in the Israel Defence Force Reserves. Avital Leibovich: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: So can you share with our listeners what it was like to hear that Iran had launched this wave of missiles and drones? Did Israelis immediately pack up and head for shelters? Avital Leibovich: I think that was one of the most dramatic nights in Israel's history. You know, we're living in an era in which everything is televised and broadcasted. And when those drones have been launched from Iran, that has been broadcasted. So you can imagine millions of Israelis sitting at home, counting the hours until those drones will hit the Israeli airspace. In addition to that there was a lot of uncertainty of which type of drones we're talking about, what kind of explosives will they carry? Will they make it or not? And also, will these drones be accompanied by other weapons? So yes, there was huge concern. It was a sleepless night, sometimes between 2am until seven in the morning, Israel has been paralyzed with this unprecedented attack. Now 200 drones that have been fired at the same time to Israel. This is something that the world have never, ever experienced, there was never a country in the world that has been attacked simultaneously by 200 drones. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, we also know that there were in addition to drones, there were ballistic missiles, there were cruise missiles. And we know that some of those ballistic missiles could have been fitted with nuclear warheads. And certainly, we know Iran's nuclear capability has been developing rapidly for more than a decade. Was that a concern? Avital Leibovich: Look,unlike terror groups, you know, they rely on funding of different countries, proxies and so on. Iran is a country with its own budget with its own economic means, and has been investing in technologies and procurement and development of weapons of different kinds for decades. So we saw some of the outcome of the Iranian weapons in Ukraine. When Iran sold some types of drones to Russia to hit Ukrainian civilians. We understood the capacity, the capability. And of course, Israeli intelligence followed closely the Iranian capabilities. Now, when you have so many options, the warheads of ballistic missiles can vary. And therefore there was also uncertainty with regard to what would those ballistic missiles carry? Will they carry conventional weapons? Will they carry non conventional weapons? In addition to that, the attack came after more than six months of the war in Israel. So the level of stress and the level of uncertainty was high to begin with. We're talking about six months in which Israel paid the heavy price of more than 600 soldiers and officers who were killed, and more than 1200 civilians. So it wasn't an isolated evening. It really came in the course of a very long war. And now, Israel is facing the big question of retaliation, yes or no, when and how? Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, we have long talked about Israel and Iran being in a proxy war, Hamas and Hezbollah being two of those terror proxies that want to destroy Israel and are already engaged in conflict, as you've said, as you pointed out, to do just that. Yet, it really was unthinkable that Iran would dare to directly launch missiles at Israel. How did this attack change the thinking and do Israelis think it is an indication of more to come? Avital Leibovich: Israel changed its thinking twice in the last six months. The first time was October 7. Israel never believed that Palestinians who entered Israel on a daily basis from Gaza as workers, would be collaborators of Hamas and would supply them with intelligence information about communities, about homes of people, about police stations in cities and so on. So we understood that we are, we need to change the concept, the operational concept, the strategic concept as well. And the second time was when Iran attacked Israel a few nights ago. And here for the first time, Iran shows to take a risk, and fire over 350 targets more than 60 tons of explosives at Israel from its own sovereign territory. So whether it's proportionate or not, whether it's a retaliation to something or not, this does not change the fact that this is a precedent and as a president, Israel, of course needs to change the way it reacts and it plans. I know that the cabinet has met a few times already, since the attack of Iran. And the cabinet is discussing different ways in which it could retaliate, prepare, better prepare the storages of munitions that we have. So they are different opportunities for Israel. And one of the questions I want to ask Manya is, how is the world looking at this? Because this is not an ordinary thing. And you know, one of the statements that came out yesterday, was from the G7 ministers meetings. And I was certain that the statement will primarily include practical steps against Iran, which is not only a problem for the Middle East and Israel, but for the entire world. And one of the leading statements said that, no, we have agreed to, to convince Israel not to retaliate. And I'm thinking to myself, haven't we learned anything? Do we want to wake up in a few months and discover that Iran has turned into a country with nuclear capabilities, with five bombs with six bombs? Now, October 7, have never would have happened if it wasn't for Iran. Hezbollah attacking Argentina, the Jewish Community Center, decades ago, and murdering a lot of Jews and diplomatic staff would not have happened if not of Iran, and a lot of terror attacks all over the world as well. So how many proofs more does the world need, in order to take concrete action concrete measures against this terror global inciter called Iran. Manya Brachear Pashman: In addition to the United States, Israel's allies and neighbors really stepped up Saturday night, the United Kingdom, France, Jordan, they all helped down some of the drones that were headed Israel's way. But the attack undoubtedly depleted some of Israel's defenses. And so what does Israel need now from its allies, particularly, you know, in the way of action by governments in the United States and the EU? What does Israel need to make sure it can defend itself if God forbid, this happens again, or another October 7, happens again? Avital Leibovich: It's not a secret that the US and Israel are very strong strategic allies. And this has two main reasons for it. The first and maybe the most important one is the shared values that we hold between us. And the second is the mutual interests. The US needs a strong Israel in the region with strong capabilities, whether its intelligence or others. And Israel needs also a very close coordination with the US. So when we are maneuvering between these islands of terror in the region, we can work together to overcome those islands of terror. Now, in this situation, I think the coalition that work together, the countries which you mentioned, preformed an amazing, orchestrated, successful operation. And part of it comes because Israel is now a part of CENTCOM, the central command. This is the command that actually gathers all the countries from the region. So in addition to being a part of that command, we share knowledge, technology,intelligence, we exercise together with other militaries. And this is the basis for future cooperation, like we've seen a few days ago within that coalition. So I think those steps are very important. I would say that continued US support for Israel's strength. And obviously, we did not plan to fight for so long. And such a long period of fighting demands a lot of ammunition. So the US support, both in budget, but in also resources, military resources, is critical for Israel to succeed and continue to defend its people and in the country. Manya Brachear Pashman: My last question, Avital, kind of references what you just said a moment ago about how the world just doesn't seem to realize the global threat that is posed by Iran. Does Israel's success matter not just to Israel, but to the world at large? Avital Leibovich: You know, Israel's success is based on the air defense system that was built for decades, with Israeli technology, Israeli know how. The ability to intercept different kinds of rockets and drones is something first of all technology we shared with the US, and we work in partnership, but also comes out of a lot of investment. Now, I believe that today in 2024, the world needs to aspire for a more stable Middle East. The Abraham Accords, was a part of that direction. And furthering and enhancing the Abraham Accords, expanding the Abraham Accords in the future, will just help the world to see a more stabilized area. Now, Iran has to be dealt with, there is no question about that. I do expect sanctions and putting on the terror list, the Revolutionary Guards and Hezbollah in its entirety, you know, Lebanon doesn't have a president for more than a year, because Hezbollah never approved the candidates, for example. So Hamas needs to be on the terror list. The Houthis need to be on the terror list, the Houthis are a problem for the world disrupting cargo movement in the Red Sea. So these are all terror groups, proxies, with different sizes with different intensities of weapons, all imminent in one troublemaker, and that is Iran. So my expectation after a few nights ago, is that the world, the Western world, the modern Western world will gather together and take concrete steps. So we do not wake up surprised in a few months and find a nuclear Iran ready to launch the rockets with nuclear warheads and we don't know exactly where–to Europe to Israel, elsewhere in the world. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Avital, I'm glad you're safe. Thank you so much for joining us. Avital Leibovich: Thank you for the opportunity and am yisrael chai.
Apr 16, 2024
Meet Modi Rosenfeld – the Comedian Helping the Jewish Community Laugh Again
Israeli-American Comedian Modi Rosenfeld, who took part in the inaugural AJC's Voices Against Antisemitism Campaign, just-released a stand-up comedy special, Know Your Audience, which reflects a principle he has always subscribed to. But what happens when you know your audience is suffering a trauma like no other? Listen to this conversation with Modi, who was in Israel on October 7, on how he jokes about antisemitism and what he sees as his mission in this difficult moment: helping the Jewish community laugh again. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Modi Rosenfeld Show Notes: Learn more: AJC's Voices Against Antisemitism: Meet the Celebrities Standing Up for the Jewish People and Israel modilive.com Photo Credits: John Cafaro Credits – Standup Clips: On Antisemitism Jewish Boyfriend Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: A Look Back: AJC's Award-Winning "Remembering Pittsburgh" Series Jewish College Student Leaders Share Their Blueprint for Combating Antisemitism Matisyahu's Message to His Fellow Jews and to the Israel Haters Trying to Cancel Him Unheard, Until Now: How Israeli Women Are Powering Israel's Resilience Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Episode with Modi: Manya Brachear Pashman: Comedian Modi Rosenfeld, known by his fans as simply Modi, is nearing the end of a live national tour, co-hosts his own podcast, and he recently released his first televised stand-up comedy special titled Know Your Audience. It's a principle the Israeli-American comedian has always subscribed to. But what happens when you know your audience is suffering a trauma like no other. Here with us to talk about how we can and why we should laugh again is Modi Rosenfeld. Modi, welcome to People of the Pod. Modi: Hi, People of the Pod. Manya Brachear Pashman: You were born in Tel Aviv and grew up on Long Island. Tell us how you found your way to comedy. Modi: I was actually just doing investment banking. And I used to imitate the secretaries. And my friends said this is really funny, you should do it on stage. And they set up an open mic night. And that was about 30 something years ago. And that's how the comedy began. Manya Brachear Pashman: The special that I mentioned was filmed nearly a year ago. It was filmed before the Hamas terrorist attack and the war. You talk about COVID, you talk about marrying your millennial husband, you talk about Shabbat elevators. I'm curious if you do feel like the material still resonates in the current climate? Modi: Ever since October 7, I've been doing my shows and not mentioning the war itself. Until the very end where I sing Hatikva with the audience. I feel like the audience needs a moment to just laugh and not think about the war. And not think about what's happening in Israel and just have a laugh about being Jewish, being Jewish, about non-Jewish people. Sometimes I tell the story about how I was October 7, while I was in Israel. And then sing Hatikva with the audience, people seem to, they're very touched and moved by it. And it reminds them, now, let's just remember where our hearts and where our prayers and where our thoughts are. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's talk about where you were on October 7. Modi: The war began at the end of the holiday of Sukkot and I was in Israel. I had six shows, sold out shows in Israel that were absolutely amazing. One of the highlights of my career. Thursday was the last show. Friday we were there for Shabbat and Saturday we were scheduled to fly out to Paris to do four shows there. And obviously Saturday morning, the alarms went off and the bombs went off. We were staying at the Setai Hotel, which is in Yafo, the Arab part of Tel Aviv. Bruno Mars was also staying at the hotel. He had three concerts in Israel and at 12 in the afternoon we saw them whisk him away to a private airplane to be taken out of Israel. And I said to Leo, my husband, I said Thank God they got put on Mars out of the hotel. He said why? I said because if a bomb hits this hotel and me and Bruno Mars die, I would get zero press coverage. And so that was you know, something light in the day, but it was a very, very stressful, scary day for everybody. We were on a scheduled flight to go to Paris. And it had a four hour delay. And we finally took off and got to Paris. And then we had to make a decision. Do we do these shows? Because the war was so fresh, people were just learning about what's happening and watching it on their phones. But the sold out shows were full. And that's when I began to do Hatikvah at the end of the shows, and I've been doing it ever since. You know, we just had an hour and 20 minutes of laughter, they just had the best time. We were all laughing. And then you just focus again, you know, yeah, we're laughing. But in Israel, there's a whole different experience happening. And even though in Israel now, the comedians there are also performing and doing shows. You've got to find a respite from being in the war. Because we are, you know, everybody's on their phones, you're 24 hours in the war, receiving news and footage and all kinds of information. And then you finally get to just take a few minutes to laugh. Manya Brachear Pashman: When you said that you were actually an investment banker, that you found comedy kind of as a career later on, but what role did humor and comedy play in your upbringing, in your family life, your childhood? Modi: Only later on in life that I realized that my father more than all is a very funny person, just by having no editing skills. I never was a class clown. I was always funny with friends, but you know, when you're a table comic, and you're a real comic it's two different things. If you can be funny with your friends at a table, you know your audience, you know everybody at the table, you know what they've gone through, you know what we all know that they went through. And so it's easier to get a joke out. When you're on stage, you don't know everybody, and you don't know what they've all been through, or how they know each other. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how do you kind of unite your audience? How do you try to kind of find that common denominator? Modi: People are kind of seeing the Jewish world through my eyes, through the eyes of a Jewish person. And they learn things, even though sometimes it gets a little specific, I always translate. My goal in comedy is to make people happy, is to bring laughter into the world, which I call Moshiach Energy. When you're standing in front of an audience of 500 to 1500 to 2000 people and you see them all laughing together. For me, that's Moshiach Energy. How I pictured the world would be when Moshiach is here. You know, the Messianic era, just people just happy, united, laughing, not arguing. And even though you can create that for an hour and a half, you wish you could create it for 24/7. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how else have you adjusted your live shows to reflect the current situation in addition to adding the anthem? Do you talk about antisemitism? Modi: I was always talking about antisemitism, not as a lecture, not as a type of Noa Tishby, but more as a comedian. Here's what's happening, here's how it's funny. You're bringing light to it, but you're bringing it with punch lines that are appropriate. And this was before the war, it's in my special, it's before the war. I don't know if you remember there was a politician in Turkey that stood up and screamed that Allah was going to kill all the Jews and destroy Israel. And then he drops, has a heart attack. I mean, the jokes sometimes just write themselves. Manya Brachear Pashman: A few weeks ago, we spoke with musician Matisyahu, who also has been on a national tour. He has encountered protests at most of his concerts, actually. And some concerts have even been canceled because of security concerns. Have you encountered any of that? Modi: In general to answer that, I would say not in the form he's had. We've had a lot of security at our shows, especially the European shows. Since the war I've performed in Berlin, Dusseldorf, Frankfurt, Vienna, Brussels, Amsterdam. I call it the Reparations Tour. And we've had an enormous amount of security both from hired security and local police and guards from the city. Our last show in Paris, we had four shows in Paris, the fourth one, the police asked us to cancel because there was a huge pro-Palestinian riot across the street. And the reason I stay riot and not protest is because it was unauthorized, and they were out of control. They had tear gas thrown in there. And that was one of the incidences. In Brussels there was a mixup in people knowing that the security would be there. So we lost about 100 people that were going to come to the show. So the show went from 900 people to 800 people. That's the worst that's happened. Manya Brachear Pashman: And did you indeed cancel that fourth Paris show because of the riot? Modi: The Paris police were so wonderful with providing security for all the other three shows, when they asked us to cancel that show, we listened to them, and we did it. And we actually moved it to the following day to a matinee. But they said this is not going to be a good idea for this insane amount of, that kind of protest to be–it was catty corner across from where our theater was. It was the Republic Square, which our theater was at the Apollo, which was you can see it. And so they said it's not a good idea to have Jews walking into a theater at that moment. Manya Brachear Pashman: Makes sense. Was it a coincidence that it was that it was located there? Or was it connected to your show in any way? Modi: No, no, no–the Republic Square is, I guess, an iconic place to do something like that. My theater happened to have been across the street from it. This was the Thursday after the Saturday, which was less than a week. Our first show in Paris was on Monday after the Saturday of the beginning of the war. So you couldn't understand how fresh this was. All the news was coming in. Everybody was finding out exactly what was going on. We didn't have all the information, we had no idea about people that were locked in bomb shelters and people that were missing, they had no idea if they were killed or kidnapped and then just doing comedy there you know, literally I'm in the back of the theater looking at people watching their phones, trying to get information on what's happening on the war and then the lights go down and the comedy starts. Manya Brachear Pashman: How have you been affected by the war? Modi: We have family in Israel that are affected by just being in Israel and the change in their lifestyles that happened. Directly, we have family that their their kids are in Gaza. Ellie Beer from United Hatzalah is a close friend of mine, his son is fighting in Gaza. So when I speak to Ellie, I'm like, how's your kid doing? When you're in Israel, you speak to people, it's like one degree of separation between you and anybody that's truly affected by the war. When we did the 100th episode of my podcast at the 92nd Street Y, my podcast, which is called And Here's Modi. I'm so used to performing at fundraisers and charities where they show a movie of something horrible, and then they bring me out, and they go, and here's Modi:. And here I am the Monday after the war, doing a show. We did a Q&A with the audiences, a pre Q&A, sent questions in, and everybody kept asking who would you want as a guest on the podcast and I said, Omer Shem Tov, which is one of the hostages. His photo for some reason I see it everywhere. And I wish he could be in front of me at the podcast and not in a tunnel somewhere being held hostage. I truly go to bed every night thinking I'm gonna wake up. When I open my phone up, it's gonna say today, all hostages were released, ceasefire has begun. And there will be an end to this soon. Manya Brachear Pashman: I think that that is what we all pray for, and hope to wake up to every morning. I'm curious if you've returned to Israel since October 7, I know you've been on tour, traveling a lot, but have you had a chance? Modi: I have been in every Jewish community from California to Florida to New York to Chicago to everywhere, with the tour. And again, it's, I think, for me, that's more important than being in Israel, because I'm connecting with these communities who are not in Israel, and bringing them a little bit of unity. The community gets together, you see people –for some reason, all our shows are starting a little late, everybody just sees each other in the lobby and like, Hi, how are you? Good to see you. And then they come into the show. I think that's more important for me to be doing that than running around Israel, saying how ridiculous this war is. Everybody's doing what they can do. And I'll be in Israel in June, and I'll be doing a show in Yerushalayim, and then I'll be back there in September doing a larger show in Tel Aviv and doing whatever I can do to help there. Manya Brachear Pashman: You often interact with audience members in your show. Have you had any interesting encounters with individuals in your audience? Especially since October 7? Modi: I'm not one of those comics who does the where are you from, what do you do and make a whole hour about trying to get something funny out of that. That's totally not my style. I do ask if anybody's not Jewish and this way I know–if you see my comedy special you see there's an extra layer of the joke. Me translating it to the person who's not Jewish. I will tell you in that aspect, beautiful things have happened. People who are let's say in an intermarriage or even converted to Judaism come up to me afterwards and say, Wow, I never felt so welcomed and accepted and feel a part of the tribe and they tell me their story about how they ended up in the Jewish world. Like my husband, who was born Catholic. And now he is coordinating with your organization, with every other UJA, JJJ, JJC, JJABC, JABC JJBC. You know, and he is on the phone speaking to people about a motzei shabbos show, a pre-shabbos show, after yuntif, before yuntif. He's coordinating with the Jewish world to make sure that they're laughing. And it's an amazing– that's one of the nicest things that I've been seeing. People who ended up in the Jewish community that weren't Jewish, feel so welcome from the show. Manya Brachear Pashman: What makes you proud to be Jewish, Modi? Modi: What makes me proud to be Jewish is, I just think that the contribution of Jews to the world is significantly larger than the size of the people that we are. And I talk about that now in the new part of my show, you know, how just everywhere you go, whether something to do with medicine, education, culture, there's always a Jewish name on the building. A part of being Jewish is not only helping the Jews in the community, it's helping the community. So not just creating something–the Lubavitcher Rebbe always spoke about that, whatever you are in the community, don't just help the Jews there, help the community in general. And you see that, you know. You go to any hospital, any museum, and you just see the Goldberg Pavilion, you see the Horowitz Wing, and they just give and help create all of that. In comparison to the size that we are in the world, we do a lot more. And something, that makes me proud. Manya Brachear Pashman: I think that you're absolutely right. And I think that your contribution of comedy and humor, and laughter, especially at a time like this is really so appreciated. Modi: You can bring humor into the world by, I always say: be the friend that brings their friends to the comedy show. If you see me coming to a theater near you, another comedian, coming to a theater, buy a few tickets. By the time the comic gets there, you'll see how all your friends are looking for tickets, and they're gonna want to have a good night of laughter. And now you can just make a night at your house, you can put my special on the TV and have a bunch of friends watching and make an evening of it, and make sure to send it and make sure that people who can't get to a show like the elderly and your parents, grandparents that don't have a way to get to a show or don't know how to set up Amazon or go to my website, help them, sit with them. Watch the comedy show with them. That's Moshiach energy. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, thank you so much, Modi. Modi: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: Last week, we re-aired excerpts from our award-winning series Remembering Pittsburgh, which marked five years since the 2018 shooting at the Tree of Life synagogue. Next week, one of the guests in that series returns. Marnie Fienberg founded 2ForSeder, an initiative to honor her mother-in-law Joyce who was one of the 11 victims murdered inside Tree of Life. Ahead of Passover, Marnie will share how inviting newcomers to our Seder table can be a powerful way to push back against antisemitism.
Apr 4, 2024
A Look Back: AJC's Award-Winning "Remembering Pittsburgh" Series
Listen to this compilation of our award-winning series Remembering Pittsburgh, exploring how the horrific shooting at the Tree of Life synagogue affected the Jewish community in Pittsburgh, the U.S., and around the world. In the four-part series, we take listeners behind the scenes of how the Pittsburgh Jewish community continues to rebuild and honor the lives lost on October 27, 2018. The anniversary came during the same month as the most lethal attack on Jews since the Holocaust: Hamas' October 7 massacre of Israelis. Rising antisemitism has led to the murder of Jews around the world, from Pittsburgh, to Paris, to Israel. All forms of antisemitism must be countered to ensure a safe and secure Jewish future. Listen to the entire series at AJC.org/TreeofLife . Episode Lineup: (0:40) Eric Lidji, Carole Zawatsky, Howard Fienberg, Marnie Fienberg, Belle Yoeli, Anne Jolly, Ted Deutch Show Notes: Music Credits: Relent by Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com), Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 Virtual Violin Virtuoso by techtheist is licensed under a Attribution 4.0 International License Tree of Life by Nefesh Mountain Shloime Balsam - Lo Lefached Hevenu Shalom - Violin Heart Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: Jewish College Student Leaders Share Their Blueprint for Combating Antisemitism Matisyahu's Message to His Fellow Jews and to the Israel Haters Trying to Cancel Him Unheard, Until Now: How Israeli Women Are Powering Israel's Resilience 152 Days Later: What the Mother of Hostage Edan Alexander Wants the World to Know Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Episode Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: Last month, the Senate earmarked $1 million in federal funding to create a curriculum for students about antisemitism and other forms of discrimination and bigotry. The recipient of that money? An organization that knows the consequences of that hatred all too well: the newly imagined Tree of Life, an education center dedicated to ending antisemitism that emerged after 11 worshipers inside Tree of Life synagogue were murdered by a white supremacist on October 27, 2018. This week, we are presenting a compilation of our award-winning series Remembering Pittsburgh, which launched on October 5, 2023 -- right before the October 7th terrorist attacks in Israel. Listen to the series at AJC.org/TreeofLife . __ Episode 1, which originally aired on October 5, takes you inside the Tree of Life building before it was demolished to make way for a new complex dedicated to Jewish life and combating antisemitism. Eric Lidji: Pittsburgh definitely is not forgetting. It's ever-present here. There are people who are healing and doing so in ways that, at least from the outside, are remarkable and very inspiring. And there are people who I'm sure have not fully reckoned with it yet. Carole Zawatsky: It's all too easy to walk away from what's ugly. And we have to remember. We can't walk away. Manya Brachear Pashman: Five years have gone by since the horrific Shabbat morning at Pittsburgh's Tree of Life Synagogue, when eleven congregants were gunned down during prayer – volunteers, scholars, neighbors, doing what they always did: joining their Jewish community at shul. Today, we take you to the Tree of Life building that stands on the corner of Shady and Wilkins Avenues in Pittsburgh's Squirrel Hill neighborhood to hear from two people in charge of preserving the artifacts and memories of the vibrant Jewish life that unfolded inside those walls until October 27, 2018. Manya Brachear Pashman: In early September, our producer Atara Lakritz and I visited the Tree of Life synagogue in Pittsburgh's Squirrel Hill neighborhood. Squirrel Hill, where Jews have settled since the 1920s, is quite literally Mister Rogers' neighborhood. We were there to interview those touched by the events of October 27. But it didn't take us long to figure out that everyone there had been affected in some way. All along Murray Avenue, in 61C Cafe, at Pinsker's Judaica Shoppe, at the Giant Eagle supermarket, when we told people why we were there, they all had a story, an acquaintance, a connection. Later, walking through the glass doors of the synagogue felt like we were stepping through a portal, traveling back five years, when life stopped, and the reality of the hatred and terror that unfolded there began to haunt every step. Atara and I were invited to accompany a final group tour of the building before it closed in order for preparations to begin for the building's demolition. The tour was painful, but we felt it necessary to share with our listeners. As we left the lobby, we were told to take the stairs to the left. The stairs to the right were off limits. Someone had been shot there. We were led to a small, dark storage room where chairs had been stacked for guests. A handful of people had hidden there as the shooter continued his rampage, but one man walked out too soon, thinking it was safe. When first responders later came to get the others, they had to step over his body. In the kitchen, there were still marks on the wall where the bullets ricocheted when he shot two women hiding underneath a metal cabinet. The calendar on the wall there was still turned to October 2018 with a list of activities that were happening that week posted alongside it. And in the Pervin Chapel where seven people died, pews punctured with bullet holes and carpet squares stained with blood were no longer there. No ark either. But remarkably, the stained glass windows remained with images and symbols of Jewish contributions to America, the land to which the ancestors of so many worshipers once inside that synagogue had fled to and found safety. Those windows will be carefully removed by the son of the man who first installed them 70 years ago. And they will return, when the reimagined Tree of Life rises again. Carole Zawatsky: The tragedy is a Pittsburgh experience. But it's also every Jew's experience. It shattered for so many of us our sense of security in America. This is our safe haven. This is where we came to. Manya Brachear Pashman: Carole Zawatsky is the inaugural CEO of the reimagined Tree of Life. Since November 2022, she has overseen the development of a new complex on the hallowed ground: an education center dedicated to ending antisemitism, including a new home for the Holocaust Center of Pittsburgh; a memorial to the lives lost that Shabbat morning; a dedicated synagogue space where the Tree of Life congregation can return. Carole Zawatsky: What can we build to enrich Jewish life, to remember this tragedy, and to show the world that we as Jews should not be known only by our killers and our haters, we should be known by our joy, our celebrations, our rituals, our resilience. __ Manya Brachear Pashman: Next, hear from the son and daughter in law of Joyce Fienberg, one of the 11 victims. In this second installment of our series, we sit down with Joyce's son, Howard Fienberg, and his wife, Marnie, as they share their journey of mourning and resilience. After her husband and mother died in 2016, Joyce Fienberg started each day at Tree of Life synagogue in Pittsburgh, to recite Kaddish, the mourner's prayer. Even when she was no longer officially considered a mourner as Jewish tradition prescribes, 11 months, she continued to attend services each morning at the synagogue. That's why Howard Feinberg knew his mother Joyce was at Tree of Life when he heard there had been a shooting there on the morning of October 27, 2018. It would be more than 12 hours before he learned she was among the 11 killed that day. Howard and his wife Marnie are with us now from their home in Northern Virginia. Howard, you followed your mother's example and recited kaddish for 11 months. Can you tell us a little bit about that experience? That experience of saying Kaddish and mourning for your mother, and also can you share with our listeners why it felt like the mourning period was extended? Howard Fienberg: I felt a huge amount of support everywhere I went, in order to be able to say Kaddish every day. Which for someone who was not the most observant of Jews, it was a big lift to be able to do that every day. In fact, even when traveling in disparate places, that I could always find, somehow, be able to pull together 10 people to be able to say Kaddish was a big deal. And I wanted to make sure that no one would struggle in similar circumstances as well. Obviously, initially, in Pittsburgh putting together 10 people was not a particularly big lift. Because the community support in that first week of Shiva was phenomenal. But it's not an easy thing in many congregations, and I think we are fortunate in mine that we always seem to pull it out every day. But I want to make sure that it happens. So in practice wise, that's one of the biggest things, my involvement with the synagogue, and prayer. The broader extension of the mourning period, in a way, was a result of the constant delay of the trial for the monster that committed the massacre. And that was a result of both just the general usual procedural delays that you would expect, combined with COVID excuses that dragged things out during the trial. And once a new judge took over responsibility for this case, things suddenly snapped into gear and it moved forward. And we're particularly grateful for the judge in this case, just for his very no-nonsense approach moving forward. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you talk about whether the guilty verdict once it did take place, and a verdict was delivered, how that verdict changed anything for you and your family? Howard Fienberg: It was a matter of relief, to a great extent. I sat through almost the entirety of the trial, heard and saw all of the evidence. A lot more than I expected to and ever wanted to, but I felt duty to do so. From an outside perspective, looking at it all, you would say this is a slam dunk case, lined up for all the federal hate crimes that were involved. And at the same time, I was in doubt until the jury came back and said, all said guilty. It's just the nature of things. I was on pins and needles. Massive relief afterwards and the same thing with the final verdict and sentencing. Massive relief for us and our families. And that did allow…nothing's ever closed. You don't finish feeling the loss of somebody, especially when they're taken in, you know, horribly violent terrorist circumstances. But you move from segment to segment. So the same as we do in the year of mourning, you're moving from shiva, which is one kind of thing, to the 30 days, and then to the end of the mourning period. And this was moving to yet another period. And what exactly this is and how long it will be, I don't know. But we're figuring that out as we go. I certainly feel a lot more relaxed. Marnie Fienberg: Feels a little lighter. Howard Fienberg: Yes, definitely lighter. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's good to hear. That's good to hear. I am curious, you said you felt a duty to listen to those details, even though you didn't want to. Can you explain why you felt that sense of obligation? Howard Fienberg: Part of it is, somebody in our family needed to. And it wasn't something that I wanted everybody to sit and hear and see. And I specifically told friends and family as much as I could, to stay far away and said, as much as you want to know, I'll let you know. But otherwise, it's horrific. And it wasn't anything that I would wish for anybody to see and hear. But at the same time, it's the reality of how my mom died. And what the circumstances were, what was going on with the antisemitic conspiracy theories that drove the monster that killed her. And what did he have in mind, and what was his intention, what did he plan, what did he do? These were important things. And the bigger picture, which I didn't even know going in, was the extent to which the police in Pittsburgh were so heroic. And while they were not able to save my mom, they saved other people, including friends of ours, and people who are now friends, who would not be alive if those cops had not tried to charge at the front door trying to charge the building and getting shot. And then the SWAT teams going into the building, and in a couple cases getting almost murdered themselves, trying to rescue the people that were inside. And they did rescue some people. And those people would most likely be dead if the SWAT had not rushed in. Equipment wise, they were not ready ordinarily for this sort of situation. But they went in anyways because they knew they needed to, and they didn't hesitate. And that's the kind of thing that you can only understand, having gone to the trial and learned what went on. ___ Manya Brachear Pashman: In the third installment, we look back at how horror drew people to solidarity. We interviewed Belle Yoeli, AJC chief advocacy officer, as well as others who showed up for Shabbat. Belle Yoeli: We saw hundreds of thousands of people show up. And we saw pictures later, after the fact, and videos, and people making speeches, and just so much solidarity. This was captured on the news. I think it really stands out as one of the most amazing responses to antisemitism that we've seen in modern history. Manya Brachear Pashman: On October 27, 2018, Americans witnessed the deadliest antisemitic attack in this nation's history. The senseless slaughter inside a house of worship devastated and shocked American senses because it was simply unAmerican. But the aftermath of the atrocity became an American moment when so many people showed up – showed up with hugs, showed up with flowers, showed up with prayers for their Jewish neighbors. The most visible expression of this came a week after the massacre with the unprecedented turnout of people of all faiths at synagogues across the nation as part of AJC's #ShowUpForShabbat campaign. Together, Americans sent a message that hate will not prevail. Belle Yoeli: Everyone wanted to do something, and the entire Jewish community mobilized to make this happen with the understanding that as AJC has always said that antisemitism is not just about the Jewish community. It starts with the Jewish community, but it's a threat to democracy, and the murder of Jews in their religious institution is such a breaking, a fracturing of everything that the United States stands for, everything that democratic society stands for. Manya Brachear Pashman: Today, Belle Yoeli is the chief advocacy officer for AJC. In 2018, she worked as the chief of staff for then AJC CEO David Harris. David had spent nearly 20 years counseling European leaders on the rise of antisemitism in their midst, calling their attention to violent crimes against Jews when conflict erupted between Israel and their Arab neighbors. Belle was on her way to a nephew's birthday party when she got the call on October 27 about what had happened in Pittsburgh. She remembers sobbing in the car on the phone with colleagues as they all grappled with the reality that whether they were regular shul-goers or had just happened to go to synagogue to celebrate a friend's bar mitzvah that day – it just as easily could've been them. For many, what they needed now was to go to shul and not be afraid, and to see others, not just their own community, but others of all faiths in the pews alongside them. What they needed most now was to know they were not alone. So they drew up a plan. Belle Yoeli: A couple members of our staff actually kind of simultaneously came up with a similar idea, which was that we need to, more than anything, rally non-Jews to come and support the Jewish community at this time, and what better time to do that than the following Shabbat. Manya Brachear Pashman: Dubbed #ShowUpForShabbat, the social media-based campaign called on both Jews and those of other faiths to flock to synagogues that coming Shabbat on the weekend of November 2 in support of the Pittsburgh Jewish community and all of American Jewry. The response across 80 countries was astounding. Manya Brachear Pashman: We connected with people who showed up that Shabbat five years ago, and ask them what the experience meant to them. Anne Jolly: An important part of what we proclaim is love God, love your neighbor, change the world. And so we believe that means, we show up for each other. We can't love each other without being present with each other. So we have to be together. You have to show up. Manya Brachear Pashman: Episcopal Bishop of Ohio Anne Jolly was serving as the rector of St. Gregory Episcopal Church in Deerfield, Illinois in October 2018. A former hospital chaplain, she was sitting in her office when she heard the news break that Saturday morning. Her first call was to her friend and colleague Rabbi Karyn Kedar down the road at the Reform temple commonly known as Congregation BJBE. Rabbi Kedar had recently preached at St. Gregory and then-Pastor Jolly was scheduled to deliver the guest sermon at BJBE the following Friday night. Anne Jolly: I called her and we talked and we prayed. And I said to Karyn, I think probably you need to preach on the Shabbat following the shooting at your temple and she said, 'I want you to do it.' She said 'I think I think we need to hear your voice and that the congregation needs to hear you. Rabbi Kedar I think thought that to hear a voice of someone who is not Jewish saying aloud, We love you, we care for you. We believe we are all created in God's image together. And that means we need to show up for each other. It means we need to be present with each other, that to hear that from someone who was not part of their community might be more powerful, more impactful, and more important for the community here at that time. Manya Brachear Pashman: When Bishop Jolly arrived that following Friday she did not expect her sudden sense of fear when she encountered armed guards. Anne Jolly: I didn't realize I was afraid until I walked in the door. And I stopped and had to take a deep breath and realize that I was afraid because I was entering into a space of people who have long been afraid. And that I had never had to experience that before in that way. And I wasn't really afraid for my congregation the same way I was for my beloveds in the synagogue, that they had more of a reason to be afraid than I did. And that was all the more reason for me to be there, and to be present with them. Manya Brachear Pashman: Bishop Jolly credits that night at BJBE for the deep connection that formed with the congregation. In fact, she returned to BJBE many more times to celebrate Shabbat. Precisely a year later, the members of the Jewish congregation showed up at her door after a pumpkin patch at St. Gregory had been destroyed by vandals. Anne Jolly: There were a bunch of them that came to our patch and we were talking about it and they said, 'We just wanted to show you that we are supporting you. And they were worried that that vandalism had been an act of aggression against us. And I just thought it was kids. And that was a really clear distinction of how our worldviews are different. For them, a vandalism thing would, of course, of course, be something hateful against them. In this case, it was children, it was just teenagers being dumb. But it reinforced that understanding that for them, fear is always in the background because of the violence perpetrated to them – again and again and again. ___ Manya Brachear Pashman: For this closing episode of the series, I sat down with AJC CEO Ted Deutch, who served as a congressman at the time of the Tree of Life massacre. We discussed this anniversary and its parallels to the October 7 attack on Israel, when once again Jews were murdered just for being Jewish. Ted, where were you on the morning of October 27, 2018 when you heard about the Tree of Life? Ted Deutch: I was a congressman who represented Parkland, where the mass shooting at Marjory Stoneman Douglas took place. And the morning of Tree of Life, I spoke to a group of high school students from all around South Florida, who participated in a program about how they can become leaders in the community. I spoke with them about what had happened a few months before in Parkland, and what I had seen from high school students in Parkland and how they responded and how you stand up to violence and try to stop it and how you respond to evil and how important it is to use the power that you have as young people. That was literally what I was doing right before I walked out of the Florida Atlantic University auditorium and saw my phone start to buzz with news of Tree of Life. Everything that I had said to the students in the discussion, that really difficult conversation we had with these students who shared with me their fears of violence, their fears of going to school–those fears hit home really hard for me and for the Jewish community. Manya Brachear Pashman: So in our first episode of this series, our producer Atara Lakritz and I went on the last tour of the Tree of Life building. You also walked through the building back in June, before many of the artifacts had been removed. Would you mind reflecting on that experience? Ted Deutch: I couldn't help but think of my synagogue where I grew up on the other side of Pennsylvania in a lovely community, like Pittsburgh. I was struck that, forget that this was a synagogue, I really couldn't stop thinking that it was inconceivable that that kind of horrible tragedy could happen in a community like that. And walking through the synagogue and seeing the site where hatred, and antisemitism, and manifestations, the worst manifestations of antisemitism were brought to this lovely place, in this wonderful synagogue. It was overwhelming to think about what was happening that Shabbat and the fear and terror that people felt as that was happening. That was number one. Secondly, I walked into the main auditorium where they were gathering all of the things that hadn't yet been taken away to be used in the museum and the memorial that's going to be constructed, that haven't been given back to families. There were lots of things that are just not identified, they don't have families to return them to. And to see tallaisim and tefillin and all kinds of items that are used for Jewish rituals and Jewish customs just sitting on this table where they didn't know what they were going to do with them because the synagogue that existed there, the life that existed there, that simple, wonderful community, that was gone. It was gone. That community will never be the same. And I think for our community, for the Jewish community, we're really never gonna be the same after what happened there. Manya Brachear Pashman: You were telling me before we started this conversation that they gave you something during your visit. Ted Deutch: As I walked through, and they saw how moved I was by this massive display. They came over and made such a kind gesture to me. And of all of the gifts that I've received in all of my travels, as a member of Congress, and now as CEO of AJC, I don't think there's anything that's as meaningful as the tefillin that they gave me. I don't know, obviously, I don't know whose it was. And it may well have been someone that was a synagogue member years and years ago. But the connection that I felt at that moment to that community at Tree of Life and the connection that I felt thinking about, not just Tree of Life, but tragedies that have befallen the Jewish people throughout our history. And knowing that I was going to return to New York, I was going to have the opportunity to join the Jewish community around the world in overcoming these tragedies, and making sure the world understands why these kinds of attacks will never, they'll never work, they'll never, they'll never defeat the Jewish community. As we endure this really challenging time now in Israel, I've been thinking the same thing. We've gone through a lot in our history, and we've constantly, constantly overcome, and have grown and have learned and have continued to enrich the world. As Tree of Life rebuilds and will help shape a national and international conversation for years to come about fighting antisemitism. And as we continue to do our work and as Jews around the country and around the world go through whatever security measures they have to to go to synagogue and to drop their kids at day school and Hebrew school and for people to show up for programs at the JCC, there is a defiance that I felt at that moment that is perhaps the most important thing I took away from that day. Because it was awful. But I'm not going to dwell on how terrible it was. We're going to think about every way we can to honor the memories of the lives that were taken, and to strengthen the Jewish people in their memory as we go forward. Manya Brachear Pashman: We planned this series and invited you to speak before the October 7th terrorist attack in Israel and the war with Hamas that has unfolded since. At first we wondered whether we should even proceed with this series. How could we focus on anything other than Israel at this moment? Of course, the parallels between the Tree of Life and October 7th are all too stark– Jews are once again being targeted simply because they are Jewish. Can you share your thoughts on this difficult moment for the Jewish people? Ted Deutch: That sense of unease that all of us felt when we heard that story, like how could that possibly happen in the United States, really, it's an unease and fear that we feel when we've watched what's happened in Israel and when a horrific and brutal and barbaric attack takes place against our family, our brothers and sisters in Israel, we feel that here, and especially when it was, it was unthinkable what happened with this Hamas attack. Just as somebody shooting up a synagogue was unthinkable in America, it again, it puts us on edge, and it makes us redouble our efforts. Not just to fight antisemitism, but to really bring the community together. What I've really been proud of since this terrible time in Israel began is the way that AJC has responded, not just in putting out meaningful information to help people get the facts and get through this, and to fight back against lies. But the way that we've really worked to bring the community together. There are 16 million Jews in the world, out of eight and a half billion people we need to stick together. Moments like Tree of Life remind us of that, and what's been happening in Israel absolutely reminds us of that. That informs so much of what AJC does, and has done in response to Tree of Life and certainly is doing in response to the current situation.
Mar 29, 2024
Jewish College Student Leaders Share Their Blueprint for Combating Antisemitism
Hear from two Jewish student leaders at Binghamton University, Seth Schlank and Eytan Saenger, on their experiences amidst rising antisemitism on college campuses in the aftermath of the October 7 massacre in Israel by Hamas. They discuss the strong sense of community among Jewish students on campus, the value of a supportive university administration, and the power of Jewish student-led movements to counter antisemitism. The students also touch on the Binghamton community's show of solidarity with hostage Omer Neutra, a friend of many, who deferred acceptance to Binghamton before spending a gap year in Israel and enlisting in the IDF. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Seth Schlank, Eytan Saenger Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: Matisyahu's Message to His Fellow Jews and to the Israel Haters Trying to Cancel Him Unheard, Until Now: How Israeli Women Are Powering Israel's Resilience 152 Days Later: What the Mother of Hostage Edan Alexander Wants the World to Know What It's Like to Be Jewish at Harvard Among Antisemites and Hamas Supporters Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Seth Schlank and Eytan Saenger: Manya Brachear Pashman: According to a recent survey by Hillel, a majority of Jewish college students (56%) say their lives have been directly touched by antisemitism on campus since October 7. Likewise, AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2023 Report found that 20% of current and recent students reported feeling or being excluded from a group or event because they're Jewish. That figure was only 12% in 2022. That's one of the reasons AJC and HIllel expanded a partnership this week to improve that climate on college campuses and make sure university administrators know how to support their Jewish students. We wanted to know what a supportive campus environment looks like. Here to give a student perspective are Eytan Saenger and Seth Schlank, two Jewish student leaders at Binghamton University, the flagship State University of New York. Seth, Eytan: welcome to People of the Pod. Seth Schlank: Thank you. Eytan Saenger: Thanks for having us. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm hoping you can share with our listeners what it's been like to be Jewish on campus there in Binghamton. Can you kind of give us a picture of Jewish life on campus both before and after the October 7 attacks on Israel by Hamas? Eytan Saenger: So the Jewish community at Binghamton is known to be one which is very strong. There's roughly over 4000 Jewish students overall. Many students are active in Jewish life. On Friday night, you can find over 500 students having dinner at Chabad, you can find hundreds of students involved in prayers, either on a daily basis or over Shabbat or different holidays and things like that. Events that you see on campus with the Jewish community are packed and bustling all the time. You walk to class, you see people with kippot, Israeli flags. Really, you know that you're a part of a college that is a place that is welcome for Jewish students. And certainly on October 7, was something that was needed for us as a community to know that we have people to turn to and, obviously, we're in the middle, we were in the midst of celebrating a holiday, which is supposed to be a joyous holiday, celebrating the beginning anew of the reading of the Torah, we were supposed to be dancing, singing, having food, having a good time. But instead that very quickly turned into a realization of the facts and things going on in Israel. Acknowledging that there was the most Jews killed in a single day since the Holocaust, which of course dampened the mood of, especially for people like myself, who had just spent a year in Israel, the previous year. And felt such a deep connection to the people of Israel, to the land, to the whole fabric of the society there, and have family there, and things like that, where it's like, really, there was a worry of everything that was going on and trouble and processing everything that was happening. Manya Brachear Pashman: What was the response on campus in the aftermath? Eytan Saenger: We saw the whole community come together. Within the first 24 hours after the holiday ended, we held a vigil in main campus with over 700 students gathered from the community, people from outside the community as well, who were there to stand united, together. Our Rabbi actually where Seth and I, where we go to a lot of the prayers on Shabbat and the community we're part of, the OU-JLIC community, he actually went back to reserves to fight in Israel within 24 hours and was fighting there and was actually away from Binghamton, away from the students in the community, away from his wife, away from his family for almost eight weeks, in the immediate aftermath. And so that definitely had an impact on us and was something on our minds continuing throughout everything that was going on. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm going to interrupt you here and note for listeners that You're talking about Rabbi Ben Menora of the Orthodox Union's Jewish Learning Initiative on Campus, a father of 5, and a commander in an IDF infantry reserve unit. Go on please. Eytan Saenger: But we were able to look towards the fellow people in our community, who you felt the responsibility for knowing that we were all going through a tough time together and knowing that we all had some connection one way or another to things that were going on. And so people were there for each other, people continue to be there for each other and people are still doing things to be there for each other as the war continues to progress. And I'm sure we'll go more into this later on, but also the fact that we had an administration who from day one showed up for the community, was at the vigil on day one was at Chabad, the first few weeks, and really went out of their way to show that we know what just happened, we acknowledge the severity of it. And we are here for the Jewish community, even when, and this has been explicitly said by the president himself, even when we know that other administrations at other universities are not there for you at the same time, but we know it's our responsibility to be there for you. Seth Schlank: Yeah, I would say in all aspects of a community, whether you're walking down the Spine, the main part of campus, you see all these Jewish students, whether it's an organization who's tabeling for event that has a connection to Israel, or it's the administration showing up at Hillel for dinner, to spend some time and just talk with you about how you're doing, and how you how the administration is doing their part in making this tragedy and calamity in Israel. Um, for us being so far away, having a very large support system and be able to have someone who we know has our back is amazing. Manya Brachear Pashman: As we've learned, no university is immune from antisemitism. I understand the Boycott Divestment and Sanctions movement has tried to make inroads there in Binghamton this year; some students have encountered antisemitism online or at protests and hostage posters have been ripped down. So it's by no means peachy keen. Eytan Saenger: So definitely, as Seth and I have both said, we are very proud of the strong Jewish community we have here. At the same time, of course, there are still things which are on the minds of students when going about their lives on campus. In terms of whether it's a rally held, chanting slogans, which obviously do not make use for students feel any more welcome on campus. Whether it's an event that was being hosted with a pro-Israel speaker that was met with signs around a room, saying that you guys are complicit in genocide or things like that, which definitely make students think twice, sometimes about, Okay, do I want to be going to this event? Am I in a class with a professor who may judge me a certain way, because I share my stance or things like that? And so that's definitely, unfortunately, not something that we can say does not exist here at Binghamton. There have been circumstances of protests, of specific incidents that have occurred, where different students feel different ways about those incidents about those protests and things like that. And some are, let's say more nervous when they walk around and things like that. But I think what we both agree on here is the fact that the overall nature of the campus climate and with the administration support has been one comparatively more welcoming towards Jewish students. I personally do not feel scared to walk around campus with my kippa on, I'm not hiding my Judaism when I'm walking around campus. Which doesn't doesn't overshadow the fact that there are incidents which cannot be ignored and cannot be understated, but it's definitely something that is presently being thought about. Manya Brachear Pashman: Eytan, you mentioned that you spent time in Israel between high school and college. Is that common among the Jewish community at Binghamton? Eytan Saenger: Yeah, so, both Seth and I have spent gap years in Israel, there's a really significant population of Jewish students here who have spent gap years. Also because Binghamton gives credit for spending a gap year in Israel, which is a really helpful tool to a lot of students, who, let's say, are really interested in taking a gap year, but are worried about it delaying their college process more. My program alone, last year, I was at Orayta, which is a yeshiva in the Old City of Jerusalem. And there's eight students at Binghamton who were on my program alone last year, and there are plenty of others from different programs across the country, who are at Binghamton as freshmen and then, of course, later on as well. And so that connection to Israel, of course, is stronger for those who spent a full year there. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I do want to highlight that there is a personal connection between Binghamton and the horrors that unfolded on October 7. Seth, you are friends with the family of Omer Neutra, one of the eight remaining American hostages being held by Hamas in Gaza. He was accepted to Binghamton with plans to attend but joined the Israel Defense Forces during his Gap Year. Seth, what else can you tell us about Omer? Seth Schlank: I've always looked up to Omer, as someone who really understood and knew what it meant to lead. I was a member of his USY chapter when he was the president, when he was on board there. And he moved up a level. And he came on the board of the division, the Long Island division. Then he eventually became the president of the entire [USY] New York region. And I think that for me, it was really always natural to see him at the forefront in the room, but also being able to have a conversation with everyone in the room and being able to make everyone there, laugh, smile, and really be proud of themselves and be proud of their Judaism. Omer also valued Israel of course, I mean, that was probably one of his, still is, one of his main connections, one of his driving forces. Both his parents are Israelis, he's the grandson of Holocaust survivors. He was always smiling. He really enjoyed, you know, friends, family, basketball, big sports guy overall. And we know that he had a connection to Binghamton, and we know that he was accepted here and we want to make sure that this was a place where we can acknowledge that and acknowledge that it's not 5000 miles away. This is something that has happened right in our own campus and someone that we know that we can bring to the forefront. Manya Brachear Pashman: And that brings me to the event in the university's basketball arena last month, it was organized by the Zionist Organization there at Binghamton and Omer Neutra's family. Can you tell us a little bit about how many people participated and who participated? Seth Schlank: Yeah sure. So before the event, we had a gathering in the parking lot of the event center where the game was being played. We had about, say 150-200 people at the game itself. So we all gather in the parking lot. We heard from Shira Kohler, who is a family friend of Omer. And whose brother [Ira] is a lone soldier in Tzanchanim, he fought in Be'eri in the first days of the war. Ira's fighting for Omer and all the hostages. Ira's time in Gaza is very personal. And Hannah Slavsky, another one of Omer's friends from Plainview, who grew up with us. As well as Bailey Kahn, whose brother was on the volleyball team, where Omer was a captain. And they all spoke about different parts of Omer and about who he was. And then we finally heard from Omer's father Ronan made the trip out to Binghamton and was able to kind of bring us all together and share a bit about his son and was able to thank us for our tireless work. Obviously we want to thank him but we were definitely doing this really, all for all Omer. Every single part of this event was something that we wanted to make sure that like Omer was present at. So from there we went down to the basketball game. Throughout the game, we held up signs,with pictures of Omer from his time in high school, where he was wearing his Binghamton gear. And showcasing him and his connection to this university, really made it a special event. We had the tagline, the hashtag Bing Stands with Omer. And really, that was the whole main part of the event was that we are here with him with his father, with his family, and we're here for you, Omer. Manya Brachear Pashman: The pictures I saw of the fans at the basketball game were so incredibly moving. The spectators holding up pictures of Omer as if they were watching the game with him, it was really quite sweet to see. Were most of the students who participated in the event Jewish? Seth Schlank: I think while we had a lot of Jewish students, there were definitely a couple non-Jewish friends who were able to join. A lot of students grew up in that New York area here. So a lot of them felt connected, Jewish students felt connected. Or they went to this camp, worked at Ramah Nyack, went to Solomon Schechter, and was part of USY. So a lot of people here know him through one facet of life or another. And so a lot of students that necessarily had that connection, and also kids who had never known him, as well as other Jewish students and non-Jewish students who joined us. Manya Brachear Pashman: How has the university's connection to Omer affected the climate there on campus? Eytan Saenger: So, as I mentioned, from the first 24 hours of October 7, the community here was immediately getting together and putting together different rallies, different vigils, different events, and things like that. But there's something a lot more special, about an event where you have a personal connection too, right? often at the rallies at the marches and things like that. You hear the phrase, right? These hostages are our brothers, sisters, friends, and things like that. And right when our peers and they're walking on campus and they see us, they see us holding signs like that as well. But for us, it's really not hyperbole to say that we have friends there we have family there, because there are people on this campus who are family friends with the Neutras, who know Omar personally, and really when they're saying they want to bring their friends home, they are talking about someone who is their friend, who is someone they've spent time with and they're talking about someone who they've played sports with and want to continue playing sports with. So it's really not an exaggeration, or just something that we're merely saying but really a reality of the situation here that there are people like Omer, who are still held hostage, who have personal connections to people across the country. The reason this issue and the reason this conflict is making such an impact and is something that people are investing so much time and advocating for is because of that reality of who is still held hostage and the connection that they have. And that has certainly shifted and shaped the way that we have come together here at Binghamton and the way we have advocated. And in fact, after we had hosted the basketball game event for Omer, which had received coverage locally, Congressman Mark Molinero, who represents Binghamton actually went to the House floor and made a speech about Omer about his situation, and about the fact that he chose to come to Binghamton University. Based on the advocacy of the community here. And based on the things that we've been doing, to really put his name at the forefront of our efforts and in the forefront of why we care about what's going on. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm curious, and this question is for you, Seth, since you played such a key role in organizing that event in the basketball arena. And you spoke about Omer being such a leader. And I'm curious if these events of the last several months and missing Omer have propelled you into kind of an unexpected leadership role that you never saw yourself in? Seth Schlank: So I think as a leader, I definitely would say, in the roles I've held since high school, whether it's been the chapter president of my USY, or the president of the Jewish student union chapter in Plainview, or now in my role on the JLIC executive board here in Binghamton. It's been something that I've always wanted to do and something I've always saw myself as someone who wants to approach people across the room and want to make sure that everyone feels like they could go up and speak. I think since October 7th, all the leaders that I've been able to look up to in addition to Omer, being able to see that each one of them has brought me to where I am today. Brought me to a place where I feel comfortable being a leader, want to grow myself as a leader even more. And someone who really I think has been a part of that is Omer. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, I'm sure his family so appreciated what the community there in Binghamton did. The pictures I saw of the event in that arena, were just incredibly moving. And I'm sure that when he sees them, he will be incredibly moved as well, when he comes home. So thank you so much, gentlemen, for joining us. Eytan Saenger: Thanks for having us. Seth Schlank: Yes, thank you really for having us. It's been a pleasure to share our story and Omer's story. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to listen to my conversation with Grammy-nominated reggae singer, rapper, and beatboxer Matisyahu. We discussed what makes him Jewish and proud, the impact of October 7 on his musical and spiritual journey and how at almost every show on his current national tour, he has faced anti-Israel protests. The prospect of such protests led three venues to cancel his shows.
Mar 21, 2024
Matisyahu's Message to His Fellow Jews and to the Israel Haters Trying to Cancel Him
"The Jewish people don't really give up. They're fighters. … a vision of peace, and a vision of hope, and of empathy. I really, truly believe that that is at the core of who we are. And that is what we are actually fighting for." Matisyahu's recent show in Chicago was canceled due to the threat of anti-Israel protests. The Jewish American singer's music has evolved alongside his Jewish identity. But one thing has always been clear: He believes in Israel's right to exist. Because of that, he has faced protests at almost every show on his current national tour, and some have even been canceled. Hear from Matisyahu on his musical and religious journey, especially since October 7, and what makes him Jewish and proud. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Matisyahu Show Notes: Song Credits, all by Matisyahu: One Day Jerusalem Fireproof Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: Unheard, Until Now: How Israeli Women Are Powering Israel's Resilience 152 Days Later: What the Mother of Hostage Edan Alexander Wants the World to Know What It's Like to Be Jewish at Harvard Among Antisemites and Hamas Supporters When Antisemites Target Local Businesses: How Communities Are Uniting in Response Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Matisyahu: Manya Brachear Pashman: Matisyahu is a Jewish American reggae singer, rapper and beatboxer, whose musical style and genre have evolved alongside how he practices and expresses his Jewish identity. But one thing has always been clear. He believes in Israel's right to exist, and he has expressed that repeatedly since the October 7 Hamas terror attack on Israel. Since then, he has performed in Jerusalem and Tel Aviv. He has performed for the families of hostages and for students at Columbia University as a show of solidarity for those who have faced a torrent of antisemitism there. But there are places where he has not performed, including Santa Fe, New Mexico, Tucson, Arizona and Chicago, but not for lack of trying. Those shows were canceled by the venue's because of the threat of protests. Matisyahu is with us now to discuss these cancellations and what's behind them. Matis, welcome to People of the Pod. Matisyahu: Hello, People of the Pod. Manya Brachear Pashman: So first of all, I want to introduce you to those in our audience who might not be familiar with your music. And we'll start with the anthem that I associate most with you. And that is One Day. Can you tell us a little bit about how that song came about–when and why? Matisyahu: Well, that song was written in around 2010, I want to say or nine, maybe 2008 or nine. And I was working on my second studio album. It's called Light. And we had turned in the album and the new record executives didn't feel like we had any hits on the album. The album had been based on this story of Reb Nachman of Breslov called The Seven Beggars. And it was a bit of a concept album. So I went to LA and I worked with a couple of writers and tried to write a hit song. And that's what we came up with was One Day, and that song got used in the Olympics in 2010, Winter Olympics on the NBC commercials. So that's kind of what propelled that song into popularity. Manya Brachear Pashman: Popular, yes. But what does One Day mean to you? Matisyahu: A lot of my music is very positive and very much connected to this vision of a Messianic future of peace. You know, at the time, I was very religious. And in my particular group, Chabad Hasidism, the idea of a Messiah was very prevalent in the philosophy. I was living in a space of a vision of a future where the wolf lies down with the lamb and people turn their weapons into plowshares. And that was the thing that I was praying for and trying to envision daily. And so that was the main message of that song at the time. Manya Brachear Pashman: It is certainly something we've always needed, especially now. You grew up in White Plains, NY, in the Reconstructionist tradition, I believe. You found your way to Chabad. Can you talk a little bit about where you are in your spiritual journey now, these days. Matisyahu: I went through a very, very intense relationship with Orthodox Judaism, Chassidus. I started from a home, from a Reconstructionist background, so not Chassidus, for anyone who doesn't know these terms. More of a reform kind of background. And I went to Israel when I was 16, on a Conservative trip where I spent three months there, which had a profound effect on me. And then when I was in college, about 21, 20 years old or so, is when I started really exploring the more Orthodox side of Judaism, and started out with the Carlebach shul, on the Upper West Side, and his music and reading books about Shlomo Carlebach, and the type of person he was and what type of work he was doing. And then from there, I pretty much jumped into Chabad, and moved to Crown Heights and lived in the yeshiva there on Eastern Parkway for a couple of years. And all of that, sort of prior to Matisyahu the singer coming out. And then I spent many years, within 10 years or so, sort of exploring Chabad and then Breslov and different types of Hasidism. Different types of Chassidus within that realm. And I guess at some point, it started to feel a little bit, not constructive for me to be there and felt more claustrophobic. And I felt that I was not really connecting so much anymore with a lot of the ideas and a lot of the rules. And so I started to just kind of live more of like a normal life, I guess, or a non-religious life. And I'm still doing my music and making my music and writing from a place of deep Jewish yearning, empathy, and hope, you know, and using lots of the canon of the Old Testament still, to use as metaphors in my lyric, writing, and stuff like that. But more focused on more of a humanistic kind of approach to the world, less concerned with my religion, or God, or being Jewish and more concerned with, you know, writing about being a father or a husband, or dealing with addiction, or dealing with loneliness, or dealing with different ups and downs of life. So that for me was a process going through that over the last maybe 15 years or so. And then after October 7, you know, I mean, I've had some issues before, in 2015, with the BDS. I was thrown off of a festival. And so there again, I felt a very strong sense of Jewish pride when that happened. And especially like, when I went to Israel, after that had happened, I felt this sort of new connection with Israelis in the sense that a lot of them, writers, singers, actors, whoever, get shut down when they go overseas to try to perform. And so I felt like I had a strong connection with them and understanding of what some of them go through. And I guess that only reinforced my connection with Israel. Then after October 7 happened, it's been this very, very strong pull back towards feeling very Jewish and feeling like that is the center and the core of who I am, and especially right now, that's what feels the most powerful and authentic to me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you have been to Israel since October 7, performing for soldiers on bases, hospitals, visiting some of the kibbutzim targeted by Hamas, the Nova festival site. Did it scare you to walk those sites? Can you share how you felt or what you took away from that experience? Matisyahu: I don't know that I was scared when I was there. I was obviously touched profoundly by the stories that I heard and what I saw firsthand, so it was more of a feeling of just destruction. And then just seeing these incredible human beings that had just survived and are just the most amazing people. And then there was this feeling of hope and this feeling of wow, look how these people come together and how I'm a part of that, and that became a really strong place for me in terms of finding hope for my tour and going out into America. And dealing with cancellations and protesters and stuff like that. So I really wanted to try to grab that feeling that I had when I was in Israel and sort of bottle it up and take it with me and sort of get drunk on it at my shows with everybody and make everyone feel like there's a place where they can feel comfortable to be Jewish, and they can feel okay with being a supporter of Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you feel that your colleagues in the music industry understand that and understand where you're coming from? Matisyahu: Well, some people seem to silently understand it, and I'll get some texts and stuff from some people here and there. But no, I don't think people do. I think there's really for the most part, as you see, the mainstream art world and music world either doesn't know where they sit, or they're not supporters of Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you think if they went to Israel, they would have a different perspective on that, that it would shift that mindset? Matisyahu: Absolutely. I mean, any person like, in my band, who's ever come to Israel, been with me, who's not Jewish, or is Jewish, but has had no connection, like didn't have parents or grandparents that taught them about Israel. Or didn't have that experience of going to Israel, like I did when I was 16. I think anyone who goes to Israel feels a connection to this, and especially, especially now, you know, there's no way to deny it. I don't think. Manya Brachear Pashman: So, is it important for Jewish celebrities in particular, or influencers, to speak out about the violence on October 7? Matisyahu: See, I think it's important, because it's important to me, you know. But what I've learned is, there's no point in getting angry at people thinking that it should be important to them, if it's not important to them. And if they're not speaking out, and it's because of fear, then the fear is larger than how important it is to them. And everyone has to deal with their own stuff, you know, but to me, it seems that the fact that there's such a lack of people speaking out is a symptom of a sickness that the Jewish people may have been carrying, that just seemed dormant for some time, which is that somehow that it wasn't important to to a lot of American Jews. So for me, it was just like, tapping into what is the feeling after October 7, and it was immediate, and it was in my bones and in the depth of the core of my being. And I feel very blessed that, on my journey in life, I was able to connect that deeply, to being Jewish, and to Israel, and realizing how those things are connected. And I went on a journey, like I didn't come necessarily from a place where that was instilled into me, you know, to some extent, it was, you know, but I went on my own journey, and I spent a lot of time you know, sifting through all of that and figuring those things out for myself. And so I feel blessed to be in the position that I'm in where I know kind of who I am and what I believe, and people can take strength from that. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I lived in Chicago for 15 years so I'm very familiar with the House of Blues as a venue. I loved going to see shows there and was heartbroken to hear that The House of Blues canceled your recently scheduled show. I understand that they paid the contractual penalty, you're going to donate that to an organization that advocates for the return of Israeli hostages held by Hamas. But can you tell us a little bit about the conversations you had with them, or with Chicago police or anyone else prior to the cancellation, and what explanations were given? Matisyahu: Well, I'll go into it a little bit. I mean, there's still some confusion as to exactly what happened. But I essentially got a call from someone high up at Live Nation saying that the show needed to be canceled because of a lack of police force. And then with a friend of mine, David Draiman, who's the lead singer for a band Disturb also from Chicago with a lot of his close friends, we were able to explore that. And it seemed as though the police department was aware there was going to be a protest, but that they were not concerned. So then it became a mystery as to where's the concern coming from really, which then led us to this whole Alderman thing, and then we thought it might have been this one. But now then, you know, turns out maybe it was other Alderman that were putting pressure on the police force or on Live Nation. And so there's, there's some mystery and honestly, as much as it is important to find out where this is coming from. And so how we can try to stop it. It has not been my main focus in this past week. This past week, I was out on tour, I played four shows, there were protesters at all of them, except one, Salisbury, Massachusetts. And all four shows went on, and they all sold out. And they were all really powerful. So what happened in Chicago was pretty devastating for us. Because, you know, it's scary to think that people are making choices and being able to shut down huge organizations, and creative expression and artistic freedom. So it was devastating. But, you know, we bounced right back and jumped right back into tour. I got another big week of shows this week. So that's basically all I know, to tell you the truth. And while I would love to point the finger and say it was this person or that person, what I'm learning is, as things start getting uncovered, you know, it's hard to know, I'm not an investigative reporter, but I'm sure that like, it's tricky finding out what the real story is a full time job probably. Manya Brachear Pashman: Were there similarly mysterious circumstances surrounding Tucson and Santa Fe? Matisyahu: No, that was less mysterious. And in those cases, it was a little more clear as to what was going on. In Santa Fe, it was literally staff members that didn't want to come to the show. And for whatever reason, let the venue know at the last minute. There may have been someone at the venue behind that, we don't really know. And then in Arizona, it was, seemed like it was more from the promoter, or the buyer of the show where people were putting pressure on her to cancel the show. Manya Brachear Pashman: I asked you a bit ago, if it was important for Jewish celebrities or influencers to speak out about October 7 violence? I'll ask you instead, is it important for them to speak out about this kind of cancellation or censorship or limitation on creative expression? Matisyahu: I think so. You know, because it's like that old story, they came for, they came from me and these people, and I didn't say anything, they came for these people. And then they came from me. I mean, that's what we see out here. You know, that's what that's what artistic expression, creativity is about, it's about being able to express your views and your ideas through music. It's peaceful, you know. So, it's unfortunate. It's what we have to deal with. There are people that realize how important it is. And those people like David are really trying to help and trying to be outspoken and there are a lot of Jews out there that understand how important this is. I'm feeling support from most people, but not enough. For sure. Manya Brachear Pashman: Speaking of creative expression, I am curious whether October 7 has influenced any of your musical creation, songwriting, how has that influenced the creative process for you? Matisyahu: One way, I have a song that's coming out it's called Ascent, and I wrote it before October 7, but after the Kanye antisemitic lash out and it's about antisemitism. So while I was in Israel, we shot the video at the site of the Nova festival and in some of the kibbutzim and with some of the survivors, so that is like one very obvious way in which I was influenced. And that video kind of takes footage from the Holocaust and World War Two and intermixes it with October 7 footage as well. And then in terms of my own music, last year, I recorded about 40 songs, and started releasing them with this EP. But I kind of like right when all this began, right as I was starting touring, so it's sort of, for me a different creative hat, like a bit of a different place than writing. So I'm not writing new material, but I'm performing the new songs along with old songs. And what I'm finding creatively is that a lot of the lyrics and a lot of the themes, even though over the years, some of them have been personal, they all kind of connect and tie into the greater story of the Jewish people, and the obstacles that we face. And our survival. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's one of the reasons why I brought up One Day, is I loved the song back when it came out. But it does take on a whole new meaning when you listen to it today. It's very powerful. This is not the first time that your shows had been canceled due to anti Israel sentiments, I believe it was in 2015, there was a music festival in Spain that canceled your appearance, when you wouldn't promise to bring up Israeli politics on stage. Instead, you toured a dozen American college campuses that year. And I'm curious what you learned from that experience that you're applying to now? And also what you've learned on some of these college tours? Matisyahu: Well, that's a great question. Because for a lot of people all this is like the first time they're experiencing it. And I feel like part of the blessing of my journey that I've had is that I have gone through this to a lesser version. Like you said in 2015. What they wanted me to do was to sign some kind of document saying that I was against the atrocities of Israel. So I wouldn't sign that and that was the same thing. It was like, No, I'm not going to do that. Like, that doesn't that doesn't line up with who I am. I mean, I don't care honestly, what this statement is, I'm not going to sign something, I'm not going to be singled out as the only artist out of hundreds. That's being forced to sign something, because I'm Jewish, or because of my belief system. So I just kind of played it cool. You know, I was just like, No, I won't do it, and they threw me off the festival. It was like this story of Purim, like, they were trying to hang Mordechai. But Haman got hung really. They were patting themselves on the back, like, we threw this guy off the festival. And then there was an uproar about it. There were backers that were pulling out of the festival. And so they ended up having to apologize. And asked me to come back and still play the festival, all this happened within three or four days. And so I did go back, and I did play the festival. And, and then I went to Israel, you know, and then I went on this college tour, with Palestinian artists. And we went and performed together because we felt that was an important thing to do. So I think from what I learned from that was sort of like this idea of sort of, like trying to just be like water. If I just sort of do what feels what the right thing is what I feel is the right thing, and just don't kind of lose my cool. And I'm able to just sort of move within it, then basically, it's going to come out in a way that hopefully, will be victorious. And that's been my strategy so far with this tour as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: So my last, my last question to you is, we talked about your journey, your faith journey and your musical journey. What makes you Jewish and proud today? Matisyahu: You know, you see, the Jewish people don't really give up. They're fighters. And there's always, in my mind, I believe, a vision of peace, and a vision of hope, and of empathy. I really, truly believe that that is at the core of who we are. And that is what we are actually fighting for. Even when the rest of the world is trying to say that we're the monsters, we won't let that stop us. Nothing will stop us. It's just who we are. Manya Brachear Pashman: Beautiful, thank you so much, Matis, for joining us. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Israeli filmmaker Shifra Soloveichik about her digital initiative Women of Valor: Women of War, portraits of individual Israeli women during this challenging moment in modern Jewish history.
Mar 14, 2024
Unheard, Until Now: How Israeli Women Are Powering Israel's Resilience
In the days following October 7, Israeli filmmaker Shifra Soloveichik felt hopeless and hated, but not helpless. Inspired by women around her, she launched a digital initiative called Women of Valor: Women of War, to spotlight unheralded women with extraordinary stories during one of the most difficult moments in modern Jewish history. To mark Women's History Month, hear from Shifra about how she is giving a voice to Israeli women whose stories have gone unheard. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Shifra Soloveichik Show Notes: Learn more: Women of Valor on Instagram Senai Geudalia's Story on YouTube Sarah Lopez's Story on Instagram Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: 152 Days Later: What the Mother of Hostage Edan Alexander Wants the World to Know What It's Like to Be Jewish at Harvard Among Antisemites and Hamas Supporters When Antisemites Target Local Businesses: How Communities Are Uniting in Response How A 10/7 Survivor is Confronting Anti-Israel Activists on College Campuses Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Shifra Soloveichick: Senai Geudalia : So I'll start from the day before. It was Friday, October 6. That night was really fun. We were dancing in the street from place to place, like you know hakafot here, hakafot there. And he was like being so like himself, times 100. Hugging me and dancing with me and just, at the sea of Yosef, like that was Yosef in a bottle, like celebrating his people, celebrating the Torah and being with his family, like that was the peak of Yosef. You know, they say the neshamah [soul] knows 40 days before. So that to me, like he was like getting all of it in. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's Senai Geudalia, whose husband Yosef was killed on Oct 7.In the uncertain days following the outbreak of the war between Israel and Hamas, Israeli filmmaker Shifra Soloveichik felt hopeless and hated, but not helpless. She used her craft to launch a digital initiative called Women of Valor: Women of War, an opportunity to lift up the Jewish women of Israel and share their stories of courage and perseverance. To mark Women's History Month, Shifra is with us now to discuss Women of Valor: Women of War. Shifra, Welcome to People of the Pod. Shifra Soloveichik: Hi, thanks for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: You have shared a little bit about the genesis of this project on your social media. You felt self conscious, scared, like a lot of us did after October 7. Can you share how you channeled that fear? Shifra Soloveichik: So on October 7, myself, and like many Israelis, we woke up to sirens. My husband was immediately call for reserve duty that morning. And it was a very scary feeling. Because I had never experienced anything like that before. I grew up in the States. I moved to Israel when I was a young teenager, so my entire relationship, my husband, he was never in the army, so I never had that sort of experience within my relationship. The only word I can describe I could use to describe how I felt was scared. It was a very scary day. I remember being scared to walk to my in-laws house that they live very close by because there were sirens every other minute. And we lived in an area in Israel where there aren't usually a lot of sirens. So we knew things were going on. We also are observant Jews. So if we couldn't check our phones, we were keeping Sabbath. So we weren't able to understand what was going on. We were just hearing from people talking on the streets. We heard that maybe there was a terrorist infiltration, but we didn't quite understand the scope of what was going on. And my husband left. I didn't know what to do. I didn't realize that from that day, he would be in reserves for four months, and our entire lives completely changed. And just the first few days of the war was incredibly terrifying, because only after Shabbat did we realize what was going on. And over the next few days, did we realize what was going on. And there were two aspects that were very fearful. One was that physically what my entire life changed within a few minutes. And I was living, I wasn't living at home, I was scared to be myself. My husband wasn't at home. There was a physical war going on. I didn't know where he was going. On October 7, we didn't know anything. So it was just a very logistic reason to be afraid. And then on top of that, I would go on social media and I would scroll through Tiktok and Instagram and see, at the beginning level of support. But even then, there were a lot of people who were saying very hateful things calling what happened on October 7 a resistance. So there was just that aspect of fear. But there was also this very genuine fear of being scared of being a Jew and experiencing a level of hate that I didn't know was humanly possible. So I had all of these feelings of, of fear, and also hopelessness. And the only thing that got me through that time was being with other women whose husbands were also in reserve duty, being with family, being within a support network where we would sit around, and we would knit and we would talk, all of our schedules were all gone. We didn't have school, we didn't have work. We didn't have anything to do except wait around all day for our husbands to call us and just be scared. So that support system is what got me through. And it inspired me. And throughout living in Israel and reading the news stories of the horrific tragic things that were happening, I was also finding so much strength and the connection between the Jewish women that I was experiencing in my community as well as stories of Jewish women who were so brave and powerful, and empowering in their own right, in different ways from the war and those women would inspire me as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I love how you describe the subjects of women of Valor, –ordinary women who do extraordinary things, because that's often how I define the religion stories that I pursue–ordinary people who do extraordinary things inspired by their faith. What are some of the other extraordinary stories you have collected so far? Shifra Soloveichik: Yes, absolutely. So, Iris Haim, the mother of Yotam Haim, who was abducted from his home in Kfar Aza, and was in Hamas captivity and ran away from his captors. He was killed by IDF friendly fire, a situation that is just so unbelievably awful and horrific. And we interviewed Iris Haim as part of the Women of Valor series, but I think she's an embodiment of looking at evil in the eyes and still saying that she doesn't blame the IDF. She doesn't blame her people. And that at this time, we need to come together and be one family, which I think is something so difficult to feel sometimes during such hard times of war. But even more so after such a horrific tragic loss, she was able to, and she continues to inspire people through her perspective and her power. And I think in general, the women that I've been bringing, that we've been wanting to show a light or showcase on the series are women who, who are not letting their pain define them. Rather, they are taking the next step to be empowered through their story. I think in general, with everything that's happened since October 7, there's been so many awful tragedies that have happened to our people, to the Jewish people. And it's very easy for us as a nation to connect through the pain and connect to each other and feel each other's pain and kind of sit in the pain. It's more so, these women are letting their power, they are choosing to let that define them. And I think that's a really beautiful part of this platform that we're creating, which is connecting other women to our strength and to the beauty that comes along with the pain but it's not letting the pain and the evil define who we are. Sarah Lopez : Two weeks after October 7, I found out I was pregnant. I was honestly shocked and the joy that I felt was such a juxtaposition to the pain that I was feeling that it almost felt kind of wrong. My husband was in miluim at the time and I surprised him when he got back. For us it was like this little flame of light and joy during such a dark time. Now I don't feel like this is just another baby or I'm just another mother. Now this feels like a mission, it feels like a shlichut, to continue our Jewish legacy and bring life after we lost so many. It's kind of like a sign to our enemies, because us Jewish women, we're not gonna stop being strong and powerful. We're not going to stop living and giving life. Because we are women of valor. Manya Brachear Pashman: How did you find the women for this project, like Sarah Lopez, who we just heard from? Shifra Soloveichik: So we have two different parts of the project. We have documentaries, as well as a social media platform. They kind of work together, but they are kind of different entities in the sense that and the documentaries, I have four interviews with women that I specifically wanted to show their narrative, and our social media is open to everyone, any Jewish woman can send in her submission of what her life has been like since October 7, or how she defines what a woman of valor is. So with the submissions, we have so many women just sending us stories and ideas and thoughts. And they send it through asocial media form, in a social media structure. So they'll send you their reels, or posts or written posts or captions, and so many different ways. And that was just very organic, we post on our stories that we would love for you to share your story. And it comes to us. And it's just a beautiful initiative and way for us all to connect and feel seen and heard. And for the documentaries that came more from a film background of just research and reaching out to specific women that I wanted to amplify their voices. And that was our production team working on that. And that was more from things I saw on the news as well as friends of friends that I was inspired by and I was like, you know what, I need to share her story. So it kind of happened in that organic route as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: This project in many ways highlights how women are overcoming the unique challenges that face them in the aftermath of October 7. Could we talk a little bit about those unique challenges but also the added affront of doubt that Israeli women faced unspeakable crimes. The UN recently validated the claims of sexual violence against women by Hamas, for example. That seemed like an additional layer of trauma that Israeli women had to endure even if they weren't directly affected by it. How do you see Israeli women responding to those kinds of challenges as well? Shifra Soloveichik: The lack of condemning the sexual violence on October 7 was very hurtful, but I wasn't. I would have seen it coming. I wasn't surprised. Because just from the general feeling that and especially that's something I experienced a lot on October 7 was that everyone is kind of out to get me, like why would anyone believe me? No one understands me. I think there's a general feeling of misunderstanding amongst Israelis in general amongst all Israelis, not women and men alike. I think it's just or it's not something I was surprised by, which is very painful to say. I think what Israeli women are experiencing, specifically is kind of an understanding of where our priorities are and what we need to focus on in order to be strong and be strong for our husbands, for our children, our parents. There are a lot of Israeli women who are, who are soldiers and are in reserve duty, but also a lot are kind of also undeserved duty from the other end of supporting the war from a more spiritual and emotional perspective. I think that is the biggest challenge of kind of just not letting anything faze you and being focused on how can we continue the conversation? How can we continue our lives in a healthy way? I think if I were to sit and think about all of the injustice since October 7, I don't think I would be able to have it within myself to create a platform like this necessarily, because it's just so disappointing. But unfortunately, not something that I would have expected otherwise. I yeah, I think that there's a lot of immense trauma going on right now. Amongst all Israelis, I think I don't know the exact statistic. But most Israelis suffer from some form of PTSD. And I think when we let the outside voices kind of define our narrative,it just makes it harder. Like it's harder for us to kind of focus on how we continue, how we grow. Manya Brachear Pashman: You have described this war as not only one of physical violence, but as a spiritual battle against the essence of our existence, those are the words that you used. The existence of the Jewish people, is that what you mean by that? Can you explain it a bit? Shifra Soloveichik: It can be defined as against the existence of the Jewish people, but I don't think you necessarily you don't have to be Jewish to be an Israeli and to be part of this narrative. I think there are so many Women of Valor, who are not necessarily Jewish, they can be Muslim, Christian, and they live in Israel, and they are also experiencing tragedy from this war. I don't think it is particularly only a Jewish concept. But I do think that the general narrative against the essence of existence as Israelis and Israeli Jews is kind of what's going on. The spiritual war is that, it's part of the narrative that Israel should not exist. And the battle that we're fighting is, why shouldn't I? I deserve to live too, I deserve to be part of this, I deserve to live freely, why is this part of the conversation? And I think that's more of the spiritual aspect of kind of standing up for our rights to exist as a Jew, wherever I want to live. If it's in America, if it's in Israel, if it's in Canada, I have a right to exist. Manya Brachear Pashman: And do you see women in particular as fighting this spiritual war? Shifra Soloveichik: I believe that women are the spiritual leaders. I think from history and from the Bible that's how I've always connected to the role of women in Judaism, is that we are spiritual warriors throughout all the generations.I see it on a on a general scale, but on a very, very personal level, just me being at home while my husband was at war. It did feel like something out of the Bible, like what people talk about. I was just at home and you think, what do you do at home, when your husband's at war, it's just such a odd concept. And it just feels so traditional in a sense. And that reality was just very eye opening, of what is my role in my home. And I think highlighting that aspect, that more traditional role as an empowering thing, because that in my personal journey, that's kind of where it brought me, has just been, I think, giving a voice to a lot of women and saying, you know, stuff like your role in whatever you choose to do, whether that's be a warrior, or be a wife, or be a mother, be a commander in the army, like these are not contradictory things. I interviewed someone named Shifra Buchris, who is a mother of 10, who's also commander in Magav, in the border police, and she's also religious, and she also, saved tons of lives on October 7, she was driving back and forth from the Nova festival, just saving lives. I think people kind of can see it as a complex idea of like, what is a woman of valor? What is what makes someone a spiritual warrior? And I think it's just, it's, it's anything, it's anything if you're a woman, and you're, and you're fighting, in whatever way you're, you're a woman of valor. And she's a great embodiment of that, that kind of like, oh, is this? Are these identities complex? Are they contradictory? And it's, it's honestly, it's not. We are all living here trying to be there for our families, be there for our our friends and our nation. Manya Brachear Pashman: Why focus on women? Shifra Soloveichik: As an Israeli Jewish woman, I see a lot of emphasis on the men in our society. And I think also as a whole. Just growing up, I haven't seen so much representation of women voices that I connected with. I think it's specifically in Israeli society, there's a big emphasis on the military, it's more of a patriarchal society, I would say not necessarily in a bad way. I think it makes sense in the context of us having a lot of wars, and there's just a lot of emphasis and an honor placed on our male soldiers, because of what they do. And it's incredible, and they are protecting Israel. And it makes sense. That idea that I had with this project was to give voices to those who are not necessarily being honored or applauded, whether that's in the general society or even within our consciousness, I think, just giving a voice to people who have inspired me and inspire countless others, but you wouldn't look at them walking down the street and think, oh, yeah, they're super inspiring, and they're so strong, because I think it's more of a internal strength as opposed to like an external battle. And I think giving a voice to those women and those and that narrative has just been very empowering for me personally, and that's really what I hope to share through this platform. Manya Brachear Pashman: Shifra, thank you so much for joining us. To learn more about Women of Valor, check out @ValorStories on Instagram and Youtube - links are in our Show Notes. Shifra Soloveichik: Thank you. Thank you for having me.
Mar 7, 2024
152 Days Later: What the Mother of Hostage Edan Alexander Wants the World to Know
"Listen to me, Edan. I'm here. I'm with you. I love you. Just protect yourself. Just be safe." These were the last words Yael Alexander spoke to her then-19 year old son, Edan, on the morning of October 7, 2023. Edan, an IDF soldier stationed on the Gaza border, was later taken hostage by Hamas terrorists. Yael joins us from her New Jersey home to tell her story of pain, uncertainty, and anguish over the past 152 days. This week, as President Joe Biden delivers his State of the Union address, she will be among the 17 American families of hostages taken by Hamas into Gaza on October 7 that will be in attendance at the U.S. Capitol. Visit AJC.org/BringThemHome to urge Congress to keep pressing for the release of the hostages. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Yael Alexander Show Notes: Music Credits: Dramatic Piano and Strings by UNIVERSFIELD is licensed under a Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . More Analysis and Resources: Hostage Families Will Attend the State of the Union. Here's What to Know. Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: What It's Like to Be Jewish at Harvard Among Antisemites and Hamas Supporters When Antisemites Target Local Businesses: How Communities Are Uniting in Response How A 10/7 Survivor is Confronting Anti-Israel Activists on College Campuses Tal Shimony Survived the Hamas Attack on the Nova Music Festival: Hear Her Story of Courage, Resilience, and Remembrance Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Yael Alexander: Yael Alexander: I told him at the end of the call: 'Listen to me, Edan. I'm here. I'm with you. I love you. Just protect yourself. Just be safe.' And that's it, we hang up. I didn't know I'm not gonna hear from him again. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's Yael Alexander, the mother of Edan Alexander, one of eight Americans still held hostage by Hamas inside Gaza. I recently visited the family's home in Tenafly, New Jersey, a small suburban town often dubbed Little Tel Aviv for its relatively large Israeli population. Throughout the town, there are reminders of the deep connection between its residents, the Jewish state, and its ongoing war with Hamas. A billboard downtown featuring Edan's picture. A weekly walk for the hostages not yet home. A moment of silence at the start of every school day. Signs of support staked in front lawns. As of this recording on March 7, 2024, it has been 152 days since Yael spoke with her son Edan. Those days have been a constant whirlwind of meetings, trips, tours—all in an effort to bring him home. Most recently, the family went to Israel for a painful look at where Edan was at the time of that last call. At the State of the Union address in Washington D.C., Yael and her husband Adi will join 15 other relatives of Americans murdered or kidnapped by Hamas, as guests of a bipartisan group of members of Congress. Yael Alexander: They told us it's gonna' be a long process, but I didn't imagine you know, I thought after four weeks max, they're gonna bring everyone out. And now we're four months, it's, I don't have words. Manya Brachear Pashman: Edan Alexander, a 2022 graduate of Tenafly High School, was one of two graduates that year who instead of going straight to college moved to a kibbutz in Israel and volunteered to serve two years defending the nation where his mother and father had been raised and his grandparents still live. Yael Alexander: August 2023, Edan came to the U.S. for four weeks. He came to visit us, to spend time with his friends from college. Everyone was here in Tenafly. So, it was like the best opportunity for him and for them, like after their graduation to be again. And it was the best vacation ever. And when I drove him to JFK. I told him: Listen, Edan, I really want to come and visit you during the holidays. And I told him: I'm gonna' come by myself, Sukkot. So please ask your commander and tell him that mommy's coming and give you some free time to spend time with me. So, October 1, I came to Israel. He came to pick me up from the airport. And we spent the two days together. Manya Brachear Pashman: After two days with his mom, 19-year-old Edan asked if he could return to the kibbutz a little early to squeeze in time with his girlfriend before returning to base. He texted with his mother throughout the rest of the week and Facetimed with her and his grandparents on Friday night, October 6th. He was stationed on the Gaza border. Yael Alexander: Friday night after the kiddush, in our house. He called me and I told him: 'Listen Edan, let's do a FaceTime. And he's like, OK, so I'm like, looking at him and he just looking so happy and great, telling me that he ate some chicken and rice and it was OK. It was fine. And now he's going to sleep because first thing in the morning on Saturday, he needs to get up to his watch.' And I'm like, 'OK, great. So say bye to Grandma and Grandpa and everyone' because we were sitting around the table. And it was very cute of him to change to the FaceTime because sometimes he doesn't want to do it. But this time he was like 'Yeah, cool. Of course. Let's do FaceTime.' And, that's it. Saturday morning, October 7, I'm waking up because my dad is opening the bedroom door and he's telling me 'Yael, you need to wake up. It's an alarm outside. It was 6:30-ish in the morning AM and we need to go to a safe place.' And the first thing that I'm thinking about, 'Oh my God, I need to check what's going on with Edan. So, I'm texting him, What's going on there? Are you OK? Are you safe? And then he's calling me. It was a few minutes before 7 AM. And he's telling me: 'Hey, Mom, we are getting a lot of bombs here. It's like a war. I'm seeing stuff. Terrible stuff. But don't worry, I'm safe. But it felt like all the conversation is start, also he spoke a little bit English. He was sound like he was screaming and full of adrenaline. And I didn't know what he's seeing or what is happening because no one knew. I told him at the end of the call, 'Listen to me, Edan. I'm here. I'm with you. I love you. Just protect yourself. Just be safe.' And that's it, we hang up. I didn't know I'm not gonna hear from him again. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yael called her husband Adi back in the States. He and Edan's younger brother Roy and sister Mika flew to Israel the next day. Still, for days, they remained in the dark, unable to get through to their son's cell phone. Unable to get any information. Yael Alexander: A lot of bad news, like you hearing, you know, all around. A lot of people murdered, horrible stories, like after a day or two you start hearing about these horrible stories from this morning of October 7, and still nothing from Edan. So we went to every forum that it was like, I don't know, it was like … one night, you don't know what's going on, the day after you're working with people on the phone that you never met, and you just trust them they're gonna find your kid. They had some you know, I don't know. Everyone was trying to help you and telling you, go to hospitals. Go and look, because there is a lot of anonymous soldiers or people. Go and look for him. So we've been everywhere like every hospital in Israel, like we went there and tried to understand where is Edan. On Thursday someone is calling me from the army and he's telling me that he's got a message for us. I didn't understand at first. What is this? What kind of message? I'm on the phone 24/7. We couldn't eat. We couldn't sleep, nothing, like in the loop. Like, try to find my son. And then I'm just catching myself like, Oh, my God, you have a message for us? Yes, yes. Where are you? So we are waiting for them. We wait for 40 minutes I think. I couldn't breathe. I remember my head like down, you know, between my knees and I'm just trying to breathe and breathe and breathe because I felt I'm going to faint. I didn't know what they want from me. We met them in this discreet room and then they told us that after they reviewed everything they know that Edan is took hostage by Hamas terrorists and they took him to Gaza. He was guarding a kibbutz that a lot of people got murdered. Thank God, they didn't touch him. They just took him from there. He was by himself. So, it wasn't like a conflict or nothing. Thank God. He was surrendering and they took him. There's something that we know. Manya Brachear Pashman: It was devastating news, but at that point in time, the best news that Yael and Adi could've received because it meant there was hope of seeing their son again. Yael Alexander: So, it's good. And they're looking at me like I'm a crazy person. Because this is the worst message you can ever get as a parent. My son is my life. He is my air, he is everything for me. But to understand that they took him and he's OK. It was like the world. Wow, wow, wow, wow. Now we can work to speak with everyone because he's OK. OK, he's a hostage. But still we have the hope that he will come back home. A day after we had a Zoom with Biden and all the American families. He was really with us, you know, he understand our pain, he could connect to this. He told us, as Americans, we are going to do whatever we can to help you to get through it. Like whatever we can, we are here and we are going to do it. And it was really comforting. It was like we felt the hug. We stayed a total of an hour and a half with the President. It was unbelievable because we were so confused. We just got a day before the message. So, we knew what is the situation with Edan, but a lot of families didn't know what happened to their loved ones. Not everyone knew if they were murdered, if they took hostage. Still it was chaos. Manya Brachear Pashman: 152 days later, eight American hostages remain missing: Edan, Itay Chen, Omer Neutra, Sagui Dekel-Chen, Keith Siegel, Hersh Goldberg-Polin, Gad Haggai, and Judith Weinstein. Both Judith and Gad are confirmed dead. Americans Liat Beinin Atzili and Avigail Idan have been released. 32 Americans lost their lives on October 7. Nearly two dozen more have lost their lives since. Yael Alexander: A few days after, I left Israel with the kids, with Mika and Roy. I felt it was very tough to stay in Israel. I wanted to stay. I didn't want to leave because I felt that I'm leaving my son behind. You know, it's the worst, really, it's the worst feeling ever. But I said to my husband: Listen, it's not healthy here. The alarms, the panic, the worry, it's too much. And they're like in jail, in their house, in my parents' house. So, it's not healthy. I'm gonna go back home to Jersey, and I'm gonna try to have a routine, you know, again, with the schools, with the friends, with the community, like I'm trying to, you know, for them, because it's not healthy. So, my husband spent I think two weeks over there without us. I came back. My sister came with me with her kids and all our friends just was here, like, you know, I'm still getting food, everyone is taking care of us and so caring and loving and you feel the hug. Manya Brachear Pashman: Though Edan's absence is palpable every day, the rhythms of life have not stopped in the Alexander home, though they are frequently interrupted. Mika is waiting to hear from colleges and shopping for shoes to wear to prom. But she's also writing columns about her brother, speaking at rallies, and holding down the fort when her parents are away advocating. Yael Alexander: It's hard. To be 17 and to handle this, and she's doing a lot. After we came back from Israel, there was a big rally in Times Square, New York. And they asked me to speak, and I couldn't. I was like, numb. I couldn't say anything. So, I asked Mika at the same day. And she did it. And it was a great speech, from the heart. And it was in front of thousands of people. And since then, I am amazed by her. It seems like this situation because I'm keeping her also busy. I know that she can handle it, she's feeling like she's helping with the fight to bring Edan home. And this is super important to her. Manya Brachear Pashman: Meanwhile, in addition to traveling with his mother and marching for his brother, Roy is attending middle school, playing basketball, and preparing for his upcoming bar mitzvah, right before Passover. Edan was supposed to come in to New Jersey for that milestone. Yael Alexander: The first time that I saw Roy put the tefillin on and I just start crying because he's not a boy. He's looking more and more like Edan. And he's like, grown up now. I'm very emotional now when I'm seeing Roy. When I'm seeing Roy, he's not my little baby anymore … and I'm remembering everything that we've been through with Edan with his bar mitzvah and how little he was and it's very emotional for me now this time because we are such in pain, but still we are preparing for this, Roy's celebration. You know, bar mitzvah boy. So, it's a lot. It's sad and happy and you still trying to be OK for the kids to see you OK every day. But it's very hard. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yael, who baked cakes out of the family's home, and Adi, a diamond wholesaler, are juggling work obligations, meetings with senators and congressmen, travels to Washington and Israel, and media interviews, all focused on bringing their son home. Yael Alexander: I don't know what's next. Every day everything is so dynamic. I don't know what's going on. Like a day we here, a day we need to go to DC, like this is the thing now. My husband is going to work maybe two days a week now because he can't. We have the zoom. We have the meetings. Suddenly this come and this came. I'm not working obviously. I'm around it all day. All day and all night. You don't want to miss anything. I feel that everyone is really working. Also with the Qataris, also America, also Egyptians like everyone is doing whatever they can to make it happen. I'm really hoping, I'm going to be in Israel next week, I'm really hoping that some kind of miracle. Now I'm praying a lot. A lot. I'm talking to Edan nonstop the whole day but I'm also praying like actual praying and I'm just asking for a miracle. And just to see him, to hug him, to just to feel his perfect face. Just to be with him because, yeah. Manya Brachear Pashman: The Alexander family no longer lives in the house where Edan spent his childhood. They moved a mile away during his sophomore year in high school. Edan never spent much time in his bedroom. He preferred to be in the center of the action, camped out on the sofa downstairs so he could greet anyone who walked through the room. But Yael took me to the room where he slept as a teen. Beside the bed there now is a giant Torah scroll delivered by the local Chabad rabbi, dressed in silver plating and finials that jingle when the scroll is lifted. A prayer shawl is draped over the top. Yael Alexander: So you can see we have a Torah here. It's a beautiful Torah and this is something guarding Edan and is giving him bless to his return. Every morning, I'm coming in here and I'm doing my prayer. And I'm just talking to Edan every morning and I'm sending him a lot of strength in his heart and his soul. And I'm just here with him. And every night I'm saying 'Good night, Edan. I love you. You know, can't wait to hold you. Manya Brachear Pashman: Edan spent most of his young life in Tenafly. A happy-go-lucky guy, champion swimmer for the high school team, and a big fan of the New York Knicks. But he was born in Israel, spoke Hebrew at home, and visited Israel often to see both sets of grandparents. He even celebrated his bar mitzvah there. Yael showed me the photographs in an album she keeps in his room. Yael Alexander: Oy yoy yoy. Yes, Edan. You see? What a celebration. Yeah it's everyone. Manya Brachear Pashman: Still, Yael was surprised when Edan announced his senior year in high school that he wanted to postpone college and try Garin Tzabar, a program founded in 1991 for young Jewish adults who want to explore serving as lone soldiers in Israel's Defense Forces. Edan and 16 other high school graduates, including a classmate in Tenafly, moved to a kibbutz and did four months of training before committing to serve in the IDF. Yael Alexander: He told us that he wants to do the Garin Tzabar. I don't know, I felt proud. You know, because I've done my army. And Adi was in the Army, everyone doing the army in Israel. So, this is something that you do for your country, you know. For me, it was a great experience. It was great for me. And I thought also for Edan because he's doing this for two years and eight months. He's coming back, doing his college. So, Edan chose to do this. I was proud. I was proud. Yeah. I am proud. Not was. Manya Brachear Pashman: Edan's 20th birthday was on December 29, 2023. To call attention to his continued captivity, Yael and his brother Roy traveled to Israel and hosted a blowout celebration with live bands and balloons and media coverage. Yael Alexander: It was really important for me to do a celebration for him, to mark this day, I wanted to everyone in the news in the radio, everyone will speak just about one thing about Edan's celebration, because if he's going to hear something or someone is going to hear it inside, it's going to be the world for me. Because for him to understand that his mom is in Israel and also his brother and we are celebrating his birthday and everyone loves him and miss him so much. It's going to be major. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yael knows she's not getting all the answers about her son's whereabouts and well-being. Still, she continues to meet with whomever will see her and listen to her pleas to bring Edan home. Yael Alexander: I don't think they can give me the answers. But it's important, because every meeting that you are opening your family, your trauma, your kid, like it's connecting them to you, and they understand it and you're still relevant. And this is something that they're gonna think about it and maybe you're hoping that they will work on it, you know, to make the stand, to connect to us. And to do this. Manya Brachear Pashman: During the pandemic, Yael started baking cakes. She loved being in the kitchen and Edan loved it too. But since he disappeared, she has not baked a single pastry. She has replaced dough with clay, sculpting in a quiet corner of the basement where she can disconnect for just a little while and think about Edan. She showed me one sculpture that started as a balloon, but collapsed in the middle. Yael Alexander: Now it looks like a heart and there is like a crack in the middle. And I think this is my perfect piece. It's so imperfect and look like it's not done but I think it's done and I can't wait to take it to do bisque and to paint it because this is how I feel right now. Like with the crack in my heart. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yael has adopted other coping mechanisms too. A chair and a coffee mug full of cigarette ash now occupy a corner of the front porch as she has resumed smoking, which she hasn't done since she herself served in the IDF. She also has tried to create the reality she wants to see. Yael Alexander: We bought a new dining table last week. It's a huge one also because I'm waiting to the celebration for Edan return home. So, I'm telling my husband: 'Listen, don't say a word. I'm doing that because I'm creating something, and this is something good. So, we need to continue and praying that this is something that's gonna happen. We just holding and hoping and praying that he's OK. That he's still strong there, in heart and in mind, in everything. I'm all the time I'm praying 'Please, Edan. Please stay strong. Don't let it break you. Even if you hear the bombing you know people are coming to save you. You're not alone. We are coming.
Feb 29, 2024
What It's Like to Be Jewish at Harvard Among Antisemites and Hamas Supporters
What's it like being a Jewish student at Harvard today? With us to tell their firsthand accounts are Nitsan Machlis, Co-Chair of the Harvard Kennedy School Jewish Caucus, and Shabbos Kestenbaum, a Harvard Divinity school student who is part of a group that sued the university–alleging that they failed to address "severe and pervasive" campus antisemitism. AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2023 Report found that 24% of current or recent college students say they felt uncomfortable or unsafe at a campus event because they're Jewish. Listen in to hear from Machlis and Kestenbaum on how Harvard's administration has made Jewish students feel unwelcome and unsupported – and what they're doing to fix it. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Nitsan Machlis, Shabbos Kestenbaum Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: The Fallout from the University Presidents Congressional Hearing: What Does it Mean for Jewish Students? When Antisemites Target Local Businesses: How Communities Are Uniting in Response How A 10/7 Survivor is Confronting Anti-Israel Activists on College Campuses Tal Shimony Survived the Hamas Attack on the Nova Music Festival: Hear Her Story of Courage, Resilience, and Remembrance More Analysis and Resources: What is Students for Justice in Palestine, the Hamas-supporting Anti-Israel Group Being Banned on College Campuses? Confronting Campus Antisemitism: An Action Plan for University Students AJC Campus Library Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Nitsan Machlis and Shabbos Kestenbaum: Manya Brachear Pashman: Since the October 7 terror attack on Israel by Hamas, it has become increasingly difficult for Jewish students to feel safe on American college campuses. AJC's state of antisemitism and America 2023 report found that 24% of current or recent college students say they felt uncomfortable or unsafe at a campus event because they're Jewish. This is even true at one of the world's top Ivy League schools. Some might even say, especially true at Harvard University. This week, the co-chair of a task force set up by Harvard to combat anti semitism resigned. The second such departure after Rabbi David Wolpe resigned from an anti semitism Advisory Committee. He cited former Harvard President Claudine Gay's congressional testimony and events on campus, which reinforced the idea that he could not make the sort of difference he had hoped. The latest event on campus: a blatantly antisemitic cartoon circulated on Instagram by pro Palestinian student groups. Here to give us some perspective on the ground are Harvard Divinity student Shabbos Kestenbaum and head of the Harvard Kennedy School Jewish Caucus, Nitsan Machlis. Shabbos, Nitsan, welcome to People of the Pod. Nitsan Machlis: Thank you. Shabbos Kestenbaum: Thank you. Good to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So as I mentioned on Sunday, Professor Raphaela Sadoon resigned from her role on the University Task Force to Combat Antisemitism. Any idea why? Shabbos Kestenbaum: Sure. So when President Garber put out that announcement, it was definitely a surprise to many of us. The official reason was she wanted to focus on her administrative and academic responsibilities as a professor at the business school. But we know that that's not true. The very next day, The Harvard Crimson wrote an article detailing from members on the antisemitism Task Force, that she was incredibly frustrated with the slow pace, with the bureaucracy. And more fundamentally, she had asked Harvard to commit themselves to actually applying the recommendations that the taskforce would issue. And Harvard was not willing to do that. And I think that speaks volumes, again, about their priorities and how serious they are about combating antisemitism, that they wouldn't even commit themselves to listening to the advice of people that they themselves appointed. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what are some of those basic obvious objectives that you think the task force–what are your expectations for this task force? Shabbos Kestenbaum: Well, my expectations for the task force is nothing. I mean, the first one was so remarkably useless. It was disbanded after, what 40 days. And this one, I'll give it, let's say 100 days tops. But in terms of what I would want to see, and what Jewish students have been asking for for years, is I'll give you an example. When all incoming students come into Harvard, they take mandatory Title Nine training, and it tells them that things like fat phobia, like sizeism, like the wrong gender pronouns are forms of abuse, and they can be disciplinary, if someone were to engage in them. Why is antisemitism not included in that type of mandatory training? And why is it that we need the largest massacre of Jews since the Holocaust for Harvard to wake up to that reality? So that's number one. Number two, we need to see the fair enforcement of the school code of conduct and the fair enforcement of school policies. If you're a student engaged in antisemitism, the way that many of them are at the moment, you will be disciplined in the same way you would be and you have been, because Harvard has a track record of doing this, if you were engaged in racism, or sexism, or homophobia. But why the double standard when it comes to Jews? And then more fundamentally, we need to really restructure and reconsider DEI, diversity, equity and inclusion initiatives on campus that have never included Jewish people. Not once. These are just three basic recommendations off the top of my head that we've been saying for so, so long. Manya Brachear Pashman: It seems like students and faculty are simply oblivious to just how vulnerable Jewish students are feeling. Case in point the cartoon last week showing a hand marked with a star of David and $1 sign holding nooses around the necks of a black man and an Arab. Can you share with our listeners, what kinds of explanations, apologies or consequences that you've heard about associated with that cartoon? Nitsan Machlis: That cartoon was really upsetting on a personal level. I'll share maybe attuned with the general theme here that I personally have never felt threatened on campus. I have friends who have had very bad experiences. I think antisemitism at an institutional level definitely exists. But I think that cartoon for me was the first time that I really felt like, wow, this is very upsetting. And this is something that could hurt me. I haven't had conversations with students about the cartoon. And I was actually surprised how many students were unaware that that cartoon had, in fact, been circulating. And many times I found that in conversations I'll have with friends, they will be very upset, but they didn't even know it was happening. So I will hear about this first from my Israeli circles or from my Jewish circles. But many students are really unaware the extent these images are circulating on campus. So I don't know if that directly answers the question of reactions. But for me, there's been this big question of how do people not know this is happening? And how can I be so upset for several days over this and my classmates are not even aware. Manya Brachear Pashman: Shabbos you, as you were saying, you're one of six students who has sued the university for not adequately protecting Jewish students. In fact, you personally encountered antisemitism. Can you share that experience with our listeners? Shabbos Kestenbaum: Sure. So unfortunately, I haven't just encountered it on a one off, but it's been pervasive and it's been consistent. But one particular example that stands out was the very first day of the spring semester here at Harvard. I was walking through Harvard Yard and I noticed that every single poster that called attention to kidnapped Jewish babies was vandalized and not just vandalized, but with horrific horrific antisemitism, saying that Jews are best friends with Jeffrey Epstein, that they're responsible for 9/11. And in fact, on Kfir Bibas, who's the one year old Jewish child, someone had written his head is still on, where's the evidence? So I, of course, reported that immediately, no action was taken. It was only after CNN and Fox News had covered the story that Harvard retroactively issue a statement. But anyways, the next morning, I get a unprompted unsolicited email from a current Harvard employee who asked me to meet him in a secluded underpass to debate whether Jews were involved in 9/11. I, of course, reported that. And then later that night, he posted a video on his social media waving a machete with a picture of my face, saying that he wants to fight and he has some master plan. And as I said, I recorded all of this, I went through all the proper channels, whether it was DEI, whether it was the police, whether it was the Office of Student Life. To this day, February 27, he is still employed at Harvard. In fact, a friend of mine told me he saw him walking through Harvard Yard just a couple of days ago. It is inconceivable that any other minority group would be treated the way that Harvard treats its Jewish student body. And that's what makes this lawsuit, unfortunately, so necessary. Manya Brachear Pashman: That sounds absolutely horrifying and terrifying for you. I'm so sorry that you're having to deal with that. And that's on social media. Have you also encountered people on campus? Have you had personal encounters as well? Shabbos Kestenbaum: Yeah, yeah, absolutely. You know, I'll just tell you the most recent incident that happened. There is a forum for Harvard students, specifically Harvard Divinity School students, and it's really just become a forum in the last couple of months to bash the Jewish state—It's genocidal, it's apartheid. And someone had posted a couple of days ago that they were going to organize an event demanding lawmakers pass a ceasefire resolution. So I responded and this is the first time I was really involved in this forum for months, I responded saying wouldn't it make more sense to ask Hamas to release all the Jewish babies that they kidnapped and to surrender and end the war and I was kicked out of the forum. So there was not space for mainstream Jewish viewpoints unless that Jewish viewpoint is anti-Zionist. Harvard does not value freedom of speech, the free exchange of ideas or intellectual discourse. what it values is a one narrative, one ideology, and the moment you are counter to that you are ostracized, you are bullied and you're isolated. Manya Brachear Pashman: Nitsan, have you encountered the same resistance to your point of view? Have you been reluctant to share that you're Jewish or Israeli? Nitsan Machlis: I have felt for the first time, uncomfortable with how I share my identity. And whenever I speak in class, either on Israel or my Jewish identity, I think twice about it. And I have friends who have had very difficult experiences in classrooms and have really been caught off guard, that constant feeling that you have to be on guard because you don't know what will be said and how he will reply to it. It's very exhausting. But again, what I want to emphasize here is that this isn't the case for everyone. On a personal level, I haven't felt unsafe on a day to day basis, and I have had overwhelmingly positive experiences with my peers in the classroom. At the same time, there's a lot of very upsetting behavior that's happening, like the cartoon we just discussed. But the reason I think it's important to also discuss these stories is because I think that that feeling of isolation can be very dangerous. So we need to separate fighting against all the awful things that are happening, but also listening to students who have had positive experiences with their peers who have stepped forward and supported them in this time. I think both from an Israeli and a Jewish perspective, the worst thing that can happen is for us to feel completely isolated from our surroundings. Manya Brachear Pashman: Nitsan, you are not part of this lawsuit. You have not been targeted in the same way. How are you trying to make a difference and change the climate there? Nitsan Machlis: I will say that my approach has been to first of all work with the administration. And I very much believe in this. I think there is value to challenging the institution from the outside, especially when they have disappointed us on so many levels. But as the chair of the Jewish caucus in the Harvard Kennedy School, we have tried with the other co chairs, to work together with administration and specifically with DEI offices. For me this is one of the most important asks to have DEI offices in Harvard and another campuses understand that religious identities and national identities are part of any policy of inclusivity. And personally, I've seen results here, I think there is a greater understanding that these offices should cater to the needs of Jewish students. And I think this is institutionally one of the most important places that we can make things better for students in the long term, and shift the mindset of how administration deals with different identities within the school. But this really requires an approach of being willing to work together with administration, even when they have disappointed us. To make the meetings, to speak to the deans, and to come with lists of of demands from our students. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned working with University officials and leaders who run the DEI programs, there on campus. And I know that there has also been a task force formed to address anti Muslim and anti Arab bias. And both that group and the antisemitism Task Force are being advised by the university's chief diversity and inclusion officer. Until now, have the DEI efforts adequately included Jewish students, or let me just say, have they addressed Jewish students' needs at all? Nitsan Machlis: So pre October 7, not at all, at all. And I found that really shocking, even from having orientation presentations, where we speak about all the different identities in school, and no religious identities would be there. And I think that we had a similar issue with Muslim students in the school who also felt like their religious identity is not something they felt comfortable talking about, or expressing or asking for accommodations. And in that sense, I think we should be building bridges with these kinds of student groups and working together because this is a dual issue. So we definitely did not see any of that pre-October 7. And a lot of our work with the DEI Deans has been making them aware that this is part of their toolkit and part of what they should be working on on campus. And some of it is really basic stuff like celebrating Jewish holidays when we're celebrating different holidays. So giving that a space on campus, having people know that a lot of the student population are celebrating a holiday right now, building courses around antisemitism, talking about antisemitism in racism classes, clarifying who we can report antisemitism to on campus. So these are small milestones. But I think what's important here is the mindset change. And understanding that if we want to talk about being inclusive, then we should be talking about religious identities, too. Manya Brachear Pashman: Shabbos, there's the strategy of working from within, and there's this strategy of putting pressure from the outside. Do you feel like you kind of maximized used up any energy you had to try to work from within? Or is that in your experience, just not a successful strategy? And how did you decide to put the pressure on from the outside in the form of this lawsuit? Shabbos Kestenbaum: My mindset from day one was let's work with the administration, let's work from the inside. And in fact, when I was working with my legal team to draft this lawsuit, which took about three months, I was quite emphatic, and quite clear that should things change, I would be willing to drop the lawsuit in a heartbeat. You know, I don't want to do this. And I don't want to go to DC. And I don't want to appear on different conferences, telling strangers how bad antisemitism is at Harvard. I want to learn. that's why I came to Harvard. But much like they say about Palestinian leadership, they never miss an opportunity to miss an opportunity. The Harvard faculty, the Harvard administration are the exact same way. They failed time and time again, not only did they fail, but they made the situation untenable, they made the situation so much worse. So my attitude in the past month or so has been these things are not amenable, we cannot change it. We have to dismantle it, we have to put pressure, outside pressure. Manya Brachear Pashman: What are some of the mistakes that you're seeing in this battle to confront antisemitism? Nitsan Machlis: The whole conversation on anti-Zionism being critical of Israel and antisemitism is a very, very, very complicated conversation. There are no easy answers. I wish I had easy answers. And we shouldn't be having a complicated conversation about it, we should not be having an easy answer to every single case of criticizing Israel is necessarily antisemitic. And when we do that, unfortunately, people take us less seriously. Again, it's very complicated conversation. And I think very much of anti semitism is tied to anti-Zionism. And these things are not separate at all. I think we need to be very careful with how we fight antisemitism on campuses. And I think the listeners of this podcast will hopefully be willing to understand that climate is very, very, very complicated. I'm very critical of Israel's policies, I was involved in a lot of political activism work, I'm also a Zionist, and I'm a proud Israeli and I will return to Israel to work within the Israeli political system. Manya Brachear Pashman: Have you taken precautions to stay safe? Have you changed any of your behavior? Shabbos Kestenbaum: Yeah. So you know, going back to this example of the current Harvard employee who taunted me with a machete, I had private armed security outside my house for three days, I had armed security follow me to synagogue on Friday night, you know, my parents are always calling and checking in on me, they very much want me to leave Cambridge and to come back home. And in the lawsuit, we also talked about how there was one instance at Widener library, which is really the heart and soul of Harvard University, where during finals week of the fall semester, there were hundreds of students chanting, globalize the Intifada, Palestine will be Arab, from the river to the sea. And Widener library's where I like to go. It's where I'm entitled to go as a Harvard student. And I, of course, made sure not to, not even go into Widener library, but to change my regular route. So I wouldn't even have to walk across these people. Because we already know as we saw in the week after October 7, these protests can get violent, they do get violent, you know, there was an incident of a physical altercation at the business school. So what has Harvard done about it? The answer is nothing. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm just curious if your sense is that this climate already existed on campus, and October 7, that just intensified it, or are we just now paying attention to something that has long been there? Shabbos Kestenbaum: That's a great question. Well, before October 7, just as one anecdote, my first semester as a Harvard student, actually my first month, with the Palestine Solidarity committee invited Mohamed El Kurd to speak, this was his second time coming to campus. This is someone who said that Jews eat the organs of Palestinians. This is someone who says that the Israeli occupying forces have adopted the ways of Nazi Germany. And this is also someone that literally last night lamented on Twitter, that it's such a shame that we can't hijack planes to pursue our cause. I mean, calling him a terrorist sympathizer puts it mildly. Harvard has a strong track record, rightly or wrongly, but a strong track record of regulating speech that they find to be harmful to students. And they have a track record of rescinding invitations and even acceptances to students and to speakers in the name of promoting peace and safety for its students. The obvious and only exception is when it comes to Jews. We went to the administration, we said this is someone who supports violence against Jewish people in the name of Palestinian resistance. And the answers we got were shrugs on the shoulder, and well, there's nothing we can do about it. The hypocrisy and the double standard is so breathtaking, is so hurtful, is so demeaning. This was my first month at Harvard. So to say that this suddenly appeared out of nowhere, really does not encapsulate the pervasive problem of antisemitism at Harvard. And it also encapsulates how Harvard has enabled and in some cases, promoted this type of discourse and behavior amongst students and faculty. Manya Brachear Pashman: Nitsan, you are a graduate student at Harvard's Kennedy School of public policy and government. Your classmates are learning how to navigate the complexities of policy negotiations and international diplomacy. Do the conversations there tend to be elevated compared to the general campus discourse? Nitsan Machlis: I think this is exactly the vacuum that I've been feeling on campus. It took a very long time to be having serious policy conversations about this topic. And this is at the top policy school in the world. So if we're not having policy conversations on a foreign policy issue, the war in Israel and Gaza, then the people who are going to enter that vacuum are going to be bad actors and are going to be extremist activists sometimes, and their voices will be heard to a disproportional extent. Now, I'm not saying these conversations aren't happening at all, because eventually people stepped up and some of my more impressive professors were brave enough to step up into that space. But they've been lone actors in a system that as a whole has not led discourse of this kind. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, they're lone actors. There's not a community, there's not a mass, critical mass that is following in their footsteps. There really are just lone voices. Nitsan Machlis: As students, we've had to push for this. And I think it isn't my role as a student to be asking a policy school to teach me policy. Manya Brachear Pashman: You're not just Jewish, you're also Israeli. Does that help or hinder your role and your ability to carry on these conversations? I mean, you just said you're very critical of Israeli policies. To me I think that would help right in, in fostering conversations and teaching people that, you know, here are, these are policy conversations. Nitsan Machlis: It's a very difficult point. And I think many times, my Israeli identity goes before me and colors anything I say, no matter what my thoughts are on the government, no matter what my thoughts are on Israeli politics. And that's very upsetting. And that's something that many Israeli students have felt on campus. I also think that we're learning how to have these conversations. And we're learning how to be strategic about the people we speak to, and the way we raise awareness. I do my best not to give attention to the extreme people, but to work with moderates. And I think most students at the end of the day are a silent majority, who either are unaware of antisemitism happening on campus or are scared to speak up. And working with them can be much more effective, in my opinion, than working with people who are shouting the loudest on the edges of the spectrum. And I can speak for the Israeli community at the Harvard Kennedy School, but that's something we've worked on together as a community, how do we target the majority, and not the people who are making us most upset and who gets the headlines, who are speaking on the margins of the campus discourse? Manya Brachear Pashman: Being from Israel I imagine it was incredibly difficult to watch abroad, what was happening in your home country? Do you have family or friends who were directly affected on October 7? Nitsan Machlis: My brother had just finished his military service. He's an officer, he had actually come to the States for a visit and to travel after his service a week before October 7. And he got on a plane on October 8, and had been in Gaza for around three months since. And this is actually a crazy story. But in one of the only times that he left Gaza during that time, he called me up and he said Nitsan, what's happening in Harvard. And I found that shocking, that someone who was actually at the frontlines and actually in a war and actually endangering their own life, was asking me what's happening on a campus on the other side of the world. And it's crazy, it really is. Manya Brachear Pashman: It speaks to the effect, the emotional impact on the Jewish community at large around the world, what's happening at such a major college campus. I'm also curious what the reaction on campus has been to you having a brother who's serving on the front lines? Nitsan Machlis: That's a good question. And to be honest, that's something I don't feel comfortable sharing with most people in school. And that's a problem. There are people who know and there are people who have been very supportive. But there are many people who I've been concerned, what will they think of me? What will they think of my family? And it's a very difficult environment to navigate. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm sure it is. That would be taxing for any college student whose family is fighting in a war anywhere in the world. Not just with this added element. Nitsan, I certainly will keep your family in my prayers. Nitsan, Shabbos: thank you both for sharing your difficult but different experiences on Harvard's campus. Nitsan Machlis: Thank you. Shabbos Kestenbaum: Thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC's, managing director of policy and political affairs on the efforts in Congress to stand in solidarity with Israeli victims of Hamas' sexual violence and what you can do to make sure the plight of Israeli women is heard.
Feb 23, 2024
Believe Israeli Women: How to Advocate for Victims of Hamas' Sexual Violence
During their murderous rampage across Southern Israel on October 7th, Hamas weaponized sexual violence. Over 138 days later, denial of these crimes runs rampant despite verified evidence and testimony from survivors of the NOVA festival, the attacked kibbutzim, and freed hostages. Hear from Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC's Managing Director of Policy and Political Affairs, on the efforts in Congress to stand in solidarity with Israeli victims of Hamas' sexual violence, and what you can do to make sure the plight of Israeli women is heard. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Julie Fishman Rayman Show Notes: Act: Urge Congress: Condemn Rape and Sexual Violence by Hamas Terrorists Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: When Antisemites Target Local Businesses: How Communities Are Uniting in Response How A 10/7 Survivor is Confronting Anti-Israel Activists on College Campuses Tal Shimony Survived the Hamas Attack on the Nova Music Festival: Hear Her Story of Courage, Resilience, and Remembrance How to Mark International Holocaust Remembrance Day in a Post-October 7th World Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Julie Fishman Rayman: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week, the Association of Rape Crisis Centers in Israel delivered a report to the United Nations detailing the systemic sexual violence committed by the Hamas terror group during and after the October 7 attack on Israel. The horrific report follows a bipartisan resolution adopted by the US House of Representatives last week, condemning the use of rape and sexual violence. Here to discuss that resolution is AJC's Managing Director of Policy and Political Affairs Julie Fishman Rayman. Julie, welcome. Julie Fishman Rayman: Thank you so much, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: So anything bipartisan on Capitol Hill is rare and worth discussing. Can you walk our listeners through the details of the resolution and explain why there was such unity around it? Julie Fishman Rayman: Absolutely. So the resolution was introduced in January. And it really came out of a concerted effort on the part of mostly female members of Congress, who were hearing about what had gone on on October 7, and what was continuing to go on in Israel as it related to gender based violence and sexual assault. And they read the tea leaves of the deafening silence on behalf of the global community and said, if people aren't believing Israeli women, we are going to show that Congress, the American Congress, is united in believing Israeli women. So there are two resolutions, in the House and in the Senate, the resolution in the House passed. And they're pretty straightforward, expressing this sense, both of outrage and outlining some next steps. So in addition to condemning rape, and all forms of sexual violence as a weapon of war by Hamas, calling on nations to criminalize rape and sexual assault and hold perpetrators accountable, including by armed groups, which is somewhat of a different take on this. Calling on international bodies to really condemn these atrocities in a way that we have seen too many of them pause or hesitate or simply remain silent. Reaffirming the US government support for an independent, impartial investigation —this is very important— into what happened on October 7th and afterwards, and reaffirming this commitment to supporting survivors, which is, I think, so critical in this moment. It's one of those things you could say, Oh, of course, we support the survivors. But recognizing the reality of what's going on in Israel today, and how this trauma continues to play for those victims, is really critical, right. In this moment, Israel is not focused on supporting the survivors of rape and sexual assault, not because it's not important, but because they're still fighting a war and focusing on you know, rebuilding and what to do with the hundreds of thousands of people who have been displaced from their homes, to elsewhere. So in the hierarchy of need, addressing all sorts of trauma, is it has to be sort of lower on the totem pole and hopefully will be addressed. But that's a piece of what the international community can do and what Congress is trying to do. Just express that support and solidarity. Manya Brachear Pashman: Calling on international bodies to condemn sexual violence, international bodies such as the UN, correct? Julie Fishman Rayman: Yes. Manya Brachear Pashman: All right. Can you tell us a little bit about the report that the Association of Rape Crisis Centers released this week? Julie Fishman Rayman: It's a really important report. Not least of which because in some ways it's the first sort of fully fleshed out credible report about the atrocities of the seven. And in a lot of ways it's important also because it pushes us to be uncomfortable, right? I think a lot of why this issue has been sidelined or pushed aside is not just because Israel continues to be fighting a war. And their myriad other issues, the release of the hostages, etc, that are really, there's all these competing needs, both in our minds, as people who are sympathetic to these causes, but also in the world, and in terms of advocacy. But it really pushes a lot of these deeply uncomfortable themes to the forefront. So for example, there's a whole section in this report about the sadistic practices of Hamas, binding and tying, mutilation or destruction of genitalia, insertion of weapons into intimate areas, destruction and mutilation of the body. It's grotesque. It is hard to read about, it's hard to say. But in some ways, I think that's sort of our responsibility, right? We who have not thank God lived through this trauma can be the voices for those who have and may not feel comfortable coming forward to tell their stories, may not have the emotional capacity or stamina, to tell their story and relive the horrific trauma that they suffered. So every time I sort of talk about this issue, I try to make whoever I'm speaking to, especially women, say the really uncomfortable things that we're taught as young children not to say in polite society, talk about vaginas, talk about rape, talk about fondling of breasts and mutilation and all of these things. Because if we're not comfortable saying it out loud, we're not going to be comfortable doing that advocacy that's so important. Manya Brachear Pashman: Has sexual violence been used or highlighted as a weapon of war elsewhere, Julie, that we know of? Julie Fishman Rayman: It's enough of an instrument of war, that it's been deemed a war crime. I think that this, like so many things that took place on October 7, it was used to such a degree that the global community at some point will have to reckon with how we treat or how we consider sexual assault as an instrument of war. But certainly in lots of other places this is the sad reality. And I would say the sad reality of sort of the treatment of women. But of course, we know from October 7, that it wasn't just women. It was women, children, accounts of men being sexually abused. Even men who are still hostage in the tunnels in Gaza, there are reports of sexual abuse against them. So we sort of think about it in terms of gender based and focused specifically and solely on females. But the sad reality is, that's also not the case. And for men, especially, I think the stigma can be that much more heightened. So knowing that it could take years or even decades for us to fully understand the full gravity of the situation of what happened on October 7th against women. When it comes to men and other victims, we may never understand the full scope of what happened and what continues to happen. Manya Brachear Pashman: What is the progress of the resolution in the Senate? Julie Fishman Rayman: It's moving. It's been introduced, it has about a quarter of the Senate as co-sponsors, which is significant. There's a need for swift movement, I would say and greater advocacy so for listeners, they can go to AJC.org and find our action alert , calling on senators to co-sponsor and support this really important resolution when it's up for a vote. This is one where again, our advocacy is critical and sometimes we shy away. But it's much easier to send an email to your Senators than it is to actually have to talk about these really awful issues. So for anyone who is looking for a 30 second way to sort of comfortably take action on this important issue, the action alert is a really good and meaningful way to do so. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you kind of walk us through the advocacy efforts that push this through the House of Representatives, but also are pushing it through the Senate? In other words, are there victims participating in this, families of victims? What kinds of stories, and again, this could be a very uncomfortable portion of our conversation, what kinds of stories are being shared with people to convince them to put their name on this resolution? Julie Fishman Rayman: A lot of the stories are coming from the family members and loved ones of current hostages. So there's there's an amazing piece of advocacy going on, in the halls of Congress nearly every week that that touches on this, but isn't entirely about the sexual assault. But it's about those families coming whether they're Americans, Israelis, or some other nationality. And they have family members who are still hostage. They are coming week after week, day after day, to speak to members of Congress to keep that issue at the forefront. And of course, for a lot of them the hostage issue is part and parcel integrally connected to the issue of gender based violence. So for example, there's a woman who has been to DC several times already. And who is coming back next week to talk specifically about gender based violence. Her name is Yarden Gonen. And she is an amazing advocate for her sister, her sister Romi, who is young, she's in her 20s. She was at the Nova festival. And she had this horrific experience of being shot, calling her mother saying I've been shot, I've been bleeding. And while she was on the phone, her mother relays that they heard screaming, screaming in Arabic, screaming in Hebrew. And then the sounds got louder and louder, the voices got louder. And then Romi shut the phone and was taken into Gaza and is still held hostage. She is one of the few women still held hostage. And so her sister tirelessly comes to tell her story. With this sort of recognition, this sad recognition that probably all of our worst fears. You know, hopefully not God forbid, but our worst fears about sexual assault are possibly happening to her sister with frequency or regularity. And she's one example you know. There's another woman who comes also to advocate in Washington, but elsewhere as well, who actually works on this issue. She works in rape centers and working on sexual assault in Israel for many years. So she comes to talk about her cousins and her family members who experienced a raid on a kibbutz but specifically through this lens and says, I know, the type of trauma that women experience. I know why they don't speak out, why it can take years, even not in war time. And this impossible situation that Israeli women are now being faced with right where they have to before they're ready before they have the emotional capacity, tell their stories because the world is not believing them. Because there needs to be this public cry, believe Israeli women. Me too unless you're a Jew, all of this you know, horrific silencing, that now they're they're forced into telling these stories and the long standing trauma that will certainly continue. not just because of what they experienced. not because of the sexual assault and rape but then also because of the the repeated trauma of sharing that with others. Manya Brachear Pashman: Of course, this advocacy is also happening in other countries as well. AJC's Berlin director Remko Leemhuis told us about Shani Louk, another Supernova festival goer, who was actually filmed by terrorists and that film was released. She was experiencing horrible treatment. Unfortunately, she did not survive her captivity. But certainly her story lives on in Germany, and her family has spoken out about some of the crimes committed against her. And there's certainly evidence of that, as well. Julie, who were the champions of this resolution on Capitol Hill, who really supported it, lobbied for it. And I'm talking about the US House of Representatives, but also which senators are indeed putting their name on it? Julie Fishman Rayman: So in the house, it was really the brainchild of Kathy Manning, Lois Frankel, Mario Díaz-Balart, and Jen Kiggans. And some of those names will probably be familiar to listeners. Kathy Manning is one of the co chairs of the bipartisan Task Force for Combating Antisemitism. Lois Frankel, another very outspoken Jewish female representative, who leads a lot of the sort of women's groups and women's caucuses on Capitol Hill. In the Senate, it's an all female cast, which I think is beautiful. In both the House and the Senate, you have two Democrats and two Republicans. But in the Senate, it's all women, Jeanne Shaheen, Kirsten Gillibrand, Doug Fisher and [Katie] Britt from Alabama. They've really emerged as champions on this issue. Especially, you know, Kirsten Gillibrand is the senator from New York. She's going to the floor nearly every week to tell the stories of hostage families, about what happened in Israel on the seventh, the sexual assault, etc. And she's not alone. There are true champions that have been kind of tapped into because of this unspeakable trauma. And their voices, I'm sure will outlive this war, certainly, the hostage crisis, I say, hopefully, and with a lot of prayers. That kind of advocacy continues. Of course, there are others. Everyone, I'm sure by this point has seen the images of Senator John Fetterman's office, where he has every single hostage poster, sort of wallpapered in his office. And his staff are tracking who's released, who's still being held, who do we know is already deceased? They're tracking it as closely as the Hostages and Missing Family Forum is in Tel Aviv. They're so on top of it. They're great friends. In Congress and the administration around the world. What you said about the work of our Berlin office is absolutely true. These issues are being raised by AJC at the EU in Brussels, in Paris, at the Vatican, really throughout the country and throughout the world. Manya Brachear Pashman: The only abstention in Congress was Congresswoman Rashida Tlaib, a woman. Has she explained why she saw problems supporting such a resolution, but also why she didn't outright object to it? Julie Fishman Rayman: Her response was really a case of classic Whataboutism. You know, how can you speak about the Israeli victims while not speaking about Palestinian victims? And that's something that we've heard increasingly on social media. Oh, there are there Palestinian victims as well of sexual abuse. It's a really twisted distortion of reality. While horrible things happen in wartime, there's there's no comparison to Hamas' systematic, targeted, brutal, sadistic, planned assault on Israeli women and anything that could be happening elsewhere. Hamas has really sort of set the benchmark and I say that with some irony for what sexual assault as a weapon of war can look like. So I'm not surprised by Congresswoman Tlaib's vote. It tracks with other votes that she's taken and other statements that she's making. And I think for her, it's very personal. You know, she has Palestinian roots, she has Palestinian family members. So I imagine for her, all of this is very, very personal, very sensitive. And she probably comes to this issue with a great degree of defensiveness as well. That said, the sheer fact that she was standing alone as the only voice not affirming this condemnation, says a great deal. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did she explain why she didn't outright object to it? Julie Fishman Rayman: I don't believe that she did. Manya Brachear Pashman: What else is AJC trying to accomplish in Washington right now? What more is needed? Julie Fishman Rayman: Certainly, we need the Senate to pass this resolution. There's this continued fight over foreign aid for Israel. How do we get Israel the support that it needs in terms of material and munitions, etc? And a lot of that is tied up in a political battle over, do we fund Israel alone? Do we find Israel and Ukraine and Taiwan and other allies who are sort of collectively fighting against forces of authoritarianism or anti democratic forces? And then, of course, then there's additional layers, do we also then fund efforts to secure our border in different ways? And the more you sort of add into this pot of money, the more additional avenues or or recipients the more opportunities there are for poisoned pills. So AJC is working really hard to try to continue the fight for Israel to get the support they need, for Ukraine to get the support that they need, as they continue to fight Russian aggression. It's an uphill battle. And so, so, so political. But those are the really the key advocacy items. And of course, we continue, as I said before, to support a number of family members and loved ones of hostages as they come week after week to tell their stories on Capitol Hill. Next week, actually, we have a delegation specifically to talk about gender based violence. And it's going to include the sister of one of the hostages who I mentioned before, a part of the Zaka search and rescue team who went and saw bodies as they were being prepared for burial and witnessed the clear and really atrocious evidence of sexual assault. A reservist for the IDF, who he was off duty, but the minute that he heard the news about the Nova festival and what had happened there, he went to help and try to try to rescue people and saw bodies that had clearly undergone sexual assault. Naked bodies, a male body with cut genitalia, talking about how it's not just women, who are victims here. A woman's body with her breast cut off a young woman with massive bleeding in and around her genitalia. And then also a survivor of the Nova festival, who saved himself by hiding in bushes, but heard repeatedly over and over again, the sounds of rapes happening. So we're bringing these people to Washington to tell their stories to members of Congress, to diplomats, to State Department officials and other members of the administration. To continue the momentum. We're really lucky that most of the audiences that we'll be reaching, do believe. They've already reached that first hurdle of believing Israeli women, but now need to be urged continuously to take those stories on as as their own to continue that advocacy and to make sure that those stories don't stand on their own, but they have echoes throughout throughout the halls of Congress, throughout Washington throughout you know, the EU, the UN, other multilaterals until this attention really gets this issue really gets the attention that it deserves. Manya Brachear Pashman: Why aren't women being believed? Julie Fishman Rayman: For all, for all conflicts like this, for any other case, massive or individual, where a woman has experienced sexual assault, our first response is supposed to be belief. We're supposed to believe, we're supposed to hear. It is the opposite of innocent until proven guilty, you are a victim until or unless it can be proven otherwise. We start with belief. So the fact that that hasn't been the case here, it defies explanation. It defies our understanding, and unfortunately, really heightens the need for the victims to tell their stories, the witnesses to tell their stories. It is horrific that these people are being put in this place where they have to continue to tell this story because people aren't believing them. I wish I had a better explanation for why they're why they're not being believed. That being said, there are reasons voiced as to why Israeli women aren't being believed. There are reasons given that to some may hold sway. And they're worth acknowledging, because that's part of the narrative that is incumbent on all of us to address and rebut. Part of it we hear is because there's not always that clear cut evidence. This was war time. The worst attack against Jews since the Holocaust. A truly traumatic moment for Israel. They were not doing the job that maybe in retrospect, they should have done in terms of rape kits, and documenting all of that evidence. For Zaka, the search and rescue team, they traditionally don't take photos, that's not a part of their mandate. And in some ways they feel it's a violation. You know, it's not a part of the holy work that they're doing in terms of collecting body parts and trying to keep victims, victims of terror of the seventh and preceding, trying to keep those victims as whole as possible. So there's this sort of dearth of evidence. But there's plenty of credible accounts. So I say that, but it doesn't explain why people aren't being believed. There's no explanation for that. ya Brachear Pashman: Well thank you so much Julie for joining us. And for those listeners out there who would like to do more and push the senate to adopt that resolution, you can go to AJC.org/BelieveIsraelis . Julie, thank you. Julie Fishman Rayman: Thank you for having me and Manya, I can't thank you enough and People of the Pod enough for shining some light on this really horrific story that needs to be at the forefront of all of our attention.
Feb 15, 2024
When Antisemites Target Local Businesses: How Communities Are Uniting in Response
One in five U.S. Jews reported that local businesses where they live have been the target of antisemitism in the past five years, revealed AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2023 Report , published this week. To dive deeper into this concerning trend, we spoke with Adam Deutsch who, since October 8, has displayed a "We Stand With Israel Sign" in the window of his Scarsdale, NY ice cream shop. In January, his storefront was spray painted with the words "genocide supporters." Hear from Deutsch on how his local community rallied against this hateful action and why he's been even more vocal about his support for the Jewish state and prouder to be Jewish. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Adam Deutsch Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: How A 10/7 Survivor is Confronting Anti-Israel Activists on College Campuses Tal Shimony Survived the Hamas Attack on the Nova Music Festival: Hear Her Story of Courage, Resilience, and Remembrance How to Mark International Holocaust Remembrance Day in a Post-October 7th World Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Adam Deutsch: Manya Brachear Pashman: The contrast was stark. The words "genocide supporters" scrawled in black spray paint across the windows. On the other side of the glass, giant stuffed animals and pillows embroidered with the abbreviation for I love you so much. This was the scene one morning in January at The Scoop Shop, an ice cream and gift store at a shopping plaza in Scarsdale, New York. The vandals also left their mark on a nearby boutique. Both stores had one thing in common: Jewish owners. This week, AJC released The State of Antisemitism in America 2023 Report, which for the first time found that one in five American Jews reported local businesses where they live had been the target of antisemitism in the past five years. With us to talk about the incident in January is the owner of the Scoop Shop, Adam Deutsch. Adam, welcome to People of the Pod. Adam Deutsch: Thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: Adam, if you wouldn't mind walking us through that morning when you discovered the graffiti on your storefront. Adam Deutsch: Sure. So my brother actually got a call, we're partners, got a call around 7am rrom the people who do the maintenance in the shopping center. They were with the police who actually noticed the graffiti. So we got a call from them saying that something was written on the store window. My brother was in the middle of getting ready to drop his kids off at school so he was planning on coming right after that. He called me. And we met over there and they were already starting to clean it off. But at first I couldn't really read what it said. The handwriting was very mishy mashy. But once we actually saw it, we realized that it was not good. Not like it would have been good anyway, graffiti on the store. But we realized it had something to do with the fact that we supported Israel or that we were Jewish or something along those lines. We weren't positive at first. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how did the vandals know to target your business? Adam Deutsch: So we have a sign that says We Support Israel with the Israeli flag in our storefront window. I think it was October 8, someone came to the shopping center and asked if we would put it up. We said absolutely. So we've had it up for a few months. A few shops in the shopping center do as well, the other store that was vandalized did also. So I don't think it had anything to do with the fact that I'm Jewish, necessarily. Because how would they know that? However, the fact of what they wrote, that they believe what's going on in Israel is genocide made them write what they wrote. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how did law enforcement respond? And I'm also curious if the shopping plaza's staff contacted law enforcement when they contacted you and your brother? Adam Deutsch: The police were actually, they do rounds in the shopping center. They do like a drive by all the time. So the police actually are the ones that saw what happened, the New Rochelle police department. They, the guys who do the maintenance of the shopping center were changing the garbages at the time. So it was like they told them, they called us. But there was a lot of police presence. And you know, the district attorney's office and there was FBI. I thought it was handled very well. Manya Brachear Pashman: So it sounds like they did report it as a hate crime. Adam Deutsch: Yeah, so it was originally being reported as a possible hate crime. So I know that they have not caught the person. But I was also told that since it was written on glass, as opposed to brick, which is not permanent. And the fact that it wasn't really derogatory towards Jews or towards any group, that it wouldn't have been a hate crime. If they got caught, they wouldn't have been arrested for a hate crime. Manya Brachear Pashman: I should add that the AJC survey found that a vast majority of American Jews and American adults, 93% of Jews, 91% of the American public, believe it's important that law enforcement report hate crimes, or even be required to report hate crimes to a federal government database. So I wonder if your incident is going to be reported and recorded since it was on glass. So bizarre. So and neighbors, how did the neighbors respond? Adam Deutsch: First of all within the first–this was at eight o'clock in the morning, by the time we got there, within the first half hour of us being there, my phone received probably 20-30 text messages. Someone created this flyer that they were planning on doing an ice cream social get together and a pro-Israel rally at four o'clock. I was planning on working by myself because it's January in an ice cream store, it's pretty quiet. I right away started texting all my employees, who are in high school. So I knew they couldn't get there until after three o'clock. But I said you got to come. I need everyone here. Not knowing exactly what it was gonna be like. But, you know, I was getting texts from everyone, people who belong to all different temples saying that their temple sent this out or, this group on Facebook sent this out. It was building a lot of steam. I was like, something's gonna be crazy today. It was already crazy what we woke up too, but I wasn't expecting it to really inflate business. But I mean, literally from 8:15 in the morning when I walked into the store until 10:30 at night, I didn't sit down once. It's still hard for me to grasp what has happened in these last few weeks. But the support from the community and the words that we're getting from everyone, and I mean, I shook hands with more rabbis in the last couple of weeks than I have since my bar mitzvah for sure. Manya Brachear Pashman: I am curious, though, if you changed anything that you did – I've been asking you, how did law enforcement respond? How did neighbors respond? How did you respond? Adam Deutsch: Aside from being an ice cream shop, we're also a custom gift store. So we do custom shirts, water bottles. We print and we do stuff for teams and schools and everything like that. So that morning, my brother had to go to our office, and he was doing an order for a bat mitzvah that weekend. So he literally went to the office, the first thing he did was, he printed five or six more signs, t-shirts that said we stand with Israel and the Scoop Shop logo and the Israeli flag. We now have five signs in the front window. He made a few thousand stickers that we were handing out to everyone. We were wearing t-shirts that said, you know that we stand with Israel. And I mean, we've doubled down and we I mean we're standing pretty strong. So that's the biggest thing that changed is that we have more support for Israel signage than we did before. Manya Brachear Pashman: Had you ever been targeted personally before by antisemitism? Adam Deutsch: Personally, no. However, in December, my daughter, there was an incident at her school where her and a couple of her friends were just sitting in class, she's in sixth grade. And a kid went up to them and started making some antisemitic comments to them. Not even knowing that they were Jewish, but like, he then asked them if they were Jewish. So the fact that this all happened, and I didn't really put two and two together at first, and I still don't think there's any connection at all. The school handled that. But I grew up in New Rochelle, and it's a very large city, and there's a lot of Jewish people in one part of town, and non-Jewish in another part of town and not like it's like, segregated like that. But like, there was always people who just didn't know or didn't understand. And, you know, just thought of us Jews as different, which is the same as it is in the world today. I knew it growing up, but I didn't think twice about it. I mean, I've never seen it as bad as it is now. Manya Brachear Pashman: What sets AJC's survey apart from others is that it measures perceptions of antisemitism, both among American Jews and the American public. And I'm curious what your perception was, before this happened or before October 7 did you sense that antisemitism was already on the rise or not so much? Adam Deutsch: I mean, it's been in the news a lot for the past few months. So like, since October 7, I mean, that's really what put it in my head more like, I always knew it was out there, but I never really thought it was more than usual or that it was more than other races or religion. You know, I didn't think it was different than other groups of people. But just seeing on the news since October 7, and everything like that, you see, I mean, literally every, every day on the news, there's something that says the word antisemitism, every day on Facebook, on Instagram, on anything I see online, it's, you hear the word antisemitism. But I never really saw it in my hometown. I didn't really think it was going to affect me personally, like, at work, or anything like that. Manya Brachear Pashman: Were you afraid? Adam Deutsch: No. Manya Brachear Pashman: Or are you afraid? Adam Deutsch: No. From what happened at the store, I mean, the person was honestly the worst vandal I've ever seen. They wrote a little spray paint on the glass that was literally taken down in five minutes, they wore masks, they were scared. During the rally, there was a rally, and someone came, a pro-Palestine person came wearing a mask, it's like, you're gonna come and talk smack, show who you are. Don't be, you know, don't hide behind something. If you have something to say, say it. I mean, I'm not a tough guy by any means. And I'm all for fun, and, you know, not controversy. But if you have a point to make, make it. These people literally came, spray painted in the morning. It's like, if you got something to say, say it to my face. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how do you talk to your children about this, especially since they've encountered some difficulty themselves? Or at least your daughter has? Adam Deutsch: Yeah. So I mean, look, I watch the news every morning. My kids are getting ready for school. And like, we have like our morning routine, where I'm sitting on the couch at one spot, drinking my coffee, my son's in one other area, getting ready for school, on his iPad, my daughter's doing her thing, my wife's doing her thing. But the news is always on in the background. And it just, you hear it. So like they ask me, you know, what does that mean when they hear the word antisemitism, and you know, we tell them, there are hateful people out there. And a lot of people don't like Jews. I mean, we tell them this has happened for a long, long time, and it's going to continue to happen, but we have to just be strong and be proud of who we are. And they get it, I think, but they're not scared. They're not worried. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you think you would have been so brave as to increase your show of support for Israel if the community hadn't rallied around you? Adam Deutsch: Look, to be honest with you, we have the sign in our window, but I haven't really thought much. I mean, I see it every day when I walk in and out of the door. But other than that, it hasn't really crossed my mind too much to be honest with you. I'm not proud of that. Because obviously what's going on over there…I mean, I hear it on the news and I know what's going on, but I'm wrapped up in what's going on in my world here. But now that this happened, and the showing of support and the amount of people coming in and thanking us, we're doubling down and putting more signs up, and just telling us how proud they are, and how much they appreciate it. I mean, all I did was put a sign in the window. I mean, I didn't do anything heroic. I had someone come up to me and said, You're a hero. I mean, that was like, what? You know, that was a little odd, I'm not gonna lie. But, you know, I understand what they're saying. Because we have a way to show to the community that we stand with Israel, because I have a big storefront window that gets a lot of eyeballs on it. But all I did was put a sign in the window and opened my store for business. I don't feel like I did anything really special. Manya Brachear Pashman: Have you been kind of part of the Jewish community? Are you part of a congregation, or not really? Adam Deutsch: Yeah, my kids go to Hebrew school. We're raising our kids in the town that we grew up in, New Rochelle. My kids went to nursery school at Kehila, which is at Temple Israel in New Rochelle. That's where we belong as congregants. My daughter is going to be Bat Mitzvahed there in two years, we just got her date a month and a half ago. I mean, we're in it. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm just curious if you've had conversations within that community. I mean, you said it was odd to be called a hero for putting a sign in your window. But I'm curious if other people have expressed reticence about showing their support for Israel, because of what's happening? Adam Deutsch: I see a lot of people in the store, from my temple and from all the different temples around just because we're right in the middle of everything. So people have come up to me and told me that they're glad that we did what we did. So I got a lot of calls at the store from different rabbis or different clergy from all different religions. When it first happened, but I got a call on my cell phone from my rabbi. So that was, a nice feeling, to get a call from your rabbi. He brought his kids to the, to the rally. I mean, it was knowing that even though I'm not really doing anything, I'm representing either my temple or my people. That's the least I can do. Manya Brachear Pashman: Have you been to Israel? Adam Deutsch: I have not. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what prompted you to show such support for a place where you've never been? Adam Deutsch: I mean, I've wanted to go for forever. I do have family that is from there. Plenty of my family members have been there. I just have never had the opportunity. When I was growing up. I mean, birthright wasn't really like a thing. It happened, like a few years after, like, I just like it started really becoming a popular thing after I was, you know, already working full time, and I didn't have time to go travel or do anything like that. But that would have been an amazing thing to do. We'cr talked about maybe doing my daughter's Bat Mitzvah in Israel. Now we're not really keen on going there at this moment, you know, but we'd love to, at some point, get there for sure. Manya Brachear Pashman: AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2023 Report found that a majority of American Jews, 8 in 10, said that when thinking about what being Jewish means to them, caring about Israel is important. Do you agree? Adam Deutsch: Yeah, I mean, it's our place, it's our land. I'm not gonna say our country because it's like, it's not my country. I'm not Israeli. But I feel like it's the land of the Jewish people. It's our homeland. It's where we could all go, we should be able to all go and feel like we belong here. We are here as one. Manya Brachear Pashman: Adam, the survey's findings that we've been talking about here certainly show that I'm not alone in occasionally feeling alone as a Jew. Isolated. Once in a while, not all the time. But not always fully free to express my Jewish identity, my anxiety and concern about what's going on. And I host a podcast in the Jewish space. So I can only imagine how others who aren't regularly in this space must feel. What do you say, especially based on what has happened, what do you say to people who have felt that way? Adam Deutsch: I just think that it's important to know that people are gonna disagree with your beliefs and your feelings and who you are. And it happens all over the world, it happens everywhere. But don't let that change how you feel or how you act because whether you don't see it or feel it on an everyday basis, you have so many people in your corner and that have your back. It's like, I can't even put into words the appreciation I have for all the people in the community that have come out and continue to come out. And my brother and I looked at each other and we knew it was going to be busy that day, because there were rumblings. We never could have imagined in a million years. That would have been what it was and continued to be what it's been. It's incredible. It's incredible. And we're so grateful for it. A terrible thing happened. Not even though they did a good job on it, because like I said, they wrote a little spray paint, they wore a mask. But the stupid thing they did turn into an amazing coming together of the community and I'm glad that I can be a part of it because it made me, it made me really just sit back and think for a second how proud I am to be Jewish and to know that my people have gone through stuff like this and a million times worse than this. And we're still here and we're not going anywhere. Manya Brachear Pashman: Adam, thank you so much for joining us and sharing your experience. Adam Deutsch: Thank you. I do appreciate it. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Israeli filmmaker Yoni Diller who escaped the Supernova Music Festival on foot, walking for hours through southern Israel's desert to safety.
Feb 8, 2024
How A 10/7 Survivor is Confronting Anti-Israel Activists on College Campuses
Yoni Diller, a 28-year-old Israeli filmmaker, arrived at the Supernova Music Festival just hours before Hamas terrorists launched their unprecedented attack on Israel that killed 1200 people, including 401 at the music festival alone. Yoni escaped the festival on foot, walking for hours through southern Israel's desert to safety. Having survived this harrowing experience, Yoni is now traveling the world to share his story with political leaders, college students, and others, providing firsthand testimony of the horrors he and his fellow festival attendees witnessed on that fateful morning of October 7th. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Yoni Diller Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: Tal Shimony Survived the Hamas Attack on the Nova Music Festival: Hear Her Story of Courage, Resilience, and Remembrance How to Mark International Holocaust Remembrance Day in a Post-October 7th World A Spider Web of Terror: How Iran's Axis of Houthis, Hezbollah, and Hamas Threaten Israel and America Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Yoni Diller: Manya Brachear Pashman: During the Grammys this past Sunday, Recording Academy CEO Harvey Mason Jr. remembered the 401 people murdered and 40 kidnapped by Hamas terrorists during the October 7 attack on the Nova Music Festival. Yoni Diller is a 28-year-old filmmaker from Ra'anana, a town outside Tel Aviv. Yoni and his friend Nadav arrived at the Supernova Music Festival just a few hours before rockets began flying overhead. At daybreak, he had expected to send up a drone camera to capture the scene of unadulterated song and dance in the desert. But he never got the chance to get his camera ready. Yoni is with us now to describe that harrowing day that started at dawn. Yoni, welcome to People of the Pod. Yoni Diller: Thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: Could you please walk us through what you saw that morning? Yoni Diller: So, when the sirens went on at 6:30, we saw hundreds of missiles heading our way. So we rushed back to our campsite. We packed up our stuff, we tried to leave, the parking lot was chaotic. And I suggested going a different way. This decision to head south towards Re'im, which is another village. I didn't think it would change or it will change everything, but it did. On the road, people originally told us to turn around, to do a u-turn. Manya Brachear Pashman: You told me earlier that was when a car riddled with bullet holes approached you and you found yourself helping a wounded women. That was 25 year old Shani Gabay whose remains were identified seven weeks later. At that time, when you were helping her, you heard gunfire in the distance and you tried to take cover in a nearby valley. Yoni Diller: Yes. I saw terrorists from a distance and continued to hide. A short moment later, mass shooting started in the Be'eri area, north of us. I checked my phone to assess our surroundings and our current location. At the same time, my friend's sister called him to check on him to check everything's okay. He promised everything's gonna be alright. And about that time about a dozen others had joined us and we start walking. But the best thing I could do at that moment is to scream for everyone to get down because bullets are flying up on top of our head. So when the gunshots stop for a second, we decided to head towards Patish, it was more than 24 kilometers away. My intuition told me that this will be safer there. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did you just say 24 kilometers away? How did you make it through an almost 15-mile walk? You're walking in fields, the open fields in the desert, without food or water for over four and a half hours. It's really really tough. The fear and uncertainty made it even harder. At some point, Nadav found a single grapefruit that gave us enough energy to finish the long walk to Patish. Throughout this journey we continued to hear automatic gunfire. Finally after 4 ½ hours we arrived at Patish. Emotions were mixed because we began to learn the enormity of what happened. Friends were missing and there were rumors of many people hurt and worse from the festival. Later on around 2 in the afternoon, a bus came to take us away, bringing us to Be'er Sheva and then to Tel Aviv. Then I arrived to Ra'anana finally. Safe and sound in one piece. I hugged my family and I understood just how lucky I had been. Manya Brachear Pashman: So can you kind of explain to our audience what is so wonderful about this festival, this trance culture and this music, this experience? Yoni Diller: So trance, psy-trance, electronic music, personally for me it's not a genre. It's like you said, it's a culture, it's the people in it. It's the free spirit people, liberal people, just all about spreading love. It doesn't have to be in a hippie way, just more in a way that everything is very simple, you know. Simply just be a good person, giving, ego's not involved, very laid back people. And that's the whole idea behind all these festivals and that's what's for me. It's about the people, it's about the music, it's about the art, everything together. I joined a group of friends, friends of friends, we were like total more than 20 people and two of them lost their lives there and two others that I know from another group that went with me to high school also. One got killed and actually the one the other one got kidnapped. These festivals, from event to event, you get to know people from everywhere. It's a small world. Manya Brachear Pashman: Your companion who was kidnapped, has he been released, any word on where they are now? Yoni Diller: No, one of them is still there. Hopefully he's still alive. I'm not even sure what's less worse, being kidnapped, or hostage, or being killed. We don't really know what they're going through over there. The best we can do is just wish for them to be released, no matter what the circumstances are. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yes, my colleagues here at AJC are working to bring about the safe return of all the hostages. Listeners can go to AJC.org/BringThemHome to learn more about those efforts. Yoni, do you feel like people outside Israel fully grasp the gravity of what happened to people there, or really how truly innocent the festival goers were? Yoni Diller: Unfortunately, you know, this generation wants to get fast news and simple news comfortably, and a lot of them consume content from, you know, platforms like Tiktok, or Instagram. And unfortunately, there's a lot of fake news out there, a lot of false accusations. And, you know, people sometimes deny that October 7 happened. And that's really unfortunate. I'll give you an example. I flew to the US after the event, I was part of this special delegation to do advocacy and telling the story to politicians in DC, in New York. And also, independently later after this delegation, I stayed another week in the States, and I took the train to these campuses. And I spoke and told my story. You know, campuses like NYU, Columbia, I went to Harvard, MIT, Yale, and Princeton. Six campuses in three days. It wasn't easy. I was really exhausted. But the fact that I had that meaning that, you know, I'm there to tell the story. Not for me, not telling the story for me. I'm telling that story for people to actually know what really happened, you know, the truth. I'm saying this for people who weren't lucky to tell them to tell the story themselves, or for the families. So what I saw, when I told the story, is a lot of people were actually in shock, like, wow, I didn't know if this would really happen. Like, how can you not know, we're in 2023. Information hasn't been easier to be delivered from place to place up until this moment, and how do you not know exactly what happened? There's videos everywhere. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned that students were actually shocked that when they heard your testimony, and what happened. What other kinds of reactions are you getting, both reassuring reactions and negative reactions? Yoni Diller: I would say that the positive reactions I had a lot, a lot of good reactions. I mean, most of the people I spoke to or through this Hillel organization and the campuses. And, you know, people come up to me after the event and they feel very sorry, and they sort of it was really nice, but I would say that the only time that I dealt with some, somebody that was maybe a negative was at Princeton, there was this guy, some 18 year old kid. Apparently he's not one of the Israeli supporters I would say, is an understatement. And he had a weird comment. It took him actually 10 minutes to ask me a question, at the end of the lecture, I asked if anyone has any questions, and he asked me something. He was very embarrassed to ask me this. But he said something about should we feel bad for the Palestinians, they've been oppressed for many years, October 7th was legitimate, it should have happened, something in that kind of way. So instead of attacking him and try to humiliate him, or trying to make him look really bad, make him look silly, I told him, Look, I can talk to you about it. No problem. I'm not here to talk about politics or give you history lessons. I'm just here to tell my story, this is what happen. Again, I can get into it, but I wasn't really interested,I wasn't sure it was really appropriate to just get into that, because he just wanted to find some action. In terms of antisemitism or just being against Israel, I see it's a very broad trend, nowadays. I had this event with Douglas Murray the other day. And he said, this generation is Gen Z, you know, everyone wants to be an activist, everyone wants to be an influencer in some way. And people calling Israel, telling them they're calling colonialist or doing genocide, all that. It's very easy to use these buzzwords, okay, but most of the people don't even know what they mean. Most of the people when they shout from the river to the sea, don't even know which sea or which river they're talking about. But a lot of these people feel a sense of meaning, oh, we're part of something, although they don't know 100%, where they're part of part of. So my mission, or one of my main meanings, is to educate people and telling them in a very simple way, what really happened because I'm the proof that October 7, I'm evidence to all this all this thing happened. So no one can actually tell me that this didn't happen. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yoni I am curious, how you are healing, how you are taking care of yourself, and whether these opportunities to speak about what happened are therapeutic, and what music is playing in your healing process? Yoni Diller: Well, as I tell the story more, at some point I feel it comes out more easy and less challenging. As I tell it more, I feel I become stronger. You know, because you just can't keep this stuff in your stomach, you gotta share this stuff, and be very careful how you share it. I've read this book Man's Search for Meaning by Viktor Frankl, I'm sure you've heard about it. And I read this book while I was doing this whole advocacy work, and, you know, doing this journey in the states, in Europe, and it gave me a lot of strength. And, and it was part of my healing process, you know, to have this meaning. But the main point wasn't really, you know, spreading the story everywhere. I mean, it was important, but how do I bridge that story to something more positive? So that was part of my healing process. In addition, I have friends and family that are very supportive. And I'm very lucky to have them. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you encounter mostly Jewish audiences with whom you speak? Or do you encounter non-Jewish audiences and recipients? Yoni Diller: It's mixed. It's mixed. Mostly mixed. A lot of them are Jews, though, because I was hosted by Hillel. So a lot of them were Jews. Also for security reasons. At that time, I decided to go to Harvard and MIT when there were all the riots. I went there by myself to speak and they had to make sure everything's secure and they had police on the outside, the inside, it really kept everything very safe. Manya Brachear Pashman: And did you get any surprising reactions from non-Jewish audience members? Yoni Diller: Just from that incident in Princeton, but if the event was more like for everyone, I'm sure I would get responses from so many other people. And it would be a disaster, it would just be a mess because it would be me probably arguing with a couple of kids screaming stuff like free Palestine and stuff, things that have no connection to what I came for. And, you know, just misses the whole purpose. So we try to do something more organized, more the Jewish crowd, because let me tell you this, okay. A lot of Jews, Israelis that live in the States, whoever it is, the campuses, they know what happened, but most of them don't know from a survivor or someone who's really there. In addition, a lot of them don't have the self confidence to combat this antisemitism and hate in their surroundings, they feel afraid to stand up. I mean, if I survived it, I'm just a simple Ashkenazi guy from Ra'anana. And, you know, I survived it. You know, I wouldn't consider myself a big hero. I mean, I was very lucky. And again, you know, I've been through hell. But the last thing I should do is be silent and just stay home. I got to speak up. Hey, guys, look this is what happened, you know, get your head up. People are in a much worse situation, you have no reason to be afraid. We went through the Holocaust, we've been through, you know, 3000 years of hell. And we've always survived. So we're resilient. And that's kind of the message that I came to convey. You know, that's one of the reasons I'm there to speak. Again, you cannot fight antisemitism with the other side's kind of method, let's say, they would scream stuff, and be violent. You can't play that game. Let them yell and play that game or spread their lies. What you should do is, you know, you gotta really pick your crowd, like I said, You got to pick your people. You got to be more united, you got to speak, you got to spread facts. That's what you should do, every Jew in the world. Because we're stronger than ever. Nothing can break us. History has shown it. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yoni, do you think that you will return to the supernova festival or any other music festival? Do you think you'll dance again? Yoni Diller: I'll even dance more. You know, this is what they want, disregarding what happened and everything. I guess that these terrorist organizations, not only they want to, like physically hurt you, they will also want to mentally break you, okay? And they want you to fear them. So the last thing you should do is be afraid of that. So you got to do the opposite. They probably would want me not to dance anymore, not to go to these festivals or just not enjoy my life. I'll do the opposite. I will go and I'll dance even more often. Or I'll just you know, create more joy. And that's one of the ways to really combat this battle. So to your question. Yes. I will not stop, maybe it'll take me some time. I'm not sure if I'm so ready. But slowly, you know, you got to really listen to yourself first. That's the most important. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yoni, thank you so much for sharing your story and I hope to see you dancing again very soon. Yoni Diller: Hey, thank you so much for having me. Hopefully, people can hear this and they can spread the word. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with another Supernova survivor Tal Shimony as she discusses the genesis of the exhibit 'Nova 6.29,' where the community aims to tell their story and honor those killed and taken hostage. Tal guides us through the horrors she witnessed during the deadliest attack on a music event in history.
Feb 2, 2024
Tal Shimony Survived the Hamas Attack on the Nova Music Festival: Hear Her Story of Courage, Resilience, and Remembrance
Dancing. Costumes. Music. Rockets. Running. Chaos. At 6:29 am on the morning of October 7, Tal Shimony went from dancing in a field outside the Southern Israeli kibbutz of Re'im at the Supernova Music Festival to running for her life as the site was attacked by Hamas terrorists. Tal guides us through the horrors she witnessed that morning, and the exhibit 'Nova 6.29,' where the community aims to tell their story and honor those killed and taken hostage, in the deadliest attack on a music event in history. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Tal Shimony Show Notes: Song credits: Clear Test Signal Artifex Remix - Nova Tribute Learn more: Tribe of Nova Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: How to Mark International Holocaust Remembrance Day in a Post-October 7th World A Spider Web of Terror: How Iran's Axis of Houthis, Hezbollah, and Hamas Threaten Israel and America Unpacking South Africa's Baseless Genocide Charge Against Israel Countering the Denial and Distortion of the 10/7 Hamas Attack Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Tal Shimony: Manya Brachear Pashman: More than 3000 people were at the Supernova Music Festival that began on Friday night October 6, and was meant to last through the next day. But at 6:29 am on October 7, it came to an end. In the horrific hours that followed, more than 400 people were killed and more than 40 kidnapped by Hamas terrorists. Survivors organized an exhibit at the Tel Aviv Expo to tell their story. 'Nova 6.29' is named for the moment when rockets began falling on the tribe of Nova desert rave. During an AJC Project Interchange Fact Finding Delegation to Israel in December 2023, my colleagues met survivor and organizer Tal Shimony. After hearing her story, we wanted you to meet her too. Tal, welcome to People of the Pod. Tal Shimony: Thank you so much for inviting me, it means a lot for me and also for my tribe. Manya Brachear Pashman: So before we begin, I'm hoping you can kind of help our audience understand your tribe and understand just what the tribe of Nova or trance culture is, and what were people celebrating that morning? Tal Shimony: Yeah, of course, I will explain to the audience about trance culture and who we are. It's named after music, electronic music. What's very interesting about this music, it came to Israel around the 80s from the area of India, and very soon became a very popular culture here and a very big scene here in Israel. Every weekend, we have around 20 parties that are happening in nature, that are celebrating this culture. The trance culture is connected in a way to the more liberal and free culture, connected to the yoga world. Which means it's a very global and international thing. We're speaking about love and peace. In all of the international trance festivals, it's not very much allowed to bring national flags. You're not allowed to bring flags of your own country. You can bring flags that are stating a peace of love or stuff that are representing your group of friends, but nothing that is representing anything national. The aim is to do a community that has no judgment. That everyone can join it. If you're a good person, and you love nature, and you love humankind, and you love the music, you can join. And that's the Nova tribe's main values. These are the things that we are standing for. And the gap between what happened to us at 6:29 that morning, and of course, the whole day after, because it's not just that moment that was horrible. It was the whole day after it and of course, until now it's still going on. And from that moment on, the gap between this and who we are and what we are and what we came to celebrate is so big. For me, this is the unbelievable thing. A lot of time I ask myself, What am I doing here? What happened? Why did it happen to us? Manya Brachear Pashman: How many festivals have you been to personally, and what took you to that one in October? Tal Shimony: I've been going to trance festivals and nature parties in Israel since I'm really young. I live in a really small village in the north that is quite hippy. So these things are a part of who I am and what I do since I'm around 15. My first International Festival was in Hungary when I was 19. So I traveled to festivals around the world when I was very young. Today, I'm 25. So this thing has been a part of my world for a while now. And Nova festival came into my world around two years ago. I went to the same festival as I went to the first time. And I didn't want to go alone. And some of my friends connected me to one of the Nova producers, Nimrod Arnin, or the way I call him, Nimi. He's a good friend. And became sort of a little love story, not in the romantic way. But in a way they opened their arms to me, this production, said come join us, just be with us as our friends. And I just fell in love with these people. They are so beautiful. The people who will lead this community are people that are full with heart, all they want to do is give good to this world. They volunteer monthly as a production. And we have another volunteering now and this week on Friday. This is something that they do all the time and, and every time and at some point, I decided that every time I'm going to come to visit Israel, I will visit in the time of the Nova festival. I've been living in Berlin for the last three and a half years. So it's not like it's been easy for me to come to the Israeli festival of Nova. But I did. I felt like it was important to me to do so. And they really produce something that is in international levels. Just like the Hungarian festival I went to or the Portuguese Boom famous festival or Universo Paralello, which is the festival that Nova worked in collaboration with in the seventh of October. The international trance community is hugging us as much as they can, because it's also very complex for them. This is for me what this thing is about. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you take us back to October 6, and then October 7, Tal, and tell our listeners what you went through that day personally? Tal Shimony: Yeah. So I was not supposed to be at that party. But I got a call from one of the producers, my friend, his name is Dov. And he needed help in a new ecological team. He's been building up this first of a kind ecological project in an Israeli festival, using reusable cups in the bar, and handing out trash bags to the audience and differentiating trash, plastic trash and non-plastic trash, things that are really revolutionary in Israel. And since I was living in Berlin, in Germany, as you know, is top one in this thing. He called me and he asked for help. I was supposed to come to Israel for the winter because the Berlin winter was too cold for me. And I decided I'm going to take my flight a bit more earlier than I planned and landed in Israel in the second of October. Which means the sixth of October was my first Friday at home after many months. I was doing a Friday dinner, shishi, Shabbat dinner with my family. Around 11 I took a ride with a friend. And we had two other friends in the car and we drove into the party. I arrived around 12:30. And I said it to you before the podcast that my boyfriend is one of the leaders of this production. He was already there. He was setting up the event, so this is why I had to take a ride. And he had his car there. And then he was really tired, he went to sleep. And I started working. At around 4am, I got a radio. And I started doing my job. And around 5:45, actually, quite exactly, my friend Yarin, he was going to play. His DJ name is Artifex, you probably know this name. He is the last DJ who played at the party. I woke up my boyfriend at 5:45, and I told him, let's go to dance, I can take my break now. And we can go and hear Yarin play on the main dance floor. It's a really big dance floor. It's one of the biggest he ever played in, so we were very excited for him. He's a good friend. And we went to dance. Now you see in the dance floors of, especially of Nova community, but generally in the trance community, you don't really need to stay next to your friends, you can walk around, everyone are friends with everyone, everyone is super friendly and nice. And I think it's a very beautiful atmosphere. As I said, no judgment, everyone was smiling at you. Manya Brachear Pashman: And then the sun starts to rise over the festival, right? Describe that for us. Tal Shimony: I don't think there are words that can express how you can feel when the sun is rising on a desert party in Israel. First of all, the Israeli sunrises in the desert are the most beautiful thing you can see. Really. I've seen a lot of sunrises, in a lot of places in the world, I'm traveling quite a lot. This is something else. The atmosphere is magical. And also, you are dancing in the dark next to people that you don't see, when suddenly the light of the sun comes in, and you can see the people around you. You can see their eyes, you can see their faces. And I think around 6:20 the sun was already starting to rise and at 6:20 my boyfriend said he's going to the bathroom and I asked to join him. He found me in the dance floor somehow, which was luck for both of us. And we went to the bathroom, we went outside the bathroom at 6:29. And I can see a missile from far away. And I asked my boyfriend, didn't you say there is a ceasefire? And the minute I finished my sentence, hundreds of rockets are already flying above my head. And when I say above my head, you need to understand it was very, very close to my head. Physically, you can really feel the echo on your body, the echo of the Iron Dome, disarming these missiles. Now we are in an open field and as an Israeli I know that open field missiles are not usually being disarmed by Iron Dome because it's protecting the villages. So we are deciding to go away from the area of the party. So if there will be any missiles exploding on the ground and heating something with electricity, so we will be safe. Like us a lot of people are doing so there is a lot of mess in the beginning. Very fast the music is turned off. Very fast our head of security, Aviv Avraham, rest in peace, who was murdered at the event after saving lots of people's life. He's calling on the speakers that there is a red alert, which means missiles, that the party's over and everyone should go outside of the party area to their cars, take their cars and go away. Now we are production members. We also meet some of the production members outside the area of the party. And we don't really know what to do. Should we go, should we help the security members take everyone outside, what should we do? We go back to the area where my boyfriend's car was, next to the police improvised tent that was there. We have 27 police officers on the job, 80 security members, private security that the Nova is hiring. And one of the police officers was screaming from the tent: everyone who has a car take your car, go away, the party's over. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did you still feel compelled to stay or did you follow his orders and flee? Tal Shimony: In the moment that these missiles are flying above my head at 6:29, I immediately get an anxiety attack. So everything I'm telling you right now are stuff that my boyfriend told me. And he was leading me through. So he was leading me out of the area of the party, and then into the car physically taking me because I was incapable of walking, my body completely froze. I couldn't speak. I couldn't say anything but the name of my dog for a while, because she was home. And this is the only thing I could think about. And also saying to him, What can we do? Can we help? He said, I also said that, which is quite funny, because who I can help to when I'm like this. The mind can be very tricky at that point. We take the car, we go inside the car, and we're driving through the emergency exit. From the left side of us, we can already see the traffic of cars coming out of the event, it's 4,000 people, around 2,000 cars. One road. There is no other way. We take the left turn towards the north, and we drive away. At that point, we decided we're going to take a safe house. We didn't know there were terrorists. We knew they were only missiles. So we decided we're going to go to the artist's house the production has rented. And we're going to go to the protected room there because this is the safest place we know. And the closest place we know. My boyfriend was also thinking about stopping on the road, in the protected houses that are on the road, protected rooms. These places became death traps that many of my friends were there and murdered. And some of our friends were there and were lucky enough to survive and tell horrible stories from there. And I am very lucky he thought that way. And then for some reason he didn't do so. Everything is very random. We arrive into this house. He's opening his phone and you can see a message in the group that says that there are terrorists in the party. I'm calling my best friend, Or. She was working in the entrance. I can hear gunshots when Or is talking to me. She's talking with me for a while, around 20 minutes, where she's been led by police officers in the field, trying to escape terrorists that have arrived. And the conversation ends with, Tal I have to ditch my car, I'll call you later, bye. And she hangs up. Manya Brachear Pashman: I hope you will tell us what happened to her later. But what is going through your mind at this point? It seems so cliche to ask, but what do you remember feeling in such a moment of confusion and utter chaos? Tal Shimony: Helplessness I think is the best way to describe the way I feel right now. I want to go out, take my take my boyfriend's car and go and save everyone I can, because this phone call is just one out of many we got at the same time. We get notified of people we know being murdered. Some of our friends saw it happening, and they are texting us. And then we realize everyone ditched their cars. At that point a couple, a friend of ours in, one girl that he managed to take with him. They're coming into this safe house and they are telling us that they saw someone completely wounded from gunshots on the way they wanted to take him and help him and he told them leave me here. I'm out. Don't take me, you will die. And they had to continue driving because they were shooting at that time. And the stories that continue to come and at some point we're being asked by our production to start gathering locations of our friends that are hiding and running away from terrorists. We are posting everywhere online that we need people to send us the locations and that we need people to help us get to our people. At that point one of our security members with some military man's that were in voluntarily arriving into the era. He managed to sort of take back the area of the party from the terrorists, because they conquered it. Even when I say it, like four months ahead, it still sounds to me like a movie. At 8:30 I get a video call from the same friend, Or, this time, she's running in an open field and I can see the terrorists running behind her. And I scream at her to run as fast as she can. And I scream at her that I love her. She doesn't really talk. She says to me, she loves me back. And she hangs up. She was saying goodbye. Now you see, I was a shooting instructor in the army. And I see my friend in an open field when terrorists are shooting at her. For me, she's dead. There is no other option. And she's a friend of mine, and also everyone else who was sitting there with me. And we all hear her in this conversation and we are completely broken at that moment. Half an hour later, I get a sign of life from her when she says to me, Sister, I got shot. She got shot in her leg. She survived. But after she got shot in her leg, she had to run 10 more kilometers with a gunshot in her leg. She survived, but I think her soul died that day and she had to rebirth. Manya Brachear Pashman: I am so relieved to hear that Or survived. When were you finally able to leave the house that you were trapped in and go home? Tal Shimony: This house is not far away from the area of the party and definitely not far away from Gaza. It's next to a city called Netivot. Netivot is a small city in the area of Sderot and Ofakim, and the terrorists are arriving there at some point. They're not arriving into the village we are. And there is a civilian squad who is protecting us. But they are getting very much closer to us all the time. We have television so we can see it on the news that they are getting closer. And this entire day, I'm trying to send locations of people that I know and people I don't know and I get phone calls from worried mothers asking me to see what's going on with their child. And this whole thing is happening while in one hand, I have my phone, and I'm calling people in the other hand, they have a knife. Because they are coming closer. And I need to protect myself. And this feeling of fear and helplessness being all the time switching, and anxiety attacks that are being escort me until this day, and on the seventh of October, I think I had around 48 hours of an extended anxiety attack that was going on and off. At 5pm, my boyfriend decided he had enough and he doesn't want to stay in this house in the dark and we want to go home. We are calling the head of the civilian squad that is protecting the little village we are in. We're telling them we want to leave. And he says to me on the phone like this, listen, I can't guarantee you're going to survive this, right, it's your choice. We have no idea where they are right now. This is your decision. I don't take responsibility for that. And we decide to leave anyway. I don't remember anything from that ride, only two burned cars. And that's it. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank God you survived that trip. Tal, how have you coped during the weeks and months since then? Tal Shimony: I think in the first week, I didn't sleep at all. Everything is very vague. The day after the seventh of October, the eighth of October was the hardest day for me because I realized how many people I know lost their life that day. And then started a week that was the most horrible week in my life. So every day I go to around three funerals of people that I know from the international festivals, from home, from other circles in my life, and some of the funerals of my friends I couldn't arrive because they were in the parallel time for another funeral. And the decision was to choose which one of my friends I'm saying goodbye to. Some of them were also in areas of risk, like the desert, like the Israeli South. And some of them were in the North that was very much involved at that point. Nimrod Arnin, my friend who welcomed me into this community, his sister, 19 years old, Ayelet Arnin, was murdered. So we went to, of course, to her funeral, and there was an alarm. And it's 30 Nova survivors in a house that doesn't really have a place for us to be protected. So we couldn't stay for this funeral. We all left. It was very sad. And that's how my first week goes. I still carry with me marks of this. Anxiety attacks that are happening. My sleepless nights, nightmares that are worse than anyone can imagine. Yeah. This is my life right now. Manya Brachear Pashman: This is so unfathomable, and Tal, and I am so grateful to you for sharing all of that, because I think it is hard for so many people to truly fathom the horrors of that day. And I imagine that is part of why this exhibit came together. Can you tell us how it came together, who's behind it, and kind of describe it to our listeners? Tal Shimony: So all the villages next to Gaza–Kibbutz Nir Oz, Kibbutz Re'im–all these beautiful places that were burned out by Hamas, they have something to show, they can show people this is what happened to us. The Nova parties, just like any other international festival, are being built and disassembled in a matter of hours or days. And we had nothing to show. Our community is the biggest community hit by this day. A third of all the victims from the seventh of October are coming from the Nova community, it's such a big number. After the seventh of October, the first thing that we did as a community was building a healing center for the community where we had body treatment, mental treatment, workshops, everything we thought about that can help people. Of course, at some point, the artists of Israel came to play music for us. And during that time, some producers in Israel came to help us because some of them are the dinosaurs of the tribe of trance in Israel, it's a big thing. And they wanted to help. And one of them came up with this idea of rebuilding the area of the party, as an exhibition for the public. And this exhibition, what you can see there, is the original party place. So it's the shadow tent, the big one that everyone can see in all the videos, is being rebuilt there. The bars, the camping area, the stages. We also have there toilets. The ones that I left from, and these toilets are now full with bullet holes, real bullet holes, from the terrorist attack. For example, we know that around 30 people were hiding in these toilets and only three came out. And you can see and bear witness with your eyes on these things. You can see how many bullets are in every cell, they really didn't let anyone survive. You can see burned cars, because Hamas just burned everything they saw with every measure they had. So if it's special explosives that burns everything very fast and at a very high temperature, if it's RPGs, if it's fuel, they used everything they had. Some people were hiding underneath the car, inside the trunk, and they were burned alive. And you can see that there. I have so many stories of friends that we found their bodies in cars. And it took so long to identify the bodies because when you burn the human body, there is nothing left. Manya Brachear Pashman: After living through what you did, what was it like to see the scene recreated and memorialized for the exhibit? Tal Shimony: For me, the first time I arrived into this exhibition was horrible. The most horrible part was not all these things. The most horrible part was the screens. We had screens of pictures of the kidnapped people, and a screen of murdered people, all the faces, pictures of them. And between these two, we had a little place of lost and found. Everything that was found in the area of the party was brought there. Some people find their stuff there. It's a very exciting moment. But there is one table that was always staying the same. I call it the fun table. So when you are going to trance party or into a Nova party, you usually bring with you stuff that makes other people happy. Because this is the tribe, this is what we do. So for example, I like to put on a costume of a fairy. So I have my wings, and I have my elf ears and I have many glitters. And some people are going around with really nice, beautiful, colorful umbrellas. Some people are going with a Hollywood sign of action and running around the dance floor and saying action to people. Some people are going with water guns and shooting at people in the dance floor. It's very warm in the Israeli desert. And people brought all these things with them. Some people bring some juggling, very expensive juggling stuff to entertain themselves and the audience. And this table was always remaining full. And at some point I realized why. I was thinking to myself, if I would lose my own juggling equipment which I bring to every party, if I would lose it in the area of the party, I would come back to take it. There is no way. It's so expensive and it's so sentimental and it's so personal. And I know that my mother would never know how it looks like. So I believe that most of the things in this table were belonging to victims because they were just staying there for so long, and they look so insignificant for someone from the outside. For me, that was the most hard table, hard area in the party, because you can see the pictures of the victims and you can see equipment that you understand that the only person who can take them is this people that belongs these things, because they are so personal. Manya Brachear Pashman: You make a really good point about the exhibit memorializing a culture that's so ephemeral, so intangible. And I'm curious if there is a therapeutic quality to the trance culture? And is there a therapeutic quality to this exhibit, both for those who have organized it, and for those who are visiting? Tal Shimony: I always end my tours there, when I was doing tours, I was always ending them with this table that I told you about in the last one and I always told them that I still see the hope. Because I know I have my festival clothes at home and also all my friends and we all have our fun stuff, waiting for us to come back dancing. Because for me, dancing means healing. Dancing means therapy. Dancing means being connected to myself. And the great Raja Ram, which is a very big DJ, famous trance DJ. When he was asked about dancing in a trance festival what it means, he was saying something very beautiful. He was saying you forget who you are. You forget your identity. You forget your job. You are just there at that moment. And that moment is so beautiful. And I think we all need to come back dancing. We have every Wednesdays now a Healing Center, a community day that has being end with two hours of trance music. And there are therapists around if someone needs help, and some people are not staying. They know that at 8pm starts a set, a set of trance, so they are not staying because it's too much for them. They're coming there for the therapy and they're coming there to meet their friends and be together and hug. And some are staying and fighting through it. And it's a beautiful thing to see. It's a beautiful thing to see but it takes time. I have to say that. We are trying to be back dancing but I have to say I tried a few times to go to nature parties, and it ended up with very big anxiety attacks. And I'm, let's say a very high-functioning survivor, I can help others, which is not something I take for granted. So yes, definitely, we will dance again. And we don't say this sentence…again together as a community. Because it's a part of our healing. I believe my friends, who are not with us, are very proud of the Nova tribe, for continuing dancing, for trying to heal and come back to the dance floors. This is what they left for us. They said to us with everything, with everything they have, dance. With everything they have. They will not die in another way. They died in the middle of one of the most beautiful things you can do. Unfortunately, a very horrible death. But if I want to remember these people, as they were, I would like to remember them dancing on the dance floor with me. And they will dance with me when I dance everywhere. Manya Brachear Pashman: Tal, the Grammy Awards are this Sunday, February 4th. Of course, it's not just an awards show. It's a platform for artists to speak out or pay tribute, and we've seen that after horrific events like the shooting at the Route 91 country music festival in Las Vegas or the bombing at an Ariana Grande concert in England. Do you feel that the music world has spoken out about Nova? Tal Shimony: Definitely not. I would expect the music industry to talk about it at the international level. You can say, we are not talking about politics, we don't talk about Israel, we just talk about Nova. I think it's something that is possible to do. But it takes some bravery. Because people are connecting what happened with Nova to what happened generally on the seventh of October, and for me going inside the music trance festival is like going into international grounds. Really, it's just like the same for me. And the thing that the music industry is forgetting is that, as you said yourself, there were so many music events that were attacked by terror before. And that can happen in every trance music festival around the world. They forget it, that each and every country, also in the US, there is many, many festivals with this type of music and this type of culture. They forget it, it could have happened everywhere else, everywhere else. And of course, I would have expected the Grammys to do something about it, but I don't. I know how it works. When it comes to Israel, it's always been separated. It's just like all the women organizations that are always talking about rape publicly. When it came to the seventh October attack, which women were raped, by the way a lot of them were raped in the rave, in the Nova party. We have testimonies of our friends. Yesterday, even some of the representatives of the UN came to our Community Day to speak with some of the witnesses, because they came here to Israel to do it. I can't understand why they need to come to believe me. There is a movement now that's called Me Too Unless You're a Jew. And when I saw even the name of it I was like, how can they separate me from the rest of the world, if I was in an international festival, music festival, just like anywhere else in the world? Manya Brachear Pashman: What would be a meaningful tribute in your eyes? What would you like to see at the Grammys on Sunday? Tal Shimony: I think they should do something similar to whatever they did on other occasions that terror attacks were happening, for any music festival or any music performance or in any other thing. I think they are creative enough and they are very good producers, they are bigger than, than whatever the Nova will ever be. So I trust them to know that they should recognize the fact that there was an attack in a music industry related festival. But I'm also not expecting them to do so because I know that this festival was in Israel. And everything that is connected to Israel or to Jews is being treated differently. People are saying it's not antisemitism, but I'm asking myself, so what is it? Manya Brachear Pashman: Will this exhibit travel, Tal? Will there be an opportunity for people around the world to see this and to memorialize this community? Tal Shimony: Yes, we are working on it, very hard, actually. I'm a part of the international team right now. It seems like the first destination might be New York or LA, but the United States. I think it's very important that everyone who can will come to this exhibition when it will arrive to an area that is close to them because it will mean a lot to the Nova community and also to the Israeli state. Manya Brachear Pashman: Tal, thank you so much for joining us. Tal Shimony: Thank you so much for inviting me. It means a lot and I'm so grateful for being here today. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Mark Weitzman from the World Jewish Restitution Organization, on how Holocaust museums worldwide and in Israel are grappling with the aftermath of October 7 in their exhibits. And tune in next week, for another conversation with a Supernova survivor, Yoni Diller. He shares his journey from that field in southern Israel that morning to American college campuses. Manya Brachear Pashman: The music heard throughout this episode was the last track played at Nova on October 7, when Hamas terrorists stormed the festival. The remix by DJ Artifex was released in dedication to all lives lost and forever changed that morning.
Jan 25, 2024
How to Mark International Holocaust Remembrance Day in a Post-October 7th World
This week, Mark Weitzman from the World Jewish Restitution Organization, joins us to discuss the links between the October 7 Hamas attack on Israel and the Holocaust, and how Holocaust museums worldwide and in Israel are grappling with the aftermath. As International Holocaust Remembrance Day approaches, we also delve into the direct connection between Holocaust denial and distortion to the denial and distortion of October 7 events, and how both are rooted in antisemitism. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Mark Weitzman Show Notes: Learn: AJC's Translate Hate Glossary: See why Holocaust denial / distortion is antisemitic. Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: A Spider Web of Terror: How Iran's Axis of Houthis, Hezbollah, and Hamas Threaten Israel and America Unpacking South Africa's Baseless Genocide Charge Against Israel Countering the Denial and Distortion of the 10/7 Hamas Attack 4-Year-Old Hostage Abigail Idan is Free–Her Family is On a Mission to #BringThemAllHome Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Mark Weitzman: Manya Brachear Pashman: One could easily say the October 7 Hamas invasion and massacre in Israel is one of the most well-documented terrorist attacks in history. Dozens of smartphone cameras and GoPros filmed Hamas terrorists crossing the border between Gaza and southern Israel murdered more than 1000 soldiers and civilians and kidnapped more than 200 others, the deadliest antisemitic attack since the Holocaust. But just like the scourge of Holocaust denial, October 7th denial is growing. Mark Weitzman is the chief operating officer of the World Jewish Restitution Organization, a nonprofit that pursues claims for the recovery of Jewish properties lost during World War Two. He's also the lead author of the working definition of Holocaust denial and distortion for the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance known as IHRA, and chairs the IHRA Working Group on museums and memorials. As we approach International Holocaust Remembrance Day, Mark has joined us to discuss how we can make sure the world does not forget or deny any atrocities committed against Jews. Mark, welcome to People of the Pod. Mark Weitzman: Thank you very much for the invitation to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: Mark, you are an expert on Holocaust denial and distortion. What does it have in common with the denial we're seeing around October 7? Mark Weitzman: I think there are clear connections between people who are downplaying or distorting the events of October 7, and those that engage in Holocaust distortion or hardcore Holocaust denial, because both are linked by an attempt to try to explain what is for them an uncomfortable historical reality that targeted Jews, whether the Holocaust or the events of October seventh, to justify their preconceived political agenda, which often includes an antisemitic conspiracy theory, either as its base or as its method to achieve their goals. One of the root causes of Holocaust denial distortion, from the antisemitic perspective, is the attempt to say that since the Holocaust, there is a certain sympathy for Jews as victims, and sometimes that turns into political sympathy or support for the State of Israel. Sometimes it turns into actions that are pro-democracy or anti-racist in terms of society and saying that we've seen what happened in Auschwitz, we don't want our society to go in that direction. So we're going to take certain positive steps. Those people who want to turn the clock back to a world where people could still be judged by their religion, their race or whatever signifier, often have to grasp with the Holocaust. It's the paradigm of what can happen when society turns evil. The same thing in the sense is at the root of October 7 denial. It's the attempt to say that, Oh, no, we don't want to allow any sympathy to Jews or Israelis, we have to justify it or explain it away in a way that allows us to accept the reality of what it happened, because denying it puts you in a really sort of cuckoo cage of denying what's obvious to everyone what happened there. So in this sense, in a particular sense, it can be by saying that, Oh, yeah, it happened there. The Israelis were killed, but they were killed by the Government of Israel. The hostages were not really taking the Gaza, they're actually hidden in Israeli buildings or holdings. That, you know, this is all part of a plot by Israel and the US government, aimed at undermining the Palestinian narrative and drive for freedom. But the goal there is similar, it's to grapple with a reality that most people would find repugnant. An anti semitic reality. The latest poll in the US shows 80% of the US population support Israel versus Hamas. And in an attempt to justify their stance, their pure antisemitic stance, they have to deal with that reality. And so you can't ignore it, you can say it didn't happen. Since as you pointed out, it's one of the most photographed and verified actions in recent memory. So you try to twist it away, and turn it on its head. Manya Brachear Pashman: But how do people wrap their heads around this fantasy fiction? Mark Weitzman: These conspiracy theories are linked. And I don't think enough people have realized this or paid attention to it, that Hamas's original charter, 1988, actually quoted, literally quoted the Protocols of the Elders of Zion, which is, as we all know, the Bible of antisemitic conspiracy theories. And they literally based their charter, it's the only western document quoted in their charter, their original charter. And it links the events of October 7, with the history of antisemitic conspiracy theories. This is not an anti-Zionist document, the protocols, it's an anti-Jewish, antisemitic document. So there's a direct connection there. The Holocaust is the most documented event in human history. There are films, there are millions and millions of pages of documents. There are so many archival records of survivors, of perpetrators, of war crimes tribunals that have, you know, judged and and entered into evidence, the effects of the Holocaust, the reality of the Holocaust, not just in the United States. But look at the David Irving trial, the famous David Irving trial. But all the war crimes trials in Europe as well, to say that it did not happen, or to twist, it requires an effort of will. And it's not just on the individual level. In our work at the WJRO, we see governments today that do not want to deal with restitution, and use manipulation of the Holocaust, to try to get out of it by claiming that it was all the Germans, the local collaborators had nothing to do with it, or that the numbers were inflated or that we don't know what the value was, what was really owned by by Jews at that time. All sorts of methods used to evade trying to make some payment, some form of restitution, and then to survivors and part of our mission is to set forth and ensure that the historical record, even in terms of the theft of Jewish property, is well established. So when we get to the events of October 7, particularly in an era where fake news, where people claim to believe all sorts of conspiracy theories, whether it's related to COVID, whether it's related to American election results, and a lot of these people kind of bond together. The underground of election denial and some of the anti-COVID extremists, and some of the Hamas or some of the October 7 deniers or distorters. Very often, they live in the same atmosphere, in the same basement, they imbibe the same fumes, they're in touch with each other. Very often they're cooperating or believe in similar conspiracy theories. And this is one of the problems that we have as a society, amplified by social media, is to separate the real from the fake, and to try to limit and minimize the impact that the fake has on real life, on mainstream society, and politics, and culture, and so on. Manya Brachear Pashman: So as I mentioned in the introduction, International Holocaust Remembrance is January 27. You just returned from a meeting with representatives of Holocaust institutions around the world. How did these museums come to be? I mean, was it a bricks and mortar movement to counter Holocaust denial, was it seen more broadly as a tool to fight antisemitism or something else entirely? Mark Weitzman: Well, I think that most of these came to be, first of all, through the efforts of survivors. In so many cases, it was the survivor community that were the driving force behind it. And yes, it was in response to antisemitism and to Holocaust denial. But those movements were not, in a sense, the dominant factors that we may think today. It was a sense, I think, more of trying to pass on what they went through, both to the Jewish community, their children and grandchildren, and so on, but more importantly, to the community writ large, meaning that to the world at large, whether it's the US or the UK or Canada. They wanted people to learn the lessons from what they had gone through and survived. They wanted people to not to have to deal with the same things that they dealt with. And it's fascinating to me, one of the most interesting things that I find in the field is that today, and not only a majority of visitors to Holocaust museums, the vast majority, are not Jewish. But the majority of people who work in these institutions are not Jewish either. There are people who have dedicated their lives to some second career, some it's, you know, a career long commitment to both studying and teaching and passing on lessons of the Holocaust. So what began sometimes within the Jewish community, as a survivor-led effort, at this point, there are very few survivors still actively involved in this, especially, you know, on that level, and it's evolved into something that is broader and larger than just the Jewish community. Manya Brachear Pashman: We had your colleague Rob Williams at the USC Shoah Foundation join us at the end of last year, and the Shoah Foundation is collecting testimonies from October 7 now. And I'm curious, are other Holocaust Memorial institutions developing programs or adding evidence from October 7, to their collections? Mark Weitzman: I think one of the things that came out at the meeting, which was at the Holocaust Museum in Washington about a month ago, was that these institutions are grappling with October 7, and it was very clear. And part of it is that most of these institutions had not tried to be politically based. In other words, they did not conceive of themselves as taking a political stance one way or the other. And the supercharged atmosphere of October 7, the events of October 7, the atmosphere post October 7, caught them, I think, by surprise, and they're still grappling with how to respond and how to react to it. There has been a tremendous amount of interest, of support. USC is leading the way with a tremendous effort of taping the survivor accounts and making them available. But I saw conversations, we had conversations from certain speakers in how to address October 7, how to deal with antisemitism in the wake of October 7. Because again, these are people who are not necessarily the the you're an expert in the Holocaust is that's really mean you're an expert in what's happening with Israel and Hamas and the Middle East, and, and so on. And it's a very different field, a very volatile field. And they're in a position that they had not anticipated. So I think that there was a shock. There's a strong sense of moral support, moral based support for Israel and the victims there, there is a strong commitment to, I think, keeping the message of releasing the hostages first and foremost in people's minds. But how exactly to go about it, what the best way to achieve those goals is still something I think some of them are wrestling with. Some are doing even little things like one museum that I know of, has in their gift shop, a sort of small section of Israeli objects for sale, that the proceeds will go back to, you know, to some of the communities or some of the people in Israel who have been evacuated or need support. So it can be a small thing like that could be educational programs. It can be public statements that could be hosting events, it could be showing the testimony. It could be learning more about the background that led up to it. There are a lot of potential paths and ways that they're engaging with. And I think each of them are finding their own path right now. But they were in the process of grappling with something that they had not anticipated. And this is somewhat novel, for them to have to deal with. Manya Brachear Pashman: Generally, do Holocaust institutions try to avoid Israel or kind of leave Israel out of their exhibitions, their collections, and really focus on the Jewish communities of their particular country? Mark Weitzman: I think it varies. I think that, you know, in a broad sense, they're not necessarily want to be seen up till now at least, as partisans in a political struggle or political battle. But there was clear recognition in so many of them you that you can't leave Israel out of the story, because you had survivors going to Israel. You had the Zionist youth groups, let's say in the Warsaw ghetto, and other places that It helps spearhead some of the revolts you, if you ignore those parts of the story of the narrative of the Holocaust, then, you know, you're not being true to the history of it. Would you show where survivors ended up after the war? Certainly, you know, a huge number of them, percentage wise ended up in Israel is one of the, you know, the prime spots for survivors to go to. You have many of them worked with Yad Vashem, for example, and have a relationship there. You have the righteous among the Gentiles, which is a story that almost all Holocaust museums wanted to have some focus on, because it's a prime example of non Jews responding in a positive way in the most dire circumstances, but the certification of who is a righteous Gentile came from Yad Vashem, in Israel. So there are, you know, inextricably linked to it, but you went, you didn't, and what they try to avoid, was taking a, you know, sort of a partisan position, should Israel do this action? Should this Israeli Government be supported against that Israeli government or, you know, so on and so forth. But the broad idea of Israel's right to exist of Israel as a place of refuge for the survivors as Israel, a change in the narrative of the history of the Jewish people in the 20th and 21st centuries, all those had to be part of the story and are dealt with, but in different ways in in many of these institutions. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you also traveled to Israel at the end of last year. And I'm curious up until now, how have Israelis talked about the Holocaust? Is it a cornerstone of their history as a modern nation, maybe not so much for the younger generations, and could October 7, connect some dots and change that? Mark Weitzman: Well, I led a small mission for the WJRO, and went down south to Kfar Aza. And also met with evacuees. And it was an incredibly moving experience. And the reality of what happened there, going to the exhibition on Nova, music festival is something that I don't think any of us who participated will ever forget. And it was interesting, because we had two guides, from the Israeli army, from the spokespersons office from the Israeli army, two young women who were with us in Kfar Aza down at the border, one of the worst hit places. And they made the connection. And we had a Holocaust survivor with us, as well. And she made the connection. And there was a resolve that, you know, this is something that we didn't think we would ever have to face firsthand. This kind of targeted destruction of Jewish civilian life. I don't think Israelis have fully come to grasp and understandably, with the implications of what happened, I think it may take even a generation or two, to kind of work this through in some ways, and I don't think…it may be premature to make judgments. But I think that there's no question that hearing over and over again, the worst act of violence since the Holocaust, gives a frame and a context that is going to keep the Holocaust as part of the conversation about this. Israel prior to this, there have been a lot of efforts. I mentioned Yad Vashem earlier, it's certainly one of the cornerstones of a historical, cultural life in Israel. But it wasn't the only place, there were other kibbutzim, such as up north, Beit Lohamei Ha-Getaot, the ghetto fighters kibbutz that had the same similar mission of educating about the Holocaust. The Israeli government that no matter which party the Prime Minister belongs to, has always been very strongly supportive of Holocaust education. Has been a partner key partner of WJRO, and its work on restitution issues and efforts. So the Holocaust has been, I think, part of the Israeli consciousness. But I think it was viewed as historical in many ways, this is what our grandparents went through. This is what happened over there in Europe. And now that reality is shifted a little bit, that, Oh, something that can be spoken about in the same sentence, not the same, not comparable in many ways. But it's here, and it's now. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how do the events of October 7 alter this year's observance of International Holocaust Remembrance Day? Mark Weitzman: Throughout the world, I think you're going to hear a lot of linkage in a way of people saying that, we can't forget that, you know, what happened, the victims. So many places are involved, for example, in the reading of names of victims names. And yet, for many of us on a weekly basis, or whenever we can, we still read the names of the hostages, and try to get them returned in those efforts. So there are going to be you know, connections like that connections made about the threat, the ongoing threat to the Jewish people. The fact that since the Holocaust 80 years ago, we haven't faced anything like this, like we're facing today. Um, certainly in the West, the in the United States, the conversation is certainly going to include the fact that Jews are in an unprecedented situation in this country in terms of anti semitism. The questions of the people trying to erode support for the existence and legitimacy of Israel take on much more significance, especially as they become much more high profile, the attempts. I'm sure there'll be part of, they are part of the political landscape for the forthcoming elections. Manya Brachear Pashman: AJC often cautions against comparing tragic events to the Holocaust because it risks trivializing the genocide of 6 million Jews. But I have heard well-meaning people make that comparison. In this case, is it a legitimate analogy? Mark Weitzman: Israel as a state, was able to strike back and respond in a way that Jews could not do during World War Two. Governments in the West–the UK, France, Germany, and so on the United States, of course, first and foremost, have responded forcefully defending Jews align themselves with Israel. Whereas governments in the West prior to World War Two, basically ignored, accepted or complicit in the Nazi actions. You know, those kinds of differences are significant. And the fact that as I said public opinion in the United States is firmly on the side of Israel compared to on the side of Hamas is also significant. So I think we have to be careful about making kind of glib historical comparisons. We're not powerless today. We were powerless in the 1930s. But that doesn't mean that our situation is not problematic and dangerous for us today it is. And we have to recognize that. But we need to do that, factually and calmly and realistically, we need to find our allies. And they're our allies, in many places, and to work together with them. Because the threat to us, particularly today, from Hamas, and allied groups like that, and their supporters, whether from the extreme left, the so called progressives, or the extreme right, is a threat to liberal society, in general. And that's something that we need to be able to share, and to work with our allies to turn that thread back. Manya Brachear Pashman: Mark, thank you for sharing your expertise and cautionary advice. Mark Weitzman: Thank you very much. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Dr. Matthew Levitt of the Washington Institute as he helped us make sense of the renewed terror threat, how Iran's terror proxies Hezbollah, Hamas and the Houthis are coordinating their strategy and attacks, and what the U.S., Israel, and its allies are doing to fight back.
Jan 19, 2024
A Spider Web of Terror: How Iran's Axis of Houthis, Hezbollah, and Hamas Threaten Israel and America
This week President Biden re-designated Yemen's Houthis as a global terrorist group amid its increasing attacks on international shipping in the Red Sea. Meanwhile, in Lebanon, the Hezbollah terror group continues to threaten Israel's northern border, and the Israel-Hamas war continues as Hamas still holds more than 100 Israeli hostages taken on 10/7. Matthew Levitt, Fromer-Wexler Fellow & Director of the Reinhard Program on Counterterrorism and Intelligence at the Washington Institute, joins us to help make sense of the renewed terror threat, how these terror groups are coordinating their strategy and attacks, and what the U.S., Israel, and its allies are doing to fight back against Iran and its terror proxies. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Matthew Levitt Show Notes: Learn: 5 Things to Know About the Houthis, Their Attacks on Israel and the U.S., and Their Treatment of Yemen's Jews Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: Unpacking South Africa's Baseless Genocide Charge Against Israel Countering the Denial and Distortion of the 10/7 Hamas Attack 4-Year-Old Hostage Abigail Idan is Free–Her Family is On a Mission to #BringThemAllHome What Would You Do If Your Son Was Kidnapped by Hamas? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Matthew Levitt: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week the US military struck a Houthi arsenal in Yemen that had threatened US Navy vessels in the Red Sea. It was America's fourth strike on Houthi turf since November 19. Meanwhile, the Hezbollah terror group continues to violate a UN Security Resolution and threaten Israel's border, and Hamas still holds more than 100 Israeli hostages taken during the October 7th invasion and massacre. What do all these terror groups have in common? Returning here to discuss is Matthew Levitt, the Fromer-Wexler Fellow & Director of the Reinhard Program on Counterterrorism and Intelligence at the Washington Institute. Matt, welcome back to People of the Pod. Matthew Levitt: Thank you so much for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's start with the terror group making the latest headlines. The Houthis? Who are they and why has the Biden administration just re-designated them a terrorist organization? Matthew Levitt: So the Houthis are a separatist group in Yemen, based in the north of the country. They are Shia, and they get support from Iran. But they're not exactly the same kind of Shia as Iran. And they aren't exactly the kind of proxy that says jump when Iran says how high. This is a relationship of convenience and my enemy's enemy. And they both hate the United States and the west and hate Israel. And the Houthis have been for years an ineffective, and for the Iranians an inexpensive and risk free way to complicate things for the Saudis. So for years, the Houthis were shooting at the Saudis when the Saudis were involved in the Yemeni war, after the Houthis had taken over. And that's one of the reasons why things are a little sensitive right now, because there have been efforts to try and negotiate a ceasefire between the Houthis and the Saudis. The Saudis aren't happy with what the Houthis are doing right now in the Red Sea. But they also don't want to rock the boat. The Houthis have as part of their mantra printed on their flag, Death to Israel, Death to America, Death to Jews, all three, they're not particularly, you know, unclear. And so they have flown drones towards Israel that have been shot down, they have fired ballistic missiles at Israel, some of which have been shut down by US Navy vessels, at least one was shut down by the Saudis. Just pause to think about that for a minute. The Saudis weren't thinking this was aimed at them, the Saudis shut down a Houthi missile aimed at Israel, which suggests that the Israel-Saudi reconciliation track, while very much on pause, is not over. And the Israelis have shot down some including for the first time ever using the arrow anti-missile system, which shot down a ballistic missile in lower outer space. Now, the Houthis have tried to leverage their position geographically by targeting ships in the Red Sea. They claim that they are targeting only those ships that are owned in whole or in part by Israel or have serviced Israeli ports. They've hit some American ships as well. They're clearly getting intelligence from the Iranians on this. And it has disruptive international freedom of navigation. And you have now a new problem in terms of getting things where we need them to be to stock our shelves, because boats that would normally go up the Red Sea and through the canal are now going around South Africa. Manya Brachear Pashman: And this volatility on the part of the Houthis is also compounded by what's going on with Hamas, and also Hezbollah. Is Iran the common denominator here, Matt? I mean, is that what all these terror groups have in common, or is there much more? Matthew Levitt: So it's true, the Houthis claimed that what they're doing is in support of the Palestinians. But what we are seeing for the first time put into action is the strategy that was developed by the late Qasem Soleimani, the head of the Quds Force, who was killed in Iraq several years ago. And that strategy was what he called uniting the fronts. And so this idea that across the spectrum, and it really is a spectrum of proxy, activity of sponsorship. Hezbollah is at one end very, very close to Iran, the Houthis, I would argue, are at the other end, and Hamas is kind of somewhere in between. Getting them all to be able to coordinate their activities, when push comes to shove. Now, Hamas for its part is very happy with the Houthis. They're quite disappointed with Hezbollah. There are reports in the Arabic press, that Hamas expected that Hezbollah would get much more involved and Hezbollah didn't when they saw the US naval presence, you know, two aircraft carriers. Whatever the specifics, Hamas have been very vocal about how displeased they are with the level of support they're getting from Hezbollah, though that has been significant. And they're pretty pleased with the support they're getting from the Houthis, which is outsized what might have otherwise been expected from the Houthis. Manya Brachear Pashman: So the alignment of these groups with Iran, what exactly does that mean? Does that mean that Iran is pulling the strings? Are they funding the activities? All of the above? I mean, you mentioned the goal of coordinating all these proxies, but does coordinating go as far as collaborating? Matthew Levitt: So I don't want to get into a semantic discussion of what exactly is the difference between collaborating and coordinating. I think what's important to understand here is that it's not like in the movies, where everybody's getting together at a meeting with evil laughs, coordinating all that they're doing. There have been some meetings, we know that for at least the past few years. Iranian Quds Force, Hamas, Hezbollah, Palestinian Islamic Jihad had been meeting at what they call, their term not mine, a joint operations room in Beirut. What all is coordinated is not entirely clear. You've had Iranian and some Shia militants from Iraq, the Ḥashd ash-Shaʿbī making statements recently about how, you know, generally things are coordinated right now. Frankly, the level of coordination took a hit with the assassination of Qasem Soleimani. And there was no one with the gravitas to kind of bring all these proxies together. So they actually leaned on Hassan Nasrallah, the Secretary General of Lebanese Hezbollah to come in and serve that role not only kind of mediating between the various Iraqi Shia militant groups, but also the others, the Hamas is that Palestinian Islamic Jihad and the Houthis. So they're not all sitting around a big conference table. And you'll do this and you'll do this, but they're all getting support–financial and often weapons from Iran. There is some significant cross pollination in some personalities. So for example, for the first time this week I've seen in the open source, Israelis say that the head of the Redwan special forces unit in southern Lebanon that has been firing anti tank guided missiles into Israel multiple times a day is a guy known as Abu 'Ali Al- Tabataba'i. He was in southern Lebanon for many years. Then he was sent to Syria, where he worked with Iraqi Shia militants and Quds Force. Then he was moved from there to Yemen, where Hezbollah had a very, very small contingent, maybe a couple of dozen. But the fact that they sent someone that senior was telling. I actually wrote a piece of Foreign Affairs about this years ago, when it came out that he was sent to Yemen. He was designated by the US Treasury, there's a Rewards for Justice from the State Department to reward out for his head. Well, he now is back from Yemen, got a promotion and is the overall head of the Redwan unit. And he has at this point, all kinds of personal relationships. And so there's a little bit of cross pollination, you might talk about the people you know, from back when you went to college together. And back in the day the Al Qaeda would talk, did you go to the duranta camp in Afghanistan? Do you remember that trainer? Well, now there's a similar thing going on in the Shia extremists milieu? Did you go to the camps together? Were you in Iran at the same time, or Iraq or Lebanon at the same time? Which trainer did you have, who did they send to you? And so there is coordination happening, but I don't think it's Houthis. Sometime this morning, you're going to be targeting a ship. On the flip side, there is some open source information about ships that you can find and their ownership. But it's clear that the Iranians are also providing them information that is not public. And they're also clearly working with Hezbollah. If you go back to October 7 itself, the plotline of October 7, fire a bunch of missiles under that cover, infiltrate across the border, take as many civilian communities as possible, kill a bunch of people, kidnap others across the border. That was the Hezbollah plan that the IDF Northern Command was preparing and training to deal with for years. And it was Hamas who used it, so you can see some of that connectivity. Manya Brachear Pashman: Ah, exchanges of strategy. Matthew Levitt: Strategy and more. It's not every tactic. It's not every every instance, but there is certainly overall strategy that they're coordinating. There certainly is communication. There certainly is movement of funds and of weapons. And, and this is the first time we're seeing that type of coordinated effort involving militants from Iraq, Iranian assets in Syria. You know, at one point, the Iranians flew a drone and crashed it into a school and a lot. The drone flew down. Jordan didn't cross into Israel until the very end went into a lot. It was a school where children evacuated from communities in the south, are being educated. I don't know if it's luck. I think it is. I don't think the Iranians had intelligence to know exactly what time class got out. But it was, you know, a couple of hours after class got out could have been much, much worse. And even just today, there are reports of things being shot towards Israel, around the Red Sea. Manya Brachear Pashman: So are we at risk of a wider war? Or does anything stand in the way of that? Matthew Levitt: Yes. We really are at the brink of a regional war. And I see a lot of people, a lot of press saying that Israel has done something which brings us to the brink of a regional war. And I challenge that Israel is responding to not only the attack on October 7, but to all kinds of attacks. Still, the United States also is not bringing the region to the brink of war, when United Kingdom strike Houthi assets in an effort to prevent them from being able or to deter them from carrying out attacks on vessels in the Red Sea. Ultimately, this really comes down to how far do Iran and its spectrum of proxies want to push the envelope. I think at the end of the day, they're actually quite happy with what's going on. So long as the fighting in the Gaza Strip continues, I think they feel justified in saying this can go on. They have said, Hezbollah and others have said, that this can stop when the fighting of the Gaza Strip stops. Whether that is what they actually mean or not is something only time will tell. But I think at the end of the day, the decision about whether or not this spills into a broader regional war doesn't rest with Israel or the United States or the United Kingdom, those that are responding to the aggression. But it's the aggressors. How far does Hezbollah want to push this? For a long time, Hezbollah was only hitting military targets in the north and now they're selectively hitting some civilian targets. Killed a mother and her son in their home in northern Israel just a few days ago. Generally, they're still hitting military targets but it's escalating a little bit in response to the Israeli assassination of Hamas leader Saleh al-Arouri, which was a big deal because they killed him in Hezbollah stronghold. They hit some pretty significant Israeli military targets, a radar installation on the Hermon mountains and Northern Command Headquarters near Safed. Those appear to be one offs. Do the Shia militias do something more? Do Iranian assets in Syria try and infiltrate more drones or rockets? Do the Houthis get lucky and hit something particularly big and bark something more. There's lots of ways for this to unintentionally, to escalate. But I do think that all parties right now don't want a regional war. That said, Hezbollah, Iran, the Houthis, the Shia militias in Iraq, certainly Hamas, Palestinian Islamic Jihad, some of the groups that we're seeing very active in the West Bank right now are quite happy to see this level of pressure on Israel and starting the first of what I think they want to be a trend, of these types of coordinated assaults. Manya Brachear Pashman: So why don't they want a wider war? What is their goal? Matthew Levitt: They all have as part of their goal, their raison d'etre, destroying Israel, kicking the United States out of the region, undermining Western powers in the region, etc. But they all also understand that you go too far, and you open up this to a much broader conflict. The United States has barely gotten involved. They've done a few very, very small things in Yemen. They have been very supportive to Israel's effort to defend itself. While the US has sent significant forces to the region, they have not done anything, for example, regarding Hezbollah in Lebanon. They've not done anything in terms of the Hashed al-Shaabi in Iraq attacking Israel, though they have responded very, very, very few times, I might add, to the significant number of times Iraqi Shia militants have struck at US military targets in Iraq and Syria. They understand that this could get much bigger. And ultimately, Iran understands that if things escalate too much, that the fight is going to come to Iran. And it won't stop. They also really don't want Hezbollah in particular, to go too far in the moment. Because all those rockets that the Iranians have provided to Hezbollah in violation of UN Security Council resolution 1701, since the 2006 war, they're not there primarily for this. They're there to deter Israel and anybody else from attacking Iran's nuclear program, which by the way, the Iranians have been pushing the envelope on throughout this period of conflict since October 7. And if anybody should attack Iran or its nuclear program, this is seen as Iran's best second strike capability. It's why Hezbollah has basically not fired almost anything other than the Kornet anti tank guided missiles, fired a couple of other short range things. But none of the precision guided missiles under the longer range missiles, that's all, but that powder is dry. That's all for now. And I think Iran doesn't want those spent right now, and also doesn't want these to escalate to the point where the Israelis go ahead and try and take them out under the cover, or in the context of this current conflict. So there's a strategic set of goals and they believe in, you know, the concept of muqawima, of resistance. There's this idea of muqawima patience, right? This, from their perspective is what God wants, it will eventually happen. This past three months, this is a huge step on the road to resistance victory. This is a huge success in terms of galvanizing multiple forces to unite the fronts. Doesn't all have to happen right now. But they believe that this is very much a sign that they're on the right path, and it's a step in what they would consider to be the right direction. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Matt, thank you so much. I appreciate you explaining who these terror groups actually are and helping our listeners better understand the headlines. Matthew Levitt: It's always a pleasure. Thanks so much for having me. And if you want more, there's plenty more at WashingtonInstitute.org. Thank you for the work you're doing and for having me on the show.
Jan 11, 2024
Unpacking South Africa's Baseless Genocide Charge Against Israel
The International Court of Justice is currently hearing South Africa's case accusing Israel of genocide in Gaza. Professor Geoffrey Corn from Texas Tech University joins us to explain how we got here, the case's significance, and why the claims of genocide are baseless. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Geoffrey Corn Show Notes: Explainer: What You Need to Know about South Africa's Baseless Genocide Accusation Against Israel Go Deeper: 5 Reasons Why the Events in Gaza Are Not "Genocide" Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: Countering the Denial and Distortion of the 10/7 Hamas Attack 4-Year-Old Hostage Abigail Idan is Free–Her Family is On a Mission to #BringThemAllHome What Happens Next: AJC's Avital Leibovich on the Hostage Deal and Challenges Ahead What Would You Do If Your Son Was Kidnapped by Hamas? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Geoffrey Corn: Manya Brachear Pashman: The International Court of Justice is holding its first hearings in a case filed by South Africa, accusing Israel of committing genocide against Palestinians in Gaza. While it could take years for the panel of judges to rule on the genocide accusation, South Africa has asked the judges to issue a restraining order of sorts in the coming weeks that could among other things, call on Israel to halt its effort to root out Hamas and bring home the remaining hostages, at least until a verdict is reached. Here to explain what's at stake and the questions that the court will need to weigh is Professor Geoffrey Corn, Director of the Center for Military Law and Policy at Texas Tech University. Professor Corn. Welcome to People of the Pod. Geoffrey Corn: Thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you are an expert in international humanitarian law and the law of war, which to some those terms might seem contradictory, or are the? Are they actually one in the same? Geoffrey Corn: No, they refer to the identical branch of international law, historically, we call this branch of law, the laws and customs of war. Before the end of World War II, it was referred to as the law of war. And then, of course, with the advent of the United Nations Charter, technically war was prohibited. And states engaged in armed conflicts. And so the name evolved for many years to be referred to as the law of armed conflict, the Loack, that's still what it's called. And in official US circles, we have the Department of Defense law of war manual, and the army law of armed conflict manual, most of the world today refers to it as international humanitarian law. And that, as you know, it can be misleading because it suggests that it's really focused on human rights. In fact, IHL, or international humanitarian law is a synonym for the law of armed conflict. It's the law that regulates the conduct of hostilities, during conflicts between states or between states and non-state groups, and protects victims of war. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's cover another basic distinction or definition that will help listeners decipher all of this, the charges that I spoke of in the introduction, they had been brought in the International Court of Justice. And now that's the 15 judge panel of the United Nations. Not the International Criminal Court, which is also in The Hague, but charges individuals with war crimes. So can you explain for our audience the purpose of the International Court of Justice? Geoffrey Corn: Sure, the International Court of Justice is part of the mosaic of the Charter of the United Nations, a treaty that was created in the aftermath of World War II, to manifest the international community's determination that wars not be the mechanism by which states resolve their disputes. So there are a variety of mechanisms built into the Charter of the United Nations, the one people are most familiar with is the Security Council, which is vested by the treaty with enforcement power. So the Security Council has the authority to authorize measures for the restoration of international peace and security. So for example, in 1991, when the coalition conducted military action against Iraq to force it out of Kuwait, that was done under the authority of the Charter of the United Nations and the Security Council resolution to restore international peace and security. One of the four components of the United Nations is the International Court of Justice. It is a successor to a prior international court that sat in the Hague, and its singular jurisdiction is over disputes between states, or to give advisory opinions on international law as requested by the Security Council or the General Assembly. But the primary function of the International Court of Justice is to serve almost like an arbitration mechanism when states have disputes so that they can resolve them in accordance with international law without resorting to force to resolve those disputes. And so it has no jurisdiction over individuals. It is, as you know, very different from the International Criminal Court, which is a treaty based criminal tribunal, and its jurisdiction is dependent on whether or not the individual is a national of one of the treaty parties, or whether the alleged crimes occurred in the territory of one of the treaty parties is Israel is not a party to that treaty, nor is the United States. But Palestine is. They've accepted Palestine as a member of the court, which means the prosecutor for the international criminal court has jurisdiction to investigate and pursue charges for any alleged war crimes that he believes have occurred in Palestinian territory, which includes Gaza. So two very different courts, very different consequences for their assertion of jurisdiction. Manya Brachear Pashman: So now, both Israel and South Africa are signatories of the 1948 Genocide Convention. That is precisely why these charges have been brought to the ICJ. It's because they are both signatories of that treaty. Geoffrey Corn: Yeah, so I wouldn't say charges, I would say accusation. Right, because when we say charge, we tend to think of a criminal accusation. Let's remember that an accusation is just that. It's not proof, it doesn't prove anything. If you read the filing by South Africa, it really is an exercise in selective fact assertion and ignoring inconvenient facts, there's a lot more to this story that we're going to see when we see the Israeli filing in response. So the Genocide Convention says, if there's a dispute between signatories or contracting parties to the treaty, they agree to allow the International Court of Justice to resolve that dispute. So one of the aspects of South Africa's filing is that they alleged that they've made a number of diplomatic forays to Israel demanding that they explain how what they're doing is legal and asserting that it's genocide. And Israel has not responded to those diplomatic forays, and therefore, that's created a dispute within the meaning of the treaty. And one of the things the court is going to have to resolve is whether there is in fact, a dispute between two members of the treaty as a jurisdictional predicate to even reaching the question of whether they should impose preliminary measures. Manya Brachear Pashman: And does that precede the ruling on provisional measures? Geoffrey Corn: It will be it will be part of the ruling. In any in any court of law, there's always a question of jurisdiction. Now, in most cases, it's not complicated. If you commit a crime where you live, the state has jurisdiction over that crime, but in the international realm, it's often a matter of debate as to whether or not the tribunal that has been requested to adjudicate an issue is actually vested under the law with the power, that's what jurisdiction means the power to resolve that issue. So the first issue that the court's going to have to resolve is whether it in fact, has jurisdiction pursuant to the terms of the Genocide Convention. And then if it says it does, then it will go to the question of whether there is a compelling case for preliminary measures. Manya Brachear Pashman: So we know South Africa has a history of anti-Israel positions, it has historically sided with the PLO, Palestinian Liberation Organization and it now appears to be supporting the Hamas terrorists that govern Gaza. There also might be some political posturing going on here ahead of a national election. But how did we get here? A genocide claim against the Jewish state. Geoffrey Corn: I think the answer to that is twofold. I mean, the first is that there is a widespread public perception that the level of carnage being inflicted as a result of Israeli Defense Force operations in Gaza is intolerable. And it's created a perception among many that the Israelis are actually not just trying to defeat Hamas' military capability–they are trying to destroy in part the Palestinian population of Gaza, that that's their intent. Now, I personally believe that that is a highly erroneous inference to draw from the facts on the ground. But this is part of Hamas' information campaign. This should be unsurprising from the inception of this conflict, they know that they cannot defeat Israel in battle. And this is one of the ironies of Israel's military struggle against Hamas. And I would say even if it occurs, Hezbollah. These highly capable organized military groups are under no delusion that they have the capability to confront the Israeli Defense Force and defeat it on the battlefield. For them, combat is not about defeating your enemy. For them combat serves their information campaign. They use combat to create conditions to advance their strategic information campaign of delegitimizing Israel, but more importantly, in creating pressure both within Israel and externally to force Israel to terminate its operations before it achieves its combat objectives, which are much more traditional, which is to defeat your enemy on the battlefield. So if you think about it, for Israel, what does operational success look like? It looks like Hamas' military capability has been completely destroyed. The word destroy is a military doctrinal term, and it means that you are combat and effective without substantial reconstitution. What is Hamas' is operational objective? It's to be there when the proverbial and literal dust settles. And that means they've got to do something that compels Israel to stop before it achieves its military objective of destroying Hamas. They can't do that by force. They can only do that by getting the international community to pressure Israel to terminate its operations before they've achieved these objectives. And the best ammunition Hamas has to do that is creating the reality and the perception of the indifference to the human suffering that's occurring in Gaza. So this is all connected to a strategic objective of Hamas. And that's why the most prominent statistic that we hear day in and day out is what? The civilian death toll in Gaza, which ironically, never apparently includes an enemy combatant. I guess the IDF is fighting shadows, because apparently they're not killing any enemy, because every casualty is asserted to be a civilian. And I don't want to, in any way, minimize the tragedy of human loss and war. But you cannot find an enemy that's determined to create conditions where you have to inflict civilian casualties without doing so. And that's the strategy from inception that has snowballed into a public perception that Israel's objective is much more nefarious than simply defeating Hamas. That's one factor. The other factor to be to be candid, is the terribly bombastic statements of certain Israeli government officials that fuel this perception that you have an ulterior motive here that's separate from just achieving a legitimate military goal, and the failure of the Netanyahu administration to be more aggressive in sanctioning or isolating the officials in the government who make those foolish statements. Manya Brachear Pashman: To be fair, I should note that Prime Minister Netanyahu did post a statement to social media after this interview was recorded in which he insisted that Israel has no intention of displacing the Palestinian population from Gaza and permanently occupying the Strip, despite those calls from some Israeli government officials. Israel's legal team is quite likely going to emphasize the extensive precautionary measures taken by the IDF to minimize civilian casualities and they will also quite likely emphasize the ongoing humanitarian relief being facilitated by Israel since mid-October – tens of thousands of tons of medical supplies , food, water, shelter equipment. Still, that doesn't change the level of carnage you mentioned, which is incredibly disturbing for all of us. You predicted early on that the notion of proportionality would become an issue. You predicted that back in October, regarding Israel's response, and I'm curious if you could kind of explain the notion of proportionality, the misconceptions about proportionality when it comes to warfare. Geoffrey Corn: So it's a critically important question, because if you read the 84-page submission by South Africa, they make what they allege to be the indiscriminate nature of Israeli military action, a centerpiece of their proof of genocide. o when we talk about proportionality in war, there are two different aspects of proportionality we have to understand. The first relates to the right of the state to defend itself. And that really functions no differently than if you were walking down the street and somebody attacked you under the law of self defense. You are allowed to take self help measures to protect yourself, but those measures have to be proportional to the threat. It is a mistake to assume that that is only limited to tit for tat response. They fire a missile, you're allowed to fire a missile. If someone swung a punch at you on the street. The law doesn't say you're only allowed to swing one punch back and then wait for them to punch you again. You're allowed to take reasonable measures. So if we think about Israel's action of self defense against Hamas, what do we know? We know Hamas represents an ongoing threat of significant military and terrorist violence against Israel. And the only way that Israel would be able to be confident that it's restored its security, the security of its population, the security of its territory, would be to take military action to completely destroy Hamas' military capability. So the way that that self defense objective is translated into military terms, in the military as a whole, you need to do what is necessary to be able to come back to the political leadership and say, the people in southern Israel are safe again. And so the idea that Israel should just terminate operations and build a wall is unrealistic, because they tried that already. They've had more limited military action against Hamas in the past, and Hamas has demonstrated over and over again, an ability to bypass their defensive measures and inflict death and injury on Israelis. Once you're fighting, there's another component of proportionality, which is the one that we're all focused on now. And that has to do with what we call the incidental or collateral consequences of attacking a legitimate target. So if I'm going to attack a building, because there's an enemy fighter in the building, and I know that in doing so, I cannot avoid killing civilians, I have to make a proportionality assessment under the law of armed conflict or international humanitarian law. For each individual attack, the commander has to make a judgment. First, the commander has to assess the military value of attacking the target, then the commander has to assess the unavoidable civilian risks that will be created by conducting that attack. If the commander concludes that the risk, the harm to civilians would be excessive, compared to the concrete and direct military advantage, then the attack would be considered disproportionate and indiscriminate within the meaning of international law. So if I were to put a question to your audience: you have an enemy commander, you identify him in a bunker, that's the enemy has put under a congregation of civilians deliberately, maybe the bunker is under a school. And he's a high-level enemy commander. And you've done everything you can to get civilians to evacuate. But you know that the only way you can kill that commander is to conduct an attack that will result in 20 civilian casualties. If we took a poll right now, is 20 civilian casualties excessive in relation to the value of attacking that target–we'd probably have as many answers as we had participants. So the reality is that when we look at an aggregate number, even if we take Hamas as numbers at face value–23,000 civilians have been killed. And we say that proves all of the attacks were indiscriminate. It's a complete distortion of the process of analysis. Because you don't do an aggregate number, you look at the individual attack, you have to decide what was the value of the attack? What was the risk that was anticipated? What measures did the attacking side do to mitigate risks? What measures did the defending side do to exacerbate risk? And you put all that into the equation. So there's been a complete distortion of the way this is actually supposed to function. And what we've created and what South Africa has done in its filing is it's created, almost a strict liability standard. If you kill X amount of civilians, your attack is indiscriminate and it violates the proportionality rule. I always ask a question in response, if you tell me that killing 100 civilians as a consequence of killing a high level enemy commander is too much. How many are okay? Can you give me a number? Is 50 okay, 20,10. There's no book. There's no manual, there's no equation. And that's why my view from inception has been the much better mechanism for mitigating civilian risks are the steps you take before the attack to reduce that risk. And when we look at that, we see no moral equivalency because you have the Israelis trying to figure out ways to reduce civilian risk, and we have Hamas deliberately engaging in conduct that exacerbates civilian risks. Manya Brachear Pashman: There's been a longstanding concern that in the United Nations, Israel faces a double standard. Other nations don't face this kind of scrutiny when they are involved in armed conflicts, though this court has taken up separate Genocide Convention cases filed by Ukraine against Russia and another filed by Gambia against Myanmar. So is this once again a double standard or is this different? Geoffrey Corn: Here's one of the ironies, because the effects of combat had been so visible in Gaza. The assumption is we should be dwelling on whether or not Israel is conducting war illegally. Hamas has fired over 10,000 rockets at Israel, they don't even pretend to be trying to attack military targets. They're just firing rockets at the civilian population, which is the blatant first level of violation. Now, fortunately, Israel has prevented most of those attacks from achieving their intended objective. But that doesn't mean they weren't illegal, because the law doesn't focus on whether you achieve your illegal result. It focuses on what you're trying to do. So when people like Bernie Sanders writes an op-ed in the New York Times and says, Okay, I can see that what Hamas did on October 7 was a war crime. Well, first off, that's, you know, I mean, that's self evident. But what's ironic is he doesn't acknowledge that what they've been doing ever since October 7 is war crimes. Every time they fire another rocket it Israel. They are the ones that are blatantly an indisputably violating the law of armed conflict. And yet it's the Israeli Defense Force that is the subject of international scrutiny persistently And it's no surprise because this is the nature of modern warfare. It's a bigotry of disparate expectations. And the Israelis know it, and they're not released from their obligation because they're fighting an illicit enemy. But it is it is corrosive to fail to acknowledge that the pernicious tactics of that enemy are largely responsible for the level of civilian suffering destruction, that is becomes unavoidable when you're fighting them. Manya Brachear Pashman: There are still more than 50 hostages still being held by Hamas, their well-being unknown. Does that change the equation for these court proceedings or the court's decision on provisional measures? Or is that a variable for the International Criminal Court to take up? Geoffrey Corn: There's no doubt that Hamas' has objectives and its stated purpose is to commit genocide of the Jewish people in Israel. There's not going to be but what about them argument. I don't see that happening. I think it becomes much more significant for the prosecutor of the International Criminal Court, because hostage taking inhumane deprivation of liberty or war crimes within the jurisdiction of the International Criminal Court. We know Hamas is not going to prosecute its own individuals. And so the credibility of that court is going to, I think, demand that they investigate and prosecute the summary execution of civilians on October 7, the sexual violence against victims, the hostage taking, the deprivation of access to the International Committee of the Red Cross. All of these are blatant violations of the law of war, and are within the jurisdiction of the International Criminal Court. So if I were the ICC prosecutor, and I would look at this as objectively as I could, I would look at the conduct of the Israeli Defense Forces and whether or not they've taken corrective measures against what I believe were violations of the law. No military is perfect. There have been examples of Israeli soldiers engaging in ill discipline and unjustified conduct in Gaza. And the Israeli Defense Forces have an obligation to investigate and discipline their own. I would look at how effectively that had been done. I would look at Hamas' actions. And if I believed there was credible evidence of a violation of the charter that was being ignored by the institutional leadership, I would indict. And if I never got them in front of the court, that's not my problem. My objective is to demonstrate that there have been violations that are worthy of being adjudicated. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much, Professor Corn. I really appreciate you breaking this down for us. Geoffrey Corn: Thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Dr. Robert Williams, Executive Director of the USC Shoah Foundation. He joined us to discuss the history and tendency to deny atrocities committed against Jews and the foundation's added mission of collecting the testimonies of October 7 survivors.
Dec 28, 2023
Countering the Denial and Distortion of the 10/7 Hamas Attack
Since October 7, the USC Shoah Foundation has added a new component to its mission: collecting the testimonies of those who survived the worst antisemitic attack since the Holocaust to counter those who deny it took place. Dr. Robert Williams, Executive Director of the USC Shoah Foundation, joins us to discuss the history and tendency to deny atrocities committed against Jews, the importance of collecting testimonies, and how they help in understanding antisemitism in all its forms. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Belle Yoeli (1:44) Robert Williams Show Notes: Take action to bring all hostages home now. To support our work today, you can visit AJC.org/donate. Or text AJC DONATE to 52886. Learn more: USC Shoah Foundation: Survivors of the October 2023 Hamas Terrorist Attacks Testimony of Shaylee Atary Winner Testimony of Maor Moravia The Testimonies Archive The Testimonies Archive Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: 4-Year-Old Hostage Abigail Idan is Free–Her Family is On a Mission to #BringThemAllHome What Happens Next: AJC's Avital Leibovich on the Hostage Deal and Challenges Ahead What Would You Do If Your Son Was Kidnapped by Hamas? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Robert Williams: Manya Brachear Pashman: Since the Hamas terror attacks on Israel on October 7, the Shoah Foundation has added a new component to its mission: collecting the testimonies of those who survived the worst antisemitic attack since the Holocaust to counter those who have dare to deny it took place. Dr. Robert Williams is the Advisor to the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance, where he served for four years as chair of the Committee on Antisemitism and Holocaust Denial. In October 2022, he became the Executive Director of the USC Shoah Foundation. Dr Williams is with us now to discuss the history and tendency to deny atrocities, in this case, those committed against Jews. Thank you for joining us. Dr. Williams, if you could begin by explaining to listeners what Holocaust denial is, and how it's similar or different from Holocaust trivialization and distortion. Robert Williams: Holocaust denial is a little easier for us to wrap our heads around, for better or worse. Holocaust deniers are essentially trying to tell people that the Holocaust didn't happen for one of two reasons. The most obvious reason is because they're antisemitic, they want to tell people that the Jewish Diaspora writ large has come together to invent this grand conspiracy to pull the wool over the eyes of non-Jews for all manner of dastardly purposes. So that's the first reason. The second reason is also antisemitic, although in a slightly different way. That is to rehabilitate national socialism as an acceptable ideology. No matter which way you slice that cake, it still ends up being antisemitism. That's why, to echo the words of people like Deborah Lipstadt, and others: Holocaust denial is antisemitism. Full stop. And it's a problem. It's something we need to deal with. But in our parts of the world, roughly speaking, the northern hemisphere, the West, it's become fortunately a bit of a microphenomenon over the last couple of decades. The bigger problem is the second part of your question: Holocaust distortion, and I use the terms trivialization and distortion interchangeably. I prefer to use distortion. But Holocaust distortion is in essence, rhetoric that minimizes, confuses, or otherwise misrepresents the Holocaust, both as something factual, and something that has relevance today. And that can take on a variety of forms, it can be something obvious like minimizing the number of victims, to something that's a little less obvious like figure skaters dressing up like concentration camp victims for their routines. Now distortion also brings with it a challenge: is somebody distorting because they're cynical antisemites? Sometimes the answer is yes. Other times, distortion of the Holocaust happens because people don't know the facts, or they think they know the facts and they don't, and they end up saying the wrong thing. But again, the end result, no matter the motivation, becomes problematic. Because if you are misrepresenting the Holocaust, you are effectively doing two things. On an ethical plane, you are disrespecting the memories of the victims and the survivors, and that's wrong. And on a practical plane, you are opening the door. I like to say Holocaust distortion kind of acts like a gateway drug to outright denial, to conspiracy thinking, and to more dangerous forms of antisemitism. So you have to tackle distortion, but you tackle distortion often in ways different from that of denial. Manya Brachear Pashman: But rather than focus on the word Holocaust, I want to focus on the word denial. You mentioned Deborah Lipstadt, for example, and she recently expressed concern that people are denying that Hamas committed so many heinous crimes on October 7. Is this a phenomenon, this denial of atrocities – do you see it more applying to atrocities against Jews? Or have we seen it in other instances? Robert Williams: Well, we've certainly seen it in other cases of mass crimes and genocides. One of the most prominent cases that predates the Holocaust is denial of the genocide of the Armenian people in the early 20th century, something that persists in certain parts of the world and is part of official state policy in some countries. Denial of the Armenian Genocide is problematic for a whole host of reasons. First, again, it's immoral visa vie the victims and survivors of that particular genocide to deny their experience, to say it never happened, to minimize it. It also has inhibited global understanding of Armenian life, history and culture since the genocide happened. So denial of mass atrocity crimes is something quite common when it comes to the denial of crimes against the Jewish people. You do see this over and over over and over again, though, you see, either excuses for the various pogroms that have claimed the lives of hundreds of 1000s of Jews over the centuries, or an attempt to minimize it, or an attempt to suppress that history. And that's separate from the denial and suppression of Holocaust history that we've seen through time. And we have seen, not just in the case of the October 7 attacks, but denial of other atrocities that were carried out against Jews through various forms of anti semitic terror violence. But we've definitely begun paying attention to it after October 7, in part due to the scale, you know, the largest act of anti semitic violence against the Jewish people since 1945. In the one place where it was never supposed to happen, people were supposed to be safe. And the international community, you know, you're used to seeing these claims of exaggeration or outright denial from certain countries in the Middle East or North Africa, but this is become widespread. Think within, was it a week, nine days after that horrible series of attacks, with people asking to see photographs of the murdered children, because they didn't believe that. So engaging in very dangerous, I would say almost pornographic rhetoric, about violence against the most innocent among us. And engaging in it in a way that encourages denial encourages doubting the veracity of these crimes, or–and we've seen this in other corners as well since October 7 –rhetoric that in turn moves from denial to outright justification for the atrocities that were committed. It's very tricky. It's not black and white. Unfortunately. Mnya Brachear Pashman: Does social media amplify Holocaust denial, and are we seeing that same trend now with the October 7 attacks? You talk about it being a post-truth world. Robert Williams: I absolutely think that's the case. Although I will say, outright denial on social media. Again, it's there. It's a problem, but it's less common than distortion and intentional manipulation. You know, I think even the term Holocaust distortion is potentially problematic, we're probably better served calling it Holocaust disinformation. And I think we're seeing some of the same dynamics at play in the post October 7, discussions that we see in online forums, including closed forums, in places like telegram or Gab or Discord, as well as in more public facing ones like X and Instagram and threads. Manya Brachear Pashman: Before we leave the topic of denial, and move on to distortion, because I do want to explore that a little bit more. I do want to ask about the role of Holocaust denial in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Palestinian Authority leader, Mahmoud Abbas, he wrote his dissertation at the University of Moscow denying the Holocaust happened to the Jews, that it was more of a product of the Jews' collusion with the Nazis. Is that a belief that is common among Palestinians or pro-Palestinian supporters. What role does that piece of disinformation play in exacerbating the sentiments? Robert Williams: There's a lot to unpack in that question. I'm going to start with the caveat that I'm a specialist on Europe, not a specialist on the Middle East. So a lot of my understanding of dynamics around distortion and denial among non Israeli Palestinians is anecdotal, and based on secondary literature. But it does seem that there is a current in some parts of the Palestinian culture where denial of the Holocaust is known to the degrees to which it's accepted, or probably vary from time and place. And it makes a certain amount of sense. Because if you can deny the reality of the Holocaust, you can then point to the State of Israel and say, the Jewish people who've never been victims were the eternal victim. It's much easier to be a victim when you're in a complex political world anyway. The more interesting thing is the origins of the Abbas dissertation, and how it's managed to spread across at least the Arabic speaking and Persian speaking worlds. To a certain degree, it's something that has been generated in Muslim society. But as scholars like Jeffrey Herf, have shown certain elements of antisemitism spread from Europe in the case of Professor Herf's work, from National Socialist Europe to parts of the Middle East, and then those forms of antisemitism spread. And as the works of people like Isabella Taparofsky have shown, particularly in the case of the Abbas dissertation, a boss wrote that dissertation in the Soviet Union and at a time when the Soviets promoted through international propaganda schemes and domestic propaganda, virulent, dangerous forms of anti-Zionist antisemitism, that also included trafficking and Holocaust denial. So the origins of it came from the Cold War, policies and practices, to a certain extent, of the Cold War policies and practices of the regime that no longer exists. A regime that sought to undermine democracy, sought to undermine solidarity in the western world sought to undermine the State of Israel, well throughout its history. And there's no acknowledgement of that. So if we're going to root out Holocaust denial, no matter where it lies, we have to begin with its origins. And those origins vary from time and place. Some of the origins lie in the National Socialist experiment. The Nazis had all manner of terms and actual formal programs to cover up their crimes. Some of those origins lie with certain French intellectuals, certain origins lie with American public figures in the 1940s. And some of the origins lie in the Soviet Union. We need to know the enemy top to bottom if we're ever going to deal with. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to move on to distortion. And I'm curious if the kind of distortion that we're talking about that is common now on social media and in conversations, especially those around October 7, does it tend to be a far right phenomenon, far left, pretty universal? Robert Williams: So Holocaust distortion, the trends have shown, cuts across all ideological, social, cultural, political and religious barriers. Now, certain forms are more common to certain groups at certain times, the forms of distortion that minimize the number of persons murdered during the Holocaust, for example, or claim that the Jewish people did something to deserve the Holocaust. Those have typically been more common on the far political right. And among some religious conservative extremists. Some of the forms that suggest that the Jewish people make use of the Holocaust for all manner of gain, everything from funding to guilt to special protections, to justifying the State of Israel – pretty much cut across the left, right divide. Certain leftist forms of Holocaust distortion through antisemitism that have emerged at least since the Second Intifada, take the form of the Jewish people using the Holocaust to justify the State of Israel or the policies of the Israeli government. But by and large, distortion of the Holocaust is unfortunately a phenomenon that is everyday. It even takes the form of particular types of commercial distortion, people engaging in it without any ideological agenda. One need think of the unfortunate situation that seems to happen every couple of years where Anne Frank Halloween costumes go up for sale in the US or in the UK, or when Chinese made ornaments depicting Auschwitz Birkenau become up for sale on on Amazon or even I think it's still possible today to buy model kits and toys of Hitler and his inner circle. People who make the subject so blase and everyday that it loses its power. That's a different form of distortion, stripped of ideology. Alright, October 7 distortion at first, and again, I'm an historian, so I like to have a wealth of evidence before me. But based on early observations and research, those forms of distortion and denial that emerged often enough were associated with in the Western world, largely the political left, and certain forms of protest movements that either had shared affinity with the Palestinian cause or would be affinity with the Palestinian cause. But what we've seen over the last couple of weeks is that is no longer the plaything only of the political left. We have seen some people on the extreme right begin engaging in similar rhetoric. Now, there's no sympathy being given to the Palestinians in that rhetoric, but claims that the State of Israel is making too much use of this, or the Jewish diaspora is using this for all manner of bad things. So it is beginning to cut across those boundaries that we've seen. Manya Brachear Pashman: The Shoah Foundation holds the world's largest video collection of Holocaust survivor and witness testimonies. And it has now begun collecting video testimonies of the atrocities committed by Hamas terrorists against the Israelis on October 7. Why? Robert Williams: So I assumed the leadership role here at the Shoah Foundation about 13 months ago, and I was brought here to establish a robust initiative focused on antisemitism. The Shoah Foundation was created as a platform so that the voices of Holocaust survivors could echo for future generations, and moreover, lead to a better world. In a sense, we engage in wish fulfillment. Survivors gave us their testimonies to bring about the world they wanted. And when you get right down to it, survivors wanted only a few things. One of those things, I guarantee you, was a world without antisemitism. So we have an obligation to those survivors to try, especially before the last of the survivors leave us, to create the conditions to bring about that better future. So we had been developing this laboratory, this multi-subject expert initiative that would deal with antisemitism as it's existed since 1945. And we were going to start, we are starting, with the development of a massive collection. Our minimum goal is 10,000 testimonies of antisemitic violence in a variety of forms. And we broke, we broke that into five categories. One of those categories was the survivors of antisemitic terror attacks. Several months ago, we thought, alright, we're gonna focus on this, our starting point is going to be the 1994 bombings in Buenos Aires. We're going to work our way forward. And then October 7 happened. So we had to swing into action immediately. Within 12 days, we had secured the first testimony on the ground. This was possible thanks in part to our already existing work in Israel and our strong partnerships with Israeli institutions, including the National Library of Israel and Yad Vashem and others. The Ghetto Fighters House as well. And very quickly utilizing our on the ground teams, our partnerships, we began to acquire testimonies using the same methodology that we did in the 1990s when we started taking Holocaust survivor testimonies. And a few things became readily apparent to us. One is just the simple tragedy, and the painful irony of this endeavor. In the 1990s, when a survivor came and gave us her testimony, the first thing you would see is a sheet. The survivors name, the date of the interview, the interviewer's name, some basic information. And we're seeing the same thing when we look at survivors of the October 7 attacks. There's true tragedy there. We've secured as of the date, as of today's recording, a little more than 250 of these testimonies. They will be put online for free, I think we have about 70 or 80 online right now. We have a partnership with some media partners, including Tablet Magazine here in the United States to make them even more available, and they will be made available to our Israeli partners for use, because this is the history of Israel and its people now. But our goal is to use these here, so that we can begin training people from a major university, how to understand antisemitism in all its forms and how to build resilience against it, how to research the subject on a deeper level, how to write better journalism around the subject, and how to respond and recognize that the victim of antisemitism is not some faceless person or somebody who lived eight or so decades ago. Somebody today, just like you, just like me, just like our children, or our parents. Manya Brachear Pashman: Before we share a clip of one of the survivors from the Shoah Foundation's October 7th Testimony Collection, I want to give listeners a chance to turn down the volume or fast forward. These testimonies are incredibly painful to listen to. This is a portion of testimony from Shaylee Atary Winner, from Kibbutz Kfar Aza, who hid for 26 hours with her newborn daughter [Shaya]. Her husband, Yahav, was killed. [Portion of testimony from Shaylee Atary Winner ] Manya Brachear Pashman: The voices and stories of the survivors are always so difficult to hear and even the bravery it takes to recount these horrors is so hard to fathom. We are talking about people who dare to deny these horrors happened. This collection serves to counter those attempts, right? Robert Williams: That's correct. There's a lot of, as we all know, the Israeli government pulled together GoPro and other footage captured from the terrorists. There's a lot of security camera footage. A number of teams have gone in, including a group at Reichman University, doing 3D scans of the atrocity sites. The physical record of this is astounding. So far, I've heard different numbers, I don't want to give a precise number, let's say tens of 1000s of videos have been made. And we're only just beginning to understand it. Manya Brachear Pashman: We're going to share another clip here. This is Maor Moravia, a 37-year-old father of two, on returning to Kibbutz Kfar Aza after the October 7 terror attacks. [Portion of testimony from Maor Moravia ] Robert Williams That the best way to counter denial and disinformation is to hear it from those who lived it, to see their experiences. And will that convince everybody? No. Those who don't want to be convinced, those who have an agenda will always be a problem. Our job is to make sure that we have this content and are reaching audiences who are vulnerable to being radicalized, vulnerable to becoming extremists, before that happens. And we're seeing that happen in a variety of spaces right now. So we have a big job to do. Manya Brachear Pashman: Rob, you mentioned being there at USC. Our December 14th episode was tied to the congressional inquiry of university presidents regarding antisemitism on college campuses. Have the students and faculty at USC taken advantage of The Shoah Foundation's presence there on campus? It seems like such a great resource, as long as people are actually utilizing it. Robert Williams: Yes, I'm very proud to be at USC, especially right now. You know, the university president has been in regular contact and dialogue not not just with us, but with Hillel, with Chabad, with the Jewish students, with the Religious Life Center, with faculty across this massive University of 22 schools. Beyond that, the Shoah Foundation has been in dialogue with different departments, including the School of Social Work right before we started this podcast. Now it had been planned in advance of October 7, but a couple weeks after October 7, we here at USC, along with our partners, and Hillel International, AJC, the local Federation, brought university administrators from across the west coast to our campus, for one reason: to learn about antisemitism and how to respond to it within a university environment. Now, we haven't crowed about this. We're just doing the work. But I think the fact that we have strong leadership from the top, we have a peerless institution in the USC Shoah Foundation here, literally in the middle of the campus, has protected us against some of the unfortunate trends that we've seen on campuses and other parts of the country. Manya Brachear Pashman: I mean, I could see being in any kind of a protest environment and hearing vile things come from the students mouths and pointing to the to your facility and saying, look over there, go in there. Robert Williams: Yeah, well, and to a certain extent that has happened. You know, we do have regular outreach to students over the summer is part of the build up to our anti semitism programming, we took a significant number of the student athletes from USC's track and field team, a track and field team that has more Olympic gold medals than most countries, to our offices for a week of training on how to understand antisemitism in all of its forms. And while they were here, they met with local Jewish community representatives, of course, our staff gave lectures as you would expect, we brought in virtual, or by remote, a very well known survivor of the Holocaust, Shaul Ladany. Mr. Ladany, for those who don't know, is one of the most remarkable and sweetest people I've ever met. He's a survivor of the Holocaust, who made his way to Israel, became an Israeli athlete. As he told me, he felt he wasn't a fast enough marathon runner. So he became a speed walker, and entered and became part of the Israeli Olympic team in 1972. And he was one of the first athletes to escape the dormitories during that horrible, horrible tragedy. So he spoke to these athletes in his sport. After that, we took them to Poland, but we didn't take them to Poland just for the reason everybody would expect. We started in Krakow, where the students learned about a thousand years of Jewish life and culture, from its origins to its challenges to its almost Renaissance today. To learn about something more than just the Shoah. They did, of course, visit Auschwitz Birkenau to learn more about the Holocaust. And they walked away from this program. more aware of the antisemitism in their midst. One student said something along the lines of, 'I didn't realize I was engaging in distortion of the Holocaust until I took part in this program.' And some of these students after October 7, started emailing us again, 'I'm hearing this, I'm hearing that, how do I respond to my friends?'. So our staff is working with them. And this is an important leadership group. This is a program that we have to continue engaging in. It will have an effect now, but I guarantee in a generation, it will have such an impact that we might start turning the tide because things have gotten so out of control in every other way. Manya Brachear Pashman: Rob, thank you so much for joining us and having this conversation. Robert Williams: I appreciate it Manya. Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Liz Hirsh Naftali whose great niece Four-year-old Abigail Mor Idan, returned home during a pause in fighting in November. The youngest U.S. citizen to have been kidnapped and held by Hamas, Abigail and her siblings are now orphans after Hamas murdered their parents. Hear about her family's continuing effort to bring the remaining 129 captives home to their loved ones.
Dec 21, 2023
4-Year-Old Hostage Abigail Idan is Free–Her Family is On a Mission to #BringThemAllHome
Four-year-old Abigail Mor Idan, the youngest U.S. citizen who was kidnapped and held by Hamas, returned home during a pause in fighting in November. But the whereabouts and well-being of 129 hostages are still unknown. Abigail's great-aunt, Liz Hirsh Naftali, joins us to recount her family's harrowing story – including the murder of Abigail's parents – and her relentless effort to bring the remaining captives home to their loved ones. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Shay Avshalom Zavdi (1:32) Liz Hirsh Naftali Show Notes: Take action to bring all hostages home now. To support our work today, you can visit AJC.org/donate . Or text AJC DONATE to 52886. Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: What Happens Next: AJC's Avital Leibovich on the Hostage Deal and Challenges Ahead What Would You Do If Your Son Was Kidnapped by Hamas? The Good, the Bad, and the Death Threats: What It's Like to Be a Jewish College Student Right Now Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Liz Hirsh Naftali: Manya Brachear Pashman: One hundred twenty-nine hostages taken from Israel by Hamas during the October 7 attack are still unaccounted for. Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has said the effort to root out Hamas from Gaza will continue until every hostage returns home. With us to discuss how her family is carrying both tremendous loss and tremendous gratitude for the return of one of their youngest family members, is Liz Hirsh Naftali. Naftali's great niece 4-year-old Abigail Mor Idan returned to her siblings on November 26. Hamas terrorists killed Abigail's parents. Liz, who lives in New York, joins us from Israel where she has been spending time with her family and advocating for the release of the remaining hostages. Liz, welcome to People of the Pod. Liz Hirsh Naftali: Hi, thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: Your family members were living on a kibbutz a half mile from Gaza. How did you hear about their fate? Liz Hirsh Naftali: First, I have two nieces with families that lived on the kibbutz, and my sister in law and her husband. My sister Mara has lived on this kibbutz Kfar Aza for over 50 years. And they raised four children and two of the children stayed, my two nieces. So on October 7, I happened to arrive on October 6 to Israel because my daughter lives in Tel Aviv. And I was coming to spend a week with her. And I was in my hotel early on the seventh when the sirens started, and we ran to the stairwell for shelter. And after like the second or third time very early in the morning, around 9, I started to hear there was something happening at the Gaza-Israel border. And so I called my sister in law who didn't answer and then I called another sister that lived on this kibbutz. And then I called another sister in law in Tel Aviv. And she said, the first thing she said was that my niece and her husband and their baby Abigail had been killed by Hamas terrorists. That was what I first learned. And basically, that's the news we had all day. And it came from the 6 and the 10 year old sister and brother, who were in the house when Hamas terrorists came in and murdered my niece. Then they went outside, and they're with their father and he was holding Abigail, their three year old, and they went to run for safety. And Hamas terrorists shot and killed her husband, my nephew. The six and 10 year old thought that their little sister and the father both were killed. So they went back to their house, they locked themselves in a closet for 14 hours. And really, the news that we got that day was from a six and a 10 year old, who basically were locked in until they were rescued by soldiers and then brought to other family members that were on this same kibbutz. And so our news that day was incredibly terrible, which was that my niece, her husband, and their three year old, were all dead. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how did you hear about what happened to Abigail, what actually happened to Abigail? Liz Hirsh Naftali: A few days later, we learned that actually, Abigail, as you refer to in the intro, had crawled out from underneath her father's body. She was covered in his blood. And she went to a neighbor that she knew. Most of the kibbutz at this time was locked down. Everybody was in their safety rooms, but they let in Abigail, they heard her voice. And they took her with their three children. And what happened is the husband decided to go out to try to defend the kibbutz. The mother and her three children and Abigail stayed hidden in the safe room, and he was injured, so he did not come back. So what we learned a few days later was that an eyewitness on the kibbutz had actually seen this mother and her three children, Abigail, being marched off of the kibbutz by Hamas terrorists. So that was the last we learned. That was the only way we learned that Abigail survived. And we then for 50 days did not have any news about where Abigail or this woman and her three children were located. Manya Brachear Pashman: What can you tell us about Abigail? We're talking about her in the abstract. But what can you tell us about that adorable little girl? Liz Hirsh Naftali: All these hostages are people. And I'm glad you said that because they are loved ones. And they are special people. And they have big characters, but we sometimes just put them down to how many numbers there are, or a picture on a screen. And so I'm wanting to say that it's very important that we actually talk about their characters because they could be our child, our grandmother, our sister, our father, our brother, or our son. Abigail turned four in captivity two days before she was released. She is this beautiful little girl who has lots of energy, big brown eyes, loves to play, loves to play with her big siblings. She is really smart. She is funny. She's just delightful. And so, you know, when we talk about the thought that she was for 50 days a hostage. It's just inconceivable that any child would be a hostage, let alone a three year old for 50 days who just became an orphan. I mean, the thought of that is just something that I still grapple with. I can't understand how it happened, how people can do that, or what the experience is like for this child. Manya Brachear Pashman: What have you learned about those 50 days about Abigail's time in captivity? I mean, has she been able to share anything about her experience, or have others who were with her? Liz Hirsh Naftali: You know, one of the things that we're very thoughtful of is, first, she is four years old. Second, there are still hostages. People are really very careful because one, they're asked not to speak a lot about the experience so that we don't get in the way of the future and hopefully very soon hostage release. But what I can tell you, which is, you know, common is that these hostages and Abigail herself are not fed properly. A three year old should be eating more than a piece of bread and some crackers and water. And that's what most hostages have come back and said they were eating. And the one thing that we held hope was that Abigail would stay with this mother and her three children. The youngest of this woman's three children was Abigail's classmate in nursery school, they knew each other. And you've just really wanted to believe that this mother was holding and hugging Abigail, and she was, and that was one of the things that we did learn afterwards. Other than that, we learned that they had moved around. And that they had been kept together because we've heard stories where hostage kids were separated from other kids and just terrible things. But in Abigail's case, she was with this mother and her three children. Manya Brachear Pashman: Has there been a birthday party for Abigail since she returned? Liz Hirsh Naftali: Yes, she had a birthday, I think every day for Abigail since she returned has been a birthday. I mean, think about a family that lost a mother, a father. And Smadar and her husband Ro'ee, were part of a big family, both in their personal families, but part of this big kibbutz family. And the two children lost their parents, the six and 10 year old, they also then found out their sister was alive, and they left her and they were in this closet. And I think that for them, that every day was just waiting for their sister to join them. And that just that moment where they were all together, was the greatest celebration, celebrating that these three children had each other and have each other. And you know, one of the things people have asked is like, how was that reunion, and I wasn't at the hospital. But what I have heard, and which I think is just beautiful, is that when Abigail saw her brother and sister and her cousins come in, she lit up. You know, this was a child that was in the dark for 50 days, didn't have family. And when she saw them, just the light came back in. And they're very close. So when you ask about a birthday, I think every day is a celebration, and every day is appreciated. And in their case you know, every day is Abigail's birthday for this family. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's beautiful. You also mentioned that you were in Israel, on October 7, you had just arrived in Israel to see your daughter. How long did you stay? And how is your daughter? Did she get called up to fight because I know that she served in the IDF at one point. Liz Hirsh Naftali: I arrived on October 6 in the evening, I went to Jerusalem with a friend, had dinner, went to shul, went back to my hotel in Tel Aviv. And I was supposed to have breakfast with my daughter, she had been away for the holiday with her boyfriend and his family. And I was really excited, I was gonna have breakfast with her and spend the week with her. In the end, I basically stayed in the hotel, we all were locked in where we were, and what I learned throughout the day from family, friends, and people, were like you need to get out of here. You'll be more helpful for us back in America. And so I basically got on a flight that Sunday, the next day on the eighth, and I came back to the States. And then I hit the ground running, one to tell the story of what happened on the seventh to our family, and what happened to this kibbutz, and what happened to Israel. So I started trying to do as much sharing of what happened because it was so atrocious. And little by little as we learned that there were hostages, and Abigail was a hostage. Then I started to do the advocacy work. And my daughter, she did serve in the IDF. But her division and her area was not called in for miluim, for reserves. But what she did do was come and be with this family and be there for them during this really hard, hard time. You know, during which they buried my niece and her husband, so she was there for shiva, she was there to support them. A lot of her friends' husbands were called to miluim. So they came and stayed with my daughter. She helped them with their children. She just really put her heart out there, she and her boyfriend to really give support to each community and especially to our family that was in such a state of limbo and grieving and tragedy. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, as you were talking, I was thinking I guess everyone has been called up to fight in some way. Everyone has. You don't have to be serving in the IDF. Liz Hirsh Naftali: If you look at what happened in Israel, one of the things that we see is that people came and they volunteered, people came and made sure that soldiers had what they needed, whether it was equipment or food in the beginning, because the country wasn't ready for that. They made sure that these families that were all of a sudden taken from being in their safe rooms for 30 hours, they needed to be taken somewhere, they had no clothes, they had no food, they had nothing. And you could just see the Israeli people rising to make this work. And these organizations that already were in existence, turning into aid and humanitarian organizations. And that is what is beautiful about Israel. And that is what is beautiful about these people: that in the darkness and in the greatest tragedy, many, many people really turned around and said, How can I help? What can I do to make people's lives better, and that is what is still happening. And I'm still seeing it here. And that's who the Israeli people are. Manya Brachear Pashman: Let's talk about your fight, Liz, your advocacy to bring the hostages home. It's reached across both aisles politically, you've been meeting with people both in as you said, Washington, DC, New York, Israel. Who have you been speaking with? And what kind of reception are you getting? Liz Hirsh Naftali: So when I learned that Abigail was a hostage, I got a picture of her. And I saw this picture and I put it on my mantel and I put it everywhere so I'd see it when I was in my apartment. And my daughter who was in Israel, she said, how can you look at that picture and just not be so sad. And I said, Oh, I'm sad. But when I look at that beautiful little girl, I am inspired to do everything I can to make sure that she comes home. And basically put everything else aside that I could and just made it my focus, which was to, one bring back Abigail. But what I shortly learned was, there were about 250 other families whose loved ones were all their children, Abigail's age and younger. And as I've said, people's children, their sons, their daughters, aunts, uncles, grandparents, mothers, fathers. And what I started to learn was that these people were coming from Israel to New York or coming to DC. And many of them were survivors themselves, and they were coming to tell their stories. So one of the roles that I could play was to give them that love and support because I was in America, and I was already doing this work. And what you realize was you became this big family, you became a family that you never expected. And so what I continue to do is work with my family to make sure that their loved ones come back. The advocacy work took on a few different levels. At first, there was a few interviews, but most of the work was basically going to Capitol Hill and talking with elected leaders, both sides of the aisle. We worked with groups that were evangelicals, we worked with Jewish groups, we worked with AJC, we worked with, as I said, Christian groups, we worked with anybody that was willing to help us set up meetings that were part of their network. There was not one person on either side [of the aisle] that was partisan. Everybody understood then and understands now that getting back these hostages, these people, is our number one priority and that we are all committed to it. But what I will tell you is that early on, I went to this meeting, and it was a group of Republican senator women. And when they heard our stories, you could just feel their hearts were broken. These are mothers. These are women. And leaders. And Susan Collins, Senator Collins, she listened to my story of Abigail and she took Abigail's picture, she put it in her purse. And about a week later she was in Israel meeting with leaders. And my daughter, Noa, who was in Israel went to this meeting with my brother in law, because they were already from the Israeli side advocating for Abigail. And Noa, my daughter started to explain to her about Abigail and she said, I have Abigail's picture and she pulled it out from her purse. And then they did a press conference when they were leaving Israel and Senator Collins picked out Abigail's picture to show people what a child is like who has been kidnapped, and is a hostage of Hamas terrorists in Gaza. And one of the things that I learned from Senator Collins throughout this was that, that image, just like it was for me, that like marching like we're going to get this little girl and all 250 hostages, Senator Collins used this photo, and it was inspiring her. And I just love that story. There's not a person I have met in an organization, on the hill or anywhere that does not understand this is an issue about humans, and that humans need to be brought home to their loved ones. Manya Brachear Pashman: So speaking of the humanity of the hostage crisis, there have been a number of pro-Palestinian protests around the United States over Israel's response. Many unfortunately have veered into anti Israel sentiments and antisemitism. Some people have torn down the posters of the hostages that are in captivity. And this has become in many cases a political or partisan issue. How are you navigating that or coping with that handling of the situation? Liz Hirsh Naftali: My role from the day one was to get Abigail back and quickly became to get back 250 hostages. So I would literally go and I would bring a poster and hand it out to political leaders, their staff, organizers, just to make sure they understood and they saw the faces of 250 people who had been kidnapped. In addition, Abigail obviously was on that and I had to hand them a picture of Abigail to really put a human face to it. And to this day, I really believe the one lane that I want to stay in until they are all back is this lane of bringing back the hostages. And as a result of that is, my telling Abigail's story, my telling that niece and nephew were murdered by Hamas terrorists in front of their children. My story of the other people whose stories that I have heard and heard about the most grotesque catastrophe, terrorism, abuse, I mean, it's just, it doesn't end. So for me, the story is what's so important. And I hope that through that story, we continue to keep the truth out there so that no matter, and I know what you've described, but no matter what the untruths are, or the convenient truths that people have done, or the historical revisionism they've done from two months ago, that those stories do not control the narrative, but the real stories of what happened to my niece and her husband, what happened to Abigail, and what happened to so many–and I say this–innocent people who are in their houses, in their neighborhoods, on the seventh, when Hamas terrorists broke a ceasefire, and came in and just murdered and savaged and raped and pillaged. I mean, the worst atrocities that one can imagine in modern times that we could even understand. So the other stuff, it's noise, but the focus for me and for so many of us hostage families, is saying, we need to bring back our loved ones. And telling that story makes it really clear what happened. And nobody can change those facts. Even if they tear down a poster, even if they say something else. Nobody can take away what really happened on October 7 in Israel, to innocent people from 30 nations, Israelis, Americans and 28 other nations, children, as young as nine, up till women and men in their 80s were kidnapped. And that doesn't even talk about the 1400 who were brutally murdered. And we don't need to go there today, but brutally murdered infants. I could cry thinking about the other atrocities that took place that day, young people at a music festival that could have been my children out there dancing in the morning to music. But again, I go back to how we get back these hostages, and telling our stories, whether it's the Nova music survivors, or the families from the kibbutzes or my family story. Those are the truths and the truths are what will control the narrative. Because people have a right to their own opinion. They just don't have a right to their own facts. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you speak to the support that Abigail, her siblings and others are receiving now that they have been returned? Liz Hirsh Naftali: There are so many people that are through professional areas going to be and have been working with survivors, both survivors of the atrocities, and those who were kidnapped and have returned. And so you see throughout the country, programs, doctors, places for people to go. And within their communities, there are social workers and specialists that are there to work with children and adults to give them what they need. But the thing that is hard to navigate is, there's not a rulebook for this, this isn't something that happened before. And that we can say, this is what we need to do. But what I can say is that the concern and the understanding, and the need for therapy, and the need for support is there. And that is something that is going to be developing and that these survivors are going to need for we don't know how long. How do you know what a three, four year old, internalized and how long it takes for that to come out. We hope and pray that Abigail has just a beautiful, normal life. And that this family, and this is the beautiful part, is that her family here, our family here is going to do everything to bring in the proper support, proper care, and the love. One of the things that we talk about is how important it is to have family to give you the love, the hugs and and just to be there for you. And Abigail has that. Manya Brachear Pashman: Why are you in Israel now? Liz Hirsh Naftali: I am in Israel to visit our family to just sit there and to look at this four year old and play memory game with hers watch her play with her siblings and just to take a moment to breathe and realize that while we worked really hard, so many of us for 50 days, and many of you out there who are listening and AJC worked really hard to make it possible that a child like Abigail could come back to her family. I thought it was important to come and have that moment. And to be here with my niece and my sister in law and all those that have, you know, lost sleep, none of us ate, none of us slept. And we were, you know, so far apart. But together in terms of what we were trying to do, which is to get Abigail back and to get these hostages back. And one of the other things that I did, is that I also went to the kibbutz to see what it looked like to see what their homes look like. So that I understood, when I speak to folks, when they talk about the destruction that took place in these people's homes, and the grenades that were thrown, and the homes that were burned and the bullet holes and just the destruction and hate that took place on the seventh. It wasn't something that I wanted to do, which was to go see this kibbutz. I needed to do it because I thought that to go and actually see what happened on this kibbutz, in my nieces home, in front of their house in other people's homes, was something to be able to understand so when I speak with people like yourselves, or people who might have a different vision of what happened on the seventh, that I can say from my own personal experience, what I saw, and what I saw was just terrible, and just devastating. But that is what happened on October 7, and we can't change that. But we have to be able to tell those stories so people understand what happened. Manya Brachear Pashman: Was there a particular takeaway list from that tour and what you saw? Liz Hirsh Naftali: I just can't understand how people survived, endured what happened in their homes. You saw the safe rooms, you saw the bullet holes in the door where people were holding on from inside to keep themselves safe to keep their family safe. And you saw the bullet holes of Hamas terrorists that wanted to get into them. There were just so many bullets, so many, you could see remnants from the grenades, you could see the burned. And you just think to yourself, how could? How could society? How could life be like that? And you know that you can for a second separate from that it's your family that was murdered and your family that went through this. But just to look at this and think, How can humans behave like this? How could this happen? But it did. And the other is how these people survived, how they were just surviving that day. And, you know, a ten and a six year old survived in a closet, my other niece, and her husband with their three kids, they were locked in a safe room in their home. And they heard the terrorists. But at one point, early in the morning, they heard a woman's voice and they opened up their safe room and there was another kibbutz member, a woman carrying a baby and holding a hammer. And they let this woman into their safe room. And you think about, it still gives me the chills. And I saw their safe room and their safe room was there in their home. But they took a chance with an infant who could have cried, had no diapers, had no food. This mother, this woman, her husband had been killed. She had a hammer, which you just think to yourselves like, she was just this innocent woman. On this day of destruction and catastrophe and such darkness, such grotesque darkness, people were fighting for their lives, and people were doing beautiful things to try to help each other. How does that work? How does that balance work? And I guess that one of the hopes is we try to keep bringing the light to this terrible darkness. Manya Brachear Pashman: Liz, Abigail has been reunited with the rest of her surviving family. Thank God. When the world sees those precious pictures of your great niece, what are they looking at? What do you hope they see, and what's the message you want them to take away from this conversation? Liz Hirsh Naftali: Abigail is four years old. She is our hope. She is our resilience. She is our resistance. She is our peace. She is what we are all trying to do, which is to make this world a better place for our children and our grandchildren. But I do ask anyone who is listening to this to understand that Abigail is back and she is free, but whatever anyone can do to help support the release of these other hostages is really what is our call right now. And there's many different things to do. But please keep that as our focus. The political stuff, many of us want to be in charge and we want to fix but we know we can't. But what we can do is keep these stories alive and keep pressure on our leaders to make sure that nobody says okay, Abigail and the kids are home. But there are women and men and still a few little children that need to come home. So that is my ask, that is my call to action, if anything, that we all partake in. And that's really why I'm here is to really share our story and Abigail's story but to ask you all to keep helping. Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: AJC certainly shares your mission of bringing all of the hostages home. To learn more about how to help make that a reality, listeners can go to AJC.org/BringThemHome . Liz, thank you so much for joining us. If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with AJC Director of Academic Affairs Dr. Sara Coodin, and AJC Director of Contemporary Jewish Life, Dr. Laura Shaw Frank about the fallout from a recent hearing on Capitol Hill about the current state of antisemitism on college campuses.
Dec 14, 2023
The Fallout from the University Presidents Congressional Hearing: What Does it Mean for Jewish Students?
As American colleges and universities struggle to foster discussions about the war between Israel and Hamas that don't veer into antisemitism and misinformation, three university presidents testified on Capitol Hill about the current state of Jew-hatred on college campuses. However, their testimony drew widespread outrage over their refusal to condemn calls for genocide against Jewish students. AJC Director of Academic Affairs Dr. Sara Coodin, and AJC Director of Contemporary Jewish Life, Dr. Laura Shaw Frank join us to break down the fallout and give us a broader view of how university leaders are handling this situation. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Avital Leibovich (1:44) Sara Coodin, Laura Shaw Frank Show Notes: Take action to bring all hostages home now. AJC has been working nonstop to support Israel, combat antisemitism, and safeguard Jewish communities worldwide. To support our work today, you can visit AJC.org/donate . Or text AJC DONATE to 52886. Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: Global Antisemitism Report Part 2: The Impact of the Hamas-Israel War in Germany, Asia, and the Arab Gulf Global Antisemitism Report Part 1: What It's Like to Be Jewish in Europe, Latin America, and South Africa Right Now What Happens Next: AJC's Avital Leibovich on the Hostage Deal and Challenges Ahead What Would You Do If Your Son Was Kidnapped by Hamas? The Good, the Bad, and the Death Threats: What It's Like to Be a Jewish College Student Right Now Learn: AJC Campus Library: Resources for Becoming a Strong Jewish Student Advocate Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Sara Coodin and Laura Shaw Frank: Manya Brachear Pashman: Since the horrific October 7 terrorist attack on Israel by Hamas and the start of Israel's counter offensive, American colleges and universities have been struggling to encourage fact based debates and demonstrations that don't veer into antisemitism and misinformation. University presidents have issued and reissued statements that originally missed the mark, and presidents from three of the nation's top universities appeared on Capitol Hill for congressional inquiry that led one to resign and put another in jeopardy. Here to discuss that inquiry and give us a broader view of how university leaders are handling this crisis is Dr. Sara Coodin, AJC's Director of Academic Affairs, and Dr. Laura Shaw Frank, AJC's Director of Contemporary Jewish Life. Laura, Sara, welcome to People of the Pod. Sara Coodin: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to start with the testimonies by three university presidents last week: Claudine Gay at Harvard, Elizabeth McGill at the University of Pennsylvania and Sally Kornbluth at MIT. Since that, since their appearance on Capitol Hill, President McGill has resigned. And President Gay has survived a debate over whether to oust her from Harvard. For those listeners who didn't follow those hearings, Sara, you were there, right? Can you summarize for us what happened? Sara Coodin: I was there, and I have to say I was really quite surprised that it went on for as long as it did. There were close to six hours from start to finish. And the kind of publicity that followed over their inability, all three of them to respond to those very pointed and basic questions by Representative [Elise] Stefanik, really happened in the 11th hour. And there was a lot that happened before. There were a lot of important questions and points that were raised before that kind of pivotal moment in the hearings. So I just want to say that, because for those of us who were sitting in the room and listening and watching, there was a lot to sit through. And there were a fair number of questions that emerged that were very onpoint. And I think as direct as Representative Stefanik's questions were, there were questions about the ability of these universities to access considerable resources. Harvard sits on a $50 billion+ endowment, 350+ years of history, and tens of thousands of faculty. So one of the questions that emerged was, why haven't they been able to address this up until now? What's new in the present commitment? And I think for me, that was a really central question. Because these are some of the most recognized elite and well endowed universities, in a country that prides itself on excellence in higher education. These are the most excellent of the excellent. So what gives? When they've suddenly decided that this is a huge problem, they're devoting their considerable resources to addressing it. But you know, to do that, convincingly, I think they have to respond to the fact that this is not something that emerged overnight. This is not something that happened simply in the wake of October 7. It's been brewing for a long time. So why the institutional silence, or turning away from these questions and issues up until now? I think that for me, it was one of the key takeaways before that moment where they were not actually able to respond in any kind of real way to that question about codes of conduct, which in a way is a very limited, very specific question. But I think their inability to come up with a convincing set of arguments and proposals for how they're going to address antisemitism on their campus, either programmatically or through structural innovations, like codes of conduct. You know, people left with very little to take away, there were very few takeaway moments for me in terms of convincing, really proactive measures that they were willing to take that could address the culture problems on their campus. Manya Brachear Pashman: Of course, you mentioned the pointed questions by Representative Stefanik. You're talking about her question about, does a call for the genocide of Jews violate the university's Code of Conduct? The presidents really stumbled to answer those questions kind of unequivocally and unequivocally denounce the mass murder, or calls for the mass murder of Jews. They kept turning back to free speech, right, and academic freedoms on campus and prioritizing that instead. Was that your takeaway? Sara Coodin: I think that they had prepared for a series of responses that were very suitable for a court of law. And I think they weren't prepared to respond to the court of public opinion, which is essentially what happened. I mean, enough people were paying attention to that hearing, and have their eyes on these universities and on this particular set of problems that's made national headlines. Before this December hearing, they should have been prepared, frankly, they should have spoken to members of the Jewish community, including representatives from AJC to address what the concerns really are, from our side of things. They seemed very well prepared to defend a very narrow, legalistic notion of what free speech is, of where it starts and where it begins. That is not incorrect. It's not an inaccurate description. But it's one that really misses the larger point. And I think the directness of those questions by Stefanik, and others, was really a kind of shot, where it where it hurt, you know, because they they weren't able to respond to those basic queries that I think really picked up on some of the basic questions that we have for the schools and for these leaders. What are you doing? And why are you so unable to draw a basic line in the sand that condemns something with a degree of moral clarity that seems convincing? Why can't any of them do that? So I think that's what that question became. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did you feel like the journalists who covered this hearing also got that? I mean, you talked about six hours of discussion, and really the stories about the hearing focused on that 11th hour, those really, very pointed questions. But did you feel like the coverage really got to the heart of this issue? And perhaps could lead to some constructive conversations going forward or not necessarily? Sara Coodin: I mean, there were some interesting moments. All three university leaders condemned antisemitism at the outset of the hearing, they were asked in a very direct fashion, Do you condemn antisemitism? Yes, yes, and yes. They were asked whether they stood in support or opposition to BDS resolutions, or to BDS full stop, and two of the three had time to answer and said, we do not support BDS. So that's also significant that they expressed that to hear a top university leader actually say those words is meaningful. Because we've seen, of course, last year with the Harvard Crimson editorial, where, you know, they came out and support of BDS. So to hear the leader of Harvard actually condemn it, and say, This is not represent our position, our perspective. That's significant. That being said, you know, having sat through the first three hours, or whatever it was, before they broke for a recess, what were the key takeaways up to that point where they had nothing to say and just sort of stumbled? Not terribly many, they seem to be sticking to a very set number of talking points, very clearly focused on saying, you know, free speech matters on campus, which means something that can include hate speech, and unless it turns into conduct behavior, there's nothing we can do. There's nothing we're willing to do. That was the line and they repeated it and they kept doubling down on it up to the point where they continue to double down on it in response to Stefanik's question. There was a lot of it, too much of that and not enough of the kind of responses that I think we were all wanting and needing to hear from these university leaders. Laura Shaw Frank: I wanted to just note that the first headline that I saw about the hearings is from the New York Times, which said, Republicans tried to put Harvard, MIT and Penn on the defensive about anti semitism. And to be honest, I just was like, they're really going to make this about a political fight, and not actually engage with the anti semitism question itself. And I actually found that to be quite a horrifying headline. It felt so egregiously ignorant, and also ignoring the substance, the very real substance of what was trying to happen and what people were trying to get at in that room. So I was really upset by that. And then afterwards, shortly afterwards, there was another headline, which I guess they noticed themselves that they had missed the mark and published another article, some of the same journalists, were the authors of that article, the second piece called college president, the headline was college presidents under fire, after dodging questions about anti semitism. So I thought that was a pretty big turnaround, where they all of a sudden realized, Oh, we really can't make this into a Republicans versus Democrats thing here. This is actually about something much more substantive, much deeper, and much more bipartisan. Manya Brachear Pashman: You said Sara that the hearing the leader of Harvard denounced that BDS is significant. These are kind of influencers, if you will, these three elite schools, they're influencers in academic circles. But can you give us a broader view about what's happening? You know, we've spoken to Jewish student leaders about what they and their peers are experiencing, but you work with administrators and faculty. I'm curious, from their point of view on smaller liberal arts campuses, state schools, community colleges, what are you? What are they saying? What are you hearing from their point of view? Sara Coodin: I think the schools that think of themselves as being part of the Harvard Extension orbit, you know, they're not quite Harvard, but they're aspirants to Harvard, they maybe have some of the same students that also applied to Harvard. They've really got their eyes fixed on public perception right now about university leadership. So they're scared frankly, I think they're worried that the next incident that's going to strike their campus is going to produce a moment that may may result in their their ouster, you know, in their being kicked to the curb, because if it can happen at the University of Pennsylvania, it can happen anywhere. And we're dealing with a large cohort of incoming presidents, all three of the presidents who testified before Congress, we're in the first year of their presidency. And that's actually not as unusual as it sounds, there's been a kind of a revolving door syndrome for about a decade now, where these positions used to be for, you know, 2030 years, you'd have presidents sitting in these positions, no more. And so we're seeing a rash of new, I will say, an experience, but new to their roles at their current campuses, university president at a lot of schools, including places like GW, where I think there's a real concern about this being a kind of formative moment for them that shapes the perception of who and what they are about as university leaders. So I think there is an awareness now that in the post-statement moment, where everyone was called upon to make these amazing, pointed, clear statements, and most university presidents failed, that this, this is potentially, you know, a series of tests for them, where there there can be real failure, you know, and they've seen what that looks like on the public stage. I think when it comes to very small colleges, they tend to operate in their own little worlds, right, their own little bubbles. And there's often a perception that the kind of media focus is not an important factor. But I think we've seen enough lawsuits being filed, enough title six complaints, to know that that's just not the world that any of these campuses are functioning in anymore. And there's more and less resistance to that as part of the new landscape. The fact is, you know, the media attention to these issues means that no one is really free to operate in an insular bubble anymore. So I think that in itself might create a kind of extended series of real deliberations on the part of administrations before they issue statements before they jump into the fray. I don't know that that's a bad thing. Thoughtfulness is good. Thoughtfulness, with a concern about messaging, you know, maybe that'll be good for the university community, maybe not. There's an argument that maybe that's not the best thing to actually solve the problem, because the problem can't be solved with messaging. It has to be solved through innovative programming through looking at things like student codes of conduct. And some schools, to be perfectly honest, seem very content to remain exactly the kinds of anti-Zionist microclimates that they've been for years now. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you give us a couple of examples of those campuses, but also some encouraging examples as well? Sara Coodin: You know, a lot of the smaller liberal arts schools in the northeast and Massachusetts, in New York State have had that reputation for a long time, including schools where the leaders themselves are actually really committed to trying to do something. So Wellesley is a perfect example of that. And the President of Wellesley, Paula Johnson, traveled to Israel with us this last summer. She's wonderful. She's incredibly thoughtful. She was such a formative figure to have on that trip, wouldn't you say, Laura? Laura Shaw Frank: Absolutely. She's an incredible president to have on the trip, who took in everything that we did with such humility and wisdom and an eagerness to learn. And she's an incredible partner for us, and at the same time for campus is a really tough place to be a Zionist. A president can't control fully, and certainly can't overturn in a minute of campus climate. Sara Coodin: They're under a title six investigation now. There's a set of ingredients there, and a pretty recent history of a bit of an echo chamber syndrome on that campus. It's really tough when you have a small school where already there's a concentrated number of voices, and they don't include a kind of diverse range of questions about Israel and Zionism. So that's not a very good recipe for inclusion, or for Jewish students who want to go and be themselves and represent their identities as Zionist fully. By all accounts, there are a lot of schools–small ones, particularly–that can foster those kinds of climates that are really not great for Jewish students. And it's a bit of a puzzle when you have a small institution where every voice matters, but there's too much agreement about Israel and Zionism. So there's no real conversation. There's no way to kind of generate real dialogue because there's no one willing to give voice to an unpopular position. Manya Brachear Pashman: And are there heartening examples? Sara Coodin: You know, there are and I''m going to name another school whose president we took to Israel this summer, Julio Frank of the University of Miami. I want Laura to speak to this particular example because she has a personal connection to that school now. Laura Shaw Frank: Absolutely, I would love to speak about the University of Miami. So Julio Frank was just also such a wise and present member of our trip to Israel this past summer. He just drank it in with such depth of character and thought, and has kept the University of Miami as a campus that– look, I don't know what it was like before. My personal connection to it is that my son is a student in their very wonderful bachelor of fine arts conservatory program in musical theater. So I hear from my son all the time, about how things are on campus. How does he feel as a Jew on campus? And he says, it's totally fine. Peaceful, wonderful. There is an SJP-like group, but it is a moderate group. It is a fairly quiet group. It has not interfered with Jewish students' ability to get everything they need to get out of their education. The Hillel and Chabad are both very active. And President Frank has spoken very, very clearly, both in his initial statement after October 7, and also in joining the Yeshiva University coalition statement, as one of the founding members of it, which was a very, very strong statement. He's also made a point of speaking on panels together with pillow leadership, like Adam Newman, who's the CEO of Hillel, and has just been a real partner to the Jewish community. He is Jewish himself. He's a Mexican Jew. He's also just a very moral person, he thinks very deeply about morality. He's actually a public health person and in his scholarship. And the University of Miami, I would say this has been a real model campus in terms of keeping the atmosphere, free of harassment, against Jews, and really with clear moral leadership from the top. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, Sara, you mentioned having very few takeaways after three hours of congressional hearing largely because it was political theater versus talking points. I am curious, what kinds of thoughtful conversations are unfolding on campuses? Is there any kind of dialogue healthy, open, maybe sometimes angry, but thoughtful dialogue, to move the needle somewhat? Sara Coodin: There is. We focused on hate speech so much as the one segment of speech that we should all be concerned about. And we should, but there's so much more to campus speech than just hate speech. There's constructive dialogue across difference, which is a term that anyone working in student-facing administrative roles is familiar with. They're familiar with dialogue across difference, and how crucial it is in today's pluralistic student community. If you want diversity on your campus, you have to figure out how to stage and model those conversations. And they have to be constructive. So schools like GW have been, you know, slowly starting to implement that kind of programming with the aim of showing incoming students what it looks like. I was part of a panel discussion this fall before, you know, before October, that tried to do exactly this. And it was an amazing model, and it was one that they've done before. And Laura was part of that rollout, which was for student-facing staff. This was for incoming students. And we just went right into it with different perspectives, different identity positions, and addressed questions about antisemitism and Zionism. And they had a parallel session going on about race and racism, that was equally, forthright, they were not saying let's talk about some version of this as watered down and irrelevant, they went straight for it. And they brought in people who could actually speak authentically to difficult questions. And we didn't agree, we didn't all agree, we didn't have to agree. That's sort of the point. So I think when it comes to programming, that's the model, is to find ways to bring people into dialogue. That model is something other than just shouting matches, reductive talking points, polarized discourse, all the stuff that's happening in the streets, or, you know, in kind of public spaces of campus. But it's probably not happening enough when it comes to these issues. And I think administrators have been loath to address this in a direct way, in many cases, because they feel like it's too hot. You know, it's too likely to inflame existing tensions, which may be true. But I think showing students through creative programming, what it means to engage on these issues. And if you're really skilled, you can create programs to actually get them involved in ways that make them take ownership of the issues and ownership of their own knowledge. Laura Shaw Frank: I want to note that the person behind the GW programs that Sara was talking about is a PI alum as well. And it's Vice Provost Colette Coleman, Vice Provost for Student Affairs, who went to Israel with us in the summer of 2022. And has been an incredible thought partner. Manya Brachear Pashman: Some terms, you and Laura were talking about how some terms just don't have a place on a college campus. Walter Russell Mead, also a previous guest on this podcast, had a column in the Wall Street Journal recently in which he argued this generation of college students has never experienced the toll of a world torn by war. And frankly, this generation of college presidents has largely been spared that experience. Claudine Gay was born four years after teach-ins protesting the Vietnam War began at the University of Michigan. Do you think that has led to a lack of moral clarity or a situation where maybe the administrators are listening to the students but the students aren't listening, and aren't learning, and aren't fully comprehending consequences of words and actions? Sara Coodin: There's always a generational divide in these conversations between faculty, you know, senior faculty, junior faculty, and then students who've grown up with different experiences, their worldview has been shaped by things like new technologies, which simply weren't even a factor, you know, 20, much less 50 years ago. I think part of the issue that we're seeing is that there is a kind of moment, a very brief one, in the larger context of Jewish history, where were American Jews have experienced a golden age where they haven't, haven't really directly confronted antisemitism, at least not in the overt ways that are so much a part of our history. A lot of American Jews consider themselves to be a pretty seamless part of the fabric of American life and culture writ large. That alone goes quite a long way to understanding some of the issues that we're dealing with on college campuses, where Jewish students might feel like they have no one to turn to, as far as Jewish mentors are concerned, on college campuses, because there's a generation in place, who achieved amazing things. But I think there was a widespread assumption that there was really no problem that this was a new golden age for American Jews where we could stop thinking about antisemitism as the central defining principle of our culture. And I think we're seeing now, which is something that we've seen many times before, if we take the long view, that antisemitism goes into a kind of dormancy, and then it it resurges, and what is old becomes new again, some of the old tropes attach themselves to new social languages, and they acquire a kind of currency that allows people to invest in them and keep promoting them. We're dealing with a generation that I am sorry to say in terms of the people who are the permanent residents of campus–the tenured faculty members, the people who are there for life–who seem insulated from the realities that the younger generation are actually dealing with in their social lives and their social interaction with their peers. I think there is a kind of awareness of it on the part of some faculty where they know that there are certain opinions on certain topics that they can't really opine about. Because there's a risk there that the social lubrication that's required to gain acceptance in their field or to have the kinds of conversations they want to have about their subject areas can't happen if they foreground Zionism, if they talk about Jewish identity in certain ways, if they express a certain range of opinions about Israel, so they kind of saw silence, and they see that as a reasonable price to pay. But I think right now, with the generation of students that's coming up, we're so invested in identity politics as a cornerstone of our identity, that that seems like an unfair trade off, it seems insane to walk into a space that's defined by identity politics, and not be able to talk about yourself as a Jew, and to talk about your relationship to Israel and Zionism, which is such an important part of that for most American Jews. So I think there is a disconnect there. I think the generation that is older, maybe it's an understanding quite the predicament that young Jews are actually in, because they've found ways to gain advancement in an era where identity politics was not really the current thing. And it's so much is for this generation of students, that they need other tools and better tools to navigate those spaces, conversations, and relationships. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to go back to teach-ins for a moment. We've seen many promoted in recent weeks as educational events and opportunities for dialogue. Are you finding that is indeed the case? Are they spaces for open and constructive conversations, or do they have open and shut agendas? Are teach-ins not what they used to be? Sara Coodin: There was one at NYU just this week that was being promoted on other campuses as a zoom event, a must-attend kind of event to help make sense of the conflict in the Middle East. There is nothing balanced or even fact based about the kinds of conversations that are happening in those spaces. And I think it's incredibly dangerous for these kinds of events to be masquerading as educational opportunities for students to learn about a very challenging and very difficult set of geopolitical questions and circumstances. These are not educators who are providing balanced fact-based opportunities for exchange. A lot of these events have taken place and have actually prevented any questions from being raised by people who are sitting on the sidelines and tuning in. Laura Shaw Frank: I think that side by side with free speech, our universities need to start focusing on what is responsible speech? What does it mean to use this wonderful right of free speech in a way that's going to be productive for our society, without restricting it necessarily. Where we can have conversations that are so difficult about verge topics, that are rooted in facts that are rooted also in listening across difference, that are rooted in empathy. And that are rooted in lacking in the opposite of ideological silos that are rooted in ideological diversity. And that's something that we've spoken about on this podcast about how much ideological diversity is lacking, how much reading and facts is lacking, and how much dialogue across difference, the skills for dialogue across difference is lacking. And all of those things in our minds are critical for the future of university campuses, not just just for Jews, but the project of higher education in this country. And the last thing I would say is, we have to wrap our minds around the fact that there is no quick fix here. We have to dig into some serious work. The campuses have to do it. The administrators have to do it. We are here to partner with them to do it. But this is not going to go away quickly. It took decades to sort of create the toxic situation that we're in, and it's going to take a little bit for us to get out of it. So we have to understand that. Manya Brachear Pashman Well, hopefully some progress will have been made by the time my children get to college. Sara, Laura, thank you for joining us. If you missed last week's pair of episodes, be sure to tune in for a roundup of reports from some of AJC's experts around the world. They shared what efforts are underway to protect Jews and counter the hate that has erupted since the October 7 massacre of Israelis by Hamas.
Dec 6, 2023
Global Antisemitism Report Part 2: The Impact of the Hamas-Israel War in Germany, Asia, and the Arab Gulf
"I cannot recall a moment where we have seen this kind of openly expressed antisemitism." Dr. Remko Leemhuis, AJC Berlin Director, sums up the state of antisemitism in Germany post-October 7 with this chilling statement. Hear from Leemhuis, along with Asia Pacific Institute (API) Assistant Director Hana Rudolph, and AJC Abu Dhabi Director Marc Sievers, on how the October 7 Hamas massacre of Israelis has impacted Jews in Germany, Asia, the Pacific Islands, and the United Arab Emirates. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Hana Rudolph (7:18) Remko Leemhuis (15:20) Marc Sievers Show Notes: Take action to bring all hostages home now. Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: Global Antisemitism Report Part 1: What It's Like to Be Jewish in Europe, Latin America, and South Africa Right Now What Happens Next: AJC's Avital Leibovich on the Hostage Deal and Challenges Ahead What Would You Do If Your Son Was Kidnapped by Hamas? The Good, the Bad, and the Death Threats: What It's Like to Be a Jewish College Student Right Now Mai Gutman Was Supposed to Be at the Music Festival: IDF Lone Soldier Recounts Harrowing Week Responding to Hamas Terror: IsraAID CEO on How You Can Help Israelis Right Now Learn: Debunking the False Equivalency Between Israeli Hostages and Palestinian Prisoners How much do you know about Hamas? Try to ace our quiz and expose the truth about the terror group today. Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Hana Rudolph, Remko Leemhuis, and Marc Sievers: Manya Brachear Pashman: American Jewish Committee has 14 international offices around the world. This week, we checked in with some of those offices to learn what they're seeing and hearing on the ground since the October 7 Hamas terrorist attack on Israel. In an earlier installment, we took you to Europe, Africa, and Latin America. Our journey continues today in Asia, Berlin, and Abu Dhabi. We started in South and East Asia, and the Pacific Islands. Since the director of the Asia Pacific Institute (API) [Shira Loewenberg] was en route to Indonesia, we caught up with Assistant Director Hana Rudolph. Hana, let's start with Indonesia, a predominantly Muslim country, the country with the world's largest Muslim population. In fact, where AJC has made tremendous inroads in recent years engaging with faith and political leaders. What has the response to the October 7 attacks been there? Hana Rudolph: The Indonesian government doesn't have ties with Israel, though it does support a two state solution. So we don't expect there to be a vocal kind of support for Israel. But the anti semitism and the conspiracy theories, the false narratives happen incredibly alarming. There was a rally on November 5, a pro Palestinian rally, and rally organizers think that there were 2 million people who turned out for that. So we're talking huge numbers. The prevailing narrative there is really that Israel is the indiscriminate aggressor, they are just killing women and children for no reason in Gaza. There's very little mention of Hamas' massacre on October 7, and that's the narrative. AJC has taken several delegations of Indonesians to Israel for our Project Interchange. A lot of our alumni had been receiving death threats. And we're not talking about death threats for posts that they're actively making right now in support of Israel. We're talking about death threats because, you know, some long time ago, when they were on this delegation, they posted something that was seen as something pro-Israel, and now they're receiving this kind of pushback and hate and condemnation for it. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned the dominant narrative. Are there other narratives developing? Hana Rudolph: One of the most, I think, notable and disappointing reactions across our region has been China. China refused to condemn Hamas' terrorist attack on October 7. And there has been a notable uptick in antisemitic rhetoric across Chinese social media platforms, which, as you know, are heavily censored when the government chooses to do so. So here the government is choosing not to censor. And in fact, several state-run institutions are actively promoting radically antisemitic content. So I'll give you a few examples. CCCB describes Jews as accounting for 3% of the US population and manipulating and controlling, in their words, 70% of the country's wealth. The China Internet Information Center compared Israel to the Nazis. And these are, of course, narratives that, you know, once they're once they're put out there, they're being actively promoted and popularized by other social media influencers. So the content that's being generated, you know, as a result goes far beyond even those examples. We've noticed that there are several major Chinese map platforms that are no longer labeling Israel as a country, you know, they'll demarcate the borders, they'll identify cities, but you don't see Israel labeled. Most likely, China is seeing the current conflicts within the context of the US versus China and this whole conflict is just another opportunity to champion itself as the leader of the developing world. You know, it's a continued strengthening of the China, Russia, Iran, North Korea bloc of malign actors. It's just very laughable, really, that China is maintaining what is described to be a position of neutrality, when one, it won't condemn Hamas' attack; two, it won't condemn antisemitism. But instead, it'll explicitly denounce Israel for quote, going beyond self defense, and, again, in the foreign minister's words, collectively punishing the Gaza people in its counterstrike. Manya Brachear Pashman: What are we seeing in Australia, where the Jewish community numbers about 100,000? I know historically, antisemitic incidents per capita have remained low there. Hana Rudolph: The Australian government has, by and large, really supported Israel in the same way that the US has. But the politics and public sentiment also look a lot like here. So there's been growing pressure for the government to call for a ceasefire, things like that. The uptick in antisemitism also looks a lot like here. It's been very alarming. There's actually a very sizable Jewish community in Australia. It's about 100,000, and Australia has the largest number of Holocaust survivors per capita, just to give some context. Since October 7, the Executive Council of Australian Jewry has documented 221 incidents of antisemitism, so we're just talking about one month. This includes threats to Jewish schools and synagogues, property damage, even a few physical assaults. There has also been large pro-Palestinian demonstrations. I think the one that probably everyone signed in the news is a demonstration on October 9. So we're talking just two days after the attack. Outside of the Sydney Opera House where pro-Palestinian protesters were chanting 'Gas the Jews.' Manya Brachear Pashman: Remarks and resolutions coming out of the United Nations General Assembly have shown little support for Israel since the beginning of this conflict. There was a resolution calling for a truce this week. There's one calling on Israel to withdraw from the Golan Heights, the buffer between Israel and yet another hostile neighbor, Syria. How have the nations in the Asia Pacific voted on these resolutions? Hana Rudolph: I would say that the most kind of encouraging signs coming out of some of these countries have really been in terms of the government's position. So I want to especially highlight Japan, South Korea, and India. These are all countries that have joined the U.S. in condemning Hamas' attack on October 7, affirming Israel's right to self defense. They all abstained from a recent UN General Assembly resolution that called for an immediate humanitarian truce. And the reason why they abstained is because there has been a Canadian amendment to unequivocally condemn Hamas terrorist attacks and demanding immediate release of hostages. This amendment was backed by the U.S. but was rejected by the resolution. And so these three countries all abstained. We see it as a positive. The Marshall Islands and Micronesia Islands, both Pacific Islands, voted against it. They have always been strong supporters of Israel. We're incredibly grateful for that relationship. …. Manya Brachear Pashman: Since October 7, AJC Berlin director Remko Leemhuis has taken two German delegations to Israel to speak with hostages' families, to see the homes raided by Hamas, and understand the military operation underway there. Remko joined us from Berlin to speak about those missions, but also to talk about what he's seeing and hearing back home. Remko Leemhuis: We had an attack on a synagogue here in the center of Berlin that was attacked with Molotov cocktails, even though there was police protection. We had the homes of people marked with a star of David. You know, where members of the Jewish community live. And these are the things that happened sort of outside of demonstrations–we had people that have been threatened, because they were wearing a kippah or are visibly Jewish. And when we look at the demonstrations, we see what we've seen, this is nothing too new. All sorts of expressions of antisemitism beginning with, from the river to the sea. People chanting that. We're also seeing that they compare what's happening in Gaza with the shoah, so, Holocaust trivialization. Again, we see attacks on police officers, and thinly veiled, classic antisemitic stereotypes. You know, they're not saying the Jews but saying, you know, the Zionist. And that's also something not too new, but the how forceful these things press. We're also seeing attacks against the press, and saying that the press is lying, and they're always, you know, portraying them in the wrong way and using chants that are hard to translate, but that, up until now, we've mostly seen right wing manifestations. So it's very weird to see how they're now using the same slogans. We've seen it across the board, in every region in every major city. We don't have numbers, over the past month or so. But I can tell you that, for example, in the first week, after October 7, we had 202, antisemitic incidents that were recorded by a different NGO. And that was just the first week after, after October 7. And we had until the end of October, 80 antisemitic crimes that have been registered with the police and the authorities. So we've seen it across the board and online, but especially during demonstrations, so called pro-Palestinian demonstrations, where we have seen violence–violence against the police, but obviously also expressions of antisemitism and very clear expressions of antisemitism. That's been frightening, to be honest, because we have seen, you know, these kinds of before during other rounds of conflict between Hamas and Israel, but this time, it's just the sheer number and the openness is pretty stunning. And I cannot recall a moment where we have seen this kind of openly expressed antisemitism. Manya Brachear Pashman: Are you also hearing it from government leaders? Remko Leemhuis: I have to say that, especially for Germany, that the government, the ministers, they are all very clear in their support for Israel. And this is obviously not a winning theme for them, oftentimes, but the chancellor is very straightforward in his support for Israel, on numerous occasions. The Economy Minister Habeck, has put out a video that got a lot of attention , where he very clearly addresses antisemitism. Antisemitism coming from the left, so sort of his own, he's from the Green Party. So when he's talking about antisemitism from the left, he's sort of talking about where he is coming from. And I think that's always a good starting point for people when they talk about antisemitism always, start by addressing it in your own sort of political spectrum and not pointing fingers at others. And so I think that this is a very good sign. And today, we're weeks after October 7, and they're still very forceful in their support for Israel, which, again, given the pictures that we unfortunately see coming out of Gaza, I wouldn't have imagined that it would be the case, but it still is. So that is, that is good. What is still lacking, in my opinion is, or something that we've seen over the past years, and now seeing much more, that there's a gap between sort of the political class, if you like to call political class and or politicians and mainstream society. Manya Brachear Pashman: But then again, government leaders have had the opportunity to see the battleground firsthand, right? I mean, you've taken two delegations now, can you tell us what they've seen, what they've heard? Remko Leemhuis: I was on two missions. The first mission, this was a delegation with members of parliament, members of the European Parliament and other national parliaments in the European Union, including two German Members of Parliament. That was my first mission to Israel since October 7. And I can say that, obviously, seeing it firsthand among, you know, we had obviously political meetings and meeting with lawmakers in Israel, members of Knesset, but we also went to Kfar Aza, one of the kibbutzim that was attacked on October 7. And we met with survivors' families from there, with families whose loved ones have been abducted, and are now hostages in Gaza. And I think that seeing this firsthand, hearing it firsthand, from the families there's nothing that can substitute for that. You can read a lot, you can watch everything that's in the news or on TV, but being there yourself really has really an impact on people and gives them a better understanding of what Israel is facing and what the enemy is that Israel is facing. My second trip was with the Chairman of the Foreign Affairs Committee, and again, it's someone to be there and be able to go into one of these, you know, small houses which seem like frozen in time. And I mean, nothing has been touched and it looks like it looked on this Saturday morning and in some houses you think, the inhabitants or the people who live there are just out for a while and will come back. Then you go through these houses and then you get to the safety room or the security room and bomb shelter. And you see what happened in that house and that obviously people have died there. And then again, speaking to the families, to the survivors, and seeing how desperate they are. It's something that no one will ever forget who was there and will impact everyone going forward and obviously will also have an impact on how they view the ongoing military operation in Gaza, differently than somebody who's just seeing it from the news. …. Manya Brachear Pashman: In addition to its Jerusalem office, AJC also has a Middle East presence in Abu Dhabi. With us to discuss how Israel's Abraham Accords partner United Arab Emirates has been reacting to the news is AJC Abu Dhabi Director Marc Sievers. Marc, welcome to People of the Pod. Marc Sievers: Hi, Manya. Great to be with you. Manya Brachear Pashman: You are right there in the region, in the neighborhood, if you will. Tell us what you're seeing or hearing and do you feel safe? What's top of mind there? Marc Sievers: Certainly there's a great concern about the potential for escalation. We hear that, it comes up in almost every discussion. Certainly, it's bad enough to see the combat and the situation in Gaza. But there's been concern from the beginning that it could spread to Israel's northern border with Lebanon, with Syria, even potentially, to Iran directly, although I think that's quite unlikely. But it's not entirely out of the realm of the possible. But I think the US military presence in that sense, in the two aircraft carrier groups that are in the waters in the Mediterranean and the Red Sea. There is a significant US military presence that's been brought into the region to help deter an escalation, an expansion of the fighting to Lebanon and Syria. Manya Brachear Pashman: Does the tiny Jewish community there feel safe? Marc Sievers: First of all, threatening or commenting in a hostile manner toward people here because of their race or their religion or their nationality is a crime. It's taken very seriously. There have been a few cases of Jewish people. Not anyone I'm directly involved with, but I heard about who took some complaints to the police and the police took legal action. So there is a legal basis to ban any expression, public expressions of antisemitism. The messages we've received are to keep a bit of a low profile, you know, avoid being obvious or provocative. But other than that, everything's normal. I walk around the city, I drive myself, I go to a lot of public places. I feel perfectly comfortable. I don't feel any particular tension. I'm sure if there were any threats, specific threats that we would be notified. I'm not aware of any. Look, it's a difficult period and emotions run high. And certainly emotions are high in Israel, but they're also high across the Arab world. There is a lot of, as I said earlier, a lot of concern for Palestinian civilians. I think, to some extent, Hamas has managed to project itself, particularly through social media, as the embodiment of the Palestinian people in a way that's kind of hard for us to understand, but it's out there. And that is a factor. Here the Israeli embassy is open and functioning. And there's also a consulate in Dubai that is open and functioning. My understanding is that at least Israeli ambassadors in the other countries, including Egypt and Jordan have been asked to come home, not because they've been kicked out, but out of security concerns. So I think it also speaks highly of the environment in the UAE, that the Israeli diplomatic missions are still here. Manya Brachear Pashman: But will the relationships that AJC has built, that Israel has built through the Abraham Accords, are they strained? Or is your work continuing through all of this? Marc Sievers: As I keep saying this is a difficult period. But I think we're all hoping that we'll all get through this together and that there will be a new situation after the military campaign is completed, that we want to see the hostages released safely. And that's very much on people's minds. A number of people here have family or friends who either died on October 7, or in some cases were kidnapped or they know somebody who was. So we share that concern and hope with all of the Jewish people around the world. That's certainly on our minds, but I'm very hopeful still that we will get past this and that there will be new opportunities to rebuild some of what's been disrupted. And there's no question that things have been disrupted, that's just a fact. Manya Brachear Pashman: Marc, Remko, Hana, thank you all for joining us. Be sure to listen to our previous episode from earlier this week featuring updates from Paris, Latin America, and Africa. And last week, before fighting resumed, we spoke with AJC Jerusalem Director Avital Leibovitch about Israel's efforts to root out Hamas and bring the rest of the hostages home.
Dec 4, 2023
Global Antisemitism Report Part 1: What It's Like to Be Jewish in Europe, Latin America, and South Africa Right Now
Following Hamas' October 7 massacre of Israelis Jews around the world have experienced a surge of antisemitism. We checked in with some of AJC's global experts to learn what they've been seeing and hearing on the ground and to understand what efforts are underway to protect Jews and counter this hate. In the first of two installments, we hear from AJC Europe Managing Director Simone Rodan Benzaquen, AJC Africa Director Wayne Sussman, and Dina Siegel Vann, Director of AJC's Belfer Institute on Latin American Affairs. Take action to bring all hostages home now. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Simone Rodan Benzaquen (7:09) Wayne Sussman (14:54) Dina Siegel Vann Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: What Happens Next: AJC's Avital Leibovich on the Hostage Deal and Challenges Ahead What Would You Do If Your Son Was Kidnapped by Hamas? The Good, the Bad, and the Death Threats: What It's Like to Be a Jewish College Student Right Now Mai Gutman Was Supposed to Be at the Music Festival: IDF Lone Soldier Recounts Harrowing Week Responding to Hamas Terror: IsraAID CEO on How You Can Help Israelis Right Now Learn: Debunking the False Equivalency Between Israeli Hostages and Palestinian Prisoners How much do you know about Hamas? Try to ace our quiz and expose the truth about the terror group today. Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Simone Rodan Benzaquen, Wayne Sussman, and Dina Siegel Vann: Manya Brachear Pashman: American Jewish Committee has 14 international offices around the world. For today's episode, we checked in with some of those offices to learn what they're seeing and hearing on the ground since the October 7 Hamas terrorist attack on Israel. Today, we take you to Europe, Africa and Latin America. We start in Paris, where years of work to combat rising antisemitism has seen a serious setback. For more than two decades, since the Second Intifada, antisemitism has been on the rise on the European continent. In fact, it was that ripple effect that prompted AJC to ramp up its advocacy there. AJC Managing Director of Europe Simone Rodan Benzaquen joined us from Paris. Simone Rodan Benzaquen: What we have seen, I think, in Europe is more or less what we've seen, everywhere, what can only be described as an explosion of antisemitism across the European continent, I would say, mostly in Western Europe, here in France in particular, but also in the United Kingdom, we have seen the same. In Germany, we have seen similar things going on in Sweden and Denmark. But of course, here in France, where antisemitism has existed for at least two decades, or at least this contemporary form of antisemitism, for the past two decades with high numbers of antisemitic hate crimes. The situation is very, very serious. We've had basically three times the number of antisemitic hate crimes, since October 7 of what we had during the entire year, last year. We have desecration of cemeteries, we have antisemitic tags. We have intimidation, we have spitting on people. It is as if the sheer horror, the violence that happened on October 7, unleashed an antisemitic passion, an antisemitic violence across the world. As if the horrible images that were filmed by the Hamas terrorists on October 7 sort of was a legitimization. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what does that mean for the Jewish community and daily life? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: We've reached a point where people are hiding every single aspect of their Jewish identity. People are changing their names on their delivery apps, people are changing their names on their doorbells, if they believe that they sound Jewish. People are hiding every single aspect of their Jewish identity. On Uber apps, on taxi apps, myself, you know, I go on TV and do interviews quite a bit and so I give a different name to the taxi, and I give a different address a few blocks down the street is to be sure that you know, just in case, the taxi driver doesn't know where I actually live. So everybody takes precautions. It's gotten to a point where we just don't live the same life as everybody else. Manya Brachear Pashman: Has the work you've done over the past two decades made a difference? For example, since the Second Intifada, there have been a number of conflicts between Israel and terrorist groups in Gaza. Do you see progress? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: We in Europe have felt like we've been doing a little bit of the work of Sisyphus over the past two decades, where we have moments of hope and things are getting better. And we say to ourselves, oh, maybe this is a wakeup call. And sort of, then we go back to, you know, before. And I hope that this this time around, given the level of violence, given the level of antisemitic hate crimes, given the number of sheer antisemitic attacks. When you actually take it down, you come to on average about 40 antisemitic acts a day. I mean, that's huge for a population that represents far less than 1% of the entire French population. I hope this will serve as a wakeup call. But there is the question of what does it mean, how do you translate it politically? How do you translate it into government action? I mean, Europe has come up with different plans, action plans against antisemitism, but it's not enough and more needs to be done. I think one of the things that we as Jewish communities were very wary about was the fact that over the past sort of two decades, there was sort of a lack of how can I say, solidarity from other French people. Again, we've had antisemitic hate crimes for the last 20 years, people have been murdered. But every single time, when you look at the demonstrations, at the marches after something horrible happened, you would mostly have a few hundred, or maybe a few thousand Jews in the streets. And so there was sort of a feeling that within the French Jewish community that they were a little bit abandoned by the rest of society. And so we know from our surveys, AJC does a survey every two years where we know that, for example, French people, and Germans as well, are convinced about the fact that antisemitism is not the problem of Jews alone, but that of the entire society. So both in Germany and in France, 73% of the population say that it is not the problem of Jews alone. But despite that number, it has never sort of translated into something concrete. So we would never have marches. We would never have like sort of big shows of solidarity with the Jewish community. And I think, since, if there's one good news, and there's not a lot of good news these days, if there's one good news is that last Sunday there were massive demonstrations across France, against antisemitism with basically the entire political class were present, with 20 government ministers who were present, with a prime minister who was present, with three former prime ministers who were present, two former presidents, plus a lot of people on the streets. We had over 180,000 people in the streets of France, basically expressing solidarity with the Jewish community and saying that they want to fight against antisemitism. So I think that was a sort of a very important sign of hope for many French Jews. …. Manya Brachear Pashman: Now we go to the continent of Africa, where AJC Africa Director Wayne Sussman joins us from the South African city of Johannesburg to explain how the war that began on October 7 affects Israel's relations with African countries. Wayne Sussman: I would say the tensest of the relationships right now is between Israel and South Africa. The Ambassador of Israel to South Africa received a démarche. So when the first two countries to recall their ambassadors were South Africa and Chad. When it comes to Chad, that was more unexpected than South Africa. Because relations were recently increasing between Chad and Israel. Sadly–and one's got to remember that the largest Jewish community in Africa by a country mile is in South Africa. But sadly, the government of South Africa has had a very adversarial relationship with the State of Israel over the last few years. And this has manifested in the last few weeks. Manya Brachear Pashman: Because of this antagonistic relationship with Israel, has the South African Jewish community faced quite a bit of antisemitism? Wayne Sussman: Even though the current government of South Africa has had an adversarial relationship with the State of Israel, levels of antisemitism are extremely low–far lower than Europe, far lower than Latin America, far lower than the United States of America, far lower than Canada, far lower than Australia. So we are working off a very low base here in South Africa. But over the last few weeks, antisemitic incidents have increased. For the time being, levels of violent incidents have been low. A turning point was on Sunday afternoon in Cape Town on the Sea Point Promenade, just to zone in on Sea Point, where the majority of Jews in Cape Town live. And the promenade is a beautiful public space, which all residents of the city use. And what we saw the day before was a pro-Palestinian demonstration through the streets of the City of Cape Town. It was a largely peaceful protest. There were pockets of the protests, which had hateful slogans and made concerning threats against the main Jewish Day School in Cape Town. And then the next day, a group of Christians at the Sea Point Promenade, which I referred to earlier, which is in the Jewish neighborhood of Sea Point, were going to have a prayer vigil for the State of Israel. They had a stage set up, microphones, etc. And a group of 200 to 300 pro-Palestinian, pro-Hamas supporters sympathizers came and disrupted it. And the police had to get involved and use water cannons. It's very rare for us to see sights like this in South Africa, particularly in Sea Point. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what I'm hearing you say is the antagonism toward Israel doesn't normally translate into antagonism that targets the Jewish community there? Wayne Sussman: One of the worrying sides we see is our threats against, first of all, multinational corporations. I think these threats will not be impactful. But what is more concerning are privately owned Jewish businesses. And we have seen specific targets in this regard. Because of the CEOs of these businesses purporting to support and stand with Israel. But I think we need to see how successful these are going to be. But I think the community is incredibly united right now. They are standing strong. And it's vital because this is a very important Jewish community in South Africa. A rich history, this community has made a remarkable contribution to the fight against apartheid, to building this economy, to creating jobs in the field of medicine and law, to arts and culture, and even some in sport. Manya Brachear Pashman: There was a United Nations resolution calling for a truce. I believe 35 African states voted in favor of that resolution but Cameroon and Ethiopia abstained. Can you shed a little light on where other African countries stand? Wayne Sussman: I would say the overwhelming amount of countries have adopted a neutral position that might change when we come to the United Nations and a multinational forum on the African continent like the African Union. But countries like Kenya, who under the new president have stood firmly and strongly with Israel. Countries, like Zambia have shown a lot of empathy towards Israel. That's a version relationship. And then we look at countries in the west of Africa, Togo and Cameroon. They've historically had very strong ties with Israel, those ties remain. And then you have countries like the Democratic Republic of Congo and Rwanda, those countries have stood firmly with Israel at this time. An interesting development. And again, this is a very fluid situation. But Indian Ocean islands like Mauritius, and Seychelles, where I was, I've been surprised at their even-handedness on this particular situation. Ethiopia is a fascinating country. It's a country which for many years had remarkable levels of economic growth, a very young population, one of the largest populations in Africa, also the center of the African Union, and also the hub of African air travel. And, of course, a country where many of Israel's citizens hail from and still maintain deep personal ties to. So I think that Ethiopia abstaining was very, very interesting in that regard. And that ties will be stronger between the two countries after this. Manya Brachear Pashman: I should note that Sudan and Morocco, two signatories of the Abraham Accords, did vote in favor of a truce. Do you see those ties weakened by all of this? Wayne Sussman: I think universally, it's going to be a challenging time for Israel. But I think once the dust settles, that you will see countries like Morocco return to embracing normalization. You'll see countries like Zambia, who are not part of the Abraham Accords, but are deepening ties, I think they will continue to do that. So I think the next few days and weeks will be very difficult. But again, back to what I was saying earlier, from a bilateral level, I think African countries are pragmatic. Those which were considering the Abraham Accords will see the benefit with regards to Israel, agritech Israel in fintech, Israel in rural health care, Israel in rural development. I think countries have seen a great benefit in deepening those ties. So it is going to be tested, certainly in places like the United Nations, certainly in forums like the African Union. What's very interesting, there was an interview in a Saudi Arabian newspaper recently with the president of Somalia. And he was very bullish, saying that if Israel and the Palestinians agreed to a two-state solution, that it would be right for Somalia to engage in peaceful relations with Israel. So even though we're in a very difficult and dark time, and it's unclear what's going to happen, we're seeing signs from Somalia, which is obviously in Africa, and also signs in Saudi Arabia, that even once the dust settles over here, that diplomatic doors will still remain open. …. Manya Brachear Pashman: In July 1994, terrorists bombed the AMIA Jewish Community Center in Buenos Aires, killing 85 people and injuring more than 300 others. From that point on, the Argentine capital became known as the site of the worst and most fatal antisemitic attack since the Holocaust. That distinction changed on October 7 when terrorists breached the border between Israel and Gaza and murdered more than 1,200 people. As the Director of AJC's Belfer Institute for Latin American Affairs Dina Siegel Vann explains, it has not been an easy time for Jews on the South American continent or other Spanish-speaking regions. Dina Siegel Vann: Some of the countries that have really concerned us the most, are countries like Colombia, which in the past used to be the most steadfast ally of the United States and of Israel. But since the arrival of President Petro, who is a leftist ideologue, I would say, this has changed. And since October 7, we have seen really the country go in a totally different direction, which is really endangering the relationship not only with Israel, but with the United States. Colombia, President Petro has tweeted on October 8, he was already tweeting, where he was comparing Gaza to Auschwitz, where he was talking about international bankers, and he was talking about, the media, international media being on the side of those who commit genocide. So, you know, that has already made for a very rarefied environment, in terms of relations, as I said, both with the United States and what Israel. He also threatened through his foreign minister, the expulsion of the Israeli ambassador who was responding to his attacks, and now he has recalled his ambassador to Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: Chile also has been unfriendly, but that's been the case for a while. It is home to the largest Palestinian diaspora outside the Middle East, and leaders of that community have expressed support for Hamas. But AJC will hold its annual strategic forum for Latin American and Iberian leaders in Santiago this month. Can you give us the lay of the land there? Dina Siegel Vann: So what has happened since is that President Boric, who, you know, who identifies with those positions of the Palestinian community has also had very hostile attitudes towards Israel. Number one, you know, he has not met with the Jewish community, he has not expressed his condolences, he hasn't expressed his condolences to Israel, and to the families of the victims. And he has also spoken, you know, mostly about what is going on in Gaza, and has characterized Israel's efforts to defend itself as genocidal as crimes against humanity, etc. And that also has created a very very vulnerable sense in the Jewish community in Chile that feels, you know, totally alone when it comes to this development. So I would say that Chile and Colombia have been the most egregious cases. Particularly because we're not talking about insignificant countries in the region, we're talking about Colombia, which is the third largest recipient of U.S. aid after Israel and Egypt. And we're talking about a country like Chile, who has always been or considers itself a paragon of human rights, not only in the region, but around the world. So their voices count, and that's why, you know, it concerns us a great deal. Manya Brachear Pashman: As I mentioned at the beginning of this conversation, until October 7, the worst antisemitic attack since the Holocaust had taken place in Argentina in 1994, carried out by Iran's terror proxy, Hezbollah. And just recently, Brazilian police detained a couple of Hezbollah operatives who were in the country with plans to attack Brazilian Jewish institutions, correct? Dina Siegel Vann: It underscores the really, really dangerous role that Iran plays in the region. And we know firsthand about it, because of course, the attacks in 1992 and 1994. But we know about it also, because of the tri-border area, where we know that Hezbollah and Hamas are very active, undertaking all kinds of money laundering activities. It's very important that we keep a focus on that. I think the U.S. is very, very keen on following very closely what's going on in that area, and in other areas in other areas of the region, including Venezuela, which has been the gateway to Iran in the region. Iran is very well positioned in that country and has ties to President Maduro. Started with President Chavez and it has continued with President Maduro. So we need to keep in focus, when we talk about, you know, potentially dangerous scenarios, not only from lead for Latin America, but for the United States for the whole hemisphere., this, you know, Iran is quite active. And is really, you know, thinking about how to create mischief, you know, whether in Brazil or elsewhere.We don't remember that, you know, that we have really a dangerous situation very close in our own neighborhood. Manya Brachear Pashman: You have told me that 30% of the hostages hail from Latin America: Brazil, Chile, Uruguay, Mexico, 15 from Argentina. Dina Siegel Vann: Yes. Well, I have to say that Argentina, for example, President Fernandez published in the New York Times a half a page with a letter an open letter demanding that the hostages be brought home and talking about their own hostages their own citizens. So yeah, absolutely. I mean, the hostages are traveling, there's some hostages from Latin American families that are traveling all around the region, meeting with members of Congress meeting with government officials and others and the media to raise more awareness about the issue and pressure the governments, their own governments to to speak up, you know, on on on, on behalf on to bring that these hostages home. Manya Brachear Pashman: Since recording this episode, many of those hostages with Latin American citizenship have been able to return home. Of course, there are still so many hostages– nearly 160. To push for their safe return, listeners can head to AJC.org/BringThemHome or follow the link in our show notes. Dina, take us back to Europe–tell us about the situation in Spain. Dina Siegel Vann: Spain has been a mixed bag, because you have President Sanchez and Foreign Minister Alvarez has come out from the very beginning with very strong signs of support towards Israel, recognizing Hamas as a terrorist organization recognizes Israel's right to defend itself. But they they were in the process of creating a government and they need some of the more radical parties, independent parties, and, you know, some other parties like Soomad, who are very anti-Israel, they needed them to form coalition's and this parties were speaking, you know, in very vile terms regarding Israel, and really indulging on some antisemitic themes, and President Sanchez, didn't come out publicly as well as, you know, Foreign Minister Robotis to denounce them. But at the same time, they made clear that everybody understood that in foreign policy, what counts is the voice of the President and the voice of the foreign minister. They met with the Jewish community, they expressed their their their solidarity, they express their concern about antisemitism, they met with the families of the kidnapped. So they have really tried to, you know, to keep a very balanced and very difficult position, vis a vis, their current situation. They formed a government yesterday, the government was finally formed. And maybe at this point, they will be more, they'll have more leeway to come out to protest this type of discourse. But at the same time, you know, in Spain, you have seen some vandalism, you have seen some intimidation in schools against Jews and Israelis. So as I said, it's a mixed bag. And we are still monitoring this very carefully. Spain wants to be a leader, wants to be a convener when it comes to negotiating some sort of peace deal, they did it in the Madrid Conference a while back, they see their role, once again, as you know, as as a liaison, as a bridge between both worlds and therefore, you know, they always try to keep a very careful stance when it comes to both communities.
Nov 29, 2023
What Happens Next: AJC's Avital Leibovich on the Hostage Deal and Challenges Ahead
From the frontlines of the Israel-Hamas War, Lt. Col. (res.) Avital Leibovich, director of AJC Jerusalem, joins us to discuss the current pause in fighting between Israel and the terror group Hamas, the release of hostages, the significance of international support for Israel, and the challenges the Jewish state faces in the West Bank. Leibovich also provides insights into the humanitarian conditions of the hostages and the broader implications of the conflict. Take action to bring all hostages home now. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Lt. Col. (res.) Avital Leibovich Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: What Would You Do If Your Son Was Kidnapped by Hamas? The Good, the Bad, and the Death Threats: What It's Like to Be a Jewish College Student Right Now Mai Gutman Was Supposed to Be at the Music Festival: IDF Lone Soldier Recounts Harrowing Week Responding to Hamas Terror: IsraAID CEO on How You Can Help Israelis Right Now Watch – Lt. Col. (res.) Avital Leibovich's War Diary How All Israelis are Affected by the Israel-Hamas War How October 7 "Changed the DNA" of Israelis Forever How Volunteers are Stepping up to Support the IDF Learn: Debunking the False Equivalency Between Israeli Hostages and Palestinian Prisoners What is Known About Israeli Hostages Taken by Hamas How much do you know about Hamas? Try to ace our quiz and expose the truth about the terror group today. Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Avital Leibovich: Manya Brachear Pashman: As the pause in fighting between Israel and Hamas terrorists nears its expiration on Thursday, Hamas continues to hold hostage 160 people. 80, including 61 women and children have been released during the pause. In exchange, Israel has freed 180 Palestinian prisoners. Lieutenant Colonel Avital Leibovich, Director of AJC Jerusalem joins us from Israel now for an update. Avital, welcome to People of the Pod and how are you? Avital Leibovich: Thank you for having me. I am doing well, considering the fact that we are in a war here in Israel. My biggest concern at this time is the well being of my family. My son is in the army, my daughter is on reserve duty. So that's my number one concern. And of course, the well being of Israel, the safety and security of Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Avital, what does this pause mean? What is being accomplished during this time? Avital Leibovich: So the pause is something that Hamas pressured Israel. It pressured Israel because the military pressure was quite significant. The pause allows a few things to happen. Number one, we, Israel will receive hostages, and in return, Israel will free from prison, women and youth that were involved in different planning of terror attacks or executed themselves terror attacks. And that's one thing. The second thing I would say, is time for Hamas to regroup. That's for their benefit. This pause allows them to regroup, rearm, reposition themselves. The third thing and I'm going back to Israel also allows Israeli army to better prepare to rearm to place itself in the right positioning and then be ready for the next stage, which is resumption of the fighting. Manya Brachear Pashman: And do you expect that fighting to resume right away? Or do you think that Israel would like to extend the pause as long as possible in order to get as many hostages back as possible? Avital Leibovich: Yesterday, there were meetings between, actually was a very interesting meeting in Qatar. In the meeting, we had the head of the Egyptian intelligence, the head of the Israeli Mossad, and the Qatari representative, and the American head of the CIA, the American CIA. And in this meeting, the discussion evolved on a few more days of pause, and in return, Hamas will release a few more hostages. So right now Israel has said that it agrees to a few more days of a pause. But we're only talking about a few more days. The ultimate goal of this war is to eliminate Hamas government in Gaza. And in order to change that government, in order to bring some sort of a new future to this region, to Israel, to Gaza, to the Palestinians living in Gaza, this takes time. So the fighting I assume will take a long time. It's going to be a long time because Gaza has been built underground and above the ground in such a way that requires inch by inch, very careful work a lot of the time other facilities are booby trapped. There is a huge array of tunnels underground, which are very long. With junctions. Some of the tunnels can even have cars inside. So this has to be a very, very careful job. We have a lot of soldiers inside Gaza right now. And so this pause I would say is temporary. Manya Brachear Pashman: What are we learning from the hostages who are being released? Avital Leibovich: That's the most heartbreaking issue. We're learning a few things. The first thing is they had to speak very, very quietly among themselves. Of course, I'm referring to those who had other hostages with them. But those who had other hostages with them had to whisper. And how do we know this because some of the kids are still whispering today, some of the kids that have been held as hostages and just returned from captivity, they're still whispering. Another thing we know is that they had very little food, very little quantities of food, which also brings a lot of worries here in Israel, because there are many elderly people held. There's still a baby inside the toddlers and a few other children. And so the nutrition issue obviously is quite critical. The third thing we learned is that some of them were held in complete seclusion. One of the children that returned two days ago is a 12 year old boy, by the name of Eitan Yahalomi. His father was murdered, his mother is still alive. And he actually was in a room by himself for at least two weeks. And imagine for a 12 year old to be in this kind of hostile environment, on his own without anybody to communicate, underground, most of the time, that's quite scary. We also know that they had very poor hygiene conditions, no running water, very, very minimal toilet facilities. We also know they never received any medical care and attention, no medicine, no doctors, nothing of that sort. And the last thing we know is that most of the time they were held underground, in an underground facility, different sizes of rooms. And all of these things are just a small indication of the cruelty of this terror organization called Hamas. Manya Brachear Pashman: Congress is debating whether to send aid to Israel to support Israel in the war. How important is it at this point? Avital Leibovich: I think it's very important. First of all, I do want to say that the support that Israel received from the US until now, it's unbelievable. The fact that there are, on the military side the fact that there are our aircraft carriers here in the region, and planes filled with different kinds of ammunition. That sends a very strong message of both deterrence and strength to the enemies in the region. And second, on the political, more strategic level. The voting, the vetoing of the different proposals on the Security Council in the UN, the multiple visits starting from President Biden to Secretary of State Blinken, which he's supposed to arrive here tomorrow. And also appointing a special envoy to this specific situation that we have here in the region. So all of these things speak volumes. So yes, I think it's very significant to Israel, and also the future decisions will be significant. Look, being at war for such a long time and 53 days have passed already has serious precautions on different issues. Economy is one of them. Obviously, tourism has stopped, small businesses have been affected and many other sectors as well. So aid would be very, very significant to Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm also curious about the security situation in the West Bank. We were so focused on terrorism coming from the West Bank before this happened. What is the situation there now, especially as hostages are being released? Avital Leibovich: It's a good question, because from where I'm sitting, the West Bank at this point of time is another front that Israel has to deal with at this specific moment. We have a serious challenge with the fact that the Palestinian Authority does not really have governance in many areas in the West Bank. And as a result of that, there are different kinds of terror groups, Hamas is one of them. But it's not the only one, trying to recruit Palestinians to commit different terror attacks. The second side of it is a lot of incitement, which is really flooding the social media platforms, and also has an effect on the mood on the streets on the mood of young people and others as well. So the IDF, the Israeli Defense Forces, actually almost on a daily basis, needs to enter certain areas where there is no prisons, unfortunately, have any Palestinian policemen, and actually arrest those terrorists on the ground. And I think in the last 50 days or so the IDF has arrested more than 1000 people that have been suspicious and with some kind of planning or plotting terror attacks against Israelis. And this does not seem to quiet down I have to say so I am concerned of this front. At this point of time Hamas is though, by the way, investing a lot of time and effort because Hamas is interest is of course, to create lack of stability here in Israel. So part of that is the instability is trying to influence what's going on in the West Bank and trying to get people out to the streets, either protesting against idea for committing some sort of terror acts against Israelis so that's really an issue of concern for us. Manya Brachear Pashman: We talked about the importance of American aid, are there other countries that are showing significant support that have been really vital in this war? Avital Leibovich: I think that we've seen some very important gestures of support by European leaders from the Czech Republic, from Bulgaria, from, from the UK, from France, from Japan, from other countries. But I think the number one country in Europe that really stood up and is still standing up supporting Israel very, very strongly, is maybe Germany. And yesterday, the President of Germany visited Israel and visited one of the kibbutzes, a kibbutz called Be'eri. And a lot of the houses there were burned and dozens of people were murdered and others were kidnapped. And he was so touched and moved. And he said that the government of Germany intends to donate 7 million euros just for the rebuilding and renovating of this community. But there are other countries as well, and I think Israel has been well supported by the international community. However, the challenge still lays ahead, because we are not at the end of this war. And in order to eliminate Hamas, we need more time. And as this time progresses, there will be a lot more pictures which are not pleasant because pictures from wars are not pleasant pictures. And this may have an impact on different kinds of world leaders. So we have to continue and explain and gain that legitimization so that Israel could complete its goal and continue to defend itself. Manya Brachear Pashman: I know in conversations with AJC's, Berlin's director Remko Leemhuis, he brought delegations of German officials to Israel. And that has made quite a difference, I think, to see it firsthand. Have there been other delegations from other countries? Avital Leibovich: So we have hosted here in Israel four delegations with very short notice. I have a great staff in the office, and they were able to create an itinerary, which I think is very experiential on one hand, but on the other hand, is also quite touching. Because how many people in such leadership positions really have the opportunity to really be on the ground and see the situation as it is. So we had here three parliamentary delegations from European countries, East and Western Europe. And we also had here the head of the, the chair of the Foreign Affairs security committee of the German parliament. And I met those three parliamentary delegations, and I briefed them. And I have to say that with all the information that is out there today in 2023, via the internet and platforms and social media, still there is not a full understanding of the situation. So taking these participants on the ground, showing them those areas, those communities that have been affected, and taking them to a base that has been turned into a morgue. Where, even today, more than 80 bodies and body parts still remain unidentified because of the terrible condition that they came with. And I explained to them the extent of the atrocities. You can only really get it when you're on the ground. Manya Brachear Pashman: Avital, once this pause expires, and I know it's unclear when that will be, but you've made it clear that it's inevitable – what comes next? Avital Leibovich: I think we are heading into a very difficult time ahead. Because once we finish the hostage exchange kind of agreements, then Israel will have to return to the actual fighting part. And Hamas, which is a very bitter psychological warfare enemy will continue and try to stop this fighting in different psychological ways. Israeli leadership will have to make here tough decisions, whether the country agrees, for example, just I'll give you just one idea of such a dilemma. Let's say Hamas tomorrow morning, or in three days time says, complete and finish the fighting altogether. Stop for the next five years, hold your fire for the next five fears, and in return, we will return all the hostages. Then what, then what do you do as a country? What kind of decision will the government take? Will it still continue with the fighting to eliminate Hamas? Or will it say okay, the life of the hostages are more important and therefore, we are canceling the original goal and stopping the fighting. I don't think that will happen. But those kinds of dilemmas, I think will escort Israeli leaders in the next couple of days. I think they will be tough, very tough questions ahead that Israel will need to deal with. Another issue that we haven't discussed, is the northern arena. Hamas is a tough enemy. is a cruel enemy. It possesses something like 20,000 rockets, which they used more or less half, maybe a bit more. Because Hezbollah is a totally different ballgame in terms of capabilities in terms of military capabilities in terms of ammunition, precise ammunition and so on. And what will be the policy visa vie Hezbollah. And this is also a question Israel will need to ask itself and I'm sure that the next week or two will have an indication where this country is heading. There's one thing that it's clear to all of us here in Israel, that we cannot go back to the same situation that existed here on October 6–53 days ago. That situation must be changed. Manya Brachear Pashman: Avital thank you so much for joining us and giving us an update. Avital Leibovich: Thank you for the opportunity.
Nov 16, 2023
The Good, the Bad, and the Death Threats: What It's Like to Be a Jewish College Student Right Now
Delve into the unsettling rise of antisemitism on American college campuses, focusing on alarming incidents at Cornell University and Columbia University. Our guests, Molly Goldstein and Elliot Sadoff, both members of AJC's Campus Global Board, share their experiences of Jewish students being targeted in the classroom, physically attacked while raising awareness about kidnapped babies in Gaza, and facing death threats for merely speaking Hebrew. Join us as Molly and Elliott share their perspectives on this surge of antisemitism following the October 7th Hamas attacks, and the solidarity and Jewish pride they are seeing on campus. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Molly Goldstein and Elliot Sadoff Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: Jewish U.S. Military Veterans' Message to IDF Soldiers Fighting Hamas: "We're With You" What Would You Do If Your Son Was Kidnapped by Hamas? Renana Gomeh's Sons Were Taken Hostage by Hamas: What She Needs You to Do to Bring Them Home Now What Biden's Wartime Visit to Israel Signals to Hamas, Iran, Hezbollah Mai Gutman Was Supposed to Be at the Music Festival: IDF Lone Soldier Recounts Harrowing Week Responding to Hamas Terror: IsraAID CEO on How You Can Help Israelis Right Now Learn: What is Known About Israeli Hostages Taken by Hamas 7 Ways Hamas Exploits Palestinian Civilians in Gaza How much do you know about Hamas? Try to ace our quiz and expose the truth about the terror group today. AJC Campus Library AJC Campus Global Board Donate: AJC.org/SupportIsrael Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Molly Goldstein and Elliot Sadoff: Manya Brachear Pashman: Throughout her studies at Cornell University, junior Molly Goldstein has become passionate about the intersection of international relations, human rights and conflict resolution. She joined AJC's Campus global board last year to develop her Jewish advocacy skills on and off campus. But nothing could have prepared her for what has unfolded this year on Cornell's campus, where nearly a fourth of the students are Jewish. An arrest has been made after a number of posts on an online discussion board threatened extreme violence and death to Jews on campus, specifically identifying the address of Cornell's kosher dining hall. Likewise, Elliot Sadoff also joined AJC's Campus global board last year. He is a dual degree student at Tel Aviv University and Columbia University, where an Israeli student was physically attacked while hanging posters of kidnapped babies trapped in Gaza. And Jewish students have received death threats and been spat upon for speaking Hebrew. Molly and Elliot are with us now to discuss what they've witnessed as antisemitism related to the Israel Hamas war has emerged at an alarming rate on a number of American college campuses across the country. Elliot, Molly, welcome to People of the Pod. Molly Goldstein: Thank you for having us. Elliot Sadoff: Yeah, thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I first have to ask, how are you both doing? And how are you coping with the intensity of all of this? Elliot Sadoff: I mean, I think you can ask anyone how they're doing these days, and it's hard to answer. But definitely holding in there. I've been very lucky the past few weeks because of the program I'm in where I have a lot of students with me who are studying at Tel Aviv University. So we've really formed a tight knit community that's able to support each other throughout these times. With everything going on on campus and around the world. It's a very good support system to have that I don't think a lot of students do. It's not easy to go to class and be looking around you thinking what's going to happen, what are people going to say, what does this professor think? But to have a support system like that is very helpful. Manya Brachear Pashman: Molly, how about you? Molly Goldstein: Over the past month, it's definitely progressed to feeling more and more afraid to be a Jew on campus. But something that doesn't make it to the media, I believe the media likes to portray, you know, all the horrible things that are happening on campus, but the Jewish community at Cornell has really come together, in one of the most beautiful ways I have ever seen during my time at Cornell. We've had the Shabbat dinners with filling capacity of the kosher dining hall. We've had, you know, Jews from Monsey coming and bringing us food for a barbecue for 200 people. We had never met them before in our entire lives. And they just decided to come up and do this wonderful, wonderful, good deed for us. And there's nothing more I could have asked to be proud of as a Jew. And I hope that Jews on campus know that, although it's scary, we will get through this time. And we should be proud and continue to be Jewish. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's really comforting to hear. And I'm sure your parents find that really comforting to hear, especially as they watch the news and wonder how their children are doing. What are you hearing from them? How are they doing? Molly Goldstein: Yeah, parents are definitely more scared than I have ever seen them before. I mean, I had people's parents coming up to get their kids and take them home. People's parents like requesting that we have to sue the University and we have to get these kids off campus and we have to take really harsh actions. And it's because they're scared, they don't know what to do. They're far away from their kids. And, you know, it's up to us to make sure that their parents know that we'll be safe and, and for them to know that everything that needs to be done is getting done for Jewish students. Manya Brachear Pashman: Elliot, anything to add to that? Elliot Sadoff: Yeah, I mean, I can just echo what Molly was saying about kind of uniting around this and being proud of, like being Jewish and rallying around the community and that my parents are scared, a lot of parents are scared. But there's also been a lot of people working together to change that environment, to change the narrative to to help students be proud of who they are. I don't know if you've seen recently there's a large Facebook group, Mothers Against College Antisemitism, which I think now is hundreds of 1000s of people. I could be mistaken there. But it shows that there are people who care about us, there are people who care about protecting their identity and supporting students and I think that's really meaningful. That's very helpful to see on campus. Manya Brachear Pashman: Molly, can you walk our listeners through what has happened at Cornell? I mean, how did you first hear about the threats that I mentioned in the introduction? And what precautions did you and other students take? Molly Goldstein: Yeah, absolutely. So I was sitting in my room actually in the Center for Jewish Living, which was the place that was threatened by a bomb threat, as well as it's right next door to the kosher dining hall, which the student threatened to shoot up. And I was sitting, you know, doing homework in my room, and all of a sudden, there's a Cornellians for Israel group chat that now has 1000s of people in it. It's progressed over the month since the war has started. And we just get a link from one of the students that found it, and said, like, look, what we have posted online, and all of a sudden, all the threats started coming in. My immediate reaction was genuine fear. I'm sitting in the building, I did not know what was going to happen to me or my fellow community members. And pretty quickly, we got Cornell Police Department on the case, we got the FBI, Homeland Security, Ithaca police and New York State Police, everybody showed up and was at the dining hall and kosher spaces. And that night, the President of the University and vice president of the university came to our house, to see how we were doing and make sure that we know they're doing everything they can to ensure our safety. And, you know, they would not have come if they really thought their lives were in danger. But it was scary. I had students, you know, weren't sleeping in the house that night. They found other places to go, whether that was other friends who had apartments or relatives, family, friends in Ithaca. And as the day went on, we had New York Governor Kathy Hochol came the next morning, the next morning, within just 12 hours was at our doorstep, talking to us, ensuring that New York State was going to do everything they can to condemn antisemitism to ensure our safety for not just Jewish students at Cornell, but Jewish students at all New York State campuses, which includes Columbia, and you know, CUNY schools, which are having a really difficult time with anti-Zionism and antisemitism. And as time went on, we were getting, you know, news media coverage. And we never went on lockdown. But we were doing everything we could to keep people safe. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did you feel that the university was doing enough to respond? It sounds like people from across the state were doing enough, or doing a lot. But was the university doing enough in your opinion? Molly Goldstein: In my opinion, yes. I think the fact that the President and the Vice President came immediately to make sure we're doing okay, they released a statement that night, and the next day they were updating their social media with everything that they were doing. And they just released actually that they are changing their antisemitism in their DEI training, so that it's more prevalent and that education can be better on that front. Manya Brachear Pashman: Eliott, can you walk our listeners through the atmosphere at Columbia, I know a student was attacked, but there have also been smaller acts of aggression. I won't say microaggressions because there's nothing micro about a swastika on a wall. But can you walk us through the general atmosphere there? Elliot Sadoff: Yeah, so I think throughout the past month, the atmosphere on campus at Columbia has generally felt unsafe for Jewish students. Obviously, there were the incidents where the physical safety of students was was under threat where the Israeli student was attacked for putting up posters of those that were kidnapped, but also reports of people yelling on campus, f the Jews or people being spit on and I think either one or two now swastikas being drawn on campus. But it just kind of fits into the broader rhetoric on campus. There seems to be the downplaying of anti semitism and anti Zionism and in class on campus, Jewish students aren't feeling safe. They aren't feeling welcomed by the professors, by their peers, by people in New York City. And the rhetoric for me from what I've seen and what my friends have seen from what I'm hearing from the pro Israel groups is that it seems the real effect and a real threat, antisemitism is being downplayed. There's an anonymous app that, obviously, it's an online platform. I think a lot of schools are dealing with this, where students sign up, can post whatever they want without consequences. And for the past few weeks, it's been riddled with antisemitism. There seems to be no consequences for anyone. People are saying again, like F the Jews, Israel should be demolished. Lives of Israelis don't matter. And there's an anti semitic incident someone posted and all the comments are saying, This is not real. It's over blasted. This isn't a real threat to Jewish students. And that I think that doesn't that doesn't help anyone. It doesn't help the Palestinian cause to do this. It doesn't help the Israeli cause to do this. It's just it's making everyone feel unsafe. Manya Brachear Pashman: What is this app that you mentioned, where there is no accountability? Elliot Sadoff: So the apps called Sidechat, but I think other campuses have different ones-Sidechat, YikYak, some other ones where you have to log in with your student university email to verify that your student at Columbia, or then you get access to a Columbia on the message board where there's posting, you can upvote or downvote, you can comment, post images. And this entire month, the app just every day, you can't scroll through it. 75% of the posts are completely antisemitic, saying Jews don't have a right to live, Jewscan't do this, that, downplaying antisemitism, minimizing it saying it's not happening, saying Jewish lives don't matter. And these things have been brought up, from my understanding, this has been brought up to the university. And obviously, it's hard for them to control. We want everyone to be able to have free speech and speak their mind. But it seems that there's a line that's been crossed here, and Jewish students feel unsafe because of this, and it continues to this day, even this morning. Manya Brachear Pashman: And who runs this app? It's not a university run app. It's a company, right? Elliot Sadoff: It's a company, but they advertise at the club fair, they're on campus, they have tables, you need your university email to log in. So it seems there should be some way to provide accountability. And obviously, it's not an official university platform. But it's an atmosphere that's not safe for Jewish students. That's part of what's going on on campus. Manya Brachear Pashman: You said that there is a feeling of danger in the classroom that you have. Have you personally encountered hostility in the classroom? Elliot Sadoff: In a lot of my classes, it's that I don't want to spark hostility. And I don't want to say what my thoughts are, I don't want to say that I might feel unsafe as a Jewish student, I don't want to tell people that I went to school in Tel Aviv. And that's the program that I'm part of. I mean, if I see some of my professors that I've had in the past signing a petition that says Hamas' actions are legitimate military action, how am I supposed to feel safe on campus? My professors are signing this, ones that I've had, they know who I am, I've had conversations with them. And this is what they're signing. And that just adds into the fact that in some of my other classes, people are kind of using free speech as a guise to promote antisemitism and that one professor at Columbia described awe and joy at Hamas' attack on Israel. And this is a pretty well known case that this professor has been espousing these ideas. And in my class, people are saying, this is free speech. You can't criticize him, you can't. You can't deny that you can't take action against him when there's a difference. It's clearly adding to a rhetorical atmosphere that's making Jewish students feel unsafe. Manya Brachear Pashman: And what about you, Molly? Has there been any hostility in classrooms at Cornell that you've, you've come across? Molly Goldstein: There are many students who have been coming out and reporting professors and other students in their classes, who are spewing anti-Israel, anti-Zionist views. And it's really toeing the line between anti-Zionism and real antisemitism. And it's scary. I mean, I know a student who has family who's in the IDF right now fighting in Gaza, and one of their cousin's just was killed and they tried to get accommodations from the professor and they weren't accommodating. There's another class on you know, colonialism and a writing seminar for first year students. So this is exactly what they're going to introduce to the university. And when they were first asked about their opinions on the Israeli Palestinian conflict, they said, you know, we feel bad for everybody, like innocent lives, nobody should be killed. This is not right. And the professor's reaction was to then say all the horrible things that Israel is doing, and tried to convince the class that they should be on the side of the Palestinians. And then they ask the question again, and almost nobody wants to talk because they were scared of disagreeing with the professor, or they were confused. And it's real propaganda that's being pushed through the university and people aren't able, people aren't able to make the distinctions and be able to freely express their opinions, their problems or opinions or their pro Jewish opinions for that matter. Manya Brachear Pashman: Has there been any kind of constructive dialogue either facilitated by faculty by students? Has there been any evidence that people are willing to understand other points of view or embrace the complexities of the conflict. Molly Goldstein: So the only experience I've had with true constructive dialogue was at the beginning, I'm like October 10, or 11th, or something like that. There was a student assembly meeting where SJP on campus, I proposed a resolution to condemn Cornell University for not speaking out for the Palestinian people. Their statement had only mentioned: Hamas is a terrorist organization and didn't say anything about the innocent Palestinian lives that are being lost. And in addition to that resolution, it was you should divest from Israel, you should deem it an occupied apartheid state. And a whole bunch of SJP people and a whole bunch of pro Israel, people came to the student assembly meeting. And after everyone showed their views, the person who had originally proposed the resolution, wanted to amend it. And they said, You know what, I can understand why this was very harmful. Let's try to change and have constructive dialogue. And at the end, we all came together. And we were all talking about our views and our notions. And that was probably the last time that there was constructive dialogue on campus. Unfortunately, that was like three weeks ago. Since then, you know, the university has had panels and other talks led by professors, but the academics are not in favor of Israel. They do not like to show both sides of the narrative. And it's always from an anti-Israel voice. And it's scary and hard to see. Manya Brachear Pashman: Elliot, how about constructive dialogue on Columbia's campus–any at all? Elliot Sadoff: I know that the School of International and Public Affairs has held a few meetings, but it hasn't been student dialogue at all. It's just been webinars from what I understand. And since a month ago, October 7, I haven't seen anything with students that's been constructive, that's been meaningful. And I think that's really the issue that I see with that, and I think a lot of other Jewish students do with that is that it doesn't help us it doesn't help anyone that there's no constructive dialogue. If someone wants to sit down with me and discuss the Israeli Palestinian conflict, I'm happy to do so. I know that there's a lot to discuss. But I haven't seen any of that. All I've seen as Israel's bad. Israel's done this. No actual discussion, and how does that help anyone? I can't sit here and, and feel safe and feel safe to discuss this. If people won't condemn Hamas. People will say: the resistance lives, I support them, they're not a terrorist organization, they didn't behead babies. Then there's no room for discussion. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, I keep using the word constructive. But I guess really, another word is compassionate. I mean, has there been compassionate dialogue? And I think one, they are one in the same in this situation. Would you characterize any of the conversations you've had with individual students as leaning toward compassionate, even if not really all that constructive? Elliot Sadoff: Personally, I've not. And I think that's what's so hurtful is that I would love to have a compassionate conversation. Recognize that right now, both Israelis and Palestinians are suffering. It's the sad truth. It's the reality. But if you can't acknowledge that, if you can't recognize that Israelis are suffering, too. There's no room for compassion. Manya Brachear Pashman: So AJC has developed an action plan for confronting campus antisemitism. It's a toolkit for students. It closely follows the US national strategy to counter antisemitism that was unveiled by the White House in May. The final step in that toolkit is recruiting and forming a task force to address antisemitism on campuses. Do you see that happening at Cornell or Columbia? Elliot Sadoff: Fortunately, Columbia, about a week and a half ago, announced that they're launching an Antisemitism Taskforce, which is welcomed, I'm very happy that you're doing it. It's something that is necessary to protect Jewish students and to protect everyone on campus. Personally, though, it is a little upsetting that it took this to happen for there to be an Antisemitism Task Force as antisemitism is not a new problem. This anti-Israel, anti-Jewish sentiment is not a new problem on campus or in the world. And the fact that it's being launched, investigated and addressed as a result of a lot of bad stuff happening as opposed to proactively protecting students on campus is a little upsetting. Obviously, it's a welcome step, it's a step in the right direction. But I don't know if I feel any safer now than I did last week before it was announced. Manya Brachear Pashman: College is hard enough. And so I'm really impressed that both of you joined us, that both of you are confronting this problem and this challenge and doing so with such bravery and such poise. Thank you so much for sharing your experiences with us and we're gonna be rooting for you and fighting for you every step of the way. Molly Goldstein: Thank you so much. Elliot Sadoff: Thank you for having us.
Nov 9, 2023
Jewish U.S. Military Veterans' Message to IDF Soldiers Fighting Hamas: "We're With You"
In honor of Veterans Day, explore the unique experiences of Jewish U.S. military veterans with Dave Warnock, U.S. Army Veteran, and Andrea Goldstein, U.S. Navy Veteran and Reservist. Our guests share what inspired them to join the military, how their Jewish heritage played a significant role in shaping their service, and what advice they have for the Israel Defense Forces soldiers fighting now against Hamas in the Gaza Strip. Warnock and Goldstein are members of AJC's ACCESS Jewish Military Veterans Affinity Group, a space to convene young Jewish professionals who have served in the American military. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Dave Warnock, Andrea Goldstein Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: What Would You Do If Your Son Was Kidnapped by Hamas? Renana Gomeh's Sons Were Taken Hostage by Hamas: What She Needs You to Do to Bring Them Home Now What Biden's Wartime Visit to Israel Signals to Hamas, Iran, Hezbollah Mai Gutman Was Supposed to Be at the Music Festival: IDF Lone Soldier Recounts Harrowing Week Responding to Hamas Terror: IsraAID CEO on How You Can Help Israelis Right Now Learn: What is Known About Israeli Hostages Taken by Hamas 7 Ways Hamas Exploits Palestinian Civilians in Gaza How much do you know about Hamas? Try to ace our quiz and expose the truth about the terror group today. Donate: AJC.org/SupportIsrael Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Dave Warnock and Andrea Goldstein: Manya Brachear Pashman: This episode pays tribute to our nation's veterans. Guest hosting is my colleague Dr. Dana Levinson Steiner, Director of ACCESS Global at AJC, where she oversees an international program to engage young professionals. In that group are a number of Jewish military veterans who have served in the American Armed Forces. Dana, the mic is yours. Dana Levinson Steiner: Thanks, Manya. I'm so happy that we're here today. It was just over two years ago that we formed the ACCESS Jewish Military Veterans Affinity Group, which is a space for us to convene young Jewish professionals who had served in the American military. And here we are now recording our first People of the Pod podcast episode in honor of and commemorating Veterans Day. With us today are: Dave Warnock, U.S. Army Veteran, joining us from his home in Seattle, Washington, and Andrea Goldstein, U.S. Navy Veteran and Reservist, who is based in Washington, D.C. Dave, Andrea, thanks for joining us today. Dave Warnock: Happy to be here, Dana. Andrea Goldstein: Yeah, I'm glad to be here. Dana Levinson Steiner: To kick off the conversation, please tell us a little bit about your journey as an American Jewish military veteran. What inspired you to join the United States Armed Forces? Dave, let's start with you. Dave Warnock: For me, there are two kind of main things when I look back on what propelled me to join the US Army. The first one was my great grandfather, Saul Fink. The family legend is like he emigrated over from the shtetl. His family settled in Harlem. And when he heard about what was going on in Texas at the time, and 1916 and 1914 with the Pancho Villa incursions, he felt so propelled by patriotism and love of America that he had to run away from home and enlist at 16 years old. Which he did. Joined the Horse Calvary, a proper Jewish cowboy chasing after Pancho Villa in New Mexico, in a forgotten war. And he made sort of a career out of the army. So that's the legend that he was propelled by patriotism, maybe hated the tenement, maybe just wanted to get out of Harlem, get some fresh air, see the American West, I don't know. But his service propelled him forward in American society, through the US Army in a way that I think would have been unavailable to a lot of Jews at the time. It's not to say that it was an easy journey. He was certainly discriminated against; he shortened his name from Finkelstein to Fink for reasons that are not kind of lost to history. One joke is that it couldn't fit on the nametag. But through this service, he was elevated in society, he became an officer in World War I. He served through World War II and in the army of occupation in Germany. And his stature, sort of the patriarch of my family, loomed large. My middle name is Solomon, I'm named after him. So that kind of tradition was part of it. Another part was, I enlisted in 2004. So three years after 91/1 when I was a freshman in high school, and that terrorist attack really did propelled, cemented my decision to serve you know, if that didn't happen, I don't know what I would have done differently. But those are the two main reasons that propelled me to join. And I joined the Army and I volunteered for the infantry because I wanted to be a soldier. Dana Levinson Steiner: In a lot of ways, it is our family that inspires us to make these kinds of decisions and we learn so much from our family history and our family lineage. Andrea, I'd love to hear a little bit more about your journey too and I'm curious if family played a role in your decision to join the Navy. Andrea Goldstein: My family decision to do the military was much more related to growing up in the United States, growing up in New York at a time actually, probably when we didn't have the NYPD outside of synagogues. I didn't really think about being Jewish, at least in New York in the 90s. But my family came here in mostly two waves, most in the early 20th century, and then another wave right before the Holocaust, and found everything they were looking for. And depending on which wave, either second generation or third generation where a sense of precarity and being American was gone. We just were American Jews. And I am currently sitting in a home that has embroidery on the wall that was sent to my great-grandmother, by family members who ended up–who perished in the shoah. This country really gave us everything and I wanted to give back to that. The value of tikkun olam is very central to everything that I do. And so serving my country and wearing the cloth of the nation to me felt like really the only way to do that. 9/11 was not a motivating factor for me, despite growing up in New York City and being in New York City on 9/11. My desire to serve in uniform predated that, in fact, 9/11 led me to really not so much reconsider, but really give even more thought to my military service, because I knew I would be serving in conflict zones, which, with the peacetime military of the 90s, that wasn't clear. But I ended up joining through an officer program. I didn't initially have any family support, because it was such a shocking choice. I had great-grandparents who'd served during World War Two great-uncles, but not from a military family at all. And what became very understood by my family, because it was, what was motivating me was, this desire to serve my country and wear the cloth of the nation, no matter what. Dana Levinson Steiner: I want to pivot a little bit, I want to get back to questions of Jewish identity in a moment. But when we're thinking about American Jews serving in the US armed forces, while there isn't a ton of data, the most recent-ish data suggests that just about 1% of the US armed forces, or the US military, is made up of American Jews. It's tiny, only 1%. And that 1% is of an already really small number of American Jews who already live in this country. So, you know, thinking about this statistic and also acknowledging American history in serving in the military. What do we make of this small number? And what would you like to tell young American Jews who may be considering joining the military but may have doubts or concerns? Andrea Goldstein: So there are a couple of things I would say to that. I would comment on that data–first of all, that's only commenting that that only includes self reported numbers because we don't collect demographic data on, it's seen as completely religious affiliation. The military does not collect demographics on Jews as being an ethnic group. So it's actually quite difficult to self-report your religion. So there's going to be an undercount, there are people who are Jewish, who may even practice privately, who are not reporting. And it also doesn't capture Jewish families. So it doesn't capture the number of people who may be not Jewish themselves, but their partner and spouse is Jewish, and they're raising Jewish children, and they're observing Jewish holidays with their families. So there's a lot that we really don't know. What I would also say is, if you were to overlay where the military struggles to recruit from, with the parts of the country where most Jews live in the United States, you would see probably some very interesting geographic trends. The military has become a family business. There has also been, there have been some comforts that the military has had in where they recruit from. And that typically is not New York, Los Angeles, Miami, Chicago, Washington, DC. So in addition to being one of the very few Jews that I know, in the military, I think I know probably even fewer people from New York City, especially officers. Dana Levinson Steiner: Dave, I'm curious, your thoughts on some of these numbers? And also maybe what you would tell–you and I have talked about this before about wanting to really engage in conversation with young American Jews about this experience and what it can mean for them, you know, acknowledging this number a while not perfect, I would imagine it's not so massive. So tell us a little bit about what you think and also maybe what you would tell a young American Jew who might be considering enlisting. Dave Warnock: Sure. First off, my mom was also very surprised when I joined, perplexed, flummoxed, aggrieved, perhaps she would have much rather me not join the army. But I just have to get that out there because she's certainly going to listen to this. Yeah, so, you know, I don't know where that number comes from, you know, the infantry's a different representation, I would say Jews were less than 1% of the infantry. But when I was at basic training, like for one station unit training, as they called it back then, after your red phase, like your hell phase, or whatever you want to call it, you are allowed to go to religious services on Sunday. So I went to Jewish services on Sunday, because, you know, it is the army. And I want to do it, like in my basic training company, there were no other Jews. So the company's like 200 guys, and then when you go to religious services, they're all of a sudden, like, 200 guys, they're like, Oh, my God, why so many Jews all of a sudden in every company in Fort Benning, except for mine? And then I realized is because they serve Kiddush lunch and you could get snacky cakes after services. And it turns out there were like three actual Jews at the services. Andrea Goldstein: I had a completely different experience in officer candidate school where we were allowed to leave on Friday nights. Dana Levinson Steiner: Oh, interesting. Dave, what was your experience? Dave Warnock: So again,, this is like 2005, things might have changed. But when you joined a Combat Arms significant you just went to one station unit training and it was a fairly intense experience. Think about Full Metal Jacket, whatever, people screaming at you, doing lots of push ups. And all your time is blocked out and accounted for. So you've trained on Saturdays and religious service time was Sunday morning. That's the time you got, so if you want to go to services, you had to do that. Something to consider if you join certain aspects of the military is, religious accommodations will be difficult. You know, I served with guys who were vegetarian. And there's one vegetarian MRE. You ate that a lot, like our rations for the field. So you eat that vegetarian ration a lot. Get real used to it. Certainly that is a consideration and it would be difficult to be religiously observant. In the infantry. I actually there was one guy in my company on the latter half of my service who was a religious Jew. And he basically got a lot of exceptions by his rabbi to serve. Because it was hard. The army would accommodate him to an extent, like, for example, we had to shave every day. And so he was allowed to use an electric razor. But it's something to consider if you are religious, that serving in the US military will be challenging. But you know, I encourage people to consider it. I don't regret my service, it's difficult to imagine my adult life without it. I'd say, I'm proud of it, too. But it carries costs. You know, when I was 19, on my first tour in Iraq, I was wounded, it took me six months to recover and get back to the line. The, almost five years I was in, I rarely saw my family because I was stationed in Germany and deployed to Iraq twice. So I was overseas, essentially, for the entire time of my service. And that's something to consider, but this is all my perspective. But the experiences you get, that will propel you forward in life in a way that I don't think you get through other things, certainly, when you're 18, or when I was. That being said, you know, a lot of soldiers in my unit did die in combat. A lot of guys, when they got out, they did struggle with PTSD and suicide. So it's not all sunshine and roses. But for me, it was the right decision. Andrea Goldstein: Military service is really incredible. My field does have more Jewish folks, especially in the reserves where I'm still serving. What's been very interesting is as an intelligence officer, the active duty component doesn't have a lot of Jewish people, but the reserve component, my last unit, we had enough people to have a minyan in a unit of 50 people. And I have found, similarly to just living in society. I mean, your exercises are not–you're going to have exercises that take place during Rosh Hashanah, you're going to be deployed around Christian holidays so that people can be home for Christmas. Maybe you'll be lucky if that's around Hanukkah. But I've also found people to who I've worked with to be incredibly accommodating up until, up to the extent that they can. So maybe I was going to be away for Rosh Hashanah or Yom Kippur. But people would change their shifts with me on watch so that I could run the service because I was the lay leader, or so that I could break my fast at the end of Yom Kippur war. And I experienced people being really curious and asking a lot of really good, in good faith questions. And I've had incredible experiences that range from serving with a lot of incredible, not just our military, but partner militaries. The most rewarding was my time with NATO where I got to teach in Norway and Greece and in Sweden and get to have these incredible experiences with people as the people who– actually the Germans all notice my last name, which was really interesting. And that's a whole other story. But you also see things you can't experience anywhere else. And it's not just the–I saw a meteor shower in the middle of the ocean, on my 26th birthday from the middle of a ship. Like there are certain experiences that you don't think about when you're going into the profession of arms. But you will get to experience these incredibly vibrant experiences just because you've, you've made this choice to go where no one else does. And so it's incredibly rewarding. I've also found that as a millennial, I mean, there are some very realistic things about the economic environment that we graduated into. And because of my military service, I have no debt, and I own a home. I have a master's degree that the GI bill paid for. So there's some other things. Dana Levinson Steiner: You talked about sort of the things that you learned and the experience that you got as a young person. Dave tell us maybe a little about some of the more rewarding experiences or things were really profoundly important to you in your service. Dave Warnock: I got out when I was 23. So 13 years ago now and memories once so vivid that I thought I would never forget him kind of faded away a little bit. One thing that I'll never forget, that was quite challenging, because after I was wounded, I was kind of serving in the rear just like in a limited duty capacity, like back in my garrison. And it was a tough tour, you know, lots of us got wounded, we had lots of members of our battalion killed. And I was asked by chain of command, as much as one can be asked in the military to escort a soldier's body back to his parents and to his burial in Arlington Cemetery. And I did that, and that was, I can't even describe just what that moment felt like to do that to be present there. It's kind of like a unit liaison. I didn't know the soldier, we were in different companies. But that was something I'll never forget. Actually escorting a soldier back to his parents. Another memory I'll never forget is like, because I have a photo of it. And it's on the wall in our living room is, the photo of me and my fire team. I was a sergeant on my second tour. And so I led like a small unit of four guys. And I have a picture when we were leaving Iraq for the last time. And just that sense of accomplishment of, everyone came home safe from my team on that tour. And that's why it's hung up on my wall. It's you know, we're smiling. We're happy. We're leaving. Yeah, so those are two things that tend to stand out in my service. Dana Levinson Steiner: So Andrea, you started off by saying that the value of tikkun olam, repairing the world is one of the things that really guides you. And what I want to ask both you and Dave is how has your identity as a Jew, also shaped your experience as a veteran, we talked a little bit about, you know, in the beginning about your experiences as Jews or maybe your family, being involved in the military not being involved, being surprised. But tell us a little bit about how your identity as a Jew has shaped your experience as a military veteran and as someone who served in our armed forces. Andrea Goldstein: So I left active duty in 2016 and stayed in the reserves but left full time service because I felt like I had reached a ceiling on what I could really do for others and that be my full time job. I wanted to keep serving, I wanted to keep serving my country. But a lot of that actually had to do with the way that I saw a lot of my teammates being mistreated by systemic issues, whether they be cultural or policy. And I wanted to spend a lot more of my time actively putting putting more good into the world versus preventing bad things from happening. Because that's what you do in the military, especially if you're in intel, you try to stop the bad you don't do anything that actively promotes the good. And so I've spent the last seven years in my civilian career, either in nonprofit or public service, doing just that. And about half of that time has been active either actively helping veterans, particularly women veterans, and people who have experienced sexual violence or other kinds of institutionalized harm, and currently serving members of the military. And I also firmly believe that our institutions need to live up to the ideals that we profess. And I want our nation to represent the ideals that my family came here believing it had. And so that's what I've been doing with my time. I spent two and a half years on the House Veterans Affairs Committee and helped write over 100 laws that particularly supported women veterans, members of the LGBTQ community, sexual trauma survivors, people living with PTSD, to help them get improved access to healthcare and benefits. And I'm also very proud that I've also had the opportunity to work with the IDF and provided some insight into the way that we've made some policy changes here in the US. Dana Levinson Steiner: Dave, tell us a little bit about your Jewish identity and how it plays into this experience. Dave Warnock: Well, my unit was very diverse in many ways, not gender, because the unit was closed to, or at the time that the MLS was close to females, so the unit was, the job was all male. And, you know, part of the pipeline and being new and being a private is your identity is kind of like stripped away and melted down, you're built up as part of this team, your individualism is kind of knocked away. So when that process happens, you know, whatever is the more like forefront of your identity kind of consumes it. In a sense that, like, if you have a very pronounced southern accent, everyone's going to call you a country guy, or whatever. And if you're from New York, there's a guy from Queens, so like, everything about him became like, you're the New York guy. And for me, it was like I was the Jew. Because that was the most forefront and center thing of my identity. Also, when you shave my head, I have a really big head. So it was all like, all my nicknames were either about having a big head or being a Jew. And then eventually, when I started to grow my hair back and settled more on the latter. So it was always very central to my service, because that was me, I was like the company's guy who was Jewish. And that was not meant in a derogatory term was more of like a statement of fact. And I think the only thing I really had to overcome was like, in 2005, when you're serving with people, like when I said it was diverse, you could be serving with people from all over the country, the US territories and guys from parts of the South I've never heard of, guys from the center of the country place have never been soldiers from Puerto Rico and Guam, like all over the world are serving in the US Army and then we have immigrant soldiers from, you know, Colombia, Nicaragua, Vietnam, like it was a very wide swath of representation and not very many of them had even met a Jew before. So in a way I was like the first Jew a lot of them had ever met. And I think, you know, rewind back 2005. If you know anything about Jews you probably know like Woody Allen and Jerry Seinfeld, which are exactly like pictures of guys you want in a foxhole with you. So I had to sort of maybe work a little harder to prove myself in the basic soldiering tasks, but like that didn't take very long. A lot of guys asked me questions about Judaism, because they genuinely didn't know. And I think one of the benefits of my service is, these guys take back their experiences with me, which I hope are positive, and then like, go back to wherever they're from. And they're like, if Judaism or Jews comes up, they're like, Hey, I served with a Jewish guy, he was pretty cool. But I think that was very important to me, and why it's so important for Jews to continue military service, because you just meet people from all over the country that you never would have met before. And it broadened my experiences too, serving with those guys. Dana Levinson Steiner: I think, hearing the story about how in many cases you might have been the first few that these folks have met is really important. I think in a lot of ways it helps to demystify, or in most important cases, maybe even act against antisemitic ideas or stereotypes. So I think that that's really important. And Dave, you and I have talked over the years, about how sort of the term of calling you a Jew was like a term of endearment. It wasn't in terms of a term of antisemitism. And in spending a lot of my time with this ACCESS Military Veterans Group, I've gotten to learn some of the interesting elements of how you communicate and what that can look like. So I have just one more question for us. And I think it's really important to acknowledge this moment that we're in. On October 7, Israel experienced one of the most horrific tragedies in its 75 year history. It was and continues to be a horrific day for Israelis and the Jewish community around the world. As of today's recording, over 300 soldiers have been killed and tens of thousands have been called up for active and reserve duty. So a question I have for both of you is, what is a message that you have, or that you can share, Jewish veteran to Jewish veteran. And I should even say just veteran to veteran because one of the amazing things about Israel is that there are many who serve in the IDF and who've been called up for reserve duty or who are in active duty who are not Jewish. They're a part of the Druze community. They're Arab Israelis. I think that's really what makes Israel such a remarkable country. So tell us a little bit about perhaps your reactions to that day. And also a message that you have for your fellow soldiers in Israel. Andrea Goldstein: I'm struggling to react because – the horror, rage, I'm just going to start crying on this podcast and not be able to actually give words. I was actually in touch on WhatsApp with several women who I've had the opportunity to work with who are veterans and reservists in the IDF. And there's definitely this kind of secret community of women around the world who have served in combat roles. Even if they weren't in combat, occupational specialties in their countries, where we know what we did, and our service has often gone unacknowledged and erased. And that service is also particularly called upon during the most desperate times, which we are in now. And the message that I have is we see you, we're with you and we want to run towards chaos with you. Dana Levinson Steiner: Thank you so much, Andrea. Dave? Dave Warnock: I mean, I can't say anything that hasn't already been said. You know, shock, anger. My wife and I are expecting our first child soon. And I didn't think we'd be having a daughter, be worried about like, I just thought, ignorantly, that these sorts of things were perhaps in the past. All I can say to those who are going to go serve is, keep your head on a swivel. Watch out for your battle buddy. All the things we used to say to each other then are still true now. Dana Levinson Steiner: Thank you. I think just knowing that you are in community with them, and that they have love and support is so powerful. And as I think both of you know, our ACCESS chapters are all over the world, including in Israel, where a huge number of our ACCESS leaders have been called up for active and reserve duty. So we're thinking of them in this moment. And we're thinking of all soldiers as we approach Veterans Day, and we're so grateful for the two of you sharing your story with us and sharing your time with us and giving a voice to the more than 1% we will hope of American Jewish veterans and perhaps even encourage some folks who may have been thinking that this is something that's been on their mind, maybe perhaps it might be the moment for them to lean into that into that journey as a Jewish member of our armed forces. So thank you both for joining us. Wishing you a restful and restorative weekend. And Shabbat Shalom. Dave Warnock: Shabbat shalom, thank you. Andrea Goldstein: Thank you so much, shabbat shalom. Manya Brachear Pashman: What would you do if your son was kidnapped by Hamas? In this heartfelt conversation with Jon Polin and Rachel Goldberg, the parents of 23-year-old Hersh Goldberg Polin, they shared what they know about their son's abduction from the Supernova music festival on October 7th and the challenges they face in trying to secure his rescue. Hamas terrorists are holding hostage more than 240 people from over 30 countries, which the couple describes as a global humanitarian crisis that world leaders are not treating as such. They shared ways that we all can keep the hostages' stories alive and bring them home. Go to AJC.org/BringThemHome to do your part.
Nov 2, 2023
What Would You Do If Your Son Was Kidnapped by Hamas?
In this heartfelt conversation with Jon Polin and Rachel Goldberg, the parents of 23-year-old Hersh, who is among the over 240 hostages held by Hamas terrorists, they detail what they know about their son's abduction from the Supernova music festival on October 7th and the challenges they face in trying to secure his rescue. They also describe their dismay that world leaders are not doing enough to bring the hostages home and share ways to keep their son and all the hostages' stories alive. Take action to bring all hostages home now. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jon Polin, Rachel Goldberg Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: Renana Gomeh's Sons Were Taken Hostage by Hamas: What She Needs You to Do to Bring Them Home Now What Biden's Wartime Visit to Israel Signals to Hamas, Iran, Hezbollah Mai Gutman Was Supposed to Be at the Music Festival: IDF Lone Soldier Recounts Harrowing Week Responding to Hamas Terror: IsraAID CEO on How You Can Help Israelis Right Now Learn: What is Known About Israeli Hostages Taken by Hamas 7 Ways Hamas Exploits Palestinian Civilians in Gaza How much do you know about Hamas? Try to ace our quiz and expose the truth about the terror group today. Donate: AJC.org/SupportIsrael Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Jon Polin and Rachel Goldberg: Jon Polin: This is a global humanitarian issue. And every day, I wonder why is the world not speaking in that way? Why is the world shoving this into a simple black and white box of Israeli-Gaza, Israeli-Palestinian? Why are 33 foreign ministers around the world not holding hands and screaming about the magnitude of this humanitarian crisis? Manya Brachear Pashman: On October 7, Hamas terrorists broke into homes and raided a music festival, murdering more than 1400 civilians and soldiers and kidnapping at least 245 from more than 30 different countries. Almost four weeks later, only five hostages have returned home. Jon Polin and Rachel Goldberg say it doesn't matter where this happened. It is an international atrocity carried out against innocent lives and families around the world, including their own. But no one is talking about the hostage situation in Gaza in those terms. Why not? Jon and Rachel are with us now to talk about their quest to bring home their 23-year-old son Hersh and the other hostages. Jon, Rachel: Welcome. Thank you for joining us. Jon Polin: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you tell our listeners what you know about your son's abduction and the circumstances? It is a widely known story I think by now but just for those few that have not heard. Rachel Goldberg: So, I'll give you a sort of quick version because as you said, I think a lot of people already are familiar with Hersh's story. But he and his best friend who were at the music festival when the massacre started, they escaped in a car with two other friends and started to try to head north to get out of harm's way. But the road was blocked by Hamas gunmen who were just shooting at point blank range anyone who even got near them. So Hersh and his friends, and many other of the young people who were also in cars trying to escape, just stopped the cars, flung the doors open, and went running to these outside, roadside bomb shelters. Hersh and his friend Amer ended up with 29, a total of what we believe to be 29 of them smushed into this cinder block reinforced windowless small bomb shelter, which Hamas started to descend upon and threw in initially, hand grenades, which Hersh's friend Amer was standing by the doorway and manage to actually retrieve, pickup before detonating and throw back out at least seven of them. Three did detonate inside causing a lot of carnage. And then Hamas brought in an RPG which they fired directly into this small room of young people. And then they sprayed the room with machine gun bullets. After a couple of minutes of the dust settling, most of those young people were dead. Many of them were severely wounded, some were trapped under the dead bodies and the dying bodies and it is from those witnesses that we heard what happened to Hersh. Which is, he was slumped with three other boys against one of the walls and they were all somewhat injured but they still appeared alive. And Hamas walked in and said, everybody you know you four stand up and come outside. And when they stood up, the eyewitnesses told us that Hersh's left arm from around the elbow down had been blown off. He had somehow managed to fashion some sort of bandage or tourniquet, and he walked out. They all walked out calmly. I'm sure they were in deep shock and dazed and traumatized by what they had just seen take place in front of them. And they were boarded onto a Hamas pickup truck which headed toward Gaza. And Hersh's last cell phone signal was found inside of Gaza at 10:25am, Saturday morning October 7. We subsequently did get a video from CNN's Anderson Cooper who had come across it in research he had been doing on a documentary about the music festival. And he shared that with us. So we've actually seen Hersh walking out of the bomb shelter using his less dominant hand. He is left-handed and now doesn't have a left hand. He uses his right hand to board the pickup truck and he turns around to sit down and it's in that moment when he turns that you can see the stump where his left arm used to be. And he sat down and that's the last that we have seen him, heard anything about him in the last 26 days. Manya Brachear Pashman: I did watch that interview with Anderson Cooper, where they showed that footage and I'm curious what your takeaways were from that video, what were your observations, and also, did it give you hope to see him? Jon Polin: So on the one hand, as you can imagine it is a video that nobody would ever want to see of their loved one, their child. So basic answer is it's horrendously terrible to see it. On the other hand, I have been in a position where we need to just look for optimism and hope anywhere we can find it in the last 26 days. And so when I saw that video, my lens on it was, and especially since I know what had preceded it for the 90 minutes before that: the carnage, seeing his best friend killed, etc. I looked at the video and I saw Hersh looking composed, walking on his own two feet, using his one remaining hand, which happens to be his weak hand, to pull himself onto this truck. And clearly in shock, as one would expect. But I took some optimism from seeing what kind of shape he appeared to be in. Manya Brachear Pashman: You said 26 days, I cannot believe it's been 26 days that they've held these hostages with no word. And Rachel, you're wearing a 26 on your shirt I saw. What kind of support are you getting? What kind of conversations are you having with policymakers, negotiators, anyone, that indicates progress? Rachel Goldberg: Well, it's kind of a two pronged question. Because what are you doing to walk through these days is, we are surrounded by a team–beyond angels, beyond friends, beyond professional people who are dragging us along when we can't drag ourselves, and they're very talented, and they're very smart and tireless and tenacious. And so that helps us. And in the bigger picture, I mean, we've had a lot of conversations with both sides in terms of, you know, we are American-Israeli, so we right away that first Saturday turned to the US Embassy. They were extremely responsive right away, partially because they could be. They weren't at war, you know, Israel, I do cut them some slack for being slow in the beginning, because I mean, there were still terrorists running around killing people in their homes. When we first heard about what happened to Hersh. So we were spread very thin. There were things happening up in the north, there were things happening down south. I mean, I understood why there was a sort of short start to that end of things. On the American side, we've had incredible conversations with you know, as high up as you could get with President Biden, with US Secretary of State Anthony Blinken, with 15 different senators. They don't care, they said, this isn't a Republican-Democrat issue. This is an American hostage issue. We don't care what stripes you're wearing, people being real adults, which is refreshing and felt very good and supported. And that is a very excellent first step. We are now on day 26. And I need a little bit more actually, information, maybe action. I'm never one of the people in this that has said tell me what you're doing and tell me what the plan is because I always think that's ridiculous. Obviously, we can't know about that stuff. But because of Hersh's grave injury, it's different, I think, than if I had known he was just kidnapped and healthy, because I have a very primal fear that maybe he didn't get the treatment he needed, and maybe I'm here on day 26, but Hersh died on day one. So that's very difficult. Or maybe he did get treated and then three days afterwards, they said, well, we don't have any more antibiotics and then he died of sepsis. You know, so there's a lot of different kind of constellations of what ifs that, you know, run through our minds, and that make it very difficult to kind of feel trust and kind of know everyone said it's gonna take a long time. And it's a process. And I feel like well, that, unfortunately, we don't have that. And it's very concerning. When we were in America, we've had conversations with ambassadors from different countries who were, I think, trying to be helpful. In Israel, we've tried to have conversations with who we can get to, and we're doing what everyone would do, I think, if they were in our situation, but this isn't our world that we're used to. And we haven't found a playbook for this situation yet. There are playbooks for lots of other situations, but we haven't found one for this yet. Manya Brachear Pashman: There have been reports that hostages with dual citizenship or foreign hostages may be released first. Considering Hersh is a dual citizen, what have you heard? Rachel Goldberg: I don't think it'll make a difference for him. My personal pontificating is that they probably will release some of these poor Thai people who were swept up in this chaos. Or the Nepalese people, there are, you know, 33 different countries that have citizens that are currently being held. And I think I would be thrilled and elated if Hirsch was released. But I would be also shocked, because my impression is that the people that they're talking about are not people like Hersh. Jon Polin: We both, Rachel and I, are elated for the hostage for their family, for the country, for the world. Anytime a hostage is released. We celebrate for a moment for all of them, and then we get back to work. The broader point here is, of course, we are most concerned about our son who's wounded. But if Hersh walked in the door five minutes from now, we'd hug him, we'd rejoice and we'd get back to work because there are 239 hostages that must be released. And the second part of that is, as Rachel talked about, these hostages represent something like 33 countries. This is not an Israeli-Palestinian, an Israeli-Gaza, an Arab-Jewish issue. This is a global humanitarian issue. And every day, I wonder why is the world not speaking in that way? Why is the world shoving this into a simple black and white box of Israeli-Gaza, Israeli-Palestinian? Why are 33 foreign ministers around the world not holding hands and screaming about the magnitude of this humanitarian crisis? Manya Brachear Pashman: Rachel said this isn't our world. I'm curious if you could share a little bit about Hirsch's world. How long has your family lived in Israel? How did you end up in Israel to begin with? And talk a little bit about Hirsch. Jon Polin: Rachel and I should say are both born and raised in Chicago, still have our mothers and other family members living in Chicago, products of the organized Jewish world in Chicago, and are feeling a lot of support from Chicago. Rachel and I moved to California, where Hirsch and one of our other children, we have three kids. Hirsch and his sister Leebie were both born in California. And then when Hersh was three or four, we moved to Virginia where we lived for four years before moving to Israel as a family. We moved to Israel because Rachel and I felt like, it's an opportunity. This is something that our great-grandparents and their parents and their parents longed for and didn't have the opportunity and we do, so how do we not join this ride, as Rachel said. Hersh is a quiet, I always say he doesn't walk in a room and make a lot of noise. But once he's been in the room for 15 minutes, he's gotten into the hearts of a lot of people. He's a really quiet, likable guy with a sharp, very smart, quick witted. Very curious, he's always been a voracious reader. He sweeps categories. When he was seven or eight, he swept the category of US presidents and knew every detail of every president and their years and their administration and so on. Not much after that he got into atlases and maps and globes, and that has been a constant in his life. He's been fascinated by the world and by traveling the world, every opportunity, including on his own dime, working, making money and taking trips. In high school, he and Amer, and a few other friends had the chance to go to a few different countries, as 17, 18 year olds on their own traveling. He's been dreaming about this around the world trip for which he has a ticket booked for December 27 to India. Rachel keeps saying, you only need one arm to travel the world so he can do it. That's who he is. I mean, it hit me over the last 26 days as people started to ask us about Hersh. And I really mean this, in 23 years of life, he's never upset me. He's super respectful. It doesn't mean he's a perfect angel, because he's not. But he's just got a very tasteful way of being mischievous with his family, with his siblings, with his parents, with his teachers. That's who he is. Manya Brachear Pashman: There was a piece written by Shoshana Gottleib for Hey Alma. Shoshana has never met Hersh in person but long before all of this came across Hersh's bar mitzvah bencher at a friend's apartment in Jerusalem and felt a real connection to him. So she instantly recognized his name when she heard he was among the hostages. Did you see that column? Rachel Goldberg: We did. It's very funny. Our family tradition is that for each of the kids' bar or bat mitzvahs, we would make a prayer book that had all of the grace after meals, the birkat hamazon. And in the covers, we had the grandmothers make up songs about that kid, to popular tunes. And as you know, sometimes these prayer books, these benchers, they're called, get sprinkled around, and somehow someone ends up with one in their apartment that isn't theirs. They don't even know the people who it belongs to. And this young woman had come across his bench, his bar mitzvah bencher years ago. And at that Shabbat table, she started to sing all the songs because the songs are to popular songs that people know. And she got a real kick out of it. And that became her whole crew's tradition Friday night, were to sing the songs from the Hersh Goldberg-Polin bencher. He tried to explain this to his grandmother to Jon's mom, and she said, doesn't this girl have anything better to do than to sing the songs from your bencher? So anyway, she wrote, since hearing about Hersh, when she heard his name 26 days ago in the news, she immediately knew who he was, because she's been singing his bencher songs for years, even though she's never met him. So she wrote a cute piece about that. Manya Brachear Pashman: There have been really intense retaliatory strikes on Gaza and the IDF has sent troops and tanks into the Gaza Strip. But the ground offensive has been limited in order to avoid endangering any efforts to free the hostages. Are you hoping for any change in approach in terms of this offensive or these retaliatory strikes? Jon Polin: It's such a hard one because we are parents of somebody who is held hostage. We are part of the family of people of 239 families who are now together in this. But even as we tried to separate ourselves from it, and we understand that there is an Israeli national interest here, and we understand that the consensus seems to be building or is already built that we must eliminate Hamas for the sake of Israel's ability to exist and to move forward. But we don't get involved in the military strategy or the military planning. We obviously are highly concerned about the safety of hostages. But we are equally concerned about the safety of all the soldiers. We've got a house full of people since October 7, who are parents of soldiers on the front lines, and starting to hit closer and closer to home as we start to see the first few names of soldiers killed coming in. And we also should say that we're concerned about innocent civilians on all sides, on the Gazan side. So it doesn't really answer your direct question other than we are hopeful that this gets resolved in minimum loss of life on all sides. I've contemplated—should they have waited longer, should they still wait longer to go in at all, and I understand both sides of the argument. But I keep coming back to: Hamas isn't going anywhere, they're holed up in there. And so if we can go very judiciously, and still try every other possible channel to get people released, I'm for it. Manya Brachear Pashman: Every Friday night on Shabbat you stand out on your porch, you face Gaza, and you bless your son. Can you tell a little bit about how that restores you, how that connects you to Hersh? Rachel Goldberg: Well, I feel like now more than ever, he probably needs a blessing. You know, and this is the traditional blessing that all Jewish parents give to their children on Friday nights. And I feel like he needs it more than ever. And I think I need to give it more than ever. And ultimately, you know, it's saying like, let God lift up God's face toward you and give you peace, which is so desperately needed. So desperately needed every single place in the world. But certainly when I picture him somewhere, you know, I don't know what to picture and I feel like I am privileged to be able to give that blessing to Hersh. I think all of us who have children, your first child is what changes you in the world. And you go from becoming a person to becoming a parent. And that's what Hersh did for me. So I will always be a different person in the world because of Hirsch. The first time, that first Shabbat when he was just a newborn baby, to give him that blessing was such a privilege that I feel like until I am told otherwise, it is my privilege to give it to him and if I have to scream it to him, because he's far away, then I will do that. And I will keep screaming that to him until he comes home or until I am told otherwise. Manya Brachear Pashman: AJC and my colleagues here at AJC, of course, have been working with your family to bring Hersh and the other hostages home. Listeners can go to AJC.org/BringThemHome to urge Congress and the United Nations to release all of the hostages. But Rachel, Jon, what more can we do to help you? Jon Polin: Well, first of all, now that you mentioned it, and it was on my mind to squeeze in as well. It's not just platitudes, like our gratitude to AJC is tremendous. CEO Ted Deutch, on down, we've been in touch with members of your team. They've been supportive. They've been guiding us. And we cannot thank AJC enough for their involvement not only for us, but for all Americans and all hostages. In terms of what people can do, we keep saying we wish we had better answers because we feel the outpouring of support from around the world and people asking us that question. We can give a few answers. And those are as follows. Number one, if this is your thing: pray. Hersh Ben Perel Chana, or Hersh ben Perel Chana v'Yonatan Shimshon. Have him in your prayers and have all the hostages in your prayers. The second thing is: awareness. We think it's critical to keep telling the story of all the hostages. In our case, it's Hersh, but it's all the hostages. News cycles in the world happen quickly, news cycles in Congress and in Washington happen quickly. And we need listeners of this podcast, we need the American Jewish community, we need everybody who can to keep this story alive, keep it front and center. When the world starts to move on from the story, don't let them. This is a global humanitarian crisis. We cannot forget these people. The third is outreach. We, in our case, put up Bring Hersh Home social channels, turnkey templates, talking points, emails that people could copy and paste, a spreadsheet of elected officials and their contact information. We are trying to make it as easy as possible. We know that it matters, it matters for your elected officials to hear not just once but to hear every single day about important issues, in this case, the importance of releasing all the hostages. We've been telling people, set your alarm for the same time every day, and take one minute and reach out to your elected officials and just don't stop hounding them. Rachel Goldberg: I think that counting is something that's very easy. I think in the Jewish tradition, we are very obsessed with, you know, we count the Omer between Passover and Shavuot. We count days of the month to make sure that we're, is it a 29 day month or 30 day month, we're very conscious. Even the days of the week, we count as the first day, the second day, the third day, we don't have names of it. We count. And I think that that one minute call to your person who can be on autodial to say, Hi, it's day 25 and the hostages are still not released, goodbye. Hi, it's day 26 and the hostages are still not released, goodbye. Now, it sounds ridiculous. But if you have 1000s of people making those calls every single day, that is annoying for the person who's getting the call. And we want to be annoying. My mother always said the squeaky wheel gets the oil or whatever. I'll say also, being distracting, I now realize, is a great thing. When we were in New York. You know, since this whole thing happened, a lot of stuff falls right into perspective. You know, I haven't worn makeup. I haven't worn jewelry. I just put my hair back. We don't sleep very well. When we were at one of the news outlets, the anchor, not even the makeup woman, the anchor said, Can we put some makeup on you? And I said no, I'm a distraught mother. And he said, Yeah, but maybe it's a little distracting. And I said, Yeah, I want to be distracting. And so I feel like I would beseech people to go out and be distracting, go out and bug people that it's day 26, and we know nothing. And you know, we get requests on this social media stuff that we're doing. People are saying can you give us updates? Yeah, the update is they're doing nothing. That's the update from today. And tomorrow–I hope I'm wrong–but the update for tomorrow might be, they didn't do anything today. Like we're working our butts off and we're trying every possible angle we can. And for people to just make a call saying: it's day 26 and I'll talk to you tomorrow if he's not home. If they're not all home. I think is a one minute ask. And I think the impact is great. Because I do think, we're a David, a mini mini molecule of David fighting a mammoth Goliath here. And I appreciate all the people that keep coming up to me and saying, he's my son too, and I believe it. So do it. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jon, Rachel, thank you so much for joining us and sharing this story. Rachel Goldberg: Thank you for having us, and I also just want to give a shout out because honest to God, I don't know what we would have done without the support of AJC so far. I mean it. I mean it from the bottom of my heart. So really, that community will always be with us, no matter what happens.
Oct 27, 2023
Remembering Pittsburgh Part 4: AJC CEO Ted Deutch On the Jewish Community's Resilience After Pittsburgh and Hamas Attacks
AJC CEO Ted Deutch joins us to discuss the significance of the Pittsburgh synagogue shooting at the Tree of Life and its aftermath, the anniversary, and what it means to Jews around the world after the October 7 attack on Israel, when once again Jews were murdered just for being Jewish. In the final episode of the Remembering Pittsburgh series, Ted reflects on what being Jewish in the United States feels like at this moment, and how the Jewish community is uniting to overcome yet another challenge. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Ted Deutch Show Notes: Listen: Remembering Pittsburgh Part 1: Behind the Scenes at the Reimagined Tree of Life Remembering Pittsburgh Part 2: What the Family of Tree of Life Victim Joyce Fienberg Wants You to Know About Her Legacy Remembering Pittsburgh Part 3: How the #ShowUpForShabbat Campaign Drew Global Solidarity Amid Tragedy Take Action: Urge Congress to Stand Against Rising Antisemitism Music credits: Hevenu Shalom - Violin Heart Fire Tree (Violin Version) - Axletree Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and review us on Apple Podcasts. Episode Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: This month, AJC set out to mark the five-year anniversary of the Pittsburgh Synagogue Shooting at the Tree of Life with a series of episodes exploring this turning point for the American Jewish community. Our first installment aired October 5. Two days later, the Jewish people faced another unprecedented deadly antisemitic attack, this time in Israel. Synagogues stepped up security and families tamped down their fears to take their children to Hebrew school or attend Shabbat services. In the second episode of our series, we sat down with Howard and Marnie Fienberg, who paid tribute to their mother Joyce. In the third installment, we looked back at how the horror drew people to solidarity. For this closing episode of the series, I sat down with AJC CEO Ted Deutch, who served as a congressman at the time of the Tree of Life massacre. We discussed this anniversary and its parallels to the October 7 attack on Israel, when once again Jews were murdered just for being Jewish. Manya Brachear Pashman: Ted, where were you on the morning of October 27, 2018 when you heard about the Tree of Life? Ted Deutch: I was a congressman who represented Parkland, where the mass shooting at Marjory Stoneman Douglas took place. And the morning of Tree of Life, I spoke to a group of high school students from all around South Florida, who participated in a program about how they can become leaders in the community. I spoke with them about what had happened a few months before in Parkland, and what I had seen from high school students in Parkland and how they responded and how you stand up to violence and try to stop it and how you respond to evil and how important it is to use the power that you have as young people. That was literally what I was doing right before I walked out of the Florida Atlantic University auditorium and saw my phone start to buzz with news of Tree of Life. Everything that I had said to the students in the discussion, that really difficult conversation we had with these students who shared with me their fears of violence, their fears of going to school–those fears hit home really hard for me and for the Jewish community. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did you view this as a significant turning point for the Jewish community in America or worldwide? Ted Deutch: This was something that we dealt with in Europe, we feared, we stood AJC's stood with the Jewish community across Europe as they, as they were attacked over years. I was a member of Congress when we had vigils with the ambassadors from European countries, in memory of lives lost, Jewish lives lost as a result of antisemitic attacks. And here, that morning is a turning point for all of us in the Jewish community, and how we respond, how we view the threat of antisemitism now as a deadly threat to the Jewish community in America, and for the rest of America to see another example of what happens when antisemitism, hatred are running rampant and where it can lead and how dangerous it is. Manya Brachear Pashman: From your vantage point as a congressman, what shifted on Capitol Hill, if anything, after October 27? Ted Deutch: Well, I was a member of Congress, but I focused so much of my work on the Jewish community. And we had started a Bipartisan Task Force to Combat Antisemitism in response to what happened in Europe. We never could have imagined something like that happening in our own country, especially in this place. I mean, this is the most idyllic, suburban, lovely neighborhood. I mean, it is, as everyone knows, it is literally Mr. Rogers Neighborhood, right? He lives just a stone's throw from Tree of Life. And so our work became that much more urgent. And we immediately refocused our efforts and those of us who were committed to fighting antisemitism, to ways that we could ensure the security of the Jewish community, and we immediately started looking at ways to find additional funding for security and and we dug deep into FBI reporting and research into what else is out there and what else they're tracking and what the fears are. And, unfortunately, whether in Congress, now at AJC, that hasn't stopped since. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did the members of Congress who are not Jewish respond differently? Ted Deutch: There was real support, and support not just for me and my fellow Jewish members, but for the Jewish community overall. Lots of members of Congress, most, know the Jewish community, many of them have Jewish communities they focus on in their own districts, sometimes large, sometimes very small. But the security concerns became real for every one of them – whether they had a large thousand-family congregation in a major city or a tiny synagogue somewhere in a remote part of the country, everyone felt it, everyone was put on edge, and every member of Congress felt an obligation to respond to that. I just remember having conversations with colleagues who were people of faith, who went to church. They were so struck by the fact that they came and went every Sunday, walked into their churches, doors were wide open. And the contrast to synagogues where you really need to be committed in so many places to get in so many places to go to synagogue, because you have to go through security, and sometimes you have to check in with the police, and in some places, you have to go through metal detectors. That really, really hit them and I think continues to, especially now. Every time something happens in Israel, we see a need for greater security at home. In the aftermath of the horrific attack by Hamas. It's affected Jews, obviously in Israel and around the world and how we view Israel, but we all fear for what could happen in the United States. Manya Brachear Pashman: You left your job on Capitol Hill and became CEO of AJC just last year. I'm curious whether the horror in Pittsburgh so soon after the Parkland shooting was an inflection point for you and your path? Ted Deutch: I wasn't thinking about leaving Congress. But when a friend reached out and asked if I'd be interested in being considered for the AJC job, I started reflecting upon the issues that I worked on, and what I had been through. And this fits into a very specific part of that thinking it was. It was the whole series of what happened, the shooting at Stoneman Douglas, and the impact that that had on the community. Then almost in immediate succession, quick succession, this horrific shooting at Tree of Life. First, there was the trauma in our own community, then there was the real trauma in the broader Jewish community. And then, not that they're directly related, but on January 6, when I was sitting in my office with the lights off, and my electronics silenced as the Capitol Police told us to do, and I was sitting in a dark cubicle in our staff office … watching what was happening in the Capitol and listening as people ran by my office and not knowing who they are. Everything was, everyone was so concerned about violence that day and my first thought that day was how grateful I was that I had just moved into this new office and had not yet had an opportunity to hang my mezuzah. And, right, so where does this fit in? I didn't decide to come to AJC because of some series of traumatic events. But just in terms of a turning point for me, what happened at Tree of Life and how that informed the remainder of my time and I was in Congress and the way I thought about my work, and, and then those fears on January 6, and realizing again, how at risk I felt even in the U.S. Capitol as a Jew. I suppose there is probably a straight line that I didn't see that started that day that led me to where I am now. Manya Brachear Pashman: So, you've been here a year now. How have these events shaped your work since you arrived? Ted Deutch: AJC's is to enhance the well-being of the Jewish people in Israel, and to advance democratic values. If we go back to Tree of Life, and think about what's transpired since and the rise in antisemitism as we saw it around the country, and on social media, and the many ways that the community has felt at risk. The week I started, Kanye West went on his antisemitic rampage on social media on Twitter. The Jewish community is not well if antisemitism is running rampant. So it's why we worked so hard with the White House, it's why we encouraged them to create a national strategy. It's why we brought in special envoys from around the world to meet with the White House to help inform the process. It's why we celebrated the release of the National Strategy to Combat Antisemitism and put together, really devoted a large part of our resources over the past six months, helping to implement the national strategy. And it's why we continue across the country here to look for ways to engage further in fighting antisemitism. By strengthening the relationships we have with others–it's why we're doing so much more in our intergroup work and interreligious work. I just recently visited a new Hindu temple in New Jersey, I think it's the largest, certainly the largest in the United States, one the largest in the world. And it was really meaningful to spend the afternoon with leaders of the Hindu community who, who very much recognize that in many ways our fates in America are intertwined. Manya Brachear Pashman: So in our first episode of this series, our producer Atara Lakritz and I went on the last tour of the Tree of Life building. You also walked through the building back in June, before many of the artifacts had been removed. Would you mind reflecting on that experience? Ted Deutch: When I walked up to the synagogue, I couldn't help but think of my synagogue where I grew up on the other side of Pennsylvania in a lovely community, like Pittsburgh. I was struck that, forget that this was a synagogue, I really couldn't stop thinking that it was inconceivable that that kind of horrible tragedy could happen in a community like that. And walking through the synagogue and seeing the site where hatred, and antisemitism, and manifestations, the worst manifestations of antisemitism were brought to this lovely place, in this wonderful synagogue. It was overwhelming to think about what was happening that Shabbat and the fear and terror that people felt as that was happening. That was number one. Secondly, I walked into the main auditorium where they were gathering all of the things that hadn't yet been taken away to be used in the museum and the memorial that's going to be constructed, that haven't been given back to families. There were lots of things that are just not identified, they don't have families to return them to. And to see tallaisim and tefillin and all kinds of items that are used for Jewish rituals and Jewish customs just sitting on this table where they didn't know what they were going to do with them because the synagogue that existed there, the life that existed there, that simple, wonderful community, that was gone. It was gone. That community will never be the same. And I think for our community, for the Jewish community, we're really never gonna be the same after what happened there. Manya Brachear Pashman: You were telling me before we started this conversation that they gave you something during your visit. Ted Deutch: As I walked through, and they saw how moved I was by this massive display. They came over and made such a kind gesture to me. And of all of the gifts that I've received in all of my travels, as a member of Congress, and now as CEO of AJC, I don't think there's anything that's as meaningful as the tefillin that they gave me. I don't know, obviously, I don't know whose it was. And it may well have been someone that was a synagogue member years and years ago. But the connection that I felt at that moment to that community at Tree of Life and the connection that I felt thinking about, not just Tree of Life, but tragedies that have befallen the Jewish people throughout our history. And knowing that I was going to return to New York, I was going to have the opportunity to join the Jewish community around the world in overcoming these tragedies, and making sure the world understands why these kinds of attacks will never, they'll never work, they'll never, they'll never defeat the Jewish community. As we endure this really challenging time now in Israel, I've been thinking the same thing. We've gone through a lot in our history, and we've constantly, constantly overcome, and have grown and have learned and have continued to enrich the world. As Tree of Life rebuilds and will help shape a national and international conversation for years to come about fighting antisemitism. And as we continue to do our work and as Jews around the country and around the world go through whatever security measures they have to to go to synagogue and to drop their kids at day school and Hebrew school and for people to show up for programs at the JCC, there is a defiance that I felt at that moment that is perhaps the most important thing I took away from that day. Because it was awful. But I'm not going to dwell on how terrible it was. We're going to think about every way we can to honor the memories of the lives that were taken, and to strengthen the Jewish people in their memory as we go forward. Manya Brachear Pashman: We planned this series and invited you to speak before the October 7th terrorist attack in Israel and the war with Hamas that has unfolded since. At first we wondered whether we should even proceed with this series. How could we focus on anything other than Israel at this moment? Of course, the parallels between the Tree of Life and October 7th are all too stark– Jews are once again being targeted simply because they are Jewish. Can you share your thoughts on this difficult moment for the Jewish people? Ted Deutch: That sense of unease that all of us felt when we heard that story, like how could that possibly happen in the United States, really, it's an unease and fear that we feel when we've watched what's happened in Israel and when a horrific and brutal and barbaric attack takes place against our family, our brothers and sisters in Israel, we feel that here, and especially when it was, it was unthinkable what happened with this Hamas attack. Just as somebody shooting up a synagogue was unthinkable in America, it again, it puts us on edge, and it makes us redouble our efforts. Not just to fight antisemitism, but to really bring the community together. What I've really been proud of since this terrible time in Israel began is the way that AJC has responded, not just in putting out meaningful information to help people get the facts and get through this, and to fight back against lies. But the way that we've really worked to bring the community together. There are 16 million Jews in the world, out of eight and a half billion people we need to stick together. Moments like Tree of Life remind us of that, and what's been happening in Israel absolutely reminds us of that. That informs so much of what AJC does, and has done in response to Tree of Life and certainly is doing in response to the current situation.
Oct 26, 2023
Remembering Pittsburgh Part 3: How the #ShowUpForShabbat Campaign Drew Global Solidarity Amid Tragedy
In the aftermath of the slaughter of 11 Jews inside the Tree of Life Synagogue in Pittsburgh, the deadliest antisemitic attack in U.S. history, American Jewish Committee (AJC) drew up a plan to galvanize Jewish communities and their allies across the world in an expression of unity and defiance: #ShowUpForShabbat. The campaign, which reached hundreds of millions of people, urged those of all faiths to attend synagogue services during the Shabbat following the attack to show solidarity with the Jewish community. In this third episode of our Remembering Pittsburgh series, hear from some of those who showed up to that Shabbat five years ago on what the experience meant to them and how the events of that week altered their perspective on antisemitism in America. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Belle Yoeli, Anne Jolly, Rachel Ain, Sharif Street, Jennifer Mendelsohn Show Notes: Listen: Remembering Pittsburgh Part 1: Behind the Scenes at the Reimagined Tree of Life Remembering Pittsburgh Part 2: What the Family of Tree of Life Victim Joyce Fienberg Wants You to Know About Her Legacy Take Action: Urge Congress to Stand Against Rising Antisemitism Music credits: Shloime Balsam - Lo Lefached Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and review us on Apple Podcasts. Episode Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: This month, AJC set out to mark the five-year anniversary of the Pittsburgh Synagogue Shooting at the Tree of Life with a series of episodes exploring this turning point for the American Jewish community. Our first installment aired October 5. Two days later, the Jewish people faced another unprecedented deadly antisemitic attack, this time in Israel. Synagogues stepped up security and families tamped down their fears to take their children to Hebrew school or attend Shabbat services. In the second episode of our series, we sat down with Howard and Marnie Fienberg, who paid tribute to their mother Joyce. In this third installment, we look back at how horror drew people to solidarity. May we see that same solidarity today. Belle Yoeli: We saw hundreds of thousands of people show up. And we saw pictures later, after the fact, and videos, and people making speeches, and just so much solidarity. This was captured on the news. I think it really stands out as one of the most amazing responses to antisemitism that we've seen in modern history. Manya Brachear Pashman: On October 27, 2018, Americans witnessed the deadliest antisemitic attack in this nation's history. Eleven worshipers inside the Tree of Life Synagogue in Pittsburgh were murdered just for being Jewish. The senseless slaughter inside a house of worship devastated and shocked American senses because it was simply unAmerican. But the aftermath of the atrocity became an American moment when so many people showed up – showed up with hugs, showed up with flowers, showed up with prayers for their Jewish neighbors. The most visible expression of this came a week after the massacre with the unprecedented turnout of people of all faiths at synagogues across the nation as part of AJC's #ShowUpForShabbat campaign. Together, Americans sent a message that hate will not prevail. Belle Yoeli: Everyone wanted to do something, and the entire Jewish community mobilized to make this happen with the understanding that as AJC has always said that antisemitism is not just about the Jewish community. It starts with the Jewish community, but it's a threat to democracy, and the murder of Jews in their religious institution is such a breaking, a fracturing of everything that the United States stands for, everything that democratic society stands for. Manya Brachear Pashman: Today, Belle Yoeli is the chief advocacy officer for AJC. In 2018, she worked as the chief of staff for then AJC CEO David Harris. David had spent nearly 20 years counseling European leaders on the rise of antisemitism in their midst, calling their attention to violent crimes against Jews when conflict erupted between Israel and their Arab neighbors. Belle was on her way to a nephew's birthday party when she got the call on October 27 about what had happened in Pittsburgh. She remembers sobbing in the car on the phone with colleagues as they all grappled with the reality that whether they were regular shul-goers or had just happened to go to synagogue to celebrate a friend's bar mitzvah that day – it just as easily could've been them. For many, what they needed now was to go to shul and not be afraid, and to see others, not just their own community, but others of all faiths in the pews alongside them. What they needed most now was to know they were not alone. So they drew up a plan. Belle Yoeli: A couple members of our staff actually kind of simultaneously came up with a similar idea, which was that we need to, more than anything, rally non-Jews to come and support the Jewish community at this time, and what better time to do that than the following Shabbat. Manya Brachear Pashman: Dubbed #ShowUpForShabbat, the social media-based campaign called on both Jews and those of other faiths to flock to synagogues that coming Shabbat on the weekend of November 2 in support of the Pittsburgh Jewish community and all of American Jewry. The response across 80 countries was astounding. More than 250 million people spread the message on social media, including celebrities Andy Cohen , Itzhak Perlman , and Mayim Bialik , and politicians Paul Ryan, Kamala Harris, and Sadiq Kahn. And hundreds of synagogues across the country and around the world, from Tokyo to Santiago to London to San Francisco, welcomed people of all faiths into their sanctuaries. Those who walked through the doors included diplomats from dozens of countries, federal, state, and local elected officials, and Christian, Muslim, Hindu clergy. Synagogues across the country reported massive crowds rivaling or exceeding those seen at High Holy Day services. Belle Yoeli: There are some times, I think before Pittsburgh, and before Tree of Life and after, where the Jewish community doesn't always feel like we are seen, and that we need defense too. When it comes to antisemitism, because Jews are viewed as white or for other reasons, or when it comes to us attacks against Israel, we don't feel like our partners are necessarily always there for us, although many are. Seeing with such clarity how people were showing up for the Jewish community, we all really needed that. And honestly, society needed that and to see that. That we will not let this stand. I think it shook everyone to their core and not just the Jewish community. That's what struck a chord with people that could have been me, that could have been hatred towards African Americans, that could have been hatred towards the Muslim community. Every single community who has a piece of them, an identity that's so strong resonated with that. Manya Brachear Pashman: We connected with people who showed up that Shabbat five years ago, and asked them what the experience meant to them, whether the events of that week altered their perspective on antisemitism in America, or changed how they show support to their Jewish neighbors. Anne Jolly: An important part of what we proclaim is love God, love your neighbor, change the world. And so we believe that means we show up for each other. We can't love each other without being present with each other. So we have to be together. You have to show up. Manya Brachear Pashman: Episcopal Bishop of Ohio Anne Jolly was serving as the rector of St. Gregory Episcopal Church in Deerfield, Illinois in October 2018. A former hospital chaplain, she was sitting in her office when she heard the news break that Saturday morning. Her first call was to her friend and colleague Rabbi Karyn Kedar down the road at the Reform temple commonly known as Congregation BJBE. Rabbi Kedar had recently preached at St. Gregory and then-Pastor Jolly was scheduled to deliver the guest sermon at BJBE the following Friday night. Anne Jolly: I called her and we talked and we prayed. And I said to Karyn, I think probably you need to preach on the Shabbat following the shooting at your temple and she said, 'I want you to do it.' She said 'I think I think we need to hear your voice and that the congregation needs to hear you. Rabbi Kedar I think thought that to hear a voice of someone who is not Jewish saying aloud, We love you, we care for you. We believe we are all created in God's image together. And that means we need to show up for each other. It means we need to be present with each other, that to hear that from someone who was not part of their community might be more powerful, more impactful, and more important for the community here at that time. Manya Brachear Pashman: When Bishop Jolly arrived that following Friday she did not expect her sudden sense of fear when she encountered armed guards. Anne Jolly: I didn't realize I was afraid until I walked in the door. And I stopped and had to take a deep breath and realize that I was afraid because I was entering into a space of people who have long been afraid. And that I had never had to experience that before in that way. And I wasn't really afraid for my congregation the same way I was for my beloveds in the synagogue, that they had more of a reason to be afraid than I did. And that was all the more reason for me to be there, and to be present with them. Manya Brachear Pashman: Bishop Jolly credits that night at BJBE for the deep connection that formed with the congregation. In fact, she returned to BJBE many more times to celebrate Shabbat. Precisely a year later, the members of the Jewish congregation showed up at her door after a pumpkin patch at St. Gregory had been destroyed by vandals. Anne Jolly: There were a bunch of them that came to our patch and we were talking about it and they said, 'We just wanted to show you that we are supporting you. And they were worried that that vandalism had been an act of aggression against us. And I just thought it was kids. And that was a really clear distinction of how our worldviews are different. For them, a vandalism thing would, of course, of course, be something hateful against them. In this case, it was children, it was just teenagers being dumb. But it reinforced that understanding that for them, fear is always in the background because of the violence perpetrated to them – again and again and again. Rabbi Rachel Ain: It was not a wake-up call that hate existed and already the hate was being felt. And at the same time, the love with my neighbors was being felt. So I was able to hold on to both emotions. But really, as I look back at these five years. Pittsburgh to Poway to Colleyville to Jersey City. I mean, I can sort of think back to all of these moments. It's here. And we need to both be proudly Jewish, and strongly protected. Manya Brachear Pashman: For Rabbi Rachel Ain, the spiritual leader of Sutton Place Synagogue, a conservative synagogue in New York City, the massacre at Tree of Life was not her first encounter with antisemitism. She knew it was simmering. A year earlier, almost to the day, vandals had spray painted swastikas across the entrance of her synagogue on the East Side of Manhattan. She knew how powerful it had been to have members of the wider community come support the congregation after that incident. Whether to invite members of the community to #ShowUpForShabbat was never a question in her mind. Rabbi Rachel Ain: It's not only that I felt supported by my neighbors, especially those that weren't Jewish. But more than anything, it was that so many of our congregation members who were not, let's say Shabbat regulars, felt the importance and the value of showing up for Shabbat and they knew that they had an address to come to both physically and spiritually to place their pain and their needs. Manya Brachear Pashman: That same weekend marked the bar mitzvah celebration of a young man in the congregation. Rabbi Ain wrestled with how to balance the sadness and shock of the prior weekend with the joy and celebration of his milestone. And a few years later, that same young man and his brother stepped up to lead the synagogue's Holocaust Remembrance event, in which teens interviewed the children of Holocaust survivors and shared the stories that have been passed down to them. She wonders if that moving show of solidarity when he was 13 and the formational years that followed had an impact. Rabbi Rachel Ain: What I really keep thinking about is how some of our teenagers who at that point, were in sixth grade or seventh grade. And now here they are seniors in high school and freshmen in college, how their teen experience has been shaped by showing up for Shabbat and showing up for shul when bad things have happened. So what I've also tried to do is, how do we ensure that our young people's experiences aren't only about the challenges of being Jewish, but the joys of being Jewish? Sharif Street: I just remember the massive amount of people that showed up and the diversity of the folks. I mean, I don't think I'd seen that many people show up for an evening Shabbat at Rodef Shalom in, well, maybe ever." Manya Brachear Pashman: Pennsylvania State Sen. Sharif Street had been in Pittsburgh the day before the shooting at the Tree of Life building. When he heard the news that Saturday morning, he scrambled to find out if his friends and colleagues were OK. He was not oblivious to hatred and its potential to lead to violence. His father had been active in the civil rights movement and Sen. Street had sponsored legislation to curb hate crimes, but he had hoped to get ahead of the trend. This seemed unfathomable. Sharif Street: I didn't really contemplate that in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, it was within the realm of reasonable possibility that someone was gonna walk into a synagogue, and commit such a vicious, horrible act of hate. I didn't see that." I thought we had moved beyond that stage of antisemitism and bigotry. And I was reminded of what my friends, older folks, and black and Jewish community always said, which is, we have to remain constantly vigilant. Because these things have a way of coming back. It took on a new air, a new level of seriousness to me. Because this is not the idea that people could be killed because of antisemitism in America. It's not just something of a bygone era. But I realized we were living in that era today. Manya Brachear Pashman: Sen. Street accompanied a friend to Temple Rodef Sholom in Philadelphia a week later and he has a few indelible memories from that night. Sharif Street: People from every walk of life. Some people who were obviously maybe were not Jewish, who just wanted to express their support and their solidarity. And the look on the faces of people who are members, who were just, who felt so troubled, so shaken. And to see all the support from people, I think, made people feel like even in this world that seems so cruel in that moment that there were many people who are good, who stood with them. And I think a lot of times, folks who are doing these kinds of acts of hate and terror want to make folks, in this case Jewish people, feel isolated and alone. And I think that the service allow people to recognize you're not alone. And that people from all walks of life stand with you and stand against these horrible acts of hate. I think those of us who were, I would say the under-50 crowd and the younger you got, the more there was a level of shock, found it more disturbing because I guess we were further removed from an era when things like this when vicious acts of violence against people for antisemitism, racism and other forms of bigotry were more commonplace. People were wanting to make sure that this is not the beginning of a new chapter. Hopefully in our lifetimes we'll remember this as a disturbing outlier, not the beginning of an era. Jennifer Mendelsohn: What really struck me about it was how simple it was, all we asked people to do was quite literally show up. You didn't have to wave a protest flag. You didn't have to donate money somewhere. You didn't have to go on a march. It was literally just saying, 'Come be with us this evening. We're hurting. And to have that answered so resoundingly was incredibly inspiring. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jennifer Mendelsohn helped create the DNA reunion project at the Center for Jewish History, which uses the power of genetic genealogy to reconnect Holocaust survivors and their children to relatives from whom they were separated. While she did not regularly attend Shabbat services, she and her husband thought it was important to show up at Fulton Street Synagogue in Baltimore on November 2, 2018. Jennifer Mendelsohn: I walked in, and there's just no way to express what it was like. There were probably 300 people there. And you know, we normally do a potluck dinner. And I looked and there was, you know, there was no room to put down all the food, there was no prayer books, there were people, you know, just packed in. And I remember seeing the faces of neighbors of ours, non Jewish neighbors, and I immediately just got so overcome, and they just sort of smiled at me. And just to know that they had taken the time on a Friday night just to say, we care, and we're here with you. It was unbelievably powerful. Manya Brachear Pashman: Clergy and congregants from across different religious traditions helped light memorial candles for the 11 victims in Pittsburgh and the congregation sang "We Shall Overcome." Jennifer Mendelsohn: I feel like every time I go back, I remember how nice it feels to be at synagogue. You always think like, Oh, it's so much easier to just, you know, sit on your couch with your fuzzy slippers. But it's, you know, it's always nice to be there. And all of the rituals are so familiar, you know, lighting candles, and, you know, welcoming the Sabbath bride and all of that, and the songs and it just reminded me that, you know, I'm not a particularly religious person in terms of practice or ritual. But it reminded me that, you know, that's where I come from, those are my people. And it was just very comforting to be in that environment at a time of such tragedy to just be around familiar sounds and smells and sights and all of that." Manya Brachear Pashman: For Mendelsohn, 2018 had already been fraught and eye-opening, as she had become the target of online antisemitism because of a political project on Twitter. As someone who deals with the Holocaust on a daily basis, her shock surprised her. Jennifer Mendelsohn: This event sort of crystallized the sense that, you know, antisemitism was still around and perhaps, you know, coming back with a new fearsome edge… It was very hard to fathom. You know you you spend this much time thinking about the Holocaust and dealing with families shattered by genocide that was, you know, spurred by just hatred. And you think, 'Well, surely this will never happen again, because everyone understands, and clearly people don't. So it was a very sobering experience to feel threatened again, as an American Jew. Manya Brachear Pashman: But #ShowUpForShabbat also crystallized that regardless of ideology, color or creed, most of America stood beside the Jewish community in this moment. Jennifer Mendelsohn: The crowd inside that synagogue was exactly the America that my ancestors came to the U.S. to be a part of, you know, they escaped political discrimination in Eastern Europe, and that's really for me what it was all about and to reinforce that that America exists that helping, kind, inclusive America, in the face of this horrific act of violence and hatred was just really the balm that my soul needed at that moment.
Oct 25, 2023
Remembering Pittsburgh Part 2: What the Family of Tree of Life Victim Joyce Fienberg Wants You to Know About Her Legacy
Join us in a tribute to the memory of Joyce Fienberg, one of the 11 victims of the 2018 shooting at the Tree of Life synagogue in Pittsburgh. In this touching second installment of our series on the events of 10/27 , we sit down with Joyce's son, Howard Fienberg, and his wife, Marnie, as they share their journey of mourning and resilience. Joyce was not only a dedicated member of the Tree of Life synagogue but also a retired university researcher, a devoted mother, and grandmother. Howard and Marnie open up about their extended period of mourning due to trial delays, offering a glimpse into the emotional toll of such a traumatic event. Marnie details how she turned her grief into 2 for Seder, an initiative to honor Joyce and push back against the hate that creates antisemitism. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Howard Fienberg, Marnie Fienberg Show Notes: Listen: Remembering Pittsburgh Part 1: Behind the Scenes at the Reimagined Tree of Life Take Action: Urge Congress to Stand Against Rising Antisemitism Music credits: Tree of Life by Nefesh Mountain Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and review us on Apple Podcasts. Episode Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: After her husband and mother died in 2016, Joyce Fienberg started each day at Tree of Life synagogue in Pittsburgh, to recite Kaddish, the mourner's prayer. Even when she was no longer officially considered a mourner as Jewish tradition prescribes, 11 months, she continued to attend services each morning at the synagogue. That's why Howard Feinberg knew his mother Joyce was at Tree of Life when he heard there had been a shooting there on the morning of October 27, 2018. It would be more than 12 hours before he learned she was among the 11 killed that day. Howard and his wife Marnie are with us now from their home in Northern Virginia to talk about their prolonged mourning period and how they have held onto and channeled that grief. Howard, Marnie, thank you so much for joining us. Howard Fienberg: Thanks for having us. Manya Brachear Pashman: Howard, you followed your mother's example and recited kaddish for 11 months. Can you tell us a little bit about that experience? That experience of saying Kaddish and mourning for your mother, and also can you share with our listeners why it felt like the mourning period was extended? Howard Fienberg: I felt a huge amount of support everywhere I went, in order to be able to say Kaddish every day. Which for someone who was not the most observant of Jews, it was a big lift to be able to do that every day. In fact, even when traveling in disparate places, that I could always find, somehow, be able to pull together 10 people to be able to say Kaddish was a big deal. And I wanted to make sure that no one would struggle in similar circumstances as well. Obviously, initially, in Pittsburgh putting together 10 people was not a particularly big lift. Because the community support in that first week of Shiva was phenomenal. But it's not an easy thing in many congregations, and I think we are fortunate in mine that we always seem to pull it out every day. But I want to make sure that it happens. So in practice wise, that's one of the biggest things, my involvement with the synagogue, and prayer. The broader extension of the mourning period, in a way, was a result of the constant delay of the trial for the monster that committed the massacre. And that was a result of both just the general usual procedural delays that you would expect, combined with COVID excuses that dragged things out during the trial. And once a new judge took over responsibility for this case, things suddenly snapped into gear and it moved forward. And we're particularly grateful for the judge in this case, just for his very no-nonsense approach moving forward. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you talk about whether the guilty verdict once it did take place, and a verdict was delivered, how that verdict changed anything for you and your family? Howard Fienberg: It was a matter of relief, to a great extent. I sat through almost the entirety of the trial, heard and saw all of the evidence. A lot more than I expected to and ever wanted to, but I felt duty to do so. From an outside perspective, looking at it all, you would say this is a slam dunk case, lined up for all the federal hate crimes that were involved. And at the same time, I was in doubt until the jury came back and said, all said guilty. It's just the nature of things. I was on pins and needles. Massive relief afterwards and the same thing with the final verdict and sentencing. Massive relief for us and our families. And that did allow…nothing's ever closed. You don't finish feeling the loss of somebody, especially when they're taken in, you know, horribly violent terrorist circumstances. But you move from segment to segment. So the same as we do in the year of mourning, you're moving from shiva, which is one kind of thing, to the 30 days, and then to the end of the mourning period. And this was moving to yet another period. And what exactly this is and how long it will be, I don't know. But we're figuring that out as we go. I certainly feel a lot more relaxed. Marnie Fienberg: Feels a little lighter. Howard Fienberg: Yes, definitely lighter. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's good to hear. That's good to hear. I am curious, you said you felt a duty to listen to those details, even though you didn't want to. Can you explain why you felt that sense of obligation? Howard Fienberg: Part of it is, somebody in our family needed to. And it wasn't something that I wanted everybody to sit and hear and see. And I specifically told friends and family as much as I could, to stay far away and said, as much as you want to know, I'll let you know. But otherwise, it's horrific. And it wasn't anything that I would wish for anybody to see and hear. But at the same time, it's the reality of how my mom died. And what the circumstances were, what was going on with the antisemitic conspiracy theories that drove the monster that killed her. And what did he have in mind, and what was his intention, what did he plan, what did he do? These were important things. And the bigger picture, which I didn't even know going in, was the extent to which the police in Pittsburgh were so heroic. And while they were not able to save my mom, they saved other people, including friends of ours, and people who are now friends, who would not be alive if those cops had not tried to charge at the front door trying to charge the building and getting shot. And then the SWAT teams going into the building, and in a couple cases getting almost murdered themselves, trying to rescue the people that were inside. And they did rescue some people. And those people would most likely be dead if the SWAT had not rushed in. Equipment wise, they were not ready ordinarily for this sort of situation. But they went in anyways because they knew they needed to, and they didn't hesitate. And that's the kind of thing that you can only understand, having gone to the trial and learned what went on. Manya Brachear Pashman: Marnie, I want to turn to you. You quit your job as a federal contractor and started a nonprofit initiative called 2 For Seder. What prompted this sudden shift in your career? Marnie Fienberg: Well, I think that I was so upset about what happened with my mother-in-law, I did take a leave of absence initially. And I wanted to volunteer. Being a Jewish woman, and having all this anger and grief and all the support that we had received from people, literally all over the world. I just couldn't sit back and do nothing. So I wanted to do something that was really in honor of Joyce, but also something that would help every single Jewish individual if they so chose to be able to take some small tikun-olam-style action, and push back against the hate that creates antisemitism. And I think 2 For Seder really accomplished that, especially that first year. And we were really on track to grow quite enormously, except for COVID. COVID stopped us in our tracks, because it is about inviting 2 people into your home, who have never been to a Seder before and really educating them and immersing them in that Jewish joy and intimacy that you create every year at Passover. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I'm really curious about the seder connection. Was Joyce known for putting together really elaborate Seders? Was she just always at the Seder table? Why Seders? Marnie Fienberg: So this is a two part sort of explanation. So one is the sort of graduation to being allowed to hold the Seder. So my mother-in-law, really for 15 years we actually had done where we started at her house, and I helped her and I learned as we went and then we flipped it. And we came to our house and she would help me and make sure that I was doing things the right way and guiding me the right way. And there's, I mean, there's so much to do, putting on a Seder and trying to of course fit, you know, 30-35 people into a house that really should only have about 20 people in it is, of course, part of the tradition. And she never blinked an eye, it was never too much. It was really mostly about making everyone at the table, regardless of their background–she always had students over, she always had people who had no place to go–every single person needed to feel like they were home. So if you had some sort of dietary restrictions, or any sort of an allergy or anything, my mother-in-law would bend over backwards, she bend herself into pretzels to make you feel 100% comfortable. And every single person who ever graced her table felt like they had never been more comfortable before. They felt like they were at their mother's house. And they commented on that many times. It was a wonderful thing. And I have to tell you, it's very hard to live up to. She was one of a kind. Howard Fienberg: If I might add in, part of this comes from looking at photo evidence. I've been going through all of the family photos, last five years, trying to digitize and you can see the progression. So early on, there are pictures of Passover seders that clearly they've invited friends and other professors at the universities, students that were Jewish, they'd invite to Passover on a regular basis. And I think there's a turn somewhere in the early 80s, my brother and I would start inviting our non-Jewish friends to the Passover Seder. And probably around about the late 80s was when it became not just bringing in Jews and my brother's friends and my friends who had never been to a Seder, it was their friends and fellow faculty, visiting graduate students from far-flung countries who knew absolutely nothing about Judaism. Certainly nothing about Passover. It was a way for them to have a comfortable introduction to what we're all about. And in all the context that my mother wanted to provide of it being a welcoming taste of being at home. Manya Brachear Pashman: We talked about how the Jewish tradition provides the process of formula, you know, the shiva and the 30 day mourning period. But this, the length of time that families have been mourning has been extended, delayed, slowed down. And I'm curious if on top of the Jewish traditions that guide people through the mourning process, if the Jewish community helped fill in some of what was missing, helped comfort you in certain ways? Marnie Fienberg: We live in two Jewish communities right now. We live in Northern Virginia, and we have our community here. And then we live in Pittsburgh, in a sense, and we have the community there. And we have been back and forth many times. The community in Pittsburgh, regardless if you were a family member, if you were a member of one of the three synagogues, or if you were a member of the greater community. There were so many ways that there were supports. And even from here we were always invited to participate in them. And some of them were done virtually actually when COVID hit which actually was very helpful for us. I don't know if the larger Jewish community is aware, but the FBI actually has a whole series of people, an entire division that's just there to support families and the communities that are affected from mass shootings, which also includes a grant to stand up an actual group that that is going to help the community at large. And that's the 10.27 Center for Healing in the Pittsburgh case, and that group is still standing and still running, still helping everyone. So there's the Jewish side, where we all still pray together, where we get together for our commemoration once a year, the families always get together in Pittsburgh. And then here in Northern Virginia, there have been a variety of commemorations, but mostly our own local community at our synagogue is extremely supportive. They're, of course, another family to us. And this has only really brought us all closer, which has been wonderful. Howard Fienberg: We've had a lot of different kinds of support structures, I wouldn't identify anything as where there was a failing, other than the broader problem that people thought it was over. The presumption on the part of everyone, when they found out that there was a trial for the monster that killed my mom, was: wasn't that done already? Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to ask you both this question, what has given you hope in the last five years? Howard Fienberg: I haven't had the time and strength to go through all of the letters and cards that we received in the month or two after mom was killed. But some of the ones that really impacted me the most, outside of people that we knew, or that knew my parents, I mean, I think we have a whole box of correspondence and cards from people who never met my mother or us. And a lot of those were from non-Jews, who were deeply impacted by this, and were moved. I mean, it's one thing that we had large groups of Jews that came to our Shiva, for example, that wanted to be there to support and during the Shiva period. There were groups of students that came from universities outside of Pittsburgh, like Ohio, and from Massachusetts, they wanted to come and be a part of it, and they weren't Jewish. They just, they felt a need to support. And that's the kind of thing that gives me great hope. Part of why we look at projects like 2 For Seder as so important, that it's not just that we're Jewish, and we're other. So I see a great load of hope there. But at the same time, the fact that, you know, trailing back to the trial, the fact that the Justice Department was willing to pursue the trial, and not just take a plea bargain, but actually present evidence and pursue a case involving such rampant antisemitism, and lay out the facts and prosecute them. That gives me great hope as well. It's not something that is an easy thing. The most reasonable response on their part probably would have been to, no matter what we wanted, would have been to pursue a plea bargain and make it all go away. Because it's expensive, and it doesn't make anybody feel good. Why would you do it? Manya Brachear Pashman: So I have to ask, if the trial had happened a century ago, do you think the jury would have reached a guilty verdict? Do you think the prosecution would have pursued the hate crime charges as they did? Marnie Fienberg: So there would never have been any hate crime charges. Hate crimes did not enter the American laws until 1964, which is when the Civil Rights Act was enacted. This is why I think that we always need to be so thankful for Martin Luther King Jr. and to be proud that we were part of that. So a century ago, would this have even been considered an anti-Jewish crime, an antisemitic crime? No. I think that you can look at Dreyfuss' case and you can say very clearly, this country, this part of the world was not ready for something like that. And they would have looked the other way. Would they have convicted as just a general murder? I don't know, there's a lot of those murders that just disappeared 100 years ago. But would it have been because it was antisemitism? Absolutely not. I would be very, very interested to learn of some other way that that would have happened. But we're very grateful that the same laws under the 1964 Civil Rights Act, that is what this was all held under. Howard Fienberg: And the other angle is that the monster that killed everybody, he killed 11 people, he was not an upstanding part of the community, he did not have a whole segment of the community cheering him on, helping him, encouraging him, protecting him. That's not the way it worked. And the reactions and the killing of my mom was part of the demonstration of that, that people were horrified and they were supportive of us. And, you know, the Justice Department pursuing the case to the fullest extent of the law, as they should, would that have happened 100 years ago? No, but again, not just because of the lack of statute, but you know, our place in society was not what it is today. And society was not the same. Manya Brachear Pashman: I know we've sprinkled details about your mother throughout this conversation, but is there anything in particular in there anything in particular that you want listeners to know about Joyce? Howard Fienberg: She twisted herself into knots and did whatever she could to help others, that starts with the rest of the family, and the amount of time and energy that she put toward helping us and helping my brother and sister in law and all of her grandkids, which were a huge focus of her life. The fact that she was able to also shoehorn in a lot of volunteer time at multiple different projects in Pittsburgh, as well as being the connector of our family and multiple sets of families, both email and letters and phone calls on a regular basis. It's an amazing thing that she was able to do that on a daily basis and still sleep and function. Not to mention, make sure that she was at minyan at Tree of Life early every morning. It was an amazing balancing act, y'know, it's a hard thing to pull off. Manya Brachear Pashman: And she picked up someone each day for minyan as well, right? Howard Fienberg: Yes, so unfortunately, he passed away. Late, late last year. Manya Brachear Pashman: May his memory be for a blessing. You know, I should ask, what does that mean to you, when this phrase, May her memory be for a blessing. What does that mean to you when someone says that about your mother? Howard Fienberg: I generally have an appreciation. Because, not just of what she meant to me, but the recognition from other people of the loss. And for some of them, they understand what that loss means. For others, they don't really, but they're trying to support. I do take comfort in that. I'm not certain that I did, certainly in the first week, I was too shell shocked to be able to appreciate all the people that were saying it to me. But, you know, over time, it makes a big difference. And I appreciate being able to do that for others, even complete strangers. If I'm supporting a minyan at someone's shiva, I like to be able to do that. Marnie Fienberg: Joyce was such a gentle, loving and caring person and to have her loss be through such an act of hate is where I think we all struggle. And I think whenever anyone talks to Howard or myself or any of the families about their losses, that they can feel that, that they can feel the shock that these people who just wanted to make the world a little bit better, a little bit of a better place, that they would be taken in such an act of hate, for no reason. I think that being able to say May their memory be a blessing really emphasizes the loss that we feel and the hope that we can fill in this space. Howard Fienberg: And I will say it's very awkward to talk to somebody who's in mourning. Just the nature of it. The fact that we have what almost a rote saying that carries so much weight is a huge benefit. And I deploy it regularly with non-Jews. They're partially taken aback, and they're very touched, because they're used to getting the awkward, Oh, I'm so sorry for your loss, which doesn't make anybody feel particularly good. We can argue about the way Judaism approaches all sorts of things. I happen to think the Jewish way of death, you know, as depressing as it may be to think about, is very practical in a lot of ways. And it's designed to be helpful. Manya Brachear Pashman: Has the rest of your family embraced that? Have they turned to the Jewish faith to cope with this, to try to make sense of it? Howard Fienberg: My brother was already what is called traditional in France, traditional Judaism, he embraced that much more fully, and is much more on the Orthodox range than he was before. And that was a huge part for him as well in coping, and coming to grips with our new life, after my mom died. And that is a piece of it for all of the family in different ways. One of the positive things along these lines, my brother dedicated a Torah in memory of my parents. And by weird twist of fate, or God's hand, in choosing a date to dedicate that Torah in Pittsburgh, the date happened to land a couple of days before the final sentencing in the Tree of Life trial. So we had just a few days before, this whole ceremony and huge celebration that my brother orchestrated, to not only involve the local community and a huge celebration and things that I've heard about, but never seen. People marching in a parade down the street, not far from Tree of Life, to introduce the new Torah to its new synagogue, but also in the final writing of the letters, finishing off the Torah, to be able to include some of the law enforcement officers that were injured in trying to rescue people at Tree of Life, as well as all of the families of the victims and the survivors. That everyone was able to participate from our family and our extended family. It was an amazing sight to behold and the simple fact that it landed right before the sentencing was kind of amazing, because there's this amazing positive outgrowth that you might not have expected. And the fact that it perfectly coincided with the darkness of the trial. It's an amazing thing. Marnie Fienberg: He had been planning this for three years. When Howard says that it was an amazing coincidence to bring them both together, to bring the one of the most Jewish things you could possibly do, dedicating a new Torah, creating and dedicating the Torah, right before the sentencing. There was never a plan for that. It just, it just happened. And it was very healing to the community. But it was also, I mean, the message of the shooter was to stop Judaism, to make us so afraid that we would never go back into the shuls, that we would never go back and be Jewish. And not only in the days right afterwards, where people flocked to go to shul. But this was just one more incredibly powerful expression, that each of the families has done so many different things, to focus on Judaism, focus on making the world a better place in memory of their loved ones. But this is just one more extraordinarily powerful example about how just being Jewish, just doing what we do best, it keeps us going. Manya Brachear Pashman: Marnie, Howard, thank you so much for joining us and sharing part of your journey with our listeners, it's really a valuable conversation to have. Marnie Fienberg: Thank you for having us. We appreciate it. Nefesh Mountain, from the song Tree of Life [singing]: O sweet friends, come and dry your eyes And hold each other by this Tree of Life I'm angry and tired of this great divide But I sing, nonetheless, with love on our side Manya Brachear Pashman: This episode is brought to you by AJC. Our producer is Atara Lakritz. Our sound engineer is TK Broderick. You can follow People of the Pod on Apple Podcasts or Spotify, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod. The views and opinions of our guests don't necessarily reflect the positions of AJC. You can reach us at peopleofthepod@ajc.org. If you appreciated this episode, please share it with friends and family and write a review on Apple Podcasts.
Oct 20, 2023
Renana Gomeh's Sons Were Taken Hostage by Hamas: What She Needs You to Do to Bring Them Home Now
At 6:30 a.m on October 7, 2023, Renana Gomeh's life changed forever when Iran-backed Hamas terrorists stormed her home in Kibbutz Nir Oz and took her two sons, Yagil and Or Yaakov, ages 12 and 16, hostage. She has not heard from them since, knows nothing about the conditions they're held in, or whether they're still alive. Listen to Renana's painful account, how she is coping, and her mission to bring them home. American Jewish Committee (AJC) and more than 110 Jewish organizations have urged the United Nations and all governments to secure the immediate and unconditional release of the hostages. Update: This conversation was recorded on October 19. On November 27, Yagil and Or Yaakov were released as part of a temporary pause in fighting. Take action to bring their father, Yair Yaakov, and all remaining hostages home now. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: What Biden's Wartime Visit to Israel Signals to Hamas, Iran, Hezbollah Mai Gutman Was Supposed to Be at the Music Festival: IDF Lone Soldier Recounts Harrowing Week Responding to Hamas Terror: IsraAID CEO on How You Can Help Israelis Right Now Learn: What is Known About Israeli Hostages Taken by Hamas AJC.org/AttackonIsrael Donate: AJC.org/SupportIsrael Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. ___ Transcript of Interview with Renana Gomeh: Manya Brachear Pashman: Over 200 hostages are being held by the Iran backed terror group Hamas after its terrorist attack against Israel and the massacre of over 1400 Israelis on October 7. American Jewish Committee and more than 110 Jewish organizations from more than 40 countries have urged the United Nations and all governments to secure the immediate and unconditional release of the hostages. The condition of many of the hostages remains unknown, yet we know some are in dire need of urgent medical care. With me to discuss her efforts to bring back her 12 year old and 16 year old sons is Renana Gomeh. Renana, thank you for joining us. Renana Gomeh: Thank you so much for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: Now, your two sons were kidnapped from Kibbutz Nir Oz by Hamas terrorists on October 7. You were on the phone with your sons, as Hamas terrorists were breaking into your home. I cannot imagine what you've been going through over the past 2 weeks. Could you please tell listeners what happened that morning at 6:30am? Renana Gomeh: Yes, I was on another kibbutz that Saturday morning, with my spouse. I have a partner living on another kibbutz in another community near the Gaza border, which is 15 minutes drive away. And I'm divorced, and my ex-husband lives 400 meters away from me. He's also a member of my kibbutz, of my community. And the boys just usually sleep at my place. You know, this is how they prefer it. And since they're not very young children anymore, we let them choose. So they were alone at home. And he was at his place with his girlfriend, with his partner, who I love to bits. And about 6:30 in the morning, we all woke up to the red alert, which is unfortunately something which became a routine and we're used to. Since I was also on our kibbutz on the Gaza border, all communities at the Gaza border had red alerts and rockets flying over, hundreds of rockets flying over on a completely surprise attack. We just didn't see it coming whatsoever. I called my boys as I was running to the safe room at the place I was in to make sure that they're in the safe room at my place. And as the safe room is the eldest son's bedroom, he was there but he made sure that his little brother was also there. So they were in the safe room. And every couple of minutes I spoke to them to see that they were okay. At a certain point they said they're starting hearing gunshots outside the house and I could hear gunshots outside the house I was in. Again, it was a completely well-planned and well-executed attack on all communities at the same time. So no one could go outside. And I told them it was probably the army defending them. You know, they're keeping us safe. 30 minutes later or so I can't remember. I've lost track of time to be honest, of that morning. We started getting text messages from other members of the community saying terrorists are walking outside freely, breaking into houses, trying to get people out. I was begging neighbors and people from the community to go and see, to go and see them, go and be with them. You know, try and help them. But no one could go outside. And there were probably over 100 terrorists walking around, getting into houses. So there was not a chance that anyone could help. At a certain point I asked my elder brother, who's also a member of the community, to call my eldest [son] and tell him how to lock the door. The doors don't lock in a safe room because the safe rooms were planned against missiles and rocket attacks and against earthquakes. So they actually want you to have the door been able to open from the outside, so they can take you out. So they don't lock. But you know, there's certain technical ways to try and keep them locked. So I asked him to call my eldest and tell him how to do it. And then I later found out that he held the door like hell. And he fought for that door. But it didn't make it. And about an hour later, about two hours after the attack started, they called me and said, they hear someone breaking in. Breaking the door, breaking in, walking in the house. And a couple of minutes later, I could hear Arabic speaking outside. The door opens. And my youngest said, Please don't take me, I'm too young. He was always good at manipulation. This time it didn't work. And they took them. That was the last I've heard from them. It's almost two weeks now. And I've nothing, I've heard nothing. I know nothing of their whereabouts. I know nothing about the conditions they're held in, whether they eat, whether they sleep, and whether they're still alive. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm so sorry to make you relive that. But I also know that it's important that you share your story with the wider world. Renana Gomeh It is, it is. I know. This is all I can do at the moment, you know. And so it means a lot to me that you're actually giving me the platform. Because what I need your audience to do is to enlist to the effort to get them released now. To get my boys home alive now. They shouldn't be there. They take children hostage, 80 people out of our small community, which only is about 400 people. 80 people were taken hostage from the age of six months to the age of 86. People who need medicine, people who need medical care. It's just plain children that need a mother. I later found out that my ex-husband and his girlfriend were also taken hostage from their house. My hope is that they've met and they're together. As 80 people were taken my hope is that someone that they know is with them, to support them and to help them. That's the story you know. As a mother to other mothers, just trying to imagine it was your child being kept there. Just for one hour, let alone 13 days. My heart goes out to every mother even in the Gaza Strip. You sometimes get in the news in Israel, you sometimes get news like a 14 year old terrorist was killed tonight at a terror attack and I always my heart goes out to them and I say you know he's 14, he's someone's child. But what kind of a mother raises such monsters? Manya Brachear Pashman: Of course, listeners who are hearing this can go to AJC.org/BringThemHome to send a letter to the United Nations, send a letter to Congress to demand swift action to release the hostages. I know that you are pushing for swift action to release your sons and the other hostages. Who have you met with, who have you talked to about bringing your sons home and what can be done? Renana Gomeh: Well I've met anyone who was willing to meet me. I was mainly trying to get the media, international media to hear my voice and to get people around the world to hear us. I think the international community has a lot of tools and there's many ways you can help by just by putting pressure, as you just suggested, by putting the right pressure in the right places, in order to release them. Obviously I want all of them to be released, there's over 200 people kept in the Gaza Strip, as far as we know, I think there's more. But, you know, it's not for me to say. What we need you to do is to approach your governments. And ask them to release those civilians that are held. We don't even know, again, in what conditions and especially released those 40 or so children. Children under the age of 18, from babies to teenagers. They're not part of this game. I'm sorry. They are not bargain chips in the war game. Get them free now without any conditions whatsoever. I can't see how anyone can think otherwise. It's just plain and simple. Manya Brachear Pashman: Renana, are you getting any explanations or theories from diplomats, people that you're speaking with, on why they're holding your sons and other children like this? Renana Gomeh: To be honest, until two weeks ago, I saw us as neighbors. And I thought there was mutuality between us, you know, that we could have a future together. Those two people have a mutual economy, have mutual relations, even have mutual cultures. But I don't think we do. I can't even try and get into these terrorists' heads and the way they think, because what they did is not just taking soldiers hostages in order to bargain them, to trade them, for prisoners. What they did was to rape and decapitate and murder, just for the sake of fun. They came in, had cameras, to have this horror filmed, and put on Facebook and on TikTok. So I can't even begin to try and understand but I reckon they probably want to bargain them for the prisoners, which as far as I'm concerned…I don't care. I think the actions they took cannot be justified in normal rules of war. I can't, I can't explain. It's not for bargaining. It's for fun. Manya Brachear Pashman: Are you being told there are limits to what diplomats can do or is anyone telling you their hands are tied, or are you getting unequivocal unbridled assurance that everything is being done? Renana Gomeh: I'm not really told anything at the moment, but I'm not an expert. I understand that not everything can be told. If there are efforts being done, which I hope there are, they can't share it with 200 families. My hopes are that anyone with the right mind understands that this situation can not go on. And the children cannot stay held by terrorists for not even one hour, let alone a day or a month. And that has to be over, no matter what. I don't care if the war still goes on after. I don't believe there's any other way to get them released, but diplomatic pressure. I think this is the way to do it. But I'm not sure there's anyone to negotiate with. So you know, the other side is so different to us. And their morales are so different from ours, apparently. Manya Brachear Pashman: Are you traveling places to meet with government officials, and do those government officials include Israel, America, beyond that? Renana Gomeh: I'm willing to do anything to get my kids back home. And to get everyone's kids back home. I have another daughter, my eldest, who's 21, who was also in Nir Oz at that horrible, horror day. And who's traumatized. Thank God, her boyfriend was around and held the door. And luckily, they got out alive but very, very deeply scarred. And I have to take that into consideration while making decisions about traveling far away. But I'm doing my best by Zoom. I'm trying to get my voice heard in any way I can, under those conditions. And I still have her to think of, she's all I have at the moment. So she deserves her mother to be around. Even [if] she's willing for me to do anything to get her father and her brothers back. Manya Brachear Pashman: Where are you staying now? Renana Gomeh: We've been evacuated to a beautiful hotel suite in Eilat. My boys love Eilat. I was here with them two months ago on summer vacation. It took me years after I got divorced to get to this point where I can take them to a summer holiday on my own. So it was very meaningful also. So I'm finding it very very hard to walk around in Eilat. But everyone from my–what's left of my community of what was Nir Oz–everyone were evacuated to this hotel and we found it very important to be together. This community, you know, it's like a big family to us. This is why we decided to stay here with them. It's very hard because it's very far away from everywhere in Israel. I know for people in the States internal flights seem like a normal bus. But for us, it's not. But at least it feels safe-ish. I don't think anyone who's now staying here could bear even one more alarm. People ran for their lives, people fought terrorists. People jumped out of burning houses, people fell out of windows, people were hiding in bushes, people were faking themselves dead. There's not even a… I can't even start to describe, you know, for me, the horror was the fact that my children were taken away. But other people experienced horrors themselves. So we're here with our big family, the kibbutz, trying to recover from ashes. Manya Brachear Pashman: Much of the world's attention is on what's going on now in Gaza. What do you have to say to journalists who are covering this war? Renana Gomeh: The last thing I want, as a human being, as a mother, as a woman–if we were to run the world, it wouldn't happen. Just saying. But the last thing I would have wanted is war. You know, we've had so many in the last few years. This is the last thing we need. This is the last thing the Gaza people need. People in Gaza are used as human shields, even their children, like I said, terrorists who are 14. Terrorists, they're children, why are they carrying guns? Why are their summer camps, teaching them how to use guns and to become terrorists? My heart goes out to every mother there. And I wish we didn't have to have a war. And I wish we could live a better life. And I think the people in Gaza had that chance. We walked out of the Gaza Strip 20 years ago, took villages, complete villages out. And it was a very difficult action to do in Israel. Which, you know, we still bleed on it nowadays, politically and socially. And we gave them the opportunity to become an independent state. And they gave the keys to a terrorist organization, which uses all the money that the EU and whoever is giving them in order to weaponize themselves and in order to become terrorists and to educate their children to become terrorists. I used to tell my children all the time: your life is so much better than children in Gaza. You have education, you have running water, you have electricity. And you have the morals that the Jewish world gives to their children: of equality, of mutuality, of giving away from yourself and no wish to get something in return. The other side does the opposite. We treasure life as Jews and they treasure death. So I'm sorry, but my sympathy is gone. I want my children back home, now, alive. Afterwards, we can speak about having a war or not having a war, the conditions they're in, the humanitarian solutions. But the world should know that what happens there is not an independent state. It's a terrorist organization, holding civilians, hostages. Their own civilians. My heart goes out to every child and every mother there. It's not their fault. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much for sharing your perspective, sharing your family's story. And I am praying and we are all doing everything we can to help you get your sons and the other hostages home. And I pray that that happens very soon. Thank you so much for joining us. Renana Gomeh: I just want them–I just want my boys back home alive now and I want you to help us do it in any way you can. Thank you so much for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you would like to help make a difference, go to AJC.org/BringThemHome. There you can urge the United Nations and members of Congress to secure the immediate and unconditional release of all hostages being held by Hamas terrorists in Gaza.
Oct 19, 2023
What Biden's Wartime Visit to Israel Signals to Hamas, Iran, Hezbollah
Jason Isaacson, AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer, joins us to break down U.S. President Joe Biden's historic wartime visit to Israel and his message to Iran and its terror proxies Hamas and Hezbollah. Jason also shares his take on the fast-moving situation, including the fallout from the explosion at the Gaza hospital, the announcement of humanitarian aid to Gaza, and the growing antisemitic attacks in the Middle East and Europe. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jason Isaacson Show Notes: Listen – People of the Pod on the Israel-Hamas War: Mai Gutman Was Supposed to Be at the Music Festival: IDF Lone Soldier Recounts Harrowing Week Responding to Hamas Terror: IsraAID CEO on How You Can Help Israelis Right Now Learn: What Everyone Needs to Know About Hamas' Lie About a Rocket Strike on a Gaza Hospital AJC.org/AttackonIsrael Donate: AJC.org/SupportIsrael Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Transcript of Interview with Jason Isaacson: President Joe Biden: October 7th, which was a sacred Jewish holiday, became the deadliest day for the Jewish people since the Holocaust. It has brought to the surface painful memories and scars left by a millennia of antisemitism and the genocide of the Jewish people. The world watched then, it knew, and the world did nothing. We will not stand by and do nothing again. Not today, not tomorrow, not ever. To those who are living in limbo waiting desperately to learn the fate of a loved one, especially to families of the hostages: You're not alone. Manya Brachear Pashman: On October 18th, 2023, President Joe Biden became the first American President to visit Israel during wartime, demonstrating his unequivocal support for the Israeli government. Here to talk about President Biden's visit is Jason Isaacson, AJC's chief policy and political affairs officer, joining us from Berlin where he's witnessed some of the European response to the crisis. Jason, welcome back to People of the Pod. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: I am always shocked when the President goes to a war zone like he did go to Ukraine in February, or in this case, Israel. What did President Biden's visit signal about his support for Israel during this time? Jason Isaacson: This is a president who has long identified himself as a strong supporter of Israel, who has spoken again and again, throughout his political career, from the time that he was a young man serving in the US Senate, of his support for, his identification with Israel. But to hear him speak, as he spoke on Wednesday, in Tel Aviv, after meeting with the Israeli war cabinet that Prime Minister Netanyahu assembled, after other meetings that took place as well, to hear him speak with such passion, such conviction about the priority for the United States, of standing by Israel, of identifying with the struggle that Israel now faces against Hamas terror. To hear him talk about "the nations of conscience," as he referred to the US and Israel together. The struggle that the Jewish people have had over the centuries, the fight against antisemitism, his references to the Holocaust. All of that, and to say that the United States was standing by Israel, in the fullest possible way, the deployment of an aircraft carrier battle group to the eastern Mediterranean. Another aircraft carrier battle group, steaming to the eastern Mediterranean as well to provide additional support. The package of additional military assistance. He described it as an unprecedented package of military assistance that he is asking Congress to approve, to help Israel through this difficult time. All of these statements and his just physical presence in Israel, in the midst of war, spoke volumes of the support that the United States has for Israel. And he also spoke frankly, about the tragedy that occurred the night before he arrived, at a hospital in Gaza. And the fact that all the indications are that this was caused by the fire of Palestinian Islamic Jihad, the rocket that misfired. It wasn't, as so much of the media and so much of the region, frankly, has alleged that it was somehow the work of Israel. Very clearly from the evidence that has been accumulated by U.S. surveillance and other means of data collection. This was something that was a misfire from the Palestinian side. All of that, packaged into a single presentation by the president at the old American Embassy in Tel Aviv, just spoke volumes of the support that the United States has for Israel, that the US is standing by Israel in this very difficult time. Manya Brachear Pashman: Let's talk about people who immediately assumed that it was an Israeli airstrike that caused that explosion at that hospital. Many did jump on board with that argument, including Jordan and Egypt. And those are countries with whom Israel has had peace agreements for quite some time, but they seem to embrace that story right away. What is going on with the the Arab nations? What has their response been to this violence? Jason Isaacson: It's profoundly disappointing. Lies have velocity and in the age of social media, enormous power, and circulation that really just can't be turned back without a huge effort to introduce the truth into the narrative. The lies that have been told about Israel for decades, have saturated the region and frankly, the world, and a lot of the international media as well, quite regrettably. Even in our own country. So it's easy to believe that if you've been told for decades, that Israel is a colonizer, Israel is an oppressor, Israel is heartless in its treatment of its Palestinian neighbors, then you see pictures of people carrying wounded people or bodies strewn about a courtyard in Gaza, knowing that Israel is attacking Gaza, because it's trying to root out the Hamas terrorists have attacked Israel just a few days before. It's easy to believe if you've got that background, and you've been hearing this and been raised on this kind of media saturation, that Israel is to blame. And it is only later that the facts come out, that the imagery that we have been now seeing on social media from a few sources, highly credible sources, what the United States government has now found through its own quite formidable means of data collection, that that this was not Israel, targeting a hospital or firing on a hospital. It was a Palestinian rocket that fell on this hospital while they were sending a barrage of rockets into Israel. There have been hundreds of Palestinian rockets and missiles that have fallen in Gaza and have killed Palestinians. This was the latest incident. It's horrible. The people of Gaza are suffering. The Palestinians are suffering because of the rule of Hamas. And the more that the region talks about that openly–instead of talking about it privately. AJC knows from our many years, including recently, of traveling across the Arab world and speaking to Arab leaders who know better, know the reality: that Israel is fighting ruthless terrorists, funded by, supported by, armed by Iran. And waging this war that is really their war, against these kinds of extremists who are hijacking a great faith and fighting in the name of a great faith when they are actually doing everything they possibly can to damage the reputation of and the standing and the principles of a great faith. And Israel is fighting this fight not only for itself and for its people, but frankly, for the possibility of peace and stability and prosperity in that region. I'm hopeful that at some point, it will be possible for the leaders of that region to step forward and say publicly what they have said so many times privately that they know that Israel's struggle is their struggle. And there have been a few assertions of this, I have to point out, in the last week and a half, there have been some statements that have identified by name, Hamas. I was struck by a statement made by the UAE ambassador to the UN. Statements that were issued on Twitter, by the Kingdom of Bahrain and by the United Arab Emirates a few days after the October 7 atrocities in Israel. But so many of the statements that we've seen in the last week, have been profoundly disappointing and hypocritical. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned the actual threat of Iran to Arab nations. I'm curious what message Biden's visit sends to Iran and its terror proxies on the border with Lebanon? Jason Isaacson: Well, I very much hope that having the USS Gerald R. Ford in the eastern Mediterranean, the USS Dwight D. Eisenhower on its way as well. There was also, I believe, a fighter squadron that was being repositioned to the region. There are enormous military assets that were already in the region. But the US has made it very clear, President Biden, Secretary Blinken and Secretary Austin, in their visits to the region as well, have made it very clear that the US is telling the region as President Biden said, again and again, you know, my message to the region is: don't. Don't even think about the possibility of adding to this fight against Israel of joining this fight against Israel. The US will step forward. Whether the US will not only provide additional military hardware, as the President has offered, and there of course are many friends in Congress who are stepping forward right now to provide for that as well. But the US could also enter this fight, depending on the circumstance, on the possibility of a widening of the war. Should Iran make the tragic blunder of deciding to somehow enter into this fight in a more direct way, there would be a powerful response. I think the President has made that quite clear. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you think Biden's visit will deter Hezbollah? Or are Iran and Hezbollah one in the same? Jason Isaacson: Closely connected, maybe not exactly one of the same, but clearly, Iran would like to see Hezbollah take a more, it appears, take a more aggressive posture. There have been some incursions that have been conducted by Hezbollah, or by people from the Hezbollah controlled territory of southern Lebanon into northern Israel, there have been the firings of certain missiles and mortars. Some of them are not the full scale kind of attack that Israel would need to respond to forcefully and that and that would actually represent a second front that hasn't happened. As of the time that you and I are speaking, let's hope that that doesn't happen. Let's hope that the messages that have been sent by the President, clearly messages sent by Israel, that it is prepared for any fight and will not allow its citizens of the North and the country as a whole to be invaded by by Hezbollah, it will resist powerfully and it will punish any incursion, any attack in a way that Israel has had to do in the past–at great cost. But Israel will defend itself, Israel will stand strong. And the United States will have its back as the President has said repeatedly and demonstrated by his latest visit, and the announcement that he made when he was in Israel this week. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know speaking of Iran, I want to go back to that, they have called for an oil embargo on Israel, how likely is that to happen? Jason Isaacson: I'd say pretty unlikely. I think that Iran's threats are hollow, and will be met by the oil suppliers from not only the region but from elsewhere, including Europe, including Azerbaijan. There are energy supplies that Israel produces, as you know, on its own through an abundant supply of natural gas in the Eastern Mediterranean. I'm not concerned about a cut off of energy to Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: In Tel Aviv, President Biden announced that humanitarian aid – food, water, medical supplies – would start to flow to Gaza from Egypt. Prime Minister Netanyahu then added that Israel would prevent any aid from reaching Hamas. Why this turn of events, Jason? Jason Isaacson: My assumption is, in the early days of the fight against Hamas, there was a sense that by putting pressure on Gaza as a whole, Hamas could be induced to release the hostages, some 200 hostages that it is holding, that the Palestinian people would put pressure on Hamas, to do so, to save themselves. I believe that there was also a concern that providing anything, allowing anything to flow into Gaza, would provide the wherewithal for Hamas to continue to build the rockets and missiles and make other preparations, build out its infrastructure, and fuel its fight against Israel. So I think the idea was, as in many war situations, you know, cut them off, then move in and try to surgically, as surgically as possible, take out the leadership and, and dismantle the infrastructure of terror. But as the situation evolves, and as it's clear that the Palestinians are, are suffering from a lack of, of food or water power, I think the thinking has shifted with, with the United States and other countries offering to provide additional assistance. I think it's very clear that Israel feels also that their intention is not to harm the Palestinian people, their intention is to eliminate Hamas. Manya Brachear Pashman: So, Jason, I am speaking to you, actually, you are in Berlin right now. Can you tell me a little bit, tell our listeners a little bit about what you're hearing, what you're seeing there on that side of the ocean. Jason Isaacson: Of course, Manya. Before I came to Berlin, I was in Paris, briefly as well. And I know the Jewish communities in Paris and Berlin, elsewhere in Europe, are on edge. There have been large street demonstrations in London and Brussels, in Paris and elsewhere. There was a firebombing the night before you and I are having this conversation at a synagogue in Berlin. There was a teacher who was stabbed to death outside of Paris, a couple of days ago. There were two people who were shot to death in Brussels, as well. There have been other acts of violence. Also within a day of our conversation, Manya, there was a firebombing of a synagogue in Tunisia, which has a small Jewish community that's been, in that country for 2000 years. So there are Jewish communities that are feeling the fallout, the impact of the propaganda that has raced across the world, about Israel being responsible for the suffering of Palestinians. And supporters of the Palestinian cause have come to the streets. And some of them have come to the streets with knives and Molotov cocktails, and have expressed their anger, and targets have been Jews, not just Israelis. And this is dangerous, and it needs to be confronted, extremely directly and forcefully as it has been, for the most part, I would say, by police authorities, by federal authorities as well across Europe. AJC is very concerned about the well-being of Jewish communities in the diaspora as a result of what's happening in Israel and Gaza. We were seeing in the first hours and days of the attacks of October 7, expressions of sympathy from across the planet, striking expressions, powerful expressions. I will not forget the statements by Prime Minister Modi, for instance of India, the most populous nation on earth, expressing solidarity with Israel. But then in the days following that, really attention has shifted entirely, the narratives have changed. And now, what we're seeing more, are demonstrations in the street. There were demonstrations in the streets of solidarity with Israel in the first day or two, including here in Berlin. But, now we're seeing a very different and a very ugly, and a completely misplaced set of priorities and angers and prejudices against Jewish communities. So we need to do what we can, working with Jewish communities, with governments to provide protection to Jewish communities that are vulnerable. And we need to hear expressions of support, solidarity, and truth from governments around the world: what really is happening, what the threats really are, and standing by Jewish communities as we stand by the State of Israel as it recovers from the trauma of October 7. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much Jason, for joining us. Jason Isaacson: Thank you. Always a pleasure, Manya. Take care. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episodes – listen to: Yotam Polizer , the CEO of IsraAID, on how Israel's leading international humanitarian organization is responding to the immediate and long-term needs on the ground. And Mai Gutman , a 28 year old graduate student and member of AJC's Campus Global Board, who planned to join her friends at the Supernova music festival near Israel's border with Gaza on Saturday, October 7. But when relatives came to visit, she decided to celebrate Shabbat and Simchat Torah in Jerusalem instead—a change of plans that saved her life.
Oct 12, 2023
Mai Gutman Was Supposed to Be at the Music Festival: IDF Lone Soldier Recounts Harrowing Week
Mai Gutman, 28, a graduate student and member of AJC's Campus Global Board, had planned to join her friends at the Supernova music festival near Israel's border with Gaza on Saturday, October 7. But when relatives came to visit, she decided to celebrate Shabbat and Simchat Torah in Jerusalem instead—a change of plans that saved her life. At least 260 young Israelis and people from all over the world were brutally murdered by Hamas terrorists at the festival. Mai, an IDF reservist who was just recently called up, joins us from her base to talk about waking up in Jerusalem the morning of October 7, the harrowing messages that she received from friends, and the four days since. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Mai Gutman Show Notes: Donate: AJC.org/SupportIsrael Learn: AJC.org/AttackonIsrael AJC.org/CampusBoard AJC.org/CampusLibrary Song credits: Pond5 : "Hatikvah (National Anthem Of Israel, Electric Guitar)"; Composer: Composer: Eli Sibony; ID#122561081 Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. ___ Transcript of Interview with Mai Gutman: Manya Brachear Pashman: The techno music festival near Israel's border with Gaza was billed as the essence of unity and love in a breathtaking location. At least 260 people were brutally killed by Hamas terrorists there on Saturday morning, October 7th. 28-year-old Mai Gutman was supposed to be there and had already joined the WhatsApp groups of friends and fellow concert goers to keep in touch. But she did not go. Mai, a member of AJC's Campus Global Board and a reservist who was just recently called up, joins us from her IDF base to talk about waking up in Jerusalem the morning of October 7th and the four days since. Mai, welcome. Where are you now? Mai Gutman: I live in Herzeliya. Currently, located in a place that I can't exactly disclose, but I am in the north of Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: Are you able to share what you're seeing and hearing all around you? Mai Gutman: Currently where I am I mean, we can hear the news, we can hear what's going on around us in the South as well. Even though we are stationed in the north. Today [October 11, 2023] was a pretty hectic day in terms of developments on the northern border. We had a day pretty much full of running to the bomb shelters and staying there, which indicated some sort of an escalation. I can't go into too many details, obviously. But we can feel the escalation coming and we're prepared for it. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you were born in Israel but grew up mostly in Melbourne, Australia. How did you end up back in Israel? Mai Gutman: I moved to Australia with my parents when I was only 18 months old, and I had grown up in Australia. But I had always felt a very strong connection to Israel. Something that really I couldn't put into words, I couldn't explain, it was just an inherent feeling. And when I was 18, I just decided that I'm going to go to Israel, I'm going to make Aliya and I'm going to draft into the army just because I think, you know, for me, it was important, if I'm going to live there, then I definitely need to carry the burden and be a part of society in that way and contribute. Because I find it difficult to comprehend living here, and not being a part of that very fundamental part of people's lives. It's a very crucial part of people's lives around here. And I feel like I wouldn't really be able to fit in and understand, you know, Israeli society, and also the Israeli mentality without having that experience. And I also just think that it's important, all in all, just to contribute. And that's I guess, how I got into the army. And I served for almost three years in a combat unit in search and rescue. For me, at the time, when I first drafted it was really the first years of women going into combat units. So it was a very kind of still a new idea. And I was really eager to jump on that and see how I go. Manya Brachear Pashman: So with no immediate family there, does that qualify you as a lone soldier? Mai Gutman: Yes, absolutely. So I enlisted with Garin Tzabar, which is a program that brings young adults from all around the world who want to make Aliyah and specifically to draft into the IDF, but don't have any immediate family with them. So Garin Tzabar provides that network of family and support, I guess, to deal with, first of all, all the bureaucracy that comes with moving to another country and drafting into the military. But also, you know, you get put on a kibbutz and you get given a host family, which is really nice. And it's just nice to have that initial support network because it might feel a little bit lonely when we first arrive. But now we're really like a one big family and we still keep in touch to this day, even though it was I think, 10 years ago, almost that we were all together on the kibbutz. Manya Brachear Pashman: So where were you when this escalation first began on October 7? Mai Gutman: I want to preface this by saying I was in Jerusalem on October 7, I was celebrating the chag of Simchat Torah, and the Sabbath with my family with my cousins. And also I had cousins that actually came from America, to join us in Jerusalem was a very big occasion. And that's really, I think, the only reason why I decided to come to Jerusalem and spend time with family because there was a very big music festival happening that weekend. And I was very keen initially, to go to that music festival. I had initially planned to go with my friend. And I joined, you know, the WhatsApp groups to try and find a good crew to go up with and find a means of transportation and all that. And then yeah, literally, you know, I think it was a couple of days later that my aunt had called me and she said, Hey, listen, you know, your cousins are coming. We're all going to be in Jerusalem at the same time. Like, let's, let's all do hog together, we really want you to come and be with us. And I said, Well, obviously, I mean, I'd rather be with family on such a unique occasion, I can go to a music festival any other time. So you know, I just kind of dropped those plans and ended up doing it in Jerusalem and ended up spent spending that weekend in Jerusalem, which was, I think the decision that ended up saving my life. And the morning of October 7, I had woken up to the sound of sirens, of Red Alert sirens, which is the sirens that go off when there's a rocket that's approaching an area in Israel, which was quite confusing to me. It was about 8am. And it was quite confusing to me, because in order for rocket sirens to be going off in Jerusalem, for me, I had to put quickly two and two in my head and say, well, that means that there's a lot more going on down south. So I you know, being a Sabbath day being a chag day as well in my family being, you know, Orthodox and observant of that day, we didn't have our phones at the ready. We didn't have the news on or anything like that. So I had decided to quickly jump on and see what was going on. Because obviously it was a lot more serious than what I thought. And I opened my phone and I'm reading the headlines in absolute disbelief, in shock. Terrorists had infiltrated into Israeli territory, they had massacred people on the streets, innocent civilians. They had burned houses, they'd gone into bomb shelters and literally just gunned people down. I think the most shocking part, though, was when my phone started pinging with those WhatsApp groups that I was saying earlier that I was part of a music festival. And the messages started coming through saying Help us help us You have no idea that here they're gunning us down. They're shooting at us. I'm bleeding, I'm hurt. Can someone call the police, call the army. My friend's dead. I think someone help me, someone help me. And other people are texting like you know some people went some people did it's pretty big Whatsapp group. What's going on? Who do we call? No one at the police station is answering. Nobody in the army bases are answering–why? Because terrorists had already commandeered their bases. They had murdered everyone. Almost everyone in those bases in order to get through. And they've made their way to this music festival of peace and love where people were celebrating. Young people my age, young people, my friend's age, my friends as well, who were there who came to have a good time. And you see them in this footage that they're sending through in the early hours of the morning, sending through footage of, of running of bullets, and they're dressed in their costumes, their beautiful faces made with colorful face paint. And you can see that they were just having a good time and tears streaming and screaming and running and shooting in the background. And it's like a war zone. It was like a scene from Armageddon. It looks apocalyptic. And I was just shaking, holding my phone shaking. What do I do? How do I feel helpless, I have nothing that I can do. And in the meanwhile, there are sirens going off in the background rocket rocket attacks on Jerusalem, rocket attacks down south. And you just feel like, Oh, my God. And you've just woken up just so you understand. Like you've just woken up. It's so overwhelming. Manya Brachear Pashman: Oh, Mai. I can't imagine your struggle in those moments to really distinguish between nightmare or reality. What did you do to try to make sense of things? Mai Gutman: I turned on the news. And on the news, they're saying, Oh, we think that, you know, there are rocket sirens. And we think that there might be something going on in the South that maybe terrorists have entered. We're not sure. And nothing about the music festival. The music festival, I think was only broadcasted the news about the music festival. In the late afternoon. It started being broadcasted. And I from the morning, I've already known about this, the people are literally bleeding out people are dying, as we speak while we're hiding in bomb shelters, people are dying. And and what do you do? What do you do? What do you do in that situation? You feel completely hopeless. And that is, I think, until now, the feeling that most Israeli civilians, if not all, are feeling we are feeling helpless, almost betrayed by a colossal failure on the part of the Israeli military on the part of the Israeli intelligence, that how could this happen? Without you know, we brag we say, you know, we've got the strongest military? And how could this possibly happen, with the most deaths–the most Jewish deaths to occur in a single day, since the Holocaust? Unfathomable. Manya Brachear Pashman: How has your IDF service impacted your connection to Judaism and your connection to Israel? Mai Gutman: It definitely changed me, it definitely strengthened I think, my Jewish identity and my Zionist identity. It gave me immense purpose. Also, as the granddaughter of Holocaust survivors, especially one of the largest families of Holocaust survivors, in Melbourne, that really, I think established the community in terms of, you know, our schools, our shows, our youth movements, we had a very family has a very big part to play, and I'm very privileged to be part of that family. But for me, it was, you know, to draft into the army. It's something that I felt as something of an obligation almost because I knew, and we can really take this situation as an example. But I knew that if I don't do something, if I'm not part of the solution, or the help, I guess, then we might not have a country, which means that we may have a Holocaust again. Ad we saw the effects today, of the very real existential crisis and threat that we face in Israel, along our borders. And if anything was to happen, if we let our guard down for even a second, this is the result. We don't have an alternative. We don't. We have a purpose. And my purpose, I feel everyone has a purpose, but my purpose that I genuinely feel, and I this was really strengthened in the army was when I swore allegiance to the army and to the state. I felt within myself that this is something that I won't only interpret in terms of my service and my physical military service, but I'll take with me to my grave I will do this in any capacity that I can. I work in Hasbara. It's my passion to defend the state because I just know that we have no other alternative without it, the alternative that we have is persecution, as the Jewish nation has faced for many years. And that's not an alternative we can accept. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you feel like you're at home right now? Mai Gutman: Absolutely. I feel at home. I've never felt more at home than I have in Israel. When I come to Israel, it's an immediate relief, a sense of relief in my heart. It's like something when I live abroad, or when I'm abroad, there's a constant sense of yearning, that I can never shake, doesn't matter what I try, it doesn't matter how many good people are surrounding me and my loving family, as much as I love them so much. It'll never fill that void that I have that's really only filled when I'm in Israel, and I can't explain it sounds–I don't know, spiritual, I guess, but that it is what it is. And I feel very comfortable here. Despite the chaos that's going on around us this is I know that I am where I need to be. Manya Brachear Pashman: But you're not just living in Israel. You're serving your nation, you're now defending it during one of its most dire moments in modern history. Mai Gutman: I mean, until I got called up, I was sitting on shpilkes, I couldn't even imagine like I was just what can I do, I went to go to the supermarket and I bought a bunch of like a huge carton worth of stuff, for the soldiers that were already serving that were already called up. I went to go help pack boxes, I felt so helpless, though I really was just waiting for the call. I had been on standby already from Saturday. Standby, obviously is just when your bags have to be packed, don't know when you're gonna be called. And it could be at any time, it could be never at all. So I am happy to just be part of a very strong nation, a very strong military. Despite what's happened recently, I do still believe that our nation is strong and our military is strong. And we will get through this, we will overcome this. Because as we can see, I mean, you know, this whole year, we've been crying over internal division over the judicial reforms in Israel. And it just goes to show you know, what tragedy, unfortunately, that it has to come to tragedy and to bring us together. But at the end of the day, when it comes to real stuff, when it comes to the existential threats and the the things that affect us all, it shows that we are bound together and we are strong together. And everybody doesn't matter what your religious political affiliations are. We are all in this together. And everybody's banding with us together. And it's so special to see and it's only in Israel that we can see such a special and unique form of unity. Manya Brachear Pashman: Is there anything else that you want Americans or Australians to know, people who are outside of Israel– anything that you want them to know about what's happening there? Mai Gutman: I just want you guys to know, whoever's listening here. I know that it's, it seems very, it is very hard, doesn't just seem, it's very hard. The situation is unlike anything that we've seen before. We've never experienced anything like this, especially not in, in our recent history. But I want you to know, and I know it feels difficult being so far away, because I've been there. It's difficult to report on things so far away, but your support, and your raising awareness, your hasbara, your social media engagement. It means a lot. Your thoughts and prayers mean a lot. We feel your prayers, we feel your presence with us, we feel you standing behind us and it's like a whole other army standing behind us. It might feel like you're not doing enough or you're not doing anything at all, really. But honestly, it's more than what you think, it's more than what you believe. So just stand by us. And don't give up hope because we certainly aren't. And we can't, we don't have that luxury of giving up hope. Our entire nation is built on hope. And that's where our resilience comes from. So be strong. We will win this, we will get through this. By hook or by crook. We'll make it through as long as we all stick together as long as we make sure that we count what's important. We remember what's important, who's important to us, hug your loved ones. Because currently there are so many there are over 1300 families around Israel that are currently grieving and mourning and they don't get that opportunity. So make sure to tell your parents you love them. Tell your kids you love them, your sisters, your brothers, your aunts, your uncles, your cousins, your friends, because not everybody has that luxury. And, and yeah, we'll do what we can over here so you do what you can over there. Manya Brachear Pashman: Mai, thank you so much. Stay safe. Thank you for your service, and we will certainly be praying for you. Mai Gutman: Thank you.Manya Brachear Pashman: American Jewish Committee's Israel Emergency Campaign has already raised more than $1.5 million. Funds that have already gone to Israeli hospitals, efforts to evacuate the elderly, NGOs such as IsraAID, providing support for children, and friends of the Israel Defense Forces. If you would like to donate, go to AJC.org/support Israel.
Oct 10, 2023
Responding to Hamas Terror: IsraAID CEO on How You Can Help Israelis Right Now
We're joined by Yotam Politzer, CEO of IsraAID, to discuss how Israel's leading international humanitarian organization is responding to the immediate and long-term needs on the ground in the wake of Iran-backed Hamas's barbaric terrorist attack in Israel. Politzer shares how American Jews can step up to support Israelis through this incredibly difficult time. American Jewish Committee (AJC) has launched an Israel Emergency Campaign to support Israeli relief organizations. Their first grantee will be IsraAID, AJC's longtime partner, which has responded to emergencies worldwide, but never before in Israel. Until now. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Yotam Politzer Show Notes: Donate: AJC.org/SupportIsrael Learn: AJC.org/AttackonIsrael Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. ___ Transcript of Interview with Yotam Politzer: Manya Brachear Pashman: On the morning of October 7th, Hamas, the terror group governing Gaza and backed by Iran's regime, launched a brutal assault against Israel, invading towns and cities across the southern border aiming to kill as many people as possible and taking more than 100 captives to Gaza. By the time of this recording, the death toll had reached 900. Thousands more are wounded. In response to this atrocity, American Jewish Committee has launched an Israel Emergency Campaign to support Israeli relief organizations. The first recipient money raised will be AJC's longtime partner IsraAID, which has responded to emergencies in more than 50 countries around the world, but never before in Israel– until now. Yotam Polizer, CEO Of IsraAID, joined us in Tel Aviv earlier this summer. He is joining us again now from New York, where he was visiting when the war broke out. While Yotam is unable to return home at the moment due to lack of flights to Israel, he is working hard to coordinate emergency response from here and is with us to discuss the efforts underway. Yotam, welcome back to People of the Pod. Yotam Politzer: Thanks for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: It must be so difficult not to be there with your team. Yotam Politzer: Thankfully, our headquarters and our emergency response team is already in full speed. So I think it's also important for me to be here for two reasons, one, to coordinate the support, and not less importantly, to communicate to people here, both in the Jewish community and in the general community, what we're seeing and hearing in terms of the humanitarian needs on the ground. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what are you hearing from your people on the ground there? What are they reporting? Yotam Politzer: I don't think I need to elaborate on the horrors because I think we've all been following the news and saw all the horrific images. But for us, as Israel's leading international humanitarian organization, we have never had a full-scale humanitarian response in Israel. This is the first time we're actually doing it. And we're doing it because the situation is indeed dire and extreme. The biggest need that we identify right now is related to mental health. And because, of course, we are not a humanitarian organization, we're not involved in the security and the military operation. And of course, there are many needs related to the operation that's going on. From a humanitarian perspective, the whole country is traumatized. I don't know of a single person who doesn't know anyone who either was murdered or kidnapped or both. And the number of people who have an immediate family member, or neighbor, who was murdered, or unaccounted for and probably kidnapped by Hamas is so high, talking about hundreds of 1000s of people. Specifically, what we consider the most vulnerable are obviously the people who lived on the frontline, the villages, the moshavim, and the kibbutzim surrounding Gaza. They have lost on average 10-20% of their population in each of these villages. In Kibbutz Be'eri, just an hour ago, it was published that they found 108 bodies– that's probably much more than 10% of the population there. And many more again, are kidnapped. So these communities who suffered the worst atrocities a person could think of are now in different shelters around the country. So supporting them in these shelters in any shape or form is the most important humanitarian mission of our time. Many of them have been evacuated specifically from this kibbutz to the Dead Sea, to the Dead Sea hotels, because it's one of the safest places in Israel. If God forbid, we will have another frontline on the north border, that's still safe enough for these people. And these hotels are now operating as shelters and evacuation centers. And the government and the local regional council and the hotel owners are currently providing the food and shelter. So there are less needs on that front. But again, when it comes to mental health support for everyone there, this is crucial. So that's what our team has been focusing on. Manya Brachear Pashman: You're also operating what are called Child Safe Spaces, which you describe as "a place for the kids to be kids." Tell us more about that. Yotam Politzer: We can't imagine what these kids went through. And we just want to give them some sense of normalcy. And let them be kids again, and let them play and let them express themselves and let them release their stress and allow their parents or whoever is left from their families a chance to finally maybe get some sleep, try to reorganize, regroup and deal with everything else that they need to deal with. Try to, you know, start thinking about rebuilding their life after these horrors, which again, will obviously take years. So when we look at the humanitarian needs, I think we need to look at the immediate needs. But even more important, we need to understand that there will be long term needs for these people, and for everyone that is related to them. And so as IsraAID it's very important for us to be first on the ground, wherever it is, in Israel, or in anywhere else in the world. In fact, our team who was responding to the earthquake in Morocco, is now on its way back to Israel to join our team that's already responding in Israel. So that's in short. Manya Brachear Pashman: In fact, some of the services that you are describing, I believe, you described to me when we spoke earlier this summer, regarding the war in Ukraine, right, many of these similar services were provided there as well, as well as other places around the world. Can you elaborate a little bit about where else around the world you have offered the same services that you're now offering everywhere? Yotam Politzer: I mean, I started my humanitarian career in Japan, again, another developed country, following the earthquake and tsunami in 2011, that killed more than 20,000 people. And they're there, the local government, the local community was very well equipped to support with infrastructure, but they didn't have any kind of emotional mental health support and trauma care. So we actually brought therapists from Sderot, who was working with children who are traumatized in Sderot and develop these models. We brought them to Japan, and we worked with the Syrian refugees with Arabic speaking therapist from Israel. We worked we work in Ukraine in partnership with the First Lady doing mental health and trauma and resilience. And, now we're in Israel. And yes, there are many great professionals doing that in Israel, but many of them were affected. And the level of trauma is so big, that we have to do it in Israel, too. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what can people here do Yotam? How can they help? Because there's certainly a feeling of helplessness as we watch these images from abroad. Yotam Politzer: Yeah and I totally understand and I think being in a position of doing is very important. Look, I think the two main things to do right now, from here from the other side of the world, which is what I'm trying to do as well, while I'm here, is supporting initiatives like IsraAID, like many other organizations who are responding, and they are great organizations, from Magen David Adom, MDA, that people know, and United Hatzalah, and many are focusing on medical services, some of the hospitals, which is very important. The other thing, which is very, very important, and I think each and every one of us can do, even if we don't have the financial resources, is to be ambassadors for the people of Israel. And we need it more than ever. And it means to do it in the Jewish community, outside the Jewish community, on social media, in synagogues, in schools, in the supermarket, everywhere, there are so many ways to become ambassadors for Israel. And this is something we can all do using our phone. And, and it's very, very important. And for the people of Israel, and especially the people who are worst affected. There's so much anger, so much frustration, so much fear, and anxiety. And showing our solidarity, in every shape or form, has a huge mental health impact on Israel. I mean, these pictures of cities, the Eiffel Tower or the Brandenburg Gate. In Kyiv. More than 20 places were displaying the Israeli flag as solidarity. I saw it shared so widely in Israel. I mean, knowing hat we have friends. And a lot of them have a huge impact, not only on the Hasbara, and advocacy, which is important, I'm not against it, but also for the mental health and well being of the people of Israel. So it's very, very important. What is less helpful at the moment, I'm not against it in general. I don't think we need to send supplies from here to Israel. I know a lot of people want to send supplies, but we can purchase supplies in Israel and support the local economy. And there's also a lot of donations going on or so I think that's less helpful. In terms of volunteers, people who want to go from here to volunteer in Israel, that may be needed in the long run. At this very specific moment. I don't think that's a big need. I think supporting organizations on the ground is more important. If you only have limited resources, rather than paying on a very expensive flight, that may or may not go, I think it's important to support organizations who are on the ground and are based there. But it may be needed in the near future, especially as this become a more long term operation. And then we will need people with specific skills and expertise. Manya Brachear Pashman: In terms of the response, what are you seeing that is giving you hope? What are you seeing that is discouraging? Yotam Politzer: I see a lot of things that are reassuring. I see the tremendous support we're getting from many, so many. Not all of them are our typical friends. And, you know, whether it's mainstream media or political leaders, political leaders. I also see some people who are not supporting or trying to paint it, you know, try to be diplomatic on both sides. I don't think at the moment that that makes any sense, to be honest. So that is disturbing. But I also don't hear enough focus on humanitarian needs. I mean, again, I'm not I think the political consequences, the security and safety are very important, but the people there and how to help them and what their needs are, are not being highlighted enough. Because maybe it's less sexy in the news, I mean, we do hear a lot of horror stories, but the people who are alive and survived and lost their loved ones and went through the worst trauma a person could think of are not being highlighted. Also the incredible story of resilience and heroism from so many people. I have seen some of these in the Israeli media, but not enough in the foreign media and not enough on social media here. So I also think we need to celebrate the resilience of the people there that have been the most resilient people before this crisis. But considering what they're going through, we need to celebrate these people, these heroes, these communities, we need to support them in whatever way we can, we need to be there for them. We need to so I don't see enough of that. Manya Brachear Pashman: Is there a particular story that comes to mind that you would like to share with our listeners of such heroism? Yotam Politzer: There are so many actually, but personally, again, and I've been following this news of so many. So many actually, not one person, hundreds of people who were you know, pulled out their sleeves and went in and pulled out people under fire. And these are people who are not in active duty. And they went in and risked their lives in these first 24 hours and pulled out people and some of them lost their lives who are doing that. I was also very touched by stories of Arab nurses and doctors who came in at even higher percentage than they are, to volunteer and to support in the hospitals. I just heard a story of this woman who was not young. But when terrorists came into her house she was so resilient, and she was able to offer – she was so smart and sharp and resilient. And she was able to offer the Hamas terrorist cookies. And to set them down until her rescuers actually came and were able to rescue her. So you know, it's unbelievable. Among the horrors, there are so many of these heroism and resilience stories and I think we should talk about them more. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yotam, thank you to IsraAID for all you're doing on the ground. AJC has been so proud to call you a partner and is so grateful that we can rely on you to help us channel our heartbreak, constructively. Yotam Politzer: Thank you so much, first of all, and we're so grateful for AJC. For everything we do together, especially now. AJC has supported us in more than 20 countries. So we have never imagined that we will need AJC to support us in Israel. But here we are. So that's number one. Number two, I do think that myself and all of us here in this part of the world have an important role to play to be the voice for the voiceless and to bring more support. Thank you very much. Manya Brachear Pashman: In less than 24 hours, AJC's Israel Emergency Campaign has raised more than one million dollars. 100 percent of which will be distributed to hospitals, trauma centers, and frontline Israeli NGOs starting with IsraAID. If you would like to donate, go to AJC.org/supportisrael.
Oct 6, 2023
Remembering Pittsburgh Part 1: Behind the Scenes at the Reimagined Tree of Life
This month, we mark the five-year anniversary of the Pittsburgh Synagogue Shooting at the Tree of Life. On October 27, 2018, 11 worshipers were murdered solely for being Jewish, in the deadliest antisemitic attack in U.S. history. As the first installment in a four-part series, we take you inside the Tree of Life building before it is demolished in the coming months to make way for a new complex dedicated to Jewish life and combating antisemitism. Hear from Carole Zawatsky, the CEO behind the reimagined Tree of Life, and Eric Lidji, director of the Rauh Jewish Archive, as they explain their mission: to preserve artifacts and memories so that the story is preserved forever. Carole shares her commitment to honoring the victims, and Eric discusses the challenges of documenting an ongoing tragedy. Together, they emphasize the power of bearing witness to history and the healing strength of remembrance. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Eric Lidji, Carole Zawatsky Show Notes: Music credits: Relent by Kevin MacLeod (incompetech.com), Licensed under Creative Commons: By Attribution 3.0 Virtual Violin Virtuoso by techtheist is licensed under a Attribution 4.0 International License Fire Tree (Violin Version) by Axletree is licensed under a Attribution 4.0 International License. Al Kol Eleh (backing track), with Yisrael Lutnick Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've appreciated this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, and rate and review us on Apple Podcasts. Episode Transcript: Eric Lidji: Pittsburgh definitely is not forgetting. It's ever present here. There are people who are healing and doing so in ways that, at least from the outside, are remarkable and very inspiring. And there are people who I'm sure have not fully reckoned with it yet. Carole Zawatsky: It's all too easy to walk away from what's ugly. And we have to remember. We can't walk away. Manya Brachear Pashman: Five years have gone by since the horrific Shabbat morning at Pittsburgh's Tree of Life Synagogue, when eleven congregants were gunned down during prayer – volunteers, scholars, neighbors, doing what they always did: joining their Jewish community at shul. This is the first installment of a series of episodes throughout the month of October devoted to remembering and honoring the lives lost that day and reflecting on how the deadliest antisemitic attack in American history changed those families, changed us, and changed our country. Today, we take you to the Tree of Life building that stands on the corner of Shady and Wilkins Avenues in Pittsburgh's Squirrel Hill neighborhood to hear from two people in charge of preserving the artifacts and memories of the vibrant Jewish life that unfolded inside those walls until October 27, 2018. In early September, our producer Atara Lakritz and I visited the Tree of Life synagogue in Pittsburgh's Squirrel Hill neighborhood. Squirrel Hill, where Jews have settled since the 1920s, is quite literally Mister Rogers' neighborhood. We were there to interview those touched by the events of October 27. But it didn't take us long to figure out that everyone there had been affected in some way. All along Murray Avenue, in 61C Cafe, at Pinsker's Judaica Shoppe, at the Giant Eagle supermarket, when we told people why we were there, they all had a story, an acquaintance, a connection. Later, walking through the glass doors of the synagogue felt like we were stepping through a portal, traveling back five years, when life stopped, and the reality of the hatred and terror that unfolded there began to haunt every step. Atara and I were invited to accompany a final group tour of the building before it closed in order for preparations to begin for the building's demolition. The tour was painful, but we felt it necessary to share with our listeners. As we left the lobby, we were told to take the stairs to the left. The stairs to the right were off limits. Someone had been shot there. We were led to a small, dark storage room where chairs had been stacked for guests. A handful of people had hidden there as the shooter continued his rampage, but one man walked out too soon, thinking it was safe. When first responders later came to get the others, they had to step over his body. In the kitchen, there were still marks on the wall where the bullets ricocheted when he shot two women hiding underneath a metal cabinet. The calendar on the wall there was still turned to October 2018 with a list of activities that were happening that week posted alongside it. And in the Pervin Chapel where seven people died, pews punctured with bullet holes and carpet squares stained with blood were no longer there. No ark either. But remarkably, the stained glass windows remained with images and symbols of Jewish contributions to America, the land to which the ancestors of so many worshipers once inside that synagogue had fled to and found safety. Those windows will be carefully removed by the son of the man who first installed them 70 years ago. And they will return, when the reimagined Tree of Life rises again. Carole Zawatsky: The tragedy is a Pittsburgh experience. But it's also every Jew's experience. It shattered for so many of us our sense of security in America. This is our safe haven. This is where we came to. Manya Brachear Pashman: Carole Zawatsky is the inaugural CEO of the reimagined Tree of Life. Since November 2022, she has overseen the development of a new complex on the hallowed ground: an education center dedicated to ending antisemitism, including a new home for the Holocaust Center of Pittsburgh; a memorial to the lives lost that Shabbat morning; a dedicated synagogue space where the Tree of Life congregation can return. Carole Zawatsky: What can we build to enrich Jewish life, to remember this tragedy, and to show the world that we as Jews should not be known only by our killers and our haters, we should be known by our joy, our celebrations, our rituals, our resilience. Manya Brachear Pashman: The founding director of the Maltz Museum in northeast Ohio, Carole has spent the last 30 years developing programs and education around the Holocaust and genocide, and overseeing projects that explore Jewish heritage from a national perspective and through a local lens. She led our tour. On October 27, 2018, the congregations of Tree of Life, New Light, and Dor Hadash, which all met in separate areas of the large, multi-story building, had just ushered in the new Hebrew year of 5779. Young students at the Hebrew school had written their own personal Ten Commandments that the teachers had hung on the walls of an upstairs classroom. Carole Zawatsky: Don't egg your neighbor's house, respect your parent. Every one of them said: Thou shalt not murder. Thou shalt not kill. And those 10 commandments that they wrote in their little student handwriting were thumbtacked up on the wall in the very classroom where the gunman was apprehended. Manya Brachear Pashman: Before the rebuilding of Tree of Life begins, Carole's no. 1 priority has been preserving the artifacts and remnants that bear witness to what happened. Artifacts include the ark, damaged by bullets, the Torah scrolls, which were remarkably unscathed but for the handles. The list of whose Yahrzeits fell on that day, still on the podium; and, of course, the children's artwork and the wall behind it. Carole Zawatsky: In the work happening here, and in my role as the CEO, I constantly ask: 'Am I doing it right? Am I doing enough?' And preserving the evidentiary material was incredibly important to me, that we have the physical evidence to bear witness. And as that drywall in the classroom in which the gunman, the murderer, was apprehended, was coming down, I found myself asking: 'Have I saved enough? Will this story be preserved forever? Have we done everything we can?' Manya Brachear Pashman: Helping Carole with this Herculean effort, is Eric Lidji, the director of the Rauh Jewish Archive at the Senator John Heinz History Center, an affiliate of the Smithsonian Museum, in downtown Pittsburgh. Eric has been collecting documentation and evidence for the archive since October 28 , 2018. Painted stones left in memory of the victims, hand-made signs, pamphlets, and prayers from vigils, sermons from interfaith services. But also a pair of tennis shoes, a guitar, a framed leaf from the Raoul Wallenberg Tree planted in Israel, a cross affixed with Stars of David -- all individual expressions of a community-wide anguish. Eric Lidji: Even before I entered the building, we knew that there were going to be pieces of the building that had historic value. Since late 2018, I've been in the building numerous times, dozens of times, doing work there. And it sort of culminated in this opportunity in early June, where we were allowed to go in and identify pieces of the building that became historic that day, and figure out how to get them out. Manya Brachear Pashman: This is no simple job for anyone involved, no less for Eric, who is accustomed to handling archival materials from generations past, not the present. Eric Lidji: It's hard for me to disentangle the work of pulling these things out of the building with the knowledge that these families that I've come to know and love, that this is sort of directly related to their loved ones passing. Pittsburgh definitely is not forgetting, it's ever present here. There are people who are healing and doing so in ways that, at least from the outside, are remarkable and very inspiring. And there are people who, I'm sure, have not fully reckoned with it yet. The stories that we're used to telling at the archive, they move much slower. You know, when you get records from 75 or 100 years ago, that's in motion too, but it's moving very slowly. And you can kind of sit there and watch it, and understand it. And get some sense of what it might mean. But when you're living through something, it's changing constantly, all around you. And it's responding to things in the world. And it's responding to people's internal resilience and their ability to grow. When I look out at the community, I see a lot of different stories. People are in a lot of different places. And it's going to be different on a month like this, where we're saying Yizkor. And it's going to be different in the early stages of the trial versus the late stages of the trial. It's assimilated into our lives now, it's a part of our lives. Manya Brachear Pashman: In 2019, Eric and journalist Beth Kissileff assembled an anthology of raw reflections by local writers about the Tree of Life massacre. It included only one essay by someone inside the building that day: Beth's husband, Rabbi Jonathan Perlman of New Light. Eric also contributed his own essay. He wrote: "I have no special insight into why this attack happened, or why it happened here. I don't know what would have prevented it from happening here or what would prevent it from happening again somewhere else. I don't understand the depth of my sorrow or the vast sorrow of others. I asked him if four years later he would still write those words. Eric Lidji: I feel the same way. You know, there's a second half to that paragraph, which is that, I do have the materials and I can describe those . The premise of an archive is that at some point, we'll all be gone. And when we're all gone, our things are what speak for us. And at the moment, there's a lot of witnesses here, emotional witnesses, I mean, who can testify to what this means. But there's going to come a time where they won't be there. And our job, I say our, I mean everybody's, our job in the present is to document our experience. So that when we're not here anymore, people in the future have the opportunity to have access to the intensity of the feelings that we had. That ultimately is how you prevent complacency. And so I don't claim any, I don't understand anything in the present. But I do understand the records. And I hope that we're being a good steward and custodian of them so that in the future, people have the opportunity to have access to real human feeling and so that they can really understand what this experience was like for people who were alive today. Manya Brachear Pashman: The Rauh Jewish Archive has collected and preserved thousands of artifacts and documents, but no physical or intellectual access has been granted yet. Cautious care has been taken to make sure families and survivors are ready and know what's involved in making the materials available to the public. Once that happens, a trove of electronic materials will be uploaded to the newly launched October 27 Archive, which will become the public face of the collection. The electronic catalog will help individuals, schools, and institutions such as Tree of Life to tell the story they're trying to tell. Carole Zawatsky: We're the only generation to bear witness to this. The next generation will not bear witness. Their children will not bear witness. We have a moral obligation to ensure that these lives are remembered and memorialized, and that we as Jews and as citizens of this earth remember what hate looks like and work toward a better world. It's all too easy to walk away from what's ugly. And we have to remember. We can't walk away. Manya Brachear Pashman: The Tree of Life building is now a shell of what it once was. The stained glass windows will soon be removed for safekeeping until the new building is ready to welcome them back. As the demolition crews arrive to remove what's left, Carole's focus has shifted. Carole Zawatsky: Our focus now is truly on working with our architect, working with the exhibition designer, and forming a new institution. This is an incredibly special moment for us, as we come together and continue to crystallize our mission, our vision, and form this new institution that will be a significant part of the Pittsburgh community, along with the national community. Manya Brachear Pashman: The architect for the project, Daniel Libeskind, a son of Holocaust survivors who is renowned for his redesign of the new World Trade Center site, has described the spiritual center of the Tree of Life as a Path of Light, which connects and organizes the public, educational, and celebratory spaces. Carole Zawatsky: We can never as Jews allow ourselves to be defined by our killers. And I'm delighted to be working with Daniel as our architect and his concept of bringing light into the darkness. Vayehi or, let there be light. We have to bring light back to the corner of Shady and Wilkins. And side by side with tragedy, as we have done throughout all of Jewish history, is also celebration. To have baby namings and B'nai Mitzvot. Celebrate Shabbat and celebrate holidays side by side. That this is the most Jewish thing we can do. When the temples were destroyed in Jerusalem, what did we do? We recreate. And that is the strength and resilience of the Jewish people. Manya Brachear Pashman: Carole also continues to build a multifaith donor base, comprised of foundations and individuals from Pittsburgh and across the country, to raise the $75 million needed to make the reimagination a reality, ideally by 2025. The reasons why donors give vary, but in most cases they're deeply personal. Carole Zawatsky: The events of 10/27 are personal for everyone. For those people who tell us: I heard the gunshots from my kitchen. I was with my children. From people across the country who experienced a sense of loss of safety. To non-Jews who say: I have to have something to tell my children why some people don't like their friends. What did I do? How did I help be a part of the solution? Manya Brachear Pashman: For generations, the Jewish people have confronted antisemitism in its many forms. But through it all, the Jewish calendar continues to guide the community through celebrations of life and beauty and wonder. Carole describes it as the bitter and the sweet. Carole Zawatsky: I've had on occasion, a Rabbi, a funder: 'How are you doing? How do you get through this?' And for me, there's often a soundtrack in my head. And one of my favorite Hebrew songs is "Al Kol Eleh," and through the bitter and the sweet. To me, it is the definition of Judaism. And it's the definition of what we're doing. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you mind sharing a bit of that song with us now? Carole Zawatsky: Al hadvash ve'al ha'okets Al hamar vehamatok Al biteynu hatinoket shmor eyli hatov Al kol eleh, al kol eleh. Manya Brachear Pashman: This podcast is dedicated to the 11 lives lost on October 27, 2018: Joyce Fienberg, Richard Gottfried, Rose Mallinger, Jerry Rabinowitz, Cecil Rosenthal, David Rosenthal, Bernice Simon, Sylvan Simon, Daniel Stein, Melvin Wax, Irving Younger. May their memories be for a blessing.
Sep 28, 2023
What Jewish Students at Penn Want You to Know About Antisemitism and the Palestine Writes Event
All eyes have been on the University of Pennsylvania and the Palestine Writes event, a gathering meant to give voice to Palestinian art, poetry, and literature on campus. However, a number of the speakers, including Roger Waters and Marc Lamont Hill, have well-documented histories of antisemitic statements. Maya Harpaz, Vice President of Israel Engagement at Penn Hillel, and Jonah Miller, a reporter for The Daily Pennsylvanian, take you through what unfolded, growing campus antisemitism, defining free speech on campus, and the responsibility of university administrators to protect Jewish students. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Maya Harpaz, Jonah Miller Show Notes: Watch: Live from Penn: Maya Harpaz of Penn Hillel on Palestine Writes Read: Everything you need to know about the Palestine Writes event at Penn and antisemitism. AJC Campus Library: Resources for Becoming a Strong Jewish Student Advocate Listen: What the UN Needs To Do To Stop Iranian and Russian Aggression Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Maya Harpaz and Jonah Miller: Manya Brachear Pashman: Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman, AJC's Senior Director of the Alexander Young Leadership Department, guest hosts this week's conversation with two Jewish college students about a situation on their campus and how they responded. Meggie, take it away. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Thanks, Manya. This past week, it seemed like all eyes were on the University of Pennsylvania in the lead up to the Palestine Writes event. The event was meant to give voice to Palestinian art, poetry, and literature- all of which are quite appropriate and indeed valuable to have on a university campus. However, a number of the announced speakers strayed from the event's purpose and instead have well-documented histories of antisemitic statements. These include Roger Waters, who was recently described by the U.S. State Department as having a long track record of using antisemitic tropes, after he desecrated the memory of Holocaust victim Anne Frank, compared Israel to the Third Reich, and recently paraded around a stage wearing an SS Nazi uniform during a concert in Berlin. It also included Marc Lamont Hill, whose public remarks as a CNN commentator called for Israel's eradication. At play were questions around growing campus antisemitism, free speech on campus, and the role of university administrators in preventing such bigotry–particularly with the release in May of the U.S. National Strategy to Counter Antisemitism, and its outsized focus on how antisemitism affects Jewish students on campus. To help us break down these events and what unfolded are two Jewish students who experienced this all firsthand and helped drive the course of events. Joining me are Maya Harpaz, a junior at Penn, and Vice President of Israel Engagement at Penn Hillel, and Jonah Miller, a junior at Penn, and a reporter for The Daily Pennsylvanian, Penn's student newspaper. Maya and Jonah, thanks for joining us on People of the Pod. Jonah Miller: Thank you so much for having me. I'm really looking forward to our discussion. Maya Harpaz: Yeah, thank you for having us. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Great. So with that, let's jump in. So there are many chapters to what happened at Penn, and I think a great deal of misinformation. So let's go back to the beginning. When did Jewish students first hear about the Palestine Writes event, and particularly its speaker lineup? And upon initially learning about it, what were the specific concerns that Jewish students had? Jonah Miller: I think that when I learned about the Palestine Writes event, I learned about it simultaneously with who some of these speakers are. Penn is a large university and institution that has countless events each day, hosted and co-sponsored by numerous different departments and facets of the university. If I had learned about this festival, solely, just about the festival, I would say, you know, great, it's great that this culture, and these literary items are being amplified on campus. Everyone and every culture should have a space on this campus. But to learn about at the same time as concerns of antisemitic speakers, that's when I as a Jewish student, started to get a little nervous. Nervous, because how could Penn allow antisemitic speakers to come speak on a campus that is close to 20% Jewish? And even without that high percentage, how could they be invited to speak at all? Maya Harpaz: Yeah, I can touch on that as well. In my role as VP Israel, a big part of that is seeing what events are going on, whether it be related to the Middle East at large, Israel, Palestinians, all of that combined. So I learned about this event A while ago, late July, early August. So before it was really even being spoken about on campus. I was having conversations as the speakers were still being finalized, as marketing materials were still being put out and discussed with a lot of the other student leaders and Hillel staff, about what our approach was going to be to handle this event. And how we were going to relay that to the Jewish community at large. So similar to what Jonah said, Jewish students definitely learned about the event and the problematic speakers hand in hand after Hillel started sending out emails about it. And after we sent our letter to the administration and after the DP coverage. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: So Maya, I want to dive into that approach in the letter that you just raised. At least from the outside, one of the first steps seemed to be a letter drafted by Penn's Jewish student leadership to President Magill, of which you were a signatory, outlining specific steps the community wanted the university to take on. So can you give us some background of how that letter came into being and can you share for our listeners what it outlined for the administration? Maya Harpaz: Yes, so this letter came to be sort of as we were having these conversations over the summer. And then once we got to campus, we all sat down with the presidents of PIPAC, SSI, Tamid, presidents of Chabad. And we sort of sat down and we were like, we know why these speakers and why this event could be problematic for our community. How do we outline that to the administration in a way that is logical and not also attacking of another group's culture. Because that's not what we wanted to do. It wasn't our goal to get this event canceled, it wasn't to blow it up in their faces. It was really just, we have specific concerns, and how do we articulate that? So we wrote this letter addressed to the president, the provost, and the dean, and sent it to high-level members of the President's administration, specifically referencing Roger Waters and Marc Lamont Hill. And we asked them to have a meeting with us so we could really sit down and have a conversation, and to make a statement about this event. And from my perspective, it was definitely a productive meeting, we voiced our concerns about the speakers, we asked them a lot of questions about what was the process of this event being welcomed on our campus, and they explained how they rented out the space and the head of the NELC department explained the process of co-sponsoring, and we really had an open dialogue about what really happened and how we can improve on that in the future. And then shortly after that, the President released her statement about the event. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: So Maya, I want to dive into a number of things that you just got at. So one is, and you alluded to this, the letter specifically did not call for the canceling of the event. And from my understanding, that's not something that Hillel was asking for. Can you talk about why that is? Maya Harpaz: Yes. So as Jonah also said, when you learn about just the event as the Palestine Writes Literature Festival, it sounds perfectly normal. Sounds like it's just a group wanting to celebrate their culture and their literature. And our goal was not to cancel that. There was over I think, 120 speakers. And our goal was to call out the ones that were problematic towards our community, not cancel their right to speak, their right to celebrate. I'm a big believer in free speech. And I didn't want to ask anyone to cancel something. I know that, I'm sure that we at Hillel and Chabad have events with proud Zionists that have maybe done questionable things or said questionable things in the past too, that maybe even some of our own Jewish students don't agree with. But Roger Waters definitely crossed the line for us. And we ended up asking for him to be uninvited and even though he was on Zoom, we were definitely very, very concerned about that, because it definitely crossed the line of our threshold of comfortableness in terms of hate speech, but it wasn't our goal to get this event canceled. And we knew it wasn't a reasonable ask either. It was a huge event that's been in the planning and in the works for a year. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: And then I want to touch on kind of the tail end of what you just described. So what did come out of that initial letter is President Magill, and her administration, indeed issued an initial statement following that letter, following what you had articulated. And that statement did have a clear condemnation of antisemitism, but it left some unsatisfied with what may not have been in there. So I'm curious from both of you, what was your interpretation of that initial statement? And can you describe what came next, particularly as the national attention started to build around Penn? Jonah Miller: Yeah, I can take this one. So in President Magill's letter, she described antisemitism as antithetical to the values of the University of Pennsylvania, which as a Jewish student was very comforting, reassuring to hear that the president of our university is very clearly against antisemitism. At the same time, she also explained how this is an event that is not being promoted or organized by the university. And at the same time, she also wrote how the university supports the notion of free speech and the free exchange of ideas. So I think what you're getting at is that, definitely a condemnation of antisemitism, which is a win. But at the same time, it doesn't really seem like there was much action that was going to be taken from the letter. It was more an acknowledgement that the Jewish voices on campus who have concerns with, as Maya said, a few of the many speakers of this festival, were being recognized, but they were not being acted upon. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: So Jonah, I mentioned at the start that you are a reporter for The Daily Pennsylvanian. So from a different lens, shortly before Shabbat and Yom Kippur, it was reported that a member of the Penn community entered Penn Hillel and in essence somewhat ransacked the lobby while also screaming antisemitic vitriol. So Jonah, can you share, first of all what we know about that, and also what it was like reporting on something that so directly affected your community? Jonah Miller: That's a great question. So in order to walk you through this timeline–to my knowledge, this is still under a form of investigation by the university, and we'll see what comes out in the next few days or weeks. But in terms of the timeline: so last Thursday morning, The Daily Pennsylvanian received information that an individual entered Penn Hillel, so all of a sudden our journalistic gears start turning, and we wanted to reach out to as many sources that have some relation to Penn Hillel, which for those of you listening is kind of the epicenter of Jewish life and culture on Penn's campus. So from what we understand now, an individual entered Penn Hillel, as someone was opening the door for early morning services, a member of the Orthodox community at Penn. Entered in to Penn Hillel a few minutes before the building officially opened for the day at 7am. So there was no security guard posted, to my knowledge. And entered the lobby, smashed a podium, flipped over a table, all while reportedly shouting antisemitic speech. So that's kind of what we understand was happening. And in terms of how it affected me, as someone who was writing it, I was really passionate and driven to make sure we have the full story. And I think as a journalist, or as an aspiring journalist, it's really important. But at the same time, as someone who I know, people from my community on campus, chances are people from my family or the extended Jewish community, in the Philadelphia area, and across the country might be reading something like this. It was really important to make sure that we had all the facts as strong and robust as possible. But at the same time, it was hard typing those words, it was hard typing how someone entered a place that I like to call a home, for me and for the rest of my Jewish community here on campus. So kind of finding that balance was definitely difficult. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: I can only imagine. And I want to turn to I guess to yet another lens, again with your journalistic hat on. Roger Waters, who Maya alluded to earlier, has a long history and well documented history of antisemitic speech, has, in recent days, basically lashed out at the paper and its coverage. I'm curious what your thoughts are about that and how that is being received by the paper. Jonah Miller: I think that, as campus journalists, it's our duty to be non biased as much as we can. And like I said, really just stick to the facts. We wrote how Penn Hillel was entered by some individual and he was yelling antisemitic speech in a clear and vivid example and trend of rising antisemitism, without a doubt. Roger Waters took this, he actually, I know the video that you're talking about, he said that he was on his way to Penn State, which first of all is not the university that we attend. But he said that he was on his way to Penn State for the Palestine Writes Festival and how the Daily Pennsylvanian commented on his history of antisemitism. But like you said, this is well documented, this is not something that we pulled out of thin air and labeled him as having a history of antisemitism. It's there, it's online, for everyone to see. And it's unambiguous. So for him to lash out at student journalists, you know, all students who are trying to do their best and maintain this journalistic integrity and share facts with our campus community members. For him to lash out at us, it's disappointing, but at the same time, we don't want to respond and kind of promote this behavior of his in any way. Maya Harpaz: And something else I'll just add is, he also mentioned in that video that he came to Philadelphia ready to speak, and then was just informed that he couldn't come to campus and posed this whole idea that Penn isn't allowing him to come on campus. And this just happened. And he came all the way here and he's ready to be here. And he wants to show his support for the Palestinian community. But as I mentioned, I've been following this event since over the summer. And I think Penn also commented this in a new article in the DP, that he was never speaking in person, it was always planned that he was going to speak on Zoom. So for him now to twist the facts and frame it as our school is his canceling him just as he arrives to speak here was definitely very misleading. Because it was never the intention of the university to have him come in person on our campus due to his extensive history of antisemitism. And he ended up coming onto our campus and rolling his window down, as I'm sure many people saw on the video, to actually articulate to participants of the conference that Penn isn't allowing him to speak. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: So I want to try and turn to something more positive, which really stems from both of you. I think, to me, what really was so inspiring to see is that instead of simply focusing on the pain, and there was tremendous pain that this caused, Jewish student leaders took a completely different path, rooted in celebrating the vibrancy and the pride of the Jewish community. And this led to the creation of Penn Unity Shabbat, which our own CEO, AJC's CEO Ted Deutch attended in solidarity. How did that come into being? And importantly, what was the feeling like in the room on Friday night? Maya Harpaz: Yeah, so this was sort of in the works from that initial meeting we had, at the beginning of the semester, when we were talking about how we want to respond to this, it was definitely always an idea that we want to have a big gathering. It's right before Yom Kippur, it's right before a very holy weekend for us. Regardless of what's going on on campus, it's important for us to feel that togetherness, and definitely because of that event, even more so. So it's been in the works for a bit and then sort of as media attention progressed on the Palestine Writes event, and as we were getting more inquiries from people about what was going on, it became really clear that this needed to be a big event and it had to go beyond just our campus community. We needed to invite leaders like Ted Deutch and leaders from Hillel International to really come and join us and to speak with them and to have their support. And the actual feeling of being in there was really awesome. I've never seen Hillel so packed before. The entire building was full, the first floor and all the rooms on the second floor. I've never seen so many people there. So it was really special. Jonah Miller: To add on, from the perspective of someone who did not have a hand in planning it, but was a proud attendee of this event, you could really feel, like you said, the vibrancy in the room and the energy where you know, in between Rosh Hashanah and Yom Kippur students from all different parts of the Jewish community were really excited to be there. I've been to my fair share of Penn Hillel shabbats. But you know, this time I had seen people who I might not have seen before at one of these events. So I think it was really, you know, I was really proud to be a member of the Jewish community at Penn and to really see people, you know, really just come together. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: What a way to bring joy to a moment that really could have just focused on the challenge, so that–it's really unbelievable. Zooming out, now that you're a few days, just a few days, away from everything. So campus issues affecting Jewish students do get press coverage, but often it is simply within Jewish news outlets, and rarely in the wider press, and certainly rarely for such an extended period of time. What we saw at Penn felt unprecedented, both in the national interest and in the last in coverage. Why do you think it led to such significant coverage? And how did that affect the campus environment at Penn? Maya Harpaz: I think one reason for that is because of Penn as an institution, as an Ivy League institution, and also as a well-known Jewish institution. Penn has a long history of a very strong Jewish community that's actually been decreasing in size pretty steadily over the years. So I think that was a big reason why we got so much attention. I also think because of the way that we responded to it, I think if we decided that we weren't going to say anything, and we were going to let antisemites come onto our campus and spew hate, and we just put our hands up, that there wouldn't have been so much attention. But I think because we pushed back on it, it became this discourse that got a lot of attention. I don't even know how to describe it still, because I'm still processing everything that's happened over the last few weeks. But me personally, I'm not a journalist. I'm not usually someone who's ever in the news or speaking to the press. But the amount of attention that that's been on us has really, really been unprecedented. As you mentioned, it's definitely been a bit overwhelming too but I'm also grateful that we've been given a platform to share what's been happening and to bring awareness to it. Because we've seen this happen at many other schools that have large Jewish communities and very strong Jewish communities. And I never thought that an event like this would or could happen here. So I've definitely been very appreciative of all of the support that we've gotten. Jonah Miller: At the same time, I think that the incident at Hillel follows a long lasting and unfortunately, growing trend of rising antisemitism. And I think that news outlets picked up on that. Secondly, to give some credit to my amazing team of reporters and copy editors at The Daily Pennsylvanian, I think that our quick and trustworthy coverage at the paper allowed news outlets, national news outlets, to cite us in their own articles. So for instance, this incident that happened at Hillel, I noticed that within 12, 24 hours, it was picked up by Fox News, and CBS News, both of which cited interviews that I myself conducted with students who were at the scene, in their own articles. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: So connected to that, in addition to the media attention, I think, many Jewish organizations, some of which had little to no relationship with the Jewish community on campus, came to campus with their own ideas of how the situation should be resolved. What advice can you give to Jewish organizations who want to help when a situation arises on campus? Maya Harpaz: The biggest advice that I can give is just talk to us. No campus is the same and although unfortunately a lot of antisemitic incidents happen on a lot of universities, the climate of each campus is very different and the wants and needs of students are very different based off of their campus. So it's definitely important to speak to students before you make an assumption about what they you think they want or make a plan for what can be done and how to solve this issue because it's really us who have a stake in this, obviously the Jewish community at large cares, but it's it's us who have to live this as our reality. Penn is our school. It's also our home. It's our social lives. So it's our everyday lives, we can't escape that. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: So while the particular event itself may have passed for right now, there is a great deal to do on Penn's campus in the wake of these events. The President has committed to implementing much of the US National Strategy to Counter Antisemitism, of which dozens of AJC recommendations were included. And Penn Hillel itself has dedicated time and resources to educational programming around antisemitism. So as student leaders, what do you want to see next? And importantly, what advice do you have for other Jewish students should something like this happen on their campus? Maya Harpaz: So something that we talked about with members of the administration and things that we want to see next is more–and this is something that President Magill mentioned, as well–is more oversight when hosting events on our campus. When this event came through, it was just listed as the Palestine Writes Literature Festival. And they were like, cool, literature festival, fine. But there definitely needs to be more work done to make sure that the lineup of any event is not including someone that is not in line with, as President Magill said, our institutional values. Something else that we discussed is further training for Penn faculty, whether that be residential advisors, or professors, to be trained on how to combat antisemitism and how to identify antisemitism and really introducing that into the other forms of training against hate that faculty go through. And a big longer term goal that I think at some point, maybe in the nearer future than I initially anticipated, is implementing the IHRA definition of antisemitism. Jonah Miller: Hopefully, an incident like this does not happen at the campuses of other Jewish students. But should something happen, my recommendation would be to just remember that our unity can overcome the hate and the vitriol being spouted at us. At the Shabbat together event at Penn Hillel, a Penn alum and someone who's very involved with the Penn community and with the Jewish community, Stuart Weitzman, spoke about how Jews have triumphed over hundreds of years and 1000s of years of banding together. I think that message remains ever-important, to remind ourselves about today. That we really as a community are stronger and can overcome this adversity when it comes right on our doorsteps. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: What a beautiful note to end on, and I have to say for myself, for us here at AJC, and certainly for the Jewish community at large, the reason we feel so hopeful about the Jewish future is because of Maya, your leadership, Jonah, your leadership, and both the courage and joy and thoughtfulness that you brought to this situation. So for all of us, I just have to say a big thank you. Jonah Miller: Thank you so much, and thank you to AJC for all the work that they're doing for students like us on campuses. Maya Harpaz: Thank you so much for having us. It really means so much to both of us to be able to have our platform and to share what's been going on at Penn. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, we went behind the scenes at the UN General Assembly with Simone Rodan Benzaquen, the Managing Director of AJC Europe.
Sep 21, 2023
What the UN Needs To Do To Stop Iranian and Russian Aggression
This week, Simone Rodan Benzaquen, Managing Director of AJC Europe, joins us to discuss AJC's leading role in the Jewish community's diplomatic efforts at the United Nations General Assembly. Simone highlights key areas of advocacy, including countering the Iranian threat, addressing antisemitism and anti-Israel bias, advancing the Abraham Accords, and supporting Ukraine against Russian aggression. We also explore the impact of addresses from Palestinian Authority President Mahmoud Abbas and Iran's President Ebrahim Raisi, who have used the UN platform to spread antisemitic and anti-Israel narratives. Simone sheds light on the challenges and progress in shaping international policies on these critical issues. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Simone Rodan Benzaquen Show Notes: Test your knowledge: About the UN, Israel, fighting antisemitism, and AJC's role Read: AJC Advocacy at UN General Assembly 2023 Top 5 Things AJC is Tracking at the United Nations General Assembly Five Things to Know About President Raisi and Human Rights in Iran and Beyond Key Takeaways From President Biden's Address to the UN General Assembly Mahsa Amini Protests One Year Later: What is the Current Human Rights Situation in Iran? Listen: Deborah Lipstadt on the Abraham Accords' Impact and the U.S. National Strategy to Counter Antisemitism Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Simone Rodan Benzaquen: Manya Brachear Pashman: All this week, leaders from 193 nations have gathered in New York, addressing the United Nations General Assembly. But there's a lot of action on the sidelines as well. That's where policy experts from the American Jewish Committee do their diplomatic outreach, urging leaders to expand and strengthen ties with Israel, and counter rising antisemitism and extremism. With us to discuss what's been happening on those sidelines is Simone Rodan Benzaquen, Managing Director of AJC Europe. Simone, welcome to People of the Pod. Simone Rodan Benzaquen: Thank you. Thank you very much for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I'll start with Iran. How are we pushing leaders to address the threat from Iran this week? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: So Iran, as you rightly point out, is a really priority issue for us in all of the meetings we've had in particular with on my end with the European leaders, and it's, and our objective is really to make sure that we are countering Iran on all fronts. Of course, there's the nuclear file. And so our objective is to push leaders to be aware and really understand that, if that was to happen, we are entering an entirely new world. If we think that the war that Russia has been waging on Ukraine was a game changer for the stability of the world, we have not seen anything yet. So our objective is to really push European and international leaders to really address the issue. The second issue is, of course, human rights. We are now a year after the murder of Mahsa Amini, and really the horrible repression that the Iranian regime has committed against its own people. And there has been a time when European international leaders were very, very clear in their support for the Iranian people, and in condemning the Iranian regime and the Islamic Republic. But these past months, we've heard a little bit less of that. So our objective is really, has really been to reengage them on that commitment. And then third of all, and this is really a very specific issue, particularly in Europe, is the Iran Revolutionary Guard. And so the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Council, the IRGC, is not listed as a terrorist organization in the EU. And that is obviously not normal. First of all, because they have been committing horrible crimes in their own country, because they have been committing terrorist acts across the world. Because they are obviously a key sponsor of terrorism across the world, because of their role also in Ukraine. They have armed Russia with Iranian drones, they have trained people on the ground. And lastly, and this is for us, very important as the Jewish advocacy organization, they have been threatening Jewish communities across Europe. There are a number of cases that are now very clear, which include in Germany, in the United Kingdom, but also in Greece and in Cyprus, where it's very clear that Iran is threatening Jewish communities and Israelis on European soil. Now, Europe for the past years, has made it very clear that it's a key priority for itself to combat antisemitism on the ground and in Europe. And that's a very important commitment. Now, if they're very, very serious about that commitment, they also have to act against the IRGC, which is today a key threat to Jewish communities on the ground. So we have been pushing European leaders to take steps to list the IRGC as a terrorist organization. As always, this will take time; it's not going to happen just during the UN General Assembly. But we've made some progress. We have had some very good conversations with a number of European countries and I hope down the line that we will be able to get there. Manya Brachear Pashman: So now what about Hezbollah? Because I know for many years we have pushed leaders at the UN General Assembly to designate Hezbollah, a terrorist organization in its entirety. This campaign has been going on for many years. Is that campaign changing in any way this year? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: No, it's not changing, it continues to be a key priority for us. By the way, the issue is linked, of course, I mean, what is Hezbollah, if not a proxy of Iran, an Iranian state within Lebanon, that is threatening, of course, Israel, but also has been committing terrorist acts across the world. So no, it has not changed. We are just trying to link the dots and explain to everybody that everything is linked. We're not there yet. There are a number of countries, as you know Manya, who have taken individual steps in Europe to list Hezbollah as a terrorist organization, because it is blocked on the EU-wide level. But you know what, we just celebrated Rosh Hashana. You know, at the end of the day, there is always hope, particularly for the Jewish people. So we will not be giving up on it and eventually we'll get there. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned the IRGC's role in Ukraine with providing weapons and we heard from Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelensky this week, warning that Russia was weaponizing essentials like food and energy, not only against Ukraine, but against every country. And I know the UN Human Rights Council created, with AJC's urging, an independent International Commission of Inquiry on Ukraine, which has already determined that Russia is responsible for war crimes. So how are we advancing that conversation on the sidelines this week? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: Listen, on the European side, I would say the conversation is very easy, because Europeans understand that if Russia is allowed to strategically win this war. That means that, though, that they, their countries, that the European Union, as such, will be threatened by Russia. Russia will not stop with Ukraine. President I hesitate always to call him president, but Putin has made it very clear that for him, the biggest catastrophe of the 20th century, is the fact that the Euro that the Soviet Union fell apart. And so he wants to go back to that scenario. So Europeans are aware of it, their commitment to Ukraine, is very much there, actually, surprisingly, because many people, when the war started, were very much afraid that that, at the end, you know, there will not be European unity, that there will not be unity in the international community and in the West, in their support for Ukraine, and finally, you know, a year and a half later, we're still there, the United States is committed in supporting Ukraine, the European Union is committed in supporting Ukraine. But more needs to be done. We need to be able to provide more help to Ukraine. And again, as you said, especially as Russia is weaponizing every single possible way, whether it's energy, whether it's food, to exert pressure, to make sure that at the end, we are faltering. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I want to switch the focus a little bit from international diplomacy and war to the IHRA working definition. This has been an ongoing conversation with the UN. AJC has been urging the UN and its member countries to use it to develop plans to counter anti semitism. How is that coming up on the sidelines this week? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: So we've had some very constructive conversations, first of all, a majority of countries now have adopted the working definition of antisemitism. And they've recognized how much an important tool it is to not only to recognize, to define, but also to apply and to combat antisemitism. So it's a very constructive conversation. But we have also had conversations with countries who have not yet adopted the working definition, who would say, we don't have a problem of antisemitism, we don't really have to do it. And after explaining to them how important it is, and what an important tool it has been for countries, and what an important signal also it would send to the world, if they were to adopt the working definition of antisemitism. I can tell you now, in advance that in a few days, a couple of countries will be announcing that they will be adopting the working definition of antisemitism because of the conversation that we have had with them. Manya Brachear Pashman: The conversation you've been having this week with them, or ongoing over a matter of time? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: Over a matter of time, but that was concluded, specifically here at the UN General Assembly this year. Manya Brachear Pashman: And what about anti-Israel bias? Has that come up? Because I know that has been a blockage for a lot of countries who won't adopt the IHRA working definition, they want to leave the door open for criticism of Israel, but there has been some pretty blatant anti-Israel bias at the UN. And that has really been a priority for AJC to address. How have you been trying to eliminate that kind of chronic one-sidedness that targets Israel? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: This is, I have to say, Manya, a complicated conversation that we've been having, obviously, for years. As you rightly point out, Israel is treated in a way that no other country is. There is a permanent agenda item at the UN Human Rights Council. There is a disproportionate number of resolutions against Israel compared to any other country in the world. Many countries we are speaking with acknowledge that fact. But often their excuse is that they are working in a multilateral environment and that is therefore complicated, because you always have to come to some sort of compromise. But I have to say that nevertheless, I think we are making progress. If you and I had had that conversation 10 years ago, most European, most countries would not have even acknowledged that that was a fundamental problem. That situation today has changed. Many countries do recognize that there is something profoundly discriminatory in that disproportionate targeting of Israel. They just are very slow in finding solutions to that approach. Manya Brachear Pashman: We also heard from Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas this week. What do you fear he is communicating? What do you fear that members of the United Nations are hearing from him and taking as truth? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: For years, I think Muhammad Abbas has been really in an endeavor to distort history by denying the link between the Jewish people and the land of Israel. He has engaged on a number of occasions in historical revisionism. He has been engaged in a number of occasions in Holocaust denial and antisemitism, in stereotypes and conspiracy theories. And I think the world needs to wake up to that reality. I mean, if any other world leader had had that kind of discourse, take away the face of Muhammad Abba, take away the voice of Muhammad Abbas and just neutrally look at what he's been saying over the years, we would not accept that. The world, the Western world, the European Union, the United States, we would not accept that, and rightfully so. So why is it that we should continue to accept these kinds of words? European leaders were right, the United States was right, to criticize Mahmoud Abbas, as they have, after his recent antisemitic remarks. But that needs to now apply all the time, we sort of have a bigotry of low expectations on Mahmoud Abbas. I mean, why is it that we consider him somehow not capable of living up to the same standards as everybody else? So I hope that the world will, at some point, wake up, and just expect of the Palestinian Authority and of Muhammad Abbas himself, to accept to have certain rules. He cannot continue to have these kinds of statements. He cannot continue to do the pay for slay, meaning to pay the families of convicted terrorists. He cannot continue to incite hatred in Palestinian schoolbooks. We have to set the same standards for everybody, including for Muhammad Abbas, including for the Palestinian Authority. Manya Brachear Pashman: And do you think the member states realize that or comprehend that and are kind of seeing through his narrative? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: There seems to be the beginning of a process. I don't know if we're there yet. But there seems to be a beginning of the process. I mean, when you have the mayor of Paris, for example, who took away the honorary medal of the city of Paris to Muhammad Abbas, when you have statements that you have never had before, by leaders of the Western world, criticizing Muhammad Abbas. I think we're maybe at the beginning of something new. I just really hope that we're not walking backwards from that, because we just simply cannot go back to that just behaving as if, you know, this wasn't happening. Some of it has to do with the fact, with this delusional idea that, you know, if the Palestinian Authority was to fall apart, if Muhammad Abbas was to fall apart and not be president anymore, there would be worse. But still, I mean, this cannot be an argument in not having the same expectations of a leader than of any other leader in the world. Manya Brachear Pashman: So speaking of narratives, the president of the Islamic Republic of Iran, Ebrahim Raisi spoke to the general assembly as well, this week. His narrative was that Iran is the model of human rights and justice. Did that surprise you? What surprised you about his sermon, if you will, to the UN? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: No, there is nothing that surprised me, the Butcher of Iran, who is president, the president of the Islamic Republic of Iran, has been lying to everybody's faces, of course, for many years. Iran is committing human rights abuses, Iran is imprisoning young people. Every single human rights organization has spoken about it. Every single western country knows it and has said it. They are committing rapes of young women in their prisons. They're abducting the families, including by the way the family of Masah Amini just a few days ago, every single day, and the fact that he is lying once again to the world is despicable. What is equally despicable is that the Council of Foreign Relations has intended to host Ebrahim Raisi. There is no way even with people who are asking difficult questions or having difficult conversations with him. That it does anything else then legitimize him and legitimize this terrible, murderous regime. So the only thing that should be done is, really be as tough as possible with this regime, and clearly impose sanctions, condemn, walk out of the room, ignore, but certainly not welcome him with open arms. Manya Brachear Pashman: And do you think the world is buying his narrative? Simone Rodan Benzaquen: Well, it depends what you mean by the world. But I don't think the western world is buying his narrative at all. I think everybody knows, you know, the reality of things. They know everything that is wrong with the regime. There might be differences in how they think they should be approaching that and they might, by the way, also be differences in perception between some Western countries and ourselves on how we think things should be approached. But nobody is naive about what is actually going on in the country. And the way this person, the Butcher of Iran, is treating his own people. Manya Brachear Pashman: Simone, thank you so much for joining us, and giving us a glimpse of what's been happening there. Simone Rodan Benzaquen: Thank you.
Sep 14, 2023
Deborah Lipstadt on the Abraham Accords' Impact and the U.S. National Strategy to Counter Antisemitism
Ambassador Deborah Lipstadt, the U.S. Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Antisemitism, joins us to discuss how she's settled into her new role and shares insights on the development of the new U.S. National Strategy to Counter Antisemitism, for which AJC has long advocated. Lipstadt, a renowned Holocaust historian and one of Time Magazine's Most Influential People of 2023, also delves into the ways in which the Abraham Accords have contributed to the fight against antisemitism in the Middle East. Additionally, she provides an insider's look into the challenges and progress associated with addressing antisemitism and how the National Strategy factors in. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Deborah Lipstadt Show Notes: Go Deeper: Test your knowledge of the National Strategy to Counter Antisemitism Read: Everything You Need To Know About The U.S. National Strategy To Counter Antisemitism And AJC's Task Force Honoring International Antisemitism Envoys AJC David Harris Award Listen: People of the Pod: Hear from America's New Antisemitism Envoy Deborah Lipstadt Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Deborah Lipstadt: Manya Brachear Pashman: Deborah Lipstadt, US Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Antisemitism is a renowned Holocaust historian, recognized earlier this year as one of Time Magazine's Most Influential People of 2023. She has written eight books, and four years ago, advised the United Nations on its unprecedented report on global antisemitism. In fact, she joined us on this podcast shortly after the report's release. Since then, she has joined the US State Department in a role that for the first time carries the rank of Ambassador. She joins us again this time in our popup Tel Aviv studio. Ambassador, welcome to People of the Pod. Deborah Lipstadt: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: America's National Strategy to Counter Antisemitism was adopted in May. Your job primarily deals with US Foreign policy to combat antisemitism. But how does this new domestic strategy affect your work? Deborah Lipstadt: Well, it affects our work and that certainly I was consulted and worked closely with the White House in the shaping of it, my team played a part in helping to shape it people to reach out to and things like that. And there are over 24 agencies involved including the State Department, we're now looking at all the other national strategies to see best practices, what America could possibly adopt. And of course, informally, I'm the administration's most knowledgeable person on antisemitism. So they turned to me quite often for advice, for ideas, etc. Manya Brachear Pashman: Okay. All right. Well, so as I said, your role is more international. Do you need a domestic counterpart? Does the United States need a domestic antisemitism czar? Deborah Lipstadt: I'm not sure. It's a lot on–the strategy is really run out of the Domestic Policy Council, which until about a week ago, was headed by Ambassador Susan Rice, who was greatly responsible for seeing this thing come to fruition. And we'll see how it works. It's up to them to decide how they want to do it. But I think it's also good that each agency from the usual suspects, as I like to say, homeland security, education, FBI, law enforcement, are involved, but so are so many others. Small Business Administration, Veterans Affairs, Smithsonian, all looking at ways to counter antisemitism, make sure there aren't barriers that are there, whether because of antisemitism or just ignorance. Manya Brachear Pashman: And second gentleman Doug Emhoff has been certainly-- Deborah Lipstadt: Even before I was sworn in, after I was confirmed, I was in Washington and he asked me if I would come in and visit with him. We had a wonderful visit. We're in touch all the time. And he really feels this very deeply. And I give him great credit because he could easily have said, Look, I'm the first Jew in this position. First second gentleman. We put up a mezuzah for the residence. We have a Hanukkah party. We have a Seder. We do other things. Don't ask me to take the lead on this. But he's taken the lead. He's traveled all over, he traveled with me to Poland and Germany, where I coordinated a meeting for him with other special envoys, just to give him a sense of what other countries were doing. And I think when he and his staff and other people in the White House who were with us saw that, it sort of energized them to say, my God, other countries have taken this really seriously. They're way ahead of us. We have to do something serious as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, with that in mind, I mean, if you think about it, your predecessors in this position have kind of made it their business to monitor, sound the alarm about antisemitism in Europe, elsewhere around the world. AJC helped convene that group of envoys at the White House. And so in many ways, the table's turned a little bit in terms of, you know, instead of the United States monitoring and sounding the alarm, these envoys came and advised the United States. Has this kind of mutual mission actually improved the relationship with some of these countries? Deborah Lipstadt: It's improved the relationship tremendously. We really work as a team, not as a team–each one has its own you know, position, certain things one can get involved in certain things. You know, I lurk and watch what's going on, but I'm not involved in it. But one of the first things I did in fact, it was the same day as last year's AJC Global Forum, which was in New York, I think, at Temple Emanuel. And I was on the stage with Katrina von Schnurbein, the amazing EU envoy on Countering Antisemitism and Enhancing Jewish Life. And then she and I left the meeting with Mr. Lottenberg, Fernando Lottenberg, who's the OAS Special Envoy, and we met with a group of us of special envoys met to talk about how we could work together. And so we've been meeting and convening. Katrina convened something that the EU others have convened, and then we meet, you know, sometimes we'll meet through the auspices, let's say, we'll be meeting here because many have come for AJC. But it is a government to government when we meet, it's not, convened by someone else. But it's people who speak for their governments coming together, which is quite amazing. I've had great predecessors in this job. They're all terrific. And were strong supporters of me taking the position, very excited about it from both sides of the aisle. And I'm very grateful for that. But there are differences. First of all, Congress elevated the position to an ambassador before I was in the picture. So it wasn't for me. And that carries weight in the world of protocol. That means you speak for the President. I see what weight it carries. In fact, I was just in conversation with a Republican senator, around the time of the rollout, because I was briefing him about the national strategy. And he had been one of those who had pushed for the elevation of it to be an ambassador. And I said, you know, when I first heard you were doing this, I said, Oh, doesn't really matter. I said, I was wrong, you were right. It really enhances the importance, and it shows how America takes this seriously. But my predecessors, certainly amongst the earlier ones, we were the first country to have a position like this. So when something happened in France, and Belgium and Germany, whatever, they would go, and they would say to the government, you know, we take this very seriously, and we think you should take it seriously. Or if they were taking it seriously, we take this very seriously, and what can we do to help you take it seriously, and say, you have a problem, we've got to address it. And now first of all, I go and I said, we have a problem, because we have acknowledged that exists in our country. And sometimes I don't have to go racing as they might have had to, because there's someone else there. There's a local person, there's a national person there, too. So the fight has become much more coordinated, enhanced, and really raised to a government level in a way that it hadn't been previously. Manya Brachear Pashman: Are there particular lessons that you can recall from any of your predecessors? Any of the envoys that you've taken to heart and realized. Deborah Lipstadt: I spoke to virtually all of them before I took the position. And they each had different advice, and I won't say one or the other, etc. But one the reasons–and I've only been in the job a year, but – building alliances in the State Department. And I'm worried a little bit not because of anything anybody tells me, just natural inclination to worry to be a pessimist so that we can be happily surprised when good things happen or the bad stuff doesn't happen. But, would I find compatriots in the State Department, would people see me as you know, an add-on, a niche? Would I be operating off by myself? And that hasn't happened. And it's really been quite amazing. Partially thanks to the advice I've gotten, partially, I think, my own interpersonal connections, but I have built really strong alliances. And I'm not saying I have personally, but people in other offices with other portfolios, see this not as a niche issue. But as a central element of American foreign policy. Manya Brachear Pashman: We hear a lot of statistics of incidents of hate crimes each month each year. And I'm curious if that's what matters most. In other words, does the perception of a community also matter whether it's a Jewish community or any other minority community, if that community perceives a rise in hatred against it? Is that enough to amplify our response? Deborah Lipstadt: The perception of a community is important, perception of an individual. Sometimes, any community, any individual can see things more dire than they are. But I think if anything, the Jewish community has become more aware of certain incidents and more aware of certain things. Give you an example, New York. I think there were a lot of Jews in New York who didn't take seriously some of the antisemitism encountered by Haredi, Hasidic Jews in Brooklyn, you know, who would walk down the street, get their hat knocked off, or get spat upon. And you could say, Okay, what's the big deal? Well, if you're walking down the street, especially walking with your kids and your hat gets knocked off, suddenly you're looking at your father, or your mother gets a little nervous because she's in, you know, other people that she sees people come in and might be dangerous or whatever. And I think now they take that much more seriously. Have that been happening on the Upper West or East Side. We would have been quicker to respond. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you think that that is enough for a government, for example, to amplify a response? Deborah Lipstadt: Well, certainly a local government, this was happening in New York, but as it became more national, and there's something else in the strategy addresses this. That government can't really deal with, but it can call out. And that's the normalization of antisemitism. And the strategy speaks very directly in the beginning, when it's something I'm paraphrasing, when politicians, when actors, when rap stars, when sports figures engage in anti semitism and amplifies it in a way that it hasn't been before. Government can't stop them. We have that pesky thing called the First Amendment and we all treasure it. Even though sometimes it can make us gnash our teeth, the good comes with the bad, or the bad comes with the good. But the normalization, so with the strategy. And when the strategy was rolled out, I spoke from the podium of the White House, one of the things I said: government can do a lot. Congress is already doing a lot and is willing to do more. But it calls for an all hands on deck and it has to be a public, the broader society has to be involved in this fight, not just because of protecting fellow American Jews, fellow citizens, but because as I think as listeners to People of the Pod know well, antsemitism is a threat to democracy. I've been talking about it now someone even said to me, the cliche, and I realized that I had been the one to really popularize it, as the canary in the coal mine of democracy. But it's a warning, it's a warning. Manya Brachear Pashman: You began your tenure with a tour of the Middle East. Saudi Arabia, Israel, United Arab Emirates, Abu Dhabi, right? Deborah Lipstadt: And Dubai. The first stop was Riyadh. Manya Brachear Pashman: Oh, right. Okay. And in fact, you were just in Abu Dhabi again just a few days ago. Deborah Lipstadt: I was for a second time, right. And where I encountered an AJC's delegation. But AJC has been present in Abu Dhabi in the Emirates for a very long time. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to talk a bit about those visits and the Abraham Accords, which is another circumstance that has changed. I mean, your immediate predecessor got to benefit a little bit from the Abraham Accords. But I'm curious if those Accords are removing barriers, helping foster relationships. And you know, that will only continue to improve the relationship between Israel and Muslim majority countries but also, their receptiveness to your message for combating antisemitism. Deborah Lipstadt: The Abraham Accords are of prime importance. And they've been wholly embraced by the State Department, this administration, and not only embrace, but I've been encouraged to build on them, in part because we see them as a good thing in terms of fostering relations in the region between Israel and these other Muslim majority countries, but also because we see them as enhancing the Middle East enhancing the economy. I mean, it's a great thing when we all go into Ben Gurion Airport and we look up and there's the flight to Atlanta and right in front of it's a flight to Abu Dhabi, you know, or the flight to Detroit, Dubai , you know, it's some people say it's Mashiach, it's the time of the Messiah in that sense. The Abraham house in Abu Dhabi, which is a mosque, a church and synagogue is magnificent, of course, that's not part of the Abraham accords. So that wasn't, that was generated in 2018, with a visit of Pope Francis to Abu Dhabi, who said, Let us build the church and a mosque, and it was the leadership of the Emirates that said, let's build a synagogue, to make it a complex of the Abraham House, of the Abrahamic faith. So and then of course, Morocco, which refers to its normalization because it's been doing this for quite a while, Morocco that expects 400,000 Israeli tourists this year. I think last year it had 225,000. And then it's just you know, everywhere. And all those things are good things. And then there are countries which are not yet and I've used not yet euphemistically, part of these things, but see them as working and see them as operating. And I think they're very important. Manya Brachear Pashman: And do you do feel that they are perhaps more receptive to your message and to listening to what you have to say? Deborah Lipstadt: Yes, of course, I mean, I think even you know, when I went to Riyadh, to Saudi Arabia, I had meetings with high ranking officials, now you can show up and you can meet with the Minister of, I don't know, keeping the paint dry or something like that. Or you can meet with higher level ministers and I met with high level ministers, very productive meetings. And one of my messages was, look, there is a geopolitical crisis in this region, we're well aware that, my country is well aware of it. I work for a government that has hundreds of people actively engaged in addressing this issue. But that's something in many respects separate and apart from prejudice, and from hatred. And the example, I had this interesting encounter in either Riyadh and Jeddah with an older imam who knew what was meeting with me and he knew what my, what my status was on my remit, was my portfolio was and he said, If Israel solved the Palestinian crisis, there'd be no antisemitism. So there was a part of me that thought, I think there was antisemitism before there was a Palestinian crisis, I think there was antisemitism, for those in Israel, I think there was antisemitism, Zionism, you need to go back and back and back. But I didn't think that was going to get me anywhere, you know, putting it on my professorial hat, my mortar board as we do at graduation and lecturing him on that. So instead, I said to him, after 9/11, in my country, there was a surge, not of Islamophobia, but Islamic hatred. And as you will remember, I'm sure, there was an attempt at one point to build a Muslim community center, opposite Ground Zero, where the World Trade Center had been. And in fact that the group that was building it consulted with the Jewish community center of Manhattan, you know, how, what's your experience? What room? Did you build enough? Should we have a gym, swimming pool, you know, et cetera, et cetera. And whatever body whether it was the city council or whatever in New York. New York, the polyglot capital of the United States, refused permission, because they said to build the Muslim community center, adjacent to Ground Zero, when it was Muslims that had destroyed the buildings and murdered the people there, would be an insult. And many of us thought that was wrong. That was prejudice. And I said, why should Muslims in lower Manhattan, a woman who wants a good place for her children to learn about their tradition, or to have an Iftar or whatever it might be a man to go to pray or whatever? Why should they be denied that right, because other Muslims had destroyed and attacked the buildings? And the man said to me, you're absolutely right. It was prejudice. I said, well, to say that antisemitism is solely dependent on what Israel does or doesn't is the same thing. And he got very quiet. I don't think I changed his mind. But he stopped arguing. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you see any progress toward people understanding it more as a territorial conflict? Deborah Lipstadt: I think so. I hope so. I think it's a continuing, it's not like you get to a point and then well, we're at this point. Now we get to the next point, you know, like I used to lift 20 pounds, I can lose 30 pounds, you know, it goes back and forth. It goes back and forth, depending on the situation. It's a volatile process. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you think that getting them to understand it as a territorial conflict would actually fulfill part of your role in terms of combating antisemitism? Deborah Lipstadt: Yes, absolutely. But I think it's also necessary not to do things that are going to aggravate or not to do things that are going to make it harder for some of these countries to follow through with the Abraham Accords, so it cuts both ways. Manya Brachear Pashman: In May, you and Ambassador Hood attended the annual Lag Ba'omer Festival at the El Ghriba synagogue. Deborah Lipstadt: In Djerba, Tunisia. Manya Brachear Pashman: The island of Djerba. Tunisia is one of dozens of Arab countries where Jews were forced out and displaced. And I'm curious if you could reflect a little on the situation of Jews in the Middle East and North African countries. Deborah Lipstadt: Tunisia is a different story than Morocco, different story than the Emirates, then Bahrain. In that it does have a very small Jewish community. I think there are 1300 Jews in Djerba, been there, hundreds, thousands you know, years. And it's much more a community in Tunis than in a number of other places. But this festival has been going on for quite a while. And it was really reasserting itself after COVID, after an attack about 20 years ago on the festival. And it was so promising. And when I heard that Ambassador Hood, our American ambassador in Tunis was going, I said, you want company, he said, I'd love it. So we went together. We visited the school there that is funded by and supported by the Joint American Jewish joint distribution committee, the joint, the JDC, one of the little students showed them how to draw an aleph. It's was very poignant. And we had a wonderful time. And then we went to the festival that night. And it was joy. The night before the deputy minister from the government catered a kosher meal for us, a kosher feast for many of the foreign representatives who were there. And we went to the festival and it was just joyous and we just loved it. We were so happy and meeting people and seeing people and meeting old friends and etc. And people are the American ambassadors here, which was very exciting. And we stood in a place and I noticed that our security guards were pretty tight security because of course Americans and back to two ambassadors and personnel from American Embassy in Tunis. We're getting nervous I said, it should relax. 24 hours later precisely in that same place, there was a shooting and two guards were killed. Two Jewish one French, Tunisian and once one Israeli Tunisian, were murdered. So it's very sober. Very, very sobering. And Tunisia was that in the beginning, what we say reluctant to acknowledge this as an anti semitic act they talked about as criminality, they talked about it as terrorism. So Ambassador Hood and I together, not together with, but also with president Macron, and the German Foreign Minister, all said this is antisemitism plain and simple. Manya Brachear Pashman: And swayed them, turned? Deborah Lipstadt: Oh, well, I don't know if we swayed them, but we got them to, he met with the President and met with the chief rabbi. And they changed a little bit, but sometimes it's criminality. Sometimes someone gets mugged on the street, and doesn't matter what they are who they are. But when this guy shot, he was on guard at a naval base. He shot his fellow guard, took a car and drove half hour across the island, to the synagogue, to attack the synagogue. And he didn't say, Oh, they're a crowd of people. I mean, he knew where he was going. And he knew what he was doing. Manya Brachear Pashman: My last question is, some listeners might not realize that there is actually a separate Special Envoy for Holocaust issues. Deborah Lipstadt: That's right, Ellen Germain. Manya Brachear Pashman: Your colleague Ellen Germain. Given the rise of Holocaust distortion, trivialization, your candidate, the loss of survivors, how much of what you do now intersects with her work? Deborah Lipstadt: Well, we're very careful. I mean, she's really handling Holocaust reparations issues, property reparations, not that we get directly involved, but in urging countries to address these things. But there's not that much overlap. But there's a great deal of cooperation with us, you know, times traveling together, working together, the more the more. Manya Brachear Pashman: Are their priorities that you can see for implementing the National Strategy since we started talking about it. Deborah Lipstadt: I think there are so many things in there that can be done large and small. I urge people to download it. Maybe you can put the link on your website. It's downloadable. It's 60 pages, read the whole thing. thing. I have to tell you, I knew it as it was emerging. But at one point when I saw a draft of it, and they asked me to go over it, I was abroad doing it in another country. So complicated. But of course, as I began to read it without going into the specifics even have different issues. I was deeply moved. Because I don't like to correct my boss, otherwise known as the President of the United States. But when he spoke about it at the White House, he called it the most momentous comprehensive plan the American government has ever addressed and he was wrong. It was the first comprehensive plan that the American government has ever addressed. Of course, when there've been tragedies and presidents from both sides of the aisle, from all perspectives have condemned, have responded, America has responded. Law enforcement has responded. But this is the first time that the United States government is taking the bull by the horns and saying, What can we do to address this scourge? And as I said, from the podium of the White House when it was rolled out, probably making history because it's the first time a mishna was quoted from the White House or talmud was quoted from the White House. I quoted from the verse from ethics of the elders, pirkei avot – lo aleicha hamlacha ligmor, v'lo ata ben chorin livatel mimenu. You're not obligated to complete the task, but you're not free from starting, from engaging in it. The United States government has now seriously engaged in it. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, thank you so much, Ambassador. Deborah Lipstadt: Thank you.
Sep 7, 2023
Sen. Joni Ernst Reflects on the Abraham Accords and the Future of Arab-Israeli Engagement
As we mark the third anniversary of the Abraham Accords, significant progress has been made in deepening Arab-Israeli engagement. With us this week is Sen. Joni Ernst (R-IA), a founding member of the Senate Abraham Accords Caucus. Ernst joins guest host Benjamin Rogers, AJC's Director for Middle East and North Africa Initiatives, to reflect on the achievements of the landmark deal, its importance to the United States, speculation over Saudi Arabia, and the crucial role of the Senate in advancing peace between Israel and its Arab neighbors. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Joni Ernst Show Notes: Engage: How much do you know about Abraham Accords? Take our quiz and put your knowledge to the test! Read: The Abraham Accords, Explained Listen: Meet 3 Women Who are Driving Change in the Middle East 'Golda': Behind the Scenes with Israeli Director Guy Nattiv on the 1973 Yom Kippur War Noa Tishby on the Abraham Accords: The Middle East Realizes Israel is Not the Enemy Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Joni Ernst Manya Brachear Pashman: As an organization, AJC has been engaged in the Middle East for more than 70 years. In fact, a senior AJC delegation first traveled to Morocco in March 1950. Since then, there have been several more milestones. AJC's own Jason Isaacson participated in the Madrid Conference in 1991, a historic effort by the international community to revive the Israeli-Palestinian peace process; and AJC opened its first Arab world office in Abu Dhabi in 2021. This week, Benjamin Rogers, AJC's Director for Middle East and North Africa Initiatives, explores one of the most significant developments in the decades-long Arab-Israeli conflict – The Abraham Accords. The conversation marks the Accords third anniversary on September 15. Benjy, the mic is yours. Benjamin Rogers: Thank you so much, Manya. And I remember the day well, I had been in the Gulf just a few months prior December 2019, talking about these issues, talking about normalization, talking about cooperation. But to see the President of the United States, the Prime Minister of Israel, the foreign ministers of the UAE and Bahrain, on the White House lawn, signing an agreement of friendship, an agreement of cooperation. It was an electrifying moment. As we prepare to celebrate the third anniversary of what is possible,when Israelis and Arabs come together and set aside their differences. I can think of no better person to help us reflect on this moment than our guests today. It is my honor to welcome Senator Joni Ernst of Iowa, founding member of the Abraham Accords Caucus to our program today. Senator, thank you so much for being here. Joni Ernst: Of course, it is an honor, a privilege and a pleasure to be with you today. I'm celebrating as well, I think it's a phenomenal achievement for the United States and for our friends in Israel and those Arab nations. Benjamin Rogers: And I think that's a great starting place for our conversation. Share with us a little bit about your story. What was your reaction when you learned of these agreements? How did that translate to saying, Hey, I'm going to work with my colleagues. I'm going to sit down with Senator Lankford, Senator Rosen, Senator Booker, and we're going to be the founding members of the Senate Abraham Accords caucus? Joni Ernst: And it goes back quite a ways. My own personal journey, I had served in the Iowa Army National Guard and had deployed to the Middle East for Operation Iraqi Freedom and, and having that experience serving in our United States Armed Forces, we have the great privilege and honor of serving with many members from other countries as well. And we have an understanding of those nations and what they're trying to achieve and how we can promote stability in certain regions. So from that basis, then I served in the Iowa State Senate, and when you think of Iowa and Israel as maybe not a natural connection, but we have a huge Christian community across the state of Iowa that is very supportive of our Jewish brothers and sisters in Israel. And so from that platform of the Senate, I was able to move into the United States Senate with a broad basis, not only the military perspective, but then also how Iowa and Israel can come together collaborate on things like agriculture, cultural exchanges, and with that basis, then finding other members of the Senate that had similar goals and objectives. And that came together really, with the incredible, really the incredible advent of the Abraham accords. And so we were able to start the caucus, those of us that have very strong feelings about stability in that region and partnership in that region. So coming together with senators, Rosen and Volker and Lankford, it was a really wonderful way for us to celebrate the Abraham Accords, and bring others from the United States Senate and House into that fold as well. Benjamin Rogers: Amazing. I was struck by what you said, you don't necessarily think of commonalities between Iowa in Israel. But the interfaith component, the agriculture cultural component, I know you're also you talked about a little bit of security, I know, energy is a huge issue. Can you walk us through how these issues that are, you know, seemingly local, actually have larger, regional and international importance? How cooperation could maybe help your average person in Iowa City say, hey, look, this makes sense to me. I get what we're trying to do here. Joni Ernst: Right. And we exist in a global economy. Of course, we, as the United States are blessed with an abundance of resources. But when we're able to partner with other nations around the globe, we find new ways of using the resources that we have at virtually at our fingertips. And what we have seen just in the exchanges and the ideas that are shared between entrepreneurs and Iowa, entrepreneurs and Israel, Israel being a huge startup nation. It has been a fascinating journey for me just explore from the realm of agriculture, the types of irrigation methods that are used in Israel. One of the visits that I had to Israel is visiting with a young entrepreneur that had developed left, a type of bandage, skin type bandage a liquid that could be applied on the battlefield. But the source of that one of the sources for that bandage, that liquid bandage that would seal the skin together, actually comes from hogs that are sourced from Iowa. So I mean, it's it. We're all connected in so many interesting and fascinating ways. But when you talk to Iowans about this, they get it, they understand how connected we are, through our everyday activities. And I love it that we've been able to work strongly and partner with Israel, now expanding that opportunity as well, and to the other narrow Arab nations of that region. It's just an incredible time period of time that we're witnessing right now. Benjamin Rogers: So that's great to hear it. Can you say a little bit more? What, when you found her the caucus? What were the hopes? As you know, we've been, as we're about to celebrate three years on what are some of the successes, AJC has been engaged with you a lot on bills like the defend act, MARITIME Act, the Regional Integration Act, what, how, what is the role of the caucus? What is the role of the US Senate in saying, Hey, we're here to support the Abraham accords? Joni Ernst: Well, you outlined a number of those goals and objectives. But the first reason bringing us together, one was to celebrate the great accomplishment of the accords. That was the baseline. But then we built off of there because between the four of us in the United States Senate that founded the caucus to Republicans to Democrats, understanding that this is an extremely bipartisan move, and how do we not just celebrate the existence of the accords? But how do we become tools to further engage with those nations, maybe expand the chords? And, you know, what we'll say is normalization of relations. And maybe sometimes that's not the right word, but just this incredible collaboration between those countries? How can we be a part of that, and really sphere, the legislation that we're working on in Congress to benefit the United States, first and foremost, always, you know, looking for ways that we can, can protect ourselves further articles. But also do that with our friends, Israel, and other Arab nations that have joined the courts or are considering joining into the courts. So we have been able to focus primarily from my perch on the Armed Services Committee then on things like the defend act, where we are working with Israel, the members of the Abraham Accords, and integrating air and missile defense systems, giving these nations a common operating picture, where they can literally save minutes seconds on an impending attack coming from, of course, main adversary in the Middle East Iran. So if we can all work together and save lives on the ground, so much the better for all of those nations. So we did have the main parts of that bill, the defend act, it was passed through the National Defense Authorization Act, last year. This year, Senator Rosen and I also have the MARITIME Act, which is yet another step forward for our caucus, our objectives of securing that region. And it does basically the same thing that you'll see with the defender Act, which was primarily focused from the air protecting from the air. Now we are focusing on the maritime domain, and making sure that as we see naval traffic through that region, that they are protected as well. So we just continue to take steps to protect that region protect buses as United States citizens, but always looking for ways to further our goals through the Abraham accords. Benjamin Rogers: That's remarkable. And in reading the legislation, being engaged with the region. You hear all these things about the Middle East, there's the Middle East is disconnected, the Middle East is not united. But then you look at some of the sources and you look at the potential and you look at the ability for all these countries that maybe would be traditional adversaries are now saying, hey, we need to worry about things like heroes. We need to worry about things like security, we need to worry about things like stability, we're going to come together, we want to work with a larger architecture. And it's been remarkable from our standpoint, to see the US as a major driving force for that. Joni Ernst: Yes. And you mentioned security, stability, they go hand in hand, and what I have witnessed and in traveling through that region, and of course, getting to know leaders throughout that region, is that they are so interconnected, they really are. And the Abraham accords really provided a path forward for them to do more together. There has been a lot of work in this area for decades now. But we're finally seeing a real breakthrough, rapid advancement of cooperation between these nations. And because of a number of these nations coming together in the Accords, we say that, maybe there's a little bit of competition now as well with some of the other nations and in the region. And I say that and maybe top of mind, we should be thinking, What about Saudi Arabia, you know, so I, I do want to say, we hope that they will join in more, and I hope that they are on that glide path to get there. It is something that I have spoken with, with many of the leaders in Saudi Arabia. And we hope that we'll continue to see that really positive movement forward. But we want to see a strong foundation to build upon and which is what we're doing right now. But it can always improve. And that's what we want to see is continuous improvement, not just with the United States. And its existing allies and partners right now than many others that we hope to bring into the fold as well. Benjamin Rogers: So, since you brought up Saudi Arabia, and that's been top of mind on the news, can you share a little bit more with us. What does it mean, from your perspective, to have the Saudis as part of this process? What does it mean, from a US security standpoint? What does it mean from Chinese influence in the region? What are some of the pitfalls there? But where are the opportunities, that clearly, there seems to be a lot of hope for? Joni Ernst: Well, let me start with the pitfalls. And I think it's pretty obvious that the largest pitfall is if we ignore Saudi Arabia, if we don't engage with Saudi Arabia, they will find another partner, and that partner is China. And so we don't want to see that happen. I think the natural alignment is for the United States and Saudi Arabia to come together. And I have always been of the thought that the Abraham accords would not have happened, if behind the scenes, Saudi Arabia had not given a signal that it was okay. So I do believe they had somewhat of a role in the Abraham accords. And I hope that they will continue working on a relationship with Israel, while maybe they won't come fully into the courts, but they will lend their leadership to the accords. And so I think that as we look forward, on the flip side, you know, that if we can avoid the pitfall of Saudi Arabia engaging completely 100% with China, we can avoid that we can move ahead in this region and have the participation of Saudi Arabia. I want them to look to the west for their partnerships. I think that's incredibly important. So I do engage heavily with leadership from Saudi Arabia, I do engage with the ambassador to the United States Ambassador Rima. We have had many, many phone and in person conversations in the US in Saudi Arabia, just continually working on the areas that we can't work on. There are things that we disagree on. But one thing I find with Ambassador Rhema is that we can be very blunt and upfront with one another and have those discussions respectfully. I have the greatest respect for Princess Rhema. And the position that she is in in negotiating in the best interests of her country. I am always going to talk and negotiate in the best interests of the United States. And the best interests of the United States are that we continue to be The best ally for Israel, and find a way for us to work with Arab nations as well, again, going back to having strong security and strong stability in that region and all partnering together against a common adversary Iran. Benjamin Rogers: This has been an absolutely fascinating discussion. We're three years out, and we're talking about Israeli Arab relations, as if this was commonplace as if this was how it's always been. If there is, you know, you do have to stop yourself. And I think an anniversary is always a good moment to say, Things did not always used to be this way. So with that reflection of the past, I know you spoke a little bit about the future. But where do you see the future of the Senate Abraham accords caucus going? If you were to look, you know, three years out, what position do you hope we are? The US, its engagement with Israel, its engagement with the Arab world and its engagement in trying to create a more interconnected Middle East? Joni Ernst: Well, I'm incredibly pleased with where we are today on this third anniversary. And if we look another three years, what are my hopes Senator Joni Ernst, from the state of Iowa, you know, co founder of the Abraham accords caucus, where do we want to be? My vision in three years is that we will have all of this, those military type protections put into place that the defend act is fully implemented, the maritime act is now passed and implemented, and that we are integrating our military resources with one another. So this is a step forward, if we can bring Saudi Arabia into this fold, that we can start working with them on military platforms, as well, the Saudi Arabia of the sides, want to engage with these platforms, if we can get them to move away from China, and really work more with the United States, I can see greater sharing of this technology, with the Saudis. And I do think that that's important. We have to have checks and balances, no doubt about it, we have to have those discussions. But if I can just say three years, this is what I want to happen. I want to have us all fully integrated, to make sure that the region is protected. And in turn, that makes us stronger in the United States, we know that we'll be protected as well for my brand. If we all are partnering together, I do want to say additional, you know, trade with that region as well. I think it's been incredibly important. As you look at UAE and Israel, the types of activities that they have been able to engage in whether it is just travel, education, and trade opportunities, there are so so many areas that are yet untouched, where we can go. And I hope that we see that in three years where we don't really differentiate ourselves as this group or that group, but that we're just common friends and partners. So I think that we've got a long ways to go. But I can act, I can, you know, actually say with this caucus, and the founders of the caucus, both in the Senate and the House, because the House members are really punching above their weight as well, is that we continue to bring members into the fold focus on this region and our opportunities there. And that we have a much more stable world because of the actions we have taken. Benjamin Rogers: Well, Senator, thank you, thank you so much for your time. It goes without saying our AGC has a huge appreciation for the work that you're doing, for the work that your colleagues Senator Rosen, Senator Lankford and Senator Booker have been engaged on. We're grateful for your house colleagues and everything that they've been doing on pushing and securing the Abraham Accords as well. AJC's shares your vision of a more interconnected region of a stronger USA of a more united front against adversaries. And we are your partners in this and we look forward to working with you to realize the vision you just spelled out. Joni Ernst: Well, I appreciate it so much and to you Benjamin and the entire team at AJC. Thank you so much for being such incredible advocates for the Abraham Accords, of course for Jewish communities all across the United States, and the work that we can all achieve together. It's pretty impressive. When we lean on each other and we move with a purpose. So thanks so much for all of the wonderful support. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with Academy Award winning film director Guy Nattiv about his latest film Golda, which opened in American theaters last week. The film examines the Yom Kippur War, a transformative moment in Israel's history.
Aug 25, 2023
'Golda': Behind the Scenes with Israeli Director Guy Nattiv on the 1973 Yom Kippur War
This week, Academy Award-winning director Guy Nattiv discusses his new film 'Golda,' which follows the journey of Israeli Prime Minister Golda Meir as she navigates the tense 19 days of the 1973 Yom Kippur War. Nattiv delves into how Helen Mirren, who portrays Golda Meir, expertly embodied the role. He also shares why, being a child of '73, he felt so compelled to tell this story. Tune in to hear the poignant anecdotes from the set and learn about the involvement of war veterans in the filmmaking process. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Guy Nattiv Show Notes: Watch: 'Golda' opens in US theaters starting August 25th from Bleecker Street / ShivHans pictures–find theater and ticket information at www.goldafilm.com Read: Tough Questions on Israel Answered Listen: Matti Friedman on How the 1973 Yom Kippur War Impacted Leonard Cohen and What It Means Today The Rise of Germany's Far-Right Party and What It Means for German Jews AJC Archives Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Guy Nattiv: Golda Meir [ from AJC Archives ]: We've suffered because of our stance, which is not just obstinacy, not just because we liked it this way. But I think it has been accepted more and more that we have something at stake, and that's our very existence. Whether the borders are such that we can defend them or not, is a question of to be or not to be. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's the late Prime Minister of Israel Golda Meir speaking with AJC about fighting wars to defend Israel's existence. The movie Golda premiering in American theaters this week tells the story of one such battle: the Yom Kippur War of 1973 when Egypt and Syria launched a surprise attack against the Jewish state. Here to talk about the movie and why it's an important story to share with the world, especially through Golda Meir's eyes is its Academy Award winning Director Guy Nattiv. Guy, welcome to People of the Pod. Guy Nattiv: Hi, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Guy, as we just heard from Golda Meir herself, Israel has been defending its very existence since its creation, in war after war after war. Why did you want to direct a film about this particular war, which turned out to be quite a turbulent moment in the life of the Jewish state? Guy Nattiv: Well, I was born into this world, in a way. I'm a child of '73. My mom ran to the shelter with me as a baby, my father went to the war. And I grew up on those stories, of Golda, of the war, and I really wanted to know more, but there wasn't any way of knowing more. And I think that 10 years ago, protocols came out and gave a sense of what really happened, protocols from the Agranat Committee, from the war rooms, from the government. All those declassified documents. And that shed a different light on what really happened there, and on Golda. And doing the research on Golda and talking to people who really knew her, gave me a sense of why we needed to tell the story. It's for my generation and for the generation of my fathers' and mothers'. Manya Brachear Pashman: So who made the decision to cast Helen Mirren as Golda Meir? Guy Nattiv: I wasn't the one who casted Helen. When I came on board, Helen was already attached. I think that Gideon Meir, the grandson [of Golda], he was the one who thought about Helen first, he said, I see my grandmother in her. And when I came she already read the script, and it was only meeting me to close the circle. Manya Brachear Pashman: And what did she bring to the role? Guy Nattiv: Humor, humanity, wisdom, charm. It's all there. But she brings a lot of human depth to the character. Manya Brachear Pashman: Were there conversations off camera during the making of the film about Israel, about its history, about the lessons learned in this moment in its history, with Helen Mirren, or other cast members? Guy Nattiv: Yeah, but the problem is that we don't really learn, right, because look what happened now in Israel. It's the Yom Kippur of democracy. So I don't think we learned enough. Where we are basically in the same situation, as '73, with a leader that is so disattached. At least Golda believed in the judicial system, she believed in High Courts, she was a humanist. She believed in democracy, full democracy. And I think the situation now is so dire. And when I went to protest in Israel, I went to protest with a lot of veterans from the war, who had the t-shirt 'This is the Yom Kippur of democracy.' We're fighting, they're almost fighting again, but this time not because of our enemies, because of ourselves. We're eating ourselves from within. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm glad you mentioned the veterans of the war because this was such a painful conflict for Israel. Such a tragic blow to the nation's psyche. More than 2,600 Israeli soldiers were killed, 12,000 injured, nearly 300 taken prisoner. What do you believe this film offers those veterans? Guy Nattiv: I think it brings a lot of humanity to Golda, who they saw as just the poster, as just a stamp, as just a statue, right? She was somebody who's not human. And I thought that Helen in the way that the film is structured is bringing Golda in a human way. And they see her struggle. And how she cared about those veterans. How she cared about every single person, every single soldier that died in this war. She wrote every name. She took it to her heart. And I thought that was something that veterans would respect. And also what I did is, when I edited the film, I brought five veterans from the front, a lot of them watched the movie in the first cut, the really first offline cut, and they helped me shape the narratives and bring their own perspective to this movie. So I thought that was very cool. Manya Brachear Pashman: You've made it clear that this is not a biopic about Golda Meir. This is really about this moment in history. Guy Nattiv: No, it's not your classical biopic, if you want to do a biopic about Golda Meir, you'll have to have a miniseries with eight episodes or more. This is an hour and a half, on a very specific magnifying glass on the requiem of a country. The requiem of a leader. The last of Golda. The last days. Manya Brachear Pashman: Let's listen to a clip from the film that really shows why Golda Meir was known as the Iron Lady of Israeli politics. Here's Helen Mirren as Golda Meir, sitting across the table from Henry Kissinger, played by actor Liev Schreiber. Clip from 'Golda': Golda Meir (portrayed by Helen Mirren): This country's traumatized. My generals are begging me to occupy Cairo. And Sharon is, is like a dog on a leash. Henry Kissinger (portrayed by Liev Schreiber): If you do that you will be on your own. Israel's long term interests will not be served by a fracturing of our relationship, Golda. Sadat has already agreed to the terms of the ceasefire. Golda Meir (portrayed by Helen Mirren): Of course he has. He's on the brink of defeat. It will give him a chance to regroup. You are the only person in the world who could possibly understand what I'm going through. Henry Kissinger (portrayed by Liev Schreiber): Yes, I know how you feel, but we need a ceasefire. Golda Meir (portrayed by Helen Mirren): I thought we were friends, Henry. Henry Kissinger (portrayed by Liev Schreiber): We will always protect Israel. Golda Meir (portrayed by Helen Mirren): Like you did in '48? We had to get our weapons from Stalin. Stalin. Our survival is not in your gift. If we have to, we will fight alone. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Guy, what would you include in a mini series, if you produced a mini-series instead? Guy Nattiv: I would go to her childhood in Ukraine, probably, I would show her family in Israel. I would show more of her relationship with Lou Kedar, they were really close, her assistant. There's a lot of things that I would do, but not in the format of a feature. Although if you want to do something like you know, a four and a half hour feature, like, used to be in the 80s or the 70s. They were massive, like Gone With the Wind. This is something else. But this is not this movie. This movie is really a specific time in history. Manya Brachear Pashman: Through her eyes, basically. Guy Nattiv: Through her eyes. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yeah. Guy Nattiv: Under her skin. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm curious, if in the making of the film, there were any kind of surprising revelations about cast members or their perspectives, their opinions, or revelations about the history itself. Guy Nattiv: One of the guys that was a stand-in, he was an extra in the movie. He was at the table of all the ministers. Ephri, Ephraim, his name is. I played the siren in the room. So everybody will get the siren, and the long siren. And he started crying. And he said, I'm sorry, I cannot really stay here for long. And I asked him, why not? He said, because I'm a veteran of the war. I was 21 when I went to the tunnel, and I fought. And he lives in the UK. And we shot the film in the UK and he came and it was amazing. And he came to Helen and me and he showed us photos of him as a 21 year old from the war. It was very emotional, it was surprising, he's only this extra. Who is a war veteran, who's playing a Minister. Manya Brachear Pashman: Wow. Did he explain why he tried out, or auditioned to be an extra, why he wanted to do this? Guy Nattiv: He's doing a lot of extra work in the UK. You know, he moved to the UK and is an extra in a lot of movies. And when he saw that this movie exists, he said, I must come, I must be one of those ministers. And we needed a desk full of ministers, you know, and he was the right age. So he's just an extra. That's what he does. I don't know if he thought that he would be in the same situation. I don't think that he thought that. Because he didn't read the script. It was a very emotional moment. And a very emotional moment for Helen. Manya Brachear Pashman: So this was filmed in the UK? Guy Nattiv: It was filmed in an Indian School, outside of London. The Indian abandoned school that was basically huge, like, massive. Arad Sawat, who is my production designer, he basically created the entire kiriya [campus/city], and war room and all the bunker and Golda's kitchen, he built it from scratch, exactly like it was in Israel. And it was crazy. It's just like walking into the 70s. Me, as a grown up, you know, and seeing Helen as Golda. And the commanders. It was surreal. Just surreal. Manya Brachear Pashman: And how did you gather those kinds of personal details about her life? In other words, like, did you have pictures, plenty of photo photographs to base that on? Guy Nattiv: My two sources were Adam, her bodyguard, that gave me all the information, and her press secretary, who's 91, who told me everything about her, and books that were available for us, and protocols. It was very specific protocols that showed us how everything went down. Manya Brachear Pashman: Did Helen spend a lot of time with those people as well to really get a sense, and I'm curious how else she prepared, if you know, how else she prepared for this role, to really embody the former prime minister? Guy Nattiv: It was her own private process. I didn't get into it so much. But I think that she read all the books. She worked with a dialect coach to understand how the Milwaukee accent, to talk in the Milwaukee accent. Walk the walk. I think she prepared also with an animal coach. There's a coach, every actor becomes, every role it's a different animal. And you behave like this animal. You take the physiques of this animal. I think she was a turtle. I think that Golda was more of a turtle. The way she spoke. Everything was so slow. So I think that she became, she did, the way she carried herself like a ship into this. So it was a lot of metaphors, a lot of stuff, a lot of tools that help actors get into the role. But when I met her, and that was after like three and a half months we didn't talk, she was Golda. It's almost like she got into the trailer as Helen and she came out as Golda. We didn't see Helen, we saw Golda. Even when we spoke and we ate lunch with her, we saw Golda. And so at the end of the 37 days of shooting, I was like, you know, I don't remember how you look like, Helen. And only in Berlin Film Festival, when she gave us Helen Mirren, is where we really saw her. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you mentioned Berlin, the film has premiered there in Berlin, also has premiered in Israel. I'm curious how audiences have received it in both places. Has it hit different chords in different countries? Guy Nattiv: When non Jews see the movie, I mean, they have lack of emotional baggage. And they see it as something foreign in a way. But for Jews, for Israelis, there's a lot of emotional aspects to it. So it's, yeah, it's different. It's a different view. But a lot of people that are not Jews are still really like, this is such an interesting, we didn't even know about her. You know, a lot of people are learning who she was. And they didn't know. It's like she paved the way to Margaret Thatcher. And to Angela Merkel. So they see now what's the origin of that. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's a really wonderful point, it being filmed in the UK and premiering in Berlin. Guy Nattiv: [Angela] Merkel said that Golda was her inspiration. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how do you expect it to resonate here in the United States? Guy Nattiv: I really feel that it's just starting out right now, we had an Academy screening, and I'm getting amazing text messages from people from that generation. But I also would love for younger generation to know about that and explore Golda. Yeah, I mean, I'm interested to know, to see how it is. But I know that it's very emotional for the Jewish community. I can feel that. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you think this film will change how people view Golda Meir and Israel's leaders in general? Guy Nattiv: I hope it will spark a nerve in a way that we are in the same situation now. And people will see that history repeats itself, in a way. It's not the same exact situation. But it's the blindness that our leaders are in right now. And I hope it will bring a different narrative to the character of Golda, and who she was, not just the poster, not just the scapegoat. Because she was the scapegoat of this war. It was easy to blame her for all the faults of her commanders and all the other human intelligence commanders and what happened there. But it's just, she's not the only one. She's not the scapegoat. She was actually very valuable for Israel, because she brought the shipments from the state, of the planes and the weapons. She was in charge of it. And I think without that, we would probably find ourselves in a different situation. Manya Brachear Pashman: Golda was the first female head of government in the Middle East. Do you think her gender had something to do with her being blamed or the being labeled the scapegoat, as you said? Guy Nattiv: Absolutely. Absolutely. I truly believe that with more female leaders in this world, the world will be a better place. I feel that men proved us wrong. You know, I want to see Tzipi Livni leading Israel again. I want to see more women in key roles and leading countries. I think the world would be a better place. Manya Brachear Pashman: Guy, thank you so much. Really appreciate you sitting down with us. Guy Nattiv: Thank you.
Aug 17, 2023
The Rise of Germany's Far-Right Party and What It Means for German Jews
Polls in Germany suggest the far-right political party Alternative for Germany, or AfD—with its antisemitic, anti-Muslim, anti-EU, and other extreme views—has support from a fifth of German voters. Hear from Felix Klein, the Federal Government Commissioner for Jewish Life in Germany and the Fight Against Antisemitism, and an AJC Project Interchange Alum, on what has contributed to the rise of AfD, why the party threatens German Jews, and the danger it presents to Germany's democracy. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Felix Klein Show Notes: Read: A Roadmap for America: AJC's Experience in Europe Is Helping the U.S. Fight Antisemitism German Antisemitism Czar Says Calling Israel 'Apartheid' Is Antisemitic Listen: What the U.S. National Strategy to Counter Antisemitism Means for Jewish College Students Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Felix Klein: Manya Brachear Pashman: Polls in Germany suggest the far right political party Alternative for Germany has support from a fifth of German voters. In some states, such as Thuringia, the AfD has the support of more than a third. This past weekend, the party met to select its candidates for the European parliament, where it has joined a far right bloc that will boost EU funding for the party. Here to discuss how that affects Germany's Jewish community is Felix Klein, Germany's first Federal Government Commissioner for Jewish Life in Germany and the Fight against Antisemitism. Felix, welcome back to People of the Pod. Felix Klein: Hello, it's a great pleasure to be here again with you. Manya Brachear Pashman: So tell us a little bit about Alternative for Germany or AfD, as it's often referred to, and explain for our audience why it was founded 10 years ago? Felix Klein: Well, AfD was founded in light of the big financial crisis. It was at the time, about 10 years ago, it was questionable at all whether the euro, as one of the most prestigious and most important European projects, could continue as a currency, as a common European currency, because countries like Greece were heavily indebted. And there was a big discussion whether to, to kick Greece out of the Euro system, or, and it was differently decided. O r to keep it in the EU, of course, and in the Euro system. And the then-Chancellor Angela Merkel said there is no alternative to that. No alternative for the solution suggested by the government. And there were many people in Germany that were not happy with that, saying, Oh, yes, there is an Alternative for Germany. And that was also the title of this new party, the Alternative for Germany. So it started really, with people who were not happy with the policy towards the European Union and the European solidarity. It didn't start so radical as it is now. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how did it become as radical as it is now? And why are we seeing a bit of a resurgence? Felix Klein: Well, in times of crisis and uncertainty people are unfortunately, I think that happens when many democracies are more open to populist ideas and parties. And that happens, many countries, including Germany, and AfD, was successful in getting support of those who were not happy with the decisions of the government in Corona, pandemic, from 2020. And now, last year, with the War of Russia, attacking Ukraine, again, we had a strike of uncertainty, energy prices went up in Germany, people are uncertain of what to do, many are not satisfied with the way the government deals with all these issues. And this is another explanation why AFD was able and successful to catch support, particularly in Eastern Germany. Manya Brachear Pashman: But it sounds like it also has values that go beyond fiscal responsibility or the economy. Felix Klein: Yes, it's beyond the economy. So as I told you, AFD started off with economic issues, but unfortunately, it was attracted by people who have very, very problematic views. And to people who would deny or distort the Holocaust. People will say it was for a long time anyway, Germany was dominated by foreign powers by the EU, and you hear what they're saying this is antisemitic thoughts and narratives. And those people became more influential by the party over time. And what we've seen now, where this party really now chose candidates for the European elections who actually are in against the European Union. Many of them want Germany to leave the EU. There you see how radical it has come, they're also anti-Muslim. This is maybe the most important narrative, anti-migration, anti-Muslim, anti-EU. And of course, with all of that comes also antisemitic narratives. So this is why I'm very, very concerned about the success of this party. And I've expressed it openly in an interview that was published in Welt am Sonntag last Sunday. Manya Brachear Pashman: You just mentioned that this party appeals to those who deny or distort the Holocaust. How so? Felix Klein: Holocaust distortion is a very common idea in this party. Up to 20% of the Germans think that we should not talk so much anymore about the atrocities committed by the Nazis, that we have to look forward, etc. So, it is not a big surprise that, of course, anything that downgrades, if I may say so, the horrors committed by Germans in the Holocaust, and in the Second World War, in general, is very common. Very prominent figures of the AfD call really for a cut, which is illogical anyway, you cannot cut yourself off of your own history as a country. But many of these voices call for a different remembrance culture, that it is a shame for Germany that it constructed the Holocaust Memorial in the heart of Berlin. Germany should not be so shameful with itself. And unfortunately, many people agree to this kind of ideas. So holocaust distortion is a big thing. Holocaust denial, it's not so much of a problem. But of course, anything that kind of makes the Holocaust less, less cruel or less incredible, as it was, is welcomed by this party. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to go back to the topic of the European Union, because one of the reasons why Alternative for Germany joined this far-right bloc was to boost EU funding for the party, but yet it's calling for the dissolution of the EU, or at least for Germany to withdraw. Can you explain that calculus? Felix Klein: Well, it's, of course very contradictory. On one hand, you call for European funds. And anyway Germany is, I think, the one of the countries that really is taking advantage of the most of the European Union, our industry is heavily export-oriented. One out of four workers in Germany depend on international trade, and of course, it would be very much against German interest to leave the EU. On the other hand, it is a very common narrative in Germany to blame the EU for many developments and decisions taken by the government and they do not have a problem calling these two things at the same time. Manya Brachear Pashman: So besides Holocaust distortion, is there other antisemitic rhetoric coming from this party that you see, or fear threatens Jewish life in Germany? Felix Klein: Yeah, one of them, clearly I see conspiracy theories being very popular within the AfD voters and a very concrete danger for Jewish life is a motion the AfD has tried to introduce into our parliament that would have banned kosher slaughtering. And fortunately, it didn't go through of course, but if you ban kosher meat, with the argument for animal protection, then of course, you violate the basic right of religion. Because the way you would like to eat is a part of the freedom of religion and fortunately, the motion didn't go through but you'll see that the AfD is really in that very concretely threatening Jewish life in Germany. Another thing is, of course, they are on first hand very anti Muslim, anti migration. But it is a common fact that anti Muslim hatred is very much linked to antisemitism actually and the way they also talk about Israel as being a big and important factor against the Muslims shows the whole narrative of, to say that Israel is there also to keep Muslims out, is very dangerous. Because I think we all agree that Israel is not against the Muslims, or it's not an anti-Arabic country, as such, but this is what the AfD would like people to believe. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, championing Israel, for motives that don't belong to Israel, in other words, assigning motives to Israel that don't even exist. Felix Klein: It triggers a discussion about Israel, which is absolutely bad, not only for Israel, but also for the Jews living here, because they then have to have an opinion about Israel. And it is complicated enough anyway for the Jews who live in Germany, to explain to non Jews that they are not ambassadors or representatives of the Jewish state here, that they are normal German citizens, and of course, they might have an opinion about Israel. But they are by no means representatives of Israel. I think you have the same discussions in the US, where many people think that American Jews represent the Jewish state. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you have also warned that there are not just antisemitic forces, but anti-democratic forces at work in this party. What do you mean by that? I mean, is that in reference to how they denigrate the EU? Or are other other things in play? Felix Klein: I refer to the conspiracy theories I already mentioned, which are as such anti democratic, because anybody who believes in a conspiracy theory thing has a problem with democracy. And I would say 99% of the conspiracy theories have an antisemitic content in the end. Because the theory is that a small group of privileged people, in brackets, the Jews, take advantage and profit from a uncertain and difficult situation at the expense of, of everybody, a small group gets an advantage. And this is what leading figures in the AfD also emanate. And of course, this is not only antisemitic, but also anti-democratic. Manya Brachear Pashman: They really are one in the same. If you're anti democratic, then you're probably anti semitic and vice versa. Felix Klein: Once again, I cannot reiterate enough, that shows that antisemitism is anti-democratic as such, and if you turn it around, every success we have in the fight against antisemitism is a fight for our democracy. It is really directly linked. I think it's like a litmus test we have in our society. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what other questions should people ask to measure a candidate or a party's democratic ideals? Certainly listening out for conspiracy theories or antisemitic rhetoric? Are there other litmus tests? Felix Klein: Yeah, of course, well first off, particularly in Germany, every politician should make it clear that he or she distances himself or herself from the horrors of the Nazi past. I mean, our democracy is the answer to the horrors of the Third Reich. And if you don't make that clear, or if you leave it uncertain, then you have a problem. And this is what voters should actively ask candidates: do you really think that the Holocaust is singular in history? Or is it an atrocity, like any other atrocity that was also committed by other people in history? This has to be made very, very clear. And I hope that in the coming elections, people will ask these questions. Manya Brachear Pashman: I love what you said about how every victory against antisemitism is a victory for democracy. They really do go hand in hand. And I want to switch gears a little bit and talk about the EU's Digital Services Act, which takes effect this month in fact. Now for our audience members who aren't familiar with this, this is a new law that will require internet platforms like Facebook and X, formerly Twitter, to not only delete unlawful content, but also provide information about those publishing that information, to the police. Some people would say this is not democratic. Others would say, Oh, yes, it is. So can you speak to that, to that criticism and whether you think this law will make a difference in the fight for democracy and against antisemitism. Felix Klein: The main number of antisemitic crimes committed in Germany happens in the internet. Holocaust distortion, particularly, but also incitement of the people. More than two thirds of all antisemitic crimes are committed there. And if you look at the antisemitic incidents below the threshold of crime rate, it's even more. So we have to get and develop new instruments in combating antisemitism online. And the idea is very simple. Whatever is punishable offline should be also punished online. So any sentence you could be punished for, like an incitement of the people in the real world should also be punishable when you do it on the internet. It's very, very simple. And that is, this is a very simple idea of the EU Digital Services Act. And in the past, of course, it was very difficult for police and prosecutors to trace the perpetrators and the main people now we want to involve, or big organizations, is the internet platforms because they have access to the IP addresses of those who spread antisemitism and hate speech. And we have to make them responsible. So I think this is a very, very good instrument in fighting antisemitism online, I would even say it is a game changer. We have had pilot projects in Germany, where prosecutors who actually then found out with their means the perpetrators who spread antisemitism and will then get counter pressure from the state. So for instance, when the police car is in front of their homes, and the neighbors are watching, these people do not spread antisemitism anymore, they are impressed that the states can defend itself or defend its citizens and go against hate speech. I think this will be very effective. And we I'm very happy that the federal police office here in Germany has now founded offices to and departments to be ready for the new law. And as you said, yeah, it is getting affected soon. And this is, I think, a very good example, that democracy is not self-evident. It has to defend itself. And freedom of speech has its limits, at least in our European concept. You cannot say anything you would like if you violate the rights of others. And this is a clear case. Manya Brachear Pashman: The White House just recently released the US national strategy to counter antisemitism. And you and other envoys traveled here to the United States to advise the officials who were developing that strategy. In fact, the last time you were on this podcast, it was to talk about that trip. Did you talk about the limits on free speech during that trip with officials, the need to hold social media platforms accountable? Because what the EU is doing is not happening here. Not yet, at least. Felix Klein: We talked about this, of course, but I'm aware of the legal situation in the US where you have a different concept of the freedom of speech, that the First Amendment of the US Constitution is, there problematic in that case to limit that. I hope that US administration finds ways nevertheless to go against, or to be effective against hate speech and antisemitism online and I think the right way is to talk to the internet platforms, to provide us– many of them have their headquarters in the US and earn much money in the US. So, there should be ways in getting them to limit or to do their responsible share of maintaining the US democracy too. Manya Brachear Pashman: Felix, thank you so much for joining us. Felix Klein: It was a pleasure. All the best, and it's always great to be together with AJC.
Aug 10, 2023
What the U.S. National Strategy to Counter Antisemitism Means for Jewish College Students
In May, the White House released its U.S. National Strategy for Countering Antisemitism. As students return to campus, hear from two student leaders who are working to share and implement the strategy's recommendations at their colleges and beyond: Sabrina Soffer, a rising junior at George Washington University and the head of the school's Presidential Task Force to Combat Antisemitism, and Abe Baker-Butler, a rising junior at Yale University and the president of the AJC Campus Global Board. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Abe Baker-Butler and Sabrina Soffer Show Notes: Learn: AJC Campus Library: Resources for Becoming a Strong Jewish Student Advocate Listen: IsraAID CEO on Sharing Israel's Expertise With the World's Most Vulnerable Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Abe Baker-Butler and Sabrina Soffer: Manya Brachear Pashman: At the end of May, weeks after most college students headed home, abroad, or to summer internships, the White House released its US National Strategy for Countering Antisemitism. But given the timing, it's unclear how many students know it exists. With me are two student leaders who not only know, they've shared it with other students with the intention of helping to implement its recommendations for college campuses, when in a few weeks they go back to school. Sabrina Soffer, a rising junior at George Washington University is the Commissioner of the Presidential Task Force to Combat Antisemitism at GW, and Abe Baker-Butler, a rising junior at Yale University is the president of the AJC Campus Global Board. Abe, Sabrina, welcome to People of the Pod. Abe Baker-Butler: Thank you for having us, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I will ask you both, when did you hear about the US national strategy? Abe Baker-Butler: So I heard about the national strategy when it was in the headlines initially. But with school ending and finals, I didn't have the time to actually sit down and read it in full until we got to AJC Global Forum. And what really stuck with me was how there are real action items in there for students, and not only Jewish students, but all students to take action to combat antisemitism. And I was very excited that as the campus global board, we had the opportunity to spend some real quality time brainstorming how we could play a meaningful role in implementing this National Strategy to Combat Antisemitism. Sabrina Soffer: So yeah, that's really interesting, I took very similar tidbits away from the strategy. But the first time that I heard about it was actually the same day that I was giving a talk to a group of women in San Diego, which is my hometown, in California. And it gave a lot of hope to the women who were listening to what I was saying, especially because the talk was about my experience on campus, which I think I'll get into a little bit later. But similar to Abe, the time I read it on the plane, actually on the way to Israel. So I had quite a bit of time to do that. And the thing that really stuck with me was exactly what Abe said, how all students, not just Jewish students, can take action and also the interfaith component. I think that having other students stand up for the Jewish community is essential and spreading awareness that way can really help in the fight to combat antisemitism. Manya Brachear Pashman: So yes, Sabrina, I do want to talk to you a little bit more about the Taskforce. But first, Abe, can you tell us about the AJC Campus Global Board? It was formed last year, but who makes up its membership? And why? Why are they on this board? Abe Baker-Butler: We're a group of 30 students, I believe, there are 20 of us from the United States, 10 of us from the rest of the world. And when I say the rest of the world, truly the whole rest of the world, Australia, to South Africa, to Europe, you name it. And our mission that we're working to pursue, is to support AJC's work on campus, and also to really ensure that AJC's work is informed from a student leader and young person's perspective. I think it's a real testament to AJC that they are taking this tangible step to prioritize us as young people and to say, you know, we want to hear you, and we want your perspectives to inform our advocacy. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what schools do students hail from? Are they all East Coast schools? Or is there geographic diversity? Abe Baker-Butler: Certainly not all East Coast schools, we have people from all over ranging from the University of Florida University of Southern California, University of Tennessee, Northwestern, and that's just in the United States. Our goal is really to ensure that we are incorporating a broad array of perspectives from across our country, from across also all parts of the Jewish community. We care deeply on the Campus Global Board about ensuring that we're embracing a pluralistic Judaism, that we have people from all denominations, all backgrounds, and we believe that by doing that we can best inform AJC's work. Manya Brachear Pashman: And what have you done so far? Abe Baker-Butler: So in the past year, we've really been building our structure and integrating ourselves into the AJC institution. A few highlights that I can think of from the past year that have been particularly meaningful to me, are well I guess this is one of the biggest ones in my mind during the development and prior to the announcement of the National Strategy to Combat Antisemitism, Holly Huffnagle, AJC's US director for combating antisemitism, her and other AJC content experts and staff took the time to meet with a contingent of our Campus Global Board members to hear their thoughts in a listening session of sorts. And then what Holly and those staff members did is they took those thoughts and used them as they were giving feedback to the White House, as it developed the National Strategy. To me that's extremely meaningful. Some other events we did is we had an event with Ted at University of Pennsylvania, which received really diverse audience in terms of Jewish denominations and observance, which I was very happy about. We also held an event with Richie Torres, at Harvard, which was also much needed, given the situation on campus there. And beyond those sorts of headline events, we've also been doing more-- we've started a mentorship program between our campus full board and ACCESS. And there's a lot more in the pipeline, too, that I can also talk about. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you talk a little bit more about what was going on at Harvard? Is the campus global board, is the primary responsibility to respond to situations? Abe Baker-Butler: Yes, so the reason I made that remark is because I think there's often a perception that you can't be both progressive and Zionist, and I think Ritchie Torres, who was our speaker there, really cuts that misconception straight through. But in terms of us responding to what's going on on campus, another really interesting part of our work that I'm proud of is our antisemitic incident response. Whenever there is an antisemitic incident on a campus, we the leadership of the campus global board, try and reach out to the Jewish leaders on that campus, whether it be the presidents of Hillel, or the head of the Chabad board. And we come saying, Hey, we're not here looking to get any kind of headlines, or press coverage, or to meet with your university administrators. You tell us what you need. And we're here as a group of 30 committed individuals to provide it to you. Manya Brachear Pashman: Sabrina, tell us about GW's task force to combat anti semitism and who makes up that group? Sabrina Soffer: Yeah, so GW's task force came about after the Lara Sheehi incident that happened in December. So basically, there was a professor who was teaching a mandatory diversity class at the grad school level. Everybody had to introduce where they were coming from. And there was a group of students from Tel Aviv. And the professor responded, it's not your fault you were born in Israel. And to make a long story short, that class became increasingly about imperialism and settler colonialism and more anti-Israel over time, and the students became more and more uncomfortable, and even after they reported it to the dean, there was no accountability. And then there was a title six complaint. And after that, there was an investigation conducted by the University, I guess, the university hired a law firm. And they found that there was not only no antisemitism, but no discrimination, because it fell within the lines of free speech, what was going on in the classroom, which I don't necessarily agree with, I think that it created a really hostile environment. Because the students did report that they couldn't sleep well, they couldn't eat because they had to turn in assignments to that professor who they couldn't trust because obviously, she disrespected them because of their identity. So something I'm trying to do with the taskforce is trying to create trust between all members of the GW community, whether they agree or disagree, and no matter their identity groups, but I'll put that aside for now. So after that incident happened, there was a student in the student government, I think he's the former legislator General. And he was friends with the president of Chabad. And I'm the vice president. So they were speaking about it. And I guess the president, who's a good friend of mine, said, Oh, I have a friend who's very much involved in the Jewish world. And she would definitely like to take on an initiative like this one, and create a taskforce to deal with these issues on campus, because we've had quite a few of them that are either similar or radically different than the Lara Sheehi incident. So you know, I took the task upon myself I, they gave me some parameters of what to do, like it had to be 10 students, which I've now expanded to 15, because I couldn't reject people who seriously sounded amazing in their interviews, and then it had to be tied to the student government in some sort. So from there, I had to pass it through three different committees on the task force, and I really wanted it to be an all encompassing group. For example, I didn't want it all Jews, like the White House National Strategy says. And I think at the back of my mind, my mom raised me with this principle of like, you can't solve a problem without making people who are a part of the problem, a part of the solution. So I said, You know what, let's go for it, Yallah, and it'll be better this way. And we'll figure out these issues together. So then it came about, it was voted on unanimously. And then we've kind of started doing some work during the summer, we started collecting data. I've gotten the whole team organized, and I'm really, really pleased. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, I'm sure there are Jewish students who are listening, who are heading to campus as freshmen this year, perhaps their parents or their grandparents are listening. And Sabrina, I'm curious, what should they expect? And how can they prepare to be a Jewish student on an American college campus? Sabrina Soffer: So I think that every campus is different. And I want to preface this by saying that no, the campuses themselves, besides a few, like, you can't label the campus as an antisemitic University, I think that's really important to note. For me, from what I've seen in conversations with administrators, with faculty and other students, is that there's a problem of systemic ignorance that breeds antisemitism, not so much a problem of systemic antisemitism. Because really, people don't have that, the majority of people don't have that much hate in their heart, you know, to like, go out and say tropes and demonize, you know, another, another person's identity for no reason. I think it really comes from people trying to advocate for something else, but they don't know how it makes other people feel, or they just don't care. And I think we have to do a better job of explaining how we feel. So that was just a little bit of a preface, but the backstory is that I came into college not having any idea what this would be like. I tried to look for a campus with a great Jewish community, which GW absolutely has. Not all campuses have it. But I'm lucky, I actually don't believe that we do have a Chabad, Hillel, Meor, GW for Israel. So groups that I really identify with, and I thought that I would have no problem. However, in some of the classes that I was taking, I would openly share my ties to Israel, where my family was from, where I got my principles and my ethics. And over time, I came to realize that my ideas were being tarnished, they were being called racist and xenophobic. This was just a quick story. We were trying to talk about Holocaust education and slavery education, and one girl told me, Oh, the Holocaust is a lot more sensitized than slavery in school, because Jews are white. And that's like, I took that very, you know, did not sit well with me. But it was a problem of ignorance. I had a conversation with the girl afterward. And you know, we reconcile the differences, but like, I think that happens a lot on campus where there's so much ignorance, that it just comes out in ways that they shouldn't. So, from then on, I really took it upon myself to become an educator, no matter what people would think of me. I would always try to spread my truth and do it in a loving way. So I would just encourage all Jewish students before they get to campus to find their community because this whole time that I was experiencing this difficulty, I was really leaning on my Chabad friends, my Hillel friends, and of course, my family back home. Always talk to your parents. I think that's a really important point. And find the people who are going to support you no matter what. So that's just my my big piece of advice as well as get yourself educated. Know your history. Know your facts, know your identity, and never stop being who you are. Manya Brachear Pashman: Abe, what about you? What advice do you have for incoming freshmen? Abe Baker-Butler: Yeah, well, I think Sabrina really hit the nail on the head here by talking about ignorance. The stories I've heard from my friends and what I've experienced on campus, I've seen that a lot of the antisemitism we see is really driven by ignorance. I've heard multiple times on my campus. ideas such as the Jews are white and privileged. Why do the Jews have so many resources in the form of their lovely Hillel building? Look how rich the Jews are-they have security guards. These kinds of ideas, these kinds of comments. I think they're not coming from. Yeah, I don't think there's such a thing as informed hatred, right. I think that's an oxymoron. But they're coming out of ignorance. And I think because these sorts of antisemitic sentiments are coming out of ignorance. It makes the work that people like Sabrina and I, like Sabrina's taskforce and our campus global board, I think it makes the work that we're doing, ever more important, extremely important. Abe Baker-Butler: In terms of my advice for Jewish students coming to campus, I would say, you should keep in mind that while you can have an extremely meaningful impact by teaching those who may be ignorant about antisemitism, you also should remember that it is not only your responsibility to fight antisemitism, it is the entire community's responsibility to fight antisemitism. That includes it, should and must include allies. And then the other advice I would give is exactly what Sabrina said, you should know that as a Jewish student, there is a community behind you both on your campus, whether it's Hillel or Chabad, or anything else. And also, nationally, there are students like Sabrina and I, who are here to support you. There are organizations like Jewish on Campus, for example, of students that have ambassador's programs on campus. So you should never feel alone as a Jewish student on campus. Because there's so many people out there who care about you and support you. And you have the facts behind you. Sabrina Soffer: I also just something that's really important for students to know is like know your rights on campus, both in the campus realm and the legal realm. Because what happened with the Lara Sheehi incident, those students, they knew how to report the incident. But there was no accountability. So it's like, where do I go from there? I've had students, I've had friends who've given up after they've had incidents, and they didn't know to go to groups, like AJC or Hillel International, maybe to help them out. So I think that knowing your rights before you get to campus is imperative. Manya Brachear Pashman: You know, I was going to add, thank you so much, Sabrina, for that. I was also going to add to what Abe said, you know, I went to a very small school. For undergraduate. I was one of two Jews on campus that I know of. There might have been more. So there was no Hillel. It was a very small, tiny Jewish community. But like you said, there are organizations like AJC, there are national organizations. Now there's a national action plan that applies to every school. Not just these larger schools that have Hillels or Chabads on campus. So we talked about engaging different points of view, and different perspectives. These are all young people, your age, still learning. I also think it's very important to build and find allies on campus. I think that right there is a potential for education. And Abe, I am curious what kind of thought the campus global board has given to engaging different points of view and finding allies? Abe Baker-Butler: So we care deeply about finding allies. One thing I do want to highlight is the AJC curriculum that we've been developing with Dr. Sara Coodin that we look to use on campuses. And in terms of finding allies. That is key if it's central to our work on the campus global board. Some ideas that we have that we're working on include collaboration, brotherhood and sisterhood events, with Black and Jewish fraternities and sororities, reading groups between black and Jewish groups on campus to understand each other's shared perspectives. Joint interfaith seders and events between Muslim and Jewish groups on campuses. We really have a responsibility to create shared communities of goodwill, who can be our allies on campus, because in addition to having the national strategy and having national organizations like AJC on campuses, like the one you attended Manya, having allies like that is perhaps the most important because they can be that community that supports you. And the other thing that I wanted to add to what we were discussing before, in terms of advice for Jewish students that I neglected to say was, you should always be proud of your Jewish identity. Always, always, always. You're the heir to an extremely rich intellectual and cultural tradition. And anyone who tries to make you feel ashamed of that or to slander that is wrong, and you should not heed what they say. Manya Brachear Pashman: I am curious if you could share how you have celebrated, enjoyed being Jewish on campus? Sabrina Soffer: This past April it was Yom Ha'atzmaut and we had Israel fest. It's a GW for Israel organized, we put Israeli flags in Cogan Plaza, the main plaza, we had loud music, falafel, shawarma, everything, and we were just dancing. And it was just the most amazing experiences not only feel like, for me, a lot of my Jewish identity comes from, like Zionism and my Israeli background. So just being able to celebrate Yom Ha'atzmaut with a bunch of my Jewish friends who also support Israel. And it was just amazing. And also like a lot of the music that I grew up with, and that I'm familiar with, that was very fun to like, have in public on campus, and also having non Jews join us in that celebration. And this was all while SJP and JVP, were sitting right in front of us for literally two hours with posters with very hostile messages about Israel. And we didn't pay any attention, we kept dancing, and they just it's like, you know, we will do our thing, we'll be proud, we block out the noise, block out the hate. So that felt pretty great. And then another experience I had was on Pesach, my parents come and visit me a lot. I brought them to Chabad for Pesach, and it was just like they fit in so nicely with all my friends, all the students and the whole GW community. Chabad was really the organization that ushered me in at the beginning, they really made me feel like home away from home, and having my parents who like literally made my home amazing, very Jewish. Like they brought me up in a Jewish home, having them in my new kind of home in college just was very rewarding. So those are two experiences. Manya Brachear Pashman: Both sound beautiful, both sound really, really lovely. And I just want to clarify for listeners, JVP stands for Jewish Voice for Peace, and SJP is Students for Justice in Palestine, which are two groups on college campuses that have engaged in a lot of anti-Israel rhetoric. Abe, I want to turn back to you for one last question. And that is, I asked you what the Campus Global Board has done and it's one year of existence, but what will it do in the year ahead? What do you envision accomplishing? Abe Baker-Butler: Probably the most central part of our plans for this year, I want to highlight is implementing the White House national strategy on combating anti semitism on campus. One idea that we're working on, not finalized yet, but that I'm hoping will become a reality is an incubator of sorts, where we'll put out a call for proposals from not only Jewish but non Jewish groups about how to fight antisemitism on campus, in line with the plan. And then our goal is that the campus goal board will sift through the proposals that we receive and figure out how we can best support, financially and otherwise, these organizations on campus in conducting activities that will help implement the plan and stem antisemitism. Some other ideas we have are, we want to bring diplomats from Abraham Accords countries to campuses to help stem the ignorance that I was talking about. And then also, we want to ensure to, the point I was making earlier about integrating young people, and really walking to talk with young people as part of AJC's advocacy. We want to ensure that young people, members of the campus cohort and others aren't as many AJC advocacy meetings and settings as possible, because we believe, and AJC believes as well, that when our voices are there, it provides for an even more persuasive advocacy, and an even more full representation of the interests of the Jewish community. Manya Brachear Pashman: Can you give examples of where that advocacy takes place? Where would these young people go? Abe Baker-Butler: Certainly. So we're planning to do it at all levels. One example would be Diplomatic Marathon alongside the UN General Assembly, meetings with diplomats there but also at the local level with legislators and others, at the regional office level. There are a lot of opportunities for young people to get involved in AJC's work. And we want to ensure that young voices are represented in all of these meetings, whether it be domestic legislators or diplomats or anyone else. Manya Brachear Pashman: Sabrina, Abe, thank you so much for joining us and discussing what your plans are for this year. I wish you both a lot of luck and I hope you most of all enjoy your junior years in college. Sabrina Soffer: Thank you so much for having us. Abe Baker-Butler: Thank you, Manya. Shabbat shalom. Sabrina Soffer: Shabbat shalom.
Aug 4, 2023
IsraAID CEO on Sharing Israel's Expertise With the World's Most Vulnerable
Tune in for a conversation with Yotam Politzer, CEO of IsraAID, a leading Israeli humanitarian aid organization and longtime partner of AJC, about the group's mission and the impact of sharing Israel's expertise and technology to help millions worldwide after crises hit. Yotam also shares his personal journey and how he found his passion for humanitarian work. Additionally, hear what our podcast community at AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv had to say when we asked: why do you love Israel? *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Podcast Listeners (2:47) Yotam Politzer Show Notes: Learn: Crossing the Red Sea: Israel and Africa in 2023 Listen: Israel's Reasonableness Law: What it Means for Israel's Democracy and Security Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Episode Transcript: Transcript of Podcast Listener Segment: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week, we bring you voices from Tel Aviv. I spoke with Yotam Politzer, the CEO of IsraAID, about the importance of sharing Israel's expertise and technology with the world's most vulnerable. But first, hear from some podcast listeners who stopped by our podcast booth at AJC Global Forum 2023 to tell us why they love Israel. Listeners, the mic is yours. Corey Sarcu: My name's Corey Sarcu, I'm from Chicago. Hannah Geller: My name is Hannah Geller, and I'm from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Irvin Ungar: My name is Irvin Ungar. I'm from Burlingame, California, which is near San Francisco. Corey Sarcu: As for why I love Israel, there are so many reasons. I think, culturally, Israel is kind of a crazy place. Everyone is very welcoming. They're almost aggressively welcoming in a way, like one of the first things, they meet you for five minutes, and they're already calling you achi, which means my brother, it goes along with the whole theme that really the Jewish people, we're all one big family, and Israel is just the natural manifestation of that in the state. Hannah Geller: I love how in Israel, I can walk on the street, I can be on the bus with someone, and a stranger will invite me to Shabbat dinner. I love how the woman at the pool will just hand her baby over to me if she has something else to be tending to–and I've never seen her in my life. Irvin Ungar: The reason I love Israel is probably-I've been here several dozen times. And the first time I arrived, I do remember feeling like I was coming home, and I'm still coming home. The question is why I left if I'm still coming home, and I've been here that many times, but nonetheless, that's the way I feel. I'm with my people. I'm with my people when I'm not in Israel. These are like my brothers. So I'm here. That's why I'm here. ___ Transcript of Interview with Yotam Politzer: Manya Brachear Pashman: Yotam Politzer joined IsraAID, Israel's preeminent humanitarian aid organization, in 2011. In fact, he was the NGO's second employee. Since then, he has flown on dozens of aid missions personally helping more than a quarter million people after some of the world's worst disasters. In 2017, he took over IsraAID as its chief executive officer and has since expanded the reach of Israeli disaster aid around the world. Earlier this year, he received the Charles Bronfman Prize, a $100,000 award given to a Jewish humanitarian under 50. Yotam is with us now, in Tel Aviv. Yotam, welcome to People of the Pod. Yotam Politzer: Thank you. Thanks for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So first, thank you for all that you are doing to quite literally repair the world. Tell us about your upbringing and what led you up that particular Jewish professional path. Yotam Politzer: So, I wasn't thinking that I would end up chasing disasters around the world in places like the tsunami in Japan, or the Ebola outbreak, or most recently, Afghanistan, where we had a very dramatic operation. I grew up in a small village, in a small Moshav in the north part of Israel. My father is a social worker, my mom was a school counselor, and had a beautiful childhood. And before my military service in the IDF, I did something-it's kind of a gap, we call it in Hebrew Shnat Sherut, which translates to service year. And it's kind of a volunteering year before the military service. And I did that with youth at risk, many of them are from Ethiopia, Ethiopian Jews. It was an incredible year, probably one of the most meaningful years of my life and I kind of developed my passion not just for service, but also for working with people from other cultures, essentially, using humanitarian work not only to save lives, but also to build bridges. And I learned so much from the Ethiopians that I worked with at that time. And then after my army service, like every Israeli, I followed what we call the hummus trail. Which is this crazy phenomenon with about 50,000 Israelis every year are traveling, backpacking after the army to kind of clear their heads from the tension of the service. Most people go to India or South America, I went to India. And it's called the hummus trail because the locals are starting to make hummus for the Israelis that are traveling. So I was following the hummus trail- hummus was not highly recommended. In India it has a bit of a curry taste to it. But ended up arriving to Nepal. And I was planning to trek in the Himalayas. And I did that for a couple of weeks. And then I saw an ad that invited backpackers to volunteer with street children in Nepal, of all places. I thought well, it sounds cool. Oh, you know, I'll do it for a couple of weeks, I'll continue to Thailand or wherever I was going. I ended up staying there for three and a half years, really fell in love with that kind of work. I came back to Israel and want to start my life and two weeks after I came back to Israel, that was 2011 the tsunami in Japan happened. Mega disaster, more than 20,000 people lost their lives, half a million people lost their homes. And IsraAID, which was at that time, a tiny organization with basically one employee and a few volunteers, offered me to lead a relief mission to Japan. And again, I was supposed to go for two weeks and I ended up staying there for three years. So that's how it kind of all started for me. And interestingly for IsraAID, it used to be a disaster response organization, and it's still part of our DNA, but in Japan we realized that for us our impact could be not just immediate relief and pulling people out of the rubble and giving them medical support, etc. Also we need to look at long term impact. In Japan, a rich country, the third-largest economy, they didn't really need our support with immediate relief. But what we supported them with was trauma care for children. Which, again, is an area that unfortunately, in Israel, not because everything is so perfect here, but because of our, you know, ongoing challenges from the trauma of the Holocaust to the ongoing conflict, we really developed this expertise to help children cope with trauma. So that's all how sort of how I started. And then from Japan, I went to the Ebola outbreak in West Africa, which was terrifying. I remember every night I used to wake up full of sweat. It's one of the symptoms of Ebola, but thank god, I'm okay. And then I led a mission in Nepal, after the earthquake they had in there, we actually had a very dramatic search and rescue operation. And we found the last survivor of the earthquake, was a woman who was trapped under the rubble for six days without food or water. And then I led a relief mission to Greece with a Syrian refugee, actually also in partnership with AJC's, some of AJC's team members actually joined me. And it was amazing, because these people were considered our enemies, and then all of a sudden, they receive support from us. We can touch base on that later. But so basically, I was chasing disasters until 2017, when I was offered to co-lead the organization, first as a co-CEO, and then from 2019, as the global CEO. So now, you know, we started as employee number two. Now we have about 350 of us in 16 countries. And it's just an amazing privilege. And I'm still learning every day. That's what keeps me going. Manya Brachear Pashman: In 16 countries, how are those countries identified and selected as locations for IsraAID? Yotam Politzer: So, so for Israel, and it may sound bad, but for us, disasters are opportunities. And it doesn't mean that we sit down and wait for disaster to happen, they will happen, whether we like it or not. And it could be, you know, climate related disasters like a hurricane or tsunami, or earthquake, or manmade disaster, like what's happening in Ukraine, or in Afghanistan, when the Taliban took over, or it could be even a pandemic, like, well, we all just experienced a global crisis. So whenever there's a crisis somewhere in the world, and it could be in a neighboring country like Turkey, where we just had an earthquake or in you know, the most remote places on earth like Vanuatu, near Fiji, we have an emergency response team that will deploy, many times in partnership with AJC. But we will send an emergency response team to essentially to do two things, one, to provide immediate relief, but to look for partners. And the partnership part is crucial, because we can't really do anything by ourselves. Manya Brachear Pashman: What about inside Israel? Yotam Politzer: So when you asked me how do we decide where to go, we decide where to go, where we have resources and partners who are interested in the type of expertise that we can provide. And this expertise is what we're bringing from Israel, whether it's water technology, trauma care that I mentioned, and other areas of response. We also know that so right now mentioned 16 countries, we have teams on the ground in Ukraine, actually responding to, you know, the bombing of the dam, just two days ago, our team was actually on the ground a few kilometers away from there. So thank God, they're safe. And but the good news is that we were able to respond immediately and we already have team on the ground. We have teams in Colombia supporting Venezuelan refugees. We have many teams in Africa, supporting the drought and some of the conflicts in South Sudan and elsewhere. The teams are not just Israelis. The Emergency Response Team deploys from here but very quickly, we identify local team members. So out of our 350 employees, many of them are actually local members of the communities that we train and support and they take the lead which is much more sustainable, because our end goal is not to be needed. Our end goal is to live the know-how and the capacity in the country, in the community, so they can support themselves. Manya Brachear Pashman: What about inside Israel? Do you do anything– Yotam Politzer: No, I mean, our mandate, IsraAID- it was established 22 years ago, actually by a group of activists and the vision was to bring Israeli expertise to the world's most vulnerable communities around the world, essentially saying, you know, Israel, again, not because everything is so perfect here, because of our challenges, we developed technologies, and techniques and methodologies that could and should be shared with disaster areas around the world. So many of the original members were actually doctors and nurses, and people who were active here on a day to day basis, but wanted to share these know-how, and expertise with the world. Manya Brachear Pashman: Why? Why not just keep it for yourselves? Yotam Politzer: First of all, for several reasons, one, because we are global citizens. And we are influenced and influencing the world. And we should be a force for good. And it's really just the right thing to do. To that one, too, because we actually have an added value. We have unique expertise and unique experience that people don't have, everyone calls Israel, the startup nation, right. So we see ourselves as the humanitarian wing of the startup nation. And we also a little bit, South Korea says we think we should do more as Israelis and as a trade. So we're doing the best we can, we are reaching millions, but we should reach billions. So and the third reason, and that's also one of the reasons the organization is called East trade is that it's also an opportunity to build bridges. And I think that's where the agency partnership is crucial, because AJC is all about building bridges, right? Between the Jews and the world, if you will. And that's where I think there's such a beautiful alignment of values and of the mission and vision of how, again, terrible crisis and tragedies could be, could become a game changer in building bridges. And these bridges are, you know, could be built with Syrian refugees who are considered our enemies. I remember, I was called a Syrian guy, you know, after we pulled out his daughter, in Greece, and we treated her, she almost drowned. She told me my worst enemy became my biggest supporter, or a group of 200 Afghans that we pulled out that are now sending me Shabbat, Shalom every every Shabbat. So that's kind of the obvious, right? But, there's a lot of bridges that needs to be built also with our friends, you know, you know, whether it's in Guatemala, which is a country that's very, you know, supportive of Israel, but like, but we are supporting them. So our goal at Israel is not to, we're not here to do diplomacy work, or we're not dealing with politics. But at the same time, we do see ourselves as representatives of the Israeli civil society. And we do see how an added value of our work is these very strong bridges that are being built both on the high level and on the People to People connection. Manya Brachear Pashman: Have you ever encountered people who are not willing to accept help from Israeli agencies? Yotam Politzer: So honestly, it almost never happened. In 99.5% of the cases, people were very happy to receive support from Israelis, and from IsraAID. Sometimes people did not expect it. So I would say they were positively shocked to receive support. But, I think they were happy for several reasons. One is because it actually helped. Two is because we're not just there for short term, we're actually staying long, longer than most organizations. So we arrived in the first 72 hours, but we are typically, you know, staying at an average of five years, in an area. So we build trust. And, and people see that it's not just, you know, a token support. Three, we have a very strong kind of multicultural team, right. When I mentioned the Syrian refugees, we had a lot of Arab Israelis, people who speak Arabic, who were able to provide the support. So it's not only professional, it's also a strong cultural understanding, and many of our local team members. The only cases I would say, which was a little bit complicated and challenging, was when we actually worked inside countries that don't have diplomatic relations with Israel. So when we worked with Syrians we didn't work inside Syria worked with Syrians who escaped. Same with Afghanistan. We help people evacuate from Afghanistan, but we didn't send our team inside. We did send our team inside Iraq, inside Bangladesh. And for security reasons, mainly, our local partners knew where we were from, but the local government didn't. So we had to be much more careful in terms of our visibility. We couldn't wear our t-shirts and our logos and you know, mainly for safety and security reasons for our staff. That's that's obviously a challenge. I mean, politics is there, whether we like it or not. Manya Brachear Pashman: So in those situations, do you feel like you make headway with the citizens with the public that you're helping, that may have a long term effect on how the governments consider Israel in the future? Or is that something that you care about? Yotam Politzer: I mean, we do care, we are from here, and your organization is called IsraAID, and probably my life would have been easier if I would be working for the UN or working for Doctors Without Borders, or for other organizations that don't have any affiliation with Israel, right. So we do care, we do care about building bridges. And we do care about changing people's perspectives. One story that I have was from Sierra Leone, West Africa, during the Ebola crisis, we worked with the First Lady. And, she was shocked to receive support from the other side of the world, from Israel. She said, you came from Israel, all the way, I promise that, you know, when Sierra Leone will be Ebola free, me and my husband will come to visit Israel, and she actually followed her promise. So you know, that was like a very clear kind of diplomatic aspect. Now, when we went to Malawi, also in partnership with AJC, following the terrible cyclone that they had, the President was the one who welcomed us and said, how excited he is for the support. When we talk about the Syrian refugees we have supported over the years, we worked there for six years, about 120,000 of them. So we do believe it goes a long way, right? It's not just one or two people. It's not just anecdotal. Whether it will lead to a political change in the Middle East, maybe hopefully, it definitely does change the perspectives of hundreds of 1000s of people. Manya Brachear Pashman: What is the budget of of IsraAID? Yotam Politzer: So this year, we're close to $23 million. Yeah. We tripled ourselves in the last two years. Again, not because everything is great, but because the world has gone mad. And it was a series of events that, you know, that we responded to whether it's, you know, Afghanistan, and Ukraine, of course, is an ongoing disaster and Turkey and others. So yeah, so we are in $24 million, we are growing, and planning to grow to $50 million in the next few years. Which is really what we believe we need in order to continue responding in the countries that we are in have some kind of an emergency fund that enables us to respond to new crisis. By the way, I want to say that that's where AJC's has been an incredible partner, because AJC, I think, supported us in more than 20 countries over the last few years. And one of the main challenges is that there's a disaster in Country X, and we need seed funding, we need to be able to deploy immediately. And that's typically what AJC provides. So and by the way, it's in places that are all over the media, like Ukraine, for instance, or in places like Malawi, that no one heard of. And that's crucial, because we know, unfortunately, that media attention equals to donor attention. So when things are in the media, it's much easier to raise funds, it's also limited, right? It's usually like a week or two, and then people move to the next tweet. When you're an expert, you probably know that. But AJC has been there on both kind of the more high profile and low profile and really has been an incredible partner that really enabled us. Because once you're on the ground, it's not only that you're saving lives, which is, you know, our main goal, it's also you build partnership and relationship and you're able to communicate to the world that you're doing that so you can raise more money. So, so deploying quickly is important for several reasons. And AJC, you know, basically enabled us to do that. So that's huge for us. Manya Brachear Pashman: If someone wants to volunteer for IsraAID, are there opportunities to do that? Yotam Politzer: There are opportunities to do that, although I do have to say something because–we were based more on short term volunteers in the past. And there's a serious problem with that. Many people who come for a short term are actually doing more damage than good. I mean, they come with great intentions. But they start something that, you know, there's no continuation or if there's a lot of pictures with children in Africa, it's a very criticized field. Now, having said that, there are still people who have specific expertise–surgeons, for example, eye surgeons, you know, in a few days of volunteering, they could save people's lives, right. So, we're not against it, it needs to be people who are highly skilled, or people who can commit for long term. And we do take insurance, for example, college students, mainly graduate students, not so much undergrad, from specific fields who are looking for professional fellowships or internships in many of the countries. So there are definitely opportunities both for younger and for people who are young at heart. But the expertise or the long term commitment is crucial. Manya Brachear Pashman: Responding to those kinds of crises, how does that reflect Jewish values? In other words, how do some of these crises contradict or violate Jewish teachings, Jewish values? And how much of a role does that play in you coming in to address it? Yotam Politzer: So I think, you know, our team, just to clarify, is not just Jewish, right? We have Jews, Christians, Muslim, Buddhist, you know, other people. So it's a very diverse team, from any perspective, definitely, from a religious perspective. However, I think many of our team members are inspired by Jewish values. I mean, there's the obvious one of tikkun olam, which, you know, I think it almost became a buzzword, I heard so many people use it. So we almost don't use it because it became such a buzzword, but essentially, how we interpret this Jewish value is our responsibility to look beyond just our community. And to support the world's most vulnerable communities and really, literally repairing the world are supporting the repairment of the world. So that's kind of the clear connection, I don't I do think that everything that related to helping the strangers, right, people who are not just from our immediate community, is something that we strongly, strongly believe in. I mean, there's a story that I always share about Ukraine. You know, if you're a Ukrainian Jew 80 years ago, you are-during the World War Two. You are at the bottom of the bottom of the barrel right? You're likely to be slaughtered by the Nazis or by their Ukrainian collaborators. And today in Ukraine, the Jewish community is a big Jewish community, they are receiving so much support, which is amazing to think about it from a historical perspective, they are entitled to support from the Israeli government and from the Jewish Agency. And from the JDC, from so many great organizations who are focusing on supporting Jews in Ukraine. I don't know if you heard that. But in the beginning of the war, when millions of people fled Ukraine, the Jews were told the Jewish refugees were told to put a sign with the letters I-L for Israel, and they were taken out of the lines, and prioritized. So it's unheard of like, the tables have turned right. Which is amazing. However, what we take from it is that we have responsibility. And that's why it's so important that now Jews and Israelis show the world that we support everyone, not just Jews. And that we are different, and that we are there for everyone. And we are there even for people who are considered our enemies. Manya Brachear Pashman: My last question is, I have to admit, every time you've talked about vulnerable people, I hear you say valuable, I just misheard you. But then I think, well valuable, vulnerable, one in the same. And I'm curious, what you have learned from the communities and people that you've served in this capacity, and also whether they have gone on to teach and volunteer and help and pay it forward? Yotam Politzer: It's a great question. And I like it, I never heard this... But that's exactly how, not only me, but all of our team members feel like–vulnerable, our communities are also extremely valuable. And in many places, we see our role, not just in bringing the expertise and know-how but actually, in a way putting a spotlight on local expertise and local know-how. And that's how, in many of our countries of operation, now, the people who are leading the response are actually local members of the community, who received some training and support from us, but actually bringing their own cultural expertise. And we've been learning so much from these people, again, from languages to cultures to how you find very innovative solutions when there are very limited resources. It's a really two way street, of learning. And now, many of our team members on the regional level, actually, when there is a crisis in a neighboring country, together with our team from Israel, they respond. So now in Malawi, for instance, we sent a team from Israel and Kenya, together, when there was another crisis in the Caribbean, we sent a team from Dominica. So, because they know they're there, so practically, it's much quicker and they understand the local culture and context. So, definitely a big part of our role is to build this global team of disaster responders who can respond to disasters, both globally and locally and in the region. So we see how that becomes more of a bigger part of our strategy now to utilize local and regional resources, to support communities at risk. So it's not only, we're coming from the west, sort of with this know-how, we're combining that with local know-how and expertise. Manya Brachear Pashman: You're not just parachuting in and imposing your solutions. Yotam Politzer: Exactly. We co-create solutions. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yotam, thank you so much, I really appreciate you sharing this time with us. Yotam Politzer: Thanks for having me. And thanks for a wonderful partnership with AJC throughout the years. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to listen to AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson break down last week's passage of Israel's Reasonableness Standard Law and what it means for Israel's democracy and security.
Aug 2, 2023
From the Black-Jewish Caucus to Shabbat and Sunday Dinners: Connecting Through Food and Allyship
Candace Bazemore and Gabby Leon Spatt, authors of the award-winning children's book Shabbat and Sunday Dinner, are traveling to Washington, D.C., this week to help AJC, the National Urban League, and ADL relaunch the bipartisan Congressional Caucus on Black-Jewish Relations. Together with Dov Wilker, AJC's Director of Black-Jewish Relations, they discuss what can be accomplished through building stronger bridges between the Black and Jewish communities and how our diversity is a source of connection, not division. More on the authors: Bazemore and Leon Spatt are members of AJC Atlanta's Black/Jewish Coalition . They are also participants of AJC's Project Understanding , which is a signature achievement of the coalition. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Candace Bazemore and Gabby Leon Spatt Show Notes: Listen: Meet 3 Women Who are Driving Change in the Middle East Watch: Learn more about the Congressional Black-Jewish Caucus relaunch Learn: Launch of Congressional Black-Jewish Caucus (2019) Project Understanding Shabbat and Sunday Dinner by Candace Bazemore and Gabby Leon Spatt Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Candace Bazemore and Gabby Leon Spatt: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week, American Jewish Committee is helping to relaunch the bipartisan Congressional Caucus on Black-Jewish Relations. Congresswoman Debbie Wasserman Schultz of Florida will join some new House leaders including Congressman Wesley Hunt of Texas and Congresswoman Nikema Williams of Georgia. The caucus aims to raise awareness of sensitivities in both the Black and Jewish communities, combat stereotypes, and showcase commonalities. And with us this week to talk about their efforts to do the same are Candace Bazemore and Gabby Leon Spatt, co-authors of the children's book Shabbat and Sunday Dinner, which was honored with the Award of Excellence from the Religion Communicators Council. Both are members of the Black/Jewish Coalition and participants in AJC's Project Understanding, a biannual weekend of dialogue to develop understanding and friendships between leaders of the Black and Jewish communities. Our guest host this week is Dov Wilker, AJC's Director of Black Jewish Relations. Dov, the mic is yours. Dov Wilker: Thank you, Manya. Candace and Gabby, welcome to People of the Pod. Candace Bazemore: Thank you. We're excited to be here. Gabby Leon Spatt: It's a great opportunity. We're really excited to chat with you. Dov Wilker: Well, wonderful, we're just gonna jump right on in. And so I'm curious, Gabby, Candace, how did y'all meet? And how did you go from being friends to co-authors? Gabby Leon Spatt: Candace and I are both transplants to Atlanta, growing up in Florida, Virginia, both moving here for college or after college. And our original meeting actually was through the Junior League of Atlanta. We served on a committee together and launched a leadership program that was trading opportunities for Junior League members. But when we really met and realized how much we really adore each other, love each other, learn from each other, was from our shared experience of both attending Project Understanding, which is a program of Atlanta's AJC office, the Black-Jewish Coalition. And once we realized we both had that experience, our conversations changed, our friendship deepened, we really had the opportunity to share to learn to have meaningful conversations. And one day, we were planning an alumni event for Project Understanding participants, and we kind of talked about writing a book. And I'll let Candace share a little bit more about that. Candace Bazemore: Yeah, well, first of all, knowing how we met is like a very cool thing, because it just showcases some of the great ways that Atlanta already has great systems and organizations in place to help people look for ways to build across different community lines. I probably would have never met Gabby otherwise, which means that the book that we wrote together would have never happened. And the way the book came about was actually really cool. During the pandemic, we got tapped to help be on a planning committee for the Project Understanding's alumni New Year's Day brunch, which was going to be virtual, since no one could go anywhere, because of COVID. In the middle of one of the planning sessions, actually, at the start of one of the planning sessions, we were waiting for the two guys to join, of course, all the ladies got on first. And... Dov Wilker: I take offense to that. Candace Bazemore: It's fine. It's okay. It's true, though. And so we were discussing what we were planning on having for the brunch, because we were encouraging everyone to find a traditional meal to have for the brunch so people could be eating and talking, even though we couldn't be in the same place. And Gabby shared, she was going to have bagels and lox and I said chicken and waffles. But I didn't know like, what's bagels and lox? And we're like, Wouldn't it be a great idea to share recipes as a way to unite people? And then that led to us to kind of discussing like, you know, well, there's tons of recipe books out there. But what if we tried to get people earlier to start thinking about it. And so that's how we got to the idea of a children's book. Dov Wilker: Wait, I have to ask, have either of you written a children's book before? Gabby Leon Spatt: Definitely not, no. Candace Bazemore: No, this is our first children's book. I've written a ton of blogs. Dov Wilker: Have you ever written a book before? Candace Bazemore: No, not since being like a little, no. Everybody does, like young authors or something like that in school, but not a book book. This is our first. Gabby Leon Spatt: We like stretch projects. We like to try new things in between taking care of our friends, our families, our full time jobs, you know. Dov Wilker: You've got boundless energy, the two of you. Gabby Leon Spatt: Yes we do. Dov Wilker: What do you hope that readers are gonna gain from the book? I mean, in the year or so since it's been released, what's been the response? Gabby Leon Spatt: The experience, the stories we hear, I mean, I'll be sitting in a meeting, and somebody says, I read that book to my granddaughter, and it's the only one she wants to read now, and she just took so much away from it. But for us, I think the big picture is when you open your stomach at a dinner table, there's a way to start to open your heart and your mind. And Candace and I have shared so many life events together, holiday dinners, Shabbat dinners, Sunday dinners, just real times, where we've had that opportunity to kind of dive in and when you taste something new or something different, and you're at someone's home or their family member cooks it–there's always a story that goes behind it. And that's really the inspiration of this book is that the dinner table is a special place that brings people, ideas, and cultures together. And we thought, how do we tell this story, and the story was about telling our own family traditions, and what we typically do when we celebrate a Friday night Shabbat dinner, or a Sunday dinner. And so the characters, you know, are loosely mirrored after us and our families, and what the dinner means to us. And so the story follows two friends through their class presentations, as they learn more about each other's family traditions. And the hope is that the book introduces readers to other cultures and communities, and that we pique some interest in learning about other traditions. And the book is a great, you know, conversation starter, not just for children, but even for adults who maybe haven't had some of those unique experiences. For us, it was really important to be able to tell them more than just the story within the book. But we tell a little bit of the history of Black-Jewish relations. And we also have a page that is continuing the conversation. Dov Wilker: I'm curious, Candace, has that been your experience as well, I mean, you sit in a meeting, and someone tells you about the book that they've read that their grandchild only wants to only wants to read that, or you got another story? Candace Bazemore: Yeah, actually, I have a couple of stories like that, I actually had an opportunity to speak at a children's center here in Virginia. And the kids were so excited, they were sharing their family dinner traditions, and things like that. So that was very cool that came from the book reading. And we've had, I was actually in a meeting last night and a program associated with AJC, and we were all talking about some plans for a program for young people. And one of the organizers mentioned about our book, and two of the people in the meeting had the book that they read to their young kids. And that's their favorite book. So it was like, very cool. I was like, Oh, my god, yeah, that's great. But one of the coolest things, I'm in a friend's group with Gabby and some other black and Jewish women. And one of the members, when we first launched the book, she ordered it on Amazon, and it got delivered to her neighbor's house by accident. And she had never met the neighbor, the neighbor just opened, because of course, it was during the pandemic, the height of everybody getting Amazon orders. And so she just was like, Oh, this must be my order. She opens it up. It's a book, she doesn't know what it is. But it's, you know, the cover was inviting, she opened it up, she read the whole book, and then she put it back in the envelope with a personal note to our friend, and said, hey, you know, I got this book by mistake, I was really excited and really love this story. The images inside, the message, and I read some of the questions at the end. I'd love to get together with you over dinner, to talk more about it, because I'd love to learn more about your community. So that's how she became friends with her neighbor through the book. So it's very cool. Dov Wilker: That's really an incredible story for so many reasons. So this Thursday, July 13, AJC's marking the relaunch of the Congressional Caucus on Black-Jewish Relations, where the two of you will be sharing your story. What do you hope our nation's leaders will gain from hearing about your experience? Gabby Leon Spatt: So we're really excited to be at the relaunch of the Congressional Caucus. I think, for us, the hope is for people to know that this work is happening, these communities are engaging already, revisiting the past, this is not a new relationship. This is one that is rooted in many, many, many years of friendship, of teaching, of learning. And it's still happening. It's just maybe happening, you know, in a new way. I hope that we're able to inspire those that are in the room, including the congressmen and the congresswomen to really make this part of the agenda, to really celebrate the relationship and show the impact we can make and that we are making. Dov Wilker: I love that. I couldn't agree more. So the goals of the caucus are to raise awareness, provide resources and unite black and Jewish, and black-Jewish communities to combat hate and stereotypes. How do you think the caucus can achieve that? Big picture here. Candace Bazemore: First of all, it's a great question. I'm gonna give you a little bit of background about myself. And the fact that I actually was in college, a Congressional Black Caucus Foundation congressional intern. So I spent a summer working on the hill, in Congressman Scott, Robert C. Scott's office, Bobby Scott, from the Third District of Virginia. And it was very cool to see some of the great things they were doing to help shape young minds and future leaders. And I think that the caucus and the role of congressional leaders and just leadership in general requires you to look at ways to unite and to get your constituents and your communities that you touch, to look for ways to work together. I mean, the goal of a congressperson is to take their district and help make it better. I know in recent years, we've seen leadership go in the wrong direction. But these leaders have the opportunity to build bridges instead of tear them down. And so they can be the catalyst for change in their communities, they have the ability to direct resources and to direct attention, as well as to put their time on these topics. So they're already doing it by obviously relaunching the program and the caucus. And so the next step is then to empower their constituents to start these dialogues, start these conversations. And, and I think this gives them a reason, and also the organizations that they touch, a reason to start looking for ways to unite these communities. Dov Wilker: Excellent. So, you know, I want to take it a little more local, before we go back to the macro national level. Can you tell us more about your experience with Project Understanding? So for those that don't know, our listeners, AJC's Atlanta office has been running this, Marvin C. Goldstein Project Understanding Black Jewish retreat, every other year, since 1990-ish. We bring together 18 black and Jewish and some black-Jewish leaders to be a part of the conversation. So 36, in total. For 24 hours of intense dialogue. So I'm wondering if you could tell us a little bit more about that experience for you. And if you've been involved since then, beyond writing this book together, and I think Candace, you even referenced a new initiative that you're a part of, so I was wondering, if you could share a little bit more about that, too. Gabby Leon Spatt: Yes. So, you know, I mentioned earlier, the retreat was just eye opening, really moving. You know, I grew up, the granddaughter of Holocaust survivors, we were told, you always love everybody. The idea in my family of not liking somebody just because of their skin color, or their culture or their religion. It just didn't exist. And I don't know that I noticed, you know, growing up, I was already kind of doing some of this work. And I had a mentor of mine in college, who was my Greek advisor. And we talked a lot about black and Jewish relations at the time, he asked me to make him, challah French toast because he always associated challah with Jewish. And I said, Sure. And I went to church with him, actually, here in Atlanta, we were here for a conference. And, you know, it just kind of happened authentically. And coming to Atlanta and getting connected with AJC, and the Black-Jewish Coalition. And then Project Understanding. I think I realized how powerful the experiences I had in the past were, and this just felt like home for me. And it's also, Dov, it's incredible to see how you've invested more into the program and opened it up to a generation above, reaching 40 to 55 year olds, but also this year, launching a high school program. And so I think the impact of the retreat, that happens immediately, but also has a long lasting impact, we've really been able to make change within the Atlanta community. Dov Wilker: Candace, how about for you? Candace Bazemore: Yeah. Well, you know, first of all, Gabby touched on all the things that are dear to my heart about, you know, what we've learned along the way in our journey together. I kind of like listening to her talk about some of the programs were a part of. I mean, to see people from Project Understanding, the Black Jewish Coalition at events for the United Way or for the Junior League. I recently hosted a fundraiser for the Amario's Art Academy, which was a sneaker ball to help this, this program that helps young kids connect with arts and art opportunities that they wouldn't normally have, because they don't have the access to afford expensive art programs. And to have Gabby and her husband show up and have such a great time, and other people from other programs that were associated. So it's great to see how much the community building how it blends across everything that helps the community grow and be more diverse. And she even mentioned the the team program, through Project Understanding, it's the Black Jewish Teen Initiative is what it's called. So applications are open for this great program where the teens get to participate, they're high school juniors and seniors from across Greater Atlanta, coming together to learn about, black Jewish relationships, to learn about, like the impact of racism, antisemitism, to learn about diversity within the black and Jewish communities. So I mean, I'm just super excited about some of the things that have come from these programs. And, and the fact that we're more forward thinking. So the idea of the book is a way to get in front of young minds, the idea of this program is to get in front of teen minds, the Project Understanding traditional program is for those emerging leaders. And now the new programs that are for people who maybe weren't around when these programs existed to instill, learn and build communities as they get older. We're looking at the whole life of people, how do you build relationships your whole life, so that those communities when you need them already there, you already know someone you can pick up the phone and say, Hey, how do I do this? What's the best way to do this? Or I made a mistake? How do I improve? How do I correct this? By having these relationships, there's more opportunity for grace. So, you know, gaps may happen, mistakes can happen. But if you have relationships, you have something that you can, dip into and say, Hey, how do we do things better? How do we do things differently? Gabby Leon Spatt: I think it's also, you know, special to point out, we're one story, we're one outcome, right? There have been other individuals who have participated in Project understanding, who have started a barbecue team at the Atlanta Kosher BBQ Festival, which happens to be the largest kosher barbecue festival in the entire country. And that, you know, became a learning experience, just for themselves to be on the team, you had to go through Project Understanding, you know, and there's this cultural experience of explaining what kosher meat is. And you don't want to put extra salt in the rub, because it's already salted right. And when you like, the, you know, the barbecue, that has to be after Shabbat on sundown on Saturday, and the mashgiach has to light it. And then it's like, Who is that, right? And so the stuff that's happening in our community is so authentic, it just is happening, and it's so nice to see people just wanting to learn and continue the conversation past just the retreat. Dov Wilker: I can also share that as an attendee of the BBQ Festival. It's not just that they're there together,they're grilling good meat. It's a very tasty experience to attend. Alright, so one final question. What are ways that we can highlight the positive worker interactions between our two communities? Candace Bazemore: Well, that's a great question. I always say the best way to highlight it is to ask people to share their individual stories. And me being a digital person, definitely utilize social media in order to get the word out about the ways that you know you're working together. If you're in a room with someone who doesn't look like you, and you're working on these tough problems and coming up with great solutions. share a post about that, encourage someone else to do that, too. If you have an event coming up, invite someone else out to come with it, that normally wouldn't be in the room. So I don't know how many times me and Gabby have been the only ones of us in a room before. A great example. I was in town during the great challah bake. And 300 Jewish women at the-was it at the Bernie Marcus center? Gabby Leon Spatt: Yes, the Jewish Community Center. Candace Bazemore: Jewish Community Center. Yeah. And so I was the only black woman or maybe one or two in the whole room? Gabby Leon Spatt: It was just you. Candace Bazemore: It was just me, okay. And was having a good old time making some challah bread. Because challah's my thing. Obviously, Gabby has shown me how to make challah bread. So I'm actually pretty good at it. She's getting good at deep fried cornbread as a matter of fact as well. Gabby Leon Spatt: Oh it's so good. I think it's opportunities like this, being able to be invited to share your story. And I think the caucus is really going to highlight a lot of what is happening across the country already, and give, you know, local advocates on the ground doing the work the opportunity to shine and to tell their story, because I think more than anything, storytelling is impactful, and it hits, at people's hearts and people's minds, and in our case, people's stomachs. Dov Wilker: Well, thank you, Gabby, and Candice, Candice and Gabby, we are so grateful for the book that you've written for the delicious food, that you're helping to inspire being made across this beautiful country, and to your participation in the relaunch of the Congressional Caucus on Black-Jewish relations. Candace Bazemore: Thank you. Dov. Gabby Leon Spatt: Thanks. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, tune in for an exclusive conversation between three women leading transformation in the Middle East and AJC Abu Dhabi Program Director Reva Gorelick onstage at AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv.
Jul 27, 2023
Israel's Reasonableness Law: What it Means for Israel's Democracy and Security
AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson breaks down what Israel's recently-enacted judicial reform means for the future of the only democracy in the Middle East. The Reasonableness Standard Law will limit the Israeli Supreme Court's ability to review the "reasonableness" of government decisions. Isaacson also provides listeners AJC's perspective on the contentious bill and takes us beyond the headlines to show AJC's support for President Herzog's efforts to reach a compromise and what's next for Israel. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jason Isaacson Show Notes: Learn: What You Need to Know About Israel's Judicial Reforms Listen: Matti Friedman on How the 1973 Yom Kippur War Impacted Leonard Cohen and What It Means Today Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Jason Isaacson: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week in Israel, a majority of Israeli lawmakers, those in the governing coalition, passed the contentious and divisive reasonableness standard law, which will limit the high court of Israel's role to limit and overturn government decisions that seem unreasonable. The new law, the first of several proposed reforms to Israel's judiciary, follows 29 weeks of protests by hundreds of thousands of Israelis, and has sparked threats by labor unions to strike, by businesses to shift investments, by military reservists to decline to serve. Joining us today to explain what the passage of this law might mean for Israel's democracy is AJC chief policy and political affairs officer Jason Isaacson. Jason, welcome to People of the Pod. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Manya. Good to be back. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Jason, for those listeners who don't quite understand the judicial reforms process in Israel, I want to steer them to our show notes to help them get up to speed. Here, I'd like to devote this time to what it means. But first I do have a fairly basic question. Would you please share AJC's perspective on the package of proposals? Jason Isaacson: Thank you for asking, Manya, when the package was put forward by the new governing coalition, the beginning of this year, we we met with senior officials of the government, including Prime Minister Netanyahu, and expressed concern that such an ambitious package should only advance with the broadest possible support in Israel if you're going to change fundamentally, the rules of the game and how Israel is governed, the balance of power, the checks and balances that exist between the legislative branch and the judicial branch. And you have to point out that in Israel, the legislative branch and the executive are virtually the same. They're in the same party. So it's the balance of power between the judiciary and the rest of the government. If you're going to make that kind of a fundamental change, you really need to strike a national consensus, the broadest possible consensus. So we encouraged the prime minister, and we also met with opposition leaders early in the year, and an urge that they get together and try to work out some kind of a compromise. It's not as though altering the system of government is a crazy thing. The Supreme Court, the High Court of Justice in Israel is an unusually empowered court. It has extraordinary power to strike down government actions. So it's not crazy. And then in the past, over the years, there have been other efforts to adjust it and adjustments have been made in this balance of power, the way the judiciary operates. That passed, there's a multistage process and passing legislation in the Israeli Knesset. If you're going to make these kinds of big changes, you really need to add, look, by the way, look, what's happened in Israeli society over the last 29 weeks, there have been protests every week, sometimes more than once a week, hundreds of 1000s of people have been out in the streets of massive display. Democracy has been on full display in Israel over this period. And it was very clear from public opinion polls, that many of these really public were not happy with this proposal and with the whole package, if it was going to be rammed through unilaterally, so unfortunately, it was pushed through unilaterally this one piece of the package. And now the question is, what happens next? Will we have other pieces move forward unilaterally? Will negotiations be reconvened? We have called for a reconvening of these talks under President Herzog, have met repeatedly with President Herzog and supported his efforts. And we're hopeful that will be where we end up. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned that democracy was on display with the many protests. But some people have said the passage of this law means that democracy in Israel is at risk. So I'm curious what your take is on that. Is democracy at risk, and why is preserving democracy so important? What's at stake? Jason Isaacson: Well, Israel is a democracy, Israel will continue to be a democracy, there have been many exaggerated obituaries of Israeli democracy. I would like to put those to rest. I'm sorry, that was kind of a terrible pun. But in fact, in our country, there are tensions, we had an uprising on January 6 of 2021. People tried to take over the US Congress and prevent the transfer of power. We have huge polarization and divisions and tensions in our own democratic system. No one would dare to say that America is not a democracy, even with these challenges, even changing voting rights laws, and gerrymandering and all the other things that happen at the state level and the national level, to make alterations in our democratic system. We have our own system of appointing Supreme Court justices, and it's possible for a party in power to prevent the appointment of a justice and to ram through other justices on weird pretexts. So it's not as though we have a perfect system, nor does Israel and Israel has shown itself to have an enduring, deeply rooted democracy. I am confident that the democratic traditions in Israel will endure even with this change in the way the balance of power is going to operate going forward. And by the way, it also must be pointed out that even though the Supreme Court, the High Court of Justice in Israel, no longer according to the As law will be able to use the reasonableness standard, in other words to say that a government action, an appointment is unreasonable and therefore cannot move forward. It has other tools that it can use. It's not as though the Supreme Court has been completely denuded and deprived of its ability to counteract, to overturn, to change government policy. But it does weaken the process that the Supreme Court has been using in the past. And it is unfortunate that it was rammed through unilaterally, does that mean that Israel is not a democracy? By no means? Does that mean that more work has to be done to shore up Israeli democracy? Yes. And by the way, ours as well, and other countries in which there are these tensions in society. We all have challenges. This is the nature of democracy. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm curious if this particular moment, even if it doesn't put Israel's democracy at risk, does it put Israel's economy or its safety? Jason Isaacson: There's a danger. We have seen reports that there are people who are withdrawing their investments in Israel, moving them to other countries. That there are Israeli companies that are moving certain operations or certain functions overseas. There are, of course, as we have seen, reports of reservists saying that they will not serve in the military, when they're called for reserve duty. All very concerning at a time when Israel's level of a threat to Israel from abroad is high. There have been attacks on Israel, not only from Gaza, which have been numerous and deadly, but also, of course, on the North. 100,000-plus missiles, maybe 150,000-plus missiles. Hezbollah every now and then someone takes a shot into Israel from there, from Syria as well. Iran continues to advance its nuclear program and its ballistic missile program, and every now and then shoot something in the sky over Israel as well. So it's not as though the threat level to Israel isn't something we should be concerned about. And therefore the security of Israel must be taken extremely seriously. If reservists are not serving. If air force pilots are not flying, Israel security is under threat. And if that is the result of changes in the governing structure of Israel, it should be a warning, a very sharp warning to the Israeli Government to go slow, as the recent American ambassador to Israel, Tom Nides famously told the Prime Minister and told us when we met him earlier this year as well, they should pump the brakes. Manya Brachear Pashman: You talked about the many threats facing Israel and for that reason, US foreign aid has been key to maintaining stability in the region. Does this development put that at risk? Jason Isaacson: I don't think so. Obviously, we watch that very closely. We're on the hill all the time. We speak frequently with members of Congress and their staff. You saw what happened the day before President Hertzog gave his address before a joint meeting of Congress, Senators and House members just last week, and that was a vote in the US House of Representatives on the essential nature of the relationship between the United States and Israel, reaffirming the strong alliance between the United States and Israel and that measure passed overwhelmingly, there were nine votes against that. One member abstained. But people talk all the time about elements of the Democratic Party, other opponents of foreign aid who speak out against aid to Israel or threaten to cut aid to Israel. You know, when push comes to shove and votes are taken, that's really not what happens at the end. I'm not saying that there isn't a concern about levels of support for Israel in the US Congress or in the broad public. Of course, that is an issue that AJC monitors closely and works very hard to make sure that there's a full appreciation of the value of the relationship, the mutually beneficial relationship between the United States and Israel. Our security is advanced when Israel security is advanced and vice versa, as president Herzog in fact, said in his speech to Congress last week. Manya Brachear Pashman: As I mentioned, hundreds of 1000s of Israelis have been on the streets protesting for 29 weeks now, even in the heat of the summer there, which is highly impressive. Some people credit those protests with slowing some of the reforms. Can you explain to our listeners what has been shelved? Jason Isaacson: It's an interesting question Manya because, in fact, as you know, the governing coalition in Israel includes elements that want to see really a complete overhaul of the judiciary and have a complete rebalancing of the relationship of the courts and in the legislature, and are not interested in shelving any aspect of the very ambitious proposal that was put forward at the beginning of this of the term of this of this government. The Prime Minister has indicated in various interviews in over the last several months, that he was not interested in advancing certain aspects, particularly the override clause, which would have empowered the legislature to counteract moves by the by the judiciary by the High Court to, to negate to cancel certain actions by the parliament or by the government. And the narrowness of that vote, that would allow a very slim majority in the legislature to overrule the court. There have been questions raised about whether other elements of his coalition feel the same way and whether they would prevail with the Prime Minister if push comes to shove. So we're waiting to see really how much is shelved, how much is just kind of shelved temporarily and will not move forward for a few months, but may come back. A lot remains to be seen. Manya Brachear Pashman: Could the High Court itself overturn this new law as unreasonable? Jason Isaacson: There's been some talk about that. And just earlier this week, colleagues and I did speak to some people in the democracy movement or the resistance, as they call it. And were given the impression that while attempts have been made, there wasn't the expectation that the court would do that. But it's possible to say that an attempt to change the reasonableness standard is unreasonable, and to therefore strike it down, and then and then who knows what happens, but I really do think that the best course of action is to bring the parties back together. Manya Brachear Pashman: So AJC has been very clear about its support of President Herzog's quest for compromise. The President's position though is largely ceremonial. Can he bring parties together that don't want to be brought together? Can he halt legislation that does not come out of compromise? Does he have any power to do that? Jason Isaacson: The legislation that passes the Knesset has to be signed by the President. But he has no power not to sign legislation that's passed by the Knesset. So in fact, there are laws that go into effect, even without the President's signature, it's an unusual system. He does have certain powers to obviously, as you know, after an election, to ask a party that believes that it can come up with a majority in the Knesset and form of government, he does have that power to empower a party to advance to form a government. But his other powers are quite limited does have the power of persuasion, he doesn't have the power of the bully pulpit, he does have the great moral authority of being the head of state of the state of Israel. He was received in the highest fashion in Washington, very important meeting in the Oval Office, an important meeting with the Vice President, of course, the address before the joint meeting of Congress. And he has played his hand, as limited as it may be on paper, he has played his hand really quite well to the point where he really is at the center of the discussions that have gone forward. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jason, why is the governing coalition so determined to restrict the high court's powers? Jason Isaacson: Whether this is a matter of protecting democracy, or protecting a nationalist agenda is a big debate that's going on right now in Israel. But whatever it is, you really cannot change the fundamental rules of how a government operates, the balance of power between the branches of government, without support from the public. And right now, the public has pretty clearly expressed great anxiety about the direction that this process is taking. It would be wiser for the long term survival and support of the current government, and of the state of Israel, if such changes are made only as a result of the national consensus. Manya Brachear Pashman: Israel is so diverse when it comes to religion and ethnicities and cultures. It's so complex, that an independent judiciary seems crucial for making sure everyone shares this land. Everyone is treated by the Golden Rule equally. You talked about the High Court protecting minority rights. Is that why this decision, this attempt at reforms seems so momentous? Jason Isaacson: Yes. And I would say there are other reasons as well. And another point that I think is important to make is that the independence of the Israeli judiciary, a judiciary that is independent from the political process, to a large degree, not completely, but to a large degree is armor for Israel legally, internationally. It is the ability of Israelis to say to those in the international community and the High Court of Justice and the internet. The Court of Justice excuse me and the International Criminal Court and the United Nations and other international bodies that say, Oh, we're going to say that Israelis are committing war crimes or we're going to hold some, some, some mock trial or some other international legal action against Israel. Israelis can say and we say in AJC, that's nonsense. You don't need to do that. Israel has an independent judiciary, if there are crimes that are being committed by Israeli soldiers or political figures, Israel will prosecute them, as they have done repeatedly, Israel will put prime ministers and presidents in jail. So don't tell us that Israelis' ability to judge themselves is somehow lacking. It's very important that Israel maintain an independent judiciary and the international recognition of the independence of the Israeli judiciary, which is another reason why this whole debate has been so frustrating to advocates for Israel like AJC, who know that the judiciary will remain independent, in most part, and democracy and Israel will continue to be strong, but just the appearance that the independence of the judiciary has been weakened, will be corrosive politically to Israel, internationally and legally to Israel internationally. And that's another reason why we have been so steadfast and trying to urge the Israelis to go slow, make this done in a way that has broad popular support and international recognition that the Judiciary's independence is being upheld and is sacrosanct. Manya Brachear Pashman: We're having this conversation on the eve of Tisha B'av, which is the saddest day on the Jewish calendar. It marks a number of tragic turning points for the Jewish people, but namely the destruction of the Second Temple, and the beginning of Jewish exile from Israel. My own rabbi reminded our congregation that the Jewish tradition teaches that division in the Jewish community is what ultimately led to the Temple's destruction. And here we are again. How likely is it that the coalition members will fast, reflect, and work to heal this rift in Israel? Jason Isaacson: That's an interesting question, and it was also interesting to see former US ambassador to Israel, David Friedman, make that same reference in a tweet the other day, and really call for a consensus, for a more deliberative process, than the unilateral approach that was being pursued. We're now about to enter a two and a half month period of summer recess basically for the Israeli Knesset. We'll see what happens when they come back in the fall. There's other legislation that will be coming down the pike as well, including a very ambitious proposal to entrench the exemption for the ultra orthodox community to conduct Torah study, rather than serve mandatory military service that other Israeli young people are required to, to attend. Whether that moves forward, whether that also sparks popular unrest, it remains to be seen. Israel is in a very interesting place right now. The democracy of Israel as we discussed is on full display. People are out there, they're motivated, they're active. And there are tensions within the society that are right on the surface in a way that does not exist in certainly any other country in the region. We're very proud of the fact that with free expression and a rambunctious free press, and people who have very strong feelings are not afraid, and have no inhibition whatsoever about stepping forward and trying to affect the policies of their government. There will also be other elections in Israel. And if the country veers too far in one direction or another, I have full confidence that the Israeli public with its strong commitment to liberal democracy will pull it back. Manya Brachear Pashman: Jason, thank you so much for your perspective, and for really helping us explain to our audience what this all means. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Manya. It was my pleasure.
Jul 21, 2023
Matti Friedman on How the 1973 Yom Kippur War Impacted Leonard Cohen and What It Means Today
Last month, we sat down with journalist and author Matti Friedman in a Jerusalem studio to talk about Leonard Cohen, the Israel-Diaspora relationship, and the turning point that was the 1973 Yom Kippur War. Selected by Vanity Fair as one of the best books of 2022, Friedman's "Who by Fire: Leonard Cohen in the Sinai," explores the late poet and singer's concert tour on the front lines of the Yom Kippur War – a historic moment of introspection for the Jewish State that continues to reverberate through events we witness today. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. __ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Matti Friedman __ Show Notes: Listen: From the Black-Jewish Caucus to Shabbat and Sunday Dinners: Connecting Through Food and Allyship How to Tell Fact from Fiction About the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict Live from Jerusalem: Exploring Israel and the Media with Matti Friedman Watch: Should Diaspora Jews Have a Say in Israeli Affairs? Learn: Four Common Tough Questions on Israel 75 Years of Israel: How much do you know about the Jewish state? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Matti Friedman: Manya Brachear Pashman: Matti Friedman has joined us on this podcast multiple times. Last year, he gave us an essential lesson on how to tell fact from fiction about Israel, and when AJC held its global forum in Jerusalem in 2018, he joined us for our first live recording, so I could not pass through Jerusalem without looking him up, Especially after learning that the writer behind Shtisel is adapting Matti's latest book, "Who By Fire" about the late great Leonard Cohen's time on the front lines of the Yom Kippur War. He joins us now in a studio in the Talpiot neighborhood of Jerusalem. Matti, welcome to People of the Pod. Matti Friedman: Thank you for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I take it you're a fan of Leonard Cohen, or just as a journalist you find him fascinating? Matti Friedman: No, of course, I'm a fan of Leonard Cohen. First of all, I'm Canadian. So if you are Canadian, you really have no choice. You have to be a Leonard Cohen fan, and certainly if you're a Canadian Jew. We grew up listening to Leonard Cohen. So absolutely, I'm a big admirer of the man and his music. Manya Brachear Pashman: What are your favorite songs? Matti Friedman: Probably my favorite Leonard Cohen song is called "If it Be Your Will." Just a prayer that came out on a Cohen album in the 80s. But I love all the Cohen you know top 10- Suzanne and So Long Marianne, Famous Blue Raincoat and Chelsea Hotel. It's a very long list. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I should clarify that your book is not a biography of Leonard Cohen. It's about just a few weeks of his life when he came in 1973, during the Yom Kippur War, and these few weeks were a real turning point in his life, also for Israel, but we can talk about that later. But I want to know, why is it important? Why do you think it's important for Leonard Cohen fans, for Jews, particularly Israelis, to know this story about him? Matti Friedman: I think that those few weeks in the fall of 1973, when Cohen finds himself at the front of the Yom Kippur War, those weeks are really an incredible meeting of Israel and the diaspora, maybe one of the ultimate diaspora figures, Leonard Cohen, this kind of universal poet and creature of the village, and this product of a very specific moment in North American Jewish life, when Jews are really kind of bursting out of the ghetto and entering the mainstream. And we can think of names like Paul Simon and Bob Dylan, even Phil Ochs, and people like that. And Cohen is very much part of that. And he comes to Israel and meets, I guess the other main trend in Jewish history, in the second half of the 20th century, which is the State of Israel, and Israelis, who are not bursting into, you know, a universal culture in the United States, they're trying to create a very specific Jewish culture–in Hebrew, in this very kind of tortured scrap of the Middle East. And the meeting of those two sides, who have a very powerful connection to each other, but don't really understand each other. It's a very interesting meeting. And the fact that it happens at this moment of acute crisis, one of the darkest moments in Israel's history, which is the Yom Kippur War, that makes it even more powerful. So I think if we take that snapshot, from October 1973, we get something very interesting about Israel, and about the Jewish world and about this artist. And in some ways, I think those weeks really encapsulate much of Leonard Cohen's story. So it's not a biography, it doesn't trace his life from birth to death. But it gives us something very deep about the guy by looking at him at this very intense and kind of traumatic moment. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you also think it sheds some light on the relationship between diaspora Jews and Israel? And how has that relationship changed and evolved since the 1970s? Matti Friedman: When Cohen embarks on this strange journey to the war, which, I mean, it's a long story, and I tell it in the book, but it starts on a Greek island or he's kind of holed up. He's in a crisis, and he's unhappy with his domestic life and he's unhappy with his creative life and he kind of needs to escape. So he gets on a ferry from the island and gets on an airplane from Athens and inserts himself into this war, by mistake, not really intending to do it. And he says in this manuscript that he writes about that time, which is unpublished until, until my own book, I published segments of it. He says, I'm going to my myth home. That's how he describes Israel. He uses this very interesting phrase myth home. And it's hard to understand exactly what he means. But I think many Jewish listeners will understand kind of almost automatically what that means. Israel is not necessarily your home. And it's possible that you've never even been there. But you have this sense that it is your mythical home or some alternate universe where you belong. And of course, that makes the relationship very fraught. It's a lot of baggage on a relationship with a country that is, after all, a foreign country. And Cohen lands in Israel and has a very powerful, but also very confusing time and leaves quite conflicted about it. And I think that is reflective, more generally of the experience of many Jews from the diaspora who come here with ideas about the country and then are forced to admit that those ideas have very little connection to reality. And it's one reason I think that I often meet Jews here from, you know, from North America, and they're not even fascinated by the country, but they're kind of thrown off by it, because it doesn't really function in the way they expect. It's a country in the Middle East. It's very different from Jewish life in North America. And as time goes on, those two things are increasingly disconnected from each other. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yeah. Which is something that I think you say, Israelis say repeatedly, that lots of people have opinions about Israel and decisions that are made and how it's run. But they have no idea what life is like here, right? That's part of the disconnect. And the reason why there's so much tumult. Matti Friedman: Yes, and runs in the other direction, too, of course. Israelis just have less and less idea of what animates Jews in the United States. So the idea that we're one people, and we should kind of automatically understand each other. That just doesn't work anymore. I think in the years after the Second World War, it might have worked better because people were more closely connected by family ties. So you'd have two brothers from Warsaw or whatever, and one would go to Rehovot, and one would go to Brooklyn, but they were brothers. And then in the next generation, you know, their children were cousins, and they kind of knew something about each other, but a few generations have gone by, and it's much more infrequent to find people who have Israeli cousins, or American cousins, you know, it might be second cousins or third cousins, but the familial connections have kind of frayed and because the communities are being formed by completely different sets of circumstances, it's much harder for Americans to understand Israelis and for Israelis to understand Americans. And we're really seeing that play out more and more in the communication or miscommunication between the two big Jewish communities here in the United States. Manya Brachear Pashman: So this is my first trip to Israel. And many people told me that I would never be the same after this trip. Was that true for Leonard Cohen? Matti Friedman: I think it was, I think it was a turning point in his life. Of course, I wrote a book about it. I would have to say that, even if it weren't true, but I happen to think that it is true. He comes here at a moment of a real kind of desperation, he had announced that he was retiring from music that year. So he had this string of hits, and he was a major star of the 60s and early 70s. And those really famous Cohen songs that I mentioned, most of them had already come out and he'd been playing at the biggest music festivals at the Isle of White, which was a bigger festival than Woodstock. And he was a big deal. And, and he just given up, he felt that he had hit a wall and he no longer had anything to say. And he was 39 years old. That's pretty old for a rock star. And he was in those days, of course, people are dying at 27. So he kind of thought he was washed up. And he came to Israel. And he writes in this manuscript, this very strange manuscript that he wrote, and then shelved, that he thinks that Israel is a place where he might be able to be born again, or just saying, again, he writes both of those thoughts. And in a very weird way, it happens. So he's too sophisticated a character to tell us exactly how that happened, or to ever say that he went to Israel and was saved or changed in some way. Leonard Cohen would never give us that moment that of course, as a journalist I'm looking for but they won't give us all we can do is look at the fact that he had announced his retirement before the war, came home from this war very rattled, not at all waving the Israeli flag and singing the national anthem or anything like that, but he came back invigorated in some way. And a few months after that war, he releases one of his best albums, which is called "New Skin for the Old Ceremony." Which is a reference, of course, to circumcision, which is itself a kind of wink toward rebirth. And that album includes Chelsea Hotel and Lover Lover Lover and Who by Fire and he's back on the horse and he goes on to have this absolutely incredible career that lasts until he's 80 years old and beyond. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's talk about Lover Lover Lover, and the line of that song. You had interviewed a former soldier on the frontlines in the Yom Kippur War. He had heard Leonard Cohen sing, was very moved by that song, which was composed on an Israeli Air Force Base, I believe originally. And then the album comes out and he hears it again. And something is different. The soldier is not happy about that. Can you talk a little bit about how you confirmed that? Matti Friedman: Right, so I spent a lot of time trying to track down the soldiers who had seen Leonard Cohen during this very weird concert tour that he ends up giving on the Sinai front of the Yom Kippur War. And it's this series of concerts, these very small concerts, mostly for just small units of soldiers who are in the sand and suddenly Leonard Cohen shows up in a jeep and plays music for them. And it's kind of a hallucinatory scene. And one of the soldiers told me that he will never forget the song that Cohen sang, and it was on the far side of the Suez Canal. So the Israeli army having kind of fallen back in the first week and a half of the war has crossed the Suez Canal, in the great counter attack that changes the course of the war, and now they're fighting on Egyptian territory. And one night, on that, on the far side of the canal, he meets Leonard Cohen, it's just kind of sitting on a helmet in the sand playing guitar, and he sang a song that would later become famous, but no one knew it at the time, because it had just been written. As you said, it was written for an audience of Israeli pilots at an Air Force base a few weeks before, or a few days before. And the song's lyrics address the Israeli soldiers as brothers. That's what the soldier remembered. And he said, I'll never forget it. He called us his brothers. And that was a big deal for the Israelis, to hear an international star like Leonard Cohen, say, I'm a member of this family, and you're my brothers. And that was a great memory. But there's no verse like that in the song Lover, Lover, Lover. And there's no reference at all that's explicit to Israeli soldiers. And the word brothers does not appear in the song. Manya Brachear Pashman: At least the one on the album, the song on the album. Matti Friedman: On the album, right. So that is the only one that was known at the time that I was writing the book. And then I kind of set it aside, I just figured that it was a strange memory that was, you know, mistaken or manufactured. And I didn't think much more about it. But I was going through Cohen's old notebooks and the Cohen archive in Los Angeles, which is where many of his documents are kept. And he had a notebook in his pocket throughout the war, and was writing down notes and writing down lyrics and writing on people's phone numbers. And in in the notebook, I found the first draft of Lover, Lover, Lover, and this verse, which had somehow disappeared from the song and the verse is a really powerful expression of identification, not uncomplicated identification, but definitely sympathy for the Israelis who was traveling with, he was traveling with a group of Israeli musicians, he was wearing something that looked a lot like an Israeli uniform, he was asking people to call him by his Hebrew name, which was Eliezer Cohen. So he was definitely, he had kind of gone native. And the verse, the verse goes, 'I went down to the desert to help my brothers fight. I knew that they weren't wrong. I knew that they weren't right. But bones must stand up straight and walk and blood must move around. And men go making ugly lines across the holy ground.' It's quite a potent verse. And it definitely places Cohen on one side of the Yom Kippur War. And when he records the song, a few months later, that verse is gone. So he obviously made a different decision about how to locate himself in the experience. And ultimately, the experience of the war kind of disappears from the Cohen story. He doesn't talk about it. Later on, he very rarely makes any explicit reference to it. The Cohen biographies mention it in passing, but don't make a big deal of it. And I think that's in part because he always played it down. And when that soldier Shlomi Groner, who I call the soldier, but he's going into his seventies, but you know, for me, he's a soldier. He heard that song when it came out on the radio, and he was waiting for that verse where Cohen called Israeli soldiers, his brothers and the verse was gone. And he never forgave Leonard Cohen for it, for erasing that expression of tribal solidarity. And in fact, the years after the war, 1976, Cohen is playing the song in Paris, you can actually find this on YouTube. And he introduces the song to a French audience by saying, he admits that he wrote the song in the war in Sinai, and he says, he wrote the song for the Egyptians, and the Israelis, in that order. So he was very careful about, you know, where he placed himself, and he was a universal poet. He couldn't be on one side of a war, you couldn't be limited to any particular war, he was trying to address the human soul. And he was aware of that contradiction, which I think is a very Jewish contradiction. Is our Judaism best expressed by tribal solidarity, or is it best expressed in some kind of universal message about the shared humanity of anyone who might be reading a Leonard Cohen poem? So that tension is very much present for him and it's present for many of us. Manya Brachear Pashman: So he replaces the line though with watching the children, he goes down to watch the children fight. Matti Friedman: So before he erases the whole verse, he starts fiddling with it. And we can actually see this in the notebook because we can see him crossing out words and adding words. So he has this very strong sentence that says, I went down to the desert to help my brothers fight, which suggests active participation in this war and, and then we see that he's erase that line held my brothers fight, and he's replaced it with, I went on to the desert to watch the children fight. So now he's not helping, and it's not his brothers, he's kind of a parent at the sandbox watching some other people play in the sand. So he's taken a step back, he's taken himself out of the picture. And ultimately, that whole verse goes into the memory hold, and it only surfaces. When I found it, and I had the amazing experience of sending it to the soldier who'd heard it and didn't quite remember the words, he just remembered the word brothers. And over the years, I think he thought maybe he was mistaken, he wasn't 100% sure that he was remembering correctly and I had the opportunity to say, I found the verse, you're not crazy, here's the verse. It was quite a moment for him. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yeah, confirmation, validation. Certainly not an expression of solidarity anymore, but I read it as an expression of critique of war, right. Your government's sending sons and daughter's off to fight you know, that kind of critique, but it changes it when you know that he erased one sentiment and replaced it with another. Matti Friedman: Right, even finding the Yom Kippur War in the song now is very complicated, although when you know where it was written, then the song makes a lot more sense. When you think a song called Lover Lover Lover would be a love song, but it's not really if you listen to the lyrics. He says, "The Spirit of the song may rise up true and free. May be a shield for you, a shield against the enemy". It's a weird lyric for a love song. But if you understand that he's writing for an audience of Israeli pilots are being absolutely shredded in the first week of the Yom Kippur War, it makes sense. The words start to make sense the kind of militaristic tone of the words and even the kind of rhythmic marching quality of the melody, it starts to make more sense, if we know where it was written, I think Cohen would probably deny. Cohen never wanted to be pinned down by journalism, you know, he wasn't writing a song about the Yom Kippur War. And I don't think he'd like what I'm doing, which is trying to pin him down and tie him to specific historical circumstances. But, that's what I'm doing. And I think it's very interesting to try to locate his art in a specific set of circumstances, which are, the Yom Kippur war, this absolute dark moment for Israel, a Jewish artist who's very preoccupied with his own Judaism, and who grows up in this really kind of rich and deep Jewish tradition in Montreal, and then kind of escapes it, but can never quite escape it and doesn't really want to escape it, or does he want to escape it and, and then here he is, in this incredible Jewish moment with the Israeli Army in 1973. And we even have a picture of him standing next to general Ariel Sharon, who is maybe the other symbolic Jew of the 20th century, right? You have Leonard Cohen, who is this universal artists, this kind of, you know, man of culture and a kind of a dissolute poet and and you have this uniform general, this kind of Jewish warrior, this kind of reborn new Jew of the Zionist imagination, and we have a photograph of them standing next to each other in the desert. I mean, it's quite an amazing moment. Manya Brachear Pashman: Yeah. I love that you use the word hallucinatory earlier to describe the soldier coming upon Leonard Cohen in the desert, because it reminded me that it was not Leonard Cohen's first tour of sorts in Israel. He had been in Israel the year before, 1972, gave a concert in Tel Aviv and Jerusalem, very different shows. Can you speak to that? Matti Friedman: So Cohen was here a year before the war. And what's amazing is that you can actually see the concerts because there was a documentary filmmaker with him named Tony Palmer. And there's a documentary that ultimately comes out very briefly, that is shelved because Cohen hates it, and then resurfaces a couple of decades later, it's called Bird on a Wire. And it's worth seeing. And you can see the concert in Tel Aviv. And then the concert in Jerusalem the next day, which are the end of this problematic European tour, which kind of goes awry, as far as Cohen is concerned. In Tel Aviv, they have to stop a concert in the middle because there's a riot in the audience and for kind of strange technical reason, which was that the arena in Tel Aviv had decided to keep the audience really far away from the stage and people tried to get close to Leonard Cohen and Cohen wanted them to come closer to the stage because they were absurdly far from the musicians and they tried to move closer but the security guards wouldn't let them and they start, you know, people start fighting, and Cohen's begging them to calm down. And you can see this in the, in the documentary and then ultimately he leaves the stage, he says, you know, it's just not I can't perform like this, and he and the whole band just walk off the stage, and you get the impression that this country is on the brink of total chaos, like it's a place that's out of control. And then the next day, he's in Jerusalem for the last concert of this tour. And the concert also goes awry. But this time, it's Cohen's fault. And he is onstage, and you can see that he can't focus, like he just can't put it together. And in the documentary, you can see that he took acid before the show. So it might have had something to do with that. But also, it's just the fact that he's in Jerusalem. And for him, that's a big deal. And he just can't treat it like a normal place. It's not a normal concert. So there's, there's so much riding on it, that it's too much for him, and he just stops playing in the middle of a concert. And he starts talking to the audience about the Kabbalah. And it's an amazing speech, it's totally off the cuff. It's not something that he prepared, but he starts to explain that, in the Kabbalistic tradition, in order for God to be seated on his throne, Adam and Eve need to face each other, or the man and the woman need to face each other in order for the divine presence to be enthroned. And he says, my male and female sides aren't facing each other, so I can't get off the ground. And it's a terrible thing to have happen in Jerusalem. That's what he says. And then he leaves, he says, I'm gonna give you your money back, and he leaves. And instead of rioting, which is what you'd expect them to do, or getting really angry, or leaving, the audience starts to sing, "Haveinu Shalom Alechem," that song from summer camp that everyone knows, I think they just assume that he would know it. And in the documentary, you see him in the dressing room trying to kind of get himself together. And hears the audience singing, a couple thousand young Israelis singing the song out in the auditorium, and he goes back out on stage and kind of just beams at that. He just kind of can't believe it, and just smiling out at them. They're entertaining him, but he's on the stage. And they're singing to him, and then the band comes back on. And they give this incredible show that ends with everyone crying. You see Cohen's crying and the band's crying and he says later that the only time that something like that had ever happened to him before was in Montreal when he was playing a show for an audience that included his family. So there was a lot going on for Cohen in Israel, it wasn't a normal place. It wasn't just a regular gig. And that's all present in his brain when he comes back the following year for the war. Manya Brachear Pashman: Makes that weird decision to get on the ferry, and come to Israel make a little more sense. I had tickets to see Leonard Cohen in 2013. He was in Chicago, and Pope Benedict the 16th decided to resign. And as the religion reporter, I had to give up those tickets and go to Rome on assignment. And I really regret that because he died in 2016. I never got the chance to see him live. Did you ever get the chance to see him live? Matti Friedman: I wonder if we should add that to the long list of, you know, Jewish claims against Catholicism, but I guess we can let it slide. I never got to see him. And I regret it to this day, of course, when he came to Israel in 2009 for this great concert that ended up being his last concert here. I had twins who were barely a year old. And I was kind of dysfunctional and hadn't slept in a long time. And I just couldn't get my act together to go. And that's when I got the idea for this book for the first time. And I said, well, you know, just catch him the next time he comes. You know, the guy was in his late 70s. There wasn't gonna be a next time. So it was a real lapse of judgment, which I regret of course. Manya Brachear Pashman: I do wonder if I should have gone to Rome for that unprecedented moment in history to cover that, kind wish I had been at the show. So you do think that the Jerusalem show played a role in him returning to Israel when it was under attack? Matti Friedman: Yeah, absolutely. Absolutely. I mean, he had this very again, complicated, powerful, not entirely positive experience in Israel. And he'd also met a woman here. And that also became clear when I was researching the book that there was, there was a relationship that began when he was here in 1972, and continued. He had a few contacts here, and it wasn't a completely foreign place. And he had some memory of it and some memory of it being a very powerful experience. But when he came in '73, he wasn't coming to play. So he didn't come with his guitar. He didn't bring any instruments. He didn't come with anyone. He came by himself. So there is no band. There's no crew, there's no PR people. He understands that there's some kind of crisis facing the Jewish people and he needs to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: I interviewed Mishy Harman yesterday about the Declaration of Independence, the series that [the I`srael Story podcast] are doing, and he calls it one of Israel's last moments of consensus. We are at a very historic moment right now. How much did this kind of centrifugal force of the Yom Kippur War, where everybody was kind of scattered to different directions, very different ways of soul searching, very Cohen-esque. How much of that has to do with where Israel is now, 50 years later? Matti Friedman: That's a great question. The Yom Kippur war is this moment of crisis that changes the country and the country is a different place after the Yom Kippur War. So until 73, it's that old Israel where the leadership is very clear. It's the labor Zionist leadership. It's the founders of the country, Ben Gurion and Golda Meir, and the people who kind of willed this country into existence against long odds and won this incredible victory in the 1967 War. And then it's all shattered by this catastrophe in 1973. And even though Israel wins the war and the end, it's a victory that feels a lot like a defeat, and 2600 soldiers are killed in three weeks in a country of barely 3 million people and many more wounded and the whole country is kind of shocked. And it takes a few years for things to play out. But basically, the old Israeli consensus is shattered. And within a few years within the war, the Likud wins an election victory for the first time. And it's a direct result of, of a loss of faith and leadership after the Yom Kippur War. That's 1977. And then you have all kinds of different voices that emerge in Israel. So you have, you know, you have Likud. You have the voice of Israelis, who came from the Arab world who didn't share the background of, you know, Eastern Europe and Yiddish and who had a different kind of Judaism and a different kind of Zionism and they begin to express themselves in a more forceful way and you have Israelis who are demanding peace now. You know, on the left, and you have a settlement movement, the religious settlement movement really kind of becomes empowered and emboldened after the Yom Kippur War after the labor Zionist leadership loses its confidence and that's when you really start seeing movements like Gush Emunim pop up in the West Bank with this messianic script and so, so the the fracturing of that that consensus really happens in wake of Yom Kippur war and you can kind of see it in in the music, which is an interesting way of looking at it because the music until 73 had really been this folk music that still maybe the only place that still sees it as Israeli music might be American Jewish summer camp, where it kind of retains its, its, its hold and yeah, that those great old songs that were sung around the campfire and the songs of early Israel and that was very much the music that dominated the airwaves. After the Yom Kippur War, it's different, the singers start expressing themselves a lot less in the collective we and much more in using the word I and talking about their own soul and you hear a lot more about God after 73 than you did before. And the country really becomes a much more heterogeneous place and a much more difficult place, I think, to run and with that consensus, you're talking about the Declaration of Independence. And that series, by the way, Israel Story, which I highly recommend, it's a wonderful series about an incredible document, which we still should be proud of, and which we should pay much more attention to than we do. But when do we have consensus, when we're under incredible pressure from the outside. The Declaration of Independence is signed, you know, as we face the threat of invasion by fighter armies. So that's basically what it takes to get the Jews to sit down and agree with each other. And, you know, there are these years of crisis and poverty after the 48 war into the 60s. And that kind of keeps the consensus more or less in place, and then it fractures. And we're in a country where it's much easier to be many different things, you know, you can be ultra-Orthodox, and you can be Mizrachi, and you can be gay, and you can be all kinds of things that you couldn't really be here in the 60s. But at the same time, the consensus is so fractured, that we can barely, you know, form a coherent political system that works to solve the problems of the public. And we're really saying that in a very dramatic and disturbing way in the dysfunction, in the Knesset and in our political system, which is, you know, has become so extreme. The political system is simply incapable of a constructive role in the society and has moved from solving the problems of the society to creating problems for a society that probably doesn't have that many problems. And it's all a reflection of this kind of fracturing of the consensus and this disagreement on what it means to be Israeli what the meaning of the state is, once you don't have those labor Zionists saying, you know, we are a part of a global proletarian revolution, and the kibbutz is at the center of our national ethos. Okay, we don't have that. But then what is this place? And if you grab 10 Israelis on the street outside the studio, they'll give you 10 different answers. And increasingly, the answers are, are at odds with each other, and Israelis are at odds with each other. And the government instead of trying to ease those divisions, is exacerbating them for political gain. So you're right, this is a very important and I think, very dark moment for the society. Manya Brachear Pashman: And do you trace it back to that kind of individualistic approach that Cohen brought with him, and that the war, not that he introduced it to Israel, and it's all his fault, that the war, and its very dark outcome, dark victory, if you will, produced? Matti Friedman: I don't want to be too deterministic about it. But definitely, that is the moment of fracture. The old labor Zionist leadership would have faded anyway. And just looking at the world, that kind of ethos, and that ideology is kind of gone everywhere, not just in Israel. But definitely the moment that does it here is that war, and we're very much in post-1973 Israel. Which in some ways is good, again, a more pluralistic society is good. And I'm happy that many identities that were kind of in the basement before '73 are out of the basement. But we have not managed to find a replacement for that old unifying ideology. And we're really feeling it right now. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much, Matti, for joining us. Matti Friedman: Thank you very, very much. That was great.
Jul 11, 2023
Meet 3 Women Who are Driving Change in the Middle East
Join us for an exclusive conversation featuring three women leading transformation in the Middle East. Ayelet Nahmias-Verbin, Chairperson of the Israeli Export Institute, speaks to promoting Israeli exports and fostering economic growth; Gadeer Kamal-Mreeh, a Senior Envoy at The Jewish Agency for Israel, discusses fostering connections and supporting Jewish communities in the region; and Aviva Steinberger, Director of Innovation Diplomacy at Start-Up Nation Central, touches on harnessing innovation and technology for positive change. Led by AJC Abu Dhabi Program Director Reva Gorelick onstage at AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv, this conversation offers valuable insights into the transformative efforts shaping the Middle East today. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Reva Gorelick, Ayelet Nahmias-Verbin, Gadeer Kamal-Mreeh, Aviva Steinberger ___ Show Notes: Listen: People of the Pod: 'Signed, Sealed, Delivered?': Exploring Israel's Declaration of Independence with People of the Pod and Israel Story Watch: AJC Global Forum: Women Driving Change in the Middle East - video of the full session, as heard on this week's episode. More sessions from AJC Global Forum 2023 Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Ayelet Nahmias-Verbin, Gadeer Kamal-Mreeh, Aviva Steinberger: Manya Brachear Pashman: The role women play in pursuing peace and progress in the Middle East is too often overlooked. But my colleague AJC Abu Dhabi Program Director Reva Gorelick is not one to leave such an important stone unturned. At AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv she led a fascinating conversation on "Women Driving Change in the Middle East." This week's podcast brings you a portion of that conversation with Ayelet Nahmias-Verbin, Chairperson of the Israeli Export Institute, Gadeer Kamal-Mreeh, a Senior Envoy at The Jewish Agency for Israel, and Aviva Steinberger, the Director of Innovation Diplomacy at Start-Up Nation Central. We open with Reva posing a question to Gadeer. Reva Gorelick: Gadeer, in your career, you have broken barriers in many ways. And I'm going to read because there's so many ways that I want to make sure that I get them right, as the first non Jewish broadcast anchorwoman here, both in Hebrew and Arabic, and then as the first Druze woman to serve as a member of Knesset, what have you learned about the appetite for change and for representation of historically marginalized communities in this part of the world specifically? And how did these trends track with what you're now seeing as an emissary for the Jewish Agency in America? Gadeer Kamal-Mreeh: Good morning. So long story short, so much, I learned so much. I'm still learning, I'm still growing, I'm still listening. And I'm still amazed to see the social impact of simply our existence, simply of being or living or achieving or talking to each other. And look at us today, this morning. The first of us, each one of us, based in different countries, speaking different language, different religion, different fields, but we are social agents. And this is what my father told me, always, as a child, you are a social agent. You are not privileged to live your life in a way that you are consuming reality, you have to shape reality. And I did social activism even without knowing that I'm doing social activism. I broadcasted my first TV show when I was 12 years old. I believe in people, I believe that we have the ability to change reality. And then being in those positions as first, as firs, as first, when you are how I always introduce myself by saying hello, my name is Gadeer. I am an Israeli but not a Jew, I am an Arab but not a Muslim, I am a minority within the Arab minority, my mother tongue is Arabic, married religion is Druze. I'm a proud Israeli citizen..good luck. So having such a unique identity, and being the first in those positions is something that a stranger would not understand the complexity and the beauty that you have. And so I started to write my book because I'm afraid that we cannot have, we don't have enough time to talk about it. But I learned so much the most important thing that I learned is engage, engage, engage. It doesn't matter where it doesn't matter how it doesn't matter with whom. Engage as a social agent and activate your role in shaping public opinion. I had so many stories in my life, Reva, in which I was amazed and telling myself, Yes, we can. Yes, we can. Being the only woman in so many rooms, I'm sure that Ayelet and Aviva also understand what does that mean to be the only woman. Nobody asked you if you want to represent women, you are a representative of women. So talk, represent, share their stories. And two weeks ago, we were in DC and we initiated some of the prestigious forum that you will hear about, and we were 18 successful leaders in Washington DC, but guess what? I was the only woman. And I told them guys, I got used to this in my villages in the Druze community, we are still a conservative community. Okay, but in DC in the 21st century, I am the only woman? Hey, wake up. Then I understood that okay, we did so much, we achieved so much in the last decades, last century, but we are not there yet. You know, like reminding ourselves in some countries we have no ability to vote, we have no ability to even, no right to be elected. Okay, we did, we promoted, we leverage our skills we went, we learned, we achieved. But even now today, we are not there. We don't have yet absolute gender equality. Look at the numbers. In our current government, there are zero CEOs of ministries, five of 33 ministers are women. 25% of MK members of parliament today are women. We are talking about 30 from 120. So the up-bottom policy is also, you know, reflecting the atmosphere. There are huge ramifications of who we are, who is working with me, who are my colleagues. So we are trying to lead. We are the head, the CEO, the founder, but we need to work much more hard to achieve. And this is our role. So the most important advice, in my opinion, that I can share here is lead. Don't wait for opportunity, take the opportunity, and I am really trying to target here, women, especially young women, excuse me, men, you have your exclusive club, you take care of each other. I believe that behind every woman, there is no man. There is a circle of women to support her, to give her the chances, to help her, to leverage her skills, to teach her. And I believe that it is our role as leaders at first, to empower women to be there for each other and to take the number much higher. Because so many researchers found that and it's proven that our ability to read reality is much better than men. We see the macro perspective, the empathy, the way of dealing things, the multitask. And all those things affect the atmosphere in our companies, in our organizations, in politics, in the Knesset. So do it, engage and lead and don't wait for the opportunity. Take the opportunity and lead. Reva Gorelick: Thank you. I want to just follow up on one point that you brought up, Ayelet, I'm gonna go off script a little bit and just ask, you brought up a question about representation in government. And we're not there in most parts of the world, we're not nearly anywhere where we where we need to be and where we should be at this point. When we're looking at government representation and gender parity in government, what should we be striving for? And how do you see that gender parity and representation as a barometer for social change and policy change? Ayelet Nahmias-Verbin: I think it is a little bit frustrating to admit the truth. We felt that we were going forward, and then we were kind of pulled back. And it's really up to us. I've got to say something, and I've got to be very frank about it. Politics is a shitty business. I worked with Yitzchak Rabin when I was 20 years old. And at 25, I had so much political power, I couldn't believe it. And I still didn't run for the Knesset, because of the men around me, you know, for them. I was 25 years old. Why should I run for the Knesset? Nowadays, it's much more reasonable to do so, to make such a crazy decision. But then I decided to go to the Knesset only after I already had three kids, a full career, a lawyer and board member and owner of a company, everything, that's when I decided, okay, now I'm gonna bring everything into the home, you know, and run to the Knesset. And it's a very, very difficult and non rewarding life. Even today, I tell people, I'm a politician, because I don't want people to think that politics is such a bad thing, you know, it's so important to understand, Gadeer, forgive me, she's also a politician, you know, this is not a bad thing. You know, this is, you know, the kind of my IP, you know, that's what I bring to the, to the table, my ability to speak to people and my ability to solve problems to, to do a lot of things, you know, that probably people with, with different skills, other people will be scientists and doctors, I really, really wanted to be an MD, but that's for another session. But what we need to do is make sure that from the very, very start at kindergarten, I'm not educating my daughter, I'm educating her brothers. Her brothers need to know that she can be Prime Minister, if she would like. That she could do anything that she could want. That's the idea. Because we used to say, once upon a time for socialization, okay, so let's take care of the girls. Nuh-uh. We need to take care of all of them, of both genders, because this is what we need to do. Because till today, and especially in a very, very complex society, like Israel, where we have both very, very strong liberalism, alongside in spite of you know, in spite of the situation in the Knesset, still very, very strong Bible values that, you know, the values that we share, and conservatism, that is not only Jewish, okay. I mean, there's no, no doubt there is, you know, is there a strong draft of conservatism from the Jewish part, but also we know well from the non Jewish parts. So the idea is, you know, people like Gadeer, I never heard you speak about what your father told you, that you should change reality. But that's exactly it. It's up to us to shape reality and shaping reality, from Facebook, from Meta, that Sheryl Sandberg used to say, speak at the table. You know, when you go through board minutes, you see that the women don't speak as much as the men. It's not only Okay, so we got to the table, but do we speak there? And I noticed once you know that Shabbat dinners, my daughter doesn't speak as much as her brothers. She's kind of reluctant. Maybe she'll make a mistake. Maybe she'll make it out and I'll correct her. God forbid I'm a terrible mom in these things. You know, I never have patience. So I say to the boys, I say, now you sush. And I give her the front seat. And this is so important to do. And up until, you know, we'll realize that and act on it, we will unfortunately, especially in such a divided society, like our own, we'll stay in the same situation. As long as people for instance, in primary parties, people still vote for one woman, you know this like, that's like the one token woman that we vote for. Now, on the other side, on the left wing, it's not as much as that. But again, we don't see as many women. I think in Yesh Atid actually, Yair [Lapid] made a huge effort. Also, Benny [Gantz] made a huge effort to bring more women on board. But these are different. You know, these are different kinds of parties. By the way, if you ask me, what's better for women? Nowadays, primaries or non primaries, you'd be surprised to hear: non primaries. Non primaries. Primaries are not necessarily the best way to bring women to the front seat. Reva Gorelick: Thank you for sharing that. And bringing that into the conversation of you, I want to come back to you. Aviva, you hold the role of Director of Innovation Diplomacy. It's not a phrase that I had heard much before we started having these conversations. And I'd love for other people to hear about it some more. From your experience in Israel's tech and startup world. Can you talk to us about the cascading effects of empowering women to be agents for change in their respective fields? Aviva Steinberger: Yeah, so innovation diplomacy is a made up term. And you know, if you think about science, diplomacy, or economic diplomacy, that's generally diplomacy that's meant to further goals around science and economics. And in this case, you're looking at focusing on innovation to further diplomacy. The idea is leveraging what's coming out of Israel in the tech sector, leveraging this brand that we have as the startup nation, to build ties. So with the signing of the Abraham Accords, really created the opportunity for normalization, as we know, and countries in the region are investing a lot of money, billions of dollars, to create their own innovation ecosystems. And they're looking at their neighbor, Israel, and Israel as a now welcome citizen of the region that everybody can play with. And saying, How can we learn from the Israel journey, Israel's journey over the last 30 years going from a resource economy where our main export was oranges, to a knowledge based economy where our main export is anyone know? Tech. Yep. So digital, we call it digital oranges, right? The drones flying over the citrus fields and around the world, measuring the health of the fruit in the trees, etc. So really this journey and what went into building an ecosystem? What did the government do 30 years ago that enabled and incentivized foreign investment, where's the academia, where is tech transfer happening both at the university level, also in hospital levels, where what is the role of incubators and accelerators and investors. So looking at the whole ecosystem, sharing that knowledge and using that, as what I call a frictionless tool to engage with our neighbors in the region, because if you're talking about some of our shared challenges, I mentioned before, water security, and energy security and the impacts of extreme weather. Those issues don't know geographic boundaries. And so we are all dealing, especially in the region, one of the most vulnerable to climate change, for example. By the way, in America, climate change is very politicized. In the region, it is not at all because if you don't pay attention to the impacts of climate change in the region, your people aren't going to have clean water, they're not going to have food, they're not going to have energy, electricity. And so these are not political issues. These are what I call frictionless issues, that we can sit around the table and say, we must collaborate in order to find solutions. So innovation diplomacy is really about focusing on the role that innovation plays to create these relationships. As it relates to women. I think women play, can play and do play a unique role into driving this forward. First of all, you know, we spoke about it a little bit and Gadeer, you mentioned this idea of women being social change agents. There's something I mean, I don't think this is unique and exclusive to women, but it's definitely emphasized in women and when we walk into a room, as professionals, we are wearing a lot of hats. You might not see them, but I think everybody on this stage is wearing a number of hats. Some of us are politicians, we're leaders in our communities, in our societies, in our companies, on boards. But we're also daughters and sisters potentially and mothers, some of us and friends, and maybe the head of a kindergarten parent group that has to worry about making sure everybody has the cake for the end of the year party. I mean, these are all things happening at once in our heads. And that's just my own. I'm sorry. I don't mean to project. Gadeer Kamal-Mreeh: The Sarah Jessica Parker cloud. Aviva Steinberger: Yeah, exactly. And I think the invitation that we're putting out to women and the engagements that we have is, bring all of those hats with you into a room. I mean, sometimes they're not necessarily relevant but the engagement at the personal level, at the business level, at the values level, sharing ideas for the vision of what the future, the region could look like. That's really where the connection I mean, I witnessed and sorry, I'm going to share I witnessed and embrace between these two friends who hadn't seen each other in a long time. And I overheard Gadeer say this is the hug of two strong women. That's something unique to women. And, I think if we create the space where that happens, those ties, then feed into trusting networks, where I know that my friend, who I just met last month and spent two and a half days with, who is running a business in Nigeria, and is looking for funding. And I'm connecting with a funder in the UAE who's looking for women-led ag-tech businesses, I'm suddenly making that connection and putting them in touch. And you create these networks of trust that create opportunity. And so it's an opportunity that leads to more women sitting around the table making decisions on investments, more women sitting around the table making decisions around what kind of solutions to pursue, and where these cross regional, cross border synergies could happen. And that I believe in my heart of hearts, is where we're charting a path to a new future for the region. I don't think it's naive to say, we are on the cusp of a new dynamic in the Middle East. Because of these opportunities, and because of these opportunities to engage. I will also say just in terms of numbers-wise. Globally, women representation we spoke about in politics, but women representation, as CEOs and founders of companies, is an abysmal 8% cap, no matter where you go, you're gonna hit that 8-9% number. When I first heard this, I immediately started checking our stats in Israel, because I was like, that's, that can't be in Israel. Israel is just hovering around 10. And we are a global leader. This is an improvement. And you're talking about after seeing efforts. And if you look at the numbers coming out of the universities, women are very well represented today at the academic level and computer sciences. You're talking about graduates that are hovering around 50%, if not more at some university. So you think, okay, you know, we're charting a path for a better future. But that doesn't translate. The reality doesn't translate into seeing more women, founding companies, leading companies. And that is a gap that needs to be addressed. And the jury's still out on what's the silver bullet to get there. But I think it is in creating opportunities. And Ayelet also spoke about this, this mentoring, I think, in particular in the region. I mean, from the United States, I'm American, living in Israel, for the last 25 years, I have not had a challenge finding women to model, women to reach out to and say, you know, I can track this path. And this is where I can see myself being as a future leader. But women in the region don't necessarily have that network, and creating these networks where you can access a vision for what future female leadership looks like and see it and get there and not be the only woman in the room, that has tremendous power. And that's really what we're driving to see in the business and tech community. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for our live recording from Tel Aviv with one of Israel's top podcasts, Israel Story. Host Mishy Harman and I joined the grandson of Moshe Kol, one of the 37 signers of Israel's Declaration of Independence as part of Israel Story's latest series, "Signed, Sealed, Delivered?" Don't miss it.
Jun 30, 2023
'Signed, Sealed, Delivered?': Exploring Israel's Declaration of Independence with People of the Pod and Israel Story
Two of the Jewish world's leading podcasts, People of the Pod and Israel Story, are teaming up to bring you inside the making of 'Signed, Sealed, Delivered?' – the latest series from Israel Story that explores the lives of the signatories of Israel's Declaration of Independence and their descendants. Recorded live at AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv, the episode features Mishy Harman, host of Israel Story, and Eran Peleg, the grandson of signatory Moshe Kol (born Moshe Kolodny). Tune in to hear Eran's lasting memories of his grandfather, the strong Zionist values he instilled in his family, and why the Declaration of Independence matters 75 years later. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Mishy Harman and Eran Peleg (42:35) Yehudit Kol Inbar and Mishy Harman ___ Show Notes: Listen: People of the Pod: Israeli President Isaac Herzog in Conversation with AJC CEO Ted Deutch People of the Pod: Two Ukrainian Refugees Reflect on Escaping War, and Life in Israel– Live from AJC Global Forum 2023 Israel Story: Episode 89 - Moshe Kol Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Mishy Harman and Eran Peleg: Manya Brachear Pashman: As many of our listeners know, People of the Pod recorded not just one but two episodes in front of a live audience at AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv. We also took the show on the road and did a few more interviews in Tel Aviv and in Jerusalem. You'll hear those episodes in the months to come. This week, we bring you our second live show in partnership with one of Israel's most popular podcasts: Israel Story. Welcome to the second live podcast recording here at AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv. So on Monday, you heard two very different perspectives from two women who fled war torn Ukraine and landed here in Israel, their new home. Today, you will hear the story of Israeli Moshe Kol, born Moshe Kolodny, in 1911, in what is now Belarus. He was one of the 37 founders of the State of Israel, who signed Israel's Declaration of Independence. We're bringing you this live show together with another podcast that you might enjoy, Israel Story. Think This American Life except it's This Israeli Life. Broadcasting in English since 2014, each episode introduces us to the wide array of characters who make up this diverse and dynamic democratic nation. In honor of Israel's 75th year of independence, the team at Israel Story set out to find the closest living relative of all 37, who signed Megilat Ha'atzmaut. In March, they began rolling out what I would call audio portraits of those 37 people. Portraits about who they met, what they could tell us about the 37 people who signed that founding document. They call the series, 'Signed, Sealed, Delivered?' And since March, we have met eight of Israel's founding mothers and fathers. Over the next several months we will meet the other 29 including Moshe Kol, through the lens of his daughter. Today, you get a special preview through the lens of his grandson. With me to talk about 'Signed, Sealed, Delivered?' is the host of Israel Story, Mishy Harman, and the grandson of Moshe Kol, Eran Peleg. Mishy, Eran, welcome to People of the Pod, live in Tel Aviv. So Mishy, I will start with you. The title is not 'Signed, Sealed, Delivered,' it's 'Signed, Sealed, Delivered?' What's with the question mark? Mishy Harman: Well, first of all, that's a good question. I mean, it's always difficult to adjust with your intonation to indicate a question mark. But I think that this is a real question. When we began this series, it was actually before the last elections which took place in November, and before this unprecedented wave of democratic, cry for democratic values in this country in light of the government's judicial reform. And we set out to ask, there is this founding document, its status, its legal status is unclear. It's the best way I think, to think of it is, it's some sort of moral compass for our country. And, you know, interestingly, the only action item that actually exists within the Declaration of Independence is to formalize the Constitution, which of course, never happened. So we want to say, to ask the question of what this document actually is in Israeli society, whether we live up to the promise of the words and the ideas that were described within it, whether we haven't. In which ways we have or we haven't, and we wanted to do this through the prism. I'm sure every citizen of Israel has something to say about this and we wanted to do it through the prism of the descendants of the people who signed this document who you know with, with strike of their pen birthed, this country. Actually Moshe Kol call was in Jerusalem at the, on the day of the declaration. There were 11 out of members from Moetzet Ha'am who were who were stuck in Jerusalem, that was besieged and didn't participate in the, in the ceremony, which was here in Tel Aviv. So I think your grandfather signed something like a month later, during the first ceasefire, the different members of Moetzet Ha'am were brought to Tel Aviv by plane actually, to sign. But we wanted to ask, well, here we have this group of people. And it's an interesting group, because the first thing to say about it is that there are no non Jews who signed Megillat Ha'atzmaut, and that's, I think, a very important thing to keep in mind. But when you look at the group of these 37 signatories, it's a little bit like a pointillist painting. So when you look from afar, it looks like a pretty monolithic group of Polish and Ukrainian and Russian Labor Party operatives. But when you come closer, you actually see that there was a dazzling diversity among the signatories. There were ultra-orthodox Jews, and there were atheists, and there were revisionists. And there were communists. And there were people who were born in the middle of the 19th century, and there were people like Moshe Kol, who was the second youngest signatory who was born in 1911, I think. And they represented very different ideologies. And we want to see if a generation and a half or two afterwards whether that diversity had expanded, or shrunken. And to what extent these people who are closest to the ones who imagines the state, how they think about the place we live in today. Manya Brachear Pashman: So 25 signed in Independence Hall, just a little ways from here, actually, here in Tel Aviv, 11, we're in Jerusalem under siege, including your grandfather, two women. Hm. But there was a lot of diversity in the group. That said, I know that they–oh, one in America, I forgot about one in America. They organized it alphabetically. When they signed it, though, even though they signed it at different times? Mishy Harman: With the exception of David Ben-Gurion, who signed first. Everyone else signed alphabetically, and they left little spaces for them. Some of them signed terribly. Like, even though it was the founding document of the state, they couldn't sign on the right line. And actually right underneath Ben-Gurion is the signature of Daniel Auster who was the mayor of Jerusalem. His surname is Auster, which begins with an aleph. So he was the first to sign. And he recalled how Ben-Gurion berated him because his signature was just like some sort of scribble and Ben-Gurion said, don't you understand the importance, the historical importance of the document you're signing. I think your grandfather's signature actually is sort of legible, right? Eran Peleg: Yeah, you can read it. Mishy Harman: I don't know if you sort of, when you were a boy, when you went up to the Declaration of Independence and sort of pointed to your grandfather's signature with pride or something. Manya Brachear Pashman: One of the women you interviewed said that her father or grandfather, I don't recall, but she remembers practicing and practicing the signature beforehand. It was an exciting, it was such an exciting moment. So going back to the organization, how did you organize the episodes? And how did you decide the sequence of how you would release the episodes? Mishy Harman: So we decided not to follow the order in which they appear on the scroll. We did start with David Ben-Gurion. An episode in which his grandson who was really his, the closest person, I would say to him in the family, including his own children, talked about Ben-Gurion. And interestingly, Yariv Ben-Eliezer, Ben-Gurion's grandson, has quite radical views about Israel today. And he thinks of Israel as an apartheid state and says that his grandfather would be very, very upset, and that the whole dream sort of went down the drain. So it was important to us in the next episode to present a pretty different view. So the next episode was the son of Zerach Warhaftig, who was one of the leaders of the Religious Zionist movement. And is a sort of mainstream right winger today. We do try to take into account, you know, gender. So even though there were only two female signatories, we obviously tried to interview as many women as we could who are descendants. Some sort of political variation, we also do try to have episodes have a theme, so whether it's economy or socialism, or tourism or you know, Yemenite Jewelry, or women's rights. So it's not just about the, about the signatory himself or herself, but also sort of about the things that were most important to that person. Manya Brachear Pashman: I tried to as we were, as we were planning this and planning this episode, I tried my hand at tracking someone down from Israeli history and tracking down descendants. And I told your producer that it just made me even more impressed by the work that went into this project, because it was damn near impossible to find who I was looking for. Tell us how you tracked everyone down? Or are there some really good stories about how you connected the dots and landed the right, right person. Mishy Harman: So all of the signatories of the Declaration of Independence are dead. The last one, who was the only one who was younger than your grandfather, Meir Vilner, died about 20 years ago. 14 of the 37 have children who are still alive. In fact, your grandfather, you were just telling me that all of his three daughters are still alive. So that was quite straightforward to find the children. When you start getting into grandchildren and great grandchildren, it becomes quite messy, there are 1000s of descendants. There were only three ultra orthodox Haredi signatories, but they have many, many descendants. And there becomes an interesting question of who you choose, right? Because depending on who you choose, you can tell a very, very different story. And we always tried to prefer people who knew their ancestor, and had firsthand experiences with them. But also to try and maybe we'll get into this a little bit later, but to try to demonstrate a variety of opinions today, too. So it is an interesting fact that the vast, and maybe maybe you'll talk about this, but it is an interesting fact that the vast majority of the descendants of the signatories of the declaration are in what you might call today, the sort of center and center left camp in in Israel, who are concerned about assaults on Israeli democracy. And in fact, the Declaration of Independence has, in recent months, become a rallying cry for the demonstrations. Suddenly the Declaration of Independence, you can't you can't escape it. It's everywhere. The municipality of Tel Aviv, hunger, massive replica, on the building. In demonstrations. There's sort of resigning of the Declaration of Independence, it's really, it's really become an icon, basically. And it was important for us to also show that there are descendants who think otherwise. And so for example, in episodes that haven't yet come out, their descendants who wonder why we even talk about Israel as a Jewish and democratic state, they say democracy is an important concept. It's some sort of Hellenistic fossil. It's not a Jewish value. We don't think that that should even be something that we aspire to. Manya Brachear Pashman: Interesting. Interesting. Eran, how did you get the call that Israel Story was putting this together? Do you recall that day? Eran Peleg: The truth is, I don't remember exactly. Because I've had numerous conversations with them. I think it was probably towards the end of last year at some point. And again, as Mishy said, it was before kind of all these events happened here in Israel. Very happy because I thought, you know, it's, as you say, now it's like the declaration is everywhere. Yeah, people talk about it all of a sudden people, you know, it's, we see it everywhere. But for many years, I mean, hasn't been much discussed, actually. So I was kind of saying, Ah, yeah, it was the 75th anniversary, the State of Israel is coming up. Some chance that we'll get something about it, but that wasn't expecting much. And I was quite happy, to have the opportunity to talk about the declaration, my grandfather, obviously. Manya Brachear Pashman: Tell us a little bit about your own upbringing and what Moshe Kol was like as a grandfather. Eran Peleg: Well, I was just telling Mishy, I mean, quite a small family. My grandfather Moshe or as we called him, Saba Misha, grandfather Misha. You know, he had three daughters. Elisa, Sari, who's my mother and Yehudit, who is the younger one. And altogether, you know, a bunch of grandchildren, seven grandchildren. But that's, that's pretty much it. And so we're a very close family. Every Friday night, for example, we would all gather at my grandparents house and have Shabbat dinner there that was like, you know, you had to be there was no discussion about it or negotiation. So even like, my friends always know that if we want to go out on Friday nights, always after dinner at Saba Misha and my grandmother Keta's house. So we spent a lot of time together. At the point when I was growing up already, my grandfather was obviously getting less involved with state affairs. When I was seven years old, he kind of retired essentially, in 1977. So I had the opportunity to spend time with him actually, both here and also they took me abroad on a couple of trips with them. So it was very interesting. He was a very kind man, very interesting man. I thought he was very smart. The Zionist project was kind of his life mission, if you like. So he was always talking in some way about it. He was always involved even after he retired he was involved in various different projects. Some of them had to do with coexistence within Israel, between Arabs and Jews, Druze, he was very involved with the Druze community, actually, he made good friends there. So even after his retirement, he continued to be active. And so I had the great privilege of kind of knowing him until I was 19 years old when he passed away. And really learned a lot from him. Manya Brachear Pashman: When did you learn that he had signed the Declaration of Independence? Eran Peleg: I don't remember exactly, frankly. And this is one of the interesting things is that I don't remember much discussion at home about the Declaration of Independence. And I think my mother and aunt as well, I don't think, I think they'll probably agree with that even at an earlier stage. And it's quite interesting that he never made a big deal about it, definitely. And I think that in a way, he, although obviously, in hindsight, it was, and maybe at the time, it was a big event, but to him it was I think, and look at here, I'm kind of interpreting, this is my perspective on it. I think to him, it was one necessary and important, obviously, but you know, one necessary step in the big project, and the big project was, you know, establishing and building the Jewish state, the state of Israel. But I don't think if you asked him probably what was the highlight of kind of what was the most important thing you did in your life? I'm not sure if he would have said signing the Declaration of Independence. For example, I think— Mishy Harman: He would have said bringing over 100,000 kids from the Diaspora. Eran Peleg: Exactly yeah, so he was head of youth Aliyah for 18 years after the Holocaust and after the establishment of the State of Israel. To him, I think that was his kind of big, the big thing he you know, he accomplished more than anything else, and he was even later a minister, a cabinet minister, and so he did you know, many other things, but I think that was probably to him, the highlight of his career, Zionist, you know, and the declaration was kind of, you know, one step, kind of a necessary step, but just, you know, one step along the way. Manya Brachear Pashman: So why was he invited to sign that day? Eran Peleg: So, and maybe Mishy, who's more of a historian can, perhaps, can you shed more light on this? But what I know is that, you know, the signatories were invited, it was based on kind of a, it was a party basis, or there were different movements, as Mishy mentioned, within, you know, Zionism or wasn't specific Zionism, because it really, it was supposed to represent the people who were living here actually ex the non Jews, right? Mishy Harman: Though interestingly, there probably would have been non Jews who would have agreed to have been part of this effort, I mean, your grandfather was involved in, in the cause of Christian Arabs from the North, who were, who were removed from their villages, Iqrit and Biram and stuff like that. Those kinds of people were actually allies of the Zionist movement in those days. And it's, it's possible, although Druze leaders- Eran Peleg: It's possible, although, I mean, it's difficult, I think, for us sitting here now to know, because we have to remember this was like, it was a very tense time and, you know, we just had the War of Independence, kind of breaking out and all that. So it's difficult to say, I think. So he was representative of one of the movements, one of the factions within the Zionist movement, he was part of the, what they called, at the time, the General Zionists, Tzionim Haklaliym. And I think he was one of six representatives, I think of the General Zionists. And already at the time, he was a prominent leader within, you know, the kind of centrist Zionism. He was very early on in his life, he was already head of the, what was called the Noar Hatzioni, the movement, the global leader of the Noar Hatzioni. From there, so he kind of knew, he attended several of the Zionist congressional,l the conferences along the years, he was already a member of the executive committee of the Jewish Agency at that point. So he already had a certain position or statue within the kind of Zionist Movement. And as one of the leaders of the General Zionist, he was invited to participate in Moetzet Ha'am, which were the signatories of the declaration. Manya Brachear Pashman: You said, I'm sorry, the first thing you said, he was the global leader of, and I didn't quite hear what you said. Eran Peleg: The Noar Hatzioni movement. Manya Brachear Pashman: What is that? Eran Peleg: It was a youth movement. One of the, at time it still exists, actually. Interestingly, less so in Israel, actually. But in some countries in South America, I know it still exists. Today it's quite small, then it was a decent youth movement. That's actually how we met my grandmother. Because my grandmother was involved in the Noar Hatzioni in Belgium in Brussels. She was one of the heads of the Noar Hatzioni there, and and he has kind of part of his job as the Global Head, whatever of the movement, he was traveling and went to see all these different, all these different places. And that's how he ended up in Brussels where he met my grandmother. Manya Brachear Pashman: You mentioned earlier that some of the descendants had evolved, drifted away from their ancestors, ideologies, political perspectives or philosophies. I'm curious, what your team found was it was did that account for most of the interviews that you did? Or a minority? I mean, did you find that in most of the interviews, the philosophies were kind of embedded in the family DNA? Mishy Harman: It's interesting. Most people are quite similar to their fathers, grandfathers, uncles, mothers, and so on, so forth. But, and, of course, I mean, the important thing to remember is that we're talking in a completely different worlds now, right? If you think about Israeli society today, and you think about our chances of ever agreeing on a single document or a single vision of this state, that's you have to be crazy, basically, to think that that's possible. I mean, we live in such a fragmented and fractured society today, that getting a group that is in some way representative of the country to agree on what this country actually is, what this project that we call Israel, really is, today seems almost unimaginable. And I think, honestly, that it was pretty unimaginable at the time too. I think that they had other things going for them that in the background that allowed them to reach this moment of agreement. Which, you know, there were, as Eran just said, that we were in the middle of a war and it was, seemed like an existential war, right. We were gonna live or die. This all came together very, very quickly. You know, people understood that this was this opportunity, the British Mandate was about to end, there was going to be a power vacuum, the Zionist movement had an opportunity to declare statehood, which was something that, you know, in the Jewish psyche, had been a dream for 2000 years, 1900 years. And they weren't going to, there was some sense of sort of, I would say, communal responsibility, which, you know, there's this word in Hebrew that is difficult to translate, really, which is Mamlachtiut, it's really some sort of sense of, of being part of a larger state collective, that that wasn't going to allow them even if they disagreed with a specific phrasing or a specific idea to be the one saying, No, I'm going to I'm going to be the sole naysayer in this otherwise historic opportunity. And that's what got a lot of people on board, right. I mean, otherwise, how, and I know, they're all these stories about sort of vague phrasings whether they refer to God or don't refer to God or whether they can be interpreted in other ways, and so on and so forth. Today, we're a much more blunt society today. People would want things to be said very, very clearly. And we just unfortunately, and then I'd be interested to hear what you think. But I don't think that as a collective we share any clear understanding of what we can agree on. At least it doesn't seem that way today. Eran Peleg: It's definitely, I agree. But I still remain optimistic, maybe it's my nature. But I do think that, you know, we've seen, you know, the huge amount we've achieved here in such a short period of time. And I do think that, you know, in some ways the values and political views are more clear now than they were back then. As you say, because of everything that was going on at the time, and they, and they were really occupied with kind of let's build this state more than anything else. You know, they put a lot of other things aside, frankly, it's not that they didn't have views about the economy about, you know, they had views about other other things about education, economy, it's just that they said, let's put this aside for now. And let's focus on the main project or the main mission. And they hope to get to the other stuff. Well, they actually promised to put together a constitution, which I guess, but the truth is, it was, frankly, with historical perspective, I think it was very difficult because they were actually set a date. I think. They said that until the, you know, the declaration was signed in May. And they said by October 1st, something like that, I think it's a very short period of time after they already want to have a constitution. And I think that probably wasn't realistic. Also because there was a war going on. And they were occupied with, you know, just existence, or survival. But also, because, you know, views were not, you know, really clear on many different issues, and they didn't have the opportunity to discuss them really yet. United States, for example, putting together a constitution, the Constitution came really only I think, like more than 150 years after people landed, with the Mayflower. So there was a long time where they were already living together. And also then, there was a very serious job around putting together the American Constitution here, they, they were trying to put it together a middle of a war and just wasn't realistic. Mishy Harman: I think that this is particularly interesting for American listeners, because 75 years is a long time, but it's also almost no time at all. And what we feel lucky about with this project is that we're able to still touch these people, who, before they sort of drift into the realm of becoming historical figures in in books and research papers and stuff like that, and we can, we can talk to two sons and daughters, who remember these people as real as real people. And I think, you know, that's unimaginable, obviously, in the American context. And we tend to, we tend to attribute so much importance to phrasings and to wordings, of these kinds of declarations of, and we forget that at the end of the day, these are people who are writing writing these words within within specific historical context and bringing themselves and you know, Moshe Kol, for example, is signing, signing his name on on this scroll of independence. You know, a few years, four years, I don't know, after, after his parents and sister are murdered in the Holocaust, and that was the story of many of the signatories. And as it was saying, it was in the middle of the war and 1% of the population was killed in this war. I mean, they're writing these words, both without sort of knowing what we know today that 75 years hence, Israel is going to be around and Israel is going to be this thriving country with a cantankerous democracy. It was, I think, in many ways, sort of a prayer or a wish, of what, of what this place could be. Many of them came from, you know, socialist backgrounds or from small villages and stuff like that, and suddenly found themselves here in this radically different environment than anything that they had known previously. And they were trying to imagine, well, what can we imagine a just society being? And another interesting thing is that, sort of patriotic symbols like the flag and like the Declaration of Independence, which for years had been essentially owned by the right in this country have in the last year. Eran Peleg: Less so the Declaration. Mishy Harman: The declaration was a little more in the right. But have been completely appropriated by the protest movement, right? I mean, if you go here to Kaplan on Saturday night, which I strongly recommend everyone to do, whether you agree with the protests, or not just because it's a really, it's an incredible, incredible sight for anyone who cares about democracy, to see what these protests are like. You'll see basically a sea of flags, of Israeli flag. So that's, for me, that's a fascinating development. Manya Brachear Pashman: But doesn't it belong to both? I mean– Eran Peleg: I mean, it definitely does. But, you know, the flag was, you know, is always perceived as a bit kind of nationalistic kind of, has this kind of flavor to it. But yeah, but you're right, it obviously belongs to both. Manya Brachear Pashman: They're just embracing it in different ways. Mishy Harman: One question that I would have to you about who things belong to is whether, sorry, I don't know if you– is whether being the grandson of one of the signatories of the Declaration of Independence, makes you feel different about your own ownership of this place? Whether it sort of casts a shadow of responsibility. Eran Peleg: I don't think I'm in a position of privilege or entitlement different from anyone else. I happen to be his grand, yeah, grand grandson. But, but what I think I do have, which maybe some other people don't, I do have, I think, a good sense of history, at least, kind of understanding where we've come from, you know, etc. And I think that's something that sometimes I see missing with other people, maybe that gives me a slightly different perspective on things. So, for example, I see, you know, because we're the generation that was already born into the state of Israel. For us, it was like a given that, right? Self-evident, it's given. And I see especially with people who, like us, some people. It does make me angry when some people might say, I don't like what's going on, I'm just gonna go elsewhere. And to me, like, that makes me angry. But I don't think it makes me angry. Because I'm the son of Moshe Kol, I think it makes me angry, because at least I have an understanding of, you know, what's been put into this project already. And the efforts that have been made, and obviously, you know, people have given their lives as well, I mean, soldiers, for us to be where we are today as well. So, just kind of thinking that, Oh, you know, Israel will always be there for us, even if we go elsewhere, then we decide to come back, right. If we want, we can always come back. But no, that's not the case. Israel wasn't always here. I mean, you have to understand that we have a very, very special situation or position where we have the State of Israel, it's such a valuable thing. We can't just give it up, you know, just like that, okay. And you can't just take it for granted that we'll be here or that it's here, that we'll be here when you decide one day to come back from wherever you're going. Manya Brachear Pashman: Maybe you don't feel that Israel belongs to you. But do you belong to Israel? Eran Peleg: Definitely. Yeah. It's definitely the case. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you ever, and I actually, I address this question to both of you. Wouldn't it be great if we could make plans. But if you had complete control over the universe, and your future, do you foresee ever leaving Israel? Mishy Harman: Eran? Eran Peleg: Again, it's very difficult to know what the future holds. But I see Israel as my home, I've actually had the opportunity to go abroad and come back. And part of the decision to come back was because this is my home. And my home also consists of the fact that my family's here, obviously. So it's a family, family reasons as well. But also, definitely, also Zionism played a role in my decision. I've lived 12 years outside of Israel, but my assumption was always that I'm there for a limited period of time, and I'm going to come back at some point. And that's actually what happened. And so, to me, Israel is where it's place for me. Mishy Harman: So I don't totally know what the word Zionism really means. Today, and something I think about a lot. My grandparents, who were of the same generation of Eran's grandparents, and also very active in the Zionist movement and in building the state. So not quite the blue-bloodedness of signing the Declaration, but they met in the early 30s. They were both students, they were both British, and they met because my grandfather, who was later on Israel's ambassador to the US for many, many years and the president of the Hebrew University, he was the he was the head of the student of design a student union at Oxford, and they met at a debate in which he debated my grandmother who was the head of the anti Zionist Student Union at the London School of Economics and she was an anti Zionist not because she had any particular beef with the Zionist movement but because she was an internationalist and she didn't believe as many others in the in the years between the wars, but leave she did believed in the concept of nation states and, of course, then spent the remainder of her life in the service of this particular nation state. But she was a tremendous presence in my life, she lived to be almost 100 and lived across the street from us. So I'll just share with you very quickly, one of the sort of formative memories of my life is that in 2006, she was already a very elderly woman in her mid 90s. She, we were and not totally with it all the time. At that point, we were watching television together and it was the Second Lebanon War. And she sort of perked up out of nowhere. And she said, Look what a strange thing we're talking about, there are hills to the north of here, that have vegetation, and have wildlife, and have flowers. And we've drawn a line in the middle of those hills. And we call one side of that line, Israel and the other side of that line Lebanon. And there are people living on both sides of that line. And what the TV is saying is that when Moti Cohen's life is destructed, or he's injured, because a Katyusha missile fell on his building, or something, we need to be deeply, deeply sad. And Ahmad Salman''s life is destructed because the Israeli Air Force bombed his village or something, no one's saying that we need to be happy, but we can basically be kind of indifferent. And she said, I don't know Moti Cohen. And I don't know Ahmad Salaman, but I'm equally saddened by the hurt that both of them are feeling. And that was that statement that stayed with me and stays with me, till today. So my connection to this place, I would say, is less from an idealistic point of Zionism, in sort of the classic sense of Jewish self determination. And more from the fact that I was born here, and I grew up here. And the park in which I played soccer, growing up still exists, and the streets, in which I, you know, walked hand in hand with my first girlfriend still exist, and my family are here, and my friends are here. And I like the food that I am accustomed to eating my entire life. And in some fundamental way, this is my home. So, you know, Madison, Wisconsin, or London are not my home in the same way. So that's what makes me want to be here and in the spirit of the Declaration of Independence, try to make our country live up to the lofty and beautiful ideals that that set out to achieve. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's beautiful, both of you. Both beautiful answers. Before we go, I do want to talk about, you've mentioned that a couple times, maybe the absence of God and democracy, those words from the declaration, and I'm just curious if you could both share your thoughts on: does that matter? And is it mattering today? If those words were embedded in the document, would anything be different today, possibly? Mishy Harman: I think the absence of the word God was very intentional. And there's a lot of historical documentation about that. And I think the absence of the word democracy was less intentional in that. I mean, I don't want to bore you with a lot of technicalities. But democracy did appear in previous drafts of of the Declaration of Independence, and was ultimately taken out but not because I think that anyone had any sense that they wanted to be less…yeah, the the intent of Israel being a democracy, I think it's very clearly stated that Israel will come into existence based on the guidelines of the United Nations and the Partition Plan that called for the creation two democratic entities here. I think the Declaration of Independence talks about equality and about freedom of religion and, and in all the main tenets of democracy. So, I think that the Declaration of Independence does, as a document does appeal to a wide variety of people even today. I think that you know, it would be more difficult Today to write a founding document, that in the current makeup of Israeli society that doesn't refer to God and doesn't refer more clearly to the divine. Eran Peleg: But there is some implicit- God is implicity present. I think there's a- Mishy Harman: Tzur yisrael (rock of Israel). Eran Peleg: Exactly, right. Mishy Harman: Which was sort of a very famous kind of pie style compromise, of saying things and not saying them at the same time. Mishy Harman: And maybe as the last thing to say, which opens up a whole other conversation with you, if you maybe want to invite us again, to the podcast, we can discuss, is that, you know, the Declaration of Independence set in place, a notion which I think to most signatories did not seem like a contradictory notion of a Jewish and democratic state. And I think we're grappling till this day with whether those terms are contradictory whether a democracy can be a Jewish state, whether a Jewish state can be a democracy, I think all of them signed the Declaration thinking that this was a possible outcome. And I don't think that they thought that these terms would come to clash in the ways that they have. And I think till today, we're dealing with that legacy of this sort of impossibly simple and yet impossibly difficult coupling of terms, which we're now living in a moment in which we're trying to understand whether the signatories were right, whether this is a possibility. Manya Brachear Pashman: Mishy, I hope you don't mind me asking you a personal question to close us out. And that is, I know you lost your father shortly before the debut of this series. It is dedicated in his memory. And you just shared a story about his mother, I believe that was your paternal grandmother. I'm curious as your team was having all of these conversations, you and your team were having these conversations with children and grandchildren, about the people they love their legacies, did that shape any of the conversations you had with your father in his final days, because you were working on it kind of simultaneously. Mishy Harman: Sure. My father would have loved this series very much because it represented his Israel. It's also Eran's Israel, which is an optimistic Israel, which sees the good in people and the potential and the dream of this project that we began here. I think he would have been very interested, he knew many of these characters who we're talking about. I think he would have also been saddened to hear that a lot of them are dismayed by where things have gone. And I think he was as well. He was the greatest Zionist that I could imagine. And that he really believed. Zionism is a sort of catchphrase in which you can insert almost anything that you want into it. But I think his most fundamental belief, which he attributed to the heart of Zionism was a belief and the quality and a belief that people are people and the belief in education, and the belief in the spirit of the Jewish people. And in this really miraculous entity that we've created that allows us to ask these fundamental, difficult questions about our past. And for me, it's very, very meaningful to be able to dedicate this series to his memory. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much to both of you for joining us. Thank you for the series. I encourage everyone here to listen to episodes of- Mishy Harman: And the next episode that's coming out on Monday is about Moshe Kol. Manya Brachear Pashman: Oh, perfect timing. Wonderful. And thank you both for joining us. Mishy Harman: Thank you. Eran Peleg: Thank you very much. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you, audience. Manya Brachear Pashman: To listen to Israel Story's special series on the Declaration of Independence or any other regular episode, you can subscribe to Israel Story wherever you get your podcasts. Just don't forget to also subscribe to People of the Pod and our award-winning series, The Forgotten Exodus. To learn more about Moshe Kol, here's a sneak peek of Israel Story's interview with his daughter, Yehudit Kol Inbar, the former director of the Museums Division of Yad Vashem in Jerusalem. Excerpt from Israel Story - Episode 89 - Moshe Kol : Yehudit Kol Inbar: He was eating grapefruit and he was crying, because for him it represented, 'wow, we are in Israel and we have a grapefruit that we ourself grew it.' He was very proud and happy with the feeling that they're building a place for the Jewish people. Mishy Harman: That's Yehudit Kol Inbar, the daughter of Moshe Kolodny, who - for nineteen years - headed the Jewish Agency's Youth Immigration Division, and was responsible for bringing more than 100,000 unaccompanied minors to Israel from eighty-five different countries. Despite being among the founders of at least seven kibbutzim and five youth villages, and later on holding senior cabinet posts, he considered that immigration effort to be his greatest public achievement. It was, he once said, a project that had no equivalent in the annals of human history. Manya Brachear Pashman: To listen to the rest of the episode, head to the link in our show notes. Our thanks once again to host Mishy Harman and the staff at Israel Story for sharing these incredible stories with us at AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv.
Jun 29, 2023
Israeli President Isaac Herzog in Conversation with AJC CEO Ted Deutch
Since his election by the Knesset in 2021, Israeli President Isaac Herzog has used his position as a platform to try to mend the social fabric of the Jewish state. At AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv, Herzog sat down with AJC CEO Ted Deutch to discuss key issues, including judicial reform, Israel-Diaspora relations, and the importance of the Abraham Accords. Herzog ends his discussion with an important message for today's youth. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Isaac Herzog ____ Show Notes: Watch: Israeli President Isaac Herzog and AJC CEO Ted Deutch's Conversation at AJC Global Forum 2023 To watch more videos from AJC Global Forum 2023, go to http://www.ajc.org/GlobalForumNews2023 Read: 3 Key Takeaways From Israeli President Isaac Herzog's Conversation with AJC CEO Ted Deutch What to Know About Israel's Judicial Reforms Listen: Two Ukrainian Refugees Reflect on Escaping War, and Life in Israel– Live from AJC Global Forum 2023 Join us next year: Attend Global Forum 2024 in Washington D.C. Register today to secure $350 off your ticket Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of interview with Isaac Herzog: Manya Brachear Pashman: Last week at AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv, AJC CEO Ted Deutch sat down with Israeli President Isaac Herzog for a conversation about a range of issues, including the controversial judicial reforms, the connection between Israel and the diaspora, and the vital relationship between the US and Israel. For listeners who didn't have a chance to see it live, we are replaying that conversation this week. Ted Deutch: As an organization that is committed to advocating for the Jewish people in its entirety, all around the world, your advocacy, your commitment to diaspora Jewry to recognizing the importance of every Jew around the world, is an inspiration to us. And for us to have this opportunity. It, I'd like to start by asking the question in all of your efforts to engage the broadest cross-section of the Jewish world, from left to right, from secular to Orthodox, you've gone out of your way to be the President of Israel, who is really representing the people of Israel. Where does that come from? Is it just part of the role you see yourself playing? It's personal to you clearly, if you could just share with us. Isaac Herzog: It is a passion. And, and I think it's also part and parcel of the role of the President, meaning the president is the head of state of the only Jewish nation, the nation-state of the Jewish people in the world. And as such, it's only natural that he will have such a role, but it also comes out of a deep passion of mine. As you know, my late father Chaim Herzog was also Israel's president was the sixth president. And I come from a family that serves the Jewish people for generations. Some of you have known my uncle Abba Eban, who was Israel's legendary foreign minister. Some of you have known My other uncle Jacob Herzog, who was a huge diplomat, some of you have known my grandfather, Rabbi Isaac Halevi Herzog, who was Israel's chief rabbi and a huge Jewish leader, you know, my brother, Mike, who's the ambassador in Washington, I can go on and on if you want to. But truly, we believe in the Jewish people. We believe that the story of the Jewish people, I believe in the story of the Jewish people, my previous role, was chairman of the world's biggest Jewish organization, The Jewish Agency. And I'm adamantly passionate me and my family, but the story of the Jewish people and we are a small nation, of about 15 million plus Jews around the globe, in a sea of 8 billion human beings, we have a role to play, we have a role, we have a story, we have a role. And therefore we should protect and preserve the unity of our people amidst all of its differences. And that's why I've launched my initiative of Voice of the People - Kol Ha'am. Well, now right now, as of this week, we are holding labs all over the Jewish world to have discussions about how do we move on? How do we care for each other? And how do we identify the future leadership of the Jewish people? Ted Deutch: Thank you, thank you for launching that effort. I just want to pause to marvel at the way that your family's history is just inextricably woven. Isaac Herzog: I haven't even told you half of it, but doesn't matter. I had one of my father's uncles was the head of the AFL CIO. He was Sidney Hillman, really and FDR would say clear it with said so now you have to understand what Shabbat dinners means in our family. There's no way you can escape this stuff. Ted Deutch: As you're sitting, you're sitting here in a room full of people who Shabbos dinners. Well, while we don't have the same personal connections throughout, throughout the history of Israel, that you have our Shabbos dinners I am comfortable saying all of us are full of conversations about Israel, about the importance of Israel, about the role that Diaspora Jewry can play how we can ensure and strengthened ties between the Jewish people in America and around the world and Israel and I know that you're just launching this really important effort. And I'm not asking you to guess what the outcome will be. But I will ask right now even as you're starting this process, as we go back when we go back to America and we go back to our 25 regional offices and our offices around the world. What can we be doing to help strengthen the relationship between diaspora Jewry and the State of Israel? Isaac Herzog: So you have a huge role to play. And I would say first that I believe that part of the problem is the lack of understanding of what Israel is all about. There's, there's a judgmental attitude in certain spheres on my American public life, in certain quarters that judges us according to certain skeleton, scale, sorry, that is not always realistic in terms of where we live in what we do. We are a small and nation which is truly challenged by a huge enemy, which works day in day out to undermine us to kill our citizens, employ, tell against us around us from all sides, and rush to the bomb and spread anti semitism and hatred. And on the other hand, we are a nation that is extremely successful, successful, reaching incredible heights in so many incredible fields that, you know, we will discuss the internal issue and the judicial reform in a minute, I'm sure. But all I'm saying is that in some places, you know, we are judged wrongly by what we do and how strategic we are. And I think you have an immense role to play in telling the story of Israeli democracy, diversity, achievements, we can, of course, deal with the faults and mistakes like any nation, I've got news for you, all nations are challenged and simmering, and, and debating, especially in the modern era. And, and of course, they need to protect and preserve our only Jewish state in the world. Ted Deutch: So we're here on a we're, we're here on a Sunday afternoon. Last night, again, there was there were massive protests around the country, democracy is really democracy in action. How, how should we be thinking about all of that? Isaac Herzog: First of all, let's understand where we're at, because the talks under my auspices, and I gave huge attention to this process, and I find it serious and important. And I also take this tells the leaders that they bear huge responsibility as to the fate and outcome of these talks. And especially as to the effort that is needed in order to reach a wide agreement on the call issues which are so important. These are critical days. And I sincerely hope that the leaders and the elected officials will take the right decisions, because not only the people of Israel want a wide agreement, consensus on the core issues, without of course, hurting the basic rules of democracy and the independence of the judiciary. But more importantly, I also feel that in this room, the Jewish world demands us not to be torn apart, and want us to move forward with a dialogue. Ted Deutch: AJC from the moment you launch your effort to bring the parties together has been as supportive as we possibly can be. We agree that this is a moment that the diaspora as a whole has to recognize why we cannot afford to let it tear us apart. Isaac Herzog: Absolutely. Look, the debate itself, on the core issue of the boundaries between the three arms of government is a legitimate debate that stems from a process of debating that has ensued 30 years ago, these are critical questions that come out when you don't have a constitution. How far can one arm of government supersede the other? That's all a very legitimate debate, the way it's done? What is unleashed, actually, perhaps it's good that it has come up now, as a public issue as a real in-depth discussion of where we are and where we are going to as a nation. I find it actually a potentially healthy process where we air out our differences and talk, talk to each other. And by the way at our home, the president's residence, both Michal and me and the entire team. We are hosting 1000s of Israelis every month while discussing these issues from all sides of Israeli multicultural society. And we have to face that reality and try our best to come to amicable solutions, which preserve our democracy, which protect our democracy, which preserve and protect the independence of our judiciary, which is a very noble arm of government and nonetheless find the right answers as to the boundaries between these arms of government, Ted Deutch: And we wish you nothing but success in reaching that compromise. Finally, Mr. President, there are over 400 young participants here high school students, college students, young adults, as you as you prepare to exit our stage-- Isaac Herzog: Do you want to say a word about the Abraham accords? Before you asked me about that? Oh, I would. Let's shift gears. I'm trying to go full of time now. I'm sorry. We'll take another few minutes. Great. So I just want to put that down, let me know when it's okay. Well, oh, then I've got a lot to ask. No, no, not a lot. Ted Deutch: But let me just ask this instead. Now, we just came from the UAE. And we heard over and over the story of your visit to the United Arab Emirates to advance Israel's place in the world. And the attacks that were launched against the UAE and the expectation as a visiting as a visiting president, that those attacks would prompt you to leave the UAE instead, you had nothing you said no to that you, you extended your stay. Talk to us about how you view your role in advancing Israel's place. Isaac Herzog: I believe that the Abraham Accords which have followed the trailblazing peace agreements with Jordan and Egypt, are a sea change, sea change in history, sea change in world affairs in the region, because there is an opening of a real dialogue between Jew and Muslim in the region. We see it all over. The interactions are huge. And I find the role of the United Arab Emirates and the Kingdom of Bahrain, which we visited as well. immensely important. And I truly believe that we should make an effort that the next chapter will be with Saudi Arabia, I also want to commend the Kingdom of Morocco, which has gone has gone and is a leap ahead dramatically in the our relations. And I believe in that relations tremendously. I also want to commend the Sudan and I hope that they will settle their affairs. But I want to say something about the UAE because the UAE is moving forward continuously in the relationship. And that is extremely important. I want to congratulate my good friend Sheikh Mohammed bin Zayed, the President of the United Arab Emirates, for assuming the leadership of the International Climate Conference known as cop 28, which will take place a few months down the road. I was extremely honored to receive a personal invitation by Sheikh Mohammed and his government and I will attend that conference together with Prime Minister Netanyahu. And I also want to add that most importantly, is that this conference is still then headed by Chef Sultan Al Jabil, by Dr. Sultana Jabber, who is the representative of the UAE in dealing with climate issues. Because I believe that the cooperation between Israel and the Arab nations, Israel and the United Arab Emirates and its neighbors, as to the issue of climate and its impact in the world, has a huge potential, and it sends a spirit of inclusiveness, of friendship, of a future of hope to all peoples. And I welcomed this wholeheartedly and I believe it will make a huge change in the future. Ted Deutch: Thank you. AJC, as you know, Mr. President, through our offices in Jerusalem, and in Abu Dhabi, remains committed to advancing this vision that you describe, as well as the opportunities to build closer relations between Jews and Muslims. And I am being told to wrap it up, but if you'd like to- Isaac Herzog: So let's take one, your final question: now, there are 400 youngsters here. Ted Deutch: Yes, yes. How did you know that was my next question. Yes. Isaac Herzog: Because that's what you say. Ted Deutch: It's not often that they get to hear from the President of the State of Israel, what would you like them to hear before you leave our stage? Isaac Herzog: So guys, you have your generation will face many challenges our parents generation faced our generation face and your generation will face you will have to take a lead role and and add another chapter in the history of the Jewish people. And I would say that one is the challenge of unity, meaning not uniformity, but unity, meaning the respect the love and affection between the nation state of the Jewish people, the State of Israel and its people and the Jewish Diaspora wherever it may be, all Jews must be able to practice their beliefs without fears, and we know harassment and be connected in their hearts to the State of Israel. And we should, we should be able to have the impact, the influence of the Jewish world, within our society within our democracy, understanding that Israel is a developing society, evolving society into a more multicultural, more diversified, fascinating, interesting and promising country. Thank you very much. Manya Brachear Pashman: People have a Pod hosted not just one but two live podcast recordings during AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv. If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for one of those live shows featuring my conversation with two Ukrainian refugees, who now call Israel home. Tune in next week for the second live show with Mishy Harman, the host of one of Israel's top podcasts, Israel Story, and Eran Peleg, whose grandfather signed Israel's Declaration of Independence.
Jun 15, 2023
Two Ukrainian Refugees Reflect on Escaping War, and Life in Israel– Live from AJC Global Forum 2023
Margo Vdovichenko and Diana Buchman, both refugees of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, have found new lives in Israel. Margo, a student from Kyiv, now plans to attend medical school, while Diana, a single mother, bravely shielded her sons during their escape from Odessa. Recorded live at AJC Global Forum 2023, this moving conversation captures their journey and adjustment to life in Israel. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Margo Vdovichenko and Diana Buchman ____ Show Notes: Watch: This conversation from AJC Global Forum 2023 Listen: Hakeem Jeffries on Israel, Ghana, and Representing Brooklyn Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jun 1, 2023
Hakeem Jeffries on Israel, Ghana, and Representing Brooklyn
This week, guest host Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC's Senior Director of Policy and Political Affairs, had the honor of connecting with Hakeem Jeffries, the leader of the House Democratic Caucus, after he led a congressional delegation to Israel and Ghana. As we approach the AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv, we have the opportunity to listen to the Democratic leader's insights on the trip, the crucial nature of the U.S.-Israel relationship, and the historical and contemporary significance of Black-Jewish relations. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Hakeem Jeffries ____ Show Notes: Learn more about AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv: AJC.org/GlobalForum Listen: 8 of the Best Jewish Podcasts Right Now From Roots to Harmony: Nefesh Mountain's Fusion of Jewish American Culture and Bluegrass Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of interview with Hakeem Jeffries: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week, Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC's Senior Director of Policy and Political Affairs, had the honor of connecting with leader of the House Democratic Caucus, Hakeem Jeffries, after he led a group of lawmakers on a recent trip to Israel. Julie, the mic is yours. Julie Fishman Rayman: Thanks, Manya. It's my pleasure to introduce Rep. Hakeem Jeffries, who represents the very diverse 8th congressional district of New York, in Brooklyn, and also serves as the Democratic Leader. He was unanimously elected to that position in November 2022, and in that capacity he is the highest ranking democrat in the US house. He is also the former chair of the democratic caucus, the whip of the congressional black caucus, and previously co-chaired the Democratic Policy and Communications committee. Also, a great friend of AJC and the Jewish community. Leader Jeffries, welcome to People of the Pod. Hakeem Jeffries: Wonderful to be on. Thanks so much for having me. Julie Fishman Rayman: I want to get started by asking you about Jewish American Heritage Month, which as you know, we celebrate in May. Many listeners may not realize that members in congressional leadership cosponsor very few bills – meaning cosign or add their name to endorse them . In this Congress–correct me if I'm wrong–you've cosponsored fewer than a dozen bills and only one resolution–the resolution commemorating Jewish American Heritage Month. Can you speak about this effort and why it was important to you to help lead it? Hakeem Jeffries: Well, thank you so much. And that is absolutely correct. The tradition has been that members and leadership sponsor very few bills and even fewer resolutions, just because the enormity of the request is large. And you want to make sure that you're being very discerning in terms of what you want to elevate as a priority. And for me, it was incredibly important to make sure that I co sponsored the resolution that commemorated Jewish American Heritage Month for a variety of reasons, including the fact that I'm privileged to represent a district that has one of the largest Jewish communities in the country. In fact, I represent the ninth most African American district in the country, and the 16th most Jewish. And so I represent. As a good friend of mine, Leon Goldenberg, once and I quote, you've got the best of both worlds. It's an honor, though, to represent the reformed Jewish community, the conservative Jewish community, the Orthodox Jewish community, the modern Orthodox Jewish community, the ultra orthodox Jewish community, and more Russian speaking Jewish immigrants from the former Soviet Union than any other member of Congress in the country. I mean, Hakeem Jeffries, who knew only in America, but that's Brooklyn, that's New York City and the Jewish community has meant so much to the country, which is why we honor and celebrate and elevate Jewish American Heritage month but particularly has meant so much to the district that I'm privileged to represent to Brooklyn and to the great city of New York. Julie Fishman Rayman: The United States has many heritage months that celebrate the various communities that form the mosaic of our country, including Black History Month, Women's History Month, Hispanic Heritage Month, and more. By celebrating heritage months, we learn about one another, we honor the richness of our diverse nation, and we strengthen the fabric of American society. Some have described JAHM as going on the offensive against rising antisemitism, do you think that's an appropriate description? Amidst rising antisemitism and hate of all forms, does this change how we think about commemorative months? Hakeem Jeffries: Yes, it's a great question. I do think AJC's leadership and certainly the leadership of my former colleague, and good friend, Ted Deutsch has been phenomenally important in this area. And your leadership, Julie, of course, and this podcast and communicating information to the American people will continue to be critical. And the fact that the Jewish community is facing a shocking rise in anti semitism and hate crimes is a cause for alarm for all of us. And it does, I think, lead to the important conclusion that we need to rethink how we lean into the celebrations and acknowledgments, such as Jewish American Heritage Month. That is not just simply an opportunity to be able to communicate to the American people about the many accomplishments, the many ways in every field of human endeavor that Jewish Americans have contributed to the growth and development of America as we know it. And that is important, and that is appropriate. And that is a central part of what celebrating Jewish American Heritage Month should be all about. But it also provides a vehicle to make sure that the appropriate narrative is in the public domain in a compelling way, as a vehicle to push back against the rise in antisemitism and hate crimes. Because it's an all hands on deck approach. And it is going to require using every tool available to us. The rise in sort of hatred and extremism, and divisive, generally should trouble us all throughout America over the last several years, and particularly, the sharp and dramatic rise, particularly given the history of the Jewish community, over 1000s of years of persecutions, and pogroms and pain and suffering, should alarm us all. And it is exactly the reason why thinking about this month as one of the tools that we can use to push back aggressively against the rise and hatred is an important and appropriate approach. Julie Fishman Rayman: In April, during your first congressional delegation trip as Leader, you traveled to Israel. You have been a great supporter, supporting Israel's right to defense and speaking out against anti-Israel sentiment time and time again. What were your biggest takeaways from this mission? What are the major challenges and opportunities for the U.S.-Israel relationship? Hakeem Jeffries: Well, that was my sixth time traveling to Israel, fifth time as a member of Congress. And the first time that I traveled to Israel, I actually was a freshman member of the New York State Legislature as part of a trip sponsored by the JCRC of New York, a wonderful opportunity. Someone said to me recently, Julie, wait, wait. You've been to Israel six times. I said, Yes. That's more than any other country you've been to in the world. I said, That would be correct. Is it isn't that a lot? I said, No, not at all. First of all, I'm from New York City, where we consider Jerusalem to be the sixth borough. And I'm just trying to catch up to my constituents. Every time I go to Israel, it's a wonderful eye opening experience. This particular trip was meaningful to me in that I was able to actually lead a delegation for the first time in this position and choose where I would go to in the world as part of my first congressional trip on foreign soil, as the House Democratic Leader. And I chose to go to Israel and to Ghana, to incredibly meaningful countries to meet personally, to the people that I represent, and, of course, to the relationship that exists between the United States and Israel. And I wanted to do it so that it was timed to the anniversary of the 75th founding of the State of Israel, because I thought that will be meaningful for the members that agreed to travel with me and certainly meaningful to me to say to the world, that we're going to continue, as we've transitioned leadership in the House of Representatives, to stand behind the special relationship between the United States and Israel. And to make it clear that that's a special relationship that we as House Democrats believe, is anchored in our shared values and our shared strategic interests. And it was incredible because of the timing of we were there, both on the day of remembrance was incredibly moving. And I was able to participate in one of the ceremonies that we're held to acknowledge those who have been lost, both to acts of terror, and in the conflicts that Israel has been made to endure throughout the 75 year history. And then, of course, on the eve of the celebration connected to the 75th anniversary, and we had a very diverse group of members, several prominent Jewish American members of Congress, of course, like Josh Gottheimer and Debbie Wasserman Schultz, Dean Phillips, Sarah Jacobs, who was a new and emerging leader, but also the chair of the Congressional Black Caucus. Steve Horsford, the chair of the Congressional Hispanic Caucus, Nanette Barragan, the first vice chair of the Congressional Black Caucus, Yvette Clarke, as well as the top Democrat on the foreign affairs committee, Greg Meeks. And so it was a wonderful experience. We had important public policy discussions with Prime Minister Netanyahu, President Herzog, with the Speaker of the Knesset, as well as the opposition leader, Lapid, they were open, they were honest, there were candid discussions about the challenges that our two countries face. But it was all anchored in our clear affirmation of Israel's right to exist as a Jewish and democratic state, and our commitment as House Democrats to continue to lift up and elevate the special relationship between our two countries. Julie Fishman Rayman: So important. How's Israel doing at 75? Hakeem Jeffries: I think Israel, it's a miracle, as has been described, that we've gotten to 75 years. And it's a testament to the strength, and the resilience and the ability, the heart, the soul, the love the intellect, of the Jewish people, and the people of the State of Israel. And I'm confident that through the challenges that we all face in Israel, the best is yet to come. You had an interesting discussion, because of the judicial reform, issues that are underway. And we've got challenges that we're working through here in the United States of America, certainly, as it relates to the Supreme Court, and what is the right, you know, balance in terms of our three branches of government. And we've got to work through that here. Many of us have been troubled by recent developments coming out of the Supreme Court, and Israel's working through trying to figure out what that right balance is, in terms of the rule of law, and the independence of the judiciary, and how that works together. I think what has been clear to me, in terms of Israel as a robust democracy, that will continue to be a robust democracy is not the challenge is that it's working through to find common ground. And those talks are being led, of course, by President Herzog. But most significantly, the fact that hundreds of 1000s of Israelis have been in the streets, exercising their right, their freedom of expression, their freedom of speech, their freedom of assembly, the right to peaceably gather and petition your government that is at the hallmark of a democratic society. And that's what we've seen, and not a single shot fired, probably nowhere else in the Middle East, would that have occurred other than in Israel, and it's an affirmation of Israel's democratic character. Julie Fishman Rayman: In just a few weeks, AJC will hold our annual Global Forum in Tel Aviv. What is one piece of advice you'd give the 1000 or so people coming from around the world to Israel at this time? Hakeem Jeffries: Well, I do think that every time I've gone to Israel, what has been a wonderful aspect of the trip was talking to the full range of people in Israeli society, to get the perspectives on the ground in terms of their views related to the challenges that Israel confront, and the opportunities that exists to continue to thrive into the future. And those are particularly relevant conversations to have now that Israel has hit this incredible milestone of 75 years in what still remains one of the toughest, if not the toughest neighborhoods in the world. And one of the reasons why sustained dialogue, sustained opportunity to engage in wonderful that AJC is hosting this forum in the next month, is that the challenges are always unique whenever one arrives in Israel. You know, it could be Hamas, it could be Hezbollah, it could be uncertainty in terms of the Iranian malign activity in Syria. It's always, you know, Iran's efforts to try to secure a nuclear weapon and we're gonna make sure that Iran never becomes nuclear capable in Gaza. There are different moments in time, where particular concern meets a level of urgency, but it's always consistently within the frame of Israel living in a very tough neighborhood, which is what I, you know, we reiterated as House Democrats directly to Prime Minister Netanyahu, our commitment to ensuring Israel maintains its qualitative military edge. My view on this thing has always been, and I grew up in central Brooklyn, came of age in the mid to late 80s, early 90s. I kind of know from tough neighborhoods. That was a tough neighborhood. I grew up in Israel, Hamas, Hezbollah, Gaza, chaos in Syria, in Iraq, Iran with nuclear aspirations, dangerous situation in the Sinai. That's a tough neighborhood. And in a tough neighborhood. The one constant, as I've consistently said, is strength. You can achieve peace, you can achieve stability, but you can only achieve it through the lens of strength. And I think, part of the dialogue that we all should continue to have and will be important for AJC to continue to have is, you know, what are the severe threats that Israel currently confronts? And how can we continue to ensure that Israel has the strength to defend itself and to provide a foundation for lasting peace moving forward building upon things like the Abraham accords? Julie Fishman Rayman: Prior to Israel, you and the members of congress who traveled with you to Israel went to Ghana, one of America's closest allies in West Africa and a nation that still bears the painful scars of the transatlantic slave trade. At AJC's 2019 Global Forum, you became the first member of the congressional Caucus on Black-Jewish Relations, I think less than an hour after it was officially launched. Did your back to back trips to Ghana and then Israel spark any insights as we continue–collectively–to try to bring Blacks and Jews closer together? Especially because Blacks and Jews were really strongly represented in your delegation? Hakeem Jeffries: Yes, you know, AJC's effort in terms of forming the black Jewish caucus was a wonderful thing, a great foundation. And in many ways, the trip to Ghana and to Israel is in that same tradition. And as you pointed out, Julie, there were a lot of African American members of Congress who on the trip and a lot of Jewish men from the members of Congress who were on the trip who visited both countries. And, you know, we were able to involve Ghana, and in Israel and Ghana, visit the Cape Coast slave castles, which were central to the horrific transatlantic slave trade. And we also were able to visit Yad Vashem and I was able to lay a wreath and make it clear that we would never forget and never again, allow the Horus of what was seen during the Holocaust to occur. And it was important that in addition to, in Ghana, for instance, meeting with President Akufo Addo, to visit the site, for a lot of the activity of the transatlantic slave trade, and, of course, the ties that then connect to the African American community in the United States of America, and to visit the door of no return. But also to make sure that, in the time that we were in Israel, almost every time that I've been there, we've always made it a point to make sure that we visited Yad Vashem, it's always a very powerful, moving experience. And it was the same and to be able to do it together with black members of Congress and Jewish members of Congress, and leaders, who were not black and Jewish, but were on the trip with us, was really a powerful experience, I think, for everyone involved. And I think it's important for us to continue to try to lean in to strengthening the relationships between the black and Jewish community. It's something that because of the district that I represent, has always been central to my time and public service. And I do you know, I am moved by the fact that at least part of the district that I represent, and that told this story during the Democratic caucus celebration of Jewish American Heritage Month, but I tried to tell it whenever I get the opportunity that I do represent a district that was once represented in part by a manual seller. And a manual seller was the longest certain Congress person in the history of the country. He served for 50 years, first elected in 1922. And served through 1972. He was a staunch ally and advocate for the special relationship between the United States and Israel from the very beginning. He was there, I believe, with Truman, when the United States first recognized Israel, and was there to support the special relationship every step of the way throughout the time that he was in Congress. But what also is little known about Manny seller, as he was affectionately known in Brooklyn, is that during the 1960s, he was also the chair of the House Judiciary Committee, which meant that he played an important role, legislatively, and making sure that the 1964 Civil Rights Act, and the 1965 Voting Rights Act, became the law of the land, to crush Jim Crow, and crushed the effort to oppress the ability of African Americans, particularly in the south to participate fully in our democracy. And then you go to civil rights museums across the country, and whenever there have been exhibits, even here in the Library of Congress, usually always an acknowledgement of the role that Manny Celler played. And I'm proud of the fact that I can represent a district that someone who was such an important link between the black and Jewish community and actually played a meaningful role in helping to advance legislation to change the course of America, in supporting the efforts and leadership of Dr. King and others, is an important thing. That's a tradition that I look forward to continuing to build upon and at the same time, to be able to represent a district as I mentioned earlier, where I serve more Russian speaking Jewish immigrants from the former Soviet Union than anyone else. And to know that Dr. King took time out from his days of leading the civil rights movement, to speak to Jewish leaders and rabbinical leaders across the country famously anchored in his guiding principle, that injustice anywhere is a justice everywhere, and it was great injustice, being directed at the Jewish community that was behind the Iron Curtain during the days of the Soviet Union, and to use his voice to speak up on behalf of what he appropriately viewed as his Jewish brothers and sisters who are facing oppression. That example that was set by Dr. King, that example that was set by Congressman Judiciary Committee Chair Manny Celler, who wasn't just focused on strengthening the relationship between the United States and Israel, but also dealt with the injustices directed at African Americans throughout the United States. That's a powerful heritage for us in Congress, or us as leaders, as AJC has promoted, to continue to build upon. Julie Fishman Rayman: Thank you so much, you've provided us with such a sweeping understanding not just of the history-everything from Manny Celler to Dr. King to Yad Vashem. But also a vision for where we can all go collectively. Whether it's in May, during Jewish American Heritage Month, or Black History Month, or every day, trying to honor the legacy of Americans from all facets who lift up our great nation and make it what it is today. Leader Jeffries, thank you for your leadership and thank you for being with us. Hakeem Jeffries: Thank you so much, what an honor Julie to be on and all the best to you and look forward to continuing to work closely with Ted, with AJC, on behalf of the issues that we all care about, particularly as it relates to the well being of the Jewish community here in the United States of America and throughout the world. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with the Jewish bluegrass duo Nefesh Mountain, featuring not one but two live musical performances, a wonderful way to wrap up our month-long series of shows honoring Jewish American Heritage.
May 30, 2023
From Roots to Harmony: Nefesh Mountain's Fusion of Jewish American Culture and Bluegrass
Driven by their message of "radical love," hear how Doni Zasloff and Eric Lindberg, the husband and wife duo behind the renowned bluegrass band Nefesh Mountain, combat antisemitism within the music industry and beyond. Join us as we delve into their remarkable journey of representing Jewish-American culture, tradition, values, and spirituality through bluegrass and Americana music. The band also treats us to intimate performances from their latest album, "Songs for the Sparrows." *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Doni Zasloff and Eric Lindberg ___ Show Notes: Learn more about: Nefesh Mountain Take our quiz: Jewish American Heritage Month Quiz Test your knowledge of the rich culture and heritage of the Jewish people and their many contributions to our nation! Start now. Read: What is Jewish American Heritage Month? Jewish American Heritage Month Resources Faces of American Jewry Amazing Jewish Americans Listen: 8 of the Best Jewish Podcasts Right Now Sen. Jon Ossoff on Jewish Resilience Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Doni Zasloff and Eric Lindberg: Manya Brachear Pashman: Nefesh Mountain arrived on the bluegrass and American music scene in 2014. The husband and wife duo of Eric Lindbergh and Doni Zasloff have since performed in hundreds of synagogues in the United States and around the world, representing Jewish American culture, tradition, values and spirituality in the world of bluegrass. Bluegrass Today magazine has described the duo as what happens when bluegrass and Jewish traditions meet and fall madly in love. In honor of Jewish American Heritage Month, Doni and Eric are with us now. Or I should say–we are with Doni and Eric now in their home in northern New Jersey, Doni, Eric, thank you for welcoming "People of the Pod." Doni Zasloff: Thank you for coming. We're so excited to have you. Eric Lindberg: What a treat. Manya Brachear Pashman: So please share with our listeners how the two of you got together. Did you have individual musical pursuits? Or did you not really find your groove until you were together as a duo. Eric Lindberg: We're both pointing at each other. You tell it. Doni Zasloff: You tell it. Eric Lindberg: Well, we both had individual pursuits. We met playing music in the New York kind of North Jersey area. Years ago, we met back in 2010. And we were playing music in various fashions. And the quick story is that our band is a love story. And we fell in love a few years later, and it became apparent to each of us that we were head over heels crazy about each other. And that we also had all of this stuff that needed to come out that we kind of needed the other person to help kind of embolden our feelings of Americana music and of Jewish life and of culture and all this stuff. So I grew up in Brooklyn. And so much of my life as a kid was part of the synagogue, my after school program, and my camp, and of course, synagogue and I had a Bar Mitzvah and I grew up with this big Jewish life in Brooklyn. But at a certain point, I became kind of just a musician, I didn't know where to put this Jewish side of myself. I went to study jazz in college and all this stuff. So when I met Doni, she kind of brought me back to this feeling of, well, you can be proud of this and you can be excited about it. And you can live a fully Jewish life, you don't have to do it, any which way. You don't have to be a quote unquote, good or bad Jew, which, we hate those terms, but people tend to use them. Even Jewish people, of course, to show how religious or observant they're being at a certain time. So she had this completely unbridled kind of cowgirl way of looking at being wild and Jewish and proud and being yourself. And ultimately, I think that is pretty much the core of our message as a band. But I guess we'll get to that a little bit later. But she brought me back to this place of really just being proud of who I was. And that was the little germ that started this band. And then I brought kind of this musical sensibility in Americana music, with the banjo, and fiddle, and all this stuff. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Doni, how about you? What was your journey? Doni Zasloff: I've always loved all different kinds of music. And I've always been very, as Eric was describing, just having a very strong Jewish spirit. And I think what Eric you know, it's exactly right. When Eric and I fell in love and started to really kind of get real with ourselves and we wanted to kind of express ourselves in the most authentic way. And I think my Jewish spirit and his massive knowledge of all kinds of music, and he just kept throwing CDs into my car–listen to this, listen to this, listen to this. And he just kind of opened my mind and my heart to so many styles of music that I--some of which I loved already, some of which I learned. It was just something about the stars aligning for Eric and I that the music that we started to write from our truest selves in that moment, came out in this Nefesh Mountain kind of a way. And it turns out, it's exactly our truth. And it's exactly the thing that we were looking for, this idea of our relationship, our connection. It is our truth and it's become our whole adventure. Manya Brachear Pashman: And are you talking about the genre of music when you say that the Nefesh Mountain sound, or something else you're referring to? Doni Zasloff: It's not, it's like our language. It's the type of music that we play. It's the stories that we tell, it's the perspective that we have. A lot of people say, you know, where is Nefesh Mountain? Is that a place? And we always say it's a place. We made it up. But it's a place that we kind of, it's like a little dream world, that bubble that Eric and I have sort of dreamt up. Where, you know, it is a little like, the free to be you and me vibes of like, just be yourself. And it's infused with this huge range of musical styles. And Eric brings that to the table. Manya Brachear Pashman: Would you describe your genre or style as bluegrass? Or would you describe it as something else? I call it bluegrass. But what do you call it? Eric Lindberg: That's a great question. Because we're right now kind of, you're catching us in the throes of exploring that. And we have been this whole time. I'm a huge fan of bluegrass music. But when I say that, like that means something to me. And it doesn't necessarily mean the same thing to everybody. Of course, it's a word out there that means different things, like being Jewish means something different to everybody. You know, is it a religion? Is it a culture? And bluegrass has the same kind of thing where there's a purest form of bluegrass, which when you're talking about Bill Monroe, Flatt and Scruggs, Stanley Brothers, etc, you know. And then you also have the Bluegrass that I grew up with, which was more of a quote, newgrass thing, and also really just ended up being kind of very fancy folk music with the likes of you know, people like Béla Fleck and Nickel Creek, and Punch Brothers and Sarah Jarosz. All these singer songwriters that are starting to write music with bluegrass instruments, and also improvising on a very high level. So bluegrass has become something that is actually more Americana. So these days, we're kind of using Americana. Manya Brachear Pashman: Talk a little bit about the original purpose of your music, or message that you wanted to convey with your music together. Or the one that's evolved over time, perhaps? Eric Lindberg: Well, the original purpose. I'll say, it was all an accident. You know, we fell in love. That's always an accident. A beautifully happy, you know, accident that is ever evolving and beautiful. We, um...sorry. Manya Brachear Pashman: Stop making lovey dovey eyes at each other. Actually, you can continue, I just wanted our listeners to know. Eric Lindberg: No, no. It's a big story. We fell in love. Your question was…say it again. Manya Brachear Pashman: You talked about wanting to be authentic, wanting to express yourselves originally. But has that purpose or intended message of your music evolved over time? Eric Lindberg: Yes, it has evolved and the purpose in the beginning, I noticed something when we first started making this music. As a fan of course, Americana, bluegrass, all this stuff. I noticed that so many artists could go out and sing songs about, about Jesus, about Christianity, about their spirituality. And it's not necessarily called religious or overtly Christian, or anything. It's just Americana. Because they are kind of synonymous. And the fact that gospel music is kind of at the core and like in the bedrock of what has laid the foundation for Americana music, it goes without saying. So any secular artists can go out there and kind of be themselves in all of that. If they want to sing a gospel tune, well, let's do Will the Circle Be Unbroken, everyone will love it, you know, even though it's a gospel song. Or even songs that we've kind of turned on their ear a little bit like Wayfaring Stranger or Down to the River to Pray, I Fly Away, gospel songs that we love. So this was our answer to that– we're gonna bring a sense of Jewish spirituality to the Americana table. And our first records, or really our first record. And then a little bit into the second dealt with some of our liturgy with some of the prayers that we had grown up singing, which, for us, meant a lot. Songs, like Henei Mah Tov, which is a whole song about how great it is to have friends and be together and, you know, celebrate each other's uniqueness and beauty. To songs like, Oseh Shalom, prayer for peace, or something like that. Through the years, we found a new purpose. And we've also, you know, been a band through a very trying time in this country. You know, no matter what side of the political fence you're on, it's been, we're all living in a world where we pretty much don't agree. And it's kind of de facto, now, that we don't agree, and we're gonna fight. And unless you see exactly eye to eye with me, I'm your enemy. And we have now kind of taken a stance, we're not politicians by any stretch. But Doni has kind of created this term that I love, and it's called radical love, which is to, regardless of our backgrounds, regardless of, our opinion on this, that, or the other, we are going to look at people in the eye and embrace them, and to put love out, because that's what the world is clearly lacking. And it's definitely a kind of hippie sentiment, peace and love, man. But we're fighting all the same things now that everyone was in the 60s, that everyone was in the 70s and 80s. And before that, and probably beyond. And we're challenged with the same issues. We're challenged with racism, antisemitism, a lack of empathy and diversity in neighborhoods and school systems and in cities and the world is still, we want to be happy. So we pretend that it's better than it is sometimes, but it's not great for so many people. And it is a Jewish ideal that I grew up with, this idea of Tikkun Olam, to make the world a little bit better. That's what we want to do through our music. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you feel like you have had opportunities to share and communicate that radical love? Are you getting through to people? Doni Zasloff: I think every time we get on a stage that is, in front of anyone really, whether it's a Jewish crowd in front of us, or whether it's a you know, a secular, diverse crowd of people, we don't know what their backgrounds are, we really are kind of stepping into a space where we are putting out this radical love. And I think that we have been blessed with an amazing response to it. People are skeptical about a lot of things. There are Jewish communities that were very skeptical about the banjo and very skeptical about the bluegrass thing. The amount of people that come up to us at a synagogue and say, I thought I hated bluegrass. I had no interest in bluegrass, I love it. Or I thought I was gonna hate you guys. Like I didn't understand what you guys were all about. But it turns out I really love it. So we're getting a lot of love wherever we go, which is kind of why no matter what's going on, we just keep doing it because, you know, we've also had responses from people of all backgrounds just hugging us, thanking us for sharing this, you know, culture with them. People have come up to me crying like thank you I, I've never met anybody Jewish, I just didn't know, I didn't know. I think that music is so powerful, that it can break down so many walls and just shift people's ideas. And so I do think that the response to our radical love has been great. It's not easy, it's a little scary sometimes. It's not always been embraced. There are a lot of bluegrass festivals that wouldn't put us on their stages, because they don't want a Jewish band up there. They don't know what their crowd's gonna think or how that would affect their bottom line, or I don't know. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do they come right out and say that? Doni Zasloff: Pretty much, yeah, we've definitely gotten that feedback. It's hard to hear, as you can imagine, it's painful. But it's the truth, that there is antisemitism everywhere. Eric Lindberg: Yeah, it used to be–we've been a band since about late 2014. And now, we're knee deep in 2023. And in the beginning stages maybe I was more naive. And I used to kind of think, because, again, the bluegrass world I had in my head was that of progressive music. But I will say that there is a flaw in the bluegrass world and some of the people who want to keep bluegrass being a certain way. And that explains part of our, you know, we will always play bluegrass. So it's not that we won't depart from the genre, but are exploring other areas as well, because we've had clear cut answers of: No, you will never be on this radio station. No, you will not be at this bluegrass festival. We don't have room for people that preach Jewish things. Which is not what we do at all. We have a big show, I think we're a good band. We've done a lot. I'm proud of what we've done. You know, if the answer was no, because we don't believe you're good enough, then that'd be one thing. But the answer is clearly a Jewish issue. It's a tough thing to live with. So a little bit of me is, it's one of those things you hope as a little kid growing up, who loves music, who is crying and dancing and laughing and learning it and loving it. And it's the most exciting thing in your life, you hope that when you grow up, that it's not going to turn around and kind of kick you in the ass. And you're not going to see some of the dark underbelly of the world that you love. And unfortunately, some of that has happened. At the same time, I've gotten to play with my heroes, our heroes, Sam Bush and Jerry Douglas and Bryan Sutton. The people, the people that I've loved as musicians have all been the most beautiful, like creatures on planet Earth. They are very much beloved to us and our family. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm not totally surprised. We love bluegrass as a family. But my kids do call it Jesus music occasionally. And we make sojourns to bluegrass jam sessions. There's one in Little Silver, New Jersey once a month that we've made the sojourn to at the little Methodist church there in town and I sing along with I Saw the Light. My eight year old wants to play the banjo, that's the musical instrument he has settled on to learn. That's why you guys stand out so much is that you have given to us, a sense of belonging. That like we belong in this world too, we belong in those seats as well. And so I'm not surprised that you have experienced that, but my heart is breaking a little as you talk. Eric Lindberg: And I want to add that there's nothing wrong at all with bluegrass music, with celebrating Christianity and that spirituality, at all. And I just want to be really clear, because that's the music that I love. And I'll sing along with those songs, too. I love those songs. And it's not, as Doni was saying before, it's not like we haven't, we're playing a lot where there are folks that are saying yes, that are embracing us. But there is something about, you know, when you're Jewish, and when you get that kind of feedback, because it speaks more to antisemitism than I think the musical world or the culture that we live around us in, in this country. I hope that I am being clear in that, the music is beautiful, and the heritage is beautiful. And we're not saying we should be like, we love bluegrass culture, bluegrass music, Americana culture, all that stuff. We love our Jewish culture. And we only want to do right by both sides of that equation, you know, make sure that they're balanced and treated with love. Doni Zasloff: But just like the world, there is, a little bit of a, not a little bit. I mean, the antisemitism that we're seeing, right now, in this country, it's everywhere, including what Eric was talking about. It doesn't just go away. We were at a big conference, and somebody came up to me, and I tell this story a lot, this guy came over to me in a big cowboy hat. And he just looked at me and he said, Why do you have to be here? Why do you have to play this music? Eric Lindberg: He actually said, you actually don't belong. Doni Zasloff: Y'all don't belong here. This Jewish thing, just basically, get out. And I remember just like, taking a deep breath, walking outside, I think I cried a little bit. I think I called my dad. You know, I was just like, What am I doing here? Like, this is nuts. You know, but then I walked back in and I'm getting, hugs and like, a lot of love. So, you know, this is part of being outwardly Jewish, I think right now. Like, it's just kind of what happens. Eric Lindberg: And that's the phrase that we haven't, we haven't said yet, because it seems like kind of a strange thing, to be outwardly Jewish. What does that mean? And I didn't grow up in a world where, where people did this, you know, and it kind of boils down to, there's a decision that we have to make that I had to make, and Doni, as musicians that are we going to be a band that is just about the music. And largely we are, actually we want to make good music first and foremost. And we also want to be a band that is, we live in this world, and we are seeing a rise in antisemitism, and we are scared about it. It troubles us and it makes my blood pressure rise and it's terrifying. And if we don't say anything about it, if we're not outwardly Jewish, if we're not openly wearing the star on our chest, you know, so to speak, or on our shoulders. I don't think we're doing ourselves a service. I think we're hiding behind something. For better or worse we're openly going out there and talking about this stuff all the time, because, you know, it won't get better if we don't. Manya Brachear Pashman: You have recorded three albums, you're getting ready to release a fourth. Is that correct? Eric Lindberg: Yeah, we actually have four albums out. One is a live one that we kind of snuck out at the end of 2021. Okay. But yeah, there's four that you can stream or buy or any of that stuff, and we have some new music coming out that we're really excited about. Manya Brachear Pashman: If you could talk a little bit about the inspiration behind those albums, because I know that they tell stories. And I'm curious if you could, you could share with our listeners. Eric Lindberg: "Songs for the Sparrows" is the most personal and adventurous recording that we've done, it was a huge undertaking. But maybe Doni, you want to tell them a little bit about the inspiration behind that record. Doni Zasloff: That record was inspired by a trip that Eric and I took with our older kids and my mother. My mom did all of this research about our family history, in Eastern Europe, and found all of this information and was able to locate the town that our families we're from. And so we did this big roots trip. It turns out I'm from Ukraine, I thought I was from Poland, but now it's Ukraine. And so we went on this trip, and we saw the town that my family was from and then we saw the forest outside of this town where some of my ancestors, we believe, were shot. We saw so many things, this trip really kind of just rocked us. I mean, it's everything that we've learned about. But to go there and to see it, it's not in a book, it's not in black and white. It's there and to see that the history was kind of almost trying to be erased, in modern times. It was hiding, we had to dig it up to even know that it had happened. Eric Lindberg: Literally hiding like we'd get there, we were in Lviv, this is of course before current day, this is back in 2018. And we were in this kind of great shopping area and parking lot and our tour guide had to say, you know, this was a cemetery. This was one of our flea markets. It was like a flea market and it was like what's going on? And there's vibrant life happening but at the same time, no one was… Doni Zasloff: Everything was destroyed, everything, you know, everything hundreds and hundreds of synagogues. I mean almost all of our ancestors, you know, this is where it all was at. But anyway, so we were on this trip. And while we were there I posted a picture on Facebook saying you know I'm on this roots trip. And then one of Eric's cousins like a distant cousin Reuvain, who had also done a lot of research on his family history, started sending email after email to Eric saying, Eric Eric, you are from six hours south of Lviv, you are from the Carpathian Mountains, that's where our family is from, you should go. So we turn the bus around, we ended up going six hours south to the Carpathian Mountains, so that we could see where Eric's family was from the next day. Eric Lindberg: And just like you thought your family was from Poland, I thought my family's from Austria-Hungary. But in '91, the borders all shifted. And so my grandma grew up, you know, grandma, where we from, she spoke a little Hungarian and, and Yiddish too. It was always Austria-Hungary. That's where we were from. And now of course, it's present day Ukraine. Doni Zasloff: Right, so we take this six hour drive south, and through the help of Reuvain, were able to find the cemetery where Eric's great grandfather was buried. Hours of looking, and we finally get there, and it had been destroyed. But somebody actually was trying to restore it. But it was little bits and pieces of stones everywhere. But at least it was kind of marked as something. So we went in there and looked for hours, we spent hours trying to find a little evidence of something with his great-grandfather's name on it. We never found anything. But there was a moment when we were walking around the cemetery that we looked up and saw all of these little birds flying above us, these tiny little sparrows. And there was just something that kind of was very breathtaking about the whole experience and kind of weird. We went through this whole trip, kind of taking it all in. It was a very emotional as you can imagine, like, just very intense trip. We got home and we're trying to like process it six weeks after we returned home was the tree of life shooting in Pittsburgh. So it was like, you know, part of our brains would like you know, that was the past that when it happened over there, this was a terrible thing. It happened over there. Then suddenly we come home and it's happening here. And there's this hate and there's this violence and so it was just like all swirling in our heads and we just kept thinking we have to do something we have to like we just felt compelled to make Now we'll basically or to do something, we didn't know what it was gonna be, we just had to write. But then we kept coming back to that moment with the bird with the sparrows, when we were walking around the cemetery. And Eric and I had this thought, well, maybe those sparrows were our ancestors. And maybe the and then the sparrow, maybe the sparrow. And we learned that sparrows live all over the world. They're small and mighty, and they live and their sparrows everywhere, there's sparrows outside of this house, there are sparrows in Ukraine, there's sparrows everywhere. So the sparrow has become, you know, became a symbol or a totem for anyone who has been discriminated against and hated for just being themselves. You know, whether it's our ancestors, or anyone, right now who's just not being accepted for the person that they were born to be. Manya Brachear Pashman: Unbelievable. I want to ask you about your upbringing. And I know Eric grew up in Brooklyn, but where did you grow up? Did you have a bat mitzvah? What's your spiritual journey? Doni Zasloff: I was born in New York. And then I lived a little bit in Boston and then I grew up in DC in the DC area and then Philadelphia and then I moved to New York so it's been you know, East Coasty. So I grew up going to Jewish camps and Jewish schools and I had this very intense connection to my Jewish spirituality. Like, I hated it, I loved it, I challenged it. It was like, I needed it. I didn't want it, you know, it was but I was in it. You know, I had this relationship with my Jewish identity. Even as a little kid, like a little girl, I remember, I wrapped to fill in when I you know, in a Jewish Day School setting, and like the rabbis were like, you know, angry at me, you know, things like that. Like, I was just like, really rebellious in my relationship with my Jewish self and going to Jewish schools and things like that. So I don't know, I felt like a Jewish cowgirl really my whole life. Manya Brachear Pashman: You have a film crew that has been shadowing you for quite a while now. Six months. And tell us a little bit about "We Sing Nonetheless." Which is the title of an upcoming documentary. Eric Lindberg: Yeah, it's really exciting. We met this awesome gentleman, Adam, up in Boston, we were playing a show, I believe that was at his synagogue. But we were, you know, it was just after the show, and I'm like, kind of sweaty, over by the merch or something, and I just start talking to this guy. And he's like, I'm a documentary filmmaker. Little did I know, he's an Emmy award winning documentary filmmaker, and his last project, Dawnland with the--Upstander Project is the name of the organization. And we became really kind of fast friends, so much in common. And we just kind of started texting a little and throwing around some, could this work.I'm kinda like, there's gonna be a documentary about us? I mean, what we do is really important, but I kind of forget that we're the ones that do it sometimes. And I'm like, You're gonna follow us around and, and do this thing. And he was serious about it. And it's turned into, it's happening. It's a project. It's gonna be a movie. And the working title is We Sing Nonetheless, which is borrowed from one of our lyrics. It's from this song called Tree of Life. It's a bigger story, because we wrote it the day of the Pittsburgh shooting. But the refrain in that song is this lyric, but we sing nonetheless. Despite this pain that we've gone through with everything we've talked about with the sparrows and all this stuff, we sing nonetheless. And it's a lyric that we of course, we love, we wrote it. But when Adam came to us and said, that could be a theme. I was kind of blown away, because that's kind of one of the core messages of the band, which is that, despite history, and what history tells us and what we've learned, we are here, so we have to sing, we have to make that choice to sing. Doni Zasloff: And it's so Jewish. I mean, it's just such a Jewish like, that's what we do. So it just feels –actually he came up with the title. And I just burst out crying. I was just like, oh, yeah, that's kind of, that's just how my life has been. It's just always that, you know. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to talk about one of my favorite songs of yours, and one of the most calming: tell us about the inspiration behind Evermore (Hashkiveinu), which is another song off your album Song For the Sparrows. Doni Zasloff: Oh, yeah. I love the gosh, every song's like another one of our babies but the song that we wrote called, Hashkiveinu, the Hashkiveinu prayer that was inspired. Eric started writing that, I think because I was having a hard time sleeping. And I think you wrote that one to try to help me get through the night. Eric Lindberg: Yeah. Doni Zasloff: When I was like, I just have a hard, sometimes I just can't, not sometimes, most times. Eric Lindberg: Still some days you're just like, I didn't sleep. That's actually a great one to bring up because it's based on this ancient prayer, Hashkiveinu. It's based on this ancient idea. And then when really reading the text and we looked through a lot of different translations and it's just beautiful that we would you know, that moment at night before sleep, first of all, we all have it's universal. And the idea that these angels come and like take us to this land and like golden shores and all this kind of like cool imagery. Doni Zasloff: [singing, acapella] Shelter, oh shelter as night... Doni Zasloff and Eric Lindberg: [singing, acapella] Shelter, oh shelter as night settles in Lay us down beside tranquil shores So we can dream of the wings That'll bring us home again For now, and evеrmore Eric Lindberg: Something like that. Manya Brachear Pashman: Beautiful. Eric Lindberg: Yeah, I mean, but that's our task. You know, sometimes if we are looking at a song from a prayer, I'm glad you brought it up because, while we're not like, the word religious can mean something different to everybody, but these prayers are based in also our culture and our heritage. And it's all one if you're living a Jewish life, and I think that this is one of these beautiful, poetic, whimsical, magical prayers, that is, that is a part of our culture that we're super proud of. And we kind of wrote this folk song around it, about being able to get yourself to sleep, despite the day you've had. Manya Brachear Pashman: Beautiful. Would you mind closing us out with another song? Doni Zasloff: [guitar playing] This song's called Where Oh Where, it was intended to be a song of hope, inspired by nature. And it's a response to all of the not so great things that we're seeing around us, to try to comfort ourselves really. But it's called Where Oh Where. Doni Zasloff and Eric Lindberg: [singing, with guitar] Where oh where are the sweetest songs Of Miriam and her daughters? They were sung beside the seas and tides So still must be out on the waters Still on the waters Where oh where is the wisdom Sung by the many before us? She was there inside the tree of life So still must reside in the forest Still in the forest Yai da dai da dai dum dai dai Dum dai ya da dum dai Ya da dai da dai dum dai dai Dum dai ya da dum dai Where oh where is the innocence From our first days in Eden? They used to rest their heads on the flowerbeds So still must be there in the gardens Still in the gardens Yai da dai da dai dum dai dai Dum dai ya da dum dai Ya da dai da dai dum dai dai Dum dai ya da dum dai Where oh where's the forgiveness From the age of the flood so long ago? Under all the rain the earth remained So it's still in the fields and the meadows In the fields and the meadows Yai da dai da dai dum dai dai Dum dai ya da dum dai Ya da dai da dai dum dai dai Dum dai ya da dum dai Where oh where's our compassion Is it somewhere we can discover? It's never too far, it's right where you are It's always been in the arms of each other Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much. Eric Lindberg: Sure thing. Manya Brachear Pashman: It's been a jam-packed Jewish American Heritage Month here on People of the Pod: we kicked off with AJC CEO Ted Deutch, popped into the kitchen with Busy in Brooklyn food blogger and cookbook author Chanie Apfelbaum, and last week, we heard from from Georgia Senator Jon Ossoff. Thank you for joining us to close out the month with Nefesh Mountain. Tune in later this week for our sit-down with House Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries.
May 18, 2023
Sen. Jon Ossoff on Jewish Resilience
Senator Jon Ossoff (D-GA), the first millennial Senator and the first Jewish member of the Senate from Georgia, joins us to honor Jewish American Heritage Month. He shares his family's survival against antisemitism and his efforts to combat it today through his work on the Senate Bipartisan Task Force for Combating Antisemitism. He also discusses his connection to Israel and feeling Jewish and proud at a recent Yom HaShoah event in his home state. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jon Ossoff ____ Show Notes: Take our quiz: Jewish American Heritage Month Quiz: Test your knowledge of the rich culture and heritage of the Jewish people and their many contributions to our nation! Start now. Read: What is Jewish American Heritage Month? Jewish American Heritage Month Resources Faces of American Jewry Amazing Jewish Americans Listen: 8 of the Best Jewish Podcasts Right Now "Busy in Brooklyn" Food Blogger Chanie Apfelbaum Talks Kosher Cuisine and Jewish Heritage Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Jon Ossoff: Manya Brachear Pashman: Jon Ossoff was a documentary filmmaker and investigative journalist before he became a United States senator representing Georgia. He is the youngest member of the Senate elected since 1980. The first millennial in fact. He's also the first Jewish member of the Senate from Georgia. In fact, the first Jewish Senator from the deep south since 1878. Senator Ossoff joins us now in honor of Jewish American Heritage Month. Senator, welcome to People of the Pod. Jon Ossoff: Manya, thank you so much for the invitation. It's an honor to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So, Israel just celebrated its 75th birthday. It's a young country, but it's twice as old as you. You are 36, I believe. How do you relate to that historic milestone, as someone who's Jewish, who's a father, as a Senator who knows Israel's strategic importance to the United States? How do you relate to Israel? Jon Ossoff: Well, I think I should begin with a reflection on how my family's story has influenced me and influenced how I think about US-Israel relations. I was sworn in to the Senate, and in my jacket pocket at that moment, had the ship's manifests, documenting the arrival of my great grandparents, Annie and Israel, at Ellis Island, from Eastern Europe, in 1911 and 1913. And they left Eastern Europe in the early 20th century, as so many European Jews did, fleeing antisemitism. And while many members of my family and ancestors managed to escape, as in so many Jewish families, there were many who did not. And of those who did not, to my knowledge, all but one perished in the Holocaust. And I remember as a very young child, spending time with my uncle Nate, I called him uncle Nate. He had escaped, and hidden in the forests around the camp and the worksite, until he was liberated. And I remember as a young child sitting with him and tracing with my finger, the numbers tattooed into his arm. And I think so many American Jews have experiences like that one, having grown up among Holocaust survivors. And growing up among survivors, and being keenly aware of the genocide of Jews, the attempt with industrial-scale brutality to extinguish the Jewish people forever, has a profound impact on all Jews, all Jews in the United States, all Jews around the world. And of course, it has a profound impact on how I view the State of Israel, recognizing that the State of Israel was established 75 years ago as Jews rebuilt in the ashes of the Holocaust, and sought to establish a secure homeland for the Jewish people. I am now, as many American Jews are, deeply concerned about Israel's future, deeply concerned about the trends and dynamics and risks in the broader Middle East. And as an American policymaker, of course, particularly focused on US national security interests and other interests in the region. So I have worked for the last couple of years, to build strong working relationships, on a foundation of trust with regional leaders in Israel, in neighboring and surrounding countries, and in the Palestinian Authority, so that I can play a constructive role advancing US interests, and working to ensure that Israel can survive as a democracy and a secure homeland for the Jewish people. And also that all people in this region can one day flourish in peace and security and freedom. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you believe that your colleagues share that understanding of the importance of Israel, the importance of Israel to the Jewish people. And as a follow up to that, you know, we deal a lot with combating and fighting antisemitism. How much of today's antisemitism is kind of disguised as anti-Israel criticism, and has to do with a lack of understanding of the role of Israel? Jon Ossoff: Look, I think that these things can and sometimes do overlap. And I think we also have to be clear that in our free society, and as we as free citizens discuss the state of the world, we also have to avoid dismissing any critical views of Israeli policy as mere antisemitism, because there are many principled people who have a diversity of views about the Middle East region, who hold those views in good faith, not born of any kind of religious hatred. You know, as for my colleagues in the Senate, I do believe that there is a growing and strong awareness of the rising tide and threat of antisemitism at this moment here in the United States, and around the world. In Georgia, just recently, there have been multiple incidents of hateful antisemitic literature being littered in the yards and driveways of Jews in different communities across the state. We've seen, of course, a significant increase in hate crimes, violent threats, and acts of violence, targeting Jews. And I was speaking recently at a Yom Hashoah event at a cemetery in Atlanta. It's an annual event that I attend, the Israeli Consul General typically attends, and local Jewish community leaders. And I heard a baby crying during the ceremony. And when I made my remarks, and as a father, my wife, Alicia, and I have an 18 month old baby daughter at home. I shared with the crowd how to me and I think to all of us how profound it was to hear a baby crying at an event remembering the unfathomable loss of the Holocaust, because that baby's voice is proof that the effort to destroy the Jewish people failed, and that we survived and that we persist. But that Jewish child is also growing up at a time when antisemitism continues to grow as a threat to Jews in the United States and around the world, which requires us to be vigilant and determined, informed by our people's history. That threats to Jews have not been permanently defeated. As they have throughout history, they rise and rise again and we have to be ever vigilant. Manya Brachear Pashman: You have confronted antisemitism in the past, some very classic conspiracy theories. I'm curious how you confront that personally. And what government's role is in combating antisemitism? Jon Ossoff: There was the widely covered, widely condemned incident during my Senate campaign. When my opponent's campaign doctored an image of my face to lengthen my nose, portray me as the sort of classic caricature, antisemitic caricature. And look, of course, as a public figure, some of the hate and ill will and sometimes threats that come my way have within them or are motivated by hatred of Jews and antisemitism. You know, I think as a public figure Manya, I have had to build the armor, personally necessary to protect myself and my family, to weather threats and insults that come with public life and leadership in the public arena. But for those who have not chosen a life in the public eye, you know, the swastika spray painted on the garage door, the hateful pamphlet dropped in the driveway, the threatening anonymous voicemail. You know, it's more than just upsetting and disturbing. It represents a threat to a family's safety. It represents a threat to children, to life, to property, and it undermines and can destroy the trust that we have, that our communities are open and tolerant, and based upon love and acceptance of one another, regardless of our faith. So it's a deeply worrying and corrosive and threatening dynamic in our society right now. Manya Brachear Pashman: So, should Jewish families build a similar armor, similar to what you have developed as a public figure? Or does the government have a role in doing something to combat it? Jon Ossoff: Private citizens should not have to weather and endure and be subjected to hatred and harassment and bigotry. And there is a role for leaders in government. I work alongside my colleague, Senator Jackie Rosen of Nevada, on the bipartisan Joint Task Force on Antisemitism to develop solutions within Congress. But at this moment of increased hatred, and violence, and division along all kinds of lines in our society: religious, racial, ethnic, political, cultural, all of us, leaders and citizens, are called upon to promote and defend and strengthen the loving and trusting and tolerant bonds between neighbors and fellow citizens to make our society more resilient to the fringe, which promotes hatred, and to ensure that the United States lives up to its highest ideals as a place where, regardless of where one came from, or how one worships one can be free and safe and treated with dignity. Manya Brachear Pashman: In fact, you called for a federal task force, an inter-agency Task Force to address Antisemitism back in December. That task force has become a reality. And I'm curious if you feel like that task force should be working toward more of a civil society response or actual government agencies, policies to really curb the spread of antisemitism? Or maybe it's a combination of both. Jon Ossoff: Look, I think that there is clearly a role for leaders in government and elected officials to promote and strengthen policies and ideals that defend the public against hate crimes, against violence, against harassment. And this also has to be a broader effort shared by leaders in all fields, business leaders, faith leaders, civic leaders, community leaders, and every ordinary citizen. The reality is that despite how hateful and divided the public discourse can seem, and is, and despite the alarming and dangerous rise in antisemitism, and various forms of hatred, most people are deeply good. Most people are kind. Most people cherish the American ideals of equal justice, freedom of religion, and the basic idea that this is a place where people from all kinds of family backgrounds coexist and live together as Americans not on the basis of one religious creed or racial identity or national origin, but on the basis of commitment to our country's fundamental values. And I think we all have a role to play in defending and lifting up that vision of our society at a time when there is so much hate in the political and cultural and social discussion. Manya Brachear Pashman: You interned in high school for the late Congressman John Lewis of blessed memory, a longtime dear friend of AJC. What is the direction of the relationship between black and Jewish communities in America? Where are the points of tension, the points of promising engagement? Where do we go from here? Jon Ossoff: You know, sort of an extraordinary 24 hours in Georgia's history and US History: January 5, to January 6, of 2021. On January 5, the state of Georgia, and you know, our complex history, as both the cradle of the Civil Rights Movement and the heart of the Old Confederacy, elected to the US Senate, the 33 year old Jewish son of an immigrant, and a black pastor, who holds the same pulpit that Dr. King did at Ebenezer Baptist Church. The first black senator in Georgia's history, the first Jewish Senator in Georgia's history, the first Jew elected to the Senate from the deep south since 1878. And that is a powerful testament to what I was describing earlier that, you know, despite the level of hatred and division that we see in our public life, this country has come so far in terms of tolerance. But it wasn't 12 hours later, that the US Capitol was being ransacked by a hateful and violent mob. In some cases, sporting neo-Nazi and Confederate symbols, who tried to use violence, to prevent the peaceful transfer of power in our democracy, a core process in our constitutional system. And so while what happened on January 5 demonstrated how far we have come, what happened the next day demonstrated the reality of the very real and present threat to those values. I mentioned that I was sworn in with, in my jacket pocket, the ship's manifests documenting my great grandparents' arrivals at Ellis Island. 2 I was also sworn in on the Tanach that had belonged to Rabbi Jacob Rothschild, who had been the longtime rabbi at the temple, the Atlanta synagogue that I attended growing up, and where I was Bar Mitzvahed. And the temple in 1958 was bombed by the Klan in retaliation for Rabbi Rothschild's alliance with Dr. King and his denunciation of segregation. And I was sworn in on that Tanach because, of course of the special role that that synagogue had played in my upbringing, but also because of the values that it represented as a possession of Rabbi Rothschild's at the moment when Senator Warnock and I had been elected. And since Congressman Lewis had been a key mentor in my life, and I, so well recall that one of the first things he ever explained to me in great detail, when we sat down together, was the historic alliance between blacks and Jews in the civil rights movement, how he had marched alongside rabbis and Jews who had come to the south in the Freedom Summer to demand civil rights and voting rights. And, you know, that's a legacy of solidarity between two peoples who have had very different, but both long-term struggles against hatred, genocide. And I think it's a bond that needs to be nourished and strengthened. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you see obstacles in the way of that? Jon Ossoff: Look in Georgia, the Jewish and black communities love one another, work closely together. And there is always room for growth. And so Manya in closing, I have to run in vote on the floor of the Senate in just a moment. I just want to, if I might, take this opportunity to reiterate what I said earlier, but at a moment like this, when there is hatred and violence, threatening and in the air, and on the ground, in reality. And when Jewish families and many American families of various minority backgrounds feel threatened by the rise in hate crimes, and religious, racial, ethnic, and cultural hatred, it's our shared obligation to make real a country that lives up to America's highest ideals. And I believe that we can, and we will, by pulling together and believing in that and working together to defend what's best about the United States. I really appreciate the opportunity to spend some time with you. And thank you for the work you do, getting information out there and connecting Jews across the country through this podcast. Manya Brachear Pashman: Wonderful. Thank you so much, Senator. Thank you so much for joining us. Jon Ossoff: Thank you, take care.
May 15, 2023
"Busy in Brooklyn" Food Blogger Chanie Apfelbaum Talks Kosher Cuisine and Jewish Heritage
To continue our Jewish American Heritage Month celebrations, guest host Laura Shaw Frank, AJC's director of William Petschek Contemporary Jewish Life, speaks with Chanie Apfelbaum, author of the popular food blog Busy in Brooklyn. Chanie joins us to discuss her new cookbook, "Totally Kosher," the intersection of Jewish culture and food, and the future of kosher cuisine. She also shares how the murder of her brother, Ari Halberstam, who was killed in a 1994 terrorist attack on the Brooklyn Bridge, has inspired her career. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Chanie Apfelbaum ____ Show Notes: Take our quiz: Jewish American Heritage Month Quiz : Test your knowledge of the rich culture and heritage of the Jewish people and their many contributions to our nation! Start now. Read: What is Jewish American Heritage Month? Jewish American Heritage Month Resources Faces of American Jewry Amazing Jewish Americans Listen: 8 of the Best Jewish Podcasts Right Now AJC CEO Ted Deutch on the Importance of Jewish American Heritage Month From Israel: AJC's Avital Leibovich Breaks Down Latest Gaza Escalation Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Chanie Apfelbaum Manya Brachear Pashman: People of the Pod is celebrating Jewish American Heritage Month by devoting all our May episodes to what makes us Jewish and proud -- food, music, and our mission to repair the world. Last week you heard from AJC CEO Ted Deutch about why we should set aside a month to celebrate. This week nods to our obsession with food. And for that, I'll turn it over to my guest co-host, Laura Shaw Frank, AJC's Director of Contemporary Jewish Life. Laura, the mic is yours. Laura Shaw Frank: Thanks, Manya. Happy Jewish American Heritage Month! As we celebrate Jewish American culture and history this month, it feels like we would be quite remiss if we didn't spend some time talking about Jewish food. Food plays an enormous role in Jewish tradition and culture. Jews have foods linked to particular Jewish holidays and of course Shabbat, ethnic foods linked to particular places where Jews lived, and of course, lots of Jews, myself included, keep kosher, follow the laws of Kashrut, which deeply influences the way we cook and eat. I think I'd be pretty safe in saying that Jewish food is really important in Jewish life. Not surprisingly, statistics bear this out. In the Pew Survey of Jewish Americans in 2020 over 70% of American Jews, young and old alike, reported cooking or eating traditional Jewish foods. Which is why I'm so excited to be joined by today's guest, Chanie Apfelbaum. Chanie is a food writer and photographer whose blog "Busy in Brooklyn" is chock full of delectable recipes and beautiful pictures of amazing Jewish foods. Her newest cookbook, Totally Kosher, hit bookstores in March 2023. Chanie, welcome to People of the Pod. Chanie Apfelbaum: Thanks so much for having me. Laura Shaw Frank: I'm thrilled to have you and really thrilled to talk to you about your new cookbook. So before we get into that, though, let's take a step backward. How did you get into kosher cooking? Chanie Apfelbaum: Well, I was born Jewish. That's the first step, always. I always say– learning your way around the kitchen is just a rite of passage when you get married. And being a Jewish housewife, obviously, we have, you know, Shabbat dinner every week, and so many holidays, and Jews are always just celebrating around food. I actually never stepped foot in the kitchen before I got married, never really helped my mom, my older sister used to help with cooking. It just looked like a chore to me. I am a very creative soul, very artistic. And it just seemed like a whole lot of rules. And I just wasn't interested. And then I got married. And I would call my mother every Friday and like, how do I make gefilte fish and potato kugel, and chicken soup. And I started hosting a lot. And people started asking me for my recipes. And I realized that I kind of had a knack for presentation. Because I've always been artistic. And you know, like composition and things like that. And my food always was presented nicely and looked beautiful. So it kind of got me you know, a little bit interested, piqued my interest. And I realized that it could be a way for me to explore my creative side. So I I started watching The Food Network a lot. And I subscribed to Bon Appetit Magazine, and started looking at cookbooks. And then when I had my third child, I didn't want to really work outside the house anymore. So I was like, What should I do with myself, I'm not the type of person that could just be a stay at home mom, I would lose my mind. So I was like, Okay, I'm gonna start a blog. And there really weren't any food blogs and no kosher food blogs. This is back in 2011. There was Smitten Kitchen, there was Pioneer Woman, those are both pioneers in the blogging world, in general. And there definitely weren't any kosher blogs. And I just, you know, I started my blog. And like I said, I wasn't cooking, you know, the traditional Jewish, heimish Ashkenazi food that I grew up with. Talking a little about being a mom. I had my crochet projects on there. And it was just like my place to get creative and have an outlet. And then feedback really started pouring in, everything I was posting, people were so interested. It didn't exist in the kosher world. And despite not being a big foodie, I just continued to just do my thing and taking terrible pictures in the yellow light of my kitchen island, on automatic, with my terrible camera. And over time, just my food started to evolve, my photography started to evolve. And fast-forward a couple of years, I went to a kosher culinary school, which really helped me kind of opened my mind to new flavors, which I was I think stuck a little bit in the Ashkenazi palate of paprika and garlic powder, as I like to say, and just tried all these Indian food and Thai food and all these flavors that I literally never ever experienced. And it just blew my mind open in so many ways. Being creative, a few of my friends kind of started blogs around the same time. And every time a holiday would come around, it was like who's going to come up with the coolest latke or the coolest humentasch, or the most creative donut. So it really pushed my competitive side and also my creative side. And I just started really thinking outside the box and doing a lot of these cool twists on tradition and fusion recipes and caught a lot of attention in mainstream media and everything went from there, I guess. Laura Shaw Frank: That's amazing. I want to pick up on one thing that you said. You said when you started blogging that so many people got in touch with you. And you were obviously bringing them content that they hadn't seen before. What do you think was missing from the conversations around kosher food before you entered the space? I mean, I'll just you know, tell you when I got married, everyone got the Spice and Spirit cookbook from Lubavitch. I still use it, by the way. It's a fantastic cookbook. It's a more traditional cookbook. And so tell us a little bit about what did you bring that was different to kosher cooking? Chanie Apfelbaum: You know what, there's one story that sticks out in my mind that really, because I've always been this person that picks up hobbies along the way, like every creative thing. I'm knitting, I'm crocheting. I'm scrapbooking, kind of all these type of things. I pick up a hobby, I do it for a couple of months and then I kind of let it go. So I always asked myself, like, what was it about food blogging that really stuck for me, and I think that I realized the power of it. One year, I made this recipe for the nine days when we don't eat meat, you know, between before Tisha B'Av, some people have accustomed not to eat any meat recipes, because it's a time of mourning, it's a serious time before the anniversary of the destruction of the Holy Temple. So wine and meat are more celebratory things that we eat. So those are restricted for nine days before Tisha B'av. So I made this recipe for Chili Pie in Jars. And it was a vegetarian chili, a layer of cheddar cheese, and cornbread, and you bake it in a mason jar in the oven. So each person has basically their own pie. So I made this recipe and I put it in on my blog, and this is before Instagram, can't DM somebody a picture, it's before smartphones, you can't just take a picture on your smartphone. So somebody took out their digital camera, took a picture of their families sitting around the table, everyone's holding their own mason jar, and like, took the SD card out, put it in their laptop and sent me an email. This is early days of my blog. I get this picture. I see a whole family sitting around the table eating my recipe and I'm like, oh my god, how powerful is this, that I have the opportunity to bring families around the table, it is so special. And I think that that's something that really stuck with me through all my years of blogging and really at the core, for me, what keeps me going because I realize the power of food. Especially, as a proud Jew, to celebrate our traditions through food, because, thank God through my platform, I get messages from people–someone sent me a message from literally Zimbabwe making Challah for the first time. It's just so special to me. So, obviously, as a mom of five, I'm always cooking dinner, and it can feel like a chore. I get cooking fatigue like everybody else. And cooking Shabbat dinner every week. I always say in the main world, they make this big deal about Thanksgiving, you know, you have to plan your menu from Sunday, and then your shopping list from Tuesday and all that but like we literally have Thanksgiving every Friday night. It's a three course or four course meal sometimes. So yeah, I get the cooking fatigue. And for me, I want to show people how to bring the love back in the kitchen. You know, how food can be more than just a way of sustaining ourselves, it could be a way of celebrating our Jewishness, it could be a way of bringing our family around the table, it could be a way of getting pleasure out of life. Food can be so delicious, and it can open your eyes and experience global cuisine. That's so cool and amazing. So I had that aha moment for myself, and I want other people to have it too. Laura Shaw Frank: That's amazing. I love that. So what you're really saying is that food and culture are really intertwined with one another. And you gave this example of the nine days before the Jewish fast day of Tisha B'Av, which takes place in the summertime, when it's traditional among religious Jews to not eat meat and wine and talking about sort of adjusting recipes. Could you give us a couple of other examples of ways that you see sort of Jewish history, Jewish culture, Jewish tradition embedded in food? Chanie Apfelbaum: Look at the holidays, right, Rosh Hashanah, we have a lot of symbolic foods. Most people know of apple and honey, but there are actually a whole range of symbolic foods that we eat. The actual names and Hebrew of those foods, point to different things that we want for our year,like we eat a fish head because we want to be like a head and not a tail. For me that really helped me kind of zone in on what is my niche here, right? I am a kosher food blogger, but how do I define my skill or who I am because every blogger kind of has their thing. And for me a lot of it is centered around the holidays because first of all for me like I have so many beautiful memories growing up. My mother is very much a traditional Ashkenazi cook, making kugel and gefilte fish and cholent and matza ball soup. She doesn't veer away from that. Those are the dishes that I grew up on and they're so nostalgic for me and there's a place for that. Our home was always open, we had so many guests. I actually grew up in Crown Heights. So I really zone in a lot on holiday foods, but putting my own spin on it, because I feel like people want something fresh and new and exciting. And I definitely think there's a place for the traditional foods. You want to mix it up and have a little bit something fresh and new and something old, that's great. We're lucky that we have that core of our heritage and our traditions throughout the year with so many Jewish holidays that allow us to get together, with family, with friends, and celebrate our Jewishness. Laura Shaw Frank: So, my husband and my three sons are all vegan. Chanie Apfelbaum: Oh, wow. Laura Shaw Frank: My daughter and I are not – but my husband and my three sons are vegan. As I was thinking about interviewing you, I was thinking about how kosher cooking is always intertwined with the places that it's located in and the time in which it's occurring. Do you feel like your cooking has been influenced by the recent trends toward vegetarian and vegan and more plant based eating? Chanie Apfelbaum: I definitely, just as someone who grew up eating a lot of heavy Ashkenazi food. Being in the food world, seeing what's out there. Besides for the fact that it's trendy. I feel like after Shabbat, I want to break from meat and animal protein. I mean, we're eating fish, we're usually having three courses. We're having fish, we're having chicken soup or having some kind of meat or chicken. Sunday we're usually having leftovers because there's just so much food from Shabbat. So come Monday we do in my house–in my first cookbook, Millennial Kosher, which came out in 2018. I had a Meatless Meals chapter. And that was really new for any kosher cookbook. You don't find it, you find definitely very heavy meat chapters. But it was important to me because I instituted that in my house many years ago. And I have it in this book as well. And I got so much amazing feedback because there's a lot of people out there who don't eat meat. There's a lot of vegetarians. There's a lot of vegans. And they were so happy that I was bringing that to the kosher world, and of course wanted to bring it again. And also my kids love it. Like come Monday they know it's Meatless Monday in my house. God forbid I didn't have time to think of something and I bring chicken they're like, What, what's going on here? Ma, it's Meatless Monday. It's like a rule. So I include this in the book where I talk about the way I structure my week because it really helped me kind of take the guesswork out of what am I making for dinner. I have a loose framework, while still allowing me the possibility to be creative because I love you know, playing Chopped with my kids, with whatever's in my fridge or my pantry. I want the possibility to be creative but I still need a little bit of framework. So Sunday's we'll have leftovers if there's no leftovers, we'll do a barbecue or sometimes a restaurant if we're out for the day. But Monday's Meatless, Tuesdays is beef. Wednesdays is chicken, Thursdays is dairy. Shabbos is Friday night, it's always a little bit different. And then, Saturday night is eggs. And it gives me the base protein, I know what I'm working off of and then from that I can kind of play around. And I think that really helps people that are like so overwhelmed with the idea of what am I making for dinner? You wake up on a Tuesday morning, you know, it's meat day, okay, I got to take out some kind of meat from the freezer. I'll figure out what I'm doing for later. Maybe I'll make tacos. Maybe I'll make spaghetti Bolognese maybe, you know, maybe I'll make burgers, but you took the meat out, you know. But going back to your question. So you know, Mondays is meatless in my house and we're a big bean family. My kids love beans. One of their favorite dinners are my refried bean tacos that are my first book. I have these amazing smashed falafel burgers in this book. Like I said, we love beans, I do curries I do, Falafel I do. Once in a while I'll try and play around with tofu. My kids don't love it too much. Tempe is something - I have tempe shawarma in the book which is really amazing. Let's not forget to mention plant based beef which I think totally revolutionized the kosher experience because when can we ever make you know, meat and dairy together because that's one of the basic rules within the kosher kitchen. You can't mix meat and dairy together in the same dish. My kids love when I make smash burgers for dinner. And I always said like, I don't love vegan dairy products if you just don't get that cheese pull, but like with the vegan meat products, with the new plant based impossible beef, it's really close to the real thing. It really is. Laura Shaw Frank: We love impossible burgers in our house and I want to try that tempe shawarma. Chanie Apfelbaum: Oh, it's really good. Laura Shaw Frank: What recipe would you say was kind of the biggest surprise for you? I mean, it seems to me like you often work from traditional Jewish recipes, but seems like you also are constantly innovating and making up your own recipes. So is there a recipe that just kind of surprised yourself and couldn't believe how it turned out? Chanie Apfelbaum: My favorite recipe in the book is my Pad Chai. And it's kind of a Middle Eastern spin on Pad Thai, where I use harissa and silan and lime and tamarind in the sauce. It almost feels like pad thai with just that little hint of Middle Eastern flavor. Pad thai is always finished with crushed peanuts, and I put crushed bamba over the top. And it's just so fun and playful. And I also love fun names. So I love just the name of it, but it's really a reflection of, first of all my favorite flavors, like I love middle eastern food, I love Thai food, marrying them together. And it's colorful and beautiful and so flavorful. Everything I love about food, and was really inspired by the pad thai made in culinary school. And it was one of the dishes that really, really transformed my palate completely. So it's kind of an ode to that. Laura Shaw Frank: You're getting me very excited to go home and make dinner for the next few nights. Chanie Apfelbaum: You see right there. Laura Shaw Frank: So your latest cookbook, Totally Kosher, is being published by Random House. And that's a really interesting thing for a kosher kind of a niche cookbook to be published by a very mainstream publisher. So I was wondering if you could tell us a little bit about how it came about that you got, first of all, that you got Random House to publish your cookbook, which is amazing. Second of all, why you left the more Jewish the more orthodox publishing world. Chanie Apfelbaum: I'm with Clarkson Potter, one of the imprints of Penguin Random House, that's an imprint. They haven't written a kosher book in many, many, many years. Thank God, I've been in this industry for 12 years. And I already wrote a very successful book. So my name is really out there. People know me as being the kosher cook. So they did approach me to write the book, which was really an honor. I had a very good experience the first time around working with Artscroll. Artscroll is like the main Jewish distributor of and publisher of Jewish books. My book was beautiful, and their distribution is really unmatched, but it's really only in the Jewish world. they'll get your book and every Judaica shop in the world, but not in Barnes and Nobles, and not in you know, in mainstream, indie booksellers. I really wanted to reach a larger demographic of Jews. As a blogger, people have come to know me and my family. I wanted to put more lifestyle photos in and most Jewish publishers don't actually publish photos of women in their books, which is something that I definitely want to see change. And I put beautiful pictures of my family, me and my daughters lighting Shabbos candles which is something that like, the moment of my week that I look forward to and a special time for me that I really feel like I connect with my Jewishness. And you know, my book is dedicated and memory of my Bubbie and to my mother and to my daughters and for me, it's really about the Jewish family and Jewish pride–not just about food, but really about family and I wanted to be able to portray that through the photos in the book. So that was another of my reasons for moving mainstream. Laura Shaw Frank: I think it's just amazing. And I just think it's so wonderful that you are illustrating your cookbook, with pictures that are not just about Jewish pride, but also about the special pride of Jewish women and the special…you know, of course, not only women cook, you know, men cook too, I have to say, my husband cooks dinner a lot more than than I do. And kids cook and lots of different people find a lot of wonderful fulfillment in the kitchen. But, of course, we do have this very long tradition of women cooking for their families, even as we change it up today. And I just think it's beautiful that you actually intentionally use pictures of women, of your family, in your cookbook. Chanie Apfelbaum: And my sons are there too. Laura Shaw Frank: Excellent. Let's make it a family experience. Chanie Apfelbaum: Exactly, exactly. Laura Shaw Frank: Speaking about family experience, you've written about why it's so important to you to encourage family meals with everyone sitting around the table together, whether it's on Shabbat or holidays or even just a weekday dinner. Could you share with us why that's so important to you? Chanie Apfelbaum: Well, I grew up in a very open home. My mom always had guests for shabbat or holidays. I grew up on the block of 770 Eastern Parkway, Chabad Lubavitch headquarters, and our house was just always open to guests. It's something of value that was instilled in me from early on. And I don't know if you know this, but my brother Ari Halbersham was actually killed in a terrorist attack on the Brooklyn Bridge in 1994. That's something that I feel like, I don't think people realize, when you lose a family member in that way, it's not like, OK, you just lost your brother. But it affects the whole family, really for generations. And I think that one of the things that I lost was having those experiences around the table. And especially so many memories with my brother at the table as well. So for me, I find so much healing–first of all healing, but also just, I see the greatness and the power to bring families around the table. To create family memories. So many that I draw great comfort from, I want other people to be able to experience that. It's important for me to do that, also as a way to remember him and celebrate what he lived for and what he died for. Laura Shaw Frank: Ok, that's incredible. And it's an incredible message to all of us to be in the moment and treasure those moments around the table. So the last thing I want to ask you is, so you have this cookbook that's being published by a mainstream publisher. And we know that not a lot of Jews keep kosher. The percentages are not that high. Do you think your cookbook appeals beyond just a kosher audience? Chanie Apfelbaum: Well, I'll tell you that I have a lot of–forget about non- kosher keeping. I have a lot of non-Jewish followers on Instagram that buy my book, because they just like my style of cooking. I know it's called Totally Kosher. And obviously, it's a celebration of kosher and celebration of our Jewish heritage, and our customs and traditions, but at the same time, it's just good food, it's just good food, despite it being kosher, and really, I really want to break that stigma that there is about kosher food - that kosher food is brown, and it is brown. You know, like I can't take it away. Matzah ball soup is beige, and gefilte fish is beige, and potato kugel's beige, and brisket's brown. And you know, there's a reason for the stereotype. Laura Shaw Frank: Cholent's brown too. Chanie Apfelbaum: It is. And if you look through my book, one thing that will pop out at you is how colorful the food is, and how beautiful the food is. And like I said earlier, I came to food by means of artistry. They say people eat with their eyes first. And it has changed and I think in the mainstream world, they haven't quite realized how kosher has evolved. I mean, there's so many different restaurants, kosher restaurants now, that celebrate different global cuisines. There's a Peruvian Japanese restaurant in the city, there's a Georgian restaurant in Queens. It's not just your Bubbie's stuffed cabbage anymore. And I want, like I said, the stigma to change and make waves in the mainstream world to see kosher a little bit differently. Laura Shaw Frank: Well, I'm for one very excited to start making some recipes from Totally Kosher. And I just want to thank you, Chanie, so much for coming to join us on People of the Pod. I think that you are bringing such a fresh take. And such a warmth, such a deep sense of Jewish culture and peoplehood, and family, and love to your work. And it's really more than just about kosher cooking. It's really about something much bigger. And I just want to thank you for that. So thanks so much for joining us today and I know we're gonna have a lot of listeners going to buy your cookbook. Chanie Apfelbaum: Thank you for having me.
May 11, 2023
From Israel: AJC's Avital Leibovich Breaks Down Latest Gaza Escalation
In a special breaking news edition, Lt. Col. (res.) Avital Leibovich, director of AJC Jerusalem, joins us to break down Israel's Operation Shield and Arrow and the threat posed by the Iranian-backed terror group Palestinian Islamic Jihad, which has fired over 500 rockets towards Israel since Tuesday. Leibovich also provides an update on how Israelis are coping with the latest escalation and efforts being made towards a ceasefire. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Avital Leibovich ___ Show Notes: Take action: Urge Congress to Stand with Israel Against Terrorism Read: What to Know About the Gaza Strip, Terrorist Rocket Attacks, and More 5 Things You Need to Know About Israel's Iron Dome Defense System and Those Who Voted Against It Listen: Israel at 75: 7 Things You Should Know About Israel : Listen to these seven episodes of AJC's People of the Pod featuring leading Israeli and American scholars, experts, and influencers that will help you learn more about the complexities, triumphs, and challenges facing Israel today. AJC CEO Ted Deutch on the Importance of Jewish American Heritage Month: This May, AJC is proud to celebrate Jewish American Heritage Month and the countless contributions that Jewish Americans have made as patriotic citizens, creative artists, brilliant scientists, and star athletes. To kick things off, we're joined by AJC CEO Ted Deutch to hear his reflections on his first several months at AJC, what he's looking forward to at AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv, and how he's marking Jewish American Heritage Month. Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Avital Leibovich Manya Brachear Pashman: Welcome to a special breaking news edition of People of the Pod to bring our listeners up to date on what's going on in Israel. Joining me is Lieutenant Colonel Avital Leibovich, Director of AJC Jerusalem. Avital, welcome, and I hope you are safe. But how are you doing? Tell me. Avital Leibovich: Thank you. It's an opportunity for me to be here with you today and to share from the ground our experiences here in Israel. This is already the third day of the operation. There's tension in the air, but I think that our resilience as Israelis is quite strong. And I'm sure we will overcome this situation as we have in the past. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what is going on there–who is firing the rockets that are now falling on Israel? Avital Leibovich: So the operation is directed towards the Islamic Jihad in Gaza. Islamic Jihad in Gaza is the smaller of two terror groups in Gaza. It's backed and funded and directed by Iran. And its charter is pretty clear, I would say. Basically, the organization believes that Israel has no right to exist. And in order to make sure that we will not exist, Iran is funding its military capabilities. They have managed to build an arsenal of rockets, of mortars, of drones. They have managed to train soldiers, militants in order to conduct anti-Israeli operations. And Israel decided to initiate an operation, following two events. The first event was a week ago, where over 100 rockets were fired by this organization, the Islamic Jihad, within 24 hours, towards Israel. And the second event actually took place on Pesach, on Passover, in which 34 rockets were fired from Lebanon within 10 minutes by factions of the Palestinian Islamic Jihad in Lebanon. So this was an opportunity to make sure that Israel is preventing further escalation and basically defending its people. Manya Brachear Pashman: So where's Hamas in all of this? Avital Leibovich: So Hamas has in the past, decided to actually sit quietly and not intervene. And this is common. We've seen this in the operation last year, we've seen this in the operation two years ago. And you may want to ask what the reason for Hamas sitting back and the reason is that Hamas has a lot to lose. Currently, Israel declared that it's only looking to target Islamic Jihad targets, namely not Hamas targets. And Hamas understands that if it will join the celebration of Islamic Jihad, then the price Hamas will pay will be very, very high, for one. There are 18,000 Palestinian workers entering Israel from Gaza on a daily basis. These kinds of workers bringing salaries back home, actually move some sort of an economic cycle inside the Gaza Strip, and the shopping power is stronger and stronger by these workers. If Hamas will join the operation, then obviously, Israel will close the border and will not allow these workers to enter. And additionally, I'll remind our listeners that Hamas is still renovating Gaza from previous operations. So it would be quite serious from their perspective, to stop the renovation and then create further damage. Because as you know, Hamas and Islamic Jihads' arsenal of weapons are very much inside densely populated areas. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what are we seeing in terms of – is the Iron Dome doing its job of protecting Israelis? Avital Leibovich: So I would say thank God for the Iron Dome, I would say thank God for the very strong and strategic partnership Israel has with the US, which is very highly valued here. The Iron Dome is basically saving their lives with a whopping success rate of 90%, the Israeli people know that there's something in the sky that will be able to protect them. There are thousands of people that have spent the last three days in shelters, their spirit is quite broken. Because sitting in a shelter, whether you're a four year old child or a 30 year old mum, and hearing constantly sounds of explosions and jets flying in the air, this is not a normal kind of atmosphere. Manya Brachear Pashman: By the time this airs, perhaps a ceasefire will be reached, wouldn't that be a blessing? Are you optimistic that that will happen? Avital Leibovich: You know, living in the Middle East, you have to be optimistic in routine times, in emergency times. Talks of a ceasefire began yesterday. But we have to keep in mind that there is a lot of fake news, a lot of false publications. And I don't see an end to the current situation, the next couple of hours, maybe in another 24 to 48 hours. And I'm just getting a report that there was a direct hit of a building in Rehovot, which is a city maybe half an hour from here, half an hour from Tel Aviv. So we're not there quite yet. I do want to mention, in this context, Egypt's role. Media has put a focus on Saudi Arabia's role in the region. But we must not forget that Egypt is a strong partner. And this is the partner who actually mediates between Israel and the different terror groups in Gaza. They have an important role. Israel respects this role. And we should not forget this very, very significant actor in our region. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well Avital, thank you for that addendum and thank you for joining us. I really hope that you're able to stay safe and that we are talking about a ceasefire very soon. Avital Leibovich: Thank you for the opportunity.
May 4, 2023
AJC CEO Ted Deutch on the Importance of Jewish American Heritage Month
This May, AJC is proud to celebrate Jewish American Heritage Month and the countless contributions that Jewish Americans have made as patriotic citizens, creative artists, brilliant scientists, and star athletes. To kick things off, we're joined by AJC CEO Ted Deutch to hear his reflections on his first several months at AJC, what he's looking forward to at AJC Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv, and how he's marking Jewish American Heritage Month. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Ted Deutch ___ Show Notes: Learn more at: AJC.org/JewishAmericanHeritageMonth Join us in Tel Aviv at AJC Global Forum 2023: AJC.org/GlobalForum Sign up for AJC CEO Ted Deutch's Video Newsletter : Receive "Ten from Ted," the biweekly video newsletter from AJC CEO Ted Deutch where he'll share ten major highlights in the work he and American Jewish Committee (AJC) are doing to make this world safer for the Jewish people and Israel. Take our quiz: Jewish American Heritage Month Quiz : Test your knowledge of the rich culture and heritage of the Jewish people and their many contributions to our nation! Start now. Listen: Israel at 75: 7 Things You Should Know About Israel : Listen to these seven episodes of AJC's People of the Pod featuring leading Israeli and American scholars, experts, and influencers that will help you learn more about the complexities, triumphs, and challenges facing Israel today. How Playing Baseball With Team Israel Transformed Ryan Lavarnway's Life : In celebration of Israel's 75th birthday, guest host Dov Wilker, AJC's Atlanta director, sits down with retired Major League Baseball catcher Ryan Lavarnway, who played for Team Israel in the World Baseball Classic and the Olympics. Lavarnway reflected on the Jewish pride he felt representing Israel on the international stage, how he has dealt with the antisemitism in his career, and the importance of building connections between the Jewish state and the Diaspora. Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Ted Deutch: Manya Brachear Pashman: This May, AJC is proud to celebrate Jewish American Heritage Month and the countless contributions that Jewish Americans have made as patriotic citizens, creative artists, brilliant scientists, lightning fast athletes, one of whom we heard from last week. Returning to the studio to help us kick off the celebration is AJC's CEO, Ted Deutch. Ted, welcome back to People of the Pod. Ted Deutch: It's great to be back. Thanks, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I want to start with a progress report. You have been CEO now for I'm going to count on my fingers here October, November, December -seven months, now? Ted Deutch: Now, you've got to get onto your second hand. Manya Brachear Pashman: Which means this time last year, you were still a congressman. So what's remarkably different about your life now, your mission and your day to day approach to that mission? Ted Deutch: Well, the day to day work is very different. And I'd start with the most obvious: I came from a place that was, by definition, political, everything about it was driven by politics. I worked really hard to focus on the issues that mattered to me and my community. But there were always political considerations. Now, as the CEO of American Jewish Committee, I have the incredible honor of spending everyday working with a supremely talented team here at AJC, remarkable volunteers and lay leaders with one mission, and that's to think about how we can do more to enhance the well being of the Jewish people and Israel and advance democratic values. And every issue I work on, I'm passionate about, and it matters to me, it matters to my core. It affects who I am, and my family and my community. And that's a big difference. And it's just a big privilege to be able to spend my days this way now. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what have some of the milestones been so far? Ted Deutch: AJC as the global advocacy organization for the Jewish people has been doing incredible work in the United States and all around the world for more than a century. But to bring those two things together, as we did in our advocacy, with the Biden administration, to urge them to create a national action plan to combat antisemitism, seeing them move forward, and announce that plan and then bringing to the White House special envoys to combat antisemitism from around the world that we had helped create. And as we worked in other countries, as they prepared their own action plans to confront anti semitism and foster Jewish life, this was an opportunity to bring their experiences together so that they could share their insight into what's worked and what hasn't in their own countries. So that our own administration can come up with something meaningful as we seek to strike back against antisemitism. That is something that I'm really proud of. And being able to travel around the country and around the world as I have to meet with Jewish communities, in all parts of America and all corners of the world and to be reminded of just how much we have in common. It sounds obvious and probably silly to say, but when you're when you're speaking with university students in Paris and you realize that the things that they're focused on, the challenges they face and antisemitism and anti-Israel sentiment that they deal with is not unlike what our campus leaders in America are dealing with and, and knowing that we can bring them together as we will at our Global Forum. Or spending time with communities from across Latin America. And when we all got together in Mexico City, to talk about the ways to ensure a strong future for the Jewish community. And meeting LFT students, our high school program, Leaders for Tomorrow, the high school students that we're helping to train to be the leaders of the next generation, and be inspired by by what they've already taken from this program, whether it's in Atlanta in Chicago, or any of the other places that I've had the opportunity to travel. There's a lot that we've done, there's a lot that I'm really excited about. And as you point out, just barely been seven months. Manya Brachear Pashman: Shortly after you began, there was kind of a torrent of antisemitic incidents, rhetoric that was on social media, in the celebrity world. And I'm curious if that kind of took you aback because it happened right after you started your position. And do you feel like you've made some progress in that sphere, as well, in terms of educating celebrities, creative artists, and the like? Ted Deutch: It happened immediately after almost as if it were planned to happen right when I started. But, I've been clear about this, as horrific as that was- there was a national conversation that started that I don't remember seeing before and to have the chance to talk about the Jewish community and antisemitism and the issues that AJC works on, on national television on a regular basis, and help elevate the importance of these issues for the broader community was an important moment for me and for AJC, and for the Jewish community to really focus on what we do, and the fact that our call to action against antisemitism is a document that the rest of the country can look to Jews and non-Jews alike for ways that they can be involved to combat antisemitism. And since all of this happened, and since we've found ourselves in the middle of this conversation, there has been a real interest in looking at all the ways that government and education and law enforcement and corporate America and social media can all play their part. And yes, there's a special opportunity for the creative community. I was in Los Angeles recently with Doug Emhoff, with the second gentleman, and we did a program for executives and agents and music and studio executives, to talk about antisemitism, the things that that they can do, all with the understanding that content really drives so much of what we think about in our country, and we want people to be aware of this rising antisemitism and make sure that there's an understanding as well of what the Jewish community is and what the Jewish community isn't, and to be careful not to advance antisemitic tropes and to reflect the diversity of the Jewish community and to acknowledge the great diversity within Israel. These are, these are conversations that are taking place there, they're taking place with media, I've met with a number of media outlets, again, just to make sure that some of these issues that we know are so challenging and sometimes complicated, deserve a full airing, and we need to start with what is true about our community and about the things we care about. We've worked hard to accomplish that. Manya Brachear Pashman: And I just just want to remind listeners that it's Kanye West. It was the comments from Kanye West that just kept coming. And yeah, you're right. It was days after you started your job that we were addressing that. It was Congress that named the month of May Jewish American Heritage Month or JAHM, as we affectionately call it around here. How did you celebrate it on Capitol Hill? Ted Deutch: Well, there were receptions and we usually made a statement in Congress. We looked for opportunities to help elevate the issue. This is an important opportunity for the community. It happens every May. Most people I'm not embarrassed to say–although I will be next year if this is still the case. But I'm not embarrassed to say that most people didn't know that May was Jewish American Heritage Month. They're obviously familiar with the steps Congress took to create Black History Month and Women's History Month and so many others. But here we are at this moment. And Congress, when I was a member of Congress, we tried to, to remind people what was happening. But there's so much more and this year, in particular, in light of what the community has been facing, the timing of Jewish American Heritage Month is really important. And it's something that we're really trying to take advantage of, frankly. Manya Brachear Pashman: So now how do you celebrate it as you lead a non Jewish nonprofit? Is that very different, what you're experiencing this year? Ted Deutch: Well, it is. And again, it means I get to spend a lot of my time thinking about all of the ways that we can draw people's attention to this month. It gives me a chance to think about the prominent Jewish Americans who contribute to our country and in so many ways, that helps strengthen it. And for us here at AJC, we've worked really hard, focusing specifically at the outset of this month, on elected officials, state, local, and federal, and business leaders just to come in and acknowledge Jewish American Heritage Month and look for their own ways to recognize the contributions that Jewish Americans have made to our country. And we have a resource to do that. It's AJC.org/JewishAmericanHeritageMonth, of all things, which helps elected officials know what this is and how they can be involved and tells business leaders how they can acknowledge this month and it's so important this year, especially when so much of the conversation has been about antisemitism, and about hatred. And about that really a debate that's being, a conversation is being driven by those who want to divide the country and to spread false stereotypes of conspiracy theories about Jews and the Jewish community. Here is the perfect opportunity for us to set the record straight. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you raise an important point that the people who should be driving the conversation about Jewish American Heritage, or driving the conversation in our community should not be the antisemites, it should be the Jewish community itself. So is this month a rare opportunity, or a platform to move the needle when it comes to awareness of antisemitism? Or is that not what this month is necessarily about? I mean, why is it on the calendar? Ted Deutch: It is not a month about antisemitism any more than Black History Month is a month about racism. These are important milestones for our two communities to celebrate the contributions of our communities to the American story, that's what Jewish American Heritage Month is. The best way to push back against the antisemites is to marginalize them, and to give more people the opportunity to actually get to know the Jewish community–who we are, the diversity within the Jewish community. The fact that the Jewish community is not just a religion, but a people, and a culture and, and a group that has contributed so much throughout our nation's history. That's what this is really about. And by the way, it's going to have the added benefit of reducing antisemitism, because antisemitism preys on false narrative conspiracy theories, and providing facts and helping to educate people about who we really are, is the great opportunity that we have in front of us. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I'm curious, you talked about traveling the world and spending time with Jewish communities around the globe, celebrating many Shabbats abroad. Have you encountered comparable commemorations, and time set aside for Jewish heritage in those countries? Or any heritage for that matter? I mean, Arab Americans in France or Asian Pacific Islanders in Germany. Ted Deutch: First, I would note that May is also AAPI Heritage Month here in the United States. And AJC is working with partners in the API community, in a number of our regions to do joint programming, because again, important contributions to American history from both of our communities. Around the world, I don't know of anything, specifically comparable. I know, in Europe, there's a Europe-wide day to acknowledge the contribution of the Jewish community. There's a Jewish culture festival in Krakow that has become fairly popular. I was in Mexico City, just recently, and I know that in Mexico and in Argentina, there are opportunities to celebrate the Jewish community. But I don't know anything quite like this. But I know that in Europe, a lot of the plans that were created to combat antisemitism also includes specific ways to foster Jewish life. And one of the ways to do that is to highlight the history of the Jewish community in each of those countries. Manya Brachear Pashman: So why does America devote an entire month to all the many diverse heritages, ethnicities, that make up our country? Why is this an American concept? Ted Deutch: Well Manya, I don't know what the thinking was in moving forward with these designations. But it is, in many ways, the most American idea. This is what America is, it's who we are. It's this great collection of all different groups and faiths and nationalities, all contributing to create this remarkable country that we're so privileged to live in, a country with challenges that we can only overcome by working together. Antisemitism, by the way, one of those challenges, that it doesn't just affect the Jewish community, it affects everyone. But having specific times to pause to think about the contributions from each of those communities. When you add them all up, suddenly, you've got a year's worth of contributions from the great diversity within our country to celebrate. And I think that's the way we need to think about it. This isn't about May. This is, as you point out, about this collection of months throughout the year where we can celebrate the contributions from individual groups, which overall, reflect and contribute to the great diversity and the great successes that we've had. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to switch gears, switch countries, and talk a little bit about Israel. Israel has been going through a pretty difficult few months between its internal political debate over judicial review and the ongoing threats of terrorism, just this week more rocket attacks from the Gaza Strip. What would be your message to American Jews who are concerned about what they're seeing here? Ted Deutch: Well, I understand the concern. Obviously, this most recent barrage of rockets is a reminder that while we're focused, and there's so much attention here in our country, to the politics in Israel, to the protests to the workings of the Knesset and the government and, whether there's going to be some sort of judicial reform, or what it looks like, to protect civil liberties and minority rights and checks and balances…while all of those conversations are taking place, 100+ rockets reminds us that we have a whole lot to be vigilant about. And Israel's security is not something that we can ever take for granted. And that it's important to note that all of those protesters in Israel, whether they're protesting, on Saturday nights, on a regular basis against judicial reform, or they were part of the big protest of people who turned out in Jerusalem to support judicial reform, all of them understand the threats that the country faces externally. And I understand concerns, I just think it's important to remember that it's, standing together in support of the country, doesn't mean that we don't have specific opinions about things that happen within the country. It doesn't mean that everyone comes at their connection to Israel the same way. But it does remind us that, being united, as rockets fall, as Israel confronts these threats is really important, not only for Israel, but I think for diaspora Jewry, as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: We are holding our first Global Forum under your leadership in Tel Aviv next month, on the occasion of Israel's 75th birthday. So what are you hoping participants take away from that event, especially in light of what we just discussed – the difficulties and the many, many tensions that have to be managed there? Ted Deutch: Well, the one thing that I know people will take away is the importance of being there. The fact that at this moment when history is being made the opportunity to be in Israel not only to focus on judicial reform and the political challenges and the security threats, but to also be in this incredibly vibrant, and diverse, and beautiful country, and to be reminded of the important place that Israel plays in the world in technology and innovation, and in humanitarian circles, and in combating climate change, and all of the ways and we go on and on, that this tiny little country is doing such remarkable things. And then all of that is continuing, even as hundreds of 1000s of people are marching in the streets. That's what people will take away from this. You want to be there when history is being written. You want to be part of the history that's being written now and showing up in Israel and coming together at AJC Global Forum is well, for me, clearly, it's the best way to do that. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, people should be excited about the democracy swirling all around them while they're experiencing Israel. Ted Deutch: I've had friends reach out to invite us to come to the protests, I've had other friends reach out to tell me that they're looking forward to talking about the challenges of the Supreme Court as it currently exists. I've told them AJC's views on the importance of where this is going and, and the importance of shared democracy between the United States and Israel. And the response, again, from everyone on whatever, wherever they are on the political spectrum in Israel is, okay, well, it's just important that you're coming. We may agree with you completely. We may disagree with you, but as American Jews, your voice matters, and this is the opportunity to share it. And it's the opportunity to hear directly from Israeli leaders and from global leaders who will be joining us literally from around the world, because they share in our commitment to safeguard Israel's place in the world. And it's those diplomatic efforts that help us do our work around the world, but at this moment, will allow all of us to focus on all that's happening in Israel. Manya Brachear Pashman: Ted, thank you so much for joining us for the party, for coming to JAHM with us. And I look forward to more celebrating in Tel Aviv. Thank you so much. Ted Deutch: Manya, I look forward to it as well, to celebrate with you and everyone who's listening. It's going to be a remarkable trip. But remember, we still have all of JAHM ahead of us. Manya Brachear Pashman: May has only just begun. Ted Deutch: All right, happy, JAHM. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much.
Apr 27, 2023
How Playing Baseball With Team Israel Transformed Ryan Lavarnway's Life
In celebration of Israel's 75th birthday, guest host Dov Wilker, AJC's Atlanta director, sits down with retired Major League Baseball catcher Ryan Lavarnway, who played for Team Israel in the World Baseball Classic and the Olympics. Lavarnway reflected on the Jewish pride he felt representing Israel on the international stage, how he has dealt with the antisemitism in his career, and the importance of building connections between the Jewish state and the Diaspora. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. __ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Ryan Lavarnway ___ Show Notes: Watch: Catch the full video conversation with Ryan Lavarnway , recorded live on Yom Ha'atzmaut as part of AJC's Advocacy Anywhere Test your knowledge: Quiz: How much do you really know about Israel? When was Israel founded? Who was the first Israeli to win a Nobel Prize? Which country was the first to recognize the State of Israel? Start the quiz ! Listen: Israel at 75: 7 Things You Should Know About Israel : Listen to these seven episodes of AJC's People of the Pod featuring leading Israeli and American scholars, experts, and influencers that will help you learn more about the complexities, triumphs, and challenges facing Israel today. Julianna Margulies on Holocaust Education and Fighting Antisemitism : Emmy Award-winning actress Julianna Margulies recently partnered with the New York's Museum of Jewish Heritage: A Living Memorial to the Holocaust, to help create the Holocaust Educator School Partnership. To date, the partnership has trained two university fellows to teach the history of the Holocaust to 1,700 middle and high school students in New York City Public Schools. In a poignant interview, Margulies shares her motivations for expanding the program, personal experiences of how antisemitism has affected her family, and reflections on her first visit to Israel and Yad Vashem. Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with Ryan Lavarnway: Manya Brachear Pashman: Sometimes it just makes more sense for my AJC colleagues to guest host. When it comes to sports, I always try to hand the mic to AJC Atlanta Director Dov Wilker. This week, in honor of Israel's 75th birthday, Dov sat down for a live conversation in front of a virtual audience with Major League Baseball Catcher Ryan Lavarnway, who played for Team Israel in the World Baseball Classic and the Olympics. Ryan talked to Dov about the pride he felt representing Israel on the international stage and the importance of building connections between the Jewish state and the Diaspora. I might not know a lot about baseball, but as someone about to visit Israel for the first time, Ryan's recollections and reflections brought tears to my eyes. Here's an instant replay. Dov Wilker: Let's get it started in the beginning, Ryan, how did you get into baseball? And does your Judaism intertwine with that, or is that a separate story? Ryan Lavarnway: So, I started playing baseball when I was five years old. And my dad always played baseball, he was always doing pickup games on the weekends playing high-pitch softball, but the story of why I got started was my kindergarten teacher told my parents that I was not good at sharing, and that I should get involved in a team sport. So they signed me up about as early as I could sign up, when I was five years old. And I took to it really quick and the rest is history. Dov Wilker: You know, that's good advice for my seven year old who is also not very good at sharing. So I appreciate that. And what about the role of Judaism in your life? Was Judaism something that was important to you from an early age? Or has that sort of become more important to you as you got older? Ryan Lavarnway: No, it really wasn't. My mom is Jewish, and she always loved Christmas. They had a white Christmas tree in her house with blue ornaments. And my dad would describe himself as a disenchanted Catholic. So growing up, we celebrated holidays from all religions. But there was no religion involved. We celebrated just to have a nice meal together, to have a reason to give presents and celebrate or light the candles. We went through the motions. Sometimes I joke that we celebrated Hallmark holidays. And it wasn't until really until high school that I started to grow into my own as an adult and start to search for more. And in high school, I ended up going to temple for the first time with a high school teammate's mother who had MS and couldn't drive herself. So we kind of needed each other because I needed someone to go with, and she needed someone to drive her. And that was really my first experience. As an adult, when I started searching for more meaning behind –Why do we celebrate these holidays? And what do they mean? And where's the community that I want to be a part of? Dov Wilker: What state did you go to high school in? Ryan Lavarnway: I grew up in California, LA County, in the valley. My wife likes to make fun of me every time I talk about home, she references that SNL skit The Californians– she's like, Oh, you, you were on the one oh one and the four oh five. So I grew up in Southern California. A lot of Jewish players on my youth league teams, on my little league teams, you know, Bar Mitzvah season for me, you know, when you're 13, 15, in that season of your life, I had a ton of friends that were Jewish, we had a great community here. But my family, again, we were more of the Hallmark holidays. Dov Wilker: So when you were in high school, when sort of you started getting more into your Judaism, but also, you know, as you were playing, did you ever experience antisemitism on the field when you were younger, or even when you were older? Ryan Lavarnway: When I was younger, not so much. And I think the reason that I was able to kind of dodge those bullets was because my dad was Catholic, and my mom was Jewish. So as we studied the Holocaust in school, I felt, you know, and to me, I'm almost embarrassed looking back, but this is my truth. I would step away and I would say, Well, I'm half Catholic, so the people that were hurt and the people that were, killed in and, and antisemitism is against, that wasn't me. But then I could also step on the other side and be like, Well, I wasn't the evil villain, either. It wasn't my people that were causing all this pain. And that helps me avoid feeling, and feeling hurt by the antisemitism as a kid. But what that also did was, it kept me from feeling the benefits of the community. And it wasn't until later, and we can get into this, when I played for Team Israel and I fully embraced being Jewish–and publicly–that I started facing antisemitism for the first time and really internalizing it and feeling it personally. But then that was also the first time, with that came, the feeling, the sense of community and feeling like I'm your brother, and you're my brother, you're my sister, and like we're all in this together. So I feel like they go hand in hand. Dov Wilker: So let's dive into that, the Team Israel stuff a little bit. Your first experience with the team came about in 2017, 2016. Ryan Lavarnway: 16, yeah. Dov Wilker: 16. So how did that all start? I mean, you're a Major League Baseball player, you're a world series champion, and you get a phone call from some guy who was like, hey, like, we've got this team we want to create it? Or, was it, the World Baseball Classic is gonna be a big thing and you want to find a way to be a part of it and you're a great catcher, but you might not be picked for team USA. How does this all work? Ryan Lavarnway: So, yeah, I got a phone call from some guy that I'd never heard of. Peter Kurtz. I don't know if it initially came through my agent or how he first got ahold of me. But I got a call in 2012. And I had just made it into the big leagues as a rookie the year before. I had like half a year of service time, still trying to prove myself and establish myself as a major leaguer. And he said, Hey, we have this Team Israel. And we play baseball, surprise, you never heard of us. Which I think was everyone's reaction. But you qualify for the team, because your mom's Jewish. So what do you think? And I was like, Well, what's the WBC because 10 years ago, it wasn't very popular yet, it's still growing. He's like, Well, we have to qualify to get into the tournament, because we only have one field in our whole country. And we're ranked 64th in the world. But we think we can do it. What do you think? The qualifier's in September, can you be there? And I was like, Well, it sounds like an amazing opportunity. Let's do it. But if I get called up again, this year, I'll be in the big leagues, so I can't be there. So September 2012, came in when I was in the big leagues. I wasn't able to go, but I had the seed planted in my mind of this, this is a possibility. This is a thing. So four years later, they just missed qualifying in 2012, they had a lead in the last inning. And my now best friend from this team, Josh Zeid, ended up blowing the lead. Flash forward four years later, 2016, I get another call, Hey, we're going to try to qualify again. We just missed it last time, we think we're really going to make it this time. Can you be there? And this time, my answer was, well, I'm probably going to be in the big leagues. But if for whatever reason I'm not, heck yeah, let's do it. And then the skies parted. It was the first year in six years, I wasn't in the big leagues in September. And I was available. And I went and played. And what I remember, showing up, when I first got there was Josh Zeid spoke very passionately to the group about how blowing that lead four years earlier, is still eating him up inside. And it was the lowest of lows for his career and everything he had done pitching in the big leagues. That was the moment he wanted to change. And his impassioned speech really spoke to the rest of us about oh, man, this is maybe more important than we thought. Dov Wilker: So I want to jump back to something that you said, which I find very profound. This random person calls you and says, Hey, your mother's Jewish, you qualified to be on the team. How do you respond to that? Right? You started off by saying that you got more into your Judaism when you were in high school and but, how do you feel, what is that? And by the way, have you ever been to Israel before? Was there any sort of connection to Israel, as all of this is sort of taking place? Ryan Lavarnway: I had not ever been to Israel. When he first called me in 2012, my wife and I were engaged to be married. By the time 2016 came around, we had been married. My wife was raised Jewish, she had a bat mitzvah, she had been on Birthright. We had a Jewish wedding. I was more involved in the Jewish community locally in Denver, and had really embraced, on a personal level, that I'm a Jewish man, and I want to raise a Jewish family. I want to be involved in the Jewish community in Denver. I still had yet to say that publicly. Because playing for the Boston Red Sox, our media training, at least 10 years ago, this was before athletes branding themselves and having their own brand was really acceptable. Especially in baseball, baseball is one of the last sports to embrace that. So the Boston Red Sox media training involved: if anything is even potentially controversial—just keep it to yourself. The Red Sox is the brand, don't tarnish it. And Boston itself as a city is a little closed minded, I would say. I think people that know Boston could agree with this, that they're not the most forward thinking city. Dov Wilker: No offense to anyone in Boston that's listening. Ryan Lavarnway: No, I love the city of Boston. Trust me, I love Boston. It's one of my favorite places. I still feel at home there. I've got my Red Sox World Series ring on the table right here. But like, I know, some of my black teammates didn't feel comfortable, and black visiting players don't feel super comfortable there. So it's just it's just the way Boston is a little bit. So I just kept to myself. When I announced I was going to play for Team Israel, was the first time that I really feel that it was public. And I feel maybe in a way that's the first time I dove all the way into the deep end of embracing it. Because you have to say to the world, right? If you are privately Jewish, in a sense, you could say that maybe it's–you're hiding it a little bit. Or it's just you're just not announcing it. So I finally announced it to the world. I finally experienced antisemitism for the first time in a way that I really internalized and personalized and I was really embraced by the Jewish community and it was really wonderful in that way. Dov Wilker: Two things --one is, AJC has a campaign that we created called Jewish and Proud. And it's something that we've been sort of pursuing as a result of the rise of antisemitism in our society. So I couldn't agree with you more. I think that that's so important. It's why, in fact, one of the reasons that I wear my kippa— one of the reasons is that I've got a hair problem in the back. But the second reason is that I feel it's an important identifier, because I'm very proud to be Jewish. And I want people to be able to know that. But I'm one of the things you just said was that, it's when you started to experience antisemitism, really publicly. So could you share a little bit about that? What was that like, or what type of experiences you might have had? Ryan Lavarnway: Yeah, so there was a couple of experiences that were more subtle. And it was more of people questioning, like, Oh, I didn't realize you were Jewish, or like, I didn't know that about you. And I felt like, I felt like they felt permission to express their questioning, or they felt like they had the right to have an opinion. Which ultimately, what's the difference? I'm the same exact person you've known for years. And now you think you have a different opinion about me. And just the fact that they even made a face or had a slight different tone when they talked to me. It made me feel like well, why? Why did something change? Why did anything have to change? There were more obvious experiences. Baseball is a very Christian sport, at least on the professional level. I think that we have 12 Jewish major leaguers this year, and that's a record. Out of 780 players in the major leagues, 12 are Jewish, so it's very much a minority. So every Sunday, a chaplain comes in and holds baseball chapel, in the dugout or in the clubhouse, for both teams, and they do it in English and in Spanish. So it's a really established institution within baseball. And it's great for those players. But it's not my thing. And I kind of established, 'that's not my thing,' was my go to response when I was invited, because they tried to include everybody. And one time I remember I was in Gwinnett, Georgia, the AAA team for the Braves. Dov Wilker: Yeah. So it's up the street from where I live right now. Ryan Lavarnway: Yeah. And I was invited to baseball chapel. And I said, Well, it's not my thing. And the chaplain really pushed back, like, why wouldn't you go? And I was like, Well, I'm Jewish. So you know, I don't need to go to baseball chapel. We have our own thing on the weekend. And, he said, Well, I've dealt with heathens like you before. And I don't remember what happened with the rest of the conversation. But it left me feeling really awful, that he would call me that. And I honestly didn't even know what heathen meant. So I went and I looked it up in the dictionary on my phone. And I think technically, by the definition, heathen just means non-believer. But the way he said it made me feel like he was talking down to me, like I was less than and, for a supposed man of God, I didn't think that was very ethical, or I didn't really like the way he handled it. So small experiences like that. And then there was one other time I was in AAA, I don't remember what team I was with. But one of my teammates in the outfield was expressing some other backwards opinions about some other groups that he thought maybe I might relate to—which I didn't. And he also went on to add –also, if we're going to be friends, I'm gonna have to tell you, you're wrong at some point. Because you don't believe in Jesus Christ. And I was like, okay, guy, well, then we're just not going to be friends after this. So there have been experiences, some of them have been more subtle, some of them have been more obvious. In my experiences, I feel like antisemitism falls into two major categories. It's either ignorance, or it comes from hate. And I approach them in two separate ways. I think if it stems from ignorance, I try to educate them. It shouldn't have to be my job and anybody that is a Jewish person, it shouldn't have to be your job either. But if we don't do it, who will? And I think it goes the same way with anybody that is the receptor of any sort of ignorant hate, you know, whether it's black people, or gay people, anybody that experiences that, it shouldn't have to be your job to educate people. But again, if you don't, who will? So when someone makes a joke that might be hurtful or someone comes from a place of not understanding why it might be hurtful, I try to educate them, like this is where the history of that joke or the history of that ignorance comes from. And then in general people, they don't want to be ignorant and they don't want to be hurtful. So most of the time they back off. The other time is when it comes from hate. And I don't know if you can necessarily change people's hearts. I take one of my cues from Hank Greenberg, who was one of the more famous baseball players in history. He was a big, strong, intimidating person, he would stand up to it. And he took the approach, at least from the stories that I've heard, of, you deal with a bully, you stand up to them, and you maybe intimidate them back, and then they'll back down. And I think that's one way or the other way is, if it stems from a place of hate so much that you're in danger, then that's when you kind of try to avoid it, or you reach out to authorities in some regard. Dov Wilker: Ryan, I appreciate you sharing that. Unfortunately, for me, it's not surprising to hear what you shared. And I'm sure for many in our audience, they wouldn't have expected it. And yet, it also might not be a surprise. It's also one of the reasons AJC created a tool. It's an online glossary called Translate Hate, for those experiences to be able to explain to people what the root of the antisemitism that they might be sharing comes from. I absolutely agree with you about the two types of antisemitism that you've experienced. I'm curious if you ever, did you ever talk to the other 11 Jewish players in the majors about their experiences? Or that you sort of just assume that they had similar ones? And did you ever experience it from the fans? Ryan Lavarnway: No, in general, a lot of most of the fans have been really supportive, or don't bring it up at all. So fan wise, it's been really, really positive. And as far as talking to other players about it, when we're with Team Israel is when I interact with the other Jewish players the most. And we're really just enjoying the experience and really positive. So any experience I speak of is really personal. And you'd have to kind of talk to them about theirs. Dov Wilker: Yeah, no, I appreciate that. So let's talk a little bit more about what it was like to represent Team Israel. What was it like? I mean, here you are, you've sort of done very cool things in the majors, you got to be a part of this team, this unique gathering of the diaspora Jews essentially to represent the Jewish homeland. Here we are again, on Yom Ha'atzmaut, Independence Day, talking about that. Was the team received well by the other countries in the World Baseball Classic? These are other ballplayers that, you know or were you sort of shunned aside a little bit? Ryan Lavarnway: So the first thing is, when I first started to play for Team Israel, I can be totally honest about this. I signed up because it was a great baseball opportunity. Playing in the World Baseball Classic was, I had never played international baseball before. So it seemed like a cool thing to do. And it would add to my baseball resume. Representing a people, a culture, and a country, it didn't even enter my mind. I didn't know what it would mean to me. So I signed up for a baseball opportunity. We played in Brooklyn in a qualifier. And it started to hit me when I stepped on the field with Israel across my chest. And we stepped onto the line for the national anthems before the game. And we took off our hats and we put on kippas. And it was the first time that a sports team had ever done that, or at least a baseball team had ever done that. It was really interesting. And I looked into the stands and there was–Brooklyn's a home game for for Israel, right, there was a bunch of Jews in Brooklyn, and there was a few yeshiva schools with kids with the tallit and the kippa. And it hit me that these kids have never had a team like this, where they can relate to every player on the field. And everything that I know about representation and how the more things you can relate to in leaders, or the more things you can relate to in role models, the more meaningful and impactful it will be for you as a young person. It really hit me that I wanted to be the person for them. I wanted to be their role model. And then it hit me again when we got to Israel, because after we qualified for the tournament, they brought us to Israel and filmed a documentary about it. They did a great job. I don't get five cents if you download it on Amazon but check it out because they did a great job. Going to Israel really, really it hit home for me. We got to Israel and we had a practice on the only field in the country. And I have this sense of meaning that's growing and my heart is expanding another size like the Grinch on Christmas, when his heart grows two sizes. And after our practice, we have a press conference with the Israeli media. And they let us have it. They were initially not excited to have us represent them. They pushed back really hard. Who are you to represent us? We don't even play baseball, you guys are outsiders. Who do you think you are? And we were all like, Oh, my God, like, we thought we would be at this press conference, and it was going to be a love fest where they were so happy that we made it into the tournament. And that was very much not the case. So that gave us pause a little bit. But we also appreciated that they didn't just accept us because we were winners. They wanted us to prove it, like prove that you mean it and prove that you're gonna represent us well. So we went to Seoul, South Korea was the first round. And we started to win. And we counted out before we started, I don't know if you remember the article that ESPN posted. They called us the Jamaican bobsled team of baseball, has-beens, wannabes, never-weres, that perfectly fulfill the role of "team that has no business being there, and somehow found a way to win minus, they haven't won yet." That was what the article said. And that was maybe the best thing that ever happened to us because we got a very, very solid collective chip on our shoulders. And we had a lot of players that felt like maybe they had been overlooked in their careers or hadn't got the opportunity or hadn't performed to their potential. So we had a lot of players that already had a chip on their shoulder. And now as a group, we had one. So we went out there, and we started to win. And we beat Korea, and we beat Taiwan, and we beat the Netherlands. And everybody's now freaking out. We're a Cinderella story. And the other teams were great. The other teams, you know, you qualified for Israel, whatever. We move on to Tokyo. And as we advance to the second round, now the Israeli media is like, we're so happy you're representing us. Thank you for being respectful and giving positive energy on the worldwide stage and for playing so great. And now we have this positive thing. So the Israel media finally embraced us, as we continued to send the message that we want it to grow the game within Israel, not just win, and not just say, wham bam, Thank you, ma'am, we're out of here. But we all had the intention to be around for a while. And then we beat Cuba. And the Cuban media was pissed. And I think they were probably embarrassed that they lost. And that was the first time that another country's media had been like, well, you guys are all American. You guys are America. American's B-team. And that was the first time we really got pushed back. But realistically, nobody on Team Israel would have made America's B-team or America's C-team or America's D-team or E-team or F-team. Like us we were a collection of has-beens, never-weres and wannabes that qualified for Israel. And then most of that team from 2017 signed up for the Olympics and we established Israeli citizenship and went back to Israel a second time. And every time that we've been to Israel, we make the commitment to grow the game we go, and we host clinics for the youth. Most of the prize money for the team has gone to building new fields or funding international tournament travel for the youth. And participation in baseball in Israel has doubled since the first time I wore an Israeli uniform. Dov Wilker: There's so much that was said. I'm so grateful that you shared all of that. Ryan Lavarnway: I have no idea if I answered your question. Dov Wilker: I'm not even sure what my question was anymore. So it's the perfect answer. By being members of the Israeli team at the Olympics, did the Israeli Olympic Committee do anything to share about the massacre of the 72 Olympics? Was that at all a part of sort of, in general, was there sort of learning, teaching, touring that that Israel did, that the the institutions there to help you all sort of have a better understanding if you'd never been there before, sort of different challenges and things like that on the global scale? Ryan Lavarnway: Yeah, there absolutely was. So we all had to go to Israel a second time to establish our citizenship, which I think was the right thing to do. You know, you can't just mail us a passport overnight, right? So we went to Israel again, we went to all the fields, we coached kids. We went to Independence Hall, we did all the things. What we also did was we had to go to their athletic Institute to be put through a battery of testing. They wanted to make sure we were healthy, and that we weren't going to die on the field. And I don't know if you remember the old Gatorade commercials, where they had a tube hooked up to your mouth and the EKG machine, all the wires coming off and you're running on a treadmill. We did that. And we're running on this treadmill. We're dripping sweat, we're panting. Our hearts are beating and we're all like, do you understand baseball? Like, we don't have to do this. But they put us through all the crazy testing. It was really awesome. And while we were at the Institute, we got to meet some of the Judo athletes, some of the windsurfer athletes and we went straight from there to the Israel Olympic Experience, which is like a museum for Olympics in Israel. It's not a very big museum. Dov Wilker: They've got some gold medals... Ryan Lavarnway: I believe, and don't quote me, because I'm not sure on the facts. But I believe they had 13 medals, before Tokyo and four gold, I want to say. Judo and windsurfing I believe, I might be wrong. But going through that Olympic experience, it really gave us context for understanding the history of Israeli athletics. And the tragedy that happened in the 70s. Dov Wilker: I'm glad to hear that. I'm curious: in Israel, what was it like for you the first time, the second time? Did your opinions change when you became an Israeli citizen? I'm not going to ask for your political analysis of the current situation there, I don't think that'd be fair. How has that experience changed for you and your family? You're married. Did anybody join you in Israel? Ryan Lavarnway: So the first time I went, my parents were nervous. Because if you watch the American news cycle, you would think that Israel feels like a dangerous place. And they were like, Are you sure you want to go, especially right now. So I went into it a little nervous. not knowing what to expect, and you land on the ground. And I was like, I've never felt more safe in my life. This place is beautiful. It's amazing. We spent, the first time I went, we spent four days in Tel Aviv first, beautiful city, right on the water, we stayed in this beautiful beachfront hotel. And then we went to Jerusalem, and going to Jerusalem. And this is going to be a pained metaphor, so please forgive me. But in the same way, the first time that I stepped into the old Yankee Stadium, or Wrigley or Fenway Park, you can just tell it's different. You can just smell the significance in the air, you just know, like, I am among history, so many important things have happened here. And I get to experience this in the modern world. And it just feels, like your heart beats different, the air smells different. So going to Jerusalem was that for me, and especially getting to the Western Wall, I swear to God, I felt God for the first time. And it was just this transformational experience. I think I cried. I think they caught it on video for the documentary, which is cool for me to live through and get to see again, because that was a really, really meaningful moment in my life. But going there, for the first time, yeah, my wife came with me. This was before we had our daughter, years before we had our daughter. But it was really, really meaningful and transformational for me to go for the first time. When I went back the second time, I got to experience it all again. You know, you don't have that transformational experience, because you've already changed as a person, and you're changed forever. So it was really cool to go back again. And then they handed me my passport. And I have this goatee so I kind of felt like Jason Bourne, where I have two passports now, like, which I am going to use. Except they both have the same name. It's very, very, very cool. Dov Wilker: So I'm gonna go for some rapid fire questions… Ryan Lavarnway: Oh wait, I have one more. I think it's a good answer. And I don't like to express my political opinions. But what I'd like to tell people is, if you either voted– in America, if you're an American citizen, you either voted for our current president, or you voted for the last president, you didn't vote for both. And either currently or four years ago, you were unhappy with the decisions that the government was making. I don't think that made you feel less proud to be an American. And I would encourage you to use the same opinion, when you think of Israel. Whether you agree with what the current current government is doing or not, does not have to color your opinion of whether you agree with the concept of Israel. When I think of Israel, I believe in what Israel is about, and it being a safe haven for the Jewish people worldwide, whether I agree with what the current government is doing or not. And I think it's very easy to judge ourselves by our intentions and others by their actions. And that goes the same with a country that you personally identify with also, so I just wanted to throw that in there. Dov Wilker: I so appreciate you saying that. I was speaking to a group of high school students recently. And I shared with them that, you know, we're talking about the current situation, and I said, you know, Israel welcomed in Ukrainians as citizens, not as refugees. If you read Israel's Declaration of Independence, it refers to the survivors of the Holocaust and those who were expelled from other lands. And so the in-gathering of the safe haven for the Jewish people is so important for us to be able to continue to remember the role that Israel plays in our lives. We're, you know, we're fortunate to live in the United States today. But we see that people need Israel more and more depending on where they live, not everybody is as fortunate and there are many people who have moved to Israel because of the antisemitism that they themselves might have experienced here. So I think it's a really powerful statement for you to make and something that I hope, I'm guessing that if you shared it here, you share it with all of your audiences, but if not, I hope that that's something you continue to share with your audiences. All right, well, it's no easy transition to my rapid fire, so I'm just gonna do it. Ryan Lavarnway: Just rip off the bandaid. Dov Wilker: There you go. Favorite Israeli snack? Ryan Lavarnway: Shawarma. Dov Wilker: Oh. Snack? You have a very different appetite than I do, my friend. Ryan Lavarnway: I have a very big appetite. Dov Wilker: Favorite city in Israel? Ryan Lavarnway: Jerusalem. Dov Wilker: Favorite baseball memory. Ryan Lavarnway: Two answers: World Series win, or my debut with Cincinnati. Dov Wilker: Okay. Most challenging part of being a catcher. Ryan Lavarnway: Hitting in the ninth inning. Dov Wilker: You know, you talked about the small numbers, the mighty numbers of Jews in Major League Baseball today. Is there an association between the Jewish ballplayers in the major leagues and other professional sports? Is there any reason, maybe it's based on a city that you live in? Or it's sort of an overall, I know like, there's the Jewish Coaches Association, something like that? Is there anything like the Jewish professional ballplayers association, that gets you together, perhaps to be able to encourage others like you to play for the Israeli teams in other sports that they're professionals in. Ryan Lavarnway: Not that I've experienced yet, but that might be a cool idea to start. I'd be up for it. If you want to talk off of this broadcast. Dov Wilker: It's my new side project at work. Ted, thank you for the approval. And I guess my final question for you, Ryan, is, we're here today, Yom Ha'atzmaut, Israel's 75th birthday. What type of closing message do you have about the importance of Israel, you already talked about the safe haven for the Jewish people, but sort of the future of American Jewry. Any parting words of wisdom that you'd like to share? Ryan Lavarnway: My biggest thing is, participate, and be proud. And you need to be public, because the only way that we can get the benefit of the community and strengthen numbers is if we support each other, and we're aware of who each other are. I've received so much benefit in my life from embracing the community and stepping out into the public. And it's really changed my life. And it's changed how I view myself as a man. And it's changed the direction that I want to raise my family. And it's been such a positive change. And I've had such a positive embrace from the community. And I want others to experience that. And I never would have experienced it if I didn't go out of my way to participate in Team Israel. So I encourage anybody watching, go out, get involved, anything in your community, a team you can get involved in. It's been so positive for me, and I hope it can be so positive for you as well. Dov Wilker: Well, Ryan, on behalf of American Jewish Committee, thank you very much for joining us for this wonderful conversation.
Apr 21, 2023
Julianna Margulies on Holocaust Education and Fighting Antisemitism
Emmy Award-winning actress Julianna Margulies recently partnered with the New York's Museum of Jewish Heritage: A Living Memorial to the Holocaust, to help create the Holocaust Educator School Partnership. To date, the partnership has trained two university fellows to teach the history of the Holocaust to 1,700 middle and high school students in New York City Public Schools. In a poignant interview, Margulies shares her motivations for expanding the program, personal experiences of how antisemitism has affected her family, and reflections on her first visit to Israel and Yad Vashem. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Julianna Margulies ___ Show Notes: Learn more about: The Museum of Jewish Heritage's exhibit The Holocaust: What Hate Can Do The Holocaust Educator School Partnership Vote: Vote for The Forgotten Exodus at The Webby Awards: AJC.org/Webby Test your knowledge: Test your knowledge of antisemitism in America : Stopping antisemitism starts with understanding how dangerous it is. Take our quiz and learn how antisemitism impacts American Jewish life. Read: Breaking Down and Fighting Holocaust Trivialization : Holocaust trivialization is not always obvious; a casual observer might miss it without an understanding of the terms, symbols, and relevant history. Here is what you need to know. Listen: Surviving the Unimaginable: A Child's Story of the Holocaust : In this powerful episode, we sit down with Sam Harris, who is one of the youngest survivors of the Holocaust. As a young child, Sam watched in horror as his family was taken to Treblinka and murdered, but he and his two older sisters were able to beat the odds. Listen as Sam recounts the unimaginable struggles he faced during one of the darkest periods in human history and how his experience motivated him to play a central role in the founding of the Illinois Holocaust Museum. What to Know About Israel's Judicial Reform Effort and Protests: Last month, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu pressed pause on a series of contentious judicial reforms that have triggered mass protests, condemnation from wide swaths of Israeli society, and expressions of concern from American leaders and Jewish organizations. Guest host Belle Yoeli, AJC's Chief Advocacy Officer, sits down with AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson to discuss what this means for the future of the Middle East's only democracy. Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Interview Transcript - Julianna Marguiles: Manya Brachear Pashman: Last year, Emmy Award winning actress Julianna Margulies hosted a Holocaust memorial special called "The Hate We Can't Forget", which featured the stories of four Holocaust survivors. In that documentary, Julianna sounded the alarm that Holocaust education across the country was severely lacking. After filming, Julianna partnered with the Museum of Jewish Heritage: a Living Memorial to the Holocaust here in New York, to help create the Holocaust Educator School Partnership, or HESP. Julianna is with us now to explain what that is and what she hopes it will accomplish. Julianna, welcome to People of the Pod. Julianna Margulies: Thank you so much for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So please tell our audience: what is the Holocaust Educator School Partnership or HESP? Julianna Margulies: HESP's an easier way to say it, actually Jack Kliger, who is the CEO of the Museum of Jewish Heritage, he calls he calls them the Hespians. So HESP is a program that I started with the Museum of Jewish Heritage after I hosted that CBS documentary on the Holocaust, when I realized how little education there was in our country. And with the rise of antisemitism and Holocaust deniers, I just felt, I felt despair, to be honest with you. I just thought it's ignorance, because people are not educated. And when you do not learn history, history repeats itself. And so after I hosted it I thought to myself, what can I do? I'm just one little person. I'm not a humongous star, but I have a bit of a platform. And I thought well, let me try and use my voice and the small platform that I have to make change. So luckily, I knew Jack Kliger. And I said, I hosted this Holocaust Remembrance documentary for CBS and MTV, and they paid me. I didn't even think I was gonna get paid to be honest with you, because it was, of course, a labor of love to do it. And I felt weird taking money for it. And so I took the hefty check that they gave me, and I said, let's figure out how to educate our children. Because these are seeds that you have to plant early. So that when these people become adults, this idea that conspiracy theories and the rest of it, they won't penetrate, because you already have that education and the knowledge inside of you to say, that's crazy, no. And also, it wasn't just about antisemitism. For me it was about–and this is how we're approaching it with HESP. It's about genocide. It's about racism. It's about homogenizing human beings. It is about putting people in a category who are different than you and saying you don't belong. So it really spans the spectrum of the entire world and all the people in it. For me, antisemitism is incredibly frightening because family members of mine were Holocaust survivors. I'm a Jew. I'm raising my son Jewish. And I just felt like I had a call to action after I hosted that documentary and watching the documentary, I learned a lot. But really, I think it's about hate. And as we like to say at HESP, never again. Manya Brachear Pashman: It's scary, right? Raising Jewish children is scary, as a mom, I mean, it's wonderful and rewarding and rich, but scary. Julianna Margulies: Well, it wasn't to me at all until I did this documentary and my girlfriend who lives right around the corner from me and her son goes to St. Ann's. She said, Well, how does your son get to school? I said, it takes the subway. We live downtown and he goes to school uptown. Her son goes to school in Brooklyn and she said, Oh, I won't let them on the subway. And I said, Why? And she said, Because he loves to wear his Star of David around his neck, and I'm afraid. And I just couldn't believe I was hearing those words. It's 2023. We live in New York City. And many people have asked me why I've started this program in New York City. Because isn't New York City the center of the Jews. They talk about that. The fact of the matter is, we're in the second semester of this program that I started, and it is shocking how many seventh, eighth and high school students do not know anything about the Holocaust. In fact, two weeks ago, one of my interns was teaching the hour course on the Holocaust and the history of the Holocaust, and an eighth grade boy up in the Bronx asked if there were any Jews still alive, after 6 million were killed. So that's where we're at. Manya Brachear Pashman: So it's an hour long course. But there's more to it than that. Can you kind of walk us through the components of this, this partnership? Julianna Margulies: Yes. So, we take college and graduate students who apply to the program in our first semester, it was just starting out, and we had to do, and it is a paid internship, where they take an eight-day crash course at the Museum of Jewish Heritage on teaching the Holocaust, through one of our professional Holocaust professors there, they then go to schools that we contact, and give, from seventh to eighth grade all the way through high school, one-hour classes, on what the Holocaust was, what it did to the Jewish race, and how it was part of what World War II is about? Manya Brachear Pashman: Do they step into the classroom and take the place of a teacher for a period basically? Julianna Margulies: So they come into the classroom, there, we talk to the principal first and the teachers and it's usually in a history period, it depends on the school's curriculum, and they step into the classroom. And they give this hour lesson and children get to ask questions. On occasion, although they are dying out now, we are able to bring in a Holocaust survivor. My idea now is, because the Holocaust survivors are dying out is, I would like to bring in the children and the grandchildren and the great-grandchildren of Holocaust survivors to tell the stories of their ancestors so that the stories don't get lost, and they don't die out. Because as we're seeing antisemitism isn't dying out. Manya Brachear Pashman: So does it go beyond the classroom, or does it stop there? Julianna Margulies: It does. So because it's affiliated with the Museum of Jewish Heritage, we desperately feel that no child money should never be an issue when it comes to education. So we then after the class, a lot of scheduling is involved, but they're so on it at the Museum of Jewish Heritage. But then we supply buses and bring the children to the museum, which is beautiful, it's downtown and all the exhibits are quite something right now. It's this incredible, The Hate We Know. And it shows the very beginning of before World War II happened and then you get to see this journey that they took all the way after. After the Holocaust and after World War II is over. So they get to go and experience what we were teaching in their class and they get to ask questions. And it's been really heartening because we had an eighth grade class. I forget if it was the Bronx or in Brooklyn, they were so taken by the class that was taught. They chose, for their eighth grade project, an entire exhibition based on the Holocaust and what Jews went through and it was absolutely just gut-wrenchingly beautiful. They made me so proud. They sent me all the pictures of it, I was away working. So I couldn't go. But these kids were beaming. And they felt like they were doing something. I think the idea for me of what HESP is, and any kind of Holocaust education, I think because there's such darkness surrounding it. And I can understand why parents would be nervous to let a seventh and eighth grader learn about it, I understand the fear. But what I'm trying to implement into the program, is this idea of heroes. Who are these heroes that stood up in the face of evil, Jews and non Jews alike. And right now, in our country, I actually feel it's more important that the non Jews are standing up for the Jews, the way that I marched for Black Lives Matter, the way that we all marched for women, you know, this is a universal problem. And we all need to stand behind it. And if all the communities that are so oppressed joined together, power in numbers, and let's look at it more as shining a light on something that will make you feel heroic, to stand up to evil. Manya Brachear Pashman: How many kids has the program reached so far? Julianna Margulies: I'll tell you what's been really amazing to watch. So the first semester, we were small. And we had our two interns who did an incredible job, and they reached over 1700 children, and I always look at any kind of philanthropy, the way I look at acting, which is if I'm on stage, and I reach just one person in the audience, then I've done my job. And that's how I feel about this program. So knowing that they've reached 1700 children, maybe half of them didn't care or weren't listening or weren't moved. But there certainly were a handful that were. And what it also did was, when I went to the museum to congratulate our interns, when they graduated, we publicized it and took some pictures. And our next semester, we had 20 applicants. And in fact, I was just talking with —AJC's been really helpful. They're helping me expand it throughout the country. But it was Laura Shaw Frank, who said, What I love about this, and she's a holocaust historian, she said is that it's young people teaching young people, because they respond, kids respond to young teachers. And so to have these 20, 21, 22 year old interns walking into a classroom, full of, you know, 9th graders, 10th graders, 11th graders, and talking at their level, is actually incredibly helpful. Manya Brachear Pashman: I learned something from the documentary. AJC has this wonderful resource called Translate Hate. It's a glossary that's online and it teaches people about antisemitic tropes and terms that have been around Yes, since the dawn of time. And new ones too. It's constantly updated. And I learned a new term in that documentary called Godwin's Law. And I hope that we add it to Translate Hate later this year. And Godwin's Law is: the longer an online conversation goes on, the likelihood of a comparison to Nazis or Adolf Hitler rises 100%. I thought that was so interesting. And so social media does play such a significant role in school children's lives. TikTok, Twitter, Snapchat, probably a few have been invented that I don't know about yet. What role do you believe social media companies should be playing in reining in this antisemitic rhetoric, if any role at all? Julianna Margulies: Well, I think that I think they need to be responsible for misinformation, and hate speech. I'm all for the First Amendment. But where do you draw the line? Where do you draw the line here? I mean, children are sponges. And you plant one little seed, and it can be a good seed or a bad seed. And it's also you know, social media is toxic. I know I'm not a big social media person. I had to join Instagram when I wrote my memoir, because Random House said, Wait, you're not on social media. So I joined the lesser of all evils, because I figured the only people following me on Instagram are people who like me, right? So I'm not gonna get a lot of hate mail there. Manya Brachear Pashman: Think again, Julianna. Julianna Margulies: I know, I know, I actually realized–don't read the comments. But I do believe that it is their job to filter out the hate and the misinformation, I really do. I do not think they should be allowed to. I'm going to peddle these incredibly damaging, and life threatening conspiracy theories. It's not helping anyone, it's making people more angry. I know how I feel just scrolling through Instagram. You know, I as an adult, who is not into any of it, and who feels very secure in who I am. And in my position in life with my family, and who I am as a person to my friends, and my child and my husband, I start feeling insecure. So if I, a confident woman in her 50s is feeling insecure, scrolling through Instagram, I can't imagine what it's doing to children. Manya Brachear Pashman: I love the way that you put it in the film, that just a little bit of Holocaust knowledge can actually be dangerous, that it's because it's just enough for someone to invoke it for political reasons or to make a point, but not enough to take responsibility and to try to prevent it from ever happening again. Was it important that this partnership that you are funding, be robust, be in depth, be more than just an hour long course? Julianna Margulies: Absolutely. I mean, obviously, it's very difficult to teach everything in an hour. So the idea is that those who hear about it and learn about it from that course, will further their interest in it, and that the schools will eventually realize this is something we need to teach. This should be a mandatory class in our history program, the same way we learn about how America was founded, you know, like this is just as important, especially because it's just not that long ago. You know, this, this is quite recent. If you look at the big scale of our world, and how many years it's existed. This is not that long ago. And I, I do believe that institutions, Holocaust museums, all over this country, are doing a tremendous job in showing what it was like, I mean, you know, we're, we're, we're doing an exhibition in October because it's the 80th anniversary of the Danish rescue. And at MGH they're doing an incredible job. I'm on the advisory board now. They're doing the Danish rescue, and it's for children and families. It's not, there's no age, it's age appropriate for everyone. And it's showing the heroes that saved 7200 Jews, and- Manya Brachear Pashman: If you could tell our listeners a little bit about what that Danish rescue is, what you're referring to. Julianna Margulies: So the Danish rescue. You know, it's interesting. I just read this book that Richard Kluger wrote, it's coming out in August, called "Hamlet's Children," and it's all about the Danish rescue. And very few people know about it. I didn't before I read the book. So Denmark was in a very tricky place in World War II. They had made a treaty with Germany and they were in a place where they were Nazi occupied, but they had made a deal with King Christian had made a deal that the Nazis could not harm their Jews because they were their Danish brothers and sisters, and they were not to be touched. Now, here's a country that is under Nazi occupation. And they hated it. And they sort of were grinning and bearing it. And then towards the end, when the Nazis realized they were losing the war, when America came in, and England came into the war, and they realized that this was going to be a losing battle. The Danes realized that their Danish Jewish brothers and sisters were in trouble. And boatload by boatload at midnight, they rescued 7200 Jews to Sweden, which was neutral. I think what's so important about that story, and I think for people who have gone to Yad Vashem, in Jerusalem, where I just was this past December, to see all these points of light, what would have been had 6 million Jews not been murdered? Where would the life, where would the tree have gone? How far would it have grown? And the 7,200 Jews that were saved, their families have lived on. And it's to show- it's about the tree of life, which was being chopped down before it could even begin. And it's such a heroic story of how they did it. We even have the actual boat that we've refurbished. That's actually in Mystic, Connecticut, because we couldn't get it to New York yet, but we will eventually. It is such a sort of miraculous story. And it wasn't just adults who saved these, these Jews. Everybody in Denmark rose to the occasion. And when you go to Yad Vashem, I mean, I, I had just finished reading the book and I walked down the path of the righteous at Yad Vashem, and I saw a plaque. So for those of you listening who don't know what the path of the righteous is, it's the path of all the heroes, the non Jews that stood up to the Nazis and protected the Jews from the Nazis. And there was this beautiful plaque to the Danish rescue, and I just, you can't help but weep. I mean, it's— where are those heroes? And so that's the light I want to shine on HESP and our Hespians is that these are heroes, let's be heroes. What's amazing to me, is in my business, you know, I'm an actress and all the big movies are about heroes. So why aren't we turning that into- Okay, so that's what makes money, right? Heroes. So let's make this about being a hero. Not about being an antisemite, or whatever labels they have for people who love the Jewish people, who are Jews. Let's turn this into a moment of heroism, and change the narrative so that our children grow up wanting to be heroes. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to hear more about this trip to Israel. I've encountered many Holocaust survivors who don't talk about their experience until they make a trip to Israel. And then they feel empowered, obligated to tell their horrific story. I'm curious what you witnessed, what you experienced in Israel, both at Yad Vashem, but also in the greater country at large. Julianna Margulies: Yeah, it was a magical experience. And we really crammed a lot in 10 days, because we wanted to make sure and when are we going to be back here? Let's do it. Right. So we actually hired a professor to take us around for 10 days. And really, we went to Tel Aviv, we went to the Negev, we went to Jerusalem. We even actually took a day trip to Jordan and went to Petra, which was mind boggling. We went to Masada. I mean, we did it all. We met with political consultants to try and understand the politics. And we went everywhere and learned about so much. And first of all, I think the thing that struck me the most– my sister was born in Jerusalem. In 1960, my big sister, and she, they left when she was one and I had never been to Israel, because we moved here. My parents moved back to New York. But I always felt this Oh, my sister was born in Jerusalem, I have to go. And we actually had meant to go for my son's Bar Mitzvah. But COVID happened and there was lockdown. So that didn't happen. Then the next year, we were gonna go and it was, Omicron. And so this year, it actually I'm glad I waited till he was 15. Because I actually think he got a lot more out of it. But one of the things that hit me the hardest was how young the country is. Manya Brachear Pashman: 75. Julianna Margulies: It is so young. Because I grew up in England for a great part of my life, and every time I'd come back home, I think how young our country is, like, God, it's so young here. You know, I love America. But some of the ideas, it's like, how can we move past this in, there's still this sort of, it's very young, we live in a young country, Israel is very young. But it's founded on such a strength of community and belonging. And I remember just landing in Tel Aviv, and I looked at my husband, we're walking through the airport. Now we are with our people, it's like, I've never felt like I belong more. Most people don't think I'm Jewish. Most people think I'm Greek or Italian because of my name. But I didn't grow up Jewish. You know, my mother, they're both 100% Jewish, but my mother's family tried to keep their Jewishness quiet. Because her grandmother, who had fled from Prussia, persecuted for being a Jew didn't want to cause any reason for someone to harm her. So they didn't celebrate Passover and Yom Kippur and Hanukkah. They just stayed very quiet. And they didn't talk about it. They spoke Yiddish and they had Jewish food but they didn't advertise their Jewishness, because that caused tremendous pain in their family. And so for me once I became an adult, I wasn't Bat Mitzvahed. And I married a Jewish man who said, I want to raise our son Jewish, and I want a Jewish wedding. And I said, Great, I'm in, let's do it. That's fine. Okay. But as I've sort of grown into the role of my life, as not just the actress and the independent woman, but also as part of a unit, part of a family. We do Shabbat on Fridays, even if it's just to light the candles, and to say goodbye to the workweek, and to say hello to our friends and family. Putting down phones. It's the tradition of Judaism. Because I'm not a religious person, I've always felt any kind of religion is a little bit sexist. And even though I played a Hasidic Jew in a movie years ago, called "The Price Above Rubies," and I went to Boro Park and and I did some research on the women there because .. I guess I was confused as to why you would love this life, because to me, it felt suffocating, incredibly sexist, and demoralizing to be a Hasidic wife. And then to see their pride and joy in their work, and how they felt about themselves. Iit was quite eye opening. You know, I was judging, I was definitely judgy about it. And I learned a really good lesson, you know. But I have found tremendous joy in the traditions of our Jewish heritage. And our son knows, Friday nights, he can invite any friend over, but we're gonna, before the pizza comes, we're going to just do our blessings, light the candles, and kiss each other. There's something about tradition that is so lost in today's world, that gives a sense of meaning. And, and a route to the family. Manya Brachear Pashman: This has been a fascinating conversation. Julianna Margulies: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: I know that it could go on for hours longer. But thank you so much for joining us. Julianna Margulies: Thank you for doing this podcast. I really love it. Manya Brachear Pashman: I really hope this program expands across the country. Julianna Margulies: Thank you so much for having me.
Apr 17, 2023
Vote for The Forgotten Exodus at the Webby Awards
The Forgotten Exodus has been nominated for a Webby Award, also known as "the Internet's highest honor" — but we need your help to win! Click here to vote for The Forgotten Exodus for "Best Limited Podcast Series." It takes less than a minute. Voting ends at 11:59 p.m. PDT on April 20, 2023. The Forgotten Exodus is the first-ever narrative podcast series devoted exclusively to the fascinating and often-overlooked history of Mizrahi and Sephardic Jewry from Arab countries and Iran. Created by American Jewish Committee (AJC), the series debuted as the top-ranked Jewish podcast in America last August. Please make sure that these fascinating and impactful stories reach an even wider audience. Vote for the series now. ____ Show notes: Pond5 : "Arabic (Middle Eastern Music)"; Composer: Andrei Skliarov; Item ID # 152407112 Vote now: AJC.org/Webby Listen to "The Forgotten Exodus": AJC.org/ForgottenExodus
Mar 31, 2023
What to Know About Israel's Judicial Reforms Effort and Protests
This week, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu pressed pause on a series of contentious judicial reforms that have triggered mass protests, condemnation from wide swaths of Israeli society, and expressions of concern from American leaders and Jewish organizations. Guest host Belle Yoeli, AJC's Chief Advocacy Officer, sits down with AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson to discuss what this means for the future of the Middle East's only democracy. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jason Isaacson ____ Show Notes: Join us in Israel June 11-14 for AJC's Global Forum 2023: AJC.org/GlobalForum Read: What to Know About Israel's Judicial Reforms American Jewish Committee, Other Jewish Organizations Welcome Suspension of Israeli Judicial Overhaul Legislation Listen: How Jewish Teens Take on Antisemitism in America Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. ____ Transcript of Interview with Jason Isaacson: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week, Israel's Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu pressed pause on a series of contentious judicial reforms that have brought scores of Israelis to the streets in protest. My guest host, Belle Yoeli, AJC's Chief Advocacy Officer, sat down with Jason Isaacson, AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer to discuss what this means for the only democracy in the Middle East. Belle, the mic is yours. Belle Yoeli: Thank you Manya, and hello, People of the Pod listeners. It's great to be with you. Jason, thanks for joining us. Jason Isaacson: Of course. Good to be with you, Belle. Belle Yoeli: I think it's fair to say that it's been anything but a dull time when it comes to Israel. And I think that applies to the past year, the past few months, and especially the past few days. I'm sure our listeners have a lot of questions and very privileged that we're going to be joined by Jason to help us to understand and analyze recent events. And I'm going to jump right in. Jason, I want to begin by reviewing the sequence of events that led to the developments this week. The Israeli government has been pursuing legislation that would fundamentally change the way the judiciary operates, which has garnered a lot of attention. What has played out since Sunday that has led to the latest state of affairs? Jason Isaacson: Well, you'd have to go back a few days before Sunday, to the meeting that took place last Thursday, I believe it was, between the defense minister Yoav Gallant, and the Prime Minister, before the Prime Minister left on his most recent European trip. And in the course of that meeting, it was widely understood that Gallant was going to present to the Prime Minister what he has found in talking to senior officers of the military, hearing about the concerns that reservists were planning not to show up or were not showing up for duty. And that there was just a severe security threat that was being posed by the protests that have been sweeping the country for the last 12 and a half, 13 weeks. And that something had to be done. And what that something was, was that we really had to slow the train and pause this process of judicial reform. He presented that argument to the Prime Minister, the Prime Minister discussed this with him. Apparently, won some kind of understanding that would not lead to Gallant leaving or making a speech that night. And then the Prime Minister took off for London. After that, two days go by and on Saturday night, the defense minister makes a speech, basically the speech that we all expected him to make last Thursday, saying just what I said about the effect that the judicial reform process, the rush to judicial reform, is having within the ranks of the military and the reserve of the military. And because of that, he is calling on the Prime Minister to halt the process, to pause the process of judicial reform. Within 24 hours, the Prime Minister fires the defense minister, much to the shock of the entire Israeli military establishment and much of the political establishment. And there were then massive protests. So of course, we've seen in Israel for the last 13 weeks, hundreds of 1000s of Israelis out in the streets, people across the political spectrum, rising up and saying this judicial reform package does not serve the interests of Israeli democracy, it actually undermines Israeli democracy. It changes the whole process of checks and balances in Israel. But it was the firing of Gallant, who is widely popular, even though a figure with a deep, honorable military background, on the right in Israeli politics, but respected across the board, which I think one could say generally has been the tradition in Israel, for those who have served in high office in the military, regardless of their politics. The fact that he was dismissed by the Prime Minister in what looked like a political act, a personal act rather than an act that would serve the interests of security and of the best interest of the country. That's the way it appeared to so many in Israel. That's why 10s of 1000s of people immediately were out in the streets. And that's what led to the following morning, a whole series of events–calling of a general strike by the Histadrut, the Labor Federation. Israeli embassies and consulates around the world honoring that strike because they worked for the federal government and they're also part of the Union, Ben Gurion airport, stopping outgoing flights. Hospitals apparently no longer scheduling non-emergency treatment. So a range of effects rippling across the Israeli economy and society. At that point, it was clear that chaos is raining. This is not possible to continue on this track. And the Prime Minister, then after a series of discussions in the course of a very long day on Monday, made an announcement that he was putting a halt temporarily, to the judicial reform process that was racing through the legislature, through the Knesset until after Passover, after the Memorial Day, and Independence Day celebrations of Israel. So we got about five weeks or so to see what can come next. There apparently is going to be a–not apparently, there is already a negotiating process that has just begun, under the auspices of President Herzog with a different political factions sitting around the table, at least trying to establish a framework in which to pursue negotiations to come up with a compromise formula on judicial reform. Belle Yoeli: Obviously, we don't have time right now to go into every different piece of reform that's being proposed there are resources on AJC's website explainers on just that if anyone's interested in more details, Obviously, they've been widely reported on. But I want to get to the heart of: what are the concerns when it comes to this legislation? Why are these so controversial? Because we've heard a lot in the reporting about these proposals that Israel's democracy is at risk, but at the same time that's being said, Israel's democracy is on full display. So break down for us with the key big picture issues here with what's being performed with changes to the judiciary. Jason Isaacson: Look, I think what what's at the heart of the issue is concern that minority rights could be trampled, that the the majority, which has now, the governing coalition has 64 seats in the Knesset, but we all remember that when the election took place in early November, it was a fairly small margin of actual votes that put this majority, put this coalition into power. That a narrow majority could trample on the rights of the minority in court cases in which a newly reconfigured Supreme Court with more justices chosen by this narrow majority in the Knesset, or the current Supreme Court, overwritten by a narrow majority in the Knesset, which is also part of the proposal, part of the proposed package put forward by the government. All of that could reduce minority rights. And I think that that's really at the core of this. In addition to of course, maybe in the context of, larger divisions within Israeli society. We all know that Israel is a very complicated society with a significant secular majority and a growing religious minority that now has greater representation than ever before in the governing coalition. And I think that there are many in the majority, who are uncomfortable with that. There are also differences of opinion, as you know, within Israeli society on what to do with the West Bank, with Palestinian rights, with the future of a possible Israeli-Palestinian peace process, which has been pushed farther and farther into the background, farther and farther into the future, if it ever happens that there was the creation of a Palestinian state. But these fundamental questions that had been kicked down the road for so long, the secular religious divide the questions of what to do with millions of Palestinians who are living in the West Bank, and a growing community of Israelis who are living in the West Bank, as well, these are these are issues that often find themselves in court. And where that court comes down, and how the legislature responds to where that court comes down, are major issues that don't have to get addressed every day. But when they are addressed, people want an assurance that minority rights are respected, that the independent judiciary will be preserved, which by the way, is of huge importance to protecting Israel from international legal action and protecting Israelis from international legal repercussions, being able to point to the independence of the Israeli judiciary. So for all of these reasons, people take very seriously what's going on and the judicial reform proposals put forward by the governing coalition. That's why hundreds of 1000s of Israelis have been out in the streets over these last weeks. And it's why it's so important that when you make such a huge change that has such impact on the future of Israel, and on the future of the Israeli people, that the process be slowed down, that a negotiation proceed to try to reach a compromise proposal. So that we can we can take this crisis, you know, off the front page, and move, frankly, to celebrate the 75th anniversary of Israel, in an Israel that is united. And that has a common commitment, shared across the society, that it will protect minority rights, and that will protect the fundamental principles of democracy that we share with Israel in our country. Belle Yoeli: Thank you, Jason. I want to ask you now about how this process and everything that's playing out is impacting Israel's relations with the United States, the US-Israel relationship, and also Israel's relations in the region, beginning with the United States. And, of course, the latest exchange between Prime Minister Netanyahu and statement by President Biden I've just seen now also vice president Harris joining concerns about the situation in Israel. What are we seeing in terms of the Israel-US relationship? Should we be concerned? What's your analysis on what's happening there? Jason Isaacson: What we have seen, what we have heard from President Biden now from Vice President Harris, from Secretary of State Blinken, from others, of course, is concerning. But these statements expressing criticism of any efforts in Israel, to weaken the independence of the Israeli judiciary, to change the balance of power in a way that is rushed through the legislature and not arrived at through a deliberative, inclusive, careful process. These are the expressions of concern of a friend. President Biden is a longtime friend of Israel for 40 plus years in politics, he has always stood by Israel, his relationship with Prime Minister Netanyahu goes back that long, and with previous prime ministers as well, and other officials, he's visited many times. He is pointing out the importance of maintaining the spirit that unites the United States and Israel in so many ways. It is not just, this is an unusual relationship, it's a special relationship. It's a relationship. It's not just built on strategic interests. It's built on a very deep emotional bond, frankly, between the people of the United States and the people of Israel. It has a religious connection, it has a historic connection. It has a love of freedom and democracy that has been the animating principles of both of our countries for decades, or in the case, United States centuries. There is something unique in that relationship. And from the point of view of this president who has a love affair with Israel going back for decades, that shared spirit of democracy is being threatened by this rush to change the system. That balances the rights of the judiciary and the rights of the elected legislature. And he has spoken about that with concern–with love of Israel, but with concern. Now, of course, no sovereign state likes a lecture from another country, from a great power. And it's not surprising that you had a sharp reaction to the President's words from Prime Minister Netanyahu and his supporters. But I would, I would point you to the long record of support that the President has expressed, which is, by the way, the tradition of US presidents in this relationship that exists between the United States and Israel, and must always exist, and that AJC has played a role in maintaining. But his words should be taken seriously. I do expect that once we get through this current crisis that there will be a visit of course by the Prime Minister. These are normal events in the life of our two countries. But right now, clearly, President Biden wanted to send a message, wanted to send a sharp message and make sure that it was heard clearly in Jerusalem. Belle Yoeli: And Jason, of course, we've spoken a lot. And we've been celebrating the Abraham Accords and thinking a lot here at AJC about what comes next and how we can expand upon that success. I would imagine that what's playing on Israel right now is potentially threatening to some of the relationships that have been built, and putting countries in the region and in sort of a precarious position in terms of their relationships with Israel. What are you hearing on that regard? Jason Isaacson: Well, you know, I think it's less of an issue, how Israel balances or rebalances the relationship between the judiciary and the legislative branch. These are issues that are really not very much on the radar screen of Israel's neighbors. What is on their radar screen, is the degree to which the Prime Minister– a figure, whom they have come to know over the years and developed relationships with and trust in. The degree to which he is in control, in control of his government and control of his society. The degree to which frankly, the high tech powerhouse of Israel remains on the course that it has been on, that has been such a beacon for the region and and a selling point of Israel in terms of the relationship that Israel's neighbors want to have with Israel, want to develop, want to nurture with Israel. And apart from that, apart from this appearance of control, or lack of control and appearance of what's going on in the Israeli economy and the high tech sector. And we all know that's all been rattled by what's been going on, is the actions and the statements of members of the governing coalition who are on the radical edge of Israeli politics and who have said some, some very sharp things about about Israel's Arab neighbors, Israel's Palestinian neighbors, the role of Israel going forward in the territories in settlement construction, in walking back the disengagement agreement through which Israel left Gaza and some settlements in the northern part of the West Bank. Some very offensive statements that have been made, including by the finance minister, who said, there was no such thing as the Palestinian people. And he did make some other statements or appeared behind a map that seemed to express the belief that Israel and Jordan were all part of one contiguous territory. These are things that have rattled some of Israel's neighbors and have led to some denunciations of Israeli behavior. Now, I don't believe that the Abraham Accords are in jeopardy, I don't believe that anyone's going to walk back from the strategic decisions that were made in 2020. To establish or in the case of Morocco reestablished diplomatic relations with Israel. What I do worry about is a cooling of these relationships at a lower trajectory of these relationships, which were soaring until just weeks ago. And AJC as you know, Belle, has been playing a role for many years in trying to open up these relations and open up civil society dialogue, we continue to do, we have a presence in Abu Dhabi, we are active across the region, we'll get back on that track. And I believe that there are so many friends and potential friends that still exist in the Arab world for a closer relationship with Israel, a mutually beneficial relationship with Israel. But the news that's been coming from the street in Israel, and from all sorts of elements of Israeli society have upset Israel's neighbors. And we need to get past this, we need to come up with a compromise that will allow this to be driven off the front page. And frankly, the more extreme elements of the Israeli governing coalition need to be reined in. Whether it means walking around the Temple Mount, a very sensitive place for many of Israel's neighbors, or it means various statements that are made. The prime minister said that he had his hands on the steering wheel, he was in control. As that is further demonstrated to Israel's neighbors, I expect that the situation will calm down, and we'll get back on the very significant upward trajectory that we've seen over the last two and a half years in the Abraham Accords process. Belle Yoeli: Jason, I'm encouraged by your optimism. And I just want to ask you one more question along the same lines. Obviously, this is a moment, this is a moment for the Israeli people. This is a moment for the Israeli government, and it's playing out and getting a lot of attention around the world. And of course, a lot of what I'll describe as Israel's enemies, or Israel's harshest critics, are in many cases monopolizing on this moment to say, everything that we've said about Israel is right, or this is the end of Israel's democracy. But as we've said, that's really not the case. What are your words of wisdom to really explain what's happening in this moment, when there is so much political polarization in Israel, there are competing visions for the state, but at the same time, we're celebrating 75 years of the wonder that is Israel and all the good that it brings to the world. How do we balance the hysteria and the concern of this moment, with optimism and what you were just talking about, that things will get back to normal, things will calm down, we will reach a compromise, we'll get there. What is the message that you really want to send about where things are going? And how we should be thinking about this going forward? Jason Isaacson: Can you imagine any other country in the region, maybe not just in the region, in which a significant portion of the population would be out on the streets to defend a governmental system, a balance of power between branches of government, in opposition to what the current elected government has put forward? Hundreds of 1000s of citizens parading through the streets, carrying the Israeli flag, no violence, no destruction of property. When they have shut down major highways, when they have surrounded the Prime Minister's house. They're dispersed. No one gets shot, people aren't being put to jail. The spirit of engagement in the political process, of making your voice heard, of getting out on the street because you're a patriot, because you believe in the country you believe in the ethics of the country, the ethic of the country. And then, after weeks and weeks of this kind of citizen engagement, having a government that says, Okay, we hear you, we're going to take a pause, we're going to come up, we're going to see if we can find an acceptable compromise, even in that crazily diverse Israeli political system that we have. I think it's a remarkable piece of evidence, remarkable testament to the democratic spirit in Israel, the respect, the mutual respect that even people on different sides of the political spectrum have for each other and for the country, and for the processes that had built this country and kept it strong. Against all odds, against multiple challenges for 75 years. I have great confidence that this democratic spirit will prevail. I believe that a compromise is within reach, could be found. It is not unreasonable that there be a reexamination of the judicial-legislative balance, I think that they'll be able to find that. And by the way, if they cannot find it, Israel is a democracy. It has elections. It has had five elections in four years, it could have a sixth election. I have no doubt that the Israeli political spirit, which is a spirit of democracy, and a protection of human rights and protection of minority rights, will prevail, will get through this, and will go on for another 75, many more than another 75 years of this great miracle that is the state of Israel. Belle Yoeli: Jason, thank you so much for that. And thank you for sharing all of your thoughts and analysis with us. I just want to make a plug to our listeners, that I think this conversation has shown you why more than ever before, it's important to show up and to engage on these issues. And I want to encourage all of you who have not yet registered to join us in Israel in June for AJC's Global Forum 2023 in Tel Aviv, June 11 through 14th, you can sign up by going to AJC.org/GlobalForum. We hope to see you there, and to be with us as we engage in this very interesting time in Israel. Jason, thank you. Jason Isaacson: Thank you, Belle.
Mar 23, 2023
How Jewish Teens Take on Antisemitism in America
Jewish teenagers in middle and high schools throughout the United States are experiencing antisemitism in various forms, including in their school premises, in the classroom, and on social media. Abi Streger, a Jewish student from suburban Atlanta, is one of the many teenagers who have faced such hatred. Joining the conversation is Aaron Bregman, Director of High School Affairs for AJC's Alexander Young Leadership Department, who speaks about how AJC empowers students and their families to stand up to antisemitism. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Aaron Bregman, Abi Streger _____ Show Notes: Test your knowledge: Test your knowledge of antisemitism in America : Stopping antisemitism starts with understanding how dangerous it is. Take our quiz and learn how antisemitism impacts American Jewish life. Read: In Washington, D.C., Jewish High School Students from AJC's Leaders for Tomorrow Gain Valuable Advocacy Skills : More than 130 of American Jewish Committee's (AJC) Leaders for Tomorrow (LFT) students – Jewish high school students from across the U.S. – gathered in Washington, D.C. this week to speak up for Israel and the Jewish people during the Susan and Bart Lewis Family Leaders for Tomorrow Advocacy Day. Listen: How Rising Antisemitism Impacts Jews on College Campuses : Unpack the findings from AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2022 report on young U.S. Jews, including those on college campuses, with the Senior Director of AJC's Alexander Young Leadership Department, Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman. We also hear from Northwestern University student Lily Cohen. A White House Meeting with Antisemitism Envoys from Around the World : Two weeks ago at the White House, a group of antisemitism envoys from around the world attended an AJC-convened gathering as part of the efforts of an interagency group created by President Biden to build a national strategy to combat antisemitism. Two of those envoys join us to discuss that meeting. Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Mar 16, 2023
A White House Meeting with Antisemitism Envoys from Around the World
Two weeks ago at the White House, a group of antisemitism envoys from around the world attended an AJC-convened gathering as part of the efforts of an interagency group created by President Biden to build a national strategy to combat antisemitism. This week, two of those envoys, senior European antisemitism officials from the EU and Germany join us to discuss that meeting and share how their governments have addressed rising antisemitism. Katharina von Schnurbein, European Commission Coordinator on Combating Antisemitism and Fostering Jewish Life, and Felix Klein, Federal Government Commissioner for Jewish Life in Germany and the Fight Against Antisemitism, also discuss their experiences fighting Jew-hatred in Europe and their impressions of the state of antisemitism in the United States . Klein is also an alumnus of Project Interchange , an AJC institute that brings global decision-makers to Israel to learn about its reality and complexity for themselves. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Katharina von Schnurbein, Felix Klein _____ Show Notes: Read: International Antisemitism Envoys Join AJC-Convened Meeting at White House - American Jewish Committee (AJC) convened a meeting at the White House of antisemitism envoys from around the world as part of the efforts of an interagency group created by President Biden to build a national strategy to combat antisemitism. American Jews Shouldn't Be Afraid to Be Jewish - In this Newsweek column, AJC CEO Ted Deutch writes that urgently creating and implementing the first-ever national action plan to effectively combat antisemitism in the U.S. is essential. The safety of Jews and the health of our society are at stake. Be Part of the Society-Wide Effort - AJC's Call to Action Against Antisemitism in America is a dynamic tool to mobilize and unite all Americans in the fight against antisemitism. Read the Call to Action . Watch: How Can Governments Win the Fight Against Antisemitism? - At AJC Global Forum 2022, Katharina von Schnurbein joined U.S. Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Antisemitism Deborah Lipstadt to share how American and European governments are responding to the frightening resurgence of antisemitism. Listen: 87 Ways to Fight Antisemitism: Inside the EU's New Plan to Combat Hate - When the EU unveiled its first Strategy on Combating Antisemitism and Fostering Jewish Life, a multi-faceted plan that incorporated many recommendations from AJC, Katharina von Schnurbein shared how that strategy is being implemented and what it means for European Jews and the entire Jewish diaspora. Women's History Month: Meet Felice Gaer, Human Rights Champion - She's one of the world's most effective champions of women's rights, human rights, and democratic values. For Women's History Month, we speak with Felice Gaer, director of American Jewish Committee's Jacob Blaustein Institute for the Advancement of Human Rights. Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Mar 8, 2023
Women's History Month: Meet Felice Gaer, Human Rights Champion
She's one of the world's most effective champions of women's rights, human rights, and democratic values. For Women's History Month, we speak with Felice Gaer, director of American Jewish Committee's Jacob Blaustein Institute for the Advancement of Human Rights. Gaer, who fights for religious freedom, the rights of women, and against antisemitism, highlights the importance of women's voices in an often-male dominated field. She has been appointed to the US Commission on International Religious Freedom, serving five terms (three as chair and two as vice chair), and was the first American elected to serve on the UN's Committee Against Torture. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. _____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Felice Gaer _____ Show Notes: Read: JBI Appeal on the One-Year Anniversary of the Russian Invasion of Ukraine Listen: 10 Trailblazing Jewish Women on AJC's People of the Pod Dr. Ahmed Shaheed on first UN human rights report wholly dedicated to antisemitism Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. _____ Transcript of Interview with Felice Gaer Manya Brachear Pashman: Felice Gaer has served as the director of AJC's Jacob Blaustein Institute for the Advancement of human rights, affectionately known here as JBI since 1993. During that time, she has specifically focused on the rights of religious freedom, the rights of women, the prohibition of torture and the struggle against antisemitism globally. She has been appointed a public member of at least nine US delegations to United Nations Human Rights negotiations, including the Vienna World Conference on human rights in 1993. And the Beijing World Conference on Women in 1995. She was the first American elected to serve on the UN's Committee Against Torture. In fact, she served five terms, and she was appointed to the US Commission on International Religious Freedom, where she served as chair and advised the President and Congress on US human rights policy. And even though she's not a lawyer or a court justice, on March 30, she receives the Honorary Member award of the American Society of International Law, the preeminent international society in this field, as we mark International Women's Day this week and women's history this month, Felice is with us now to discuss today's human rights challenges and the challenges she has faced as a woman in the Human Rights world. Felice, welcome to People of the Pod. Felice Gaer: Thank you, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's start with the beginning. Can you share with our listeners a little about your upbringing, and how Jewish values shaped what you do today? Felice Gaer: Well, I had a fairly ordinary upbringing in a suburb of New York City that had a fairly high percentage of Jews living in it–Teaneck, New Jersey. I was shaped by all the usual things in a Jewish home. First of all, the holidays. Secondly, the values, Jewish values, and awareness, a profound awareness of Jewish history, the history of annihilation, expulsion, discrimination, violence. But also the Jewish values of universality, respect for all human life, equality before the law, sense of realism, sense that you can change your life by what you do, and the choices that you make. These are all core Jewish values. And I guess I always have found the three part expression by Rabbi Hillel to sum up the approach I've always taken to human rights and most other things in life. He said, If I'm not for myself, who will be, and if I'm only for myself, what am I? And if not now, when? So that's a sense of Jewish particularism, Jewish universalism, and realism, as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: You went to Wellesley, class of 1968, it's an all-women's college. Was there a strong Jewish presence on campus there at a time? And did that part of your identity even play a role in your college experience? Felice Gaer : Well, I left, as I said, a town that had a fairly sizable Jewish population. And I went to Wellesley and I felt like I was in another world. And so even as long ago as 1964-65, that era, I actually reached out to Hillel and participated in very minor activities that took place, usually a Friday night dinner, or something like that. But it really didn't play a role except by making me recognize that I was a member of a very small minority. Manya Brachear Pashman: Here on this podcast, we've talked a lot about the movement to free Soviet Jewry. As you pursued graduate work at Columbia, and also during your undergrad days at Wellesley, were you involved in that movement at all? Felice Gaer: Well, I had great interest in Russian studies, and in my years at Wellesley, the Soviet Union movement was at a very nascent stage. And I remember arguments with the Soviet Ambassador coming to the campus and our specialist on Russian history, arguing about whether this concern about the treatment of Soviet Jews was a valid concern. The professor, who happened to have been Jewish, by the way, argued that Jews in the Soviet Union were treated badly, but so was everybody else in the Soviet Union. And it really wasn't something that one needed to focus on especially. As I left Wellesley and went to Columbia, where I studied political science and was at the Russian Institute, now the Harriman Institute, I found that the treatment of Soviet Jews was different in many ways, and the capacity to do something about it was serious. We knew people who had relatives, we knew people who wanted to leave. The whole Soviet Union movement was focused around the desire to leave the country–not to change it–that was an explicit decision of Jewish leaders around the world, and in the Soviet Union itself. And so the desire to leave was something you could realize, document the cases, bring the names forward, and engage American officials in a way that the Jewish community had never done before with cases and examples demanding that every place you went, every negotiation that took place, was accompanied by lists of names and cases, whose plight will be brought to the attention of the authorities. And that really mobilized people, including people like me. I also worked to focus on the agenda of internal change in the Soviet Union. And that meant also looking at other human rights issues. Why and how freedom of religion or belief was suppressed in this militantly atheist state, why and how freedom of expression, freedom of association, and just about every other right, was really severely limited. And what the international standards were at that time. After I left Columbia, that was around the time that the famous manifesto from Andrei Sakharov, the world famous physicist, Nobel Prize winner, was made public. It was around the time that other kinds of dissident materials were becoming better known about life inside the Soviet Union post-Khrushchev. Manya Brachear Pashman: So you left Colombia with a master's degree, the Cold War ends, and you take a job at the Ford Foundation that has you traveling all around Eastern Europe, looking to end human rights abuses, assessing the challenges that face that region. I want to ask you about the treatment of women, and what you witnessed about the mistreatment of women in these regions. And does that tend to be a common denominator around the world when you assess human rights abuses? Felice Gaer: Well, there's no question that the treatment of women is different than the treatment of men. And it's true all over the world. But when I traveled in Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union in the height of those years, height of the Cold War, and so forth, the issues of women's rights actually weren't one of the top issues on the agenda because the Soviet Union and East European countries appeared to be doing more for women than the Western countries. They had them in governance. They had them in the parliament. They purported to support equality for women. It took some years for Soviet feminists, dissidents, to find a voice and to begin to point out all the ways in which they were treated in the same condescending, patriarchal style as elsewhere. But in those years, that was not a big issue in the air. It was unusual for me, a 20-something year old woman from the United States to be traveling around Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union, meeting with high officials and others, and on behalf of the Ford Foundation, trying to develop programming that would involve people to people contacts, that would involve developing programs where there was common expertise, like management training, and things of that sort. And I was really an odd, odd duck in that situation, and I felt it. Manya Brachear Pashman: I mentioned in my introduction, the Beijing World Conference on Women, can you reflect a little on what had a lasting impact there? Felice Gaer: Well, the Beijing World Conference on Women was the largest, and remains the largest conference that the United Nations has ever organized. There were over 35,000 women there, about 17,000 at the intergovernmental conference. I was on the US delegation there. The simple statement that women's rights are human rights may seem hackneyed today. But when that was affirmed in the 1995 Beijing Outcome Document, it was a major political and conceptual breakthrough. It was largely focused on getting the UN to accept that the rights of women were actually international human rights and that they weren't something different. They weren't private, or outside the reach of investigators and human rights bodies. It was an inclusive statement, and it was a mind altering statement in the women's rights movement. It not only reaffirmed that women's rights are human rights, but it went further in addressing the problems facing women in the language of human rights. The earlier world conferences on women talked about equality, but they didn't identify violations of those rights. They didn't demand accountability of those rights. And they said absolutely nothing about creating mechanisms by which you could monitor, review, and hold people accountable, which is the rights paradigm. Beijing changed all that. It was a violations approach that was quite different from anything that existed before that. Manya Brachear Pashman : Did anything get forgotten? We talked about what had a lasting impact, but what seems to have been forgotten or have fallen to the wayside? Felice Gaer: Oh, I think it's just the opposite. I think the things that were in the Beijing conference have become Fuller and addressed in greater detail and are more commonly part of what goes on in the international discourse on women's rights and the status of women in public life. And certainly at the international level that's the case. I'll give you just one example, the Convention Against Torture. I mean, when I became a member of the committee, the 10 person committee, I was the only woman. The committee really had, in 11 years, it had maybe said, four or five things about the treatment of women. And the way that torture, ill treatment, inhuman, degrading treatment may affect women. It looked at the world through the eyes of male prisoners in detention. And it didn't look at the world through the eyes of women who suffer private violence, gender based violence, that is that the state looks away from and ignores and therefore sanctions, and to a certain extent endorses. And it didn't identify the kinds of things that affect women, including women who are imprisoned, and why and where in many parts of the world. What one does in terms of education or dress or behavior may lead you into a situation where you're being abused, either in a prison or outside of prison. These are issues that are now part of the regular review, for example, at the Committee Against Torture, issues of of trafficking, issues of gender based violence, the Sharia law, the hudud punishments of whipping and stoning, are part of the concern of the committee, which they weren't before. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, having that woman's perspective, having your perspective on that committee was really important and really changed and broadened the discussion. Felice Gaer: Absolutely. When I first joined the committee, the first session I was at, we had a review of China. And so I very politely asked a question about the violence and coercion associated with the population policy in China, as you know, forced abortions and things of that sort. This was a question that had come up before the women's convention, the CEDAW, and I thought it was only appropriate that it also come up in the Committee Against Torture. In our discussion afterwards, the very stern chairman of the committee, a former constable, said to me, 'You know, this might be of interest to you, Ms. Gaer, but this has nothing to do with the mandate of this committee.' I explained to him why it did, in some detail. And when I finished pointing out all of those elements–including the fact that the people carried out these practices on the basis of state policy–when I finished, there was a silence. And the most senior person in the room, who had been involved in these issues for decades, said, 'I'm quite certain we can accommodate Ms. Gaer's concerns in the conclusions,' and they did. That's the kind of thing that happens when you look at issues from a different perspective and raise them. Manya Brachear Pashman: You talked about being an odd duck in your 20s, as a woman traveling around Eastern Europe, trying to address these challenges. I'm curious if that woman in her 20s would have been able to stand up to this committee like that, and give that thorough an explanation? Or did it take some years of experience, of witnessing these issues, perhaps being ignored? Felice Gaer: Well, I think as we go through life, you learn new things. And I learned new things along the way. I learned about the universal norms, I learned about how to apply them, how they had been applied, and how they hadn't been applied. And in that process, developed what I would say is a sharper way of looking at these issues. But the Bosnian conflict in particular, made the issue of gender based violence against women, especially in war, but not only in war, into a mainstream issue, and helped propel these issues, both inside the United Nations and outside, the awareness changed. I remember asking the International Red Cross representatives in Croatia, just across the border from Bosnia, if they had encountered any victims of gender based violence or rape, and they said, 'No.' And I said, 'Did you ask them about these concerns?' And they sort of looked down and looked embarrassed, looked at each other and looked back at me and said, 'Oh.' There were no words. There were no understandings of looking at the world this way. And that has changed. That has changed dramatically today. I mean, if you look at the situation in Ukraine, the amount of gender based violence that has been documented is horrifying, just horrifying, but it's been documented. Manya Brachear Pashman So is the world of human rights advocacy male-dominated, female-dominated, is it fairly balanced these days? And has that balance made the difference in what you're talking about? Felice Gaer: You know, I wrote an article in 1988, the 40th anniversary of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, about why women's rights weren't being addressed. And one of the points I drew attention to was the fact that the heads of almost all the major organizations at the time were all male. And that it wasn't seen as a concern. A lot of that has changed. There's really a real variety of perspectives now that are brought to bear. Manya Brachear Pashman: So we've talked a lot about the importance of [a] woman's perspective. Does a Jewish perspective matter as well? Felice Gaer: Oh, on every issue on every issue and, you know, I worked a great deal on freedom of religion and belief, as an issue. That's a core issue of AJC, and it's a fundamental rights issue. And it struck me as surprising that with all the attention to freedom of religion, the concern about antisemitic acts was not being documented by mainstream human rights organizations. And it wasn't being documented by the UN experts on freedom of religion or belief either. I drew this to the attention of Dr. Ahmed Shaheed, who was recently ending his term as Special Rapporteur on Freedom of religion or belief. And he was really very struck by this. And he went, and he did a little bit of research. And he found out that since computerized records had been prepared at the United Nations, that there had been no attention, no attention at all, to cases of alleged antisemitic incidents. And he began a project to record the kinds of problems that existed and to identify what could be done about it. We helped him in the sense that we organized a couple of colloquia, we brought people from all over the world together to talk about the dimensions of the problem and the documentation that they did, and the proposals that they had for addressing it. And he, as you may recall, wrote a brilliant report in 2019, setting out the problems of global antisemitism. And he followed that up in 2022, before leaving his position with what he called an action plan for combating antisemitism, which has concrete specific suggestions for all countries around the world as to what they can do to help combat antisemitism and antisemitic acts, including and to some extent, starting with adopting the working definition on antisemitism of the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance, but also activities in in the area of education, training, training of law enforcement officials, documentation and public action. It's a real contribution to the international discourse and to understanding that freedom of religion or belief belongs to everyone. Manya Brachear Pashman: And do you believe that Dr. Shaheed's report is being absorbed, comprehended by those that need to hear it that need to understand it? Felice Gaer I've been delighted to see the way that the European Union has engaged with Dr. Shaheed and his report has developed standards and expectations for all 27 member states, and that other countries and other parts of the world have done the same. So yeah, I do think they're engaging with it. I hope there'll be a lot more because the problem has only grown. Manya Brachear Pashman: On the one year anniversary of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, JBI issued a report that sounded the alarm on the widespread violations committed against Ukrainians, you mentioned the amount of gender based violence Since that has taken place, and the other just catastrophic consequences of this war. Felice, you've been on the front row of Eastern European affairs and human rights advocacy in that region. From your perspective, and I know this is a big question: How did this war happen? Felice Gaer: I'll just start by saying: it didn't start in 2022. And if you have to look at what happened, the events of 2014, to understand the events of 2022. Following the breakup of the Soviet Union, or even during the breakup, there was a period where the 15th constituent Union republics of the Soviet Union developed a greater national awareness, really, and some of them had been independent as some of them hadn't been, but they developed a much greater awareness. When the Soviet Union collapsed, the 15 countries, including Russia, as one of the 15, became independent entities. And aside from having more members in the United Nations and the Council of Europe and places like that, it led to much more robust activity, in terms of respecting human rights and other areas of endeavor in each of those countries. The situation in Russia, with a head of state who has been there, with one exception, a couple of years, for 20 years, has seen an angry desire to reestablish an empire. That's the only thing you can say really about it. If they can't dominate by having a pro-Russian group in charge in the country, then there have been invasions, there have been Russian forces, Russia-aligned forces sent to the different countries. So whether it's Georgia, or Moldova, or Ukraine, we've seen this pattern. And unfortunately, what happened in 2022, is the most egregious and I would say, blatant such example. In 2014, the Russians argued that it was local Russian speaking, little green men who were conducting hostilities in these places, or it was local people who wanted to realign with Russia, who were demanding changes, and so forth. But in the 2022 events, Russia's forces invaded, wearing Russian insignia and making it quite clear that this was a matter of state policy that they were pursuing, and that they weren't going to give up. And it's led to the tragic developments that we've all seen inside the country, and the horrific violence, the terrible, widespread human rights violations. And in war, we know that human rights violations are usually the worst. And so the one good spot on the horizon: the degree to which these abuses have been documented, it's unprecedented to have so much documentation so early in a conflict like this, which someday may lead to redress and accountability for those who perpetrated it. But right now, in the middle of these events, it's just a horror. Manya Brachear Pashman: What other human rights situations do we need to be taking more seriously now? And where has there been significant progress? Felice Gaer: Well, I'll talk about the problem spots if I may for a minute. Everyone points to North Korea as the situation without parallel, that's what a UN Commission of Inquiry said, without parallel in the world. The situation in Iran? Well, you just need to watch what's happened to the protesters, the women and others who have protested over 500 people in the streets have died because of this. 15,000 people imprisoned, and Iran's prisons are known for ill treatment and torture. The situation in Afghanistan is atrocious. The activities of the Taliban, which they were known for in the 1990s are being brought back. They are normalizing discrimination, they are engaged in probably the most hardline gender discrimination we've seen anywhere where women can't work outside the home, girls can't be educated, political participation is denied. The constitution has been thrown out. All kinds of things. The latest is women can't go to parks, they can't go to university, and they can't work for NGOs. This continues. It's a major crisis. Well, there are other countries, from Belarus, to Sudan to Uzbekistan, and China, that we could also talk about at great length, lots of problems in the world, and not enough effort to expose them, address them and try to ameliorate them. Manya Brachear Pashman So what do we do about that? What can our listeners do about that, when we hear this kind of grim report? Felice Gaer: Work harder. Pay attention when you hear about rights issues. Support rights organizations. Take up cases. Seek redress. Be concerned about the victims. All these things need to be done. Manya Brachear Pashman: I don't know how you maintain your composure and your cool, Felice, because you have faced so much in terms of challenges and push back. So thank you so much for all you have done for women, for the Jewish people, and for the world at large. Thank you, thank you, thank you. Felice Gaer: Thank you, Manya.
Feb 28, 2023
How to Support Jews of Color
Rabbi Sandra Lawson, Reconstructing Judaism's first director of racial diversity, equity and inclusion, joins us to talk about how you can support Jews of color. The social media influencer uses her platform both online and off as a queer Jew of color to drive hard conversations around racism, homophobia, and antisemitism. Rabbi Lawson, who feels a deep responsibility to serve American Jews, is full of Jewish pride amid a rise in anti-Jewish hate. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Rabbi Sandra Lawson ____ Show Notes: Check out: AJC's State of Antisemtism in America Report 2022 Take this quiz to test your knowledge of how antisemitism impacts America and its Jewish population The Power of Joy: Reflections on the Jewish Month of Adar by Rabbi Sandra Lawson Listen: Our most recent podcast episode: The Jewish Experience in Ukraine Amidst Russia's Invasion Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Feb 23, 2023
The Jewish Experience in Ukraine Amidst Russia's Invasion
One year after Russia's illegal invasion of Ukraine, Vladislav Davidzon, European culture correspondent for Tablet Magazine, shares what he's witnessed as a war correspondent on the frontlines, and predicts the future for his beloved country and the Jewish community he's proud to call home. We last spoke to Davidzon hours before the Russia-Ukraine war began, when he was on the ground in Kyiv – listen now to his dispatch a year on, as he joins us live from our New York studio. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Vladislav Davidzon ____ Show Notes: Read: What You Need to Know About the Wagner Group's Role in Russia's War Against Ukraine Preorder: Jewish-Ukrainian Relations and the Birth of a Political Nation Watch: Kiyv Jewish Forum: Ted Deutch, AJC CEO, Addresses Kyiv Jewish Forum 2023 Panel: Ukraine as the Israel of Europe with Simone Rodan-Benzaquen, Managing Director of AJC Europe, Bernard Henry Levi, philosopher, and Josef Joffe, Stanford University Listen: Podcast episode with Vladislav Davidzon, recorded February 23, 2022: Live from Kyiv: The Future of Ukraine and its Large Jewish Community Our most recent podcast episode: How Rising Antisemitism Impacts Jews on College Campuses Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. ______ Transcript of Interview with Vladislav Davidzon : Manya: On February 24th, 2022, just hours before the Russian invasion of Ukraine began, Vladislav Davidzon, founding editor of The Odessa Review and contributor to Tablet Magazine, joined us live from Kiyv to share the mood on the ground as Russian forces were closing in. Now, one year later, Vladislav joins us again, this time in person, in our studio to share what he has seen, heard, and experienced this past year since the Russian invasion of his home. Vladislav, it is so good to see you alive and well and in person. Vladislav: Thank you so much. This is so surreal. I'm so grateful, first of all, for your interest, for your affection, for your graciousness, for your respect. But I'm grateful to be here exactly one year later. It was the last thing that I did in the workday before the war began, before the old world ended. And I went off to dinner with my friend, now of blessed memory, Dan Rappaport, who was an American Latvian born Jewish financier. It was also the last time I saw him. He died under very suspicious circumstances. He died falling out of a window in Washington, DC, or of a roof, on the seventh floor, three months later. I just have extremely intense emotions about that six hour period because…I was talking to my wife, my wife's French Ukrainian, she was back in Paris. I said, if anything happens tonight, I'll call you in the morning. Things are gonna go down tonight. And then I did this podcast with you. And so, it's really amazing to be back with you a year later. Manya: Yes. I mean, I am so grateful to see you because I really was very worried. I worried that that was going to be our last conversation, and that I would not get a chance to meet you in person after that. And in addition to everything, you've been working on a book, The Birth of a Political Nation, which we'll talk a little bit more about shortly. But, first tell me, tell our listeners how you have managed to survive and tell the stories that need to be told. Vladislav: It's not pretty. I mean, it's just, it's not elegant. I'm a Ukrainian Russian Jew, so I kind of went into primordial, bestial mode, like Russian Ukrainian, Jewish survival mode, like my grandfathers and great-grandfathers during World War II. I just, you know, something clicked and your your training and your skillset and your deep cultural characteristics click in and you just go full on Hemingway, Lord Byron, and then you just go to war. Like a lot of other people, I went to war. I burned out after about six months and I needed some months off. I was just rnning around like a madman, reporting, getting my own relatives out, helping whatever way I could, helping my family close down their businesses, helping run guns, going on t radio, you know, just collecting money, going to the front, just, going off on an adrenaline rush. And it's admixture of rage, testosterone. Adrenaline, survival, rage, all the cocktail of horrific, let's say toxic masculine character [laughs]. I know you can't, I I know. I'm ironic about that. I live in Eastern Europe, so you can, you can still make fun of all that stuff in Eastern Europe. I don't know if you can here, but, you know, jokes aside. I just went into this deeply primordial state of Ukrainian Russian civilizational structures of brutal survival and fighting. And that went on for about six months, at which point I just crashed and collapsed and needed some off time. Manya: How much of your journalistic instincts also fueled your push on, your forging ahead and surviving just to tell the story, or was it more a familial connection? Vladislav: I have skin in the game. I'm from there. I mean, my ancestors are from there, two of my grandparents were born there. My family lived there for hundreds of years. I'm married to a Ukrainian Jewish girl. I have family there. My friends are, these are my people. I'm deeply tribal. Obviously you take the opportunity as a journalist reporting on a country for 10 years and almost no one cares about it. And you're an expert on it. You know all the politicians and you know all the, all the stories and you know all the storylines. And you, you have contacts everywhere. You know, of a country like the back of your hand. And suddenly it becomes the focal point of the world's attention and it becomes the greatest story in the entire world. And of course, you're prepared in a way that all, all these other people who paratroop in are not prepared, and you have to make the best of it. And you have to tell stories from people who wouldn't otherwise have access to the media. And you have to explain, there's so much bad stuff in terms of quality of reporting coming out of Ukraine because so many amateurs went in. In any given situation, there are lots of people who come to a war zone. You know, in wars, people, they make their bones, they become rich, they become famous, they get good looking lovers. Everyone gets paid in the currency that they want. Right? But this is my country. I've been at this for 10, 12 years. I don't begrudge anyone coming to want to tell the story. Some people are opportunists in life and some people are extraordinarily generous and gracious. And it almost doesn't matter what people's motivations are. I don't care about why you came here. I care about the quality of the work. And a lot of the work was pretty bad because people didn't have local political context, didn't have language skills. And a lot of that reporting was so-so. I made the most of it, being an area expert. And also being a local, I did what I had to do. I wish I'd done more. I wish I went 500% as opposed to 250%. But everyone has their limits. Manya: What got lost? With the poor reporting, what do you think with the stories that you captured, or what do you wish you had captured, giving that additional 250%? Vladislav: Yeah. It's a great question. I wish that I had known now what I know a year ago, but that's life in general. About where the battles would be and what kinds of people and what kinds of frontline pounds would have particular problems getting out to particular places. For example, I know now a lot more about the evacuation of certain ethnic communities. The Gagauz, the Greeks. Ukraine is full of different kinds of people. It's a mosaic. I know now a lot about the way that things happened in March and April. Particular communities went in to help their own people. Which is great. It's fine. a lot of very interesting characters wound up in different places. Much of Ukrainian intelligentsia, they wound up outside the country. A lot stayed, but a lot did wind up in different places like Berlin and the Baltics. Uh, amazing stories from, uh, the volunteers like the Chechens and the Georgians and the Lithuanians and the Belarus who came to fight for Ukraine. Just, you know, I wish I'd kept up with the guys that I was drinking with the night before. I was drinking with like six officers the night before, and two of 'em are alive. Mm or three alive now. I was with the head of a Georgian Legion two nights before the war. Hang out with some American CIA guys and people from the guys from the American, actually a couple of girls, also hardcore American girls from the US Army who were operatives and people at our embassy in Kyiv who didn't get pulled out. These are our hardcore people who after the embassy left, told whoever wanted to stay on the ground to stay. I met some very interesting people. I wish I'd kept up with them. I don't, I don't know what happened with them or what, what their war experiences were like. So, you know. Yeah. Life is full of regrets. Manya: You talked a little bit about the ethnic communities coming in to save people and to get them out. How did the Jewish communities efforts to save Ukrainian Jews compare to those efforts? Did you keep tabs on that? Movement as well. Vladislav: Oh, yeah. Oh, in fact, I worked on that actually, to certainly to a smaller extent than other people or whatever. I certainly helped whatever I could. It was such a mad scramble and it was so chaotic in the beginning of a war. The first two weeks I would be getting calls from all over the world. They would call me and they would say this and this and this person, I know this person needs to get out. There were signal groups of volunteers, exfiltration organizations, special services people, my people in the Ukrainian Jewish community who were all doing different things to get Jews out. Tens of thousands of people were on these lists. And I would figure out to the extent possible with about 50 people, 40 to 50 people, what their risk level was. And I would give 'em advice. I have a gay friend, one of my wife's business partners, who was the head of a major television station. And he would, he would've been on the Kill list because he was in part of intelligentsia and he was gay. I gave him particular advice on where to go. I said, go to this village–and men aren't allowed of the country, and he wasn't the kind of guy who was gonna fight. I said, go to a particular place. I told him, go to this village and sit here and don't go anywhere for two months. And he did this. Other people needed to be gotten out. Holocaust survivors, especially. We have horrific incidents of people who survived Stalin's war and Hitler's war and who died of heart attacks under their beds, hiding from Russian missiles. There were many stories of Holocaust survivors. Typically, it's old women by this point. It's not it's not gentleman. Women do live longer. Older women in their nineties expiring in a bunker, in an underground metro station or under their bed hiding from missiles, you know. Horrific stories. but people who survived Auschwitz did get killed by the missiles. We have stories like that. And so to continue, there were many people working on getting elderly Jews out. Getting Jewish women out. Jewish kids out. There were, in fact, there were people working on getting all sorts of people out. And that's still going on. And I met a Jewish member of the Ukrainian parliament last night who did this for two months. Uh, I saw, I saw my acquaintance who I hadn't seen in two years. Yeah. There are a lot of people I haven't seen in a year, obviously, for the obvious reasons. I saw an acquaintance who's an Israeli educated Ukrainian member of parliament. He spent the first three months just evacuating Jews, driving convoys of special forces guys, former Mossad guys, special operatives into cities like Mariupol, Chernigev to get Jews out. Literally driving through minefields at a certain point with buses full of elderly Jews. And he told me last night that they got 26,000 Jews out. Just in his organization, which was Special Forces guys, Ukrainian police volunteers, Ukrainian Jewish guys who came back from Israel with IDF training, a motley collection of people. But they set up an organization and they went in, and they got people out. Manya: That's amazing. So I know before, when we spoke before you were splitting your time between Ukraine and France, because your wife is of French descent as well. For your most recent piece for Tablet, the most recent one that I've read, you were in Tel Aviv doing an interview. So where have you spent most of your time, in this past year? Vladislav: In my head. Manya: Yeah. Understandable. Vladislav: I've spent, if I had to count up the dates of my passport, 40 to 50% of my time in Ukraine, over the last, less than the last three months for various family reasons and, you know, working on my book But half the time in Ukraine, in and out. I've been all over, spent a lot of time on the front. That was intense. That was really intense. Manya: You mean as a war correspondent on the front lines? Vladislav: Yeah,I was in Sievierodonetsk, Kharkiv, Kherson, Lysychansk, Mykolaiv. I was all over the front. I was with the commanding general of the Southern front in a car, driving back from the battle of Kherson, and we got stripped by a Russian sniper three times and they hit our car. They just missed by like a couple of centimeters, side of a thing. And the guy actually usually drove around in an armored Hummer. But the armored Hummer was actually in the shop getting repaired that day and was the one day he had an unarmored Hummer. And we were just in an unarmed car, in an unarmed command car, black Mercedes, leaving the war zone a couple of kilometers out, just a Russian reconnaissance sniper advanced group just, you know, ambushed us. They were waiting for us to, maybe they were just taking pot shots at a command car, but they were waiting for us as we were leaving. Took three shots at us and the car behind us with our bodyguards radioed, they're shooting, they're shooting. I heard three whooshes and three pings behind it. Ping, ping, ping. And we all thought in the car that it was just rocks popping off the the wheels. But actually it was a sniper. So, you know, there, there was a lot of that. It was very intense. Manya: Did you wear flak jackets? Vladislav: Yeah, well, we took 'em off in the car. When, when you're on the front line, you wear everything, but when you get out of the front line, and you're just driving back, you don't wanna drive around with it, so you just take it off in the car. And that's exactly when they started shooting us. Yeah. They would've gotten us, if they'd been a little bit luckier. Manya: Well, you moderated a panel at the Kiev Jewish Forum last week. Our CEO, Ted Deutch and AJC Europe Director Simone Rodan-Benzaquen, were also there. Your panel focused on the new Ukraine. What does that mean, the new Ukraine? What does that look like? Vladislav: Thank you for asking about that. Let me start with talking a little bit about that conference. Along with Mr. Boris Lozhkin, the head of Ukrainian Jewish Confederation. I put together with Tablet where I'm the European culture correspondent, wonderful, wonderful conference. It is the fourth annual Kiyv Jewish Forum. It took place in Kiyv for the last three years, but today, obviously this year, it won't be for the obvious reason and we put together a conference so that people understand the issues at stake, understand the position of Ukrainian Jewish community, understand the myriad issues involved with this war. Just a wonderful, wonderful conference that I really enjoyed working on with remarkable speakers. Running the gamut from Leon Panetta, Boris Johnson. Your own Mr. Deutch. Just wonderful, wonderful speakers. And, six really great panels, and 20 wonderful one-on-one interviews with really interesting people. So please go to the website of the Kiev Jewish Forum or Tablet Magazine and/or YouTube, and you'll find some really interesting content, some really interesting conversations, dialogues about the state of war, the state of Ukrainian Jewry, the state of Ukrainian political identity and the new Ukraine. Manya: I should tell our listeners, we'll put a link to the Kiyv Jewish Forum in our show notes so that they can easily access it. But yeah, if you don't mind just kinda elaborating a little bit about what, what does the new Ukraine look like? Vladislav: Well, we're gonna see what the new Ukraine will look like after the Russians are driven out of the country. It's gonna look completely different. The demographic changes, the political changes, the cultural changes will play out for decades and maybe a hundred years. These are historical events, which will have created traumatic changes to the country and to Eastern Europe, not just to Ukraine, but all of eastern Europe. From along the entire crescent, from Baltics to Poland, down to Hungary, through Moldova, Belarus. Everything will be changed by this war. This is a world historical situation that will have radically, radically changed everything. And so Ukraine as a political nation has changed dramatically over the last seven years since the Maidan revolution. And it's obviously changed a lot since the start of the war a year ago. It's a completely different country in many ways. Now, the seeds of that change were put into place by the political process of the last couple of years, by civil society, by a deep desire of the resilient Ukrainian political nation to change, to become better, to transform the country. But for the most part, the war is the thing that will change everything. And that means creating a new political nation. What that will look like at the end of this, that's hard to say. A lot of these values are deeply embedded. I know it's unfashionably essentialist to talk about national character traits, but you know, again, I'm an Eastern European, so I can get away with a lot of things that people can't here. And there are such things as national character traits. A nation is a collection of people who live together in a particular way and have particular ways of life and particular values. Different countries live in different ways and different nations, different people have different traits. Just like every person has a different trait and some are good and some are bad, and some are good in certain situations, bad in other situations. And everyone has positive traits and negative traits. And you know, Ukraine like everyone else, every other nation has positive traits. Those traits of: loving freedom, being resilient, wanting to survive, coming together in the times of war are incredibly generative in the middle of this conflict. One of the interesting things about this conflict that is shown, the way that all the different minorities in the country, and it's a country full of all kinds of people, all sorts of minorities. Not just Jews, but Greeks and Crimean Tatars, Muslims, Gagauz, Turkish speaking Christians in my own Odessa region, Poles on the Polish border, Lithuanian Belarus speakers on the Belarusian border. People who are of German descent, though there are a lot fewer of them since World War II. All sorts of different people live in Ukraine and they've come together as a political nation in order to fight together, in a liberal and democratic way. Whereas Russia's also an empire of many different kinds of people, And it's also been brought together through autocratic violence and authoritarian, centralized control. This is a war of minorities in many ways, and so a lot of the men dying from the Russian side are taken from the minority regions like Dagestan, Borodyanka, Chechnya. Disproportionate number of the men dying from the Russian side are also minorities, disproportionate to their share of the Russian Federation's population. In some circles it's a well known fact, one of the military hospitals on the Russian side, at a certain point, the most popular name amongst wounded soldiers, was Mohammed. They were Muslim minorities, from Dagestan, other places. There are a lot of Muslims in Russia. Manya: That is truly a heartbreaking detail. Vladislav: And they're the ones that are the poorest and they're the ones who are being mobilized to fight Ukrainians. Manya: So you're saying that literally the face of Ukraine, and the personality, the priorities of the nation have been changed by this war. Ukrainians have become, what, more patriotic, more militant? Militant sounds … I'm afraid that has a bad connotation. Vladislav: No, militant's great. You know, Marshall virtues. . . that's good. Militant is, you know, that's an aggressive word. Marshall virtues is a good word. Surviving virtues. It's amazing the way Ukrainian flags have encapsulated a kind of patriotism in the western world, which was in many ways unthinkable for large swaths of the advanced population. I mean, you see people who would never in a million years wave an American or British or French flag in Paris, London, and New York and Washington, wave around Ukrainian flags. Patriotism, nationalism have very bad connotations now in our decadent post-industrial West, and, Ukrainians have somehow threaded that needle of standing up for remarkable values, for our civilization, for our security alliances after the war, for the democratic world order that we, that we as Americans and Western Europeans have brought large swaths of the world, while also not becoming really unpleasantly, jingoistic. While not going into, racism for the most part, while not going into, for the most part into unnecessary prejudices. They fight and they have the best of traditional conservative values, but they're also quite liberal in a way that no one else in eastern Europe is. It's very attractive. Manya: They really are unified for one cause. You mentioned being shot at on the front lines of this war. This war has not only changed the nation, it has changed you. You've become a war correspondent in addition to the arts and culture correspondent you've been for so many years. And you've continued to report on the arts throughout this horrific year. How has this war shaped Ukrainian artists, its literary community, its performing arts, sports? Vladislav: First of all, unlike in the west, in, in Eastern Europe. I mean, these are broad statements, but for the most part, in advanced western democracies, the ruling classes have developed different lifestyles and value systems from much of the population. We're not gonna get into why that is the case, but I, as a insider-outsider, I see that. It's not the case in Eastern Europe yet, and certainly not in Ukraine. The people who rule the country and are its elites, they are the same culturally, identity wise as the people that they rule over. So the entire, let's say ruling elite and intelligentsia, artistic class. They have kids or sons or husbands or nephews at war. If we went to war now in America, much of the urban population would not have a relative who died. If a hundred thousand Americans died right now would not be, you would probably not know 10 people who died, or 15 people who died. Manya: It's not the same class system. Vladislav: Correct. America and the western world, let's say western European world from Canada down to the old, let's say Soviet borders or Polish borders, they have developed a class system, a caste system that we don't have. You could be a billionaire, and still hang out with your best friend from high school who was a worker or a bus driver. That doesn't happen here so often, for various reasons. And so a larger proportion of the intelligentsia and the artistic classes went to fight than you would expect. I know so many writers and artists and painters, filmmakers who have gone off to fight. A lot, in fact, I'd say swabs of the artist elite went off to fight. And that's very different from here. And this will shape the arts when they come back. Already you have some really remarkable, interesting things happening in, in painting. Not cinema because cinema's expensive and they're not really making movies in the middle of a war. Certain minor exceptions. There's going to be a lot, a lot of influence on the arts for a very long time. A lot of very interesting art will come out of it and the intelligentsia will be strengthened in some ways, but the country's losing some of its best people. Some of its very, very, very best people across the professions are being killed. You know, dozens of athletes who would've been competing next year in the '24 Olympics in Paris are dead on the front lines. Every week I open up my Twitter on my Facebook or my social media and I see another athlete, you know, pro skater or a skier or Cross Country runner or someone who is this brilliant 19, 20 year old athlete who's supposed to compete next year, has just been killed outside of Bakhmut or just been killed outside of Kherson or just been killed outside of Sloviansk or something like this. You read continuously and there's a picture of this beautiful, lovely, young person. who will never compete next year for a gold medal at the Olympics. You see continuously people with economics degrees, people who went to art school being killed at the front. So just as the army, as the Ukrainian army has lost a lot of its best men, a lot of its most experienced soldiers have been killed recently in Bakhmut and in other places, the intelligentsia is taking a wide scale hit. Imagine like 20-30% of America's writers, artists, people who went to art school getting killed at the front or something like that. I don't have statistics, but 10 to 15, 20%. Can you imagine that? What would that do to the society over the long term, If some of its best writers, people who won Pulitzer prizes, people who won national book awards wound up going to the army and getting killed? Manya: When this war ends… Vladislav: When we win, when we win. Manya: When you win, will there be a Ukrainian Jewish community like there was before? What do you see as the future of the Ukrainian Jewish community and how do you think the trauma of this conflict will impact that community? Vladislav: There will be a Jewish Ukrainian community, whether there will be a Russian Jewish community remains to be seen. There will be survivors of the community. A lot of people will go back, we'll rebuild. We will get our demographics back. A lot of people in Ukraine will have already stayed where they're going. There are already a lot of people who have left and after a year their kids got into a school somewhere in the Czech Republic or France or Germany. They're not coming back. There will be a lot of people who will have roots somewhere else. Within the community, certain cities, Jewish life will die out. What was left of the Lugansk, Donetsk Jewish communities is gone now. What was left of Donetsk Jewry is gone. There were a lot of Jews in Mariupol, thousands of Jews. Many of them who survived World War II. Certainly the Mariupol Jewish community has no future. None. Absolutely none. For the obvious reasons. The demographics of the Jewish communities have all changed and we're gonna see over time how all this plays out and sorts itself out. A lot of Jews from Odessa went into Moldova and they will come back. A lot of Jews from Dnipro have been displaced, although the city has not been touched. And they had the biggest Jewish community of like 65-70,000 Jews in Dnipro, and the wealthiest Jewish community and the best financed, the most synagogues. I actually went, before the battle of Sievierodonetsk, I went and I asked the rabbi of Dnipro for his blessing, cause I knew it was going to be a bloodbath. I didn't really want to die, so, you know, I'll try anything once. and it worked. Proofs in the pudding. I'm still here. He's done tremendous work in order to help Jewish communities there. One of the interesting parts of this is that little Jewish communities that had been ethnically cleansed by the Holocaust, which were on their way to dying, which did not have enough Jews in order to reproduce on a long timeline in Western Ukraine. Now because of the influx of Jews from other parts of the country, from the south especially and from the east, now have enough Jews in order for them to continue on. I don't know if anyone knows the numbers and it's too early to say. Places like Lviv had a couple of hundred Jews. They now have several thousand. There are at least three or four minor towns that I can think of in Western Ukraine, which were historically Jewish towns. which did not after the Holocaust, after, Soviet and Post-soviet immigration have enough of a Jewish population in order to have a robust community a hundred years from now, they now do. Now that is a mixed blessing. But the demographics of Jews inside Ukraine have changed tremendously. Just that the demographics of everything in Ukraine has changed tremendously when 40% of a population have moved from one place to another. 8 million refugees, something like 25- 40% of the country are IDPs. Lots of Jews from my part of Ukraine, from the South, have moved to West Ukraine. And those communities, now they're temporary, but nothing is permanent as a temporary solution, as the saying goes. I think Chernowitz, which never had the opportunity, I really love their Jewish community and they're great. And the rabbi and the head of community is a wonderful man. It did not seem to me, the three or four times that I'd visited before the war, Chernowitz, where my family's from, that this is a city that has enough Jews or Jewish institutional life to continue in 50 years. It does now. Is that a good thing, I don't know. That's a different question, but it's certainly changed some things, for those cities. Manya: Vladislav, thank you. Thank you for your moving reports and for joining us here in the studio. It has been such a privilege to speak with you. Please stay safe. Vladislav: Thank you so much for having me. I really appreciate it. It's really great to check in with you again one year after the last time we spoke.
Feb 13, 2023
How Rising Antisemitism Impacts Jews on College Campuses
Unpack the findings from AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2022 report on young U.S. Jews, including those on college campuses, with the Senior Director of AJC's Alexander Young Leadership Department, Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman. We also hear from Northwestern University student Lily Cohen, whose efforts to encourage constructive dialogue following a disturbing antisemitic encounter on her college campus has sparked hostility, friendship, and above all, a renewed sense of Jewish pride. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman and Lily Cohen ___ Show Notes: Read: AJC's State of Antisemtism in America Report 2022 Take this quiz to test your knowledge of how antisemitism impacts America and its Jewish population Cohen: I am more proud of my Jewish identity than anyone can ever hate me for it Listen: Our most recent podcast episode: Breaking Down the Headlines from Israel: From Secretary Blinken's Visit, to Terror Attacks, Protests, and More Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. ____ Transcript of Interview with Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman and Lily Cohen Manya Brachear Pashman: This week, AJC released its State of Antisemitism in America 2022 report, its fourth annual look at the perceptions of antisemitism among American Jews and the American public. So much has happened since AJC launched the annual survey in 2019, one year after the mass shooting at the Tree of Life synagogue in Pittsburgh, and so much has been learned, given the rise of antisemitism and anti-Zionism on college campuses. This year survey included new questions directed toward current and recent college students and their parents. Here to discuss the findings of those questions and more is an occasional guest host of this podcast, Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman. AJC 's Senior Director of the Alexander Young Leadership department. Meggie, thank you for bringing your expertise to that side of the mic. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Thanks for having me. Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: And with Meggie to share her own personal experience with antisemitism on campus. This school here is Lily Cohen, a junior at Northwestern University, whose efforts to encourage constructive dialogue on her college campus has sparked both hostility and friendship. Lily, welcome to People of the Pod. Lily Cohen: Thanks, Manya. Happy to be here. Manya Brachear Pashman: So, Meggie, I want to start with you. If you could please share with our listeners why this annual report is important, and what some of the more significant findings were? Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Thanks, Manya. So part of what makes our survey really unique is we're both looking at how antisemitism affects the lives, of the actions of American Jews, but we also compare that to how the American general public perceives that threat. And over the last year, it really feels like we're experiencing a surge in antisemitism that's particularly affecting young Jews within the campus space. But to actually gain a better understanding, we specifically surveyed those who are current students, or recent graduates, or parents of current students. And what we found supports those feelings, it really provides data, and in certain areas, unfortunately, a more dire picture. Some of our topline findings are: more than a third of current or recent Jewish college students encountered challenges on campus related to their Jewish identity. And what we found is that growing antisemitism is affecting the behaviors and decisions of young Jews today, both in person and online. One out of every five Jewish college students reported feeling unsafe on their university campus because of their Jewish identity. A staggering 85% of U.S. Jews between the ages of 18 to 29 have seen or were themselves targets of antisemitism online. Manya Brachear Pashman: 85%, wow, that is staggering. How much of that had to do with students' support for the existence of Israel? Or was that a separate finding? Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: I would say this is intrinsically linked to what we will hear from Lily, is that there's pushback students experienced when publicly supporting Israel, 14% say they have felt or have been excluded from a campus event or group because of assumed or actual connection to Israel. So these findings really speak to that level of fear and intimidation that we can't allow to become normalized on the college campus. Manya Brachear Pashman: Of course, AJC has been doing this report for four years, the questions for college students, about the college experience were new this year. But what are some of the constants that keep emerging each year that AJC does the report? Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: The constant, which is an unfortunate one, to be frank, is that antisemitism remains a real problem in American society. We found that 41% of American Jews reported the status of Jews being less secure than a year ago. That's 10 percentage points higher than 2021. That's a big number, a big jump. One in five feel unsafe when attending Jewish institutions with which they're affiliated. You mentioned what changed. And I think a reality is that the growing rate and feelings of antisemitism are creating a broader awareness within the American ecosystem. So over nine in 10 U.S. adults say that antisemitism is a problem for everyone and affects society as a whole. Fewer adults this year have discussed never hearing or knowing the term antisemitism, that went down from 16% in 2021, to nine this year. Manya Brachear Pashman: Meggie, in January of last year, someone entered a synagogue and Colleyville, Texas, and there was a hostage situation. Many people heard about this in the news, how did that affect people's anxieties when responding to this survey? Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Yeah, so that's something we asked about specifically. And the reality there is that it both increased concern around antisemitism within the Jewish community, while simultaneously raising awareness in broader society. And for those who might not remember all the details of that really harrowing experience, someone came into Congregation Beth Israel in Colleyville, Texas, a group was doing Shabbat services like so many of us do. He then took Rabbi Cytron-Walker and other Jewish worshipers hostage for 11 hours. And that motive, which is a really important part for us to understand here, was the release of someone named Aafia Siddiqui, herself in prison on terror charges, because he thought that due to antisemitic beliefs in Jewish control, that Jews would be able to make her release possible. And that false notion that Jews control media, banks, governments, that antisemitic conspiracy theory showcases how theories like that move into tangible threat. And of course, the heroism of Rabbi Cytron-Walker ultimately allowed for his escape and the escape of his fellow Jews inside. But that was a harrowing experience for Jews in this country and something where it felt like it could have been any of us. And our data shows that. So for American Jews who had heard of Colleyville, were aware of it, the majority said it made them feel less safe today. One in five American Jewish respondents feel unsafe attending Jewish institutions that they are affiliated with, because of fears of antisemitism. I personally think about that when I drop my daughter off at Jewish daycare. And I know I'm not alone in that. So the reality of the attack and growing attacks, just like in Colleyville, is that it's both adding very real fears to American Jewry, while simultaneously leading to increased awareness of antisemitism within the broader American public. Manya Brachear Pashman: As counterintuitive as it might seem, the finding that more people, more adults have heard the term and know the definition of antisemitism. That's actually a good thing when you can't take a stand against something or avoid it if you don't know what it is. And I think part of that awareness was because of Colleyville. But also because of the many other issues that were in the headlines. Kanye West's very high profile, antisemitic tirades, Kyrie Irving's endorsement of an antisemitic film, the FBI warning that was issued to New Jersey synagogues, including my own back in the fall. And in fact, this survey research was done during that time period, correct? Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Yes, exactly. And I think Manya, that kind of reality or that predicament, however you want to look at it is exactly right. So both of those incidents, like you mentioned, both with Kanye and with Kyrie Irving happened while our survey was in the field. So, you know, my presumption is that they really did raise awareness on these issues. And that's reflected in our data. We also saw that after, we saw that with celebrities speaking out, we saw it with the NBA's response to Kyrie. What also can't be overlooked with Kanye specifically and I'll also say particularly before he had his kind of like broader cultural downfall, there today or something like 15 million Jews here across the world. Kanye, before his Twitter was banned had 30 million followers. His reach can't be stated enough, especially when we have cultural figures, who are peddling deeply antisemitic tropes. And I think our data shows that. Our data shows that that bleeds over into the broader American public. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to talk a little bit about the statistics, the findings, about how young people seemed especially affected by these fears by these anxieties, and actually experienced more of the hate out there, than adults our age, older than 30, that is, right? Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: So that was a feeling that many of us had going into the survey, but it was just that: a feeling. And one of the profound things about this year's survey is that we were able to understand empirically, not just anecdotally, that American Jews are experiencing antisemitism differently than other generations, often at a higher rate. So among young Jews 18 to 29, who experienced antisemitism online, one in four said that that online encounter made them feel physically threatened. That's compared to only 14% in the over 30 set. We found that 85% of American Jews are experienced antisemitism online or on social media, as compared to only 64% of Jews who are in that over 30 set. And I think what's also really important here is that these anxieties are leading to behavioral changes within Jewish college students. And these are often changes that they feel forced to make. So one in five current or recent students avoided wearing items that could identify them as Jewish. 18% felt uncomfortable or unsafe at a campus event because they were Jewish. And I think students feel singled out for who they are and what they believe in. That's not okay. More colleges and universities need to acknowledge and ensure that Jewish students feel safe and are protected. And also, our data shows that young students are noticing they feel unseen, almost six and 10 of Jewish young adults think antisemitism is taken less seriously than other forms of hate. And I hope that's a number that people hold on to because if we're creating and have a generation who feel unseen, clearly more work needs to be done by broader society. Manya Brachear Pashman: Lily, this is probably a good time to bring you in since we're talking about your peers. You are a junior at Northwestern University in suburban Chicago, my old stomping ground. You started attending there nearly three years ago, what have you witnessed since you arrived? Lily Cohen: Something that I have noticed frequently over the past about two and a half years was this sense on campus, similar to what Meggie was talking about, of Jewish students feeling a little bit concerned sometimes about sharing all of the parts of their Jewish identity specifically when it came to talking about Israel. And the other side of this was seeing a lot of sort of activist students on campus, very active and vocally anti-Israel, and sort of creating a climate that made it uncomfortable for Jewish students to be loudly and proudly in support of Israel. And the result of that, that I noticed among a lot of my friends, was sort of shying away from maybe posting when they were traveling to Israel, or posting in support of Israel. And a lot of this was on social media. But as things have moved back in person on campus, as we've come out of the pandemic, I think a lot of both the anti-Israel activism and the fears about displaying our pride in our Judaism and in supporting the State of Israel, have also sort of turned more in person. And so in a lot of senses, this has looked like anti-Israel students on campus, adorning walls and different areas of campus with phrases like 'from the river to the sea, Palestine will be free,' calling Israel an apartheid state, calling it a genocidal state, and equating Zionists of all forms- American Zionists, and Israelis in the IDF and the Israeli government- sort of as one. And so I think that has likely contributed to a lot of the statistics that Meggie was mentioning, just because all of this combined is making, at least in my case of what I've noticed here, it's making at least my college campus feel like a more hostile environment for Jewish students. Manya Brachear Pashman: So when you first arrived, almost three years ago, were you expecting that level of hostility? And did you feel compelled to speak up, or not so much? Lily Cohen: Quite honestly, coming in, I didn't expect this as much because I'd spoken to a lot of Jewish students before getting to campus. And I had asked them what their experiences had been like. And if they had seen or witnessed or experienced antisemitism on campus, and very few of them really had anything to share. Some of them mentioned that sometimes Israel comes up in conversation, and some people agree with you, and some people don't. But it didn't really seem to be as pressing of an issue. But then early on my freshman year, in the fall, before I was even on campus, since we were at home, online, for COVID reasons, there was some action going on on campus. It ended up becoming this complicated thing. But the organization that had organized this action, which originally had nothing to do with Israel, with antisemitism, with anti-Zionism, but this organization came out sort of against all forms of hate. And in that list of types of hatred, included both antisemitism and Zionism, and sort of saying that both of those were very problematic and hateful ideologies. And this was kind of before I had a Northwestern community at all, I was still in my childhood bedroom in New Jersey, kind of watching this unfold on social media, and especially seeing this happen for the first time before I had a community and while I was not even on campus, I very much shied away from speaking up. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what changed this year to break your silence? Lily Cohen: I think it was sort of just by nature of this is my third year here, my second year now fully in person. So I feel pretty established in my communities, the organizations I'm a part of, especially the ones sort of outside of Hillel and the Jewish spaces, which were the ones that I was originally more hesitant to be publicly pro-Israel in. I'm a little bit less worried about the backlash, because I know that I have foundations in a lot of great communities on campus that know me, for me, know and like who I am. And that won't necessarily jump to judgments about me once I started talking about these things that are important to me. Manya Brachear Pashman: I want to talk about a very specific incident that happened to you in the fall. But before we do, Meggie, I want to ask you, if that's typical, what Lily is describing? Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Well, I don't know if I can necessarily divide it based on where you are within your undergraduate career. But I do think the one part that is very true, and I think similar is that it takes a lot of courage to speak up. And I think often we forget that we think exactly like you outlined, like you see something antisemitic, of course, you would speak up. But you know what, when you are in that instance, right, especially if you don't have people around you to provide that community and support. That's a really lonely place to be, right? And it takes a lot of courage to say, I'm going to raise my hand, I'm going to call this out, whether it comes with social kind of isolation in certain places, whether it comes with professional conflict, which you know, of course, we would hope does not, but you cited certain student groups, that's been the experience of some. And I think, I always say that all not in any way to discourage I hope I'm encouraging people to follow your bravery. But just to zoom out for a moment and say, our student leaders on campus who speak up for what's right, deserve a whole lot of credit, and really are showcasing a lot of courage. Manya Brachear Pashman: So kudos to you, Lily, because you have been very outspoken this year at Northwestern, especially after a particular incident last fall, can you tell listeners about the rock, what it symbolizes on Northwestern campus, kind of what the customs are in terms of of respecting free speech and different messaging, and what happened. Lily Cohen: So, that messaging that I'd mentioned earlier, that students have frequently been adorning around campus, such as 'from the river to the sea, Palestine will be free,' I saw coming up a lot more this past fall, the fall of 2022. We have a rock on campus that is sort of a symbol of free speech. So the idea is that student groups can paint the rock with whatever message it is they want to share. So whether that is to advertise an event or to spread awareness about an issue. And there are some unwritten rules and traditions about the rock, specifically that student groups, in order to paint the rock, have to camp out and guard the rock for 24 hours beforehand. In the fall, I had been part of a group of students that a couple of days before the midterm elections, we painted the rock, encouraging passers-by to vote with gun safety and reproductive rights in mind. I believe it was five or six hours later, we saw that another group was painting over our message on the rock. And the language that our rock painting was being covered with was indeed this, 'from the river to the sea, Palestine will be free,' and a lot of those other similar phrases. And that I think, was part of what really motivated me to write the piece that I wrote, just the fact that it was this time covering up something that I had worked to create, really hit me in a different way and motivated my decision to ultimately publish something very publicly talking about my Jewish identity and my connection to Israel and how that specific phrase that is around campus a lot is hurtful to me as a Jewish student. Manya Brachear Pashman: You did write a column for The Daily Northwestern, which is the campus newspaper there, and we'll put a link to that column in our show notes for listeners to read. And in that column. I thought it was quite lovely, the way that you framed it. It really talked about, it really comes across as a love letter to your Jewish traditions, your Jewish values, your Jewish upbringing, your Jewish pride that you hold quite dear. And you also did call on the university to condemn the slogan 'From the river to the sea' as an antisemitic slogan, and you explained why. I'm curious, Meggie do other activists and college students frame the response, or frame their explanations, their fight against antisemitism in a similar way to how Lily did it? Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Well, I think, you know, the responses to antisemitism certainly vary, first of all, for anyone who has not read it yet, Lily's piece is beautiful. And I think Manya, you put it just right, where it is really a love letter to what the beauty of Judaism on campus can be. The reason why I think that is so important. And it is an equation within antisemitism that we have to think about is, you know, at the start of our conversation, we were talking about a lot of statistics, a lot of things that can feel, that are indeed actually quite concerning for Jewish students today. What happened to Lily, which we'll get to after that, too, is quite concerning. But part of also, Jewish peoplehood, is that, yes, we need to acknowledge the real challenges that exists, if not, our silence is normalizing it. But it's actually the most Jewish of ways to say there are challenges. But also we're going to talk about vibrancy, we're going to talk about the power of our community. We're going to talk about the beauty that Judaism is and we're not going to let other people, including people actually, who not only want to limit our voices, but actually want to be detrimental to the Jewish experience, we're not going to let them do that. And I think, Lily, in particular in what you wrote, you capture just that, of acknowledging that campus life for most Jews is indeed really vibrant and thriving. Again, we're not glossing over the real challenges that you know, doing that enters a space for normalization, normalizing antisemitism, which none of us are in any way giving any legitimacy to. But we do need to remember that there's so much joy and positivity within Jewish life on campus. Manya Brachear Pashman: So yes, as Meggie alluded to, this is not the end of the story. I would love to say that framing it in that context kind of kept the opposing voices and the naysayers from lashing out. But it didn't. Let's tell listeners what happened, Lily. Lily Cohen: So pretty immediately after I published my op-ed, as I had sort of expected, there was this first wave of social media backlash. In these tweets, I was called a terrorist, a colonizer, I was called violent, I was called a white supremacist, I was called an array of expletives. And this immediate backlash was really just students who don't know me, jumping to assumptions about me, making judgments about my character, and taking attacks at my character, solely for this one part of my piece, which was that I found this phrase 'from the river to the sea,' to be problematic, and to be sort of at odds with my Jewish identity and my comfort as a Jewish student on campus. And while I had hoped that sort of cushioning this within this piece, really about how much I love being Jewish, and how much I love being able to share that on campus, unfortunately, that still wasn't enough to avoid all of the negative response. After the social media had started dying down a little bit, and the weekend was coming. And I was feeling like by Monday, most people would have forgotten about this, especially those who had a problem with it, and we would move on. Unfortunately, that was not the case. And early Monday morning, I received a call from one of my friends that there had been a banner put up on the main street of our campus in front of the library that was made up of about 40 copies of my article, and painted over all of those copies was the phrase 'from the river to the sea, Palestine will be free,' in red paint. It wasn't just a banner sort of in response to my op-ed, but it was directly targeted at me and my words, because they put it on top of my name and my words. Manya Brachear Pashman: Not everyone who disagreed handled it this way, right. The daily Northwestern also published a column by a senior by the name of Hamza Mahmood, who disagreed with always condemning that slogan from the river to the sea. Can you talk a little bit about your interaction with him and how it went beyond the counter column? Lily Cohen: Part of what I was trying to do with publishing my piece was find the people willing to have conversations on campus. And because while there is sort of this echo chamber of the very vocally anti-Israel voices, especially on Twitter and putting up these messages around campus, I know that there are students here that are willing to engage, but I just haven't been able to find them. And it really was a very respectful piece. The place where it sort of diverged a little bit, not from respect, but just from what I had written, was that he had a different understanding of the phrase 'from the river to the sea' and had a different opinion about what activists were intending when they were putting it up around campus. And I read his piece and wanted to reach out, we grabbed coffee a couple of days later, and we very quickly bonded. Before we even got to talking about the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, about activism on campus, about literally anything related, we just got to know each other as people. He's a Muslim student, I'm obviously a Jewish student, one of the first conversations we had was about how we both don't eat pork. And we bonded over that. And when we did get to the topic of conversation that had brought us together in the first place, and we started talking about our different understandings of what that phrase means, though I didn't agree with him, and though he didn't agree with me, we asked each other questions, we really tried to understand each other's perspectives. And so I walked away from that coffee, not feeling frustrated that I hadn't changed his mind, but feeling grateful that I had had a conversation with someone that was both willing to listen, and willing to share. Manya Brachear Pashman: I'm curious, did he have thoughts on that banner? Did he have thoughts on the response, including that banner? Lily Cohen: He did think that it was completely wrong. He thought it was bullying. He thought it was absolutely terrible that anyone would do that. But he wasn't completely convinced that it was an act of antisemitism, more than just an act of bullying and disrespect. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Meggie, I'm curious, in terms of allies on campus, do college students share similar stories of having difficulty finding the allies on campus? And what advice do you have for students who are searching for those people who aren't necessarily going to agree, but are at least willing to listen? Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: First of all, what a beautiful story, and Lily, I think, Manya to your question, it's, I think, indicative by the way of campus culture today, but I also think of our broader society, right? Where dialogue I mean, let's go back to campus. Campus is supposed to be the bastion of free exchange of ideas, right? That is often where most people come and experience people who are from different walks of life. But for that to work, you need to have an environment where that dialogue, where open exchange is accepted. And I think what we're seeing on campus, and within the broader society, you mentioned, Twitter. Twitter's probably the most extreme of this, of that, even if the number of people are small, the loud voices dominate. And often those voices they want silo, right? They don't want to sit down, they don't want to actually have that exchange. And I think kind of the power in the calling for all of us, Jewish students included, on campus, and in broader society, is to find those allies, those friends, those partners, who do want to sit down and have actual conversation, even if-and this is a part I think we all need to get behind-even if you know they're not the ones who are on the quads screaming the loudest, making the biggest show, you know, finding people who will actually talk and build those bridges with you is really important. Manya Brachear Pashman: Finally, Lily, I want to ask you about your winter break, during which you went to Israel, with other college students from across the country. And you felt a little differently about sharing pictures and posts from your trip than they did as a result of this incident, if I'm not mistaken. Can you share a little bit about that? Lily Cohen: I think one of the best things, I guess, to come out of this situation is sort of the sense of relief that I'm not hiding this part of myself anymore. And so when I went on Birthright over winter break, I had no hesitations about sharing pictures on social media showing that I was in Israel, because I had kind of already ripped the band aid off on that one. I had already sort of announced to everyone at least at Northwestern that I support Israel's existence. Whereas both speaking with other students on my trip and with Northwestern students in years past, there has been a different sense of comfort with sharing that information about going to and spending time in Israel. For example, over the summer, there were a lot of Northwestern students in Israel on a variety of different programs or just traveling there with friends. And going back to Twitter, there were tweets about people making lists of all of the Northwestern students that were partying in Israel. I was on a trip with students from several different schools, and so I found that many of my friends on the trip who go to different schools, were very hesitant to share with peers from their school, that they were in Israel, and that they were on Birthright, because they were worried about how it would be received and how they would be treated sort of in response to that. Whereas I think one thing that the whole experience I went through in the fall sort of helped with was, I didn't have to worry about that anymore. I just didn't feel like I needed to hide anymore, that I would spend time in Israel, that I was there, and that I was having a great time there. Manya Brachear Pashman: Meggie, does that reflect what the survey found as well, when it comes to college students and young adults on social media? Are they also hesitant to post? Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Yeah, well, what we found certainly within the campus space is that over one in 10, college students feel like they have been penalized, for doing just that for talking about their ties with Israel. I would say, Lily, I keep singing your praises, but they're deserved. I hope that more and more students can get to the place that you're at now, where no one should have to hide part of their identity. And again, acknowledging that in certain environments, it can be daunting, but there are kind of two lenses. One just in principle, we shouldn't be in a position in 2023, where any Jewish student should feel like they have to hide who they are, because of repercussions. The second part is, I'm not denying that that happens in certain corners. But I think what's so important, and your story speaks to this, both through Hillel, both through the friendships you've made with some people because of it, find your community. Find your community so that you're not standing alone. And I think that's a really important step. Manya Brachear Pashman: And not just on social media. Don't just find the community on Twitter or on Facebook, find it on the ground. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: In-person community. Exactly. Thanks, Manya. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Meggie, Lily, thank you both for joining us to talk about the data for putting a voice to it. These are not just numbers and statistics. Lily, they are you and your peers and our people, our peers. So thank you both so much for having this conversation. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Thanks, Manya. It was a pleasure. Lily Cohen: Thanks for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: Think you know the state of antisemitism in America? Take AJC's quiz and test your knowledge of how antisemitism impacts America and its Jewish population. Find it at ajc.org/antisemitismreport2022. We'll include a link in our show notes. And if you missed last week's episode, be sure to tune in for my conversation with AJC Paris director Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache, about France's most recent upgrades to its plan for fighting antisemitism.
Feb 8, 2023
The New Ways France is Combating Antisemitism
France just released its latest national plan for combating antisemitism. AJC Paris Director Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache joins us to break down this new initiative, share how French Jews are impacted by rising antisemitism, and give us a behind-the-scenes look at the role AJC played in helping craft the plan. In April 2015, AJC praised the French government for launching its first comprehensive plan to fight antisemitism and racism, and a year earlier for establishing the position of Inter-ministerial Delegate to Fight Racism and Antisemitism, reporting directly to the prime minister. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache ___ Show Notes: Read: AJC Paris Welcomes Updated National Action Plan to Combat Racism, Antisemitism, and Discrimination in France Listen: Our most recent podcast episode: Breaking Down the Headlines from Israel: From Secretary Blinken's Visit, to Terror Attacks, Protests, and More Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Feb 2, 2023
Breaking Down the Headlines from Israel: From Secretary Blinken's Visit, to Terror Attacks, Protests, and More
The Jerusalem Post's Lahav Harkov joins us this week to help us understand all of the big news from Israel, from U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken's visit, to rocket attacks from Gaza, terror attacks in Jerusalem, ultimatums from Russia, massive protests, and proposed changes to Israel's Law of Return. Harkov is the senior contributing editor and diplomatic correspondent for The Jerusalem Post . *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Lahav Harkov ___ Show Notes: Read: What You Need to Know About the Palestinian Terror Attacks in Jerusalem Listen: Our most recent podcast episode: Surviving the Unimaginable: A Child's Story of the Holocaust Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript: Manya Brachear Pashman: This week, US Secretary of State Antony Blinken arrived in Jerusalem as Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu dealt with more rocket fire from terrorists in Gaza, ultimatums from Moscow, and protests to propose judicial reforms and changes to Israel's Law of Return. Here to share what she sees and hears on the ground is Lahav Harkov, senior contributing editor and diplomatic correspondent for The Jerusalem Post . Lahav, welcome back to People of the Pod . Lahav Harkov: Hi. Manya Brachear Pashman: So let's begin with the visit by Blinken. His jaunt to Jerusalem was on the calendar for a while. But given the escalation of violence in recent days, and the Cabinet support for legalizing more settlements, did Blinken's agenda change? Lahav Harkov: Yeah, I mean, I'm sure that you know, it's updated according to whatever is going on at the time, he has to be, you know, have his finger on the pulse. And so the issue of terrorism did come up. And he did make some really important remarks, just about how horrific it is and how just completely unacceptable it is to attack a place of worship, as a Palestinian terrorist did on Friday night. But of course, that was followed by another terrorist attack the next morning, in which two people were killed. Manya Brachear Pashman: So his original agenda included a strategy of how to deal with the nuclear situation in Iran. Can you kind of update us on where Israel stands on that situation right now and how it's dealing with hostilities from Iran? Lahav Harkov: Yeah, you know, it's not so different from what it was in the previous government, right. There's some nuances that are different, but overall, Netanyahu opposes the Iran deal. But that deal is not so much on the table anymore anyway. Netanyahu openly says that Israel has done things to stop Iran from developing certain weapons, which seems to be a hint at an attack in Isfahan, which is a city in Iran, in what apparently was a drone manufacturing site. But of course, Netanyahu would not get into that level of detail. But there's been reports, it was first reported in The Wall Street Journal, that it was Israel that did it, sort of in coordination with the US. Manya Brachear Pashman: In other words, taking matters into Israel's own hands and taking care of the situation within Iran. Lahav Harkov: All the reports say generally that it is in coordination with the US. So you know, Israel is doing it. But I guess you could say Israel is taking matters into its own hands, but it's not acting, like at cross-purposes with the US. Manya Brachear Pashman: So was there progress made in the conversations between Netanyahu and Blinken? I mean, are the United States and Israel still on the same page when it comes to Iran or were there sticking points? Lahav Harkov: Overall, I think that Netanyahu would like a more aggressive approach to Iran. You know, more sanctions, more willingness to strike, but I think that they're still in a good place. Overall, they're sort of, again, working towards similar purposes, working in the same direction. It's not a point, you know, if Netanyahu was Prime Minister, I don't know, a year ago, and the Biden administration was really actively pursuing the Iran deal something Netanyahu thinks is a great danger to Israel and in the world. That's not where we are, right. The Biden administration has all but dropped the deal. And with the massive protests and the violent suppression by the regime, you know, the Biden administration is not in a place where it's looking to cut Tehran any slack. So, the differences, I guess, are, maybe they're not small, but they're not as big as they could have been, even just six months ago. Manya Brachear Pashman: So another topic that Blinken had hoped to discuss this week was diplomatic relations between Israel and Saudi Arabia. I don't know what that did end up on the agenda as significantly as was intended, but how likely is that to happen? And if it's likely, what's the timeline and what are the caveats? Lahav Harkov: So I think it's very premature to talk about a timeline. The Saudis themselves, in any public statement, when the top officials are asked about this issue, they say that there needs to be some sort of movement on the Palestinian file before there can be peace with the Saudis. That being said, that was the case for the entire Arab world for the past 23 years or so, and yet Israel established relations with four different Arab countries in 2020. And so it's possible that Netanyahu can once again make the seemingly impossible happen. And certainly, you know, I think we saw maybe a baby step in that direction after Friday night's terrorist attack. One of the countries that condemned that attack was Saudi Arabia, which is not the usual thing. And so that was very interesting. But I still think that it's very premature to be talking about timelines. I don't know when it's gonna happen. But Netanyahu is really, really intent on trying. Manya Brachear Pashman: So, Secretary Blinken also hinted that the proposed judicial reforms could undermine Israel's democracy, and that this common connection with the United States, this democratic connection, right. Let's talk about those reforms, which many legal scholars have said, could weaken the Israeli Supreme Court? Can you walk us through those proposed changes and why there's so much concern? And frankly whether that concern is overblown? Lahav Harkov: Yeah, I mean, first of all, I take a little bit of issue with the premise because there certainly were a lot of headlines that said that blinkin said what you said he did. But when you look at what he actually said, which anyone can find on the State Department website. He said that Israel and the US share democratic values. He said that the sort of very robust debate going on about the judicial issue, but he didn't actually mention the judicial issue, but it was in response to questions about it. And it's sometimes not, but he said the robust debate is indicative of a strong democracy. So none of these things to me sounded like Blinken chiding Israel, I think he was being very cautious. And I would be surprised if he did support these judicial reforms, although really, he shouldn't take a position this way or other. But I think that he was a lot more cautious, and a lot more neutral in his statement than the way it had been reported in a lot of places. Now, I understand that behind the scenes, he did express caution. But I think the way that this was reported on was sort of slanted and inaccurate, almost everywhere. But moving forward, look, the judicial reform, it goes very far in the opposite direction of where things stand in Israel right now. But where things stand in Israel right now is also extremely unbalanced. You know, you're supposed to have checks and balances between the different parts of government. And, there's only checks and no balances right now, like the court can really check anything that the government and the Knesset does. But the Knesset and the government have no bearing, no influence practically on what happens. The process of selecting judges, for example, is there's a joint committee, that includes politicians and judges and the Bar Association. And essentially, it's slanted so that the judges have, you know, outsized influence, for example. And all kinds of things like that. It takes a really long time to explain it. So I'm not gonna take our whole half hour to explain the judicial reform. But I will say two things. First of all, I often find it deeply ironic when Americans criticize the reform, because certain parts of it will just make it more like America's system. Right? So when people say like, oh, it's not democratic, you know, to have politicians having too much of an influence on the judicial selection process, I think to myself, well, how do you think Supreme Court justices are chosen in America, right? And then there's just like, another thing that happens in the Supreme Court in Israel is that you have an extremely broad concept of standing in the court, like an NGO can bring a case before the court, even though they have nothing to do with it. Like let's say, I don't know, an NGO can say that Israel is building on property that actually belongs to Palestinians, even if the Palestinians aren't suing, and haven't spoken to that NGO. And in the US, right, the idea of who can have standing before the Supreme Court is much narrower than that. So to me, it's like people are hearing what's being said by certain figures that they like to read or hear from in the media and they're just echoing out without really thinking. That being said, I do think that the reform swings, it does like a one ad, right where you have an extremely powerful judiciary and you want to fix that unjust injustice of an imbalance. But this reform, the way it stands now, creates a new imbalance, it's just in the opposite direction. But I think that, Israel's system is built on compromise. We have a coalition system, you have a lot of different parties there. They're sort of push and pull and in the end, you have to agree on something. Now, it's true that this coalition, they all want to make big changes to the courts. But I think that in the parliamentary process, which of course, includes the opposition, that they are active parts of the committee that's legislating this reform, I think it will end up more moderate than it is now. And you know, and people can debate about the degree right, like to what level should there be reform? Netanyahu says that it's not going to be exactly as it was proposed at first, he says that I will hear the opposition out, and that there will be changes made. I know a lot of people just don't believe him. You know, he is a polarizing figure. But he's not the only person involved with this bill who says that. And so my hope is that that's what will happen in the end. And that, as Blinken, actually himself said, that hopefully they will be able to reach some kind of consensus or if not consensus, than just a broad section of the Knesset working together. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what is fueling the protests? The direction of the imbalances is particularly sensitive. Is it just the polarizing nature of it being a Netanyahu administration? What's fueling the protests? Lahav Harkov: I actually think there's a little bit of both. I think first of all, there is a subsection of the protesters who are genuinely outraged by the reform, and maybe not the concept of reform itself, maybe they think it just goes way too far and puts too much of the power in the hands of the politician, as opposed to the courts. You know, there are people like that, certainly, you have a lot of figures from the legal world who joined the protest and speak at the various protests. On the other hand, for basically the entire time since we started our whole crisis where we had five elections in four years, there's been protests outside the Prime Minister's residence as Netanyahu was Prime Minister. So you know, almost the entire time, minus a year and a bit. And there was a protest movement, and it ebbed and flowed. There were bigger protests and smaller protests. But I just think that this is an outgrowth of that. And honestly, it's been every week since the government was formed. I guess that's like six weeks now. And the first protests were not really so focused on the judicial issue, they were focused on other sort of social issues, which that's also something that we could discuss about this government. But, they then shifted to the judiciary, which I think gave them like, an intellectual gloss, sort of, it made it seem more serious than just people who are angry at this government. But I do think that it certainly was a building on an existing, anti Netanyahu protest movement. Manya Brachear Pashman: So what are the social concerns causing concern and fueling protests? Lahav Harkov: There is a lot of sort of homophobic and very strongly anti-gay rhetoric coming from this coalition, coming from specifically within the religious Zionist party, and some of the things being said are very ugly, and I think like hurtful to people who are gay and there is a lot of concern about that. And I would also add that there's misogyny coming from the same people as well, in terms of not even just women in the army, because I think it's fair to have a debate about, you know, whether it's appropriate for women to be in combat roles, et cetera. Like there's a debate to be had there. And I wouldn't jump to saying that's misogyny, but other things just about like women's roles in society that, you know, I wonder what year it is when you hear those people say these things. What's interesting is that it's not the Haredim who are saying either the homophobic or the misogynistic things for the most part, because they, their idea is sort of, we have our community and we do things within our community one way and sort of, even if they disapprove of what other communities do, they're less involved. Let's put it that way. But it's the religious Zionist party, which is, for many years, sort of a bridge between those two parts of society. But I would say in recent years, at least, the political religious Zionism, if not the actual communities, leads towards the Haredi direction. So anyway, it's been coming from them. Netanyahu has said that there's not going to be any anti gay laws, and nothing's going to change. I believe him that that's what he wants. I would say that between the judicial stuff, and also, you know, these things about LGBT people, you know, Netanyahu can't say no to everything that his partners want, because then he won't have a coalition anymore, they'll quit, and we'll go to another election. And so I don't know where the breaking point is going to be. But in order for Netanyahu to maintain his coalition, there will be a breaking point somewhere. Somewhere, he's going to have to say yes, even though he really wants to say no. Manya Brachear Pashman: So another change, proposed change, that has sparked tremendous concern among Jews, at least here in the diaspora, is the possibility that people who are not recognized as Jewish under Jewish law will be restricted. Right now the Law of Return allows every Jew to emigrate to and live in Israel as long as they have at least one Jewish grandparent. The definition of a Jew was based on the Nuremberg laws, in the original law of return. Now, there have been amendments since then that have extended Aliyah, to spouses to children, regardless of whether they're Jewish, how likely is this law to change? Lahav Harkov: So I think it is actually pretty low priority for this coalition. And if it's low priority, then there's always the chance that just with the passage of time, other things will happen. And this won't. So for starters, there's that like, I just don't think there's going to be some sort of rapid change there. That being said, I do think that it is something that people in this coalition want. And again, it's another thing Netanyahy doesn't want. And also Likud really doesn't want it. I mean, Likud doesn't want rights to be rolled back for gay people either. Don't get me wrong, but like, Likud doesn't want this, it goes against their voter base, a lot of Russian speaking Israelis vote for Likud. And this is viewed by them, and rightly so I think, as a way to stop immigration from the former Soviet Union. Because especially now with the war going on, you have many people coming here who, let's say, probably didn't ever see themselves living in Israel and don't really see themselves as Jewish, but because they're sanctions on Russia, life is increasingly difficult there, it's easier for them to come to Israel. It's one of these things where, the law of unintended consequences where where the politicians are thinking about one thing, but there are a lot of Jews in the Western world and you know, the majority of American Jews are married to marrying non Jews, you know, the numbers get higher all the time, and it affects people more people I think, than they were thinking about. So moving forward, they're gonna have to have that discussion and they're gonna have to think about it, you know, if they're gonna move forward with this, but I do think that politically they just don't have the numbers for it. I don't think Likud will want that. And Likud is half the seats in this coalition. So you need Likud in order for it to happen. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I want to shift gears a little bit and go back to Secretary Blinken, who doubled down on the United States support for a two state solution, both Israel and Palestinian state. But there are signs that public support for a two state solution is waning there. Is there really a lack of public support for that solution? Lahav Harkov: Polls have shown that support is waning, both among Israelis and even more dramatically among Palestinians. I don't think it's overblown. Netanyahu talks like someone who does not want a two state solution at all, but the Trump per parameters the Trump plan was, practically, it was exactly what Netanyahu would have wanted it, it's exactly what you're saying- I would accept any plan, which is that Israel can keep all of the communities in Judea and Samaria, and, and applied sovereignty to them. And the Palestinian state would be on parts of the West Bank that, you know, Israelis don't live on. And it would be a demilitarized state that would essentially be surrounded on all ends by Israelis. Now, that's not a two state solution that Palestinians will ever accept. But that is a two state solution that I think the majority of Israelis would accept if they were presented with that, right. So a lot of it really depends on how you ask the question. But if you talk about a two state solution based on pre-1967 lines, then I think the vast majority of Israelis would not want that. Manya Brachear Pashman: Okay, Lahav, the last time you came on this podcast, we discussed the really difficult spot that Israel was in, they were offering safety to Ukrainian refugees, they were providing humanitarian aid inside Ukraine, with Russia, right there on Israel's border with Syria. A lot has transpired since then, not least of which Israel has a new administration. So has Israel's position shifted? Lahav Harkov: Israel's position has not shifted openly. Israel's not like sending weapons to Ukraine right now. That being said, the attack on the drone manufacturing site in Iran, which is something that, reportedly Israel did, is something that helps Ukraine a lot. And so Netanyahu admitted it that also in the interview on CNN with Jake Tapper, he says something, you know, like that we we hit back at, you know, Iran's development of different weapons, and those are weapons that are also being used against Ukraine. And I believe it was Ukraine's defense minister, some important Ukrainian official. It slipped my mind now exactly who it is but after that attack tweeted something to like, We warned you Iran, which sort of hints to you that maybe Ukraine knew something about what was going on as well. So it seems to me that there are things happening behind the scenes. But Israel's not saying it upfront, in order not to antagonize Russia, which really is sitting on Israel's northern border. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, Lahav, thank you once again for coming and sharing your perspective from on the ground there. I think that's really important because a lot of people are interpreting and reporting things without actually being there and there's always holes when you try to do that, so thank you so much. Lahav Harkov: All right. Thank you.
Jan 26, 2023
Surviving the Unimaginable: A Child's Story of the Holocaust
In this powerful episode, we sit down with Sam Harris, who is one of the youngest survivors of the Holocaust. As a young child, Sam watched in horror as his family was taken to Treblinka and murdered, but he and his two older sisters were able to beat the odds. Listen as Sam recounts the unimaginable struggles he faced during one of the darkest periods in human history and how his experience motivated him to play a central role in the founding of the Illinois Holocaust Museum. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC. __ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Sam Harris __ Show Notes: Read: Sammy - Child Survivor of the Holocaust by Sam Harris Watch: Full live recording of this episode Listen: Interview with Howard Reich, as mentioned in this week's episode: The Art of Inventing Hope: Elie Wiesel's Masterclass for Humanity Our most recent podcast episode: 'Leopoldstadt' Actor David Krumholtz Sees Tom Stoppard's Holocaust Play as the Role of a Lifetime Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jan 19, 2023
'Leopoldstadt' Actor David Krumholtz Sees Tom Stoppard's Holocaust Play as the Role of a Lifetime
Since its Broadway opening last fall, Tom Stoppard's "Leopoldstadt," a play about a multigenerational Jewish family in Vienna, based on Stoppard's own family history, has been met with critical acclaim. Hear from celebrated actor David Krumholtz, who plays the patriarch of the family, on how his Jewish identity has been transformed by the role, why he speaks to his young children about antisemitism, and the importance of Holocaust education today. _ Episode Lineup: (0:40) David Krumholtz __ Show Notes: Leopoldstadt: Tickets and more information Photo credit: Joan Marcus Listen to: Our most recent podcast episode: Shabbat Shalom No More? One Year Later, Colleyville Synagogue Wrestles with Impact of Hostage Crisis Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Transcript of Interview with David Krumholtz: Manya Brachear Pashman: Since its official Broadway opening on October 2 2022, Tom Stoppard's latest play Leopoldstadt has received widespread acclaim. One of the hottest tickets in town, it has been extended through July 2023. The drama follows multiple generations of a Viennese Jewish family over half a century, beginning in 1899. Through the Holocaust and beyond, the fictional family and the story is based on Stoppard's own. When he was in his 50s, the playwright learned that he was Jewish and had lost his grandparents and many other family members in the Shoah. With us now to discuss his role in the play is actor David Krumholtz, who plays Hermann Merz, the tragic patriarch of this fictional family who has converted to Catholicism for purposes of social and professional mobility, but discovers in the end it is to no avail. David, welcome to People of the Pod . David Krumholtz: Thank you so much. Thanks for having me. Manya Brachear Pashman: So I described your character as tragic, but it is a play about the Holocaust. So would you say all of the characters in this play are tragic? Would you agree? Walk our audience through Hermann Merz's approach to life, to his Judaism. David Krumholtz: I don't see the character as tragic at all, which is sort of a conversation I needed to have with Patrick Marber, our director before I even auditioned for the role. I think he's heroic in many ways. He's doing the very best he can for his family, and for the future generations of his family, and in doing so, he has had to shed his Judaism. You get the sense, though, that he was kind of raised in the religion of business. The most important thing he inherited, this textile factory from his father, and his father did very well. And it seems to me that he was groomed to take over and bring it to great success, build it farther than his father could have ever imagined. And for the sake of his family, and for the sake of future generations. So, certainly converting to Catholicism in late 19th century Austria, was one of the ways to do that, you know, he wasn't labeled anymore, it opened up channels that he probably would have had a harder time getting in on. He did all that he possibly could do to benefit from the choice. And it's a choice, ultimately, that he must have known broke his mother's heart, and alienated him from his family, from the more religious members of his family. And yet, he did it anyway. And he does suffer for it. And it seems to me he's willing to suffer for it. But when we learn about him, is that at the very core of who he is, he is Jewish. At the first instance, of someone challenging his Judaism or, you know, mocking his Catholicism, he's ready to kill the guy, literally. So we get the sense that this is a very, very deep seated issue that comes from, as he explains through a story about his grandfather being bullied for being Jewish. It's true. There's a trauma there that he is doing this from, it's not all just business-minded and flippant. This is something that he has been tortured by his whole life by the time we meet him. Which is why he has so many strong opinions on Israel and the future of Jews, and assimilation in Austria. Vienna, being at the time, the cultural center of the world with an emperor king who emancipated Jews from all wrongdoing. And was a sort of Jewish sympathizer who gave Jews quite a lot of leeway that they didn't have prior to his reign. So things are looking up when we meet Hermann Merz, looking up not only for his business and his family, but for Jews in Vienna. I think he has every right to feel positively about the future, think positively about the future, and not want to move his entire family to the middle of the desert. He's righteous in that indignation. And sadly, time tells a different story. The next, you know, 40 years of his life, teach him that his ideals and his hopes for the future were obsolete or were futile. And that's the tragedy of the story of Hermann Merz. But I don't view him as a tragic figure. Manya Brachear Pashman: But what you're referring to is there's a kind of an ongoing debate through the play between Ludvig, his brother in law, if I'm not mistaken, and Hermann, and that debate is about assimilation and what the definition of assimilation is. Ludvig says assimilation doesn't mean to stop being a Jew. Assimilation means to carry on being a Jew without insult. Would you agree with that definition? And would you consider yourself assimilated, by that definition or another? David Krumholtz: I think for the time in which the play is set, that is a very keen definition. The idea of being anything other than what religion you're raised in, identifying with a nationality, let's say, was a novel concept at the time. The term thrown around by Ludvig in that scene a couple times is the word ordinary Jew, ordinary Jews, meaning not rich, middle class Jews who don't have access to all the luxuries that my character does. And that's an interesting little phrase there. ordinary jew, What is an ordinary Jew, what separates us? What makes you know, a Hasidic Jew a Hasidic Jew, what makes an assimilated Americanized for instance Jew, the same Jew or a different Jew? What's the difference? I personally like to think that there is only a matter of degrees of religiosity between the two. I would hope that as appreciative of I am as I am as an assimilated Americanized Jew, as appreciative as I am of the Hasidic community of the religiosity of the ultra Orthodox community, the Orthodox community, that those communities would be as appreciative of me, that there'd be no judging. Especially at this point, 80 years, past a genocide that we all suffered through, where it didn't matter how religious you were, at the end of the day, all that mattered was what was on your birth certificate. And one would hope that, 80 years later, we're all sort of on equal footing with one another. And we've all carried on being Jews without insult in one way or another. I grew up in New York City. I grew up in Queens, which is the most multi-ethnic, multinational place on Earth, believe it or not, per capita. Queens represents more nationalities than any place on Earth. Just the borough of Queens alone, not to mention the entire city of New York. So for me, there wasn't any corner to fit into, it was all a melting pot, and I could be whatever I wanted to be. And so over time, after Hebrew school, and having had my Bar Mitzvah, I felt strongly that I didn't necessarily relate or feel attracted to the more religious tenets of Judaism. But that culturally I was Jewish. And I've taken great pride in playing Jewish characters, and telling the story of Jewish people over the last 30 years, in my work, when I get the chance to. and so in that way, I've carried on being a Jew without insult, you know, it is part of my identity, this play has made me sort of realize how much of that identity I maybe took for granted at times. But for the most part, it's nice to be a part of something that makes a clear statement. And that statement is that Judaism is more than just a religion, it's a cultural existence, it is something unique unto itself. And there are, there's a lot to be proud of, there's a lot of amazing history to be cherished and celebrated, and to be celebrated as well. Manya Brachear Pashman: So how did you find your way to Leopoldstadt? And I will follow that up with a question of, how have you found your way to your Jewish heritage, kind of discovering what you might have taken for granted through Leopoldstadt? David Krumholtz: Patrick Marber, the director of Leopoldstadt, had his sights set on me. It flabbergasted me to be honest, I haven't done a stitch of theater in 30 years. I'm not your sort of prototype for the role on paper. And yet, he was enamored with my work and sensed that it would all pan out nicely. And so I don't look a gift horse in the mouth. So I took the opportunity. My father would have loved this play. My father was a deeply devout Jewish culturalist at heart. You know, he grew up in the Lower East Side of Manhattan. He was surrounded by Jewish people, his upbringing was surrounded by old world Jews who had settled in America prior to the war, and Jewish survivors of the Holocaust who had just come back. That was his reality growing up as a kid in New York. And so these themes were an obsession for him his whole life. So I thought, well, one way to connect was to evoke the memory of my father, and so I did that, and in doing so, I came to some pretty tough realizations, one being my father was quite frustrated with me, and how I sort of abandoned the religion, early on in my life. There comes a time in, I think, in a lot of people's lives where they question the existence of God, they question the existence of biblical history. And that was happening to me and it frustrated my father a great deal, because he had a tremendous amount of faith. And it's only recently that I've had to take on quite a bit of faith in my life now that I'm a father and being an actor is a leap of faith. It took me a long time to realize that. I just know from doing this play, that it would have made my father very, very proud. And that if he could tell a story this is the story he would tell. And so, for me, rediscovering my Judaism, through this story, as a tribute to his life, is the formula for success. And for me finding greater pride and being Jewish than perhaps I've ever had before. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's beautiful. This was not a typical role for you, and you hadn't done a stitch of theater for 30 years. I believe I read somewhere that, in fact, when you're making your commute into the city to do these shows, you call someone to kind of share how intimidated you are by this play, and that that call settles you down. Do you still do that? David Krumholtz: There are certain days I just have to do that. The weight of this role is heavy. This is a heavy responsibility. In many ways, the role of Hermann is kind of, along with other roles in the play, but he's one of the anchors of this ship that is sailing to great success on Broadway, and that's not lost on me and you know, when I walk out of the theater at night and, and get teary eyed thank yous from our patrons, who clearly have been deeply impacted by what they've just seen. It's not lost on me. And so yes, you know, little old me on the way in, in my car to the city has to sometimes call anyone. But typically, my family, someone in my family and just sort of say, Hey, this is quite a mountain to climb and hang in here. But there are moments certainly where the pressure is enormous, and I feel unworthy of the glory of playing this role. It's just part of who I am. It's what motivates me. Those feelings of insecurity actually motivate a great performance, or what I hope is a great performance. And, so I make those calls. And, you know, and like I said, they're family mostly because to me, family is just deeply important, and they know me better than anyone. Manya Brachear Pashman: Well, that leads me to ask about the family tree in Leopoldstadt, which plays a very important role. It's published in the program, so that you can study it. In fact, someone told us to study it before we even watch the play. I don't know if it made that much of a difference. It made so much more sense afterward. But there are, I believe, 31 characters in Leopoldstadt, is that right? 24 of them are members of this extended family. And even in the play, there's a reference to how confusing that family tree can be. Why? What's the point of that kind of complicated, many branches of that family tree? David Krumholtz: Well, it's a stroke of brilliance by Tom Stoppard who's written quite a few pieces that are strokes of brilliance. It's purposeful. It's so that at the end of the play, when your frustration mounts at not knowing exactly who every character is, there's so many characters, and how they're related to each other. When that frustration mounts, you can equate that frustration with the fact that each one of those people, each one of those characters, individualism didn't matter. At the end of the day, they were killed for being something they couldn't help but be. They were killed for being Jewish. It didn't matter what their hopes were, what their dreams were, what their aspirations were, it didn't matter whose mothers were, who's who, you know, whose sons had mothers and whose mothers had sons. none of it mattered. Death is the final, there's so much finality in death. And at the end of the play, we get a sense of that finality, that there is no coming back. There's only memory, there's only memory. And memory, for as impactful as memory can be at times, is also a thinly veiled representation of the real person. And so when our audiences walk out of the theater going, I didn't get to know that character, I didn't get to know that character…you knew as much as they knew about themselves, before they were killed, before their life ended. The frustration you feel with the frustration of generations worth of Jewish families that lost their loved ones. And that's the point. Yeah, Manya Brachear Pashman: You talk a lot about walking out of the theater and how you encounter audience members. My husband and I walked out of the theater, and we kind of stood off to the side, just really in stunned silence. We were still processing everything we had just watched and heard. And these two ladies came by and they were taking smiling selfies outside the right by the poster. And my husband and I were like, Did you just see the same play that we saw? shocked that, you know, they show it was there, you know, maybe first time on Broadway and you know, this was a Tom Stoppard play, it's exciting. But we were so kind of emotionally drained. David Krumholtz: We've been told by a lot of audiences that they're not prepared to clap for us, when we take our vows, that the ending in the play is so deeply tragic and so stunning that suddenly there are these actors on stage taking their vows. And, our crowds aren't quite ready to process. The difference between what they just saw and reality, the difference between 1900 and 2023. And we feel it as well. And we are as a cast somewhat desensitized to the trauma of the play. But during the rehearsals, and during our first couple of weeks of runs, we all had a very, very, very difficult time processing the different, more depressing aspects of the play. There were countless tears shed. It was amazing for us to bond over something that we all clearly felt so moved by. So we're not surprised, we often have to remind ourselves, oh, this is the first time these people are seeing the show. And how it felt the first time we read it, or how it felt the first time we heard it out loud, or how it felt the first time we got it up on its feet and looked into each other's eyes and performed it. You know, we have to remind ourselves of how deeply impactful The show is. And it doesn't take much because at the end of most performances, we hear audible weeping in the in the crowd and we see it in the eyes of people standing to give us you know, an ovation and It's some of the most important work. You know, you always strive as an actor or an artist of any sort to do relevant work. So much of the work you do in between relevant work is down to whatever reasons, you know, whether it be to make a living or to, you know, to cement some future for yourself or whatever. And then in between, and then once in a while very rarely do you get to do something that is truly timeless, if you will. And that's what I believe about this play. It's timeless, in its impact. It tells the story of humanity in a very unique time. It's historical, and so the pride we all feel is just incredibly palpable. Manya Brachear Pashman: And you should really, it is truly incredible. I also want to ask you how you've changed your behavior, what you have done, if anything. As a result of being part of this play, this is a very small thing I shared with you before we started recording, one of the lines during that comedic scene actually really pierced me and that was when the grandmother was looking through the photo album. And they don't know who people are here. She says, Well, here's a couple waving goodbye, but who are they? It's like a second death to lose your name and a family photo album. And I immediately burst into tears. And came home and started writing names on the back of photos in our family photo album because I realized, oh my goodness, what truth that line delivered. David Krumholtz: Well, yeah, I think that theme of that desperation of clinging to memory desperately, is made all the more impactful when you realize that lives were meaninglessly lost. When tragedy strikes, memory both takes on more and less meaning. You know, because you're clinging so desperately to it, because you've lost something that you felt wasn't complete. And you're completing it in your memory, if you will. And yet it's just a memory. It's a Central as a memory, it exists here, maybe in your heart. But, there's no tangible proof that that person existed any longer. Again, it's Tom Stoppard hitting you over the head with a very, very bleak truth about the nature of murder of genocide, about the robbing of individual individuality, about the discounting of a person's dreams, of a person's hopes, of a person's family, of people's reliance on each, other dependence on each other. Just wiping people out of this general blanket of death. That memory becomes a more desperate thing. It's haunting, it's terribly haunting. And at the end of the play, we see the ghosts. What we essentially see, live in the flesh, is the new family photo album, filled with people that we just hope we can remember. And if we can't, then well, that's even more tragic. Manya Brachear Pashman: Do you do anything different? Do you talk to your children differently about your Jewish traditions, history? David Krumholtz: You know, I grew up incredibly frustrated by racism, because as I'm in my mid 40s, my generation grew up with the stories and the harrowing sort of, the wagging- be careful, you never know, this could happen again. I could touch and feel my great grandmother, I could see the tears in her eyes in recalling her memories. She lost 11 brothers and sisters in the Holocaust. And so I can see it. My kids can't.... So for me, it's just important. I debated – my daughter's eight, this is heavy fare for an eight year old. And I debated whether or not it was important that she see the play. I don't want to hurt her. I don't want to scare her. And at the same time, it's important that she knows and that the message is delivered by me. And so we're gonna have her come see the play before I'm done with it, and hopefully, that impacts the way it should. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's a wonderful point. I wrestle every day with how much to share with my children, because you don't want to scare them. Because you don't want them to run away from their Jewish traditions and heritage either out of here. I'm really grateful to the rabbi at our synagogue who, every Shabbat during the Mourners' Kaddish, will share six names of the 6 million killed. And my children will often look up at me when he mentions the name and age of a child that was killed during the Holocaust. It just highlights the importance of remembering, but doing so in a safe space, in a community, in a sacred space where we're all together, illustrating: we all survived, but it's important to remember those who didn't. When are you done with Leopoldstadt? David Krumholtz: I'm done March 12. Play is going through, as of right now it's extended to July 2, it may extend again, another wonderful actor is going to come in and take my place. I can't tell you who that is yet. I will have done six months. Something like 175 performances, for me, is plenty. This is a hard play to live through and live in the skin of and so, you know, I'm going to take my leave, but it's been transformative and the role of my life. It's just, for someone like Patrick Marber and Tom Stoppard, Sonia Friedman, to have believed in me, to the extent that they did to take on such a huge responsibility just means the world. And hopefully I can take that with me through to the next important job. Manya Brachear Pashman: Why is it important for people to see this play now? David Krumholtz: Well, we live in a time when, unfortunately or fortunately, where we can openly communicate our deepest darkest feelings to one another. Sometimes, those feelings are feelings of hatred. Sometimes those feelings are ignorant feelings of hatred, that are blanket generalizations based on small experiences that people may have had. People tend to use social media, for instance, to make things a lot more, a lot bigger than they are. And so something like a man with 11 million followers saying something anti semitic, can snowball very, very quickly into this kind of real world danger that the show presents that actually happened not too long ago. And so it's very important that now that people of all races, religions, creeds, this could happen to anyone. As Jew as Jews, we have to make sense of what happened to us. Part of making sense of what happened to us, I believe, is telling the story in order to warn not only our own people, but all minorities, all people that this could happen again, that this actually happened, that humanity did this, that hate created murder, can create genocide. And it's our responsibility to pay the lesson we've learned forward, the painful lesson. It's easier to turn a blind eye, or to say, well, that's just Jewish people's problem. The truth is, it's a problem for all humanity. And so hopefully, we're not playing to a bubble of people who need to see this, want to see this, or are Jewish enough to see it.. And I think it has the power to be a play that's impactful for all people. And we found that to be true thus far, it's a really clearly communicated olive branch in a way to say, hey, we went through this, we're telling you this could happen. And stay safe, be smart, and love one another before your time's up. Manya Brachear Pashman: Thank you so much, and thank you for joining us to talk about it today. David Krumholtz: All right. My pleasure. Thanks for having me.
Jan 12, 2023
Shabbat Shalom No More? One Year Later, Colleyville Synagogue Wrestles with Impact of Hostage Crisis
One year ago, Jeff Cohen was taken hostage during Shabbat services by an antisemitic attacker. Hear from Cohen, who is now the president of Congregation Beth Israel synagogue in Colleyville, about all that has transpired since that traumatic day and how the attack has impacted him and the Colleyville Jewish community. Bradley Orsini, the Secure Community Network's senior national security advisor, also joined the conversation to share what steps American Jews can take to protect and empower their communities amid increasing antisemitism. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jeff Cohen, Bradley Orsini ____ Show Notes: Register here for: Surviving Hostage Situations - SCN event on January 19, 2023 Sunday marks one year since attack on Colleyville synagogue TranslateHate.com : Stopping antisemitism starts with understanding it Listen to: Our 2022 podcast episode, right after the Coleyville situation: Inside the Colleyville, Texas Synagogue Hostage Crisis: Hear from 3 Local Jewish and Muslim Leaders on What It Was Like on the Ground Our most recent podcast episode: How Hanukkah's Americanization Became a Show of Jewish Pride Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Dec 22, 2022
How Hanukkah's Americanization Became a Show of Jewish Pride
This Hanukkah, we hear from Rabbi Yael Buechler, a writer, educator, entrepreneur, and Hanukkah merch maven. She's also a Hanukkah historian who has tracked how the festival of lights helped reinvent Jewish culture in America and how it became a gift-giving occasion alongside Christmas. Rabbi Beuchler joins us to discuss how American Jews can take advantage of the marketplace to express their Jewish pride authentically during the Hanukkah season, despite increasing antisemitism–with inflatable menorahs, dreidel nail decals, holiday pajamas, and more. Also, hear from listeners on the Hanukkah traditions they are finding meaning in this year. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:00) Jessica Bernton (1:52) Listener Hanukkah Voicemails (3:28) Rabbi Yael Buechler ___ Show Notes: If you're alarmed by rising antisemitism, you can take action right now by supporting AJC: visit AJC.org/donate , or text AJC DONATE to 52886. Music credits: Lille by johnny_ripper is licensed under a Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 (Will Not Appear in Vimeo Music Store) License. Please Stop Rebranding Christmas Items for Hanukkah by Rabbi Yael Bucheler Listen to: 5 Hanukkah Podcasts to Light Up Your Holiday 7 Podcasts to Help You Understand, Respond To, and Prevent Antisemitism Our latest podcast episode: What Does NYC's Office for the Prevention of Hate Crimes Do?; An Elton John Hanukkah Celebration Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Dec 15, 2022
What Does NYC's Office for the Prevention of Hate Crimes Do?; An Elton John Hanukkah Celebration
Earlier this week, New York City Mayor Eric Adams insisted on the end of plea bargains for the perpetrators of antisemitic attacks and called out all forms of hate. To discuss New York City's efforts to combat the alarming rise in Jew hatred, Hassan Naveed, executive director of New York City's Office for the Prevention of Hate Crimes (OPHC), joins to explain how his office coordinates agencies across the city to curb the rise of antisemitic hate crimes, the importance of tracking these crimes accurately to inform those efforts, and what motivates him to do this work. Then, we're joined by Mike Boxer, one of the members of the Jewish a capella group Six13, to share the group's new Elton John parody song just in time for Hanukkah: Elton Johnukah. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:00) Joshua Kramer (2:10) Hassan Naveed (24:37) Mike Boxer ___ Show Notes: If you're alarmed by rising antisemitism, you can take action right now by supporting AJC: visit AJC.org/donate , or text AJC DONATE to 52886. AJC's State of Antisemitism in America report 2021 Do you decorate for Hanukkah, or leave the decorating to the Christmas crowd? Call us at 212-891-1336 and leave a voicemail of 1 minute or less, and you may hear your voice on next week's episode! Music credits: Together We Stand by Scott Holmes Music is licensed under a Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. Six13 - Elton Johnukah 'No plea bargaining': Adams calls for hate crime reform amid antisemitic violence in NYC NYPD Hate Crimes Dashboard Listen to our latest podcast episode: How Young Jews and Muslims are Advancing Israeli-Moroccan Peace Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Dec 8, 2022
How Young Jews and Muslims are Advancing Israeli-Moroccan Peace
This week marks the second anniversary of the normalization of relations between Israel and Morocco as part of the Abraham Accords. Building on this peace, three young adults hailing from Israel, Morocco, and the U.S. join us to discuss their visit earlier this year to Israel and Morocco. The first-of-its-kind tour was part of the Michael Sachs Emerging Leaders Fellowship, sponsored by AJC and the Mimouna Association, a Muslim nonprofit in Morocco devoted to preserving Jewish-Moroccan heritage. Hillary Jacobs, ACCESS Global and ACCESS NY President, Reda Ayadi, Program Director of Muslim-Jewish dialogue for the Mimouna Association, and Itiel Biran, Head of Operations in the Mayor's office for the municipality of Rahat, Israel, talk about what they learned about Morocco, Israel, and each other, what impact the Abraham Accords have had, and what progress they hope to see continue. __ Episode Lineup: (0:00) Aaron Bregman (2:05) Hillary Jacobs, Itiel Biran, and Reda Ayadi __ Show Notes: If you're alarmed by rising antisemitism, you can take action right now by supporting AJC: visit AJC.org/donate , or text AJC DONATE to 52886. Music credit: Humanity by Scott Holmes Music is licensed under a Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. Listen to our latest podcast episode: What Lessons Can We Learn From the Past to Fight Antisemitism Today? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. __ Episode Transcript Manya Brachear Pashman: Two years ago, Morocco normalized relations with Israel becoming the sixth Arab country to do so. Earlier this year, a group of 22 young Americans, Israelis and Moroccans toured Morocco together, a first of its kind experience for everyone involved. The tour was part of the Michael Sachs Emerging Leaders Fellowship. The fellowship is sponsored by AJC, and the Mimouna Association, a Muslim nonprofit in Morocco devoted to preserving Jewish Moroccan heritage. The first cohort included members of Morocco's parliament, as well as civic, business, and technology leaders in Israel and the United States. With us to talk about this unprecedented venture are three members of that cohort: Hilary Jacobs, president of AJC's young professionals group ACCESS Global, Reda Ayadi, Program Director of Muslim Jewish Dialogue for the Mimouna Association, and Itiel Biran, Head of Operations in the Mayor's office, for the municipality of Rahat, Israel. Welcome to all of you. Hilary Jacobs: Thank you. Itiel Biran: Thank you, hi. Reda Ayadi: Thank you. Manya Brachear Pashman: So Hilary, I will start with you. How did your involvement in the Sachs Fellowship come about? Was it a curiosity about Morocco, curiosity about Israel, or just an opportunity to continue pursuing better Jewish-Muslim relations? Hilary Jacobs: I think all of the above for those. And in addition to that, one, I love traveling, and I love getting to know and experience other cultures, from the people who are from there, and who live there, so less on vacation, and where I can really understand the culture, the geopolitics of the region. And this seemed like a great opportunity. It also felt like a way that, we talk a lot about in the US and in the different activities with AJC about the Abraham accords and about these different relationships, it felt like a real chance for me to do something actionable, and really learn about what that meant. Manya Brachear Pashman: Itiel, had you been to Morocco? Itiel Biran: No, no, this was my first time. Manya Brachear Pashman: Okay, had you even wanted to go? And just could not? Or did this plant the idea in your head? Itiel Biran: To be honest, I don't think it was in my radar,, in my point of view, or thinking. Mostly, I think because even my background in the army and you look outside, you don't really look at it, until the last couple of years don't really look and say like, I'm going to visit whatever, Egypt or Morocco or something like that. We need to be frank and say that a lot of Israelis visited Morocco in the last decade. A lot of them. But for me personally, it wasn't like an opportunity until it became more real in the area, in the region. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Reda, had you been to Israel? because that was part of this as well, right, a trip to Israel? Reda Ayadi: That's correct. The second part, right after Morocco, we flew from Casablanca to Tel Aviv, for the second part of the trip. Before that I had been to Israel, it was almost 10 years to the day, so 2012 was the first time I went, before the Abraham Accords and the situation was a little different than it is today. Manya Brachear Pashman: How so? I mean, was it different for you as a traveler? Personally or geopolitically in the broader scope? Reda Ayadi: It was different, more geopolitically was different. And also as a traveler, I'll explain both sides. 2012 there were no Abraham Accords, there was no open dialogue between the countries in the region. So it was a purely civil society kind of grassroots organization talking to each other. So we didn't have the necessary framework within which we can operate. On a personal level, as a traveler it's also quite different, back then I remember in 2012 I had to fly to Istanbul and meet someone from Israel to give me my Israel visa, but now you can just go to the Israeli office in Rabat and submit your application and get your visa to travel. So, quite a different situation. Manya Brachear Pashman: So, let's summarize for our listeners kind of the Jewish history of Morocco, there has always been a kind of a quiet connection. Excuse me, there's always been kind of a quiet connection between Israel and Morocco, particularly the Moroccan diaspora in the Jewish state and then kind of the new kind of 21st century approach there in Morocco to celebrating interfaith relations, celebrating its Jewish history. Reda Ayadi: Morocco had the largest Jewish community in the Muslim world, and the largest outside of the Ashkenazi world, with almost 300,000 Jews, up until the 60s, quite a large flow migration started one way, and I guess, yes, there was definitely a strong connection that were maintained between Moroccan monarchy and heads of state in Israel. Some of it was indeed behind closed doors. But others were more in the open, like the trip to Shimon Peres to Morocco or Yitzchak Rabin, and others. So, I think, the 21st century as you said, there are two things: Morocco's approach, and its relationship with its Jewish community, like the 2011 constitution that finally recognized it as an essential component of Moroccan identity, its Jewish part, its Jewishness. But at the same time, Abraham Accords now that gave a new kind of strong impetus to go beyond what you said, you know, those kinds of closed door connections, usually between security officials, that now it's, you know, accorded across the whole spectrum of agricultural, technology, lots of people to people relations. So it's, yeah, it's a very significant change that we're seeing now. Hilary Jacobs: Unlike most other countries, Jews were never kicked out of Morocco. In fact, originally, during the Spanish Inquisition, they were asked to come to Morocco. And were wanted to be there. And the people that we met and spoke with felt the loss of the Jewish community there when they migrated to Israel. And so I think that's something that's really special. And I'm the granddaughter of two Holocaust survivors, and then Russian on the other side, so a lot of persecution and to think about Jews being in a country in a region, and especially we don't think about in the Arab world, as one that is welcoming to Jewish people, and beyond welcoming, to really see them as their fellow citizens, Manya Brachear Pashman: Itiel, did you have something to add? Itiel Biran: Yeah, I want to add two things. One, and I think, from Israel's society point of view, there's some interesting collision of the vector of what happened in Israel, to the Moroccan Jews in Israel, in the last seventy years, that I think relates very much to what happened these days between Morocco and Israel. And I think we should speak and when we look at the history of Israel, the Moroccan Jews a lot of the Mizrahim, a lot of the people from Africa, and not the Ashkenazi people were pretty much pushed aside from the decision-making places. And there's some big changes in Israel in the decades that follow, that I think influenced a lot of how not only Moroccan but also the whole society in Israel, look at the heritage, the big and amazing heritage that Moroccan Jews bring to Israel. And I think these days, what we've seen is a combination between what Israels look up and look on the history of themselves. You know, the Moroccan Jews in Israel are a half a million people. There's a lot of people, the heritage is enormous, amazing, a lot of culture. And for decades Israeli society looks at them and the very good foods or something like that. And I think this change impacts a lot. And it's very helpful. This is the first thing I want to say, of course, to relate to what Reda said, the Abraham Accords is the peak of process. I think in Morocco, not in other countries. In other countries, I think it's the start of a process. In Morocco and in the relationship between Morocco and Israel is, it's some kind of a peak, because there was an ongoing relationship for a lot of the time. But there was never, from up-down, always from down to up, only from top to bottom. This is a point of view that will really help you understand why this peak of relationship between Morocco and Israel is so strong, and why the changing of how many Israelis come to Morocco, it changed in two, three years from 50,000 to 200,000 a year. I think because it's a peak, not a start. Manya Brachear Pashman: That's a really interesting point. In other words, you're saying that the renewed interest in the Jewish history of Morocco plus the renewed look at how Moroccan Jews are treated in Israel, both of those paved the way toward this normalization. Itiel Biran: Yes, with all of the other things, the business opportunities, etc. Manya Brachear Pashman: Right. That is, that's really a very good point, Itiel, I appreciate you making that. I'm curious, both of you, Itiel, Hillary, what did you learn about the Jewish community in Morocco, and the efforts on behalf of both Jewish and Muslim communities there to better understand each other. Itiel Biran: First of all, for sure what I mentioned before, for me is the continuous process of my friend for me, there is not a good translation for this, but I'm very a fan of the Arabs in Morocco, and the identity, and I'm looking at myself as Israeli, as a combination of a lot of identities. And a lot of them are more like an African identity. And I think there's a continuous process in a lot of Israelis to embrace this identity, even more. And I think when I went to Morocco, it was a big, strong feeling of this heritage and how it's related to me. And to be honest, the absence of similar heritage from my own places I'm from. I'm Ashkenazi, from Poland and from Germany, etc. And there's nothing there. There's nothing there left, there's nothing there to see what my ancestors were talking about, and what this big proud communities were. When you go to Morocco, you see all the stories in real life. It's blown my mind. It's amazing. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Hillary, what did you learn about the Jewish community in Morocco, when you went? Hilary Jacobs: You know, it's very humbling. I also grew up in a very Ashkenazi centric world, or around Sephardic Jews, mostly from Iran, and there was maybe like one or two, you know, Moroccan Jews, and I never really got to learn about any of their traditions at all, and so on this trip, getting to see those and also seeing how our Moroccan counterparts were as excited about participating in those cultural traditions. I mean, the Mimuna Association is called the Mimouna Association for a reason, after one of those specifically Moroccan holidays after Pesach. So, that was kind of amazing. I think the fact that an organization that started out simply as an on campus group that has blossomed into an NGO, would go around and preserve Jewish sites and culture. Manya Brachear Pashman: What is the Mimouna Association? Reda Ayadi: The Mimouna Association is now a Moroccan NGO. It started in 2007 at my university, as Student Club, right. Just a group of students decided that they want to learn more about Moroccan Jewish heritage. So 10 of them got together and created the club and started pretty small. Just once a month or once every other month, they will do an event, like Moroccan Jewish days, or something of the sort where they would turn the whole campus Jewish for a day, you know, like Moroccan Jewish food within the the cafeteria, the library would show books from Moroccan Jewish writers or scholars, and things of the sort. And I guess it evolved quite a bit from 2007 until 2012, when a lot of us graduated, and we registered what was then a student club into a Moroccan NGO that exists outside of the university, present in a few cities. And also we started different tiers, student branches in other universities besides the one where it started. The big chunk of the work that's done is education, really working in universities and high schools with students to learn more about their own history that most people are not very much aware of. That's one. Two, we work on Holocaust education as well. The Holocaust is not necessarily a chapter that Moroccans are very familiar with. But with partners in the US and others we developed a Holocaust curriculum specifically for an Arab audience. So we focus on that. And also we work on Muslim-Jewish relations with both the Jewish community in Morocco and outside, in the US, Israel and other countries. So that's just a few of the things that we focus on. Now it's been more than 15 years doing the work. And we continue, there is plenty that needs to be done. Manya Brachear Pashman: Since Israel and Morocco did establish diplomatic relations, I think more than 30 agreements have been brokered having to do with a variety of things: water management, renewable energy, security. I'm curious if there were any particular collaborations that you explored during this fellowship that intrigued you or or kind of struck you as particularly beneficial for the region? And Reda, I'll start with you. Reda Ayadi: I think a critical issue is really the water management in both. Morocco right now is suffering from a very heavy drought that's been ongoing for a long time. And both the well-being of everyone in the country depends on water resources. So like cooperating in that space, I think it is excellent. And I think could be a good platform for both Morocco and Israel to pursue similar agendas in other countries, because water scarcity is not just an issue for Morocco, it's an issue for the whole region. So I think it could be a way to work with countries that are also in such a need. Manya Brachear Pashman: Hilary, I'll pose the same question to you. Hilary Jacobs: From what I experienced, there's so many different opportunities. Tourism is something that we talked a lot about as it being something very immediate that we could do as individuals, encouraging people to go there, we met with the tourism office. And so how we can encourage Israelis and Americans to go there. Also, one of the things that I learned that was really helpful in terms of thinking about the region as a whole, and as Morocco as a gateway to Africa, and that being so essential and important for the future of Israel, and there's a lot of contention often in African countries, and its relationship to Israel. Like, considering the vote of the African Union to potentially kick out the delegates from Israel. And so to really be championing these new sorts of relationships in Morocco, I think is an excellent starting point to open up a whole new region of possibilities. And so, there's just kind of endless opportunities that can come through, starting with Morocco and moving out all over Africa. Manya Brachear Pashman: And Itiel, are there particular collaborations that you find very beneficial? Itiel Biran: For me myself, to be honest, what's very unique, look at governmental, municipality and governance. And I think I told this to my friends from Morocco. I was very surprised and very interested about the way of managing and the way of handling pretty much the same issues in a different country with different rules and different government, and I think there's a lot of potential there. Manya Brachear Pashman: So these past couple of weeks, we've been watching the first World Cup hosted in the Arab world in Qatar, yet it was quite an ordeal to arrange for Israelis and Palestinians to fly directly from Israel. And since some of the Israeli journalists have arrived there, they've been harassed simply because of where they're from. And I'm curious if your participation in this program, your engagement in these these kinds of relationships, if it changed how you view tensions like this? Itiel Biran: Every experience that we experience as an Israeli comes across Arab people all around the world or in Israel, or in Morocco, or you come across Israelis, or what you're facing back home. And when you speak on your relationship or what your projects are. I think most of this experience speaks pretty much the same language. And the same language is: peace is coming from people, from face to face, from long relationships, from knowledge, from understanding, from business and actions, and not from papers and not from anything else. And you can say from the point of view of Israel: yeah, we have a peace agreement with some countries – is there any peace with them? Yeah, peace agreement, there is. But has there been peace with them? And for my personal view, I came to Morocco with my arms up, ready to argue, ready to defend my point of view as an Israeli. Ready to, whatever. And I was blown away by the fact that I didn't have to do it. That some some root or some foundation of coexistence, even though there's a lot of misunderstanding. There's a lot of mania. There's a lot of things that people on both sides think and hear and don't understand. When you have some foundation of warmth, there's something to build on. And when you don't have it--whatever agreement you're going to do, and whatever speaking you're going to do is going to stay in the area of speaking, of talking. Enough. And I think this statement that I just said, it's going through our delegation, and our friendship, and continuing after this program to, to do things together and speak together and discuss. Because I think all of us, when we met in this delegation, it wasn't something for one time and meeting. All of us felt, I think, and agreed without talking about it, that when you do this day to day speaking and working and action, you make with your own hands, the warm peace, that you can actually build on. Manya Brachear Pashman: Have you encountered pushback from others for participating in this program? And if so, how do you respond to that kind of pushback? Reda Ayadi: Trust is very hard, if we have learned for generations to mistrust, to distrust each other. It's hard to just like one day wake up and be, 'Oh, you know, it's all good, it's easy to go back and forth without any issue.' If we would just give up after any pushback after any, being stopped at the checkpoint or at an airport for two hours, nobody would be doing anything, you know. Since my first trip and my second trip and my third trip to Israel, every time I would spend at least two hours in a room waiting for someone to come question me. But I understand that it takes this many times and this many years for the other to become less other, to become something someone that's familiar. And I hope that both Israelis and Palestinians go into the World Cup and everyone else traveling back and forth between these countries, to not give up after the first difficult experience trying to travel and build bridges between these peoples. And to continue doing. Manya Brachear Pashman: Excellent. Well, thanks to all of you for making the trip, for participating in this fellowship, and for coming and sharing your experience with our listeners. Itiel Biran: Thank you for the opportunity.
Dec 1, 2022
What Lessons Can We Learn From the Past to Fight Antisemitism Today?
Before, during, and after the Holocaust, antisemitism spread throughout American society. AJC's innovative multimedia campaign to counter this rising hatred is the subject of "Confronting Hate: 1937-1952," an exhibit at the New York Historical Society. With posters, comic books, newspaper advertisements, radio spots, and television cartoons, that, since 1952, have not been seen by the public, join Charlotte Bonelli, Director of AJC's Archives and Records Center, and Debra Schmidt Bach, Curator of Decorative Arts and Special Exhibitions at the New-York Historical Society, for a behind-the-scenes tour, recorded live from the exhibit. Hear original radio clips: "Uncle Don's All-American Contest," "Dear Adolf," and a historic, moving 1944 NBC Radio broadcast in cooperation with AJC, which aired the first Jewish religious broadcast from Germany since the rise of Hitler, straight from a battlefield in Aachen, Germany. __ Episode Lineup: (0:00) Dana Steiner (2:00) Charlotte Bonelli and Debra Schmidt Bach __ Show Notes: If you're alarmed by rising antisemitism, you can take action right now by supporting AJC: visit AJC.org/donate , or text AJC DONATE to 52886. Visit the New York Historical Society to see "Confronting Hate 1937–1952" open through January 1, 2023. Interested in bringing "Confronting Hate 1937–1952" to your museum or institution, free or charge? Contact Emily Croll, Deputy Museum Director at travelingexhibitions@nyhistory.org , or (212) 873-3400 x527. AJC's William E. Wiener Oral History Library : listen to the oral histories of Milton Krents, Richard Rothschild and Ethel Phillips, which helped inform the exhibit. AJC Archives Uncle Don's All American Contest Broadcasting from the Battlefield Music credit: Lille by johnny_ripper is licensed under a Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 (Will Not Appear in Vimeo Music Store) License. Listen to our latest podcast episode: From "Chopped" to the White House: TikTok Chef Eitan Bernath on Being a Loud and Proud Jew Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Nov 30, 2022
Celebrating Mizrahi Heritage Month with The Forgotten Exodus: Iran
Too few people know that parts of the Arab world and Iran were once home to large Jewish communities. This Mizrahi Heritage Month, let's change the story, with the final episode of the first season of The Forgotten Exodus , the first-ever narrative podcast series devoted exclusively to the rich, fascinating, and often-overlooked history of Mizrahi and Sephardic Jewry. Thank you for lifting up these stories to celebrate Mizrahi Heritage Month. If you enjoy this episode, be sure to listen to the rest of The Forgotten Exodus, wherever you get your podcasts. __ Home to one of the world's oldest Jewish communities, the story of Jews in Iran has been one of prosperity and suffering through the millennia. During the mid-20th century, when Jews were being driven from their homes in Arab lands, Iran assisted Jewish refugees in providing safe passage to Israel. Under the Shah, Israel was an important economic and political ally. Yet that all swiftly changed in the 1979 Iranian Revolution, which ushered in Islamic rule, while chants of "Death to Israel" and "Death to America" rang out from the streets of Tehran. Author, journalist, and poet Roya Hakakian shares her personal story of growing up Jewish in Iran during the reign of the Shah and then Ayatollah Khomeini, which she wrote about in her memoir Journey From the Land of No. Joining Hakakian is Dr. Saba Soomekh, a professor of world religions and Middle Eastern history who wrote From the Shahs to Los Angeles: Three Generations of Iranian Jewish Women between Religion and Culture. She also serves as associate director of AJC Los Angeles, home to America's largest concentration of Persian Jewish immigrants. In this sixth and final episode of the season, the Hakakian family's saga captures the common thread that has run throughout this series – when the history of an uprooted community is left untold, it can become vulnerable to others' narratives and assumptions, or become lost forever and forgotten. How do you leave behind a beloved homeland, safeguard its Jewish legacy, and figure out where you belong? __ Show notes: Listen to The Forgotten Exodus and sign up to receive updates about future episodes. Song credits: Chag Purim · The Jewish Guitar Project Hevenu Shalom · Violin Heart Pond5 : "Desert Caravans": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI), Composer: Tiemur Zarobov (BMI), IPI#1098108837 "Oud Nation": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI); Composer: Haygaz Yossoulkanian (BMI), IPI#1001905418 "Persian": Publisher: STUDEO88; Composer: Siddhartha Sharma "Meditative Middle Eastern Flute": Publisher: N/; Composer: DANIELYAN ASHOT MAKICHEVICH (IPI NAME #00855552512), UNITED STATES BMI Zarobov (BMI), IPI#1098108837 "Sentimental Oud Middle Eastern": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI), Composer: Sotirios Bakas (BMI), IPI#797324989. "Frontiers": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI); Composer: Pete Checkley (BMI), IPI#380407375 "Persian Investigative Mystery": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI); Composer: Peter Cole (BMI), IPI#679735384 "Persian Wind": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Sigma (SESAC); Composer: Abbas Premjee (SESAC), IPI#572363837 "Modern Middle Eastern Underscore": Publisher: All Pro Audio LLC (611803484); Composer: Alan T Fagan (347654928) "Persian Fantasy Tavern": Publisher: N/A; Composer: John Hoge "Adventures in the East": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI) Composer: Petar Milinkovic (BMI), IPI#00738313833. ___ Episode Transcript: ROYA HAKAKIAN: In 1984, when my mother and I left and my father was left alone in Iran, that was yet another major dramatic and traumatic separation. When I look back at the events of 1979, I think, people constantly think about the revolution having, in some ways, blown up Tehran, but it also blew up families. And my own family was among them. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: The world has overlooked an important episode in modern history: the 800,000 Jews who left or were driven from their homes in Arab nations and Iran in the mid-20th century. This series, brought to you by American Jewish Committee, explores that pivotal moment in Jewish history and the rich Jewish heritage of Iran and Arab nations as some begin to build relations with Israel. I'm your host, Manya Brachear Pashman. Join us as we explore family histories and personal stories of courage, perseverance, and resilience. This is The Forgotten Exodus. Today's episode: Leaving Iran MANYA: Outside Israel, Iran has the largest Jewish population in the Middle East. Yes, the Islamic Republic of Iran. In 2022. Though there is no official census, experts estimate about 10,000 Jews now live in the region previously known as Persia. But since the 1979 Iranian Revolution, Jews in Iran don't advertise their Jewish identity. They adhere to Iran's morality code: women stay veiled from head to toe and men and women who aren't married or related stay apart in public. They don't express support for Israel, they don't ask questions, and they don't disagree with the regime. One might ask, with all these don'ts, is this a way of living a Jewish life? Or a way to live – period? For author, journalist, and poet Roya Hakakian and her family, the answer was ultimately no. Roya has devoted her life to being a fact-finder and truth-teller. A former associate producer at the CBS news show 60 Minutes and a Guggenheim Fellow, Roya has written two volumes of poetry in Persian and three books of nonfiction in English, the first of which was published in 2004 – Journey From the Land of No, a memoir about her charmed childhood and accursed adolescence growing up Jewish in Iran under two different regimes. ROYA: It was hugely important for me to create an account that could be relied on as a historic document. And I did my best through being very, very careful about gathering, interviewing, talking to, observing facts, evidence, documents from everyone, including my most immediate members of my family, to do what we, both as reporters, but also as Jews, are called to do, which is to bear witness. No seemed to be the backdrop of life for women, especially of religious minorities, and, in my own case, Jewish background, and so I thought, what better way to name the book than to call it as what my experience had been, which was the constant nos that I heard. So, Land of No was Iran. MANYA: As a journalist, as a Jew, as a daughter of Iran, Roya will not accept no for an answer. After publishing her memoir, she went on to write Assassins of the Turquoise Palace, a meticulously reported book about a widely underreported incident. In 1992 at a Berlin restaurant, a terrorist attack by the Iranian proxy Hezbollah targeted and killed four Iranian-Kurdish exiles. The book highlighted Iran's enormous global footprint made possible by its terror proxies who don't let international borders get in the way of silencing Iran's critics. Roya also co-founded the Iran Human Rights Documentation Center, an independent non-profit that reports on Iran's human rights abuses. Her work has not prompted Ayatollah Khameini to publicly issue a fatwa against her – like the murder order against Salman Rushdie issued by his predecessor. But in 2019, one of her teenage sons answered a knock at the door. It was the FBI, warning her that she was in the crosshairs of the Iranian regime's operatives in America. Most recently, Roya wrote A Beginner's Guide to America: For the Immigrant and the Curious about the emotional roller coaster of arriving in America while still missing a beloved homeland, especially one where their community has endured for thousands of years. ROYA: I felt very strongly that one stays in one's homeland, that you don't just simply take off when things go wrong, that you stick around and try to figure a way through a bad situation. We came to the point where staying didn't seem like it would lead to any sort of real life and leaving was the only option. MANYA: The story of Jews in Iran, often referred to as Persia until 1935, is a millennia-long tale. A saga of suffering, repression, and persecution, peppered with brief moments of relief or at least relative peace – as long as everyone plays by the rules of the regime. SABA SOOMEKH: The history of Jews in Iran goes back to around 2,700 years ago. And a lot of people assume that Jews came to Iran, well at that time, it was called the Persian Empire, in 586 BCE, with the Babylonian exile. But Jews actually came a lot earlier, we're thinking 721-722 BCE with the Assyrian exile which makes us one of the oldest Jewish communities. MANYA: That's Dr. Saba Soomekh, a professor of world religions and Middle Eastern history and the author of From the Shahs to Los Angeles: Three Generations of Iranian Jewish Women between Religion and Culture . She also serves as associate director of American Jewish Committee in Los Angeles, home to America's largest concentration of Persian Jewish immigrants. Saba's parents fled Iran in 1978, shortly before the revolution, when Saba and her sister were toddlers. She has devoted her career to preserving Iranian Jewish history. Saba said Zoroastrian rulers until the 7th Century Common Era vacillated between tolerance and persecution of Jews. For example, according to the biblical account in the Book of Ezra, Cyrus the Great freed the Jews from Babylonian rule, granted all of them citizenship, and permitted them to return to Jerusalem to rebuild their Temple. The Book of Esther goes on to tell the story of another Persian king, believed to be Xerxes I, whose closest adviser called Haman conspires to murder all the Jews – a plot that is foiled by his wife Queen Esther who is Jewish herself. Esther heroically pleads for mercy on behalf of her people – a valor that is celebrated on the Jewish holiday of Purim. But by the time of the Islamic conquest in the middle of the 7th Century Common Era, the persecution had become so intense that Jews were hopeful about the new Arab Muslim regime, even if that meant being tolerated and treated as second-class citizens, or dhimmi status. But that status had a different interpretation for the Safavids. SABA: Really things didn't get bad for the Jews of the Persian Empire until the 16th century with the Safavid dynasty, because within Shia Islam in the Persian Empire, what they brought with them is this understanding of purity and impurity. And Jews were placed in the same category as dogs, pigs, and feces. They were seen as being religiously impure, what's referred to as najes . MANYA: Jews were placed in ghettos called mahaleh, where they wore yellow stars and special shoes to distinguish them from the rest of the population. They could not leave the mahaleh when it rained for fear that if water rolled off their bodies into the water system, it would render a Shia Muslim impure. For the same reason, they could not go to the bazaars for fear they might contaminate the food. They could not look Muslims in the eye. They were relegated to certain artisanal professions such as silversmithing and block printing – crafts that dirtied one's hands. MANYA : By the 19th century, some European Jews did make their way to Persia to help. The Alliance Israélite Universelle, a Paris-based network of schools founded by French Jewish intellectuals, opened schools for Jewish children throughout the Middle East and North Africa, including within the mahalehs in Persia. SABA: They saw themselves as being incredibly sophisticated because they were getting this, in a sense, secular European education, they were speaking French. The idea behind the Allianz schools was exactly that. These poor Middle Eastern Jews, one day the world is going to open up to them, their countries are going to become secular, and we need to prepare them for this, not only within the context of hygiene, but education, language. And the Allianz schools were right when it came to the Persian Empire because who came into power was Reza Pahlavi, who was a Francophile. And he turned around and said, 'Wow! Look at the population that speaks French, that knows European philosophy, etc. are the Jews.' He brought them out of the mahaleh , the Jewish ghettos, and said 'I don't care about religion. Assimilate and acculturate. As long as you show, in a sense, devotion, and nationalism to the Pahlavi regime, which the Jews did—not all Jews—but a majority of them did. MANYA: Reza Pahlavi took control in 1925 and 16 years later, abdicated his throne to his son Muhammad Reza Pahlavi. In 1935, Persia adopted a new name: Iran. As king or the Shah, both father and son set Iran on a course of secularization and rapid modernization under which Jewish life and success seemed to flourish. The only condition was that religious observance was kept behind closed doors. SABA: The idea was that in public, you were secular and in private, you were a Jew. You had Shabbat, you only married a Jew, it was considered blasphemous if you married outside of the Jewish community. And it was happening because people were becoming a part of everyday schools, universities. But that's why the Jewish day schools became so important. They weren't learning Judaism. What it did was ensure that in a secular Muslim society, that the Jewish kids were marrying within each other and within the community. It was, in a sense, the Golden Age. And that will explain to you why, unlike the early 1950s, where you had this exodus of Mizrahi Jews, Arab Jews from the Arab world and North Africa, you didn't really have that in Iran. MANYA: In fact, Iran provided a safe passage to Israel for Jewish refugees during that exodus, specifically those fleeing Iraq. The Pahlavi regime considered Israel a critical ally in the face of pan-Arab fervor and hostility in the region. Because of the Arab economic boycott, Israel needed energy sources and Iran needed customers for its oil exports. A number of Israelis even moved to Tehran, including farmers from kibbutzim who had come to teach agriculture, and doctors and nurses from Hadassah Hospital who had come to teach medicine. El Al flew in and out of Tehran airport, albeit from a separate terminal. Taking advantage of these warm relations between the two countries, Roya recalls visiting aunts, uncles, and cousins in Israel. ROYA: We arrived, and my mom and dad did what all visiting Jews from elsewhere do. They dropped to their knees, and they started kissing the ground. I did the same, and it was so moving. Israel was the promised land, we thought about Israel, we dreamed about Israel. But, at the same time, we were Iranians and, and we were living in Iran, and things were good. This seems to non-Iranian Jews an impossibility. But I think for most of us, it was the way things were. We lived in the country where we had lived for, God knows how many years, and there was this other place that we somehow, in the back of our minds thought we would be going to, without knowing exactly when, but that it would be the destination. MANYA: Relations between the Shah and America flourished as well. In 1951, a hugely popular politician by the name of Mohammad Mosaddegh became prime minister and tried to institute reforms. His attempts to nationalize the oil industry and reduce the monarchy's authority didn't go over well. American and British intelligence backed a coup that restored the Shah's power. Many Iranians resented America's meddling, which became a rallying cry for the revolution. U.S. officials have since expressed regret for the CIA's involvement. In November 1977, President Jimmy Carter welcomed the Shah and his wife to Washington, D.C., to discuss peace between Egypt and Israel, nuclear nonproliferation, and the energy crisis. As an extension of these warm relations, the Shah sent many young Iranians to America to enhance their university studies, exposing them to Western ideals and values. Meanwhile, a savvy fundamentalist cleric was biding his time in a Paris basement. It wouldn't be long before relations crumbled between Iran and Israel, Iran and the U.S,. and Iran and its Jews. Roya recalls the Hakakian house at the corner of Alley of the Distinguished in Tehran as a lush oasis surrounded by fragrant flowers, full of her father's poetry, and brimming with family memories. Located in the heart of a trendy neighborhood, across the street from the Shah's charity organization, the tall juniper trees, fragrant honeysuckle, and gold mezuzah mounted on the door frame set it apart from the rest of the homes. Roya's father, Haghnazar, was a poet and a respected headmaster at a Hebrew school. Roya, which means dream in Persian, was a budding poet herself with the typical hopes and dreams of a Jewish teenage girl. ROYA: Prior to the revolution, life in an average Tehran Hebrew Day School looked very much like life in a Hebrew Day School anywhere else. In the afternoons we had all Hebrew and Jewish studies. We used to put on a Purim show every year. I wanted to be Esther. I never got to be Esther. We had emissaries, I think a couple of years, from Israel, who came to teach us how to do Israeli folk dance. MANYA: There were moments when Roya recalls feeling self-conscious about her Jewishness, particularly at Passover. That's when the family spent two weeks cleaning, demonstrating they weren't najes , or dirty Jews. The work was rewarded when the house filled with the fragrance of cumin and saffron and Persian dishes flowed from the kitchen, including apple and plum beef stew, tarragon veal balls stuffed with raisins, and rice garnished with currants and slivers of almonds. When her oldest brother Alberto left to study in America, a little fact-finding work on Roya's part revealed that his departure wasn't simply the pursuit of a promising opportunity. As a talented cartoonist whose work had been showcased during an exhibition in Tehran, his family feared Alberto's pen might have gone too far, offending the Pahlavi regime and drawing the attention of the Shah's secret police. Reports of repression, rapid modernization, the wide gap between Tehran's rich and the rest of the country's poor, and a feeling that Iranians weren't in control of their own destiny all became ingredients for a revolution, stoked by an exiled cleric named Ruhollah Khomeini who was recording cassette tapes in a Paris basement and circulating them back home. SABA: He would just sit there and go on and on for hours, going against the Shah and West toxification. And then the recordings ended up in Iran. He wasn't even in Iran until the Shah left. MANYA: Promises of democracy and equality galvanized Iranians of all ages to overthrow the Shah in February 1979. Even the CIA was surprised. SABA: I think a lot of people didn't believe it. Because number one, the Shah, the son, was getting the most amount of military equipment from the United States than anyone in the Middle East and in the Persian Gulf. And the idea was: you protect us in the Gulf, and we will give you whatever you need. So they never thought that a man with a beard down to his knee was able to overthrow this regime that was being propped up and supported by America, and also the Europeans. Khomeini comes in and represents himself as a person for everyone. And he was brilliant in the way he spoke about it. And the reason why this revolution was also successful was that it wasn't just religious people who supported Khomeini, there was this concept you had, the men with the turbans, meaning the religious people, and the you know, the bow ties or the ties, meaning the secular man, a lot of them who were sent by the Shah abroad to Europe and America to get an education, who came back, saw democracy there, and wanted it for their country. MANYA: Very few of the revolutionaries could predict that Tehran was headed in the opposite direction and was about to revert to 16th Century Shia Islamic rule. For almost a year, Tehran and the rest of the nation were swept up in revolutionary euphoria. Roya recalls how the flag remained green, white, and red, but an Allah insignia replaced its old sword-bearing lion. New currency was printed, with portraits bearing beards and turbans. An ode to Khomeini became the new national anthem. While the Shah had escaped on an Air France flight, corpses of his henchmen graced the front pages of newspapers alongside smiling executioners. All celebrated, until the day one of the corpses was Habib Elghanian, the Jewish philanthropist who supported all of Iran's Hebrew schools. Charged and convicted as a Zionist spy. Elders in the community remembered the insurmountable accusations of blood libel during darker times for Iran's Jews. But younger generations like Roya's, who had not lived through the eras of more ruthless antisemitism and persecution, continued to root for the revolution, regardless of its victims. Meanwhile, Roya's Jewish day school was taken over by a new veiled headmistress who replaced Hebrew lessons with other kinds of religious instruction, and required robes and headscarves for all the students. ROYA: In the afternoons, from then on, we used to have lessons in a series of what she called: 'Is religion something that you inherit, or is it something that you choose?' And so I think the intention, clearly, was to convince us that we didn't need to inherit our religions from our parents and ancestors, that we ought to consider better choices. MANYA: But when the headmistress cut short the eight-day Passover break, that was the last straw for Roya and her classmates. Their revolt got her expelled from school. Though Jews did not universally support Khomeini, some saw themselves as members of the Iranian Communist, or Tudeh Party. They opposed the Shah and the human rights abuses of his monarchy and cautiously considered Khomeini the better option, or at least the lesser of two evils. Alarmed by the developments such as Elghanian's execution and changes like the ones at Roya's school, Jewish community leaders traveled to the Shia holy city of Qom to assure the Supreme Leader of their loyalty to Iran. SABA: They did this because they wanted to make sure that they protected the Jewish community that was left in Iran. Khomeini made that distinction: 'I am not against Jews, I'm against Zionists. You could be Jewish in this country. You cannot be a Zionist in this country.' MANYA: But that wasn't the only change. Right away, the Family Protection Law was reversed, lifting a law against polygamy, giving men full rights in divorce and custody, and lowering the marriage age for girls to nine. Women were banned from serving as judges, and beaches and sports events were segregated by gender. But it took longer to shut down universities, albeit for only two years, segregate public schools by gender, and stone to death women who were found to have committed adultery. Though Khomeini was certainly proving that he was not the man he promised to be, he backed away from those promises gradually – one brutal crackdown at a time. As a result, the trickle of Jews out of Iran was slow. ROYA: My father thought, let's wait a few years and see what happens. In retrospect, I think the overwhelming reason was probably that nobody believed that things had changed, and so drastically. It seemed so unbelievable. I mean, a country that had been under monarchy for 2,500 years, couldn't simply see it all go and have a whole new system put in place, especially when it was such a radical shift from what had been there before. So I think, in many ways, we were among the unbelievers, or at least my father was, we thought it could never be, it would not happen. My father proved to be wrong, nothing changed for the better, and the conditions continued to deteriorate. So, so much catastrophe happened in those few years that Iran just simply was steeped into a very dark, intense, and period of political radicalism and also, all sorts of economic shortages and pressures. And so the five years that we were left behind, that we stayed back, changed our perspective on so many things. MANYA: In November 1979, a group of radical university students who supported the Iranian Revolution, took over the U.S. Embassy in Tehran, seized hostages, and held them for 444 days until President Ronald Reagan's inauguration on January 20, 1981. During the hostages' captivity, Iraqi President Saddam Hussein invaded Iran. The conflict that ensued for eight years created shortages on everything from dairy products to sanitary napkins. Mosques became distribution centers for rations. ROYA: We stood in line for hours and hours for eggs, and just the very basic things of daily life. And then it became also clear that religious minorities, including Jews, would no longer be enjoying the same privileges as everyone else. There were bombings that kept coming closer and closer to Tehran, which is where we lived. It was very clear that half of my family that was in the United States could not and would not return, because they were boys who would have been conscripted to go to war. Everything had just come apart in a way that was inconceivable to think that they would change for the better again. MANYA: By 1983, new laws had been passed instituting Islamic dress for all women – violations of which earned a penalty of 74 lashes. Other laws imposed an Islamic morality code that barred co-ed gatherings. Roya and her friends found refuge in the sterile office building that housed the Jewish Iranian Students Association. But she soon figured out that the regime hadn't allowed it to remain for the benefit of the Jewish community. It functioned more like a ghetto to keep Jews off the streets and out of their way. Even the activities that previously gave her comfort were marred by the regime. Poetry books were redacted. Mountain hiking trails were arbitrarily closed to mourn the deaths of countless clerics. SABA: Slowly what they realize, when Khomeini gained power, was that he was not the person that he claimed to be. He was not this feminist, if anything, all this misogynistic rule came in, and a lot of people realize they, in a sense, got duped and he stole the revolution from them. MANYA: By 1984, the war with Iraq had entered its fourth year. But it was no longer about protecting Iran from Saddam Hussein. Now the Ayatollah wanted to conquer Baghdad, then Jerusalem where he aspired to deliver a sermon from the Temple Mount. Meanwhile, Muslim soldiers wounded in the war chose to bleed rather than receive treatment from Jewish doctors. Boys as young as 12 – regardless of faith – were drafted and sent on suicide missions to open the way for Iranian troops to do battle. SABA: They were basically used as an army of children that the bombs would detonate, their parents would get a plastic key that was the key to heaven. And the bombs would detonate, and then the army would come in Iranian army would come in. And so that's when a lot of the Persian parents, the Jewish parents freaked out. And that's when they were like: we're getting out of here. MANYA: By this time, the Hakakian family had moved into a rented apartment building and Roya was attending the neighborhood school. Non-Muslim students were required to take Koran classes and could only use designated water fountains and bathrooms. As a precaution, Roya's father submitted their passports for renewal. Her mother's application was denied; Roya's passport was held for further consideration; her father's was confiscated. One night, Roya returned home to find her father burning her books and journals on the balcony of their building. The bonfire of words was for the best, he told her. And at long last, so was leaving. With the help of the Hebrew Immigrant Aid Society, Roya and her mother, Helen, fled to Geneva, and after wandering in Europe for several months, eventually reunited with her brothers in the United States. Roya did not see her father again for five years. Still unable to acquire a passport, he was smuggled out of Iran into Pakistan, on foot. ROYA: My eldest brother left to come to America in the mid-70s. There was a crack in the body of the family then. But then came 1979, and my two other brothers followed. And so we were apart for all those very, very formative years. And then, in 1984, when my mother and I left and my father was left alone in Iran, that was yet another major dramatic and traumatic separation. So, you know, it's interesting that when I look back at the events of 1979, I think, people constantly think about the revolution having, in some ways, blown up Tehran, but it also blew up families. And my own family was among them. MANYA: While her father's arrival in America was delayed, Roya describes her arrival in stages. She first arrived as a Jewish refugee in 1985 and found her place doing what she had always done – writing in Persian – rebuilding a body of work that had been reduced to ashes. ROYA: As a teen I had become a writer, people were encouraging me. So, I continued to do it. It was the thing I knew how to do. And it gave me a sense of grounding and identity. So, I kept on doing it, and it kind of worked its magic, as I suppose good writing does for all writers. It connected me to a new community of people who read Persian and who appreciated what I was trying to do. And I found that with each book that I write, I find a new tribe for myself. MANYA: She arrived again once she learned English. In her first year at Brooklyn College, she tape-recorded her professors to listen again later. She eventually took a course with renowned poet Allen Ginsberg, whose poetry was best known for its condemnation of persecution and imperial politics and whose 1950s poem "Howl" tested the boundaries of America's freedom of speech. ROYA: When I mastered the language enough to feel comfortable to be a writer once more, then I found a footing and through Allen and a community of literary people that I met here began to kind of foresee a possibility of writing in English. MANYA: There was also her arrival to an American Jewish community that was largely unaware of the role Jews played in shaping Iran long before the advent of Islam. Likewise, they were just as unaware of the role Iran played in shaping ancient Jewish life. They were oblivious to the community's traditions, and the indignities and abuses Iranian Jews had suffered, continue to suffer, with other religious minorities to keep those traditions alive in their homeland. ROYA: People would say, 'Oh, you have an accent, where are you from?' I would say, 'Iran,' and the Jews at the synagogue would say, 'Are there Jews in Iran?' MANYA: In Roya's most recent book A Beginner's Guide to America , a sequel of sorts to her memoir, she reflects on the lessons learned and the observations made once she arrived in the U.S. She counsels newcomers to take their time answering what might at first seem like an ominous or loaded question. Here's an excerpt: ROYA: "In the early days after your arrival, "Where are you from?" is above all a reminder of your unpreparedness to speak of the past. You have yet to shape your story – what you saw, why you left, how you left, and what it took to get here. This narrative is your personal Book of Genesis: the American Volume, the one you will sooner or later pen, in the mind, if not on the page. You must take your time to do it well and do it justice." MANYA: No two immigrants' experiences are the same, she writes. The only thing they all have in common is that they have been uprooted and the stories of their displacement have been hijacked by others' assumptions and agendas. ROYA: I witnessed, as so many other Iranian Jews witness, that the story of how we came, why we came, who we had been, was being narrated by those who had a certain partisan perspective about what the history of what Jewish people should be, or how this history needs to be cast, for whatever purposes they had. And I would see that our own recollections of what had happened were being shaded by, or filtered through views other than our own, or facts other than our own. MANYA: As we wrap up this sixth and final episode of the first season of The Forgotten Exodus , it is clear that the same can be said about the stories of the Jewish people. No two tales are the same. Jews have lived everywhere, and there are reasons why they don't anymore. Some fled as refugees. Some embarked as dreamers. Some forged ahead without looking back. Others counted the days until they could return home. What ties them together is their courage, perseverance, and resilience–whether they hailed from Eastern Europe, North Africa, the Middle East, or parts beyond. These six episodes offer only a handful of those stories–shaped by memories and experiences. ROYA: That became sort of an additional incentive, if not burden for me to, to be a witness for several communities, to tell the story of what happened in Iran for American audiences, to Jews, to non-Iranian Jews who didn't realize that there were Jews in Iran, but also to record the history, according to how I had witnessed it, for ourselves, to make sure that it goes down, as I knew it. MANYA: Iranian Jews are just one of the many Jewish communities who in the last century left their homes in the Middle East to forge new lives for themselves and future generations. Many thanks to Roya for sharing her family's story and for helping us wrap up this season of The Forgotten Exodus . If you're listening for the first time, check out our previous episodes on Jews from Iraq, Yemen, Egypt, Libya, and Sudan. Go to ajc.org/theforgottenexodus where you'll also find transcripts, show notes, and family photos. There are still so many stories to tell. Stay tuned in coming months. Does your family have roots in North Africa or the Middle East? One of the goals of this series is to make sure we gather these stories before they are lost. Too many times during my reporting, I encountered children and grandchildren who didn't have the answers to my questions because they never asked. That's why one of the goals of this project is to encourage you to find more of these stories. Call The Forgotten Exodus hotline. Tell us where your family is from and something you'd like for our listeners to know such as how you've tried to keep the traditions and memories alive. Call 212.891.1336 and leave a message of 2 minutes or less. Be sure to leave your name and where you live now. You can also send an email to theforgottenexodus@ajc.org and we'll be in touch. Tune in every Friday for AJC's weekly podcast about global affairs through a Jewish lens, People of the Pod , brought to you by the same team behind The Forgotten Exodus . Atara Lakritz is our producer, CucHuong Do is our production manager. T.K. Broderick is our sound engineer. Special thanks to Jon Schweitzer, Sean Savage, Ian Kaplan, and so many of our colleagues, too many to name, for making this series possible. And extra special thanks to David Harris, who has been a constant champion for making sure these stories do not remain untold. You can follow The Forgotten Exodus on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you listen to podcasts, and you can sign up to receive updates at AJC.org/forgottenexodussignup. The views and opinions of our guests don't necessarily reflect the positions of AJC. You can reach us at theforgottenexodus@ajc.org. If you've enjoyed the episode, please be sure to spread the word, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review to help more listeners find us.
Nov 17, 2022
From "Chopped" to the White House: TikTok Chef Eitan Bernath on Being a Loud and Proud Jew
Jewish chef and content creator Eitan Bernath joins us this week to explain why he wears a Star of David necklace in public and how he uses his platform of seven million followers to fight anti-Israel bias and antisemitism. Named to Forbes' 30 Under 30 and the author of the cookbook " Eitan Eats The World ," the 20-year-old also discusses attending last year's White House Hanukkah Party, interviewing Second Gentleman Doug Emhoff, the Jew-hatred normalized by celebrities like Kanye West, and why it's so important to be a loud and proud Jew. Finally, Eitan tells us what Thanksgiving and Hanukkah recipes he's whipping up this holiday season. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Eitan Bernath ___ Show Notes: Eitan Eats the World: A Cookbook / Free Books for Non-Profits Recipes mentioned in the episode: Vegetarian Wellington with Green Peppercorn Gravy / Tahini Honey Glaze Donuts With Halva Celebrate Mizrahi Heritage Month with The Forgotten Exodus Listen to our latest podcast episode: U.S. and Israeli Election Results: What American Jews Need to Know Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Nov 10, 2022
U.S. and Israeli Election Results: What American Jews Need to Know
This week's episode focuses on the Israeli and U.S. elections, their implications, and what impact they could have on U.S.-Israel ties, the spread of antisemitism, and advancing democratic values. We start in the U.S., where razor-thin margins left control of Congress still up in the air at the time of recording. But as the votes continued to be counted, Marc Rod, Capitol Hill correspondent for Jewish Insider , joined us to discuss some of the unexpected results and those that are still pending, along with the implications for American Jews. Then, in Israel, after five elections in the last four years, former and future Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has apparently ended the political gridlock through a victory for the right wing-religious bloc and is now in the process of assembling a coalition. Here to provide her perspective on the Israeli election and what it means for the Jewish state and U.S.-Israeli relations is Lahav Harkov, the Senior Contributing Editor at The Jerusalem Post . __ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Marc Rod (14:15) Lahav Harkov __ Show Notes: Listen to our latest podcast episode: Why Auburn Basketball's Trip to Israel Was Personal for Coach Bruce Pearl Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Nov 3, 2022
Why Auburn Basketball's Trip to Israel Was Personal for Coach Bruce Pearl
Basketball coach Bruce Pearl is on a mission both on and off the court. This summer, Coach Pearl, who is Jewish, took his Auburn University men's basketball team to Israel on a first-of-its-kind "Birthright for College Basketball" trip to play against Israeli national teams, and visit sites across the country, from the Mount of Olives to the Western Wall and the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. As the college basketball season gears up, Dov Wilker, Regional Director of AJC Atlanta, sat down with Coach Pearl to talk about being a passionate pro-Israel Jew at a large Southern university, what it was like being in Israel with his team during the conflict in August, and the reaction he received from the trip. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Bruce Pearl ___ Show Notes: Photo credits: Auburn Athletics. AJC's Call to Action Against Antisemitism Listen to our latest podcast episode: Pittsburgh's Response to the Tree of Life Synagogue Shooting: An Oral History Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Oct 27, 2022
Pittsburgh's Response to the Tree of Life Synagogue Shooting: An Oral History
Today marks four years since America's deadliest antisemitic attack at the Tree of Life synagogue in Pittsburgh, which left 11 dead and wounded six others. Over the last few weeks, the appalling antisemitic conspiracy theories and threats from rapper Kanye West serve as a reminder of the normalization of antisemitism in America and how hate can be translated into action or violence. Listen to former Pittsburgh Mayor Bill Peduto on what it was like to witness the pain inflicted on a community, a city, the country when a stranger walked into a prayer service, declared "All Jews must die," and ended 11 lives that Shabbat morning. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Bill Peduto ___ Show Notes: Tree of Life Synagogue Shooting: 4th Anniversary video 5 of Kanye West's Antisemitic Remarks, Explained Music credit: Sad Child by Dee Yan-Key is licensed under a Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Listen to our latest podcast episode: Campus Antisemitism – What's Happening at UC Berkeley? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Oct 21, 2022
Campus Antisemitism – What's Happening at UC Berkeley?
Controversy erupted at the UC Berkeley Law school this fall over the decision by a handful of student groups to adopt bylaws that would ban Zionist speakers. In response, American Jewish Committee (AJC) united with 35 other Jewish organizations to condemn the ban as a "vicious attempt to marginalize and stigmatize the Jewish, Israeli, and pro-Israel community… This is unabashed antisemitism." This week, Dr. Ethan Katz, Associate Professor of History and Jewish Studies at Berkeley, and co-founder of the Antisemitism Education Initiative, and Charlotte Aaron, a Berkeley Law student and board member of the Jewish Student Association (JSA), sat down with Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman, AJC's Senior Director of the Alexander Young Leadership Department, to discuss the situation on campus, how it has affected their work as Jewish activists, and why they remain hopeful for the future of Jews on campus. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Ethan Katz and Charlotte Aaron ___ Show Notes: Exclusive: Pro-Israel Groups Release a Statement on Berkeley Controversy Listen to our latest podcast episode: Unpacking the Origins of Kanye's Antisemitism Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. ___ Episode Transcript Manya Brachear Pashman: At the start of this academic year, members of Law Students for Justice in Palestine at the University of California's Berkeley campus persuaded nine student groups to adopt a bylaw banning speakers who support Zionism. 35 Jewish organizations, including AJC, wrote an open letter to the university pointing out this discrimination and demanding action. When Jewish student leaders expressed their gratitude to AJC earlier this week, CEO Ted Deutch assured them that AJC's efforts would not end there. For this week's episode, we invited a Berkely educator and law student to discuss what the controversy means for them and their fellow Jewish faculty and students on campus. They sat down with my occasional co-host Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman, AJC's Director of the Alexander Young Leadership Department. Take it away, Meggie. Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman: Joining me today on People of the Pod: Dr. Ethan Katz, Associate Professor of History and Jewish Studies at UC Berkeley. And Charlotte Aaron, who is a second year law student at UC Berkeley. Ethan & Charlotte, thank you for joining me. Ethan Katz: Thanks for having us. Charlotte Aaron: Thank you. Meggie: So, in the last few weeks, there has been significant coverage about events at UC Berkeley Law School, and particularly about what appears to be exclusionary, anti Israel adoptions made by a handful of student groups. So for our listeners who may not have the full story, Ethan, can you paint a brief picture for us of what has unfolded? Ethan: Sure. So in August, I believe it was actually on the first day of classes. There was a decision by several student clubs, eight, I believe, at UC Berkeley Law to adopt a set of bylaws that had been proposed to them, by Students for Justice in Palestine, at the law school, the SJP chapter at the law school. Now that was a proposal made to dozens of clubs at Berkeley law. So it was a relatively small number who adopted these bylaws, but the bylaws were very discriminatory in that they said, these clubs would not invite any speaker who had expressed, continue to express support for Zionism, or what the bylaws referred to as the apartheid regime in Israel, or the occupation of Israel, occupation of Palestine, excuse me, what they clearly mean by that last clause is not what many observers refer to as the occupation of the West Bank, it is just the presence of Israeli sovereignty, in portions of the historical plan of Israel-Palestine. So these were met with tremendous concern by not only many Jewish law students, but many others of us who were involved in efforts on campus to support Jewish students, I co-run an antisemitism education program at Berkeley, Berkeley Law has a very large Israel studies program. And the dean of Berkeley Law came out very strongly to say that he found these to be very problematic, to be against the principles of community of the university, you know, say that every club has the right to free speech, but that becomes very concerning when students are excluded. And he said, I thought, forcefully that, you know, himself, if these bylaws were to be followed to the letter, would not be able to speak at these clubs as someone who himself is a Zionist. He also reminded clubs of the fact that the Chancellor of the University has come out in writing multiple times against the BDS movement. We were sort of waiting to see what was going to happen next in terms of what was going to be the full impact of these and also what was going to hopefully be the impact of the Dean's response, in curbing this or maybe making some groups reconsider. We did not hear a lot more about this controversy after the initial week or so that it came out until an editorial published in the Jewish Journal of LA almost exactly three weeks ago, claiming in its headline and in its content that Berkeley was developing so-called Jewish free zones. This quickly ignited a firestorm in the media and major controversy. And it brought the issue much more into focus not only on campus but off. That had various impacts on campus. One of them was that we felt the need to try to explain what had happened, what we already have in place, which is considerable, to try to support your students and raise awareness about antisemitism. And also to try to better understand where things stood for the Jewish students. and figure out ways that we have not sufficiently met their needs. I also think it's important to note that many Jewish undergraduate students who had been unaware or vaguely aware of the initial bylaws became very nervous and concerned in ways that they had not been before about Jewish life on campus. So, the impact of the article was also to create a great deal more anxiety and fear among many students on campus, despite the fact that Jewish life on this campus, generally speaking, is very robust, and in many ways thriving in terms of the success of Hillel and student Chabad, and the number of student clubs and Jewish Studies and Israel studies. So that's sort of a rough timeline. Meggie: Charlotte, anything to add there? Charlotte: I think I'll just add the way I felt when I found out what had happened. I arrived at the library Monday morning, first day of school and sat down and five minutes into reading for class, I got a text message from my friend screenshotting the fact that the women of Berkeley Law organization had passed this bylaw. And I think it was a mix of heartbreaking and frustrating. I was heartbroken because I spoke to a lot of people on these boards after this happened. And they acknowledged that they themselves didn't really know much about this issue. And wanted to be supportive to their Palestinian classmates, which is incredibly important, and I so support that. But it was heartbreaking to me that we're at a place where people think that this is how you do that, which is just an indication of a lot of misinformation. And, you know, I for the last decade, almost, I've been worried about social media, and it's especially ramped up in the last five years, and how information is spread and shared. And I think, particularly with this issue, there's a lot of misinformation. And this was a clear demonstration of that, and the impact of that. That law students who, theoretically are pretty informed of what's going on in the world, and what issues are complex and which ones are not, and how to handle those types of issues, weren't even able to take a moment and recognize like, oh, maybe, maybe we should, like do a little bit of research or engage in this issue before we take such an extreme stance, which is what that bylaw was. So I think that that was heartbreaking. And I was frustrated, because the Jewish students weren't contacted about this. I would have hoped that they would have reached out or somebody would have reached out or I would have heard about it, and I didn't, and a lot of my Jewish friends didn't. And I think that was really frustrating that we weren't being included in this conversation. And it could have been a really great opportunity to engage before creating harm. And that didn't happen. But hopefully, it's a learning experience for everyone. Meggie: So Charlotte, I want to focus in more on that. You mentioned that heartbreak. And I think sadly, that is something that certainly in different scenarios and other campuses, there have been instances where Jewish students do feel that, that that exclusionary, I guess, kind of heartbreak. I want to focus in on kind of the timeline that Ethan painted of this initially, kind of being adopted months ago, and then having greater coverage brought in recent weeks. So as a student, as a member of the Jewish Law Students Association at Berkeley, what did students feel, what are they feeling now? Or did they even know about it initially months ago, when this was passed. Can you kind of talk about those two stages? Charlotte: Yeah, so I will say that it was initially really challenging for the Jewish Student Association, because we work, and continue to work really, really hard to be an organization that is welcoming of all Jewish students, regardless of their perspectives on this issue. We issued, the board of the Jewish student organization, published a letter, we first send it to our members, and then to the organizations, to all the student organizations who are invited to add the bylaws to their constitutions, basically saying: Look, this hurts Jewish students, because it forces them to choose between either, you know, denying a part of who they are, or, to be part of an organization or to, you know, exclude themselves. And we're not asking our members to do that. And we hope that you guys also don't ask your members to do that. After that, the Jewish student organization kind of stepped back, mostly because we don't want to be an organization about Israel. And that's not our purpose. Our purpose is to be there for all Jewish students. So that organization stopped engaging in this issue. As individuals, there are four of us who still were very concerned about what happened. And we're continuing to work behind the scenes on how to best address this, because it's a really challenging issue. And we wanted to make sure – three out of four of us are board members, how are we going to do this in a way that doesn't make it look like our organization is taking a stance. That was a really big concern to the other board members who, you know, don't want our organization to take a stance, which none of us do. But the optics of that were very challenging. So we are navigating that? Do we start a new organization? You know, are we trying to write a letter? Are we directly reaching out to these students? How do we do that? The Dean has been super supportive and offered to help us, but what can he actually do? Like, what do we want him to do? These were really hard questions. And so even before the article came out, the four of us were thinking about these things, and meeting and talking and we went to the Palestine 101 event that was put on, and we had students coming up to us at Jewish events, not at Jewish events, saying that they were individually concerned about what had happened. And this was even before the article came out. So yes, it drew public attention. But I do think that students were still quite concerned about what was going on. It just wasn't vocalized. Meggie: So I want to get to some of those responses once that article came out, and there was greater coverage. So Ethan, you wrote a piece that has been widely shared that in a very eloquent way, expressed your frustrations with how some of these incidents are being portrayed in the broader media. What led you to pen that piece? Ethan: In the most basic sense, I think the claims made as a headline of that article are false. I share the deepest concerns about what's happened at the law school. And we're doing a lot and we're trying to do more. And, Charlotte, as you know, we're having a meeting this afternoon. There've been a lot of meetings. And so there's no question that what's happened needs to be addressed in the most effective way possible. We're not on a campus where the administration or large numbers of students are trying to ban Jews from large portions of the campus, which I believe was the implication of such a headline. And so we wanted both to express the fact that we were really disgusted by these bylaws and that they are unquestionably, nakedly discriminatory and many of us believe antisemitic. But to say that this kind of coverage, that it paints a false picture of the campus, and that it's fundamentally unhelpful in the end. We started the antisemitism education initiative that I helped to run three years ago, we put on a lot of programs on campus, we do trainings, we respond to incidents, we created a training module, a training video, a lot of other campuses use the resources that we created. And we do that to support students. And we do that based on conditions on the ground. If people from outside want to support Jewish students here, that's fantastic. But part of what we're trying to say is, we have this program already in the system, we have this Israel studies program, we have Jewish studies, we have really strong community organizations, come talk to us and say, How can you best support our efforts, rather than effectively throwing a grenade from the outside? And I have to say, I mean, you know, what happened most recently, last week on campus, which I think many people have heard about by now was a truck going around the campus with a hologram on it, of Adolf Hitler, saying something like, you know, if you believe that Jews should be banned from Berkeley, raise your right hand. This was done by an organization that claimed to be looking out for Jewish students and to be very concerned. And just like that initial article raised a lot of alarm among Jewish students, both off campus and on campus, this, of course, scared many Jews on campus. And I know that it wasn't the intention of the articles that have been written. But by now five articles have been written continuing to claim there are Jewish free zones at Berkeley. Without those articles, those trucks would never have been circling our campus. So, we remain alarmed by the effect of this, and we don't think it's actually helping us respond the most effectively to what's taking place. Meggie: So along with the response on campus, there is kind of an inherent issue, or I would say, challenge that is always trying to be examined in situations like this. You had mentioned Charlotte earlier, Dean Chemerinsky, who himself wrote a piece in The Daily Beast. And in it, he acknowledges this tension, he talks about the need to honor free speech, which takes I think, renewed importance at a law school, honor, free speech, but also acknowledge that some of these tactics, including those of banning students who identify as Zionists are indeed at odds with free speech and can fracture student discourse. So these are tough questions. But my question and maybe Charlotte we'll start with you. And then Ethan, I'd love your perspective. Do you see this manifesting at Berkeley beyond just this incident? And have you seen these trends in academia more broadly? Charlotte: I do think free speech is an issue. When I was a student at Brandeis, I was the undergraduate representative on a university task force for free expression. And the purpose of the task force was to create a set of policies or principles that the university would abide by, to ensure that every student felt like they could have their voices heard and share their perspectives. And I'm a firm believer that, you know, more speech is how we get to the right answers. And if people have really extreme opinions on the left, the right, up, down, and aren't sharing those, then they can never be addressed. And, I mean, I think that this is, this is a perfect example of that, that, only one narrative is being heard. Hopefully from this, and I think it's sad that, you know, what I am, Adam, Billy and Noah are trying to do, is being portrayed as silencing Palestinian voices, because what we're trying to do is quite the opposite. And, you know, I went to Law Students for Justice in Palestine events last year, like I want to go to their events. So that A, I know what they're saying, and, you know, know what i might be up against B, maybe there's actually some common ground, which would be great, you know, if we can find common ground, maybe they agree with me on something that I didn't know about. And we can run from there. And C, quite frankly, what a great way to sharpen my tools. I can't possibly prepare to advocate for something I care about if I have no idea what other people are saying. Meggie: Ethan, I want to turn to you. How are you seeing this issue of a want to safeguard free speech, but be balanced with the reality that for many Jewish and pro-Israel students, they feel like their ability to proudly speak about their views is being limited because of social implications? How are you seeing this manifest within your work, in particularly so as the co-chair of AJS's Task Force on Antisemitism and Academic Freedom? Ethan: Yeah, I mean, I think Charlotte nailed a lot of it. The fact is, we're living in an age where a whole slew of actors across the political spectrum, and also in our own Jewish community, in different perspectives, have a very hard time with robust debate about issues that are dear to them. And the impetus for the creation of that [AJS Task Force on Antisemitism and Academic Freedom] task force was the feeling among certain of our Jewish colleagues, pretty far to the left, that certain conversations about antisemitism on campus, more from the right, were making them feel they could not be critical of Israel without being called antisemitic. And I know Palestinian voices are very upset about some of those efforts to shut down conversation. I think, justifiably so. So of course, it is really the height of irony and misfortune to then see the same tactic deployed by pro-Palestinian organizations to say, we can't harbor any kind of real conversation either. I think it's important to note, I mean, we all have, I think some sympathy for the fact that organizations want to create so-called safe spaces for those in solidarity with their causes. But these bylaws are not bylaws that say, unless you support the right of the Palestinians to a state you won't be allowed to speak, or unless you recognize the Palestinians are a people, you won't be allowed to speak. Those, I think whilst they would be controversial, some people, most Jewish students would not be offended by those. And I think we would all understand those more as really a matter of sort of visceral sense of safety for Palestinian students. This is so much more sweeping than that. And it really is to just silence the vast majority of Jewish students effectively, and to silence any kind of live debate on these issues. And one of the things that I'm concerned about, and I hear Charlotte is concerned, and that many of us are concerned about is that we will become so kind of siphoned off from each other in our own echo chambers. And that doesn't help anyone's problems. Meggie: I know that there are immense challenges, but there are also, and both of you highlighted these in the articles you wrote, there's a lot of opportunity and a lot of positivity happening on campus. So I want to turn to both of you, Charlotte, you are a budding lawyer. So you see both sides of the coin. And Ethan, given your professional purview, you have a long lens of Jewish history, you have seen the many ups and downs of our people. So I want to pose to both of you: what makes you hopeful about the Jewish student experience at Berkeley today, and more broadly, about Jewish life today? Maybe Ethan, we'll start with you. Ethan: Well, very honestly, I think one of the things that makes me hopeful, and what young Jews today, in many cases, are doing to pursue challenging and complex conversations on these and a host of other issues. We can always find examples of shrill voices and people who don't want to listen to each other. But there are a lot of examples that I think are quite inspiring, brave. You know, I very much appreciated the article that Charlotte and other law students wrote in The Daily Beast, and the clarity with which they have repeatedly said, We're not against Palestinians, we're not against the notion of the rights of Palestinians, what we really want is the opportunity to be engaged in conversation, and to feel that we as Jews, our identities, are able to have a space, there also for their full expression. And I think, you know, there are a lot of people across the country, particularly young, young people who are doing this kind of work, to try to push back on multiple extremes. Charlotte: The way that, you know, the bylaws have played out on our campus has, for people who don't really know much about the topic made it look really, really bad to be a Zionist, and I think that's really scary. And a lot of students don't want to engage with that, and, you know, identify themselves as somebody who supports Israel, but a lot of students have and, you know, undergraduates, other graduate students, graduate students at the law school, have come out in a really respectful and I guess proud way to engage in this and, and I was feeling bad for myself before Yom Kippur war like, oh, I'm spending so much time on this I'm not having as much time to work on school like, this is such a bummer and and I did some reflecting on the holiday which I suppose is what it's for. And it's like, you know what, what a great group of Jewish students that I have the privilege of working with and great Jewish professors and a fantastic Jewish Dean and, Rabbi Adam at Hillel has been phenomenal. And I feel really lucky and encouraged to be surrounded by and working with really great people who share a common goal to just be good, and make the world a better place. And so that's been, that's been really nice. And then, you know, in terms of Jewish life more broadly, I somehow got swept into the Jewish graduate student initiative last year and did like a six-week Jewish learning, ethical learning class online. And it was amazing. And I just was so blown away by how many young Jewish people there were, who wanted to engage with the texts and debate about what we're supposed to be taking away from these and how we can apply them to our lives. I am learning about an aspect of Judaism that is so rich and meaningful, and I do think is making me a better person. And that feels really good. And I think it's doing the same for other young Jewish people. And I'm, that gives me hope about the future. Meggie: Thank you both for making time to share your wisdom with our audiences, for the activism and the leadership you're showcasing at Berkeley. And we wish you the best for the rest of the semester. Thank you. Charlotte: Thank you. Manya: If you missed last week's episode, be sure to listen to my conversation with Holly Huffnagle, AJC's US Director for Combatting Antisemitism. She helps unpack the origins of Kanye West's conspiracy theories and stereotypes, and why the rapper's hateful words matter to all of us.
Oct 14, 2022
Unpacking the Origins of Kanye's Antisemitism
Rapper Kanye West's recent antisemitic outbursts during a primetime Fox News interview and on social media to his over 31 million followers have provided another example of the normalization of Jew-hatred in the American public sphere. While his comments elevating antisemitic conspiracy theories, Jewish stereotypes, and threats of violence have been met with outrage and condemnation, they demonstrate the continuing challenge of combating the world's oldest hatred in the media and online. AJC's U.S. Director for Combating Antisemitism Holly Huffnagle joins us to break down his vile statements and explain how they are part of longstanding rhetoric that targets Jews. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Holly Huffnagle ___ Show Notes: AJC resources: 5 of Kanye West's Antisemitic Remarks, Explained Call to Action Against Antisemitism: A Society-Wide Nonpartisan Guide for America Translate Hate Glossary Listen to our latest podcast episode: AJC CEO Ted Deutch on Building a Brighter Jewish Future Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Oct 6, 2022
AJC CEO Ted Deutch on Building a Brighter Jewish Future
After more than 12 years in the U.S. House of Representatives, Ted Deutch recently stepped down to become the CEO of American Jewish Committee (AJC), the leading global Jewish advocacy organization. In this special episode, learn about the Jewish values instilled in Ted by his parents, growing up in the working-class town of Bethlehem, Pennsylvania where he was one of only three Jewish students in his high school. From his summers at Camp Ramah in the Poconos to his Jewish leadership as a student at the University of Michigan – Ted's experiences as a Jewish leader inspired him to become a fierce advocate against antisemitism and in support of Israel in the halls of Congress. As he begins this exciting new chapter at the helm of AJC, Ted describes his commitment to enhancing the well-being of the Jewish people and Israel, and how he will help AJC build a brighter Jewish future. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Ted Deutch ___ Show Notes: 6 Things to Know About AJC CEO Ted Deutch Listen to our latest podcast episode: Synagogue Security Expert on the Importance of Volunteer-Led Protection Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us. ____ Episode transcript MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: This week, American Jewish Committee enters a new chapter with a new CEO. Ted Deutch served seven terms in Congress and during that time emerged as a powerful voice for democratic values and the Jewish people. He also became an outspoken defender of the U.S.-Israel alliance, when that defense was needed more than it ever had been. While Ted has been a guest on our podcast before, he joins us now for the first time as AJC's CEO. Ted, welcome back to People of the Pod . TED DEUTCH: Well, thanks. MANYA: So, we have a lot to get to because we want to introduce you to our audience and really let them get to know you. So, let's launch right into it. Tell us about your upbringing. TED: I grew up in Bethlehem. I'm the youngest of five. There is an 11 year gap between me and the next closest sibling, my sister and then my three brothers are older still, and 19 years between my oldest brother and me. I am, as my mother eventually came to refer to me, a pleasant surprise. My father was a painting contractor. They lived in Bethlehem because after he grew up in Chicago, he enlisted in the army after he graduated from high school, was sent by the army to the army specialized training program that was at Lehigh University in Bethlehem. He met my mother at, I think not surprisingly, at a bagel brunch at the synagogue at the JCC where I grew up, and it's a long story of what happened after. My dad went to fight in the Battle of the Bulge. My mother wound up befriending his family in Chicago and one thing led to another and he wound up moving back to Bethlehem, where he married my mother and raised our whole family. MANYA: I imagine Bethlehem, Pennsylvania was much like the small town blue collar communities where I grew up. Describe Bethlehem for us. TED: Bethlehem is home to Bethlehem Steel, which was the company that helped make the steel that helped us win World War II, that was the way we always talked about it when I was a kid. And the steel company, it was the largest employer in Bethlehem. So many people, either their families had some connection to Bethlehem Steel or they either worked at Bethlehem Steel. In my dad's case, he was a painting contractor. He painted the offices of Bethlehem Steel, he painted the houses of Bethlehem steel execs. Had an enormous impact on the community. Over the course of my high school years it started winding down. It was also sort of the end of a great American company which we watched happen in real time. But down Main Street, Broad street downtown, there was one movie theater downtown, there were two actually for a while. And yes, there were little shops and there was a magic shop that I used to ride my bike to after school, when I was little. It was a nice place, a nice community to grow up in. MANYA: Did Bethlehem have a sizable Jewish community? TED: Not a large Jewish community by any stretch. There was a very close knit Jewish community that had been there for a long time, multiple generations of families. It was the old model where in one building, we had the JCC and our synagogue. So, on the first floor, where you walked in, we actually had the gym and the pool. And then the second floor were the classrooms in the auditorium and the third floor was the sanctuary. So we spent a lot of time there, between Hebrew school and basketball and Shabbat and the rest. So it was a really nice community but definitely not large. And fortunately for me, it was a community that welcomed a new Rabbi when I was a kid, and one of the first things he decided was that the synagogue needed to send kids to Camp Ramah and it was Rabbi Judah's decision to encourage that. And I was one of the first, I think it might have been the first to go, and that had an unbelievably significant impact on my Jewish life and the way I view the world and everything else I've done since. My first year at Ramah, I was 12. I was not quite a Bar Mitzvah, that I know for sure, because I invited camp friends to my bar mitzvah, where I gladly sang Ramah tunes, hoping and expecting that they would all join in and found myself doing a lot of solos during my Bar Mitzvah. My friends didn't quite step up to the moment, but very good memories. MANYA: You mentioned that Bethlehem Steel helped win World War II and your father fought in the Battle of the Bulge, for which he won a purple heart, I believe. Can you talk a little about how he balanced his American patriotism and his Jewish pride? TED: He went off and fought in World War II and fought the Nazis and, and took with him these two books, both of which I still have. One, a prayer book, the small prayer book, one, a small book of Jewish thoughts that they gave to all of the Jewish members of the armed forces in World War II. The fact that he carried those around with him, still had them and the fact that I have them now is really special. In the siddur, there's a page where there's a small tear right down the middle. And if you look, and he explained this to me, it was torn down just so that he could have a small sheet that had a Shin on it. And this was what he taped above his bunk when he was in the army, and it was his way of having a little Mezuzah, just to reflect the fact that -- here's a Jewish soldier who was there, as an American and as a Jew. MANYA: You were telling me earlier about United States Army Specialist Daniel J. Agami, back in 2007. He did something very similar. TED: There's a family who lost their son in recent combat, who went to war and had an Israeli flag that he hung above his bunk and refused to take down despite the fact that they were fighting in a Muslim country. I think about that some, in that straight line from my Dad's experience to this Jewish soldier and the kind of patriotism that the Jews have shown for the country that we live in for so long. MANYA: You were one of three Jews in a class of more than 2,000 students. Did you encounter antisemitism growing up? TED: There were neighborhoods in my community that still had deed restrictions, where people weren't allowed to sell their houses to Jews. There occasional experiences I had, with people who made comments that were antisemitic. I, for a lot of people, was the only Jew that they knew. I was the Jewish kid. So it's just something that I dealt with from time to time. Which is when my father would share some of his stories. MANYA: And in addition to sharing his own experiences, what advice did your parents give you about confronting that antisemitism? TED: That's a really good question, Manya, that I haven't been asked and haven't really thought about in a while. My father's advice was clear. Obviously we're talking a lot about my dad, but my mother, she was very smart, had a very strong Jewish identity, she was a very strong woman. And the advice from both of them was to always stand up for yourself and never let people get away with it, and to be strong and be proud and to let them know that. That's a hugely important lesson that I've taken with me my whole life. It's frankly, one of the most important things that AJC does, is to help create strong proud members of the Jewish community, who also won't simply back down and let people get away with it. MANYA: You went to the University of Michigan for undergrad as well as Law school, and it's where you met your wife, Jill. How did you end up going from Bethlehem to Ann Arbor? TED: It's interesting, my sister went to Penn State, I loved visiting her and the big college experience. I thought I might like to do that. And everybody I talked to had only good things to say about Michigan. It was also by the way, right about the time that The Big Chill came out. Not that my life was guided by fiction, by a movie. But it was literally right at that moment we were making college decisions. And here's his movie about this group of friends that come together for a sad occasion. I don't know if you saw it or are familiar with it, but, boy do they love Michigan. It's when I heard from everyone I talked to, I had friends from my Israel trip the summer before who were going to school there. And it just became the natural destination, and everybody was right. It's an amazing place. And I had an incredible experience there. And met Jill there, which of course makes it the best of all. MANYA: You chaired the University Hillel's governing board, and you were co-editor of Consider magazine, which was launched by Hillel. And this was a magazine that made it its mission to solicit compelling arguments on multiple sides of an issue. Kind of, stoking conversation, right? TED: I was proud to do it when I was in college, but thinking about where we are now in this time where everyone has their own social media feed that plays to the things that they're interested in passionate about, criticizes the things that they don't like. Everyone has their own, their own feed, their own cable news channel. They are more and more associated with people who believe the things that they believe we were, I think doing an important service that I don't want to overstate it. But when you look back, we could, I think, benefit from a willingness to engage a little more with people whose views are different than ours. And that's what it was about. It's interesting to think about the conversations, the debates we have today, where we always want to just make this a black and white issue. You either believe this or you believe that and as you point out, in almost every occasion there are substantially more than two sides and there's nuance and engaging in a sophisticated way, requires a lot more than then simply throwing down the gauntlet and saying I'm right and you're wrong, or as is troubling these days- I'm right and you're terrible or you're an idiot or you're evil or all of the other things that people say now instead of engaging in meaningful debate. MANYA: But I have to ask, how does that jibe with AJC's advocacy role? I mean, journalists foster conversation. But as an advocacy organization, AJC picks a side. TED: There are different sides on different issues. When a conversation is really appropriate, occasionally there are things that are just so clear, that it becomes paramount that you stop trying to look for some competing argument and stand on the side of what is clearly just and right, and in the best interest of a better world. The best example is when you take the position that we should deny life-saving support to an ally in Iron Dome, the Iron Dome replenishment debate. When you say that you can't support funding for that program, which saves the lives of Israelis and Palestinians, and has prevented conflicts from escalating, and has been used to protect civilians when terrorists from Hamas and Palestinian Islamic Jihad are sending rockets, aimed indiscriminately, but meant to to kill civilians? If you can't support that, if your position is such that this particular ally, only one ally, Israel, which happens to be the only Jewish nation in the world, that if your position is that you can't even support the kind of program that saves the lives of civilians against terror attacks, then there's only so much I'm going to engage on. MANYA: Of course, you're talking about the debate about the Iron Dome funding last spring that pitted you against Rep. Rashida Tlaib. She was actually in your own party. I want to talk about that a little more. AJC is nonpartisan. And while you were in Congress, you earned a reputation for sometimes bucking party lines. You didn't side with Democrats on the Obama administration's Iran nuclear deal, you supported the Trump Administration's Abraham Accords. Why did you break rank like that? TED: At a time when partisanship rages, fighting antisemitism can't, we can't allow that to fall prey to that to partisanship. And likewise, defending the US-Israel relationship and supporting Israel and in handling Israel's position in the world also shouldn't fall prey to partisanship. And that means being very clear, when people take positions that are for partisan reasons or anything else, are outside of the broad consensus that has existed and continues to exist in Congress and in America, that we should support our allies. And, then when it comes to fighting antisemitism, as we've already discussed, that we should come together for the benefit of security of the Jewish people, but also because we're ultimately protecting much more than that when we fight antisemitism. MANYA: You first went to Israel before your senior year in high school with Camp Ramah and you believe being on the ground there really is important to comprehend its significance, its complexities. I personally have not been, so I'm sincerely looking forward to AJC Global Forum in Tel Aviv next June. Since that first trip as a high school student, you've been to Israel countless times now – what memories stick with you? TED: When you have the opportunity, when you go to Israel and you go to Jerusalem and the Kotel and everything that you've done, whatever connection you've had to Judaism, it immediately comes to life. I remember the conversations that we had with Israelis while we were there, which is still something that I think is really important to do every time you visit, that it's not just about looking at sites, but to actually understand the connection that we have as Jews, with people who live in Israel. And to think that this is a place that we're praying about, hoping for, for 2000 years. And every time I go back, I walk into someone's house for Shabbat dinner and some of the shuls and various minyans. Some had already ended, some were ramping down. You could hear from everywhere you walked, people davening. You just think about how unique that is, to be in a Jewish state like that. Every time, I mean, every time that's something that I'm thinking about. MANYA: You introduced a number of your congressional colleagues –both Republican and Democrat – to the Jewish state. But I'd like for you to tell our listeners about one trip in particular that you took with fellow Floridian Ileana Ros Lehtinen – a Republican congresswoman at the time – back in 2014. While you were there, the bodies of three Israeli teenagers were found. Kidnapped and killed by Palestinian terrorists linked to Hamas. TED: Ileana and I went on an official trip together. The first time we were there, the timing was such that we were there for Jill's, my wife's cousin's son's Bar Mitzvah. So we went to this bar mitzvah dinner, and celebration. And we were there just after we had all participated in events all over the country all over the world, about the three boys that had been missing, and all these events took place, and everybody was praying for their safe return. And it was during the bar mitzvah, that all at this one moment, everyone's phones went off. And everybody looked. It was this incredible moment where the news broke that the bodies of the boys had been discovered, and that they had been killed by terrorists, and which is what so many people had feared. And so first, there's this moment where, where people didn't know what to do, but because it's Israel, and most importantly, it's a simcha. There was almost this defiance, that even having just received this terrible news. People were more passionate about dancing the hora, and about celebrating this bar mitzvah. And that was a really powerful moment. And then we completely rearranged our schedule for the next day, so that we could attend the funeral for the boys. And there was so much that was so powerful about it, when we pulled up and it looked like literally half of the nation of Israel was walking toward this funeral. And, and Ileana and I had the opportunity, we were privileged to sit in the front. And the funeral itself was so powerful, the whole experience was so powerful, but then we made a shiva call. And we had the chance, it was a of all the things I've been able to do in Israel, this was a such a powerful moment for me, because we had the opportunity to pay respects, not just because we were on this trip, but we were on an official trip and we could pay our respects, offer our condolences on behalf of the American people, on behalf of the Jewish community that had been that had been praying all over the world. And as I explained to some of the students who were there, the fellow students of those who were killed. And as I explained in the best Hebrew that I could, that I wanted them to understand that it's one thing to say that, you're not alone at this moment. But having participated in these massive events the week before in my community and in Washington. I wanted them to know that I knew exactly what I was saying and that there were people all over the world who were literally mourning with them. MANYA: You did that here as well in the United States as well, attended shivas I mean, after the school shooting that killed 17 in Parkland. TED: I haven't ever thought of that parallel. In both cases. I was an elected official. I was in a place that I desperately wanted to avoid, or I would, I desperately would have prayed that, that the circumstances that led me there never happened. And in both instances, and so in Florida, I went to a lot of funerals after February 14, and a lot of them were Jewish funerals. That's a moment when emotion is the rawest that it can possibly be and, in both cases, we did what we're told to do at shiva: we sat and we listened. We listened to stories about, in both cases by the way, the young lives cut short and all the things that these kids had done in their short lives, and all the things that they would have done if they hadn't been killed. There are a lot of similarities. And coming out of both of those is the rededication to the important work. MANYA: So, what's in store for AJC with you at the helm? Do you have big ideas you want to implement? TED: It's not my plan to come in and, and start to make drastic changes, I'm going to come in and I'm going to listen to everyone, and understand at a deeper level, the work that's done. But the one thing I know for sure, is that that the effort to defend the interests of the Jewish people, to create resilient Jews, wherever they live, to defend all 15 million Jews in the world, by fighting antisemitism, educating people on antisemitism, advocating because ultimately AJC is an advocacy organization, building the relationships that will help to strengthen the community, and speaking out boldly, when it's necessary to make sure people understand what's at stake here. Those are the things that I look forward to doing. But more than anything else, there is so much work that AJC does to advocate for the Jewish community around the world. And, and to, to enhance Israel's place in the world. And to speak out for human rights, and democracy. There's so much work that's done that people don't know about. And when you have an organization that's engaged in advocacy, that means you're advocating on a whole host of different issues. And sometimes, we forget that- not we, AJC. But the world forgets that they're all related. And so when it comes to, to supporting Israel and standing up for the Jewish community, to be able to know that that we are advocating for the community wherever they live, from Seattle to Chicago, to New York, Buenos Aires, Paris, Jerusalem, and to do it by building the relationships at the local level, at the federal level in Washington, with the ambassadorial corps in Washington and Consuls General around the country. At the UN, where AJC is on the ground every day, at in capitals around the world with with foreign ministers and heads of state, those relationships everywhere in the world that AJC has built that its its volunteers and leaders have spent so much time engaged in, the intergroup work that has come from from that work. All of that strengthens the Jewish community. And, and, and helps to lift up Israel and its place in the world in a way that is unique. MANYA: You're coming from a role in Congress in which you fought for measures to slow climate change, curb gun violence, have peace with other countries, balancing the nation's budget – a plethora of issues. Here, at AJC, you'll be a little more focused on Israel and the Jewish people. But how are both jobs similar? TED: We talked earlier about Tikkun Olam. And it's important and we're all engaged in that in all of the ways that we choose to be. But when I think about AJC's work, if I'm looking to if I'm looking to our text, it's really it's it's called Kol Yisrael Arevim Ze Bazeh , right - We're all responsible one for another– it's all about Jewish peoplehood and the connections that we have, not just to our fellow Jews in our communities, but everywhere in the world. In the United States, that means making sure that we all understand where we come from, which is both all of the things that our history has provided us –the contributions that we've made to history as a whole, and the impact that history has had on us. MANYA: You are a father of three young'ns in their 20s. Very accomplished, young'ns in their own right, I should add. Why should AJC be paying more attention to their generation? TED: AJC has this unique opportunity to take the existing program than it does for young people, early in their careers, the programming to create well-educated, passionate advocates, who are and will continue to be leaders in their respective communities, from their schools to their campus, to wherever it is they move when they graduate. That program is so exciting to me and the opportunity to see that continue to grow, so that all of these leaders can then engage in the work that we've just been discussing. For AJC, for everyone, it means not just providing lessons, it means listening, and engaging with young people who have the capacity to lead right now. And we see it on Instagram, with some of the accounts that young people have set up. We've seen it all over social media, we see it in things that people write, we have to help build that up, meet them where they are, recognize that they're already leaders, contribute to their future growth. That's an enormous opportunity. And I think that the way that AJC goes about its work can help do that. Last thing I'll say is this. There are young people who have been so engaged on their campuses, on social media, sometimes feeling, and I had spoken to a number of them, sometimes feeling like they're on an island, and providing a real home for them to come together to confront these issues that they're facing. To help them understand what we can do to change the narrative by lifting up their voices. That's the moment that we're in that I think we really need to capitalize on. MANYA: After the Parkland shooting, you really raised your voice about addressing the forces and circumstances that led to this horrific act of violence. How will that experience, which I know was life changing for so many including yourself, how will that inform the direction you lead AJC? TED: I think the most important thing I learned during that whole experience was the power of young people, high school kids, who helped to start this whole movement from their dining room table and the leadership role that they play. If we're not talking about the threat, then it's going to make it a whole lot harder for all of us who want to prevent these things from happening to succeed. So, yes, we've got to be clear, as we as we talk about, as we acknowledge this rise in antisemitism, and we have to focus on it wherever it comes from, and we need to be clear that the the threats that rising antisemitism pose are threats to the entire community. I talked about this at the UN several years ago, the the fact is when there's antisemitism in the country that is festering and it affects not just the Jews, it is never just the Jews. The guy who went into that Walmart in El Paso. These are people who, so many of them at their core antisemites, you see it and what they've said and what they've written. So we should all be paying close attention to the rise in antisemitism. And we should be working with everyone we can to help educate them about the threat that it poses. Yes, to the Jewish community, first and foremost, and so that the Jewish community understands that, that there is this recognition and that they can feel safe and and we can build resilience in the Jewish community. But also, for everyone else to understand that we're by tackling antisemitism, we're also helping to make our country and ultimately this is a worldwide phenomenon, clearly, we're helping to create a safer world for everyone. MANYA: Ted, thank you so much for joining us, in your first week on the job, no less. TED: Thanks. This is really fun by the way. MANYA: Well, it's been a pleasure getting to know you and I'm sure we'll have you back on the air again soon. TED: I look forward to it.
Sep 29, 2022
Synagogue Security Expert on the Importance of Volunteer-Led Protection
Did you know that Jewish communities outside the U.S. have long viewed security as a communal responsibility and do not solely rely on law enforcement? Is a shift toward this viewpoint emerging in America? This week, amid the High Holiday season, we spoke to Evan Bernstein, CEO and national director of The Community Security Service, a volunteer-led national organization that trains community members to protect their synagogues and events. We discuss the manifestations of antisemitism and hate crimes plaguing all denominations of Jewish life in the U.S. and the growing importance of volunteer security in keeping communities safe. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Evan Bernstein ___ Show Notes: AJC's Call to Action Against Antisemitism Listen to our latest podcast episode: Ken Burns Explores U.S. Inaction During the Holocaust Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Sep 22, 2022
Ken Burns Explores U.S. Inaction During the Holocaust
Filmmakers Ken Burns and Lynn Novick, in conversation with AJC's Director of Contemporary Jewish Life Dr. Laura Shaw Frank, join us this week to discuss their groundbreaking historical documentary, "The U.S. and the Holocaust." This latest installment from the acclaimed filmmaker, which debuted this past Sunday on PBS, explores America's reaction – or lack thereof – to the Nazi genocide as it was unfolding in Europe as part of a critical addition to our understanding of the past. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Ken Burns and Lynn Novick ___ Show Notes: Watch "The U.S. and the Holocaust" How to Combat Holocaust Trivialization Moving Toward Never Again: State of Holocaust Education in the United States Listen to our latest podcast episode: Noa Tishby on the Abraham Accords: The Middle East Realizes Israel is Not the Enemy Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Sep 15, 2022
Noa Tishby on the Abraham Accords: The Middle East Realizes Israel is Not the Enemy
Israeli-American actress Noa Tishby didn't set out to be Israel's first special envoy for combating antisemitism and the delegitimization of Israel. But since being appointed by then-Israeli Foreign Minister Yair Lapid in April 2022, Tishby has been a powerful voice when it comes to combating hatred against Jews and misinformation about Israel. Amid the paperback release of her book " Israel: A Simple Guide to the Most Misunderstood Country on Earth," Tishby joins us to discuss the impact of the Abraham Accords two years on, how she's raising her son to love Israel, and why she doesn't view antisemitism as a "problem to solve." ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Noa Tishby ___ Show Notes: To register for Global Forum 2023, visit AJC.org/GlobalForum " Israel: A Simple Guide to the Most Misunderstood Country on Earth ," By Noa Tishby Listen to our latest podcast episode: Here's Why All of Society Must Take Action Against Antisemitism Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Sep 7, 2022
Here's Why All of Society Must Take Action Against Antisemitism
It is no secret that antisemitism is on the rise in the United States. American Jewish Committee's (AJC) 2021 State of Antisemitism in America report revealed that 90% of Jewish respondents believe antisemitism is a problem. Until now, there has not been a single resource for American society to tackle the world's oldest hatred. In a just-released mobilization tool, AJC's Call to Action Against Antisemitism in America highlights a path forward for all sectors of society, including government, corporations, the media, college campuses, and more. Listen as Holly Huffnagle, AJC's U.S. Director for Combating Antisemitism, breaks down this resource and explains why addressing antisemitism requires a bold, targeted, and cohesive strategy to understand, respond to, and prevent it. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Holly Huffnagle ___ Show Notes: Learn more about AJC's Call to Action Against Antisemitism: ajc.org/call-to-action Check out season 1 of The Forgotten Exodus: ajc.org/forgottenexodus Listen to our latest podcast episode: What a Restored Deal with Iran Could Mean for Israel and the Entire Middle East Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Sep 1, 2022
What a Restored Deal with Iran Could Mean for Israel and the Entire Middle East
Israeli Prime Minister Yair Lapid has voiced sharp criticism of reports claiming that the final text of a restored Iranian nuclear deal will soon be accepted by Tehran and Washington, reigniting debate about key components of the nuclear deal - sanctions against Iran's energy exports, IAEA monitoring, unfreezing blocked Iranian assets, among others - and whether the United States should even be negotiating with Iran in the first place. Fresh off a recent escalation with the Iranian-backed Palestinian Islamic Jihad terror group, Israel has been vocal with the Biden administration about these concerns as well as Iran's continued malign behavior. Behnam Ben Taleblu,, a senior fellow at the Foundation for Defense of Democracies (FDD), joins AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson to break down the specifics of the emerging deal and explain why the nuclear threat is only one element of the broader danger posed by Iran. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jason Isaacson and Behnam Ben Taleblu ___ Show Notes: For more Iran news and analysis, visit AJC.org/Iran Listen to our latest podcast episode: BDS on Campus: What Should Jewish Students Expect? Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Aug 25, 2022
BDS on Campus: What Should Jewish Students Expect?
Natalie Kahn, a Jewish student at Harvard University and editor at The Harvard Crimson , was stunned late last spring when the editorial board of the campus newspaper that had been so central to her college experience had endorsed the antisemitic Boycott, Divestment, and Sanctions (BDS) movement. Jeffrey Greenberg, AJC's Assistant Director of Campus Affairs, said that Natalie's feelings of betrayal are an increasingly common experience for pro-Israel college students. While BDS has had numerous setbacks and even been outlawed by many states and countries, on campus it has seen more success, where it is framed as a social justice opportunity to fight for an oppressed minority, playing on the emotions of students who aren't fully informed. Joined by guest host Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman, Senior Director of AJC's Alexander Young Leadership Department, Natalie and Jeffrey discuss what Jewish and pro-Israel students can expect as they head back to campus this fall. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Natalie Kahn and Jeffrey Greenberg ___ Show Notes: I Am a Crimson Editor and I Stand with Israel - oped by Natalie Kahn Learn more about AJC's work in Campus Affairs Listen to our latest podcast episode: Walter Russell Mead: Debunking Myths and Misconceptions About the U.S.-Israel Relationship Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Aug 18, 2022
Walter Russell Mead: Debunking Myths and Misconceptions About the U.S.-Israel Relationship
Today, Israel is one of America's top global allies. How did this relationship develop? Why does this alliance have such widespread support in America? To answer these questions and more, Walter Russell Mead, Fellow in Strategy and Statesmanship at the Hudson Institute and columnist for The Wall Street Journal , joins guest host, Melanie Maron Pell, AJC's chief field operations officer, to discuss his latest book, "The Arc of a Covenant: The United States, Israel, and the Fate of the Jewish People." In their discussion, we delve into what fuels America and Israel's alliance, debunk myths about the relationship, including antisemitic tropes and memes, and why it's important not to take it for granted. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Melanie Maron Pell and Walter Russel Mead ___ Show Notes: The Arc of a Covenant: The United States, Israel, and the Fate of the Jewish People by Walter Russell Mead Listen to our latest podcast episode: Operation Breaking Dawn: Analyzing and Assessing the Latest Gaza Conflict Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Aug 17, 2022
The Forgotten Exodus: Egypt
One of the top Jewish podcasts in the U.S., American Jewish Committee's (AJC) The Forgotten Exodus , is the first-ever narrative podcast to focus exclusively on Mizrahi and Sephardic Jews. In this week's episode, we feature Jews from Egypt. In the first half of the 20th century, Egypt went through profound social and political upheavals culminating in the rise of President Gamal Abdel Nasser and his campaign of Arabization, creating an oppressive atmosphere for the country's Jews, and leading almost all to flee or be kicked out of the country. Hear the personal story of award-winning author André Aciman as he recounts the heart-wrenching details of the pervasive antisemitism during his childhood in Alexandria and his family's expulsion in 1965, which he wrote about in his memoir Out of Egypt, and also inspired his novel Call Me by Your Name . Joining Aciman is Deborah Starr, a professor of Near Eastern and Jewish Studies at Cornell University, who chronicles the history of Egypt's Jewish community that dates back millennia, and the events that led to their erasure from Egypt's collective memory. Aciman's modern-day Jewish exodus story is one that touches on identity, belonging, and nationality: Where is your home when you become a refugee at age 14? Be sure to follow The Forgotten Exodus before the next episode drops on August 22. ___ Show notes: Sign up to receive podcast updates here . Learn more about the series here . Song credits: Rampi Rampi , Aksaray'in Taslari , Bir Demet Yasemen by Turku, Nomads of the Silk Road Pond5 : "Desert Caravans": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI), Composer: Tiemur Zarobov (BMI), IPI#1098108837 "Sentimental Oud Middle Eastern": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI), Composer: Sotirios Bakas (BMI), IPI#797324989. "Frontiers": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI); Composer: Pete Checkley (BMI), IPI#380407375 "Adventures in the East": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI) Composer: Petar Milinkovic (BMI), IPI#00738313833. "Middle Eastern Arabic Oud": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI); Composer: Sotirios Bakas (BMI), IPI#797324989 ___ Episode Transcript: ANDRÉ ACIMAN: I've lived in New York for 50 years. Is it my home? Not really. But Egypt was never going to be my home. It had become oppressive to be Jewish. MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: The world has overlooked an important episode in modern history: the 800,000 Jews who left or were driven from their homes in Arab nations and Iran in the mid-20th century. This series, brought to you by American Jewish Committee, explores that pivotal moment in Jewish history and the rich Jewish heritage of Iran and Arab nations as some begin to build relations with Israel. I'm your host, Manya Brachear Pashman. Join us as we explore family histories and personal stories of courage, perseverance, and resilience. This is The Forgotten Exodus. Today's episode: leaving Egypt. Author André Aciman can't stand Passover Seders. They are long and tedious. Everyone gets hungry long before it's time to eat. It's also an unwelcome reminder of when André was 14 and his family was forced to leave Egypt – the only home he had ever known. On their last night there, he recounts his family gathered for one last Seder in his birthplace. ANDRÉ: By the time I was saying goodbye, the country, Egypt, had essentially become sort of Judenrein. MANYA: Judenrein is the term of Nazi origin meaning "free of Jews". Most, if not all of the Jews, had already left. ANDRÉ: By the time we were kicked out, we were kicked out literally from Egypt, my parents had already had a life in Egypt. My mother was born in Egypt, she had been wealthy. My father became wealthy. And of course, they had a way of living life that they knew they were abandoning. They had no idea what was awaiting them. They knew it was going to be different, but they had no sense. I, for one, being younger, I just couldn't wait to leave. Because it had become oppressive to be Jewish. As far as I was concerned, it was goodbye. Thank you very much. I'm going. MANYA: André Aciman is best known as the author whose novel inspired the Oscar-winning film Call Me By Your Name – which is as much a tale of coming to terms with being Jewish and a minority, as it is an exquisite coming of age love story set in a villa on the Italian Riviera. What readers and moviegoers didn't know is that the Italian villa is just a stand-in. The story's setting– its distant surf, serpentine architecture, and lush gardens where Elio and Oliver's romance blooms and Elio's spiritual awakening unfolds – is an ode to André's lost home, the coastal Egyptian city of Alexandria. There, three generations of his Sephardic family had rebuilt the lives they left behind elsewhere as the Ottoman Empire crumbled, two world wars unfolded, a Jewish homeland was born, and nationalistic fervor swept across the Arab world and North Africa. There, in Alexandria, his family had enjoyed a cosmopolitan city and vibrant Jewish home. Until they couldn't and had to leave. ANDRÉ: I would be lying if I said that I didn't project many things lost into my novels. In other words, to be able to re-experience the beach, I created a beach house. And that beach house has become, as you know, quite famous around the world. But it was really a portrait of the beach house that we had lost in Egypt. And many things like that, I pilfer from my imagined past and dump into my books. And people always tell me, 'God, you captured Italy so well.' Actually, that was not Italy, I hate to tell you. It was my reimagined or reinvented Egypt transposed into Italy and made to come alive again. MANYA: Before he penned Call Me By Your Name , André wrote his first book, Out of Egypt , a touching memoir about his family's picturesque life in Alexandria, the underlying anxiety that it could always vanish and how, under the nationalization effort led by Egypt's President Gamel Abdel Nassar, it did vanish. The memoir ends with the events surrounding the family's last Passover Seder before they say farewell. ANDRÉ: This was part of the program of President Nasser, which was to take, particularly Alexandria, and turn it into an Egyptian city, sort of, purified of all European influences. And it worked. As, by the way, and this is the biggest tragedy that happens to, particularly to Jews, is when a culture decides to expunge its Jews or to remove them in one way or another, it succeeds. It does succeed. You have a sense that it is possible for a culture to remove an entire population. And this is part of the Jewish experience to accept that this happens. MANYA: Egypt did not just expunge its Jewish community. It managed to erase Jews from the nation's collective memory. Only recently have people begun to rediscover the centuries of rich Jewish history in Egypt, including native Egyptian Jews dating back millennia. In addition, Egypt became a destination for Jews expelled from Spain in the 15th Century. And after the Suez Canal opened in 1869, a wave of more Jews came from the Ottoman Empire, Italy, and Greece. And at the end of the 19th Century, Ashkenazi Jews arrived, fleeing from European pogroms. DEBORAH STARR: The Jewish community in Egypt was very diverse. The longest standing community in Egypt would have been Arabic speaking Jews, we would say now Mizrahi Jews. MANYA: That's Deborah Starr, Professor of Modern Arabic and Hebrew Literature and Film at Cornell University. Her studies of cosmopolitan Egypt through a lens of literature and cinema have given her a unique window into how Jews arrived and left Egypt and how that history has been portrayed. She says Jews had a long history in Egypt through the Islamic period and a small population remained in the 19th century. Then a wave of immigration came. DEBORAH: We have an economic boom in Egypt. Jews start coming from around the Ottoman Empire, from around the Mediterranean, emigrating to Egypt from across North Africa. And so, from around 5,000 Jews in the middle of the 19th century, by the middle of the 20th century, at its peak, the Egyptian Jews numbered somewhere between 75 and 80,000. So, it was a significant increase, and you know, much more so than just the birth rate would explain. MANYA: André's family was part of that wave, having endured a series of exiles from Spain, Italy, and Turkey, before reaching Egypt. DEBORAH: Egypt has its independence movement, the 1919 revolution, which is characterized by this discourse of coexistence, that 'we're all in this together.' There are images of Muslims and Christians marching together. Jews were also supportive of this movement. There's this real sense of a plurality, of a pluralist society in Egypt, that's really evident in the ways that this movement is characterized. The interwar period is really this very vibrant time in Egyptian culture, but also this time of significant transition in its relationship to the British in the various movements, political movements that emerge in this period, and movements that will have a huge impact on the fate of the Jews of Egypt in the coming decades. MANYA: One of those movements was Zionism, the movement to establish a Jewish state in the biblical homeland of the Jews. In 1917, during the First World War, the British government occupying Egypt at the time, issued a public statement of support for the establishment of a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine, still an Ottoman region with a small minority Jewish population. That statement became known as the Balfour Declaration. DEBORAH: There was certainly evidence of a certain excitement about the Balfour Declaration of 1917. A certain amount of general support for the idea that Jews are going to live there, but not a whole lot of movement themselves. But we also have these really interesting examples of people who were on the record as supporting, of seeing themselves as Egyptians, as part of the anti-colonial Egyptian nationalism, who also gave financial support to the Jewish project in Palestine. And so, so there wasn't this sense of—you can't be one or the other. There wasn't this radical split. MANYA: Another movement unfolding simultaneously was the impulse to reclaim Egypt's independence, not just in legal terms – Egypt had technically gained independence from the British in 1922 – but suddenly what it meant to be Egyptian was defined against this foreign colonial power that had imposed its will on Egypt for years and still maintained a significant presence. DEBORAH: We also see moves within Egypt, toward the 'Egyptianization' of companies or laws that start saying, we want to, we want to give priority to our citizens, because the economy had been so dominated by either foreigners or people who were local but had foreign nationality. And this begins to disproportionately affect the Jews. Because so many of the Jews, you know, had been immigrants a generation or two earlier, some of them had either achieved protected status or, you know, arrived with papers from, from one or another of these European powers. MANYA: In 1929, Egypt adopted its first law giving citizenship to its residents. But it was not universally applied. By this time, the conflict in Palestine and the rise of Zionism had shifted how the Egyptian establishment viewed Jews. DEBORAH: Particularly the Jews who had lived there for a really long time, some of whom were among the lower classes, who didn't travel to Europe every summer and didn't need papers to prove their citizenship, by the time they started seeing that it was worthwhile for them to get citizenship, it was harder for Jews to be approved. So, by the end, we do have a pretty substantial number of Jews who end up stateless. MANYA: Stateless. But not for long. In 1948, the Jewish state declared independence. In response, King Farouk of Egypt joined four other Arab nations in declaring war on the newly formed nation. And they lost. The Arab nations' stunning defeat in that first Arab-Israeli War sparked a clandestine movement to overthrow the Egyptian monarchy, which was still seen as being in the pocket of the British. One of the orchestrators of that plot, known as the Free Officers Movement, was Col. Gamel Abdel Nassar. In 1952, a coup sent King Farouk on his way to Italy and Nassar eventually emerged as president. The official position of the Nassar regime was one of tolerance for the Jews. But that didn't always seem to be the case. DEBORAH: Between 1948 and '52, you do have a notable number of Jews who leave Egypt at this point who see the writing on the wall. Maybe they don't have very deep roots in Egypt, they've only been there for one or two generations, they have another nationality, they have someplace to go. About a third of the Jews who leave Egypt in the middle of the 20th century go to Europe, France, particularly. To a certain extent Italy. About a third go to the Americas, and about a third go to Israel. And among those who go to Israel, it's largely those who end up stateless. They have no place else to go because of those nationality laws that I mentioned earlier, have no choice but to go to Israel. MANYA: Those who stayed became especially vulnerable to the Nassar regime's sequestration of businesses. Then in 1956, Egypt nationalized the Suez Canal, a 120-mile-long waterway that connected the Mediterranean Sea to the Indian Ocean by way of the Red Sea – that same waterway that created opportunities for migration in the region a century earlier. DEBORAH: The real watershed moment is the 1956 Suez conflict. Israel, in collaboration with France, and Great Britain attacks Egypt, the conflict breaks out, you know, the French and the British come into the war on the side of the Israelis. And each of the powers has their own reasons for wanting, I mean, Nasser's threatening Israeli shipping, and, threatening the security of Israel, the French and the British, again, have their own reasons for trying to either take back the canal, or, just at least bring Nassar down a peg. MANYA: At war with France and Britain, Egypt targeted and expelled anyone with French and British nationality, including many Jews, but not exclusively. DEBORAH: But this is also the moment where I think there's a big pivot in how Jews feel about being in Egypt. And so, we start seeing larger waves of emigration, after 1956. So, this is really sort of the peak of the wave of emigration. MANYA: André's family stayed. They already had endured a series of exiles. His father, an aspiring writer who copied passages by Marcel Proust into his diary, had set that dream aside to open a textile factory, rebuild from nothing what the family had lost elsewhere, and prepare young André to eventually take over the family business. He wasn't about to walk away from the family fortune – again. DEBORAH: André Aciman's story is quite, as I said, the majority of the Jewish community leaves in the aftermath of 1956. And his family stays a lot longer. So, he has incredible insights into what happens over that period, where the community has already significantly diminished. MANYA: Indeed, over the next nine years, the situation worsened. The Egyptian government took his father's factory, monitored their every move, frequently called the house with harassing questions about their whereabouts, or knocked on the door to issue warrants for his father's arrest, only to bring him in for more interrogation. As much as André's father clung to life in Egypt, it was becoming a less viable option with each passing day. ANDRÉ: He knew that the way Egypt was going, there was no room for him, really. And I remember during the last two years, in our last two years in Egypt, there wAs constantly references to the fact that we were going to go, this was not lasting, you know, what are we going to do? Where do we think we should go? And so on and so forth. So, this was a constant sort of conversation we were having. MANYA: Meanwhile, young André encountered a level of antisemitism that scarred him deeply and shaped his perception of how the world perceives Jews. ANDRÉ: It was oppressive in good part because people started throwing stones in the streets. So, there was a sense of 'Get out of here. We don't want you here.' MANYA: It was in the streets and in the schools, which were undergoing an Arabization after the end of British rule, making Arabic the new lingua franca and antisemitism the norm. ANDRÉ: There's no question that antisemitism was now rooted in place. In my school, where I went, I went to a British school, but it had become Egyptian, although they taught English, predominantly English, but we had to take Arabic classes, in sort of social sciences, in history, and in Arabic as well. And in the Arabic class, which I took for many years, I had to study poems that were fundamentally anti-Jewish. Not just anti-Israeli, which is a big distinction that people like to make, it doesn't stick. I was reading and reciting poems that were against me. And the typical cartoon for a Jew was a man with a beard, big tummy, hook nose, and I knew 'This is really me, isn't it? OK.' And so you look at yourself with a saber, right, running through it with an Egyptian flag. And I'll never forget this. This was, basically I was told that this is something I had to learn and accept and side with – by the teachers, and by the books themselves. And the irony of the whole thing is that one of the best tutors we had, was actually the headmaster of the Jewish school. He was Jewish in very sort of—very Orthodox himself. And he was teaching me how to recite those poems that were anti-Jewish. And of course, he had to do it with a straight face. MANYA: One by one, Jewish neighbors lost their livelihoods and unable to overcome the stigma, packed their bags and left. In his memoir, André recalls how prior to each family's departure, the smell of leather lingered in their homes from the dozens of suitcases they had begun to pack. By 1965, the smell of leather began to waft through André's home. ANDRÉ: Eventually, one morning, or one afternoon, I came back from school. And my father said to me, 'You know, they don't want us here anymore.' Those were exactly the words he used. 'They don't want us here.' I said, 'What do you mean?' 'Well, they've expelled us.' And I was expelled with my mother and my brother, sooner than my father was. So, we had to leave the country. We realized we were being expelled, maybe in spring, and we left in May. And so, for about a month or so, the house was a mess because there were suitcases everywhere, and people. My mother was packing constantly, constantly. But we knew we were going to go to Italy, we knew we had an uncle in Italy who was going to host us, or at least make life livable for us when we arrived. We had obtained Italian papers, obtained through various means. I mean, whatever. They're not exactly legitimate ways of getting a citizenship, but it was given to my father, and he took it. And we changed our last name from Ajiman, which is how it was pronounced, to Aciman because the Italians saw the C and assumed it was that. My father had some money in Europe already. So that was going to help us survive. But we knew my mother and I and my brother, that we were now sort of functionally poor. MANYA: In hindsight, André now knows the family's expulsion at that time was the best thing that could have happened. Two years later, Israel trounced Egypt in the Six-Day War, nearly destroying the Egyptian Air Force, taking control of the Gaza Strip and the entire Sinai Peninsula, as well as territory from Egypt's allies in the conflict, Syria and Jordan. The few remaining Jews in Egypt were sent to internment camps, including the chief rabbis of Cairo and Alexandria and the family of one of André's schoolmates whose father was badly beaten. After three years in Italy, André's family joined his mother's sister in America, confirming once and for all that their life in Egypt was gone. ANDRÉ: I think there was a kind of declaration of their condition. In other words, they never overcame the fact that they had lost a way of life. And of course, the means to sustain that life was totally taken away, because they were nationalized, and had their property sequestered, everything was taken away from them. So, they were tossed into the wild sea. My mother basically knew how to shut the book on Egypt, she stopped thinking about Egypt, she was an American now. She was very happy to have become a citizen of the United States. Whereas my father, who basically was the one who had lost more than she had, because he had built his own fortune himself, never overcame it. And so, he led a life of the exile who continues to go to places and to restaurants that are costly, but that he can still manage to afford if he watches himself. So, he never took cabs, he always took the bus. Then he lived a pauper's life, but with good clothing, because he still had all his clothing from his tailor in Egypt. But it was a bit of a production, a performance for him. MANYA: André's father missed the life he had in Egypt. André longs for the life he could've had there. ANDRÉ: I was going to study in England, I was going to come back to Egypt, I was going to own the factory. This was kind of inscribed in my genes at that point. And of course, you give up that, as I like to say, and I've written about this many times, is that whatever you lose, or whatever never happened, continues to sort of sub-exist somewhere in your mind. In other words, it's something that has been taken away from you, even though it never existed. MANYA: But like his mother, André moved on. In fact, he says moving on is part of the Jewish experience. Married with sons of his own, he now is a distinguished professor at the Graduate Center of City University of New York, teaching the history of literary theory. He is also one of the foremost experts on Marcel Proust, that French novelist whose passages his father once transcribed in his diaries. André's own novels and anthologies have won awards and inspired Academy Award-winning screenplays. Like Israel opened its doors and welcomed all of those stateless Egyptian Jews, America opened doors for André. Going to college in the Bronx after growing up in Egypt and Italy? That introduced him to being openly Jewish. ANDRÉ: I went to Lehman College, as an undergraduate, I came to the States in September. I came too late to go to college, but I went to an event at that college in October or November, and already people were telling me they were Jewish. You know, 'I'm Jewish, and this and that,' and, and so I felt 'Oh, God, it's like, you mean people can be natural about their Judaism? And so, I began saying to people, 'I'm Jewish, too,' or I would no longer feel this sense of hiding my Jewishness, which came when I came to America. Not before. Not in Italy. Not in Egypt certainly. But the experience of being in a place that was fundamentally all Jewish, like being in the Bronx in 1968, was mind opening for me, it was: I can let everything down, I can be Jewish like everybody else. It's no longer a secret. I don't have to pretend that I was a Protestant when I didn't even know what kind of Protestant I was. As a person growing up in an antisemitic environment. You have many guards, guardrails in place, so you know how not to let it out this way, or that way or this other way. You don't speak about matzah. You don't speak about charoset. You don't speak about anything, so as to prevent yourself from giving out that you're Jewish. MANYA: Though the doors had been flung open and it felt much safer to be openly Jewish, André to this day cannot forget the antisemitism that poisoned his formative years. ANDRÉ: I assume that everybody's antisemitic at some point. It is very difficult to meet someone who is not Jewish, who, after they've had many drinks, will not turn out to be slightly more antisemitic than you expected. It is there. It's culturally dominant. And so, you have to live with this. As my grandmother used to say, I'm just giving this person time until I discover how antisemitic they are. It was always a question of time. MANYA: His family's various displacements and scattered roots in Spain, Turkey, Egypt, Italy, and now America, have led him to question his identity and what he calls home. ANDRÉ: I live with this sense of: I don't know where I belong. I don't know who I am. I don't know any of those things. What's my flag? I have no idea. Where's my home? I don't know. I live in New York. I've lived in New York for 50 years. Is it my home? Not really. But Egypt was never going to be my home. MANYA: André knew when he was leaving Egypt that he would one day write a book about the experience. He knew he should take notes, but never did. And like his father, he started a diary, but it was lost. He started another in 1969. After completing his dissertation, he began to write book reviews for Commentary , a monthly American magazine on religion, Judaism and politics founded and published, at the time, by American Jewish Committee. The editor suggested André write something personal, and that was the beginning of Out of Egypt . In fact, three chapters of his memoir, including The Last Seder , appeared in Commentary before it was published as a book in 1994. André returned to Egypt shortly after its release. But he has not been back since, even though his sons want to accompany him on a trip. ANDRÉ: They want to go back, because they want to go back with me. Question is, I don't want to put them in danger. You never know. You never know how people will react to . . . I mean, I'll go back as a writer who wrote about Egypt and was Jewish. And who knows what awaits me? Whether it will be friendly, will it be icy and chilly. Or will it be hostile? I don't know. And I don't want to put myself there. In other words, the view of the Jews has changed. It went to friendly, to enemy, to friendly, enemy, enemy, friendly, and so on, so forth. In other words, it is a fundamentally unreliable situation. MANYA: He also doesn't see the point. It's impossible to recapture the past. The pictures he sees don't look familiar and the people he used to know with affection have died. But he doesn't want the past to be forgotten. None of it. He wants the world to remember the vibrant Jewish life that existed in Cairo and Alexandria, as well as the vile hatred that drove all but a handful of Jews out of Egypt. Cornell Professor Deborah Starr says for the first time in many years, young Egyptians are asking tough questions about the Arabization of Egyptian society and how that affected Egyptian Jews. Perhaps, Israel and Zionism did not siphon Jewish communities from the Arab world as the story often goes. Perhaps instead, Israel offered a critical refuge for a persecuted community. DEBORAH: I think it's really important to tell the stories of Mizrahi Jews. I think that, particularly here we are speaking in English to an American audience, where the majority of Jews in North America are Ashkenazi, we have our own identity, we have our own stories. But there are also other stories that are really interesting to tell, and are part of the history of Jews in the 20th and 21st centuries. They're part of the Jewish experience. And so that's some of what has always motivated me in my research, and looking at the stories of coexistence among Jews and their neighbors in Egypt. MANYA: Professor Starr says the rise of Islamist forces like the Muslim Brotherhood has led Egyptians to harken back toward this period of tolerance and coexistence, evoking a sense of nostalgia. DEBORAH: The people are no longer living together. But it's worth remembering that past, it's worth reflecting on it in an honest way, and not, to look at the nostalgia and say: oh, look, these people are nostalgic about it, what is it that they're nostalgic for? What are some of the motivations for that nostalgia? How are they characterizing this experience? But also to look kind of critically on the past and understand, where things were working where things weren't and, and to tell the story in an honest way. MANYA: Though the communities are gone, there has been an effort to restore the evidence of Jewish life. Under Abdel Fattah Al-Sisi, Egypt's president since 2014, there have been initiatives to restore and protect synagogues and cemeteries, including Eliyahu Hanavi Synagogue in Alexandria, Maimonides' original yeshiva in old Cairo, and Cairo's vast Jewish cemetery at Bassatine. But André is unmoved by this gesture. ANDRÉ: In fact, I got a call from the Egyptian ambassador to my house here, saying, 'We're fixing the temples and the synagogues, and we want you back.' 'Oh, that's very nice. First of all,' I told him, 'fixing the synagogues doesn't do anything for me because I'm not a religious Jew. And second of all, I would be more than willing to come back to Egypt, when you give me my money back.' He never called me again. MANYA: Anytime the conversation about reparations comes up, it is overshadowed by the demand for reparations for Palestinians displaced by the creation of Israel, even though their leaders have rejected all offers for a Palestinian state. André wishes the Arab countries that have attacked Israel time and again would invest that money in the welfare of Palestinian refugees, help them start new lives, and to thrive instead of using them as pawns in a futile battle. He will always be grateful to HIAS, the Hebrew Immigrant Aid Society, for helping his family escape, resettle, and rebuild their lives. ANDRÉ: We've made new lives for ourselves. We've moved on, and I think this is what Jews do all the time, all the time. They arrive or they're displaced, kicked out, they refashion themselves. Anytime I can help a Jew I will. Because they've helped me, because it's the right thing to do for a Jew. If a Jew does not help another Jew, what kind of a Jew are you? I mean, you could be a nonreligious Jew as I am, but I am still Jewish. And I realize that we are a people that has historically suffered a great deal, because we were oppressed forever, and we might be oppressed again. Who knows, ok? But we help each other, and I don't want to break that chain. MANYA: Egyptian Jews are just one of the many Jewish communities who in the last century left Arab countries to forge new lives for themselves and future generations. Join us next week as we share another untold story of The Forgotten Exodus . Many thanks to André for sharing his story. You can read more in his memoir Out of Egypt and eventually in the sequel which he's working on now about his family's life in Italy after they left Egypt and before they came to America. Does your family have roots in North Africa or the Middle East? One of the goals of this series is to make sure we gather these stories before they are lost. Too many times during my reporting, I encountered children and grandchildren who didn't have the answers to my questions because they had never asked. That's why one of the goals of this project is to encourage you to find more of these stories. Call The Forgotten Exodus hotline. Tell us where your family is from and something you'd like for our listeners to know such as how you've tried to keep the traditions alive and memories alive as well. Call 212.891-1336 and leave a message of 2 minutes or less. Be sure to leave your name and where you live now. You can also send an email to theforgottenexodus@ajc.org and we'll be in touch. Atara Lakritz is our producer, CucHuong Do is our production manager. T.K. Broderick is our sound engineer. Special thanks to Jon Schweitzer, Sean Savage, Ian Kaplan, and so many of our colleagues, too many to name really, for making this series possible. And extra special thanks to David Harris, who has been a constant champion for making sure these stories do not remain untold. You can follow The Forgotten Exodus on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you listen to podcasts, and you can sign up to receive updates at AJC.org/forgottenexodussignup. The views and opinions of our guests don't necessarily reflect the positions of AJC. You can reach us at theforgottenexodus@ajc.org. If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to spread the word, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review to help more listeners find us.
Aug 11, 2022
Operation Breaking Dawn: Analyzing and Assessing the Latest Gaza Conflict
On Friday, August 5, the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) launched Operation Breaking Dawn in response to days of threats from the Iranian-backed Palestinian Islamic Jihad (PIJ) that it would attack Israel. The conflict, which lasted nearly three days, saw over 1,100 rockets launched towards Israel by PIJ. The IDF killed several high-ranking PIJ operatives and destroyed much of the terror group's military capabilities. Listen to AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson, in conversation with AJC Jerusalem Director Lt. Col. (res.) Avital Leibovich, analyze the latest conflict and the steps moving forward. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jason Isaacson and Avital Leibovich ___ Show Notes: Photo credits: Kobi Alkotser/GPO Watch the full discussion: Briefing on the Situation in Israel - AJC Advocacy Anywhere Learn more about The Forgotten Exodus at AJC.org/ForgottenExodus Listen to our latest podcast episode: Behind the Scenes of AJC's New Podcast Series The Forgotten Exodus Follow People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Aug 4, 2022
Behind the Scenes of AJC's New Podcast Series The Forgotten Exodus
Hear behind-the-scenes details about AJC's new podcast series The Forgotten Exodus, featuring its host Manya Brachear Pashman and cartoonist and musician Carol Isaacs, who shares more about her family's flight from rising antisemitism in Iraq, as depicted in her graphic memoir and animated film, The Wolf of Baghdad . The Forgotten Exodus , which has ranked number one on Apple's Jewish podcast chart since it was launched on August 1, is the first-ever podcast series focused exclusively on the rich, yet little-known heritage of Jews from Arab nations and Iran. This discussion, hosted by AJC's Dr. Saba Soomekh, highlights the importance of learning Mizrahi and Sephardic stories to better understand the Jewish experience. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Saba Soomekh, Carol Isaacs, and Manya Brachear Pashman ___ Show Notes: Learn more about The Forgotten Exodus at AJC.org/ForgottenExodus Watch the rest of the discussion: The Forgotten Exodus Leaving Iraq - AJC Advocacy Anywhere Listen to our latest podcast episode: James Carville and Leslie Sanchez on the Battle Between Extremists and Moderates in U.S. Politics Follow to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Aug 1, 2022
The Forgotten Exodus: Iraq
Listen to the premiere episode of a new limited narrative series from American Jewish Committee (AJC): The Forgotten Exodus . Each Monday, for the next six weeks, AJC will release a new episode of The Forgotten Exodus , the first-ever narrative podcast series to focus exclusively on Mizrahi and Sephardic Jews. This week's episode focuses on Jews from Iraq. If you like what you hear, use the link below to subscribe before the next episode drops on August 8. Who are the Jews of Iraq? Why did they leave? And why do so many Iraqi Jews, even those born elsewhere, still consider Iraq their home? Join us to uncover the answers to these questions through the inspiring story of Mizrahi Jewish cartoonist Carol Isaacs' family. Feeling alienated growing up as the only Jew in school from an Arab-majority country, Carol turned her longing for Iraq and the life her family left behind into a gripping graphic memoir, The Wolf of Baghdad . Meanwhile, Zvi Ben-Dor Benite, professor of History and Middle Eastern and Islamic Studies at New York University, delves into the fascinating, yet the little-known history of Iraqi Jewry, from its roots in the region 2,600 years ago, to the antisemitic riots that led them to seek refuge in Israel, England, and the U.S. ____ Show Notes: Sign up to receive podcast updates here . Learn more about The Forgotten Exodus here . Song credits: Thanks to Carol Isaacs and her band 3yin for permission to use The Wolf of Bagdad soundtrack . Portions of the following tracks can be heard throughout the episode: 01 Dhikrayyat (al Qasabji) 02 Muqaddima Hijaz (trad) 03 Che Mali Wali (pt 1) (trad) 05 Fog el Nakhal (trad) 11 Balini-b Balwa (trad) 12 Al Effendi (al Kuwaiti) 14 Dililol (trad) 15 Che Mail Wali (pt 2) (trad) Pond5 : "Desert Caravans": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI), Composer: Tiemur Zarobov (BMI), IPI#1098108837; "Sentimental Oud Middle Eastern": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI), Composer: Sotirios Bakas (BMI), IPI#797324989.; "Adventures in the East": Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI) Composer: Petar Milinkovic (BMI), IPI#00738313833. ____ Episode Transcript: CAROL ISAACS: A lot of businesses were trashed, houses were burnt. It was an awful time. And that was a kind of time when the Jews of Iraq had started to think, 'Well, maybe this isn't our homeland after all.' MANYA BRACHEAR PASHMAN: Welcome to the premiere of the first ever podcast series devoted exclusively to an overlooked episode in modern history: the 800,000 Jews who left or were driven from their homes in Arab nations and Iran in the mid-20th century. Some fled antisemitism, mistreatment, and pogroms that sparked a refugee crisis like no other, as persecuted Jewish communities poured from numerous directions. Others sought opportunities for their families or followed the calling to help create a Jewish state. In Israel, America, Italy, wherever they landed, these Jews forged new lives for themselves and future generations. This series explores that pivotal moment in Jewish history and the rich Jewish heritage of Iran and Arab nations as some begin to build relations with Israel. Each week, we will share the history of one Jewish family with roots in the Arab world. Each account is personal and different. Some include painful memories or elegies for what could've been. Others pay homage to the conviction of their ancestors to seek a life where they were wanted. To ground each episode, we rely on a scholar to untangle the complexities. Some of these stories have never been told because they wished to leave the past in the past. For those of you who, like me, before this project began, never read this chapter in Jewish history, we hope you find this series enlightening. And for those who felt ignored for so many decades, we hope these stories honor your families' legacies. Join us as we explore stories of courage, perseverance, and resilience. I'm your host, Manya Brachear Pashman, and this is The Forgotten Exodus. Today's episode: Leaving Iraq. CAROL: All my life, I've lived in two worlds – one inside the family home, which is a very Jewish world, obviously, but also tinged with Iraqi customs like Iraqi food, a language we spoke—Judeo Arabic. So, I've always known that I'm not just British. I've lived in these two worlds, the one at home, and then the one at school. And then later on at work, which was very English. I went to a terribly English school, for example, there were about a thousand girls. Of those thousand girls, 30 were Jewish, and I was the only Mizrahi, the only non-European Jew. So, there's always been that knowing that I'm not quite fitting into boxes. Do you know what I mean? But I never quite knew which box I fit into. MANYA: Carol Isaacs makes her living illustrating the zeitgeists of our time, poking fun at the irony all around us, reminding us of our common quirks. And she fits it all into a tiny box. You might not know Carol by her given name, but you've probably seen her pen name, scrawled in the corner of her cartoons published by The New Yorker and Spectator magazines: TS McCoy, or The Surreal McCoy. Carol is homesick for a home she never knew. Born and raised Jewish in London, she grew up hearing stories of her parents' life in Baghdad. How her family members learned to swim in the Tigris River using the bark of palm trees as life preservers, how they shopped in the city sooks for dates to bake b'ab'e b'tamer. Millions of Jews have called Iraq home for more than 2,600 years, including many of their children and grandchildren who have never been there, but long to go. Like Carol, they were raised with indelible stories of daily life in Mosul, Basra, Baghdad – Jewish life that ceased to exist because it ceased to be safe. CAROL: My mother remembered sitting with her mother and her grandmother and all the family in the cellar, going through every single grain of rice for chometz. Now, if you imagine that there were eight days of Passover, I don't know 10, 12 people in the household, plus guests, they ate rice at least twice a day. You can imagine how much rice you'd have to go through. So little things like that, you know, that would give you a window into another world completely, that they remembered with so much fondness. And it's been like that all my life. I've had this nostalgia for this, this place that my parents used to . . . now and again they'd talk about it, this place that I've never visited and I've never known. But it would be wonderful to go and just smell the same air that my ancestors smelled, you know, walk around the same streets in the Jewish Quarter. The houses are still there, the old Jewish Quarter. They're a bit run down. Well, very run down. MANYA: Carol turned her longing for Iraq and the life her family left behind into a graphic memoir and animated film called The Wolf of Baghdad . Think Art Spiegelman's Maus , the graphic novel about the Holocaust, but for Jews in Iraq who on the holiday of Shavuot in 1941 suffered through a brutal pogrom known as the Farhud, followed by decades of persecution, and ultimately, expulsion. Her research for the book involved conversations with family members who had never spoken about the violence and hatred they witnessed. They had left it in the past and now looked toward the future. There's no dialogue in the book either. The story arc simply follows the memories. CAROL: They wanted to look forward. So, it was really gratifying that they did tell me these things. 'Cause when my parents came, for example, they came to the UK, it was very much 'Look forward. We are British now.' My father was the quintessential city gent. He'd go to the office every day in the city of London with his pinstriped suit, and a rose plucked from the front garden, you know, a copy of The Guardian newspaper under his arm. He was British. We listened to classical music. We didn't listen to the music of my heritage. It was all Western music in the house. MANYA: But her father's Muslim and Christian business associates in Iraq visited regularly, as long as they could safely travel. CAROL: On a Sunday, every month, our house would turn into little Baghdad. They would come and my mother would feed them these delicacies that she spent all week making and they'd sit and they'd talk. MANYA: As Carol said, she had heard only fond memories throughout her childhood because for millennia, Jews in Iraq lived in harmony with their Muslim and Christian neighbors. CAROL: Jews have always lived in Mesopotamia, lived generally quite well. There was always the dimmi status, which is a status given to minorities. For example, they had to pay a certain tax, had to wear certain clothing. Sometimes, they weren't allowed to build houses higher than their neighbor, because they weren't allowed to be above their neighbor. They couldn't ride a horse, for example, Jews. I mean, small little rules, that you were never quite accorded full status. But then when the Brits arrived in 1917, things became a bit easier. MANYA: But 20-some years later, life for Jews took a turn for the worse. That sudden and dramatic turning point in 1941 was called The Farhud. ZVI BEN-DOR BENITE: Jews have been living in Iraq for thousands of years. If we start with the Farhud, we are starting in the middle of the story, in fact, in the middle of the end." MANYA: That's Zvi Ben-Dor Benite, a professor of history and Middle Eastern and Islamic Studies at New York University. The son of Iraqi Jewish parents who migrated to Israel in the early 1950s, he carries in his imagination maps of old Jewish neighborhoods in Mosul and Baghdad, etched by his parents' stories of life in the old country. He shares Carol's longing to walk those same streets one day. ZVI: Iraqis, even those who were born in Israel, still self-identify as Iraqis and still consider that home to a certain extent – an imaginary home, but home. And you can say the same thing, and even more so, for people who were born there and lived there at the time. So here's the thing: if I go there, I would be considering myself a returnee. But it would be my first time. MANYA: As a Jew, Zvi knows the chances of his returning are slim. To this day, Iraq remains the only Arab country that has never signed a ceasefire with Israel since Arab nations declared war on the Jewish state upon its creation in 1948. Jews are not safe there. Really, no one has been for a while. The dictatorship of Saddam Hussein, ISIS, and general civil unrest have made modern-day Iraq dangerous for decades. The region is simply unstable. The centuries leading up to the Farhud in 1941 were no different. The territory originally known as Mesopotamia flipped from empire to empire, including Babylonian, Mongol, Safavids, Ottoman, British. Just to name a few. But during those centuries, Iraq was historically diverse – home to Muslims, Jews, Assyrian Christians. Yes, Jews were a minority and faced some limitations. But that didn't change the fact that they loved the place they called home. ZVI: We zoom in on the Farhud because it is a relatively unique event. Jews in Iraq were highly integrated, certainly those who lived in the big cities and certainly those who lived in Baghdad. Few reasons to talk about this integration. First of all, they spoke Arabic. Second of all, they participated in the Iraqi transition to modernity. In many ways, the Jewish community even spearheaded Iraqi society's transition into modernity. Of course, you know, being a minority, it means that not everything is rosy, and I'm not in any way trying to make it as a rosy situation. But if you compare it to the experiences of European Jews, certainly Europeans in the Pale of Settlement or in Eastern Europe, it's a much lovelier situation. Many Jews participate in Iraqi politics in different ways. Many Jews joined the Communist Party, in fact, lead the Communist Party to a certain extent. Others join different parties that highly identify in terms of Iraqi nationalism. MANYA: Very few Iraqi Jews identified with the modern Zionist movement, a Jewish nationalist movement to establish a state on the ancestral homeland of the Jews, then known as Palestine. Still, Iraqi Jews were not immune from Arab hostility toward the notion of Jewish self-determination. Adding to that tension: the Nazi propaganda that poured out of the German embassy in Baghdad. CAROL: Mein Kampf was translated into Arabic and published in all the newspapers there. There were broadcasts coming from Radio Berlin, in Arabic, politicizing Islam and generally manipulating certain texts from the Quran, to show that Jews were the enemies of Islam. So, there was this constant drip, drip of antisemitism. ZVI: Another factor is, of course, the British. There is an anti-British government in Baghdad at the time, during the period of someone who went down in history as a Nazi collaborator, Rashid Ali. And Rashid Ali's been removed just before the British retake Iraq. We should remember that basically, even though Iraq is a kind of constitutional monarchy, the British run the show behind the scenes for a very, very long time. So, there is a little bit of a hiatus over several months with Rashid Ali, and then when he is removed, you know, people blame the Jews for that. MANYA: On the afternoon of June 1, 1941, Jews in Baghdad prepared to celebrate the traditional Jewish harvest festival of Shavuot. Violent mobs descended on the celebrants. CAROL: In those two days the mobs ran riot and took it all out on the Jews. We don't, to this day, we don't know how many Jews died. Conservative estimates say about 120. We think it was in the thousands. Certainly, a lot of businesses were trashed, houses were burnt, women raped, mutilated, babies killed. It was an awful time. And that was a kind of time when the Jews of Iraq had started to think, 'Well, maybe this isn't our homeland after all.' MANYA: The mobs were a fraction of the Iraqi population. Many Muslim residents protected their Jewish neighbors. CAROL: One of my relations said that during the Farhud, the pogrom, that her neighbors stood guard over their house, Muslim neighbors, and told the mobs that they wouldn't let them in that these people are our family, our friends. They wouldn't let them in. They looked after each other, they protected each other. MANYA: But the climate in Iraq was no longer one in which Jews could thrive. Now they just hoped to survive. In the mid-to-late 40s, Carol's father, who worked for the British army during World War II, left for the United Kingdom and, as the eldest son, began to bring his family out one by one. Then came 1948. Israel declared independence and five Arab nations declared war. ZVI: So, Iraq sent soldiers to fight as part of the Arab effort in Palestine, and they began to come back in coffins. I mean, there's a sense of defeat. Three deserters, three Iraqi soldiers that deserted the war, and crossed the desert back to Iraq, and they landed up in Mosul on the Eve of Passover in 1949. And they knocked on the door of one of my uncles. And they said, they were hosted by this Jewish family. And they were telling the Jews, who were their hosts that evening, about the war in Palestine, and about what was going on and so on. This is just an isolated case, but the point is that you know, it raises the tension in the population, and it raises the tensions against Jews tenfold. But there's no massive movement of Iraqi Jews, even though the conditions are worsening. In other words, it becomes uneasy for someone to walk in the street as a Jew. There is a certain sense of fear that is going on. And then comes the legal action. MANYA: That legal action, transacted with the state of Israel and facilitated by Zionist operatives, set the most significant exodus in motion. In 1950, the Iraqi government gave its Jewish citizens a choice. Renounce their Iraqi citizenship, take only what fits in a suitcase, and board a flight to Israel, or stay and face an uncertain future. The offer expired in a year, meaning those who stayed would no longer be allowed to leave. ZVI: If you're a Jew in Iraq in 1950, you are plunged into a very, very cruel dilemma. First of all, you don't know what the future holds. You do know that the present, after 1948, suggests worsening conditions. There is a sense that, you know, all the Jews are sort of a fifth column. All of them are associated with Zionism, even though you know, the Zionist movement is actually very small. There are certain persecutions of Zionists and communists who are Jews as well. And, you know, there have been mass arrests of them, you know, particularly of the young, younger Jewish population, so you don't know. And then the state comes in and says, 'Look, you get one year to stay or to leave. If you leave, you leave. If you stay, you're gonna get stuck here.' Now, just think about presenting someone with that dilemma after 1935 and the Nuremberg Laws, after what happened in Europe. MANYA: In all, 120,000 Iraqi Jews leave for Israel over nine months – 90% of Iraqi Jewry. For the ten percent who stayed, they became a weak and endangered minority. Many Iraqis, including the family on Carol's mother's side, eventually escaped to America and England. CAROL: My mother and my father were separated by a generation. My father was much older, 23 years older than my mother. So, he had a different view of life in Baghdad. When he was around, it was generally very peaceful. The Jews were allowed to live quite, in peace with their neighbors. But with my mother's generation and younger, it was already the beginning – the rot had started to set in. So, she had a different view entirely. CAROL: My grandmother, maternal grandmother, was the last one to come out of our family, to come out of Iraq. She left in '63. And my dad managed to get her out. MANYA: After Israel defeated another Arab onslaught in 1967, thousands more fled. ZVI: This was a glorious community, a large community, which was part of the fabric of society for centuries, if not millennia. And then, in one dramatic day, in a very, very short period, it just basically evaporated. And what was left is maybe 10 percent, which may be elite, that decided to risk everything by staying. But even they, at the end, had to leave. MANYA: Remember, Carol said she was one of 30 Jewish girls at her school, but the only Mizrahi Jew. The term Mizrahi, which means "Eastern" in Hebrew, refers to the diaspora of descendants of Jewish communities from Middle Eastern countries such as: Iraq, Iran, and Yemen, and North African countries such as: Egypt, Libya, and Morocco. CAROL: It's been interesting. A lot of people didn't even know that there were Jews living in Arab lands. I mean, for all my life, I've been told, 'Oh, you're Jewish, you speak Yiddish, you come from Poland. You eat smoked salmon and bagels. You say 'oy vey,' which is great if you do all those things and you do come from Eastern Europe, but I don't. Almost 1 million Jews of Arab lands, nobody knows about what happened to them, that they were ethnically cleansed, removed from their homes, and dispersed across the world. It's our truth. And it's our history and make of it what you will, just add it to other family histories that we know. MANYA: Carol has discovered that even Iraqis did not know of their country's rich Jewish past, nor the fate of its Jewish citizens. Since the animated version of The Wolf of Baghdad premiered at the Israeli and Iraqi embassies in London, accompanied by Carol's accordion and other musicians playing its Judeo-Arabic soundtrack, Iraqis in the audience have been moved to tears. CAROL: At one Q&A, after we did a performance, one Iraqi gentleman stood up at the front. He was crying. He said, 'I'm really sorry for what we did to you. I'm so sorry.' And that was immensely moving for me. It was like, well, you know what? We're talking now. It's wonderful. We can sit down together. We can talk in a shared language. We can talk about our shared culture, and we've got more that ties us together than separates us. We've got more in common, right? So, I'm always looking for that, that kind of positive, and so far it's come back to me, multiplied by a million, which has been brilliant. The truth is coming to light, that people know that the Jews of Iraq contributed so much, not just culturally but also socially, in the government too. So, it's this reaching out from Iraq to its lost Jews saying 'Well where are you? What happened to you? Tell us your story. We want to see where you are. Come back even,' some of them are saying. MANYA: Carol has continued to give a voice to the Jewish refugees of Iraq. Most recently, she has been adapting The Wolf of Baghdad for younger, middle school-aged readers to better understand the story. And high schools in London and Canada have added The Wolf of Baghdad to their history curriculum. CAROL: Leaving Iraq was called the silent exodus for a reason. We just left quietly and without fuss, and just went and made our lives elsewhere. I do know that life was difficult for them wherever they went, but they just got on with it, like refugees will do everywhere. MANYA: These Jews are just one of the many Jewish communities who, in the last century left Arab countries to forge new lives for themselves and future generations. Join us next week as we share another untold story of The Forgotten Exodus . Many thanks to Carol Isaacs for sharing her family's story and to her band 3yin for the music. Throughout this episode, you have been listening to pieces of the soundtrack from The Wolf of Baghdad motion comic performed by 3yin, a groundbreaking London based band that plays Jewish melodies from the Middle East and North Africa. The soundtrack is available at thesurrealmccoy.com. Atara Lakritz is our producer, CucHuong Do is our production manager. T.K. Broderick is our sound engineer. Special thanks to Jon Schweitzer, Sean Savage, Ian Kaplan, and so many of our colleagues, too many to name really, for making this series possible. And extra special thanks to David Harris, who has been a constant champion for making sure these stories do not remain untold. You can subscribe to The Forgotten Exodus on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you listen to podcasts, and you can learn more at AJC.org/forgottenexodus. The views and opinions of our guests don't necessarily reflect the positions of AJC. You can reach us at theforgottenexodus@ajc.org. If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to spread the word, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review to help more listeners find us.
Jul 28, 2022
James Carville and Leslie Sanchez on the Battle Between Extremists and Moderates in U.S. Politics
As antisemitism persists on both political extremes, are moderate forces strong enough to steer us in the right direction? Can lawmakers actually reach across the aisle in today's political climate? James Carville, Democratic strategist and political icon, and Leslie Sanchez, a Republican strategist and award-winning political commentator, joined AJC Senior Director of Policy and Political Affairs Julie Fishman Rayman in a discussion about the state of U.S. politics today at AJC Global Forum 2022. The two explained how rising extremism in both parties affects critical issues like Israeli security and antisemitism. They also weighed in on the importance of talking to voters in their own language - as opposed to national talking points. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) The Forgotten Exodus Teaser Trailer (2:42) Julie Fishman Rayman, James Carville, Leslie Sanchez ___ Show Notes: Learn more about The Forgotten Exodus at AJC.org/ForgottenExodus Theme song credit: Publisher: Pond5 Publishing Beta (BMI); Composer: Tiemur Zarobov (BMI), IPI#1098108837 Watch the AJC Global Forum 2022 session: Extremists or Moderates - Who's Driving American Politics Today? - The Leonard Greenberg Forum for Domestic Policy Issues View additional highlights from AJC Global Forum 2022: AJC.org/GlobalForumNews Listen to our latest episode: How Can Governments Win the Fight Against Antisemitism? An AJC Global Forum 2022 Conversation Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jul 21, 2022
How Can Governments Win the Fight Against Antisemitism? An AJC Global Forum 2022 Conversation
U.S. Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Antisemitism Deborah Lipstadt and European Commission Coordinator on Combating Antisemitism and Fostering Jewish Life Katharina von Schnurbein discussed, in a conversation moderated by Managing Director of AJC Europe Simone Rodan-Benzaquen, how to fulfill their governments' bold promises to fight antisemitism. When every day, it seems a new instance of antisemitism appears in the headlines, how are American and European leaders working to counter these global threats? Listen to this discussion, recorded at AJC Global Forum 2022, for answers to this pressing question and more. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Simone Rodan-Benzaquen, Deborah Lipstadt, Katharina von Schnurbein ___ Show Notes: Watch the AJC Global Forum 2022 session: Can Governments Win the Fight Against Antisemitism? A Discussion With Ambassador Deborah Lipstadt and Katharina von Schnurbein - The Max Fisher Annual Program View additional highlights from AJC Global Forum 2022: AJC.org/GlobalForumNews Listen to our latest episode: Building on the Abraham Accords: President Biden's Trip to the Middle East, and Its Implications for Israeli-Saudi Relations Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jul 14, 2022
Building on the Abraham Accords: President Biden's Trip to the Middle East, and Its Implications for Israeli-Saudi Relations
This week, President Joe Biden is visiting the Middle East on a tour that includes Israel, the West Bank, and Saudi Arabia. Amid looming Iranian nuclear concerns, a shaky U.S.-Saudi relationship, and continued Israeli-Palestinian uncertainty, much work needs to be accomplished. How can President Biden strengthen the United States' strategic presence in the region? What needs to be done to improve the United States' connection to Saudi Arabia? How close are Israel and Saudi Arabia to normalization? Retired U.S. Ambassador Marc Sievers, Director of American Jewish Committee's office in Abu Dhabi: The Sidney Lerner Center for Arab-Jewish Understanding, joins us this week to discuss these matters. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Marc Sievers ___ Show Notes: Photo by Israeli Government Press Office (GPO)/Handout Watch the AJC Global Forum 2022 session: Winds of Change: The New Middle East View additional highlights from AJC Global Forum 2022: AJC.org/GlobalForumNews Listen to Marc Sievers on People of the Pod : The Historic Israel-UAE Meeting Learn more on Global Voice: What to Draw From President Biden's Middle East Visit Listen to our latest episode: Antisemitism in Latin America: The Lasting Impact of the AMIA Attack Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jul 7, 2022
Antisemitism in Latin America: The Lasting Impact of the AMIA Attack
It is the deadliest antisemitic attack outside of Israel since the Holocaust: On July 18, 1994, Iranian-backed terrorists drove a bomb-laden truck into the Argentine Israeli Mutual Association (AMIA) Jewish Center in Buenos Aires, killing 80 and wounding 300. 28 years later, how has the attack on AMIA impacted the continent, its Jewish population, and its approach to combating antisemitism? This week, Fernando Lottenberg, the first Organization of American States (OAS) Commissioner to Monitor and Combat Antisemitism, and Dina Siegel Vann, Director of AJC's Arthur and Rochelle Belfer Institute for Latino and Latin American Affairs, join us to discuss the progress that's been made since the attack, and the work left to do in Latin America. Then, Manya Brachear Pashman reflects on the deadly shooting in Highland Park, IL over the 4th of July weekend. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Dina Siegel Vann and Fernando Lottenberg (23:39) Manya Brachear Pashman ___ Show Notes: A Bomb in Argentina: 'The Jewish community is standing and fighting.' Listen to our latest episode: Is the Golden Age of American Jewry Over? An AJC Global Forum Great Debate Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jun 30, 2022
Is the Golden Age of American Jewry Over? An AJC Global Forum Great Debate
Today, American Jews have reached unparalleled levels of success in areas such as business, academia, and culture. But with rising antisemitism, Jewish demographic changes, and shifting norms, some are pessimistic about the future for American Jewry. Tune into AJC's signature AJC Global Forum 2022 session: The Great Debate: Is the Golden Age of American Jewry Over? The debate features guests Bret Stephens, Op-Ed Columnist, The New York Times , Editor-in-Chief, Sapir ; and Pamela Nadell, Patrick Clendenen Chair in Women's and Gender History; Director, Jewish Studies Program, American University, and is moderated by Laura Shaw Frank, AJC Director, William Petschek Contemporary Jewish Life. We also hear from AJC Global Forum 2022 participants about meeting other young Jews and learning from featured panelists, while also reflecting on their connections to Judaism and Israel. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Manya on the Street (3:37) Pamela Nadell and Bret Stephens ___ Show Notes: Watch the full session: The Great Debate: Is the Golden Age of American Jewry Over? To view additional videos and highlights from AJC Global Forum 2022, go to AJC.org/GlobalForumNews Listen to our latest episode: What is the BDS Mapping Project and Why Should All Jews Be Concerned? Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jun 23, 2022
What is the BDS Mapping Project and Why Should All Jews Be Concerned?
A map published online earlier this month by BDS activists claims to list organizations and institutions in the Boston area that they say are responsible for harm against Palestinians. In actuality, the project is targeting and threatening the Jewish community. AJC New England Director Rob Leikind joins us to explain what's being done to raise awareness and counter the project, and why it's not just the Jewish community that's in danger. Then, Ian Kaplan, a student at Tufts University near Boston, and one of AJC's 2022 Goldman Fellows, shares his perspective on the BDS Mapping Project, and his approach to navigating campus discourse on Israel, demonstrated by a recent conversation he had with a fellow student. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Rob Leikind (14:31) Manya Brachear Pashman and Ian Kaplan ___ Show Notes: BDS Mapping Project: How can you help? Ensure Massachusetts Stands Against BDS 5 Reasons Why the BDS Mapping Project is Dangerous for Jews (and Everyone Else) Translate Hate Listen to our latest episode: Are Jews, Israel, and Progressive Spaces Compatible? Live from AJC Global Forum 2022 Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jun 16, 2022
Are Jews, Israel, and Progressive Spaces Compatible? Live from AJC Global Forum 2022
In America today we are faced with the rise of extremism at both ends of the political spectrum. This week, we examine the interplay between progressive groups and American Jews, who are being increasingly excluded and targeted by so-called progressives, especially over ties to Israel, the Middle East's only liberal democracy. David Baddiel, Comedian, Author, Screenwriter, and Television Presenter; Rachel Fish, Co-Founder, Boundless; and Yair Rosenberg, Contributing Writer, The Atlantic, delve into this important topic in a thought-provoking conversation, recorded live at AJC Global Forum 2022. The episode opens with short interviews featuring AJC Global Forum 2022 participants about their top highlights. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Manya on the Street: Live from Global Forum 2022 (3:54) David Baddiel, Rachel Fish, Yair Rosenberg ___ Show Notes: AJC Global Forum 2022 Sessions referenced in the episode: Official Address from Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky to AJC Global Forum 2022 AJC Presents Moral Courage Award to Masih Alinejad Introduced By Lisa Pruzan Winds of Change: The New Middle East Jews, Israel, and Progressive Spaces: Are They Compatible? - Full Video To view additional videos and highlights from AJC Global Forum 2022, go to AJC.org/GlobalForumNews Urge the White House to Combat Domestic Antisemitism Listen to our latest episode: Bari Weiss on How Antisemitism Became Normalized; Gearing Up for AJC Global Forum 2022 Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jun 9, 2022
Bari Weiss on How Antisemitism Became Normalized; Gearing Up for AJC Global Forum 2022
As we look ahead to AJC Global Forum 2022, the premier global Jewish advocacy gathering of the year (June 12-14 in New York City), we look back at some highlights from AJC Virtual Global Forum 2021, including conversations with U.S. Sens. Cory Booker (D-NJ), Tim Scott (R-SC), and Jacky Rosen (D-NV), on the launch of the Senate Caucus on Black-Jewish Relations, columnists Bret Stephens and Bari Weiss discussing the mainstreaming of antisemitism, and crucial advice from two young activists on how to combat anti-Jewish hatred on campus and beyond. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Cory Booker (D-NJ), Tim Scott (R-SC), and Jacky Rosen (D-NV) (8:37) Bret Stephens and Bari Weiss (14:41) Talia Rosenberg and Julia Jassey ___ Show Notes: Can't make it to AJC Global Forum 2022, June 12-14, in New York? We've got the next best thing! Sign up at AJC.org/webcast to receive email reminders for the four AJC Global Forum live webcasts, featuring world leaders, the Great Debate, AJC CEO David Harris, and more! Watch full sessions from Virtual Global Forum 2021: The Launch of the Senate Caucus on Black-Jewish Relations with U.S. Sens. Cory Booker (D-NJ), Tim Scott (R-SC), and Jacky Rosen (D-NV) The Mainstreaming of Antisemitism: How Should We Respond? With Bret Stephens, Bari Weiss, and Simone Rodan Benzaquen The View from Campus with Talia Rosenberg and Julia Jassey Urge the White House to Combat Domestic Antisemitism Listen to our latest episode: Yossi Klein Halevi on the Convergence of Politics and Religion at Jerusalem's Temple Mount Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
May 26, 2022
Yossi Klein Halevi on the Convergence of Politics and Religion at Jerusalem's Temple Mount
Yom Yerushalayim, or Jerusalem Day, celebrates the reunification of Jerusalem in June 1967 at the end of the Six-Day War. This week, we hear from journalist and author Yossi Klein Halevi on the triumph of that historic day, the current wave of terrorist attacks in Israel, the tensions on the Temple Mount, and the trauma that continues to shape Israel's spiritual and political life. Also, as we wrap up #JewishandProud month, Halevi, along with some of our listeners, share what being Jewish means to them. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) #JewishAndProud Listener Segment (2:32) Yossi Klein Halevi ___ Show Notes: Urge the White House to Combat Domestic Antisemitism Urge Congress to Stand with Israel Urge Congress to Counter Russian Aggression Listen to our latest episode: Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Programming's Antisemitism Failures; Buffalo Shooting and Great Replacement Theory Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
May 19, 2022
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Programming's Antisemitism Failures; Buffalo Shooting and Great Replacement Theory
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) programs aim to foster belonging and unity among diverse workplaces and campus communities. However, in doing so, they often misunderstand who Jews are, view all Jews as privileged, and ignore or downplay blatant cases of antisemitism. AJC's U.S. Director for Combating Antisemitism and guest host Holly Huffnagle sits down with Dr. Saba Soomekh, Associate Director of AJC Los Angeles, to break down the issues surrounding DEI, and what needs to change to properly address prejudice against Jews. Then, Holly Huffnagle reflects on the May 14th shooting at a grocery store in Buffalo, New York, and how the perpetrators behind this and other recent shootings, including those in Christchurch, Pittsburgh, and El Paso, cited the same white supremacist belief: the Great Replacement theory. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) #JewishAndProud Listener Segment (2:33) Saba Soomekh (26:13) Holly Huffnagle ___ Show Notes: What does being Jewish mean to you? We want to know your answer. Call the People of the Pod hotline at 212-891-1336 and leave a message of a minute or less in our voicemail inbox. Don't forget to include your name and city with your answer. You may hear your voice on a future episode! Translate Hate Urge the White House to Combat Domestic Antisemitism Urge Congress to Stand with Israel Urge Congress to Counter Russian Aggression Listen to our latest episode: X Troop: The Inspiring Untold Story of Jewish Resistance During WWII Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
May 12, 2022
X Troop The Inspiring Untold Story of Jewish Resistance During WWII
Author and Jewish historian Leah Garrett shares the powerful but little-known story at the heart of X Troop , her newest book, about a group of Jewish refugees from Eastern Europe, tapped to become clandestine commandos and counterintelligence agents for the British Army during World War II. A professor and Director of Jewish Studies at Hunter College, Garrett also discusses her painful decision to resign from the trade union that represents the faculty of the City University of New York after it adopted a virulently antisemitic resolution denouncing Israel, the battle she continues to fight with the union, and how the experience has changed her Jewish identity. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Listeners on #JewishAndProud (2:16) Leah Garrett ___ Show Notes: What does being Jewish mean to you? We want to know your answer. Call the People of the Pod hotline at 212-891-1336 and leave a message of a minute or less in our voicemail inbox. Don't forget to include your name and city with your answer. You may hear your voice on a future episode! By Leah Garrett: X Troop: The Secret Jewish Commandos Who Helped Defeat the Nazis Young Lions: How Jewish Authors Reinvented the American War Novel I resigned from the CUNY union because of its antisemitism Urge the White House to Combat Domestic Antisemitism Urge Congress to Stand with Israel AJC's Emergency #StandWithUkraine Fund Urge Congress to Counter Russian Aggression Listen to our latest episode: Rabbi Ammiel Hirsch on How Support for Israel is Key to the Future of Reform Judaism Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
May 5, 2022
Rabbi Ammiel Hirsch on How Support for Israel is Key to the Future of Reform Judaism
As the senior rabbi of Stephen Wise Free Synagogue in New York City, Rabbi Ammiel Hirsch believes Zionism is a core value of Judaism. Rabbi Hirsch sat down with guest host Laura Shaw Frank, AJC's Director of Contemporary Jewish Life, to discuss the danger of a waning commitment to Israel among a portion of Reform Judaism, a recent delegation to the Poland-Ukraine border, and how being #JewishAndProud is as important to him as breathing. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Listeners on #JewishAndProud (2:59) Rabbi Ammiel Hirsch ___ Show Notes: What does being Jewish mean to you? We want to know your answer. Call the People of the Pod hotline at 212-891-1336 and leave a message of a minute or less in our voicemail inbox. Don't forget to include your name and city with your answer. You may hear your voice on a future episode! Urge the White House to Combat Domestic Antisemitism Urge Congress to Stand with Israel AJC's Emergency #StandWithUkraine Fund Urge Congress to Counter Russian Aggression Listen to our latest episode: How Do American Millennial Jews Feel About Israel? Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Apr 28, 2022
How Do American Millennial Jews Feel About Israel?
What are American millennial Jews' attitudes towards Israel and how has anti-Israel activism on U.S. college campuses changed that relationship? AJC surveyed American and Israeli millennial Jews to better understand their experiences, attitudes, and opinions about Jewish identity, connection to Israel, and attachment to one another. In a special live People of the Pod recording, AJC Director of Alexander Young Leadership Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman sits down with AJC ACCESS Global Director Dana Steiner, AJC ACCESS Israel Manager Lironne Koret, and Opinion, Analytics, and Communications Strategist Philippe Assouline, to unpack this data and discuss the implications for the Jewish community. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Naomi Ravick (2:23) Dana Steiner, Lironne Koret, and Philippe Assouline ___ Show Notes: As part of Jewish American Heritage Month, American Jewish Committee has named May as #JewishandProud Month to celebrate the Jewish people's united bravery and resilience in the face of adversity. People of the Pod will take part in this month-long campaign with a special lineup of guests, and we would love for you to join us! What does being Jewish mean to you? We want to know your answer. Call the People of the Pod hotline at 212-891-1336 and leave a message of a minute or less in our voicemail inbox. Don't forget to include your name and city with your answer. You may hear your voice on a future episode! Watch the full program "Bonds and Divides: Surveys of American and Israeli Millennial Jews" here Urge Congress to Stand with Israel AJC's Emergency #StandWithUkraine Fund Urge Congress to Counter Russian Aggression Listen to our latest episode: How to Tell Fact from Fiction About the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Apr 20, 2022
How to Tell Fact from Fiction About the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict
Amid rising tensions in Israel, Canadian-Israeli journalist Matti Friedman shares candid advice for all who are trying to understand the complex situation that is the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Friedman takes listeners behind the scenes of media reporting on Israel to demonstrate the sometimes corrosive impact that news outlets have when they attempt to oversimplify the conflict. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Matti Friedman ___ Show Notes: Register here for a live People of the Pod recording on April 26th Bonds and Divides: American and Israeli Millennial Jews Eight Tips for Reading About Israel by Matti Friedman Pumpkinflowers by Matti Friedman Urge Congress to Stand with Israel AJC's Emergency #StandWithUkraine Fund Urge Congress to Counter Russian Aggression Listen to our latest episode: France's Presidential Elections: Implications for French Jews and U.S. Politics Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Apr 14, 2022
France's Presidential Elections: Implications for French Jews and U.S. Politics
AJC Chief Field Operations Officer and guest host Melanie Maron Pell sits down with AJC Europe Managing Director Simone Rodan-Benzaquen to break down the results from the first round of the French presidential election, why both the far right and far left are a danger to French society and Jews in particular, and why France may be a barometer for the U.S. political landscape. Then, AJC's Director of the Alexander Young Leadership Department Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman joins us to discuss the unprecedented increase in antisemitic activity on campus, which was the focus of this week's University Presidents Summit hosted by AJC, Hillel International, and the American Council on Education (ACE), where college and university leaders gathered from across the United States. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Simone Rodan Benzaquen (16:34) Melanie Maron Pell and Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman ___ Show Notes: Urge Congress to Stand with Israel AJC's Emergency #StandWithUkraine Fund Urge Congress to Counter Russian Aggression Listen to our latest episode: Solving the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: A New Perspective Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Apr 7, 2022
Solving the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: A New Perspective
When it comes to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the pathway to peace has typically been presented as a choice between a one-state or a two-state solution. Guest host Jason Isaacson, AJC's Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer, speaks with Avi Melamed, Israeli intelligence and strategic affairs analyst and author of Inside the Middle East: Entering a New Era, about possible other solutions, the impact of the Abraham Accords on the region, and why the story of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict is not separate from the story of the Middle East. Then, Natalia Mahmud, AJC Associate Director of U.S. Muslim-Jewish Relations and Program Director of the Muslim-Jewish Advisory Council, joins us to share the traditions she practices with her family during the month of Ramadan. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Avi Melamed (17:03) Manya Brachear Pashman and Natalia Mahmud ___ Show Notes: Signup here to attend a Muslim-Jewish Advisory Council Iftar on April 22, 2022 near Dallas, Texas Urge Congress to Stand with Israel AJC's Emergency #StandWithUkraine Fund Urge Congress to Counter Russian Aggression Listen to our latest episode: "We Lost a Lot of Leverage": Freed Iranian Hostage Speaks Out on Iran Negotiations Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Mar 31, 2022
"We Lost a Lot of Leverage": Freed Iranian Hostage Speaks Out on Iran Negotiations
The Washington Post's Jason Rezaian, who was held hostage by Iran for nearly two years and was released in a prisoner swap the day the 2015 Iran nuclear deal (JCPOA) went into effect, joins us to share his unique perspective on the reported nuclear deal emerging in negotiations between Tehran and world powers. Rezaian weighs in on what's at stake in the talks and discusses the potential impact of the lifting of a number of sanctions and the removal of America's terrorist designation of the Iranian regime's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC). Then, we hear from AJC Abu Dhabi Program Director Reva Gorelick, who just returned from Israel where she accompanied AJC Project Interchange's first delegation of Middle East and North African (MENA) leaders. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jason Rezaian (24:19) Manya Brachear Pashman and Reva Gorelick ___ Show Notes: What is Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps and Why is it Designated a Terror Group by the United States? Learn about AJC's Project Interchange Urge Congress to Stand with Israel AJC's Emergency #StandWithUkraine Fund Urge Congress to Counter Russian Aggression Listen to our latest episode: Setting the Record Straight on Israel's Support for Ukraine Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Mar 24, 2022
Setting the Record Straight on Israel's Support for Ukraine
A false narrative has emerged about Israel's alleged neutrality over Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Lahav Harkov, senior diplomatic correspondent for The Jerusalem Post and co-host of their weekly podcast, joins us to set the record straight. Harkov explains how Israel is supporting Ukraine and the Ukrainian people, while avoiding provoking Syrian-based Russian troops on the democratic nation's northern border. Then, AJC Jerusalem Director Avital Leibovich shares a touching account of the AJC-sponsored plane that brought 101 Jewish Ukrainians to Israel and how Israel is welcoming Ukrainian refugees. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Lahav Harkov (15:26) Manya Brachear Pashman and Avital Leibovich ___ Show Notes: AJC's Emergency #StandWithUkraine Fund Urge Congress to Counter Russian Aggression Watch: Ukrainian Refugees Arrive in Israel! Listen to our latest episode: Clouded Futures and Big Hearts: What Life is Really Like for Ukrainian Refugees Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Mar 17, 2022
Clouded Futures and Big Hearts: What Life is Really Like for Ukrainian Refugees
A mother and her son in need of help. The extraordinary decision of the great-granddaughter of a Polish Resistance Movement fighter. Go behind the scenes of American Jewish Committee's humanitarian mission to the Ukraine-Poland border crossings and refugee reception centers and discover what it's really like to be a Ukrainian fleeing Russia's invasion and find out how Poland and its citizens are giving a masterclass in welcoming refugees. Aldona Zawada of AJC's Warsaw-based Shapiro Silverberg Central Europe Office shares the emotional story of how the AJC delegation helped a mother and son who were fleeing Ukraine, and how her great-grandfather's experience in the Polish Resistance Movement in World War II informed her own family's decision to open their home to refugees. Then, AJC Director of Social Media Julie Lenarz recounts what images have stayed with her from her time at the border, and how AJC is using social media to assist refugees and hold Russia accountable. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Aldona Zawada (15:40) Manya Brachear Pashman and Julie Lenarz ___ Show Notes: AJC's Emergency #StandWithUkraine Fund Urge Congress to Counter Russian Aggression Listen to our latest episode: The Historical Irony of Jews Fleeing into Poland Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Mar 10, 2022
The Historical Irony of Jews Fleeing into Poland
Among the 1.2 million Ukrainians that have crossed the border into Poland over the last two weeks are many Ukrainian Jews. This week, guest host Laura Shaw Frank, AJC's Director of Contemporary Jewish Life, speaks to the Chief Rabbi of Poland Michael Schudrich, who has been coordinating a Jewish relief effort on the ground. Rabbi Schudrich speaks about the most pressing needs that Jews fleeing Ukraine have right now and how he has been inspired by the Jewish community's unity during this crisis. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Rabbi Michael Schudrich (11:18) Manya Brachear Pashman and Laura Shaw Frank ___ Show Notes: AJC's Emergency #StandWithUkraine Fund Urge Congress to Counter Russian Aggression Listen to our latest episode: AJC CEO David Harris on Putin, Babyn Yar, and "Denazification" Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Mar 3, 2022
AJC CEO David Harris on Putin, Babyn Yar, and "Denazification"
American Jewish Committee CEO David Harris joins us to discuss the tragedy unfolding in Ukraine. Harris takes on Russian President Vladimir Putin's claim about the need to "denazify" Ukraine, shares what everyone, especially the Jewish community, needs to know about Babyn Yar, Ukraine's Holocaust memorial which was partially damaged by Russian forces, and issues a warning that Putin's tactics are drawn from Hitler's playbook. Then, Manya Brachear Pashman sits down with AJC Philadelphia Director Marcia Bronstein to talk about her personal connection to Ukraine and the rallies she has attended in support of the country over the past week. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:41) David Harris (19:02) Manya Brachear Pashman and Marcia Bronstein ____ Show Notes: AJC's Emergency #StandWithUkraine Fund Urge Congress to stand with Ukraine Listen to our latest episode: Live from Kyiv: The Future of Ukraine and its Large Jewish Community Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Feb 24, 2022
Live from Kyiv: The Future of Ukraine and its Large Jewish Community
Just hours before the Russian invasion of Ukraine began, Vladislav Davidzon, founding editor of The Odessa Review and contributor to Tablet Magazine, joined us live from Kyiv for a fascinating analysis and unique perspective on the mood on the ground, what Russian President Vladimir Putin is trying to accomplish, and the future of Europe's fourth largest Jewish community. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Vladislav Davidzon ____ Show Notes: Urge Congress to stand with Ukraine AJC's statement on Russian invasion of Ukraine Listen to an update from Vadislav Davidzon with AJC Europe Director Simone Rodan Benzaquen on the current situation in Ukraine The Odessa Review From Odessa With Love: Political and Literary Essays in Post-Soviet Ukraine Listen to our latest episode: Black, Jewish, and Proud: Rapper Nissim Black on Israel, Antisemitism, and Racism Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Feb 17, 2022
Black, Jewish, and Proud: Rapper Nissim Black on Israel, Antisemitism, and Racism
In a candid conversation, Israeli-American musician and recording artist Nissim Black discusses the roots of his career as a rapper, the struggles he faced when he moved to Israel and tried to find acceptance for his children, and how his connection to his Jewish faith shapes his music. Black explores how his music and spirituality have presented opportunities for constructive conversations on racism and antisemitism. Then, Manya Brachear Pashman and Sam Kliger, AJC Director of Russian and Eurasian Affairs, examine the situation in Ukraine and the recent AJC solidarity visit to Kyiv. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Nissim Black (22:46) Manya Brachear Pashman and Sam Kliger ___ Show Notes: Photo credit: @greycoat_ph Tziporah Litman Higher , The Hava Song , Mothaland Bounce , Change , Hashem Melech | Nissim Black We Stand With Ukraine | David Harris | AJC.org Listen to our latest episode: Does Hollywood Tolerate Antisemitism? With Jessica Shaw, Sirius XM host Listen to the our Hanukkah segment with Nissim Black: Nissim Black's "Eight Flames" (32:49 into the episode) Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Feb 10, 2022
Does Hollywood Tolerate Antisemitism?
Should only Jewish actors play Jewish roles? Was Whoopi Goldberg's apology enough? Should Mel Gibson work in Hollywood ever again? What does a greater emphasis on diversity in the entertainment industry mean for Jewish representation on the silver screen? On the same week the Oscar nominations were announced, Jessica Shaw, a host for Sirius XM's pop culture talk channel, joins us to discuss the debates, misunderstandings, and, in Gibson's case, the blatant antisemitism rippling through Hollywood. Then, Manya Brachear Pashman talks to AJC Paris Director Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache on the yahrzeit of Ilan Halimi, a 23-year-old Jewish Parisian who was kidnapped and tortured in 2006, and the troubling findings of AJC's 2022 Survey on Antisemitism in France. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jessica Shaw (14:23) Manya Brachear Pashman and Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache ___ Show Notes: American Jewish Committee Surveys French Jewish, Muslim, and General Populations' Perspectives on Antisemitism Listen to our latest episode: Why Whoopi Goldberg's Holocaust Views Shouldn't Surprise Us; Daniel Pearl's 20th Yahrzeit Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Feb 4, 2022
Why Whoopi Goldberg's Holocaust Views Shouldn't Surprise Us; Daniel Pearl's 20th Yahrzeit
This week on "The View," co-host Whoopi Goldberg wrongly claimed that the Holocaust "isn't about race." Though she apologized, ABC suspended her for two weeks. Writer Daniella Greenbaum, an Emmy award-winning former producer for "The View," joins us to discuss how Goldberg's comments demonstrate a widespread failure to understand Judaism but also present an opportunity to discuss the diversity of Judaism and comprehend antisemitism in its many forms. Then, on Daniel Pearl's 20th yahrzeit (anniversary of his death), Manya Brachear Pashman pays moving tribute to the slain reporter. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Daniella Greenbaum (21:43) Manya Brachear Pashman ____ Show notes: Whoopi Goldberg isn't the only one who doesn't understand antisemitism | Daniella Greenbaum | The Washington Post Are Jews a Race? | Yair Rosenberg | The Atlantic How Whoopi Became Today's Hot Topic On "The View" | The Late Show with Stephen Colbert | CBS/YouTube What America Taught the Nazis | Ira Katznelson | The Atlantic Violin Instrumental | Royalty Free Music | Lion Free Music | YouTube Listen to our most recent episode: Recovering a Town's Lost Sephardic Jewish Culture 77 Years After the Holocaust Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org . If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jan 27, 2022
Recovering a Town's Lost Sephardic Jewish Culture 77 Years After the Holocaust
What would it be like to return to the village your ancestors called home, to walk in their footsteps, and try to recover their stories and culture? Ladino singer and songwriter Sarah Aroeste did just that for her seventh album, which honors what was once the largest Jewish community in the country now known as North Macedonia. In the mountainous city of Bitola, formerly known as Monastir, 98% of the Jewish population that remained after the Balkan Wars was deported in 1943, and murdered by the Nazis and their collaborators. To mark International Holocaust Remembrance Day, Aroeste talks about her experiences in Monastir, explains why Sephardic culture is Jewish culture, and performs her song " Mi Monastir." Then, Manya Brachear Pashman talks about the challenge of confronting and processing the antisemitic attack on a synagogue in Colleyville, Texas. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Sarah Aroeste (27:53) Manya Brachear Pashman ____ Show notes: Episode photos, courtesy of Sarah Aroeste: Sarah Aroeste's cousin Rachel Nachmias (bottom left) and family, c. 1922. Nahmias family, c. 1922. Songs in this episode are from: Monastir . Listed in order of appearance: Espinelo Jovano, Jovanke (feat. Odelia Dahan Kehila and Gilan Shahaf) Mi Monastir Liner notes for Monastir , with lyrics and translations Listen to our most recent episodes: AJC CEO David Harris on the Deborah Lipstadt Holocaust Denial Trial and AJC's Critical Role in the Fight Inside the Colleyville, Texas Synagogue Hostage Crisis: Hear from 3 Local Jewish and Muslim Leaders on What It Was Like on the Ground Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod Tune in next week for a tribute to slain Jewish reporter Daniel Pearl, 20 years after his death. You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jan 20, 2022
AJC CEO David Harris on the Deborah Lipstadt Holocaust Denial Trial and AJC's Critical Role in the Fight
In 2000, renowned Holocaust scholar Dr. Deborah Lipstadt was sued by David Irving for defamation, because she called Irving a Holocaust denier and falsifier of history in her 1994 book Denying the Holocaust: The Growing Assault on Truth and Memory. Expert witnesses combed through Irving's research since the 1980s and found that Lipstadt was correct - Irving had deliberately manipulated the historical record, to support his ludicrous claims that most of the evidence of the Holocaust had been invented after the war. Listen to AJC CEO David Harris discuss the impact of the trial, and the quiet, global, multi-year effort he led to generate support for Lipstadt's trial defense, making sure the world never forgets the murder of six million Jews – a historical fact. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) David Harris ___ Show Notes: Take action. Join AJC in calling for the White House to convene a taskforce that will develop a national action plan to fight anti-Jewish hate. Urge the Senate to confirm Deborah Lipstadt as the Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Antisemitism . Listen to our most recent episode: Inside the Colleyville, Texas Synagogue Hostage Crisis: Hear from 3 Local Jewish and Muslim Leaders on What It Was Like on the Ground Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod Keep an eye out for our next episode marking International Holocaust Remembrance, in which we learn about the lost Jewish community of Monastir from Ladino singer and songwriter Sarah Aroeste. You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jan 18, 2022
Inside the Colleyville, Texas Synagogue Hostage Crisis: Hear from 3 Local Jewish and Muslim Leaders on What It Was Like on the Ground
On January 15th, the world watched in horror as an armed attacker, spewing antisemitic hatred and seeking the release of a convicted terrorist from prison, took a rabbi and three worshippers hostage at Congregation Beth Israel in Colleyville, Texas. As the situation unfolded, local Muslim, Jewish, and Christian clergy gathered with the families of the hostages inside a nearby church to pray for a safe resolution to the stand-off. Joining us today are Joel Schwitzer, Director of AJC Dallas, Mohamed Elibiary, former Adviser to the Department of Homeland Security and Co-Chair of the Dallas Fort Worth Muslim-Jewish Advisory Council, and Rabbi Andrew Paley, a Dallas police chaplain, Senior Rabbi at Temple Shalom in Dallas. Hear from these three local leaders as they reflect on that day's events, the interfaith work they do in their communities, and the hope they have for moving forward. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Joel Schwitzer, Mohamed Elibiary, and Rabbi Andrew Paley ___ Show Notes: Listen to our most recent episode: The Fight for Religious Equality at the Western Wall Just Got Tougher Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jan 13, 2022
The Fight for Religious Equality at the Western Wall Just Got Tougher
When Israel's coalition government took shape last summer, all signs pointed to progress on an expanded egalitarian prayer site at Jerusalem's Western Wall. But now that plan appears to be stalled, due to tensions within that coalition. We are joined by Dr. Laura Shaw Frank, AJC's Director of William Petschek Contemporary Jewish Life, who shares the special connection she has to the Western Wall (Kotel), why its egalitarian prayer site has become a flashpoint within the Israeli government, and the deep meaning it has to diaspora Jews. Then, tune into our closing segment to hear Manya and Laura on how the coronavirus pandemic and ensuing border closures have impacted American Jewish-Israeli relations, particularly for young and unaffiliated Jews, whose ties to Israel may not be as strong as previous generations. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Laura Shaw Frank (22:03) Manya Brachear Pashman and Laura Shaw Frank ____ Show Notes: Listen to our most recent episode: How Antisemitism Undermines Democracy Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod on your favorite podcast app, and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review, to help more listeners find us.
Jan 6, 2022
How Antisemitism Undermines Democracy
On January 6, 2021, a violent mob stormed the U.S. Capitol, disrupting the joint session of Congress assembled to count electoral votes that would formalize President-elect Joe Biden's victory. Among the rioters were members of white supremacist groups, and symbols and signs of anti-Jewish hate. In a discussion guest hosted by Melanie Maron Pell, AJC's Chief Field Operations Officer, we are joined by Holly Huffnagle, AJC's U.S. Director for Combating Antisemitism, and Rebecca Klein, AJC's Director of National Outreach, to unpack how the forces that fuel antisemitism also endanger American democracy. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Holly Huffnagle and Rebecca Klein (27:12) Manya Brachear Pashman and Melanie Maron Pell ___ Show Notes: Listen to our most recent episode: That Time Jewish Comedian Alex Edelman Went to a White Nationalist Gathering Don't forget to subscribe to People of the Pod and learn more at AJC.org/PeopleofthePod You can reach us at: peopleofthepod@ajc.org If you've enjoyed this episode, please be sure to tell your friends, tag us on social media with #PeopleofthePod, and hop onto Apple Podcasts to rate us and write a review to help more listeners find us.
Dec 23, 2021
That Time Jewish Comedian Alex Edelman Went to a White Nationalist Gathering
Hear from comedian and writer Alex Edelman about his new off-Broadway hit, "Just for Us," which explores his Jewish identity through the lens of a white nationalist meeting he attended in New York City. Edelman discusses the antisemitism he's faced as a performer and throughout his life, how to use humor to broach difficult topics, and the paradox of the present Jewish experience in America: embracing the joy but also reckoning with the world and outsiders that view Judaism as something very different. It's that time of year again when Jewish families make their traditional plans to indulge in Chinese food on Christmas. But if you think that's the most significant intersection of Asian and Jewish cultures, think again. For our closing segment, Shabbat Table Talk, we're joined by Hana Rudolph, Assistant Director of AJC's Asia Pacific Institute, to discuss how, throughout history, members of the Jewish diaspora have called parts of Asia their home and members of the Asian community have made Judaism their spiritual home. ____ Episode Lineup: (1:38) Alex Edelman (26:06) Manya Brachear Pashman and Hana Rudolph ____ Show Notes: Image credit: Monique Carboni Join us as we fight anti-Jewish hate and take on those who threaten Israel. Your gift to AJC before December 31 will be matched, dollar-for-dollar. To support our work, visit AJC.org/donate. Or, text AJC DONATE to 52886. "Just For Us" will take an unexpected hiatus due to the rising cases of COVID-19. Rather than ending its run on January 8th, the show will be dark beginning immediately and resume performances on January 24 for an extended run through February 19, 2022. For tickets, visit www.JustForUsShow.com Going Beyond Chinese Food on Christmas: Five New Books Celebrating Jewish-Asian Relations : https://www.ajc.org/news/going-beyond-chinese-food-on-christmas-five-new-books-celebrating-jewish-asian-relations
Dec 16, 2021
A New Middle East: The Historic Israel-UAE Meeting; How to Help Victims of Deadly Kentucky Tornadoes
Israeli Prime Minister Naftali Bennett made history this past week when he became the first Israeli premier to be officially welcomed to the United Arab Emirates. Retired U.S. Ambassador Marc Sievers, inaugural Director of AJC Abu Dhabi: The Sidney Lerner Center for Arab-Jewish Understanding, joins us to discuss the importance of this visit and what it holds for the future of the region. Then, AJC Chief Field Operations Officer Melanie Maron Pell joins us from her home state of Kentucky to share what's happening on the ground in the aftermath of deadly tornadoes that slammed six states, what Israel has done to bring aid, and how listeners can help those impacted. ___ Episode Lineup: (1:30) Ambassador Marc Sievers (19:42) Manya Brachear Pashman and Melanie Maron Pell ___ Show Notes: Join us as we fight anti-Jewish hate and take on those who threaten Israel. Your gift to AJC before December 31 will be matched, dollar-for-dollar. To support our work, visit AJC.org/donate. Or, text AJC DONATE to 52886. Kentucky Tornado Relief Funds: 1.Team Western Kentucky Tornado Relief Fund: https://secure.kentucky.gov/formservices/Finance/WKYRelief 2. Jewish Federation of Louisville Kentucky Tornado Relief Fund: https://jewishlouisville.abilafundraisingonline.com/ky-tornado-relief Stay tuned for next week's episode featuring Alex Edelman, on his new off-Broadway comedy show, "Just For Us". To purchase tickets, visit https://www.justforusshow.com/ and use the discount code ALEX . Photo credit: Israeli Government Press Office (GPO)
Dec 9, 2021
Yad Vashem Chairman: Those Comparing Public Health Policies to Holocaust "Completely Out of Touch With Reality"
Dani Dayan, the newly appointed chairman of Yad Vashem – Israel's official memorial to the victims of the Holocaust – and former Consul General of Israel in New York, joins this week's People of the Pod with critical and timely messages for the world, including why remembering the Holocaust is more important than ever and the concerning trend of weaponizing the Holocaust for political purposes. Then, AJC Director of William Petschek Contemporary Jewish Life Laura Shaw Frank shares her inspiring experience at the Freedom Sunday for Soviet Jews rally 34 years ago and what a unifying moment it was to be in a crowd of over 250,000 people on the National Mall in Washington, D.C. _____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Dani Dayan (16:50) Manya Brachear Pashman and Laura Shaw Frank
Dec 3, 2021
How to Combat Jew-Hatred: Shine a Light on Antisemitism; Nissim Black's "Eight Flames"
What can modern day advocates learn from the Hanukkah story to fight antisemitism and anti-Zionism? What can be done to make combating antisemitism a priority for elected officials? As part of an unprecedented Jewish community Hanukkah initiative called Shine a Light, hear from Holly Huffnagle, AJC U.S. Director for Combating Antisemitism, Melanie Maron Pell, AJC Chief Field Operations Officer, and Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC Senior Director, Policy and Political Affairs, on answers to these questions and more. We also speak with Nissim Black, Israeli-American musician and recording artist to discuss his spiritual journey and how the themes of Hanukkah, highlighted in his song "Eight Flames," inspire him year-round. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Holly Huffnagle, Melanie Maron Pell, and Julie Fishman Rayman (32:49) Nissim Black ____ Show Notes: Full AJC Advocacy Anywhere program: Action Not Apathy: Shine a Light on Antisemitism Urge the Senate to Replenish Israel's Life-Saving Iron Dome System at https://www.ajc.org/FundIronDome 87 Ways to Fight Antisemitism: Inside the EU's New Plan to Combat Jew Hatred - with Katharina von Schnurbein Historic UN Report on Antisemitism, Behind the Excavation of the Pilgrims' Path - with Ahmed Shaheed Nissim Black's Hanukkah Song - Eight Flames THE DEAL podcast with Nissim Black
Nov 18, 2021
87 Ways to Fight Antisemitism: Inside the EU's New Plan to Combat Jew Hatred
Can the European Union effectively combat antisemitism? Meet the woman leading the bloc's efforts to do just that: European Commission Coordinator on combating antisemitism Katharina von Schnurbein. Last month, the EU unveiled its first Strategy on Combating Antisemitism and Fostering Jewish Life, a multi-faceted plan that incorporated many recommendations from AJC. Hear from von Schnurbein how that strategy is being implemented and what it means for European Jews and the entire Jewish diaspora. Then, for our closing segment, Shabbat Table Talk, host Manya Brachear Pashman and Shira Loewenberg, Director of AJC's Asia Pacific Institute (API), reflect on Jewish journalist Danny Fenster's release from prison in Myanmar and the dire situation in the country. __ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Katharina von Schnurbein (19:39) Manya Brachear Pashman and Shira Loewenberg __ Show Notes: Tune in on December 2 at 12PM ET for a special live People of the Pod recording, "Action Not Apathy: Shine a Light on Antisemitism." You can register for the program at AJC.org/AdvocacyAnywhere Everything You Need to Know About Antisemitism in Europe: https://www.ajc.org/AntisemitismInEurope EU Strategy on combating antisemitism and fostering Jewish life (2021-2030): https://ec.europa.eu/info/files/eu-strategy-combating-antisemitism-and-fostering-jewish-life-2021-2030_en Paul Salopek's Out of Eden Walk: https://www.nationalgeographic.org/projects/out-of-eden-walk/
Nov 11, 2021
Meet the Disrupters of Antisemitism
Meet two young, innovative, and award-winning U.S. Jews who are confronting a climate of antisemitism and anti-Zionism: Jason Kessler, lead anchor for Jew or False, a satirical news show that fights antisemitism and calls out misinformation, and Eddie Chavez Calderon of Uri L'Tzedek, an Orthodox Jewish social justice organization that tackles antisemitism in progressive spaces. Guest host AJC Chief Advocacy Officer Belle Yoeli sat down with both to hear how antisemitism has impacted their lives and how they developed their antisemitism-fighting models. This week, AJC's Disrupt Antisemitism Incubator awarded $50,000 to Kessler, Chavez Calderon, and three other young American Jews who have developed bold ideas to take on Jew-hatred. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jason Kessler, Eddie Chavez Calderon (21:13) Manya Brachear Pashman, Belle Yoeli ___ Show Notes: Jew or False, a satirical news show that fights antisemitism and calls out misinformation: https://www.jeworfalse.com/ Uri L'Tzedek, a national Orthodox Jewish social justice organization that tackles antisemitism in progressive spaces : https://utzedek.org/
Nov 4, 2021
Martin Indyk on his New Book: Master of the Game: Henry Kissinger and the Art of Middle East Diplomacy
Ambassador Martin Indyk gives listeners a behind-the-scenes look at one of the most consequential figures in modern Middle East diplomacy: former United States Secretary of State and National Security Advisor Henry Kissinger. In this riveting conversation with guest co-host Jason Isaacson, AJC's chief policy and political affairs officer, Indyk discusses his just-released book about Kissinger, Master of the Game: Henry Kissinger and the Art of Middle East Diplomacy , highlighting the veteran diplomat's lessons for Arab-Israeli stability and the antisemitism that he faced in his career. Indyk himself is no stranger to Middle East diplomacy, having served twice as the U.S. Ambassador to Israel and the Assistant Secretary of State for Near East Affairs during the Clinton Administration, and as America's special Middle East envoy for renewed peace talks between Israel and the Palestinian Authority during the Obama administration. __ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Martin Indyk (18:48) Manya Brachear Pashman and Jason Isaacson __ Show Notes: Master of the Game: Henry Kissinger and the Art of Middle East Diplomacy by Martin Indyk
Oct 25, 2021
What You Need to Know About the Largest Survey Ever on Antisemitism in the U.S.
Receive an in-depth look at the American Jewish Committee's just-released State of Antisemitism in America 2021 report, which includes the largest-ever surveys of American Jews and the United States general public on antisemitism. Listen as Avi Mayer, AJC's Managing Director of Public Affairs and Senior Spokesperson, and Holly Huffnagle, AJC's U.S. Director for Combating Antisemitism, break down the report's findings and discuss what Americans should do to confront the normalization of Jew-hatred. Then, we're joined by the winner of our audience survey drawing for a guest spot on our closing segment, Shabbat Table Talk. Listener Jim Ramenofsky speaks with Manya Brachear Pashman about what the findings of the report mean to him, and reflecting on his close friend, Lori Gilbert Kaye, who was murdered in the attack on the Poway Chabad in 2019. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Avi Mayer and Holly Huffnagle (22:45) Manya Brachear Pashman and Jim Ramenofsky ____ Show Notes: Read the results from the 2021 State of Antisemitism in America report: https://www.AJC.org/2021Report Share your encounters with antisemitism on social media with the hashtag #AntisemitismReport
Oct 21, 2021
The Tree of Life Synagogue Shooting: An Oral History with Pittsburgh Mayor Bill Peduto
On Wednesday, October 27, Pittsburgh Mayor Bill Peduto will ask residents to observe a moment of silence and reflection at 9:54 a.m. That was the moment the shooting started at the Tree of Life Synagogue in Pittsburgh's Squirrel Hill neighborhood in 2018. The antisemitic attack left 11 worshippers dead, and wounded two other congregants and police officers. Listen to Mayor Peduto recount what it was like to comfort and protect not just the city he led, but his neighbors and friends, after America's deadliest antisemitic attack three years ago. Then, for our closing segment, Shabbat Table Talk, Manya Brachear Pashman speaks with Liel Leibovitz of Tablet Magazine's podcast Unorthodox , to discuss how the Pittsburgh community united following the tragedy. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40): Mayor Bill Peduto (20:46): Manya Brachear Pashman and Liel Leibovitz ____ Show Notes: Crossover with Tablet's Unorthodox: How the Jews Went Right in Britain
Oct 19, 2021
Crossover with Tablet's Unorthodox: How the Jews Went Right in Britain
This special podcast collaboration with Tablet's Unorthodox unpacks the political shift of British Jews in the wake of Jeremy Corbyn's antisemitic scandal-filled five-year tenure as Labour party leader. This live podcast is hosted by Liel Leibovitz of Tablet's Unorthodox and Manya Brachear Pashman of AJC's People of the Pod , and features comedian and author of Jews Don't Count David Baddiel; Lecturer in Sociology at Goldsmiths University of London and author of Contemporary Left Antisemitism David Hirsh; Man Booker Prize novelist and journalist Howard Jacobson; and Research Fellow at International Centre for the Study of Radicalisation and former Union of Jewish Students president Hannah Rose. Did the Corbynization of the Labour party move Jews to the right or leave them politically homeless? Has current party leader Keir Starmer been able to regain the confidence of the country's Jewish population? Listen for answers to these pressing questions and more. Episode Lineup: (0:40) David Baddiel, David Hirsch, Howard Jacobson, and Hannah Rose Show notes: This program is part of a new program series: American Jewish Committee (AJC) and Tablet Magazine are coming together to host a four-part series titled "21st Century Europe and the Jews," which aims to address timely issues related to Jewish life and the protection of democracies in Europe. Throughout these four programs, we'll delve into the most pressing issues in the United Kingdom, Poland, France, and Germany. Don't miss a single program on these critical topics. Head to AJC.org/AdvocacyAnywhere to sign up. This episode featured the following guests: David Baddiel , comedian and author of Jews Don't Count David Hirsh , Lecturer in Sociology at Goldsmiths University of London and author of Contemporary Left Antisemitism Howard Jacobson , Man Booker Prize novelist of The Finkler Question and journalist Hannah Rose , Research Fellow at International Centre for the Study of Radicalisation and former Union of Jewish Students president
Oct 14, 2021
Advocating for Living Jews When "People Love Dead Jews"
Dara Horn is angry. And the award-winning author of five novels wants you to know why. This week, she's sitting down with guest co-host Laura Shaw Frank, AJC's Director of William Petschek Contemporary Jewish Life, to discuss why People Love Dead Jews , which is the title of her first work of nonfiction, and what that obsession means for modern-day Jewry, Israel, and efforts to counter rising antisemitism. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Dara Horn (24:09) Manya Brachear Pashman and Laura Shaw Frank Show notes: Head to AJC.org/AdvocacyAnywhere to register for the first in a four-part series by Tablet Magazine and AJC titled "21st Century Europe and the Jews", which aims to address timely issues related to Jewish life and the protection of democracies in Europe. The series will delve into the most pressing issues in the United Kingdom, Poland, France, and Germany. The first program on October 19th, 12-1pm ET, "How the Jews Went Right in Britain," will start with the UK, and will be moderated by Manya Brachear Pashman and Liel Leibovitz of Tablet Magazine's Unorthodox podcast. Go to AJC.org/AdvocacyAnywhere to register, and for more details.
Oct 7, 2021
Can You Sue a Nazi?
Four years ago hundreds of torch-bearing far-right demonstrators marched through the University of Virginia campus. The Unite the Right rally/antisemitic hatefest in Charlottesville, Virginia featured chants of "Jews will not replace us" and Nazi flags. Self-identified white supremacist James Fields perpetrated the car ramming attack that killed Heather Heyer and injured countless others. While Fields was held accountable for his actions in court, what about those who meticulously organized the rally? Who will hold them accountable? Our guest for this week, Executive Director of Integrity First for America (IFA) Amy Spitalnick, previews the upcoming trial of Sines v. Kessler —IFA's lawsuit against the rally's organizers—and shares how she is working to push far-right extremists back into the shadows where they belong. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Amy Spitalnick (19:51) Manya Brachear Pashman and Melanie Maron Pell ___ Show notes: What All Jews Need to Know About the EU's New Strategy to Combat Antisemitism
Oct 5, 2021
What All Jews Need to Know About the EU's New Strategy to Combat Antisemitism
Today, a new strategy for combating antisemitism was announced by the European Union. Does it have a chance to help Jews in Europe? What are the plan's implications for diaspora Jewish communities outside of the continent? Two of AJC's leaders in Europe who have worked closely with the EU and member state governments in the effort to counter rising Jew-hatred, Simone Rodan-Benzaquen, Managing Director of AJC Europe, and Daniel Schwammenthal, Director of AJC's Transatlantic Institute, answer these questions and more in this special bonus episode of AJC's People of the Pod . Throughout the month of October, AJC's People of the Pod will focus on the rise of antisemitism around the world and what it means for all diaspora Jewish communities and Israel. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Simone Rodan-Benzaquen and Daniel Schwammenthal ___ Show Notes: To learn more about the antisemitism in Europe that led to this report, go to AJC.org/antisemitismineurope . Tune in on Thursday for our conversation with Amy Spitalnick, Executive Director of Integrity First for America on how to sue a Nazi, a deep dive into the effort to sue white supremacists who marched in the Unite the Right rally in Charlottesville in 2017 .
Sep 30, 2021
Iron Dome Debate: What to Make of "the Squad's" Anti-Israel Efforts
When the U.S. House of Representatives voted last week 420-9-2 to replenish Israel's Iron Dome defense system, it ended debate about America's short-term support for the program and simultaneously sparked a conversation about the future of bipartisan support for the U.S.-Israel relationship. Mark Mellman, President and CEO of Democratic Majority for Israel, joins us to address that topic and more, including whether Democratic support for Israel is shifting and trends in attitudes towards Israel on both sides of the aisle. Julie Rayman, AJC's Senior Director of Policy and Political Affairs, guest hosts this week's episode. AJC is a nonpartisan, 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization. As such, AJC does not endorse or oppose political parties or candidates. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Mark Mellman (20:58) Manya Brachear Pashman and Julie Rayman ____ Show notes: Integrity First for America's "Unite Against Nazis": A Virtual Rally in Support of IFA's Groundbreaking Charlottesville Lawsuit - September 30, 7:30pm ET
Sep 14, 2021
Hitler, Nazis, and Swastikas: What It Was Like To Be a Jew At the UN's 2001 Durban Conference
Ahead of the UN's upcoming 20th anniversary event commemorating the antisemitic and anti-Israel 2001 UN Durban Conference, we hear from Joelle Fiss, who, as a Jewish student 20 years ago, attended the Conference. While the 2001 UN Durban Conference was meant to offer the chance for the international community to address racism, it quickly devolved into a platform for antisemitic hate. Fighting racism is a noble cause, one American Jewish Committee (AJC) joins actively. But there can be no room for antisemitism in the fight against other forms of bigotry. So far, 18 nations have announced plans to skip the September 22 event. In this poignant conversation, Fiss shares her horrific experience from the event and details how it contributed to today's rapid spread of antisemitism. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Joelle Fiss ___ Show Notes: Learn more about AJC's efforts urging nations to skip the UN's 20th anniversary Durban event at AJC.org/Durban. The Durban Diaries: What really happened at the UN Conference against Racism in Durban (2001)
Sep 9, 2021
How 9/11 Changed America's Jewish and Muslim Communities, And Brought Them Closer Together
People of the Pod guest co-host Laura Shaw Frank, director of AJC's William Petschek Contemporary Jewish Life and the acting director of AJC New York, is a Jewish American. Saeed Khan, Senior Lecturer in the Department of Near East and Asian Studies at Wayne State University-Detroit, Michigan, and a Research Fellow at the Center for the Study of Citizenship, is a Muslim American. Twenty years after the September 11th terror attacks, the two sit down to discuss the profound implications that day had on themselves, their respective Jewish and Muslim communities, and the strides they have seen in interfaith relations over the last two decades. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Saeed Khan and Laura Shaw Frank (33:24) Manya Brachear Pashman and Laura Shaw Frank Show Notes: To register for the AJC Advocacy Anywhere program, "AJC Remembers: The Twentieth Anniversary of 9/11," visit: www.AJC.org/AdvocacyAnywhere
Sep 2, 2021
Chef Jake Cohen on the Diversity of Jew-ish Food and Countering Antisemitism with His Own Brand of Advocacy
This week, guest host Dana Steiner, director of AJC ACCESS Global, American Jewish Committee's young professional division, sat down with Jake Cohen, food writer and author of New York Times bestseller Jew-ish: A Cookbook: Reinvented Recipes from a Modern Mensch , to discuss the convergence between food and Judaism, the antisemitism he has faced throughout his career, and how sharing recipes and their connected stories from across the Jewish world is his form of advocacy. Then, Manya Brachear Pashman, Dana Steiner, and Dan Pashman, host of The Sporkful podcast and who also spoke to Jake Cohen this week, dig into their Rosh Hashanah menus. _____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jake Cohen (20:21) Manya Brachear Pashman, Dana Steiner, and Dan Pashman ____ Show notes: The State of Jewish Life on College Campuses : last week's episode with University of Michigan's Tilly Shemer and American Jewish University's Dr. Jeffery Herbst The Rice Cooker That Changed Jake Cohen's Life : The Sporkful episode with Jake Cohen, hosted by Dan Pashman
Aug 26, 2021
The State of Jewish Life on College Campuses
As students head back to campus, Tilly Shemer, Executive Director of University of Michigan Hillel, joins guest host Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman, Director of AJC's Alexander Young Leadership Department, to discuss the difficult realities, as well as the wealth of opportunities, that are awaiting American Jews on campus. Then, Dr. Jeffrey Herbst, President of American Jewish University, shares his advice on how universities can combat antisemitism on campus. _____ Episode Lineup: (0:55) Tilly Shemer (24:15) Jeffrey Herbst (35:54) Manya Brachear Pashman and Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman _____ Show Notes: Fighting Campus Anti-Semitism Before It Explodes: Op-ed by Jeff Herbst
Aug 19, 2021
Afghan Jewish Leader on the Taliban's Takeover
Following the Taliban's takeover of Afghanistan, we are joined by Afghanistan-born Jack Abraham, the president of Congregation Anshei Shalom, a synagogue for Afghan Jews located in Queens, New York, to discuss the Jewish history and future of his native country. Afghanistan was once home to an estimated 40,000 Jews, centered in Herat, where they played an important role along the ancient Silk Road trading route. But starting in 1933, the community faced antisemitism, persecution and exile influenced by Nazi ideology, and Muslim solidarity with Palestinians and suspicion that Soviet Jews who sought refuge there were "Bolshevik agents." By the middle of the last century, there were fewer than 5,000. By the time the Taliban came to power in 1996, the country's Jewish population had dwindled to single digits, and today only one remains. Then, Manya Brachear Pashman shares what she will be talking about at her Shabbat table this week: the recently released study Beyond the Count: Perspectives and Lived Experiences of Jews of Color. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Jack Abraham (15:04) Manya Brachear Pashman ____ Show notes: Visit our website for photos mentioned throughout the interview.
Aug 12, 2021
How the Abraham Accords Has Changed Hearts and Minds: A Sit-Down with Israel's Top Official in the UAE
This week marks the one-year anniversary of normalized relations between Israel and the United Arab Emirates. This historic agreement, known as the Abraham Accords, would soon grow to include Bahrain, Morocco, and Sudan. In one fell swoop, the number of Arab countries Israel had formal relations with tripled from two (Egypt and Jordan) to six. With us to discuss this pivotal moment and the future of Israeli-Arab engagement is Ambassador Eitan Na'eh, head of mission at the Israeli Embassy in Abu Dhabi - formally dedicated just six weeks ago. Then, Manya Brachear Pashman and Avi Mayer discuss Jews in sports and the Jewish Olympic athletes that brought them pride and joy in the games that ended last week in Tokyo, including Linoy Ashram, Artem Dolgopyat, and Jessica Fox. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Eitan Na'eh (19:10) Manya Brachear Pashman and Avi Mayer
Aug 5, 2021
Israel's Diaspora Minister on Surfside Visit and the Israel-Diaspora Relationship
Joining us for a second time on People of Pod is Nachman Shai, Israel's Minister of Diaspora Affairs, to discuss his new role and his critical work supporting Jews around the world, including a recent visit to Surfside, Florida, following the tragic collapse of Champlain Towers South. Then, stick around for a special tribute from colleagues and friends to our longtime co-host Seffi Kogen, including Congressman Ted Deutch (D-FL) and AJC CEO David Harris, as Seffi ends his tenure at AJC. ____ Episode Lineup (0:40) Nachman Shai (24:00) Seffi Kogen (27:26) Manya Brachear Pashman (28:55) Special guests including Ted Deutch and David Harris ____ Fill out our audience survey here Check out Nachman Shai's first appearance on People of the Pod
Jul 30, 2021
Hear from America's New Antisemitism Envoy Deborah Lipstadt
President Joe Biden has appointed Deborah Lipstadt, one of America's preeminent Jewish historians and Holocaust scholars, to serve as the U.S. State Department's special envoy to monitor and combat antisemitism. Listen to our conversation with Lipstadt, which is being re-aired for this special episode, about the troubling rise of contemporary antisemitism from multiple sources and what we can do to stop it. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Deborah Lipstadt ____ Show Notes: Fill Out Our Audience Survey Here
Jul 22, 2021
Antisemitism in the Kidlit World; Ben & Jerry's Shameful Surrender
In the wake of vicious attacks on American Jews, the Society of Children's Book Writers and Illustrators joined a chorus of organizations that condemned antisemitism then, after pushback, apologized for not condemning Islamophobia or other forms of hatred in the same statement. Jewish Insider Reporter Gabby Deutch joins us to discuss her discovery that the controversial apology underscored a wider and equally troubling challenge facing Jewish authors. Then, Manya Brachear Pashman weighs in on the controversy surrounding Ben & Jerry's decision to stop selling their ice cream in the territories captured by Israel in the 1967 war, and how Jewish advocates, including those at AJC, are urging state lawmakers to invoke their anti-BDS statutes. ______ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Gabby Deutch (19:09) Manya Brachear Pashman _____ Show notes: Fill out our podcast audience survey here!
Jul 22, 2021
Antisemitism in the Kidlit World; Ben & Jerry's Shameful Surrender
In the wake of vicious attacks on American Jews, the Society of Children's Book Writers and Illustrators joined a chorus of organizations that condemned antisemitism then, after pushback, apologized for not condemning Islamophobia or other forms of hatred in the same statement. Jewish Insider Reporter Gabby Deutch joins us to discuss her discovery that the controversial apology underscored a wider and equally troubling challenge facing Jewish authors. Then, Manya Brachear Pashman weighs in on the controversy surrounding Ben & Jerry's decision to stop selling their ice cream in the territories captured by Israel in the 1967 war, and how Jewish advocates, including those at AJC, are urging state lawmakers to invoke their anti-BDS statutes. ______ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Gabby Deutch (19:09) Manya Brachear Pashman
Jul 22, 2021
Antisemitism in the Kidlit World; Ben & Jerry's Shameful Surrender
In the wake of vicious attacks on American Jews, the Society of Children's Book Writers and Illustrators joined a chorus of organizations that condemned antisemitism then, after pushback, apologized for not condemning Islamophobia or other forms of hatred in the same statement. Jewish Insider Reporter Gabby Deutch joins us to discuss her discovery that the controversial apology underscored a wider and equally troubling challenge facing Jewish authors. Then, Manya Brachear Pashman weighs in on the controversy surrounding Ben & Jerry's decision to stop selling their ice cream in the territories captured by Israel in the 1967 war, and how Jewish advocates, including those at AJC, are urging state lawmakers to invoke their anti-BDS statutes. ______ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Gabby Deutch (19:09) Manya Brachear Pashman
Jul 22, 2021
Antisemitism in the Kidlit World; Ben & Jerry's Shameful Surrender
In the wake of vicious attacks on American Jews, the Society of Children's Book Writers and Illustrators joined a chorus of organizations that condemned antisemitism then, after pushback, apologized for not condemning Islamophobia or other forms of hatred in the same statement. Jewish Insider Reporter Gabby Deutch joins us to discuss her discovery that the controversial apology underscored a wider and equally troubling challenge facing Jewish authors. Then, Manya Brachear Pashman weighs in on the controversy surrounding Ben & Jerry's decision to stop selling their ice cream in the territories captured by Israel in the 1967 war, and how Jewish advocates, including those at AJC, are urging state lawmakers to invoke their anti-BDS statutes. ______ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Gabby Deutch (19:09) Manya Brachear Pashman
Jul 22, 2021
Antisemitism in the Kidlit World; Ben & Jerry's Shameful Surrender
In the wake of vicious attacks on American Jews, the Society of Children's Book Writers and Illustrators joined a chorus of organizations that condemned antisemitism then, after pushback, apologized for not condemning Islamophobia or other forms of hatred in the same statement. Jewish Insider Reporter Gabby Deutch joins us to discuss her discovery that the controversial apology underscored a wider and equally troubling challenge facing Jewish authors. Then, Manya Brachear Pashman weighs in on the controversy surrounding Ben & Jerry's decision to stop selling their ice cream in the territories captured by Israel in the 1967 war, and how Jewish advocates, including those at AJC, are urging state lawmakers to invoke their anti-BDS statutes. ______ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Gabby Deutch (19:09) Manya Brachear Pashman
Jul 16, 2021
Hear From the Woman Iran Tried to Kidnap
Earlier this week, four Iranian operatives were charged in the attempted kidnapping of the U.S.-based Iranian exile Masih Alinejad, a human rights activist and journalist. Alinejad was kicked out of her native country nearly a decade ago for her anti-veiling advocacy. This week on the podcast, we're joined by AJC Europe Managing Director Simone Rodan Benzaquen, who recently interviewed Alinejad about her activism and the harrowing experiences she faced in Iran. Then, Juan Dircie, Associate Director of AJC's Belfer Institute for Latino and Latin American Affairs, shares his personal reflections on the upcoming anniversary of the bombing at the AMIA Jewish Center in Buenos Aires, Argentina, and why we must never stop fighting for justice. ______ Lineup: (0:40) Masih Alinejad, Simone Rodan Benzaquen (16:47) Juan Dircie (20:15) Manya Brachear Pashman ______ Show Notes: Win a guest spot on the podcast by filling out our Audience Survey! "Le Sursaut : 3 Questions" featuring AJC Europe Managing Director Simone Rodan in conversation with Masih Alinejad
Jul 8, 2021
Launch of the Senate Caucus on Black-Jewish Relations; The Startup Nation: "Failure is Not an Option"
This week, we bring you highlights from an important announcement made at AJC Virtual Global Forum 2021. Three U.S. Senators, Cory Booker (D-NJ), Jacky Rosen (D-NV), and Tim Scott (R-SC), announced the launch of the Senate Caucus on Black-Jewish Relations. This bipartisan caucus, the first of its kind in the United States Senate, will bring together elected leaders from the Black and Jewish communities, and both sides of the aisle, to strengthen Black-Jewish relations, bolster mutual understanding, and work to combat antisemitism and racism. Then, in the decade-plus since Israel was branded the Start-Up Nation, we have seen still more dazzling successes come out of the Jewish state, like Google's billion-dollar acquisition of the navigation company Waze, Intel's $15 billion acquisition of the self driving car technology company Mobileye, and the NASDAQ initial public offering last month of team management software company Monday.com, which now has a market cap of $10 billion. Joining us this week to talk about the state of the Start-Up Nation is Barak Rabinowitz, Managing Partner of F2 Venture Capital. Episode Lineup: (0:40) Cory Booker, Jacky Rosen, and Tim Scott (18:12) Barak Rabinowitz (36:00) Manya Brachear Pashman (39:21) Seffi Kogen ____ Show Notes: Fill out our audience survey for a chance to win a spot on the podcast! Full recording of The Launch of the Senate Caucus on Black-Jewish Relations at AJC Virtual Global Forum 2021
Jul 1, 2021
"We Refuse to Choose Among Our Identities": A Wider Bridge's Ethan Felson on Antisemitism at the Chicago Dyke March
In 2017, the Chicago Dyke March ejected Jewish marchers carrying rainbow flags emblazoned with Stars of David. This year, it promoted its upcoming event with a cartoon image showing the burning of Israeli and American flags. To discuss why the Chicago Dyke March has been exhibiting such hostility towards supporters of Israel, we sit down with Ethan Felson, a progressive activist for more than thirty years and Executive Director of A Wider Bridge, a nonprofit that connects American and Israeli LGBTQ communities and works to strengthen LGBTQ inclusion in Israel. Then, AJC Miami/Broward County Director Brian Siegal shares his personal reflections on the collapse of the Champlain Towers South building in Surfside, Florida, and how the community has come together in the wake of this immense tragedy. ______ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Ethan Felson (16:32) Brian Siegal (19:19) Manya Brachear Pashman (22:22) Seffi Kogen ______ Show Notes: Fill out our audience survey for a chance to win a spot on the show! www.AJC.org/PodcastSurvey
Jun 24, 2021
The Butcher of Tehran; The Great Debate Over the West Bank
Last week, Ebrahim Raisi, a hardline cleric known as "the Butcher of Tehran" for having overseen thousands of executions, was chosen to succeed Hassan Rouhani as Iran's president. Daniel Schwammenthal, Director of AJC's Brussels-based Transatlantic Institute, joins us to discuss what Raisi's selection means for the future of Iran and ongoing nuclear talks. Over in Israel, the country's new prime minister, Naftali Bennett, has reportedly met several times in recent months with leading public Israeli intellectual Micah Goodman, who previously sat down with us on the podcast. Listen as Goodman discusses his book Catch-67 , which focuses on "decreasing the conflict" until a permanent deal can be reached. Please note that this episode contains depictions of violence that some people may find disturbing. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:41) Daniel Schwammenthal ( Please note that this segment contains depictions of violence that some people may find disturbing.) (14:53) Micah Goodman (30:46) Manya Brachear Pashman (33:42) Seffi Kogen ___ Show notes: Take our People of the Pod Audience Survey for a chance to win a guest spot on the show! ( https://www.ajc.org/news/podcast/www.AJC.org/PodcastSurvey ) Full Micah Goodman interview ( https://www.ajc.org/news/passport/the-great-debate-over-the-west-bank )
Jun 17, 2021
What You Need to Know About Israel's Diverse New Government; The Mainstreaming of Antisemitism
For the first time since 2009, Israel has a new prime minister, Naftali Bennett. The Jerusalem Post Senior Diplomatic Correspondent Lahav Harkov joins us this week to shed some light on the new prime minister and help us understand what we can expect from Israel's new government. Then, we bring you one of the most-discussed sessions from AJC Virtual Global Forum 2021. Bret Stephens, op-ed columnist for The New York Times , Bari Weiss, journalist and author of How to Fight Antisemitism , and Simone Rodan-Benzaquen, Director of AJC Europe, discuss rising Jew-hatred in a session titled "The Mainstreaming of Antisemitism: How Should We Respond?" Finally, AJC Director of Contemporary Jewish Life and Acting Director of AJC New York Laura Shaw Frank explains what we need to know about AJC's annual survey of American Jewish opinion and its companion survey capturing the views of Israeli Jews. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Lahav Harkov (20:48) Bret Stephens, Bari Weiss, and Simone Rodan-Benzaquen (43:11) Laura Shaw Frank (45:42) Manya Brachear Pashman (49:52) Seffi Kogen ____ Show notes: Please fill out our audience survey and be a part of shaping the future of the podcast! The Mainstreaming of Antisemitism: How Should We Respond? AJC 2021 Survey of American and Israeli Jewish Opinion
Jun 10, 2021
How Interfaith Relations Helped Drive the Abraham Accords; A View From Campus
This week, we bring you highlights from AJC Virtual Global Forum 2021. First, in a conversation moderated by Manya Brachear Pashman, we hear from H.E. Dr. Ali Rashid Al Nuaimi, Chairman of Hedayah, and Rabbi David Rosen, AJC Director of International Interreligious Affairs, in The Siegler Family Annual Muslim-Jewish Symposium on How Interfaith Relations Helped Drive the Abraham Accords . Then, two college student activists, Julia Jassey, University of Chicago '23, and Talia Rosenberg, University of Pennsylvania '21, help us understand today's challenges and opportunities on campus for pro-Israel students during the AJC Virtual Global Forum's session, The View from Campus , moderated by Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman, AJC Deputy Director of Young Leadership. ___ Episode Lineup: (0:40) H.E. Dr. Ali Rashid Al Nuaimi, Rabbi David Rosen, Manya Brachear Pashman (21:38) Julia Jassey, Talia Rosenberg, and Meggie Wyschogrod Fredman
May 27, 2021
High Stakes: What's Next for U.S. Policy on Iran?
Have American, European, and Israeli policymakers learned anything since signing the 2015 Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), known as the Iran nuclear deal? We sat down this week with AJC Jerusalem Director Avital Leibovich, AJC Transatlantic Institute Director Daniel Schwammenthal, and AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson to analyze what the next few months could bring. We were also joined by AJC CEO David Harris for a closing message on Iran. Then, in our closing segment, Shabbat Table Talk , we hear from co-host Manya Brachear Pashman on Kim Kardashian's response to the violence in Israel and co-host Seffi Kogen shares his thoughts on the recent surge in antisemitism. _____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Avital Leibovich, Daniel Schwammenthal, and Jason Isaacson (33:41) David Harris (41:25) Manya Brachear Pashman (43:45) Seffi Kogen _____ Show Notes: AJC.org/GlobalForum High Stakes: What's Next for U.S. Policy on Iran? - AJC Advocacy Anywhere
May 20, 2021
Talking Israel with Congresswoman Wasserman Schultz and AJC CEO David Harris
This week, we engage Rep. Debbie Wasserman Schultz (D-FL) in conversation about the violence in Israel and Gaza and about Jewish American Heritage Month, with a special salute to another trailblazing Jewish congresswoman, Bella Abzug. Then, as Israel comes under attack from Hamas-ruled Gaza, we hear from AJC CEO David Harris on the immense challenges facing the Jewish state, the importance of confronting misinformation, and the need for solidarity. __ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Debbie Wasserman Schultz (17:24) David Harris (30:35) Doreen Rosenblum (33:31) Manya Brachear Pashman (36:11) Seffi Kogen __ Show Notes: Urgent Briefing on the Situation in Israel - AJC Advocacy Anywhere PaleyImpact: Media's Role in Identifying, Explaining, and Combating Antisemitism (with AJC's U.S. Director for Combating Antisemitism Holly Huffnagle) Photo credit: Israel Police Spokesperson
May 14, 2021
Israel Under Attack: What You Need to Know
Israel is under attack, with over 1,500 rockets fired from Gaza, millions of Israelis in bomb shelters, and the threat of further violence continuing in Jerusalem and throughout the country. In this week's episode, we bring you highlights from AJC's live Advocacy Anywhere online event with AJC Jerusalem Director Avital Leibovich and i24news Senior Correspondent Owen Alterman. Hear their front-line report on the evolving crisis and AJC CEO David Harris' inspiring closing message. Then, AJC Director of Contemporary Jewish Life Laura Shaw Frank joins us to explain what we need to know about the Pew Research Center's just-released Jewish Americans in 2020 report. ____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Avital Leibovich and Owen Alterman (19:32) David Harris (26:31) Laura Shaw Frank (38:40) Avi Mayer (41:29) Manya Brachear Pashman (44:25) Seffi Kogen ____ Show Notes: Frontline Report: Escalation in Israel - AJC Advocacy Anywhere Pew Research Center: Jewish Americans in 2020 report More information on the May 20th Advocacy Anywhere program can be found here
May 6, 2021
Breaking Down the Facebook Ban and Celebrating American Jewish Heritage Month
This week, we speak to Emi Palmor, former Director-General of Israel's Ministry of Justice and a current member of The Oversight Board, which makes binding policy decisions on Facebook and Instagram, to discuss the board's ruling on Facebook's indefinite ban of former President Trump and other recent decisions. Then, leading American Jewish historian Jonathan Sarna, a professor of American Jewish history at Brandeis University and the author of American Judaism: A History and When General Grant Expelled the Jews , joins us to kick off Jewish American Heritage Month and reflect on what advocates can and should draw from the history of Jews in America. _____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Emi Palmor (7:40) Jonathan Sarna (27:24) Holly Huffnagle (29:42) Manya Brachear Pashman (33:07) Seffi Kogen ___ Show notes: Music: " Hava Nagila" by Sam Bikov Translate Hate and Quiz
Apr 29, 2021
What You Should Know About the Iran Nuclear Talks
Earlier this month, six world powers reopened negotiations with Iran over the 2015 nuclear deal, known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), from which the United States withdrew in 2018. Washington Institute Director of Research Patrick Clawson, a longtime friend of American Jewish Committee, joins us to discuss the implications of those talks and the threat posed by Iran. Then, AJC Project Interchange Director Nisha Abkarian joins us to share her grandmother's harrowing story of survival during the Armenian Genocide and the significance of President Biden's recognition of the events of 1915. ___ Episode Lineup (0:40) Patrick Clawson (21:51) Nisha Abkarian (26:00) Manya Brachear Pashman (29:06) Seffi Kogen
Apr 22, 2021
"I Will Never Forget That Day": Poway's Mayor on the Second Anniversary of the Chabad Shooting
On April 27, 2019, in the middle of Passover, a white supremacist burst through the doors of a Chabad synagogue in Poway, California and opened fire, killing congregant Lori Gilbert-Kaye and injuring three others. As we approach the second anniversary of the shooting, we speak to Mayor Steve Vaus, a Grammy-winning country music singer, who was serving his first term as Poway's mayor at the time. Then we're joined by AJC Paris Director Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache to talk about the case of Sarah Halimi, a 65-year old French woman who was murdered in 2017 because she was Jewish. France's highest court has ruled that her killer will not stand trial due to his "delirious state" from smoking marijuana. _____ Episode Lineup: (00:40) Mayor Steve Vaus (15:32) Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache (19:02) Manya Brachear Pashman (22:15) Seffi Kogen ____ Show Notes: Episode Transcript One Candle by Steve Vaus
Apr 15, 2021
Yossi Klein Halevi on The Third Era of Jewish History
Author and journalist Yossi Klein Halevi joins us to talk about the wisdom of the Israeli calendar in how Israel remembers the fallen on Yom HaZikaron, followed by celebrating its independence on Yom HaAtzma'ut the very next day. __ Show Notes: A Conversation with Yossi Klein Halevi about His New Best Seller Orthodox Jewish Women Can't Sing In Front of Men. Instagram Is Giving Them a Voice Music: Hatikvah (National Anthem Of Israel) - Beta Records - United States Navy Band
Apr 8, 2021
The Art of Inventing Hope: Elie Wiesel's Masterclass for Humanity
Elie Wiesel walked out of Buchenwald, one of the largest concentration camps in Germany, on April 11, 1945, the same day as the late father of journalist Howard Reich, the legendary former jazz critic for The Chicago Tribune . Reich never talked to his father or mother, both survivors, about their Holocaust experiences. But in 2001 Reich's mother began to relive those experiences, and his quest to piece together the stories he never knew about led to his book and subsequent film, Prisoner of Her Past . Nearly a decade later, Reich sat down to interview Elie Wiesel and discovered an instant connection, which he wrote about in The Art of Inventing Hope . Reich joins us to discuss all this, plus how jazz helped him confront his family's past. Then, in honor of Yom HaShoah, we're joined by Lilli Platt, AJC Senior Development Director and Director of Women's Leadership Board, who was born in a Displaced Persons (DP) camp and is the child of Holocaust survivors. _____ Episode Lineup: (00:40) Howard Reich (23:01) Lilli Platt (25:29) Manya Brachear Pashman (29:05) Seffi Kogen _____ Show Notes: Prisoner of Her Past The Art of Inventing Hope: Intimate Conversations with Elie Wiesel The Four Questions in Irish, and 4 More Great Moments from AJC's 2021 Diplomatic Seders
Apr 1, 2021
What We Can All Learn from Rabbi Heschel on Confronting Injustice
This week we hear from Martin Doblmeier, the director of Spiritual Audacity: The Abraham Joshua Heschel Story on the history of one of the most inspiring and preeminent scholars of the 20th Century. Doblmeier discusses Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel's profound impact on the civil rights movement, the relationship between Jews and the Roman Catholic Church, and the "evil of indifference." Then, Natalia Mahmud, AJC's Associate Director of U.S. Muslim-Jewish Relations, speaks about the Jabara-Heyer NO HATE Act, ahead of its reintroduction in Congress, and in honor of baseball's Opening Day, we dip into AJC's Oral History Library to hear directly from one of the greatest Jewish baseball players ever, Hall of Famer Hank Greenberg, also known as "The Hebrew Hammer." Greenberg recounts what it was like to be a Jewish baseball player in the 1930s and 1940s and the level of antisemitism he had to endure. _____ Episode Lineup: (00:40) Martin Doblmeier (16:55) Natalia Mahmud (19:36) Manya Brachear Pashman (23:00) Seffi Kogen _____ Show Notes: Episode Transcript AJC's William E. Wiener Oral History Library Learn more about the Jabara-Heyer NO Hate Act at AJC.org/TakeAction Music: Take Me Out to the Ballgame by Kevin MacLeod ( Link; License )
Mar 26, 2021
The Israeli Election: What Just Happened and What Comes Next
This week we're joined by Allison Kaplan Sommer, Ha'aretz journalist and panelist for The Promised Podcast, to discuss some of the headliners from the Israeli election: potential kingmaker and Ra'am Party leader Mansour Abbas and Rabbi Gilad Kariv, who will be the first Reform rabbi to serve in the Knesset. Kaplan Sommer also discusses how democracy plays out in Israel and the United States and what it's like to live in Israel, a complex, multicultural society. Then, AJC CEO David Harris shares a moving Passover message about his first-hand involvement in the Soviet Jewry movement and modern-day exoduses. _____ Episode Lineup: (00:40) Allison Kaplan Sommer (18:26) David Harris (20:27) Manya Brachear Pashman (23:34) Seffi Kogen ___ Episode Transcript
Mar 18, 2021
This Is Why Israel is Having Its Fourth Election in Two Years
Ahead of the March 23rd elections in Israel, we're joined by Haviv Rettig Gur, The Times of Israel's senior political analyst. Gur discusses the highly polarized sentiment around Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, the conflict within the Haredi community over pandemic restrictions, and the gap between the positions of the political parties that represent Arab Israelis and the concerns of Arab Israelis themselves. Then, Dina Siegel Vann, Director of AJC's Belfer Institute for Latino and Latin American Affairs, reflects on the anniversary of the 1992 suicide bombing attack on the Israeli embassy in Buenos Aires, Argentina, which left 29 dead. _____ Episode Lineup: (00:40) Haviv Rettig Gur (23:16) Dina Siegel Vann (26:23) Manya Brachear Pashman (29:45) Seffi Kogen ___ Episode Transcript
Mar 12, 2021
The Nazi Hunter: Eli Rosenbaum on Tracking Down the World's Most Wanted Criminals
This week, we're in conversation with Eli Rosenbaum, Director of Human Rights Enforcement Strategy and Policy at the Department of Justice. For 40 years, Rosenbaum has helped the department track down former Nazis and hold them accountable for their World War II crimes, a role that has earned him the moniker of "Nazi Hunter". Then, Shira Loewenberg, Director of AJC's Asia Pacific Institute (API) speaks about the wide-scale democracy protests across Myanmar in the weeks since the local military's February 1 coup d'état. _____ Episode Lineup: (00:40) Eli Rosenbaum (19:45) Shira Loewenberg (22:37) Manya Brachear Pashman (25:31) Seffi Kogen ___ Episode Transcript
Mar 5, 2021
Non-Orthodox Conversion in Israel: Dividing or Uniting the Jewish World?
This week, the Israeli Supreme Court handed down a ruling on conversions conducted by non-Orthodox rabbis. We hear from AJC's Director of Contemporary Jewish Life Laura Shaw Frank, a leading thinker on this important issue, about how this decision will affect the Israel-Diaspora relationship. Then, in celebration of International Women's Day, Director of AJC's Jacob Blaustein Institute for the Advancement of Human Rights Felice Gaer reflects on what it means to see the world and human rights through women's eyes. _____ Episode Lineup: (00:40) Laura Shaw Frank (17:10) Felice Gaer (19:38) Manya Brachear Pashman (23:34) Seffi Kogen ___ Episode Transcription
Feb 25, 2021
Soraya Nadia McDonald on Being Black and Jewish; NBC's No Good, Very Bad Week
Journalist Soraya Nadia McDonald is the Culture Critic for The Undefeated , ESPN's platform for exploring the intersection of sports, race, and culture. She is a Pulitzer Prize finalist for her essays on theater and film, including The Unbearable Whiteness of Oklahoma . Last year, when her fellow Howard University alumnus Nick Cannon made antisemitic remarks, Soraya wrote a more personal essay about being Black and Jewish. Soraya sat down with us for a conversation about confronting antisemitism as a Black Jewish woman. Then AJC Chief Advocacy Officer Dan Elbaum reflects on his 11 years at AJC, Manya Brachear Pashman discusses Michael Che's antisemitic joke on Saturday Night Live, and Seffi Kogen on criticism of a Jewish storyline on the NBC show "Nurses". _____ Episode Lineup: (00:40) Soraya Nadia McDonald (19:14) Dan Elbaum (22:28) Manya Brachear Pashman (25:40) Seffi Kogen _____ Show Notes: Tell NBC: Antisemitism Isn't Funny - Petition Episode Transcription
Feb 19, 2021
Israel and the International Criminal Court; The Power of Music
Last weekend, the International Criminal Court at The Hague determined that it has jurisdiction in the West Bank and Gaza, taking a major step toward prosecuting Israelis for alleged war crimes. To help us unpack what's been happening and what it means for Israel, we're joined by Barak Ravid, Contributing Correspondent for Axios and Diplomatic Correspondent for Walla News. Then we hear from AJC Chief Innovation Officer Belle Yoeli on the power of song during the pandemic, Manya Brachear Pashman on how Israel expects the unexpected, and Seffi Kogen on how snow is affecting both the United States and Israel. _____ Episode Lineup: (00:40) Barak Ravid (17:22) Belle Etra Yoeli (19:26) Manya Brachear Pashman (22:12) Seffi Kogen _____ Show Notes: Episode Transcript
Feb 11, 2021
The Real Danger of QAnon; Telling the Jewish Story in Arabic
This week, we're in conversation with Joel Finkelstein, cofounder and director of the Network Contagion Research Institute, a nonpartisan, multidisciplinary research group of experts who study online disinformation, and Pamela Paresky, a senior scholar at the Institute who focuses on the psychology of thriving in a liberal democracy. Both have been sounding the alarm about the dangers of the antisemitic conspiracy theory movement QAnon and they join us to discuss what we can expect next from the movement and how we can take steps to stop it. Then we hear from AJC Managing Director of Global Communications Avi Mayer on storytelling and AJC's Arabic video series, Manya Brachear Pashman on President Biden and Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, and Seffi Kogen on the second impeachment trial of former President Donald Trump. ____ Episode Lineup: (00:40) Pamela Paresky and Joel Finkelstein (19:05) Avi Mayer (21:18) Manya Brachear Pashman (24:15) Seffi Kogen _____ Show Notes: Arabic Video on Protocols of the Elders of Zion Episode Transcript
Feb 4, 2021
The Problem with California's Ethnic Studies; Mayors United Against Antisemitism
A controversial curriculum for teaching ethnic studies in California public schools will face a final vote in March. Since the first draft came out in 2019, a coalition of Jewish organizations has advocated for content that meaningfully includes Jews and other groups, discusses antisemitism, and avoids perpetuating stereotypes that put Jews in danger. We sit down with Director of AJC Northern California Rabbi Serena Eisenberg about the curriculum and why it should matter to all of us. Then, on Shabbat Table Talk, AJC's Chief Field Operations Officer Melanie Maron Pell joins us to speak about AJC's Mayors United Against Antisemitism initiative, Manya Brachear Pashman on why she isn't laughing at the Representative Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-GA) jokes, and Seffi Kogen on antisemitism on college campuses. ____ Episode Lineup: (00:40) Rabbi Serena Eisenberg (13:24) Melanie Maron Pell (18:15) Manya Brachear Pashman (20:27) Seffi Kogen _____ Show Notes: We need your help before California's Ethnic Studies Model Curriculum is finalized Mayors United Against Antisemitism AJC Arabic video - Protocols of the Elders of Zion Seffi Kogen's Op-Ed in Inside Higher Ed Episode Transcript
Jan 29, 2021
International Holocaust Remembrance Day with Mandy Gonzalez; Israel's COVID-19 Vaccine Rollout and the Palestinians
In honor of International Holocaust Remembrance Day, the Museum of Jewish Heritage held a special event, "18 Voices: A Liberation Day Reading Of Young Writers' Diaries From The Holocaust ." We sit down with Broadway actress Mandy Gonzalez, who read diary excerpts during the virtual reading, and Alexandra Zapruder, curator of " 18 Voices" and author of " Salvaged Pages." Then, we speak to Lahav Harkov, Senior Contributing Editor and Diplomatic Correspondent for The Jerusalem Post , about Israel's record-shattering vaccine rollout and the controversy over access for Palestinians. Finally, to close out the episode, past president of AJC Westchester/Fairfield Beverly Block Rosenbaum shares the story of her mother, a survivor of multiple concentration camps who was told by a Nazi officer that she was "too pretty to be a Jew," to which she bravely replied: "I am a Jew and I'm proud of it." ___________________ Episode Lineup (00:45) Mandy Gonzalez (11:28) Alexandra Zapruder (27:41) Lahav Harkov (38:15) Beverly Block Rosenbaum (43:32) Manya Brachear Pashman (46:48) Seffi Kogen ___________________ Show notes: Watch Museum of Jewish Heritage's 18 Voices event Transcript of Interview with Lahav Harkov
Jan 22, 2021
The Biden Administration Gets Underway and Post-Inauguration Reflections
One day after inauguration, we sit down with AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson to discuss President Joe Biden's inaugural address and what to expect from the new administration. Then, we hear from AJC Senior Director of Policy and Political Affairs Julie Fishman Rayman on how to engage with those with whom we disagree, Manya Brachear Pashman on President Biden's call for truth and his condemnation of white supremacy, and Seffi Kogen on the photo of Senator Bernie Sanders (I-VT) that launched a million memes. _____ Episode Lineup: (0:41) Jason Isaacson (16:10) Julie Fishman Rayman (19:26) Manya Brachear Pashman (21:46) Seffi Kogen
Jan 14, 2021
Inside America's Far Right; Congressman Ritchie Torres
This week, we sit down with Daniel Lombroso, director of The Atlantic 's first feature documentary, White Noise, an inside story of the far right in America. Lombroso, who spent four years with the leaders of white supremacist and antisemitic movements, joins us to discuss how that period informs his perspective on the horrific events of January 6 at the United States Capitol and the ensuing fallout. Then, if you missed our special episode yesterday, freshman Congressman Ritchie Torres (D-NY) shares his reflections on the antisemitism, racism, and white supremacy he witnessed on January 6; impeachment proceedings in Congress; and how the nation can move forward. _____ Episode Lineup: (0:40) Daniel Lombroso (24:42) Ritchie Torres (39:11) Holly Huffnagle (41:50) Manya Brachear Pashman (44:44) Seffi Kogen ________ Show Notes: White Noise on Amazon Prime Video: https://www.amazon.com/White-Noise-Lauren-Southern/dp/B08M5XPRLT White Noise on Apple TV: https://tv.apple.com/us/movie/white-noise/umc.cmc.6m36k2zgurb8lhdg4na0nw55s
Jan 13, 2021
A Special Conversation with Congressman Ritchie Torres
Tune in for an exclusive conversation with freshman Congressman Ritchie Torres (D-NY) about the horrific events of January 6 at the United States Capitol. Listen as he shares his reflections on the antisemitism, racism, and white supremacy he witnessed that day; impeachment proceedings in Congress; and how the nation can move forward. _____ Show notes: We must not ignore the presence of antisemitism in the January 6 attack on the U.S. Capitol - Instagram post: https://www.instagram.com/p/CJywbSQLJuV/
Jan 7, 2021
Ambassador Daniel Shapiro on Biden's Foreign Policy; Responding to the Attack on the Capitol
Earlier this week, we spoke to former U.S. Ambassador to Israel Daniel Shapiro, who served alongside President-elect Joe Biden in the Obama administration and was an advisor to his presidential campaign. Ambassador Shapiro broke down what we can expect from the Biden administration when it comes to Israel, Iran, the Palestinians, and the Abraham Accords. Then, as our nation reels from Wednesday's mob attack on the United States Capitol, AJC Director of Contemporary Jewish Life Dr. Laura Shaw Frank, Manya Brachear Pashman, and Seffi Kogen share their reactions to the riots on Shabbat Table Talk. _____ Episode Lineup: (00:40) Daniel Shapiro (23:17) Laura Shaw Frank (26:48) Manya Brachear Pashman (29:29) Seffi Kogen _____ Show Notes: 12/17 Episode with UN Mideast Envoy Nickolay Mladenov: https://www.ajc.org/news/podcast/un-mideast-envoy-nickolay-mladenov-celebrating-hanukkah
Dec 23, 2020
Georgia Runoff Elections and Tackling Hate in America
This week, Atlanta Journal-Constitution political reporter Greg Bluestein joins us to break down the January 5 runoff elections in Georgia that will decide which party controls the United States Senate. Next, we hear from Melanie Maron Pell, AJC's Managing Director of Regional Offices, on an antisemitic attack over this Hanukkah at the University of Kentucky and the importance of passing the NO HATE act, Manya Brachear Pashman on the new Wonder Woman movie, and Seffi Kogen on two Israeli TV recommendations for the long winter nights ahead. _____ Episode Lineup: (01:52) Greg Bluestein (19:36) Melanie Maron Pell (25:07) Manya Brachear Pashman (27:56) Seffi Kogen
Dec 17, 2020
UN Mideast Envoy Nickolay Mladenov; Celebrating Hanukkah
As United Nations Special Coordinator for the Middle East Peace Process, Nickolay Mladenov works to stave off escalations, speak up against violence, and promote peace between Israel and the Palestinians. Before he leaves his posting, Mladenov joins us on People of the Pod to reflect on his vital work. Then, AJC's Director of Interreligious and Intergroup Relations Rabbi Noam Marans shares his thoughts on the COVID-19 vaccine, and Manya Brachear Pashman recalls reporting on an attempt to break the world record for simultaneous dreidel spins at Indiana University in Bloomington, Indiana. _____ Episode Lineup: (01:50) Nickolay Mladenov (13:56) Noam Marans (16:53) Manya Brachear Pashman
Dec 11, 2020
Israeli Political Rumblings; Jersey City Attack: One Year Later
This week, Tal Schneider, political correspondent at the Times of Israel, joins us to unpack the latest in Israeli politics as Israel hurtles toward its fourth election in two years. Then, Rabbi David Levy, regional director of AJC New Jersey, reflects on the one-year anniversary of the attack at the JC Kosher Supermarket in Jersey City, Manya Brachear Pashman shares her thoughts on what Hanukkah means to her family, and Seffi Kogen shares a story about sufganiyot (Hanukkah jelly doughnuts). _____ Episode Lineup: [01:51] Tal Schneider [18:40] David Levy [22:41] Manya Brachear Pashman [25:36] Seffi Kogen
Dec 3, 2020
Intrigue in Iran and the Stories of Mizrahi Jews
Sima Shine, former head of the Mossad's research division and current senior researcher at Israel's Institute for National Security Studies (INSS), joins us to discuss recent developments related to Iran, including the recent death of Mohsen Fakhrizadeh, who headed the country's nuclear weapons program. Then, AJC Los Angeles Associate Director Saba Soomekh talks about the importance of telling the stories of Mizrahi Jews, Manya Brachear Pashman shares the story of a very important menorah, and Seffi Kogen delves into the political rumblings happening in Israel this week. _____ Episode Lineup: [1:20] Sima Shine [13:50] Saba Soomekh [17:53] Manya Brachear Pashman [21:42] Seffi Kogen _____ Show Notes: The Forgotten Jewish Refugees: Three Personal Stories – AJC Advocacy Anywhere: https://www.ajc.org/news/the-forgotten-jewish-refugees-three-personal-stories-ajc-advocacy-anywhere
Nov 25, 2020
Talking Racial Justice with Eric Ward and Rabbi Angela Buchdahl
In this special Thanksgiving throwback episode, we revisit two important conversations from this past summer. First up is Eric Ward, Executive Director of the Western States Center, who discusses his experience as a leader in the Black community committed to fighting antisemitism and how the Black and Jewish communities can work together to combat hate. Then, we hear from Rabbi Angela Buchdahl, Senior Rabbi of Manhattan's Central Synagogue and member of AJC's Board of Governors, about her experiences as a Jew of Color and the Jewish community's obligation to social justice. _____ Episode Lineup: [3:00] Eric Ward [15:36] Rabbi Angela Buchdahl _____ Show Notes: To make your year-end gift to AJC, go to AJC.org/Donate Eric Ward's Full Interview: https://www.ajc.org/news/podcast/eric-ward-on-racial-justice-a-conversation-with-benny-gantz Angela Buchdahl's Full Interview: https://www.ajc.org/news/podcast/rabbi-angela-buchdahl-on-jews-and-race-election-2020-debate Skin in the Game by Eric Ward: https://www.politicalresearch.org/2017/06/29/skin-in-the-game-how-antisemitism-animates-white-nationalism
Nov 19, 2020
Religion and Politics in the 2020 Election with The Atlantic's Emma Green
This week, The Atlantic's Emma Green joins us to discuss the intersection of religion and politics in the 2020 election. Then, AJC Atlanta Regional Director Dov Wilker weighs in on the importance of the January runoff election in his home state of Georgia. _____ Episode Lineup: [0:39] Emma Green [21:19] Shabbat Table Talk with Dov Wilker _____ Show Notes: America's Table - A Program of AJC's Community of Conscience: https://www.ajc.org/AmericasTable
Nov 13, 2020
Election 2020 Analysis: Bethany Mandel, Ron Kampeas
This week, we take a deep dive into the results of the 2020 election. First, we're joined by writer and commentator Bethany Mandel to discuss what pre-election polls got wrong and why. Then, we hear from the Jewish Telegraphic Agency's Washington Bureau Chief, Ron Kampeas, to break down the results of the congressional election and hear what the 117th Congress will look like. _____ Episode Lineup: [0:39] Bethany Mandel [9:27] Ron Kampeas [25:00] Shabbat Table Talk with Simone Rodan-Benzaquen
Nov 6, 2020
Election 2020: A Bipartisan Analysis and a Focus on Florida
This week, Ira Sheskin, a professor at the University of Miami and editor of the American Jewish Year Book, joins us to break down what we know so far about the results of the 2020 election, with a focus on the Jewish vote in Florida. Then, we hear from Senator Norm Coleman, National Chairman of the Republican Jewish Coalition, and Mark Mellman, President and CEO of the Democratic Majority for Israel, on what the outcome means for America, the Jewish community, Israel, and the world. _____ Episode Lineup: [0:36] Interview with Ira Sheskin [17:00] Norm Coleman and Mark Mellman [27:42] Shabbat Table Talk Show Notes: Decision 2020: Analyzing the Impact for the Jewish World – AJC Advocacy Anywhere Event with Senator Norm Coleman and Mark Mellman: https://www.ajc.org/news/decision-2020-analyzing-the-impact-for-the-jewish-world-ajc-advocacy-anywhere
Oct 29, 2020
Debra Messing; AJC's Groundbreaking State of Antisemitism in America Report
This week's episode features a conversation with actress and philanthropist Debra Messing about her new podcast, The Dissenters, and how her experiences with antisemitism shaped her identity. Then, in a live podcast recording with the Temple Emanu-El Streicker Center in New York earlier this week, we break down the results from AJC's groundbreaking report, The State of Antisemitism in America 2020, with Avi Mayer, AJC's Managing Director of Global Communications, and Holly Huffnagle, AJC's U.S. Director for Combating Antisemitism. ____ Episode Lineup: [0:37] Debra Messing [13:06] Live Recording with Temple Emanu-El Streicker Center [33:53] Shabbat Table Talk Show Notes: The Dissenters episode with Dr. Edith Eve Eger: https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast/dr-edith-eva-eger-healing-survivor-on-trauma-healing/id1510623465?i=1000494818306 The Dissenters website: https://www.thedissenters.com/ AJC's State of Antisemitism in America 2020 Report: https://www.ajc.org/AntisemitismReport2020 Full Live Recording with Temple Emanu-El Streicker Center: https://www.emanuelnyc.org/streickercenter/past-events/#473232802
Oct 22, 2020
COVID-19 in NY's Ultra-Orthodox Community with Jacob Kornbluh; Iran Sanctions with Mark Dubowitz
This week we're joined by Jewish Insider National Politics Reporter Jacob Kornbluh, who has spent months reporting on the state of COVID-19 in New York's ultra-Orthodox communities. On October 7, Kornbluh, a resident of Borough Park, was attacked while reporting on anti-lockdown protests in his neighborhood. We'll hear a portion of this special live podcast recording, on why the ultra-Orthodox community has been so hard-hit by the pandemic, what is fueling the recent protests, and where the community should go from here. Then, we sit down with Mark Dubowitz, CEO of the Foundation for the Defense of Democracies, to talk about the ramifications of this week's end to the UN arms embargo on Iran. Episode Lineup: [2:06] Jacob Kornbluh [26:21] Mark Dubowitz [39:35] Shabbat Table Talk Be sure to tune into a special live podcast recording, "The Antisemitism Gap: The Startling Results from AJC's Groundbreaking Report" on October 28 at 4:00pm EST. Click here to register: https://streicker-center.ticketleap.com/the-antisemitism-gap-the-startling-results-from-ajcs-groundbre/. Show notes: https://www.ajc.org/news/covid-19-in-new-yorks-ultra-orthodox-community-a-conversation-with-jacob-kornbluh-ajc-advocacy https://rabbisacks.org/noach-5781/ https://mitzvahproject.causevox.com/lev-rudoren?fbclid=IwAR08cJKJDvIGVQXw0SrS5wfGxF_0MClmavefGt0CC7oV-ACUqseplHqWFSg
Oct 15, 2020
Facebook Bans Holocaust Denial Content
This week, Facebook announced that it would ban Holocaust denial content from the platform. We're joined this week by Jordana Cutler, Facebook's Head of Policy for Israel and the Jewish Diaspora, to discuss this important decision and the role AJC played in making it happen. Be sure to tune into a special live podcast recording, "COVID-19 in New York's Ultra-Orthodox Community: A Conversation with Jacob Kornbluh" on October 20 at 4:00pm EST. Click here to register: https://bit.ly/2SYOs2
Oct 8, 2020
Josh Kraft on Together Beat Hate
This week, we speak to Josh Kraft, a community leader, a seasoned nonprofit executive, and through his family, a six-time Super Bowl champion. He recently took the helm of the Kraft family's philanthropic efforts, and he joins us to discuss "[tbh]," or "together beat hate," an initiative of the Foundation to Combat Antisemitism, an organization focused on creating replicable models for fighting antisemitism and other forms of prejudice, racism, and hate. Show notes: https://www.togetherbeathate.org/
Oct 2, 2020
White Supremacy in America and David Duke
White supremacy has featured prominently in the public discourse in recent years and during the current election cycle. In this week's episode, we sit down with the creators of two podcasts to explore the history of white supremacy in the United States in order to better understand the state of this hateful ideology today. First, Odette Yousef, host of WBEZ Chicago's 'Motive,' speaks to us about the podcast's third season, which examines the origins of Nazi skinhead culture. Then, we hear from Josh Levin, host of Slate's 'Slow Burn,' the fourth season of which explores how David Duke, America's most famous white supremacist, rose to prominence.
Sep 24, 2020
Remembering Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg
This week, we sit down with Abbe Gluck, a former clerk to Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg, who passed away last week, on the eve of Rosh Hashanah. A professor of law and founding faculty director of the Solomon Center for Health Law and Policy at Yale Law School, she and fellow former clerk Gillian Metzger penned an op-ed in The New York Times just days after Justice Ginsburg's passing, recalling her impact on them and on gender equality in the United States. Professor Gluck joins us to reflect on that legacy.
Sep 17, 2020
Talking Arab-Israeli Peace with Acting Consul General Israel Nitzan
Following Tuesday's historic signing of the Abraham Accords between Israel, Bahrain, and the United Arab Emirates at the White House, we sit down with Israeli Acting Consul General Israel Nitzan to help us break down this exciting development and what it means for Israel. Then, in our closing segment, Shabbat Table Talk, AJC Associate Director for Policy and Middle East Initiatives Benjy Rogers shares why the Abraham Accords give him hope for the region.
Sep 10, 2020
AJC UAE Office; Reflections on #BlackJewishUnity Week
AJC, which for more than 25 years has advanced understanding and fostered cooperation between Arab states and the Jewish people, last week announced its plans to open an office in the United Arab Emirates – the organization's first permanent presence in the Arab world. The move comes in the wake of the historic announcement last month by U.S. President Donald Trump, His Highness Crown Prince Mohammed bin Zayed Al Nahyan of the UAE, and Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu that the UAE and Israel would establish full diplomatic relations. On this week's episode, we're joined by AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson, who has long led AJC delegations to the Gulf and maintains close ties with senior Emirati officials, to speak about this historic announcement. Then, in our closing segment, Shabbat Table Talk, we hear from AJC Young Leadership Program Associate Naomi Ravick on her thoughts during #BlackJewishUnity Week, a partnership between AJC and the National Urban League. Show notes: https://www.ajc.org/news/challenges-and-opportunities-of-being-black-and-jewish-in-america-blackjewishunity-week
Sep 4, 2020
Celebrating #BlackJewishUnity Week with the National Urban League
In celebration of the enduring ties between America's Black and Jewish communities, AJC and the National Urban League are partnering to designate the week of September 7th Black-Jewish Unity Week. To kick off #BlackJewishUnity week, we're collaborating for an exciting crossover event with the National Urban League's podcast, For the Movement. This week, we sit down with Clint Odom, the National Urban League's Senior Vice President for Policy and Advocacy, Executive Director of the National Urban League's Washington Bureau, and co-host of For The Movement, to talk about the connections between the Black and Jewish communities and how we can use #BlackJewishUnity week to strengthen those ties. Then, in our closing segment, Shabbat Table Talk, we hear from AJC Director of Black-Jewish Relations and AJC Atlanta Regional Director Dov Wilker and what he'll be discussing at his Shabbat table this week. Show notes: Be sure to check out For the Movement's episode with AJC Chief Advocacy Officer Dan Elbaum: http://bit.ly/3jMsb2JFTM_BlackJewishUnityWeek.
Aug 27, 2020
Election 2020: The Republican National Convention
On the sidelines of the Republican National Convention, we speak with Matt Brooks, Executive Director of the Republican Jewish Coalition, about his takeaways from the week and what Jews should know about the Republican platform and ticket this year. Then, we're joined by AJC Los Angeles Associate Director Saba Soomekh to hear about the ongoing battle over California's ethnic studies curriculum.
Aug 20, 2020
Election 2020: The Democratic National Convention
On the heels of the 2020 Democratic National Convention, we sit down with Halie Soifer, Executive Director of the Jewish Democratic Council of America, who previously served as National Security Advisor to Senator Kamala Harris. We talk about support for Israel within the Democratic Party and other issues of importance to the Jewish community ahead of the upcoming election. Then, AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson, who has long engaged with leaders throughout the Arab world, joins to discuss last week's historic announcement of a peace treaty between Israel and the United Arab Emirates.
Aug 13, 2020
Election 2020: VP Candidate Kamala Harris; Upheaval in Lebanon
This week, we're joined by JTA Washington Bureau Chief Ron Kampeas to unpack former Vice President Joe Biden's selection of Senator Kamala Harris (D-CA) as his running mate. Then, in the wake of the fatal explosion in Beirut in last week, we speak to Matthew Levitt, Director of the Reinhard program on Counterterrorism and Intelligence at the Washington Institute for Near East Policy, about the dire need to reform Lebanon's political system due to the pernicious role played by Iranian proxy Hezbollah. Show notes: https://www.AJC.org/TakeAction https://www.AJC.org/Conventions https://www.washingtoninstitute.org/policy-analysis/view/lebanese-hezbollah-select-worldwide-activities-interactive-map-and-timeline https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/2020/08/07/four-israeli-women-who-have-broken-new-political-ground/?arc404=true https://www.ajc.org/news/the-plight-of-the-uyghurs-in-china-a-conversation-with-nury-turkel-ajc-advocacy-anywhere
Aug 7, 2020
Election 2020: Biden's VP Pick
This week, we're joined by Jewish Insider National Politics Reporter Jacob Kornbluh for a discussion of the choice facing former Vice President Joe Biden as he selects a running mate ahead of the November presidential election. Then AJC Asia Pacific Institute Japan Representative Jerry Rosenberg joins us to talk about the legacy of Chiune Sugihara, a Japanese diplomat who helped save the lives of thousands of Jews during the Holocaust.
Jul 31, 2020
The George Soros Saga: Antisemitism, Conspiracies, and Influence
First, we hear from Emily Tamkin, author of "The Influence of Soros: Politics, Power, and the Struggle for Open Society," on why the Jewish billionaire philanthropist has become a political target and an easy mark for antisemitism. Then, in our closing segment, Shabbat Table Talk, we sit down with AJC Director of Contemporary Jewish Life Laura Shaw Frank to hear what she'll be discussing at her Shabbat table this week.
Jul 23, 2020
Remembering Congressman John Lewis
This week, we sit down with Sherry Frank, who served as Director of AJC Atlanta for 26 years and was a close friend of civil rights icon and Congressman John Lewis, who passed away on July 17. Together, Frank and Congressman Lewis founded the Atlanta Black-Jewish Coalition in 1982. Frank joins us to share some of her memories of this American giant.
Jul 16, 2020
Rep. Deutch on Annexation; Daniel Gordis on Two-State Solution; Rabbi Horvilleur on Antisemitism
This week, we speak to Representative Ted Deutch (D-FL) about the letter he and fellow representatives wrote in opposition to unilateral annexation, and what the future holds for the U.S.-Israel relationship. Then, we're joined by Daniel Gordis, Senior Vice President and Koret Distinguished Fellow at Shalem College, on why the two-state solution is still worth pursuing. We close out with Rabbi Delphine Horvilleur, France's foremost female rabbi, speaking about how to have conversations about antisemitism, racism, and interfaith relations in a secular society. Show notes: https://blogs.timesofisrael.com/end-the-jewish-state-lets-try-some-honesty-first/
Jul 9, 2020
Antisemitic Conspiracy Theories; Coronavirus Resurgence in Israel
This week, we hear from Holly Huffnagle, AJC's U.S. Director for Combating Antisemitism, and Dave Rich, Director of Policy at the UK's Community Security Trust, on the rise of antisemitic conspiracy theories amid the coronavirus pandemic and following the killing of George Floyd in Minneapolis. Then, we hear an update on the resurgence of the pandemic in Israel from Dr. Yonatan Freeman, an international relations expert and professor of political science at The Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
Jul 2, 2020
Rabbi Angela Buchdahl on Jews and Race; Election 2020 Debate
On this week's episode of People of the Pod, we are joined by Rabbi Angela Buchdahl, Senior Rabbi of Manhattan's Central Synagogue and member of AJC's Board of Governors, to discuss the Jewish community's obligation toward Jews of color and to social justice. Then, in one of the most compelling sessions from AJC Virtual Global Forum, we hear a foreign policy debate between Antony Blinken, Deputy Secretary of State under President Barack Obama and now an adviser to Democratic presidential candidate Joe Biden, and KT McFarland, past Deputy National Security Advisor under President Donald Trump.
Jun 25, 2020
Eric Ward on Racial Justice; A Conversation with Benny Gantz
As the United States continues to grapple with racial injustice, we are joined by Eric Ward, Executive Director of the Western States Center, who discusses being a leader in the black community committed to fighting antisemitism, which he identifies as a leading driver of other forms of bigotry. Then, fresh from the AJC Virtual Global Forum stage, we hear from Alternate Prime Minister and Minister of Defense of Israel Benjamin (Benny) Gantz, in conversation with AJC Jerusalem Director Lt. Col. (res.) Avital Leibovich, his first major public appearance before an international audience since the formation of Israel's government. Show notes: https://www.politicalresearch.org/2017/06/29/skin-in-the-game-how-antisemitism-animates-white-nationalism
Jun 18, 2020
Highlights from the First-Ever AJC Virtual Global Forum
This week, AJC held its first-ever Virtual Global Forum, taking the premier annual global Jewish advocacy gathering online. Here we showcase some of the most memorable moments from the star-studded, five-day event. First we hear an excerpt from a historic public dialogue with United Arab Emirates Minister of State for Foreign Affairs Dr. Anwar Gargash about how his country can work with Israel despite political differences. Then, New Jersey Senator Cory Booker discusses racial injustice in America and the importance of Black-Jewish cooperation in tackling that national challenge. Finally, AJC Managing Director of Global Communications Avi Mayer moderates a fiery debate on the future of the West Bank between Member of Knesset Merav Michaeli of Israel's Labor Party and veteran Israeli diplomat Dr. Dore Gold, President of the Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs. 942436
Jun 11, 2020
Virtual Global Forum Preview with AJC CEO David Harris, a Conversation with Jeffrey Goldberg
Ahead of next week's AJC Virtual Global Forum 2020, we're joined by AJC CEO David Harris for a preview of this historic event, which marks the first time the premier global Jewish advocacy event will take place online. Then, we hear from Jeffery Goldberg, acclaimed journalist, Editor in Chief of The Atlantic, and friend of AJC, on the role of the media in the current pandemic and the vital importance of a free press in democratic societies. Show Notes: AJC.org/GlobalForum 942436
Jun 4, 2020
Lonnie Bunch on Race Relations; Isaac Herzog on Israel and the Diaspora
Protests have erupted across the United States following the killing of George Floyd by police in Minneapolis. Lonnie G. Bunch III, Secretary of the Smithsonian Institution, Founding Director of the National Museum of African American History and Culture, and AJC Project Interchange alumnus, joins us for a comprehensive discussion on race relations and Black-Jewish cooperation in the United States. Then, we're joined by Isaac 'Bougie' Herzog, Chairman of The Jewish Agency for Israel, to discuss Israel-Diaspora relations - where we are, how we got here, and the future we must build together.
May 28, 2020
A Conversation with Mayor Eric Garcetti and Mayor Betsy Price; Moroccan Jewish Heritage
This week on People of the Pod, we sit down with Mayor Eric Garcetti of Los Angeles and Mayor Betsy Price of Fort Worth to discuss the impact of the coronavirus crisis on their cities, the role of political leadership in a time of crisis, and their experiences visiting Israel with AJC's Project Interchange. Then we hear from Elmehdi Boudra, Founder and President of the Mimouna Association, a nonprofit founded by young Muslim students dedicated to preserving Jewish heritage and culture in Morocco, about his group's inspiring work.
May 22, 2020
Israel's New Government, Facebook's New Oversight Board
Earlier this week, Israel's new government was sworn in. The government will be jointly led by Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and Benny Gantz, leader of the Blue and White Party, after the two signed a coalition agreement in April. Gil Hoffman, Chief Political Correspondent and Analyst for The Jerusalem Post, joins us to explain what we can expect from this new government. Then, we sit down with Emi Palmor, former Director-General of Israel's Ministry of Justice and one of the first appointees to an independent oversight board charged with making policy recommendations about Facebook content, to discuss her new role.
May 15, 2020
Changing U.S. Political Landscape; Recovering Nazi-Looted Art
This week, we sit down with Seth Mandel, Executive Editor of Washington Examiner Magazine, and Batya Ungar-Sargon, Opinion Editor at The Forward, to discuss the changing U.S. political landscape and what's at stake for American Jews. Then, 75 years after the end of World War II, the fight to recover art and heirlooms looted by the Nazis and return them to their rightful owners and heirs continues. Joining us to discuss this important mission are Dr. Wesley Fisher, Director of Research for the Conference on Jewish Material Claims Against Germany and the World Jewish Restitution Organization, and Olaf Ossman, the lawyer for the heirs of Richard Semmel, a family in South Africa that has been fighting since 1999 to recover lost art.
May 8, 2020
Colorado Governor on the Coronavirus; 75 Years Since the End of WWII
This week on People of the Pod, Colorado Governor Jared Polis joins us to talk about the state's approach to fighting the coronavirus and the emergence of antisemitism during the pandemic. Then, Dr. Kurt Graham, Director of the Harry S. Truman Library and Museum, joins us to mark the 75th anniversary of the end of World War II and shares what we can learn from President Truman's leadership during a crisis.
May 1, 2020
Celebrating Israel with Sharansky, Germany's Hezbollah Ban, New UK Labour Leader
This week on People of the Pod, former refusenik, Israeli government minister, and Chairman of The Jewish Agency Natan Sharansky joins us to reflect on Israel's 72nd Independence Day. Then, AJC CEO David Harris sits down with us to explain the significance of Germany's decision to ban Hezbollah's activities on the country's soil. Finally, we speak to Hannah Rose, former President of the UK's Union of Jewish Students, about the newly elected leader of the Labour Party, Keir Starmer. Show notes: Natan Sharansky's Tips for Quarantine: https://youtu.be/wdyHlYpRvko Never Alone: Prison, Politics, and My People: https://www.amazon.com/Never-Alone-Prison-Politics-People/dp/1541742427/
Apr 24, 2020
Israeli Government Agreement, Arabic Video on the Holocaust
After three elections in less than a year, Israel may soon have a new government. This week, Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and Benny Gantz, leader of the Blue and White party, announced an agreement to jointly govern the country. Joining us is Tal Schneider, political and diplomatic correspondent at Globes, to discuss the agreement, including its more controversial elements. Then, we hear from AJC Director of U.S. Muslim-Jewish Relations Ari Gordon on the release of a new Arabic-language video about the Holocaust. The new video is the third in AJC's highly successful Arabic video series, 'An al-Yahud ("About the Jews"), which has reached tens of millions across the Arab world. Show Notes: https://www.ajc.org/news/ajc-releases-arabic-video-on-the-holocaust-ahead-of-yom-hashoah
Apr 3, 2020
Road to a New Israeli Government; Passover Prep
After three elections in the space of a year, Israel now appears to be on the verge of having a functioning government again. Joining us to discuss the latest developments is New York Times Jerusalem Bureau Chief David Halbfinger. Then we hear from Tablet Senior Writer Yair Rosenberg, AJC Director of Interreligious and Intergroup Relations Rabbi Noam Marans, and AJC Associate Director of Contemporary Jewish Life Laura Shaw Frank on how to make Passover especially meaningful this year. Show Notes: https://www.ajc.org/news/this-wont-be-the-first-social-distancing-passover
Mar 27, 2020
Coronavirus in the U.S.; Israeli Political Drama
This week, Tablet Senior Writer Yair Rosenberg joins us to discuss the U.S. government's response to the growing novel coronavirus (COVID-19) crisis and the release of his new Shabbat music album. Then, Times of Israel Senior Analyst Haviv Rettig Gur joins us to break down the ongoing political drama in Israel and the chances that Israelis may finally get a new government.
Mar 20, 2020
Israel's Response to the Coronavirus; Creatively Quarantined
As the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) sweeps the globe, Israeli doctors, researchers, and entrepreneurs are working diligently to help find a cure and improve treatment options. Joining us to discuss these efforts, as well as Israel's own strategies to prevent the spread of the virus, are Dr. Daniel Landsberg, who serves as Regional Medical Director of Maccabi Health Services, and Dr. Kira Radinsky, Chair and Chief Technology Officer of Diagnostic Robotics. Then, staying in Israel, we speak to Joyce Franco and Stephanie Graber, the creators of the Instagram account, Creatively Quarantined, which has become an incubator for those searching for inspiration in isolation.
Mar 13, 2020
Quarantine in Israel, Jews in the UAE
This week, Israel imposed a blanket 14-day self-quarantine on everyone arriving from outside the country in order to control the spread of the novel coronavirus. Joining us to discuss the quarantine and the other efforts to protect the country is Dr. Yonatan Freeman, an international relations expert and lecturer in the Department of Political Science at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Then, Ross Kriel, President of the Jewish Community of the Emirates, joins us from Dubai to shed light on the small but thriving Jewish community in the United Arab Emirates.
Mar 6, 2020
Elections in the U.S. and Israel
On this week's episode of People of the Pod, JTA's Washington Bureau Chief Ron Kampeas joins us to discuss Super Tuesday results, Senator Bernie Sanders' decision to boycott AIPAC, and other significant developments in the U.S. presidential contest. Then Tal Schneider, an award-winning political correspondent for the Israeli daily Globes, helps us break down the inconclusive results from Israel's third election in a year.
Feb 28, 2020
New Antisemitism Documentary; Israeli Election Update
On this week's episode of People of the Pod, we sit down with director Andrew Goldberg to discuss his new documentary, "Viral: Antisemitism In Four Mutations." Then, as Israelis prepare to head back to the polls on Monday for the third time in a year, we speak to Times of Israel Senior Analyst Haviv Rettig Gur to break down what's important to Israeli voters.
Feb 21, 2020
Black-Jewish Congressional Caucus, Israeli Election Update, Education in Israel
On this week's episode of People of the Pod, we talk to three founders of the Congressional Caucus on Black-Jewish Relations—Rep. Brenda Lawrence (D-MI), Rep. Debbie Wasserman Schultz (D-FL), and Rep. Lee Zeldin (R-NY)—about how the purpose of the caucus has evolved since it was launched at the AJC Global Forum this past summer. We also hear from Avital Leibovich, Director of AJC Jerusalem, as she shares the latest developments on Israel's third election in less than a year. Finally, we sit down with Professor Yaffa Zilbershats, chair of the Planning and Budgeting Committee for Israel's Council for Higher Education, to discuss a new initiative to double the number of international students in Israel's colleges and universities.
Feb 14, 2020
75 Years After Anne Frank, Israel-Sudan Relations
On this week's episode of People of the Pod, we commemorate the 75th anniversary of Anne Frank's death by asking young people whether they know who she was. Then, Eliseo Neuman, Director of AJC's Africa Institute, explains the latest developments between Israel and Sudan.
Feb 7, 2020
Behind the Assassination of Yitzhak Rabin, "Goy Friendly"
On this week's episode of People of the Pod, Israeli filmmaker Yaron Zilberman joins us to talk about his movie,Incitement, and to share his perspective on the state of politics and extremism in Israel. Then, Orthodox Jewish comedian Ashley Blaker joins us in the studio to discuss his new show, Goy Friendly, now running at Soho Playhouse theater in New York.
Jan 31, 2020
Peace Plan, Historic Auschwitz Visit, Last Stop: Auschwitz
On this week's episode of People of the Pod, we talk to Dr. Einat Wilf, a member of Israel's Knesset until 2013, about the Israeli-Palestinian peace plan proposed by President Trump and what it means for the future of Israel. Then, Rabbi David Rosen, AJC Director of International Interreligious Affairs, joins us to discuss the historic visit to Auschwitz-Birkenau by Muslim World League Secretary General Dr. Mohammad bin Abdulkarim Al-Issa and a group of Islamic religious leaders, organized by AJC and accompanied by the organization's leadership. Finally, we hear from Melcher de Wind, the son of author Eddy de Wind, about his father's book, "Last Stop: Auschwitz," the only novel written inside the death camp in the days following its liberation, 75 years ago this week.
Jan 24, 2020
French Antisemitism Survey, 75 Years After Auschwitz
On this week's episode of People of the Pod, we talk to AJC Europe Director Simone Rodan-Benzaquen about the findings of a new AJC survey on antisemitism in France. Then, to mark International Holocaust Remembrance Day, we go to the Museum of Jewish Heritage – A Living Memorial to the Holocaust to tour its current exhibit on Auschwitz and discuss its recent decision to offer free admission to any New York City public school student and up to three family members in response to the uptick in antisemitic attacks on the streets of Brooklyn. Show notes: AJC Survey on Antisemitism in France: https://www.ajc.org/news/ajc-paris-survey-french-jews-non-jews-agree-on-scope-of-antisemitism
Jan 17, 2020
Future of the Labour Party, ICC Investigation, Black-Jewish Relations
Liam Hoare, Europe Editor for Moment Magazine, has been covering the British Labour Party's antisemitism scandal since 2015. He joins us this week to discuss the future of the party and how it will affect British Jews. Then, Times of Israel Diplomatic Correspondent Raphael Ahren shares the latest developments on the International Criminal Court's investigation into aspects of the Israel-Palestinian conflict. Finally, we hear from Bishop Ken Ulmer, pastor at Faithful Central Bible Church in Los Angeles, who, troubled by recent attacks on Jews in New York and New Jersey, invited the Jewish community to his church for a prayer service on the eve of Martin Luther King, Jr. Day. Bishop Ulmer also discusses the Israel-inspired institute he started to provide resiliency training to youth traumatized by gun and gang violence.
Jan 10, 2020
U.S.-Iran Crisis; Hate Crimes in NY; #JewishandProud Day
This week on People of the Pod, we sit down with Middle East experts Patrick Clawson, research director at the Washington Institute for Near East Policy, and Tamara Cofman Wittes, a senior fellow in the Center for Middle East Policy at the Brookings Institution, to talk about the rising tensions between the U.S. and Iran. Then Deborah Lauter, executive director of New York's new Office for the Prevention of Hate Crimes, joins us to discuss efforts to curb the rash of antisemitic attacks across the city. Finally, in honor of AJC's #JewishandProud Day, we went around New York City to ask people what makes them proud to be Jewish.
Jan 3, 2020
Wave of Attacks Against Orthodox Jews; A Look at 55 Years of Fiddler
This week on People of the Pod, we sit down with Jacob Kornbluh, national politics reporter for Jewish Insider, to talk about the recent spate of antisemitic attacks against Orthodox communities across the New York area. Then, before the curtain falls on the Yiddish-language Fiddler on the Roof this weekend, we speak to Max Lewkowicz, director of the documentary "Fiddler: A Miracle of Miracles," about how the show became a global phenomenon. Show notes: https://twitter.com/Israelcohen911/status/1211553439924273153 www.AJC.org/JewishandProud
Dec 20, 2019
An Impeachment Conspiracy Theory, Jersey City Shooting, International Criminal Court
On this week's episode of People of the Pod, Eric Cortellessa, Washington correspondent for The Times of Israel, explains how antisemites are blaming a Jewish conspiracy for President Trump's impeachment. Then Rabbi David Levy, AJC New Jersey Regional Director, discusses the ongoing efforts to fight antisemitism after two shooters targeted a kosher supermarket and murdered four people last week in Jersey City. Finally, Jacob Magid, settlements correspondent for The Times of Israel, gives us an update on the International Criminal Court's inquiry into various parts of the Israel-Palestinian conflict. Show notes: AJC Survey of American Jews on Antisemitism in America https://www.ajc.org/AntisemitismSurvey2019
Dec 13, 2019
UK Election, Antisemitism on College Campuses, Third Israeli Election
On this week's episode of People of the Pod, the President of the UK's Union for Jewish Students Esther Offenberg joins us to discuss how the British Jewish community is feeling after the Conservative Party's landslide victory in yesterday's general election. Then AJC Chief Legal Officer Marc Stern breaks down President Trump's executive order aimed at strengthening efforts to combat antisemitism on college campuses. Finally, Raoul Wootliff, political correspondent for The Times of Israel, explains why Israel is set to hold its third election within a single year.
Dec 6, 2019
Defining Antisemitism in France; Refugees Around the World
On this episode of People of the Pod, we speak to Simone Rodan-Benzaquen, Director of AJC Europe, about this week's decision by the French National Assembly to adopt the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance's Working Definition of Antisemitism. Then we're joined by Aboud Dandachi, a former Syrian refugee, to share his perspective on the wave of anti-Zionism sweeping college campuses, and Yotam Polizer, CEO of IsraAID, an Israeli NGO that serves refugees and others in need around the world. Lastly, we sit down with Naomi Steinberg, Vice President of Policy and Advocacy for the Hebrew Immigration and Aid Society (HIAS), which is suing the Trump administration over the latest restriction on refugee resettlement in the United States.
Nov 28, 2019
Nita Lowey Retires; Tension on College Campuses; Quizzing New Yorkers
On this week's episode of People of the Pod, U.S. Congresswoman Nita Lowey joins us to discuss her decision to retire after 32 years on Capitol Hill. We also talk to Ilan Orzy, Director of Advocacy for Hillel Ontario, and Zev Hurwitz, AJC Director of Campus Affairs, to compare the challenges facing Jewish students on American and Canadian college campuses. And finally, we hit the streets of Manhattan with AJC's new glossary of antisemitic terms, Translate Hate, to give New Yorkers a pop quiz. Music from https://filmmusic.io "Sad Trio" by Kevin MacLeod (https://incompetech.com) License: CC BY (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) Music from https://filmmusic.io "Wish Background" by Kevin MacLeod (https://incompetech.com) License: CC BY (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Nov 22, 2019
Netanyahu's Indictment; Live from Atlanta
On Thursday, Israel's Attorney General Avichai Mandelblit announced that Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu will be formally charged with corruption, making Netanyahu the first serving prime minister in Israel's history to face criminal charges. Ronen Bergman, staff writer for The New York Times, national security senior correspondent for Yedioth Ahronoth, and author of "Rise and Kill First: The Secret History of Israel's Targeted Assassinations," joins us to break down the charges against the prime minister and what it means for the future of Israeli politics. Then we'll hear a conversation with Jodi Rudoren, editor in chief of the Forward and former Jerusalem bureau chief for the New York Times, and Nachman Shai, former member of Knesset and IDF spokesman, that was recorded earlier this week during a special live show in Atlanta.
Nov 15, 2019
Gaza Flare-Up, Fiddler in Yiddish
Earlier this week, terrorists fired hundreds of rockets from Gaza into Israel following the targeted killing of a top Palestinian Islamic Jihad leader. We are joined by Avi Issacharoff, Middle East analyst for The Times of Israel and Walla News, and Judah Ari Gross, The Times of Israel's Military Correspondent, to discuss the events of the past week. Then we sit down with Zalmen Mlotek, musical director of the Yiddish-language Fiddler on the Roof, and Steven Skybell, who stars in the show, to discuss the success behind the smash off-Broadway hit.
Nov 8, 2019
Jewish Life in Belgium, China-Israel Relations
This week Daniel Schwammenthal, Director of AJC's Transatlantic Institute, joins us from Brussels to talk about Jewish life in Belgium, which has seen a string of antisemitic incidents in recent years, and about AJC's efforts to combat antisemitism across Europe. Then we sit down with Ambassador Matan Vilnai, Israel's former envoy to China, to discuss the Jewish state's relationship with the ascendant Asian power and what it means for Israel's future.
Oct 31, 2019
The Sources of Antisemitism; Lebanon Protests; Israeli Politics Update
This week, we sit down with Deborah Lipstadt, Dorot Professor of Modern Jewish History and Holocaust Studies at Emory University, to discuss her new book focusing on the sources of antisemitism and what we can do to stop it. We also speak to Dr. Matthew Levitt, Fromer-Wexler Fellow at The Washington Institute for Near East Policy, about the protests in Lebanon that led to Prime Minister Saad Hariri's resignation earlier this week. Finally, Times of Israel Political Correspondent Raoul Wootliff gives us a post-election update on coalition building efforts.
Oct 25, 2019
One Year After Pittsburgh Synagogue Attack, Survey on Antisemitism in America
Sunday, October 27, will mark exactly one year since the deadly shooting at Pittsburgh's Tree of Life synagogue building. This week, we speak to Jeff Finkelstein, President and CEO of the Jewish Federation of Greater Pittsburgh, to get a sense of how the Pittsburgh Jewish community is doing one year after the attack. Then we're joined by Avi Mayer, AJC's Managing Director of Global Communications, to discuss the results of the organization's unprecedented survey of American Jews on the subject of antisemitism in America.
Oct 18, 2019
Historic UN Report on Antisemitism, Behind the Excavation of the Pilgrims' Path
Last month, Dr. Ahmed Shaheed, UN Special Rapporteur on Freedom of Religion or Belief, released the first UN human rights report wholly dedicated to antisemitism. In his report, Dr. Shaheed found that antisemitic incidents have created a "climate of fear" among Jews and refers to antisemitism as a threat that is "toxic to democracy." Today he joins us in the studio to share the findings of his report and offer recommendations to states, civil society actors, and the UN. Then, The Times of Israel's Jewish Times Editor Amanda Borschel-Dan takes us on a tour of the newly-excavated Pilgrims' Path at Jerusalem's City of David, exploring the site and the reasons it has captured the attention of so many around the world.
Oct 11, 2019
Attack on German Synagogue, Historic Pact with Gulf States, New Book on Israeli Prime Ministers
On this week's episode, we are joined by AJC Berlin Acting Director Remko Leemhuis to discuss the horrific antisemitic attack on Yom Kippur targeting a synagogue in Halle, Germany. Then, we hear from Raphael Ahren, Diplomatic Correspondent for the Times of Israel, to break down Israeli Foreign Minister Israel Katz's efforts to advance non-aggression treaties with several Arab countries in the Gulf. Finally, we sit down with David Makovsky, Ziegler Distinguished Fellow at The Washington Institute, to discuss his new book, Be Strong and of Good Courage, co-authored with Ambassador Dennis Ross, which profiles the courageous leadership of four Israeli prime ministers.
Oct 4, 2019
Ukrainian President Zelensky; Blood Libel in America
Volodymyr Zelensky emerged on the scene in 2019 when he was elected president of Ukraine. Now he is embroiled in American domestic politics as his phone call with President Trump is at the center of the impeachment inquiry currently taking place in Congress. Cnaan Liphshiz, European news reporter for JTA, breaks down who Volodymyr Zelensky is, where Ukraine is headed, and what the controversial call means. Then we are joined by NYU Professor of History Edward Berenson to examine how an incident of a missing child led to America's only blood libel case. Finally, ahead of Yom Kippur, The Times of Israel's Jewish Times Editor Amanda Borschel-Dan takes listeners on a journey to Israel's National Library, where Dr. Gila Flam, director of the Music Department of the National Library, helps us delve into the emotional pull and significance of Kol Nidre, an ancient Ashkenazi musical setting of a prosaic Aramaic vow of renunciation.
Sep 27, 2019
Backstage with "Our Boys" Creator; Israeli Elections and the Arab Party
This week, we're joined for a special live show by Joseph Cedar, creator and executive producer of HBO's "Our Boys." Cedar shared his firsthand account of how he translated the tragedies of summer 2014 into television, his analysis of the social and political climate that led to those attacks, and the critical reception the show has received from some prominent Israelis. Then Adam Rasgon, Palestinian Affairs and Arab World Correspondent for The Times of Israel, explains how the Joint List, Israel's Arab-majority party, was formed, what its success in last week's election means for Israeli politics, and what impact its decision to endorse Blue and White Leader Benny Gantz could have on the outcome of the current coalition negotiations.
Sep 20, 2019
Israeli Election Results, Sarah Hurwitz on Her New Book, Antisemitism in NY
Earlier this week, Israel held its second national election in five months after Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu was unable to form a governing coalition in April. On this week's episode, Times of Israel political correspondent Raoul Wootliff joins us to recap the complicated election results and help us understand what they mean for Israel's future. Then we speak to Sarah Hurwitz, former head speechwriter for First Lady Michelle Obama, to discuss how she rediscovered a connection to Judaism, the focus of her new book, "Here All Along: Finding Meaning, Spirituality, and a Deeper Connection to Life – in Judaism (After Finally Choosing to Look There)." Finally, Avital Chizhik-Goldschmidt, Life/Features Editor at The Forward, joins us to discuss the recent spate of attacks against Orthodox Jews in New York.
Sep 12, 2019
Israelis Head Back to the Polls
This Tuesday, Israelis will head back to the polls for an unprecedented second national election in a single year. In this special pre-election episode, we sit down with three public figures representing the Israeli left, right, and center, to get a sense of what Israelis across the political spectrum are thinking as they cast their ballots. Joining us are Oded Revivi, Mayor of Efrat; Yossi Klein Halevi, author and Senior Fellow at the Shalom Hartman Institute; and Ksenia Svetlova, former member of Knesset for the Zionist Union Party. Then, Times of Israel political correspondent Raoul Wootliff gives us an update on what to expect from the election results.
Sep 6, 2019
AJC CEO David Harris and Times of Israel Founding Editor David Horovitz in Conversation
Launching People of the Pod, AJC CEO David Harris and Times of Israel Founding Editor David Horovitz join us to discuss the significance of this new partnership between AJC and TOI, as well as some of the most pressing issues facing America, Israel, the Jewish people, and the world.
Aug 29, 2019
Welcome to People of the Pod!
In today's inaugural episode, Times of Israel Jewish World Editor Amanda Borschel-Dan joins us from the publication's Jerusalem newsroom to discuss how People of the Pod came to be and what you can expect from this exciting new partnership between AJC and TOI. Then we're joined by Leah Goldin, together with her husband Simcha, to talk about her son, Lt. Hadar Goldin, who was killed by Hamas terrorists in 2014 and whose body has yet to be returned to Israel. Finally, we hear from Shoshanna Keats Jaskoll, a writer, activist, and co-founder of Chochmat Nashim, an NGO fighting extremism and raising the voices of women in the larger societal conversation in Israel.
Aug 28, 2019
Special Announcement
We're launching a new podcast, People of the Pod, in partnership with The Times of Israel!
Aug 23, 2019
AJC Passport: American Jews and the Democratic Party; President Truman and Israel's Founding
This week on AJC Passport, Congressman Brad Schneider (D-IL), the Democratic co-sponsor of the anti-BDS bill recently passed by the House, discusses President Trump's characterization of Jewish Democrats as "disloyal," as well the controversial move by the Israeli government to bar Reps. Omar and Tlaib from entering Israel. We also sat down with Dr. Kurt Graham, director of the Harry S. Truman Library and Museum, to discuss President Truman's role in the birth of Israel in 1948.
Aug 16, 2019
AJC Passport: Israel Blocks Members of Congress; California's Ethnic Studies Curriculum
On Thursday morning, Israel decided to bar two U.S. congresswomen, Reps. Ilhan Omar and Rashida Tlaib, from entering the country due to their support for the anti-Israel boycott movement. We sat down with AJC CEO David Harris shortly after the news broke to discuss the short- and long-term implications of this decision. We were then joined by Senator Ben Allen, who chairs the California Legislative Jewish Caucus, to discuss the high-profile controversy surrounding the state's proposed Ethnic Studies Model Curriculum.
Aug 9, 2019
AJC Passport: Israel-Diaspora Relations, Return of the Battle for Balfour
Dr. Steven Bayme, AJC's Director of Contemporary Jewish Life, recently returned from a fact-finding mission in Israel. He sat down with us to share what he learned on his trip and to discuss the current state of Israel-Diaspora relations. Then on "The Battle for Balfour," we are joined by Benjy Rogers, AJC Associate Director for Policy and Middle East Initiatives, to discuss the latest political developments in Israel ahead of the September 17 national election.
Aug 1, 2019
AJC Passport: Cooperation in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Democratic Presidential Debates
This week on AJC Passport, Endy Zemenides, Executive Director of the Hellenic American Leadership Council, joins us to discuss how the cooperation among Israel, Greece, and Cyprus, with support from the U.S., has the power to project stability and democratic values throughout the Middle East and strengthen Israel's maritime border with the Mediterranean. Then AJC's Political Outreach Director Julie Fishman Rayman comes on to break down this week's Democratic presidential debates.
Jul 26, 2019
AJC Passport: 25th Anniversary of AMIA, Trump Takes on "the Squad"
This week on AJC Passport, Dina Siegel Vann, Director of AJC's Arthur and Rochelle Belfer Institute for Latino and Latin American Affairs, joins us to discuss her most recent trip to Buenos Aires to mark the 25th anniversary of the bombing of the Asociación Mutual Israelita Argentina (AMIA) building and to update us on recent developments in Argentina's approach to Hezbollah, the terrorist group that carried out the attack. Then, JTA Washington Bureau Chief Ron Kampeas joins us to break down recent Israel-related legislation on Capitol Hill and the ongoing feud between President Trump and four Democratic congresswomen known as "The Squad."
Jul 19, 2019
AJC Passport: U.S. Antisemitism Summit and LGBT Rights in Israel
Earlier this week, AJC Chief Policy and Political Affairs Officer Jason Isaacson addressed the U.S. Department of Justice Summit on Combating Antisemitism. He sat down with us on AJC Passport to share an inside look on this high-level conference and the U.S. administration's increased efforts to combat resurgent antisemitism. Then, we were joined by Tyler Gregory, Executive Director of A Wider Bridge, who shared his thoughts on Israeli Education Minister Rabbi Rafi Peretz's controversial statements on gay conversion therapy, accusations of "pinkwashing," and Israel's first openly gay cabinet minister.
Jul 12, 2019
AJC Passport: Ethiopian Israeli Protests and Singapore-Israel Relations
The shooting and killing of Ethiopian Israeli Solomon Teka by an off-duty police officer last month sparked protests across Israel. Joining us is Director of Interfaces and Synergy at The Jewish Agency for Israel Pnina Agenyahu to update us on the latest developments and discuss how Israel is addressing the challenges facing its Ethiopian community. Then, Ambassador Bilahari Kausikan, former Permanent Secretary at the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Singapore and former Permanent Representative of Singapore to the United Nations, joins us to discuss the strengthening ties between Singapore and Israel as we mark the 50th anniversary of diplomatic relations between the two countries.
Jul 3, 2019
AJC Passport: Welcoming AJC's First Female President and a Conversation with Michael Anton
Last month, AJC bade farewell to our former President, John Shapiro, and welcomed our new President, Harriet Schleifer. Today Schleifer, the first woman to lead the organization, joins us to discuss her new role and share her vision for the future of AJC. Two weeks ago, we heard from one of President Trump's most outspoken Republican critics, Bill Kristol. This week, we're bringing you another conversation recorded on the sidelines of AJC Global Forum 2019 with Michael Anton, a former deputy assistant to President Trump and one of the foremost proponents of his agenda.
Jun 28, 2019
AJC Passport: Combating Anti-Semitism Around the World
Are governments across the world doing enough to combat the threat of anti-Semitism? U.S. State Department Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Anti-Semitism Elan Carr, British Member of Parliament for the Labour Party John Mann, and European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights Director Michael O'Flaherty, joined us on the AJC Global Forum stage to address this question. Listen as they share their insights on the dangers of rising anti-Semitism and the need to step up efforts to confront it.
Jun 20, 2019
AJC Passport: Hezbollah's Activities in Germany and a Conversation with Bill Kristol
This week on AJC Passport, Dr. Remko Leemhuis, Assistant Director for Policy and Public Affairs at AJC's Berlin Ramer Institute for German-Jewish Relations, joins us to discuss Hezbollah's nefarious activities in Germany and the urgent need to designate the Iranian proxy in its entirety as a terrorist organization. Then, we continue our behind the scenes look at this year's AJC Global Forum in Washington, where we caught up with Bill Kristol, founder of The Weekly Standard and a leading political analyst. Kristol shares his insights into American politics and U.S. foreign policy in the Trump era. Show notes: Dr. Remko Leemhuis' Op-ed in International Politics and Society: https://www.ajc.org/news/germany-do-not-give-into-fanaticism
Jun 14, 2019
AJC Passport: Exploring Trump's Foreign Policy, Israel Goes Back to the Polls
Last week, we brought you onto the AJC Global Forum stage with a special live episode of AJC Passport. This week, we bring you backstage where we sat down with Dr. James Carafano, Vice President at The Heritage Foundation, for an exclusive conversation on U.S. foreign policy under President Trump, including immigration reform and the Middle East peace process. Then, we're joined by AJC Jerusalem Director Lt. Col. (Res.) Avital Leibovich to explain why Israel is heading back to the polls for an unprecedented second election in a single year. Show notes: AJC 2019 Surveys of American, French, and Israeli Jewish Opinion: www.AJC.org/survey2019
Jun 6, 2019
AJC Passport: Live from AJC Global Forum: Fighting Anti-Semitism in the UK Labour Party
Earlier this week, nearly 2,500 leaders, activists, and guests from across the United States and more than 50 countries gathered in Washington, D.C., for AJC Global Forum 2019. There, British Members of Parliament Joan Ryan and Ian Austin sat down with us for a special episode of AJC Passport. Recorded in front of our largest-ever live audience, our conversation with Ryan and Austin centered on the rampant anti-Semitism plaguing the Labour Party and how they're fighting back.
May 24, 2019
AJC Passport: The View from Both Sides of the Aisle
This week, we bring you a special Florida-themed episode of AJC Passport. We spoke to two members of Congress from Florida, Representative Ted Deutch (D-FL) and Representative Brian Mast (R-FL), and discussed the importance of pro-Israel support on both sides of the aisle and the need to confront the threat of anti-Semitism in America.
May 16, 2019
AJC Passport: Hannah Rosenthal's Fight Against Anti-Semitism
Last week, former U.S. State Department Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Anti-Semitism Hannah Rosenthal joined us for a special AJC Passport live show in Atlanta to celebrate 75 years since the creation of AJC's Atlanta office. Rosenthal discussed her time in government and her work fighting hatred of the Jewish people around the world.
May 10, 2019
AJC Passport: Israel-Gaza Flare-up and a Conversation with Congressman Eliot Engel
The recent flare-up between Palestinian terrorist groups in Gaza and Israel over saw more than 650 rockets slam into Israel's south, killing four Israeli civilians and paralyzing much of the country. The assault drew over 300 retaliatory strikes against terrorist infrastructure in Gaza by the Israel Defense Forces. Joining us today is AJC Jerusalem Director Avital Leibovich to fill us in on the latest round of violence and its aftermath. Then we'll hear a conversation with Congressman Eliot Engel, Chairman on the House Foreign Affairs Committee, recorded last week during a special AJC Passport live show in New York.
May 3, 2019
AJC Passport: Muslim-Jewish Relations and the NYTimes's Anti-Semitic Cartoon
Imam Mohamed Magid is the spiritual leader and executive director of the All Dulles Area Muslim Society Center, which serves 5,000 Muslim families in Northern Virginia, making him one the most important imams in America. He is also a member of the Muslim-Jewish Advisory Council, convened by AJC and the Islamic Society of North America. Imam Magid joins us this week to discuss Islam in America and the state of Muslim-Jewish relations. Also joining us this week is AJC Transatlantic Institute Director Daniel Schwammenthal to analyze what went wrong at The New York Times when its international edition published an anti-Semitic cartoon last week.
Apr 25, 2019
AJC Passport: Exploring Israel and the Media with Matti Friedman
With AJC Global Forum 2019 rapidly approaching, we're throwing it back to last year's Global Forum in Jerusalem. There, we recorded the first-ever AJC Passport live show in a room filled with hundreds of college students. Journalist Matti Friedman joined us to discuss one of the least reported-on angles of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict: the press that covers the struggle. Drawing on his years of experience as an AP reporter and editor, Friedman talked with us about how the editorial process shapes coverage of the conflict.
Apr 19, 2019
AJC Passport: The War of Words Between President Trump and Congresswoman Omar
September 11 was a traumatic and defining moment for Americans, so it comes as little surprise that questionable comments about the attack by a controversial member of Congress would generate a firestorm. JTA Washington Bureau Chief Ron Kampeas joins us to explain the war of words between Congresswoman Ilhan Omar and President Trump. Also joining us this week is Stephanie Guiloff, Deputy Director of AJC's Arthur and Rochelle Belfer Institute for Latino and Latin American Affairs, to discuss a new AJC campaign to urge the European Union to designate the entirety of Hezbollah a terrorist organization.
Apr 12, 2019
AJC Passport: The Results Are In
Israelis went to the polls earlier this week to elect the members of the 21st Knesset and choose a prime minister. Days after the polls closed, the final results have been announced. On this special post-election episode of AJC Passport, we are joined by David Makovsky, former senior advisor to the Secretary of State's Special Envoy for Israeli-Palestinian Negotiations and Ziegler Distinguished Fellow at The Washington Institute for Near East Policy, and AJC Jerusalem Director Avital Leibovich to break down the results of the election and what impact it will have on the future of Israel.
Apr 5, 2019
AJC Passport: Hate Crimes in the U.S. and the Battle Over the Bots
In recent years, Europe has been rocked by reports of increasing anti-Semitism. But what is happening within our own borders? Brian Levin, Director of California State University's Center for the Study of Hate and Extremism, joins us to share his latest findings, analyze the trends in hate crimes in the United States, and explore effective responses. Then, with the national election in Israel less than a week away, Haaretz journalist Allison Kaplan Sommer joins us on "The Battle for Balfour" to discuss the social media bots scandal and share her prediction of who will be Israel's next prime minister.
Mar 29, 2019
AJC Passport: Black-Jewish Relations and Flare-Up in Gaza
The African American and American Jewish communities have a long and storied history of cooperation. But is there still a shared Black-Jewish agenda today? Joining us is Dr. Lonnie Bunch III, Founding Director of the Smithsonian National Museum of African American History and Culture, to discuss the past, present, and future of Black-Jewish relations in America. Then, on "The Battle for Balfour," we are joined by Jerusalem Post Senior Contributing Editor Lahav Harkov for an update on the latest flare-up in Gaza and what impact it might have on the upcoming Israeli election.
Mar 22, 2019
AJC Passport: A New President in Mexico and Arab Israeli Voters
President Andrés Manuel López Obrador, known by his initials as AMLO, swept into office as president of Mexico with great fanfare and big promises. Will he be able to live up to them? Joining us today to discuss what we can expect from López Obrador's presidency is Dina Siegel Vann, director of AJC's Arthur and Rochelle Belfer Institute for Latino and Latin American Affairs, who accompanied a high-level AJC delegation that met with him in Mexico City last week. Then on "The Battle for Balfour," we are joined by Arik Rudnitsky, a scholar on Israeli Arab society at the Israel Democracy Institute and the Moshe Dayan Center of Tel Aviv University, for a discussion on voter turnout among Arab citizens of Israel in the upcoming national election and how it might help determine who becomes prime minister.
Mar 14, 2019
AJC Passport: Anti-Semitism and the UK Labour Party Split
On February 18, seven members of the British Parliament resigned from the Labour Party, citing what they called "institutional anti-Semitism." Two more followed just days later. Though dramatic, the split came as little surprise: the Labour Party has been rocked by charges of anti-Semitism since Jeremy Corbyn became party leader in 2015. Ella Rose, former National Director of the Jewish Labour Movement, joins us to discuss the political fallout of the split and what it means for the future of the Labour Party. Then, on "The Battle for Balfour," Walla! News Political Correspondent Tal Shalev joins us to discuss the latest political developments in Israel ahead of the April 9 national election.
Mar 7, 2019
AJC Passport: An Audience with the Pope
Rabbi David Rosen lives in Jerusalem, but he spends much of his time traveling the world as AJC's Director of International Interreligious Affairs. He joins us this week from the Vatican, where he is accompanying a senior AJC delegation in meetings with Pope Francis and other high-level Church officials. We spoke with him about the history of Catholic-Jewish relations, the breaking news that the Church will unseal WWII-era archives, and the future of interreligious dialogue. Then, on "The Battle for Balfour," we spoke with AJC Managing Director of Global Communications Avi Mayer about several controversial decisions by Israel's Central Elections Committee ahead of the April 9 election. And on "Good for the Jews," we listened in to Rep. Ted Deutch's (D-FL) stirring floor speech about recent anti-Semitic incidents in Congress.
Mar 1, 2019
AJC Passport: A Conversation with Mitch Landrieu, Introducing "The Battle for Balfour"
Mitch Landrieu's second term as Mayor of New Orleans may have ended in 2018, but the impact of his eight years in office will be felt for years to come. He helped revive a city still recovering from Hurricane Katrina and led the fight to take down four Confederate statues. In December, Landrieu traveled to Israel with AJC Project Interchange while serving as President of the U.S. Conference of Mayors. He joins us now to discuss the trip, the value of centrism in America's political discourse, and what's in store for the 2020 presidential race. This week, we're launching a new segment on the Israeli election, titled "The Battle for Balfour." Each week through Election Day on April 9, we will bring you an exclusive update on the race to determine the next Prime Minister of Israel. Joining us today is AJC Jerusalem Director Avital Leibovich.
Feb 22, 2019
AJC Passport: Mayor Pete Joins the Race
Last May, we were joined by Mayor Pete Buttigieg of South Bend, Indiana, to talk about his experience visiting Israel as part of our annual AJC Project Interchange delegation of U.S. mayors. Since then, Buttigieg, who is helping to reinvigorate his Midwest city, took a giant leap onto the national political stage when he declared his candidacy for the 2020 Democratic presidential nomination. With this enhanced spotlight on Mayor Pete, we are rerunning this pertinent interview to share his thoughts on Israel and what the Democratic party stands to learn from the Jewish state.
Feb 15, 2019
AJC Passport: Fallout from Rep. Omar's Tweets, Staggering Data on Antisemitic Incidents in France
Last weekend, freshman Congresswoman Ilhan Omar (D-MN) used her Twitter account to promote a classic anti-Semitic trope, accusing American Jews of paying off elected officials to maintain the U.S.-Israel relationship. Omar issued an apology after her remarks were met with widespread condemnation, including from the Democratic leadership. Was her apology sincere? Will she learn from this episode and become an ally in the fight against anti-Semitism? AJC CEO David Harris joins us to discuss the incident and the urgent need to confront anti-Semitism in all its forms. Meanwhile, this week, the French government released a report showing a 74% increase in anti-Semitic incidents in 2018 amidst a wave of vandalism against Jewish sites in Paris. AJC Paris Director Anne-Sophie Sebban-Bécache joins us to discuss the staggering statistics and AJC's role in urging French authorities to redouble their efforts to tackle the sources of anti-Semitism.
Feb 7, 2019
AJC Passport: Pro-Israel Democrats and a New Anti-Semitism Envoy
Is the Democratic Party still pro-Israel? Leading public opinion researcher and political strategist Mark Mellman joins us to address a question being asked by many and discuss how his newly-formed group, the Democratic Majority for Israel, plans to counter those trying to pull the party away from the Jewish state. Also joining us is AJC Assistant Director of International Relations Holly Huffnagle, who previously served as Policy Advisor to the U.S. State Department's Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Anti-Semitism. Huffnagle offers an inside look at the Special Envoy's vital role in fighting anti-Semitism and shares her thoughts on Elan Carr, who was nominated by Secretary Pompeo to fill the role earlier this week.
Feb 1, 2019
AJC Passport: Upheaval in Venezuela
Last week, Venezuelan opposition leader Juan Guaidó declared himself president after years of economic turmoil in what was once one of the most prosperous countries in Latin America. Tens of thousands of Venezuelans took to the streets to show their support for Guaidó and their opposition to the repressive regime of Nicolás Maduro. Will this dramatic turn of events help restore democracy and freedom to the country? Dany Bahar, an Israeli and Venezuelan economist serving as a David M. Rubenstein Fellow in the Global Economy and Development program at the Brookings Institution, joins us to break down these developments and what it could mean for the future of Venezuela and its Jewish community.
Jan 25, 2019
AJC Passport: Antisemitism and the Women's March
Last weekend, demonstrators took to the streets for the 2019 Women's March, but this year's event was mired in controversy. This week on AJC Passport, we hear from two leading Jewish figures who support the aims of the March, but disagree on whether to participate in light of the ongoing anti-Semitism scandals surrounding its leadership. Carly Pildis, political organizer and contributing editor at Tablet Magazine, and Rabbi Sarah Bassin, Assistant Rabbi of Temple Emanuel of Beverly Hills, discuss their decisions and suggest ways to mitigate tensions between the Jewish community and the leaders of the Women's March.
Jan 18, 2019
AJC Passport: Live from Washington, D.C.: The Freshman Perspective
This week's episode comes to you live from the nation's capital. We were joined by two freshman members of Congress, Representative Donna Shalala (D-FL) and Representative Van Taylor (R-TX). We talked with them about the key issues they plan to tackle while in Congress, including strengthening U.S.-Israel relations and building bipartisanship. The episode was recorded in front of a live audience as part of AJC's National Leadership Council Advocacy Fly In, featuring a series of meetings with thought leaders, foreign diplomats, and members of Congress.
Jan 11, 2019
AJC Passport: Congress Takes on BDS, State of the EU-Israel Relationship
The BDS movement has climbed its way up the Hill in the form of a bill targeting proponents of the anti-Israel boycott campaign. On this week's episode, AJC General Counsel Marc Stern sheds light on the bill and other legislative measures against boycott efforts. Also joining us is AJC Transatlantic Institute Director Daniel Schwammenthal, who discusses the state of the relationship between the EU and Israel and the steps needed to mend it.
Jan 3, 2019
AJC Passport: We're Off to the Races
In a shocking move last week, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu announced the dissolution of the current Knesset. With early elections now set for April 9th, join us as Lahav Harkov, Senior Contributing Editor of The Jerusalem Post, dives into recent developments, analyzes the political turmoil, and suggests what we can expect in the short months leading up to the elections for the 21st Knesset.
Dec 21, 2018
AJC Passport: The Great Debate on the West Bank
Remain in the West Bank or withdraw from the territories? Micah Goodman, director of Beit Midrash Yisraeli-Ein Prat and senior fellow at the Shalom Hartman Institute in Jerusalem, tackles this controversial debate in his book, Catch-67, which was recently published in English. Goodman navigates us through the complexity of this issue and explores alternatives for moving forward on this week's AJC Passport.
Dec 14, 2018
AJC Passport: Rising Anti-Semitism Across Europe
Earlier this week, the European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights released its second survey on discrimination and hate crimes against Jews in the EU. The survey's troubling results are a reminder of the pervasive problem of anti-Semitism in Europe. Katharina von Schnurbein, Coordinator on Combating Anti-Semitism for the European Commission, joins us to discuss the findings from this survey. Our second conversation is with AJC CEO David Harris, who joins us to share his insights on how European governments have reacted to anti-Semitism and the need to step up efforts to confront it.
Dec 6, 2018
AJC Passport: A New Path Forward for Gaza, and the Freshman Class in Congress
Is it possible to bring stability and reconstruction to Gaza? Ilan Goldenberg and his team from the Center for a New American Security and the Brookings Institution set out to answer this question in their new report, "Ending Gaza's Perpetual Crisis: A New U.S. Approach." Ilan Goldenberg, Senior Fellow and Director of the Middle East Security Program at the Center for a New American Security, joins us to discuss the report's recommendations and the state of U.S. policy towards Gaza. We are also joined by Julie Fishman Rayman, AJC Director of Political Outreach, to help guide us through the incoming freshman class in Congress.
Nov 29, 2018
AJC Passport: Stunning Report on European Antisemitism
One in three Europeans knows little or nothing about the Holocaust, one in four thinks Jews have too much influence in finance, and one in five thinks Jews have too much influence over the media and global politics. A devastating new report by CNN has found that antisemitism is alive and well in Europe. Joining us to discuss the troubling findings is CNN's Chief International Correspondent Clarissa Ward, who led the network's investigation. Our second guest is AJC Europe Director Simone Rodan-Benzaquen, who joined us to discuss how European governments have been responding to antisemitism across the continent and what steps still need to be taken.
Nov 16, 2018
AJC Passport: Rockets Slam into Israel and Trigger a Political Crisis
This week, Israel experienced the worst bombardment since 2014 as Hamas fired over 450 rockets into cities and communities across southern Israel. The assault left one dead and scores wounded as tens of thousands of Israeli families huddled in bomb shelters. After a ceasefire was reached, Israeli Defense Minister Avigdor Liberman announced his resignation in protest of the agreement, destabilizing the governing coalition and drawing calls for a new election. Joining us this week to discuss the security dimensions of the latest round of fighting is AJC Jerusalem Director Avital Leibovich. Our second guest is Jerusalem Post Chief Political Correspondent Gil Hoffman, who joins us to discuss the political fallout of the week's events.
Nov 9, 2018
AJC Passport: The Midterm Election with Norm Ornstein
In a dramatic election that saw a record number of voters flock to the polls, both parties had reason to celebrate. For the first time in over eight years, Democrats will take control of the House. In the Senate, Republicans have expanded their control of the chamber. Joining us this week to discuss the trends of the election and what it means for U.S.-Israel relations is Norm Ornstein, resident scholar at the American Enterprise Institute and author of One Nation After Trump: A Guide for the Perplexed, the Disillusioned, the Desperate, and the Not-Yet Deported. Show notes: Norm's book: https://www.amazon.com/One-Nation-After-Trump-Disillusioned/dp/1250164052/ref=as_li_ss_tl?ie=UTF8&qid=1504014479&sr=8-1&keywords=norman+ornstein&linkCode=sl1&tag=aeor-20&linkId=cd84123a5a3664f2cb56fa463965d22a
Nov 2, 2018
AJC Passport: The Pittsburgh Attack and Brazil's New President
In the wake of the horrific attack at a Pittsburgh synagogue on Saturday that left eleven dead and six wounded, AJC launched a global campaign called #ShowUpForShabbat to show solidarity with Pittsburgh's Jews and send the message that Jews will not be intimidated away from their synagogues. Joining us to discuss the tremendous response to the campaign is AJC Associate Execute Director and Managaing Director of Global Communications Avi Mayer. Our second guest is Fernando Lottenberg, President of the Confederation of Jewish Communities of Brazil (CONIB), who joins us to discuss the recent election of Jair Bolsonaro, a controversial right-wing populist who was elected President of Brazil this week.
Oct 26, 2018
AJC Passport: Sino-Israeli Relations and Pro-Israel Evangelicals
This week on AJC Passport, we talk about Chinese Vice President Wang Qishan's visit to Israel and what it means for relations between the Jewish state and China. We're joined by Mercy Kuo, President of the Washington State China Relations Council and member of the advisory council of AJC's Asia Pacific Institute to discuss the visit and China's growing influence in the Middle East. Our second conversation is from one of our first episodes. It features The Atlantic's McKay Coppins on Vice President Mike Pence's Evangelical faith and the role Evangelicals play in U.S.-Israel relations.
Oct 19, 2018
AJC Passport: A Disappeared Journalist and Rising Extremism in Germany
The grisly murder of Saudi journalist and U.S. resident Jamal Khashoggi inside the Saudi consulate in Istanbul two weeks ago has prompted unprecedented backlash in Washington, D.C. against the Saudi government. Joining us to discuss the fallout is Hady Amr, a Visiting Fellow at the Brookings Institution and former senior diplomat in the State Department under President Obama. Our second conversation is with AJC Berlin Ramer Institute Director Deidre Berger, who joined us to discuss Chancellor Angela Merkel's recent visit to Israel as well as issues of rising political extremism in Germany. Show notes: Good for the Jews article:https://www.nytimes.com/2018/10/15/opinion/sugihara-moral-heroism-refugees.html
Oct 12, 2018
AJC Passport: Nikki Haley's Surprise Move and Joint Muslim-Jewish Activism
In a surprise move earlier this week, Nikki Haley announced that she would be stepping down from her role as U.S. Ambassador to the United Nations. The statement prompted an immediate flurry of speculation in D.C. and on social media regarding her next steps. For the pro-Israel community, Haley's departure also raises questions on who will replace her as America's voice at the UN and whether the next ambassador will be able to fill Haley's shoes in combating rampant anti-Israel bias at the UN. Joining us to discuss Haley's departure is Ron Kampeas, the Jewish Telegraphic Agency's Washington Bureau Chief. We're also joined by Rabbi Noam Marans, AJC Director of Interreligious and Intergroup Relations, to discuss the AJC-convened Muslim-Jewish Advisory Council (MJAC) and the successful passage of a hate crimes bill backed by both AJC and MJAC. Show notes: Article from Good for the Jews: https://www.tabletmag.com/scroll/272249/the-flight-of-the-righteous-gentile
Oct 5, 2018
AJC Passport: Defending the Transatlantic Alliance
At the height of the Second World War, U.S. President Franklin Roosevelt and British Prime Minister Winston Churchill articulated a vision of a world living at peace, with free trade, human rights, and democracy at its center. After the war, their nations helped bring that vision—dubbed the Atlantic Charter—into being, creating the world we know today. But now, seven decades later, the charter and the global system it envisioned are under assault. This week on AJC Passport, we're joined by journalist, author, and visiting fellow at the Brookings Institution James Kirchick to do a deep-dive into what's undermining the transatlantic alliance and the close ties between fellow liberal democracies. We're also joined by AJC Associate Executive Director for Policy Jason Isaacson to discuss AJC's newest initiative to reaffirm the transatlantic partnership with the help of a few prominent friends. Show notes: James's Yale campaign in the WSJ: https://www.wsj.com/articles/im-running-to-restore-yale-values-1528054042 AJC's transatlantic partnership: https://www.ajc.org/TransatlanticUnity
Sep 21, 2018
AJC Passport: The World Comes to New York
Each year, leaders from around the world descend on New York City for the UN General Assembly. For the NYPD, these world leaders leave behind a slew of unpaid parking tickets. But for AJC, that all of them are in one place presents an unparalleled opportunity to advocate for the Jewish people globally. Our guest this week is our chief advocate, AJC CEO David Harris, who joins us to explain what happens at the UN General Assembly and what AJC does when it meets with visiting leaders behind closed doors.
Sep 13, 2018
AJC Passport: Middle East Peace with negotiator Aaron David Miller
Twenty-five years ago this week, Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) Chairman Yasser Arafat joined U.S. President Bill Clinton on the White House lawn to sign the Oslo Accords, the first-ever peace agreement between the two sides. This week, the Trump administration announced that it is closing the PLO's office in Washington, D.C. What happened? We're joined by Aaron David Miller, Vice President for New Initiatives and Middle East Program Director at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars. Miller previously served as a peace process advisor to U.S. administrations of both parties. He joins us to talk about the legacy of the Oslo Accords, the Trump administration's decision to shutter the PLO's D.C. office, and the future of negotiations between Israel and the Palestinians.
Sep 6, 2018
AJC Passport: How the Mossad Targets Terrorists and Why a Controversial Leader Came to Israel
This week on AJC Passport we're bringing you a special segment: a deep dive into the Mossad's use of targeted killings. Joining us to discuss the secretive agency's tactics is Ronen Bergman, an investigative journalist and New York Times Magazine staff writer who spent years combing through archives and conducting interviews with Mossad officials to write the best-selling book Rise and Kill First: The Secret History of Israel's Targeted Assassinations. Our second guest is AJC Asia Pacific Institute Director Shira Loewenberg, who joined us to discuss controversial Philippine President Rodrigo Duterte's visit to Israel.
Aug 31, 2018
AJC Passport: Trump Cuts Aid to Palestinians, Jews Cut Ties to Corbyn
The Trump administration is cutting $200 million in aid meant for the Palestinians. The move comes on the heels of previous cuts to U.S. funding for projects in the Palestinian territories. We sat down with Tamara Cofman Wittes, Senior Fellow at the Brookings Institution and former Deputy Assistant Secretary of State for Near Eastern Affairs at the U.S. State Department, to analyze what impact the cut will have and what it reveals about the administration's strategy. Our second guest is Josh Glancy, a correspondent for the British publication The Sunday Times. Glancy recently wrote a searing indictment of Jeremy Corbyn in The New York Times following the latest anti-Semitic scandal involving Corbyn where a 2013 video that was discovered showed him questioning whether 'Zionists' were truly British. Josh Glancy's article: https://www.nytimes.com/2018/08/27/opinion/jeremy-corbyn-anti-semitism-labour-britain.html John McCain's speech at AJC Global Forum 2014: https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=183&v=uHcr2baBftE
Aug 24, 2018
AJC Passport: Gaza Ceasefire, Netanyahu's Future, and the U.S.-Turkey Crisis
Is a long-term ceasefire between Israel and Hamas in the offing? How did the United States and Turkey—NATO allies—find themselves in a trade war? We answer those questions and more on this week's edition of AJC Passport. Joining us to talk about the Gaza ceasefire, growing election talk in Israel, and his biography of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu is Haaretz writer Anshel Pfeffer. We are also joined by Dr. Henri Barkey, a professor at Lehigh University and former Middle East Program Director at Princeton's Woodrow Wilson Center, who describes his harrowing encounter with the Turkish government after the attempted coup in 2016 and how the country found itself at odds with the U.S. government. Show notes: Anshel's Netanyahu biography: https://www.amazon.com/Bibi-Turbulent-Times-Benjamin-Netanyahu/dp/0465097820
Aug 17, 2018
AJC Passport: What Are the Best Colleges for Jews?
If you're a high school senior or the parents of one, you're about to embark on a wonderfully stressful journey: picking the right college. If you're Jewish, that comes with a few extra considerations: Is there a Jewish a cappella group? How's the kosher food? What about BDS on campus? To answer these questions and more, we spoke with Laura Adkins and Aiden Pink, two young journalists at The Forward who designed a comprehensive guide that ranks over 200 colleges across the country based on what they offer Jewish students. Show notes: The Forward College Guide: www.forward.com/college Rabbi Aaron Lerner's Essay: http://jewishjournal.com/opinion/189597/
Aug 10, 2018
AJC Passport: Rockets Batter Israel, White Supremacists Descend on D.C., Druze Fight for Equality
As we recorded this episode on Thursday morning, southern Israel was battered by rockets from the Hamas-controlled Gaza Strip. Our guest, former IDF spokesperson Lieutenant Colonel (res.) Peter Lerner, briefed us on the attacks before diving into the topic of the week: the Druze community's protest against the Nation-State Law and why he joined it. Our second guest was AJC Washington Director Alan Ronkin, who discussed how AJC joined forces with the Urban League to speak out against white supremacists ahead of this weekend's racist rally in our nation's capital. Peter's piece: https://forward.com/opinion/407409/israel-s-nation-state-bill-shamed-the-minorities-who-give-us-pride/ Alan's statement with the Urban League: https://www.ajc.org/news/greater-washington-urban-league-and-american-jewish-committee-ajc-stand-united-against-hate
Aug 3, 2018
AJC Passport: Talking to Tehran and Negotiating Jewish Numbers
Is President Trump trying to get Iran to come back to the negotiating table? During a press conference on Monday with Italian Prime Minister Giuseppe Conte, Trump indicated that he would be ready to meet with Iranian leaders without preconditions. We therefore decided to open up the AJC vault and share with you a conversation we recorded with Emily Landau, a senior research fellow at the Institute for National Security Studies in Tel Aviv, who talked about precisely this strategy. Landau leads the institute's Arms Control and Regional Security Program and is an expert on Iran's nuclear efforts. Our second segment is on a topic that comes up regularly and generates a fair amount of anxiety: Jewish demographics in Israel and America.
Jul 27, 2018
AJC Passport: Israel on the "Woke Left" and Saving the White Helmets
Is Israel becoming a litmus test on the "woke" left? This week, Teen Vogue published an article that sought to tie issues of police brutality in the United States to Israel's conflict with the Palestinians. Our guest this week is journalist Emily Shire, who joins us to explain the evolution of Teen Vogue and give us a follow-up on her viral New York Times article from 2017, which asked if feminism still has room for Zionist women. For our second segment, we are joined by AJC Jerusalem Director Lt. Col. (Res.) Avital Leibovich to discuss Israel's heroic effort to save the 'White Helmets'—Syrian medics who have themselves saved countless Syrian lives during the country's brutal civil war.
Jul 20, 2018
AJC Passport: The Trump-Putin Summit and Israel's Nation-State Bill
President Trump had a headline-grabbing visit to Europe. During the trip, he called the European Union a foe of the United States and received sharp blowback for his deferential approach to contentious questions such as whether Russia interfered in the 2016 election. Over in Israel, a controversial bill that would define the character of the state passed over the objections of Israel's president and leading Jewish organizations around the world, including AJC. Joining us to discuss the reaction to the Trump-Putin summit is Andrew Weiss, Vice President at the Carnegie Institute and long-time Russia expert, who spent years serving in administrations of both parties advising on Russia policy. We're also joined by Dr. Stephen Bayme, AJC Director of Contemporary Jewish Life and American Jewish-Israeli relations to discuss Israel's nation-state bill, what it means for Israel, and what it means for Israel-diaspora relations. Full nation-state law: https://www.jpost.com/Israel-News/Read-the-full-Jewish-Nation-State-Law-562923 AJC Press Release: https://www.ajc.org/news/ajc-criticizes-knesset-adoption-of-nation-state-bill
Jul 12, 2018
AJC Passport: Trump's SCOTUS Nominee, Supporting Israel in the Academic World
A confirmation battle is brewing. This week on AJC Passport, we dive into the world of U.S. Supreme Court nominations. Joining us to discuss this hot-button issue is AJC General Counsel Marc Stern, who has appeared four times before the Supreme Court and is one of the Jewish community's experts on the court, the separation of church and state, and religious liberty. Stern talks to us about Brett Kavanaugh, and what everyone gets wrong about confirmation fights. The segment is followed by a conversation with Eric Kaler, president of the University of Minnesota and esteemed chemical engineer, who recently traveled to Israel with AJC Passport host Seffi Kogen as part of an AJC Project Interchange delegation. Hear his take on what Israeli universities do well and why he openly supports ties with the Jewish state despite the anti-Israel activism among his students.
Jul 6, 2018
AJC Passport: Mexico Elects a New President, Poland Amends Controversial Holocaust Law
A political earthquake just shook Mexico. This week, in a landslide victory, political outsider and left-wing nationalist Andrés Manuel López Obrador won the Mexican presidency with an anti-establishment and anti-corruption campaign. Joining us to discuss this dramatic development is Dina Siegel Vann, Director of the AJC Belfer Institute for Latino and Latin American Affairs. Our second guest this week is our Warsaw-based Director of AJC Central Europe, Agnieszka Markiewicz, who is joining us to discuss recent changes to Poland's controversial Holocaust law and the recent "No to Hatred" conference AJC Central Europe co-hosted with the city of Warsaw.
Jun 29, 2018
AJC Passport: Conversations with Amb. Daniel Shapiro and UN Special Coordinator Nickolay Mladenov
Last week, we took you front and center at AJC Global Forum in Israel by bringing you the much-anticipated Great Debate. This week, we take you behind the scenes and bring you some exclusive conversations from our biggest event earlier this month. First up, friend of AJC Passport and U.S. Ambassador to Israel Daniel Shapiro (2011-17) discusses the outcomes of the embassy move to Jerusalem and Israel's endgame in Syria. We also explore the implications of potential U.S. recognition of Israeli sovereignty over the Golan Heights. The Ambassador is followed by UN Special Coordinator for the Middle East Peace Process Nickolay Mladenov, who leads the UN efforts related to Israeli-Palestinian peace. We discuss the major challenges of the peace process.
Jun 20, 2018
AJC Passport: Special Global Forum Episode - The Great Debate
For those of you who were unable to join us in Jerusalem for the AJC Global Forum—or for those who want to relive the moment—we're bringing you this year's Great Debate. In the 2018 iteration of this AJC Global Forum staple, Member of Knesset Stav Shaffir of the Labor party faced off against Mayor Oded Revivi of the West Bank settlement of Efrat. Their question: "One State or Two States, Is There a Solution?"
Jun 13, 2018
AJC Passport: Live from Jerusalem - Exploring Israel and the Media with Matti Friedman
AJC Passport hits the road! This week's episode comes to you from Jerusalem. Recorded in front of a live audience for the first time, we sat down with journalist and author Matti Friedman to discuss one of the least reported-on angles of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict: the press that covers the struggle. Drawing on his years of experience as an AP reporter, Friedman talked with us about how the editorial process shapes coverage and fielded questions from the audience of more than 350 college students who participated in the AJC Global Forum 2018.
Jun 6, 2018
AJC Passport: A Conversation with Yossi Klein Halevi about His New Best Seller
Can the stories Israelis and Palestinians tell about their history help them achieve peace? It's a question that keeps acclaimed author Yossi Klein Halevi up at night. This week's AJC Passport features a special conversation with Klein Halevi. He discusses grappling with this question and how it led him to write his latest book, Letters to My Palestinian Neighbor. Hear him explain what he wants Palestinians to know about Israel's national narrative and how this knowledge might help both peoples understand each other. Klein Halevi also contributed an essay titled "The Future of the American Jewish-Israeli Relationship" for the recently-released 2018 AJC publication, Twenty-Five Essays about the Current State of Israeli-American Jewish Relations which you can check out at ajc.org/diasporasymposium.
Jun 1, 2018
AJC Passport: Congress Takes on Antisemitism, Anti-Israel Activists Hijack the Presbyterian Church
Is Congress stepping up its efforts to combat rising anti-Semitism? In recent days, calls have rung out from Capitol Hill to fill the long-vacant position of Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Anti-Semitism at the U.S. State Department. Also, a new bill was introduced that would help define anti-Semitism to better fight it in schools and on college campuses across the nation. Joining us to share his insights from Washington, D.C., is AJC Associate Executive Director for Policy Jason Isaacson, who has worked closely with members of Congress on both issues. We are also joined by Emily Soloff, AJC National Associate Director for Interreligious and Intergroup Relations, to discuss how the General Assembly of the Presbyterian Church (U.S.A.) has become a ritual of anti-Israel demonization and consider what that means for Presbyterian-Jewish relations.
May 25, 2018
AJC Passport: Pro-Israel Support in the Democratic Party; Anti-Israel Hostility in Chile
What does the future of the Democratic party look like? There are competing visions and some cause more anxiety in Jewish voters than others. Joining us this week from South Bend, Indiana is Pete Buttigieg, a young mayor with an impressive list of accomplishments. Mayor Pete, as his constituents call him, is helping to reinvigorate his Midwest city. Hailed by President Obama as a rising star of the Democratic party, Pete talks with us about his recent experience visiting Israel and what the party stands to learn from the Jewish state. We were also joined by Stephanie Guiloff, Deputy Director of AJC's Belfer Institute for Latino and Latin American Affairs, to talk about an aggressive anti-Israel campaign in Chile, which borders on anti-Semitism.
May 18, 2018
AJC Passport: What to Make of Violence in Gaza?
What's happening in Gaza? Is it a protest? An assault? A cynical media ploy? Some combination of the above? Join us for this week's episode of AJC Passport as we examine the disturbing news of renewed violence out of Gaza. We're joined by New York Times correspondent Isabel Kershner, whose coverage of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict for the past 28 years gives her a unique vantage point on this week's events.
May 11, 2018
AJC Passport: America Exits the Iran Deal, Hezbollah Wins Big in Lebanon
The "fix it or nix it" question has been answered. On Tuesday, President Trump announced that the U.S. is withdrawing from the JCPOA and reinstating crippling sanctions against Iran. The reaction in Israel and the Gulf was positive; Europe responded with a mix of disappointment and anger. But the question everyone is asking now is: what comes next? Joining us this week is Mark Dubowitz, CEO of the Foundation for Defense of Democracies (FDD). As an Iran expert who advised the Trump, Obama, and Bush administrations, Mark offers us a unique vantage point on the flaws of the Iran deal and what lies ahead. We also spoke with Dr. Matthew Levitt, author of Hezbollah: The Global Footprint of Lebanon's Party of God and Director on Counterterrorism and Intelligence at the Washington Institute for Near East Policy, about the recent elections in Lebanon and the escalating confrontation between Israel and Iran in Syria.
May 4, 2018
AJC Passport: Where Does Europe Stand as the Iran Deal Deadline Looms?
As May 12 nears, President Trump has a decision to make: will he or won't he waive sanctions on Iran as part of the nuclear deal (JCPOA)? In January, the President told the world that he would extend sanctions relief one last time so Europe and the U.S. could fix the deal's flaws. Now, as the next deadline approaches, leaders from Europe have visited the White House in an attempt to persuade the Commander in Chief not to scrap the deal. On this week's AJC Passport we were joined by Daniel Schwammenthal, Director of the Brussels-based AJC Transatlantic Institute, to discuss the European perspective on the future of the JCPOA as well as reactions to Israel's recent intel coup, which proved unequivocally that Iran lied about the nature of its nuclear program. Show notes: https://www.nytimes.com/2018/05/02/opinion/abbas-palestine-israel.html
Apr 27, 2018
AJC Passport: Germans Say No to Anti-Semitism, Portman Says No to Genesis Prize
This week on AJC Passport, we turn our eyes to Berlin where 2,000 Jews, Muslims, Christians, and others rallied in response to a bizarre anti-Semitic assault last week…against a young Arab man who had donned a kippah to prove to his Jewish friend that it was safe to wear one on the streets of Berlin. Deidre Berger, director of AJC Berlin joined us to explain exactly what happened and to discuss the state of anti-Semitism in Germany. She also walked us through AJC Europe's 3i conference that dealt with the critical issues of immigration, integration, and identity. We also spoke with Haaretz staff writer and The Promised Podcast panelist Allison Kaplan Sommer regarding the recent controversy surrounding Natalie Portman's decision to back out of receiving the Genesis Prize in Israel. Show notes: The post-WWII AJC cartoon that Deidre mentioned: http://ajcarchives.org/main.php?DocumentId=11590
Apr 19, 2018
AJC Passport: Three Perspectives as Israel Turns 70
This week on AJC Passport we celebrated a historic milestone: 70 years since the founding of the State of Israel. On this special occasion, we spoke with three figures—a politician, a historian, and an advocate—to hear their thoughts on Israel's anniversary, and their hopes for Israel's future. For a political perspective, we were joined by Israeli Member of Knesset Tzipi Livni, the leader of the Hatnuah party and former Foreign Minister. For a historical analysis, we spoke with Francine Klagsbrun, a writer and activist whose most recent work, Lioness, is a nuanced biography of Golda Meir. Finally, for an advocate's take on Israel's future, we sat down with AJC CEO David Harris, who has decades of experience promoting Israel's place in the world. Show notes: Israel at 70 eBook: https://www.ajc.org/Israelat70 Koolulam's cover of "Al Kol Eleh" https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oxzR9Z-kG6Q
Apr 13, 2018
AJC Passport: What's Ahead for the State Department and the Iran Deal?
This week on AJC Passport, we're bringing you rapid reaction to the hearings the Senate Foreign Relations held this week to determine whether to advance the nomination of CIA Director and former Congressman Mike Pompeo. Jason Isaacson, AJC's Associate Executive Director for Policy, joined us from Washington, D.C., to analyze the potentially contentious confirmation process and what Pompeo's transition into this new role would mean for American foreign policy. Then, listen in on our conversation with Ambassador Dennis Ross about Iran's adventurism in the Middle East and the future of the Iran nuclear deal.
Apr 5, 2018
AJC Passport: Protests in Gaza, Asylum Seekers in Israel
As Jews across the world celebrated Passover, Palestinians in Gaza staged a massive protest on Israel's border. Armed Hamas terrorists fired on Israeli soldiers and tried to breach the border fence. Israel responded to the violence, prompting a great deal of international scrutiny. In this week's AJC Passport, we spoke with Ambassador Dennis Ross, a career diplomat who has spent much of his career working first-hand on Israeli-Palestinian peace, about the hardships Gazans must cope with, the security challenges Israel faces, and the prospects for the Trump administration's peace proposal. We also spoke with Haaretz's Washington D.C. correspondent Amir Tibon on this week's short-lived deal to keep more than half of the African asylum seekers in Israel while sending the rest to other western countries for resettlement. Just 20 hours after Prime Minister Netanyahu announced the agreement he had reached with the UN to a great deal of fanfare—and much right-wing opposition—he backtracked and formally canceled it.
Mar 29, 2018
AJC Passport: A Cabinet Reshuffle in Washington and a Murder in Paris
In just a few short weeks, President Trump has reshuffled key foreign policy roles in his administration. In the latest episode of AJC Passport, we spoke with Elliott Abrams, Senior Fellow at the Council on Foreign Relations and a former Deputy Assistant to the President and Deputy National Security Advisor in the George W. Bush administration. We discussed the import of these changes, and how they'll affect the upcoming U.S.-North Korea meeting and the upcoming decision on the future of the Iran nuclear deal. AJC Europe Director Simone Rodan-Benzaquen also joined us to discuss the horrific anti-Semitic murder of 85-year-old Holocaust survivor Mireille Knoll in Paris.
Mar 23, 2018
AJC Passport: How Will Britain's Labour Party Fix Its Anti-Semitism Problem?
As hate incidents against Jews in Britain reach record levels, its Labour Party continues to be plagued by one anti-Semitism scandal after another. In our latest episode of AJC Passport, we speak with John Mann, Labour Party MP and chair of the All-Party Parliamentary Group Against Anti-Semitism, to explore the deeply rooted anti-Semitic views of certain party members, and whether party leader Jeremy Corbyn can find his way out of the scandal. Belle Yoeli, Assistant Director of AJC's Office of Political Outreach, also joined us to discuss the impending passage of the Taylor Force Act.
Mar 16, 2018
AJC Passport: Why the Women's March Can't Quit Farrakhan
When Tamika Mallory attended an event hosted by the head of the Nation of Islam, notorious anti-Semite Louis Farrakhan, she exposed the Women's March movement she co-chairs to a torrent of criticism. In their belated response, the leaders of the Women's March distanced themselves from Farrakhan's anti-Semitism, but declined to reject him outright. We talked with Adam Serwer, Senior Editor at The Atlantic on Farrakhan's influence in the Black community, and the pitfalls he represents for the progressive leaders of the Women's March. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC.
Mar 8, 2018
AJC Passport: Netanyahu and Trump, feat. Amb. Dan Shapiro
President Trump and Prime Minister Netanyahu met this week in Washington, to discuss issues critical to the U.S.-Israel relationship. In this week's AJC Passport, we unpacked the visit and checked in on the state of the crucial bilateral tie with former U.S. Ambassador Dan Shapiro, who served as U.S. Ambassador to Israel from 2011-2017. We also chatted with The Jerusalem Post's Washington Bureau Chief Michael Wilner about the political objectives of both leaders and how their domestic challenges are playing with one another's audience. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC.
Mar 2, 2018
AJC Passport: The Rising Tide of Anti-Semitism
From Nazis marching in Charlottesville to attacks on Jews in the streets of Europe, anti-Semitism persists around the world. In this week's AJC Passport, we talked with Ira Forman, the former Special Envoy to Monitor and Combat Anti-Semitism at the U.S. State Department, about the international trends in anti-Semitic attitudes. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC.
Feb 21, 2018
AJC Passport: Israeli Red Lines and Polish Headlines
In our latest episode, we discuss the Munich Security Conference, a premiere meeting of global political and military leaders. Prime Minister Netanyahu made headlines at the conference by warning Iran not to "test Israel's resolve" in response to recent Iranian provocations. Polish Prime Minister Morawiecki responded to an Israeli journalist's question about the country's Holocaust law by invoking "Jewish perpetrators." AJC Berlin-Ramer Director Deidre Berger was at the conference and joins us to discuss its outcomes. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC.
Feb 16, 2018
AJC Passport: Olympic Tensions, Iranian Intentions
Join us for a conversation with North Korea expert Jamie Metzl, a Senior Fellow at the Atlantic Council, on North Korea's Olympic charm offensive. Then, we talk with Lt. Col. (res.) Avital Leibovitch, Director of AJC Jerusalem, about the recent violent flare-up on Israel's northern border. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC.
Feb 9, 2018
AJC Passport: Americans and Israel
The strength of the U.S.-Israel relationship has long been rooted in bipartisan support for an alliance based on shared interests and values. But is the bipartisan consensus on Israel fading away? In this episode of AJC Passport, we speak with Tamara Cofman Wittes, Senior Fellow in the Center for Middle East Policy at The Brookings Institution. Tamara, who previously served as Deputy Assistant Secretary of State for Near Eastern Affairs in the Obama Administration, recently co-authored an essay in The Atlantic that examines polling data and probes this question. Our second guest is Dr. Steven Bayme, AJC's Director of Contemporary Jewish Life, who discussed present-day American Jewish attitudes towards Israel. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC.
Feb 2, 2018
AJC Passport: Poland's Bill and Holocaust Blame
On the eve of International Holocaust Remembrance Day, the Polish government initiated a bill making it illegal to assert that Poland or Polish citizens bear responsibility for Holocaust crimes. Under this legislation, even the utterance of the words "Polish death camps" can be punished by up to three years in jail. The move has sparked outrage around the world, especially in Israel. In this week's episode, we talk to Poland's Chief Rabbi Michael Schudrich on the reaction in the Polish-Jewish community and to AJC's Gosia Szymanska Weiss regarding the political and diplomatic fallout. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC.
Jan 28, 2018
AJC Passport: Evangelicals and Israel
Vice President Mike Pence traveled to Israel last week and was warmly received. Throughout his political career, Pence has cited his Evangelical faith as the foundation of his support for the Jewish state. Our guests are McKay Coppins, staff writer for The Atlantic, who recently profiled Pence for the magazine, as well as Rabbi Noam Marans, AJC's Director of Interreligious and Intergroup Relations. Join us as we examine the dynamics undergirding Evangelical support for Israel. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC.
Jan 24, 2018
AJC Passport: Germany and Austria Respond to the Far-Right
In 2017, far-right parties rode a wave of anti-immigrant and xenophobic sentiment to new electoral heights across Europe. In Germany, the far-right Alternative for Germany party (AfD) became the first far-right party to enter the Bundestag since the 1960s. Meanwhile, the Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ), which was founded by former Nazis, entered Austria's parliament for the second time. In this episode, we examine the societal responses to these two political developments. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC.
Jan 24, 2018
AJC Passport: Hyper Cacher - Three Years Later
It's been three years since an Islamist terrorist attacked Hyper Cacher, a kosher supermarket in Paris, murdering four Jews. In this episode, we examine how the French government, society, and Jewish community have responded since the attack. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC.
Jan 24, 2018
AJC Passport: The Trump Administration and Israel
Year one of the Trump administration is in the books. How did it approach Israel and the Arab-Israeli peace process? Did the administration's Middle East policy evolve as the year wore on? We explore both questions this week. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC.
Jan 24, 2018
AJC Passport: Reactions to the Iran Protests
In late December, Iranians took to the streets across the country to protest against their government. The regime cracked down harshly—dozens were killed and hundreds were arrested. In this episode, we examine the surprisingly muted reaction in Europe and how the Iranian diaspora has responded. *The views and opinions expressed by guests do not necessarily reflect the views or position of AJC.